⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
Multi-modal Mutual-Guidance Conditional Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Shijun Yang, Xiang Zhang, Wanqing Zhao, Hangzai Luo, Sheng Zhong, Jinye Peng, Jianping Fan
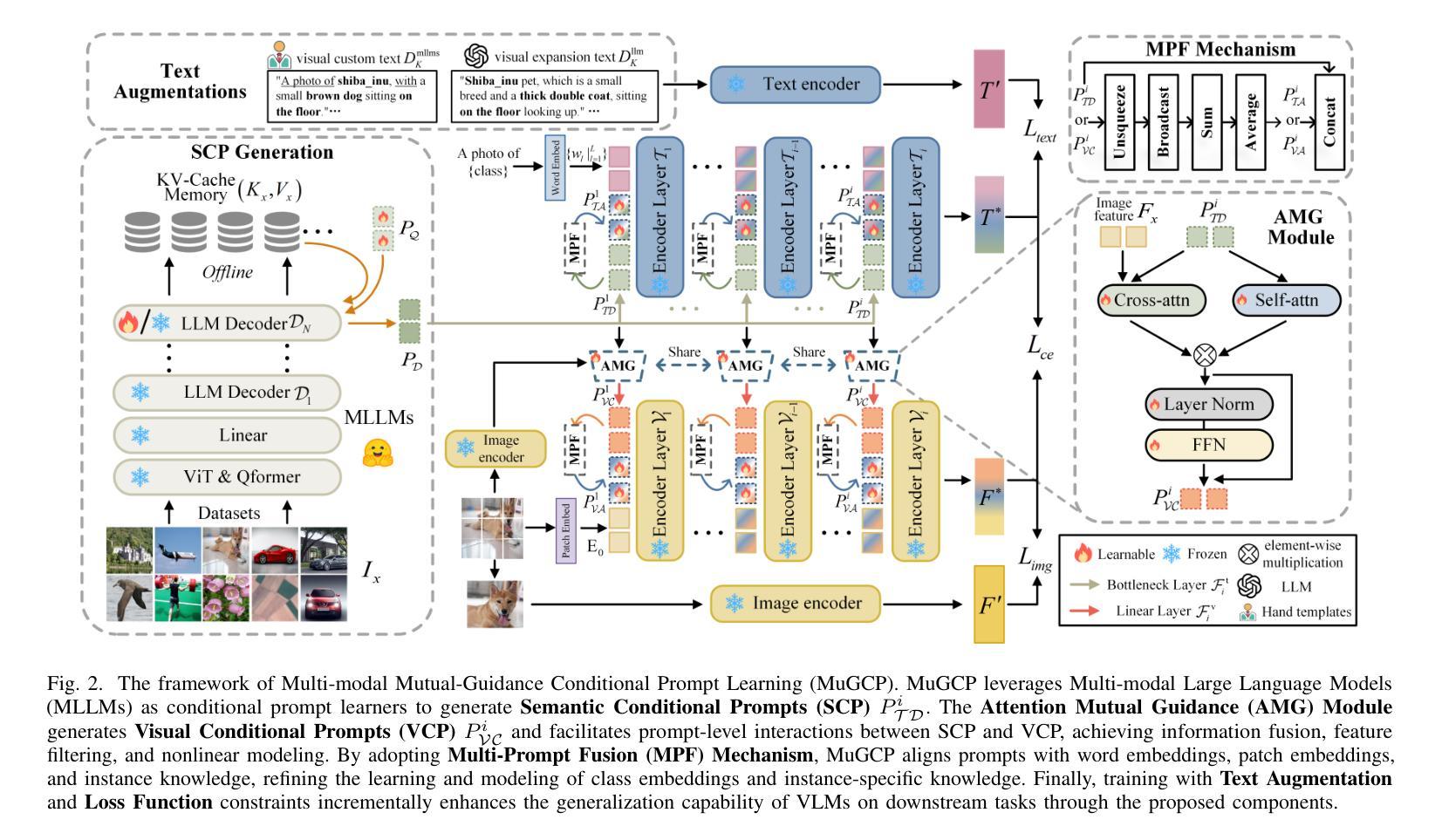
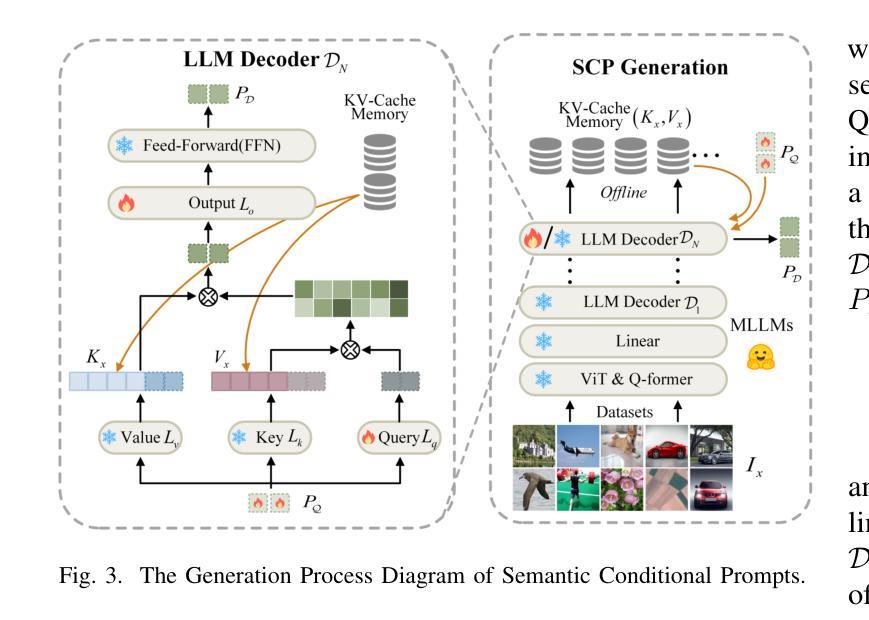
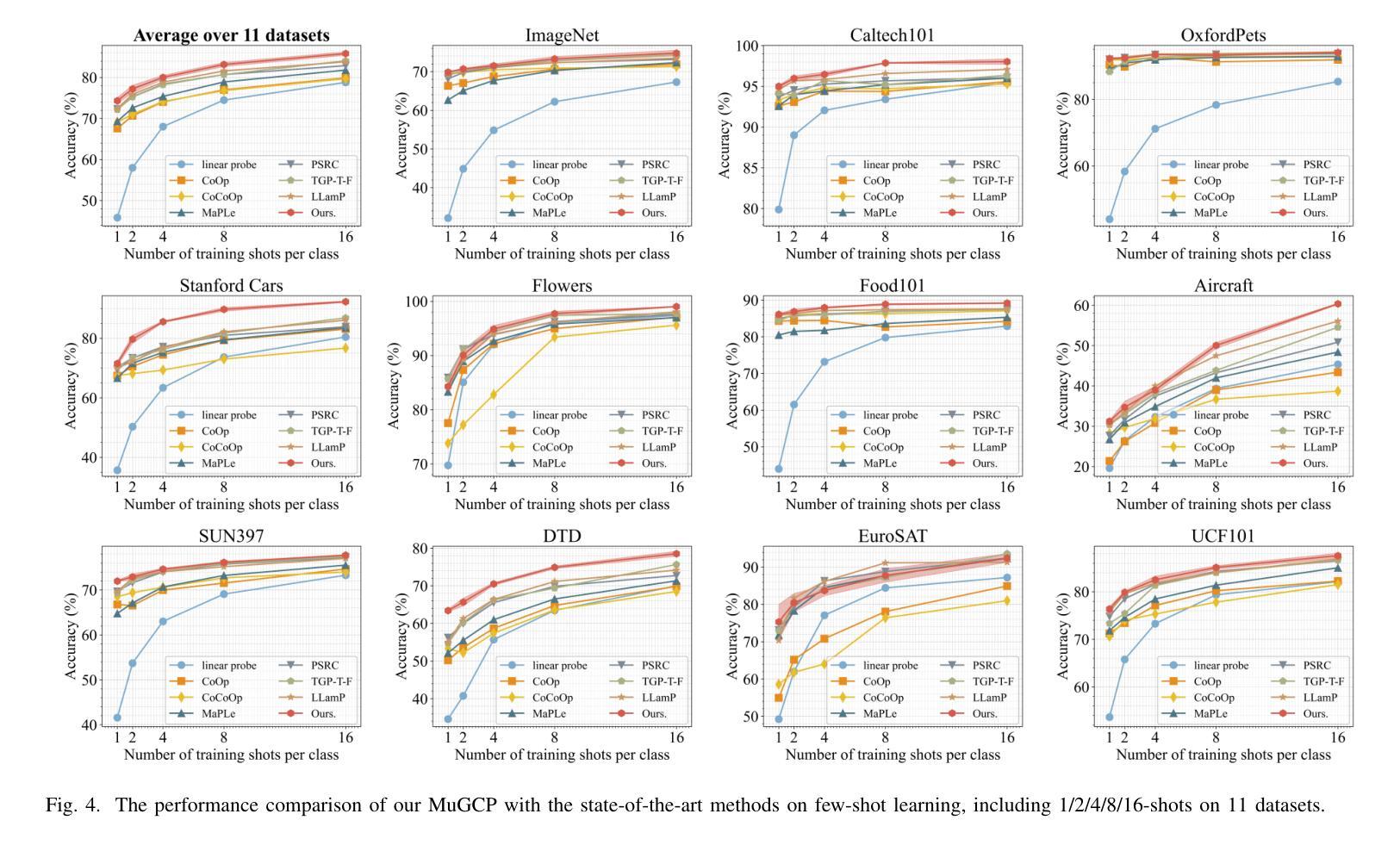
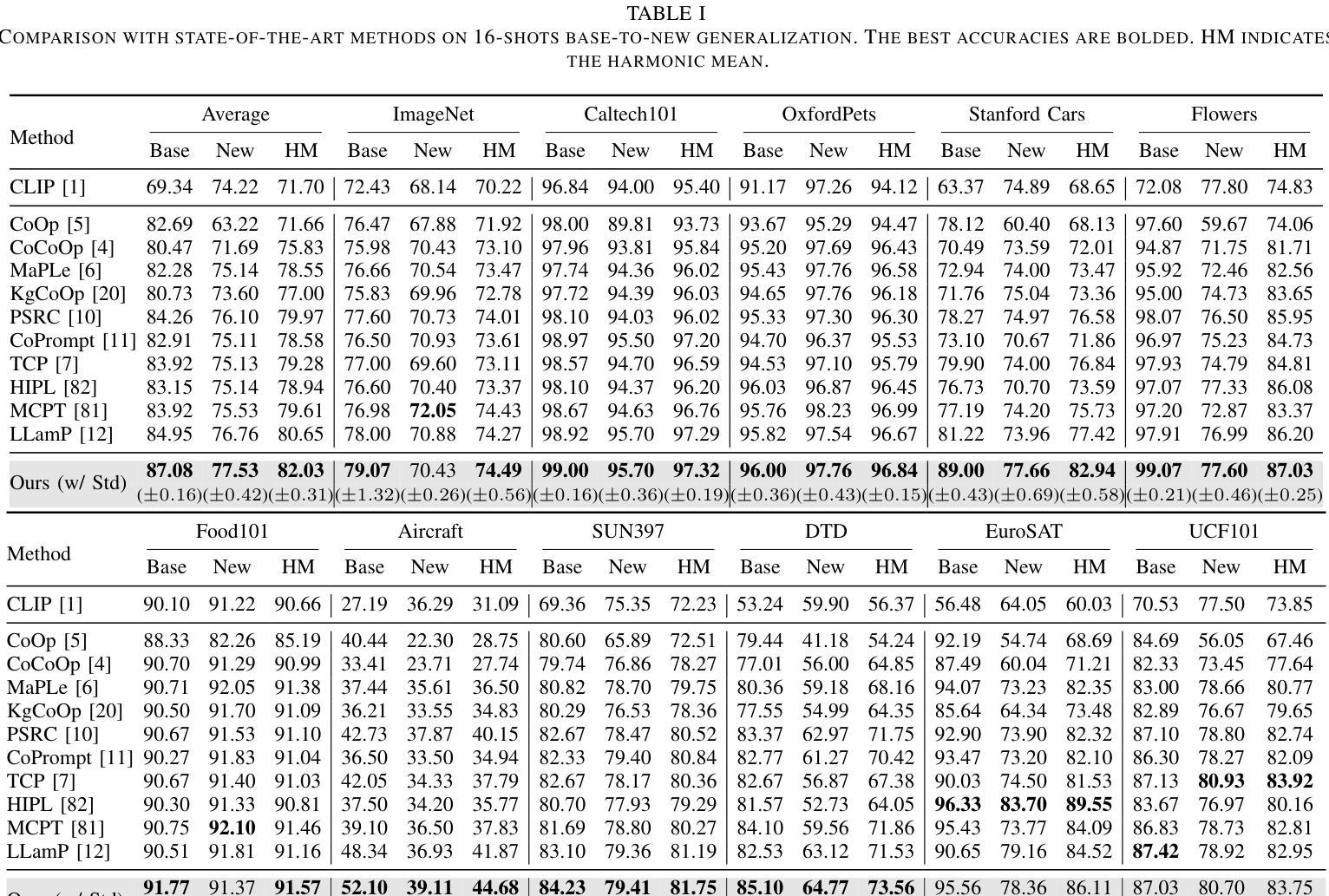
Prompt learning facilitates the efficient adaptation of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to various downstream tasks. However, it faces two significant challenges: (1) inadequate modeling of class embedding distributions for unseen instances, leading to suboptimal generalization on novel classes; (2) prevailing methodologies predominantly confine cross-modal alignment to the final output layer of vision and text encoders, which fundamentally limits their capacity to preserve topological consistency with pre-trained multi-modal embedding spaces. To this end, we introduce MuGCP (Multi-modal Mutual-Guidance Conditional Prompt Learning), a novel paradigm designed for conditional prompt generation. MuGCP leverages Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) as conditional prompt learners to adaptively generate Semantic Conditional Prompts (SCP) that incorporate rich, fine-grained high-level semantic knowledge for image instances. To ensure effective alignment and interaction across the multi-modal space of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), we introduce the Attention Mutual-Guidance (AMG) module, which facilitates interactions between visual and semantic information. Through mutual guidance, the AMG module generates Visual Conditional Prompts (VCP), enhancing the model’s performance in multi-modal tasks. Additionally, we present a Multi-Prompt Fusion (MPF) mechanism that integrates SCP and VCP with contextual prompts, ensuring seamless coordination among the different prompts and enhancing the modeling of class embeddings and instance-specific knowledge. Our MuGCP outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on 14 different datasets. The code will be made available after publication.
提示学习有助于视觉语言模型(VLM)高效适应各种下游任务。然而,它面临两大挑战:(1)对未见实例的类别嵌入分布建模不足,导致在新类别上的泛化性能不佳;(2)现有的方法主要将跨模态对齐局限于视觉和文本编码器的最终输出层,这从根本上限制了其与预训练的多模态嵌入空间保持拓扑一致性的能力。为此,我们引入了MuGCP(多模态相互引导条件提示学习),这是一种旨在为条件提示生成而设计的新型范式。MuGCP利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为条件提示学习者,自适应生成语义条件提示(SCP),这些提示融入了丰富的、精细的高级别语义知识,用于图像实例。为确保视觉语言模型(VLM)多模态空间的有效对齐和交互,我们引入了注意力相互引导(AMG)模块,该模块促进了视觉和语义信息之间的交互。通过相互引导,AMG模块生成视觉条件提示(VCP),提高模型在多模态任务中的性能。此外,我们提出了一种多提示融合(MPF)机制,将SCP和VCP与上下文提示相结合,确保不同提示之间的无缝协作,并增强对类别嵌入和实例特定知识的建模。我们的MuGCP在14个不同的数据集上的表现优于现有的最新方法。代码将在发表后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了MuGCP(多模态相互引导条件提示学习)这一新范式,用于解决视觉语言模型在处理下游任务时的两大挑战。MuGCP通过生成语义条件提示(SCP)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的融合来优化模型对未见实例的类嵌入分布建模。同时,通过注意力相互引导(AMG)模块实现视觉和语义信息的有效对齐和交互。此外,还引入了多提示融合(MPF)机制,确保不同提示之间的无缝协调,增强对类嵌入和实例特定知识的建模。MuGCP在多个数据集上的性能超过现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- MuGCP解决了视觉语言模型在处理下游任务时面临的挑战,包括类嵌入分布建模不足和对新类泛化性能不佳的问题。
- MuGCP通过生成语义条件提示(SCP)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的融合来提升模型性能。
- 注意力相互引导(AMG)模块实现视觉和语义信息的有效交互,增强了模型的性能。
- 多提示融合(MPF)机制确保了不同提示之间的无缝协调,增强了类嵌入和实例特定知识的建模。
- MuGCP在多个数据集上的性能超过了现有最先进的方法。
- 该方法将语义条件提示(SCP)与视觉条件提示(VCP)相结合,实现了多模态任务的协同优化。
点此查看论文截图

From Enhancement to Understanding: Build a Generalized Bridge for Low-light Vision via Semantically Consistent Unsupervised Fine-tuning
Authors:Sen Wang, Shao Zeng, Tianjun Gu, Zhizhong Zhang, Ruixin Zhang, Shouhong Ding, Jingyun Zhang, Jun Wang, Xin Tan, Yuan Xie, Lizhuang Ma
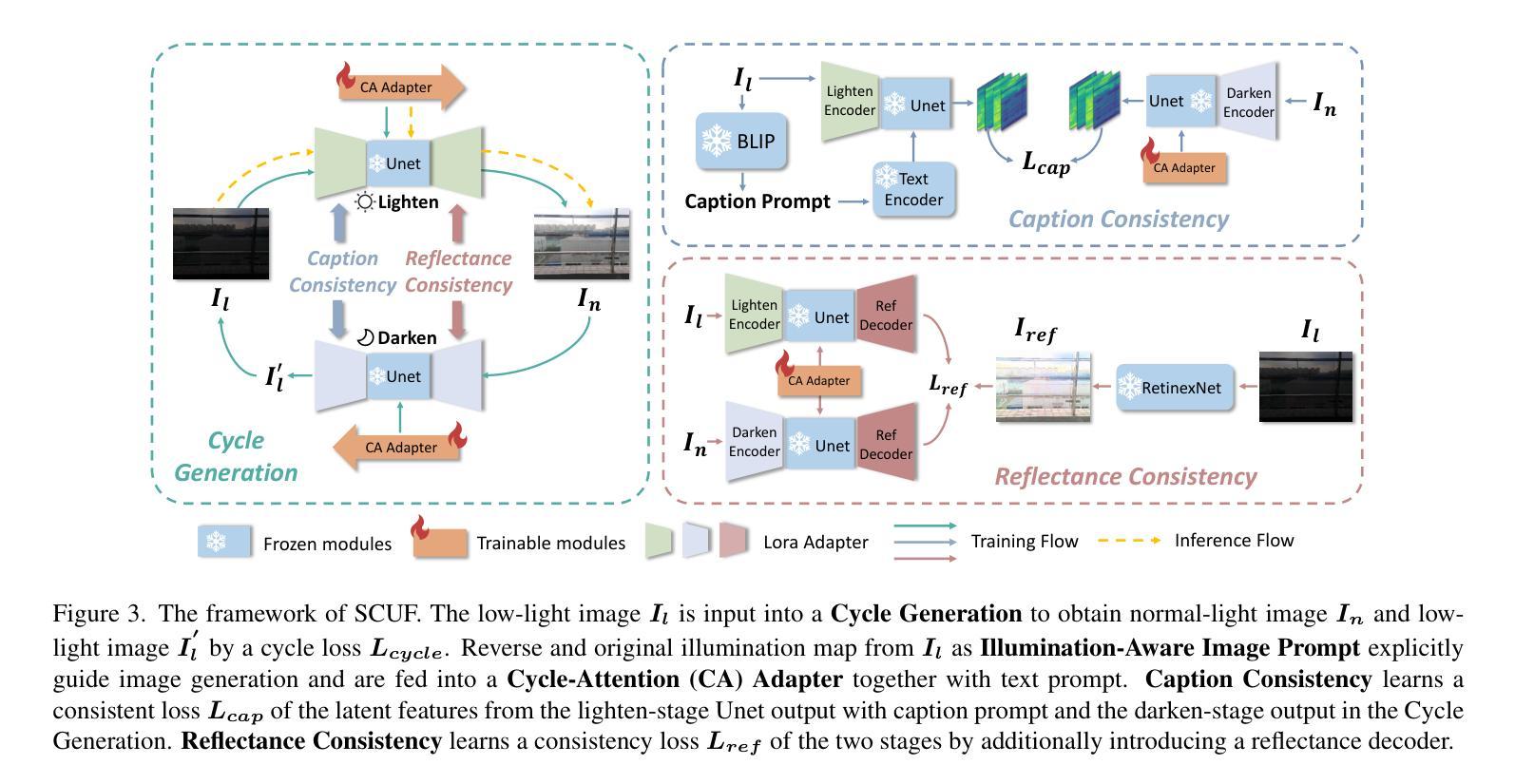
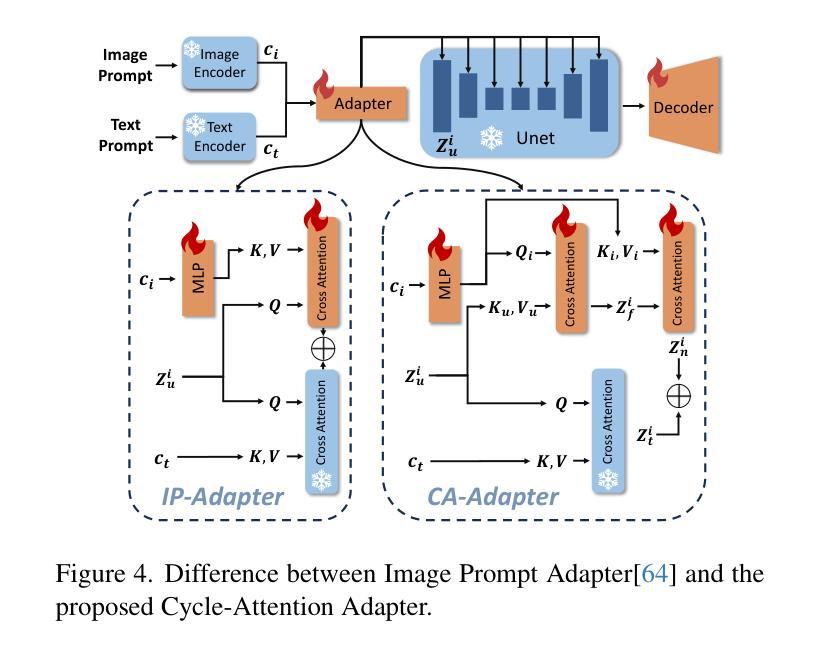
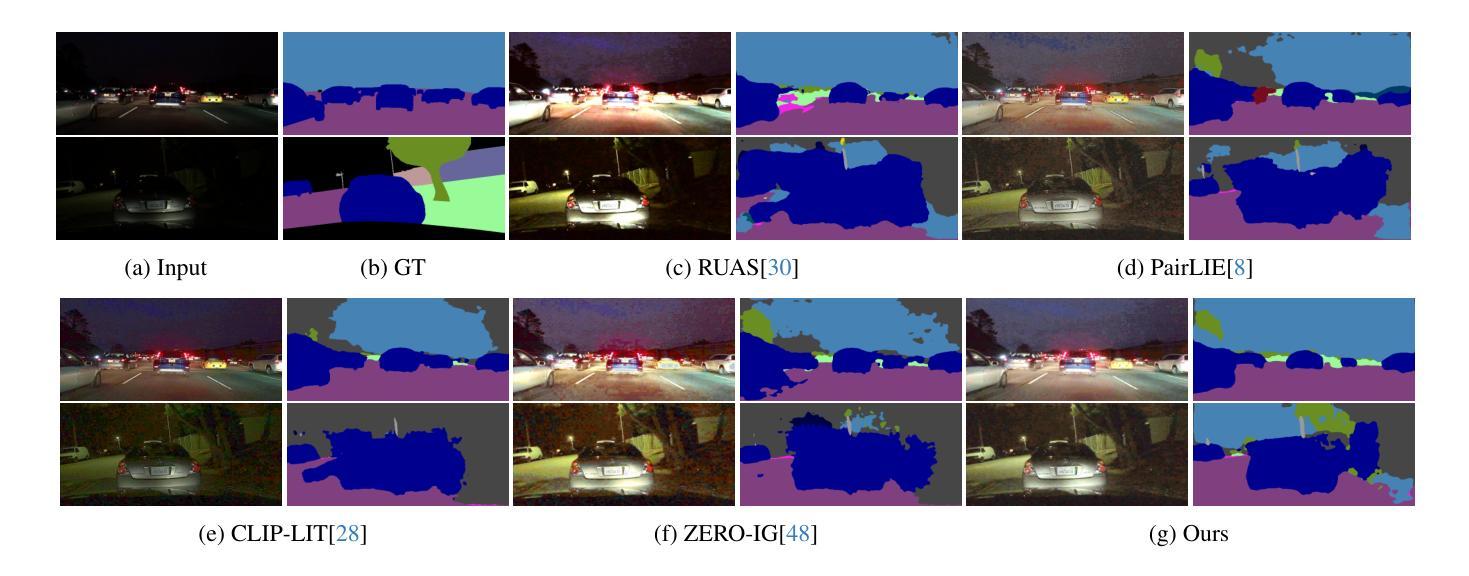
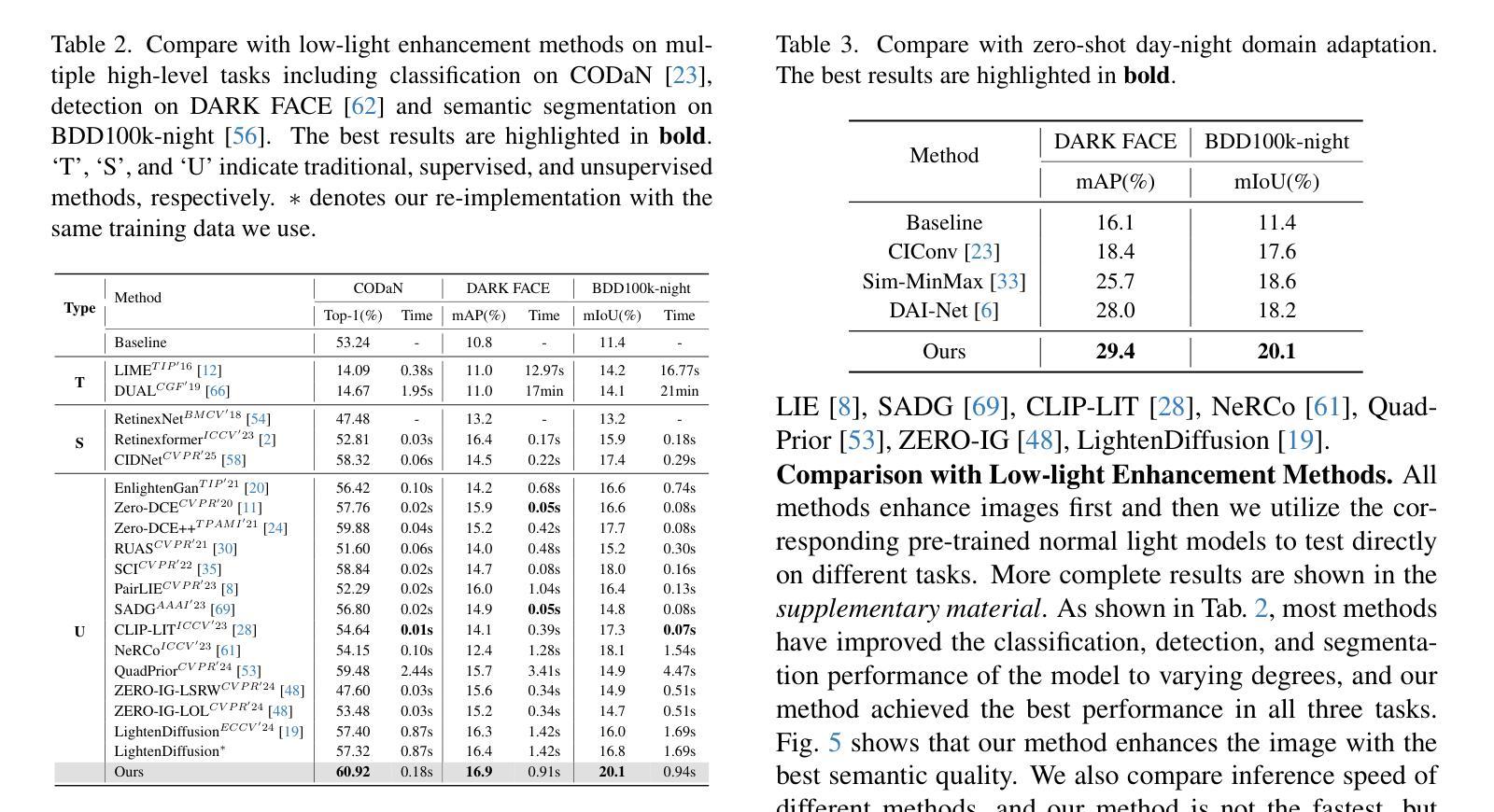
Low-level enhancement and high-level visual understanding in low-light vision have traditionally been treated separately. Low-light enhancement improves image quality for downstream tasks, but existing methods rely on physical or geometric priors, limiting generalization. Evaluation mainly focuses on visual quality rather than downstream performance. Low-light visual understanding, constrained by scarce labeled data, primarily uses task-specific domain adaptation, which lacks scalability. To address these challenges, we build a generalized bridge between low-light enhancement and low-light understanding, which we term Generalized Enhancement For Understanding (GEFU). This paradigm improves both generalization and scalability. To address the diverse causes of low-light degradation, we leverage pretrained generative diffusion models to optimize images, achieving zero-shot generalization performance. Building on this, we propose Semantically Consistent Unsupervised Fine-tuning (SCUF). Specifically, to overcome text prompt limitations, we introduce an illumination-aware image prompt to explicitly guide image generation and propose a cycle-attention adapter to maximize its semantic potential. To mitigate semantic degradation in unsupervised training, we propose caption and reflectance consistency to learn high-level semantics and image-level spatial semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in traditional image quality and GEFU tasks including classification, detection, and semantic segmentation.
在低光环境下的视觉感知中,传统上低级图像增强和高级视觉理解是被分开处理的。低光增强虽然可以改善下游任务中的图像质量,但现有方法依赖于物理或几何先验知识,限制了其泛化能力。评估主要集中在视觉质量上,而不是下游性能。由于缺乏大量标注数据,低光视觉理解主要使用针对特定任务的领域适应方法,缺乏可扩展性。为了应对这些挑战,我们建立了低光增强与低光理解之间的通用桥梁,我们称之为广义增强理解(GEFU)。这种范式提高了泛化能力和可扩展性。为了解决低光退化的多种原因,我们利用预训练的生成扩散模型来优化图像,实现了零样本泛化性能。在此基础上,我们提出了语义一致的无监督微调(SCUF)。具体来说,为了克服文本提示的局限性,我们引入了光照感知图像提示来显式地引导图像生成,并提出了循环注意力适配器来最大限度地发挥其语义潜力。为了缓解无监督训练中的语义退化问题,我们提出了标题和反射一致性来学习高级语义和图像级空间语义。大量实验表明,我们的方法在包括分类、检测和语义分割等传统的图像质量和GEFU任务上,均优于当前的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
低光环境下的图像增强与视觉理解长期分开处理,现有方法依赖物理或几何先验,缺乏通用性。为解决这个问题,我们提出了广义增强理解(GEFU)框架,利用预训练的生成扩散模型优化图像,实现了零样本通用性能。此外,我们介绍了语义一致无监督微调(SCUF)方法,通过光照感知图像提示和循环注意力适配器,克服文本提示的限制。同时,我们引入标题和反射一致性来学习高级语义和图像级空间语义,减轻无监督训练中的语义退化问题。实验证明,我们的方法在图像质量和GEFU任务上超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 低光环境下的图像增强与视觉理解长期分开处理,存在通用性和数据标注稀缺的问题。
- 提出了广义增强理解(GEFU)框架,整合低光增强与理解,提高通用性和可扩展性。
- 利用预训练的生成扩散模型优化图像,实现零样本通用性能。
- 克服文本提示限制,引入光照感知图像提示和循环注意力适配器。
- 通过标题和反射一致性学习高级语义和图像级空间语义。
- 方法在图像质量、分类、检测和语义分割等任务上表现优越。
- 广泛实验证明了我们方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图