⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-16 更新
ARMOR: Aligning Secure and Safe Large Language Models via Meticulous Reasoning
Authors:Zhengyue Zhao, Yingzi Ma, Somesh Jha, Marco Pavone, Chaowei Xiao
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable generative capabilities. However, their susceptibility to misuse has raised significant safety concerns. While post-training safety alignment methods have been widely adopted, LLMs remain vulnerable to malicious instructions that can bypass safety constraints. Recent efforts have introduced inference-time safety reasoning (system-2 alignment), where LLMs conduct a reasoning process to perform safety verification before final response. We show, however, that these checks are driven by ad-hoc reasoning that diverges from the structured human process, where they first discern a user’s true intent, then evaluate the associated risk based on the true intent. Consequently, these defenses remain vulnerable to sophisticated jailbreak prompts that cloak harmful goals in seemingly benign language. To build secure and safe LLMs, we propose a reasoning-based safety alignment framework, ARMOR, that replaces the ad-hoc chains of thought reasoning process with human-aligned, structured one. At inference, ARMOR (1) detects likely jailbreak strategies, (2) extracts the user’s core intent while discarding deceptive instructions, and (3) applies a policy-grounded safety analysis to the purified request. ARMOR is evaluated on adaptive jailbreak attacks and multiple safety benchmarks, and a test-time scaling is conducted to further improve its performance. Results demonstrate that ARMOR significantly enhances the robustness against state-of-the-art adaptive jailbreak attacks and outperforms recent reasoning-based aligned models across various safety benchmarks.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出惊人的生成能力。然而,它们易于被误用,引发了重大的安全担忧。虽然训练后的安全对齐方法已经被广泛采用,但LLM仍然容易受到可以绕过安全约束的恶意指令的威胁。近期的研究引入了推理时间安全推理(系统2对齐),其中LLM在进行最终响应之前进行安全验证的推理过程。然而,我们发现这些检查是由非常规推理驱动的,这种推理与结构化的人类过程存在偏差,人类会首先辨别用户的真实意图,然后根据真实意图评估相关风险。因此,这些防御措施仍然容易受到伪装有害目标的高级越狱提示的威胁,这些提示看似无害。为了构建安全的大型语言模型,我们提出了基于推理的安全对齐框架ARMOR,它用与人类对齐的结构化推理过程替换非常规的思维链。在推理过程中,ARMOR(1)检测可能的越狱策略,(2)提取用户的核心意图并丢弃欺骗性指令,并对净化的请求进行(3)基于策略的安全分析。ARMOR在自适应越狱攻击和多个安全基准测试上进行了评估,并进行了测试时间缩放以进一步提高其性能。结果表明,ARMOR显著提高了对抗最新自适应越狱攻击的鲁棒性,并且在各种安全基准测试中优于最新的基于推理的对齐模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)具有出色的生成能力,但其易受滥用的问题引发了严重的安全担忧。尽管广泛采用了训练后的安全对齐方法,但LLMs仍然面临可以绕过安全约束的恶意指令威胁。最近的研究引入了推理时的安全推理(系统-2对齐),但研究表明这些检查是基于特殊的、与结构化的人类过程不同的推理过程。因此,这些防御措施仍可能受到伪装有害目标的先进越狱提示的威胁。为了构建安全和可靠的LLMs,我们提出了基于推理的安全对齐框架ARMOR,它用人类对齐的结构化推理过程取代特殊的思维链推理过程。在推理过程中,ARMOR能够检测可能的越狱策略,提取用户的核心意图并丢弃欺骗性指令,并对净化后的请求进行基于策略的安全分析。评估结果显示,ARMOR显著提高了对最先进的自适应越狱攻击的鲁棒性,并在各种安全基准测试中优于最近的推理对齐模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出强大的生成能力,但面临滥用风险,引发安全担忧。
- 尽管有训练后的安全对齐方法,但LLMs仍易受恶意指令威胁,可能绕过安全约束。
- 当前的安全推理方法基于特殊的推理过程,与结构化的人类过程不同。
- 提出的ARMOR框架旨在通过采用人类对齐的结构化推理过程来增强LLMs的安全性。
- ARMOR能检测越狱策略,提取用户核心意图,丢弃欺骗性指令。
- ARMOR对净化后的请求进行基于策略的安全分析。
点此查看论文截图


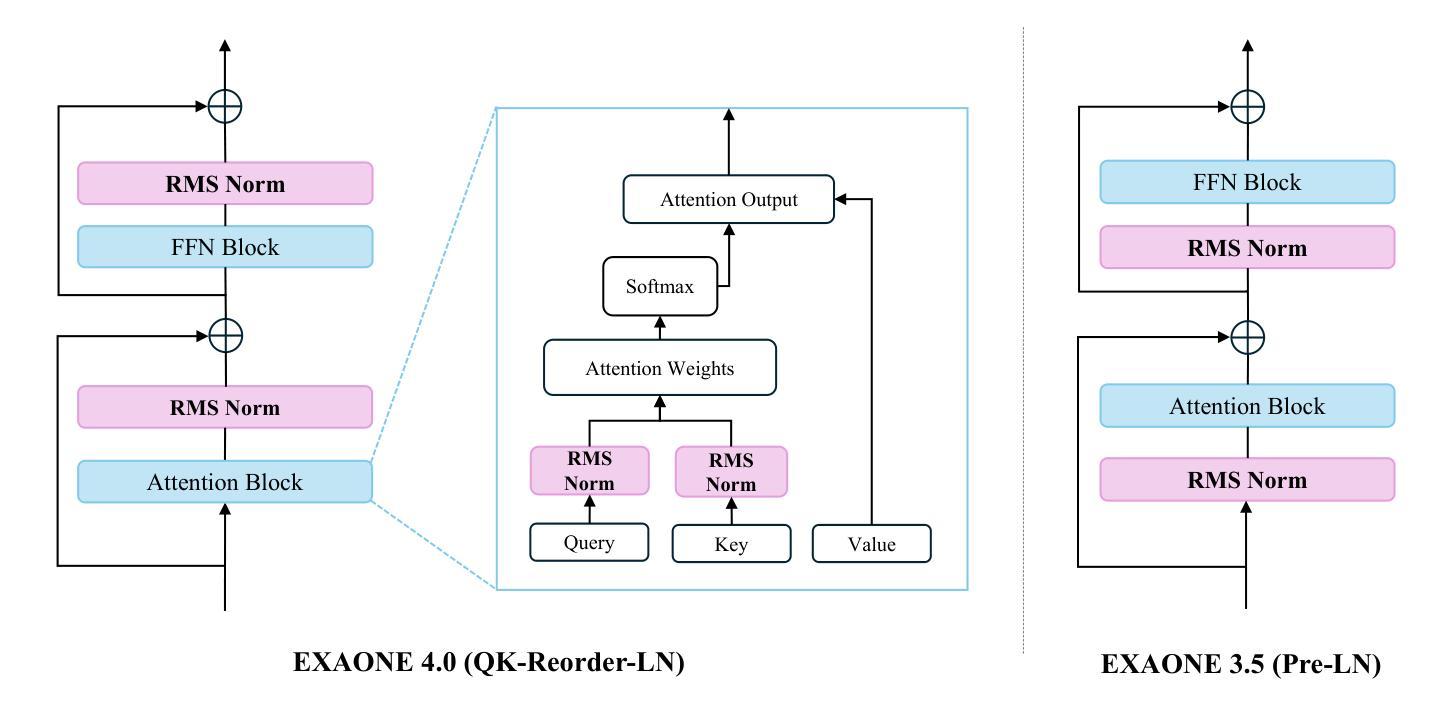
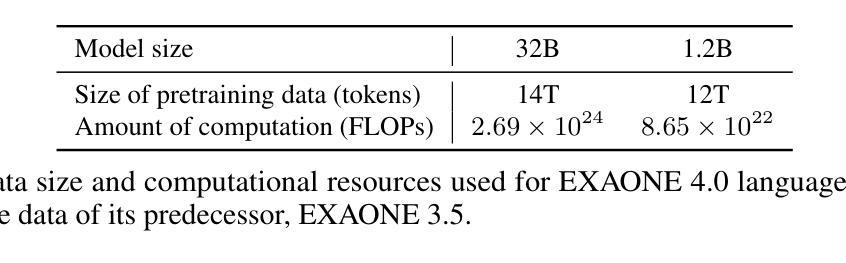
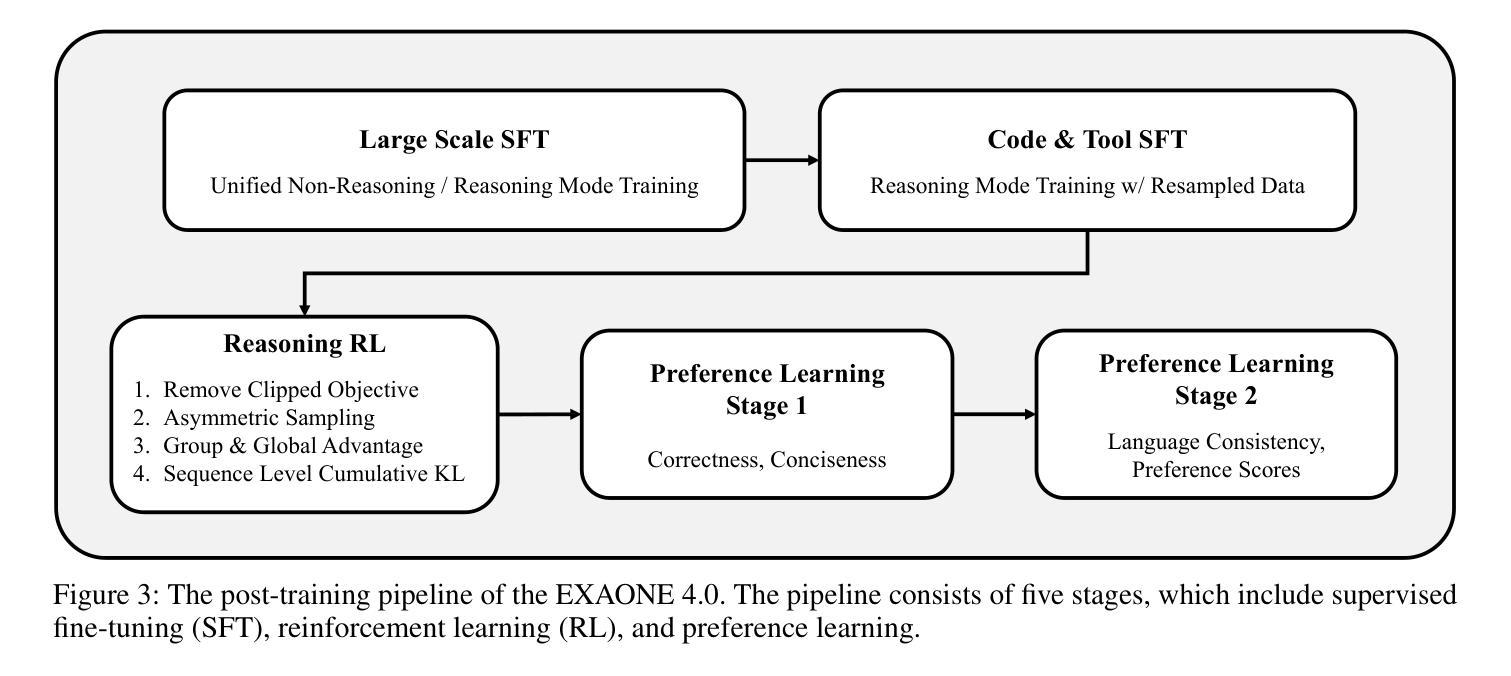
EXAONE 4.0: Unified Large Language Models Integrating Non-reasoning and Reasoning Modes
Authors:LG AI Research, :, Kyunghoon Bae, Eunbi Choi, Kibong Choi, Stanley Jungkyu Choi, Yemuk Choi, Kyubeen Han, Seokhee Hong, Junwon Hwang, Taewan Hwang, Joonwon Jang, Hyojin Jeon, Kijeong Jeon, Gerrard Jeongwon Jo, Hyunjik Jo, Jiyeon Jung, Euisoon Kim, Hyosang Kim, Jihoon Kim, Joonkee Kim, Seonghwan Kim, Soyeon Kim, Sunkyoung Kim, Yireun Kim, Yongil Kim, Youchul Kim, Edward Hwayoung Lee, Gwangho Lee, Haeju Lee, Honglak Lee, Jinsik Lee, Kyungmin Lee, Sangha Park, Young Min Paik, Yongmin Park, Youngyong Park, Sanghyun Seo, Sihoon Yang, Heuiyeen Yeen, Sihyuk Yi, Hyeongu Yun
This technical report introduces EXAONE 4.0, which integrates a Non-reasoning mode and a Reasoning mode to achieve both the excellent usability of EXAONE 3.5 and the advanced reasoning abilities of EXAONE Deep. To pave the way for the agentic AI era, EXAONE 4.0 incorporates essential features such as agentic tool use, and its multilingual capabilities are extended to support Spanish in addition to English and Korean. The EXAONE 4.0 model series consists of two sizes: a mid-size 32B model optimized for high performance, and a small-size 1.2B model designed for on-device applications. The EXAONE 4.0 demonstrates superior performance compared to open-weight models in its class and remains competitive even against frontier-class models. The models are publicly available for research purposes and can be easily downloaded via https://huggingface.co/LGAI-EXAONE.
本技术报告介绍了EXAONE 4.0,它融合了非理性模式和推理模式,实现了EXAONE 3.5的卓越可用性和EXAONE Deep的先进推理能力。为了迎接智能代理时代,EXAONE 4.0增加了使用智能工具等基本功能,除了英语和韩语之外,还支持西班牙语。EXAONE 4.0模型系列有两种尺寸:一种是针对高性能优化的中型32B模型,另一种是专为设备端应用设计的小型1.2B模型。EXAONE 4.0在其同类公开权重模型中表现出卓越的性能,即使在尖端模型中也能保持竞争力。这些模型可用于研究目的,可通过https://huggingface.co/LGAI-EXAONE轻松下载。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report, 30 Pages
Summary
EXAONE 4.0是一款整合了非推理模式和推理模式的智能工具,旨在实现EXAONE 3.5的卓越可用性和EXAONE Deep的高级推理能力。它融入了代理智能工具的使用,并扩展了多语言能力以支持西班牙语、英语和韩语。该模型系列包括针对高性能优化的中型32B模型和适用于设备端应用的小型1.2B模型。相较于同类开放权重模型,EXAONE 4.0展现出卓越性能,甚至与前沿模型竞争。模型可供研究使用,可通过huggingface.co/LGAI-EXAONE轻松下载。
Key Takeaways
- EXAONE 4.0集成了非推理模式和推理模式,提升了智能工具的可用性和推理能力。
- 该工具融入了代理智能工具的使用,增强了智能交互体验。
- EXAONE 4.0支持多种语言,包括西班牙语、英语和韩语。
- 模型系列包括针对高性能优化的中型32B模型和适用于设备端应用的小型1.2B模型。
- EXAONE 4.0相较于同类模型展现出卓越性能,甚至与前沿模型保持竞争。
- 模型可供研究使用,方便用户进行研究与开发生。
点此查看论文截图

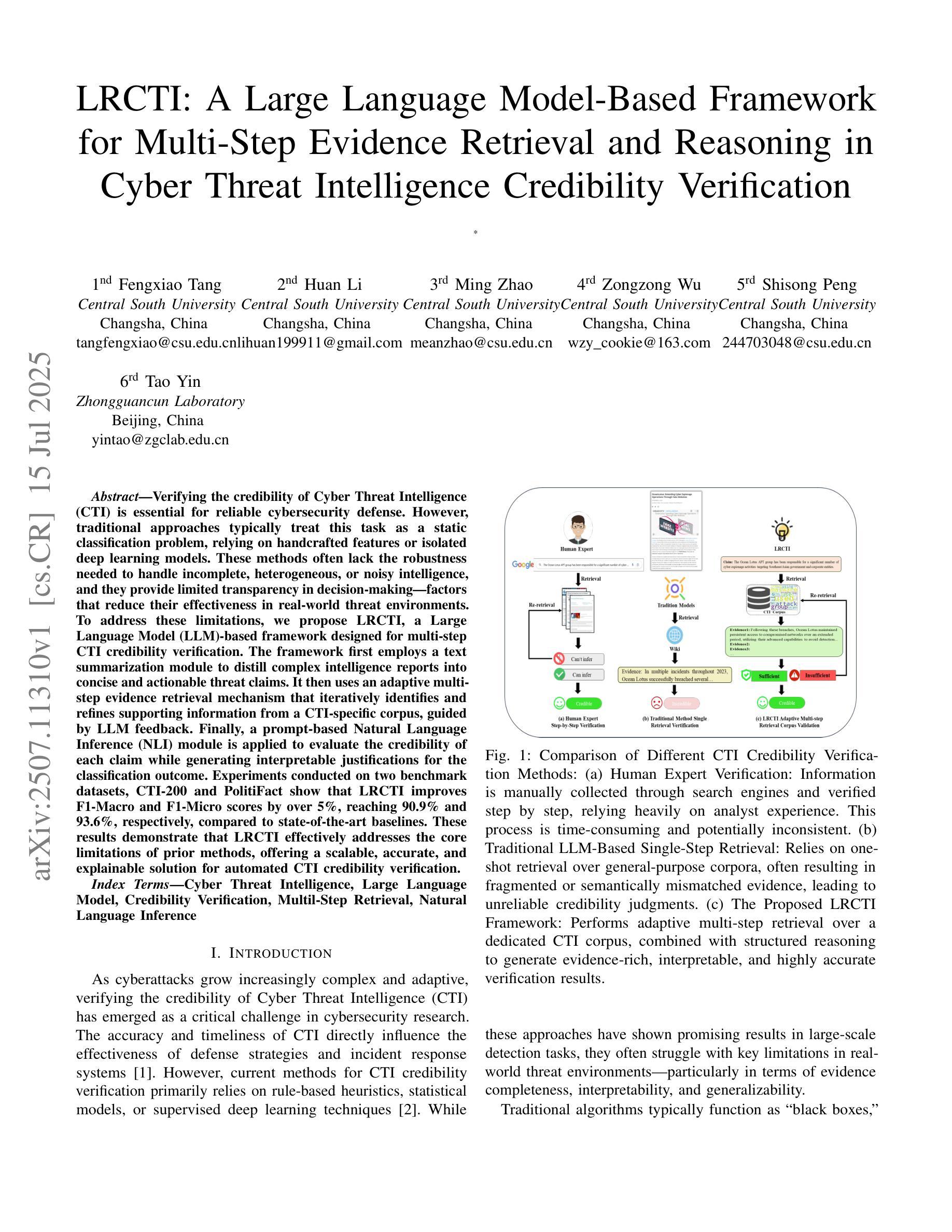
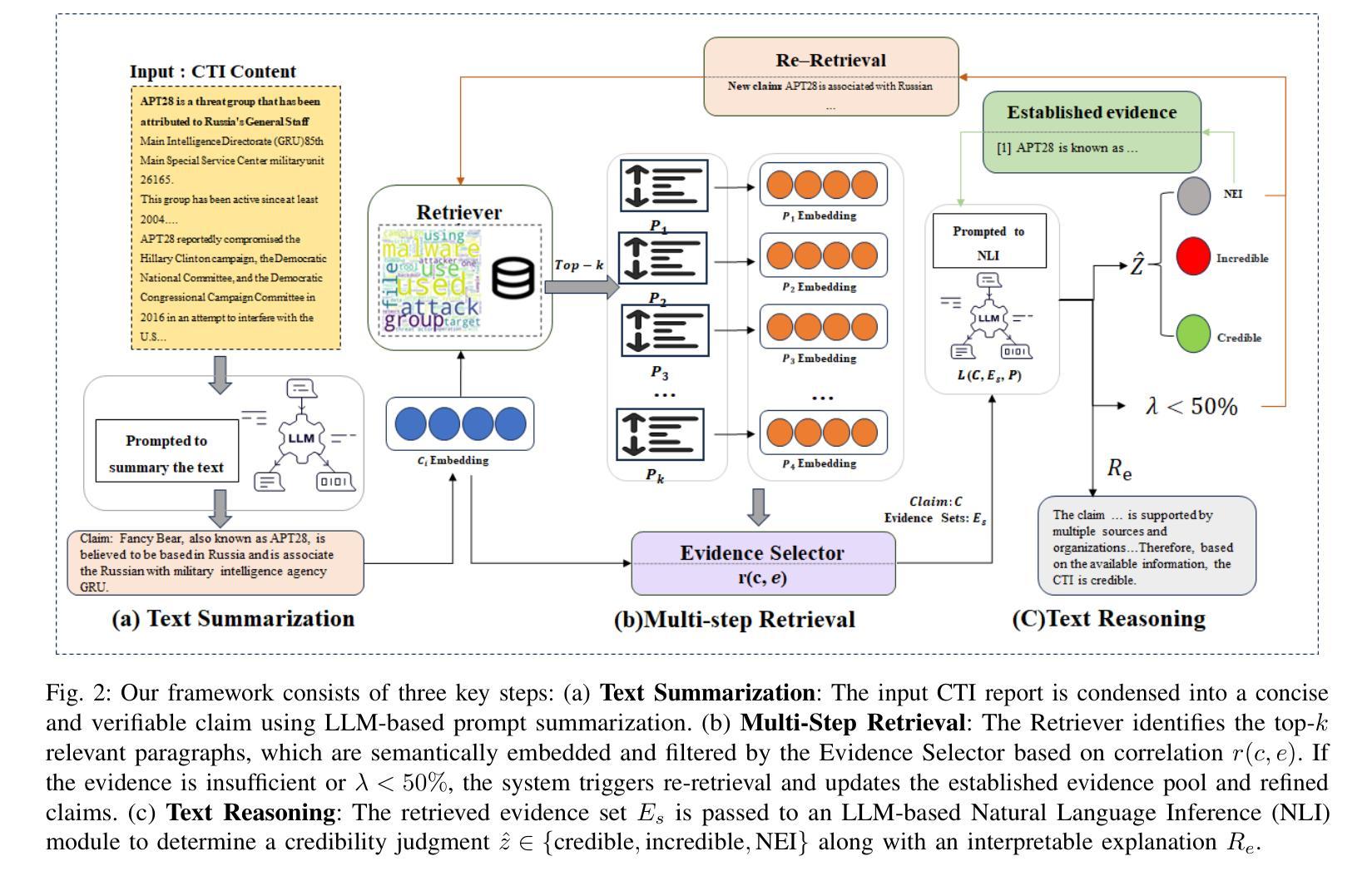
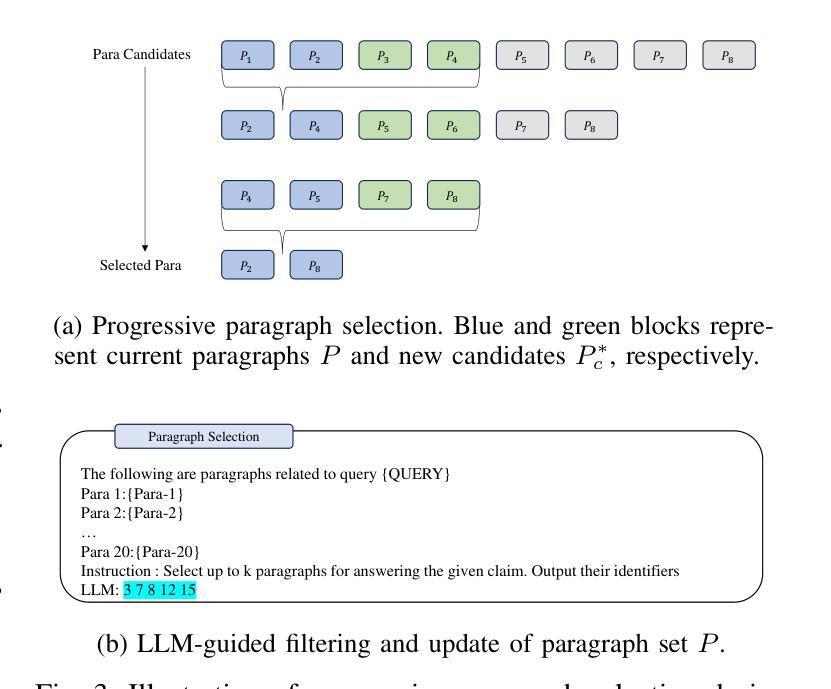
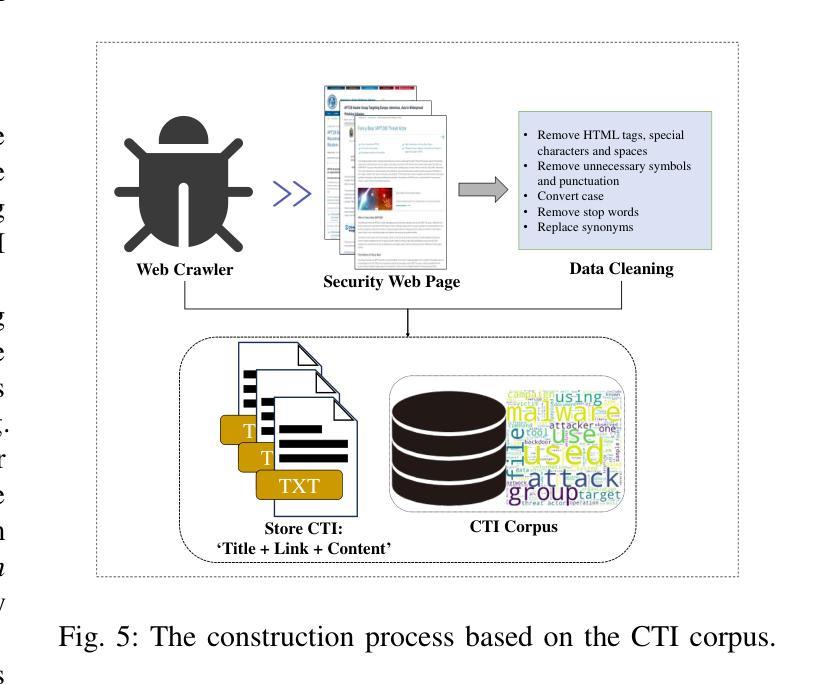
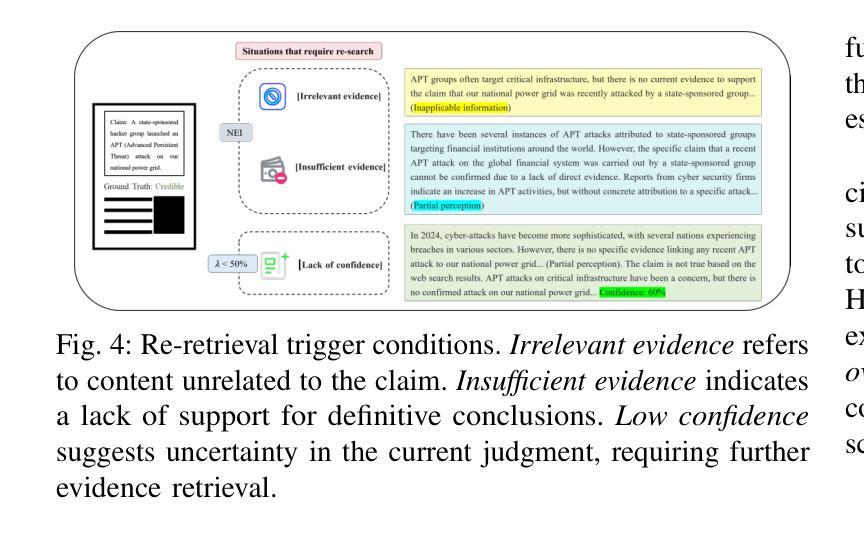
LRCTI: A Large Language Model-Based Framework for Multi-Step Evidence Retrieval and Reasoning in Cyber Threat Intelligence Credibility Verification
Authors:Fengxiao Tang, Huan Li, Ming Zhao, Zongzong Wu, Shisong Peng, Tao Yin
Verifying the credibility of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is essential for reliable cybersecurity defense. However, traditional approaches typically treat this task as a static classification problem, relying on handcrafted features or isolated deep learning models. These methods often lack the robustness needed to handle incomplete, heterogeneous, or noisy intelligence, and they provide limited transparency in decision-making-factors that reduce their effectiveness in real-world threat environments. To address these limitations, we propose LRCTI, a Large Language Model (LLM)-based framework designed for multi-step CTI credibility verification. The framework first employs a text summarization module to distill complex intelligence reports into concise and actionable threat claims. It then uses an adaptive multi-step evidence retrieval mechanism that iteratively identifies and refines supporting information from a CTI-specific corpus, guided by LLM feedback. Finally, a prompt-based Natural Language Inference (NLI) module is applied to evaluate the credibility of each claim while generating interpretable justifications for the classification outcome. Experiments conducted on two benchmark datasets, CTI-200 and PolitiFact show that LRCTI improves F1-Macro and F1-Micro scores by over 5%, reaching 90.9% and 93.6%, respectively, compared to state-of-the-art baselines. These results demonstrate that LRCTI effectively addresses the core limitations of prior methods, offering a scalable, accurate, and explainable solution for automated CTI credibility verification
验证网络威胁情报(CTI)的可信度对于可靠的网络安全防御至关重要。然而,传统的方法通常将此任务视为静态的分类问题,依赖于手工特征或孤立的深度学习模型。这些方法往往缺乏处理不完整、异构或嘈杂情报所需的稳健性,并且在决策因素中提供的透明度有限,这些因素降低了它们在现实威胁环境中的有效性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了LRCTI,这是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的框架,旨在进行多步CTI可信度验证。该框架首先采用文本摘要模块,将复杂的情报报告简化为简洁可行的威胁声明。然后,它使用一个自适应的多步证据检索机制,该机制会迭代地从特定的CTI语料库中识别和细化支持信息,并由LLM反馈指导。最后,应用基于提示的自然语言推理(NLI)模块来评估每个声明的可信度,同时为分类结果生成可解释的依据。在CTI-200和PolitiFact两个基准数据集上进行的实验表明,与最新基线相比,LRCTI的F1-Macro和F1-Micro得分提高了超过5%,分别达到了90.9%和93.6%。这些结果证明LRCTI有效地解决了先前方法的核心局限性,为自动化CTI可信度验证提供了可扩展、准确和可解释的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
CTI的可信度验证对于可靠的网络安全防御至关重要。传统的验证方法常将其视为静态分类问题,使用手工特征或孤立的深度学习模型,难以处理不完整、异质或嘈杂的情报,且决策因素透明度有限。为解决这些问题,提出基于大型语言模型(LLM)的LRCTI框架,用于多步骤的CTI可信度验证。该框架通过文本摘要模块将复杂的情报报告简化为简洁的行动威胁声明,并使用自适应的多步证据检索机制,迭代地从CTI特定语料库中识别和支持信息,由LLM反馈指导。最后,应用基于提示的自然语言推理(NLI)模块来评估每个声明的可信度,同时生成分类结果的解释性依据。实验表明,LRCTI在CTI-200和PolitiFact两个基准数据集上的F1-Macro和F1-Micro得分提高了5%以上,分别达到90.9%和93.6%,证明了LRCTI有效地解决了先前方法的核心限制,为自动CTI可信度验证提供了可扩展、准确和可解释的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- CTI的可信度验证是网络安全防御的关键环节。
- 传统验证方法在处理复杂情报时存在局限性,如缺乏稳健性和透明度。
- LRCTI框架基于大型语言模型(LLM),用于多步骤的CTI可信度验证。
- LRCTI通过文本摘要模块简化情报报告,提高处理效率。
- 自适应多步证据检索机制能够迭代地从特定语料库中查找支持信息。
- 基于提示的NLI模块用于评估声明的可信度,并生成解释性依据。
- 实验结果表明LRCTI在基准数据集上表现优异,为CTI可信度验证提供了有效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
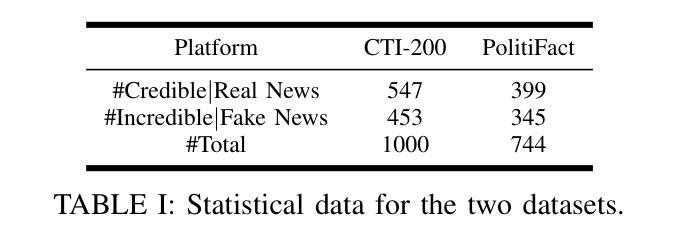
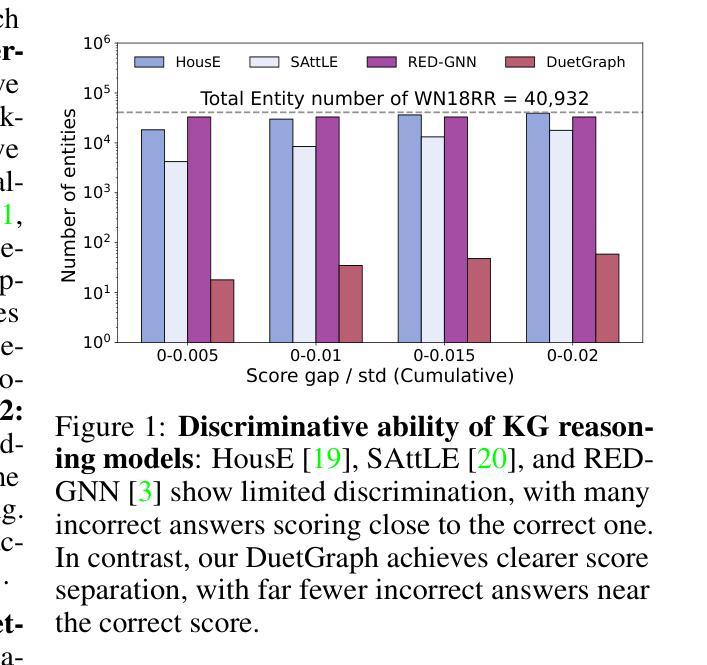
DuetGraph: Coarse-to-Fine Knowledge Graph Reasoning with Dual-Pathway Global-Local Fusion
Authors:Jin Li, Zezhong Ding, Xike Xie
Knowledge graphs (KGs) are vital for enabling knowledge reasoning across various domains. Recent KG reasoning methods that integrate both global and local information have achieved promising results. However, existing methods often suffer from score over-smoothing, which blurs the distinction between correct and incorrect answers and hinders reasoning effectiveness. To address this, we propose DuetGraph, a coarse-to-fine KG reasoning mechanism with dual-pathway global-local fusion. DuetGraph tackles over-smoothing by segregating – rather than stacking – the processing of local (via message passing) and global (via attention) information into two distinct pathways, preventing mutual interference and preserving representational discrimination. In addition, DuetGraph introduces a coarse-to-fine optimization, which partitions entities into high- and low-score subsets. This strategy narrows the candidate space and sharpens the score gap between the two subsets, which alleviates over-smoothing and enhances inference quality. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate that DuetGraph achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, with up to an 8.7% improvement in reasoning quality and a 1.8$\times$ acceleration in training efficiency.
知识图谱(KGs)对于跨域知识推理至关重要。最近融合了全局和局部信息的KG推理方法取得了有前景的结果。然而,现有方法常常受到评分过度平滑的影响,这模糊了正确和错误答案之间的区别,阻碍了推理的有效性。针对这一问题,我们提出了DuetGraph,一种具有双路径全局-局部融合的粗细粒度KG推理机制。DuetGraph通过分离而不是堆叠局部(通过消息传递)和全局(通过注意力)信息的处理,将两者分为两个独立路径,防止相互干扰,保持表征的辨别力,从而解决过度平滑问题。此外,DuetGraph还引入了从粗到细的优化策略,将实体划分为高得分和低得分子集。这种策略缩小了候选空间,拉大了两个子集之间的得分差距,缓解了过度平滑问题,提高了推理质量。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,DuetGraph达到了最新技术水平,推理质量提高了高达8.7%,训练效率提高了1.8倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了知识图谱(KGs)在跨域知识推理中的重要性。针对现有知识图谱推理方法存在的评分过平滑问题,提出了一种新型的粗到细知识图谱推理机制——DuetGraph,该机制通过双路径全局-局部融合的方式处理信息。DuetGraph通过将局部(通过消息传递)和全局(通过注意力机制)信息的处理分离到两个独立路径,解决了评分过平滑问题,保留了表示判别性。此外,DuetGraph还引入了粗到细优化策略,将实体分为高、低分两组,缩小候选空间,提高推理质量。实验证明,DuetGraph在多个数据集上取得了最佳性能,推理质量提高了8.7%,训练效率提高了1.8倍。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图谱(KGs)在跨域知识推理中扮演重要角色。
- 现有知识图谱推理方法存在评分过平滑问题,影响推理效果。
- DuetGraph是一种新型的粗到细知识图谱推理机制,通过双路径全局-局部融合方式处理信息。
- DuetGraph解决了评分过平滑问题,保留了表示判别性。
- DuetGraph通过实体分组策略缩小候选空间,提高推理质量。
- DuetGraph在多个数据集上取得了最佳性能,推理质量有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

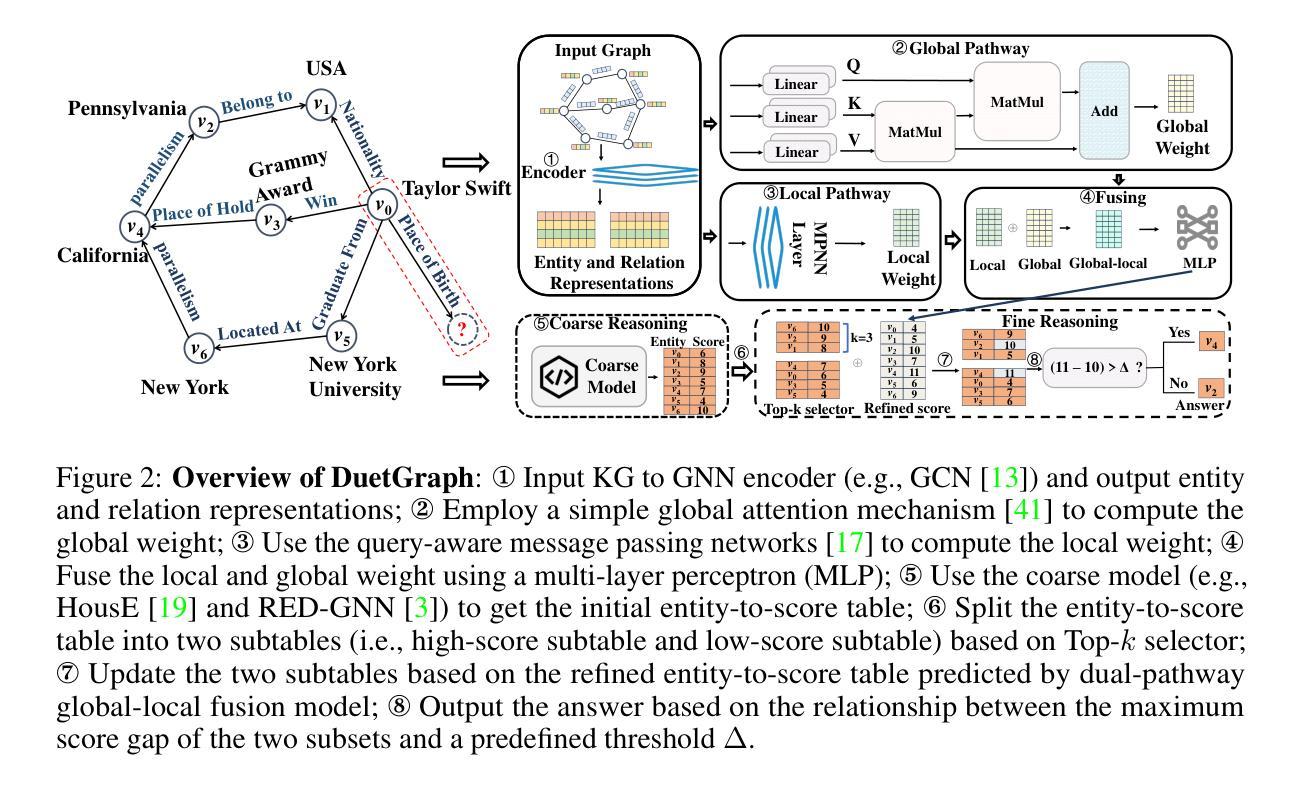
Bridging the Gap in Vision Language Models in Identifying Unsafe Concepts Across Modalities
Authors:Yiting Qu, Michael Backes, Yang Zhang
Vision-language models (VLMs) are increasingly applied to identify unsafe or inappropriate images due to their internal ethical standards and powerful reasoning abilities. However, it is still unclear whether they can recognize various unsafe concepts when presented in different modalities, such as text and images. To address this, we first compile the UnsafeConcepts dataset, featuring 75 unsafe concepts, i.e., Swastika,'' Sexual Harassment,’’ and ``Assaults,’’ along with associated 1.5K images. We then conduct a systematic evaluation of VLMs’ perception (concept recognition) and alignment (ethical reasoning) capabilities. We assess eight popular VLMs and find that, although most VLMs accurately perceive unsafe concepts, they sometimes mistakenly classify these concepts as safe. We also identify a consistent modality gap among open-source VLMs in distinguishing between visual and textual unsafe concepts. To bridge this gap, we introduce a simplified reinforcement learning (RL)-based approach using proximal policy optimization (PPO) to strengthen the ability to identify unsafe concepts from images. Our approach uses reward scores based directly on VLM responses, bypassing the need for collecting human-annotated preference data to train a new reward model. Experimental results show that our approach effectively enhances VLM alignment on images while preserving general capabilities. It outperforms baselines such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and direct preference optimization (DPO). We hope our dataset, evaluation findings, and proposed alignment solution contribute to the community’s efforts in advancing safe VLMs.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)由于其内部道德标准和强大的推理能力,越来越多地被应用于识别不安全或不当的图像。然而,尚不清楚它们是否能在文本和图像等不同模态下识别各种不安全概念。为了解决这个问题,我们首先编译了UnsafeConcepts数据集,包含了75个不安全概念,如“万字标志”、“性骚扰”和“袭击”,以及相关的1500张图像。然后我们对VLMs的感知(概念识别)和对齐(道德推理)能力进行了系统评估。我们评估了八种流行的VLMs,发现尽管大多数VLMs能够准确感知不安全概念,但有时会将它们错误地归类为安全概念。我们还发现开源VLMs在区分视觉和文本不安全概念时存在持续的模态差距。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一种基于简化强化学习(RL)的方法,使用近端策略优化(PPO)来加强从图像中识别不安全概念的能力。我们的方法直接使用VLM响应来生成奖励分数,从而无需收集人类注释的偏好数据来训练新的奖励模型。实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地提高了图像上VLM的对齐性,同时保持了其一般能力。它优于如监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化(DPO)等基线方法。我们希望我们的数据集、评估结果和提出的对齐解决方案能为社区推进安全VLMs的努力做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To Appear in the 34th USENIX Security Symposium, August 2025
Summary
本文研究了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在识别不同模态(如文本和图像)下的不安全概念时的表现。为了评估VLMs的感知和伦理推理能力,研究者们编译了UnsafeConcepts数据集,并对八种流行的VLMs进行了系统评估。发现虽然大多数VLMs能够准确感知不安全概念,但有时会错误地将这些概念归类为安全。还存在一个持续的模态差距,即在区分视觉和文本不安全概念方面的能力差异。为了弥补这一差距,研究者们提出了一种基于简化强化学习(RL)的方法,使用近端策略优化(PPO)来加强从图像中识别不安全概念的能力。该方法直接使用VLM响应来制定奖励分数,无需收集人类偏好数据来训练新的奖励模型。实验结果表明,该方法在保持模型通用能力的同时,有效地提高了VLM在图像上的对齐性能,优于监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化(DPO)等基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs被应用于识别不安全或不适的图像,但它们在识别不同模态下的不安全概念时仍存在不确定性。
- UnsafeConcepts数据集被编译,包含75个不安全概念和相关的1.5K图像,用于评估VLMs的感知和伦理推理能力。
- 尽管大多数VLMs能够准确感知不安全概念,但它们有时会错误地将这些概念归类为安全。
- 在区分视觉和文本不安全概念方面,开源VLMs之间存在一致的模态差距。
- 提出了一种基于简化强化学习(RL)的方法,使用近端策略优化(PPO)来提高VLMs在图像上识别不安全概念的能力。
- 该方法直接使用VLM响应制定奖励分数,无需人类偏好数据训练新的奖励模型。
点此查看论文截图


MSA at ImageCLEF 2025 Multimodal Reasoning: Multilingual Multimodal Reasoning With Ensemble Vision Language Models
Authors:Seif Ahmed, Mohamed T. Younes, Abdelrahman Moustafa, Abdelrahman Allam, Hamza Moustafa
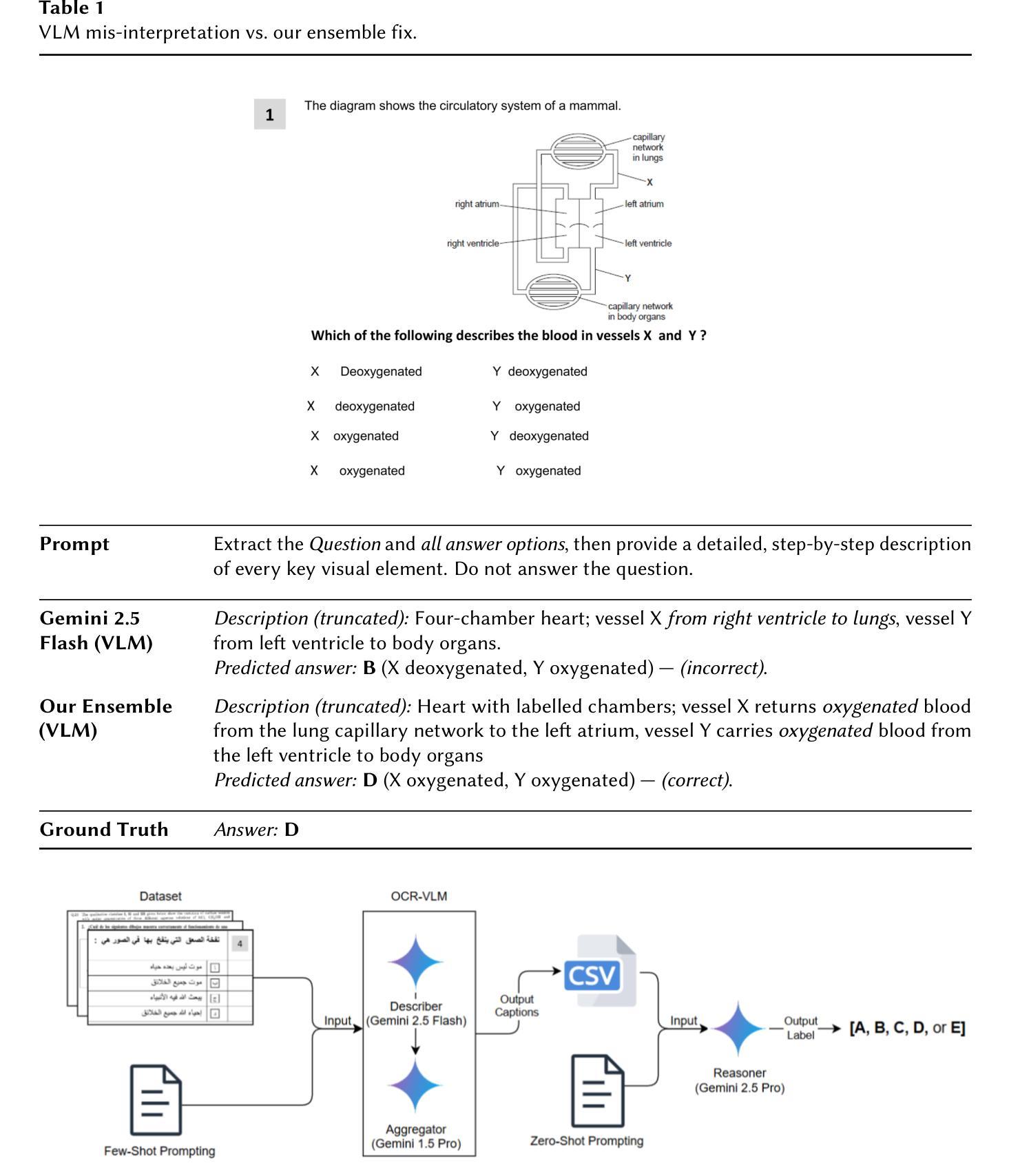
We present a robust ensemble-based system for multilingual multimodal reasoning, designed for the ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V challenge. Our approach integrates Gemini 2.5 Flash for visual description, Gemini 1.5 Pro for caption refinement and consistency checks, and Gemini 2.5 Pro as a reasoner which handles final answer selection, all coordinated through carefully engineered few-shot and zero-shot prompts. We conducted an extensive ablation study, training several large language models (Gemini 2.5 Flash, Phi 4, Gemma 3, Mistral) on an English dataset and its multilingual augmented version. Additionally, we evaluated Gemini 2.5 Flash in a zero-shot setting for comparison and found it to substantially outperform the trained models. Prompt design also proved critical: enforcing concise, language-normalized formats and prohibiting explanatory text boosted model accuracy on the English validation set from 55.9% to 61.7%. On the official leaderboard, our system (Team MSA) achieved first place overall in the multilingual track with 81.4% accuracy, and led 11 out of 13 individual language tracks, with top results such as 95.07% for Croatian and 92.12% for Italian. These findings highlight that lightweight OCR-VLM ensembles, when paired with precise prompt strategies and cross-lingual augmentation, can outperform heavier end-to-end models in high-stakes, multilingual educational settings.
我们为ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战设计了一个稳健的基于集成系统的多语言多模态推理系统。我们的方法融合了Gemini 2.5 Flash进行视觉描述、Gemini 1.5 Pro进行字幕优化和一致性检查,以及Gemini 2.5 Pro作为推理器处理最终答案的选择,所有这些都通过精心设计的少量和零样本提示进行协调。我们对几个大型语言模型(Gemini 2.5 Flash、Phi 4、Gemma 3、Mistral)进行了广泛的消融研究训练,训练数据集包括英语及其多语言增强版本。此外,我们还对Gemini 2.5 Flash进行了零样本设置下的比较评估,发现其性能大大优于训练模型。提示设计也被证明是关键的:通过执行简洁、语言规范化的格式并禁止解释性文本,模型在英语验证集上的准确率从55.9%提高到了61.7%。在官方排行榜上,我们的系统(MSA团队)在多语言轨道上以81.4%的准确率获得第一名,并在13个单一语言轨道中的11个轨道上名列前茅,如在克罗地亚语的95.07%和意大利语的92.12%。这些发现表明,当轻量级的OCR-VLM集成与精确的提示策略和跨语言增强相结合时,可以在高风险的多语言教育环境中表现优于更重的端到端模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要基于团队MSA所设计的稳健的集成系统,该系统采用多语言多媒体模式推理,适用于ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战。该系统融合了Gemini 2.5 Flash视觉描述、Gemini 1.5 Pro进行描述精炼和一致性检查,以及Gemini 2.5 Pro作为推理器进行最终答案选择,所有这些功能都通过精心设计的少量和零样本提示进行协调。通过大量实验和评估,团队在英文数据集及其多语言增强版本上训练了大型语言模型,并在官方排行榜上取得了第一名的成绩。研究结果表明,当配以精确提示策略和跨语言增强时,轻量级的OCR-VLM集成系统可以在高风险的多元语言教育环境中表现出超越重型端到端模型的能力。本研究的最大亮点在于对于特定场景下使用混合语言技术路线的模型的新发现和推广,并通过不断的训练和修正来提升模型的性能。整体表现卓越,为相关领域提供了有力的参考依据。此外,团队的克罗地亚和意大利语言的准确率达到了惊人的高水平。此研究将为多语言环境下的视觉描述与推理带来重大影响。这一研究展现了融合各种技术的强大集成系统的优势。其核心优势在于创新性的系统设计和精准的提示策略。它在教育环境中的准确性和鲁棒性非常引人注目。简而言之,本研究展示了轻量级OCR-VLM集成系统在多语言环境中的卓越性能,以及其如何在外语理解和分析上展现出高度智能化和自主性,使其成为学术研究及行业实践领域的一种全新而强有力的解决方案。综合来看本论文的方法具有高度的创新性、实用性以及广阔的应用前景。该摘要简洁明了地总结了论文的核心内容和主要发现。它强调了该系统的有效性、准确性和在多语种环境中的优越性。Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一个稳健的集成系统,专为ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战设计,用于多语言多媒体模式推理。
- 系统融合了多种技术模块包括视觉描述、描述精炼和一致性检查以及推理处理。
- 通过大量实验和评估,验证了系统的有效性。在官方排行榜上取得了第一名的好成绩。
- 研究发现轻量级OCR-VLM集成系统在高风险的多元语言教育环境中表现出超越重型端到端模型的能力。精准提示策略和跨语言增强提高了模型性能。
点此查看论文截图


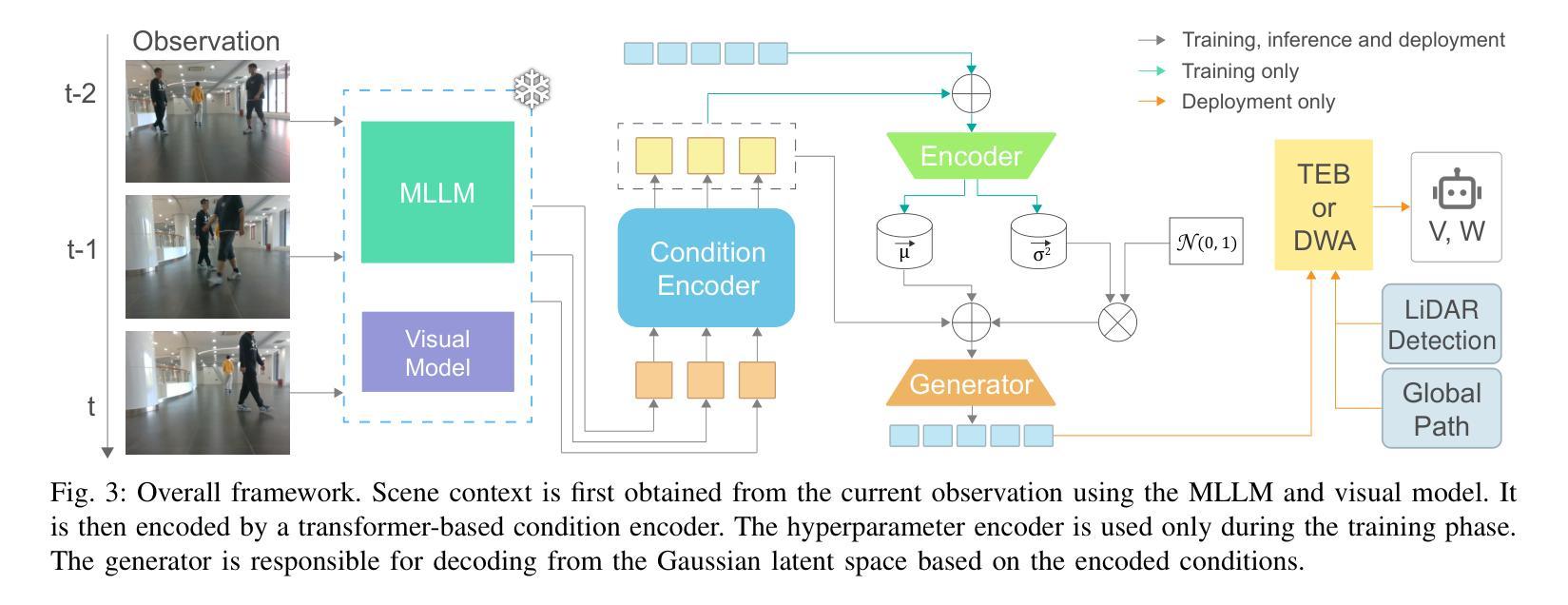
Learning to Tune Like an Expert: Interpretable and Scene-Aware Navigation via MLLM Reasoning and CVAE-Based Adaptation
Authors:Yanbo Wang, Zipeng Fang, Lei Zhao, Weidong Chen
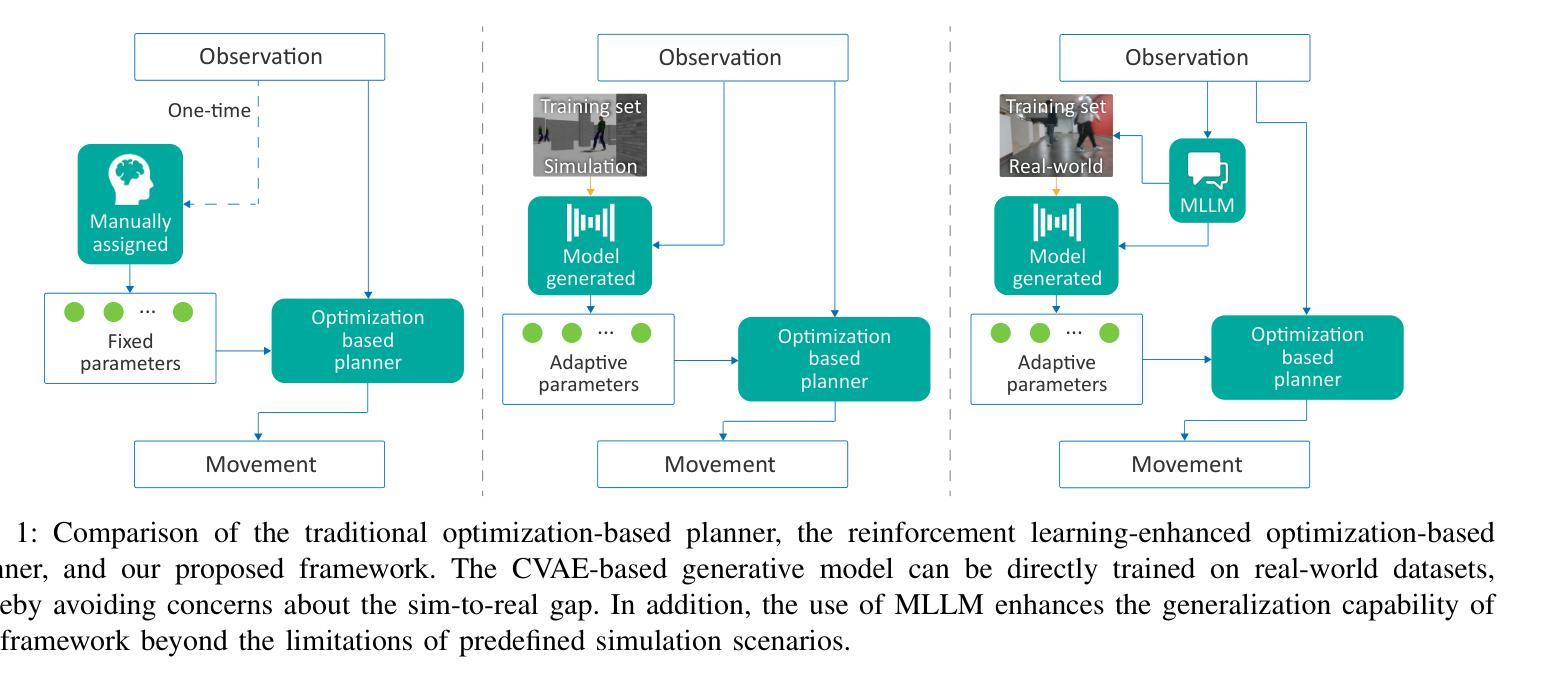
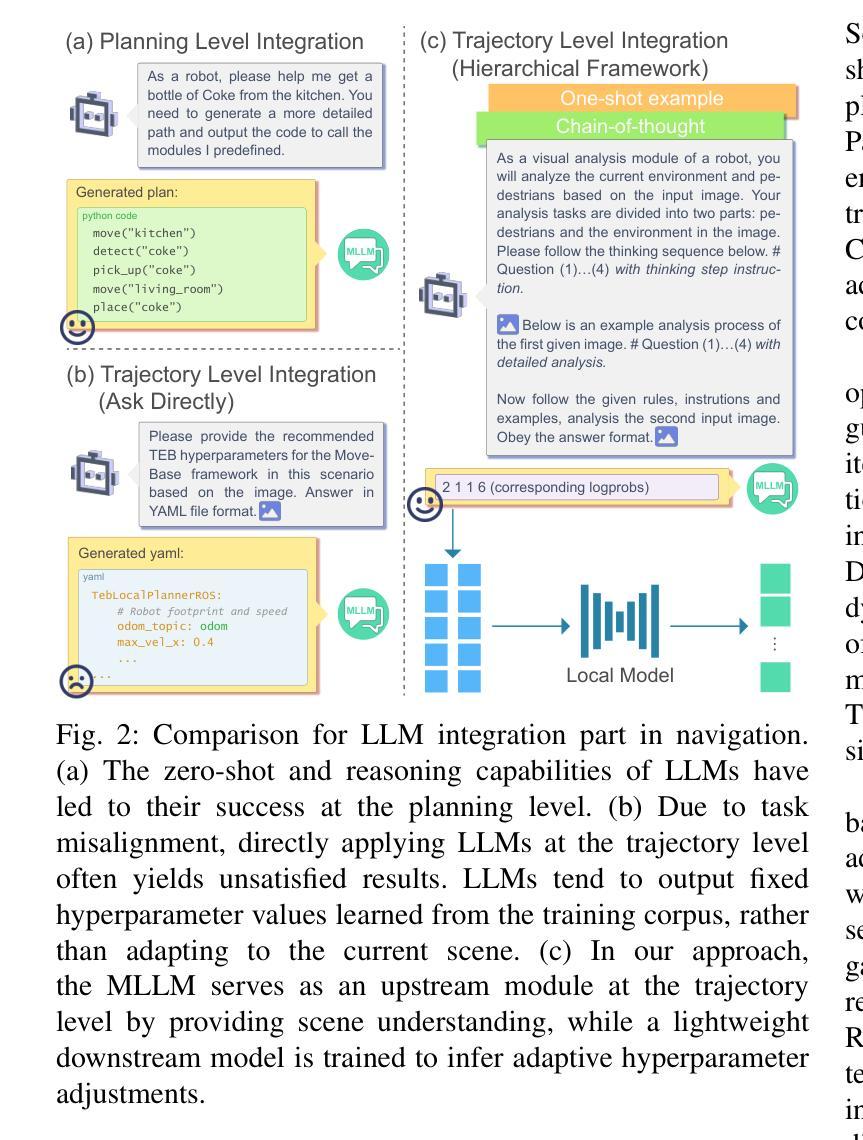
Service robots are increasingly deployed in diverse and dynamic environments, where both physical layouts and social contexts change over time and across locations. In these unstructured settings, conventional navigation systems that rely on fixed parameters often fail to generalize across scenarios, resulting in degraded performance and reduced social acceptance. Although recent approaches have leveraged reinforcement learning to enhance traditional planners, these methods often fail in real-world deployments due to poor generalization and limited simulation diversity, which hampers effective sim-to-real transfer. To tackle these issues, we present LE-Nav, an interpretable and scene-aware navigation framework that leverages multi-modal large language model reasoning and conditional variational autoencoders to adaptively tune planner hyperparameters. To achieve zero-shot scene understanding, we utilize one-shot exemplars and chain-of-thought prompting strategies. Additionally, a conditional variational autoencoder captures the mapping between natural language instructions and navigation hyperparameters, enabling expert-level tuning. Experiments show that LE-Nav can generate hyperparameters achieving human-level tuning across diverse planners and scenarios. Real-world navigation trials and a user study on a smart wheelchair platform demonstrate that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods on quantitative metrics such as success rate, efficiency, safety, and comfort, while receiving higher subjective scores for perceived safety and social acceptance. Code is available at https://github.com/Cavendish518/LE-Nav.
服务机器人越来越多地被部署在多样化和动态的环境中,这些环境的物理布局和社会背景会随时间和地点的变化而变化。在这些非结构化设置中,依赖固定参数的传统导航系统往往无法在不同场景之间进行泛化,导致性能下降和社会接受度降低。尽管最近的方法已经利用强化学习来增强传统规划器,但这些方法在现实世界的部署中经常失败,因为泛化能力较差和模拟多样性有限,这阻碍了有效的模拟到现实的转移。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了LE-Nav,这是一个可解释的、场景感知的导航框架,它利用多模态大型语言模型推理和条件变分自动编码器来适应性地调整规划器超参数。为了实现零射击场景理解,我们采用一次射击的范例和思维链提示策略。此外,条件变分自动编码器捕捉自然语言指令和导航超参数之间的映射关系,实现专家级调整。实验表明,LE-Nav可以生成在不同规划器和场景上达到人类级调整的超参数。在智能轮椅平台上的现实导航试验和用户研究证明,它在成功率、效率、安全性和舒适性等定量指标上优于最新技术方法,同时在感知安全性和社会接受度方面获得更高的主观评分。代码可在https://github.com/Cavendish518/LE-Nav获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
服务机器人在动态环境中部署日益普遍,面临场景多变、社会背景复杂等挑战。传统导航系统依赖固定参数,难以适应不同场景,性能和社会接受度受限。强化学习虽被用于改进传统规划器,但在实际部署中因缺乏通用性和仿真多样性而失效。为解决这些问题,提出LE-Nav框架,结合多模态大型语言模型推理和条件变分自编码器,自适应调整规划器超参数。利用一范例和思维链提示策略实现零镜头场景理解。实验显示LE-Nav可生成人类级别调整的超参数,在不同规划和场景下表现优越。在智能轮椅平台上的真实世界导航试验和用户研究证明,其在成功率、效率、安全性和舒适性等方面优于现有方法,主观感知安全性和社会接受度更高。
Key Takeaways
- 服务机器人在动态环境中部署面临诸多挑战,包括场景变化和复杂的社会背景。
- 传统导航系统依赖固定参数,难以适应不同场景,导致性能下降和社会接受度降低。
- 强化学习在机器人导航中的应用受到限制,主要由于缺乏通用性和仿真多样性。
- LE-Nav框架结合多模态大型语言模型推理和条件变分自编码器,能够自适应调整规划器超参数。
- LE-Nav利用一范例和思维链提示策略实现零镜头场景理解,提高导航适应性。
- 实验显示LE-Nav在生成人类级别调整的超参数方面表现优越,适用于多种规划和场景。
- LE-Nav在真实世界导航试验和用户研究中表现出较高的成功率、效率、安全性和舒适性,主观感知安全性和社会接受度更高。
点此查看论文截图


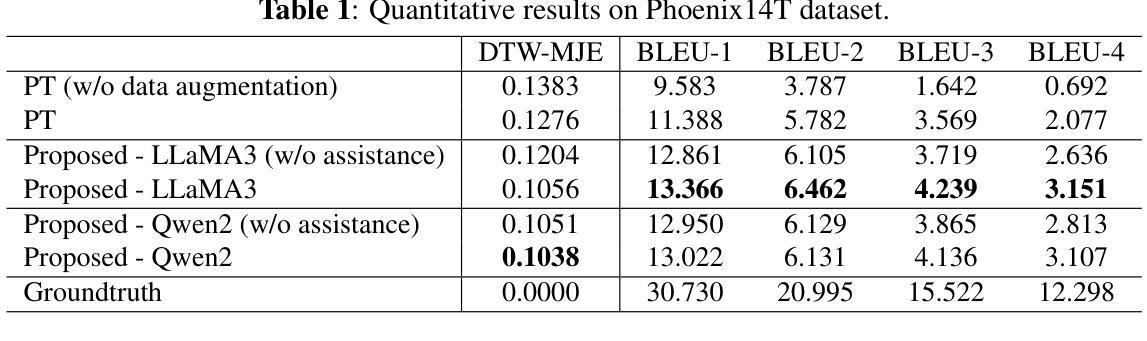
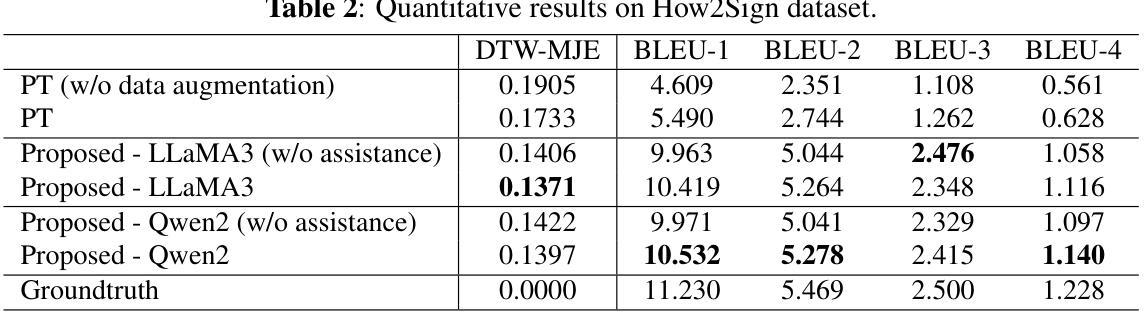
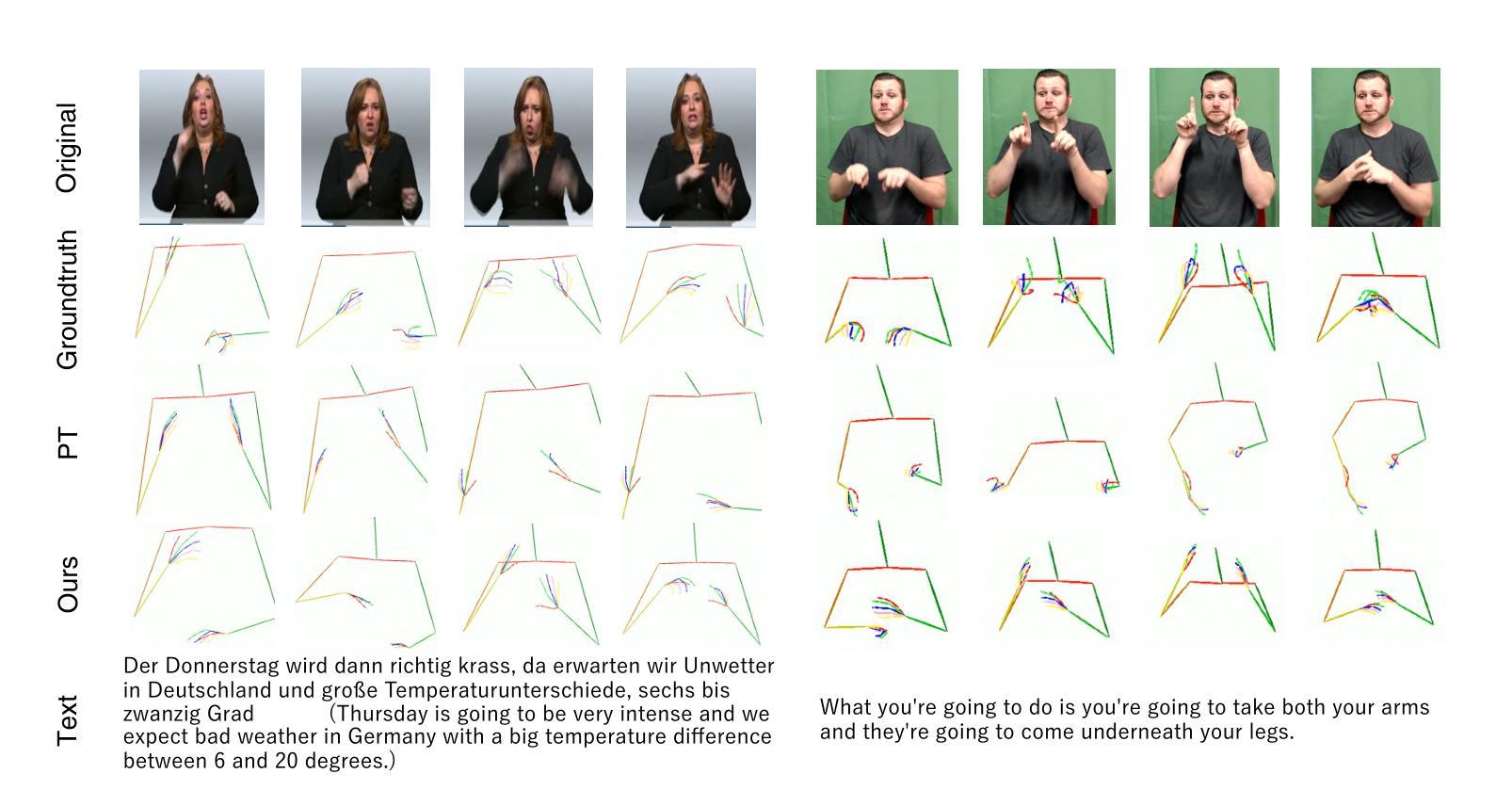
Teach Me Sign: Stepwise Prompting LLM for Sign Language Production
Authors:Zhaoyi An, Rei Kawakami
Large language models, with their strong reasoning ability and rich knowledge, have brought revolution to many tasks of AI, but their impact on sign language generation remains limited due to its complexity and unique rules. In this paper, we propose TEAch Me Sign (TEAM-Sign), treating sign language as another natural language. By fine-tuning an LLM, we enable it to learn the correspondence between text and sign language, and facilitate generation. Considering the differences between sign and spoken language, we employ a stepwise prompting strategy to extract the inherent sign language knowledge within the LLM, thereby supporting the learning and generation process. Experimental results on How2Sign and Phoenix14T datasets demonstrate that our approach effectively leverages both the sign language knowledge and reasoning capabilities of LLM to align the different distribution and grammatical rules between sign and spoken language.
大型语言模型凭借其强大的推理能力和丰富的知识,在AI的许多任务中带来了革命性的变革,但由于手语本身的复杂性和独特规则,其在手语生成方面的影响仍然有限。在本文中,我们提出“教导我手语”(TEAch Me Sign,简称TEAM-Sign)的方法,将手语视为另一种自然语言。通过微调大型语言模型(LLM),使其学习文本和手语之间的对应关系,并促进生成。考虑到手语和口语之间的差异,我们采用分步提示策略来提取LLM中的内在手语知识,从而支持学习和生成过程。在How2Sign和Phoenix14T数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地利用了LLM的手语知识和推理能力,对齐了手语和口语之间不同的分布和语法规则。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ICIP 2025
Summary
大规模语言模型因其强大的推理能力和丰富的知识而在人工智能的许多任务中引发了革命,但其在手语生成方面的影响由于手语的复杂性和独特规则而受限。本文提出TEAch Me Sign(TEAM-Sign)方法,将手语视为另一种自然语言。通过微调大型语言模型(LLM),使其学习文本和手语之间的对应关系,并促进生成。考虑到手语和口语之间的差异,我们采用分步提示策略,从LLM中提取内在的手语言知识,从而支持学习和生成过程。在How2Sign和Phoenix14T数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地利用了LLM的手语知识和推理能力,对齐了手语和口语之间不同的分布和语法规则。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在AI的多个任务中展现出强大的能力,但对手语生成的影响有限。
- TEAM-Sign方法旨在通过微调大型语言模型,使其能够学习文本和手语之间的对应关系。
- 手语与口语之间存在差异,因此采用分步提示策略来提取LLM中的手语言知识。
- 实验结果表明,该方法能有效对齐手语和口语之间的不同分布和语法规则。
- TEAM-Sign方法利用LLM的手语知识和推理能力,提高了手语生成的效果。
- 提出的方法在How2Sign和Phoenix14T数据集上进行了实验验证。
点此查看论文截图


Modeling Understanding of Story-Based Analogies Using Large Language Models
Authors:Kalit Inani, Keshav Kabra, Vijay Marupudi, Sashank Varma
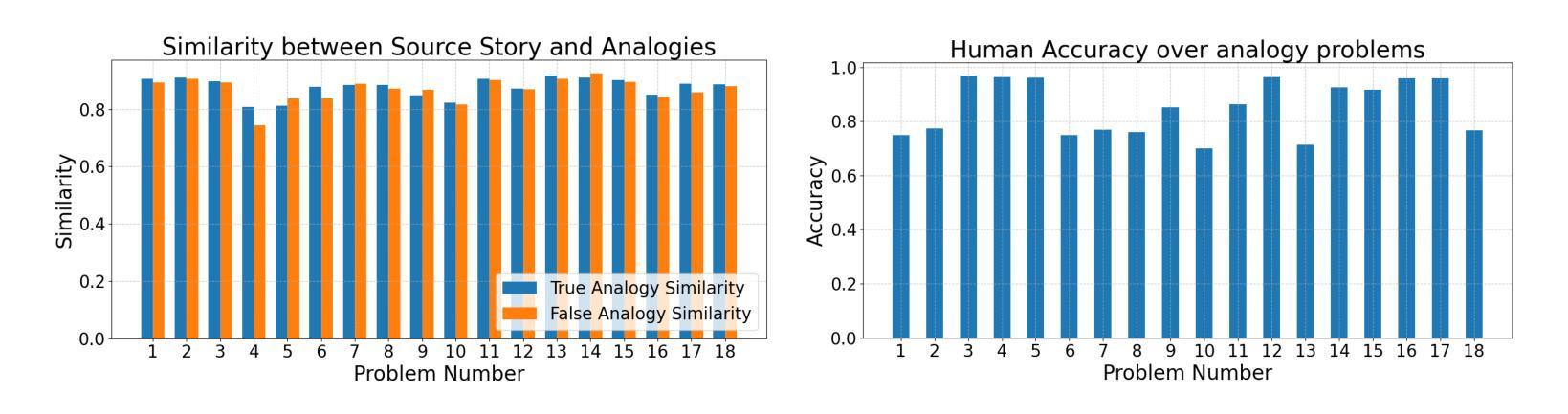
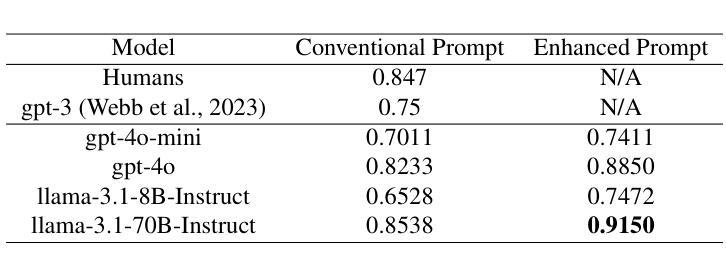
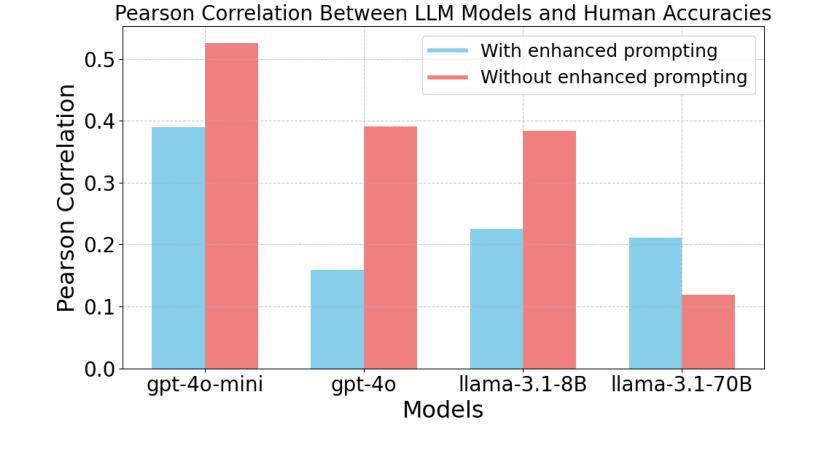
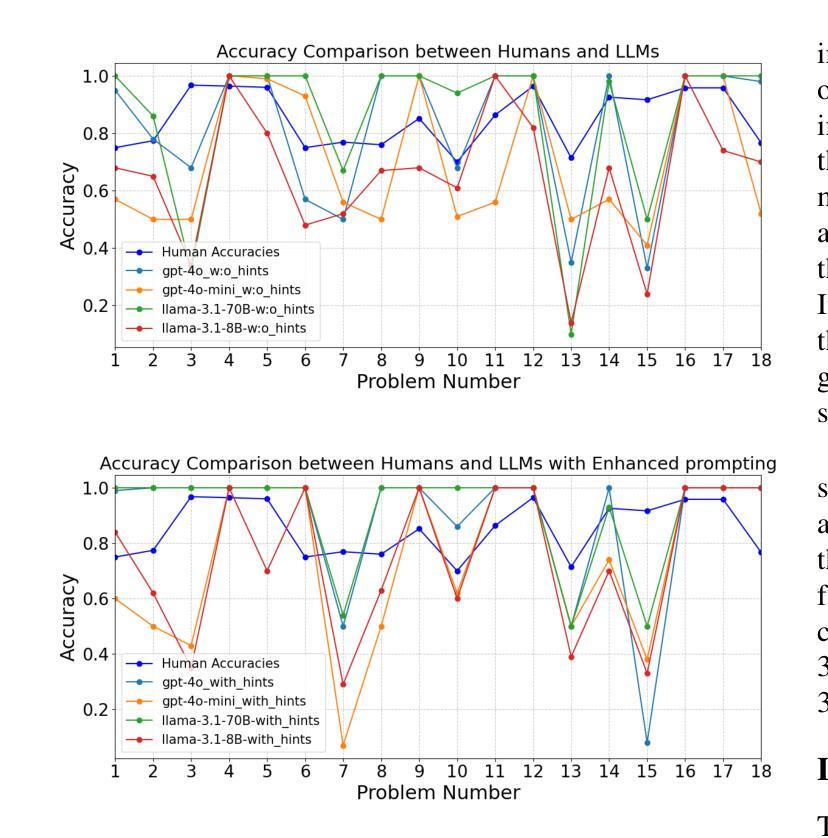
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have brought them closer to matching human cognition across a variety of tasks. How well do these models align with human performance in detecting and mapping analogies? Prior research has shown that LLMs can extract similarities from analogy problems but lack robust human-like reasoning. Building on Webb, Holyoak, and Lu (2023), the current study focused on a story-based analogical mapping task and conducted a fine-grained evaluation of LLM reasoning abilities compared to human performance. First, it explored the semantic representation of analogies in LLMs, using sentence embeddings to assess whether they capture the similarity between the source and target texts of an analogy, and the dissimilarity between the source and distractor texts. Second, it investigated the effectiveness of explicitly prompting LLMs to explain analogies. Throughout, we examine whether LLMs exhibit similar performance profiles to those observed in humans by evaluating their reasoning at the level of individual analogies, and not just at the level of overall accuracy (as prior studies have done). Our experiments include evaluating the impact of model size (8B vs. 70B parameters) and performance variation across state-of-the-art model architectures such as GPT-4 and LLaMA3. This work advances our understanding of the analogical reasoning abilities of LLMs and their potential as models of human reasoning.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步让它们在各种任务中与人类认知的匹配程度更高。这些模型在检测和映射类比方面与人类表现的对齐程度如何?先前的研究表明,LLM可以从类比问题中提取相似性,但缺乏像人类一样的稳健推理。本研究以Webb、Holyoak和Lu(2023)的研究为基础,重点关注基于故事的类比映射任务,对LLM的推理能力进行精细评估,并与人类表现进行比较。首先,它探索了LLM中类比的语义表示,使用句子嵌入来评估它们是否捕获了类比中源文本和目标文本之间的相似性,以及源文本和干扰文本之间的不相似性。其次,它调查了明确提示LLM解释类比的有效性。在整个过程中,我们通过评估单个类比层面的推理,而非仅仅评估整体准确性(如先前研究所做),来检查LLM是否表现出与人类相似的性能特征。我们的实验包括评估模型大小(8B与70B参数)的影响,以及在最先进技术架构(如GPT-4和LLaMA3)之间性能的差异。这项工作推动了我们对于LLM的类比推理能力及其作为人类推理模型潜力的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at CogSci 2025
Summary:
近期大型语言模型(LLM)在类比检测与映射任务上的表现逐渐接近人类认知。研究关注故事类类比映射任务,细致评估了LLM推理能力与人类表现的差异。研究首先探索了LLM中类比的语义表示,使用句子嵌入评估其捕捉源文本与目标文本间相似性以及源文本与干扰文本间差异的能力。其次,调查了明确提示LLM解释类比的有效性。我们评估了LLM在单个类比层面的推理表现,而非仅关注总体准确率。实验还包括评估模型规模(8B与70B参数)的影响以及不同先进模型架构(如GPT-4和LLaMA3)的表现差异。此研究有助于增进对LLM类比推理能力的理解,并推动其作为人类推理模型的发展。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在类比检测与映射任务上的表现逐渐接近人类认知。
- 研究关注故事类类比映射任务,并进行了细致的评估。
- LLM的语义表示能力对于捕捉类比中的源文本与目标文本之间的相似性是关键。
- 明确提示LLM解释类比的有效性得到调查。
- 评估了LLM在单个类比层面的推理表现。
- 实验显示模型规模与架构对LLM的类比推理能力有影响。
点此查看论文截图

MalCodeAI: Autonomous Vulnerability Detection and Remediation via Language Agnostic Code Reasoning
Authors:Jugal Gajjar, Kamalasankari Subramaniakuppusamy, Noha El Kachach
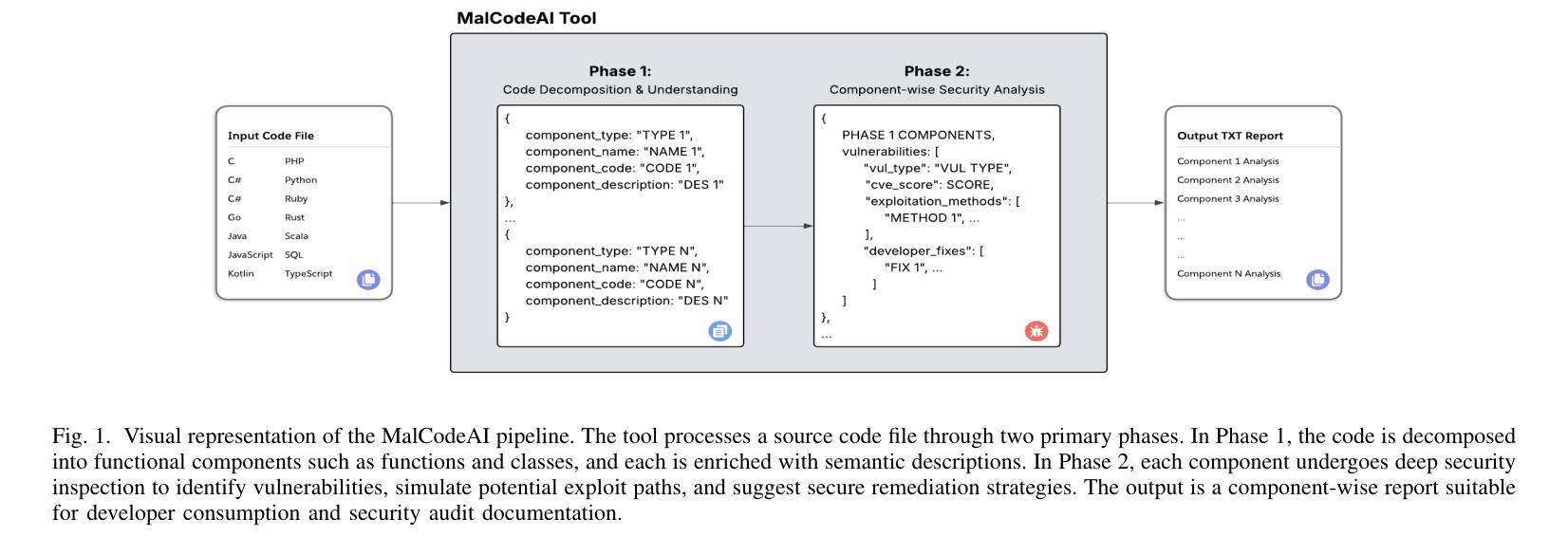
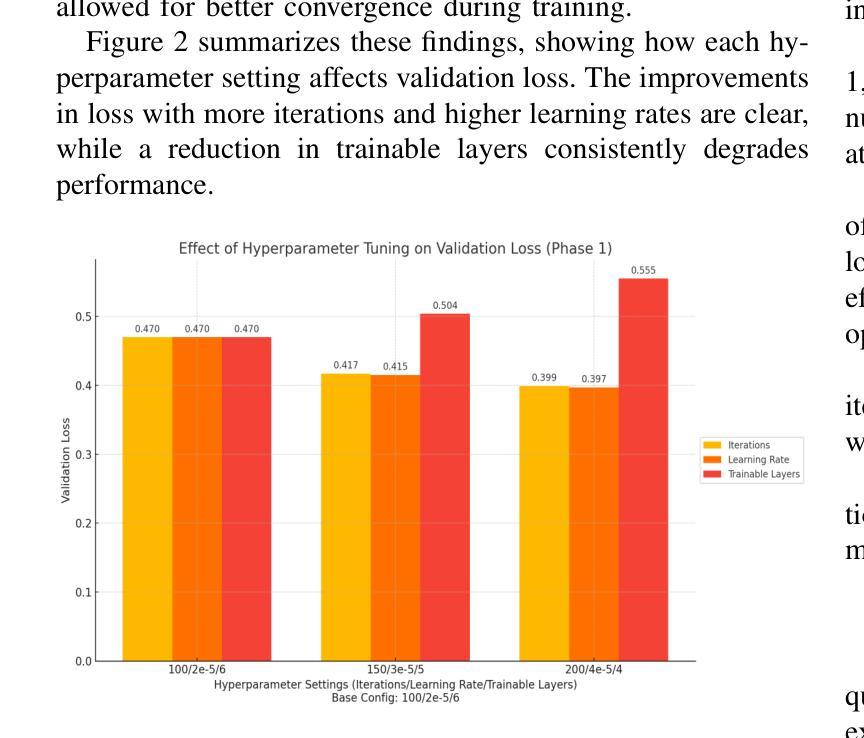
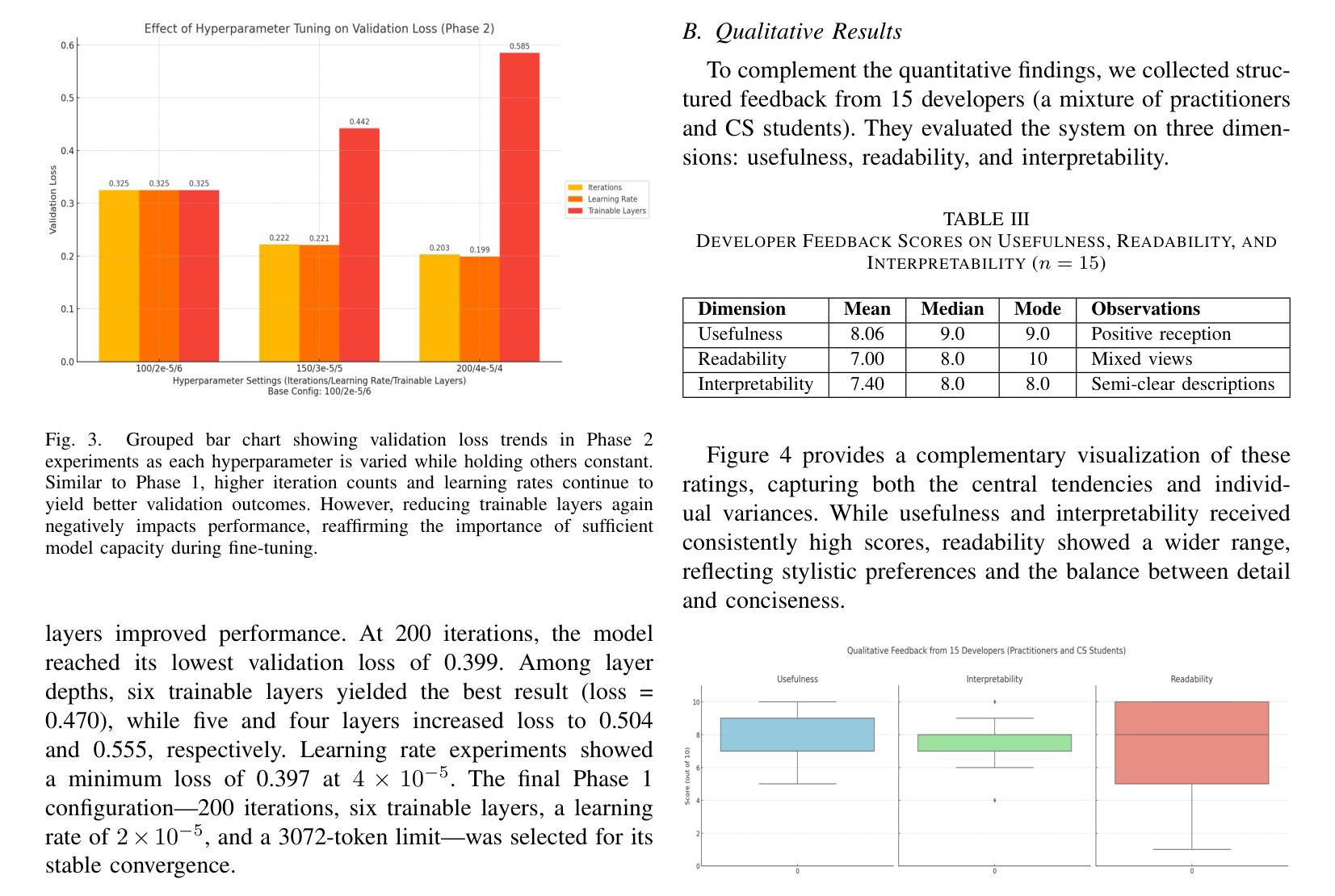
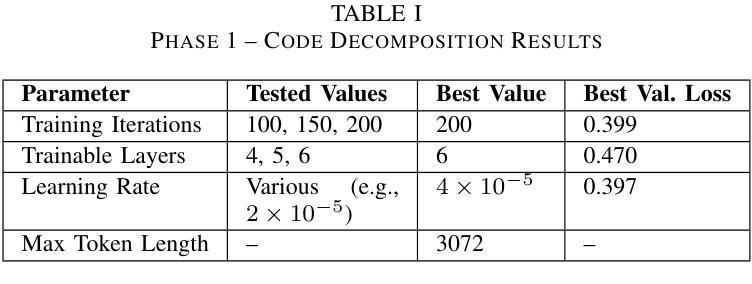
The growing complexity of cyber threats and the limitations of traditional vulnerability detection tools necessitate novel approaches for securing software systems. We introduce MalCodeAI, a language-agnostic, multi-stage AI pipeline for autonomous code security analysis and remediation. MalCodeAI combines code decomposition and semantic reasoning using fine-tuned Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct models, optimized through Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) within the MLX framework, and delivers scalable, accurate results across 14 programming languages. In Phase 1, the model achieved a validation loss as low as 0.397 for functional decomposition and summarization of code segments after 200 iterations, 6 trainable layers, and a learning rate of 2 x 10^(-5). In Phase 2, for vulnerability detection and remediation, it achieved a best validation loss of 0.199 using the same number of iterations and trainable layers but with an increased learning rate of 4 x 10^(-5), effectively identifying security flaws and suggesting actionable fixes. MalCodeAI supports red-hat-style exploit tracing, CVSS-based risk scoring, and zero-shot generalization to detect complex, zero-day vulnerabilities. In a qualitative evaluation involving 15 developers, the system received high scores in usefulness (mean 8.06/10), interpretability (mean 7.40/10), and readability of outputs (mean 7.53/10), confirming its practical value in real-world development workflows. This work marks a significant advancement toward intelligent, explainable, and developer-centric software security solutions.
随着网络威胁的日益复杂和传统漏洞检测工具的局限性,我们需要采用新型方法来保障软件系统的安全。我们推出了MalCodeAI,这是一款语言无关、多阶段的AI管道,用于自主代码安全分析和修复。MalCodeAI结合了代码分解和语义推理,使用在MLX框架内通过Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)优化的fine-tuned Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct模型,并在14种编程语言中提供可扩展、准确的结果。在第一阶段,经过200次迭代、6层可训练层和2x10^(-5)的学习率,该模型在功能分解和代码段摘要方面的验证损失降低到了0.397。在第二阶段,用于漏洞检测和修复,使用相同的迭代次数和可训练层数,但将学习率提高到4x10^(-5),取得了最佳的0.199验证损失,有效地识别了安全漏洞并提出了可行的修复建议。MalCodeAI支持红帽式漏洞追踪、基于CVSS的风险评分,并具备零样本泛化能力,可检测复杂、零日漏洞。在涉及15名开发者的定性评估中,系统在实用性(平均分8.06/10)、可解释性(平均分7.40/10)和输出可读性(平均分7.53/10)方面获得了高分,这证实了它在现实开发流程中的实用价值。这项工作标志着朝着智能、可解释和面向开发者的软件安全解决方案迈出了重要的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, accepted for publication in IEEE 26th International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration (IRI 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了MalCodeAI,一种用于自主代码安全分析和修复的多阶段人工智能管道。它结合了代码分解和语义推理,使用精细调整的Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct模型,并通过MLX框架中的低阶适应(LoRA)进行优化,可在14种编程语言中提供可扩展和准确的结果。在阶段1和阶段2的验证中,该模型分别实现了低至0.397和0.199的验证损失,展现出强大的代码段功能分解、摘要编写、漏洞检测和修复能力。MalCodeAI支持红帽风格漏洞利用追踪、基于CVSS的风险评分,并能零日通用化检测复杂、零日漏洞。开发者评价中,系统在实用性、解释性和输出可读性方面均获得较高评分,证明其在实际开发流程中的实用价值。标志着软件安全解决方案向智能化、可解释性和开发者为中心的方向迈出重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- MalCodeAI是一个多阶段的人工智能管道,用于自主代码安全分析和修复。
- 结合代码分解和语义推理,使用精细调整的Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct模型。
- 在MLX框架中通过Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)优化,支持14种编程语言。
- 阶段1和阶段2的模型验证损失分别低至0.397和0.199。
- MalCodeAI具备强大的功能分解、摘要编写、漏洞检测和修复能力。
- 支持红帽风格漏洞利用追踪、基于CVSS的风险评分,并能零日通用化检测复杂、零日漏洞。
点此查看论文截图

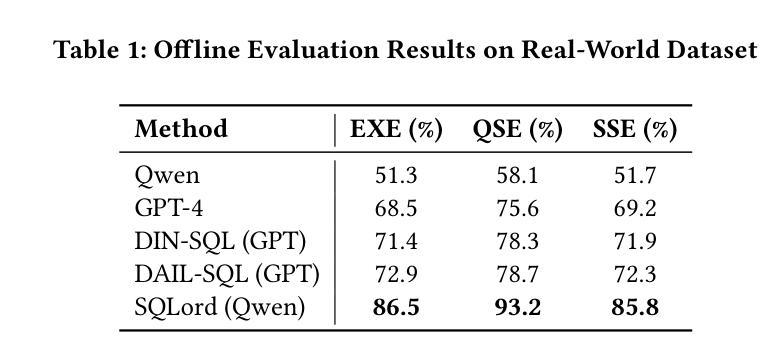
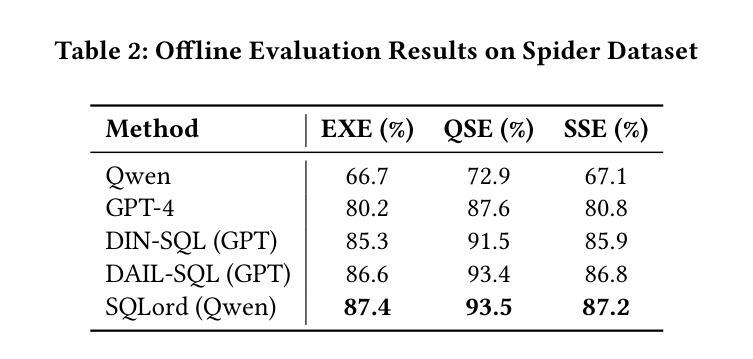
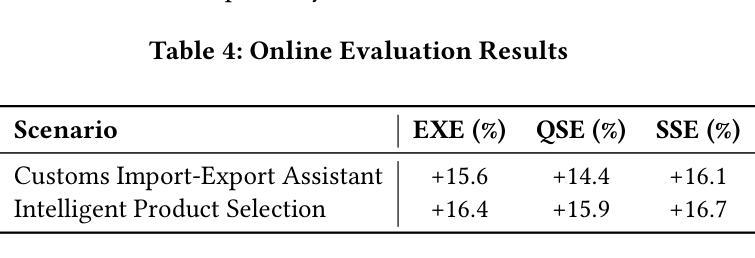
SQLord: A Robust Enterprise Text-to-SQL Solution via Reverse Data Generation and Workflow Decomposition
Authors:Song Cheng, Qiannan Cheng, Linbo Jin, Lei Yi, Guannan Zhang
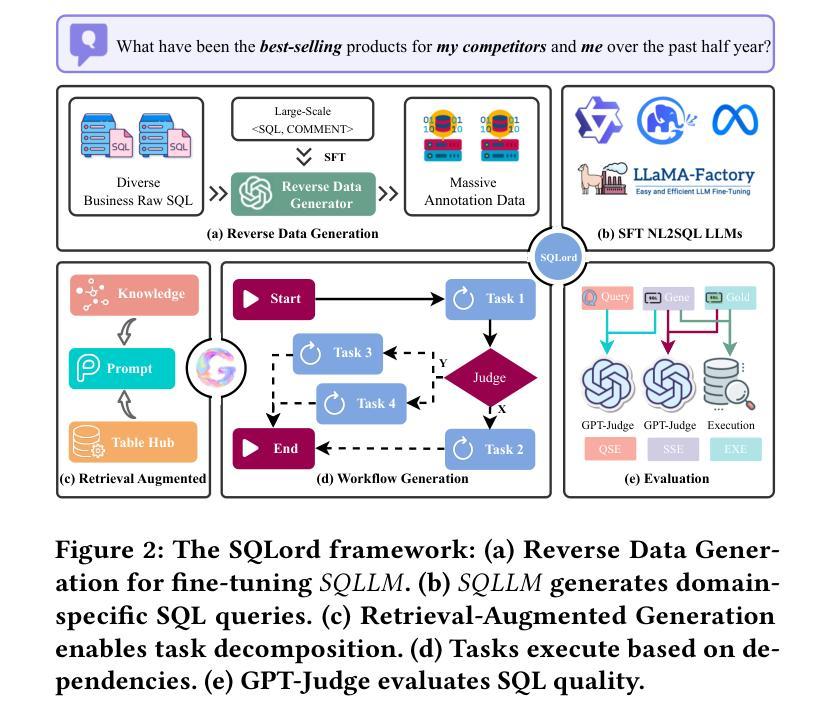
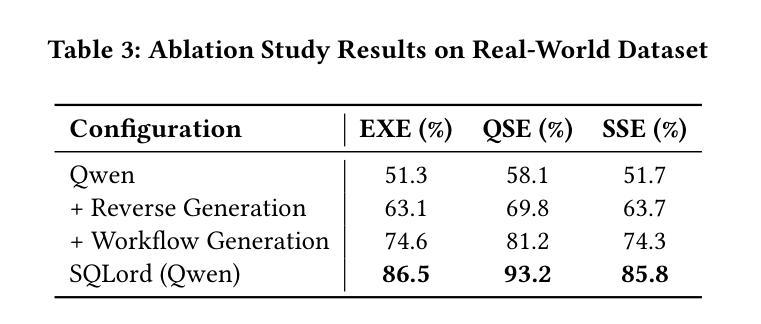
Transforming natural language into SQL queries (NL2SQL) is crucial for data-driven business applications. Existing frameworks, trained on open-source datasets, struggle with complex business logic and lack domain-specific data for fine-tuning. Additionally, evaluation methods often require annotated data and executable database environments, which are scarce in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose SQLord, an enterprise-level NL2SQL framework. First, SQLord introduces a data reverse generation approach to convert raw SQL statements into annotated data for supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Second, it proposes a decomposition method for complex queries using an automated workflow generator. Additionally, SQLord features a comprehensive GPT-Judge evaluation framework, including Execution Evaluation (EXE), Query-SQL Evaluation (QSE), and SQL-SQL Evaluation (SSE), tailored to diverse scenarios. Offline tests significantly outperform state of the art baselines, and online accuracy consistently exceeds 90, highlighting SQLord’s advantages and effectiveness in complex real world scenarios. SQLord has been successfully applied across multiple scenarios on the world’s largest B2B e-commerce platform.
将自然语言转换为SQL查询(NL2SQL)对于数据驱动的业务应用程序至关重要。现有框架在开源数据集上进行训练,难以应对复杂的业务逻辑,并且缺乏特定领域的数据进行微调。此外,评估方法通常需要注释数据和可执行的数据库环境,这在现实世界中非常稀缺。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了企业级NL2SQL框架SQLord。首先,SQLord引入了一种数据反向生成方法,将原始SQL语句转换为注释数据,用于监督微调(SFT)。其次,它提出了一种使用自动化工作流程生成器对复杂查询进行分解的方法。此外,SQLord还包含一个全面的GPT-Judge评估框架,包括执行评估(EXE)、查询SQL评估(QSE)和SQL-SQL评估(SSE),适用于各种场景。离线测试显著优于最新基线,在线准确率持续超过90%,突显了SQLord在复杂现实世界场景中的优势和有效性。SQLord已在全球最大的B2B电子商务平台上的多个场景中得到成功应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WWW ‘25: Companion Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2025 Pages 919 - 923 https://doi.org/10.1145/3701716.3715541
Summary
基于自然语言到SQL查询(NL2SQL)转换的重要性,针对现有框架在处理复杂业务逻辑和缺乏特定领域数据微调方面的挑战,提出了SQLord这一企业级NL2SQL框架。它采用数据反向生成方法将原始SQL语句转换为注释数据,支持监督微调(SFT)。此外,SQLord还提出了复杂查询的分解方法,并利用自动化工作流程生成器实现。其全面的GPT-Judge评估框架包括执行评估(EXE)、查询SQL评估(QSE)和SQL-SQL评估(SSE),适应不同场景。离线测试表现优于现有技术基线,在线准确率超过90%,表明SQLord在复杂现实场景中的优势和有效性。该框架已在世界最大的B2B电子商务平台上的多个场景成功应用。
Key Takeaways
- SQLord是一个针对自然语言转换为SQL查询的企业级框架,旨在解决现有框架在处理复杂业务逻辑和特定领域数据微调方面的挑战。
- SQLord通过数据反向生成方法,将原始SQL语句转换为注释数据,支持监督微调(SFT)。
- 框架具有分解复杂查询的能力,通过自动化工作流程生成器实现。
- SQLord配备了全面的GPT-Judge评估框架,包括执行评估、查询SQL评估和SQL-SQL评估,以适应不同的应用场景。
- 离线测试表现优于现有技术基线,在线准确率超过90%。
- SQLord已成功应用于世界最大的B2B电子商务平台上的多个场景。
点此查看论文截图
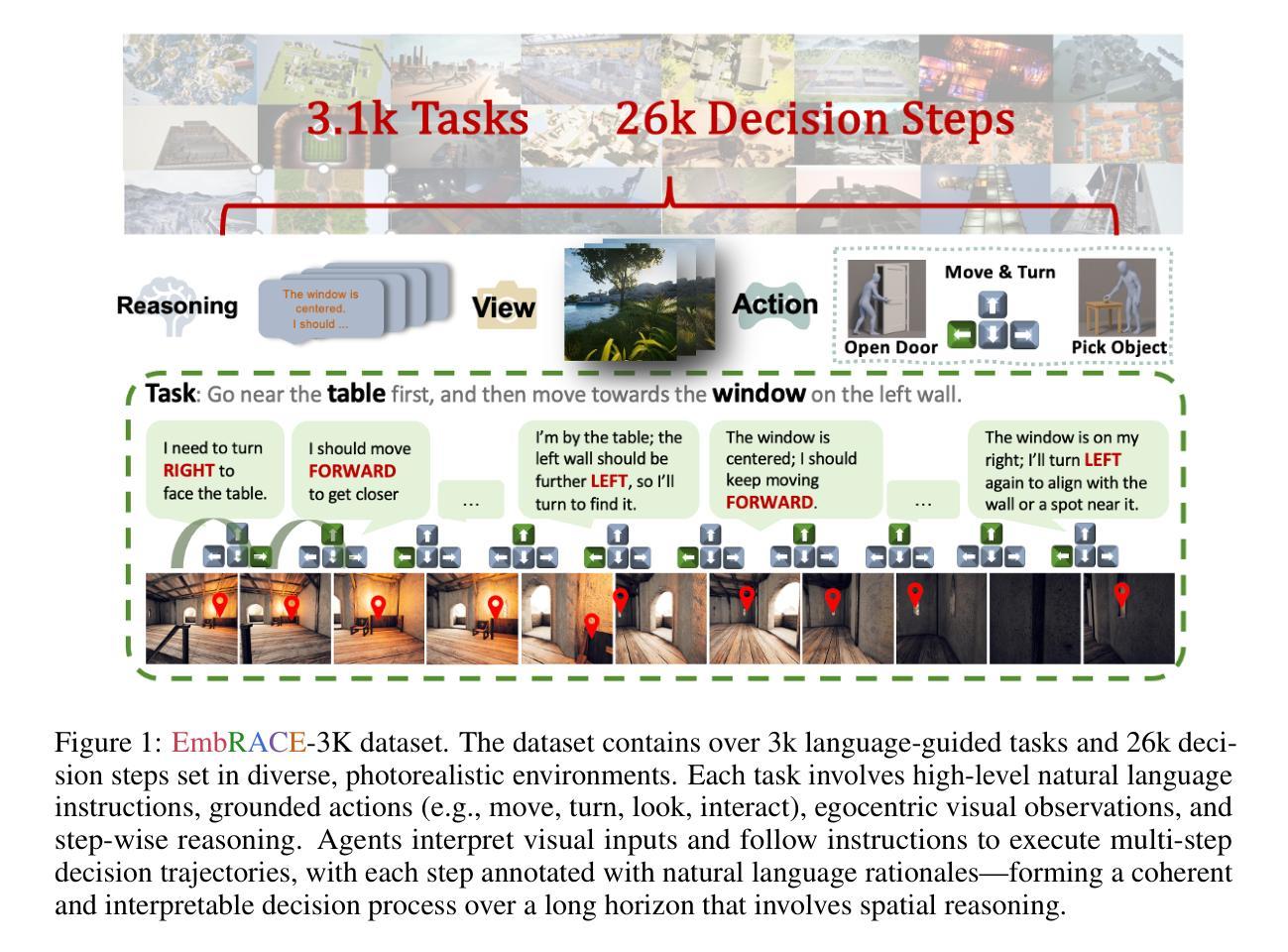
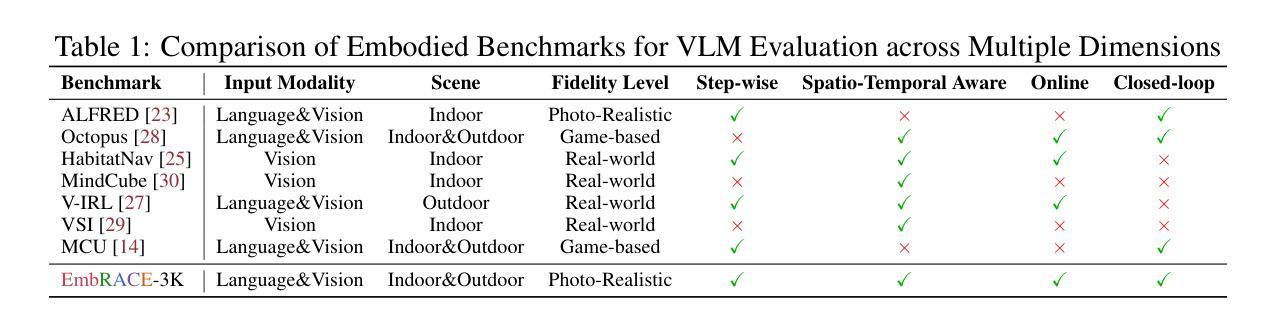
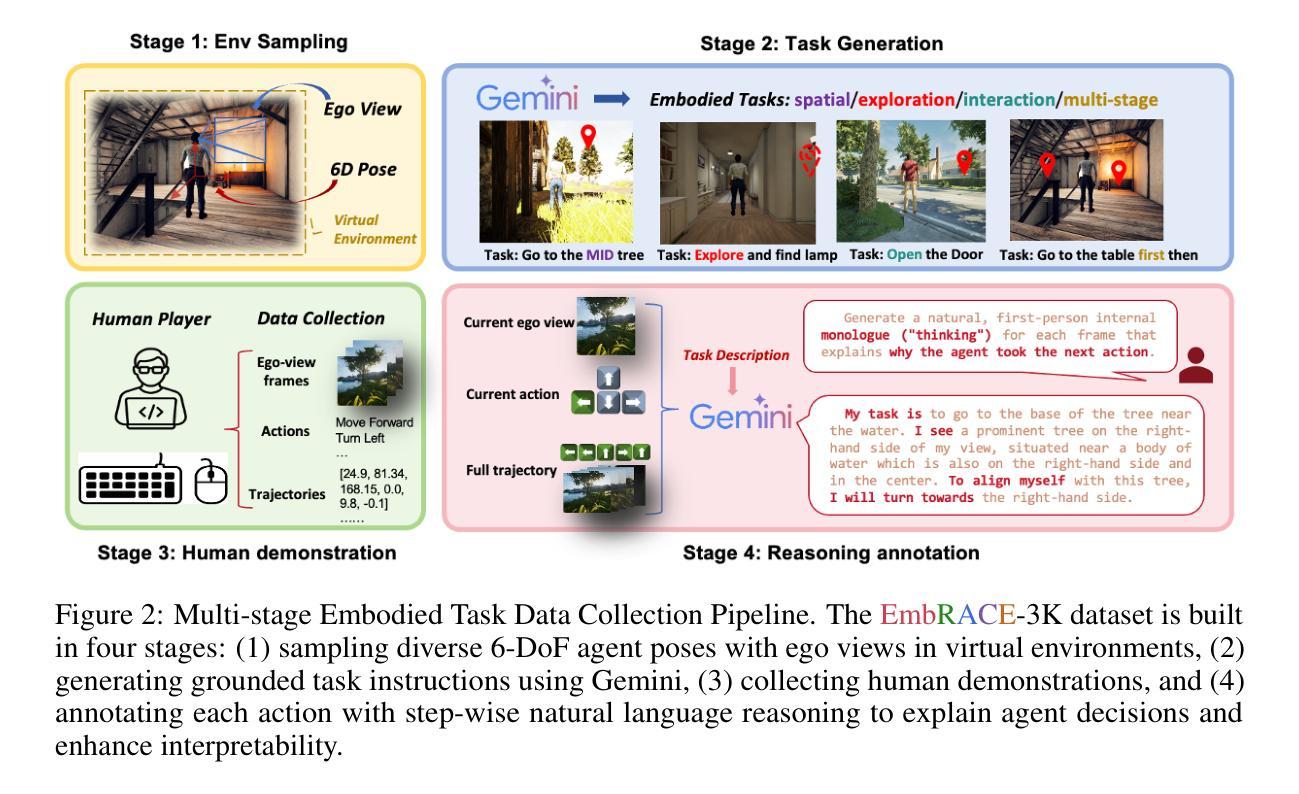
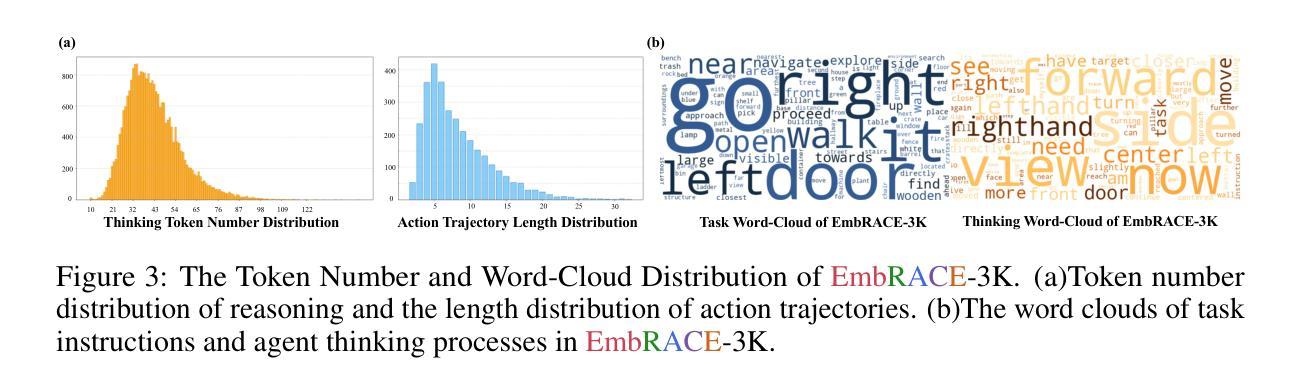
EmbRACE-3K: Embodied Reasoning and Action in Complex Environments
Authors:Mingxian Lin, Wei Huang, Yitang Li, Chengjie Jiang, Kui Wu, Fangwei Zhong, Shengju Qian, Xin Wang, Xiaojuan Qi
Recent advanced vision-language models(VLMs) have demonstrated strong performance on passive, offline image and video understanding tasks. However, their effectiveness in embodied settings, which require online interaction and active scene understanding remains limited. In such scenarios, an agent perceives the environment from a first-person perspective, with each action dynamically shaping subsequent observations. Even state-of-the-art models such as GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro struggle in open-environment interactions, exhibiting clear limitations in spatial reasoning and long-horizon planning. To address this gap, we introduce EmRACE-3K, a dataset of over 3,000 language-guided tasks situated in diverse, photorealistic environments constructed using Unreal Engine and the UnrealCV-Zoo framework. The tasks encompass a wide range of embodied challenges, including navigation, object manipulation, and multi-stage goal execution. Each task unfolds as a multi-step trajectory, pairing first-person visual observations with high-level instructions, grounded actions, and natural language rationales that express the agent’s intent at every step. Using EmRACE-3K, we establish a benchmark to evaluate the embodied reasoning capabilities of VLMs across three key dimensions: Exploration, Dynamic Spatial-Semantic Reasoning, and Multi-stage Goal Execution. In zero-shot settings, all models achieve success rates below 20%, underscoring the challenge posed by our benchmark and the current limitations of VLMs in interactive environments. To demonstrate the utility of EmRACE-3K, we further fine-tune Qwen2.5-VL-7B using supervised learning followed by reinforcement learning. This approach yields substantial improvements across all three challenge categories, highlighting the dataset’s effectiveness in enabling the development of embodied reasoning capabilities.
最新的先进视觉语言模型(VLMs)在被动、离线图像和视频理解任务上表现出强大的性能。然而,它们在需要在线交互和主动场景理解的嵌入设置中的有效性仍然有限。在此类场景中,代理从第一人称视角感知环境,每个行动都会动态地影响随后的观察。即使是最先进的模型,如GPT-4o、Claude 3.5 Sonnet和Gemini 2.5 Pro在开放环境交互中也存在困难,在空间推理和长期规划方面存在明显的局限性。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了EmRACE-3K,这是一个由超过3000个语言指导任务组成的数据集,这些任务位于使用Unreal Engine和UnrealCV-Zoo框架构建的多姿多彩、逼真的环境中。这些任务涵盖了广泛的嵌入挑战,包括导航、对象操作和多阶段目标执行。每个任务都展开为多步轨迹,将第一人称视觉观察与高级指令、实际行动和自然语言理性相结合,表达代理每一步的意图。使用EmRACE-3K,我们建立了一个基准测试,以评估VLMs在三个关键维度的嵌入推理能力:探索、动态空间语义推理和多阶段目标执行。在零射击设置中,所有模型的成功率都低于20%,这突显了我们的基准测试所构成的挑战以及VLMs在交互式环境中的当前局限性。为了证明EmRACE-3K的实用性,我们进一步使用监督学习和强化学习对Qwen2.5-VL-7B进行微调。这种方法在三个挑战类别中都取得了实质性的改进,突显了数据集在培养嵌入推理能力方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://mxllc.github.io/EmbRACE-3K/
Summary
新一代视觉语言模型在处理被动、离线图像和视频理解任务方面表现卓越,但在需要在线互动和主动场景理解的实体场景中,其效果有限。为解决这一差距,推出EmRACE-3K数据集,包含超过3000个语言指导任务,涵盖广泛的实体挑战,包括导航、对象操作和分阶段目标执行等。利用此数据集评估视觉语言模型的实体推理能力,并建立基准测试。当前模型在零样本环境下的成功率低于20%,显示其对挑战性和当前模型在互动环境中的局限性。经过精细化训练后的模型性能有所提升,凸显数据集在培养实体推理能力方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 先进视觉语言模型在被动任务上表现良好,但在实体场景中的在线互动和主动场景理解方面存在局限性。
- EmRACE-3K数据集包含多样化的语言指导任务,涵盖导航、对象操作和多阶段目标执行等实体挑战。
- 使用EmRACE-3K数据集评估视觉语言模型的实体推理能力,建立基准测试。
- 当前模型在零样本环境下的成功率较低,显示其面临的挑战和局限性。
- 通过精细化训练可以提升模型性能,凸显数据集在培养实体推理能力方面的有效性。
- EmRACE-3K数据集对于推动视觉语言模型在实体场景中的发展具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

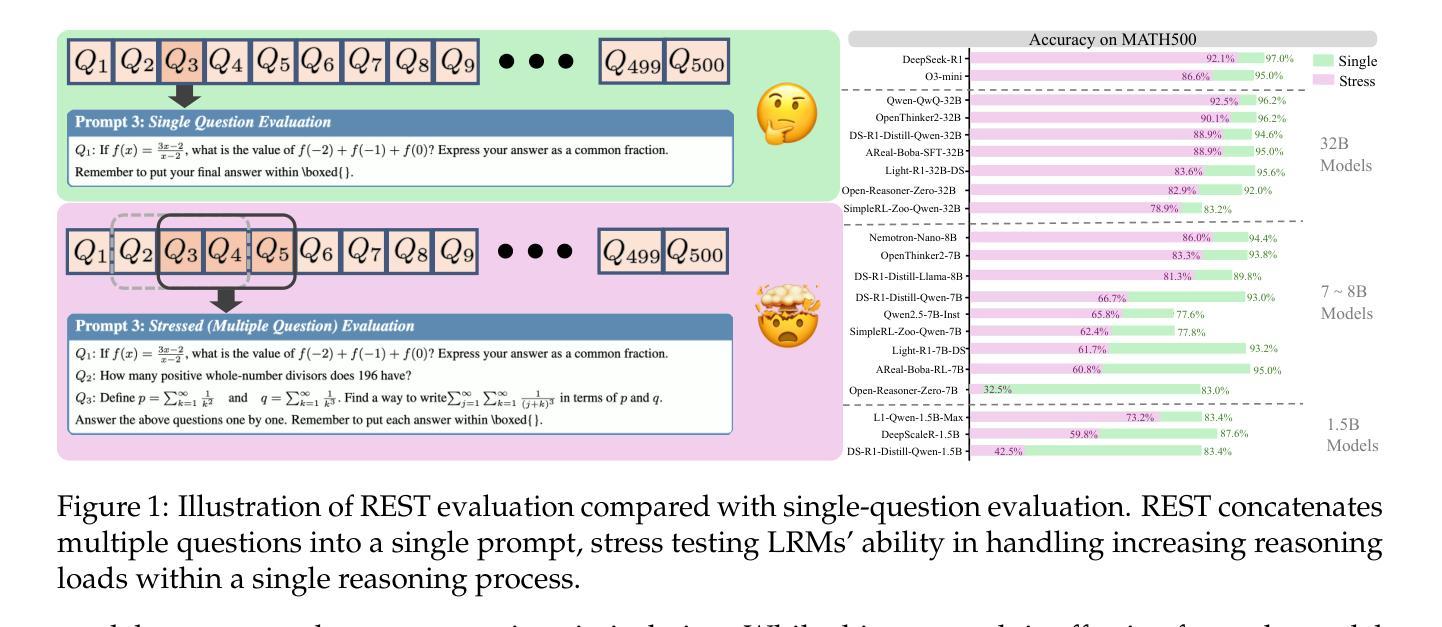
REST: Stress Testing Large Reasoning Models by Asking Multiple Problems at Once
Authors:Zhuoshi Pan, Qizhi Pei, Yu Li, Qiyao Sun, Zinan Tang, H. Vicky Zhao, Conghui He, Lijun Wu
Recent Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have achieved remarkable progress on task-specific benchmarks, yet their evaluation methods remain constrained by isolated problem-solving paradigms. Existing benchmarks predominantly assess single-question reasoning through sequential testing, resulting critical limitations: (1) vulnerability to data contamination and less challenging (e.g., DeepSeek-R1 achieves 97.0% on MATH500), forcing costly creation of new questions with large human efforts, (2) failure to evaluate models under multi-context pressure, a key requirement for real-world deployment. To bridge this gap, we present REST (Reasoning Evaluation through Simultaneous Testing), a stress-testing framework that exposes LRMs to multiple problems simultaneously. Beyond basic reasoning, REST evaluates several under-tested capabilities: contextual priority allocation, cross-problem interference resistance, and dynamic cognitive load management. Our evaluation reveals several striking findings: Even state-of-the-art (SOTA) models like DeepSeek-R1 exhibit substantial performance degradation under stress testing. Crucially, REST demonstrates stronger discriminative power than existing benchmarks, revealing pronounced performance differences among models that exhibit similar, near-ceiling performance under single-question evaluations. Some key insights emerge from our analysis: (1) the “overthinking trap” is a critical factor contributing to the performance degradation; (2) the models trained with “long2short” technique preserve more accuracy of their single-problem performance under REST, outperforming standard-trained counterparts. These results establish REST as a cost-efficient, future-proof evaluation paradigm that better reflects real-world reasoning demands while reducing reliance on continuous human annotation. Code and results are available at https://opendatalab.github.io/REST.
最近的推理大模型(LRMs)在特定任务的基准测试中取得了显著的进步,但它们的评估方法仍然受到孤立的问题解决模式的限制。现有基准测试主要通过序列测试评估单一问题的推理能力,导致关键局限性:(1)容易受到数据污染,且缺乏挑战性(例如,DeepSeek-R1在MATH500上达到97.0%),需要花费高昂成本创建新的问题需要大量的人力投入;(2)无法在多上下文压力下评估模型,这是现实世界部署的关键要求。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了REST(通过同时测试进行推理评估),这是一种压力测试框架,可以同时暴露多个问题给LRMs。除了基本的推理能力外,REST还评估了几种未经充分测试的能力:上下文优先级分配、跨问题干扰抵抗和动态认知负荷管理。我们的评估揭示了一些惊人的发现:即使是最先进的模型,如DeepSeek-R1,在压力测试下也会出现显著的性能下降。重要的是,REST显示出比现有基准测试更强的辨别力,揭示了单问题评估下表现相似、接近上限的模型之间的明显性能差异。从我们的分析中得出了一些关键见解:(1)“过度思考陷阱”是导致性能下降的关键因素之一;(2)采用“长转短”技术训练的模型在REST下保持了更高的单问题性能准确性,超越了标准训练的对等模型。这些结果确立了REST作为一种经济高效、面向未来的评估模式,更能反映现实世界的推理需求,同时减少了对持续人工注释的依赖。代码和结果可在https://opendatalab.github.io/REST上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF REST (Reasoning Evaluation through Simultaneous Testing), a stress-testing framework that concurrently exposes LRMs to multiple problems simultaneously
Summary
该文探讨了当前大型推理模型(LRMs)在任务特定基准测试上取得了显著进步,但其评估方法仍受限于孤立的问题解决模式。现有基准测试主要通过串行测试评估单一问题的推理能力,存在关键局限性。为此,本文提出了REST(通过同时测试进行推理评估)这一压力测试框架,该框架使LRMs暴露于多个问题之中,并评估了模型在基本推理之外的几项能力。研究发现,即使在压力测试下,最先进的模型也会出现显著的性能下降。REST展现出比现有基准测试更强的鉴别力,揭示了模型间显著的性能差异。本文分析揭示了一些关键见解,如“过度思考陷阱”是性能下降的关键因素之一,“长转短”技术训练的模型在REST下保持较高的准确性。总体而言,REST作为一种高效、面向未来的评估模式,更好地反映了现实世界的推理需求,并降低了对人类持续标注的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型(LRMs)在任务特定基准测试中表现出显著进步,但评估方法受限。
- 现有基准测试主要评估单一问题的推理能力,存在数据污染和缺乏多上下文压力测试的问题。
- REST框架是一种压力测试框架,能够同时暴露模型面对多个问题,评估模型的多种能力。
- 先进模型在压力测试下性能显著下降。
- REST展现出更强的鉴别力,能揭示模型间的性能差异。
- “过度思考陷阱”是性能下降的关键因素之一。
- 使用“长转短”技术训练的模型在REST评估下表现较好。
点此查看论文截图

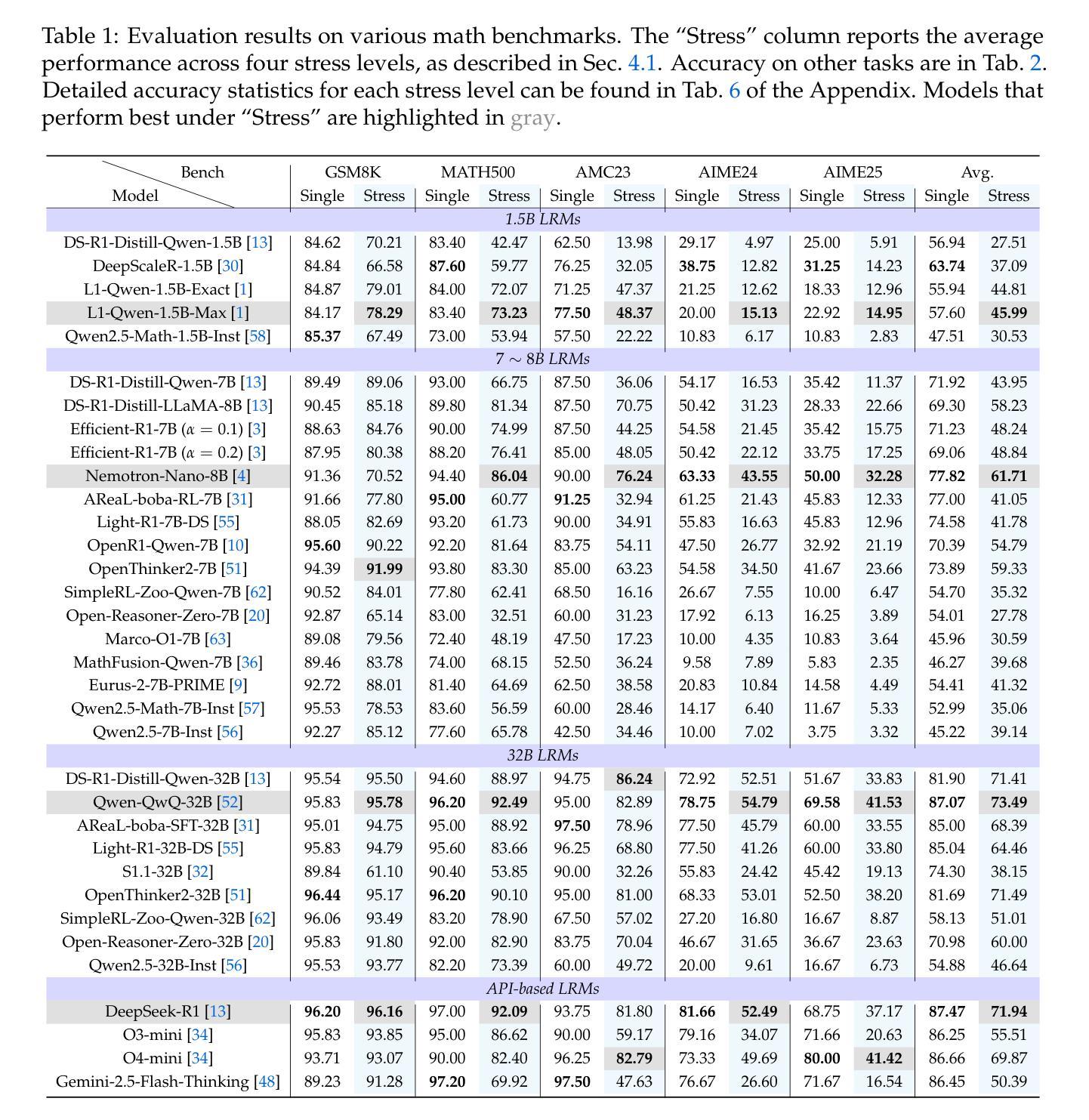
Reasoning or Memorization? Unreliable Results of Reinforcement Learning Due to Data Contamination
Authors:Mingqi Wu, Zhihao Zhang, Qiaole Dong, Zhiheng Xi, Jun Zhao, Senjie Jin, Xiaoran Fan, Yuhao Zhou, Yanwei Fu, Qin Liu, Songyang Zhang, Qi Zhang
The reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have been a longstanding focus of research. Recent works have further enhanced these capabilities using reinforcement learning (RL), with many new methods claiming significant improvements with minimal or no external supervision. Surprisingly, some studies even suggest that random or incorrect reward signals can enhance reasoning performance. However, these breakthroughs are mostly reported on the Qwen2.5 model family and evaluated on well-known benchmarks such as MATH-500, AMC, and AIME, while failing to achieve similar gains on other models like Llama, which warrants further investigation. Our analysis shows that although Qwen2.5 achieves strong mathematical reasoning performance, its pretraining on large-scale web corpora makes it vulnerable to data contamination in popular benchmarks. As a result, results derived from these benchmarks may be unreliable. To address this, we introduce a generator that produces fully synthetic arithmetic problems of arbitrary length and difficulty, yielding a clean dataset we call RandomCalculation. Using these leakage-free datasets, we show that only accurate reward signals consistently improve performance, while noisy or incorrect signals do not. We advocate for evaluating RL methods on uncontaminated benchmarks and across diverse model families to ensure trustworthy conclusions.
大型语言模型的推理能力一直是研究的重点。近期的研究工作通过使用强化学习(RL)进一步增强了这些能力,许多新方法声称在几乎没有或没有外部监督的情况下取得了显著的改进。令人惊讶的是,一些研究甚至表明,随机或错误的奖励信号可以增强推理性能。然而,这些突破大多是在Qwen2.5模型家族上报道的,并在MATH-500、AMC和AIME等著名基准测试上进行了评估,而在其他模型(如Llama)上未能实现类似的收益,这需要进行进一步的调查。我们的分析表明,尽管Qwen2.5在数学推理方面表现出色,但其在大规模网络语料库上的预训练使其容易受到流行基准测试中的数据污染。因此,从这些基准测试中得出的结果可能不可靠。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一个生成器,该生成器可以生成任意长度和难度的完全合成算术问题,从而得到一个我们称为RandomCalculation的干净数据集。使用这些无泄漏的数据集,我们证明只有准确的奖励信号才能持续提高性能,而嘈杂或错误的信号则不能。我们主张在未被污染的基准测试和各种模型家族中评估RL方法,以确保得出可靠的结论。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages
Summary
大型语言模型的推理能力一直是研究的重点。最近的研究使用强化学习进一步增强了这些能力,并在一些基准测试中取得了显著进展,甚至表明随机或错误的奖励信号可能增强推理性能。然而,这些成果主要集中在Qwen2.5模型家族上,对其他模型如Llama的适用性尚待进一步研究。分析表明,Qwen2.5虽然在数学推理方面表现出色,但由于其在大规模网络语料库上的预训练,使其容易受到流行基准测试中的数据污染影响,导致结果可能不可靠。为解决这一问题,研究团队引入了生成器,生成无泄漏的随机计算数据集。研究证实,只有准确的奖励信号才能持续提高性能,而噪声或错误的信号则不能。建议对未受污染的数据集和不同模型家族使用强化学习方法进行评估,以确保结果的可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的推理能力持续受到关注,强化学习用于增强其性能。
- Qwen2.5模型家族在特定基准测试中表现突出,但其他模型适用性尚待研究。
- Qwen2.5在数学推理方面表现出色,但预训练使其容易受到数据污染影响。
- 数据污染可能导致基准测试结果不可靠。
- 引入生成器创建无泄漏的随机计算数据集以应对数据污染问题。
- 准确的奖励信号对提高模型性能至关重要,噪声或错误信号无效。
点此查看论文截图


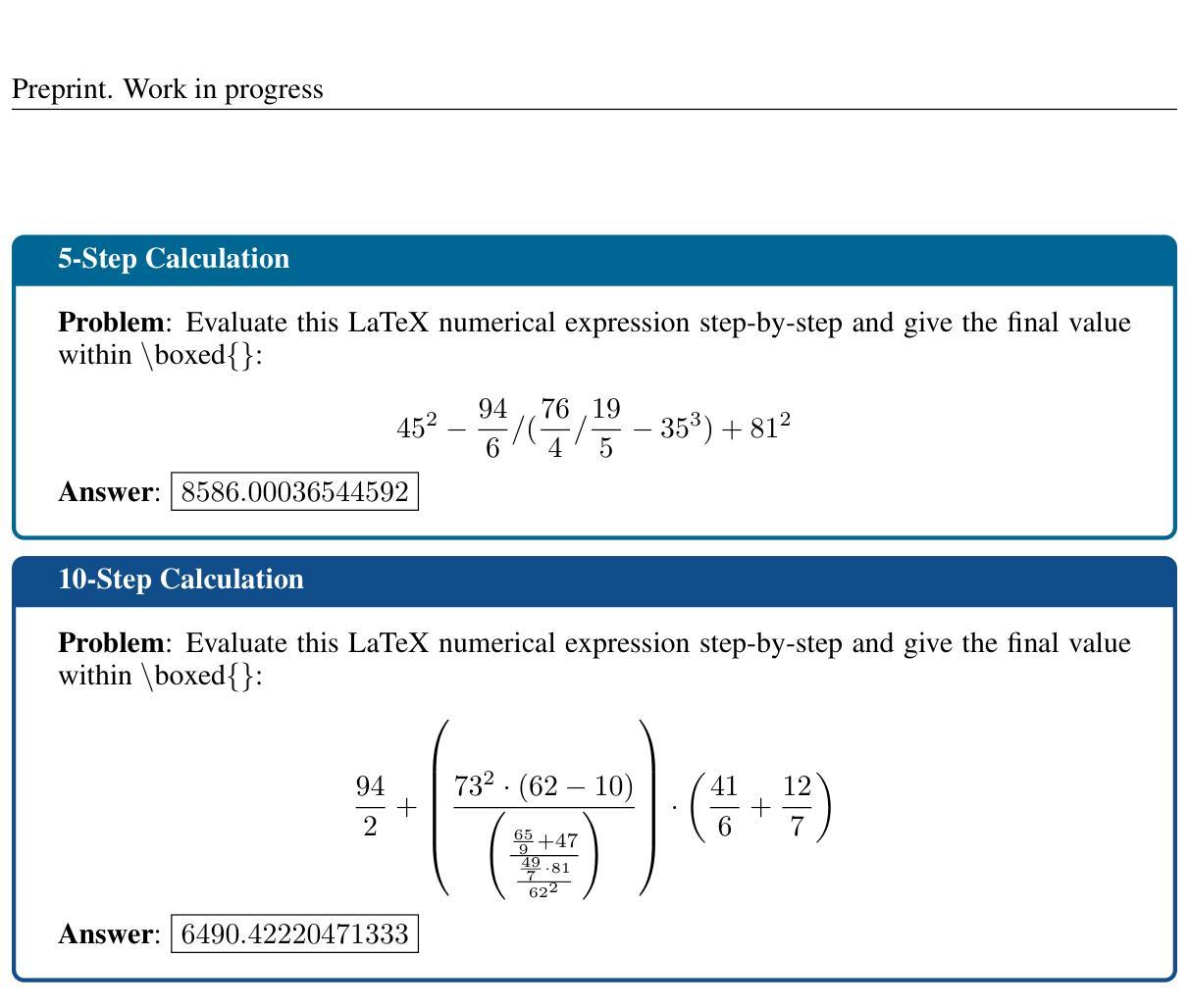
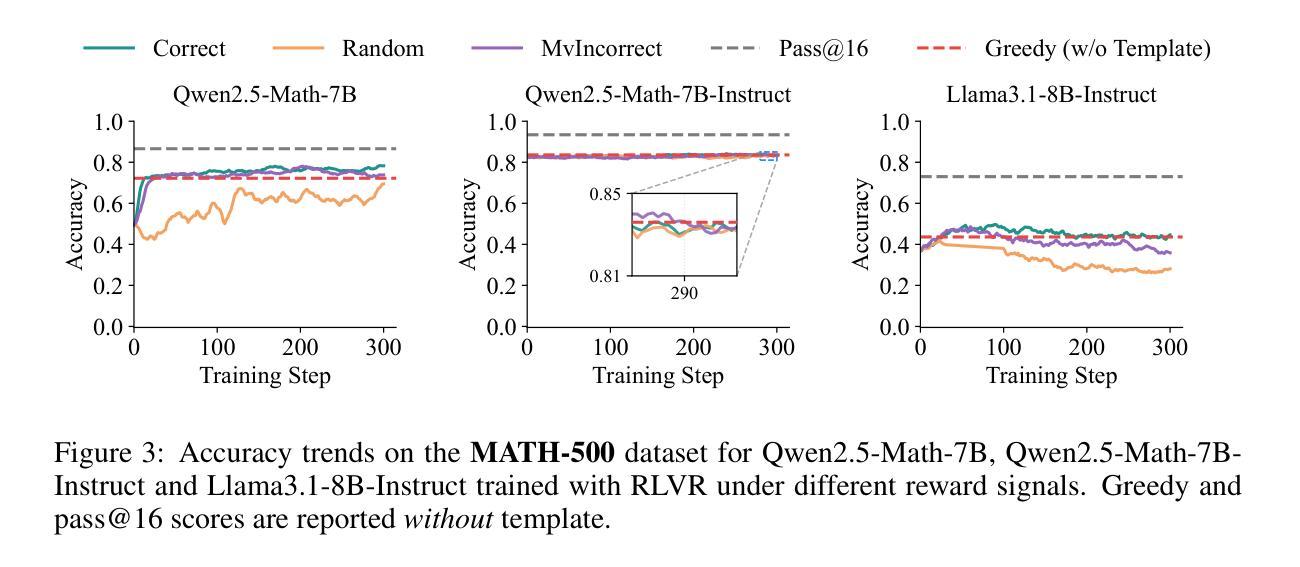
Grammar-Guided Evolutionary Search for Discrete Prompt Optimisation
Authors:Muzhaffar Hazman, Minh-Khoi Pham, Shweta Soundararajan, Goncalo Mordido, Leonardo Custode, David Lynch, Giorgio Cruciata, Yucheng Shi, Hongmeng Song, Wang Chao, Pan Yue, Aleksandar Milenovic, Alexandros Agapitos
Prompt engineering has proven to be a crucial step in leveraging pretrained large language models (LLMs) in solving various real-world tasks. Numerous solutions have been proposed that seek to automate prompt engineering by using the model itself to edit prompts. However, the majority of state-of-the-art approaches are evaluated on tasks that require minimal prompt templates and on very large and highly capable LLMs. In contrast, solving complex tasks that require detailed information to be included in the prompt increases the amount of text that needs to be optimised. Furthermore, smaller models have been shown to be more sensitive to prompt design. To address these challenges, we propose an evolutionary search approach to automated discrete prompt optimisation consisting of two phases. In the first phase, grammar-guided genetic programming is invoked to synthesise prompt-creating programmes by searching the space of programmes populated by function compositions of syntactic, dictionary-based and LLM-based prompt-editing functions. In the second phase, local search is applied to explore the neighbourhoods of best-performing programmes in an attempt to further fine-tune their performance. Our approach outperforms three state-of-the-art prompt optimisation approaches, PromptWizard, OPRO, and RL-Prompt, on three relatively small general-purpose LLMs in four domain-specific challenging tasks. We also illustrate several examples where these benchmark methods suffer relatively severe performance degradation, while our approach improves performance in almost all task-model combinations, only incurring minimal degradation when it does not.
提示工程已被证明是发挥预训练大型语言模型(LLM)在解决各种现实世界任务中的关键作用的关键步骤。已经提出了许多解决方案,这些方案试图使用模型本身来编辑提示,从而实现提示工程的自动化。然而,大多数最先进的评估方法都是在需要很少提示模板的任务以及对非常大且功能强大的LLM上进行的。相比之下,需要详细信息的复杂任务增加了需要优化的文本量。此外,较小的模型已被证明对提示设计更为敏感。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种两阶段的进化搜索自动化离散提示优化方法。在第一阶段,通过语法引导遗传编程,通过搜索由基于语法的函数组合、基于字典和基于LLM的提示编辑函数组成的程序空间来合成创建提示的程序。在第二阶段,对表现最佳的程序的邻近区域进行局部搜索,以进一步微调其性能。我们的方法在三个相对较小的通用LLM上,在四个特定领域的挑战任务中,超越了三种先进的提示优化方法:PromptWizard、OPRO和RL-Prompt。我们还举了几个例子来说明这些基准方法在相对较大的性能下降中遭受的损失,而我们的方法在几乎所有的任务模型组合中都提高了性能,只在极少数情况下会出现轻微的性能下降。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for Publication at ECAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于进化搜索的自动化离散提示优化方法,用于解决大型预训练语言模型(LLMs)在实际任务中的提示工程问题。该方法分为两个阶段,第一阶段使用语法引导的遗传编程来合成提示创建程序,第二阶段对表现最佳的程序进行局部搜索以进一步优化性能。在四个特定领域的挑战任务中,该方法优于三种先进的提示优化方法,并在大多数任务模型组合中提高了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提示工程是预训练大型语言模型(LLMs)解决各种实际任务的关键步骤。
- 自动化提示优化方法旨在使用模型本身编辑提示,但现有方法主要在任务需要少量提示模板和高度功能强大的LLMs上进行了评估。
- 对于需要详细信息的复杂任务,提示设计更加重要,且小型模型对提示设计更为敏感。
- 本文提出了一种基于进化搜索的自动化离散提示优化方法,包括语法引导的遗传编程和局部搜索两个阶段。
- 该方法在四个特定领域的挑战任务中,相比三种先进的提示优化方法表现出更好的性能。
- 在大多数任务模型组合中,该方法提高了性能,仅在少数情况下出现轻微的性能下降。
点此查看论文截图


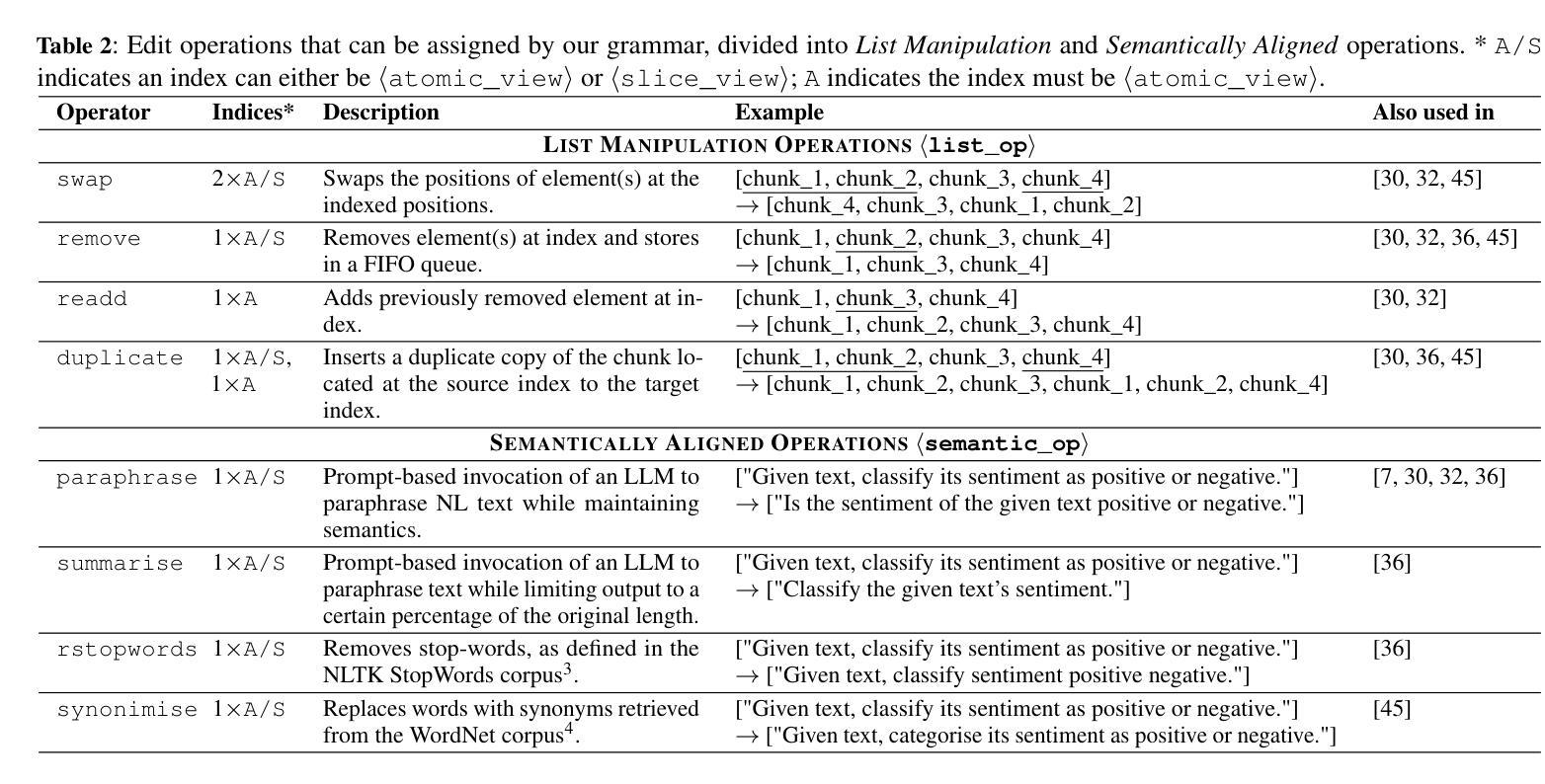
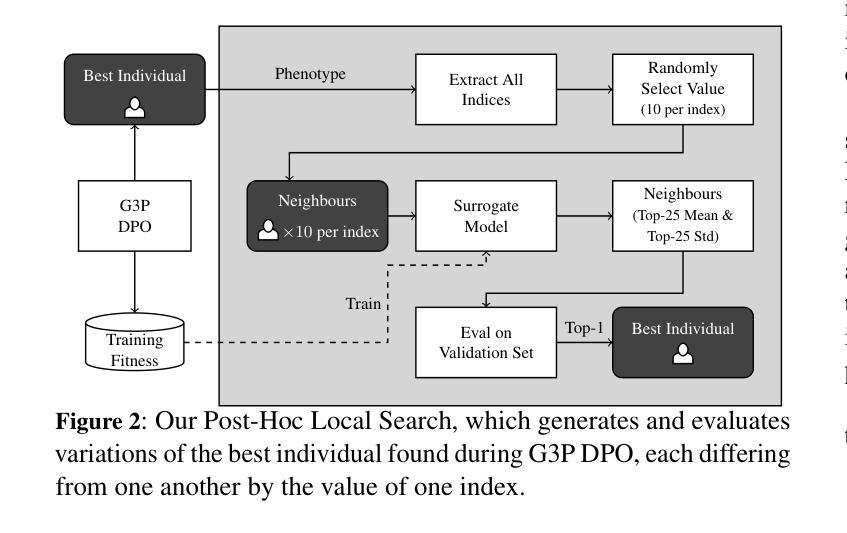
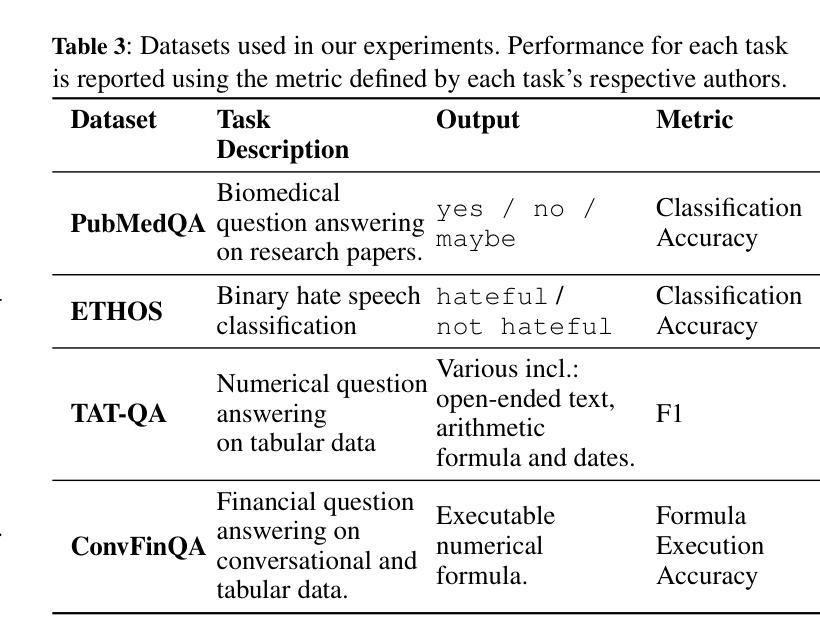
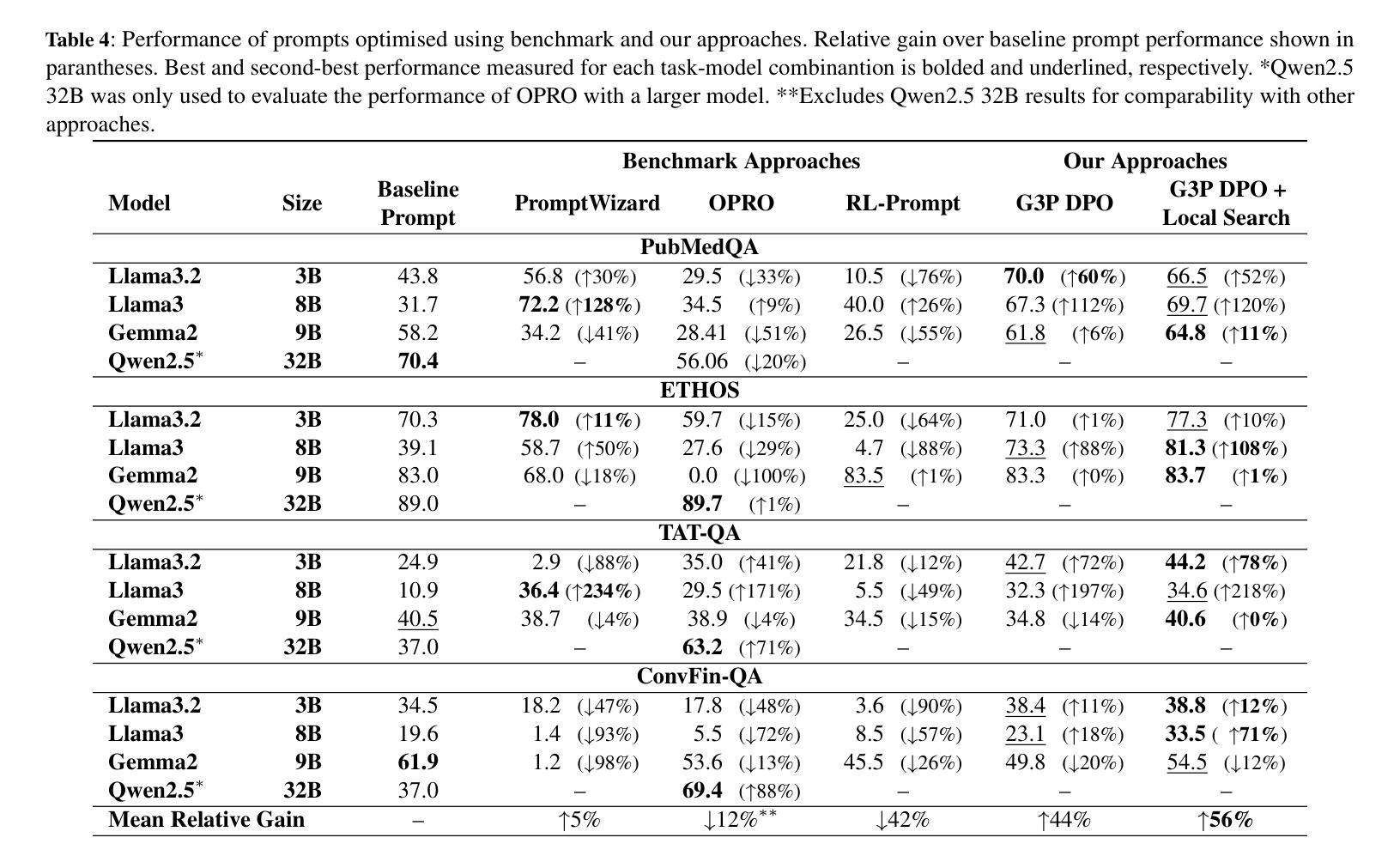
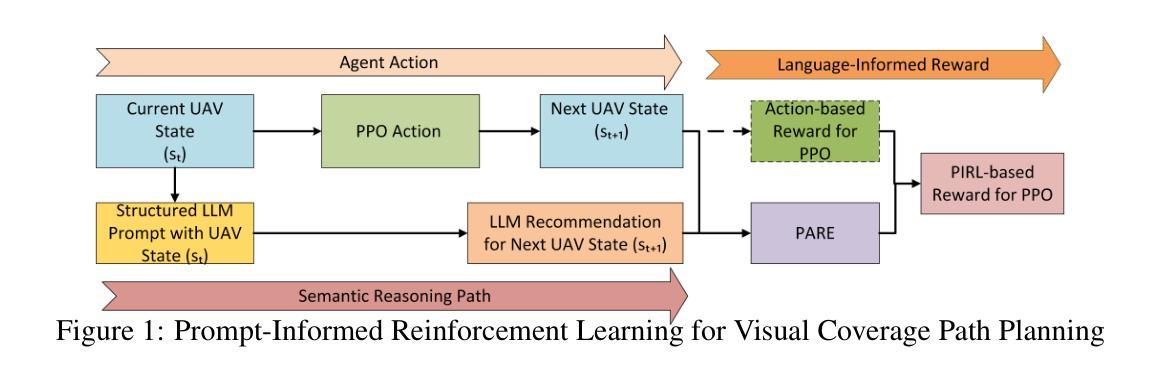
Prompt Informed Reinforcement Learning for Visual Coverage Path Planning
Authors:Venkat Margapuri
Visual coverage path planning with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) requires agents to strategically coordinate UAV motion and camera control to maximize coverage, minimize redundancy, and maintain battery efficiency. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) methods rely on environment-specific reward formulations that lack semantic adaptability. This study proposes Prompt-Informed Reinforcement Learning (PIRL), a novel approach that integrates the zero-shot reasoning ability and in-context learning capability of large language models with curiosity-driven RL. PIRL leverages semantic feedback from an LLM, GPT-3.5, to dynamically shape the reward function of the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) RL policy guiding the agent in position and camera adjustments for optimal visual coverage. The PIRL agent is trained using OpenAI Gym and evaluated in various environments. Furthermore, the sim-to-real-like ability and zero-shot generalization of the agent are tested by operating the agent in Webots simulator which introduces realistic physical dynamics. Results show that PIRL outperforms multiple learning-based baselines such as PPO with static rewards, PPO with exploratory weight initialization, imitation learning, and an LLM-only controller. Across different environments, PIRL outperforms the best-performing baseline by achieving up to 14% higher visual coverage in OpenAI Gym and 27% higher in Webots, up to 25% higher battery efficiency, and up to 18% lower redundancy, depending on the environment. The results highlight the effectiveness of LLM-guided reward shaping in complex spatial exploration tasks and suggest a promising direction for integrating natural language priors into RL for robotics.
无人机(UAV)的视觉覆盖路径规划要求代理战略性地协调无人机的运动和相机控制,以最大化覆盖,最小化冗余并维持电池效率。传统的强化学习(RL)方法依赖于特定环境的奖励公式,缺乏语义适应性。本研究提出了提示强化学习(PIRL),这是一种将大型语言模型的零镜头推理能力和上下文学习能力与基于好奇心的RL相结合的新方法。PIRL利用来自大型语言模型GPT-3..的语义反馈,动态地形成近端策略优化(PPO)RL策略的奖励功能,以指导代理进行位置和相机调整以实现最佳视觉覆盖。PIRL代理使用OpenAI Gym进行训练,并在各种环境中进行评估。此外,通过Webots模拟器操作代理测试了其仿真到现实的能力和零镜头泛化能力,该模拟器引入了逼真的物理动态。结果表明,PIRL在多个学习基准测试中表现优于基于静态奖励的PPO、具有探索权重初始化的PPO、模仿学习和仅使用大型语言模型的控制器。在不同的环境中,PIRL在OpenAI Gym上实现了高达14%的视觉覆盖和Webots上的高达27%的视觉覆盖超越表现最佳的基准测试,电池效率提高了高达25%,冗余度降低了高达18%,这取决于环境。结果突出了大型语言模型引导奖励形状在复杂的空间探索任务中的有效性,并为将自然语言先验知识融入机器人强化学习提出了一个有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
无人机视觉覆盖路径规划需要智能体协调无人机运动和相机控制,以最大化覆盖面积、最小化冗余并维持电池效率。本研究提出一种结合大型语言模型的零次推理能力和上下文学习能力的Prompt-Informed强化学习(PIRL),与好奇心驱动的强化学习相结合。PIRL利用GPT-3.5的语言模型语义反馈来动态塑造奖励函数,指导无人机位置和相机调整,以达到最佳视觉覆盖效果。PIRL智能体在OpenAI Gym和Webots模拟器中进行训练和评估,展现出强大的性能。结果表明,PIRL在多种环境中优于其他学习基线方法,如静态奖励的PPO等。在OpenAI Gym中,PIRL的覆盖面积比最佳基线高出高达14%,在Webots中高出27%,电池效率提高高达25%,且冗余度降低高达18%。这突显了大型语言模型引导奖励塑造在复杂空间探索任务中的有效性,并为整合自然语言先验信息进入机器人强化学习指明了方向。
关键见解
- UAV视觉覆盖路径规划需要协调无人机运动和相机控制,以提高覆盖效率。
- PIRL方法结合了大型语言模型的零次推理能力和上下文学习能力。
- GPT-3.5语义反馈用于动态塑造奖励函数,指导无人机位置和相机调整。
- PIRL智能体在OpenAI Gym和Webots模拟器中展现出优越性能。
- 在多种环境中,PIRL显著优于其他学习基线方法。
- 结果突显了大型语言模型在复杂空间探索任务中的有效性,特别是在奖励塑造方面的作用。
点此查看论文截图

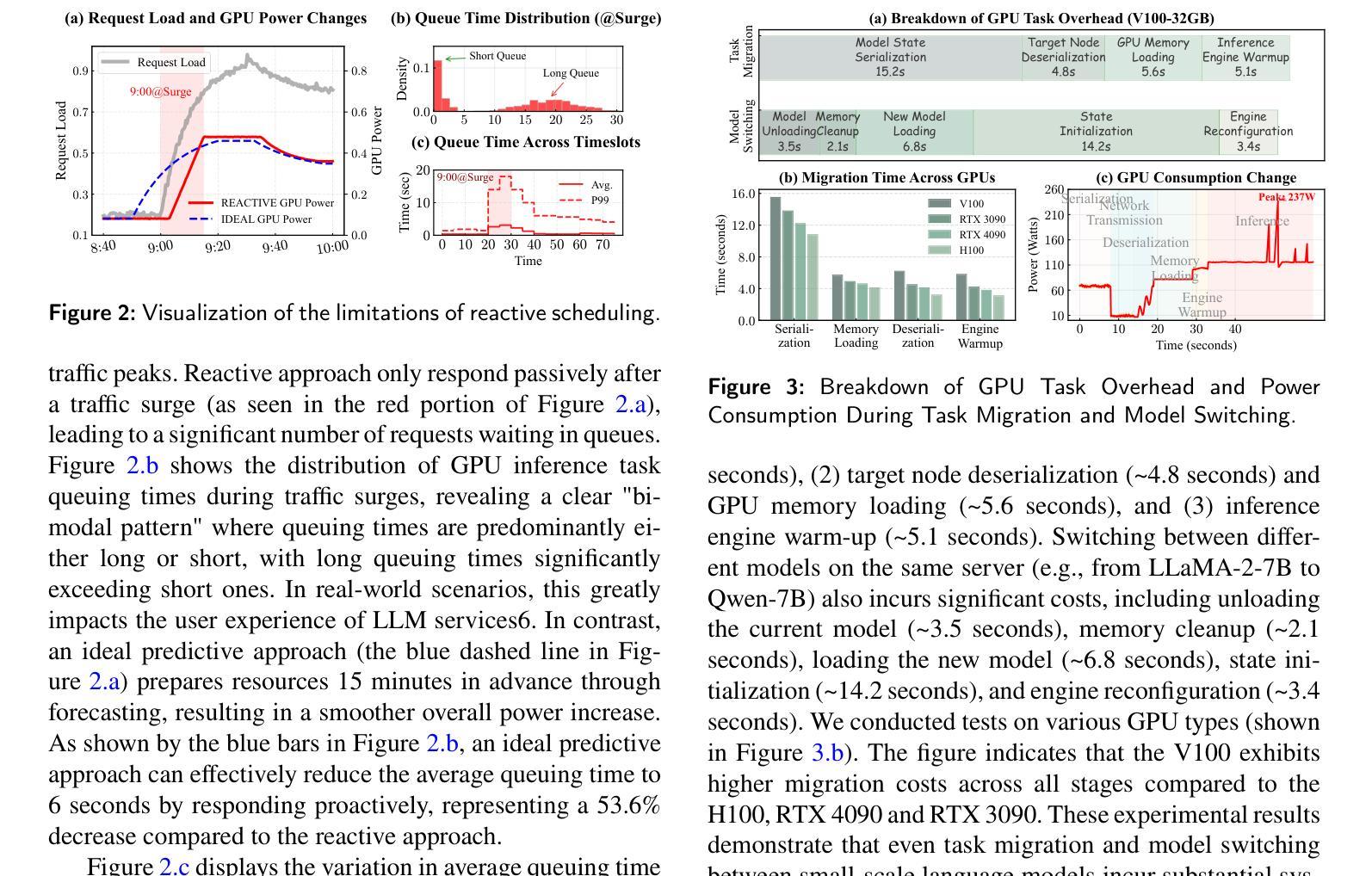
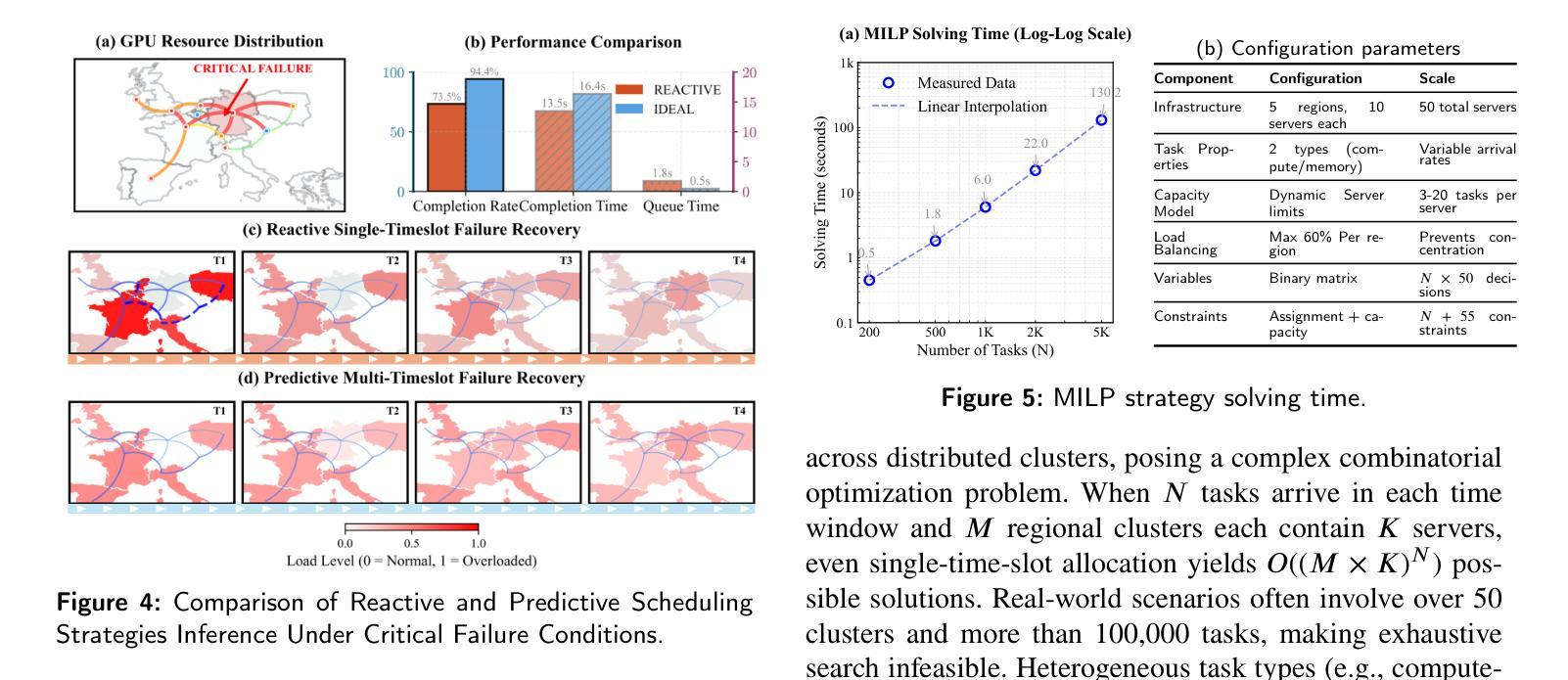
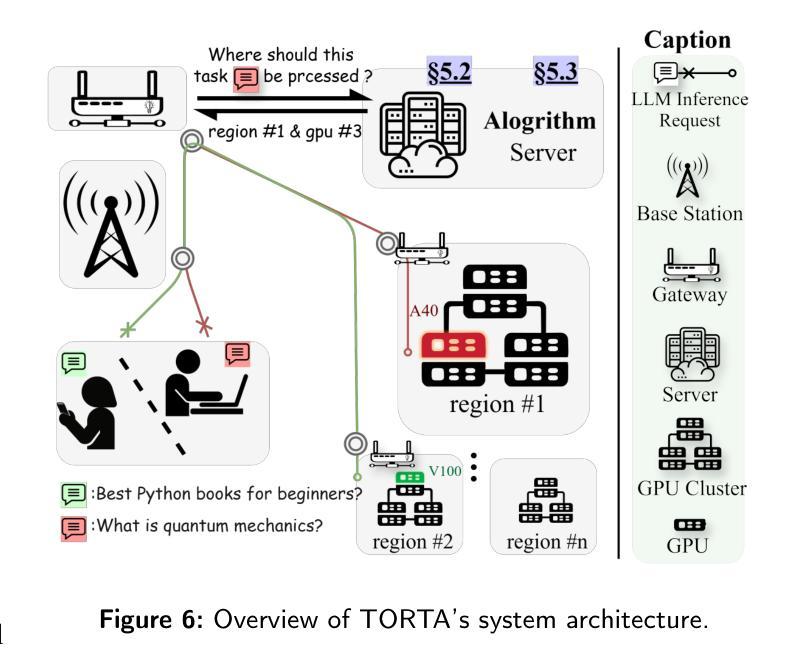
Cross-Timeslot Optimization for Distributed GPU Inference Using Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Chengze Du, Zhiwei Yu, Heng Xu, Haojie Wang, Bo liu, Jialong Li
The rapid growth of large language model (LLM) services imposes increasing demands on distributed GPU inference infrastructure. Most existing scheduling systems rely on the current system state to make decisions, without considering how task demand and resource availability evolve over time. This lack of temporal awareness leads to inefficient GPU utilization, high task migration overhead, and poor system responsiveness under dynamic workloads. In this work, we identify the fundamental limitations of these instantaneous-state-only scheduling approaches and propose Temporal Optimal Resource scheduling via Two-layer Architecture (TORTA). TORTA introduces a spatiotemporal scheduling framework that captures both long-term workload patterns and short-term execution constraints. It adopts a two-layer design: a macro-level scheduler leverages reinforcement learning and optimal transport to coordinate inter-region task distribution, while a micro-level allocator refines task-to-server assignments within each region to reduce latency and switching costs. Experimental results across multiple network topologies show that TORTA reduces average inference response time by up to 15%, improves load balance by approximately 4-5%, and cuts total operational cost by 10-20% compared to state-of-the-art baseline methods.
大规模语言模型(LLM)服务的快速增长对分布式GPU推理基础设施提出了更高的要求。大多数现有的调度系统仅依赖于当前系统状态来做出决策,而没有考虑到任务需求和资源可用性的时间演变。这种缺乏时间意识的调度方法导致了GPU利用率低下、任务迁移开销高以及在动态工作负载下系统响应性差的问题。在这项工作中,我们确定了这些仅基于瞬时状态的调度方法的根本局限性,并提出了通过两层架构进行时间最优资源调度(TORTA)。TORTA引入了一个时空调度框架,该框架能够捕捉长期工作负载模式和短期执行约束。它采用了两层设计:宏观调度器利用强化学习和最优传输来协调区域间的任务分布,而微观分配器则在每个区域内对任务到服务器的分配进行微调,以减少延迟和切换成本。跨多种网络拓扑的实验结果表明,与最先进的基准方法相比,TORTA将平均推理响应时间减少了高达15%,负载平衡提高了约4-5%,总运营成本降低了10-20%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 12 figures
Summary
基于自然语言模型(LLM)服务的快速增长对分布式GPU推理基础设施提出了更高要求。现有的调度系统缺乏时间意识,导致GPU利用率低下、任务迁移开销高以及在动态工作负载下的系统响应性差。本研究提出一种时空最优资源调度两层架构(TORTA),该架构结合了长期工作负载模式和短期执行约束。宏观调度器利用强化学习和最优传输来协调区域间的任务分配,而微观分配器则细化区域内任务到服务器的分配以减少延迟和切换成本。实验结果表明,与最新基线方法相比,TORTA平均推理响应时间减少15%,负载平衡提高约4-5%,总运营成本降低10-20%。
Key Takeaways
- LLM服务的增长对分布式GPU推理基础设施提出了更高的要求。
- 现有调度系统缺乏时间意识,导致GPU利用率低下。
- TORTA架构提出一种结合长期工作负载模式和短期执行约束的时空最优资源调度方法。
- TORTA采用两层设计,宏观调度器和微观分配器分别负责协调任务分配和细化任务到服务器的分配。
- 实验结果表明,TORTA相比现有方法能提高负载平衡、降低响应时间和运营成本。
- TORTA的宏观调度器利用强化学习和最优传输来进行区域间的任务协调。
点此查看论文截图

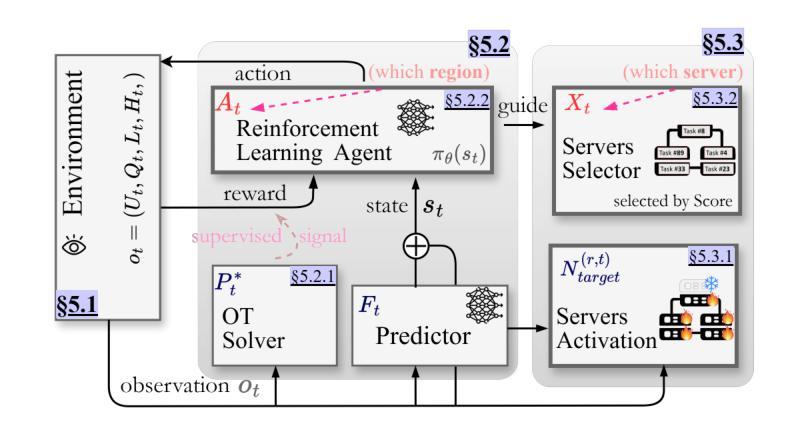
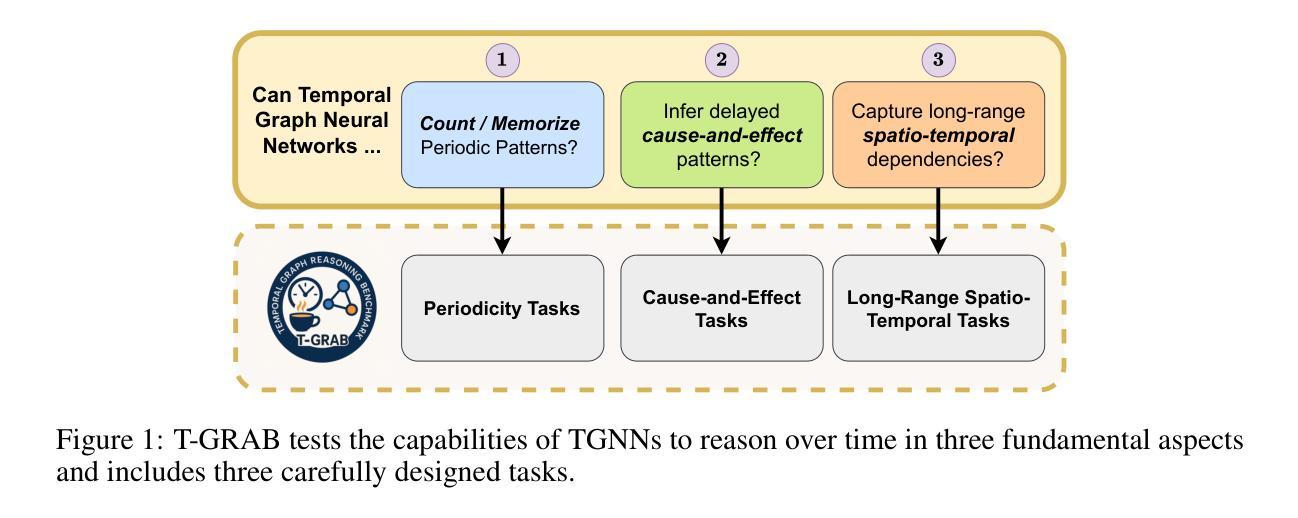
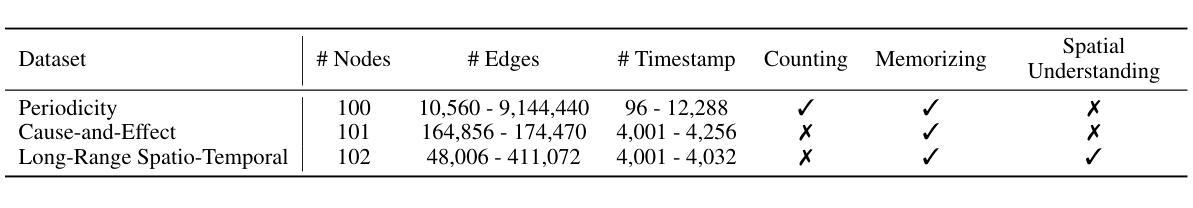
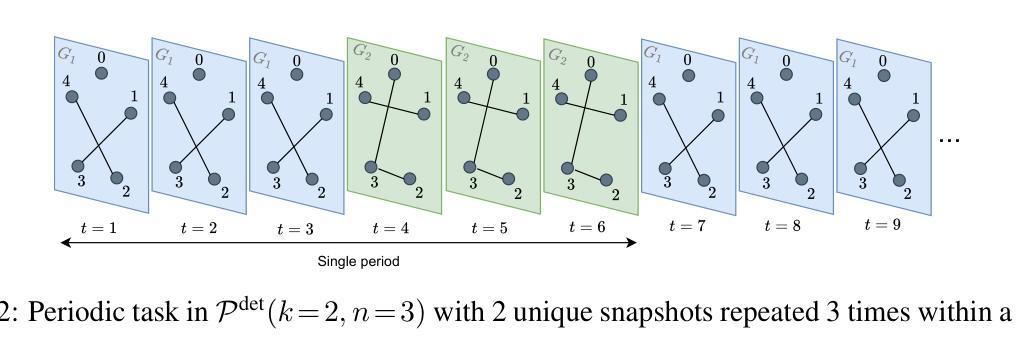
T-GRAB: A Synthetic Diagnostic Benchmark for Learning on Temporal Graphs
Authors:Alireza Dizaji, Benedict Aaron Tjandra, Mehrab Hamidi, Shenyang Huang, Guillaume Rabusseau
Dynamic graph learning methods have recently emerged as powerful tools for modelling relational data evolving through time. However, despite extensive benchmarking efforts, it remains unclear whether current Temporal Graph Neural Networks (TGNNs) effectively capture core temporal patterns such as periodicity, cause-and-effect, and long-range dependencies. In this work, we introduce the Temporal Graph Reasoning Benchmark (T-GRAB), a comprehensive set of synthetic tasks designed to systematically probe the capabilities of TGNNs to reason across time. T-GRAB provides controlled, interpretable tasks that isolate key temporal skills: counting/memorizing periodic repetitions, inferring delayed causal effects, and capturing long-range dependencies over both spatial and temporal dimensions. We evaluate 11 temporal graph learning methods on these tasks, revealing fundamental shortcomings in their ability to generalize temporal patterns. Our findings offer actionable insights into the limitations of current models, highlight challenges hidden by traditional real-world benchmarks, and motivate the development of architectures with stronger temporal reasoning abilities. The code for T-GRAB can be found at: https://github.com/alirezadizaji/T-GRAB.
动态图学习方法最近涌现为建模随时间变化的关系数据的强大工具。然而,尽管进行了大量的基准测试,但目前仍不清楚当前的时序图神经网络(TGNNs)是否能有效地捕捉周期性、因果关系和长期依赖等核心时间模式。在这项工作中,我们引入了时序图推理基准测试(T-GRAB),这是一组综合的合成任务,旨在系统地检测TGNNs的跨时间推理能力。T-GRAB提供可控、可解释的任务,孤立出关键的时间技能:计算/记忆周期性的重复、推断延迟的因果关系、捕捉时空的长期依赖。我们在这些任务上评估了11种时序图学习方法,揭示了它们在推广时间模式方面的基本缺陷。我们的研究为当前模型的局限性提供了可行的见解,突出了传统现实世界基准测试所隐藏的挑战,并推动了具有更强时间推理能力的架构的发展。T-GRAB的代码可以在以下网址找到:https://github.com/alirezadizaji/T-GRAB。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MLoG-GenAI Workshop @ KDD 2025 (Oral)
Summary
动态图学习方法已成为建模随时间变化的关系数据的强大工具。然而,尽管进行了大量的基准测试,但目前仍不清楚当前的时序图神经网络(TGNNs)是否能有效地捕捉周期性、因果性和长范围依赖等核心时间模式。在这项工作中,我们引入了时序图推理基准测试(T-GRAB),这是一组综合的合成任务,旨在系统地检测TGNNs的时间推理能力。T-GRAB提供可控、可解释的任务,隔离关键的时间技能,包括计数/记忆周期性重复、推断延迟的因果关系和捕捉空间和时间维度上的长期依赖关系。我们对11种时序图学习方法进行了这些任务的评估,发现它们在推广时间模式方面的基本缺陷。我们的研究为当前模型的局限性提供了可操作的见解,突出了传统现实世界基准测试所隐藏的挑战,并推动了具有更强时间推理能力的架构的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 动态图学习方法用于建模随时间变化的关系数据。
- 时序图神经网络(TGNNs)在捕捉核心时间模式方面仍存在不明确性。
- 引入时序图推理基准测试(T-GRAB),以评估TGNNs的时间推理能力。
- T-GRAB包括可控、可解释的任务,专注于隔离关键的时间技能。
- 通过T-GRAB对11种时序图学习方法进行评估,发现其在推广时间模式方面的不足。
- 当前模型的局限性需要改进,以更好地捕捉时间模式。
点此查看论文截图

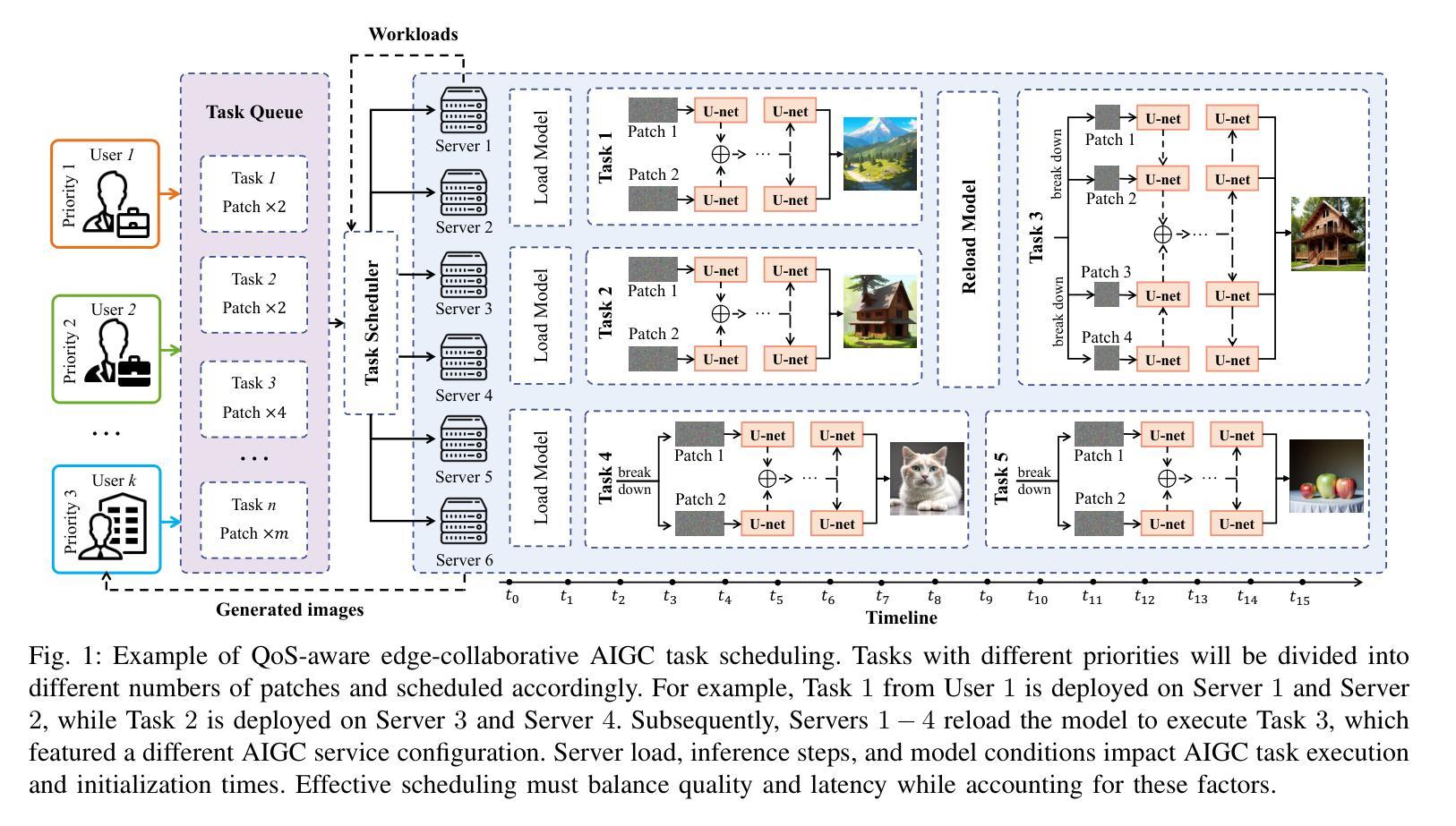
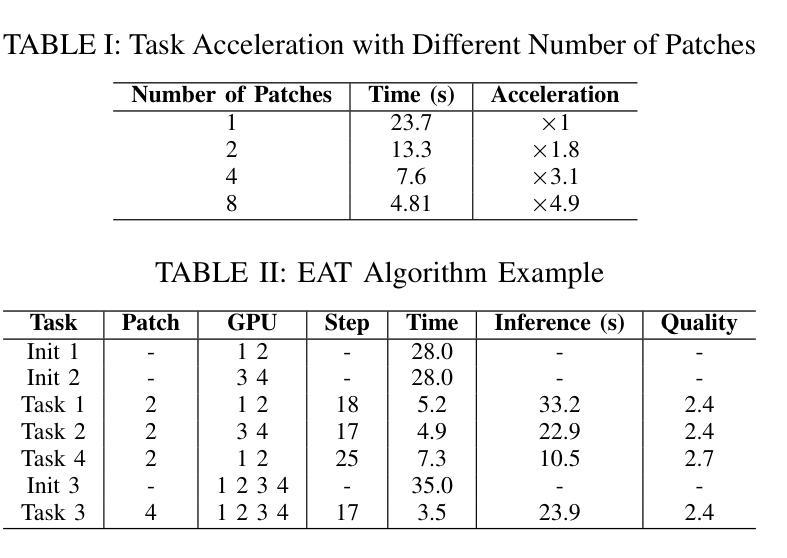
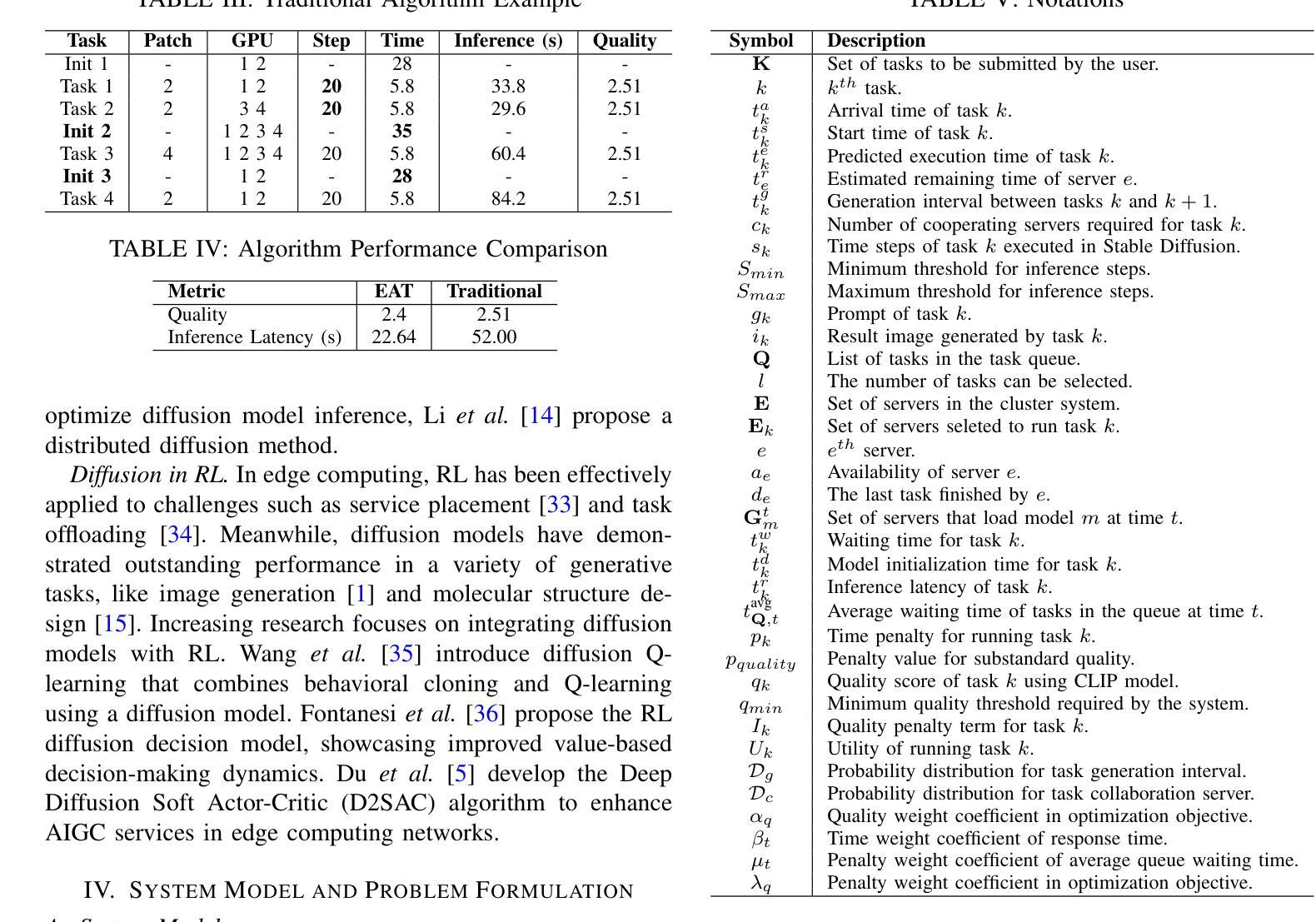
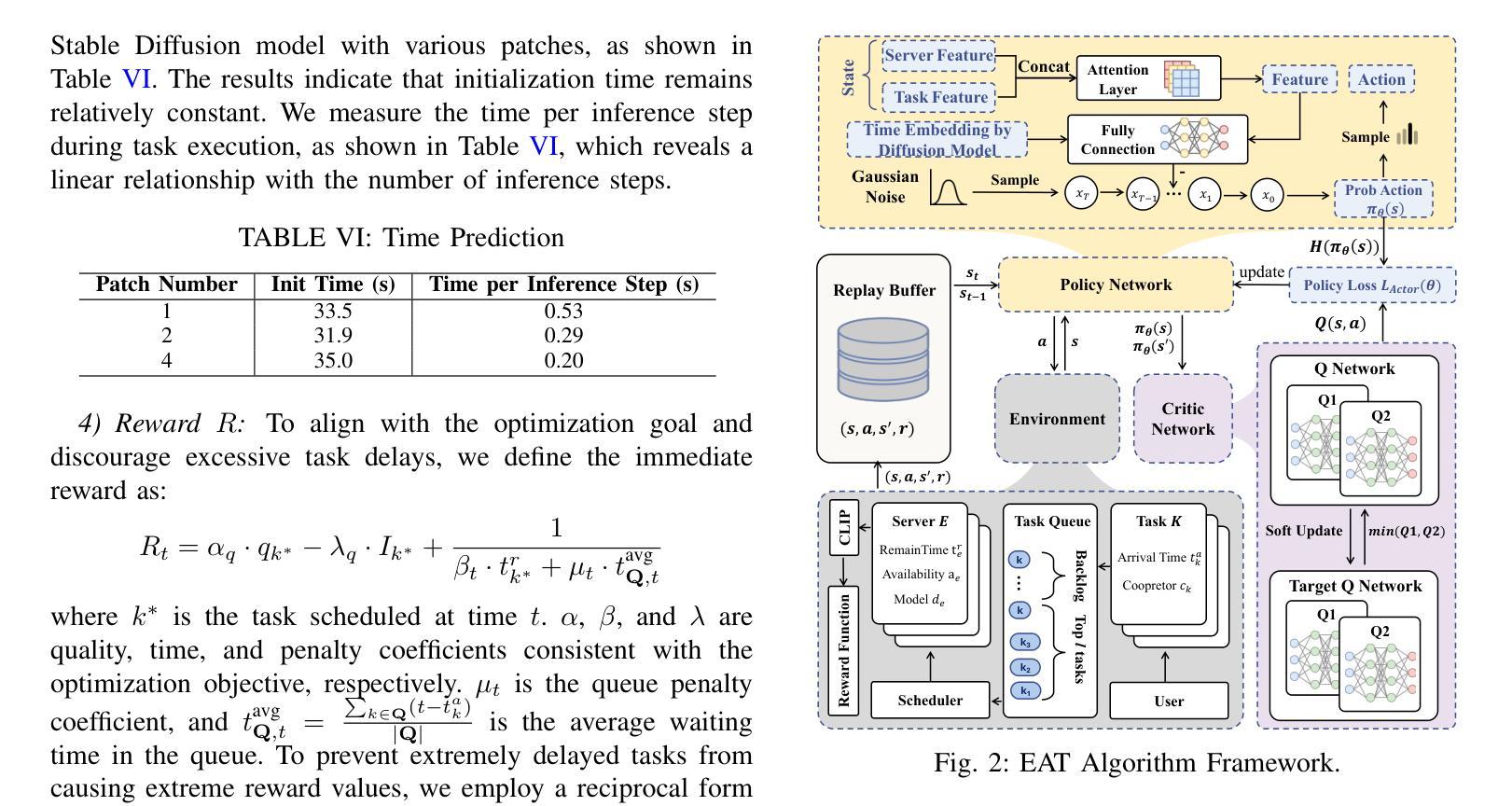
EAT: QoS-Aware Edge-Collaborative AIGC Task Scheduling via Attention-Guided Diffusion Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhifei Xu, Zhiqing Tang, Jiong Lou, Zhi Yao, Xuan Xie, Tian Wang, Yinglong Wang, Weijia Jia
The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and large language models has enabled the use of Generative AI (GenAI) in cloud data centers for diverse AI-Generated Content (AIGC) tasks. Models like Stable Diffusion introduce unavoidable delays and substantial resource overhead, which are unsuitable for users at the network edge with high QoS demands. Deploying AIGC services on edge servers reduces transmission times but often leads to underutilized resources and fails to optimally balance inference latency and quality. To address these issues, this paper introduces a QoS-aware \underline{E}dge-collaborative \underline{A}IGC \underline{T}ask scheduling (EAT) algorithm. Specifically: 1) We segment AIGC tasks and schedule patches to various edge servers, formulating it as a gang scheduling problem that balances inference latency and quality while considering server heterogeneity, such as differing model distributions and cold start issues. 2) We propose a reinforcement learning-based EAT algorithm that uses an attention layer to extract load and task queue information from edge servers and employs a diffusion-based policy network for scheduling, efficiently enabling model reuse. 3) We develop an AIGC task scheduling system that uses our EAT algorithm to divide tasks and distribute them across multiple edge servers for processing. Experimental results based on our system and large-scale simulations show that our EAT algorithm can reduce inference latency by up to 56% compared to baselines. We release our open-source code at https://github.com/zzf1955/EAT.
随着人工智能(AI)和大型语言模型的增长,生成式AI(GenAI)在云数据中心被广泛应用于各种AI生成内容(AIGC)任务。像Stable Diffusion这样的模型会带来不可避免的延迟和大量资源开销,对于网络边缘有高质量服务(QoS)需求的用户来说并不适合。在边缘服务器部署AIGC服务虽然可以减少传输时间,但往往导致资源利用不足,无法很好地平衡推理延迟和质量。为了解决这些问题,本文介绍了一种基于QoS 的边缘协同 AIGC 任务调度(EAT)算法。具体来说:1)我们对AIGC任务进行分段,并将补丁调度到不同的边缘服务器,将其制定为一个集群调度问题,在平衡推理延迟和质量的同时考虑服务器异构性,如不同的模型分布和冷启动问题。2)我们提出了一种基于强化学习的EAT算法,该算法使用注意力层从边缘服务器提取负载和任务队列信息,并采用基于扩散的策略网络进行调度,从而有效地实现模型重用。3)我们开发了一个AIGC任务调度系统,该系统使用我们的EAT算法来分割任务并将它们分布在多个边缘服务器上进行处理。基于我们的系统和大规模模拟的实验结果表明,与基线相比,我们的EAT算法可以将推理延迟减少高达56%。我们在https://github.com/zzf1955/EAT上发布了我们的开源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人工智能(AI)的发展以及大型语言模型的应用,生成式人工智能(GenAI)在云数据中心被广泛应用于各种AI生成内容(AIGC)任务。然而,模型如Stable Diffusion带来的延迟和资源消耗问题对于网络边缘的高QoS 需求用户来说是不可接受的。边缘服务器部署AIGC服务虽然减少了传输时间,但往往导致资源利用率不足,无法很好地平衡推理延迟和质量。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种面向QoS 的边缘协同 AIGC 任务调度(EAT)算法。通过分割AIGC任务并调度到不同的边缘服务器,平衡推理延迟和质量,同时考虑服务器差异性。算法采用基于强化学习的EAT算法,使用注意力层提取边缘服务器的负载和任务队列信息,并采用扩散策略进行任务调度,实现模型复用。实验结果表明,与基线相比,EAT算法可降低推理延迟达56%。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能(GenAI)在云数据中心广泛应用于多种任务。
- 现有模型如Stable Diffusion在网络边缘带来延迟和资源消耗问题。
- 边缘服务器部署AIGC服务虽减少传输时间但资源利用率不足。
- 引入了一种面向QoS 的边缘协同 AIGC 任务调度(EAT)算法来解决上述问题。
- EAT算法通过分割任务并调度到不同边缘服务器来平衡推理延迟和质量,考虑服务器差异性。
- EAT算法采用强化学习和注意力机制进行任务调度,实现模型复用。
点此查看论文截图

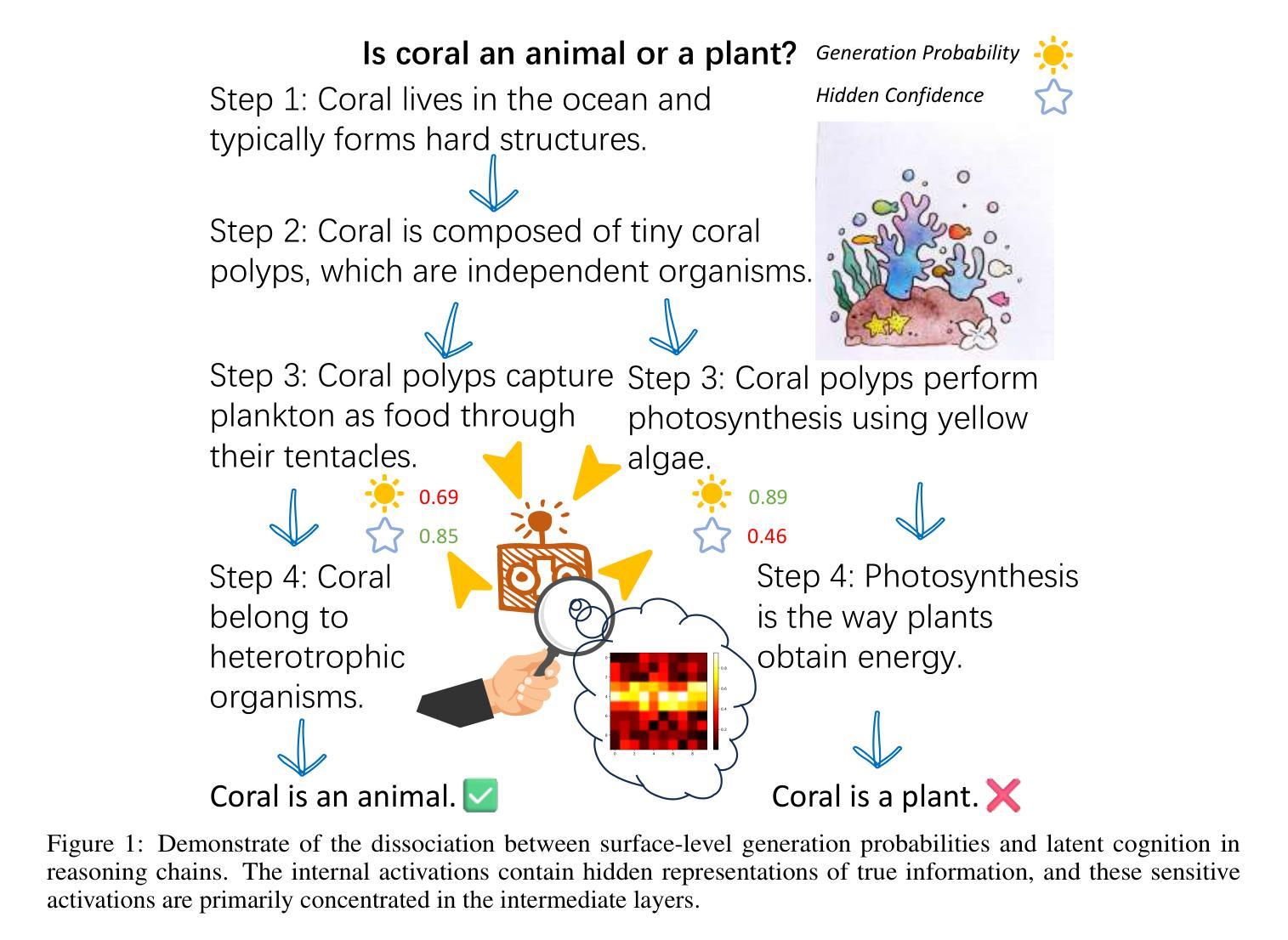
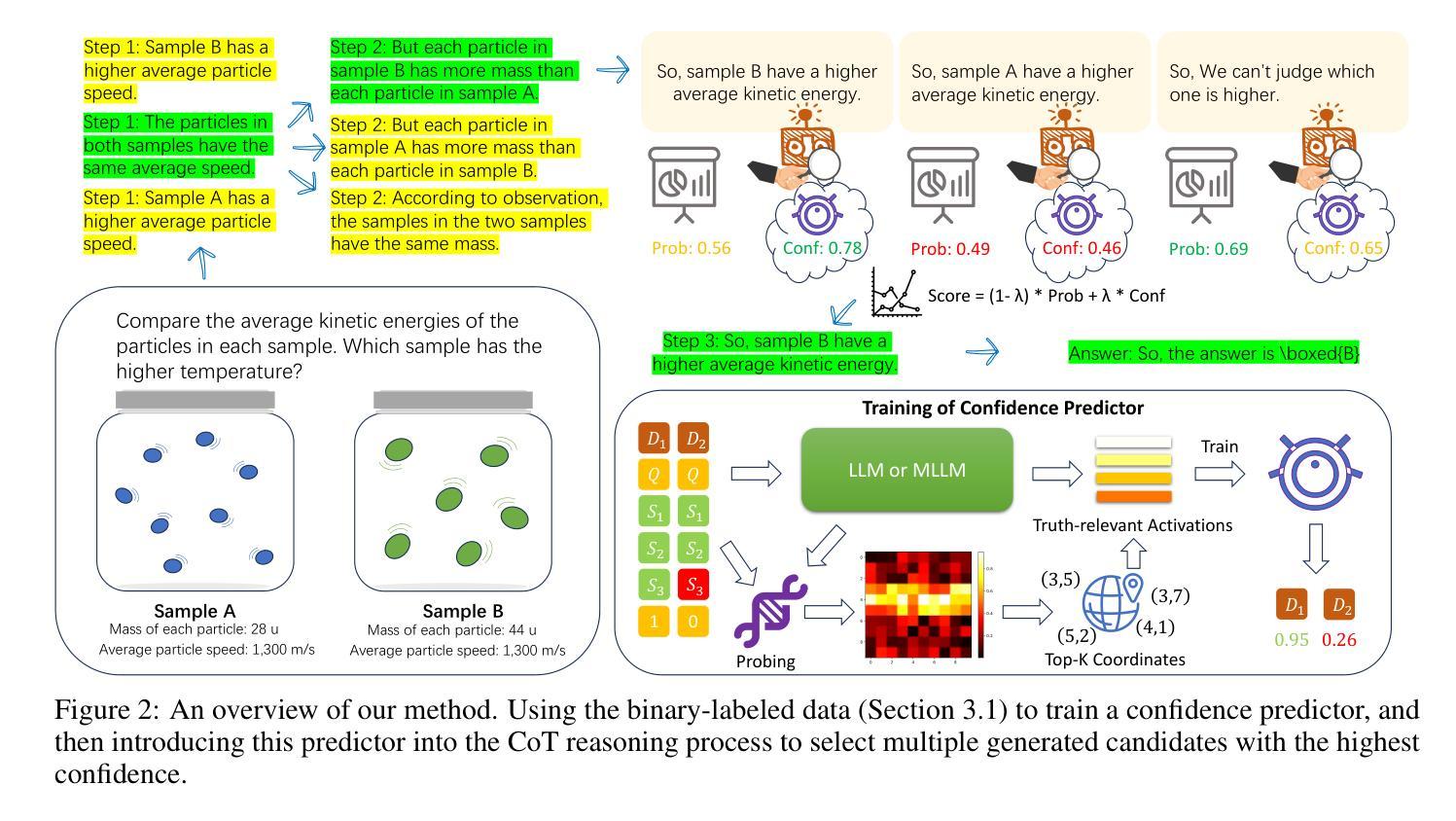
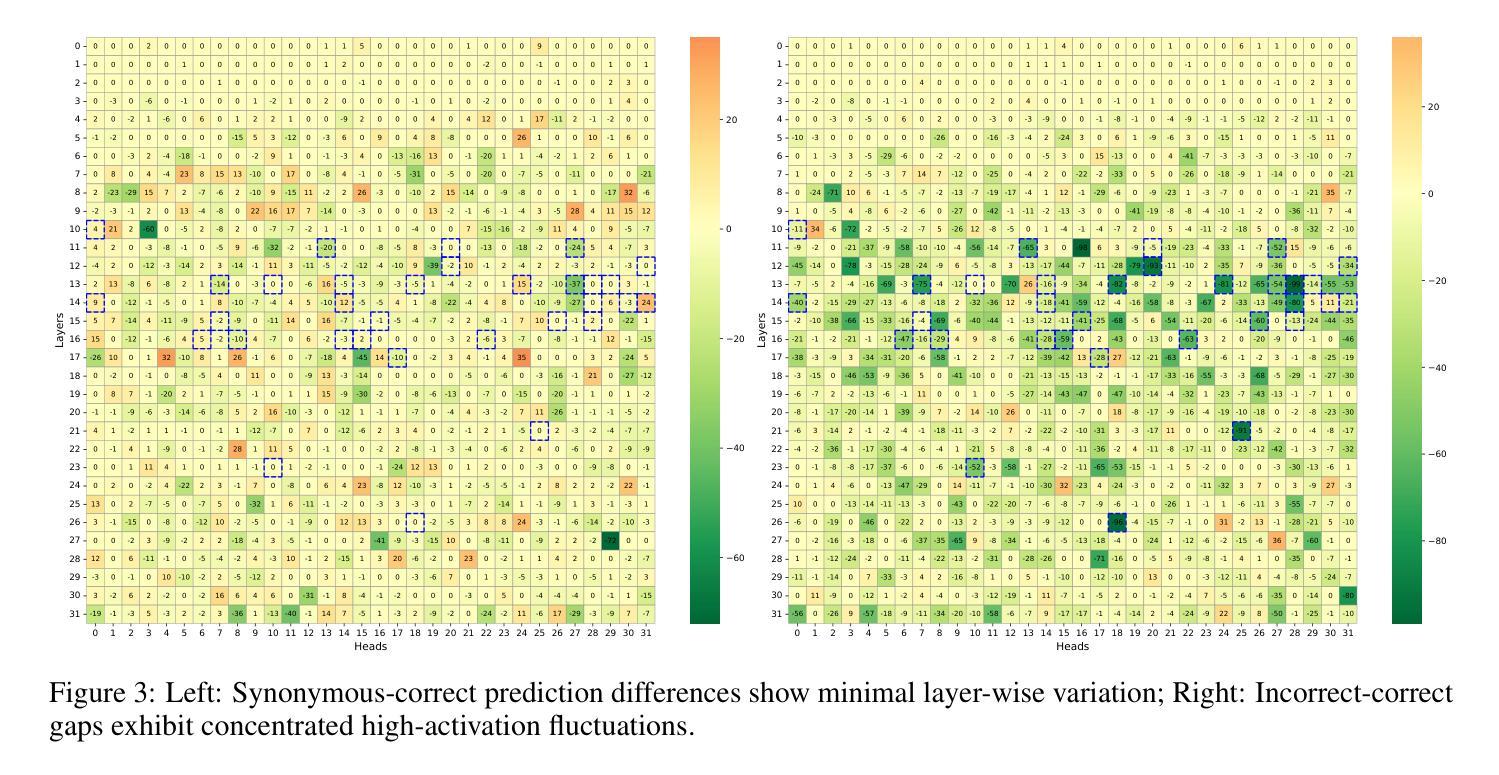
Deep Hidden Cognition Facilitates Reliable Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Zijun Chen, Wenbo Hu, Richang Hong
Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning has demonstrated remarkable deep reasoning capabilities in both large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, its reliability is often undermined by the accumulation of errors in intermediate steps. This paper introduces an novel approach to calibrate the CoT reasoning accuracy by leveraging the model’s intrinsic veracity encoding. We discover that specific attention head activations reliably reflect the truthfulness of reasoning steps in CoT. Based on this insight, we train a confidence predictor to evaluate the correctness of each reasoning step using these truthfulness-sensitive activations, dynamically selecting the most plausible reasoning path via beam search. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines (e.g., Few-Shot CoT, Self-Consistency, and Self-Evaluation Guided Beam Search) across the mathematical, symbolic, and commonsense reasoning tasks, exhibiting superior accuracy and reliability in both unimodal and multimodal settings. We further validate the approach on large reasoning models, confirming its applicability to specialized reasoning models. Additionally, we explore the role of the model’s self-correction ability in CoT reasoning. This work provides a novel reliability improvement path for CoT reasoning with broad application potential.
“链式思维(Chain of Thought,简称CoT)推理在大规模语言模型(LLM)和多模态大规模语言模型(MLLM)中都表现出了显著的深度推理能力。然而,其可靠性常常受到中间步骤中累积错误的影响。本文介绍了一种利用模型内在真实性编码来校准CoT推理精度的新方法。我们发现特定的注意力头激活能够可靠地反映CoT中推理步骤的真实性。基于这一发现,我们训练了一个置信度预测器,利用这些真实性敏感的激活来评估每个推理步骤的正确性,并通过集束搜索动态选择最合理的推理路径。实验结果表明,我们的方法显著优于最新的基线方法(如少样本CoT、自我一致性、自我评估引导集束搜索等),在数学、符号和常识推理任务中表现出更高的准确性和可靠性,在单模态和多模态环境中都是如此。我们在大型推理模型上进一步验证了该方法,证实了它在专用推理模型中的适用性。此外,我们还探索了模型中自我纠正能力在CoT推理中的作用。这项工作为CoT推理提供了一种新的可靠性提升路径,具有广泛的应用潜力。”
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用模型内在真实性编码来校准链式思维(Chain of Thought,CoT)推理准确性的新方法。研究发现特定注意力头激活能可靠反映CoT推理步骤的真实性,并基于此训练了信心预测器来评估每个推理步骤的正确性。该方法通过束搜索动态选择最合理的推理路径,在数学、符号和常识推理任务上显著优于现有方法,在单模态和多模态设置中都表现出较高的准确性和可靠性。同时,本文还探索了模型在CoT推理中的自我校正能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种利用模型内在真实性编码来校准CoT推理的新方法。
- 特定注意力头激活能可靠反映CoT推理步骤的真实性。
- 训练了信心预测器评估每个推理步骤的正确性。
- 通过束搜索动态选择最合理的推理路径。
- 在数学、符号和常识推理任务上显著优于现有方法。
- 在单模态和多模态设置中都表现出较高的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图