⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
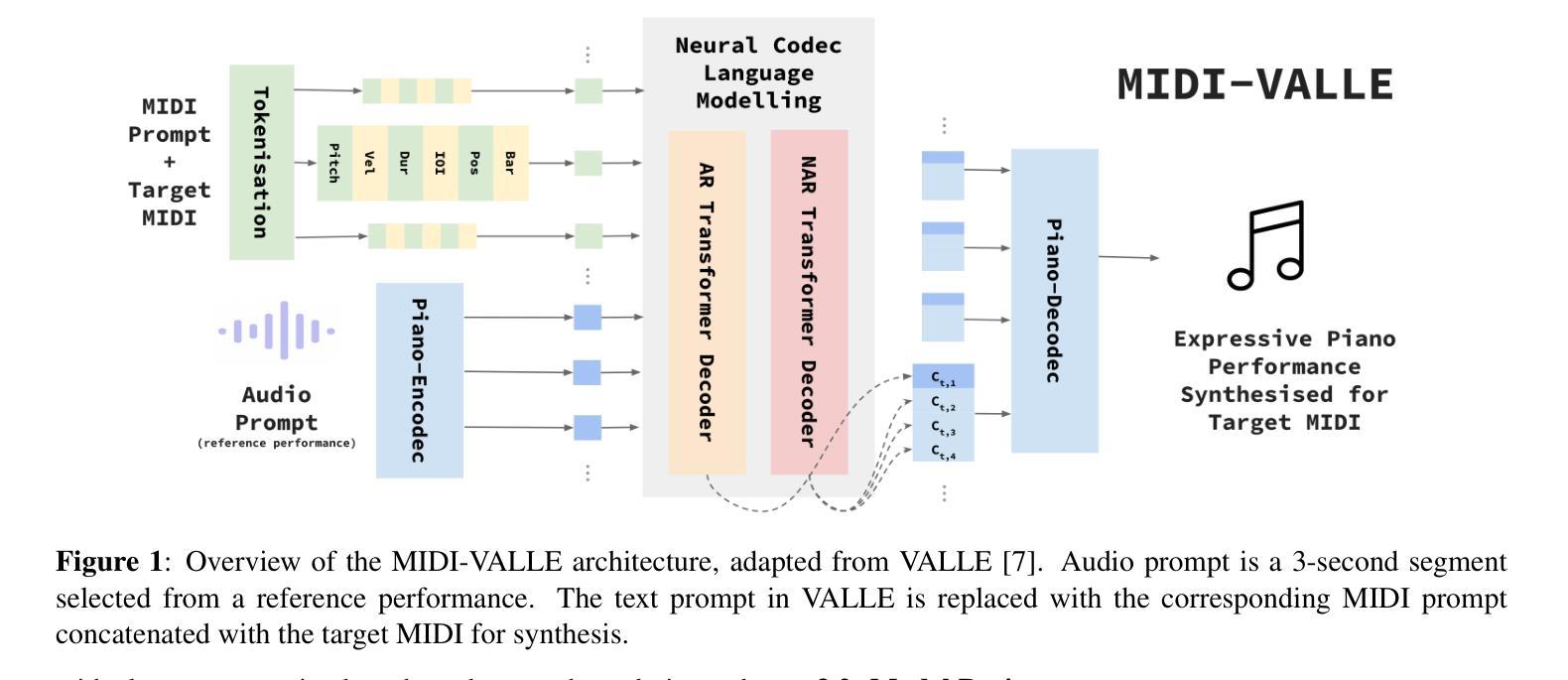
MIDI-VALLE: Improving Expressive Piano Performance Synthesis Through Neural Codec Language Modelling
Authors:Jingjing Tang, Xin Wang, Zhe Zhang, Junichi Yamagishi, Geraint Wiggins, George Fazekas
Generating expressive audio performances from music scores requires models to capture both instrument acoustics and human interpretation. Traditional music performance synthesis pipelines follow a two-stage approach, first generating expressive performance MIDI from a score, then synthesising the MIDI into audio. However, the synthesis models often struggle to generalise across diverse MIDI sources, musical styles, and recording environments. To address these challenges, we propose MIDI-VALLE, a neural codec language model adapted from the VALLE framework, which was originally designed for zero-shot personalised text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. For performance MIDI-to-audio synthesis, we improve the architecture to condition on a reference audio performance and its corresponding MIDI. Unlike previous TTS-based systems that rely on piano rolls, MIDI-VALLE encodes both MIDI and audio as discrete tokens, facilitating a more consistent and robust modelling of piano performances. Furthermore, the model’s generalisation ability is enhanced by training on an extensive and diverse piano performance dataset. Evaluation results show that MIDI-VALLE significantly outperforms a state-of-the-art baseline, achieving over 75% lower Frechet Audio Distance on the ATEPP and Maestro datasets. In the listening test, MIDI-VALLE received 202 votes compared to 58 for the baseline, demonstrating improved synthesis quality and generalisation across diverse performance MIDI inputs.
从乐谱生成富有表现力的音频表演需要模型捕捉乐器的声学特性和人类解释。传统音乐表演合成管道遵循两阶段方法,首先根据乐谱生成富有表现力的性能MIDI,然后将MIDI合成音频。然而,合成模型往往难以在多种MIDI源、音乐风格和录音环境中进行推广。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MIDI-VALLE,这是一个基于VALLE框架改编的神经编码语言模型,VALLE框架最初是为零样本个性化文本到语音(TTS)合成而设计的。对于性能MIDI到音频合成,我们改进了架构,使其依赖于参考音频表演及其对应的MIDI。与之前的基于TTS的系统不同,MIDI-VALLE将MIDI和音频都编码为离散标记,从而更一致、更稳健地建模钢琴表演。此外,通过在广泛且多样的钢琴表演数据集上进行训练,增强了模型的泛化能力。评估结果表明,MIDI-VALLE显著优于最先进的基线模型,在ATEPP和Maestro数据集上的Frechet Audio Distance降低了超过75%。在听力测试中,MIDI-VALLE获得了202票,而基线模型获得了58票,表明其合成质量和在不同性能MIDI输入的泛化能力都有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISMIR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了音乐表演合成面临的挑战以及一种新的解决方案——MIDI-VALLE模型。该模型基于VALLE框架的神经编解码器语言模型,首先生成音乐的MIDI表现,再将其转化为音频。MIDI-VALLE模型能处理不同的MIDI源、音乐风格和录音环境,其表现超越了现有的先进基线模型。该模型使用一种广泛的钢琴表演数据集进行训练,显著提高了合成质量和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- MIDI-VALLE模型结合了音乐分数和人的解读,生成具有表现力的音频表演。
- 传统音乐表演合成流程分为两个阶段:生成表现性MIDI和合成音频。但合成模型在多样化MIDI源、音乐风格和录音环境上的泛化能力有限。
- MIDI-VALLE模型基于VALLE框架的神经编解码器语言模型,用于MIDI到音频的合成。
- MIDI-VALLE通过编码MIDI和音频为离散令牌,提高了钢琴表演的建模一致性。这与传统的基于TTS的系统不同。
- 模型通过广泛的钢琴表演数据集进行训练,增强了泛化能力。
- MIDI-VALLE在ATEPP和Maestro数据集上的表现显著优于现有基线模型。
点此查看论文截图

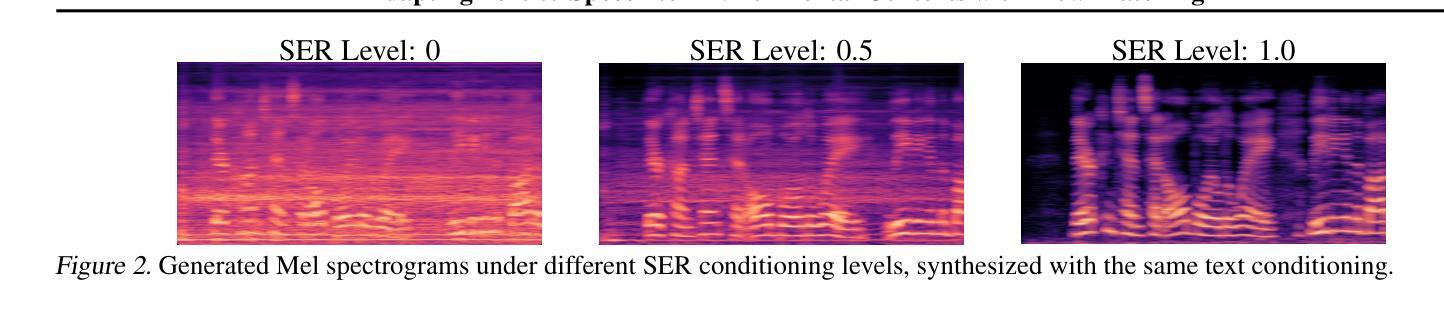
RepeaTTS: Towards Feature Discovery through Repeated Fine-Tuning
Authors:Atli Sigurgeirsson, Simon King
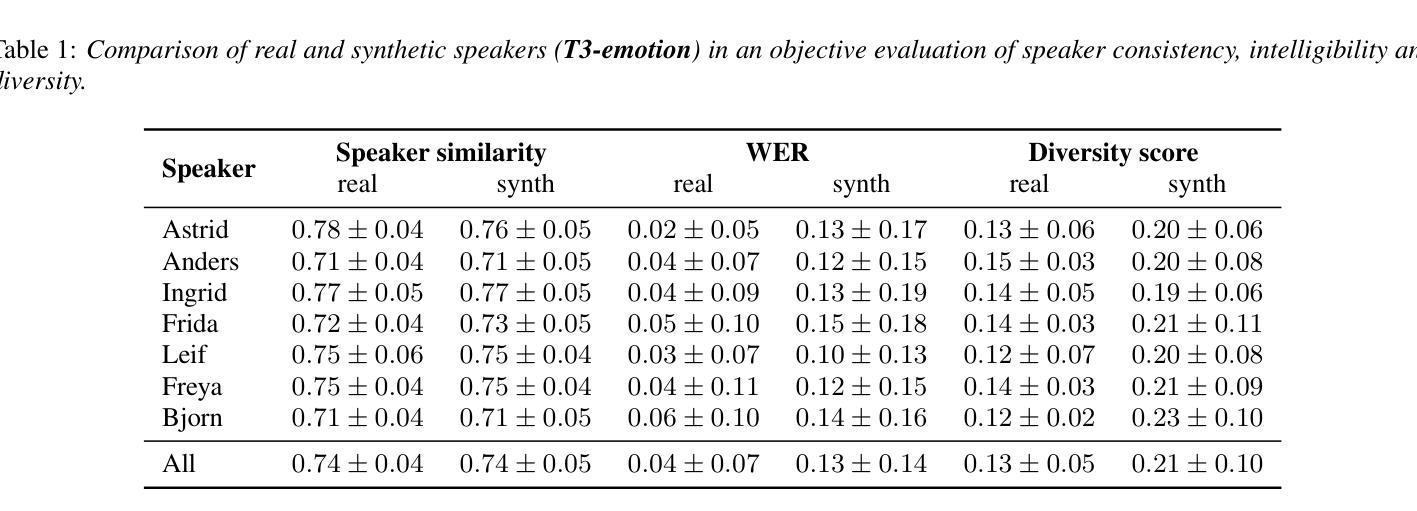
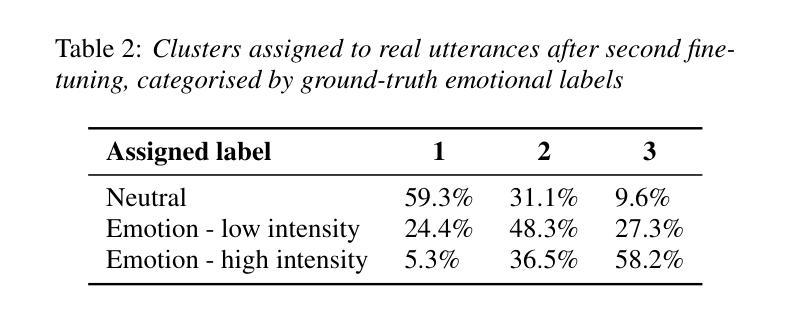
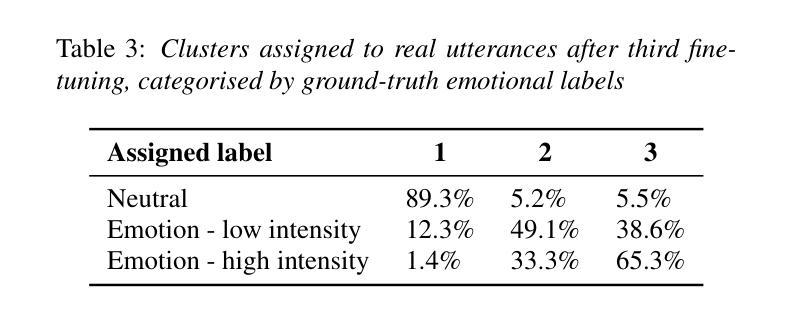
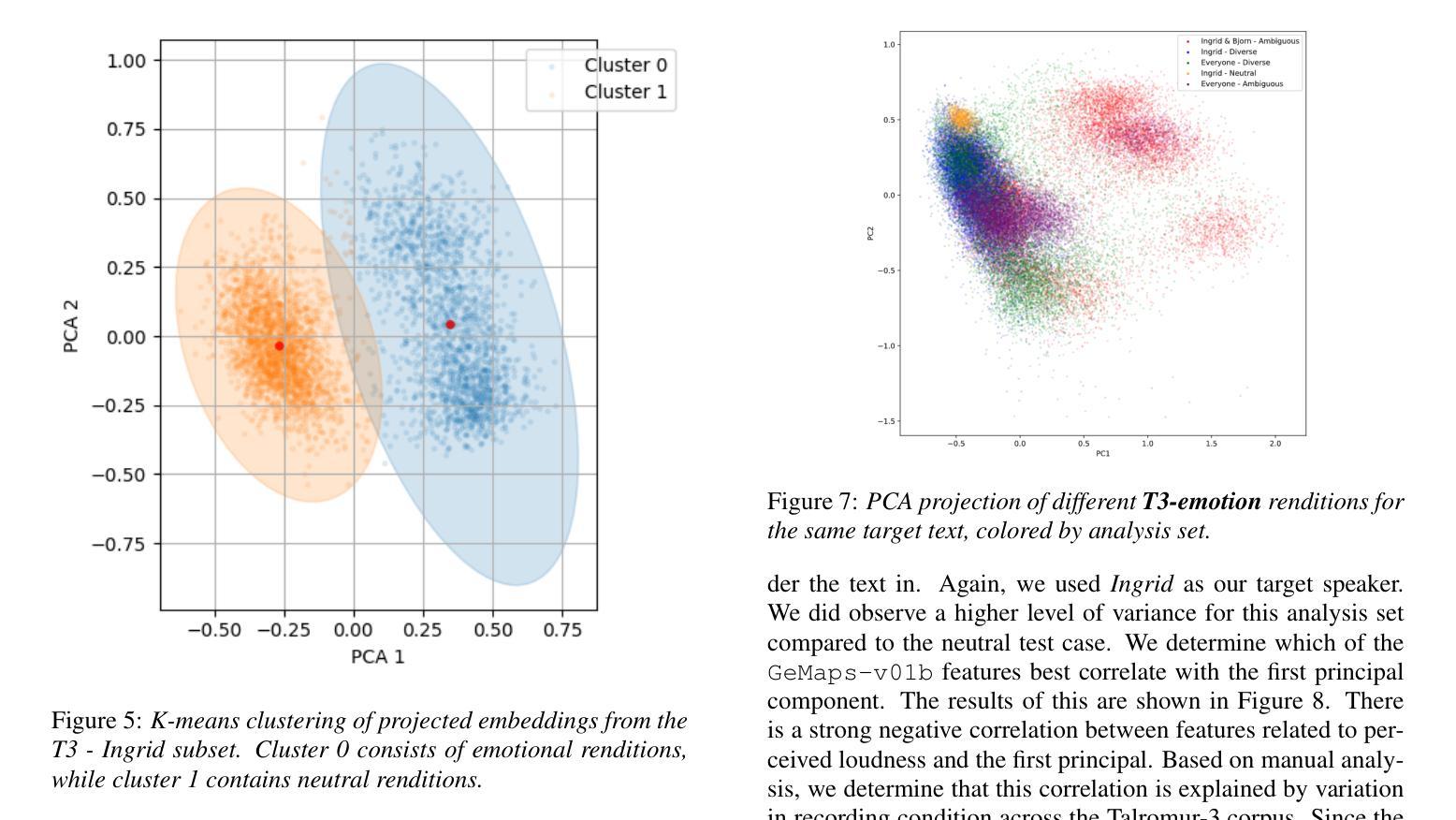
A Prompt-based Text-To-Speech model allows a user to control different aspects of speech, such as speaking rate and perceived gender, through natural language instruction. Although user-friendly, such approaches are on one hand constrained: control is limited to acoustic features exposed to the model during training, and too flexible on the other: the same inputs yields uncontrollable variation that are reflected in the corpus statistics. We investigate a novel fine-tuning regime to address both of these issues at the same time by exploiting the uncontrollable variance of the model. Through principal component analysis of thousands of synthesised samples, we determine latent features that account for the highest proportion of the output variance and incorporate them as new labels for secondary fine-tuning. We evaluate the proposed methods on two models trained on an expressive Icelandic speech corpus, one with emotional disclosure and one without. In the case of the model without emotional disclosure, the method yields both continuous and discrete features that improve overall controllability of the model.
基于提示的文本转语音模型允许用户通过自然语言指令控制语音的各个方面,如语速和感知的性别。虽然用户友好,但这种方法一方面受到限制:控制仅限于模型在训练期间接触到的声学特征;另一方面过于灵活:相同输入会产生不可控制的变异,反映在语料库统计数据中。我们通过利用模型的不可控制变化来研究一种新型微调机制,同时解决这两个问题。通过对数千个合成样本进行主成分分析,我们确定了占输出变化最高比例的潜在特征,并将它们作为次要细调的标签。我们在两个冰岛表达性语音语料库训练的模型上评估了这些方法,一个有情感披露的模型和一个没有的模型。对于没有情感披露的模型,该方法产生了连续和离散的特征,提高了模型的总体可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了一种基于提示的文本到语音模型,该模型通过自然语言指令控制语音的不同方面,如语速和感知性别。然而,这种方法存在局限性,控制仅限于模型训练期间暴露的声学特征,且同一输入产生的输出不可控。为了解决这个问题,研究人员采用了一种新型的微调方法,利用模型的不可控变量来识别主要的潜在特征并将其纳入次要微调的新标签中。评估结果表明,在不涉及情感披露的情况下,该方法能够改善模型的连续和离散特征,从而提高模型的总体可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 基于提示的文本到语音模型允许用户通过自然语言指令控制语音的不同方面。
- 这种方法的局限性在于控制仅限于模型训练期间暴露的声学特征。
- 同一输入产生的输出存在不可控性。
- 研究人员采用新型微调方法来解决这些问题。
- 通过主成分分析合成的样本,确定输出方差中占最大比例的潜在特征。
- 将这些潜在特征纳入次要微调的新标签中。
点此查看论文截图

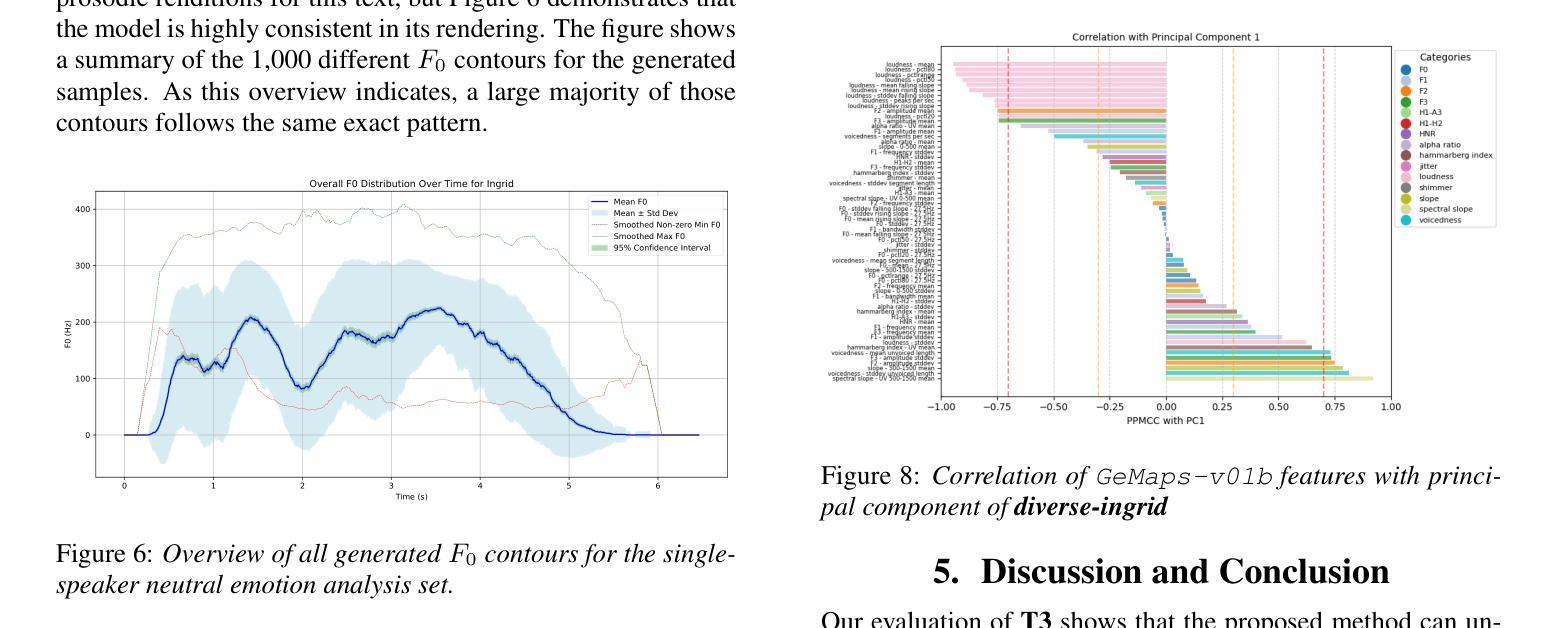
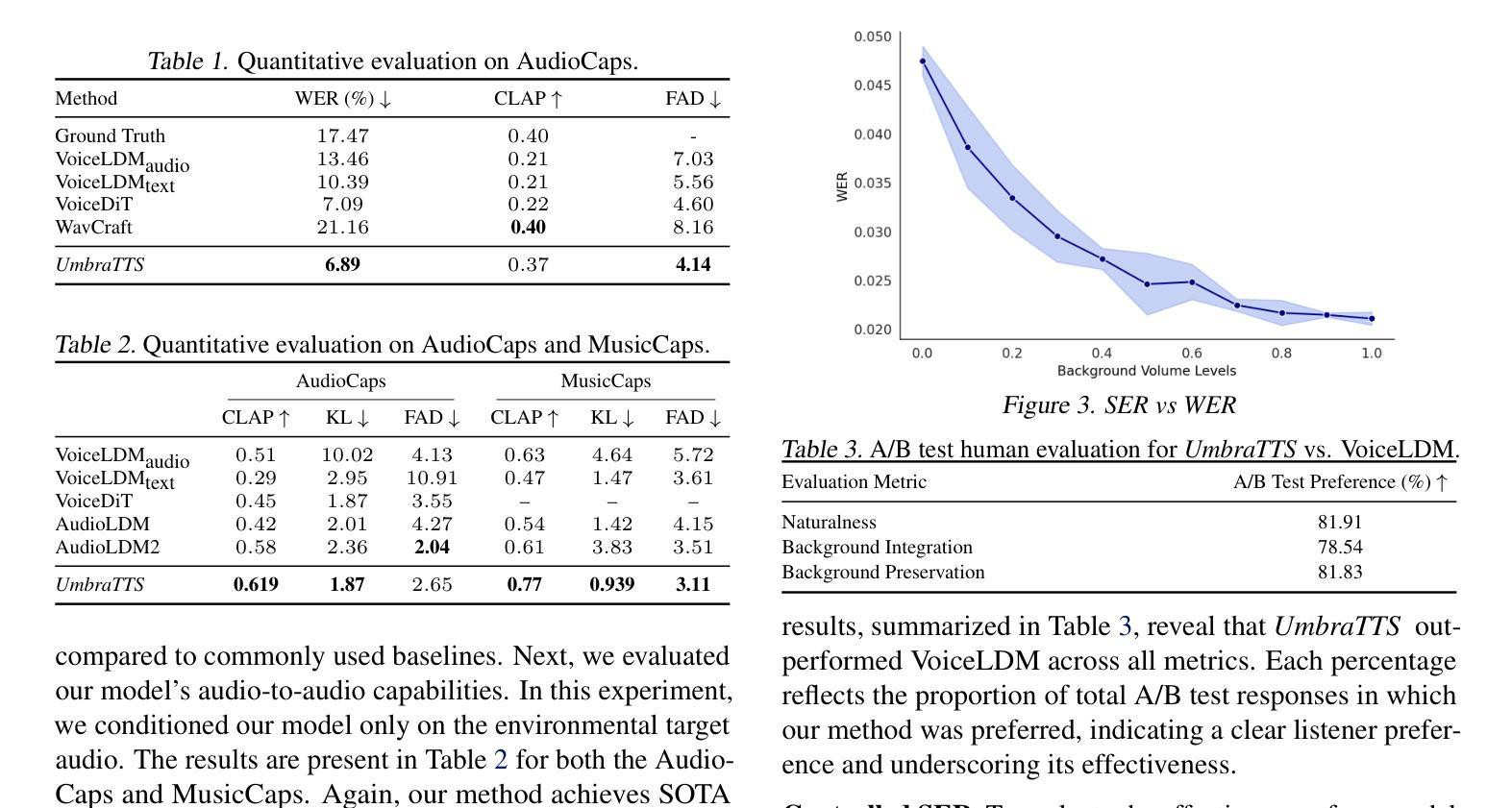
UmbraTTS: Adapting Text-to-Speech to Environmental Contexts with Flow Matching
Authors:Neta Glazer, Aviv Navon, Yael Segal, Aviv Shamsian, Hilit Segev, Asaf Buchnick, Menachem Pirchi, Gil Hetz, Joseph Keshet
Recent advances in Text-to-Speech (TTS) have enabled highly natural speech synthesis, yet integrating speech with complex background environments remains challenging. We introduce UmbraTTS, a flow-matching based TTS model that jointly generates both speech and environmental audio, conditioned on text and acoustic context. Our model allows fine-grained control over background volume and produces diverse, coherent, and context-aware audio scenes. A key challenge is the lack of data with speech and background audio aligned in natural context. To overcome the lack of paired training data, we propose a self-supervised framework that extracts speech, background audio, and transcripts from unannotated recordings. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that UmbraTTS significantly outperformed existing baselines, producing natural, high-quality, environmentally aware audios.
近期文本转语音(TTS)的进步已经实现了高度自然的语音合成,然而,将语音与复杂的背景环境相结合仍然是一个挑战。我们引入了UmbraTTS,这是一种基于流匹配的TTS模型,能够根据文本和声学上下文联合生成语音和环境音频。我们的模型可以对背景音量进行精细控制,并生成多样化、连贯、上下文感知的音频场景。一个关键挑战是缺乏在自然环境下语音和背景音频对齐的数据。为了克服配对训练数据的缺乏,我们提出了一种自监督框架,可以从未标注的录音中提取语音、背景音频和字幕。广泛评估表明,UmbraTTS显著优于现有基线,生成自然、高质量、环境意识音频。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML Workshop on Machine Learning for Audio 2025
Summary
在文本转语音(TTS)领域,近期进展虽已实现高度自然的语音合成,但将语音与复杂背景环境融合仍具挑战。为此,我们推出UmbraTTS,一款基于流匹配的TTS模型,能根据文本和声音背景联合生成语音和环境音频。该模型允许对背景音量进行精细控制,并能生成多样、连贯、语境感知的音频场景。面临的关键挑战是缺乏自然语境下语音与背景音频对齐的数据。为克服配对训练数据的缺乏,我们提出一种自监督框架,可从未标注录音中提取语音、背景音频和转录信息。评估结果显示,UmbraTTS显著优于现有基线,能生成自然、高质量、环境感知的音频。
Key Takeaways
- UmbraTTS是一款基于流匹配的TTS模型,能联合生成语音和环境音频。
- 该模型实现了对背景音量的精细控制。
- UmbraTTS能生成多样、连贯、语境感知的音频场景。
- 缺乏自然语境下对齐的语音和背景音频数据是TTS领域的主要挑战。
- 为解决数据缺乏问题,提出了自监督框架,可从未标注录音中提取所需数据。
- UmbraTTS性能显著,优于现有基线。
点此查看论文截图

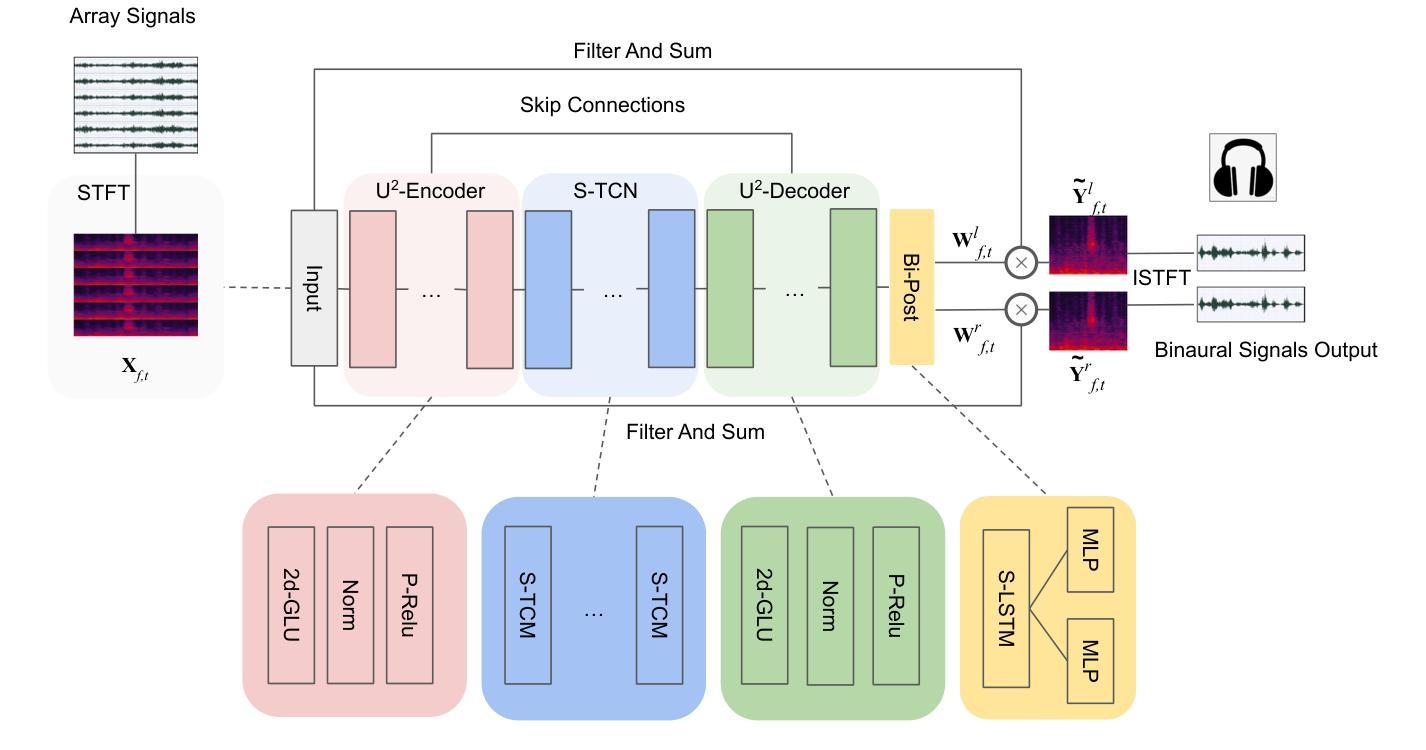
End-to-end multi-channel speaker extraction and binaural speech synthesis
Authors:Cheng Chi, Xiaoyu Li, Yuxuan Ke, Qunping Ni, Yao Ge, Xiaodong Li, Chengshi Zheng
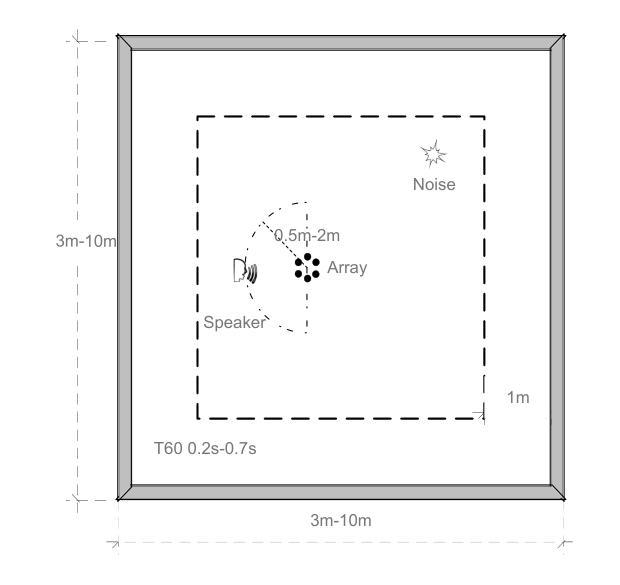
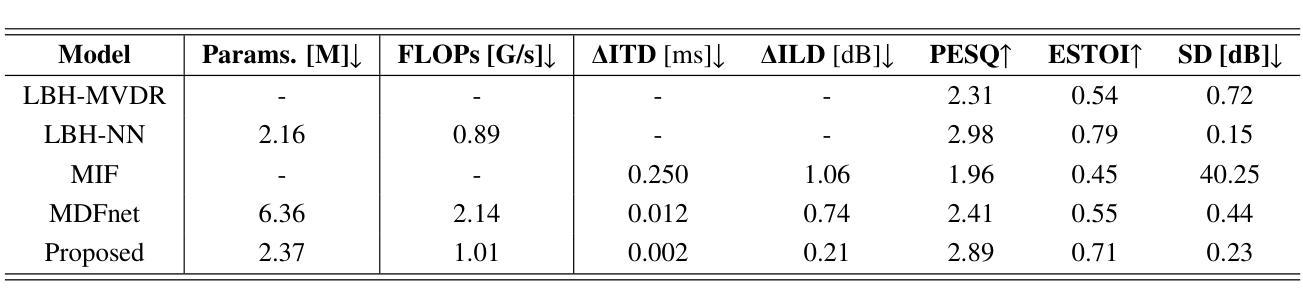
Speech clarity and spatial audio immersion are the two most critical factors in enhancing remote conferencing experiences. Existing methods are often limited: either due to the lack of spatial information when using only one microphone, or because their performance is highly dependent on the accuracy of direction-of-arrival estimation when using microphone array. To overcome this issue, we introduce an end-to-end deep learning framework that has the capacity of mapping multi-channel noisy and reverberant signals to clean and spatialized binaural speech directly. This framework unifies source extraction, noise suppression, and binaural rendering into one network. In this framework, a novel magnitude-weighted interaural level difference loss function is proposed that aims to improve the accuracy of spatial rendering. Extensive evaluations show that our method outperforms established baselines in terms of both speech quality and spatial fidelity.
远程会议体验中,语音清晰度和空间音频沉浸感是两个至关重要的因素。现有的方法往往存在局限性:要么是因为只使用单个麦克风而缺乏空间信息,要么是因为使用麦克风阵列时的性能高度依赖于到达方向估计的准确性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个端到端的深度学习框架,该框架具有将多通道噪声和混响信号直接映射到干净和立体化的双耳语音的能力。该框架将源提取、降噪和双耳渲染集成到一个网络中。在该框架中,提出了一个新的幅度加权跨耳电平差损失函数,旨在提高空间渲染的准确性。大量评估表明,我们的方法在语音质量和空间保真度方面都优于既定的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注远程会议体验的提升,指出语音清晰度和空间音频沉浸感是关键因素。现有方法常受限,如单麦克风缺乏空间信息,或使用麦克风阵列时性能高度依赖于到达方向估计的准确性。为此,本文提出一种端到端的深度学习框架,能够直接将多通道噪声和混响信号映射为干净且空间化的双耳语音。该框架将音源提取、降噪和双耳渲染集成到一个网络中,并引入一种新的幅度加权耳间水平差损失函数,旨在提高空间渲染的准确性。评估表明,该方法在语音质量和空间保真度方面均优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 远程会议中,语音清晰度和空间音频沉浸感对于体验至关重要。
- 现有方法在使用单麦克风或多通道麦克风阵列时存在局限性。
- 深度学习框架能够处理多通道噪声和混响信号,直接生成干净且空间化的双耳语音。
- 框架集成了音源提取、降噪和双耳渲染。
- 引入新的幅度加权耳间水平差损失函数以提高空间渲染的准确性。
- 该方法在语音质量和空间保真度方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

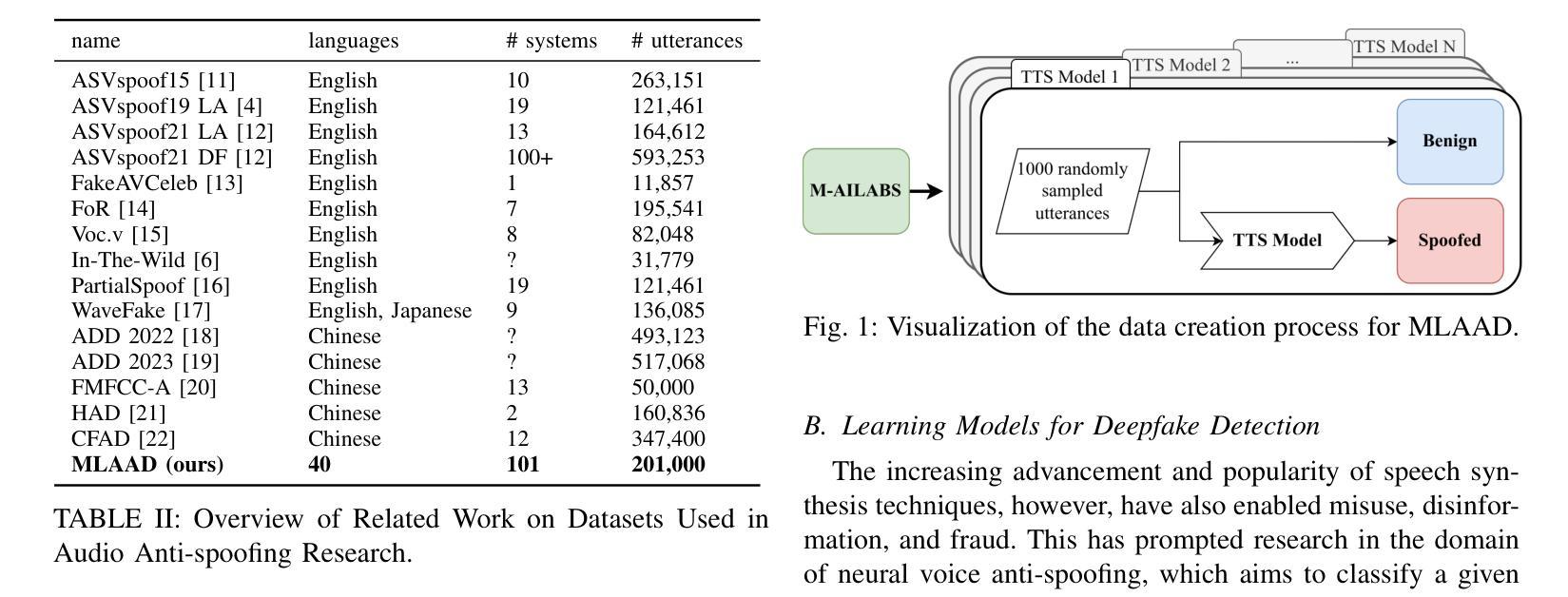
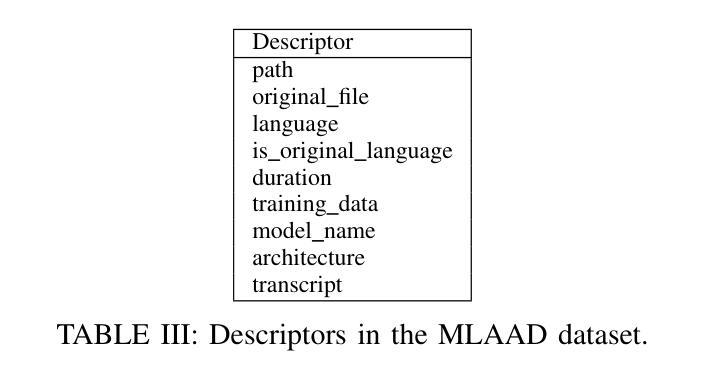
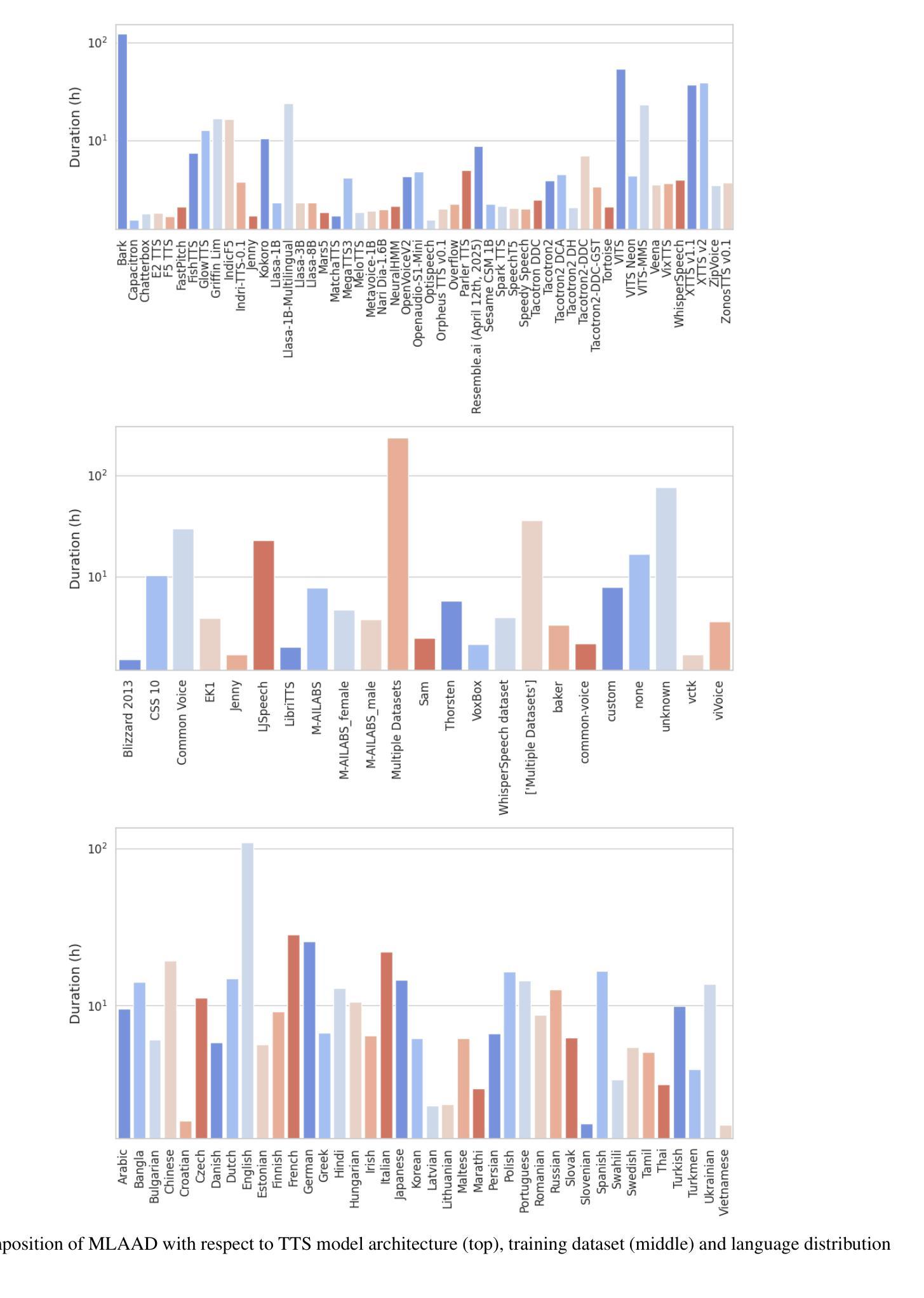
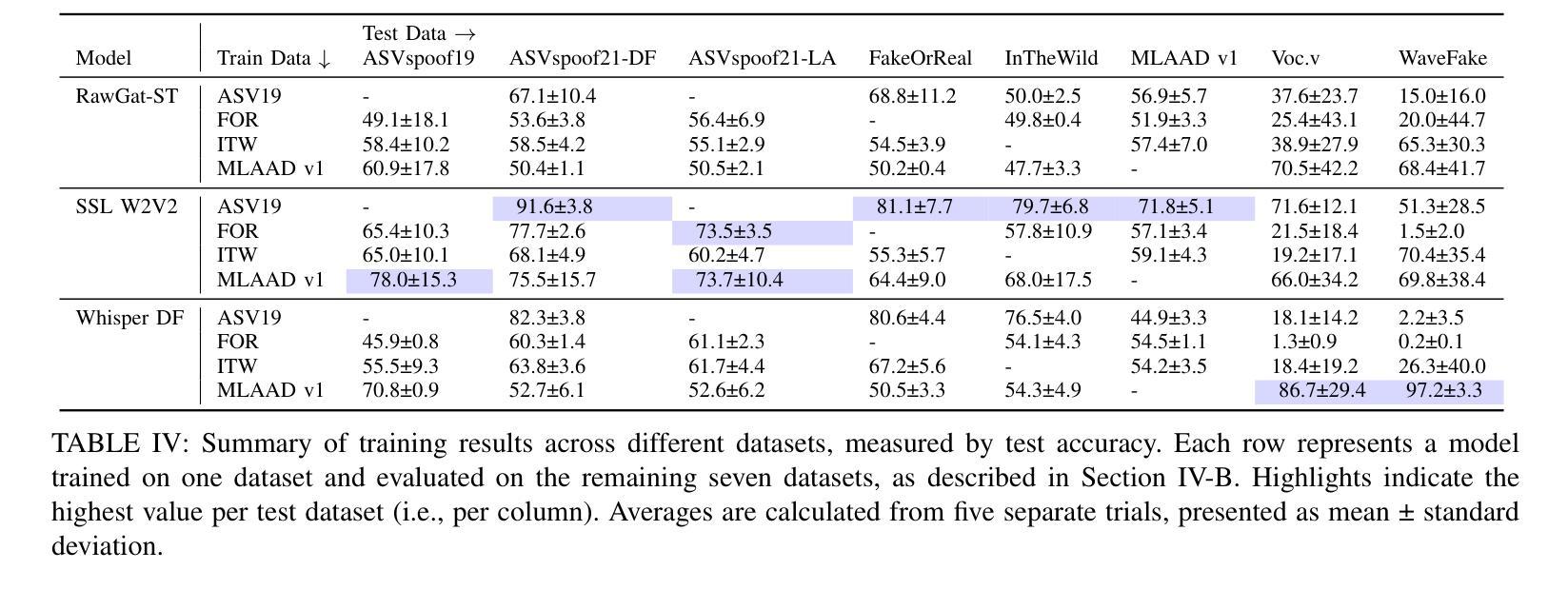
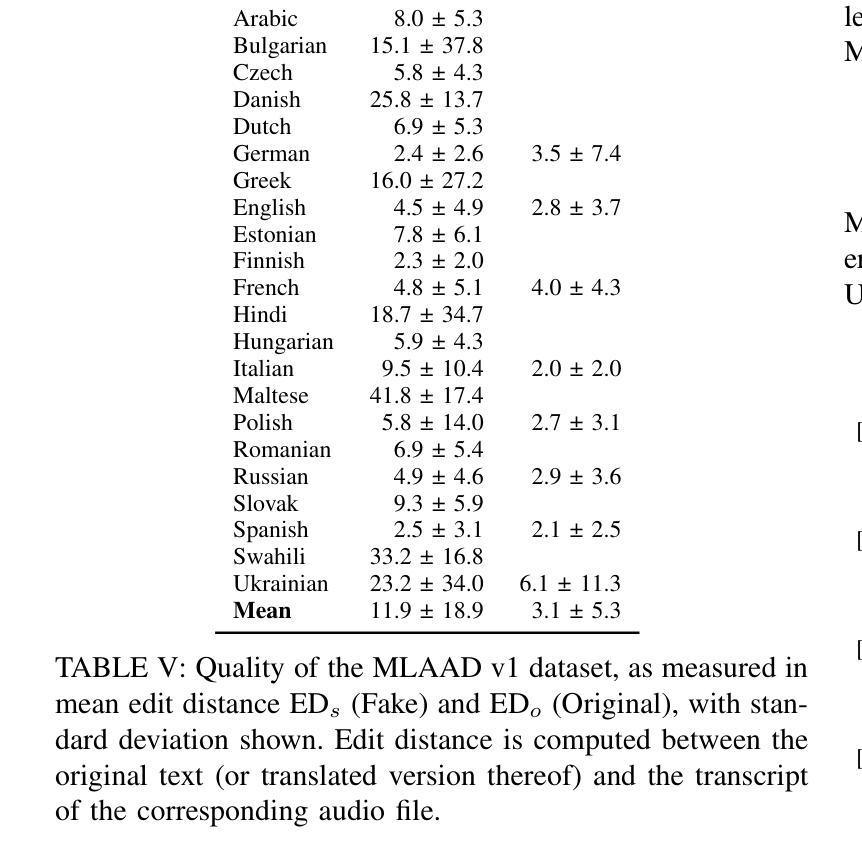
MLAAD: The Multi-Language Audio Anti-Spoofing Dataset
Authors:Nicolas M. Müller, Piotr Kawa, Wei Herng Choong, Edresson Casanova, Eren Gölge, Thorsten Müller, Piotr Syga, Philip Sperl, Konstantin Böttinger
Text-to-Speech (TTS) technology offers notable benefits, such as providing a voice for individuals with speech impairments, but it also facilitates the creation of audio deepfakes and spoofing attacks. AI-based detection methods can help mitigate these risks; however, the performance of such models is inherently dependent on the quality and diversity of their training data. Presently, the available datasets are heavily skewed towards English and Chinese audio, which limits the global applicability of these anti-spoofing systems. To address this limitation, this paper presents the Multi-Language Audio Anti-Spoofing Dataset (MLAAD), version 7, created using 101 TTS models, comprising 52 different architectures, to generate 485.3 hours of synthetic voice in 40 different languages. We train and evaluate three state-of-the-art deepfake detection models with MLAAD and observe that it demonstrates superior performance over comparable datasets like InTheWild and Fake-Or-Real when used as a training resource. Moreover, compared to the renowned ASVspoof 2019 dataset, MLAAD proves to be a complementary resource. In tests across eight datasets, MLAAD and ASVspoof 2019 alternately outperformed each other, each excelling on four datasets. By publishing MLAAD and making a trained model accessible via an interactive webserver, we aim to democratize anti-spoofing technology, making it accessible beyond the realm of specialists, and contributing to global efforts against audio spoofing and deepfakes.
文本转语音(TTS)技术提供了显著的益处,例如为言语障碍者提供声音,但它也促进了音频深度伪造和欺骗攻击的产生。基于人工智能的检测方法可以有助于缓解这些风险;然而,此类模型的性能本质上取决于其训练数据的质量和多样性。目前,可用的数据集严重偏向于英语和中文音频,这限制了这些防伪系统的全球适用性。为了解决这一局限性,本文介绍了多语言音频防伪数据集(MLAAD)第7版,该数据集使用101个TTS模型创建,包含52种不同的架构,生成了485.3小时的不同语言的合成语音。我们使用MLAAD训练并评估了三个最先进的深度伪造检测模型,并观察到当它用作训练资源时,其在InTheWild和Fake-Or-Real等可比数据集上表现出卓越的性能。而且,与著名的ASVspoof 2019数据集相比,MLAAD证明是一种补充资源。在八个数据集的测试中,MLAAD和ASVspoof 2019交替表现出各自的优势,各自在四个数据集上表现出色。我们旨在通过发布MLAAD并通过交互式网站提供训练有素的模型访问权限来使防伪技术民主化,使其超出专家领域变得触手可及,并为全球对抗音频欺骗和深度伪造做出努力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCNN 2024
Summary
本文介绍了多语言音频防伪数据集(MLAAD)的创建与应用。该数据集旨在解决现有防伪系统主要依赖英语和中文音频数据的问题,通过采用101种文本转语音(TTS)模型生成合成语音,以提高防伪系统的性能。研究结果表明,MLAAD数据集在多个测试集上的表现优于其他数据集,如InTheWild和Fake-Or-Real。此外,通过与知名的ASVspoof 2019数据集比较,发现MLAAD是一个互补资源,能够在不同数据集上表现出优异的性能。最后,通过发布MLAAD数据集和通过交互式网站提供训练模型,研究旨在使防伪技术民主化,使其易于公众使用,并有助于全球对抗音频伪造和深度伪造的努力。
Key Takeaways
- TTS技术虽然有助于为言语障碍者提供声音,但也促进了音频深度伪造和欺骗攻击的产生。
- AI检测方法是缓解这一风险的有效手段,但其性能依赖于训练数据的质量和多样性。
- 当前可用的数据集主要偏向英语和中文音频,限制了反欺骗系统的全球适用性。
- MLAAD数据集通过采用多种语言和TTS模型生成合成语音,旨在解决上述问题。
- MLAAD数据集在多个测试集上的性能优于其他数据集,如InTheWild和Fake-Or-Real。
- MLAAD和ASVspoof 2019数据集是互补的,能够在不同任务上表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图