⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
Clustering-Guided Multi-Layer Contrastive Representation Learning for Citrus Disease Classification
Authors:Jun Chen, Yonghua Yu, Weifu Li, Yaohui Chen, Hong Chen
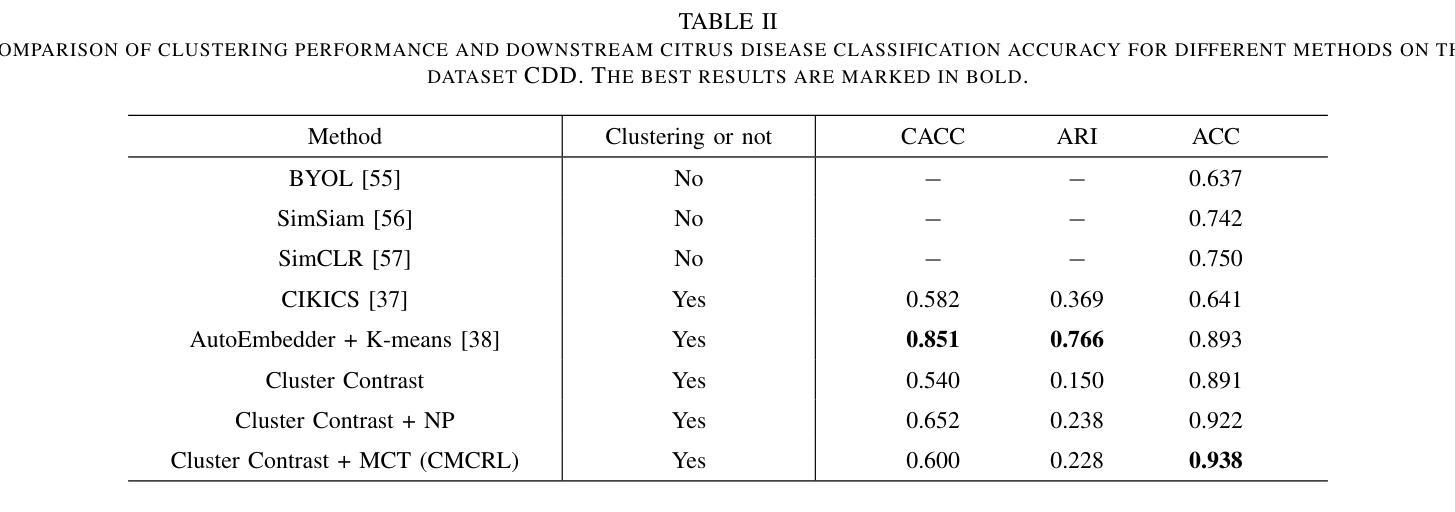
Citrus, as one of the most economically important fruit crops globally, suffers severe yield depressions due to various diseases. Accurate disease detection and classification serve as critical prerequisites for implementing targeted control measures. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly deep learning-based computer vision algorithms, have substantially decreased time and labor requirements while maintaining the accuracy of detection and classification. Nevertheless, these methods predominantly rely on massive, high-quality annotated training examples to attain promising performance. By introducing two key designs: contrasting with cluster centroids and a multi-layer contrastive training (MCT) paradigm, this paper proposes a novel clustering-guided self-supervised multi-layer contrastive representation learning (CMCRL) algorithm. The proposed method demonstrates several advantages over existing counterparts: (1) optimizing with massive unannotated samples; (2) effective adaptation to the symptom similarity across distinct citrus diseases; (3) hierarchical feature representation learning. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the public citrus image set CDD, outperforming existing methods by 4.5%-30.1% accuracy. Remarkably, our method narrows the performance gap with fully supervised counterparts (all samples are labeled). Beyond classification accuracy, our method shows great performance on other evaluation metrics (F1 score, precision, and recall), highlighting the robustness against the class imbalance challenge.
柑橘作为全球经济最重要的果树作物之一,因各种疾病而遭受严重的产量损失。准确的疾病检测和分类是实施有针对性的控制措施的关键前提。最近人工智能的进展,特别是基于深度学习的计算机视觉算法,在保持检测与分类精度的同时,大大降低了时间和劳动力的要求。然而,这些方法主要依赖于大量高质量的有标注训练样本,才能获得有前景的性能。本文通过引入两个关键设计:与聚类中心进行对比和多层对比训练(MCT)范式,提出了一种新颖的聚类引导自监督多层对比表示学习(CMCRL)算法。该方法相对于现有方法具有几个优点:(1)利用大量未标注样本进行优化;(2)有效地适应不同柑橘疾病症状之间的相似性;(3)分层特征表示学习。该方法在公共柑橘图像集CDD上实现了最先进的性能,较现有方法提高了4.5%~30.1%的准确率。值得注意的是,我们的方法与全监督方法(所有样本都已标注)之间的性能差距缩小了。除了分类精度外,我们的方法在其他的评估指标(F1分数、精确度和召回率)上也表现出良好的性能,突显了该方法在应对类别不平衡挑战时的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于聚类引导的自监督多层对比表示学习(CMCRL)算法,该算法通过引入对比聚类中心和多层对比训练(MCT)范式,实现了对柑橘病害的自动检测与分类。该算法能够利用大量未标注样本进行优化,有效适应不同柑橘病害症状间的相似性,并实现了分层特征表示学习。在公共柑橘图像集CDD上,该方法达到了最先进的性能,相比现有方法提高了4.5%~30.1%的准确率,并且在其他评估指标(如F1分数、精确度和召回率)上也表现出色,尤其是在类不平衡挑战中展现了稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 柑橘作为全球经济重要的水果作物之一,遭受各种疾病的严重影响,准确的疾病检测和分类是实施有针对性的控制措施的关键。
- 最近人工智能的进步,尤其是基于深度学习的计算机视觉算法,已经大大减少了检测和时间要求,同时保持了准确性。
- 提出的CMCRL算法通过引入对比聚类中心和多层对比训练范式,实现了优化大量未标注样本、适应不同柑橘病害症状间的相似性以及分层特征表示学习。
- CMCRL算法在公共柑橘图像集CDD上达到了最先进的性能表现。
- 与现有方法相比,CMCRL算法的准确率提高了4.5%~30.1%。
- CMCRL算法在其他评估指标(如F1分数、精确度和召回率)上也表现出稳健性。
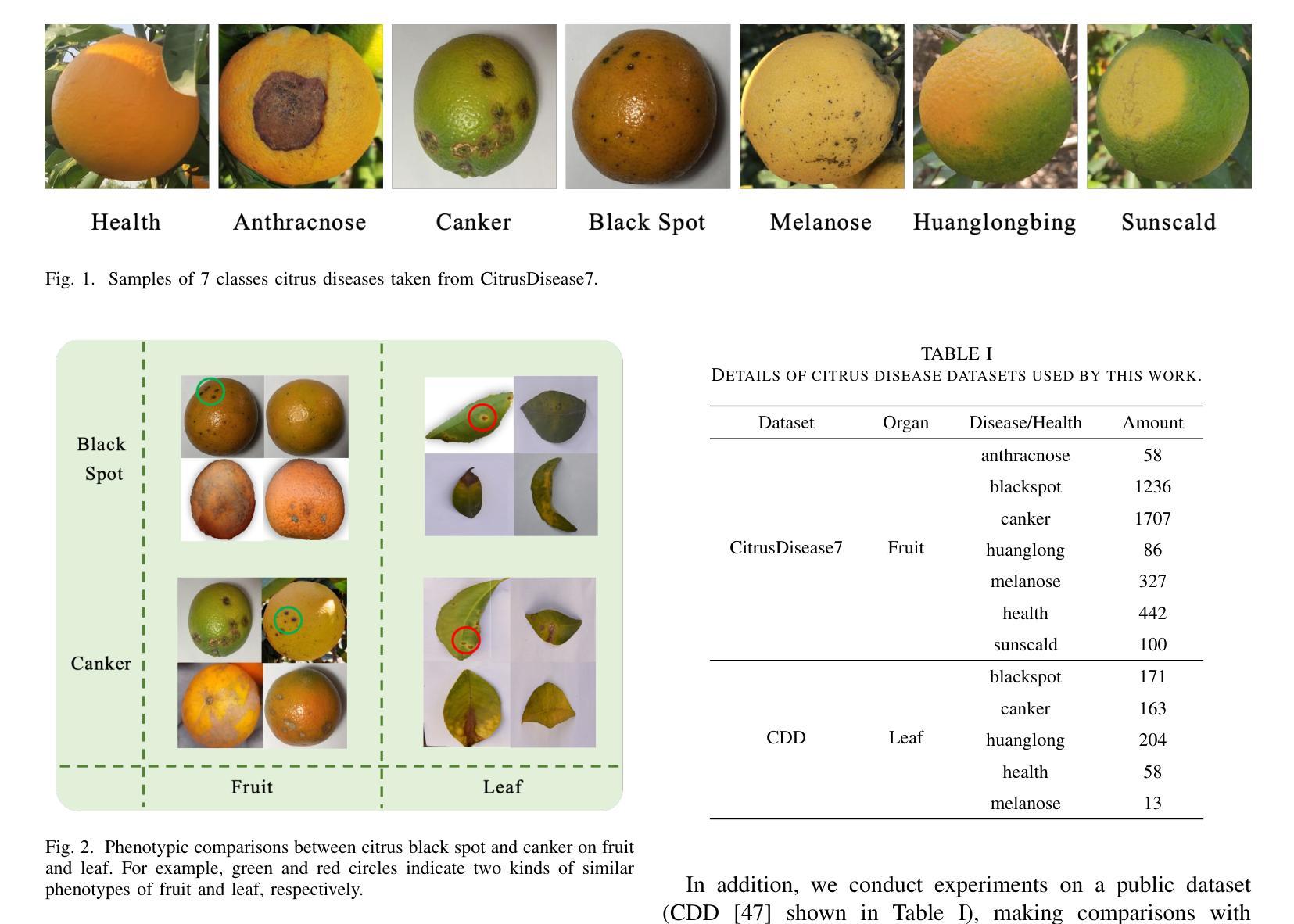
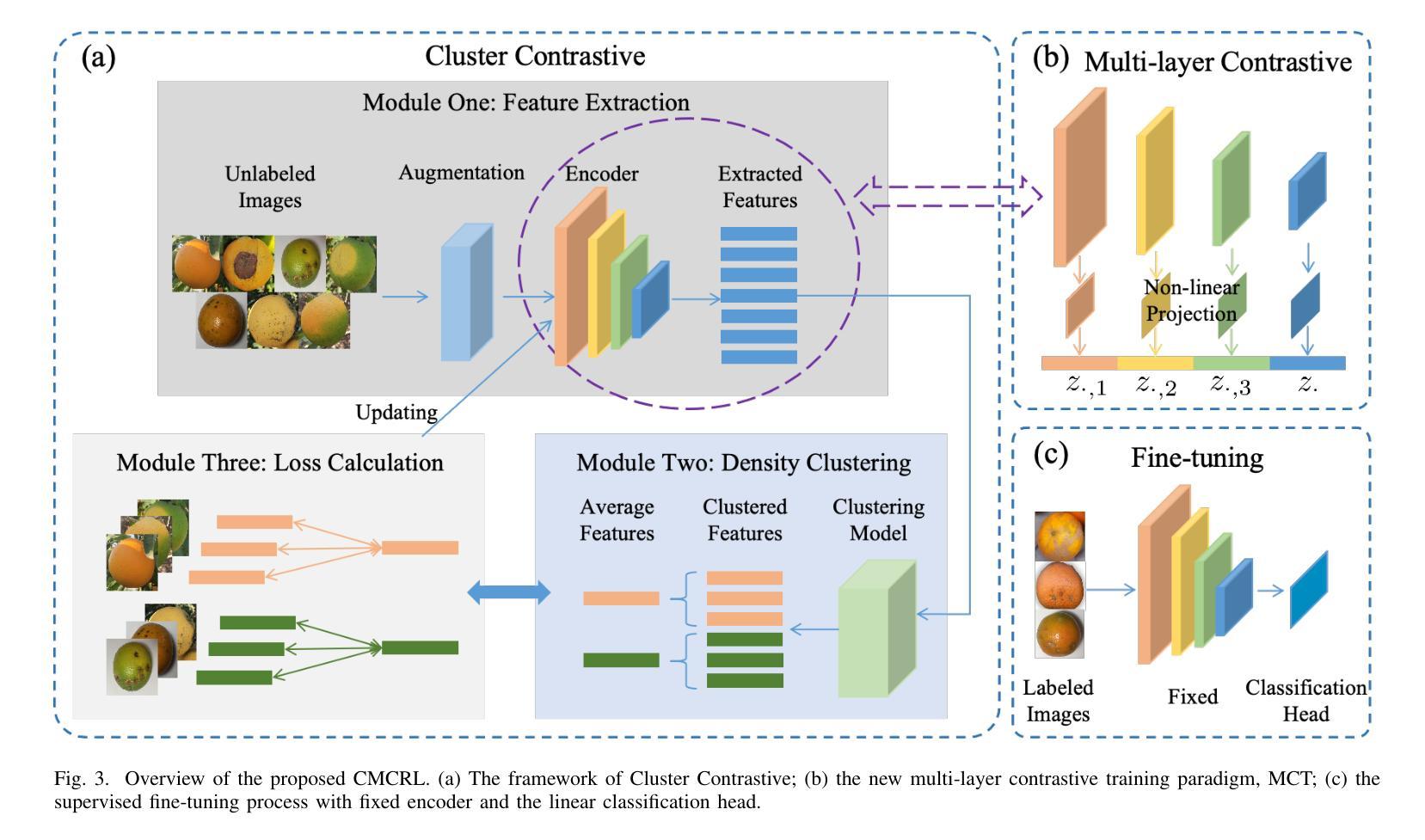
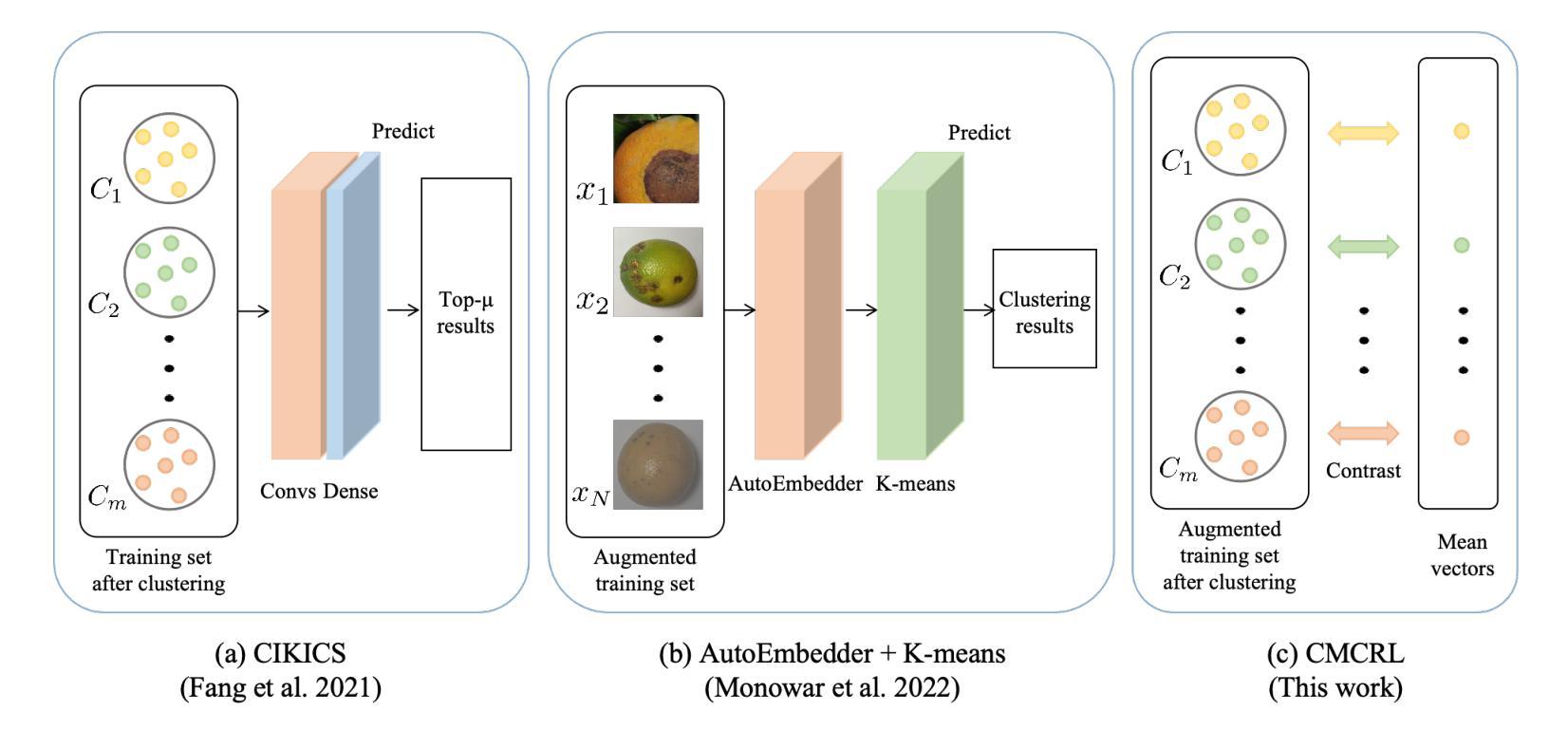
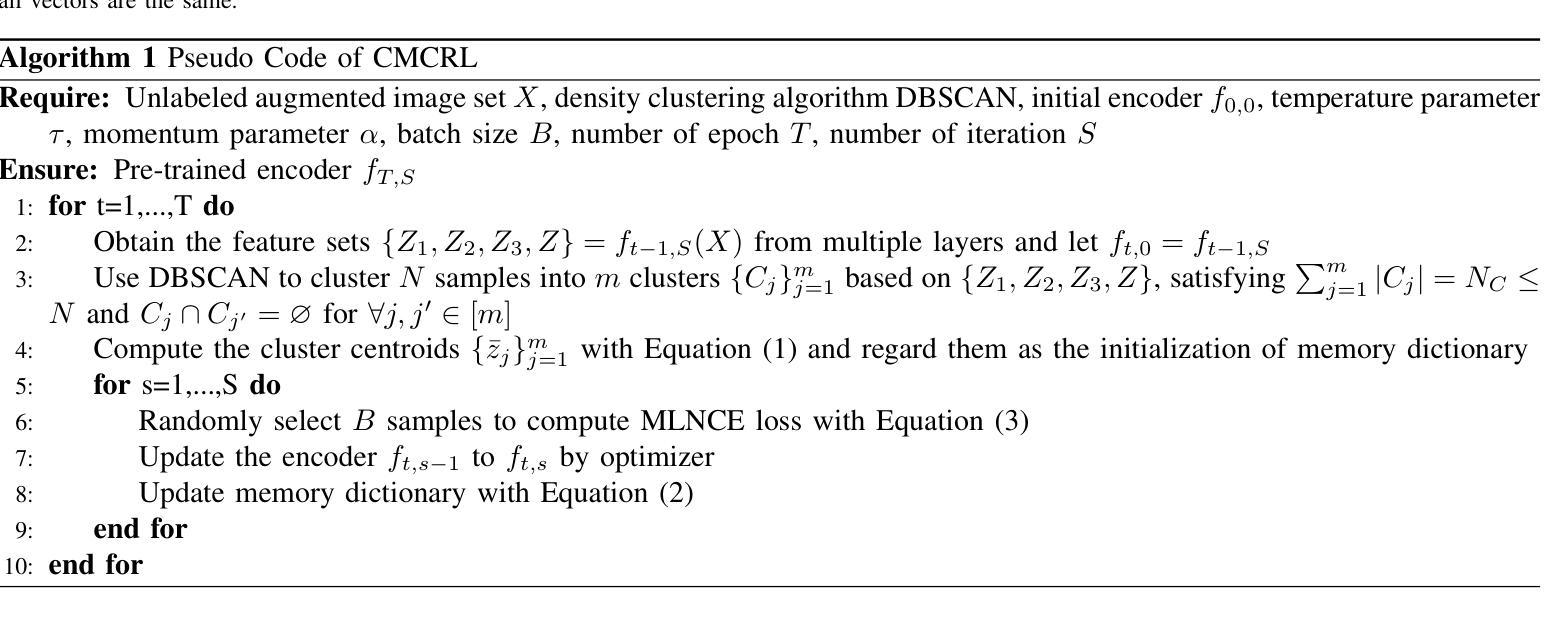
点此查看论文截图

FIX-CLIP: Dual-Branch Hierarchical Contrastive Learning via Synthetic Captions for Better Understanding of Long Text
Authors:Bingchao Wang, Zhiwei Ning, Jianyu Ding, Xuanang Gao, Yin Li, Dongsheng Jiang, Jie Yang, Wei Liu
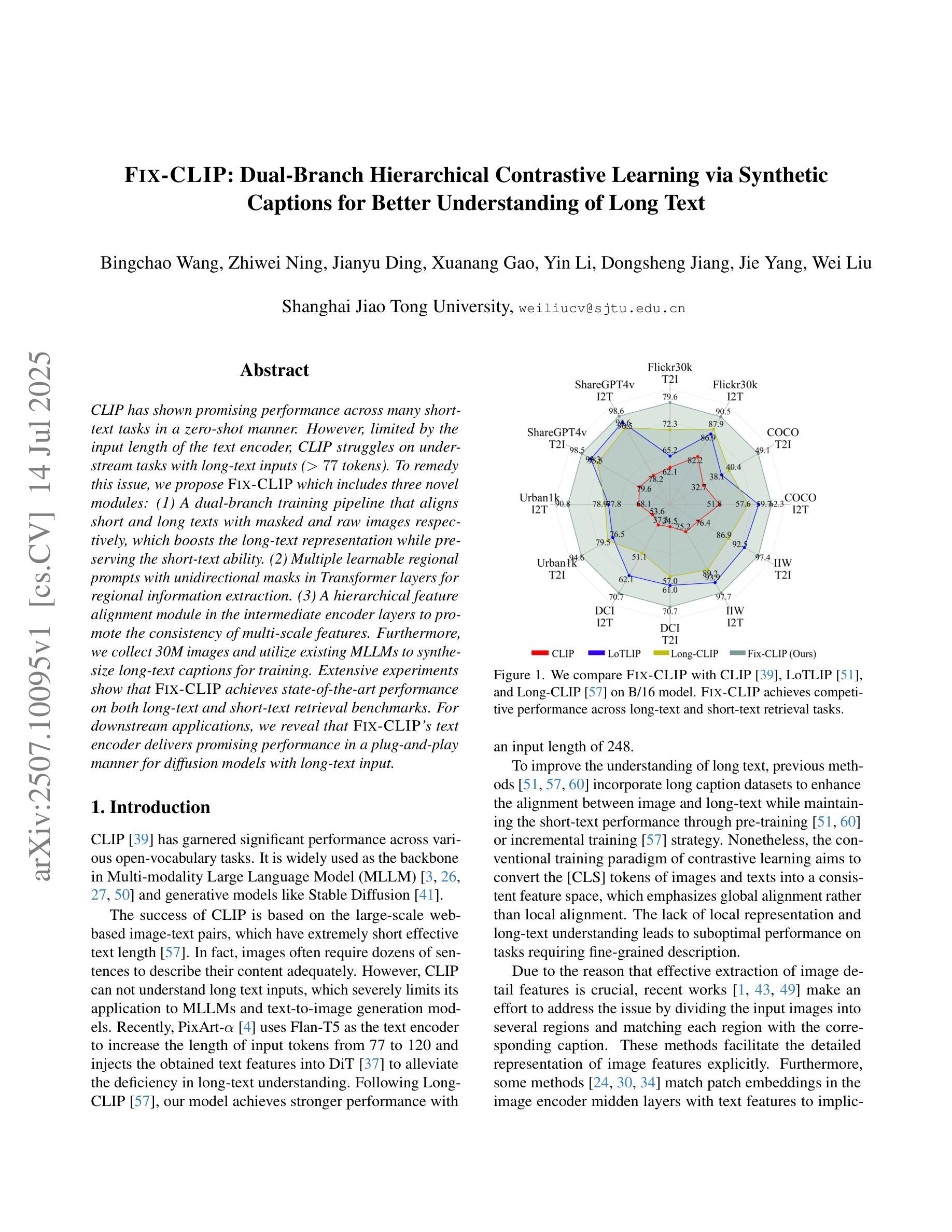
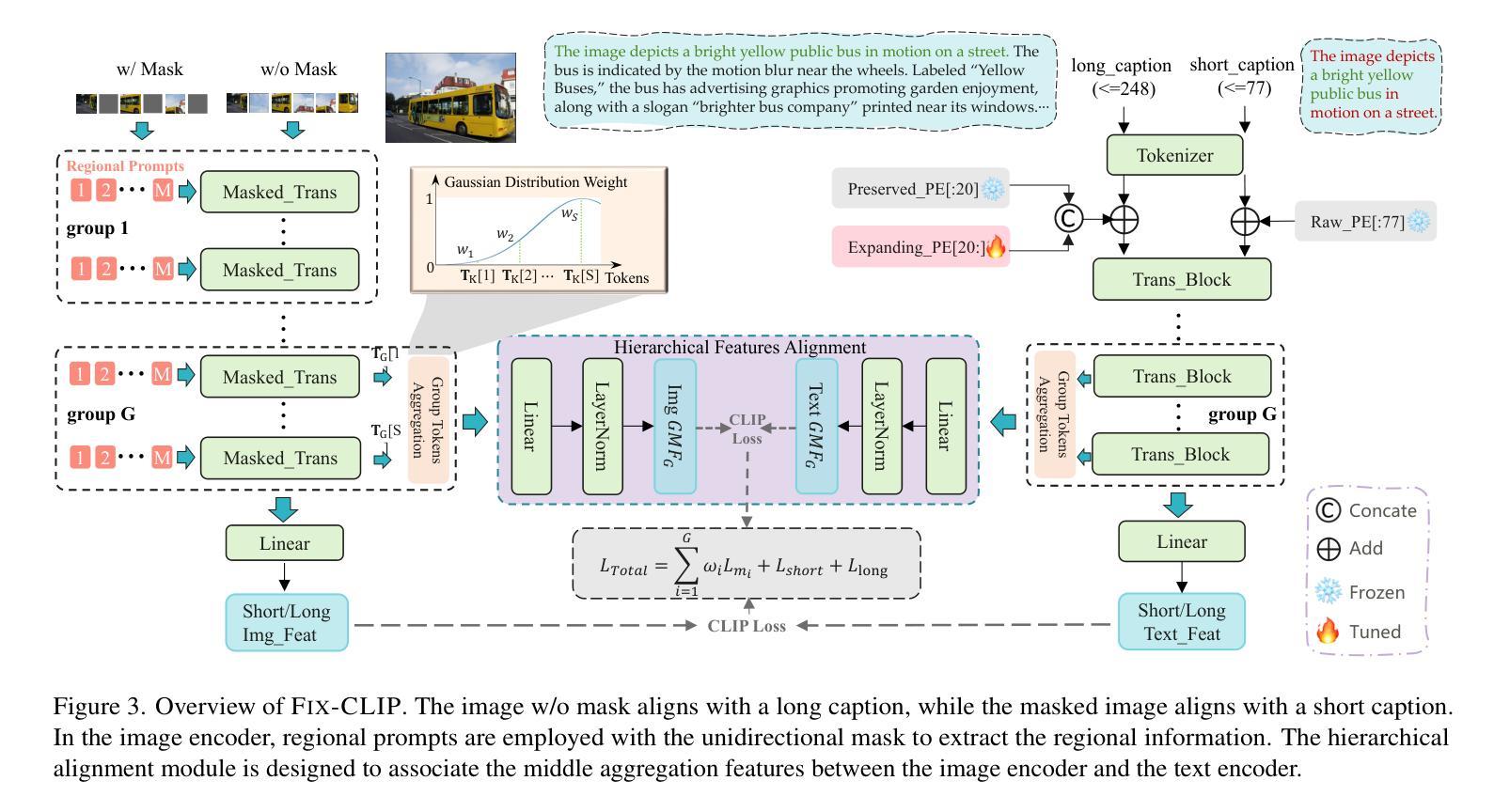
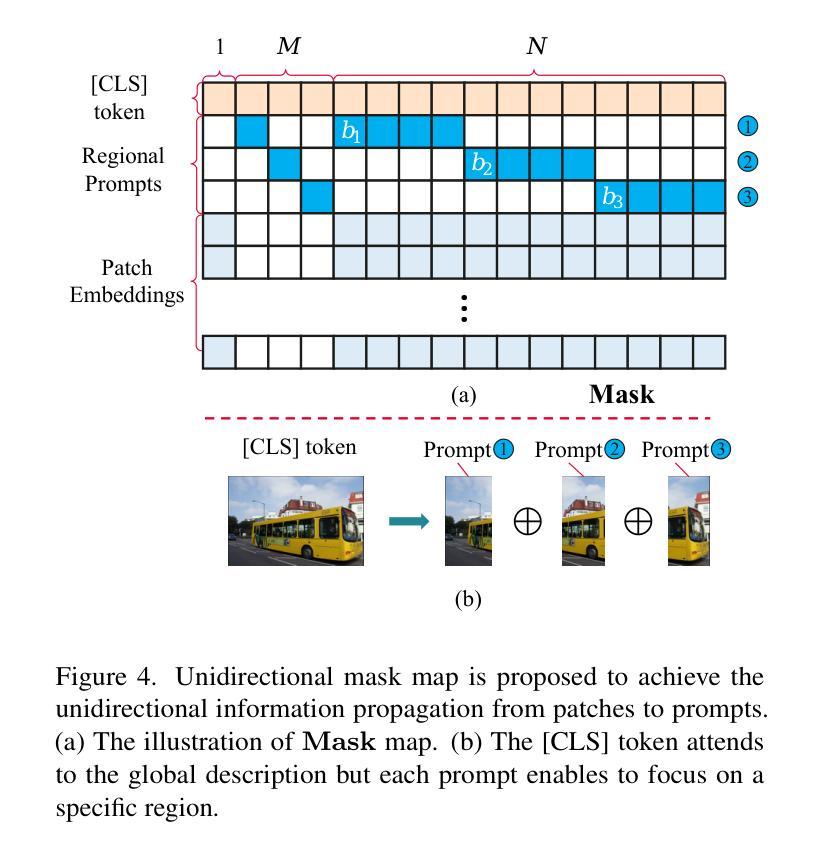
CLIP has shown promising performance across many short-text tasks in a zero-shot manner. However, limited by the input length of the text encoder, CLIP struggles on under-stream tasks with long-text inputs (>77 tokens). To remedy this issue, we propose FIX-CLIP which includes three novel modules: (1) A dual-branch training pipeline that aligns short and long texts with masked and raw images respectively, which boosts the long-text representation while preserving the short-text ability. (2) Multiple learnable regional prompts with unidirectional masks in Transformer layers for regional information extraction. (3) A hierarchical feature alignment module in the intermediate encoder layers to promote the consistency of multi-scale features. Furthermore, we collect 30M images and utilize existing MLLMs to synthesize long-text captions for training. Extensive experiments show that FIX-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on both long-text and short-text retrieval benchmarks. For downstream applications, we reveal that FIX-CLIP’s text encoder delivers promising performance in a plug-and-play manner for diffusion models with long-text input.
CLIP在许多零样本短文本任务中表现出良好的性能。然而,由于文本编码器的输入长度限制,CLIP在处理长文本输入(>77个令牌)的流式任务时遇到了困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP,它包括三个新模块:(1)双分支训练管道,该管道分别通过掩码和原始图像对齐短文本和长文本,在提高长文本表示能力的同时保持短文本能力。(2)在Transformer层中使用多个可学习的区域提示和单向掩码进行区域信息提取。(3)在中间编码器层中引入层次特征对齐模块,以促进多尺度特征的一致性。此外,我们收集了3000万张图像,并利用现有的大型语言模型来合成长文本描述进行训练。大量实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长文本和短文本检索基准测试中都达到了最先进的性能。对于下游应用,我们证明了FIX-CLIP的文本编码器在具有长文本输入的扩散模型中具有良好的即插即用性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP在零样本方式下在许多短文本任务中表现出良好的性能,但在处理长文本输入(>77个令牌)时面临挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP,包括三个新颖模块:1)双分支训练管道,分别对齐短文本和长文本与掩码和原始图像,提升长文本表示能力的同时保留短文本能力;2)在Transformer层中使用多个可学习的区域提示和单向掩码进行区域信息提取;3)在中间编码器层中引入分层特征对齐模块,以促进多尺度特征的一致性。此外,我们收集了3亿张图像,并利用现有的MLLMs进行长文本描述的训练。实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长短文本检索基准测试中实现了业界领先的性能,并且在具有长文本输入的扩散模型中具有可插拔的良好表现。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在许多短文本任务中表现良好,但在处理长文本输入时存在局限性。
- FIX-CLIP通过三个新颖模块解决这一问题:双分支训练管道、使用区域提示和单向掩码进行信息提取、以及中间编码器层的分层特征对齐。
- FIX-CLIP收集大量图像数据并使用MLLMs合成长文本描述进行训练。
- 实验显示FIX-CLIP在长短文本检索基准测试中表现领先。
点此查看论文截图

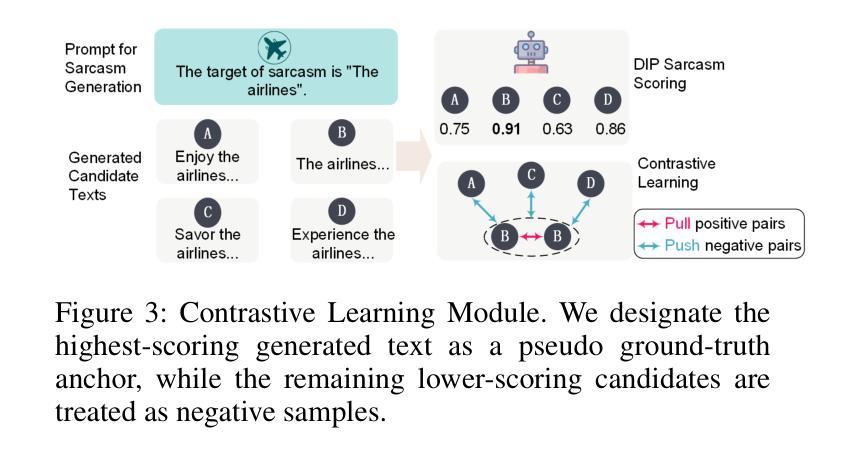
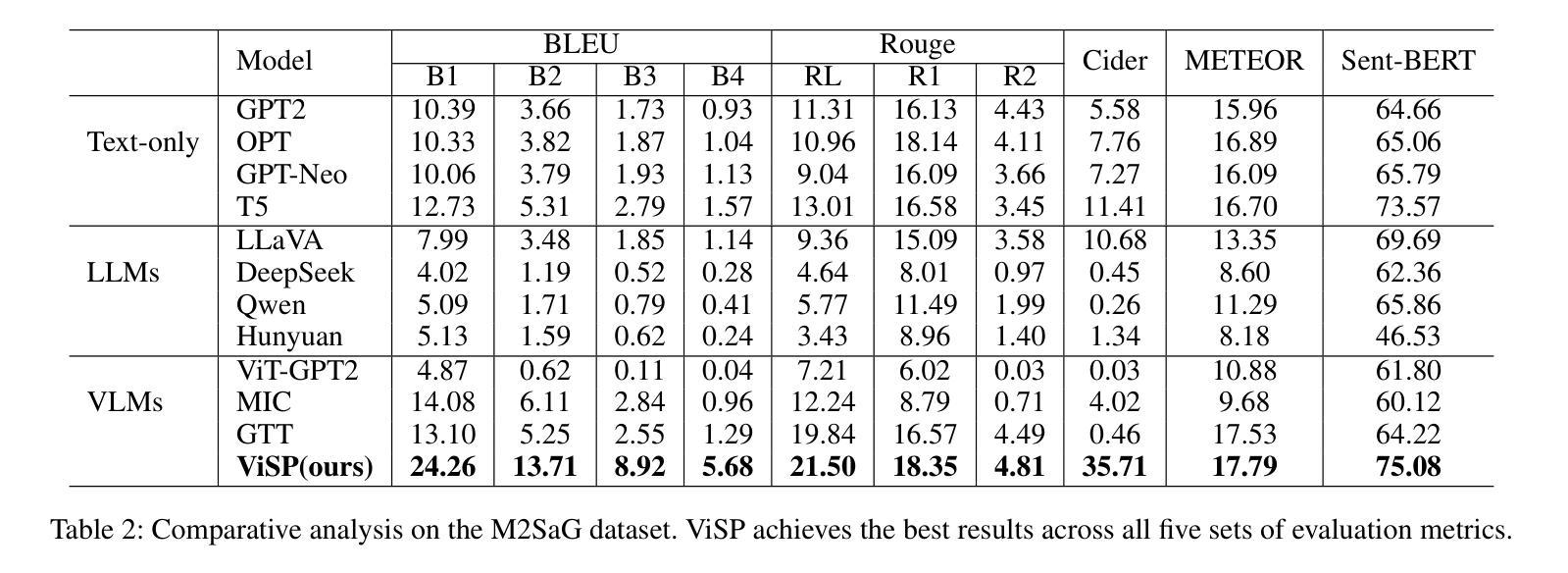
ViSP: A PPO-Driven Framework for Sarcasm Generation with Contrastive Learning
Authors:Changli Wang, Rui Wu, Fang Yin
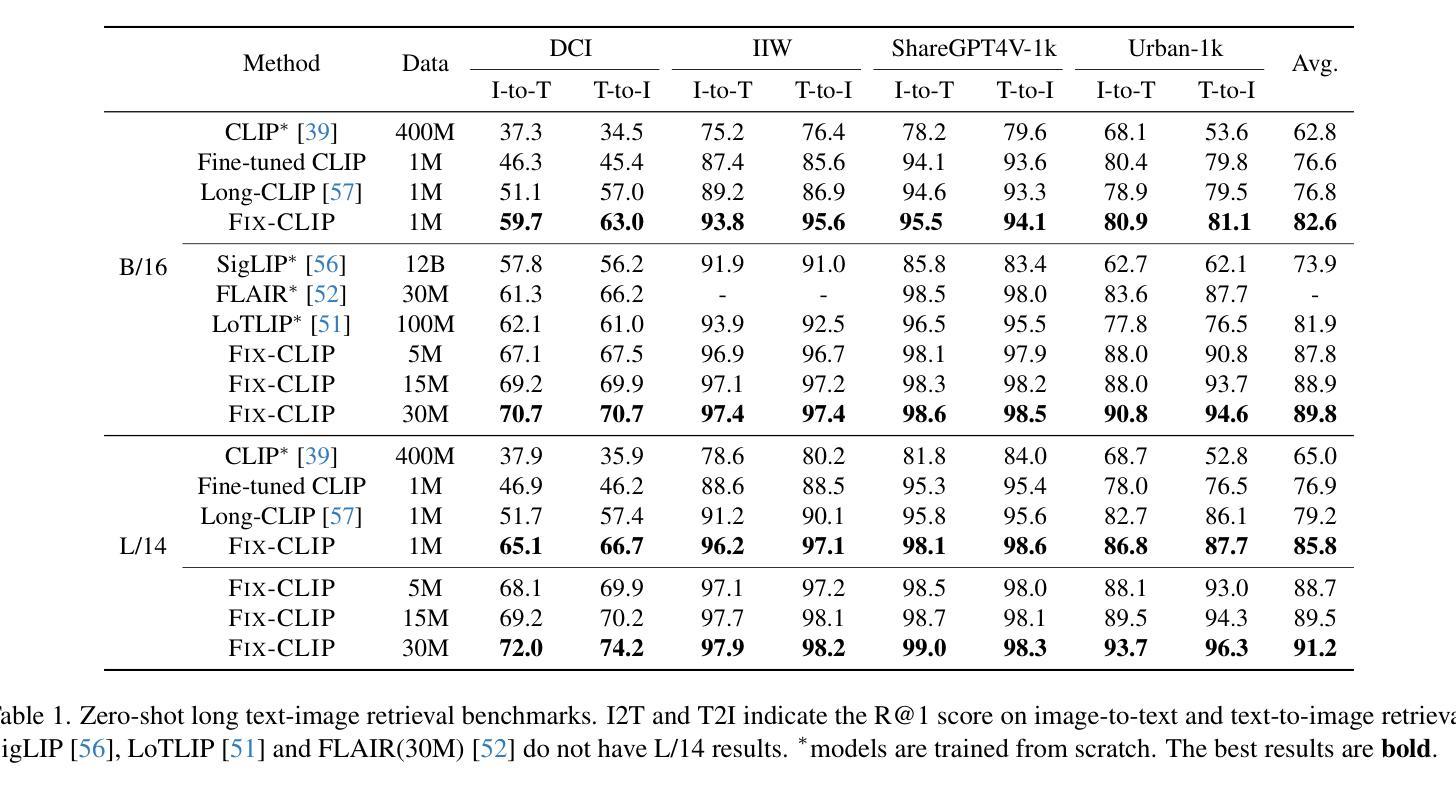
Human emotions are complex, with sarcasm being a subtle and distinctive form. Despite progress in sarcasm research, sarcasm generation remains underexplored, primarily due to the overreliance on textual modalities and the neglect of visual cues, as well as the mismatch between image content and sarcastic intent in existing datasets. In this paper, we introduce M2SaG, a multimodal sarcasm generation dataset with 4,970 samples, each containing an image, a sarcastic text, and a sarcasm target. To benchmark M2SaG, we propose ViSP, a generation framework that integrates Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and contrastive learning. PPO utilizes reward scores from DIP to steer the generation of sarcastic texts, while contrastive learning encourages the model to favor outputs with higher reward scores. These strategies improve overall generation quality and produce texts with more pronounced sarcastic intent. We evaluate ViSP across five metric sets and find it surpasses all baselines, including large language models, underscoring their limitations in sarcasm generation. Furthermore, we analyze the distributions of Sarcasm Scores and Factual Incongruity for both M2SaG and the texts generated by ViSP. The generated texts exhibit higher mean Sarcasm Scores (0.898 vs. 0.770) and Factual Incongruity (0.768 vs. 0.739), demonstrating that ViSP produces higher-quality sarcastic content than the original dataset. % The dataset and code will be publicly available. Our dataset and code will be released at \textit{https://github.com/wclapply/ViSP}.
人类情绪复杂,讽刺是一种微妙而独特的表达形式。尽管讽刺研究已取得进展,但讽刺生成仍然被低估,这主要是因为过度依赖文本模式而忽视视觉线索,以及现有数据集中图像内容与讽刺意图之间的不匹配。在本文中,我们介绍了M2SaG,这是一个多模态讽刺生成数据集,包含4970个样本,每个样本包含一张图像、一段讽刺性文本和一个讽刺目标。为了评估M2SaG,我们提出了ViSP,这是一个结合了近端策略优化(PPO)和对比学习的生成框架。PPO利用DIP的奖励分数来引导讽刺文本的产生,而对比学习则鼓励模型优先选择奖励分数更高的输出。这些策略提高了整体的生成质量,产生了更具讽刺意味的文本。我们在五个度量集上评估了ViSP,发现它超越了所有基线,包括大型语言模型,凸显了它们在讽刺生成方面的局限性。此外,我们分析了M2SaG和ViSP生成的文本的讽刺分数和事实不一致性的分布。生成的文本具有更高的平均讽刺分数(0.898 vs. 0.770)和事实不一致性(0.768 vs. 0.739),表明ViSP生成的讽刺内容比原始数据集更高质量。数据集和代码将在公开平台上发布,可通过网址访问:\ul{https://github.com/wclapply/ViSP}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个多模态讽刺生成数据集M2SaG,包含图像、讽刺文本和讽刺目标。提出ViSP框架,集成近端策略优化(PPO)和对比学习以改进讽刺文本的生成质量。通过对比不同指标集评估ViSP表现,证明其在讽刺生成上的优越性。公开数据集和代码以推动研究进步。
Key Takeaways
- 引入多模态讽刺生成数据集M2SaG,融合图像和文本信息。
- 提出ViSP框架用于改善讽刺文本的生成质量。
- 集成近端策略优化(PPO)进行强化学习控制文本生成过程。
- 使用对比学习策略促使模型偏向更高奖励得分的输出。
- 通过多项评估指标验证了ViSP相较于其他基准模型和大型语言模型的优越性。
- 分析表明,ViSP生成的文本在讽刺分数和事实上的不一致性上表现出更高质量。
点此查看论文截图
Can Contrastive Learning Improve Class-Imbalanced Diffusion Model?
Authors:Fang Chen, Alex Villa, Gongbo Liang, Xiaoyi Lu, Meng Tang
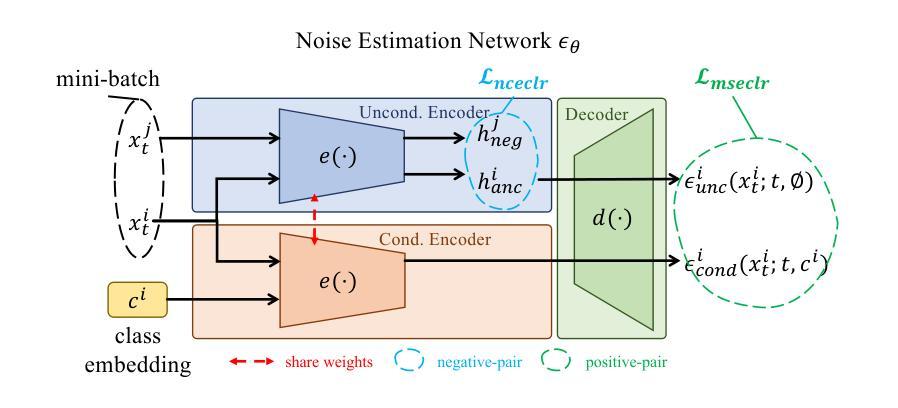
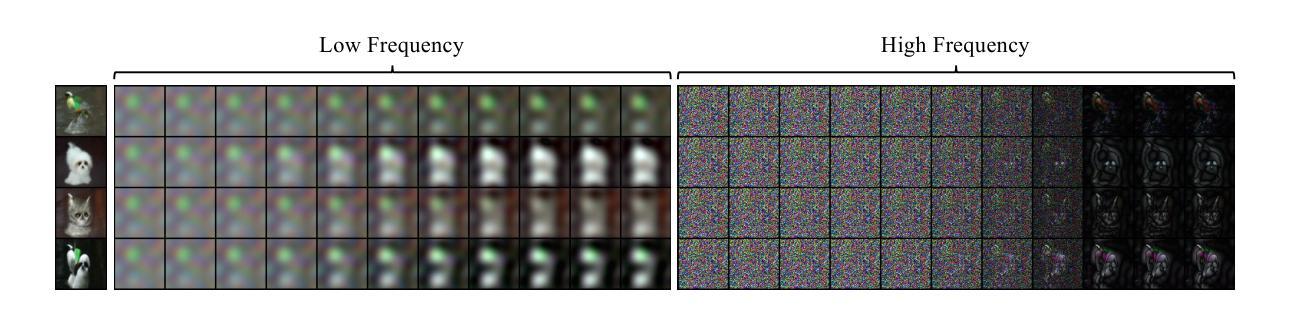
Training data for class-conditional image synthesis often exhibit a long-tailed distribution with limited images for tail classes. Such an imbalance causes mode collapse and reduces the diversity of synthesized images for tail classes. For class-conditional diffusion models trained on imbalanced data, we aim to improve the diversity of tail class images without compromising the fidelity and diversity of head class images. We achieve this by introducing two deceptively simple but highly effective contrastive loss functions. Firstly, we employ an unsupervised InfoNCE loss utilizing negative samples to increase the distance/dissimilarity among synthetic images, particularly for tail classes. To further enhance the diversity of tail classes, our second loss is an MSE loss that contrasts class-conditional generation with unconditional generation at large timesteps. This second loss makes the denoising process insensitive to class conditions for the initial steps, which enriches tail classes through knowledge sharing from head classes. Conditional-unconditional alignment has been shown to enhance the performance of long-tailed GAN. We are the first to adapt such alignment to diffusion models. We successfully leveraged contrastive learning for class-imbalanced diffusion models. Our contrastive learning framework is easy to implement and outperforms standard DDPM and alternative methods for class-imbalanced diffusion models across various datasets, including CIFAR10/100-LT, PlacesLT, TinyImageNetLT, and ImageNetLT.
针对类别条件图像合成的训练数据通常呈现长尾分布,尾部类别的图像数量有限。这种不平衡会导致模式崩溃,并降低尾部类别合成图像的多样性。对于在不平衡数据上训练的类别条件扩散模型,我们的目标是在不损害头部类别图像的保真度和多样性的情况下,提高尾部类别图像的多样性。我们通过引入两个具有欺骗性简单但非常有效的对比损失函数来实现这一目标。首先,我们采用无监督的InfoNCE损失,利用负样本增加合成图像之间的距离/不相似度,特别是尾部类别的图像。为了进一步提高尾部类别的多样性,我们的第二个损失是一个MSE损失,它对比了大类条件下生成和无条件下生成的结果在大时间步长时的差异。第二个损失使得初始步骤的降噪过程对类别条件不敏感,通过从头部类别共享知识来丰富尾部类别。有条件-无条件的对齐已被证明可以提高长尾GAN的性能。我们是首次将这种对齐方法适应于扩散模型。我们成功地将对比学习应用于类别不平衡的扩散模型。我们的对比学习框架易于实现,并且在各种数据集上,包括CIFAR10/100-LT、PlacesLT、TinyImageNetLT和ImageNetLT,对于类别不平衡的扩散模型,其性能优于标准的DDPM和其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对类别条件扩散模型在训练数据不平衡问题上的改进方法。通过引入两种对比损失函数,提高了尾类图像的多样性,同时不损害头类图像的保真度和多样性。采用无监督的InfoNCE损失和MSE损失,通过对比合成图像之间的距离和不相似性,特别是在尾类上,来增强尾类的多样性。该框架易于实现,在各种数据集上均优于标准DDPM和其他针对类别不平衡扩散模型的替代方法。
Key Takeaways
- 针对类别条件图像合成中的长尾分布问题,提出了改进方法。
- 引入两种对比损失函数:InfoNCE损失和MSE损失。
- InfoNCE损失利用负样本增加合成图像间的距离/不相似性,特别是尾类图像。
- MSE损失通过对比类别条件生成与无条件生成在大时间步的生成结果,进一步增强了尾类的多样性。
- 该方法通过知识共享丰富尾类,使去噪过程对初始步骤的类别条件不敏感。
- 首次将条件-无条件对齐适应于扩散模型,提高了长尾GAN的性能。
点此查看论文截图