⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
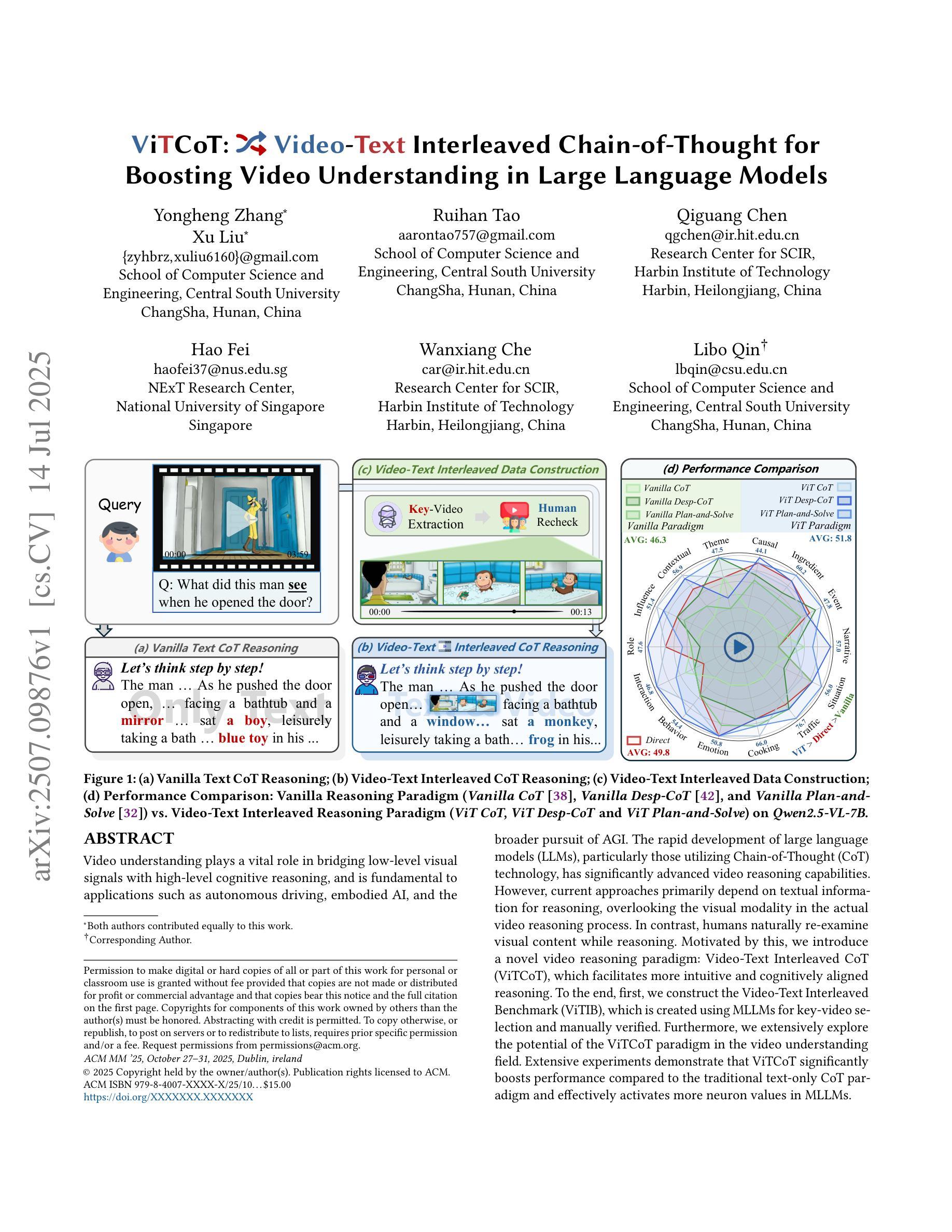
ViTCoT: Video-Text Interleaved Chain-of-Thought for Boosting Video Understanding in Large Language Models
Authors:Yongheng Zhang, Xu Liu, Ruihan Tao, Qiguang Chen, Hao Fei, Wanxiang Che, Libo Qin
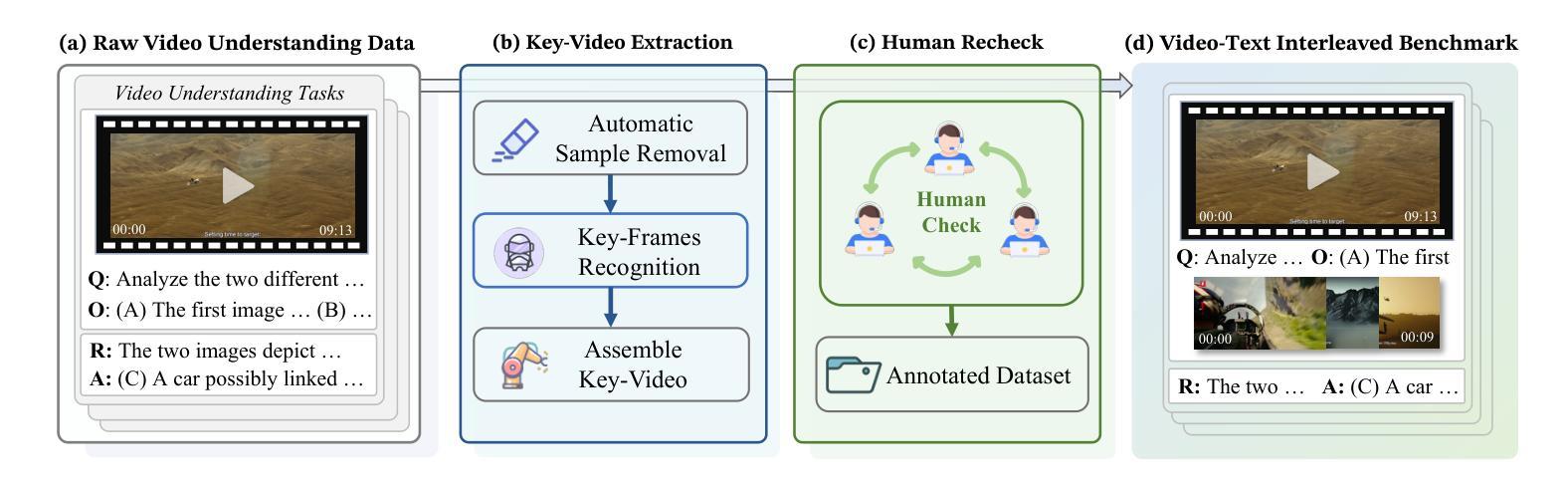
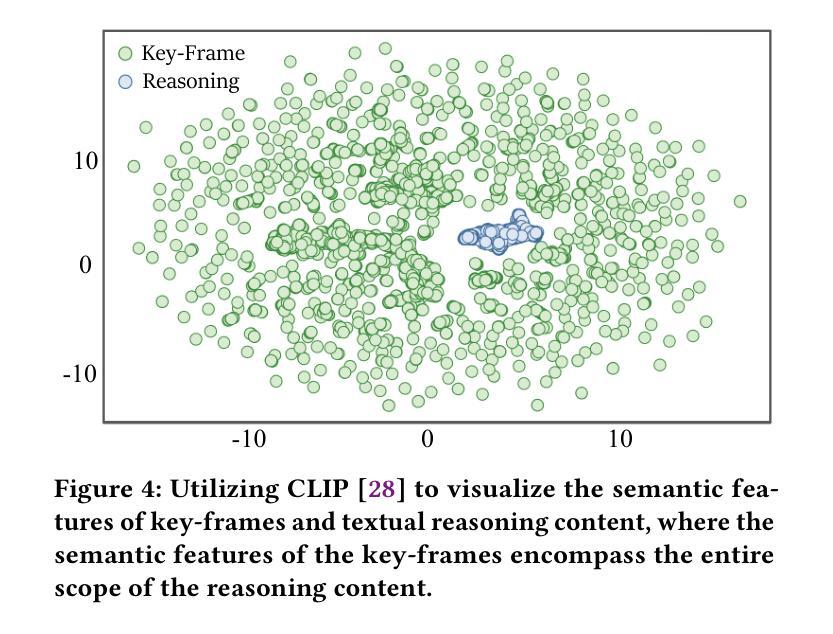
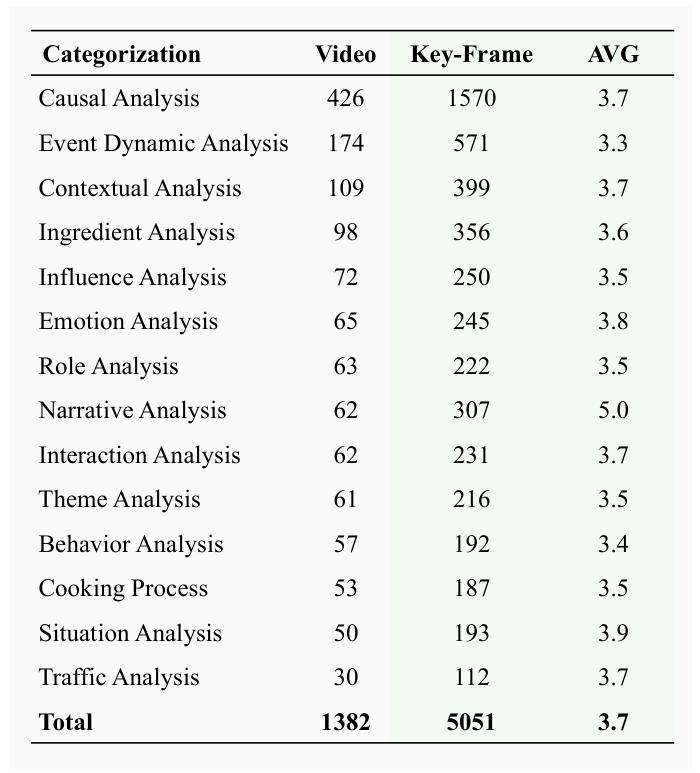
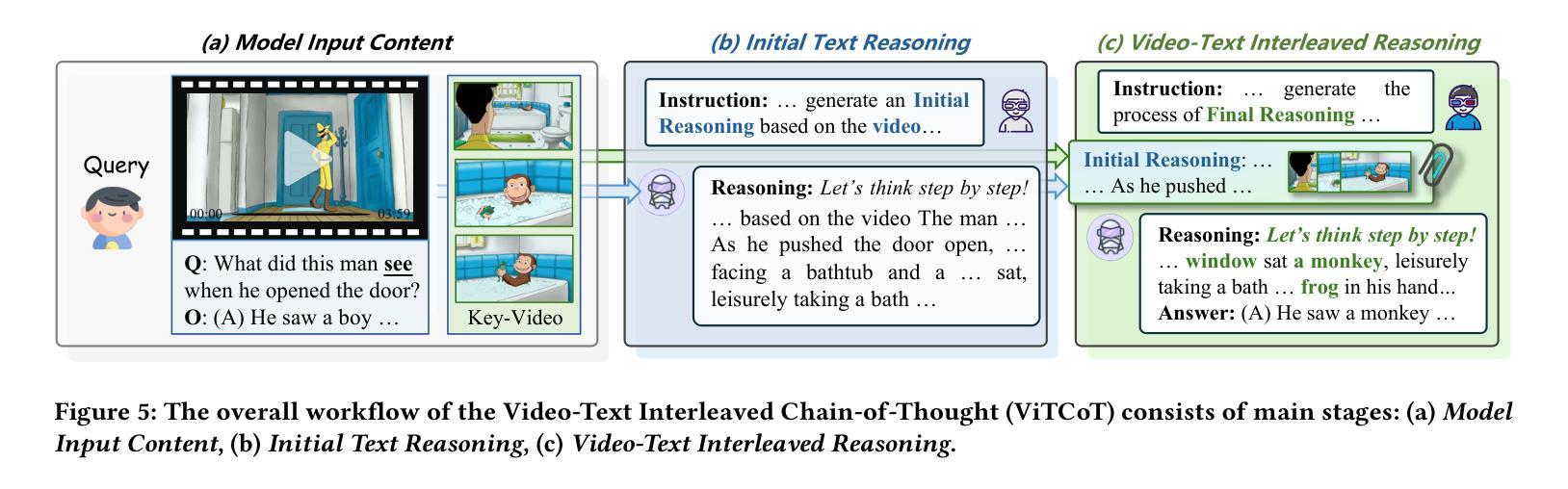
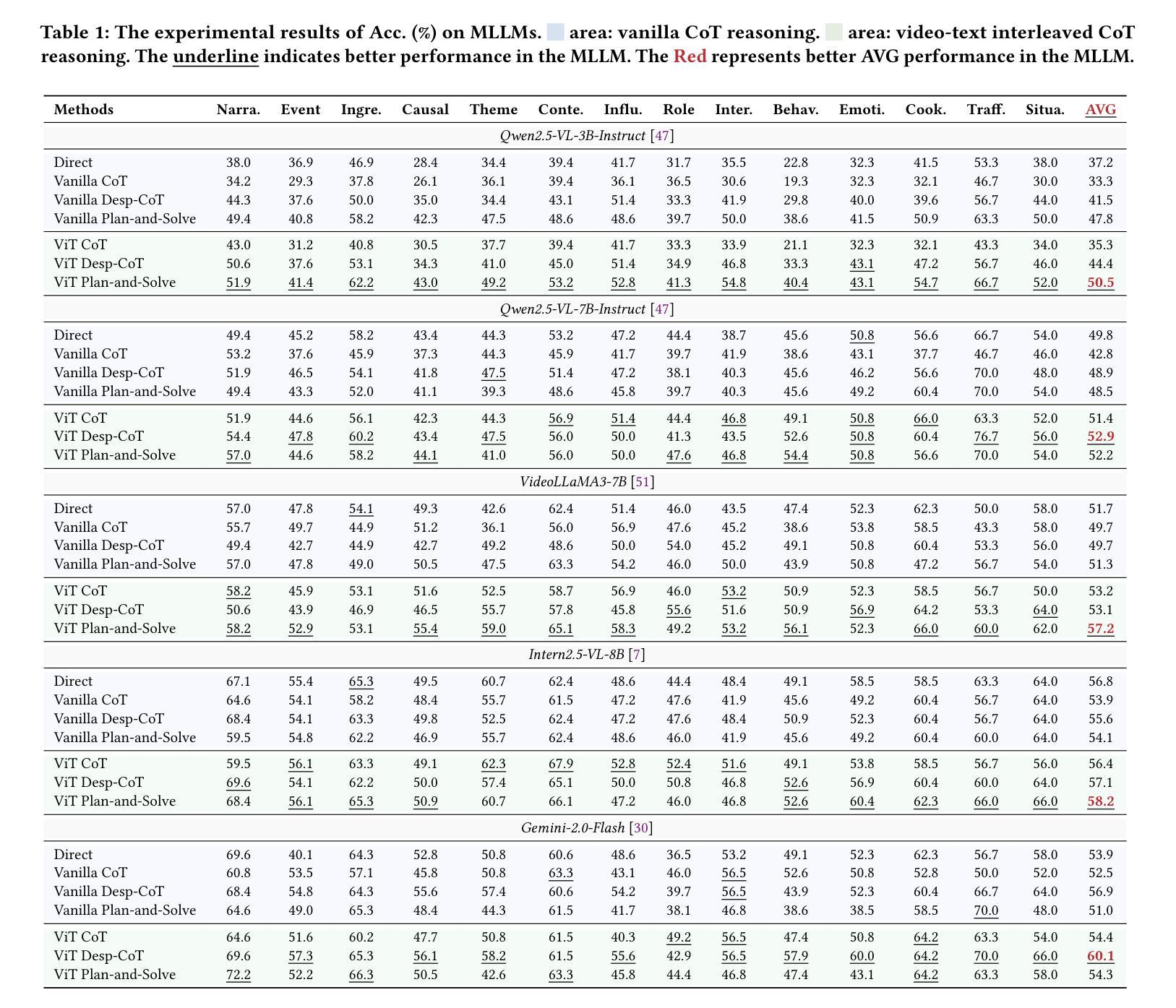
Video understanding plays a vital role in bridging low-level visual signals with high-level cognitive reasoning, and is fundamental to applications such as autonomous driving, embodied AI, and the broader pursuit of AGI. The rapid development of large language models (LLMs), particularly those utilizing Chain-of-Thought (CoT) technology, has significantly advanced video reasoning capabilities. However, current approaches primarily depend on textual information for reasoning, overlooking the visual modality in the actual video reasoning process. In contrast, humans naturally re-examine visual content while reasoning. Motivated by this, we introduce a novel video reasoning paradigm: Video-Text Interleaved CoT (ViTCoT), which facilitates more intuitive and cognitively aligned reasoning. To the end, first, we construct the Video-Text Interleaved Benchmark (ViTIB), which is created using MLLMs for key-video selection and manually verified. Furthermore, we extensively explore the potential of the ViTCoT paradigm in the video understanding field. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViTCoT significantly enhances performance compared to the traditional text-only CoT paradigm and effectively activates more neuron values in MLLMs.
视频理解在连接低层次视觉信号与高层次认知推理方面扮演着至关重要的角色,对于自动驾驶、实体人工智能以及更广泛的通用人工智能追求等应用来说是根本性的。随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展,特别是那些采用思维链(CoT)技术的模型,视频推理能力得到了显著的提升。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于文本信息进行推理,忽视了实际视频推理过程中的视觉模式。与此相反,人类在推理时会自然地重新检查视觉内容。受此启发,我们引入了一种新的视频推理范式:视频文本交织思维链(ViTCoT),它促进了更直观和认知一致性的推理。为此,我们构建了视频文本交织基准测试(ViTIB),它使用MLLMs进行关键视频选择并经过手动验证。此外,我们还广泛探索了ViTCoT范式在视频理解领域的潜力。大量实验表明,与传统的仅文本CoT范式相比,ViTCoT显著提高了性能,并有效地在MLLMs中激活了更多的神经元值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
视频理解在将低层次的视觉信号与高层次认知推理之间建立桥梁方面起着至关重要的作用,对于自动驾驶、嵌入式人工智能和更广泛的通用人工智能追求等应用是基础。随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展,特别是利用思维链(CoT)技术的模型,视频推理能力得到了显著提升。然而,当前的方法主要依赖文本信息进行推理,忽略了实际视频推理过程中的视觉模式。相比之下,人类在推理时会自然重新审查视觉内容。受此启发,我们引入了一种新型视频推理范式:视频文本交织思维链(ViTCoT),促进更直观和认知相符的推理。为此,我们建立了视频文本交织基准测试(ViTIB),利用MLLMs进行关键视频选择并经过人工验证。同时,我们广泛探索了ViTCoT范式在视频理解领域的潜力。实验表明,与传统的仅文本CoT范式相比,ViTCoT显著提高了性能,并有效激活了MLLMs中的更多神经元值。
Key Takeaways
- 视频理解在连接低层次视觉信号与高层次认知推理方面起关键作用,对自动驾驶和通用人工智能等领域至关重要。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展已经显著推动了视频推理的进步。
- 当前视频推理方法过于依赖文本信息而忽视视觉模式。
- 人类在推理过程中会重新审查视觉内容。
- 新型视频推理范式——视频文本交织思维链(ViTCoT)旨在更直观地促进认知相符的推理。
- 建立了视频文本交织基准测试(ViTIB),通过MLLMs进行关键视频选择并经过人工验证。
点此查看论文截图
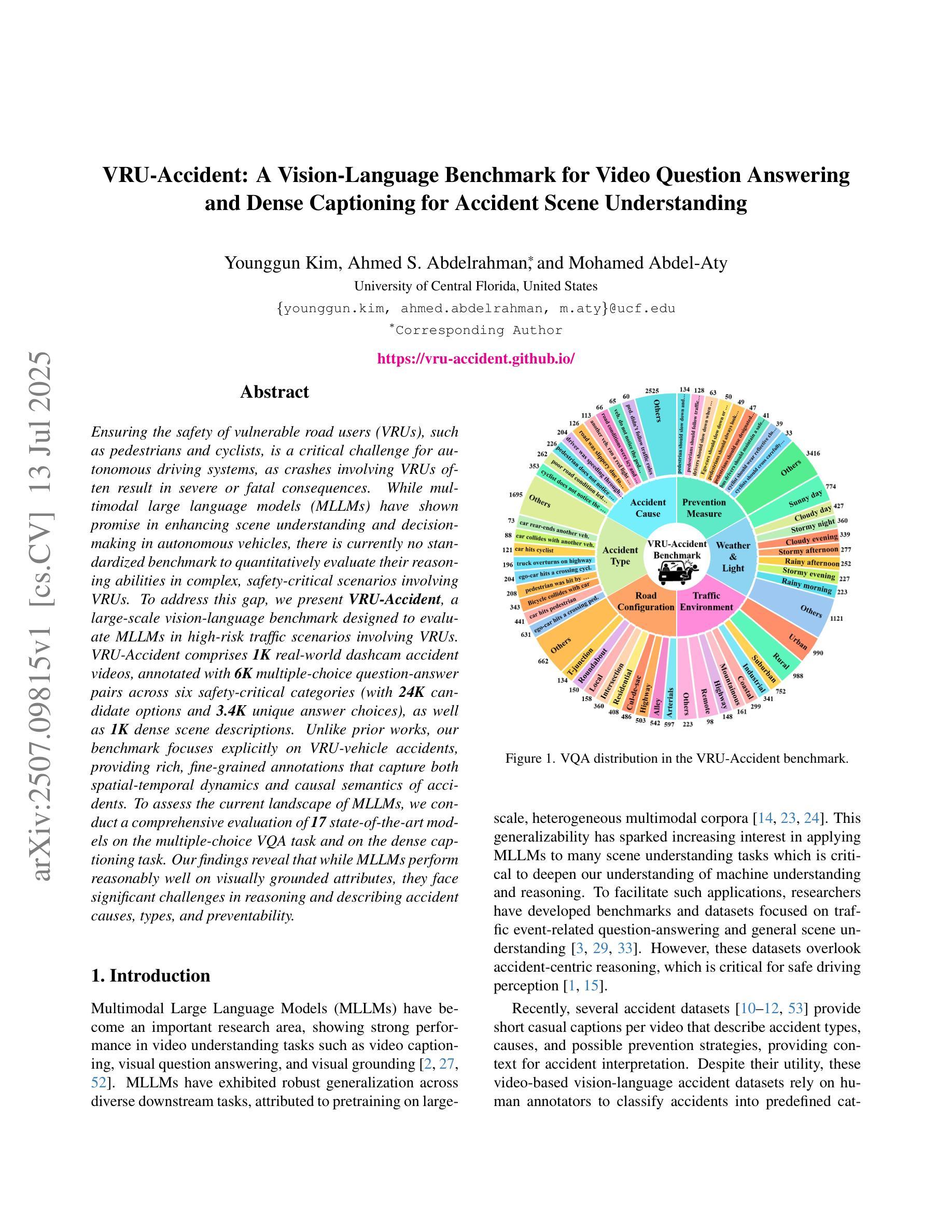
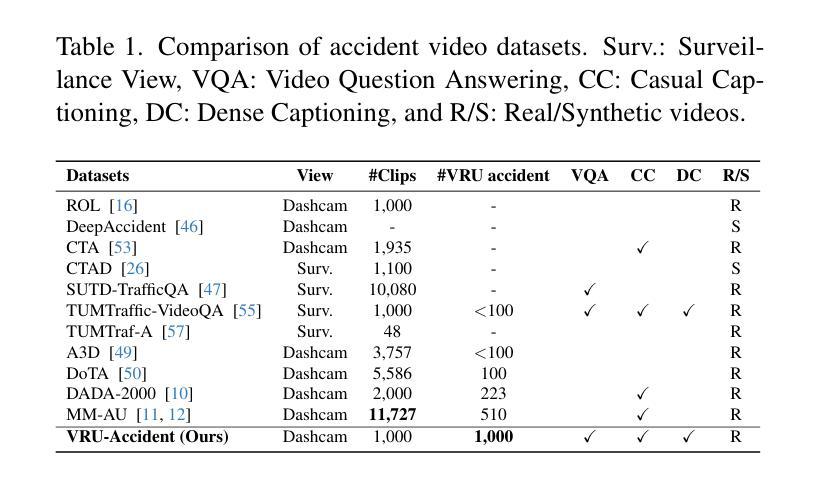
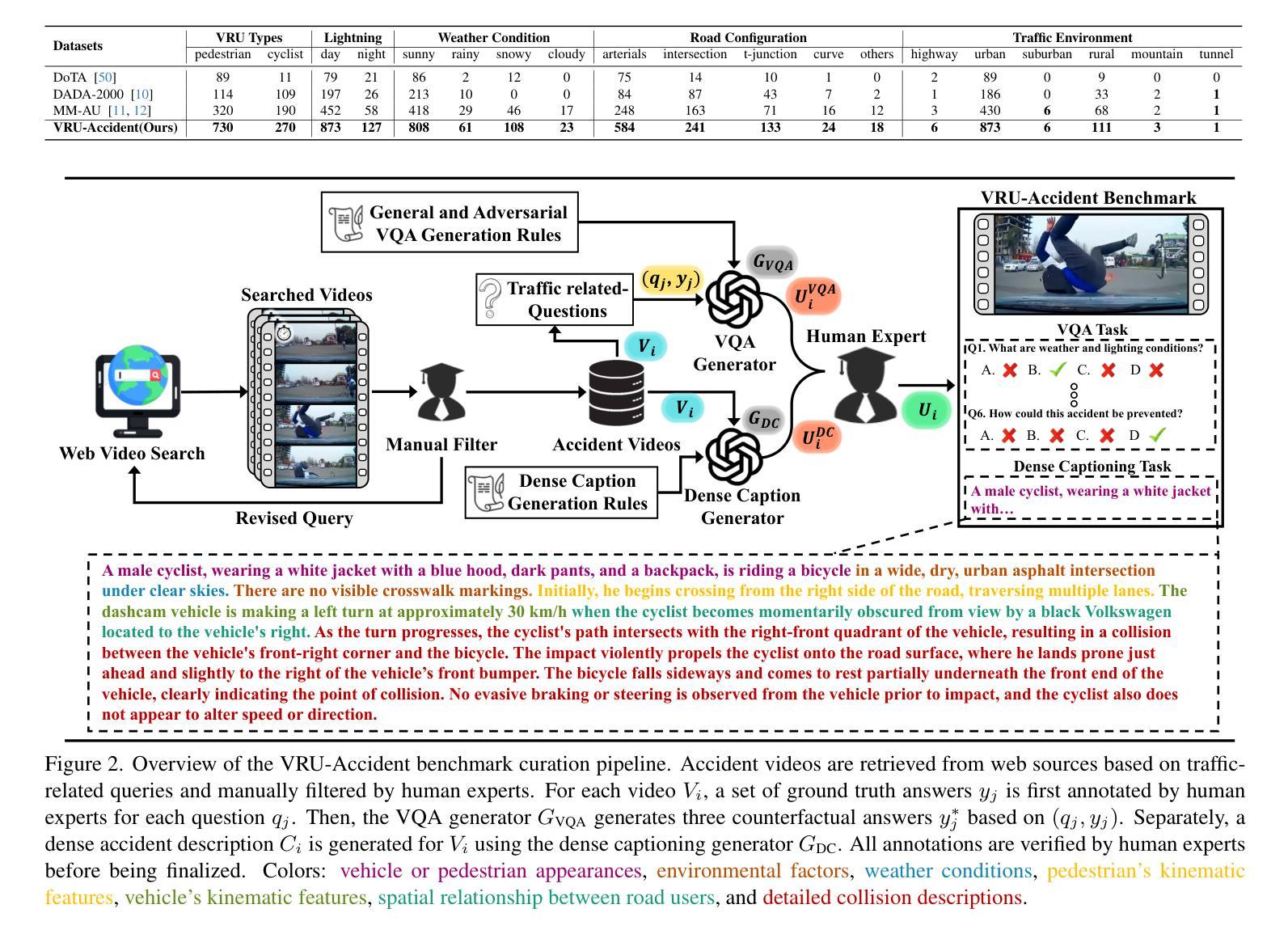
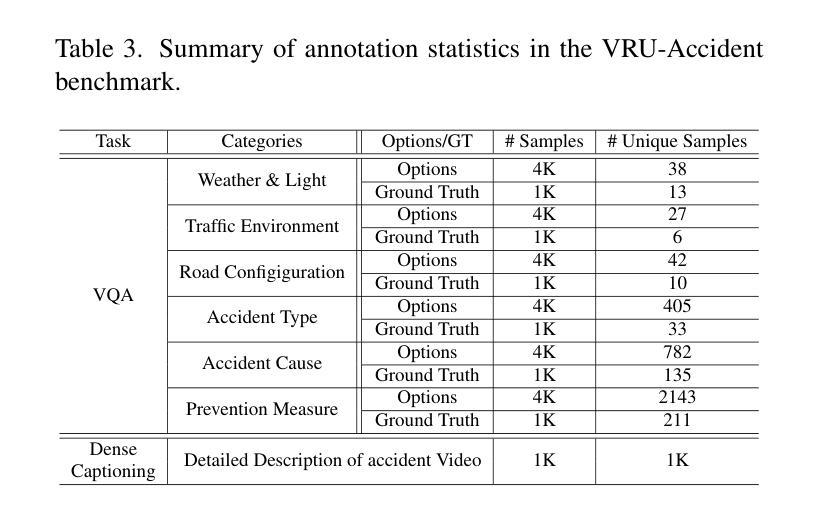
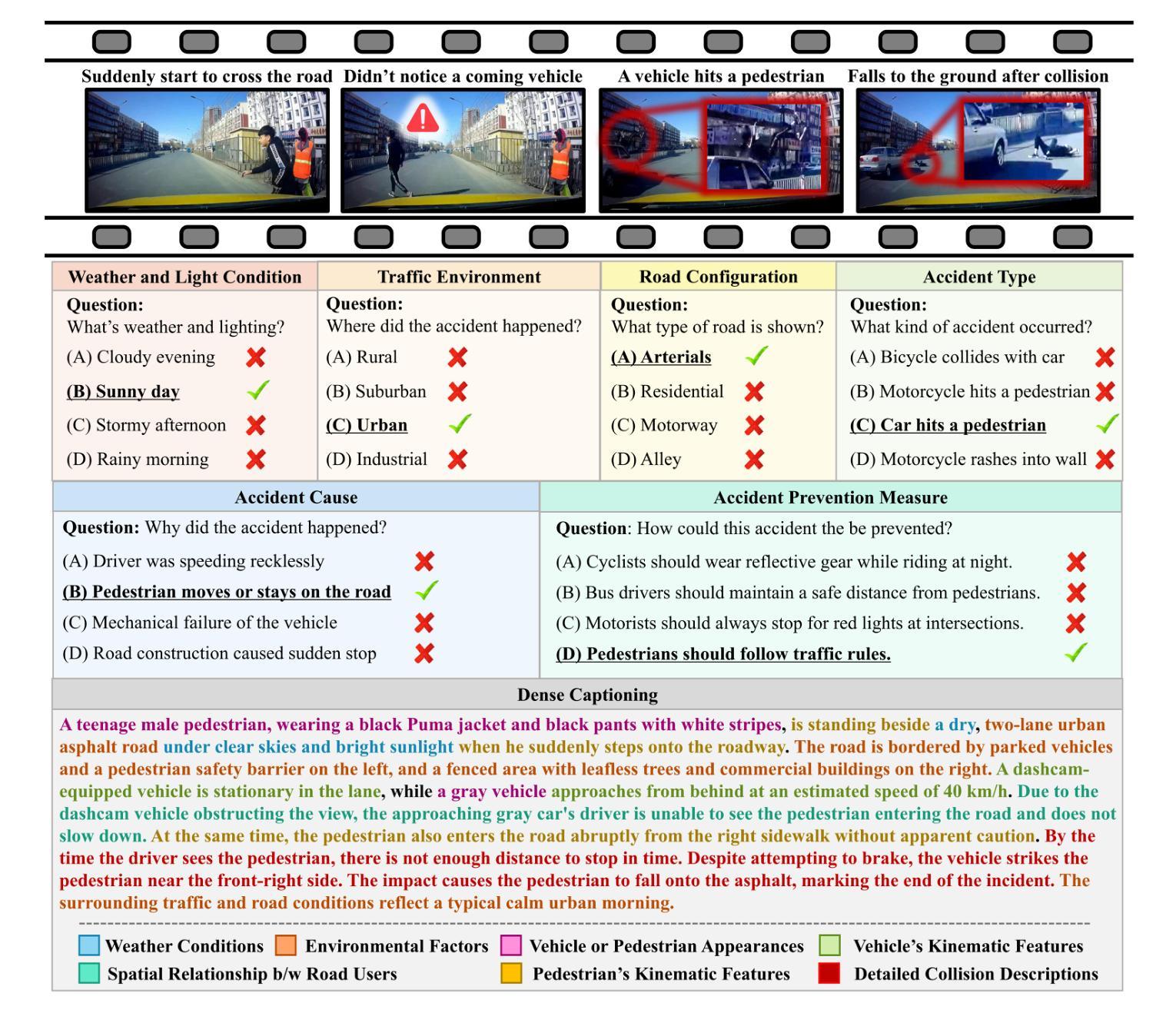
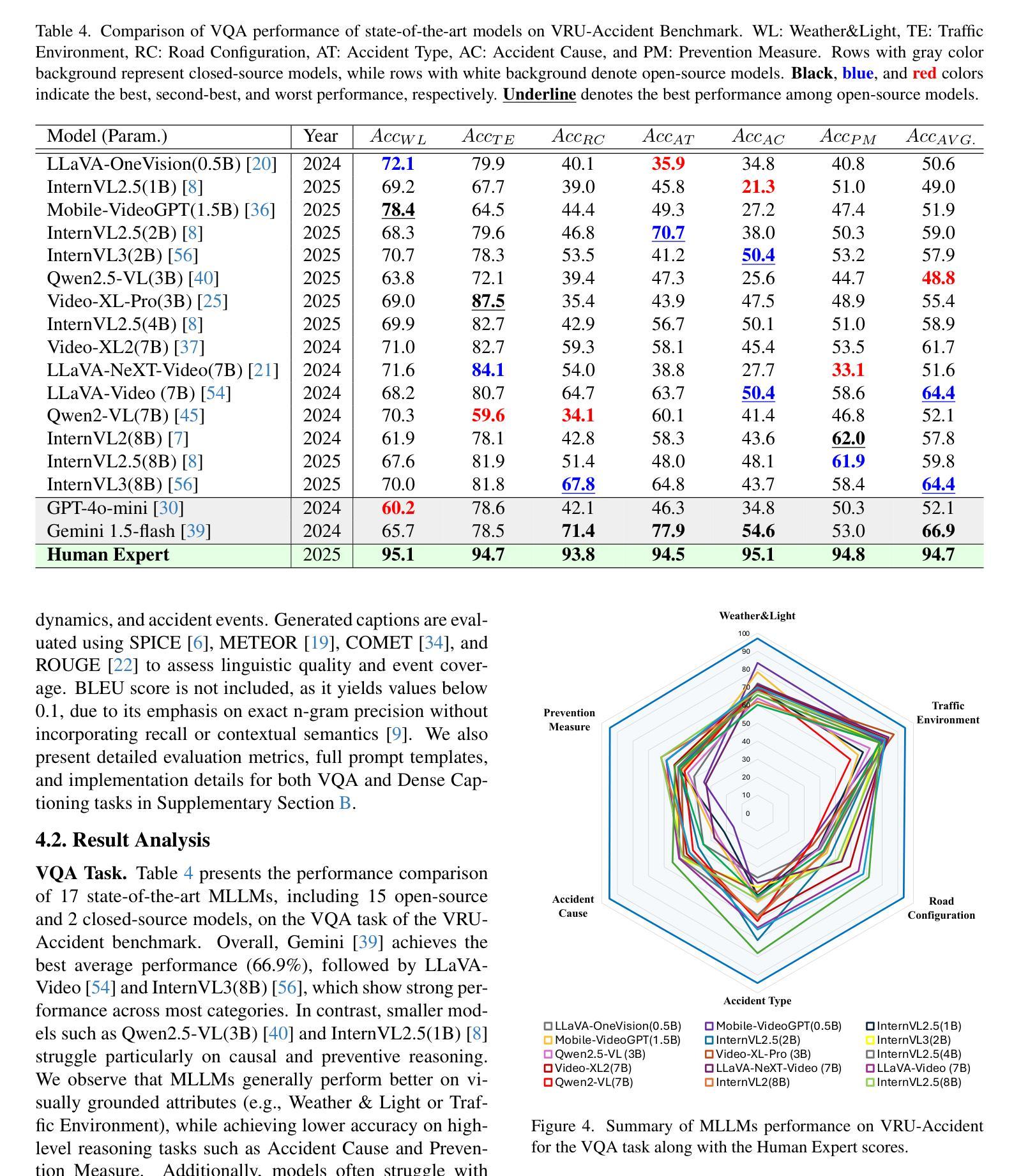
VRU-Accident: A Vision-Language Benchmark for Video Question Answering and Dense Captioning for Accident Scene Understanding
Authors:Younggun Kim, Ahmed S. Abdelrahman, Mohamed Abdel-Aty
Ensuring the safety of vulnerable road users (VRUs), such as pedestrians and cyclists, is a critical challenge for autonomous driving systems, as crashes involving VRUs often result in severe or fatal consequences. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown promise in enhancing scene understanding and decision making in autonomous vehicles, there is currently no standardized benchmark to quantitatively evaluate their reasoning abilities in complex, safety-critical scenarios involving VRUs. To address this gap, we present VRU-Accident, a large-scale vision-language benchmark designed to evaluate MLLMs in high-risk traffic scenarios involving VRUs. VRU-Accident comprises 1K real-world dashcam accident videos, annotated with 6K multiple-choice question-answer pairs across six safety-critical categories (with 24K candidate options and 3.4K unique answer choices), as well as 1K dense scene descriptions. Unlike prior works, our benchmark focuses explicitly on VRU-vehicle accidents, providing rich, fine-grained annotations that capture both spatial-temporal dynamics and causal semantics of accidents. To assess the current landscape of MLLMs, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of 17 state-of-the-art models on the multiple-choice VQA task and on the dense captioning task. Our findings reveal that while MLLMs perform reasonably well on visually grounded attributes, they face significant challenges in reasoning and describing accident causes, types, and preventability.
确保脆弱道路使用者(如步行者和骑自行车的人)的安全对于自动驾驶系统来说是一个关键挑战,因为涉及脆弱道路使用者的交通事故常常会导致严重或致命的后果。虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在增强自动驾驶场景理解和决策制定方面显示出潜力,但目前还没有一个标准化的基准来定量评估它们在涉及脆弱道路使用者的复杂、安全关键的场景中的推理能力。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了VRU-Accident,这是一个大规模视觉语言基准测试,旨在评估涉及脆弱道路使用者的高风险交通场景中的MLLMs。VRU-Accident包含1000个真实世界的行车记录仪事故视频,标注了6000个跨六个安全关键类别的多项选择题对(总计24000个候选选项和3400个独特答案),以及1000个密集场景描述。与以前的工作不同,我们的基准测试明确关注于脆弱道路使用者与车辆之间的事故,提供丰富、精细的标注,捕捉事故的时空动态和因果语义。为了评估当前MLLMs的状况,我们在多项选择问答任务和密集描述任务上对17个最先进模型进行了全面评估。我们的研究发现,虽然MLLMs在视觉基础上的属性表现良好,但在推理和描述事故原因、类型和可预防性方面仍面临重大挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 11 figures, 5 tables
Summary
该文关注自主驾驶系统中对脆弱道路使用者(VRUs)如行人及骑行者的安全保障问题。针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在复杂、安全关键的VRU场景中的推理能力缺乏标准化评估的问题,提出了一种大规模视觉语言基准测试VRU-Accident。该基准测试包含1000个真实世界行车记录仪事故视频,包含6000个涉及六种安全关键类别的选择题答案对,以及1000个密集场景描述。评估发现,MLLMs在视觉属性上的表现较好,但在推理和描述事故原因、类型及可预防性等方面存在显著挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 自主驾驶系统需确保脆弱道路使用者(VRUs)的安全,因为涉及VRUs的事故常导致严重或致命后果。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在增强自主车辆场景理解和决策方面具潜力。
- 目前缺乏标准化基准评估MLLMs在复杂、安全关键的涉及VRUs场景中的推理能力。
- VRU-Accident是一个新的大规模视觉语言基准测试,用于评估MLLMs在高风险VRU交通场景中的表现。
- VRU-Accident包含真实事故视频、选择题和密集场景描述,注重VRU与车辆事故。
- MLLMs在视觉属性上的表现良好,但在事故推理和描述方面存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图
Infinite Video Understanding
Authors:Dell Zhang, Xiangyu Chen, Jixiang Luo, Mengxi Jia, Changzhi Sun, Ruilong Ren, Jingren Liu, Hao Sun, Xuelong Li
The rapid advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and their multimodal extensions (MLLMs) have ushered in remarkable progress in video understanding. However, a fundamental challenge persists: effectively processing and comprehending video content that extends beyond minutes or hours. While recent efforts like Video-XL-2 have demonstrated novel architectural solutions for extreme efficiency, and advancements in positional encoding such as HoPE and VideoRoPE++ aim to improve spatio-temporal understanding over extensive contexts, current state-of-the-art models still encounter significant computational and memory constraints when faced with the sheer volume of visual tokens from lengthy sequences. Furthermore, maintaining temporal coherence, tracking complex events, and preserving fine-grained details over extended periods remain formidable hurdles, despite progress in agentic reasoning systems like Deep Video Discovery. This position paper posits that a logical, albeit ambitious, next frontier for multimedia research is Infinite Video Understanding – the capability for models to continuously process, understand, and reason about video data of arbitrary, potentially never-ending duration. We argue that framing Infinite Video Understanding as a blue-sky research objective provides a vital north star for the multimedia, and the wider AI, research communities, driving innovation in areas such as streaming architectures, persistent memory mechanisms, hierarchical and adaptive representations, event-centric reasoning, and novel evaluation paradigms. Drawing inspiration from recent work on long/ultra-long video understanding and several closely related fields, we outline the core challenges and key research directions towards achieving this transformative capability.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)及其多模态扩展(MLLM)的快速发展,视频理解领域已经取得了显著的进步。然而,仍存在一项基本挑战:有效处理和理解超过分钟或小时的视频内容。尽管最近的努力,如Video-XL-2,已经展示了极端效率的新型架构解决方案,以及HoPE和VideoRoPE++等位置编码的进步旨在提高大范围上下文中的时空理解,但当前最先进的技术模型在面对长时间序列的大量视觉标记时,仍面临重大的计算和内存约束。此外,尽管在诸如Deep Video Discovery等智能推理系统中取得了进展,但维持时间连贯性、追踪复杂事件以及在延长时期内保持精细细节仍是艰巨的障碍。这篇立场论文认为,多媒体研究的一个逻辑上虽然雄心勃勃但全新的前沿领域是无限视频理解——模型连续处理、理解和推理任意潜在无限持续时间的视频数据的能力。我们认为,将无限视频理解作为蓝海研究目标,为多媒体和更广泛的AI研究社区提供了一个关键的北极星,推动流架构、持久记忆机制、分层和自适应表示、事件中心推理以及新型评估范式等领域的创新。我们从最近关于长/超长视频理解和几个相关领域的作品中汲取灵感,概述了实现这一变革性能力的核心挑战和关键研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)及其多模态扩展(MLLMs)的快速发展,视频理解领域取得了显著进步。然而,处理和理解超过分钟或小时的视频内容的挑战仍然存在。当前最先进模型在处理长时间视频时面临计算量和内存约束问题,且维持时间连贯性、追踪复杂事件、保留精细细节仍是难题。本文提出无限视频理解作为多媒体和更广泛的人工智能研究社区的重要研究方向,并概述了实现这一变革性能力的核心挑战和关键研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态扩展(MLLMs)的进展推动了视频理解领域的快速发展。
- 处理和理解超过分钟或小时的视频内容仍存在挑战。
- 当前先进模型在处理长时间视频时面临计算量和内存约束问题。
- 维持时间连贯性、追踪复杂事件、保留精细细节是视频理解的难题。
- 无限视频理解是多媒体和AI研究的重要方向。
- 实现无限视频理解需要研究流媒体架构、永久记忆机制、层次化和自适应表示、事件中心推理和新评估范式等关键领域。
点此查看论文截图

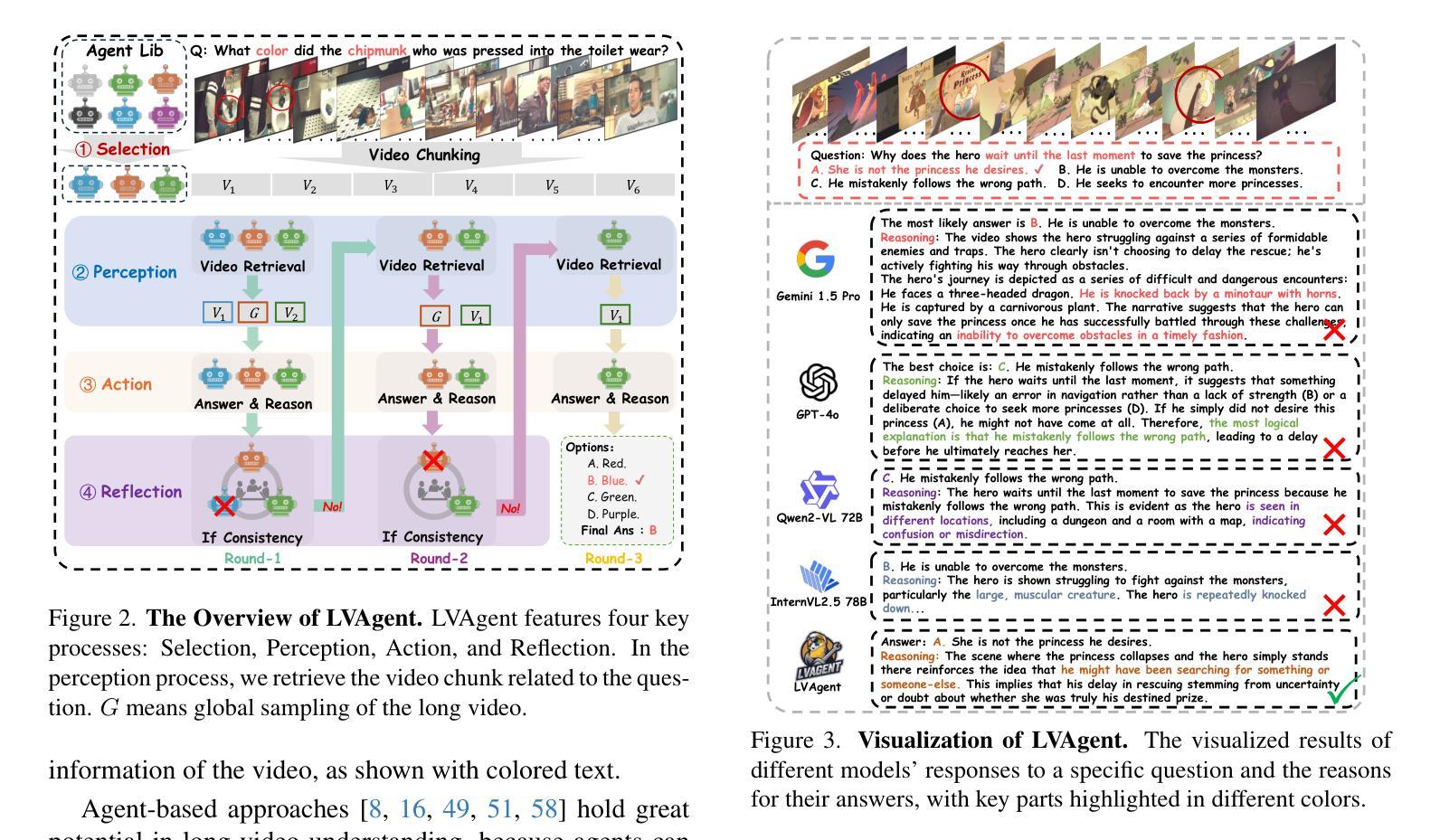
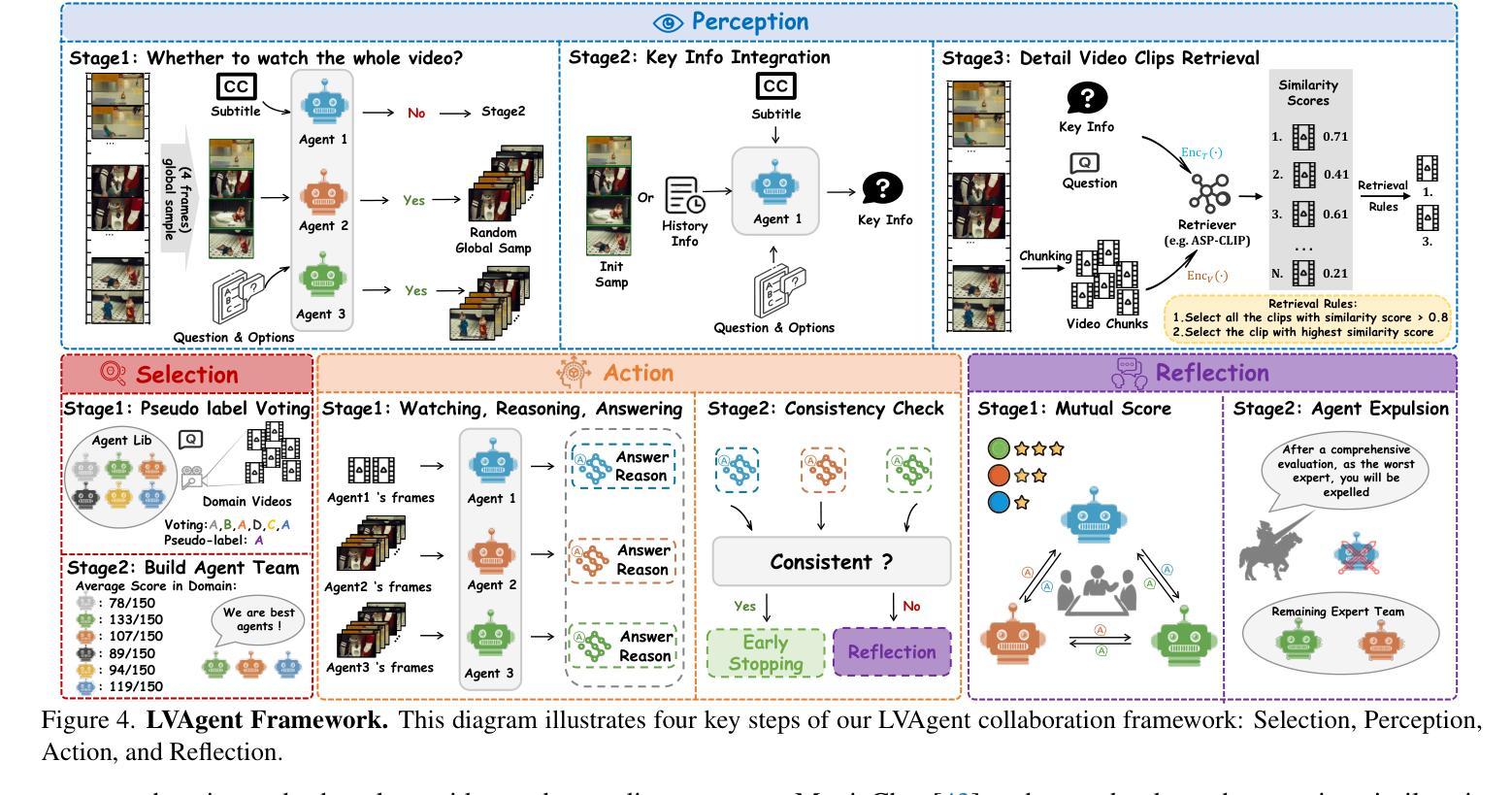
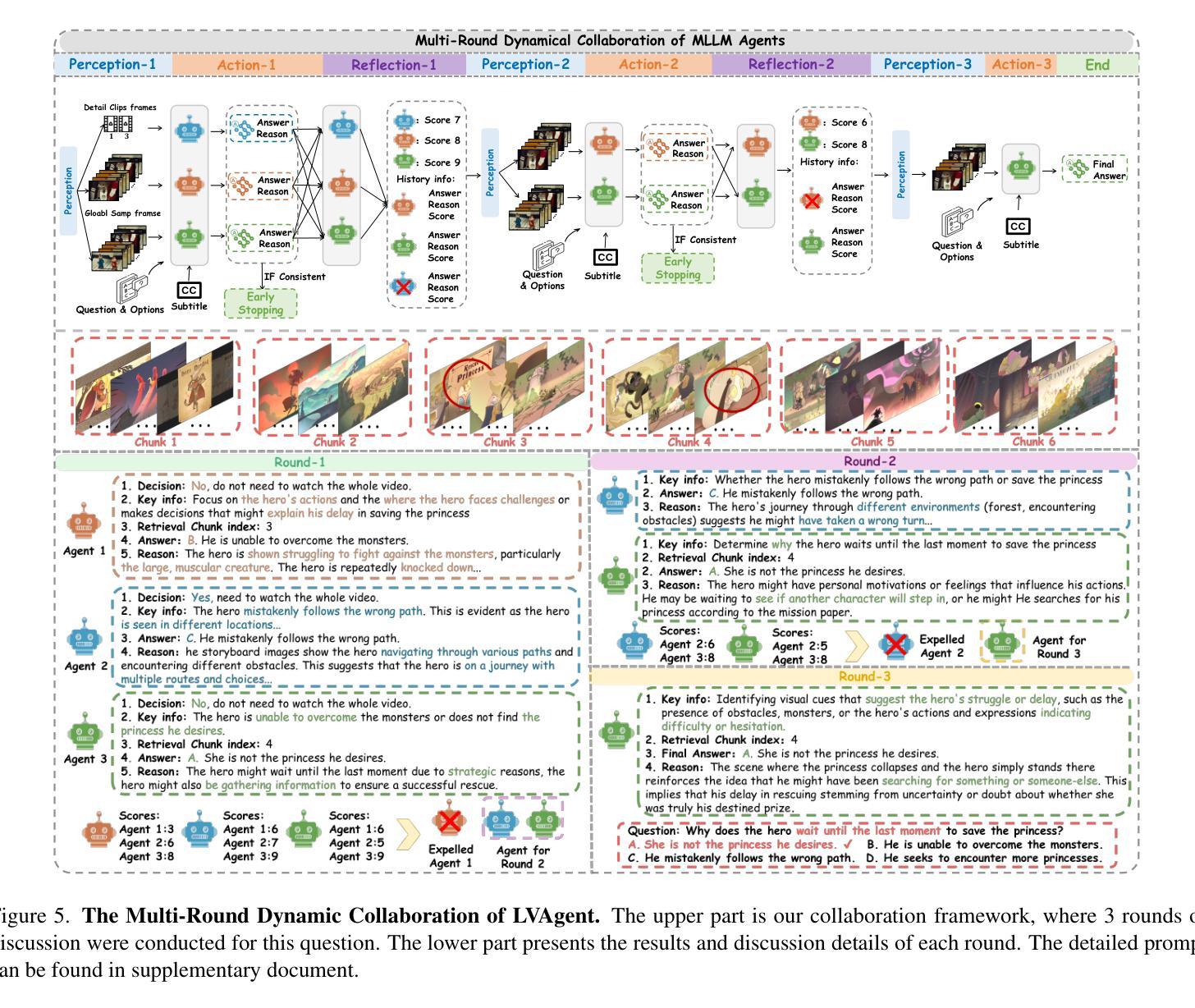
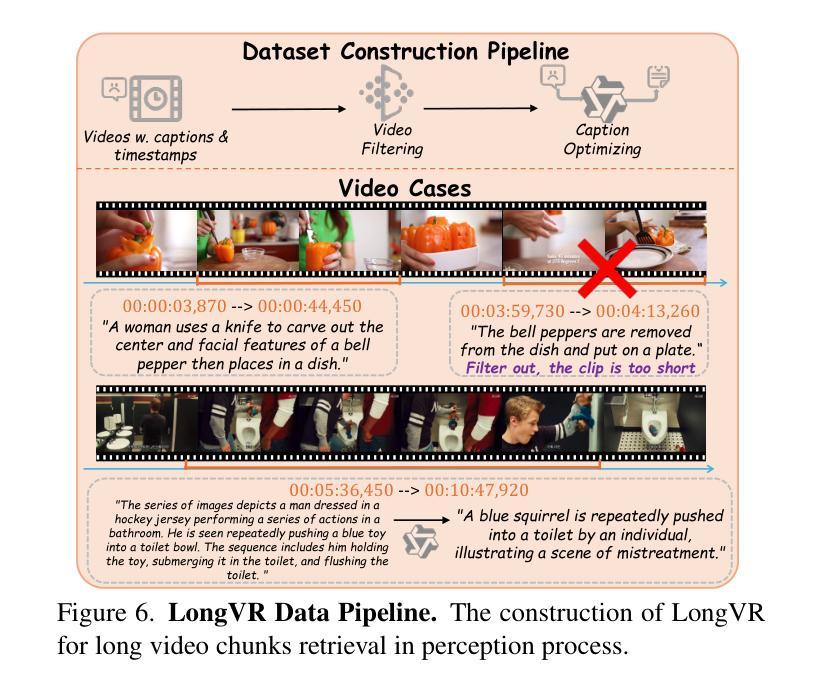
LVAgent: Long Video Understanding by Multi-Round Dynamical Collaboration of MLLM Agents
Authors:Boyu Chen, Zhengrong Yue, Siran Chen, Zikang Wang, Yang Liu, Peng Li, Yali Wang
Existing MLLMs encounter significant challenges in modeling the temporal context within long videos. Currently, mainstream Agent-based methods use external tools to assist a single MLLM in answering long video questions. Despite such tool-based support, a solitary MLLM still offers only a partial understanding of long videos, resulting in limited performance. In order to better address long video tasks, we introduce LVAgent, the first framework enabling multi-round dynamic collaboration of MLLM agents in long video understanding. Our method consists of four key steps: 1) Selection: We pre-select appropriate agents from the model library to form optimal agent teams based on different tasks. 2) Perception: We design an effective retrieval scheme for long videos to improve the coverage of critical temporal segments while maintaining computational efficiency. 3) Action: Agents answer long video questions and exchange reasons. 4) Reflection: We evaluate each agent’s performance in each round of discussion and optimize the agent team for dynamic collaboration. The agents iteratively refine their answers by multi-round dynamical collaboration of MLLM agents. LVAgent is the first agent system method that outperforms all closed-source models (like GPT-4o) and open-source models (like InternVL-2.5 and Qwen2-VL) in the long video understanding tasks. Our LVAgent achieves an accuracy of 80% on four mainstream long video understanding tasks. Notably, LVAgent improves accuracy by 13.3% on LongVideoBench. Code is available at https://github.com/64327069/LVAgent.
现有大型多模态语言模型(MLLMs)在模拟长视频中的时间上下文时面临重大挑战。目前主流的基于代理的方法使用外部工具来辅助单个MLLM回答长视频问题。尽管有基于工具的支持,单个MLLM仍然只能对长视频有局部理解,导致性能有限。为了更好地处理长视频任务,我们引入了LVAgent,这是第一个使多个MLLM代理在长视频理解中进行多轮动态协作的框架。我们的方法包括四个关键步骤:1)选择:我们从模型库中预先选择适当的代理,根据不同的任务形成最优代理团队。2)感知:我们为长视频设计了一种有效的检索方案,旨在提高关键时间段的覆盖率,同时保持计算效率。3)行动:代理回答长视频问题并交流理由。4)反思:我们评估每个代理在每轮讨论中的表现,优化代理团队以进行动态协作。通过MLLM代理的多轮动态协作,代理们可以迭代优化答案。LVAgent是首个在长视频理解任务中表现优于所有闭源模型(如GPT-4o)和开源模型(如InternVL-2.5和Qwen2-VL)的代理系统方法。我们的LVAgent在四个主流的长视频理解任务上达到了80%的准确率。值得注意的是,LVAgent在LongVideoBench上的准确率提高了13.3%。代码可在https://github.com/64327069/LVAgent上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted in ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在处理长视频理解任务时,现有MLLM面临的挑战。为此,提出了一种新的框架LVAgent,它通过多轮动态协作的MLLM代理来实现对长视频的更好理解。LVAgent包括选择、感知、行动和反思四个关键步骤,并能在长视频理解任务中取得优异性能,准确率高达80%。
Key Takeaways
- MLLM在处理长视频理解任务时存在挑战,需要更全面的模型架构来解决。
- LVAgent是首个实现多轮动态协作的MLLM代理框架,用于长视频理解。
- LVAgent包括选择、感知、行动和反思四个关键步骤,以提高对长视频的理解。
- LVAgent通过优化代理团队和动态协作,实现了对长视频的全面理解。
- LVAgent在主流的长视频理解任务上取得了显著的性能提升,准确率高达80%。
- LVAgent相较于闭源模型(如GPT-4o)和开源模型(如InternVL-2.5和Qwen2-VL)具有更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图