⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
CRMAgent: A Multi-Agent LLM System for E-Commerce CRM Message Template Generation
Authors:Yinzhu Quan, Xinrui Li, Ying Chen
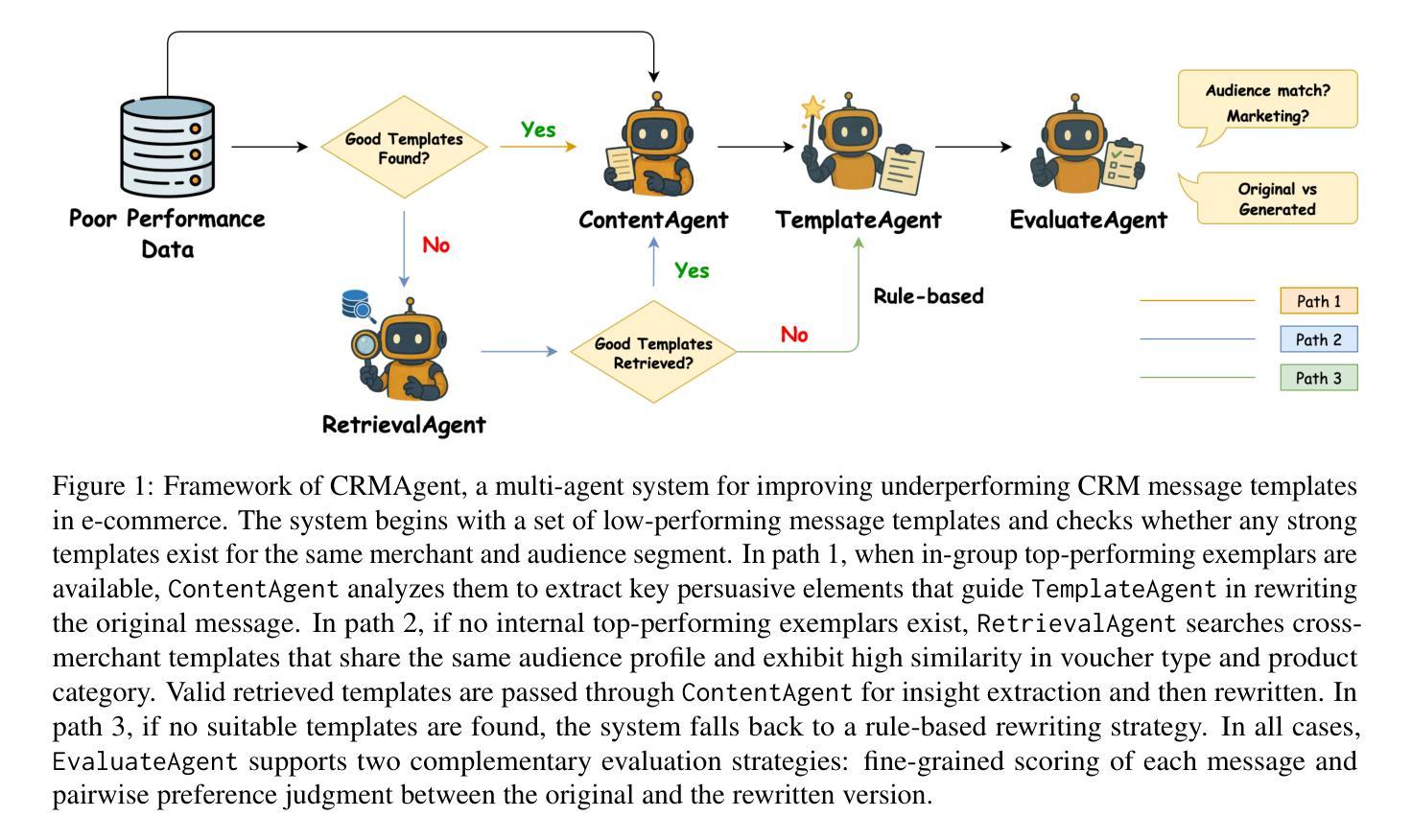
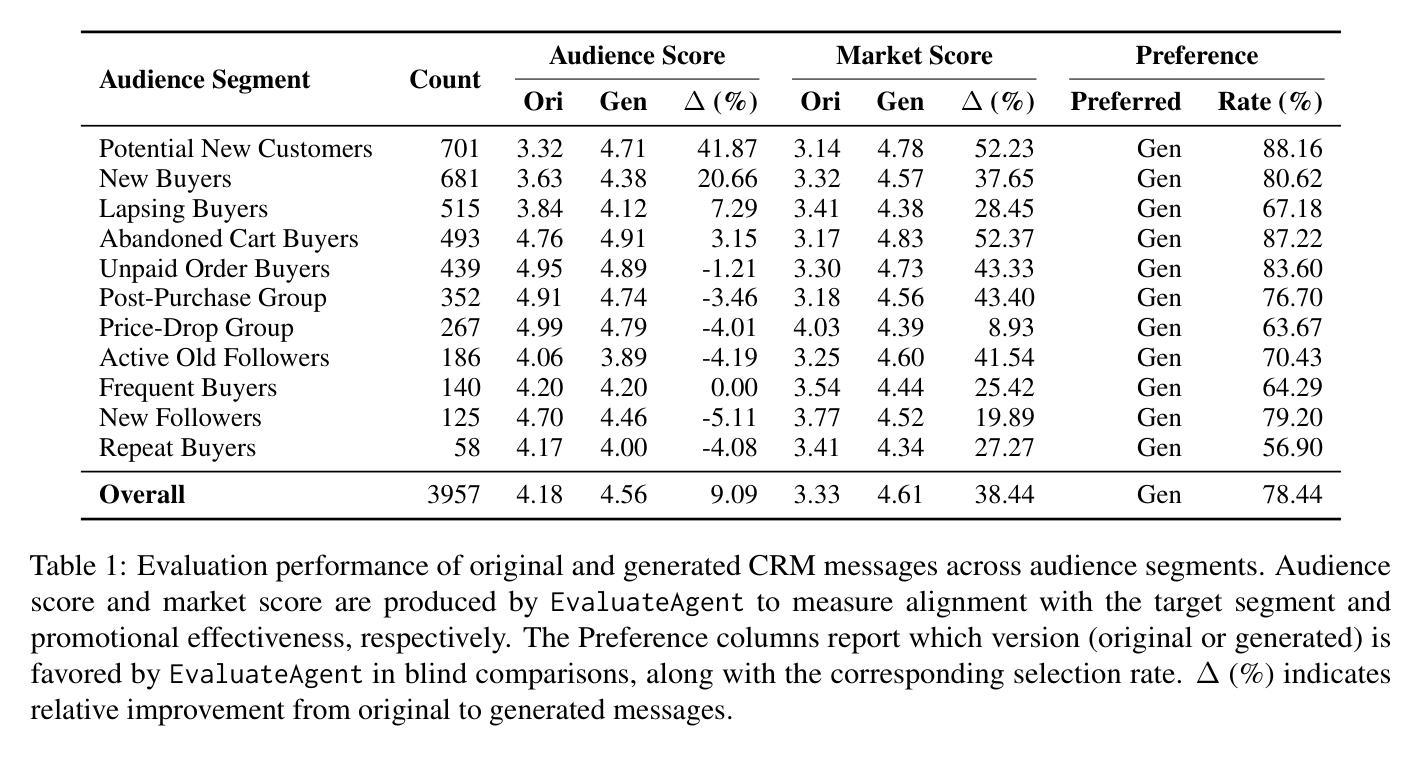
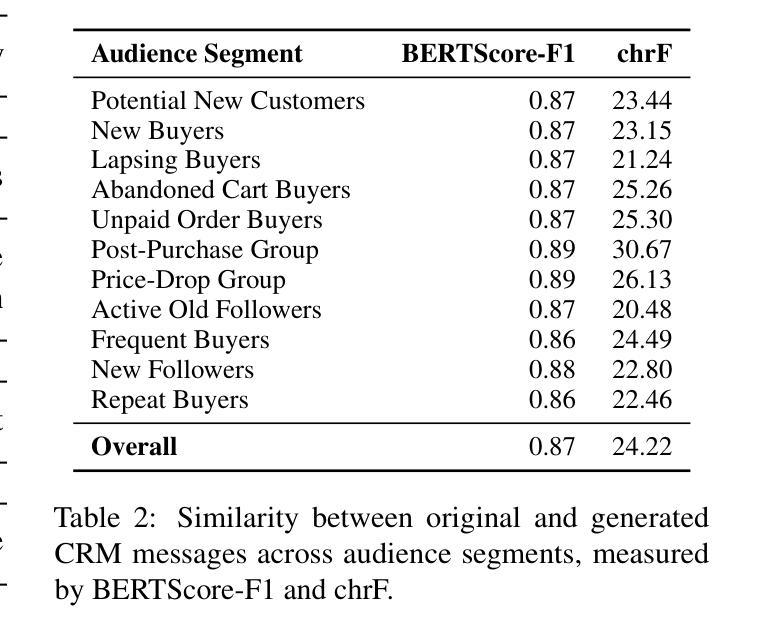
In e-commerce private-domain channels such as instant messaging and e-mail, merchants engage customers directly as part of their Customer Relationship Management (CRM) programmes to drive retention and conversion. While a few top performers excel at crafting outbound messages, most merchants struggle to write persuasive copy because they lack both expertise and scalable tools. We introduce CRMAgent, a multi-agent system built on large language models (LLMs) that generates high-quality message templates and actionable writing guidance through three complementary modes. First, group-based learning enables the agent to learn from a merchant’s own top-performing messages within the same audience segment and rewrite low-performing ones. Second, retrieval-and-adaptation fetches templates that share the same audience segment and exhibit high similarity in voucher type and product category, learns their successful patterns, and adapts them to the current campaign. Third, a rule-based fallback provides a lightweight zero-shot rewrite when no suitable references are available. Extensive experiments show that CRMAgent consistently outperforms merchants’ original templates, delivering significant gains in both audience-match and marketing-effectiveness metrics.
在电子商务私域渠道,如即时通讯和电子邮件中,商家会将其作为客户关系管理(CRM)计划的一部分,直接与客户进行互动,以促进客户留存和转化。虽然一些表现突出的商家擅长制作外发消息,但大多数商家在撰写有说服力的文案时感到困难,因为他们既缺乏专业知识,又没有可规模化使用的工具。我们在此介绍CRMAgent,这是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统,它通过三种互补模式生成高质量的消息模板和可操作的写作指导。首先,基于群体学习可以让智能体从同一受众群体内部商家表现最佳的消息中学习,并改写表现不佳的消息。其次,检索与适应模式会检索与当前受众群体相同、优惠券类型和商品类别高度相似的模板,学习它们的成功模式并适应当前活动。最后,基于规则的备用方案在没有合适的参考可用时提供一种轻便的零样本重写方法。大量实验表明,CRMAgent始终优于商家的原始模板,在受众匹配和营销有效性指标上取得了显著的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
电商私域渠道如即时通讯和电子邮件中,商家通过CRM计划直接与客户沟通以驱动用户留存和转化。虽然顶级商家擅长编写外发消息,但多数商家由于缺乏专业和可扩展工具在撰写说服性文案方面面临挑战。我们推出CRMAgent多智能体系统,基于大型语言模型生成高质量信息模板和可操作的写作指导,通过三种模式进行互补。实验证明,CRMAgent在受众匹配和营销有效性指标上表现优于商家原始模板,实现了显著增长。
Key Takeaways
- 商家在CRM计划中通过私域渠道直接与客户沟通以提高用户留存和转化。
- 虽然部分顶级商家擅长撰写外发消息,但大多数商家面临编写说服性文案的挑战。
- 缺乏专业和可扩展的文案工具是商家面临的主要问题。
- CRMAgent是一个多智能体系统,基于大型语言模型生成高质量信息模板和写作指导。
- CRMAgent通过三种模式进行互补:基于群组学习、检索和适应以及规则基础回退。
- 实验证明CRMAgent在受众匹配和营销有效性方面表现优于商家原始模板。
点此查看论文截图



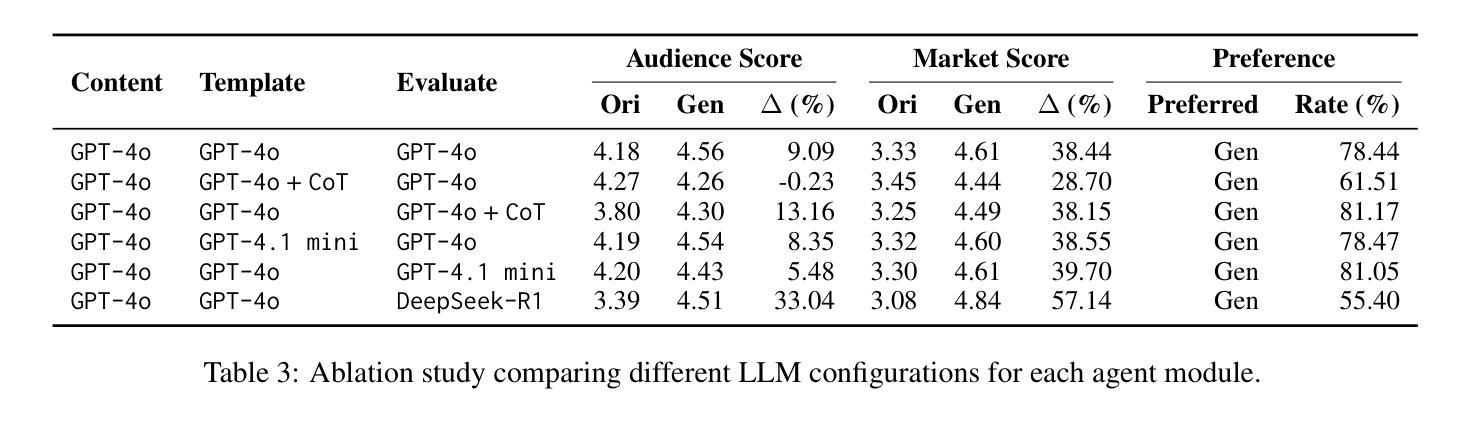

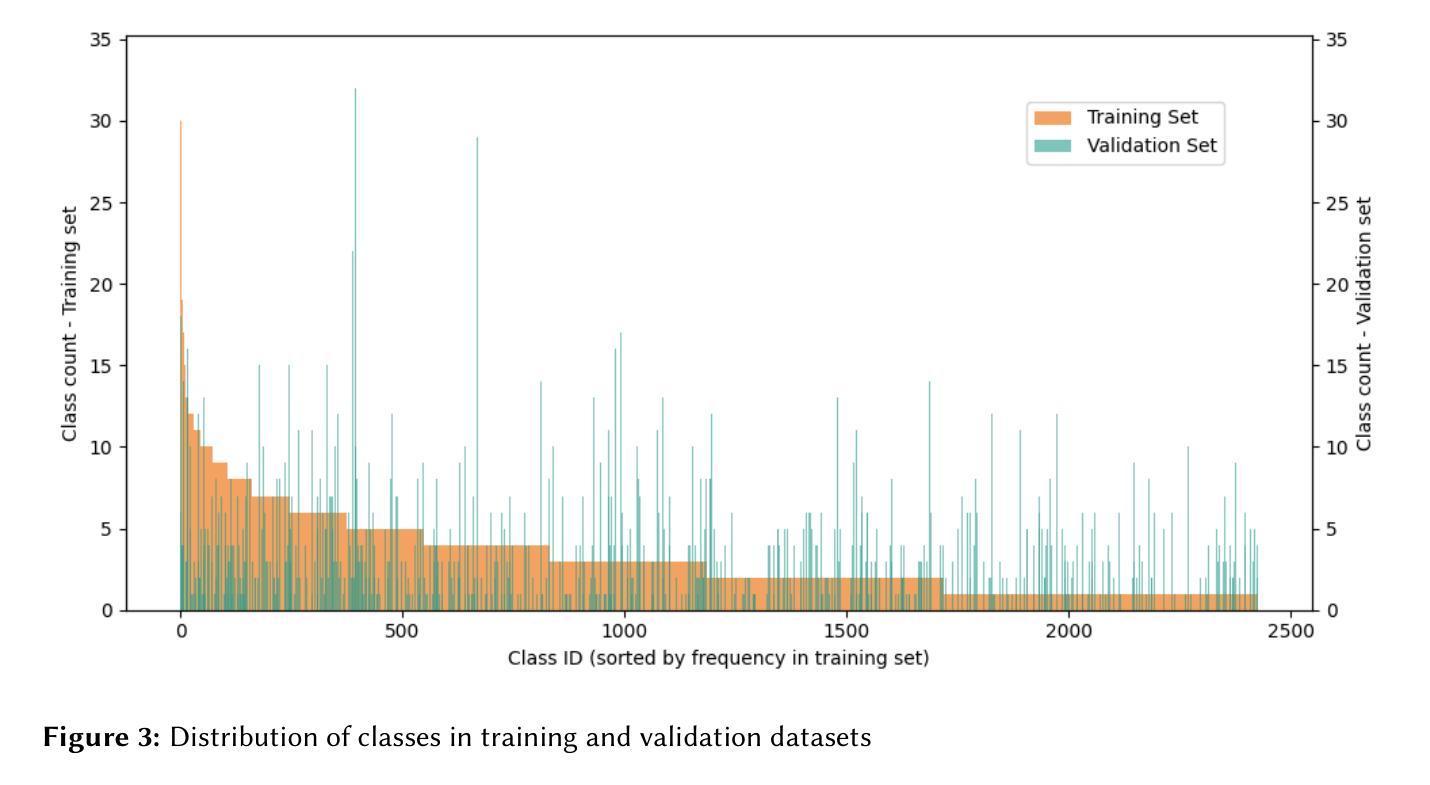
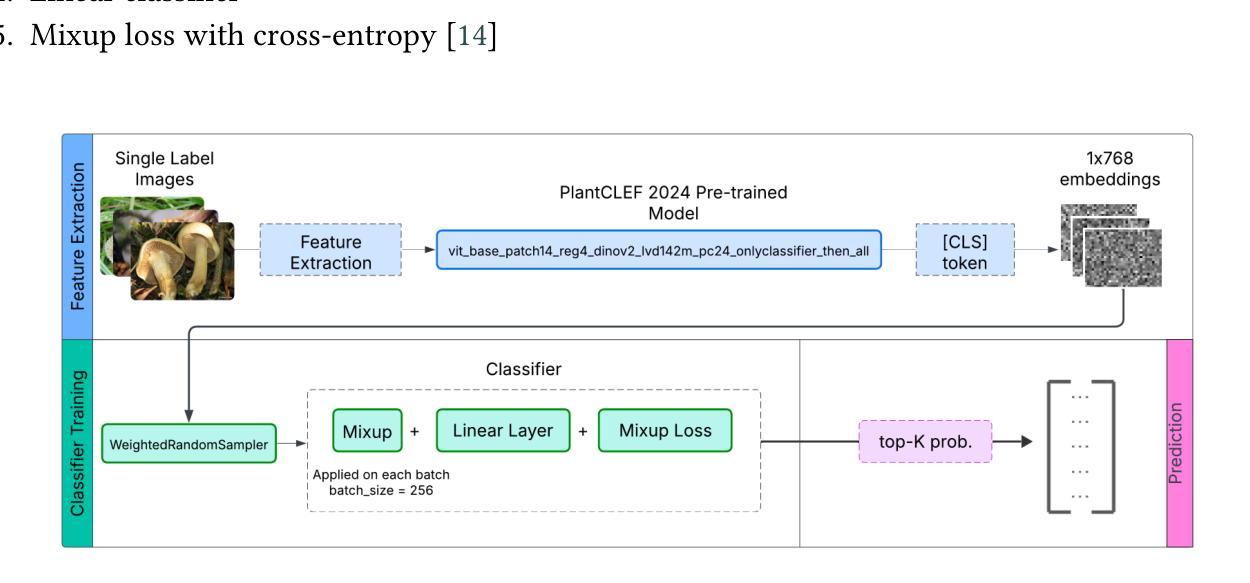
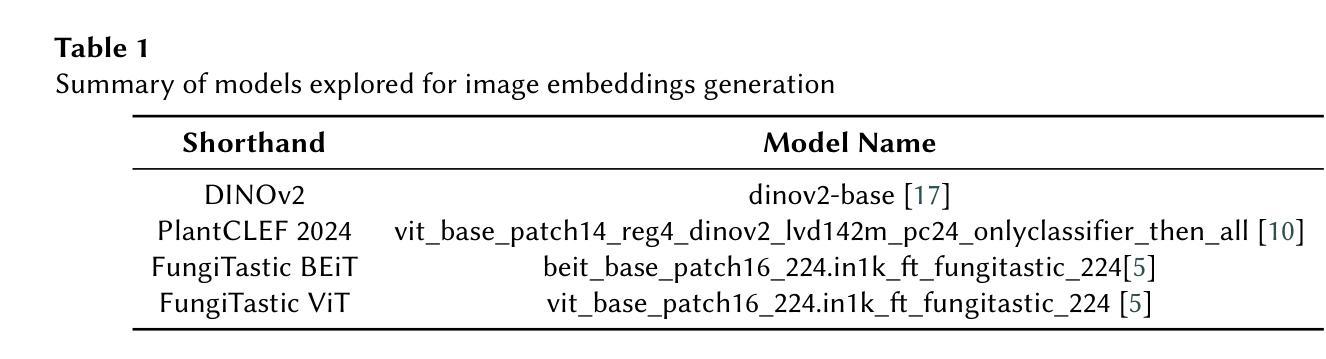
Transfer Learning and Mixup for Fine-Grained Few-Shot Fungi Classification
Authors:Jason Kahei Tam, Murilo Gustineli, Anthony Miyaguchi
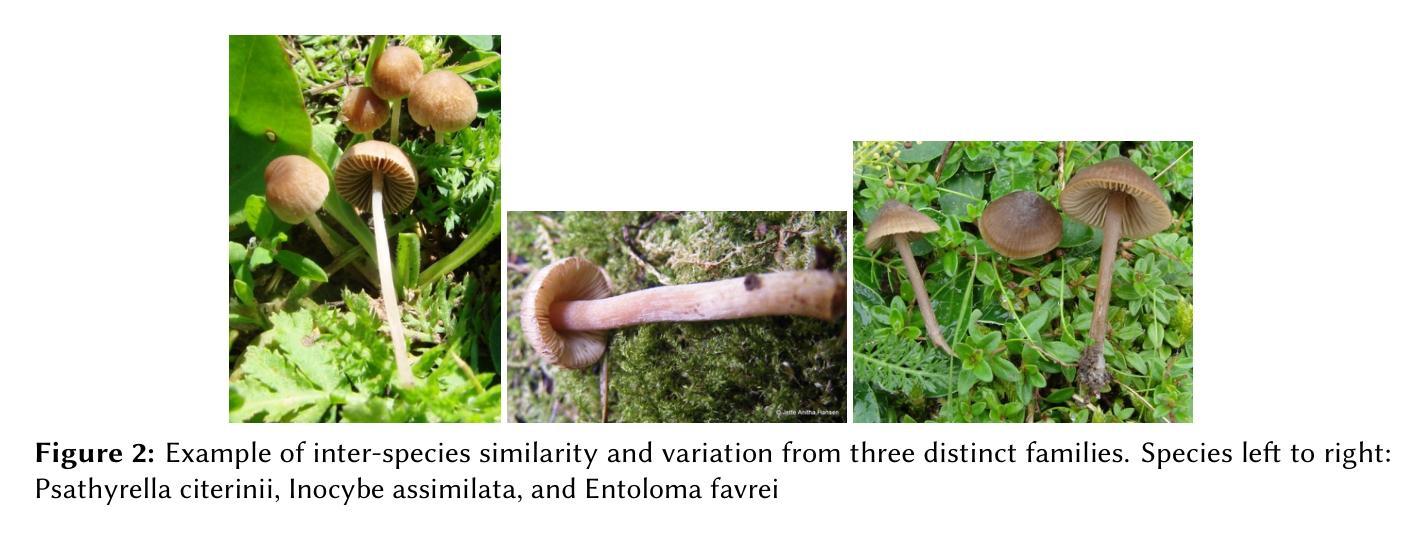
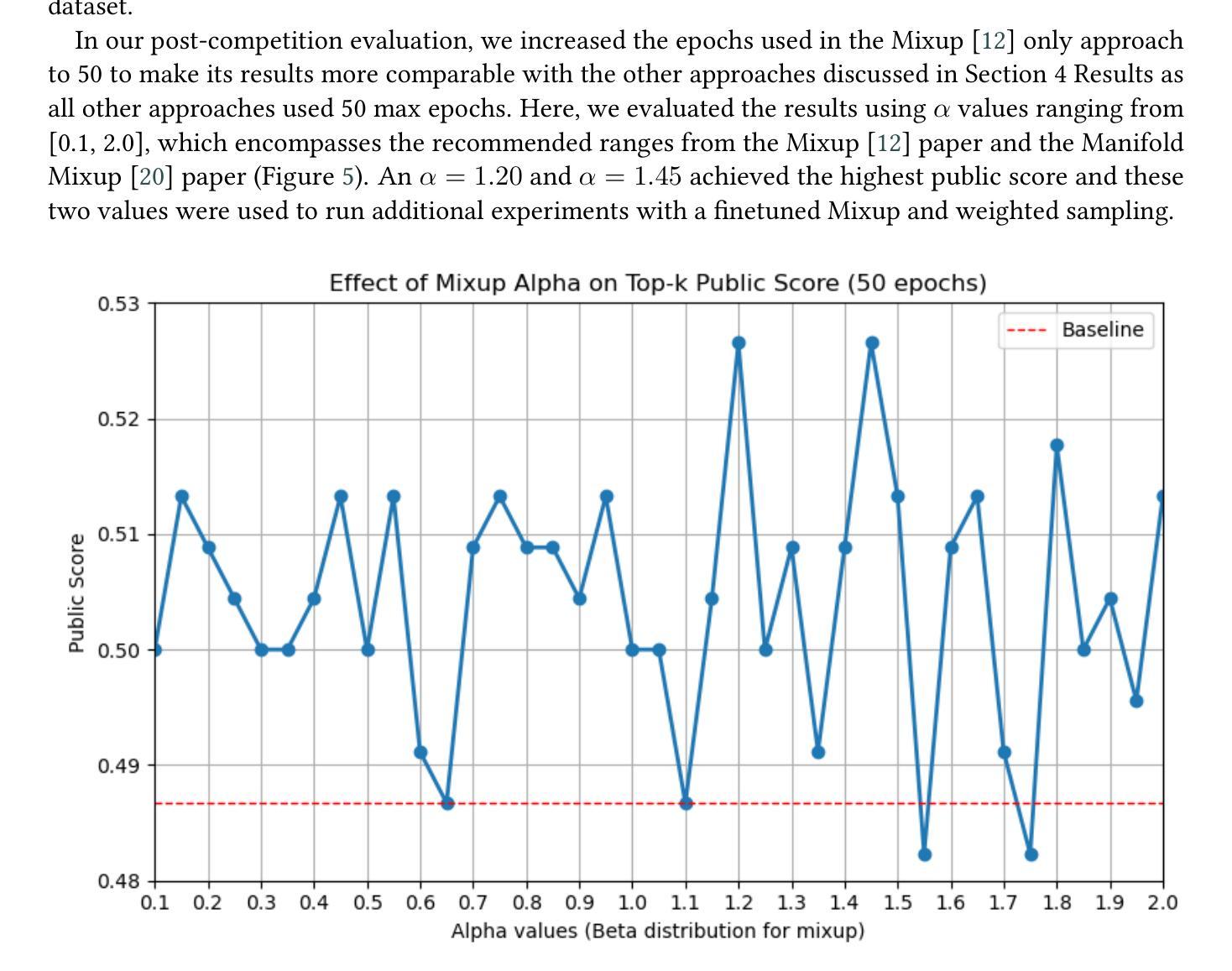
Accurate identification of fungi species presents a unique challenge in computer vision due to fine-grained inter-species variation and high intra-species variation. This paper presents our approach for the FungiCLEF 2025 competition, which focuses on few-shot fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) using the FungiTastic Few-Shot dataset. Our team (DS@GT) experimented with multiple vision transformer models, data augmentation, weighted sampling, and incorporating textual information. We also explored generative AI models for zero-shot classification using structured prompting but found them to significantly underperform relative to vision-based models. Our final model outperformed both competition baselines and highlighted the effectiveness of domain specific pretraining and balanced sampling strategies. Our approach ranked 35/74 on the private test set in post-completion evaluation, this suggests additional work can be done on metadata selection and domain-adapted multi-modal learning. Our code is available at https://github.com/dsgt-arc/fungiclef-2025.
真菌物种的精确识别在计算机视觉领域是一项独特的挑战,因为存在物种间的细微差异和物种内部的巨大差异。本文针对FungiCLEF 2025竞赛提出了一种方法,该方法聚焦于使用FungiTastic Few-Shot数据集的少样本精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)。我们团队(DS@GT)对多种视觉转换器模型、数据增强、加权采样和文本信息融合进行了实验。我们还探索了基于生成式人工智能模型的零样本分类,使用结构化提示,但发现与基于视觉的模型相比,其性能显著较差。我们的最终模型超越了竞赛基线,突显了领域特定预训练和平衡采样策略的有效性。在完成后评估的私有测试集上,我们的方法排名第35/74,这表明可以在元数据选择和领域适应的多模式学习方面做进一步的工作。我们的代码可在https://github.com/dsgt-arc/fungiclef-2025找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文针对FungiCLEF 2025竞赛提出了一种基于视觉的少样本精细分类方法。研究团队尝试使用多种视觉Transformer模型、数据增强、加权采样和文本信息融合等技术。尽管探索了基于生成式AI的零样本分类方法,但发现其性能显著落后于视觉模型。最终模型在竞赛中的表现优于基线模型,突显了领域特定预训练和平衡采样策略的有效性。排名为第35名,表明在元数据选择和领域自适应多模态学习方面还有提升空间。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 论文针对FungiCLEF 2025竞赛,提出了基于视觉的少样本精细分类方法。
- 研究团队使用了多种视觉Transformer模型进行尝试。
- 数据增强和加权采样技术被用于提升模型性能。
- 融合了文本信息,但基于生成式AI的零样本分类方法表现不佳。
- 最终模型表现优于竞赛基线,凸显了领域特定预训练和平衡采样策略的重要性。
- 模型在私有测试集上的排名为第35名,提示需要在元数据选择和领域自适应多模态学习方面进行进一步的研究。
点此查看论文截图


GRASP: Generic Reasoning And SPARQL Generation across Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Sebastian Walter, Hannah Bast
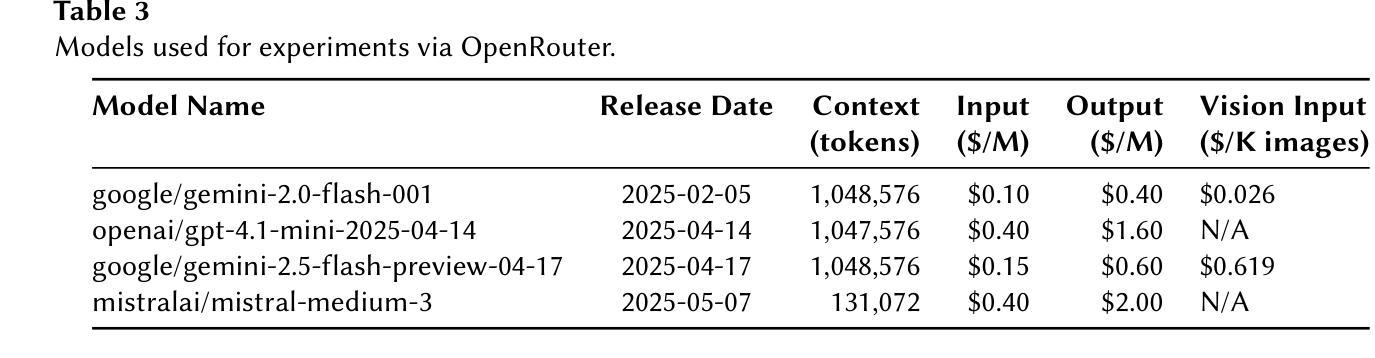
We propose a new approach for generating SPARQL queries on RDF knowledge graphs from natural language questions or keyword queries, using a large language model. Our approach does not require fine-tuning. Instead, it uses the language model to explore the knowledge graph by strategically executing SPARQL queries and searching for relevant IRIs and literals. We evaluate our approach on a variety of benchmarks (for knowledge graphs of different kinds and sizes) and language models (of different scales and types, commercial as well as open-source) and compare it with existing approaches. On Wikidata we reach state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks, despite the zero-shot setting. On Freebase we come close to the best few-shot methods. On other, less commonly evaluated knowledge graphs and benchmarks our approach also performs well overall. We conduct several additional studies, like comparing different ways of searching the graphs, incorporating a feedback mechanism, or making use of few-shot examples.
我们提出了一种新的基于大规模语言模型的自然语言的SPARQL查询生成方法,用于在RDF知识图上构建查询。我们的方法无需精细调整。相反,它通过策略性地执行SPARQL查询并搜索相关的IRI和字面量来探索知识图谱。我们在各种基准测试集(针对不同类型和规模的知识图谱)和语言模型(不同规模和类型,包括商业和开源)上评估了我们的方法,并将其与现有方法进行了比较。在WikiData上,尽管我们采用了零样本设置,但在多个基准测试集上取得了最新结果。在Freebase上,我们的表现接近最佳的小样本方法。在其他较少评估的知识图谱和基准测试集上,我们的方法总体上表现良好。我们还进行了其他额外研究,如比较不同的图形搜索方式、引入反馈机制或利用小样本示例等。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法,利用大型语言模型从自然语言问题或关键词查询生成SPARQL查询语句,对RDF知识图谱进行查询。该方法无需精细调整,而是通过执行战略性的SPARQL查询和搜索相关的IRI和字面量来探索知识图谱。该方法在不同的知识图谱和多种语言模型上进行了评估,并与现有方法进行了比较。在Wikidata上,该方法在多个基准测试上达到了最新的技术成果水平;在Freebase上的性能也接近最先进的几种技术;对于其他知识图谱和基准测试的表现整体也较好。本研究还包括各种额外的研究分析,比如对比不同图谱搜索方式、加入反馈机制和利用少数样例进行学习等。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于大型语言模型的生成SPARQL查询的新方法,适用于RDF知识图谱的自然语言查询。
- 方法无需精细调整,而是通过执行战略性SPARQL查询和探索知识图谱来工作。
- 在多种基准测试上进行了评估,包括不同类型和规模的知识图谱以及不同规模和类型的语言模型。
- 在Wikidata上的性能达到了最新的技术成果水平。
- 在Freebase上的性能接近最先进的少数技术。
- 对于其他知识图谱的查询性能整体表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

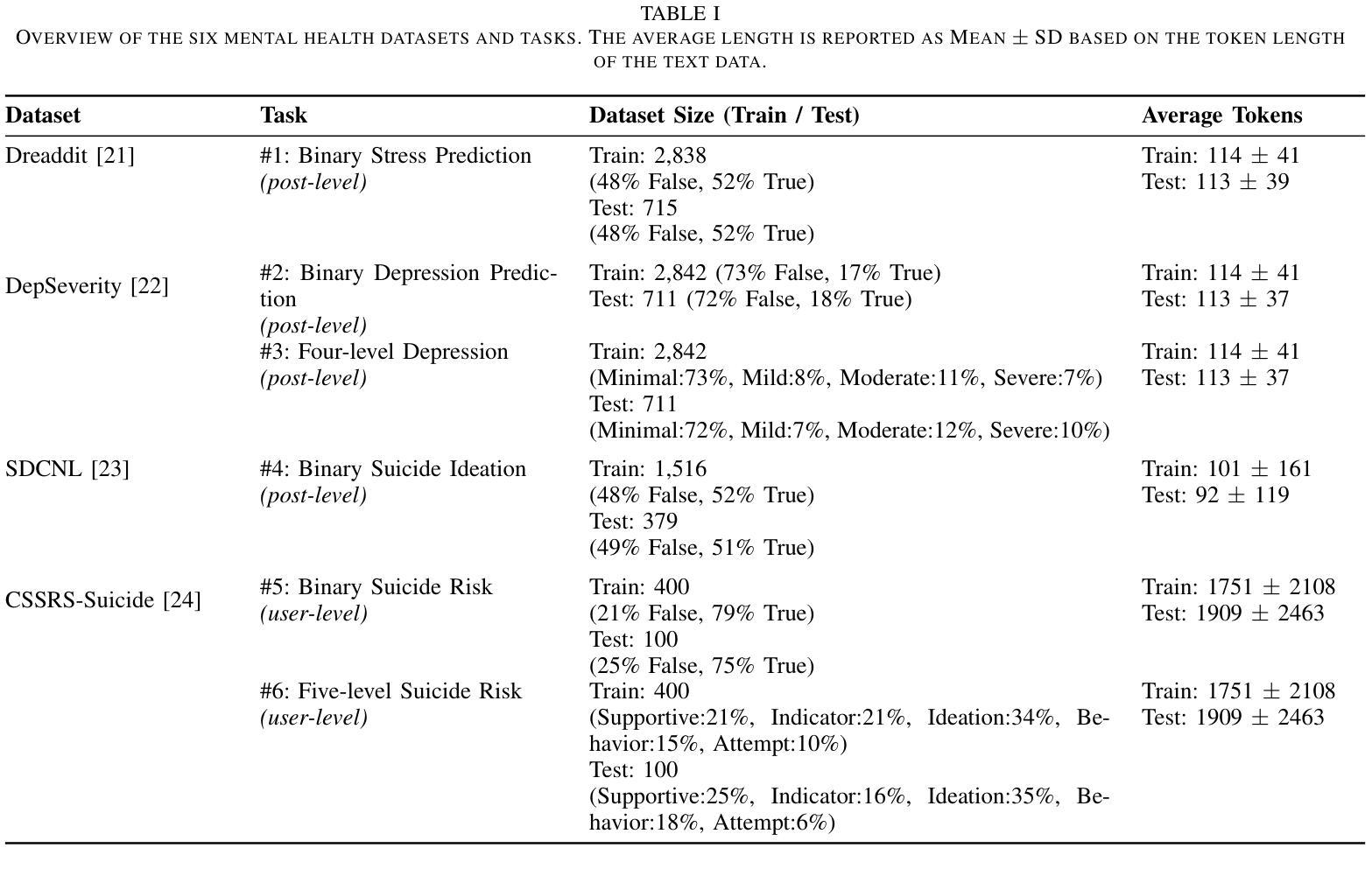
Beyond Scale: Small Language Models are Comparable to GPT-4 in Mental Health Understanding
Authors:Hong Jia, Shiya Fu, Vassilis Kostakos, Feng Xia, Ting Dang
The emergence of Small Language Models (SLMs) as privacy-preserving alternatives for sensitive applications raises a fundamental question about their inherent understanding capabilities compared to Large Language Models (LLMs). This paper investigates the mental health understanding capabilities of current SLMs through systematic evaluation across diverse classification tasks. Employing zero-shot and few-shot learning paradigms, we benchmark their performance against established LLM baselines to elucidate their relative strengths and limitations in this critical domain. We assess five state-of-the-art SLMs (Phi-3, Phi-3.5, Qwen2.5, Llama-3.2, Gemma2) against three LLMs (GPT-4, FLAN-T5-XXL, Alpaca-7B) on six mental health understanding tasks. Our findings reveal that SLMs achieve mean performance within 2% of LLMs on binary classification tasks (F1 scores of 0.64 vs 0.66 in zero-shot settings), demonstrating notable competence despite orders of magnitude fewer parameters. Both model categories experience similar degradation on multi-class severity tasks (a drop of over 30%), suggesting that nuanced clinical understanding challenges transcend model scale. Few-shot prompting provides substantial improvements for SLMs (up to 14.6%), while LLM gains are more variable. Our work highlights the potential of SLMs in mental health understanding, showing they can be effective privacy-preserving tools for analyzing sensitive online text data. In particular, their ability to quickly adapt and specialize with minimal data through few-shot learning positions them as promising candidates for scalable mental health screening tools.
随着小型语言模型(SLMs)作为敏感应用的隐私保护替代方案的出现,关于它们与大型语言模型(LLMs)的内在理解能力的比较,提出了一个根本性的问题。本文通过系统评估各种分类任务来研究当前SLMs在心理健康理解方面的能力。我们采用零样本学习和小样本学习范式,以既定的LLM基线为标准来衡量它们在关键领域的性能表现,以阐明它们在心理健康领域的相对优势和局限性。我们评估了五个最先进的小型语言模型(Phi-3、Phi-3.5、Qwen2.5、Llama-3.2、Gemma2)与三个大型语言模型(GPT-4、FLAN-T5-XXL、Alpaca-7B)在六个心理健康理解任务上的表现。研究结果显示,小型语言模型在二元分类任务上的平均性能表现接近大型语言模型,二者的零样本模式下F1得分分别为0.64和0.66,表现出显著的竞争力,尽管参数数量方面差距巨大。在多元严重程度分类任务上,两个模型类别的表现均出现类似下降(下降幅度超过30%),这表明微妙的临床理解挑战超越了模型规模。小样本提示为小型语言模型提供了实质性的改进(最多提高了14.6%),而大型语言模型的收益则更加多变。我们的工作突出了小型语言模型在心理健康理解方面的潜力,表明它们可以作为分析敏感在线文本数据的有效隐私保护工具。尤其值得一提的是,它们通过小样本学习快速适应和专门化的能力,使它们成为可扩展心理健康筛查工具的绝佳候选者。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
当前文本探讨了小型语言模型(SLMs)在心理健康理解方面的能力,通过与大型语言模型(LLMs)的对比研究,发现SLMs在二元分类任务中表现出较强的性能,并在少样本学习场景下实现了显著的提升。研究结果表明,SLMs在心理健康领域具有潜在的应用价值,尤其在于其能够快速适应并专业化处理少量数据的能力,使其成为心理健康筛查工具的有力候选者。
Key Takeaways
- SLMs作为隐私保护工具在敏感应用中的兴起,与LLMs相比具有内在理解能力的挑战。
- 通过系统评价,研究了SLMs在心理健康理解方面的能力。
- 在二元分类任务中,SLMs性能与LLMs相近,F1分数在零样本场景中达到0.64。
- 少样本学习范式为SLMs带来了显著的性能提升。
- 在多类严重性任务中,两类模型都出现了类似的性能下降,表明临床理解的复杂性超越了模型规模。
- SLMs在心理健康领域具有潜在应用价值,尤其在快速适应和处理少量数据方面表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

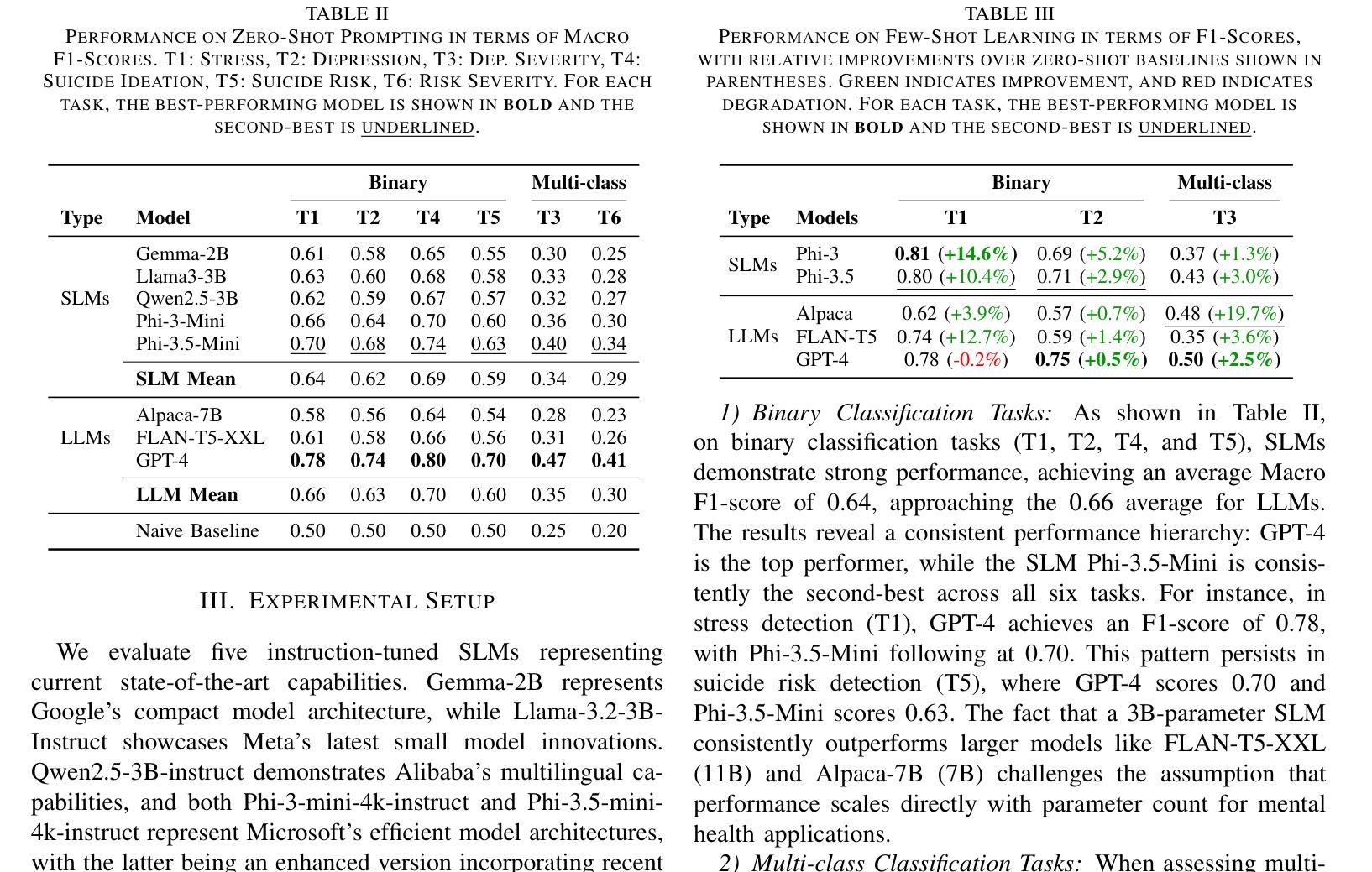
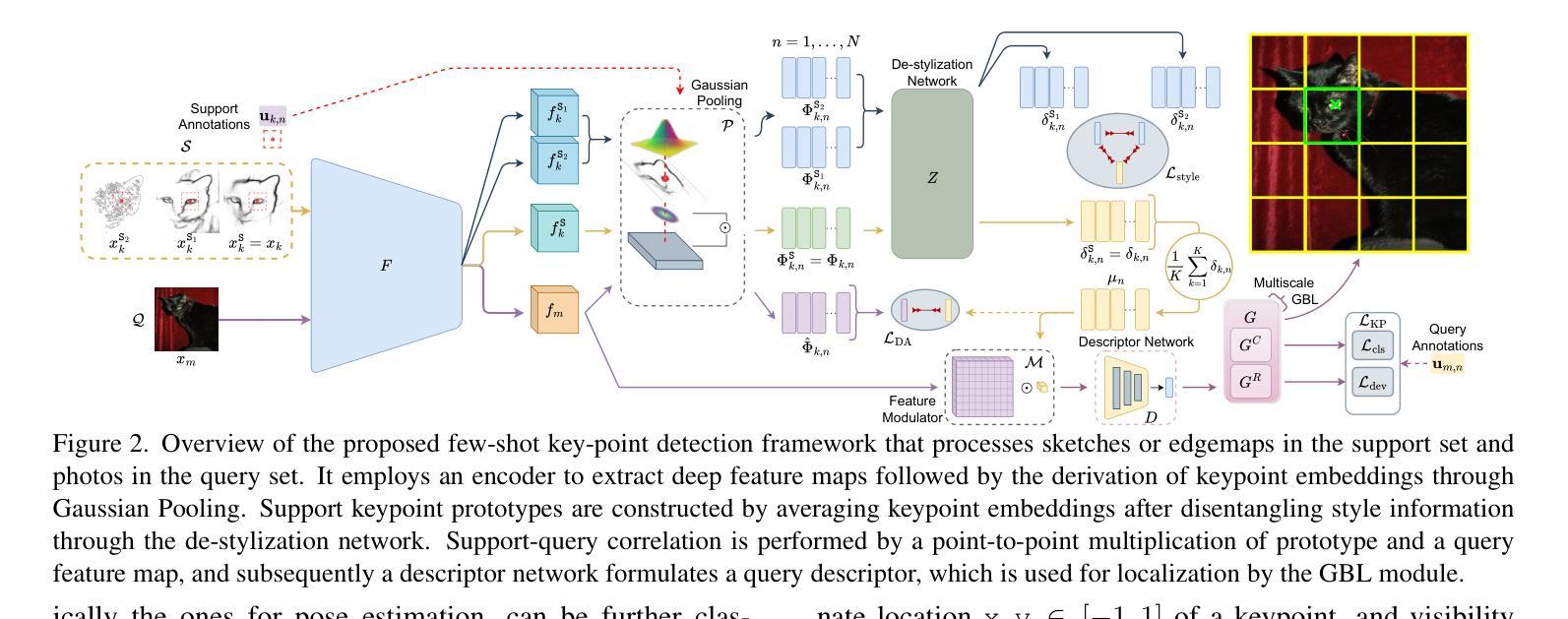
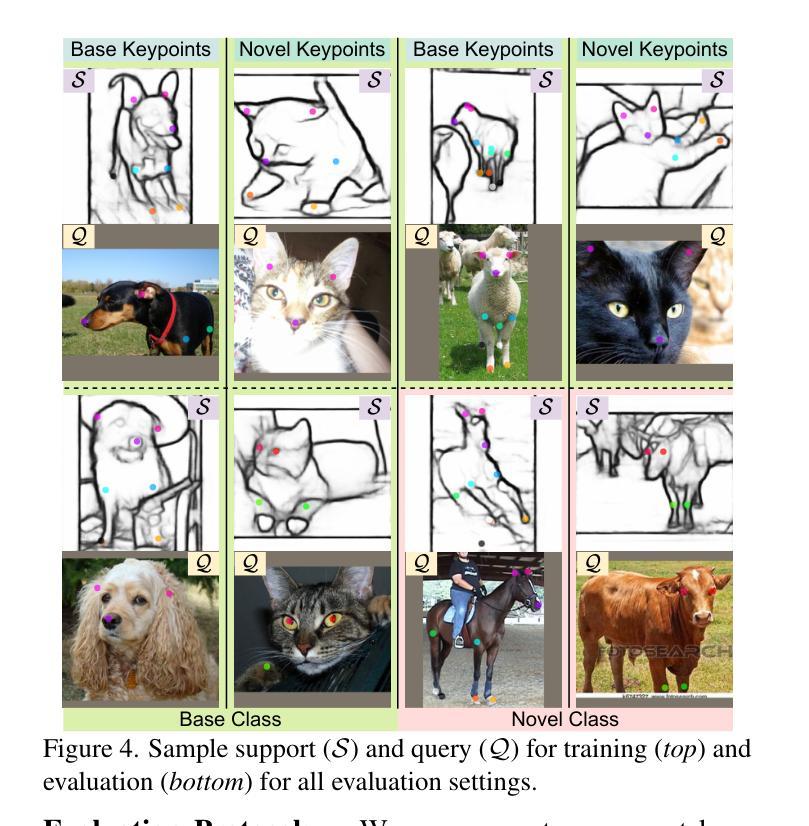
Doodle Your Keypoints: Sketch-Based Few-Shot Keypoint Detection
Authors:Subhajit Maity, Ayan Kumar Bhunia, Subhadeep Koley, Pinaki Nath Chowdhury, Aneeshan Sain, Yi-Zhe Song
Keypoint detection, integral to modern machine perception, faces challenges in few-shot learning, particularly when source data from the same distribution as the query is unavailable. This gap is addressed by leveraging sketches, a popular form of human expression, providing a source-free alternative. However, challenges arise in mastering cross-modal embeddings and handling user-specific sketch styles. Our proposed framework overcomes these hurdles with a prototypical setup, combined with a grid-based locator and prototypical domain adaptation. We also demonstrate success in few-shot convergence across novel keypoints and classes through extensive experiments.
关键点检测是现代机器感知的核心,在少样本学习中面临挑战,尤其是在无法获取与查询相同分布的源数据时。为解决这一空白,本研究利用流行的人类表达形式——草图,提供一种无源的替代方案。然而,掌握跨模态嵌入和处理用户特定的草图风格存在挑战。我们提出的框架通过原型设置与基于网格的定位器和原型域适应相结合,克服了这些障碍。我们还通过大量实验证明了在新关键点和新类别上的少样本收敛成功。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://subhajitmaity.me/DYKp
Summary
在现代化机器感知中,关键点检测在面临少量学习数据挑战时尤其重要。由于缺乏与查询数据分布相同的来源数据,这一领域存在问题。本研究采用草图(一种常见的人类表达方式)作为无源的替代方案来解决此问题。然而,存在掌握跨模态嵌入和处理用户特定草图风格方面的挑战。本研究提出的框架通过原型设置、网格定位器和原型域适应克服了这些障碍,并通过大量实验成功实现了跨新型关键点和类别的少量收敛。
Key Takeaways
- 现代机器感知中的关键点检测面临了少数情况下的学习挑战。
- 缺乏与查询数据分布相同的来源数据成为了主要难题。
- 草图作为一种人类表达形式被用作解决此问题的无源的替代方案。
- 存在掌握跨模态嵌入和处理用户特定草图风格的挑战。
- 研究提出了一种基于原型的框架来解决这些挑战。
- 该框架结合了网格定位器和原型域适应技术。
点此查看论文截图

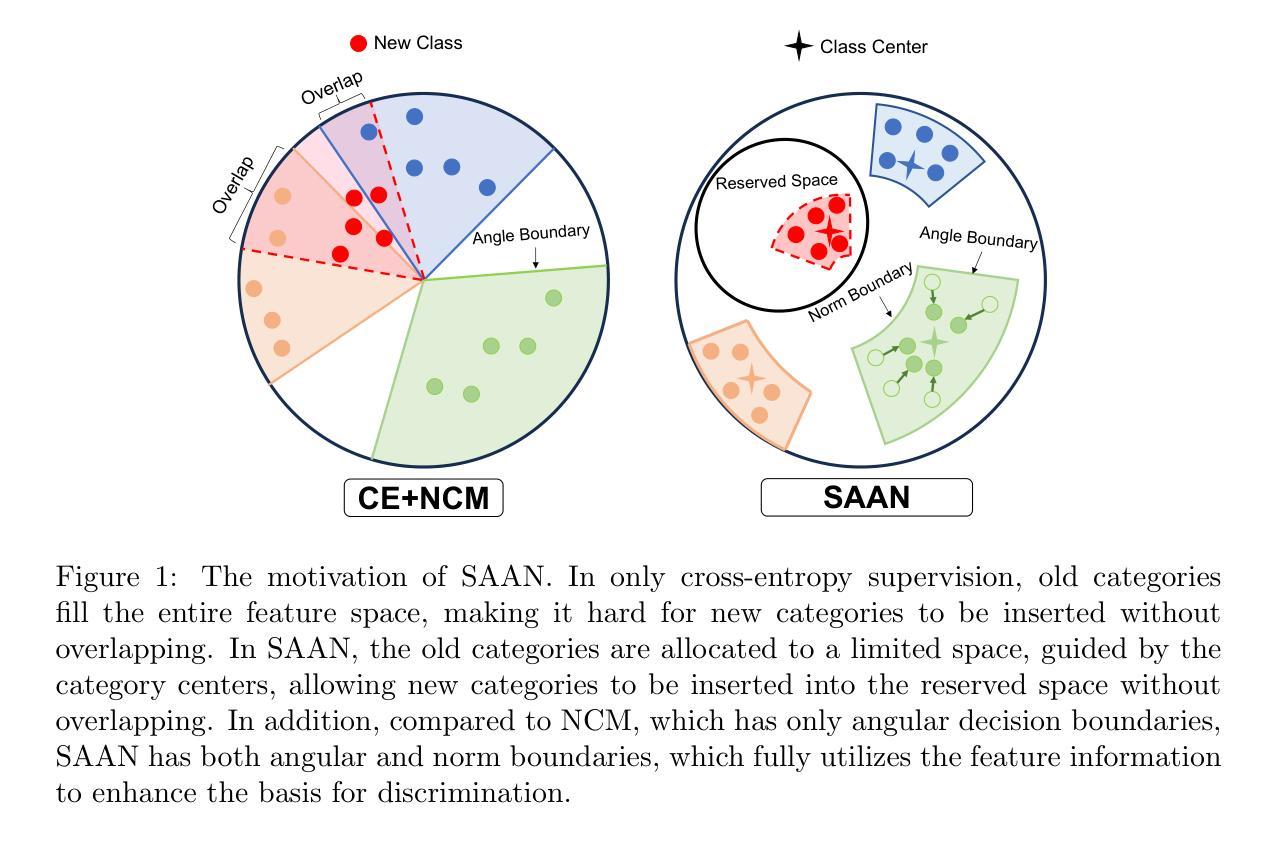
Embedding Space Allocation with Angle-Norm Joint Classifiers for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Dunwei Tu, Huiyu Yi, Tieyi Zhang, Ruotong Li, Furao Shen, Jian Zhao
Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) aims to continually learn new classes from only a few samples without forgetting previous ones, requiring intelligent agents to adapt to dynamic environments. FSCIL combines the characteristics and challenges of class-incremental learning and few-shot learning: (i) Current classes occupy the entire feature space, which is detrimental to learning new classes. (ii) The small number of samples in incremental rounds is insufficient for fully training. In existing mainstream virtual class methods, for addressing the challenge (i), they attempt to use virtual classes as placeholders. However, new classes may not necessarily align with the virtual classes. For the challenge (ii), they replace trainable fully connected layers with Nearest Class Mean (NCM) classifiers based on cosine similarity, but NCM classifiers do not account for sample imbalance issues. To address these issues in previous methods, we propose the class-center guided embedding Space Allocation with Angle-Norm joint classifiers (SAAN) learning framework, which provides balanced space for all classes and leverages norm differences caused by sample imbalance to enhance classification criteria. Specifically, for challenge (i), SAAN divides the feature space into multiple subspaces and allocates a dedicated subspace for each session by guiding samples with the pre-set category centers. For challenge (ii), SAAN establishes a norm distribution for each class and generates angle-norm joint logits. Experiments demonstrate that SAAN can achieve state-of-the-art performance and it can be directly embedded into other SOTA methods as a plug-in, further enhancing their performance.
少量样本类增量学习(FSCIL)旨在从仅有的少量样本中持续学习新的类别,同时不遗忘之前学过的内容,这需要智能代理适应动态环境。FSCIL结合了类增量学习和少量样本学习的特性和挑战:(i)当前类别占据了整个特征空间,这对学习新类别是不利的。(ii)增量轮次中的样本数量很少,不足以进行充分训练。在现有的主流虚拟类方法中,为了解决挑战(i),他们尝试使用虚拟类作为占位符。然而,新类别并不一定与虚拟类别对齐。对于挑战(ii),他们基于余弦相似性,用可训练的全连接层替换最近类均值(NCM)分类器,但NCM分类器并没有解决样本不平衡问题。为了解决之前方法中的这些问题,我们提出了类中心引导嵌入空间分配与角度范数联合分类器(SAAN)学习框架,它为所有类别提供了平衡的空间,并利用样本不平衡引起的范数差异来增强分类标准。具体来说,对于挑战(i),SAAN将特征空间划分为多个子空间,并通过预设的类别中心引导样本,为每一轮分配一个专用的子空间。对于挑战(ii),SAAN为每一类建立范数分布,并生成角度-范数联合逻辑。实验表明,SAAN可以达到最先进的性能,并且可以作为插件直接嵌入到其他SOTA方法中,进一步提高其性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted to Neural Networks
Summary:
本文介绍了面向持续学习的Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)技术,该技术旨在从少量样本中持续学习新类别而又不遗忘已学类别。针对当前类别占据整个特征空间不利于学习新类别以及样本量不足的问题,本文提出了一个名为SAAN的学习框架,通过划分特征空间为多个子空间并为每个会话分配专用子空间来解决第一个问题;通过建立每个类别的范数分布并生成角度范数联合对数来解决第二个问题。实验表明,SAAN可以达到最新技术水平,并且可以嵌入到其他先进方法中作为插件来提高性能。
Key Takeaways:
- Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL)的目标是在不断变化的动态环境中,从有限的样本中学习新的类别,同时保留对旧类别的知识。
- 当前的主流方法使用虚拟类作为占位符来解决特征空间占用问题,但新类别可能与虚拟类不匹配。
- 现有方法采用基于余弦相似度的最近类均值(NCM)分类器解决样本数量不足的问题,但忽略了样本不平衡的问题。
- SAAN学习框架通过划分特征空间并引导样本到预设的类别中心来解决特征空间占用问题。
- SAAN建立每个类别的范数分布并生成角度范数联合对数来解决样本不平衡和数量不足的问题。
- 实验表明SAAN在性能上达到了最新技术水平,并且可以与其他先进方法结合使用以提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

SQLNet: Scale-Modulated Query and Localization Network for Few-Shot Class-Agnostic Counting
Authors:Hefeng Wu, Yandong Chen, Lingbo Liu, Tianshui Chen, Keze Wang, Liang Lin
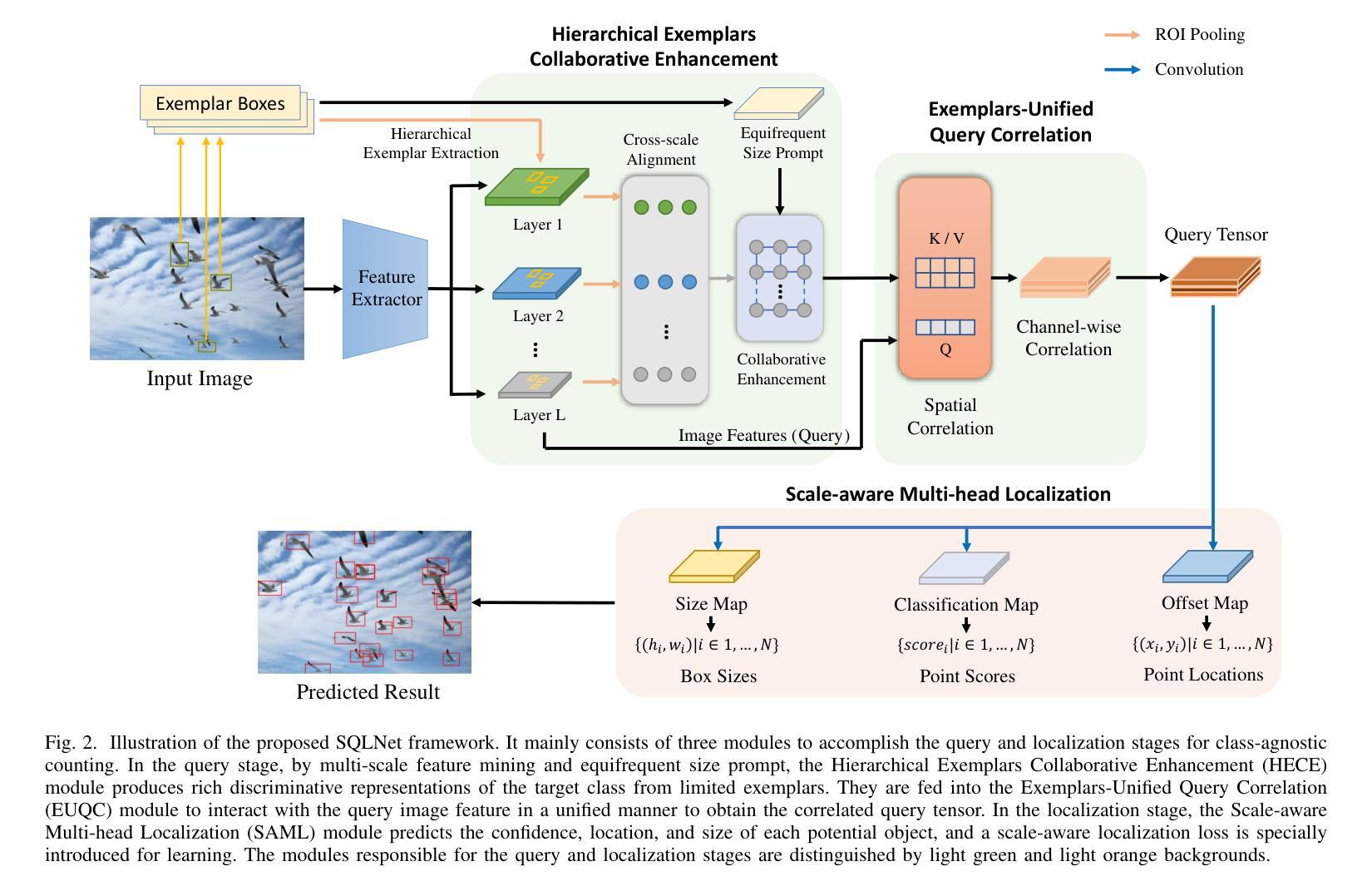
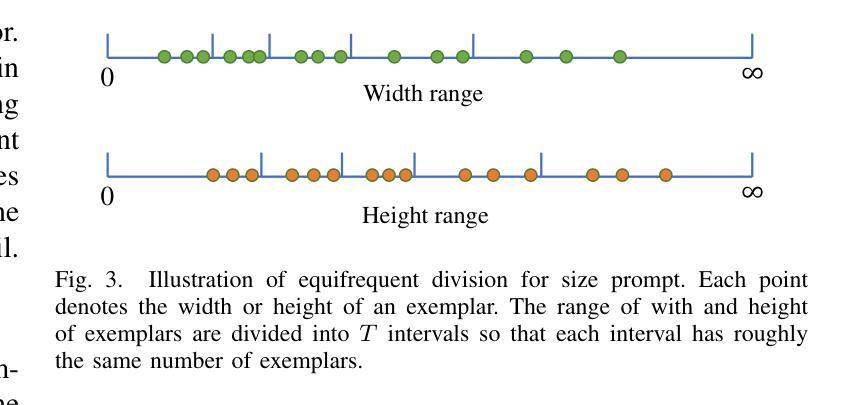
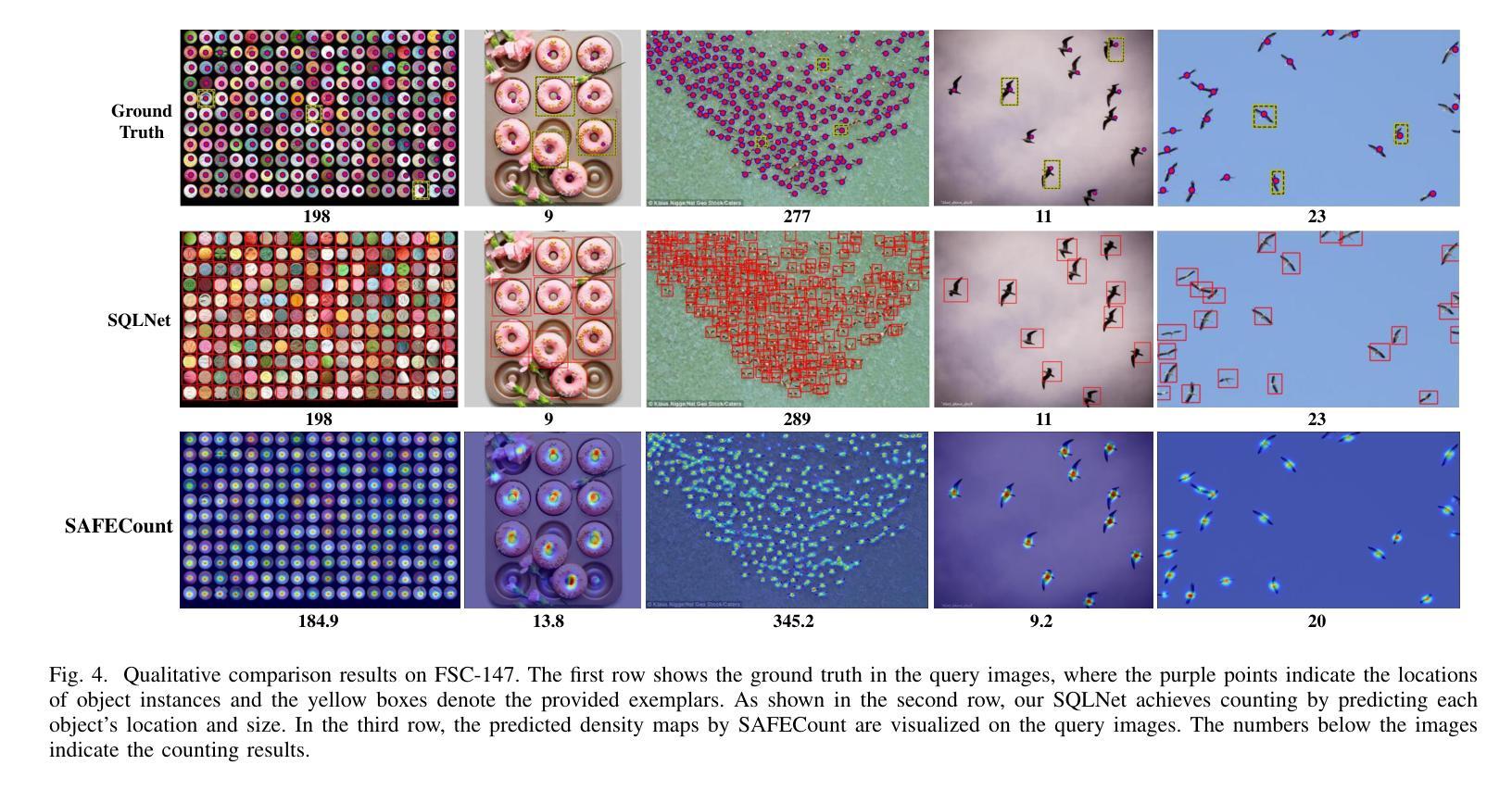
The class-agnostic counting (CAC) task has recently been proposed to solve the problem of counting all objects of an arbitrary class with several exemplars given in the input image. To address this challenging task, existing leading methods all resort to density map regression, which renders them impractical for downstream tasks that require object locations and restricts their ability to well explore the scale information of exemplars for supervision. To address the limitations, we propose a novel localization-based CAC approach, termed Scale-modulated Query and Localization Network (SQLNet). It fully explores the scales of exemplars in both the query and localization stages and achieves effective counting by accurately locating each object and predicting its approximate size. Specifically, during the query stage, rich discriminative representations of the target class are acquired by the Hierarchical Exemplars Collaborative Enhancement (HECE) module from the few exemplars through multi-scale exemplar cooperation with equifrequent size prompt embedding. These representations are then fed into the Exemplars-Unified Query Correlation (EUQC) module to interact with the query features in a unified manner and produce the correlated query tensor. In the localization stage, the Scale-aware Multi-head Localization (SAML) module utilizes the query tensor to predict the confidence, location, and size of each potential object. Moreover, a scale-aware localization loss is introduced, which exploits flexible location associations and exemplar scales for supervision to optimize the model performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SQLNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods on popular CAC benchmarks, achieving excellent performance not only in counting accuracy but also in localization and bounding box generation. Our codes will be available at https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/SQLNet
类不可知计数(CAC)任务最近被提出,以解决在输入图像中给定多个范例时计数任意类所有对象的问题。针对这一具有挑战性的任务,现有的领先方法都依赖于密度图回归,这使得它们对于需要对象位置的下游任务不实用,并限制了它们探索范例规模信息的能力以进行监督。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于定位的新颖CAC方法,称为Scale-modulated Query and Localization Network(SQLNet)。它在查询和定位阶段充分探索了范例的规模,并通过准确定位每个对象和预测其近似大小来实现有效的计数。具体来说,在查询阶段,通过多层次范例协同增强(HECE)模块从少量范例中获取目标类的丰富判别表示,通过多尺度范例合作和等频大小提示嵌入获得这些表示。然后,这些表示被送入范例统一查询关联(EUQC)模块,以统一的方式与查询特征进行交互,并产生相关查询张量。在定位阶段,规模感知多头定位(SAML)模块利用查询张量来预测每个潜在对象的置信度、位置和大小。此外,引入了一种规模感知定位损失,它利用灵活的定位关联和范例规模进行监督,以优化模型性能。大量实验表明,SQLNet在流行的CAC基准测试中优于最新方法,不仅在计数精度方面表现出色,而且在定位和边界框生成方面也表现出色。我们的代码将在https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/SQLNet上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
Summary
本文提出了一种基于定位的经典无关计数(CAC)任务新方法,名为Scale-modulated Query and Localization Network(SQLNet)。该方法在查询和定位阶段充分利用了范例的尺度信息,通过精准定位每个对象并预测其大致尺寸,实现了有效的计数。实验表明,SQLNet在流行的CAC基准测试上优于现有方法,不仅在计数精度上表现优异,而且在定位和生成边界框方面也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 经典无关计数(CAC)任务旨在解决在输入图像中计数任意类所有对象的问题。
- 现有领先方法主要依赖密度图回归,这不适用于需要对象位置的下游任务,且限制了范例尺度信息的探索。
- SQLNet方法提出一种基于定位的解决方案,在查询和定位阶段充分利用范例的尺度信息。
- SQLNet通过精准定位每个对象并预测其大小来实现有效计数。
- Hierarchical Exemplars Collaborative Enhancement(HECE)模块通过多尺度范例合作和等频尺寸提示嵌入,获取目标类的丰富判别表示。
- Exemplars-Unified Query Correlation(EUQC)模块以统一的方式与查询特征进行交互,产生相关的查询张量。
点此查看论文截图