⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
From Enhancement to Understanding: Build a Generalized Bridge for Low-light Vision via Semantically Consistent Unsupervised Fine-tuning
Authors:Sen Wang, Shao Zeng, Tianjun Gu, Zhizhong Zhang, Ruixin Zhang, Shouhong Ding, Jingyun Zhang, Jun Wang, Xin Tan, Yuan Xie, Lizhuang Ma
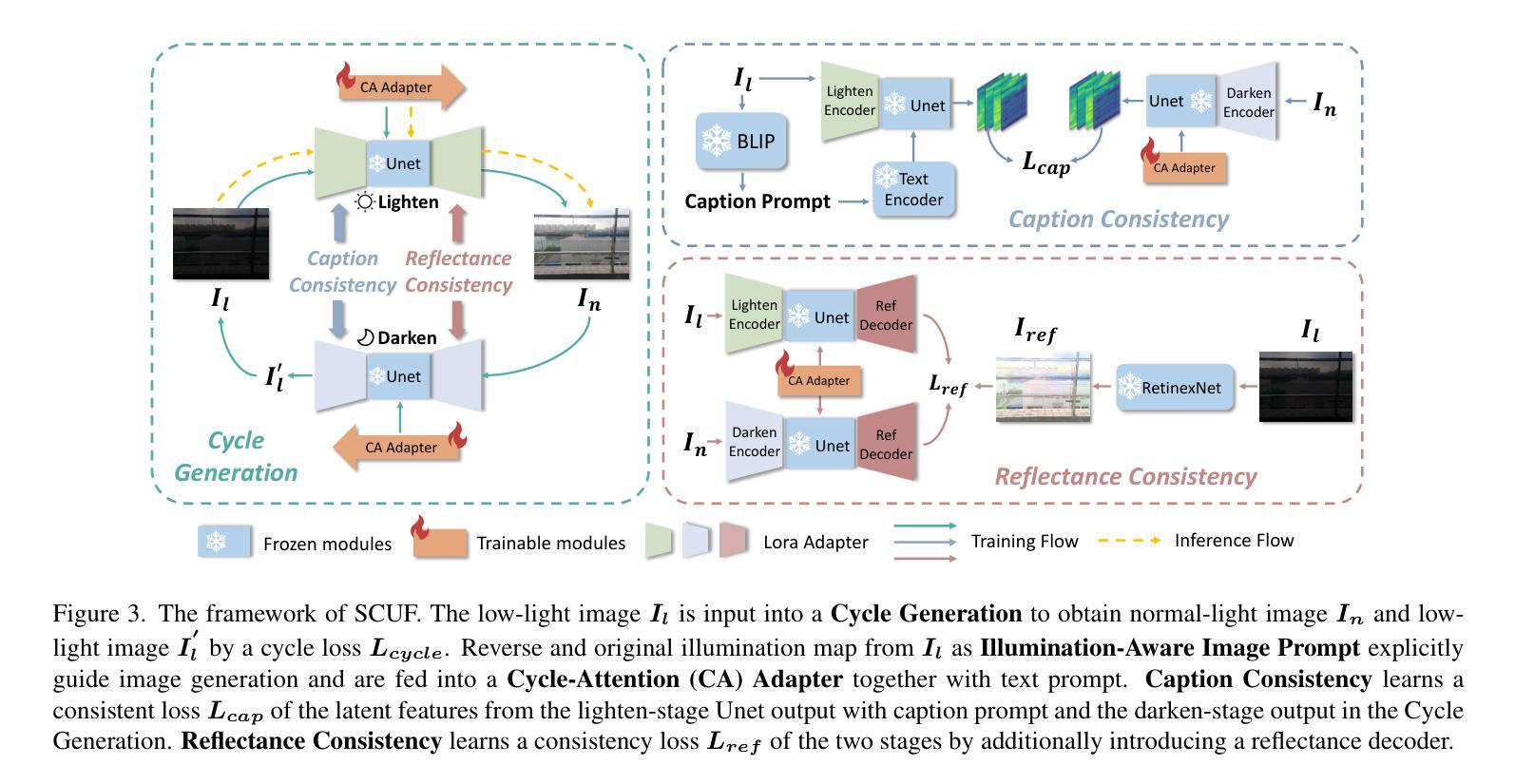
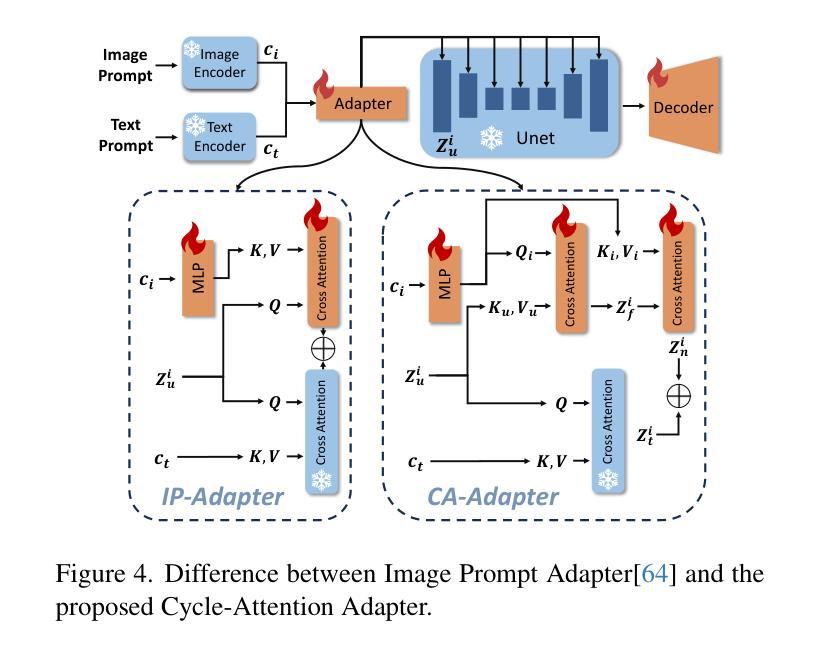
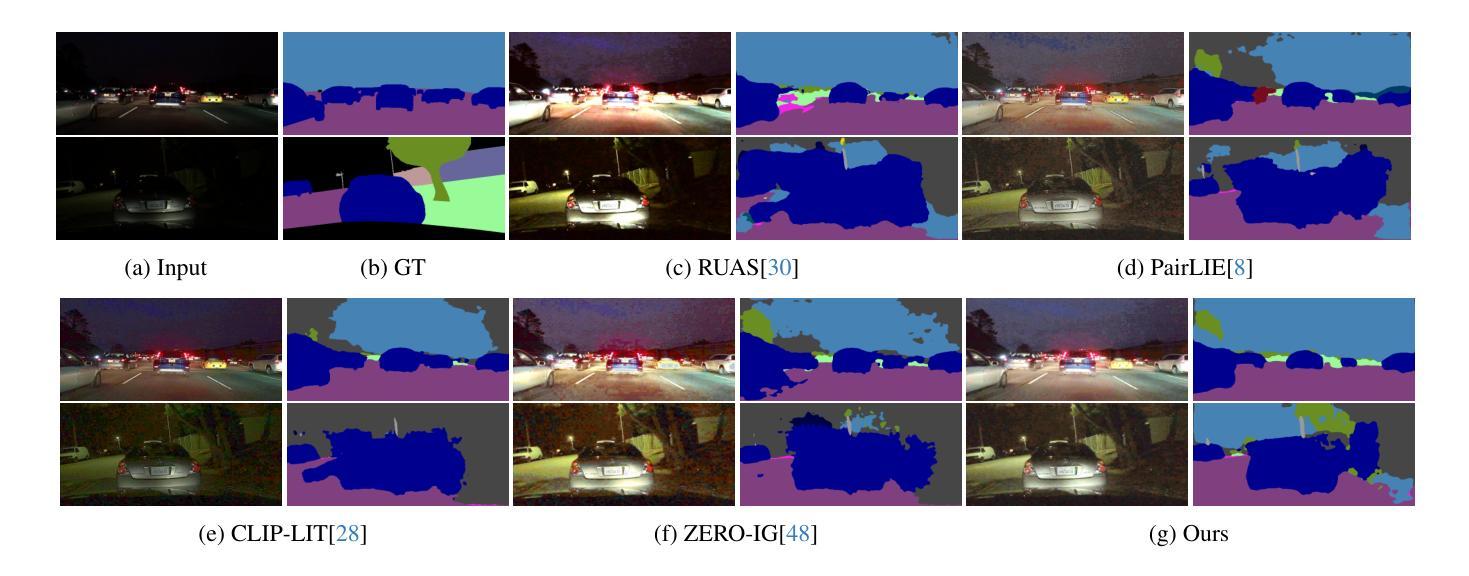
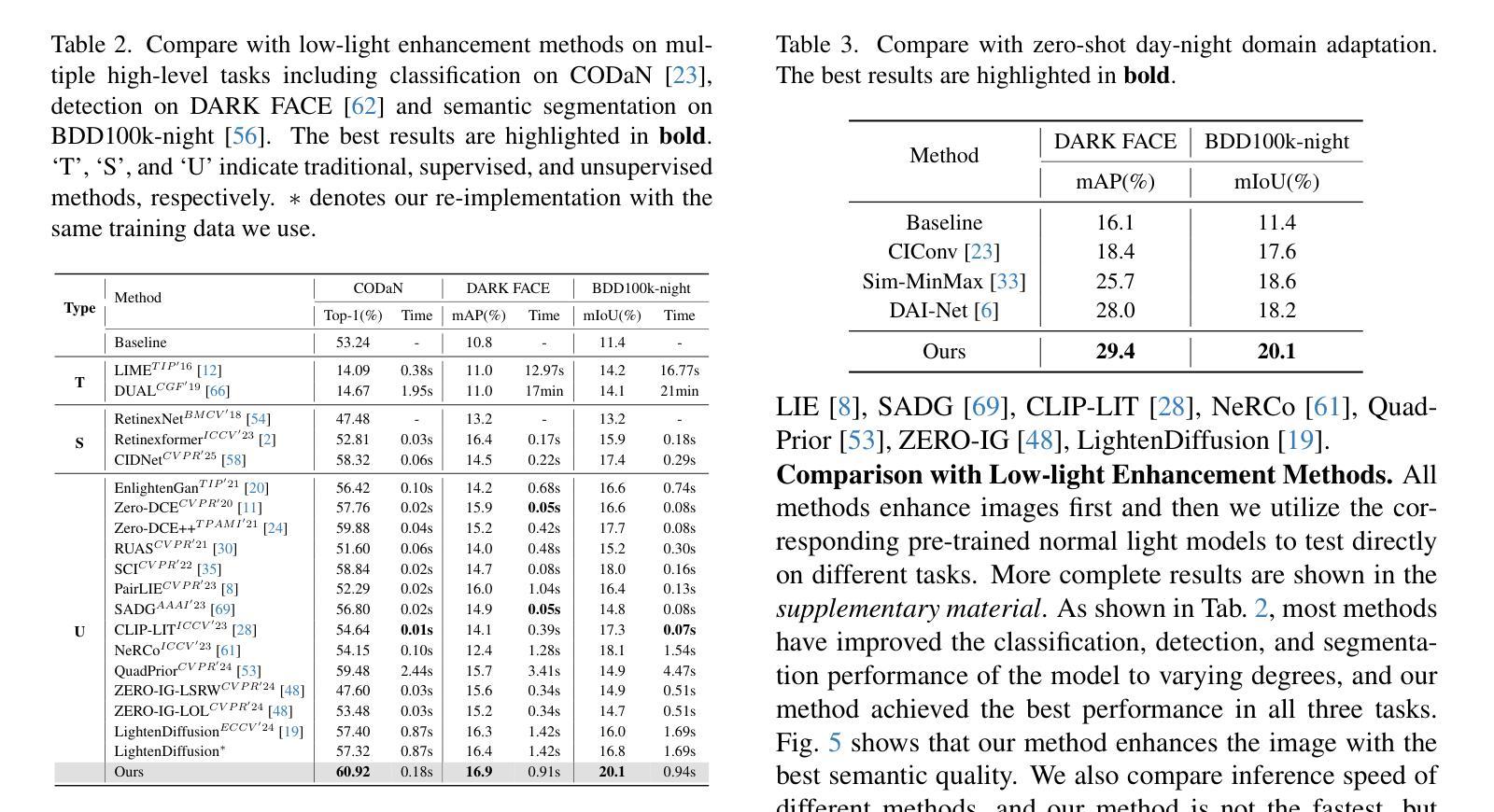
Low-level enhancement and high-level visual understanding in low-light vision have traditionally been treated separately. Low-light enhancement improves image quality for downstream tasks, but existing methods rely on physical or geometric priors, limiting generalization. Evaluation mainly focuses on visual quality rather than downstream performance. Low-light visual understanding, constrained by scarce labeled data, primarily uses task-specific domain adaptation, which lacks scalability. To address these challenges, we build a generalized bridge between low-light enhancement and low-light understanding, which we term Generalized Enhancement For Understanding (GEFU). This paradigm improves both generalization and scalability. To address the diverse causes of low-light degradation, we leverage pretrained generative diffusion models to optimize images, achieving zero-shot generalization performance. Building on this, we propose Semantically Consistent Unsupervised Fine-tuning (SCUF). Specifically, to overcome text prompt limitations, we introduce an illumination-aware image prompt to explicitly guide image generation and propose a cycle-attention adapter to maximize its semantic potential. To mitigate semantic degradation in unsupervised training, we propose caption and reflectance consistency to learn high-level semantics and image-level spatial semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in traditional image quality and GEFU tasks including classification, detection, and semantic segmentation.
在低光环境下,低层次的图像增强和高层次的视觉理解传统上被视为两个独立处理的任务。低光增强旨在提高图像的下游任务性能,但现有的方法依赖于物理或几何先验知识,这限制了其泛化能力。评估主要集中在视觉质量上,而不是下游性能。由于标注数据的稀缺,低光视觉理解主要依赖于特定任务的域适应方法,这缺乏可扩展性。为了应对这些挑战,我们在低光增强和低光理解之间建立了一个通用的桥梁,我们称之为“广义增强理解(GEFU)”。这种范式提高了泛化能力和可扩展性。为了应对低光降质的多种原因,我们利用预训练的生成扩散模型来优化图像,实现零样本泛化性能。在此基础上,我们提出了语义一致的监督微调方法(SCUF)。具体来说,为了克服文本提示的局限性,我们引入了光照感知图像提示来明确指导图像生成,并提出了循环注意力适配器来最大化其语义潜力。为了缓解无监督训练中的语义退化问题,我们提出了标题和反射一致性来学习高级语义和图像级别的空间语义。大量实验表明,我们提出的方法在图像质量和GEFU任务(包括分类、检测和语义分割)上的表现均优于当前最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary:
传统上,低光环境下的图像增强与视觉理解是分开处理的。低光增强旨在提高图像质量以便后续任务,但现有方法依赖于物理或几何先验,限制了其泛化能力。评价主要关注视觉质量而非后续任务性能。而低光视觉理解受限于稀缺的标签数据,主要使用任务特定的域适应方法,缺乏可扩展性。为应对这些挑战,我们建立了一座连接低光增强与理解的桥梁——我们称之为通用增强理解(GEFU)范式,以提高泛化能力和可扩展性。为解决低光降质的多种原因,我们利用预训练的生成扩散模型优化图像,实现零样本泛化性能。在此基础上,我们提出了语义一致的无监督微调(SCUF)。为克服文本提示的局限性,我们引入了光照感知图像提示来明确指导图像生成,并提出循环注意力适配器来最大化其语义潜力。为减轻无监督训练中的语义退化问题,我们提出标题和反射一致性来学习高级语义和图像级空间语义。实验证明,我们的方法在图像质量及包括分类、检测和语义分割的GEFU任务上均优于当前先进方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 传统上,低光环境下的图像增强与视觉理解是分开处理的,存在泛化性和数据瓶颈问题。
- 提出了一种新的范式——广义增强理解(GEFU),连接低光增强与理解,提高泛化性和可扩展性。
- 利用预训练的生成扩散模型优化图像,实现零样本泛化性能。
- 引入光照感知图像提示和循环注意力适配器,以克服文本提示的局限性并最大化语义潜力。
- 提出语义一致的无监督微调(SCUF)方法,结合标题和反射一致性,学习高级和图像级空间语义。
- 实验证明,该方法在图像质量和多种任务(包括分类、检测和语义分割)上均表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


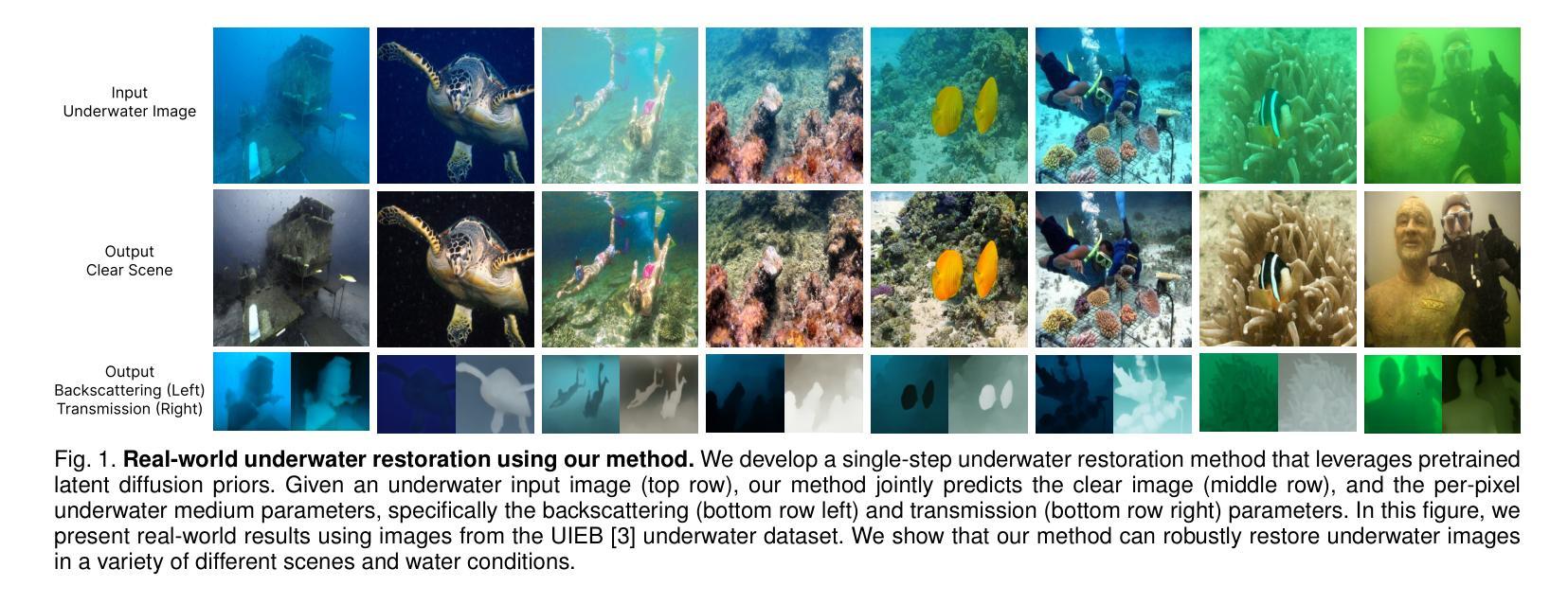
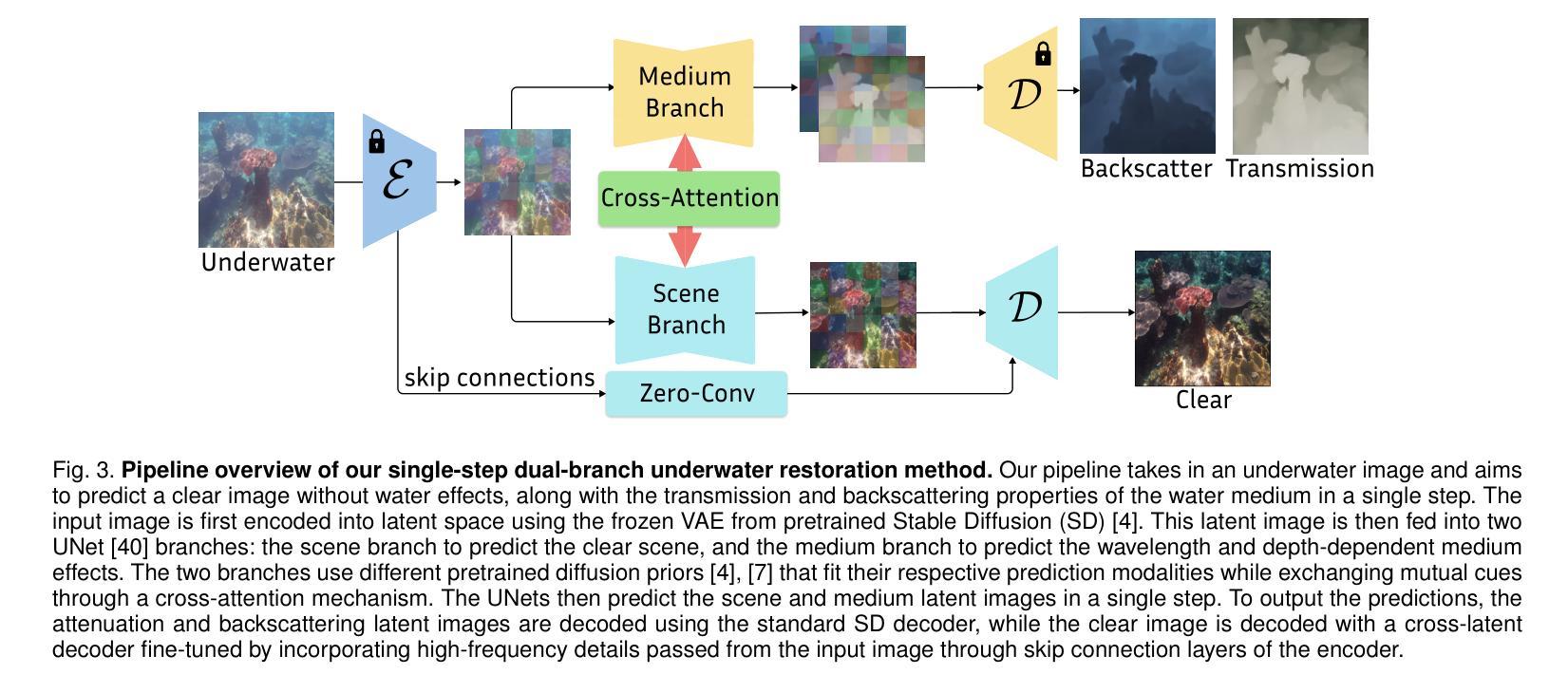
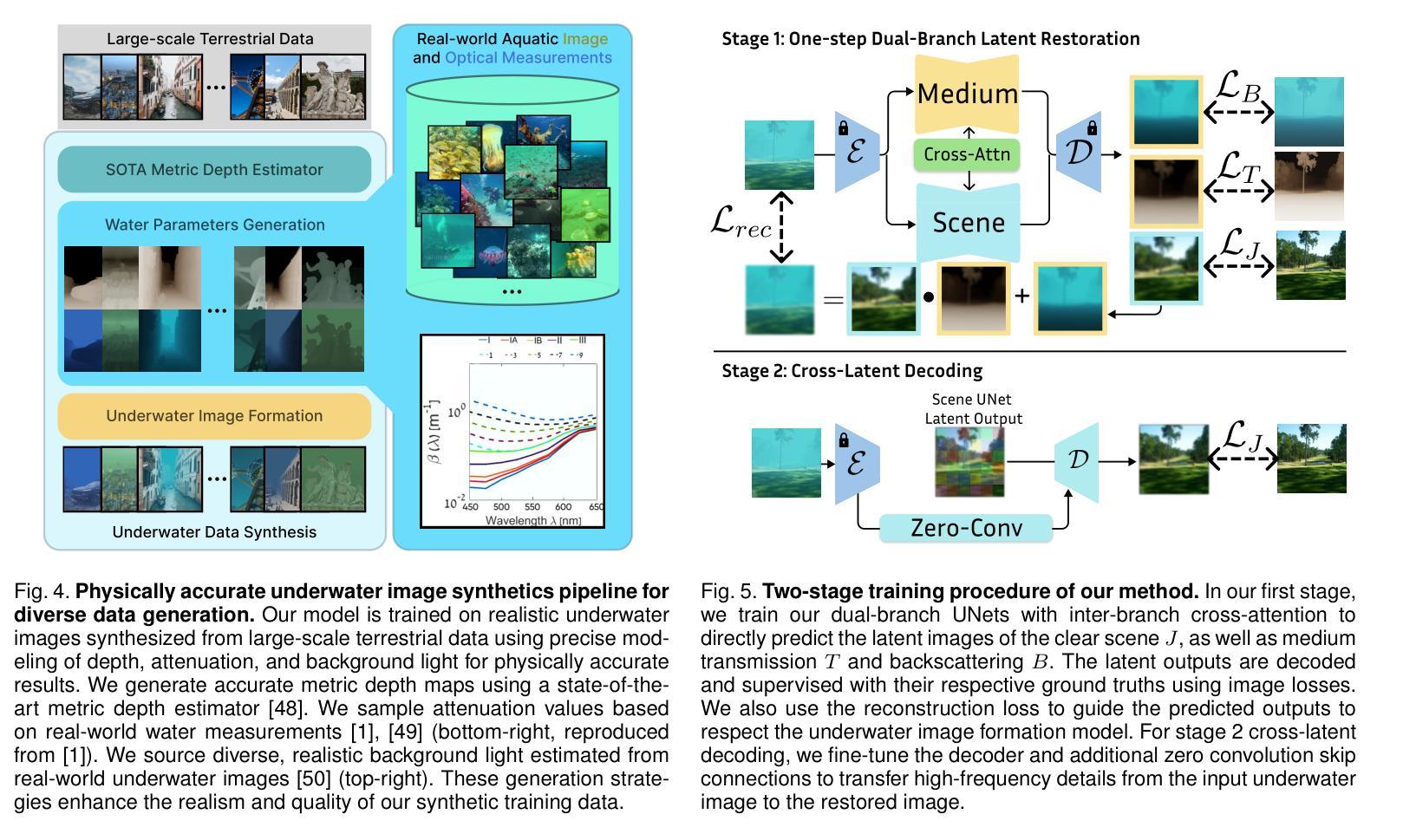
Single-Step Latent Diffusion for Underwater Image Restoration
Authors:Jiayi Wu, Tianfu Wang, Md Abu Bakr Siddique, Md Jahidul Islam, Cornelia Fermuller, Yiannis Aloimonos, Christopher A. Metzler
Underwater image restoration algorithms seek to restore the color, contrast, and appearance of a scene that is imaged underwater. They are a critical tool in applications ranging from marine ecology and aquaculture to underwater construction and archaeology. While existing pixel-domain diffusion-based image restoration approaches are effective at restoring simple scenes with limited depth variation, they are computationally intensive and often generate unrealistic artifacts when applied to scenes with complex geometry and significant depth variation. In this work we overcome these limitations by combining a novel network architecture (SLURPP) with an accurate synthetic data generation pipeline. SLURPP combines pretrained latent diffusion models – which encode strong priors on the geometry and depth of scenes – with an explicit scene decomposition – which allows one to model and account for the effects of light attenuation and backscattering. To train SLURPP we design a physics-based underwater image synthesis pipeline that applies varied and realistic underwater degradation effects to existing terrestrial image datasets. This approach enables the generation of diverse training data with dense medium/degradation annotations. We evaluate our method extensively on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Notably, SLURPP is over 200X faster than existing diffusion-based methods while offering ~ 3 dB improvement in PSNR on synthetic benchmarks. It also offers compelling qualitative improvements on real-world data. Project website https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/.
水下图像恢复算法旨在恢复水下场景的色调、对比度和外观。它们在海洋生态、水产养殖、水下建筑和考古等应用中都是关键工具。虽然现有的像素域扩散图像恢复方法在恢复深度变化有限的简单场景方面非常有效,但它们在处理具有复杂几何和显著深度变化的场景时计算量大,并且经常产生不现实的伪影。在这项工作中,我们通过结合新型网络架构(SLURPP)与精确合成数据生成管道来克服这些限制。SLURPP结合了预训练的潜在扩散模型(对场景的几何和深度具有强烈的先验信息)和明确的场景分解(允许对光的衰减和后向散射进行建模和补偿)。为了训练SLURPP,我们设计了一个基于物理的水下图像合成管道,该管道对现有的陆地图像数据集应用了多样化和现实的水下退化效果。这种方法能够生成具有密集介质/退化注释的多样化训练数据。我们在合成和实际基准测试上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估,并展示了其卓越的性能。值得注意的是,SLURPP的速度是现有扩散方法的逾两百倍,同时在合成基准上提供约提高PSNR达约等于减少到百分之零点五虚比重的保真度的优势。它在实际数据上还拥有引人注目的定性改进。项目网站:[https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了水下图像恢复算法的重要性及其应用场景,如海洋生态、水产养殖业、水下建设和考古等。针对现有像素域扩散型图像恢复方法在复杂场景和显著深度变化方面的局限性,本文提出了一种新型网络架构SLURPP和精确合成数据生成管道的结合。SLURPP结合了预训练的潜在扩散模型和对场景进行明确分解的方法,以模拟和解释光线衰减和背散射的影响。本文还设计了一个基于物理的水下图像合成管道来训练SLURPP,通过对现有地面图像数据集应用各种现实的水下退化效应,生成具有密集介质/退化注释的多样化训练数据。在合成和真实世界基准测试上,该方法均表现出卓越的性能,尤其是速度比现有扩散方法快200倍以上,同时在合成基准测试上提高了约3dB的PSNR。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像恢复算法在多个领域有广泛应用,如海洋生态、水产养殖业等。
- 现有像素域扩散型图像恢复方法在复杂场景和显著深度变化方面存在局限性。
- 本文提出了新型网络架构SLURPP,结合了预训练的潜在扩散模型和场景明确分解方法。
- SLURPP通过结合物理模型,能够模拟和解释光线衰减和背散射的影响。
- 设计了一个基于物理的水下图像合成管道来训练SLURPP,生成具有密集介质/退化注释的多样化训练数据。
- SLURPP在合成和真实世界基准测试上都表现出卓越性能。
- SLURPP相比现有扩散方法,速度更快,同时在性能上也有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图



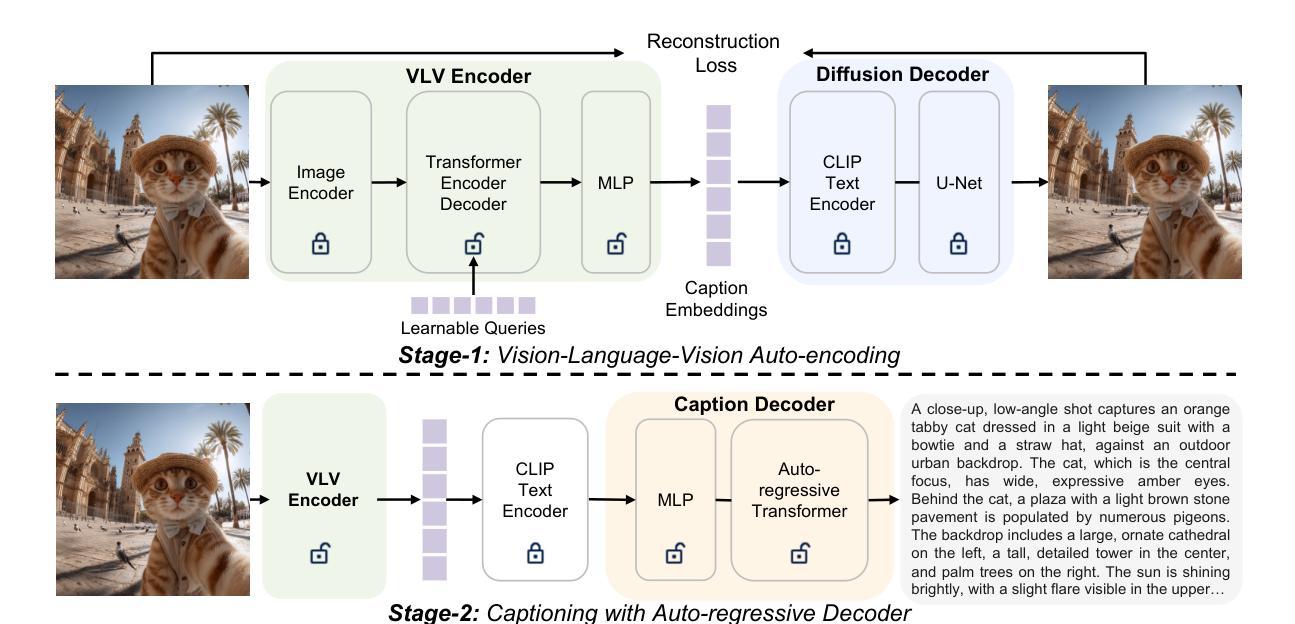
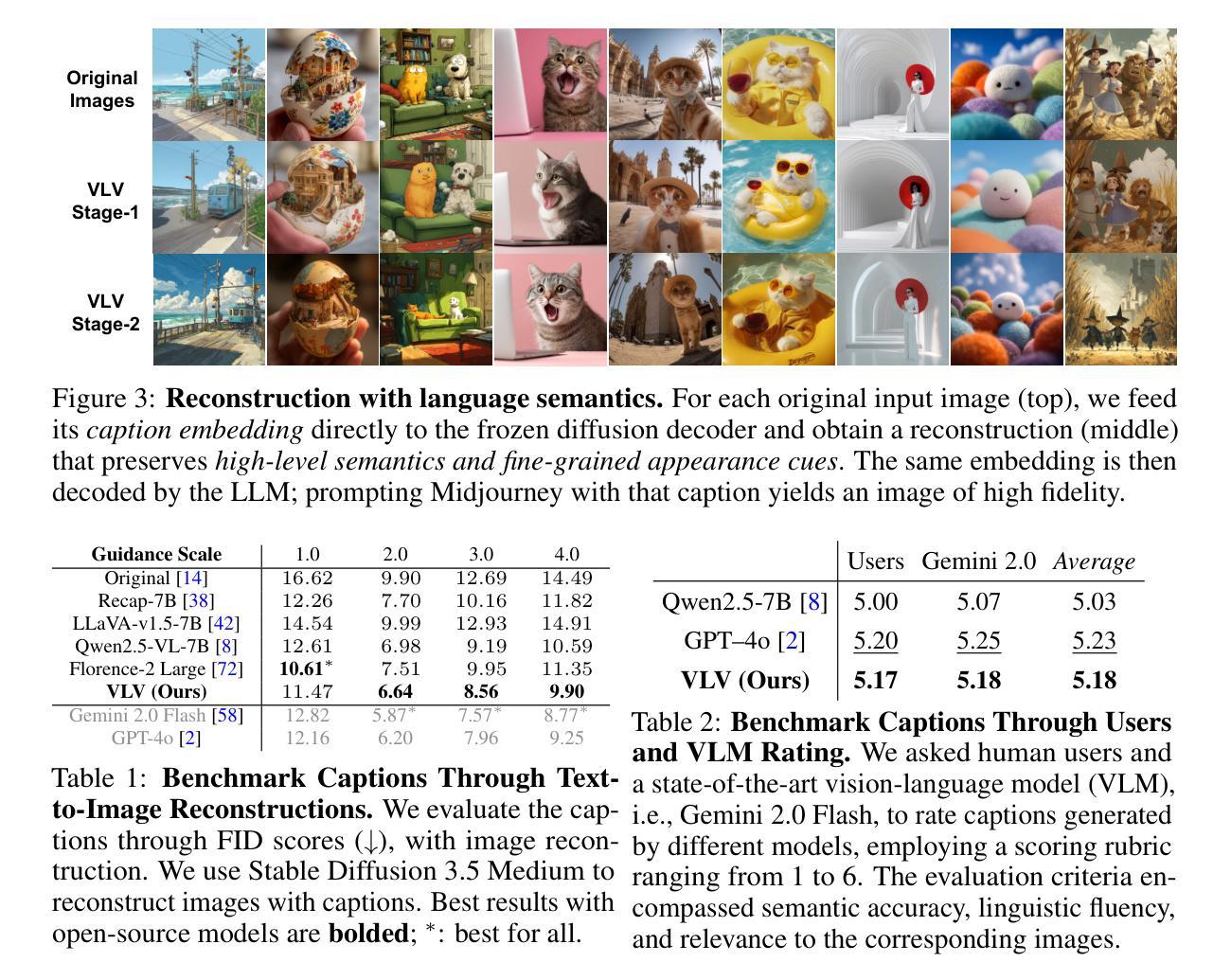
Vision-Language-Vision Auto-Encoder: Scalable Knowledge Distillation from Diffusion Models
Authors:Tiezheng Zhang, Yitong Li, Yu-cheng Chou, Jieneng Chen, Alan Yuille, Chen Wei, Junfei Xiao
Building state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs) with strong captioning capabilities typically necessitates training on billions of high-quality image-text pairs, requiring millions of GPU hours. This paper introduces the Vision-Language-Vision (VLV) auto-encoder framework, which strategically leverages key pretrained components: a vision encoder, the decoder of a Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion model, and subsequently, a Large Language Model (LLM). Specifically, we establish an information bottleneck by regularizing the language representation space, achieved through freezing the pretrained T2I diffusion decoder. Our VLV pipeline effectively distills knowledge from the text-conditioned diffusion model using continuous embeddings, demonstrating comprehensive semantic understanding via high-quality reconstructions. Furthermore, by fine-tuning a pretrained LLM to decode the intermediate language representations into detailed descriptions, we construct a state-of-the-art (SoTA) captioner comparable to leading models like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash. Our method demonstrates exceptional cost-efficiency and significantly reduces data requirements; by primarily utilizing single-modal images for training and maximizing the utility of existing pretrained models (image encoder, T2I diffusion model, and LLM), it circumvents the need for massive paired image-text datasets, keeping the total training expenditure under $1,000 USD.
构建具有强大描述功能的最新视觉语言模型(VLMs)通常需要训练数十亿高质量图像文本对,并需要数百万GPU小时。本文介绍了视觉语言视觉(VLV)自动编码器框架,该框架战略性地利用了关键预训练组件:视觉编码器、文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的解码器,以及随后的大型语言模型(LLM)。具体来说,我们通过正则化语言表示空间来建立信息瓶颈,这是通过冻结预训练的T2I扩散解码器来实现的。我们的VLV管道有效地从文本条件扩散模型中蒸馏知识,使用连续嵌入来展示高质量重建的综合语义理解。此外,我们通过微调预训练的大型语言模型来解码中间语言表示以生成详细描述,从而构建了一个与GPT-4o和Gemini 2.0 Flash等领先模型相当的最先进(SoTA)描述器。我们的方法展示了出色的成本效益,并大大降低了数据要求;它主要通过使用单模态图像进行训练并最大限度地利用现有预训练模型(图像编码器、T2I扩散模型和LLM),从而避免了需要大量配对图像文本数据集的需求,将总训练费用控制在1000美元以内。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://lambert-x.github.io/Vision-Language-Vision/
Summary
本文提出了Vision-Language-Vision(VLV)自编码器框架,通过战略性地利用关键预训练组件,如视觉编码器、文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的解码器以及大型语言模型(LLM),实现了具有强大描述能力的视觉语言模型(VLM)。通过冻结预训练的T2I扩散解码器,建立信息瓶颈,并通过连续嵌入从文本条件扩散模型中蒸馏知识。该方法能够生成高质量重建,展现了全面的语义理解。通过微调预训练LLM以解码中间语言表示,构建了一个与GPT-4o和Gemini 2.0 Flash等领先模型相当的最先进(SoTA)描述器。该方法具有卓越的成本效益,显著降低了数据要求,主要利用单模态图像进行训练并最大化现有预训练模型(图像编码器、T2I扩散模型和LLM)的效用,无需大规模配对图像文本数据集,总培训费用低于1000美元。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Vision-Language-Vision(VLV)自编码器框架,融合了视觉编码器和文本到图像扩散模型的解码器。
- 通过建立信息瓶颈和冻结预训练的T2I扩散解码器,实现了高效知识蒸馏。
- 利用连续嵌入生成高质量重建,展现了全面的语义理解。
- 通过微调预训练的大型语言模型(LLM),构建了先进的描述能力,与现有领先模型相竞争。
- 方法具有卓越的成本效益,显著降低了数据要求。
- 主要利用单模态图像进行训练,最大化现有预训练模型的效用。
- 该方法无需大规模配对图像文本数据集,总培训费用低于1000美元。
点此查看论文截图

Lighting the Night with Generative Artificial Intelligence
Authors:Tingting Zhou, Feng Zhang, Haoyang Fu, Baoxiang Pan, Renhe Zhang, Feng Lu, Zhixin Yang
The visible light reflectance data from geostationary satellites is crucial for meteorological observations and plays an important role in weather monitoring and forecasting. However, due to the lack of visible light at night, it is impossible to conduct continuous all-day weather observations using visible light reflectance data. This study pioneers the use of generative diffusion models to address this limitation. Based on the multi-band thermal infrared brightness temperature data from the Advanced Geostationary Radiation Imager (AGRI) onboard the Fengyun-4B (FY4B) geostationary satellite, we developed a high-precision visible light reflectance generative model, called Reflectance Diffusion (RefDiff), which enables 0.47\mu\mathrm{m}, 0.65\mu\mathrm{m}, and 0.825~\mu\mathrm{m} bands visible light reflectance generation at night. Compared to the classical models, RefDiff not only significantly improves accuracy through ensemble averaging but also provides uncertainty estimation. Specifically, the SSIM index of RefDiff can reach 0.90, with particularly significant improvements in areas with complex cloud structures and thick clouds. The model’s nighttime generation capability was validated using VIIRS nighttime product, demonstrating comparable performance to its daytime counterpart. In summary, this research has made substantial progress in the ability to generate visible light reflectance at night, with the potential to expand the application of nighttime visible light data.
地球静止卫星的可见光反射数据对于气象观测至关重要,并在天气监测和预报中扮演重要角色。然而,由于夜间缺乏可见光,无法连续进行全天候天气观测使用可见光反射数据。本研究率先使用生成式扩散模型来解决这一限制。基于风云四号B(FY4B)地球静止卫星上的高级地球静止辐射成像仪(AGRI)的多波段热红外亮度温度数据,我们开发了一种高精度可见光反射生成模型,名为Reflectance Diffusion(RefDiff),该模型能够在夜间生成0.47μm、0.65μm和0.825μm波段的可见光反射。与传统的模型相比,RefDiff不仅通过集合平均显著提高精度,还提供不确定性估计。具体来说,RefDiff的SSIM指数可达到0.90,在具有复杂云结构和厚云区域表现出特别显著的改进。该模型的夜间生成能力已使用VIIRS夜间产品进行了验证,表现出与日间产品相当的性能。总之,这项研究在夜间生成可见光反射方面取得了实质性进展,有可能扩大夜间可见光数据的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Title corrected (Lightning to Lighting); terminology updated (retrieval to generative)
Summary
基于地球静止卫星的可见光反射数据对于气象观测至关重要,但夜间缺乏可见光导致无法全天候持续观测。本研究创新性地使用生成扩散模型来解决这一问题,利用风云四号B卫星上的高级地球静止辐射成像仪的多波段热红外亮度温度数据,开发出高精度可见光反射生成模型——Reflectance Diffusion(RefDiff)。该模型能够在夜间生成0.47μm、0.65μm和0.825μm波段的可见光反射,相比传统模型,不仅通过集成平均显著提高精度,还提供不确定性估计。RefDiff的SSIM指数可达0.90,在复杂云结构和厚云区域表现尤其显著。该模型夜间生成能力已使用VIIRS夜间产品验证,表现出与日间相当的性能。总之,该研究在夜间生成可见光反射方面取得显著进展,有望扩大夜间可见光数据的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 可见光反射数据对于气象观测、天气监测和预报至关重要。
- 夜间缺乏可见光导致无法全天候进行天气观测。
- 研究使用生成扩散模型解决这一问题。
- 开发的高精度可见光反射生成模型RefDiff,基于多波段热红外亮度温度数据。
- RefDiff能在夜间生成特定波段的可见光反射。
- RefDiff相比传统模型有更高的精度和不确定性估计能力。
点此查看论文截图

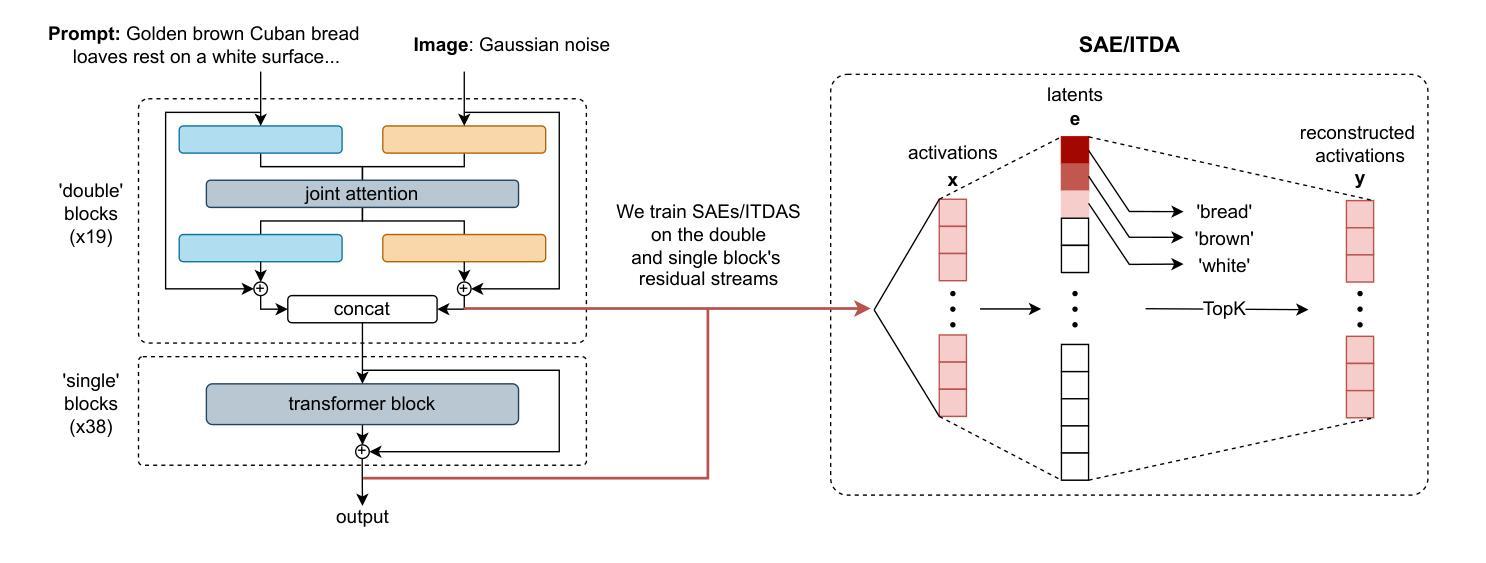
Interpreting Large Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Dictionary Learning
Authors:Stepan Shabalin, Ayush Panda, Dmitrii Kharlapenko, Abdur Raheem Ali, Yixiong Hao, Arthur Conmy
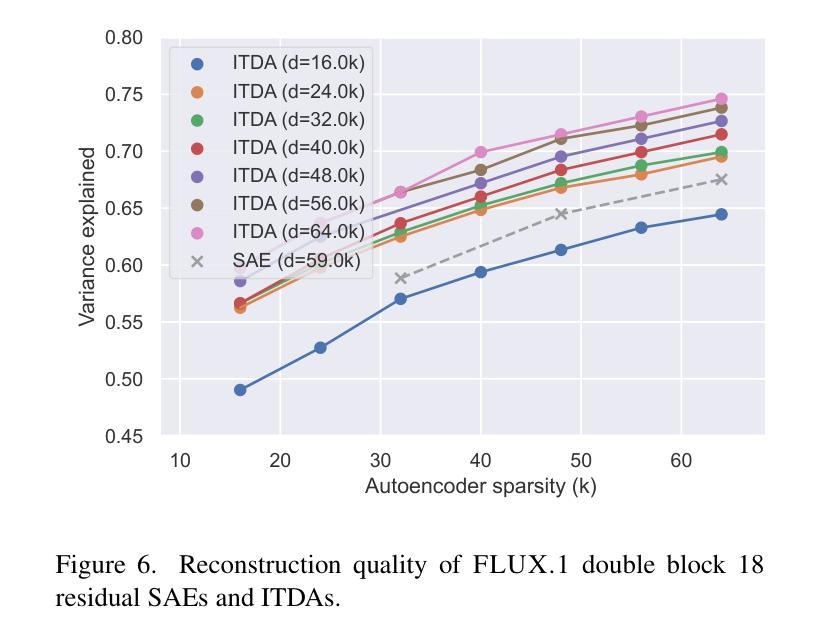
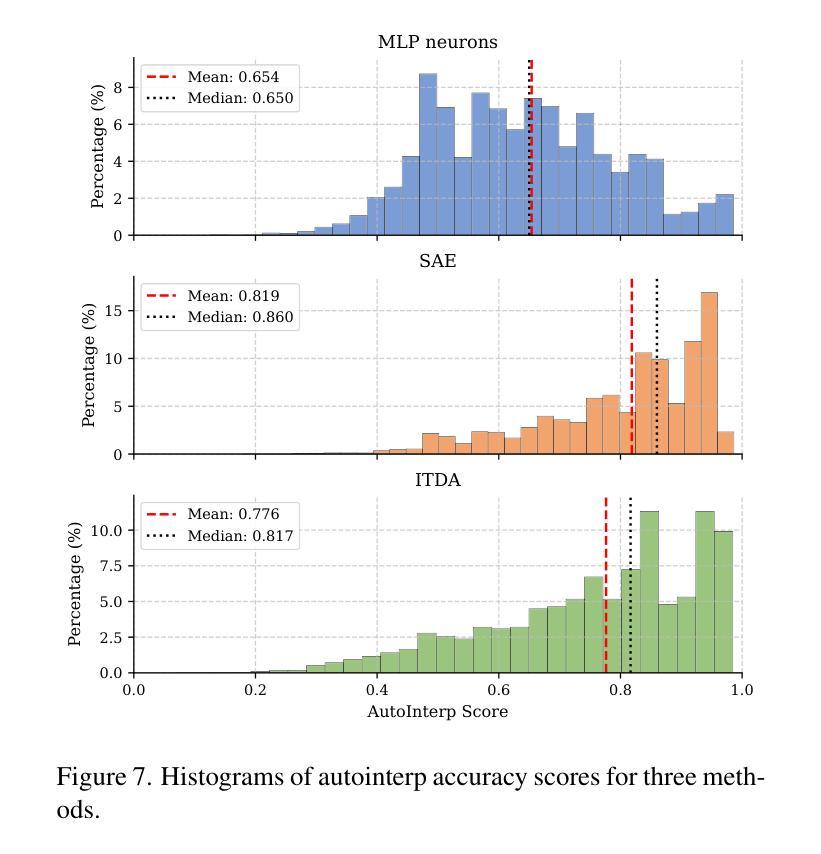
Sparse autoencoders are a promising new approach for decomposing language model activations for interpretation and control. They have been applied successfully to vision transformer image encoders and to small-scale diffusion models. Inference-Time Decomposition of Activations (ITDA) is a recently proposed variant of dictionary learning that takes the dictionary to be a set of data points from the activation distribution and reconstructs them with gradient pursuit. We apply Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) and ITDA to a large text-to-image diffusion model, Flux 1, and consider the interpretability of embeddings of both by introducing a visual automated interpretation pipeline. We find that SAEs accurately reconstruct residual stream embeddings and beat MLP neurons on interpretability. We are able to use SAE features to steer image generation through activation addition. We find that ITDA has comparable interpretability to SAEs.
稀疏自动编码器是一种很有前途的新方法,用于分解语言模型的激活,以进行解释和控制。它们已成功应用于视觉转换图像编码器和小规模扩散模型。推理时间活动分解(ITDA)是最近提出的词典学习变体,它将词典视为激活分布中的数据点集,并通过梯度追求进行重建。我们将稀疏自动编码器(SAE)和ITDA应用于大型文本到图像的扩散模型Flux 1,并通过引入视觉自动化解释管道来考虑两者的嵌入解释性。我们发现SAE能够准确重建残差流嵌入,在解释性方面优于MLP神经元。我们能够使用SAE特性通过激活添加来引导图像生成。我们发现ITDA的解释性与SAE相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 10 figures, Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision at CVPR 2025
Summary
稀疏自编码器是一种新兴的有前途的方法,用于分解语言模型的激活以实现解释和控制。它已成功应用于视觉转换器图像编码器和小型扩散模型。我们将其应用于大型文本到图像扩散模型Flux 1,并通过引入视觉自动化解释管道来考虑两者的嵌入解释性。研究发现,稀疏自编码器能准确重建残差流嵌入,在解释性方面优于多层感知机的神经元。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏自编码器(SAE)是一种新兴方法,用于分解语言模型的激活,以提高解释性和控制性。
- ITDA是字典学习的一种新变体,使用数据点重建激活分布。
- SAEs能准确重建残差流嵌入,且在解释性方面优于MLP神经元。
- ITDA在解释性与SAE特征上具有相当性。
- SAE特征可用于通过激活添加来引导图像生成。
- 在大型文本到图像扩散模型Flux 1中应用SAE和ITDA,考虑了它们的嵌入解释性。
点此查看论文截图

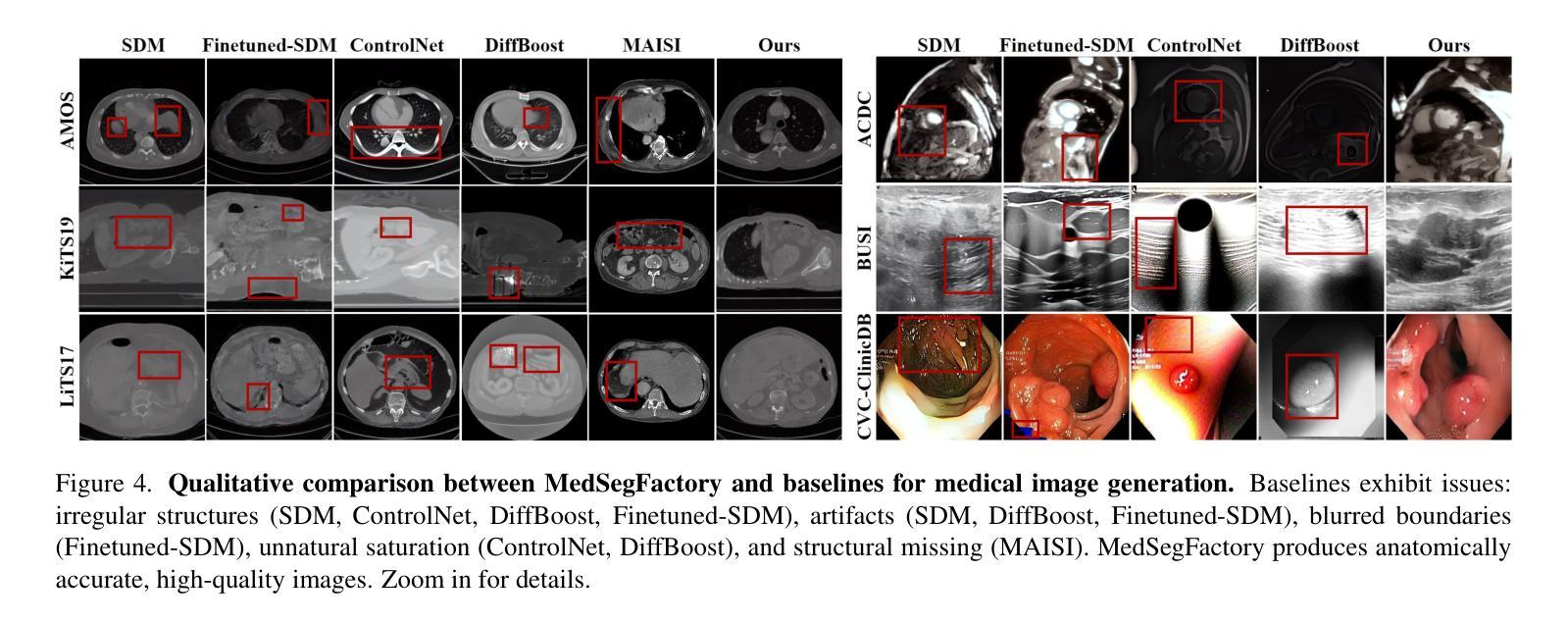
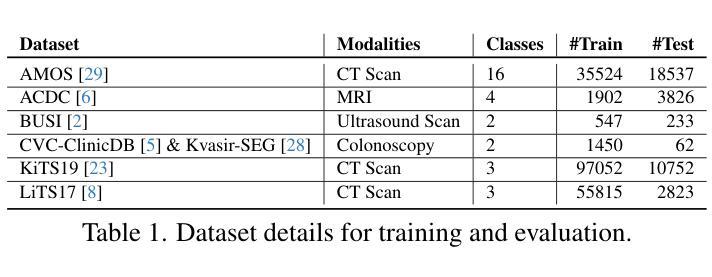
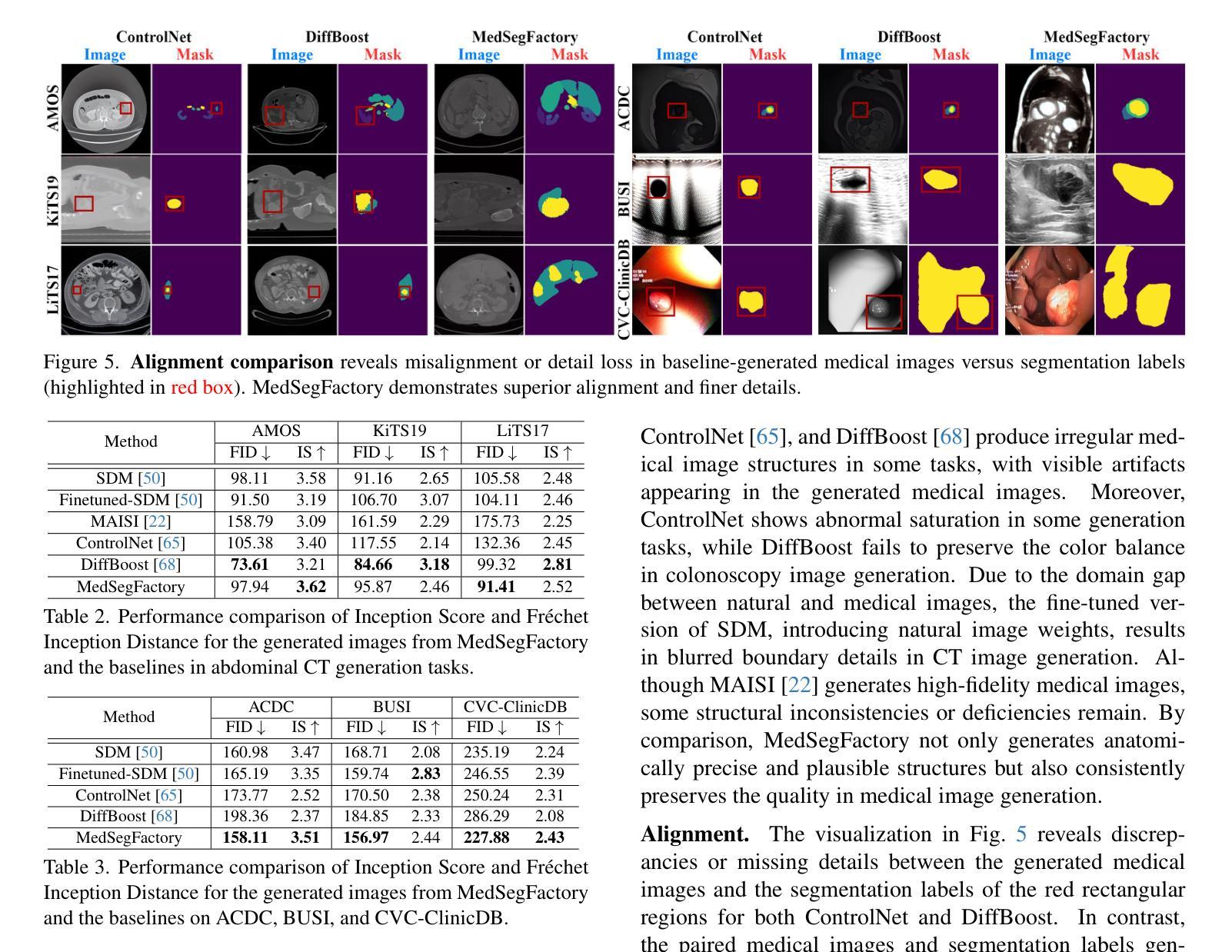
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
Authors:Jiawei Mao, Yuhan Wang, Yucheng Tang, Daguang Xu, Kang Wang, Yang Yang, Zongwei Zhou, Yuyin Zhou
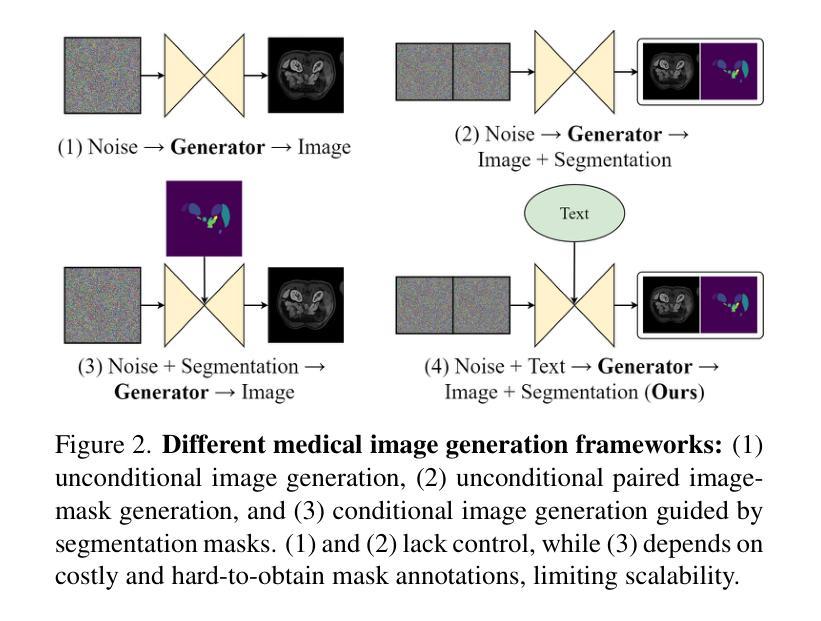
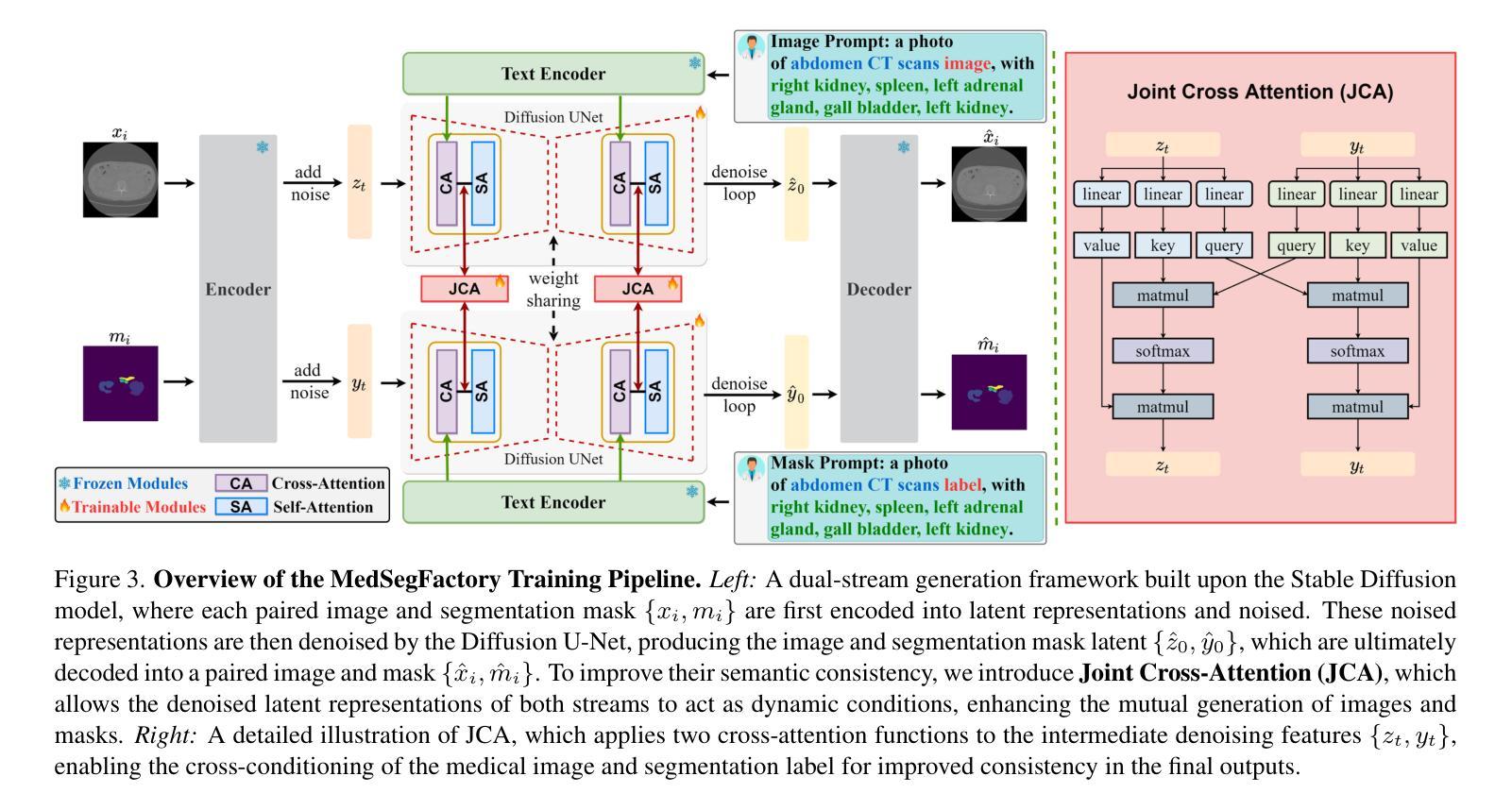
This paper presents MedSegFactory, a versatile medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across modalities and tasks. It aims to serve as an unlimited data repository, supplying image-mask pairs to enhance existing segmentation tools. The core of MedSegFactory is a dual-stream diffusion model, where one stream synthesizes medical images and the other generates corresponding segmentation masks. To ensure precise alignment between image-mask pairs, we introduce Joint Cross-Attention (JCA), enabling a collaborative denoising paradigm by dynamic cross-conditioning between streams. This bidirectional interaction allows both representations to guide each other’s generation, enhancing consistency between generated pairs. MedSegFactory unlocks on-demand generation of paired medical images and segmentation masks through user-defined prompts that specify the target labels, imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and pathological conditions, facilitating scalable and high-quality data generation. This new paradigm of medical image synthesis enables seamless integration into diverse medical imaging workflows, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments show that MedSegFactory generates data of superior quality and usability, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints.
本文介绍了MedSegFactory,这是一个通用的医学合成框架,能够生成跨模态和任务的高质量配对医学图像和分割掩膜。它的目标是作为一个无限的数据仓库,提供图像-掩膜对,以增强现有的分割工具。MedSegFactory的核心是一个双流扩散模型,其中一个流用于合成医学图像,另一个流用于生成相应的分割掩膜。为了确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐,我们引入了联合交叉注意(JCA)机制,通过流之间的动态交叉条件,实现协同去噪范式。这种双向交互允许两种表示形式相互引导生成,增强生成对之间的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义的提示(指定目标标签、成像模式、解剖区域和病理状况)解锁按需生成的配对医学图像和分割掩膜,促进可扩展和高质量的数据生成。这种新的医学图像合成范式能够无缝地融入各种医学成像工作流程,提高效率和准确性。大量实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据具有卓越的质量和可用性,在二维和三维分割任务中达到了竞争或最先进的性能,同时解决了数据稀缺和监管约束的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, The project page can be accessed via https://jwmao1.github.io/MedSegFactory_web
Summary
MedSegFactory是一个通用医疗合成框架,能生成跨模态和任务的配对高质量医疗图像和分割掩膜。它旨在作为一个无限的数据仓库,为现有的分割工具提供图像-掩膜对以增强其性能。该框架的核心是双重流扩散模型,一个流负责合成医疗图像,另一个流生成相应的分割掩膜。通过引入联合交叉注意(JCA)机制,确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐。JCA实现了流之间的动态交叉条件,推动协同去噪模式。这种双向交互允许两个表示相互引导生成,增强生成配对的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义提示实现按需生成配对医疗图像和分割掩膜,提示可指定目标标签、成像模式、解剖区域和病理状况等。这一全新的医疗图像合成模式可无缝融入多样化的医疗成像工作流程,提高效率和准确性。实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据质量高、实用性强,在二维和三维分割任务上表现优异,解决了数据稀缺和监管约束问题。
Key Takeaways
- MedSegFactory是一个医疗合成框架,能生成高质量配对医疗图像和分割掩膜。
- 它作为一个无限数据仓库,为现有分割工具提供图像-掩膜对。
- 双重流扩散模型是框架的核心,包括图像合成流和分割掩膜生成流。
- 引入的联合交叉注意(JCA)机制确保图像和掩膜之间的精确对齐。
- 用户可以通过定义提示(如目标标签、成像模式等)实现按需生成图像和掩膜。
- MedSegFactory能提高医疗成像工作流程的效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

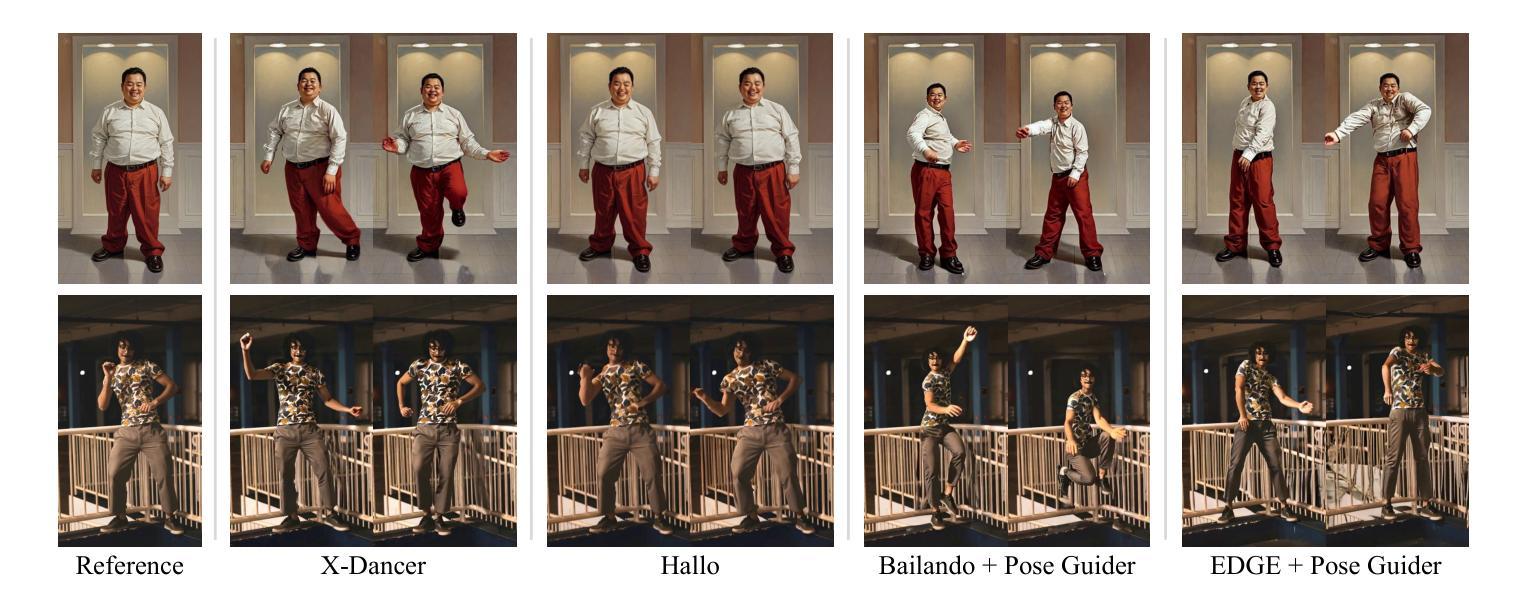
X-Dancer: Expressive Music to Human Dance Video Generation
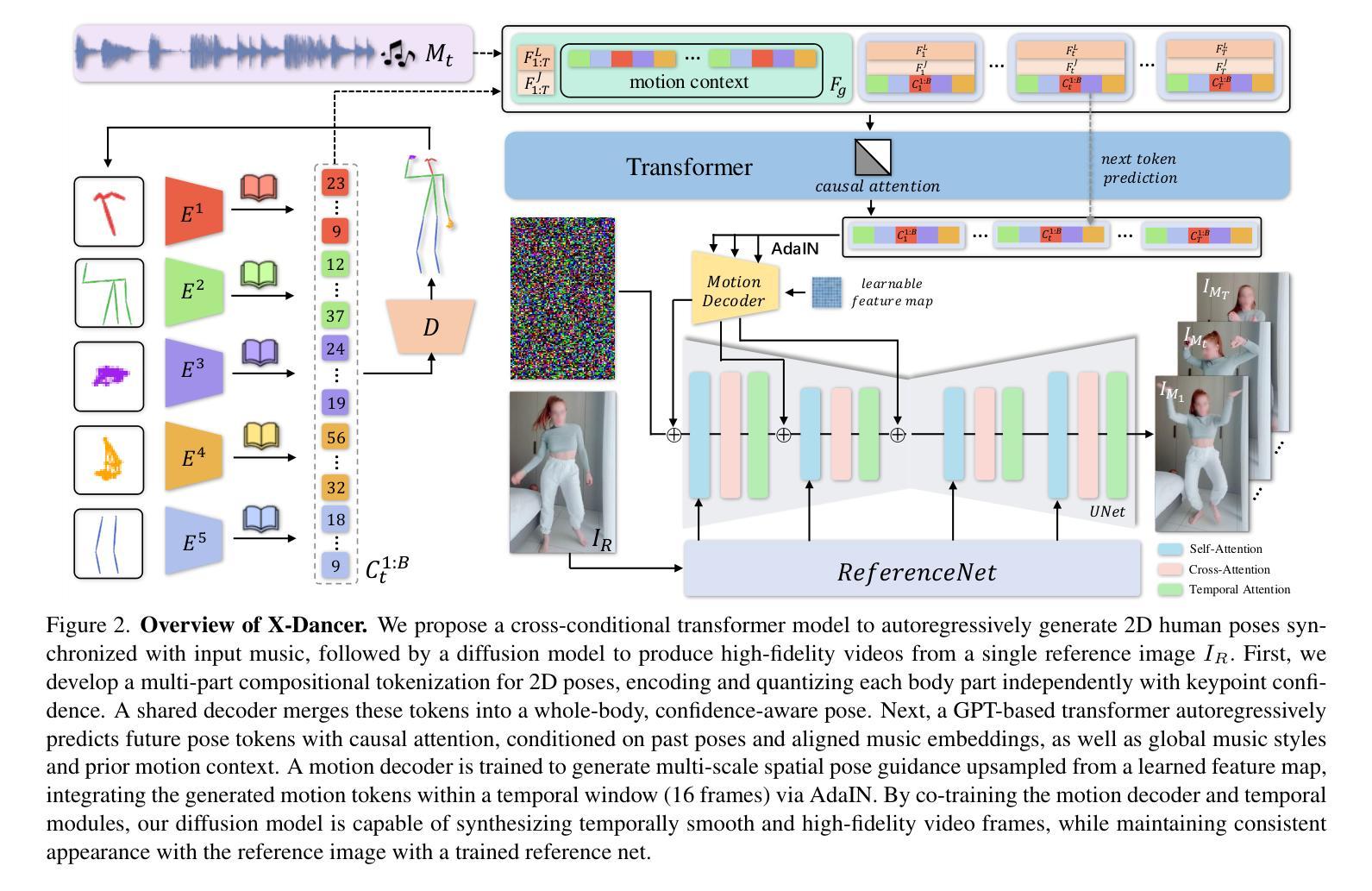
Authors:Zeyuan Chen, Hongyi Xu, Guoxian Song, You Xie, Chenxu Zhang, Xin Chen, Chao Wang, Di Chang, Linjie Luo
We present X-Dancer, a novel zero-shot music-driven image animation pipeline that creates diverse and long-range lifelike human dance videos from a single static image. As its core, we introduce a unified transformer-diffusion framework, featuring an autoregressive transformer model that synthesize extended and music-synchronized token sequences for 2D body, head and hands poses, which then guide a diffusion model to produce coherent and realistic dance video frames. Unlike traditional methods that primarily generate human motion in 3D, X-Dancer addresses data limitations and enhances scalability by modeling a wide spectrum of 2D dance motions, capturing their nuanced alignment with musical beats through readily available monocular videos. To achieve this, we first build a spatially compositional token representation from 2D human pose labels associated with keypoint confidences, encoding both large articulated body movements (e.g., upper and lower body) and fine-grained motions (e.g., head and hands). We then design a music-to-motion transformer model that autoregressively generates music-aligned dance pose token sequences, incorporating global attention to both musical style and prior motion context. Finally we leverage a diffusion backbone to animate the reference image with these synthesized pose tokens through AdaIN, forming a fully differentiable end-to-end framework. Experimental results demonstrate that X-Dancer is able to produce both diverse and characterized dance videos, substantially outperforming state-of-the-art methods in term of diversity, expressiveness and realism. Code and model will be available for research purposes.
我们介绍了X-Dancer,这是一种新型零样本音乐驱动图像动画管道,它可以从单个静态图像中创建多样且长程的逼真人类舞蹈视频。其核心是统一transformer扩散框架,它采用自回归transformer模型合成扩展的与音乐同步的令牌序列,用于二维身体、头部和手部姿势。然后这些序列引导扩散模型生成连贯且逼真的舞蹈视频帧。与传统的主要在3D中生成人类运动的方法不同,X-Dancer通过建模大量的二维舞蹈动作来解决数据限制并增强可扩展性,通过可获得的单目视频捕捉其与音乐节奏的微妙对齐。为实现这一点,我们首先根据与关键点置信度相关的二维人体姿势标签构建空间组合令牌表示,编码大型关节身体运动(例如上下身体)和精细运动(例如头部和手部)。然后我们设计了一个音乐到运动的transformer模型,该模型自回归地生成与音乐对齐的舞蹈姿势令牌序列,并融入全局注意力以关注音乐风格和先前的运动上下文。最后我们利用扩散主干通过这些合成的姿势令牌对参考图像进行动画处理,形成一个完全可微分的端到端框架。实验结果表明,X-Dancer能够产生多样且具特色的舞蹈视频,在多样性、表现力和逼真度方面大大优于现有先进技术的方法。代码和模型将用于研究目的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://zeyuan-chen.com/X-Dancer/
Summary
本文介绍了X-Dancer,一种新颖的零样本音乐驱动图像动画管道,能够从单张静态图像创建多样且长程逼真的舞蹈视频。其核心是统一transformer-diffusion框架,包含一个自回归transformer模型,用于合成扩展且与音乐同步的token序列,用于指导扩散模型生成连贯且逼真的舞蹈视频帧。不同于传统方法主要在3D中生成人体运动,X-Dancer解决了数据限制并增强了可扩展性,通过建模丰富的2D舞蹈动作并捕捉其与音乐节奏的微妙对齐,通过可获得的单目视频实现。
Key Takeaways
- X-Dancer是一种零样本音乐驱动图像动画管道,能从单张静态图像创建舞蹈视频。
- 它采用统一的transformer-diffusion框架,包含自回归transformer模型,用于合成扩展且与音乐同步的token序列。
- X-Dancer通过建模丰富的2D舞蹈动作并捕捉其与音乐节奏的微妙对齐,实现了数据限制和可扩展性的增强。
- 它通过关联人体关键点置信度的空间组合token表示来编码大型关节运动和精细动作。
- X-Dancer设计了一个音乐到运动的transformer模型,能够自回归地生成与音乐风格和历史运动上下文对齐的舞蹈姿势token序列。
- 通过利用扩散模型和后端动画技术,X-Dancer能够以合成的姿势token激活参考图像,形成一个完全可微分的端到端框架。
点此查看论文截图


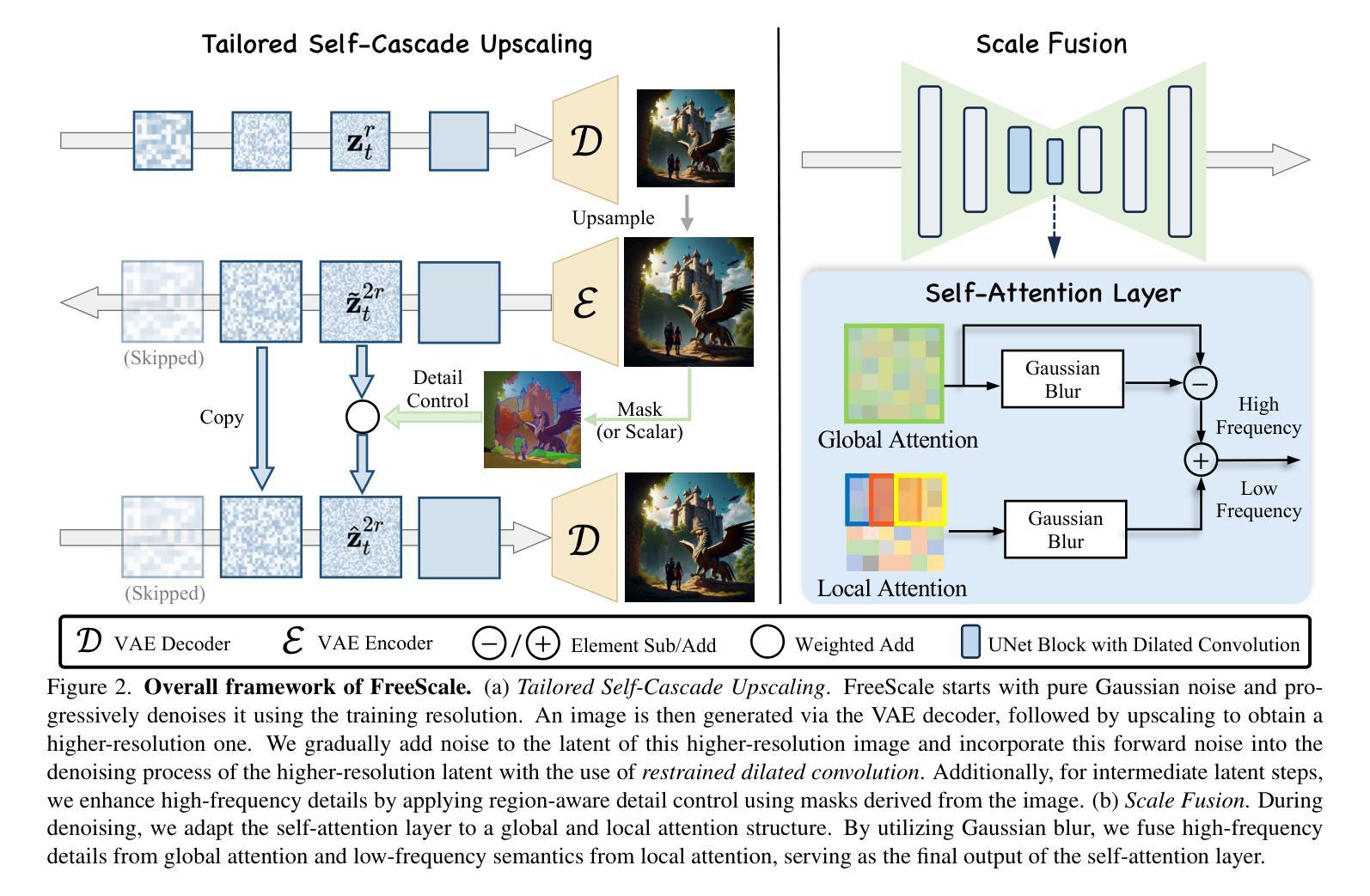
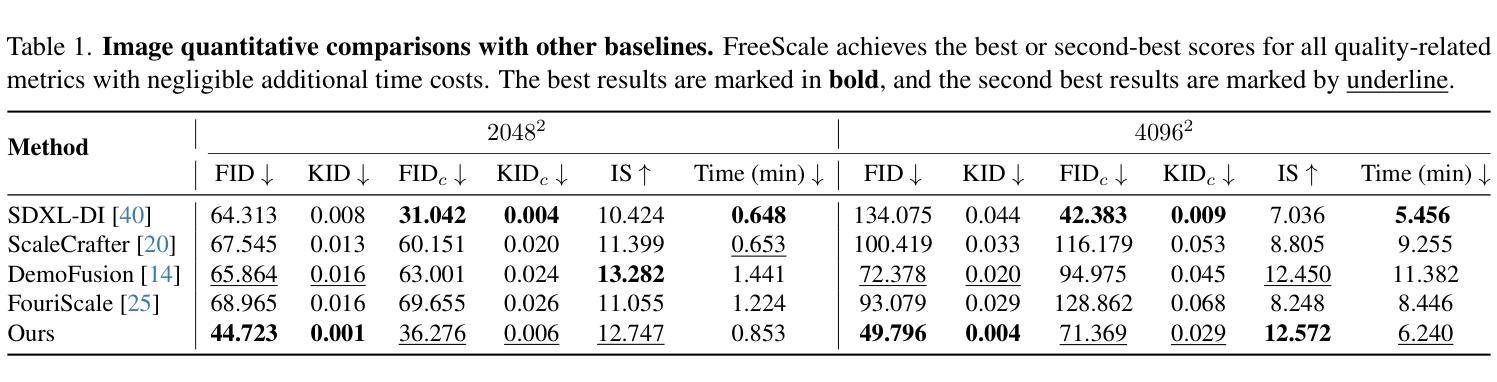
FreeScale: Unleashing the Resolution of Diffusion Models via Tuning-Free Scale Fusion
Authors:Haonan Qiu, Shiwei Zhang, Yujie Wei, Ruihang Chu, Hangjie Yuan, Xiang Wang, Yingya Zhang, Ziwei Liu
Visual diffusion models achieve remarkable progress, yet they are typically trained at limited resolutions due to the lack of high-resolution data and constrained computation resources, hampering their ability to generate high-fidelity images or videos at higher resolutions. Recent efforts have explored tuning-free strategies to exhibit the untapped potential higher-resolution visual generation of pre-trained models. However, these methods are still prone to producing low-quality visual content with repetitive patterns. The key obstacle lies in the inevitable increase in high-frequency information when the model generates visual content exceeding its training resolution, leading to undesirable repetitive patterns deriving from the accumulated errors. To tackle this challenge, we propose FreeScale, a tuning-free inference paradigm to enable higher-resolution visual generation via scale fusion. Specifically, FreeScale processes information from different receptive scales and then fuses it by extracting desired frequency components. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of our paradigm in extending the capabilities of higher-resolution visual generation for both image and video models. Notably, compared with previous best-performing methods, FreeScale unlocks the 8k-resolution text-to-image generation for the first time.
视觉扩散模型取得了显著的进步,但由于缺乏高分辨率数据和计算资源的限制,它们通常只能在有限的分辨率上进行训练,这阻碍了它们在更高分辨率下生成高保真图像或视频的能力。近期的研究工作已经探索了无微调策略,以展示预训练模型未开发的高分辨率视觉生成潜力。然而,这些方法仍倾向于产生带有重复模式的低质量视觉内容。关键障碍在于模型生成超过其训练分辨率的视觉内容时不可避免的高频信息增加,这会导致由累积误差引起的不可取的重复模式。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了FreeScale,这是一种无需微调推理范式,通过尺度融合实现高分辨率视觉生成。具体来说,FreeScale处理来自不同感受尺度的信息,然后通过提取所需的频率成分将其融合。大量实验验证了我们的范式在扩展图像和视频模型的分辨率视觉生成能力方面的优越性。值得注意的是,与以前表现最佳的方法相比,FreeScale首次实现了8k分辨率的文本到图像生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, Project Page: http://haonanqiu.com/projects/FreeScale.html, Code Repo: https://github.com/ali-vilab/FreeScale
Summary
视觉扩散模型虽有所进展,但由于缺乏高分辨率数据和计算资源的限制,通常只在有限的分辨率上进行训练,这限制了其生成高分辨率图像或视频的能力。最近的研究尝试采用无微调策略来展示预训练模型在更高分辨率视觉生成方面的潜力,但这些方法仍易产生带有重复模式的低质量视觉内容。关键在于,当模型生成超过其训练分辨率的视觉内容时,高频信息的增加是不可避免的,这会导致由累积误差引起的重复模式。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了FreeScale,一种无需调参的推理范式,通过尺度融合实现更高分辨率的视觉生成。实验证明,我们的范式在图像和视频模型的更高分辨率视觉生成能力方面具有优越性。值得注意的是,与以前表现最佳的方法相比,FreeScale首次实现了8k分辨率的文本到图像生成。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉扩散模型因缺乏高分辨率数据和计算资源限制而通常在有限分辨率下训练。
- 缺乏高分辨率训练限制了视觉扩散模型生成高质量图像和视频的能力。
- 现有研究尝试采用无微调策略来优化预训练模型在更高分辨率视觉生成方面的表现。
- 当前方法仍面临生成低质量视觉内容的问题,包含重复模式。
- 模型生成超过训练分辨率的视觉内容时,高频信息的增加会导致重复模式的问题。
- 提出的FreeScale方法通过尺度融合实现无需调参的更高分辨率视觉生成。
点此查看论文截图


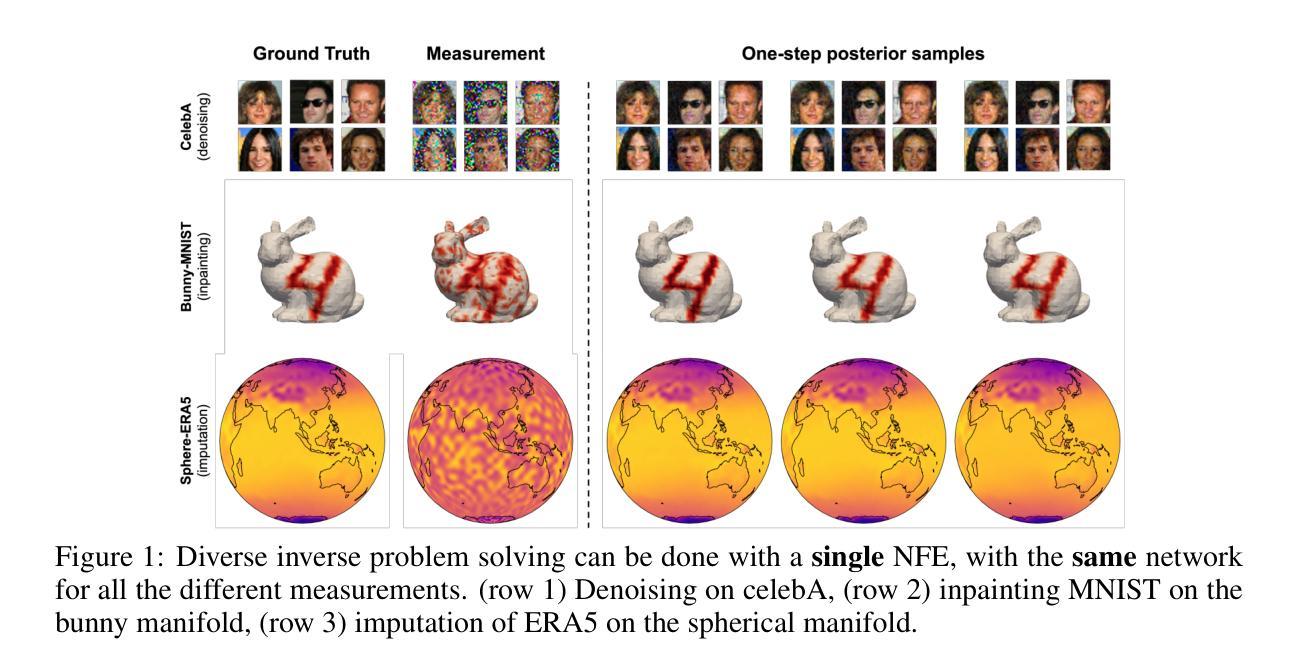
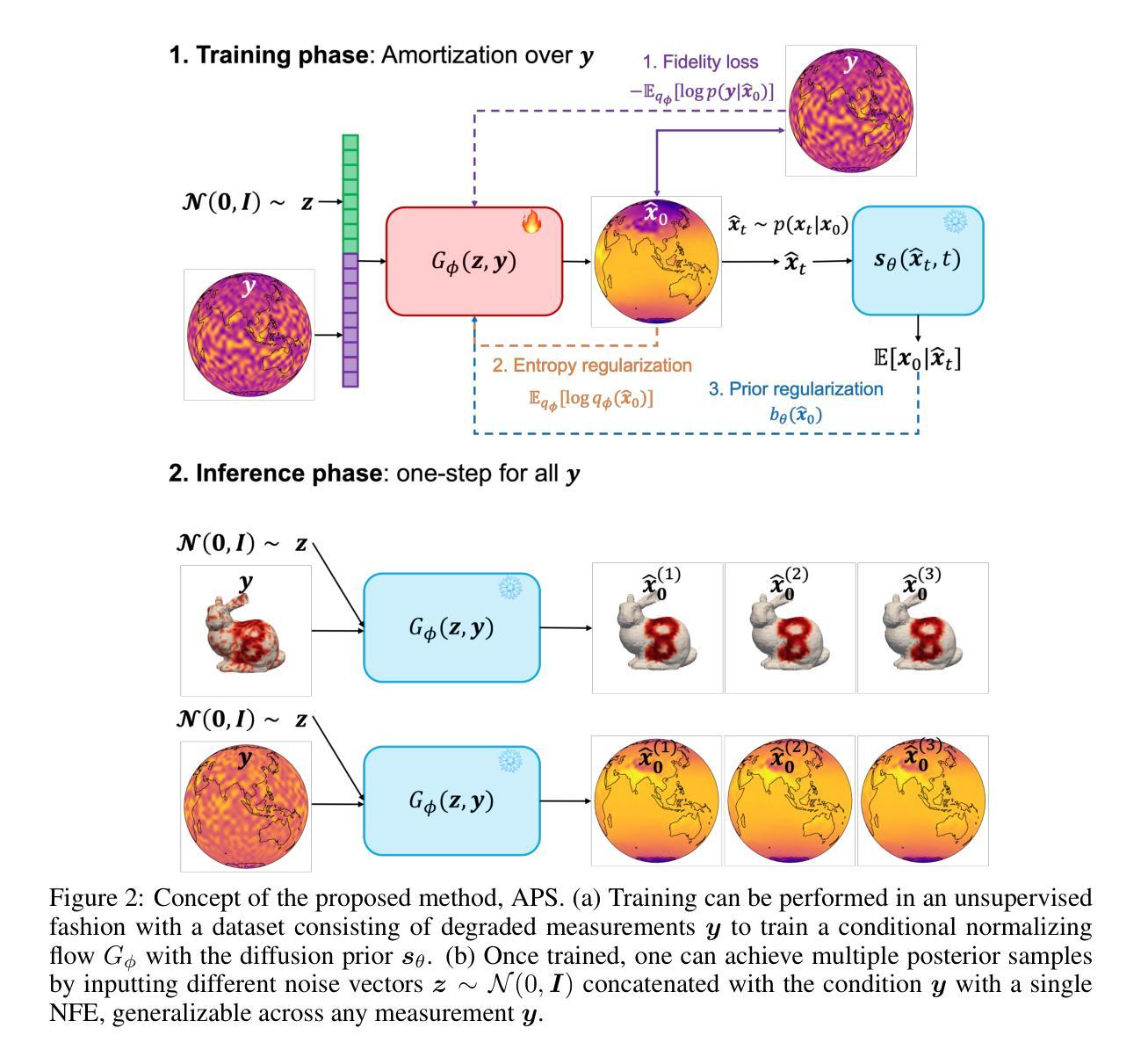
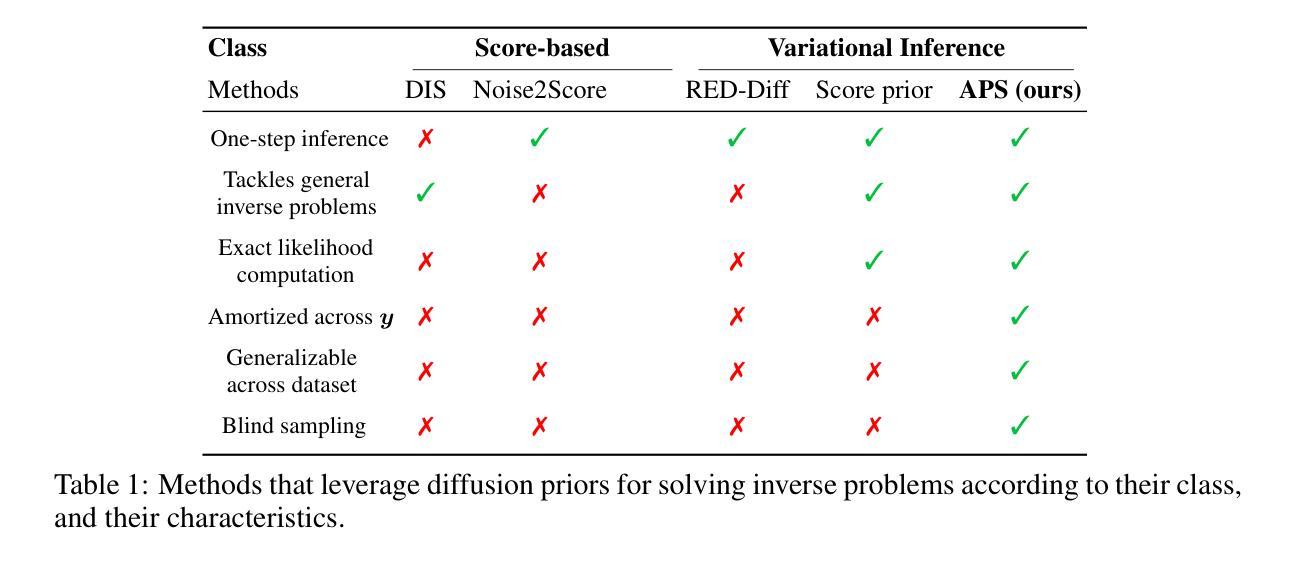
Amortized Posterior Sampling with Diffusion Prior Distillation
Authors:Abbas Mammadov, Hyungjin Chung, Jong Chul Ye
We propose Amortized Posterior Sampling (APS), a novel variational inference approach for efficient posterior sampling in inverse problems. Our method trains a conditional flow model to minimize the divergence between the variational distribution and the posterior distribution implicitly defined by the diffusion model. This results in a powerful, amortized sampler capable of generating diverse posterior samples with a single neural function evaluation, generalizing across various measurements. Unlike existing methods, our approach is unsupervised, requires no paired training data, and is applicable to both Euclidean and non-Euclidean domains. We demonstrate its effectiveness on a range of tasks, including image restoration, manifold signal reconstruction, and climate data imputation. APS significantly outperforms existing approaches in computational efficiency while maintaining competitive reconstruction quality, enabling real-time, high-quality solutions to inverse problems across diverse domains.
我们提出了摊销后采样(Amortized Posterior Sampling,APS),这是一种针对反问题中有效后验采样的新型变分推断方法。我们的方法训练了一个条件流模型,以最小化变分分布与扩散模型隐式定义的后验分布之间的散度。这产生了一个强大的摊销采样器,能够在一次神经网络函数评估中生成多样化的后验样本,并可在各种测量中通用。与现有方法不同,我们的方法是无监督的,不需要配对训练数据,适用于欧几里得和非欧几里得领域。我们在图像恢复、流形信号重建和气候数据插补等一系列任务中展示了其有效性。APS在计算效率方面显著优于现有方法,同时保持有竞争力的重建质量,为不同领域的反问题提供实时高质量解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种名为Amortized Posterior Sampling(APS)的新型变分推断方法,用于高效解决反问题中的后采样问题。通过训练条件流模型,最小化变分分布与扩散模型隐式定义的后验分布之间的分歧,从而创建一个强大的、一次性采样器,能够在单一神经网络函数评估中生成多样化的后验样本,并广泛应用于各种测量。该方法无需监督,无需配对训练数据,适用于欧几里得和非欧几里得领域。在图像恢复、流形信号重建和气候数据插补等任务上表现出色,在计算效率上显著优于现有方法,同时保持竞争力的重建质量,为不同领域的反问题提供实时高质量解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 引入Amortized Posterior Sampling(APS)方法,一种针对反问题中后采样的新型变分推断方法。
- 通过训练条件流模型,最小化变分分布与扩散模型后验分布之间的分歧。
- APS方法创建一个强大的、一次性采样器,能够在单一神经网络函数评估中生成多样化后验样本。
- APS方法具有通用性,可应用于各种测量、图像恢复、流形信号重建和气候数据插补等任务。
- 该方法无需监督,无需配对训练数据,适用于欧几里得和非欧几里得领域。
- APS在计算效率上显著优于现有方法,同时保持竞争力的重建质量。
点此查看论文截图