⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
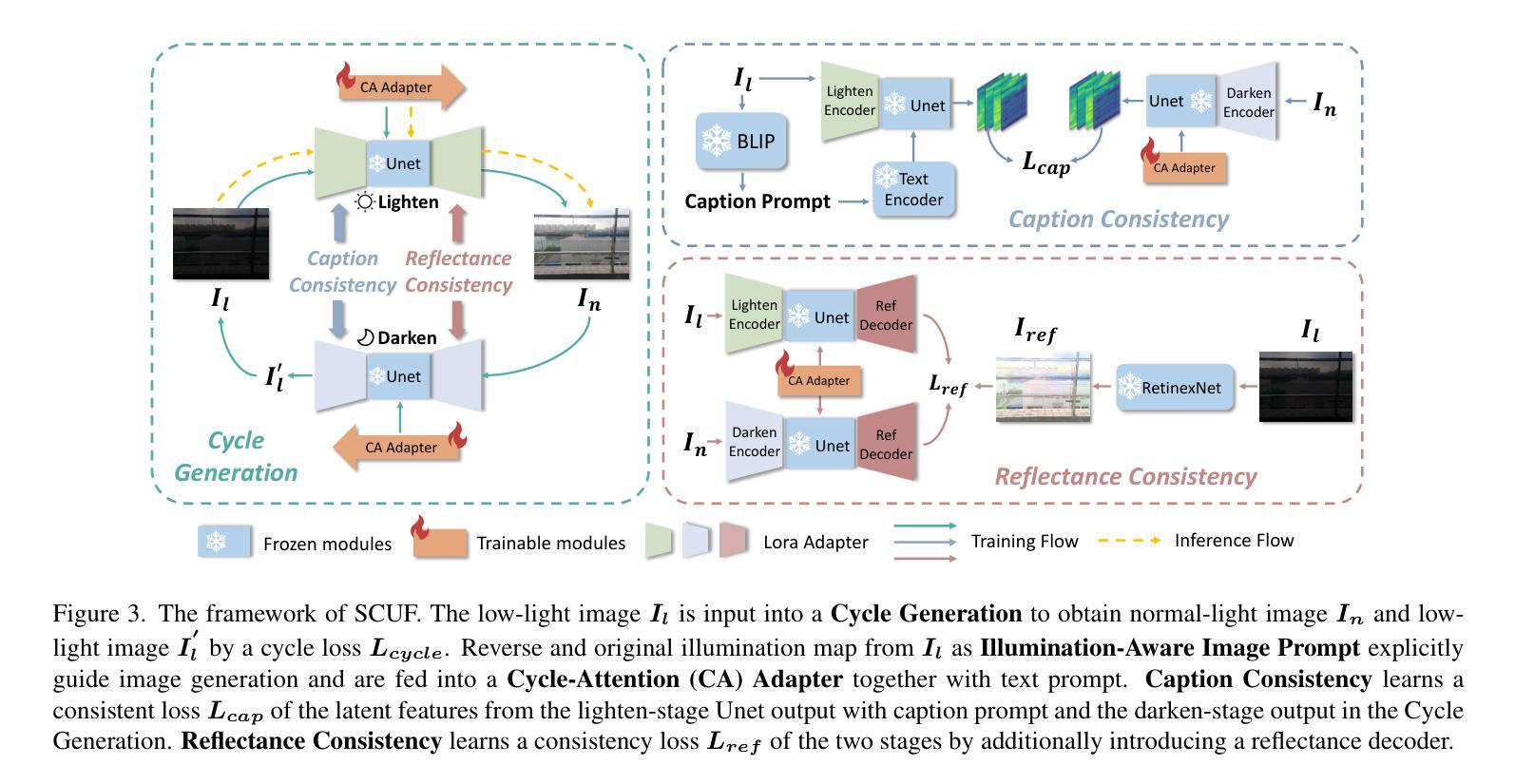
Image Translation with Kernel Prediction Networks for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Cristina Mata, Michael S. Ryoo, Henrik Turbell
Semantic segmentation relies on many dense pixel-wise annotations to achieve the best performance, but owing to the difficulty of obtaining accurate annotations for real world data, practitioners train on large-scale synthetic datasets. Unpaired image translation is one method used to address the ensuing domain gap by generating more realistic training data in low-data regimes. Current methods for unpaired image translation train generative adversarial networks (GANs) to perform the translation and enforce pixel-level semantic matching through cycle consistency. These methods do not guarantee that the semantic matching holds, posing a problem for semantic segmentation where performance is sensitive to noisy pixel labels. We propose a novel image translation method, Domain Adversarial Kernel Prediction Network (DA-KPN), that guarantees semantic matching between the synthetic label and translation. DA-KPN estimates pixel-wise input transformation parameters of a lightweight and simple translation function. To ensure the pixel-wise transformation is realistic, DA-KPN uses multi-scale discriminators to distinguish between translated and target samples. We show DA-KPN outperforms previous GAN-based methods on syn2real benchmarks for semantic segmentation with limited access to real image labels and achieves comparable performance on face parsing.
语义分割依赖于大量的密集像素级标注来实现最佳性能,但由于现实世界数据获得准确标注的难度,实践者通常在大型合成数据集上进行训练。无配对图像翻译是一种方法,用于在低数据情况下生成更现实的训练数据,从而解决由此产生的领域差距问题。当前的无配对图像翻译方法训练生成对抗网络(GANs)执行翻译,并通过循环一致性强制像素级别的语义匹配。这些方法并不能保证语义匹配成立,对于对噪声像素标签敏感的语义分割来说,这就成了一个问题。我们提出了一种新型图像翻译方法,即领域对抗核预测网络(DA-KPN),它保证了合成标签与翻译之间的语义匹配。DA-KPN估计轻量级简单翻译函数的像素级输入变换参数。为确保像素级变换的真实性,DA-KPN使用多尺度鉴别器来区分翻译样本和目标样本。我们在有限的真实图像标签访问权限下,展示了DA-KPN在语义分割的syn2real基准测试上的性能优于之前的基于GAN的方法,并在面部解析方面取得了相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF OOD-CV Workshop at ECCV 2024
Summary
本文提出一种名为Domain Adversarial Kernel Prediction Network(DA-KPN)的新型图像翻译方法,用于解决语义分割中的合成数据与现实数据域差异问题。DA-KPN通过估计像素级的输入转换参数,实现简单而轻量级的翻译功能,同时利用多尺度鉴别器确保翻译结果的现实性。在有限的真实图像标签下,DA-KPN在语义分割的syn2real基准测试中表现出优于基于GAN的方法的性能,并在面部解析中实现了相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割需要大量密集像素级注释以达到最佳性能,但获取现实世界数据的准确注释非常困难。
- 实践者通常在大型合成数据集上进行训练,但合成数据与真实数据之间存在域差距。
- 当前的无配对图像翻译方法使用生成对抗网络(GANs)进行翻译,并通过循环一致性强制执行像素级语义匹配,但不保证语义匹配的有效性。
- 这对语义分割构成问题,因为性能对噪声像素标签很敏感。
- 提出的Domain Adversarial Kernel Prediction Network(DA-KPN)方法保证了合成标签和翻译之间的语义匹配。
- DA-KPN通过估计像素级的输入转换参数,使用轻量级和简单的翻译功能。
点此查看论文截图

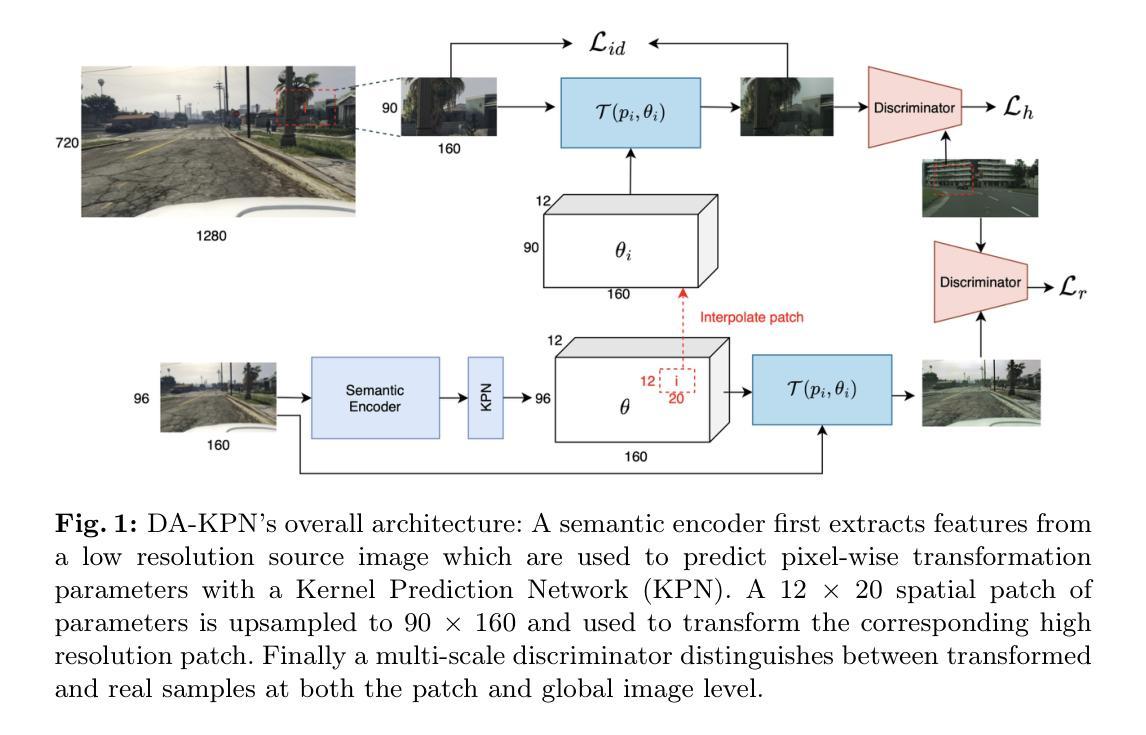

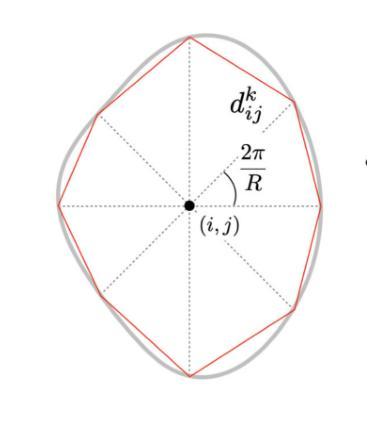
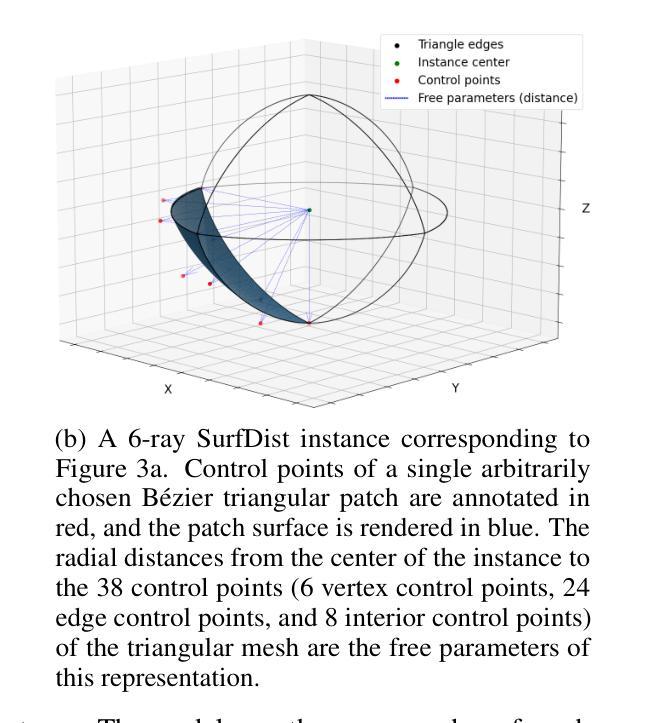
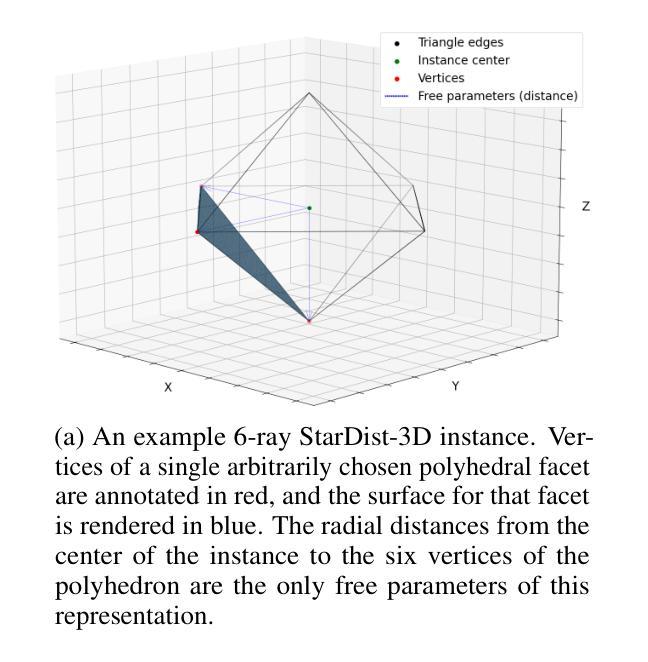
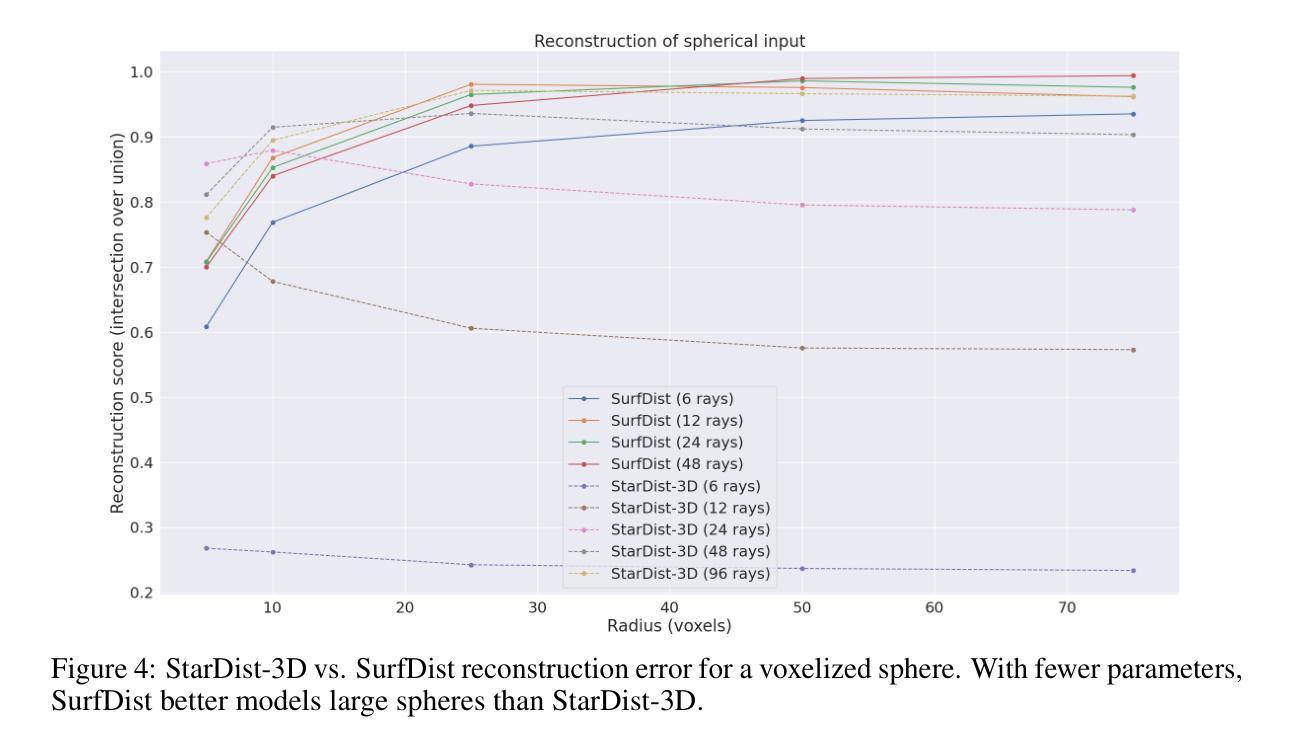
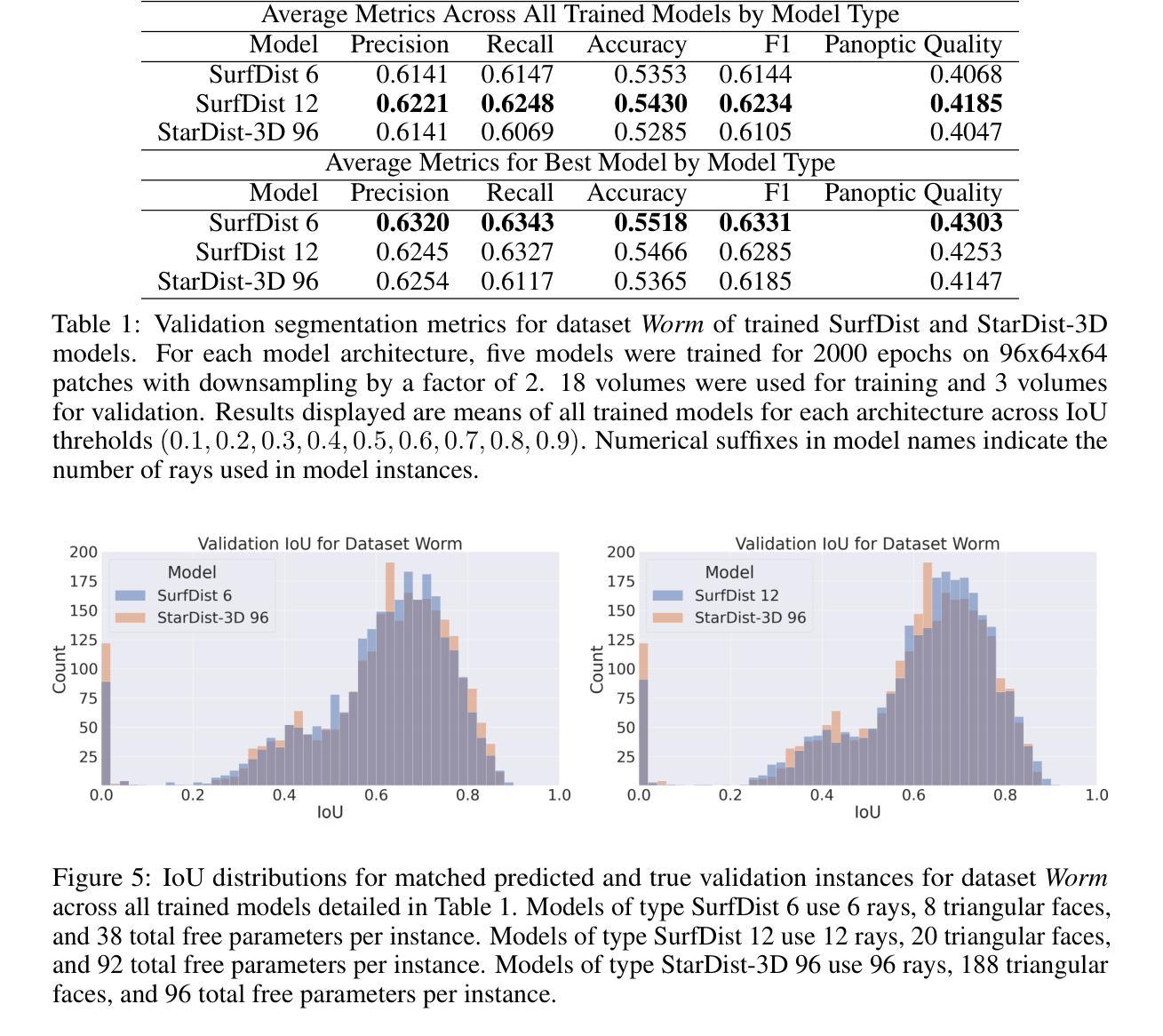
SurfDist: Interpretable Three-Dimensional Instance Segmentation Using Curved Surface Patches
Authors:Jackson Borchardt, Saul Kato
We present SurfDist, a convolutional neural network architecture for three-dimensional volumetric instance segmentation. SurfDist enables prediction of instances represented as closed surfaces composed of smooth parametric surface patches, specifically bicubic B'ezier triangles. SurfDist is a modification of the popular model architecture StarDist-3D which breaks StarDist-3D’s coupling of instance parameterization dimension and instance voxel resolution, and it produces predictions which may be upsampled to arbitrarily high resolutions without introduction of voxelization artifacts. For datasets with blob-shaped instances, common in biomedical imaging, SurfDist can outperform StarDist-3D with more compact instance parameterizations. We detail SurfDist’s technical implementation and show one synthetic and one real-world dataset for which it outperforms StarDist-3D. These results demonstrate that interpretable instance surface models can be learned effectively alongside instance membership.
我们提出了SurfDist,这是一个用于三维体积实例分割的卷积神经网络架构。SurfDist能够预测以平滑的参数曲面补丁组成的封闭表面表示的实例,特别是双三次Bézier三角形。SurfDist是流行模型架构StarDist-3D的改进版,它打破了StarDist-3D实例参数化维度和实例体素分辨率之间的耦合,并产生预测结果,可以无体素化伪影地提升到任意高分辨率。对于在生物医学成像中常见的点状实例数据集,使用更为紧凑的实例参数化,SurfDist的表现优于StarDist-3D。我们详细描述了SurfDist的技术实现,并展示了一个合成数据集和一个真实世界数据集,在这些数据集上它的性能优于StarDist-3D。这些结果表明,可以有效地学习与实例成员资格相关的可解释的实例表面模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures
Summary
SurfDist是一种用于三维体积实例分割的卷积神经网络架构。它可预测以光滑参数曲面补丁(特别是三次贝塞尔三角形)组成的闭合表面表示的实例。SurfDist改进了流行的模型架构StarDist-3D,打破了实例参数化维度和实例体素分辨率之间的耦合,并产生可上采样到任意高分辨率的预测结果,而不会引入体素化伪影。对于在生物医学成像中常见的具有blob形状的实例数据集,SurfDist使用更紧凑的实例参数化可以超越StarDist-3D的性能。我们详细介绍了SurfDist的技术实现,并展示了一个合成数据集和一个真实世界数据集,在该数据集上它的性能优于StarDist-3D。
Key Takeaways
- SurfDist是一个用于三维体积实例分割的卷积神经网络架构。
- SurfDist可以预测由光滑参数曲面补丁组成的闭合表面表示的实例。
- SurfDist改进了StarDist-3D模型架构,打破了实例参数化维度和实例体素分辨率之间的耦合。
- SurfDist产生的预测结果可以进行上采样,达到任意高分辨率,且不会引入体素化伪影。
- 对于具有blob形状的实例数据集(常见于生物医学成像),SurfDist的性能优于StarDist-3D。
- SurfDist的技术实现包括了详细的解释和说明。
点此查看论文截图

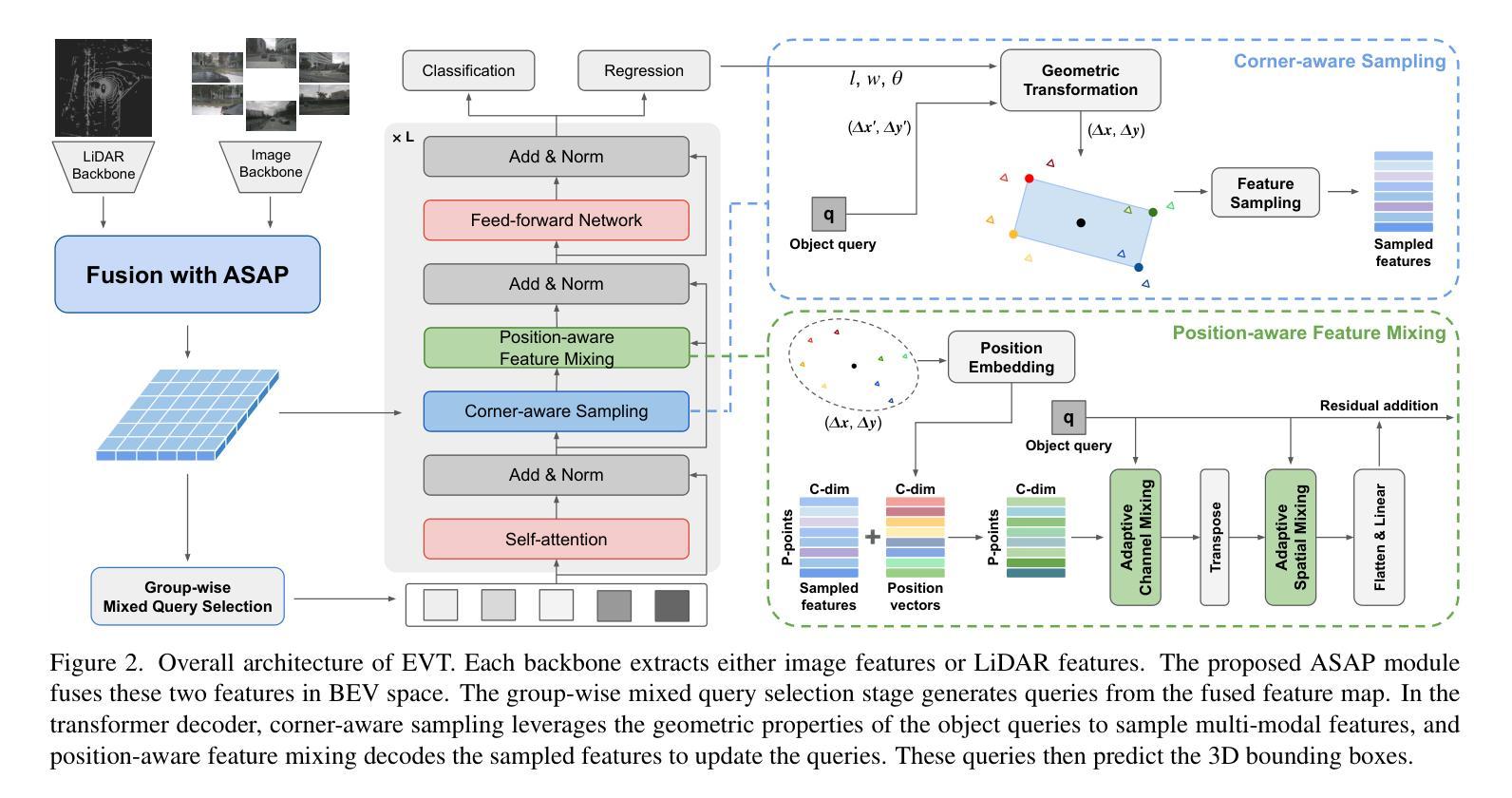
EVT: Efficient View Transformation for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yongjin Lee, Hyeon-Mun Jeong, Yurim Jeon, Sanghyun Kim
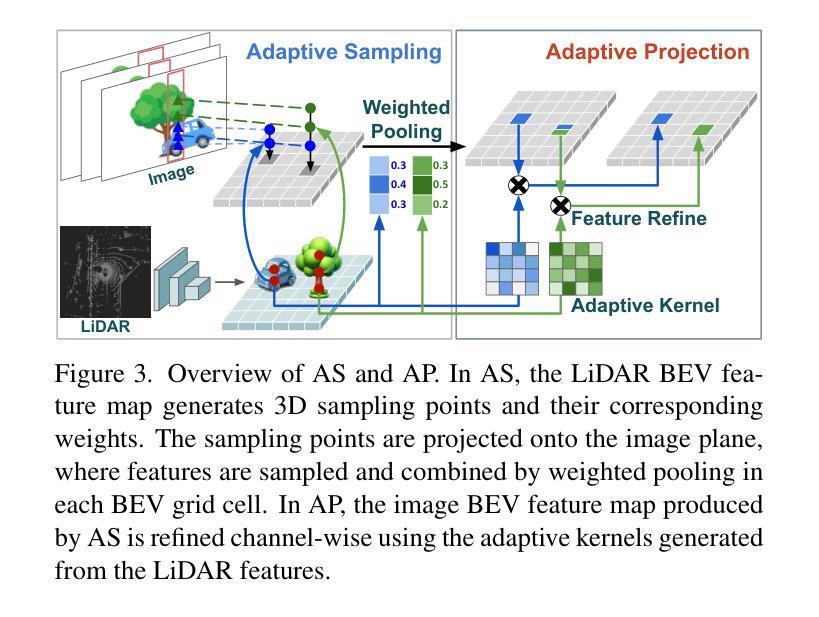
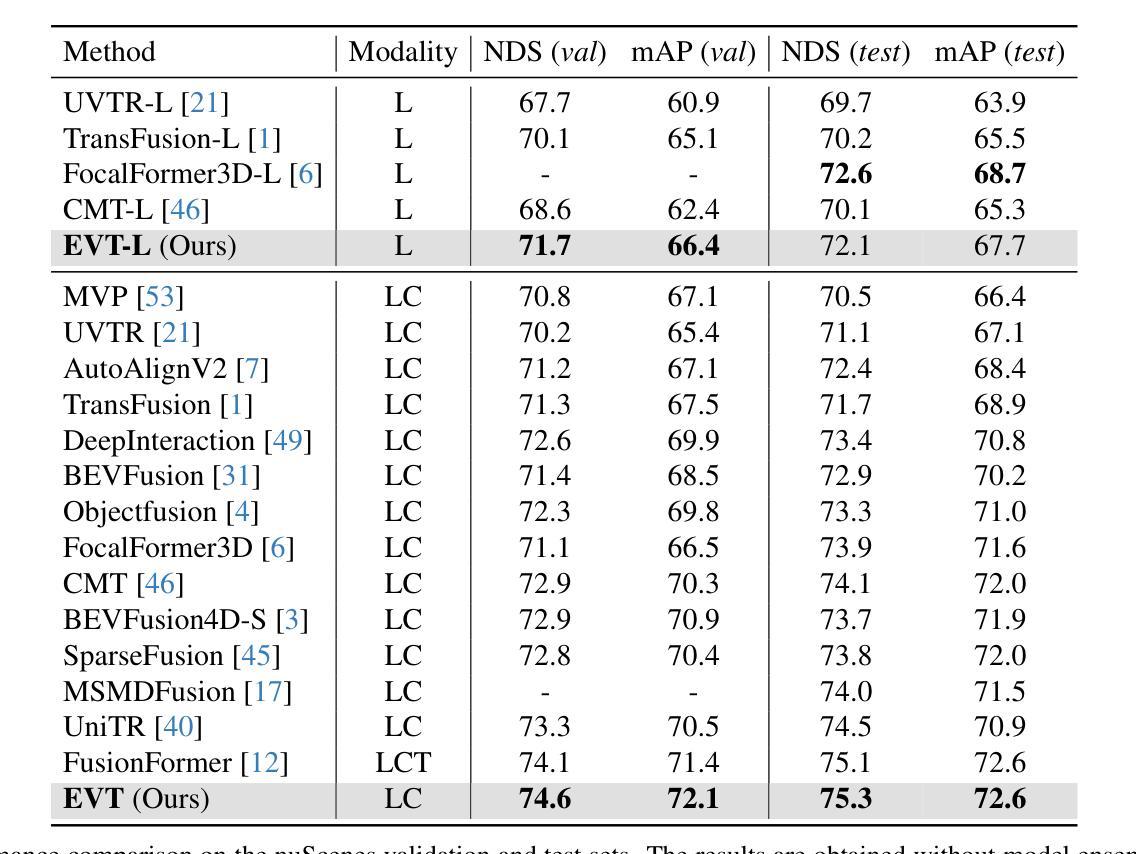
Multi-modal sensor fusion in Bird’s Eye View (BEV) representation has become the leading approach for 3D object detection. However, existing methods often rely on depth estimators or transformer encoders to transform image features into BEV space, which reduces robustness or introduces significant computational overhead. Moreover, the insufficient geometric guidance in view transformation results in ray-directional misalignments, limiting the effectiveness of BEV representations. To address these challenges, we propose Efficient View Transformation (EVT), a novel 3D object detection framework that constructs a well-structured BEV representation, improving both accuracy and efficiency. Our approach focuses on two key aspects. First, Adaptive Sampling and Adaptive Projection (ASAP), which utilizes LiDAR guidance to generate 3D sampling points and adaptive kernels, enables more effective transformation of image features into BEV space and a refined BEV representation. Second, an improved query-based detection framework, incorporating group-wise mixed query selection and geometry-aware cross-attention, effectively captures both the common properties and the geometric structure of objects in the transformer decoder. On the nuScenes test set, EVT achieves state-of-the-art performance of 75.3% NDS with real-time inference speed.
鸟瞰图(BEV)表示中的多模态传感器融合已成为3D目标检测的主流方法。然而,现有方法通常依赖于深度估计器或变压器编码器将图像特征转换为BEV空间,这降低了鲁棒性或引入了巨大的计算开销。此外,视图变换中几何指导的不足导致射线方向错位,限制了BEV表示的有效性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Efficient View Transformation(EVT),这是一种新型3D目标检测框架,构建了结构良好的BEV表示,提高了准确性和效率。我们的方法侧重于两个方面。首先,自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP)利用激光雷达指导生成3D采样点和自适应内核,实现了更有效的图像特征到BEV空间的转换和更精细的BEV表示。其次,改进的基于查询的检测框架,结合分组混合查询选择和几何感知交叉注意力,有效地捕获了目标的一般属性和几何结构在变压器解码器中的表现。在nuScenes测试集上,EVT达到了最先进的性能,实时推理速度为75.3%NDS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个高效、准确的三维物体检测框架Efficient View Transformation(EVT),它构建了一个结构良好的鸟瞰图(BEV)表示。该框架通过自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP)以及改进的基于查询的检测框架,解决了现有方法在转换图像特征到BEV空间时的不足,实现了图像特征更有效的转换和更精细的BEV表示。在nuScenes测试集上,EVT实现了具有实时推理速度的最优性能,达到NDS分数为75.3%。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态传感器融合在鸟瞰图(BEV)表示中的方法在三维物体检测中处于领先地位。然而,现有的方法依赖深度估计器或变换编码器将图像特征转换为BEV空间,这降低了稳健性或增加了计算开销。
- 现有方法的几何指导不足导致射线方向的误对齐,限制了BEV表示的有效性。
- 本文提出的Efficient View Transformation(EVT)框架通过两个关键方面解决了这些挑战:自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP),利用激光雷达指导生成三维采样点和自适应核,更有效地将图像特征转换为BEV空间;改进的基于查询的检测框架,结合分组混合查询选择和几何感知交叉注意力,有效地捕捉了物体的共同属性和几何结构。
点此查看论文截图