⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
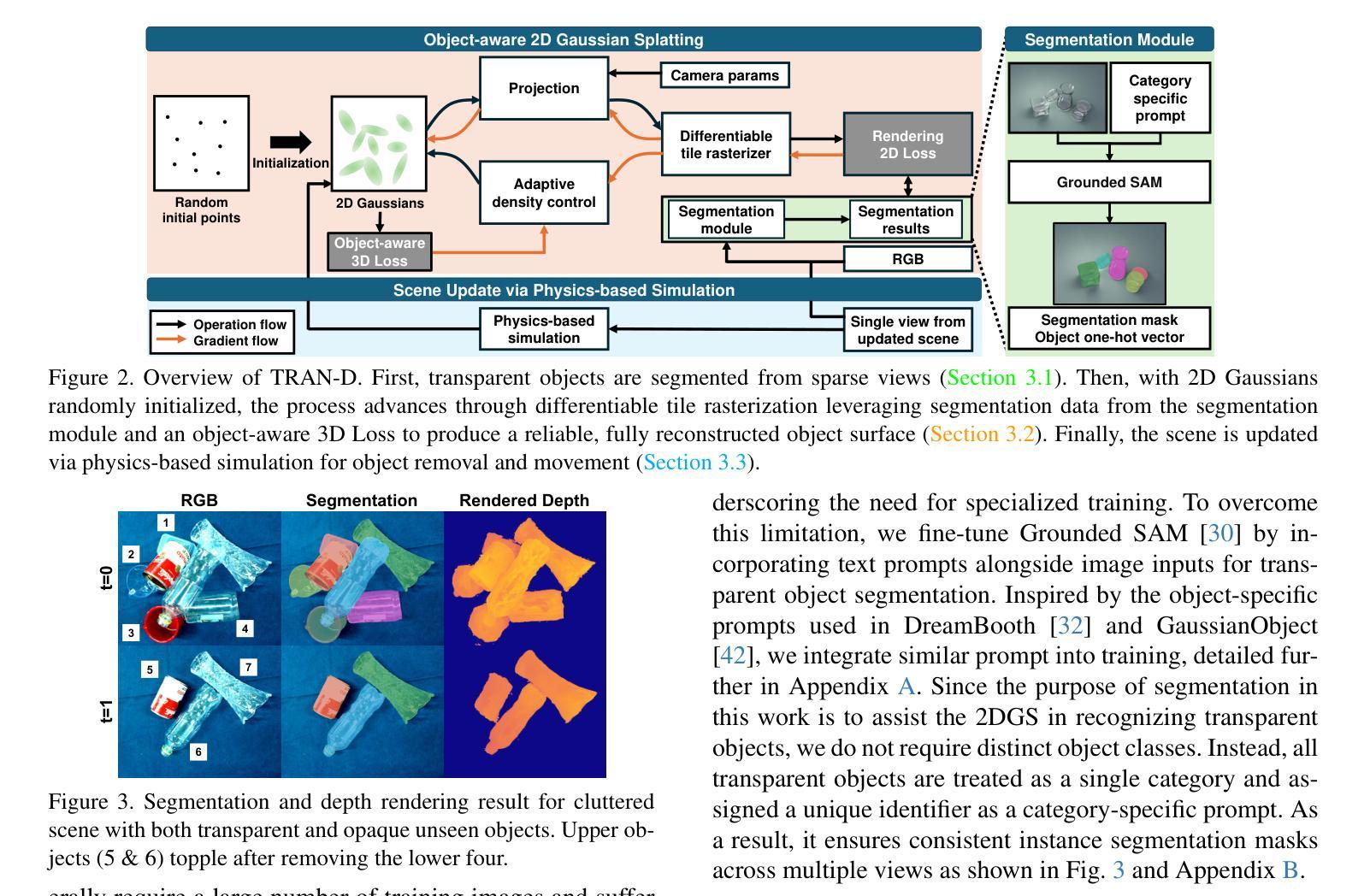
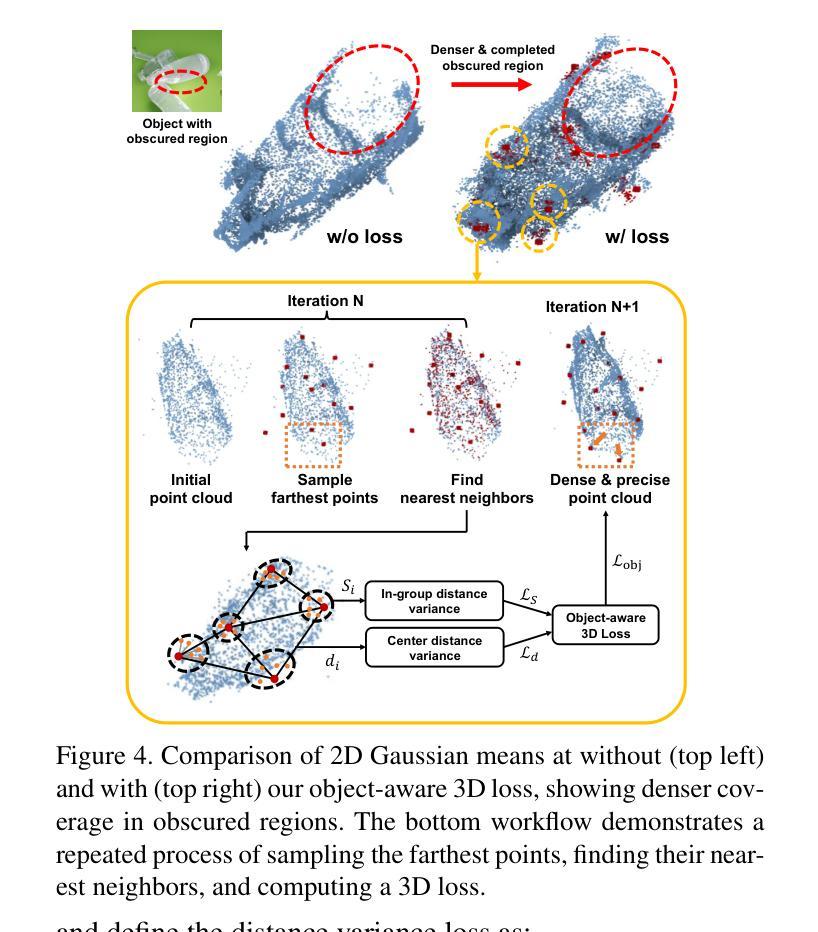
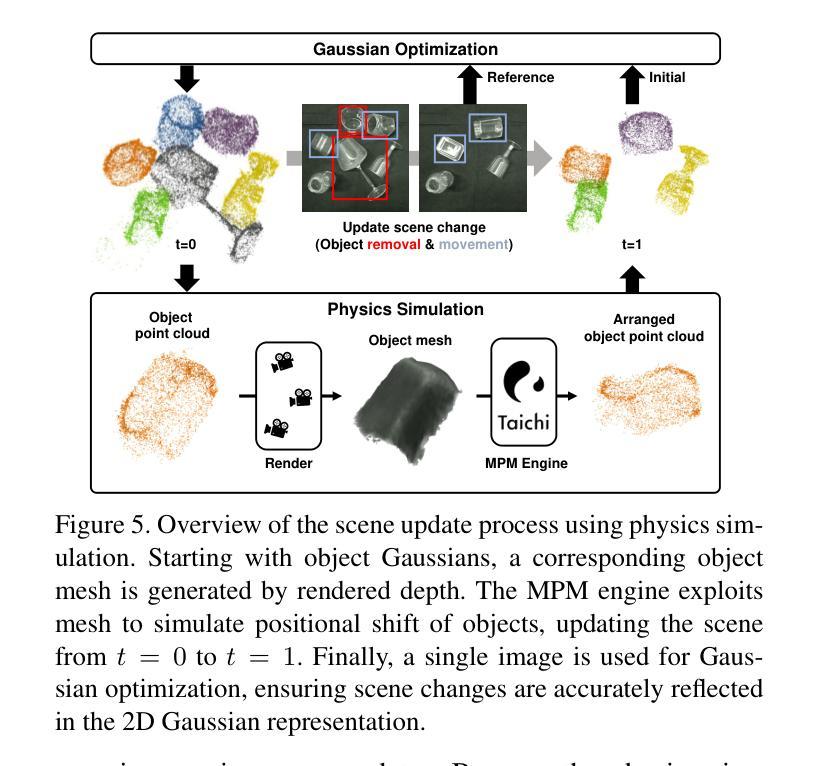
TRAN-D: 2D Gaussian Splatting-based Sparse-view Transparent Object Depth Reconstruction via Physics Simulation for Scene Update
Authors:Jeongyun Kim, Seunghoon Jeong, Giseop Kim, Myung-Hwan Jeon, Eunji Jun, Ayoung Kim
Understanding the 3D geometry of transparent objects from RGB images is challenging due to their inherent physical properties, such as reflection and refraction. To address these difficulties, especially in scenarios with sparse views and dynamic environments, we introduce TRAN-D, a novel 2D Gaussian Splatting-based depth reconstruction method for transparent objects. Our key insight lies in separating transparent objects from the background, enabling focused optimization of Gaussians corresponding to the object. We mitigate artifacts with an object-aware loss that places Gaussians in obscured regions, ensuring coverage of invisible surfaces while reducing overfitting. Furthermore, we incorporate a physics-based simulation that refines the reconstruction in just a few seconds, effectively handling object removal and chain-reaction movement of remaining objects without the need for rescanning. TRAN-D is evaluated on both synthetic and real-world sequences, and it consistently demonstrated robust improvements over existing GS-based state-of-the-art methods. In comparison with baselines, TRAN-D reduces the mean absolute error by over 39% for the synthetic TRansPose sequences. Furthermore, despite being updated using only one image, TRAN-D reaches a {\delta} < 2.5 cm accuracy of 48.46%, over 1.5 times that of baselines, which uses six images. Code and more results are available at https://jeongyun0609.github.io/TRAN-D/.
理解透明物体的3D几何结构从RGB图像是一项挑战,因为它们的固有物理属性,如反射和折射。为了解决这些困难,特别是在视图稀疏和动态环境场景中,我们引入了TRAN-D,一种基于二维高斯展开的新型透明物体深度重建方法。我们的关键见解在于将透明物体与背景分离,从而能够对对应于物体的高斯进行有针对性的优化。我们通过对象感知损失减轻了伪影,该损失将高斯放置在遮挡区域,确保隐形表面的覆盖,同时减少过度拟合。此外,我们采用基于物理的模拟,在短短几秒钟内对重建进行细化,有效地处理对象移除和剩余对象的连锁反应移动,无需重新扫描。TRAN-D在合成和真实世界序列上进行了评估,与基于GS的现有最先进的方法相比,它始终表现出稳健的改进。与基线相比,TRAN-D将合成TRansPose序列的平均绝对误差减少了超过3 9%。此外,尽管仅使用一张图像进行更新,但TRAN-D达到了δ<2.5 cm的精度为48.46%,这是基线使用六张图像时的1.5倍以上。代码和更多结果可在https://jeongyun0609.github.io/TRAN-D/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对透明物体从RGB图像理解其3D几何结构的问题,提出了一种新的基于二维高斯溅射的深度重建方法——TRAN-D。该方法能够分离透明物体与背景,优化对应物体的高斯分布,并减少遮挡区域的伪影。此外,还结合了物理模拟,可快速处理物体移除和剩余物体的连锁反应移动,无需重新扫描。在合成和真实世界序列上的评估表明,TRAN-D较基于高斯溅射的现有先进方法有明显改进。相较于基线方法,TRAN-D在合成TRansPose序列上的平均绝对误差降低了超过39%。尽管仅使用一张图像进行更新,但TRAN-D的精度达到了小于2.5厘米,是基线方法(使用六张图像)的1.5倍以上。
Key Takeaways
- TRAN-D是一种针对透明物体的二维高斯溅射深度重建方法。
- 通过分离透明物体与背景,实现对物体对应的高斯分布优化。
- 使用对象感知损失减少遮挡区域的伪影。
- 结合物理模拟,快速处理物体移除和连锁反应移动。
- TRAN-D在合成和真实世界序列上的表现优于现有方法。
- 在合成TRansPose序列上,TRAN-D较基线方法的平均绝对误差降低了超过39%。
点此查看论文截图


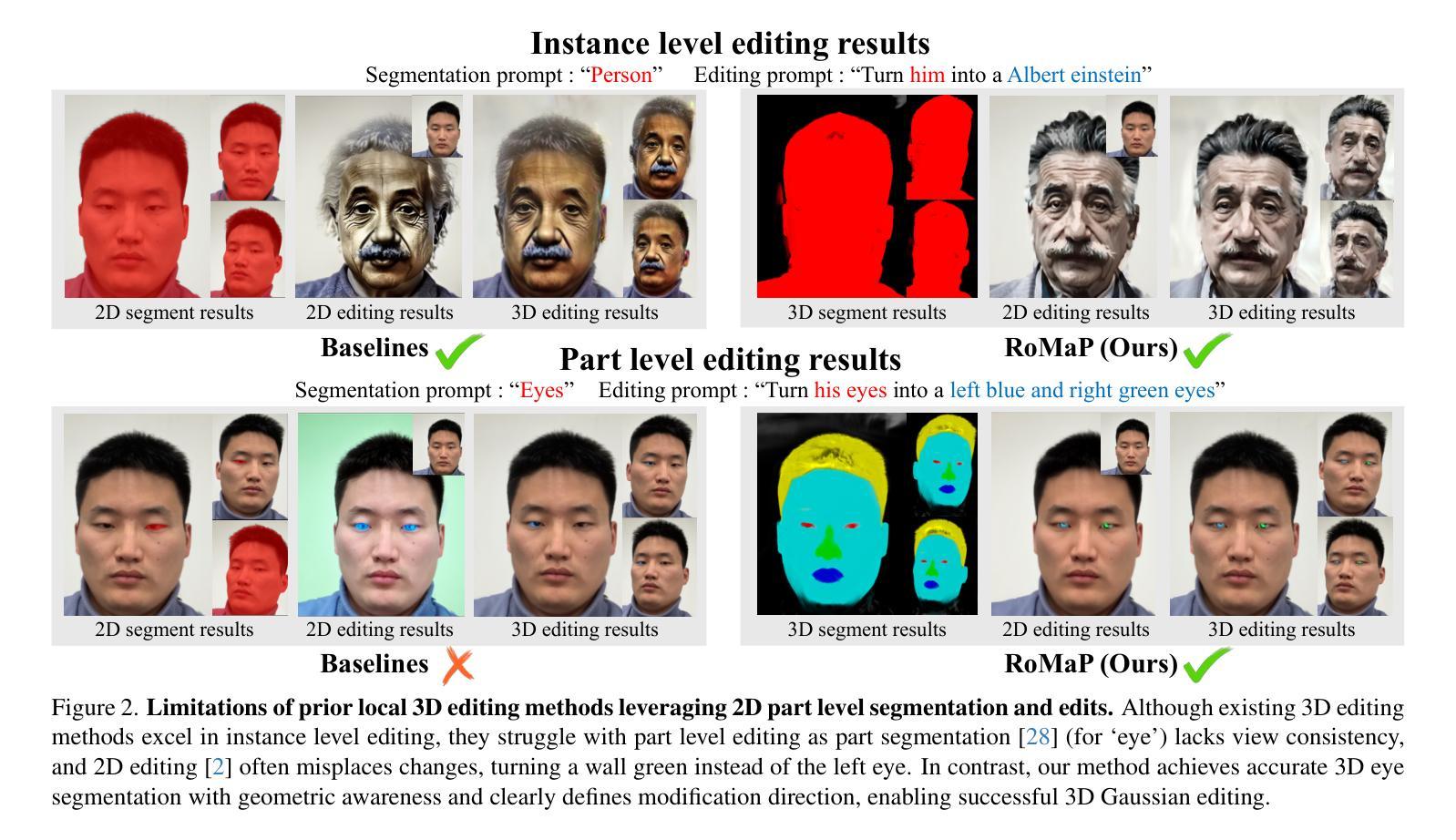
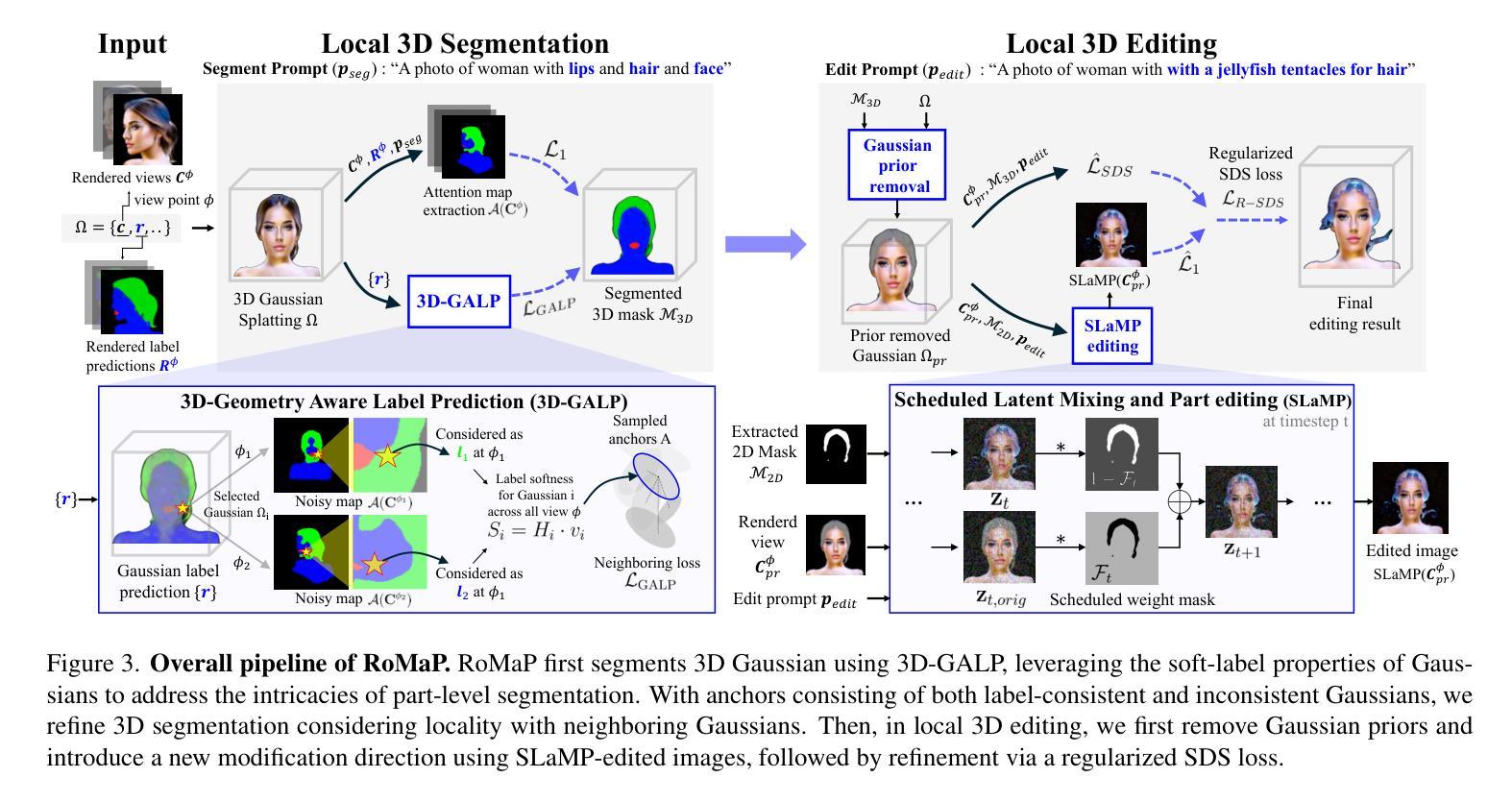
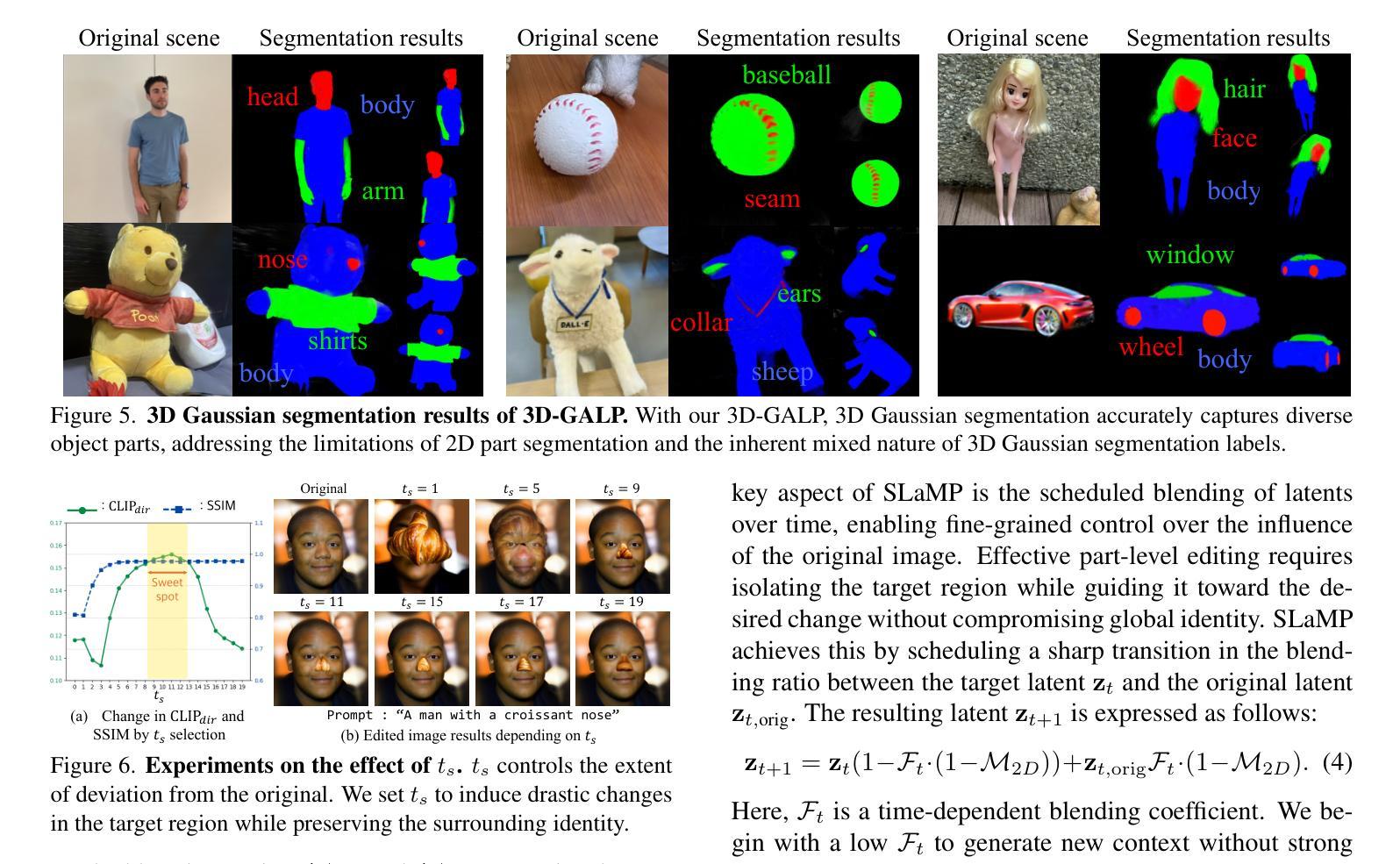
Robust 3D-Masked Part-level Editing in 3D Gaussian Splatting with Regularized Score Distillation Sampling
Authors:Hayeon Kim, Ji Ha Jang, Se Young Chun
Recent advances in 3D neural representations and instance-level editing models have enabled the efficient creation of high-quality 3D content. However, achieving precise local 3D edits remains challenging, especially for Gaussian Splatting, due to inconsistent multi-view 2D part segmentations and inherently ambiguous nature of Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss. To address these limitations, we propose RoMaP, a novel local 3D Gaussian editing framework that enables precise and drastic part-level modifications. First, we introduce a robust 3D mask generation module with our 3D-Geometry Aware Label Prediction (3D-GALP), which uses spherical harmonics (SH) coefficients to model view-dependent label variations and soft-label property, yielding accurate and consistent part segmentations across viewpoints. Second, we propose a regularized SDS loss that combines the standard SDS loss with additional regularizers. In particular, an L1 anchor loss is introduced via our Scheduled Latent Mixing and Part (SLaMP) editing method, which generates high-quality part-edited 2D images and confines modifications only to the target region while preserving contextual coherence. Additional regularizers, such as Gaussian prior removal, further improve flexibility by allowing changes beyond the existing context, and robust 3D masking prevents unintended edits. Experimental results demonstrate that our RoMaP achieves state-of-the-art local 3D editing on both reconstructed and generated Gaussian scenes and objects qualitatively and quantitatively, making it possible for more robust and flexible part-level 3D Gaussian editing.
最近,三维神经表征和实例级编辑模型的进步使得高质量的三维内容创作效率大大提高。然而,实现精确局部三维编辑仍然是一个挑战,尤其是在高斯拼贴技术中,由于多视角二维部分分割的不一致性和得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失的本质模糊性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了RoMaP,这是一种新型局部三维高斯编辑框架,能够实现精确且大幅的部分级修改。首先,我们引入了一个稳健的三维掩膜生成模块,配合我们的三维几何感知标签预测(3D-GALP),使用球面谐波(SH)系数来建模视图相关的标签变化和软标签属性,从而在各个视点上实现准确且一致的部分分割。其次,我们提出了一种正则化的SDS损失,它将标准SDS损失与额外的正则化器相结合。特别是,我们通过计划的潜在混合和部分(SLaMP)编辑方法引入了L1锚损失,该方法生成高质量的部分编辑二维图像,并将修改限制在目标区域,同时保留上下文连贯性。额外的正则化器,如高斯先验移除,通过允许超出现有上下文的更改来提高灵活性,而稳健的三维掩膜则防止了意外的编辑。实验结果表明,我们的RoMaP在重建和生成的高斯场景和对象上实现了先进的三维局部编辑效果,无论是从主观质量评估还是定量评估方面。这为更稳健和灵活的部分级三维高斯编辑提供了可能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为RoMaP的新型局部3D高斯编辑框架,解决了精确局部3D编辑的难题。通过引入基于3D几何感知标签预测的掩膜生成模块,并采用正则化的SDS损失函数,实现了精确的局部修改。实验结果显示,RoMaP框架在重建和生成的Gaussian场景和对象上实现了先进的局部3D编辑效果,使得鲁棒性和灵活的局部级别3D高斯编辑成为可能。
Key Takeaways
- RoMaP框架解决了精确局部3D编辑的难题,尤其是在高斯绘图领域。
- 提出了一种基于3D几何感知标签预测的掩膜生成模块,能够准确且一致地分割跨不同视角的部分。
- 引入了一种正则化的SDS损失函数,结合了标准SDS损失和其他额外的正则器。
- L1锚损失通过特定的Scheduled Latent Mixing和Part(SLaMP)编辑方法引入,可以生成高质量的部分编辑后的2D图像并保持上下文连贯性。
- 通过引入高斯先验移除和其他附加正则化技术,提高了框架的灵活性和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


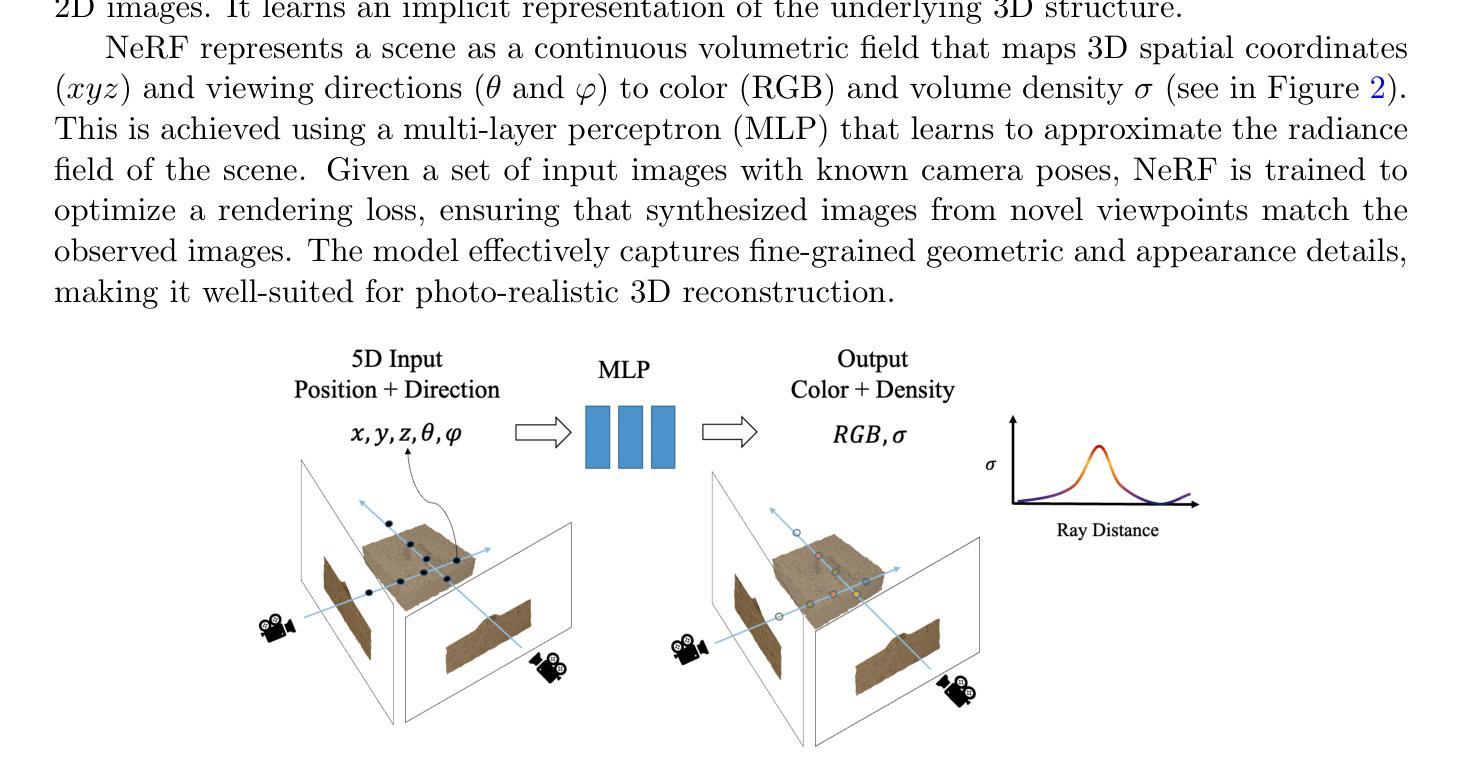
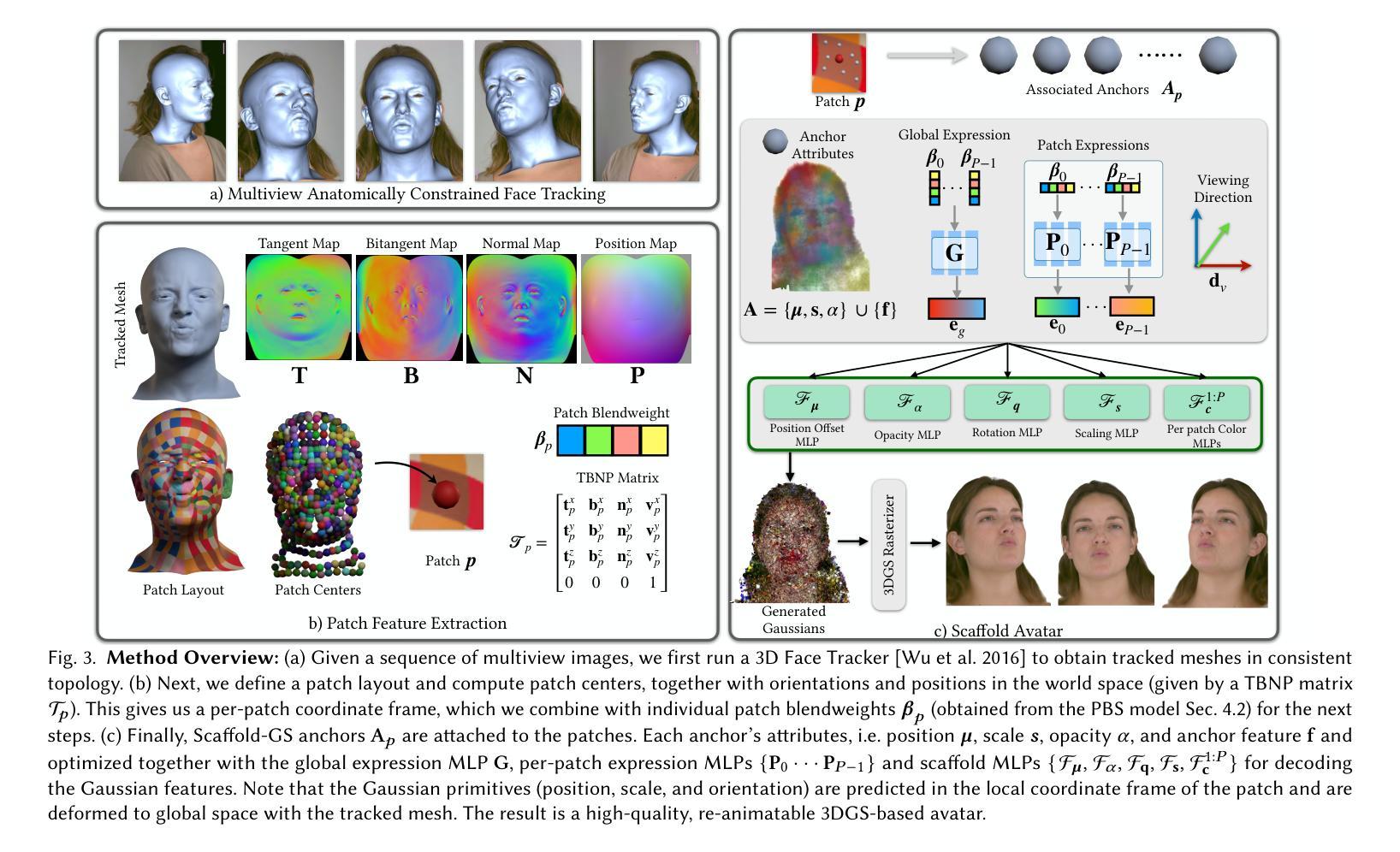
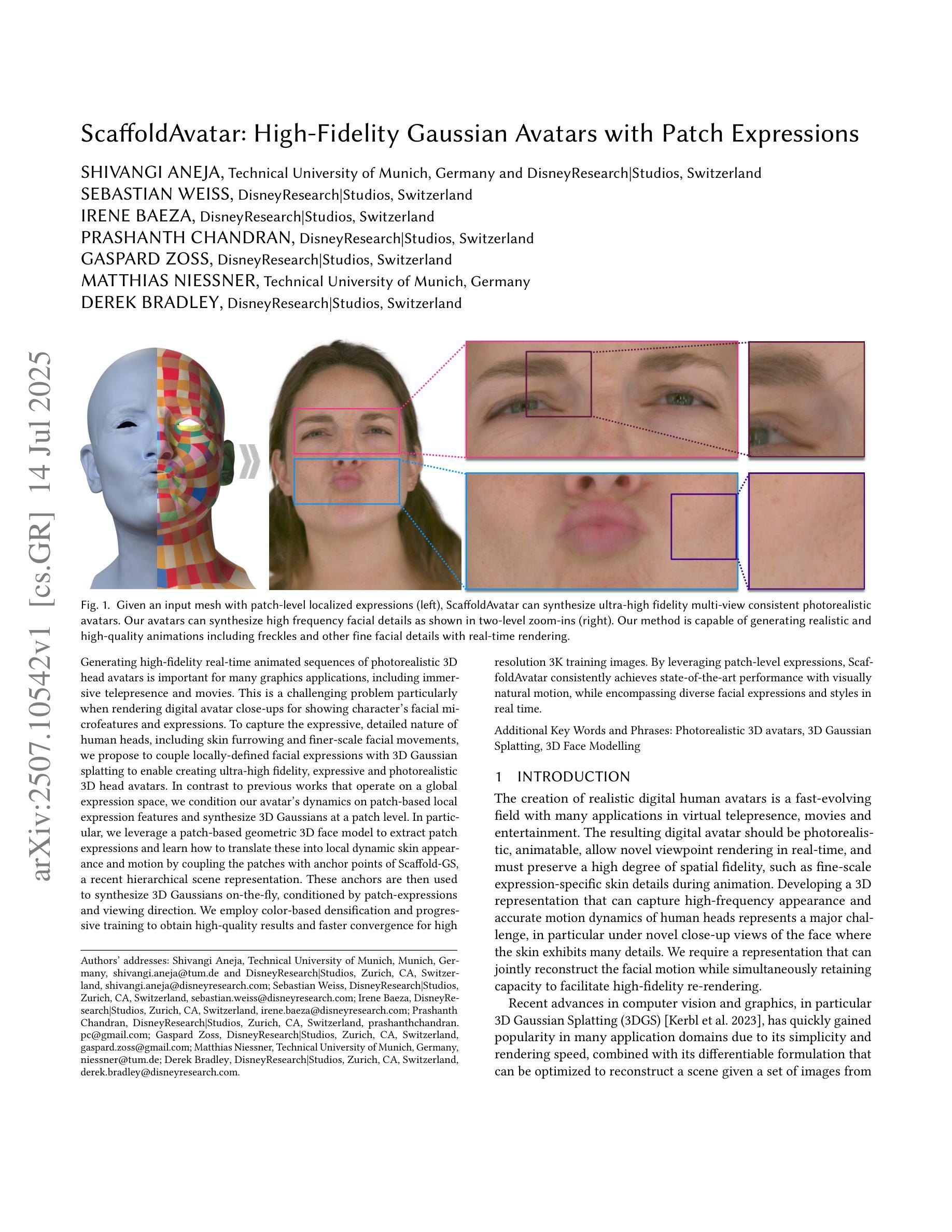
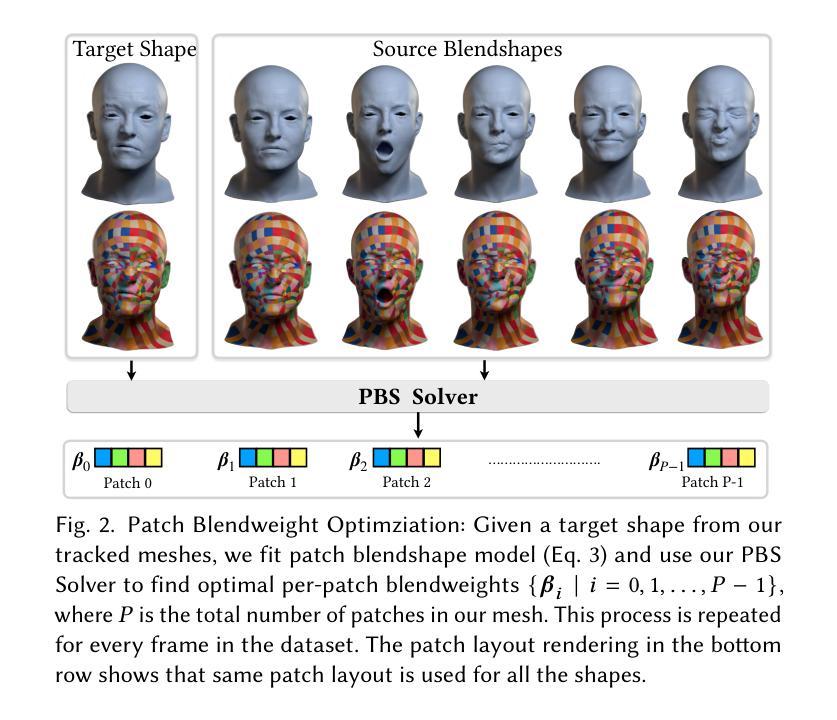
ScaffoldAvatar: High-Fidelity Gaussian Avatars with Patch Expressions
Authors:Shivangi Aneja, Sebastian Weiss, Irene Baeza, Prashanth Chandran, Gaspard Zoss, Matthias Nießner, Derek Bradley
Generating high-fidelity real-time animated sequences of photorealistic 3D head avatars is important for many graphics applications, including immersive telepresence and movies. This is a challenging problem particularly when rendering digital avatar close-ups for showing character’s facial microfeatures and expressions. To capture the expressive, detailed nature of human heads, including skin furrowing and finer-scale facial movements, we propose to couple locally-defined facial expressions with 3D Gaussian splatting to enable creating ultra-high fidelity, expressive and photorealistic 3D head avatars. In contrast to previous works that operate on a global expression space, we condition our avatar’s dynamics on patch-based local expression features and synthesize 3D Gaussians at a patch level. In particular, we leverage a patch-based geometric 3D face model to extract patch expressions and learn how to translate these into local dynamic skin appearance and motion by coupling the patches with anchor points of Scaffold-GS, a recent hierarchical scene representation. These anchors are then used to synthesize 3D Gaussians on-the-fly, conditioned by patch-expressions and viewing direction. We employ color-based densification and progressive training to obtain high-quality results and faster convergence for high resolution 3K training images. By leveraging patch-level expressions, ScaffoldAvatar consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance with visually natural motion, while encompassing diverse facial expressions and styles in real time.
生成高保真实时动画序列的光照真实三维头像对于许多图形应用程序非常重要,包括沉浸式远程存在和电影。这是一个具有挑战性的问题,尤其是在渲染数字头像特写以展示角色的面部细微特征和表情时。为了捕捉人类头部的表情和细节特征,包括皮肤褶皱和更精细的面部动作,我们提议将局部定义的面部表情与三维高斯喷涂相结合,以创建超高保真、表情丰富且光照真实的三维头像。与以前在全球表达空间上操作的工作不同,我们将头像的动态特性建立在基于补丁的局部表情特征上,并在补丁级别上合成三维高斯。特别是,我们利用基于补丁的三维几何面部模型来提取补丁表情,并学习如何将它们转化为局部动态皮肤外观和运动,通过将补丁与支架GS的锚点相结合来实现这一目标。支架是一种最新的分层场景表示。然后,这些锚点被用来即时合成受补丁表达和观察方向影响的三维高斯。我们采用基于颜色的增密和渐进训练法,以获得高质量的结果并加快对高分辨率3K训练图像的收敛速度。通过利用补丁级别的表达,支架头像一直实现了最先进的性能,具有视觉上自然的运动,同时包含实时中的多种面部表情和风格。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF (SIGGRAPH 2025) Paper Video: https://youtu.be/VyWkgsGdbkk Project Page: https://shivangi-aneja.github.io/projects/scaffoldavatar/
摘要
本文研究了基于局部定义的表情与三维高斯展平技术的高保真实时动态三维头像制作技术。该技术对于图形应用中的沉浸式远程出席和电影制作等领域具有重要意义。通过利用局部表情特征和三维高斯展平技术,能够在超高分辨率下创建具有表情和真实感的动态头像。该技术采用基于补丁的几何面部模型提取表情特征,并将这些特征转化为局部动态皮肤外观和运动。通过实时合成三维高斯图像,实现了高质量、自然运动的头像制作,具有多样化的面部表情和风格。
要点摘要
- 生成具有真实感的高保真实时动态三维头像对于图形应用至关重要。
- 技术重点研究如何在细节丰富且表达真实的头像制作中展现面部微观特征和表情。
- 提出了一种基于局部表情与三维高斯展平技术的方法,用于创建超高分辨率的头像。
- 采用基于补丁的几何面部模型提取表情特征,并转化为局部动态皮肤外观和运动。
- 利用补丁级别的锚点合成三维高斯图像,实现实时合成高质量的头像。
- 采用颜色密集化和渐进式训练技术提高头像质量和收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图

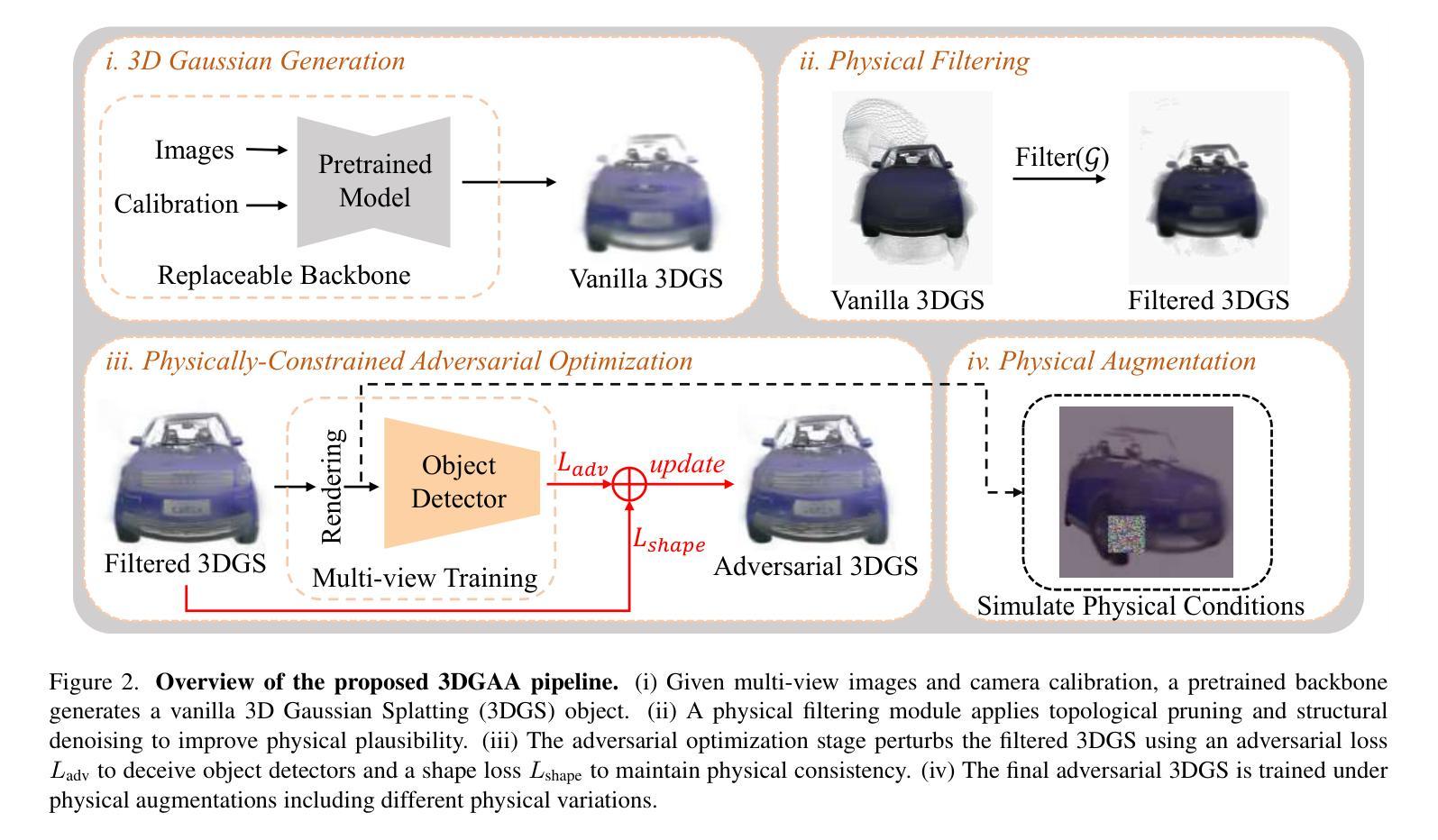
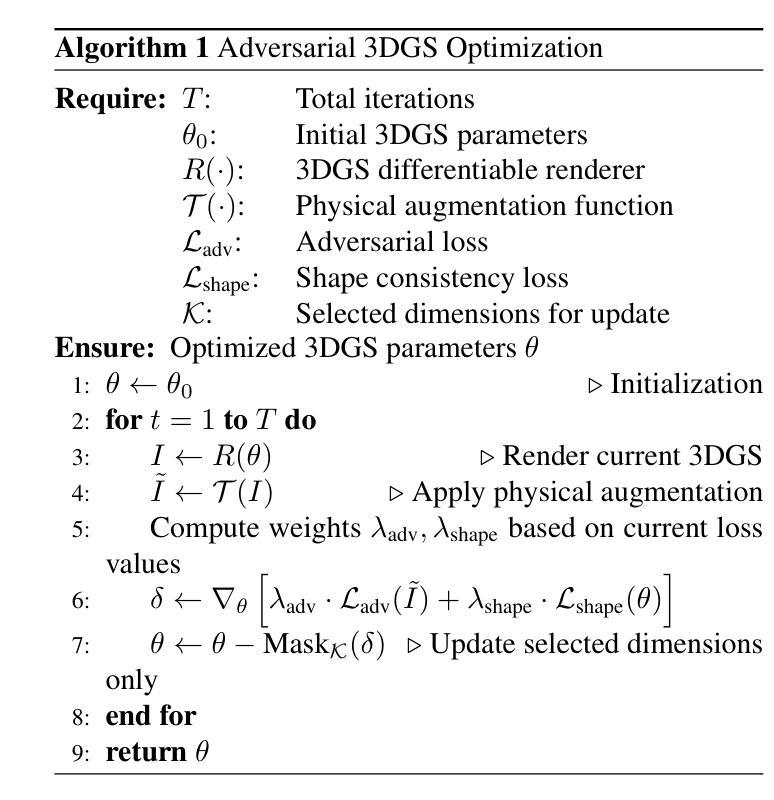
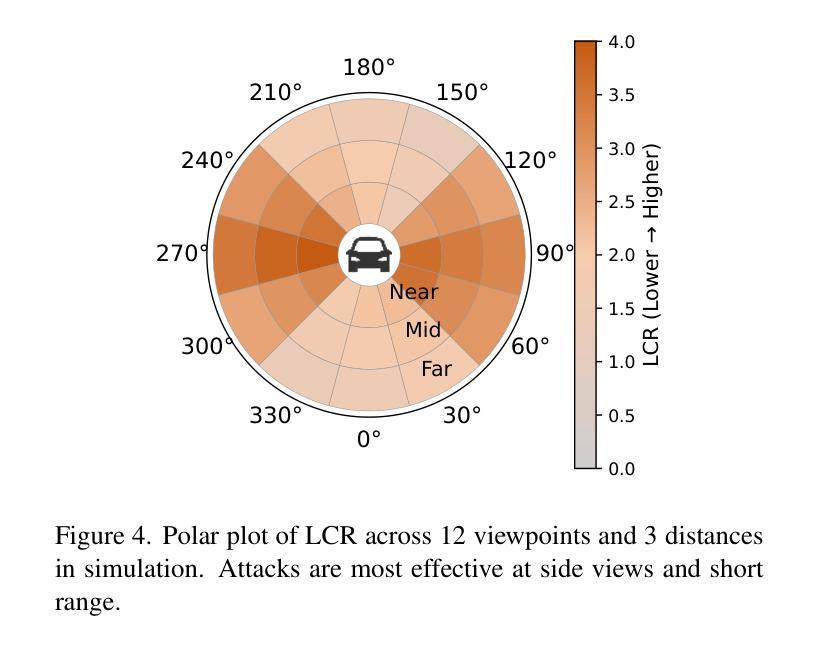
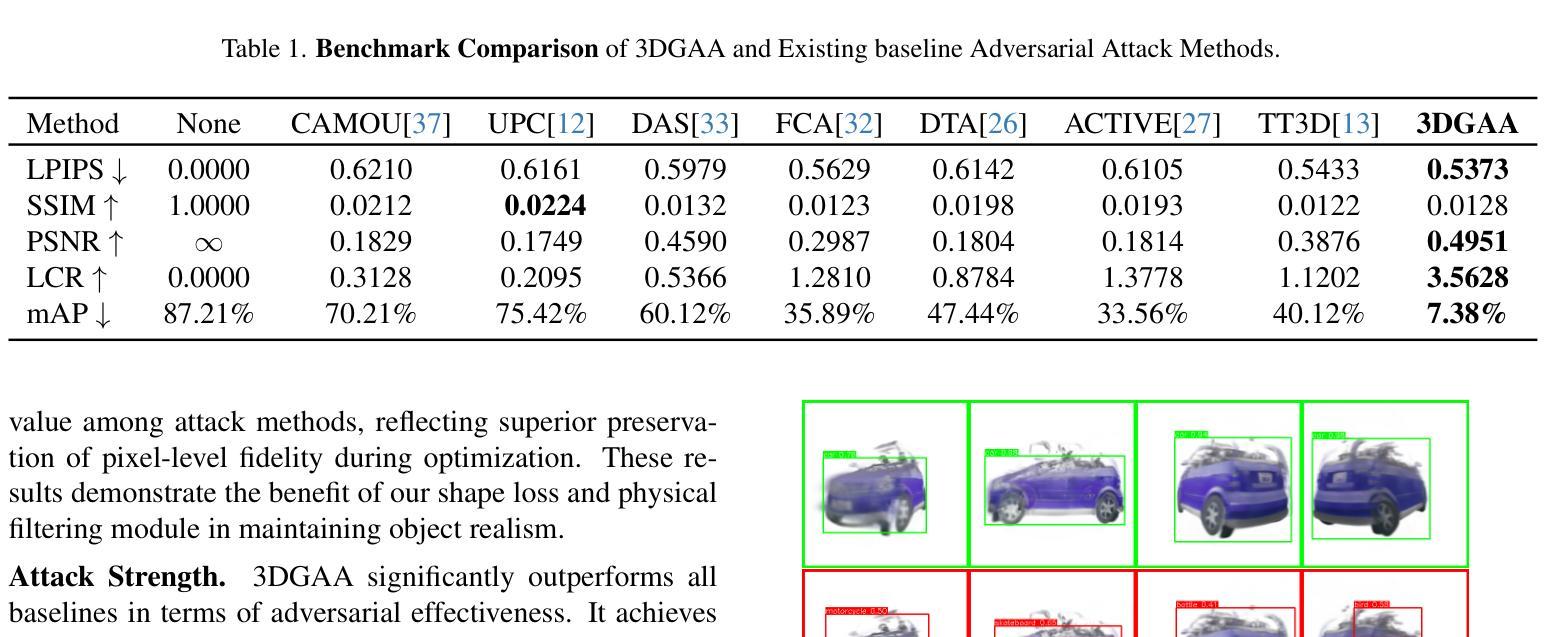
3DGAA: Realistic and Robust 3D Gaussian-based Adversarial Attack for Autonomous Driving
Authors:Yixun Zhang, Lizhi Wang, Junjun Zhao, Wending Zhao, Feng Zhou, Yonghao Dang, Jianqin Yin
Camera-based object detection systems play a vital role in autonomous driving, yet they remain vulnerable to adversarial threats in real-world environments. While existing 2D and 3D physical attacks typically optimize texture, they often struggle to balance physical realism and attack robustness. In this work, we propose 3D Gaussian-based Adversarial Attack (3DGAA), a novel adversarial object generation framework that leverages the full 14-dimensional parameterization of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to jointly optimize geometry and appearance in physically realizable ways. Unlike prior works that rely on patches or texture, 3DGAA jointly perturbs both geometric attributes (shape, scale, rotation) and appearance attributes (color, opacity) to produce physically realistic and transferable adversarial objects. We further introduce a physical filtering module to preserve geometric fidelity, and a physical augmentation module to simulate complex physical scenarios, thus enhancing attack generalization under real-world conditions. We evaluate 3DGAA on both virtual benchmarks and physical-world setups using miniature vehicle models. Experimental results show that 3DGAA achieves to reduce the detection mAP from 87.21% to 7.38%, significantly outperforming existing 3D physical attacks. Moreover, our method maintains high transferability across different physical conditions, demonstrating a new state-of-the-art in physically realizable adversarial attacks. These results validate 3DGAA as a practical attack framework for evaluating the safety of perception systems in autonomous driving.
基于摄像头的物体检测系统对自动驾驶起着至关重要的作用,但在现实世界中,它们仍面临对抗性威胁的脆弱性。尽管现有的2D和3D物理攻击通常优化纹理,但它们往往难以在物理真实性和攻击稳健性之间取得平衡。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于3D高斯的对抗攻击(3DGAA),这是一种新型的对抗性物体生成框架,它利用3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)的14维参数化,以物理可实现的方式联合优化几何和外观。不同于以往依赖于补丁或纹理的工作,3DGAA同时扰动几何属性(形状、尺度、旋转)和外观属性(颜色、透明度),以产生物理真实且可迁移的对抗性物体。我们进一步引入物理滤波模块以保持几何保真度,并引入物理增强模块来模拟复杂的物理场景,从而增强现实条件下的攻击通用性。我们在虚拟基准测试和物理环境设置中使用小型车辆模型对3DGAA进行了评估。实验结果表明,3DGAA将检测mAP从87.21%降低到7.38%,显著优于现有3D物理攻击。此外,我们的方法在不同物理条件下保持了高可迁移性,在物理可实现的对抗攻击方面展现了最新的技术水平。这些结果验证了3DGAA作为评估自动驾驶感知系统安全的实际攻击框架的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to WACV 2026
摘要
本文提出了一种基于三维高斯(3DGAA)的新型对抗性攻击框架,该框架利用三维高斯展开(3DGS)的完整十四维参数化来联合优化几何和外观,以物理可实现的方式实现。不同于依赖补丁或纹理的先前工作,它通过联合扰动几何属性和外观属性来生成物理真实的对抗性物体。实验结果表明,相较于现有的三维物理攻击,本文提出的攻击框架在虚拟基准测试和物理世界设置中均表现出显著优势,将检测mAP从87.21%降低到7.38%,并且在不同物理条件下具有良好的可迁移性。这为评估自动驾驶感知系统的安全性提供了新的实用攻击框架。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新型对抗性攻击框架(3DGAA),基于三维高斯展开(3DGS)技术。
- 利用完整的十四维参数化联合优化几何和外观,实现物理真实的对抗性物体生成。
- 通过扰动几何属性和外观属性联合生成对抗性物体,突破了传统攻击方法的局限。
- 引入物理过滤模块以保持几何保真度,并引入物理增强模块模拟复杂物理场景,增强了攻击在现实条件下的通用性。
- 在虚拟基准测试和物理世界设置中进行了实验验证,显著降低了目标检测性能。
- 攻击框架在不同物理条件下表现出良好的可迁移性,为评估自动驾驶感知系统安全性提供了实用工具。
点此查看论文截图


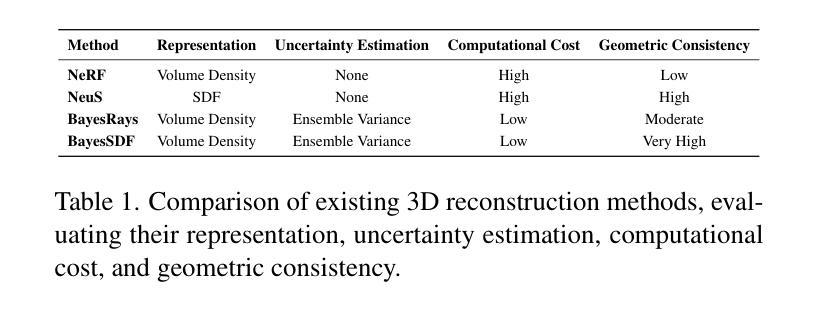
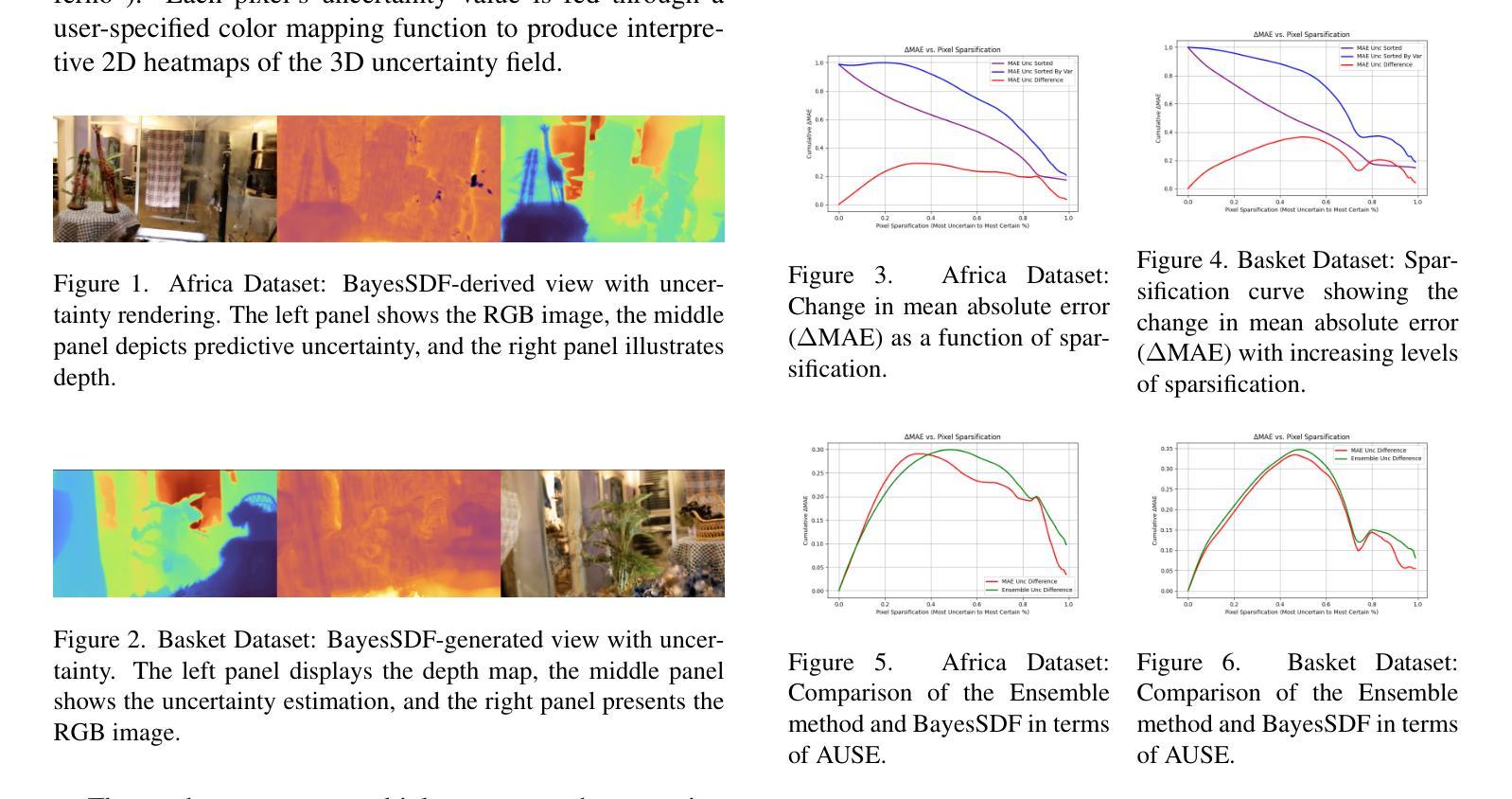
BayesSDF: Surface-Based Laplacian Uncertainty Estimation for 3D Geometry with Neural Signed Distance Fields
Authors:Rushil Desai
Quantifying uncertainty in neural implicit 3D representations, particularly those utilizing Signed Distance Functions (SDFs), remains a substantial challenge due to computational inefficiencies, scalability issues, and geometric inconsistencies. Existing methods typically neglect direct geometric integration, leading to poorly calibrated uncertainty maps. We introduce BayesSDF, a novel probabilistic framework for uncertainty quantification in neural implicit SDF models, motivated by scientific simulation applications with 3D environments (e.g., forests) such as modeling fluid flow through forests, where precise surface geometry and reliable uncertainty estimates are essential. Unlike radiance-based models such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian splatting, which lack explicit surface formulations, Signed Distance Functions (SDFs) define continuous and differentiable geometry, making them better suited for physical modeling and analysis. BayesSDF leverages a Laplace approximation to quantify local surface instability using Hessian-based metrics, enabling efficient, surfaceaware uncertainty estimation. Our method shows that uncertainty predictions correspond closely with poorly reconstructed geometry, providing actionable confidence measures for downstream use. Extensive evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that BayesSDF outperforms existing methods in both calibration and geometric consistency, establishing a strong foundation for uncertainty-aware 3D scene reconstruction, simulation, and robotic decision-making.
在神经隐式三维表示中量化不确定性,特别是那些使用带符号距离函数(SDFs)的表示,仍然是一个巨大的挑战,主要是由于计算效率低下、可扩展性问题以及几何不一致性问题。现有方法通常忽略了直接的几何集成,导致校准不良的不确定性映射。我们引入了BayesSDF,这是一种用于神经隐式SDF模型中不确定性量化的新型概率框架,其灵感来源于具有三维环境的科学模拟应用程序(例如森林模拟),如森林中的水流建模,其中精确的曲面几何和可靠的不确定性估计是必不可少的。与基于辐射的模型(例如神经辐射场(NeRF)或三维高斯平铺)不同,后者缺乏明确的表面公式,带符号距离函数(SDFs)定义了连续且可微分的几何形状,使其更适合物理建模和分析。BayesSDF利用拉普拉斯近似值来量化基于Hessian度量的局部表面不稳定性,从而实现高效、面向表面的不确定性估计。我们的方法表明,不确定性预测与重建不良的几何形状紧密对应,为下游应用提供了可行的置信度度量。在合成和真实数据集上的广泛评估表明,在校准和几何一致性方面,BayesSDF优于现有方法,为不确定性感知的3D场景重建、模拟和机器人决策制定建立了坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Workshops (8 Pages, 6 Figures, 2 Tables)
Summary
神经网络隐式三维表示中的不确定性量化,特别是在使用符号距离函数(SDFs)的情况下,仍然是一个巨大的挑战,因为计算效率低下、可扩展性问题以及几何不一致性。忽视直接几何集成导致不确定性映射校准不良。我们提出BayesSDF,一个用于神经网络隐式SDF模型的不确定性量化的新型概率框架,其灵感来源于需要精确表面几何和可靠不确定性估计的3D环境模拟应用(如森林中的水流)。不同于基于辐射的模型(如神经辐射场或3D高斯拼贴),符号距离函数定义连续可微的几何形状,使其更适合物理建模和分析。BayesSDF利用拉普拉斯近似值,使用基于Hessian的度量来衡量局部表面不稳定性,从而实现高效、关注表面的不确定性估计。我们的方法显示,不确定性预测与重建不良的几何形状紧密对应,为下游应用提供了可行的置信度度量。在合成和真实数据集上的大量评估表明,BayesSDF在校准和几何一致性方面优于现有方法,为不确定性感知的3D场景重建、模拟和机器人决策提供了坚实的基础。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络隐式三维表示中的不确定性量化面临计算效率、可扩展性和几何不一致性的挑战。
- 现有方法忽视直接几何集成,导致不确定性映射校准不良。
- BayesSDF是一个新型概率框架,用于神经网络隐式SDF模型的不确定性量化。
- BayesSDF适用于需要精确表面几何和可靠不确定性估计的3D环境模拟应用。
- 符号距离函数能定义连续可微的几何形状,使其更适合物理建模和分析。
- BayesSDF利用拉普拉斯近似和Hessian度量衡量局部表面不稳定性,实现高效、关注表面的不确定性估计。
点此查看论文截图

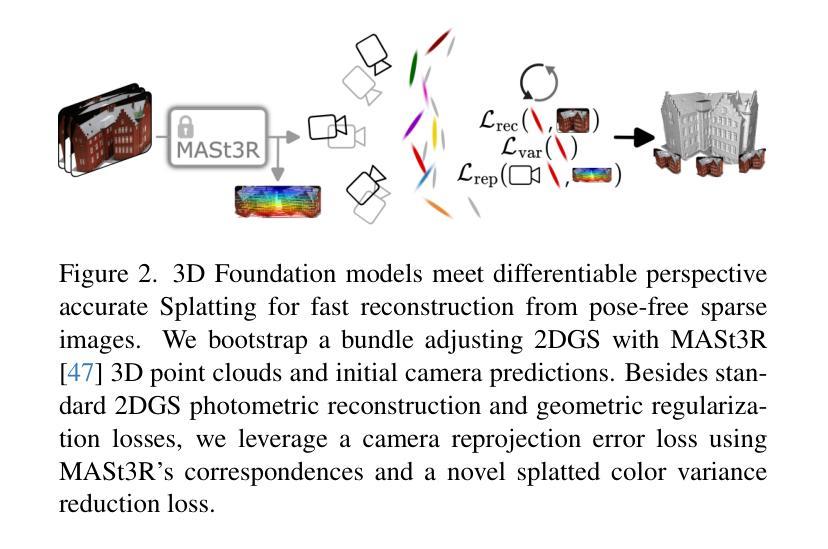
Sparfels: Fast Reconstruction from Sparse Unposed Imagery
Authors:Shubhendu Jena, Amine Ouasfi, Mae Younes, Adnane Boukhayma
We present a method for Sparse view reconstruction with surface element splatting that runs within 3 minutes on a consumer grade GPU. While few methods address sparse radiance field learning from noisy or unposed sparse cameras, shape recovery remains relatively underexplored in this setting. Several radiance and shape learning test-time optimization methods address the sparse posed setting by learning data priors or using combinations of external monocular geometry priors. Differently, we propose an efficient and simple pipeline harnessing a single recent 3D foundation model. We leverage its various task heads, notably point maps and camera initializations to instantiate a bundle adjusting 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) model, and image correspondences to guide camera optimization midst 2DGS training. Key to our contribution is a novel formulation of splatted color variance along rays, which can be computed efficiently. Reducing this moment in training leads to more accurate shape reconstructions. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performances in the sparse uncalibrated setting in reconstruction and novel view benchmarks based on established multi-view datasets.
我们提出了一种基于表面元素拼贴技术的稀疏视图重建方法,该方法在消费级GPU上运行时间不超过3分钟。尽管已有少数方法解决了从噪声或未校准的稀疏相机中学习稀疏辐射场的问题,但在这种情况下,形状恢复的探索仍然相对较少。一些辐射和形状学习测试时间优化方法通过学习数据先验或使用外部单眼几何先验的组合来解决稀疏定位设置问题。与之不同,我们提出了一种高效且简单的流程,利用最新的单一3D基础模型。我们利用其各种任务头,特别是点图和相机初始化来实例化调整束的二维高斯拼贴(2DGS)模型,并利用图像对应关系来指导2DGS训练过程中的相机优化。我们贡献的关键在于沿射线拼贴颜色方差的新公式,该公式可以高效计算。在训练中减少这一时刻会导致更准确的形状重建。我们在稀疏未校准设置下的重建和基于现有多视图数据集的新视图基准测试中展示了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page : https://shubhendu-jena.github.io/Sparfels-web/
摘要
本文提出了一种基于表面元素拼贴技术的稀疏视角重建方法,该方法在消费级GPU上运行时间不超过3分钟。尽管已有一些方法解决了稀疏辐射场学习的问题,但在噪声或无姿态稀疏相机的情况下,形状恢复的探索相对较少。我们的方法不同于现有的测试时间优化方法,这些方法通过数据先验或外部单眼几何先验的组合来解决稀疏定位设置的问题。我们提出一种高效且简单的管道,利用最新的单一3D基础模型。我们利用其各种任务头,特别是点图和相机初始化来实例化束调整二维高斯拼贴模型,并利用图像对应关系指导相机优化在二维GS训练期间。我们工作的关键创新在于沿射线拼贴颜色方差的新公式,该公式可以高效计算。在训练中减少这一时刻会导致更准确的形状重建。我们在稀疏未校准环境中展示了在重建和基于多视角数据集的新视角基准测试中的最佳性能表现。
关键见解
- 提出了一种基于表面元素拼贴技术的稀疏视角重建方法,能在消费级GPU上快速运行。
- 现有方法主要解决稀疏辐射场学习问题,而该研究在噪声或无姿态稀疏相机条件下对形状恢复的探索具有创新性。
- 与其他测试时间优化方法不同,该研究利用单一3D基础模型,利用其点图和相机初始化等任务头来实现高效重建。
- 研究中提出了沿射线拼贴颜色方差的新公式,可高效计算以提高形状重建的准确性。
- 该方法在稀疏未校准环境中的重建和新视角基准测试中表现出最佳性能。
- 利用图像对应关系来指导相机优化在二维GS训练期间的过程。
点此查看论文截图

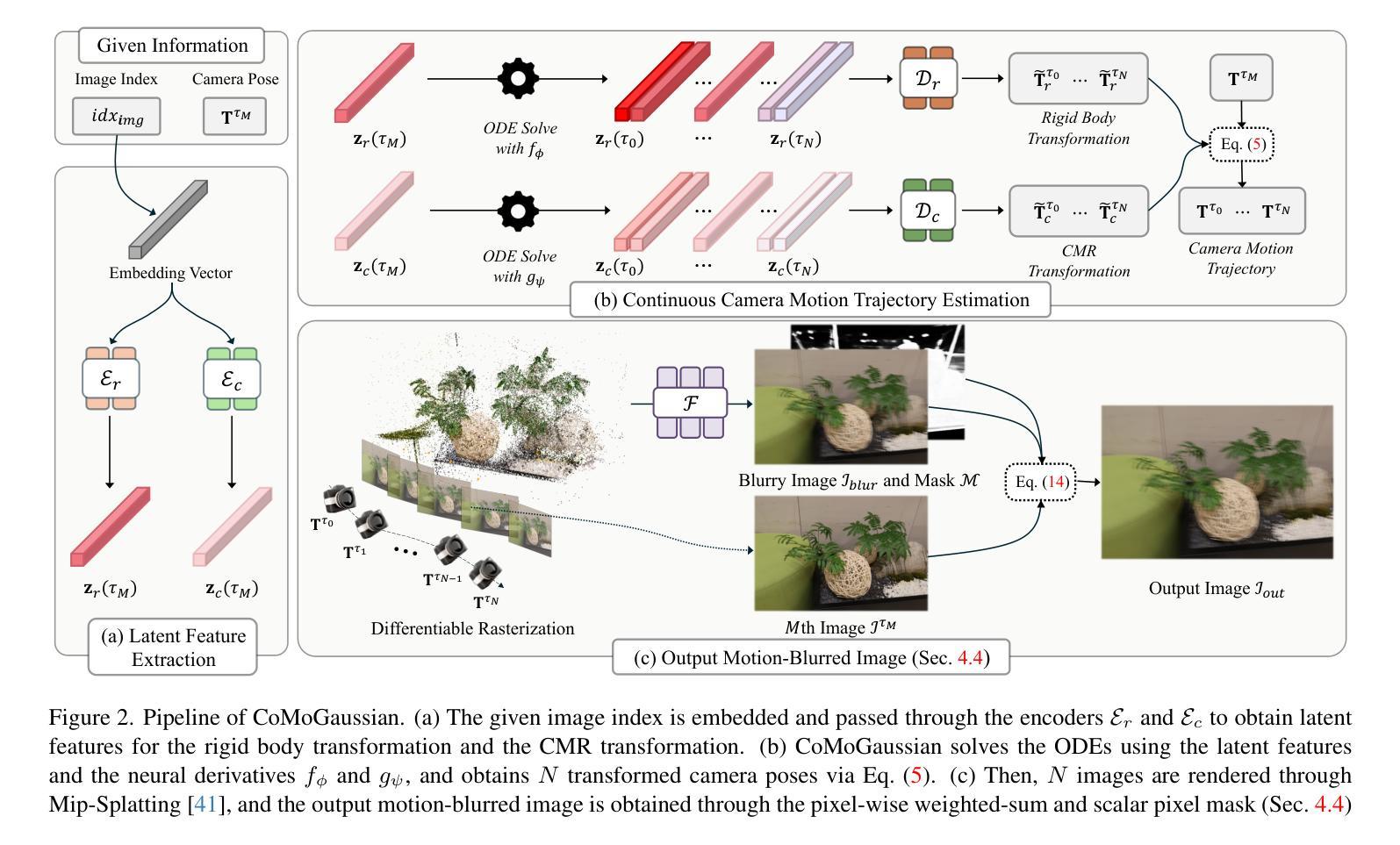
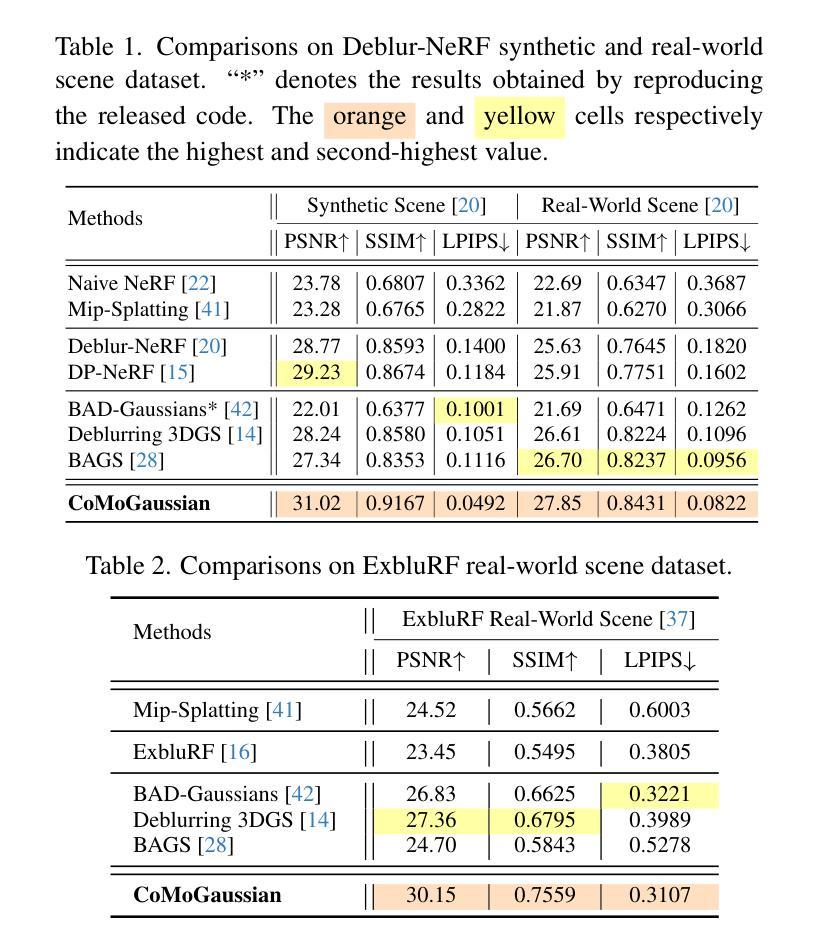
CoMoGaussian: Continuous Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting from Motion-Blurred Images
Authors:Jungho Lee, Donghyeong Kim, Dogyoon Lee, Suhwan Cho, Minhyeok Lee, Wonjoon Lee, Taeoh Kim, Dongyoon Wee, Sangyoun Lee
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention due to its high-quality novel view rendering, motivating research to address real-world challenges. A critical issue is the camera motion blur caused by movement during exposure, which hinders accurate 3D scene reconstruction. In this study, we propose CoMoGaussian, a Continuous Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting that reconstructs precise 3D scenes from motion-blurred images while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Considering the complex motion patterns inherent in real-world camera movements, we predict continuous camera trajectories using neural ordinary differential equations (ODEs). To ensure accurate modeling, we employ rigid body transformations, preserving the shape and size of the object but rely on the discrete integration of sampled frames. To better approximate the continuous nature of motion blur, we introduce a continuous motion refinement (CMR) transformation that refines rigid transformations by incorporating additional learnable parameters. By revisiting fundamental camera theory and leveraging advanced neural ODE techniques, we achieve precise modeling of continuous camera trajectories, leading to improved reconstruction accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively on benchmark datasets, which include a wide range of motion blur scenarios, from moderate to extreme blur.
3D高斯贴图技术(3DGS)因其高质量的新视角渲染而备受关注,从而激励研究者应对真实世界的挑战。一个关键问题是曝光过程中运动造成的相机运动模糊,这阻碍了准确的3D场景重建。本研究提出了CoMoGaussian,一种连续运动感知高斯贴图技术,能够从运动模糊图像重建精确的3D场景,同时保持实时渲染速度。考虑到真实世界相机运动所固有的复杂运动模式,我们使用神经常微分方程预测连续的相机轨迹。为了确保准确建模,我们采用刚体变换,保持物体的形状和大小不变,但依赖于采样帧的离散积分。为了更好地近似运动模糊的连续性,我们引入了连续运动细化(CMR)变换,通过引入额外的可学习参数来优化刚体变换。通过重新研究基本的相机理论并利用先进的神经常微分方程技术,我们实现了对连续相机轨迹的精确建模,提高了重建的准确性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在基准数据集上在定量和定性方面都达到了最新技术水平,涵盖了从轻度到重度模糊的广泛运动模糊场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Revised Version of CRiM-GS, Project Page: https://Jho-Yonsei.github.io/CoMoGaussian
Summary
本文介绍了针对相机运动模糊问题提出的连续运动感知高斯融合技术(CoMoGaussian)。该技术能够重建精确的3D场景,并维持实时渲染速度。通过利用神经常微分方程预测连续相机轨迹,并结合连续运动细化技术(CMR),实现对复杂运动模式的精确建模,从而提高了重建准确性。实验结果表明,在包含多种运动模糊场景的基准数据集上,其性能达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了三维高斯融合技术(3DGS)在新型视图渲染中的应用及其对现实世界挑战的意义。
- 强调了相机运动模糊对准确三维场景重建的影响。
- 提出了一种名为CoMoGaussian的连续运动感知高斯融合技术来解决运动模糊问题。该技术可在重建过程中维持实时渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图

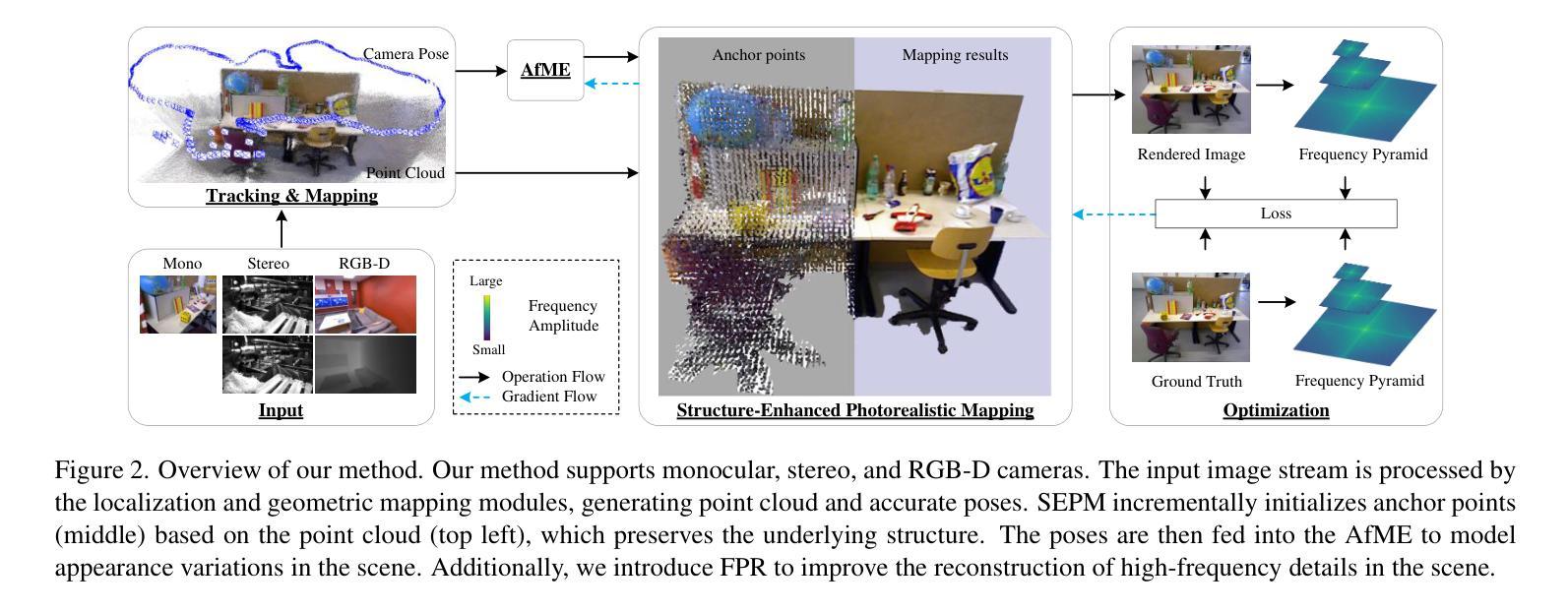
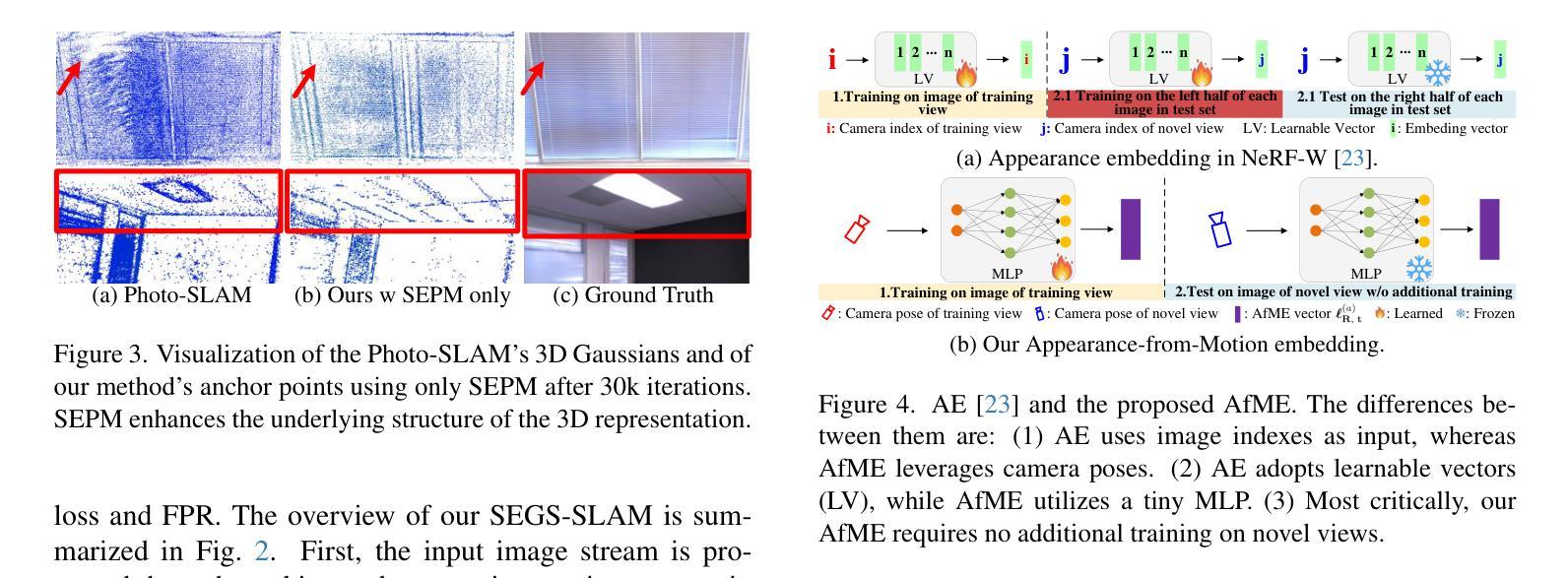
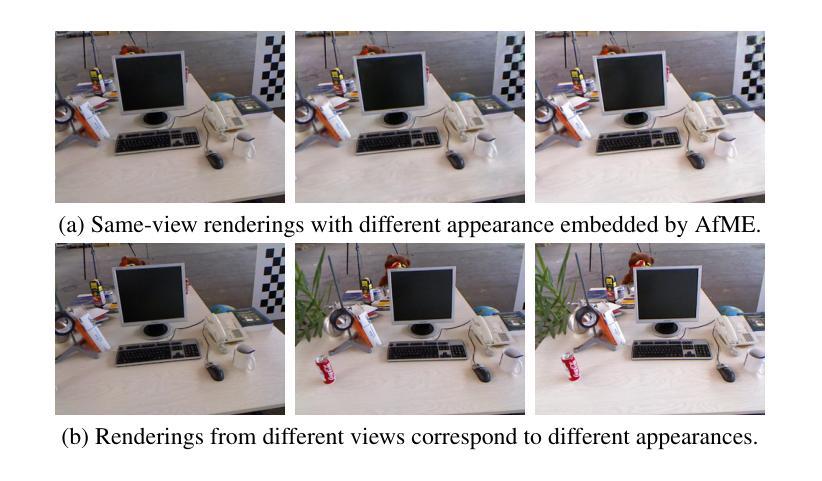
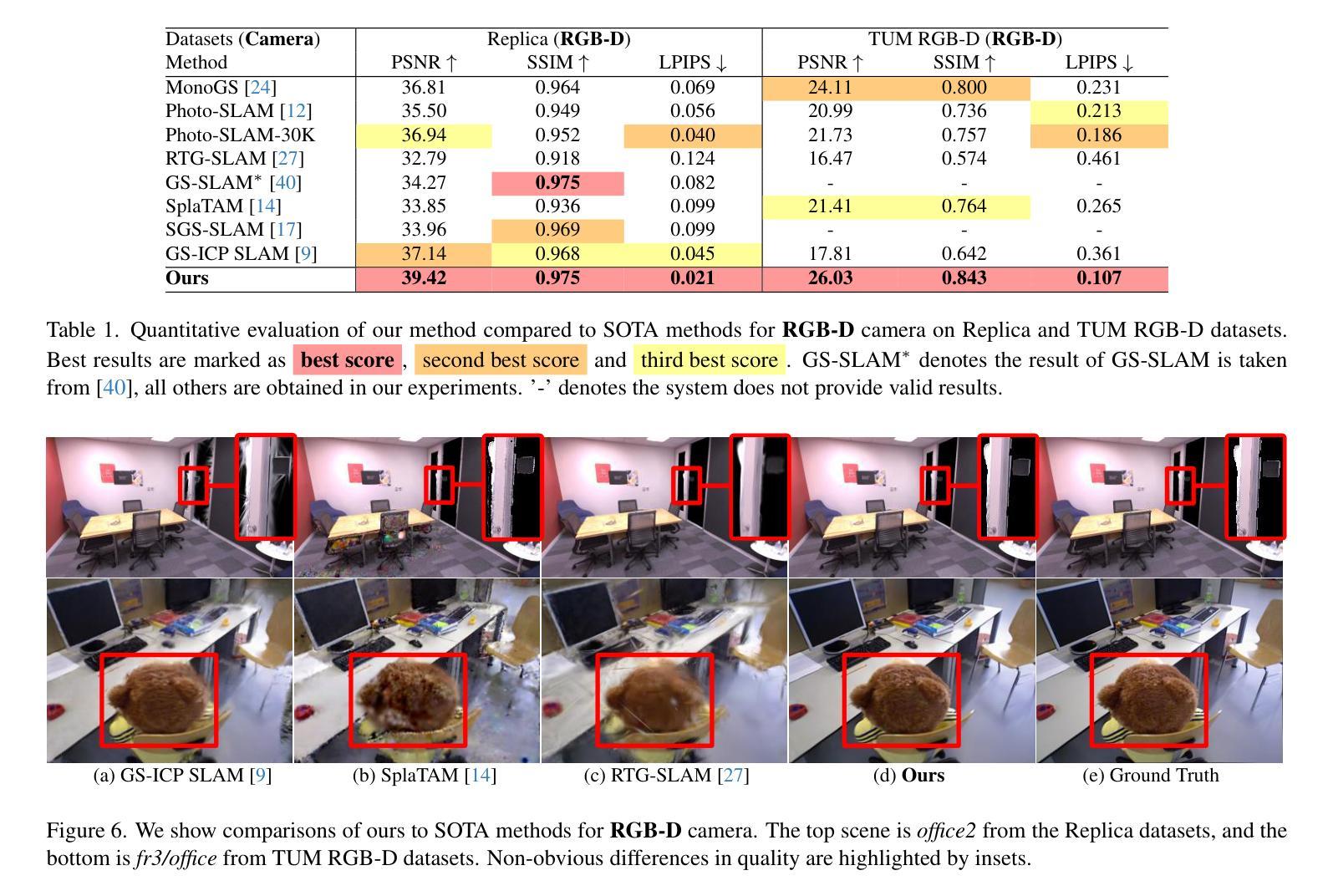
SEGS-SLAM: Structure-enhanced 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Appearance Embedding
Authors:Tianci Wen, Zhiang Liu, Yongchun Fang
3D Gaussian splatting (3D-GS) has recently revolutionized novel view synthesis in the simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) problem. However, most existing algorithms fail to fully capture the underlying structure, resulting in structural inconsistency. Additionally, they struggle with abrupt appearance variations, leading to inconsistent visual quality. To address these problems, we propose SEGS-SLAM, a structure-enhanced 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM, which achieves high-quality photorealistic mapping. Our main contributions are two-fold. First, we propose a structure-enhanced photorealistic mapping (SEPM) framework that, for the first time, leverages highly structured point cloud to initialize structured 3D Gaussians, leading to significant improvements in rendering quality. Second, we propose Appearance-from-Motion embedding (AfME), enabling 3D Gaussians to better model image appearance variations across different camera poses. Extensive experiments on monocular, stereo, and RGB-D datasets demonstrate that SEGS-SLAM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in photorealistic mapping quality, e.g., an improvement of $19.86%$ in PSNR over MonoGS on the TUM RGB-D dataset for monocular cameras. The project page is available at https://segs-slam.github.io/.
3D高斯喷溅(3D-GS)最近为同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)问题中的新型视图合成带来了革命性的变化。然而,大多数现有算法无法完全捕捉底层结构,导致结构不一致。此外,它们还难以应对突发的外观变化,导致视觉质量不一致。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了SEGS-SLAM,一种结构增强的3D高斯喷溅SLAM,实现高质量的照片级映射。我们的主要贡献有两点。首先,我们提出了结构增强的照片级映射(SEPM)框架,该框架首次利用高度结构的点云来初始化结构化3D高斯,从而在渲染质量方面实现了显著改进。其次,我们提出了运动中的外观嵌入(AfME),使3D高斯能够更好地模拟不同相机姿态下图像的外观变化。在单目、立体和RGB-D数据集上的大量实验表明,SEGS-SLAM在照片级映射质量方面显著优于最先进的方法,例如在TUM RGB-D数据集上的单目相机PSNR提高了19.86%。项目页面可在[https://segs-slam.github.io/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 accept;code, video, demos, and project are available at Project page https://segs-slam.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了SEGS-SLAM(结构增强三维高斯映射SLAM)技术,该技术解决了同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)问题中的结构不一致性问题。文章的核心技术包括利用结构化点云初始化结构化三维高斯(SEPM框架)和从运动获取外观嵌入(AfME)。在多个数据集上的实验证明SEGS-SLAM在渲染质量方面优于最新方法。文章还对技术的潜在应用领域做了介绍。关于SEGS-SLAM项目,可在官网https://segs-slam.github.io上获取更多信息。
Key Takeaways
- SEGS-SLAM解决了现有SLAM算法无法完全捕捉底层结构的问题,实现了高质量的光栅化映射。
- SEGS-SLAM通过SEPM框架首次利用结构化点云初始化结构化三维高斯,提高了渲染质量。
- SEGS-SLAM通过AfME技术使三维高斯更好地模拟不同相机姿态下的图像外观变化。
- 实验结果表明,SEGS-SLAM在单目、立体和RGB-D数据集上的光栅化映射质量优于现有技术。例如,在TUM RGB-D数据集上,相较于MonoGS,SEGS-SLAM在PSNR上提高了19.86%。
- SEGS-SLAM具有广泛的应用前景,包括增强现实、虚拟现实和自动导航等领域。
- 用户可以通过在线项目页面了解更多关于SEGS-SLAM的信息和技术细节。该项目页面的链接是:https://segs-slam.github.io。
点此查看论文截图

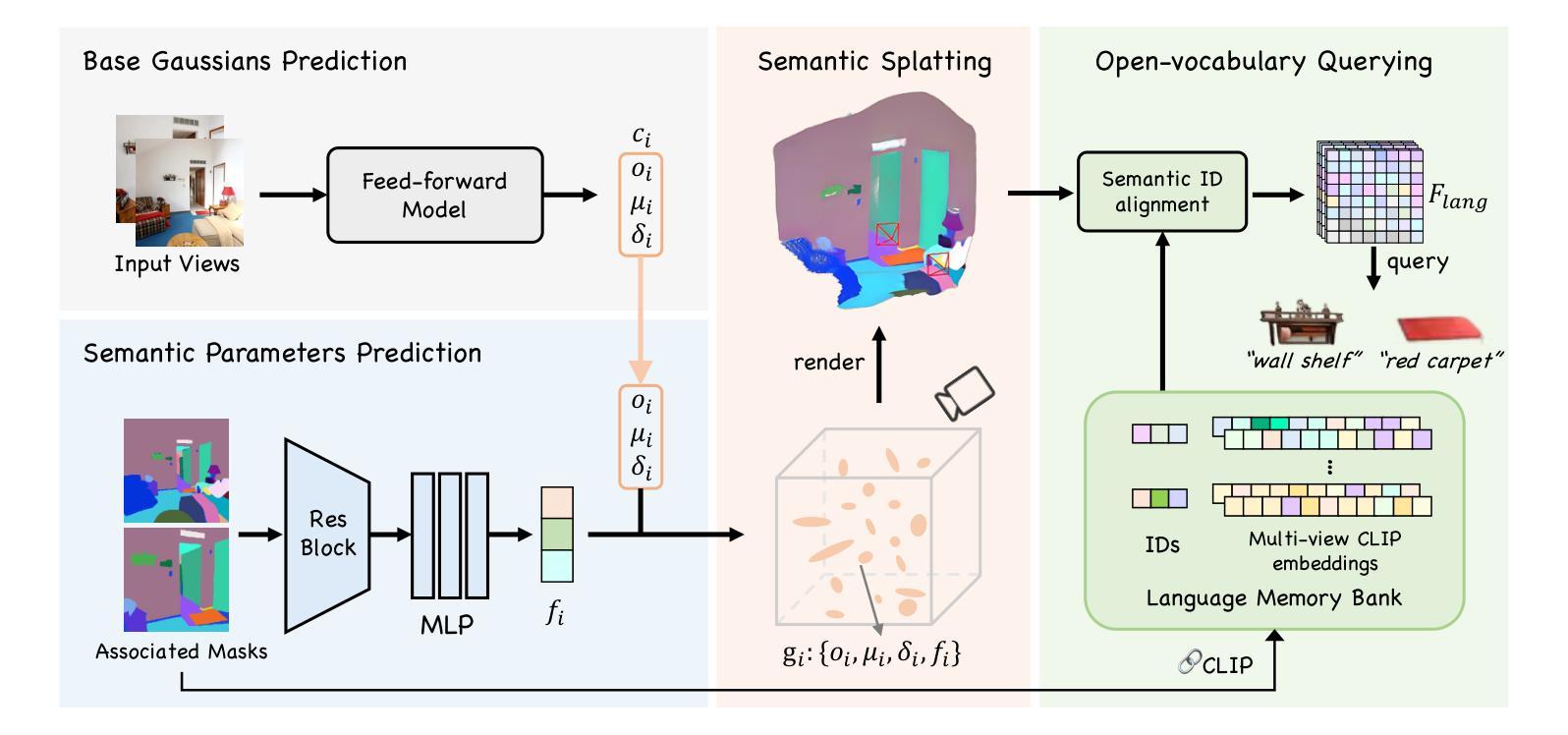
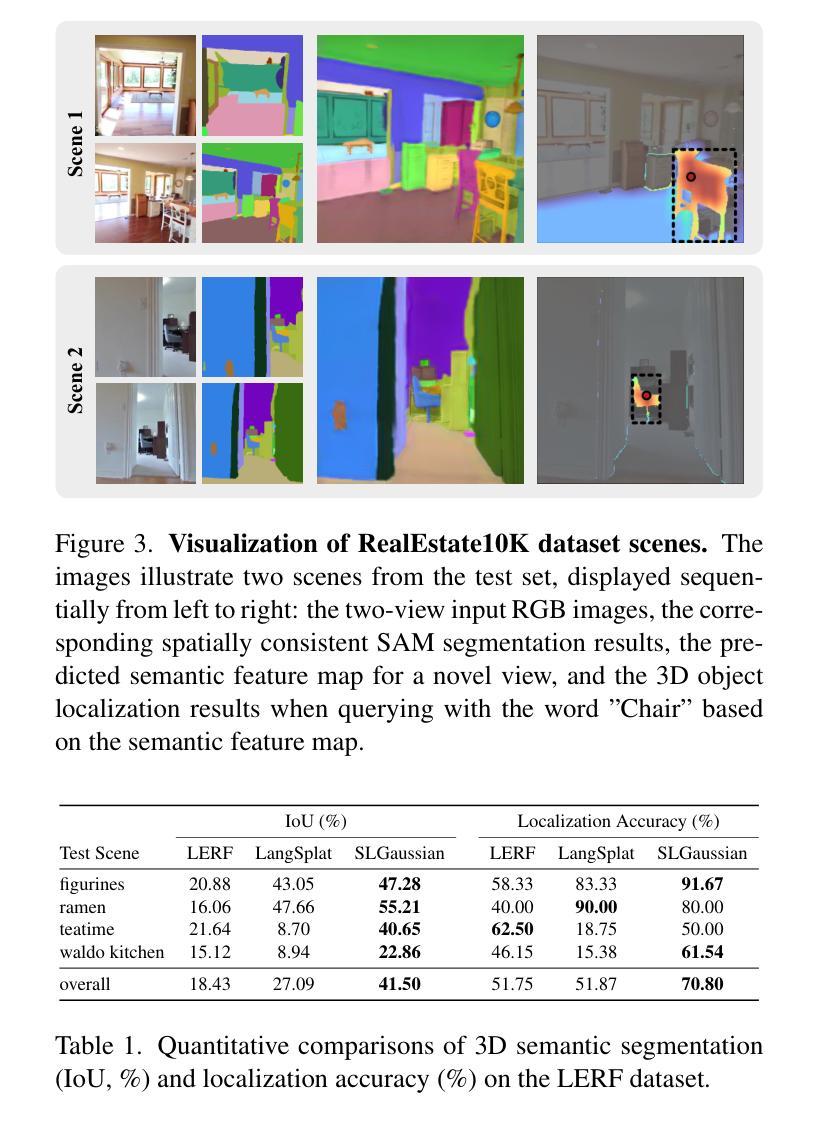
SLGaussian: Fast Language Gaussian Splatting in Sparse Views
Authors:Kangjie Chen, BingQuan Dai, Minghan Qin, Dongbin Zhang, Peihao Li, Yingshuang Zou, Haoqian Wang
3D semantic field learning is crucial for applications like autonomous navigation, AR/VR, and robotics, where accurate comprehension of 3D scenes from limited viewpoints is essential. Existing methods struggle under sparse view conditions, relying on inefficient per-scene multi-view optimizations, which are impractical for many real-world tasks. To address this, we propose SLGaussian, a feed-forward method for constructing 3D semantic fields from sparse viewpoints, allowing direct inference of 3DGS-based scenes. By ensuring consistent SAM segmentations through video tracking and using low-dimensional indexing for high-dimensional CLIP features, SLGaussian efficiently embeds language information in 3D space, offering a robust solution for accurate 3D scene understanding under sparse view conditions. In experiments on two-view sparse 3D object querying and segmentation in the LERF and 3D-OVS datasets, SLGaussian outperforms existing methods in chosen IoU, Localization Accuracy, and mIoU. Moreover, our model achieves scene inference in under 30 seconds and open-vocabulary querying in just 0.011 seconds per query.
三维语义场学习对于自主导航、增强现实/虚拟现实和机器人等应用至关重要,在这些应用中,从有限视角准确理解三维场景至关重要。现有方法在稀疏视图条件下表现困难,依赖于低效的针对每个场景的多视角优化,这在许多现实任务中不切实际。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SLGaussian方法,这是一种前馈方法,可以从稀疏视角构建三维语义场,允许直接推断基于3DGS的场景。通过确保通过视频跟踪进行一致的SAM分割,并使用针对高维CLIP特征的低维索引,SLGaussian有效地将语言信息嵌入三维空间,为稀疏视图条件下的准确三维场景理解提供了稳健的解决方案。在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的两视图稀疏三维对象查询和分割实验中,SLGaussian在选择的IoU、定位精度和mIoU方面均优于现有方法。此外,我们的模型在不到30秒内实现场景推断,每个查询的开放词汇查询时间仅为0.011秒。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025. Project page: https://chenkangjie1123.github.io/SLGaussian.github.io/
摘要
针对稀疏视点下的三维语义场学习问题,提出SLGaussian方法。该方法通过前馈方式构建三维语义场,支持从稀疏视点进行直接推理,有效嵌入语言信息,提升在稀疏视点条件下的三维场景理解准确性。在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的实验表明,SLGaussian在IoU、定位精度和mIoU等指标上优于现有方法,场景推理时间小于30秒,开放词汇查询每秒可达0.011次。
要点
- 3D语义场学习在自主导航、AR/VR和机器人等应用中至关重要,其中从有限视角准确理解3D场景是关键。
- 现有方法在稀疏视图条件下表现不佳,依赖于低效的每场景多视图优化,不适用于许多真实任务。
- SLGaussian是一种从稀疏视点构建3D语义场的馈送方法,支持直接推理3DGS场景。
- SLGaussian通过视频跟踪确保SAM分割的一致性,并使用高维CLIP特征的低维索引,有效嵌入语言信息。
- 在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的实验表明,SLGaussian在IoU、定位精度和mIoU等指标上优于现有方法。
- SLGaussian实现了场景推理时间的优化,小于30秒。
- 开放词汇查询效率高,每秒可达0.011次查询。
点此查看论文截图

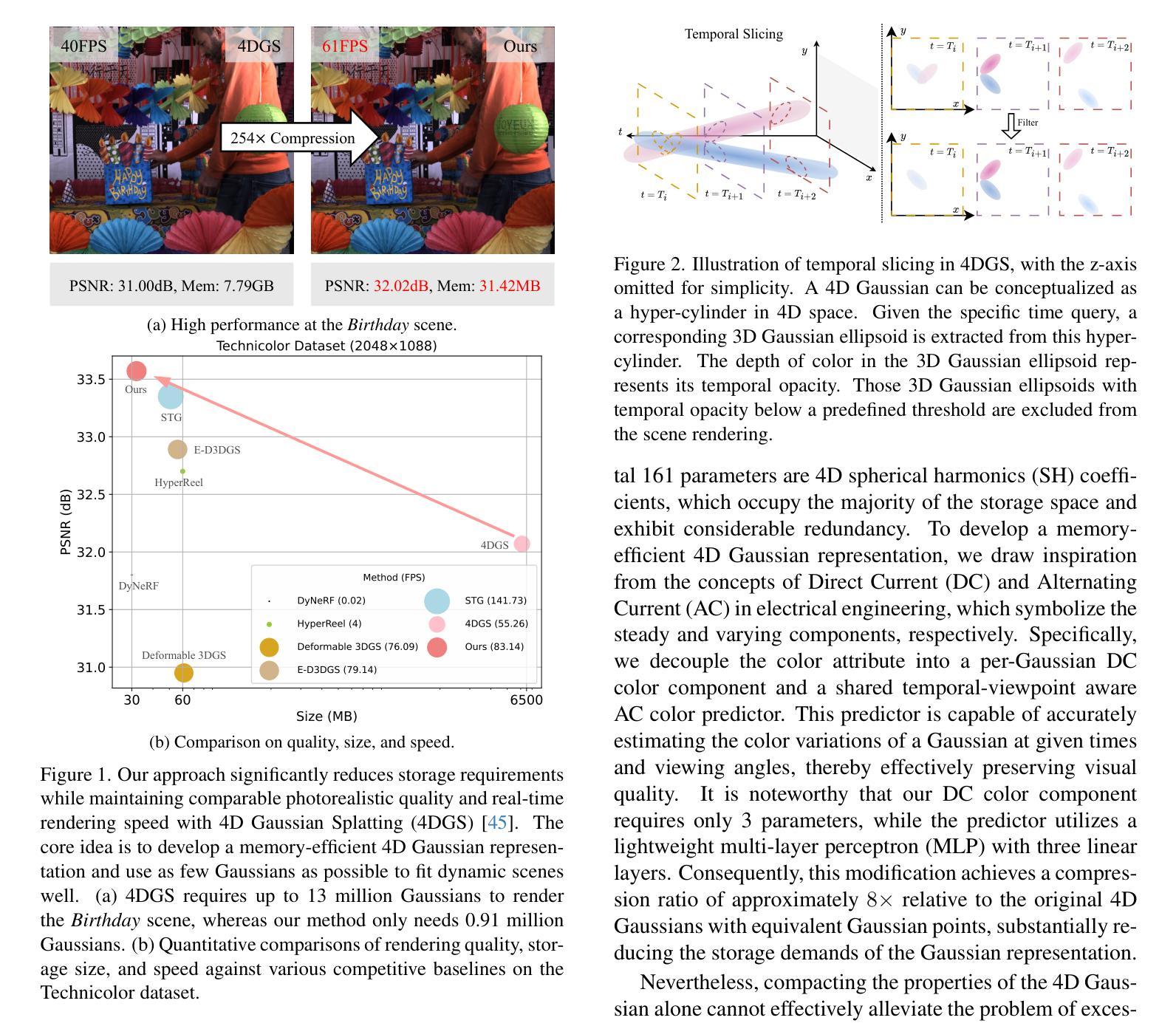
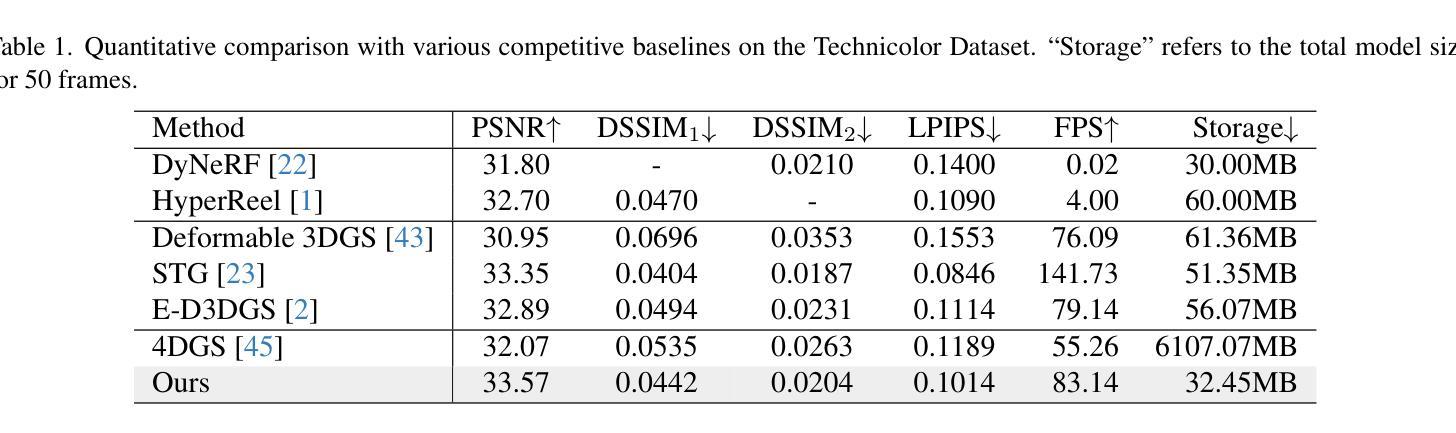
MEGA: Memory-Efficient 4D Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scenes
Authors:Xinjie Zhang, Zhening Liu, Yifan Zhang, Xingtong Ge, Dailan He, Tongda Xu, Yan Wang, Zehong Lin, Shuicheng Yan, Jun Zhang
4D Gaussian Splatting (4DGS) has recently emerged as a promising technique for capturing complex dynamic 3D scenes with high fidelity. It utilizes a 4D Gaussian representation and a GPU-friendly rasterizer, enabling rapid rendering speeds. Despite its advantages, 4DGS faces significant challenges, notably the requirement of millions of 4D Gaussians, each with extensive associated attributes, leading to substantial memory and storage cost. This paper introduces a memory-efficient framework for 4DGS. We streamline the color attribute by decomposing it into a per-Gaussian direct color component with only 3 parameters and a shared lightweight alternating current color predictor. This approach eliminates the need for spherical harmonics coefficients, which typically involve up to 144 parameters in classic 4DGS, thereby creating a memory-efficient 4D Gaussian representation. Furthermore, we introduce an entropy-constrained Gaussian deformation technique that uses a deformation field to expand the action range of each Gaussian and integrates an opacity-based entropy loss to limit the number of Gaussians, thus forcing our model to use as few Gaussians as possible to fit a dynamic scene well. With simple half-precision storage and zip compression, our framework achieves a storage reduction by approximately 190$\times$ and 125$\times$ on the Technicolor and Neural 3D Video datasets, respectively, compared to the original 4DGS. Meanwhile, it maintains comparable rendering speeds and scene representation quality, setting a new standard in the field. Code is available at https://github.com/Xinjie-Q/MEGA.
4D高斯模糊技术(4DGS)作为一种新兴技术,在高保真捕捉复杂动态三维场景方面表现出巨大潜力。它采用4D高斯表示和GPU友好的光栅化器,实现快速渲染速度。尽管具有优势,但4DGS面临重大挑战,尤其是需要数百万个具有大量相关属性的4D高斯,导致内存和存储成本高昂。本文介绍了一个高效的内存管理框架用于4DGS。我们通过将颜色属性简化为每个高斯仅具有三个参数的直接颜色组件和一个共享的轻量级交流颜色预测器来优化流程。这种方法消除了需要使用球面谐波系数,传统4DGS通常需要高达144个参数,从而创建了一个内存高效的4D高斯表示。此外,我们引入了一种基于熵约束的高斯变形技术,该技术使用变形场扩展每个高斯的作用范围,并结合基于不透明度的熵损失来限制高斯数量,从而迫使我们的模型尽可能使用最少的高斯来适应动态场景。通过简单的半精度存储和zip压缩,我们的框架在Technicolor和Neural 3D Video数据集上实现了约190倍和125倍的存储缩减,同时保持相当的渲染速度和场景表示质量,为这一领域设定了新的标准。代码可在https://github.com/Xinjie-Q/MEGA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
该文介绍了新型的4D高斯混合技术(4DGS),用于捕捉复杂的动态三维场景。为提高效率,该文提出一种内存优化的框架,通过简化颜色属性和引入基于熵约束的高斯变形技术,实现了显著的内存节省。该框架在保持渲染速度和场景表示质量的同时,显著减少了所需的内存空间。
Key Takeaways
- 4DGS技术能够捕捉复杂的动态三维场景并具备高保真度。
- 为解决内存和存储成本问题,论文提出了一种内存优化的框架。
- 通过简化颜色属性和引入熵约束的高斯变形技术,实现了高效的内存使用。
- 框架采用半精度存储和zip压缩,实现了显著的存储缩减,同时保持渲染速度和场景表示质量。
- 该技术对于动态场景的拟合能力强大,使用的高斯数量尽可能少。
点此查看论文截图



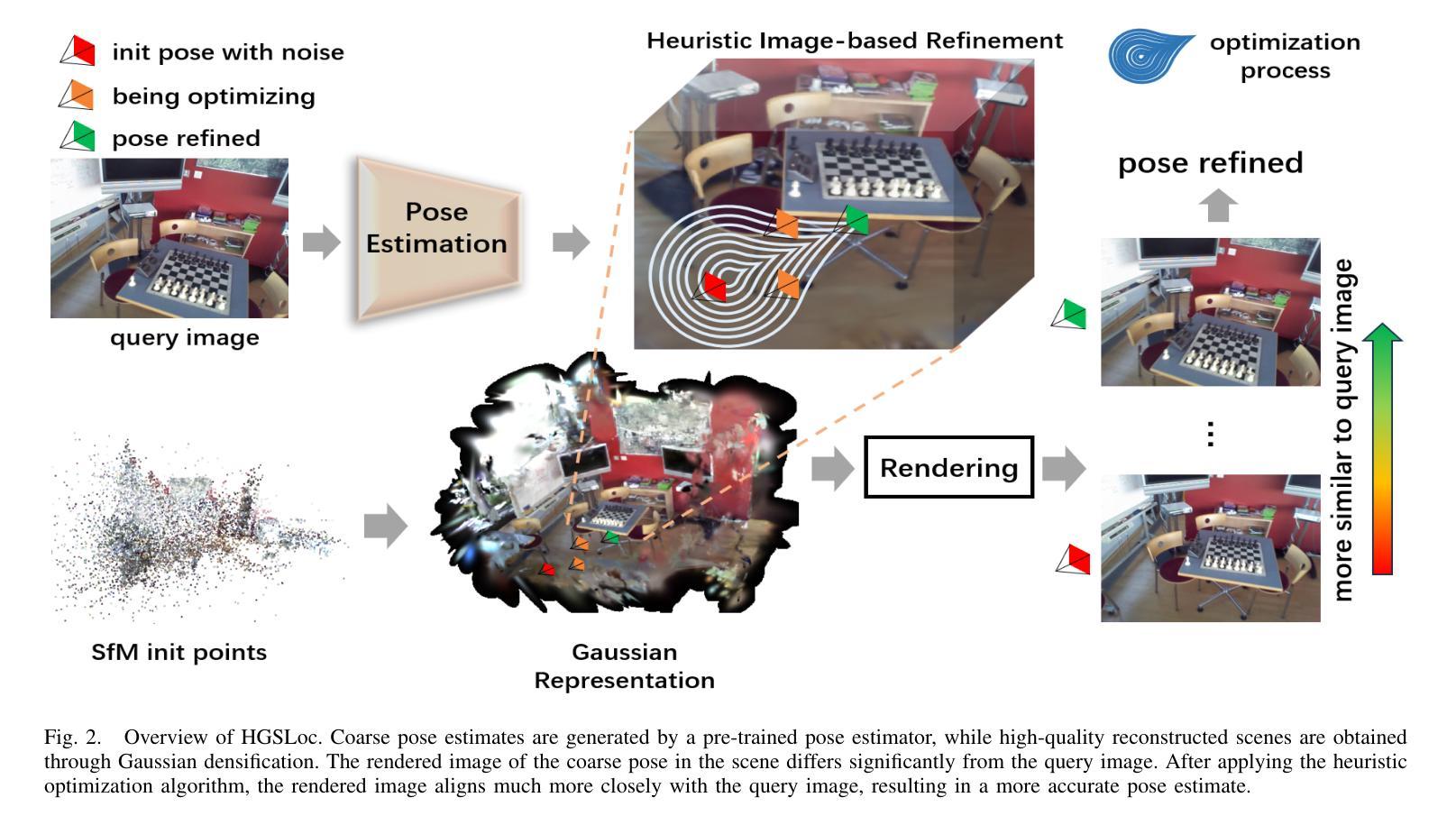
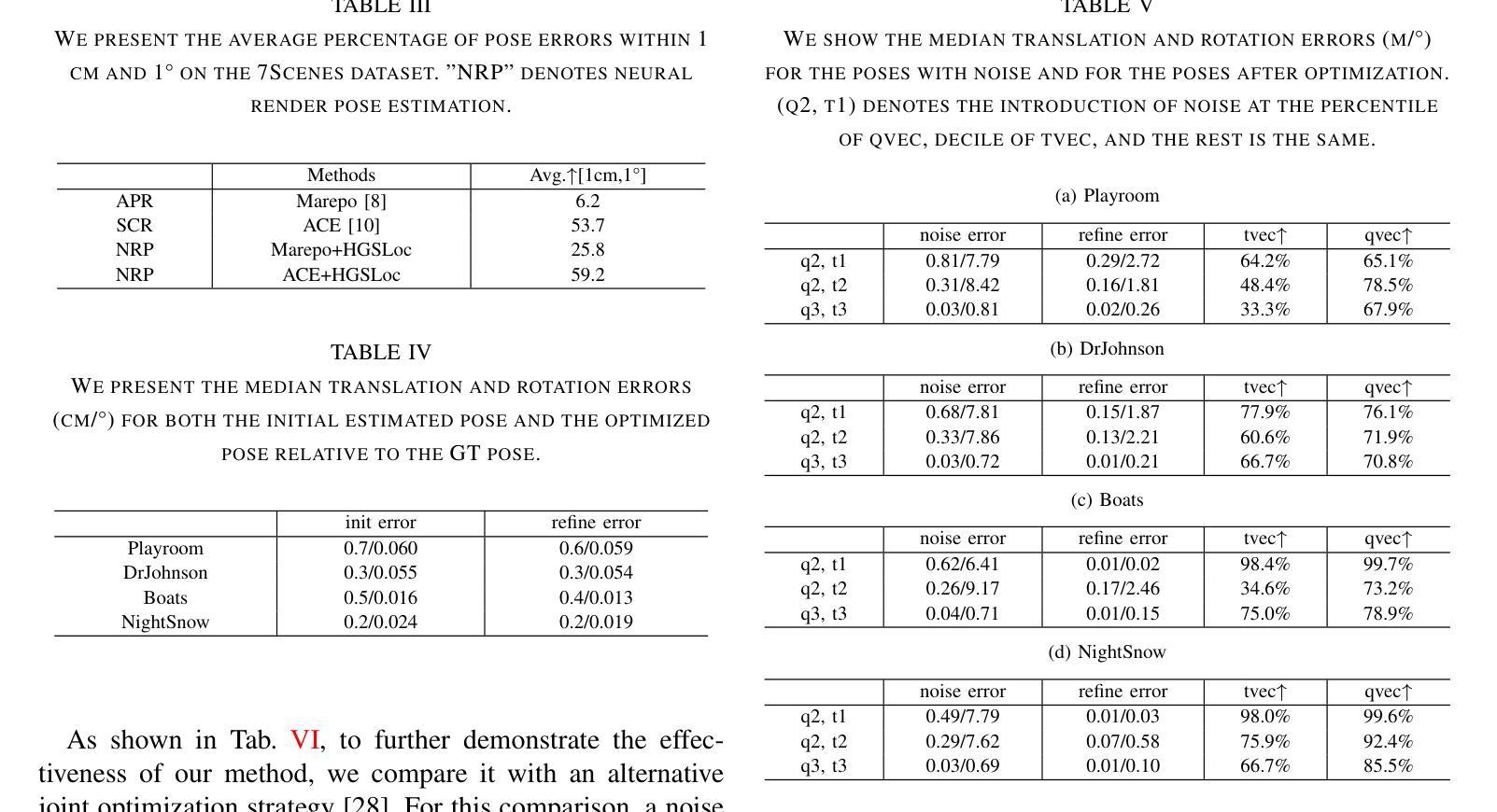
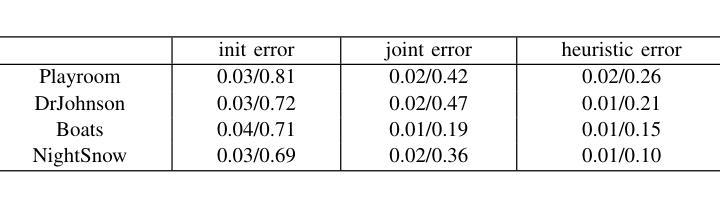
HGSLoc: 3DGS-based Heuristic Camera Pose Refinement
Authors:Zhongyan Niu, Zhen Tan, Jinpu Zhang, Xueliang Yang, Dewen Hu
Visual localization refers to the process of determining camera poses and orientation within a known scene representation. This task is often complicated by factors such as changes in illumination and variations in viewing angles. In this paper, we propose HGSLoc, a novel lightweight plug-and-play pose optimization framework, which integrates 3D reconstruction with a heuristic refinement strategy to achieve higher pose estimation accuracy. Specifically, we introduce an explicit geometric map for 3D representation and high-fidelity rendering, allowing the generation of high-quality synthesized views to support accurate visual localization. Our method demonstrates higher localization accuracy compared to NeRF-based neural rendering localization approaches. We introduce a heuristic refinement strategy, its efficient optimization capability can quickly locate the target node, while we set the step level optimization step to enhance the pose accuracy in the scenarios with small errors. With carefully designed heuristic functions, it offers efficient optimization capabilities, enabling rapid error reduction in rough localization estimations. Our method mitigates the dependence on complex neural network models while demonstrating improved robustness against noise and higher localization accuracy in challenging environments, as compared to neural network joint optimization strategies. The optimization framework proposed in this paper introduces novel approaches to visual localization by integrating the advantages of 3D reconstruction and the heuristic refinement strategy, which demonstrates strong performance across multiple benchmark datasets, including 7Scenes and Deep Blending dataset. The implementation of our method has been released at https://github.com/anchang699/HGSLoc.
视觉定位是指确定相机在已知场景表示中的姿态和方向的过程。这个任务通常受到光照变化和观看角度变化等因素的影响。在本文中,我们提出了HGSLoc,这是一种新型轻量级的即插即用姿态优化框架,它将3D重建与启发式细化策略相结合,以实现更高的姿态估计精度。具体来说,我们引入了用于3D表示的显式几何地图和高保真渲染,以生成高质量合成视图,支持精确视觉定位。我们的方法与基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法相比,展示了更高的定位精度。我们引入了一种启发式细化策略,其高效的优化能力可以快速定位目标节点,同时我们设置了步骤级优化步骤,以提高在错误较小的场景中的姿态精度。通过精心设计的启发式函数,它提供了高效的优化能力,能够在粗略的定位估计中快速减少误差。我们的方法减轻了对于复杂的神经网络模型的依赖,同时展示了在噪声环境中的鲁棒性和在具有挑战性的环境中的更高定位精度,这与神经网络联合优化策略相比。本文提出的优化框架通过整合3D重建和启发式细化策略的优点,为视觉定位引入了新颖的方法,它在多个基准数据集(包括7Scenes和Deep Blending数据集)上均表现出强大的性能。我们的方法的实现已发布在https://github.com/anchang699/HGSLoc。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的视觉定位方法HGSLoc,它结合了三维重建和启发式优化策略,以提高姿态估计的准确性。通过构建明确的几何地图进行三维表示和高保真渲染,生成高质量合成视图以支持精确视觉定位。相较于基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法,HGSLoc具有更高的定位精度。此外,其启发式优化策略能迅速定位目标节点,并在存在小误差的场景中通过步级优化步骤提高姿态估计的准确性。HGSLoc方法避免了依赖复杂的神经网络模型,在噪声环境下表现出更强的鲁棒性,并在具有挑战性的环境中实现了更高的定位精度。
Key Takeaways
- HGSLoc是一种新型的视觉定位方法,结合了三维重建和启发式优化策略。
- 通过构建几何地图进行高保真渲染,提高了姿态估计的准确性。
- HGSLoc具有更高的定位精度,相较于基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法。
- 启发式优化策略能迅速定位目标节点,并能在存在小误差的场景中提高姿态估计的准确性。
- HGSLoc避免了依赖复杂的神经网络模型,具有更强的鲁棒性。
- HGSLoc在具有挑战性的环境中实现了更高的定位精度。
- HGSLoc已在多个基准数据集上进行了验证,包括7Scenes和Deep Blending数据集。
点此查看论文截图




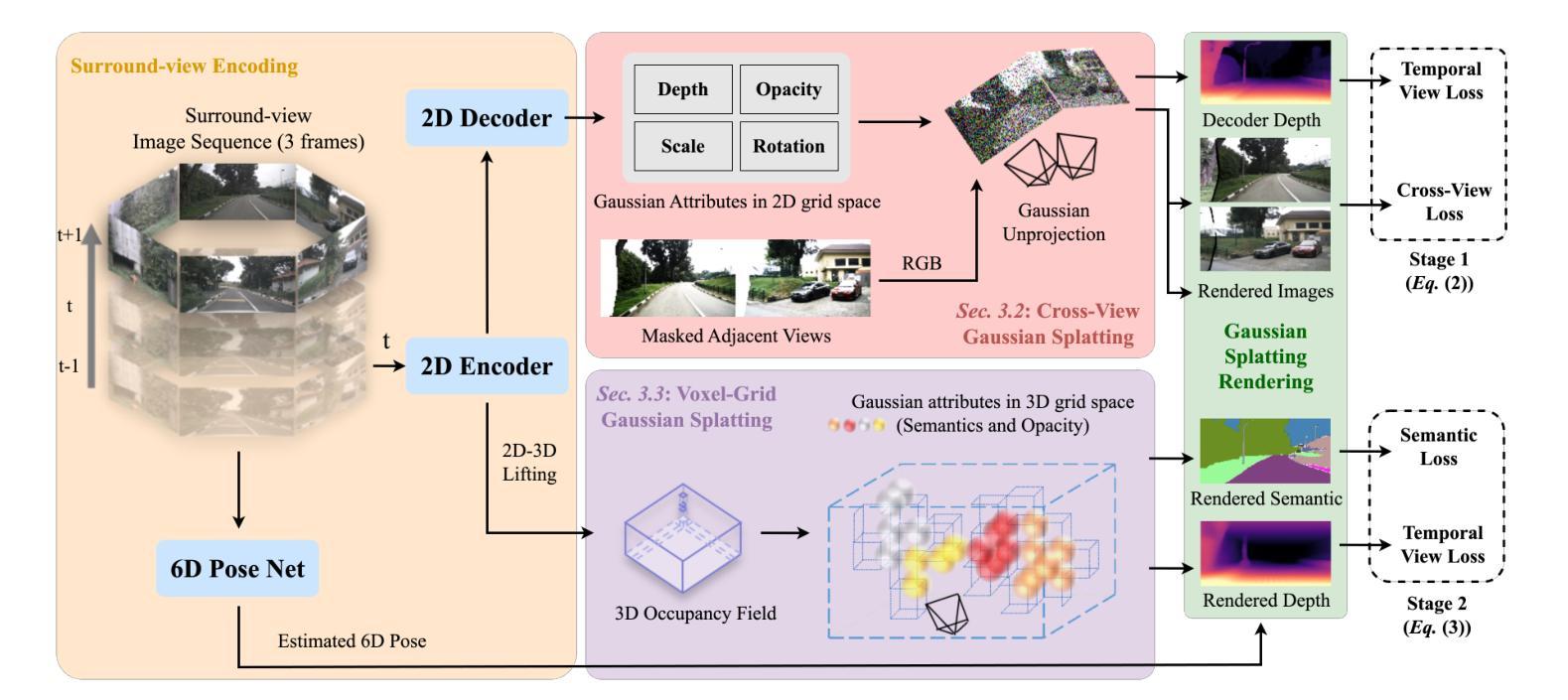
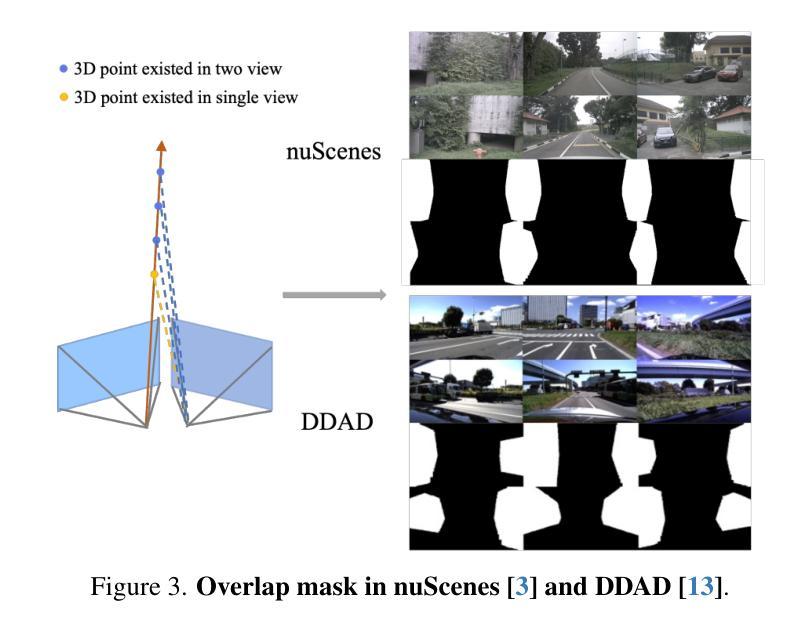
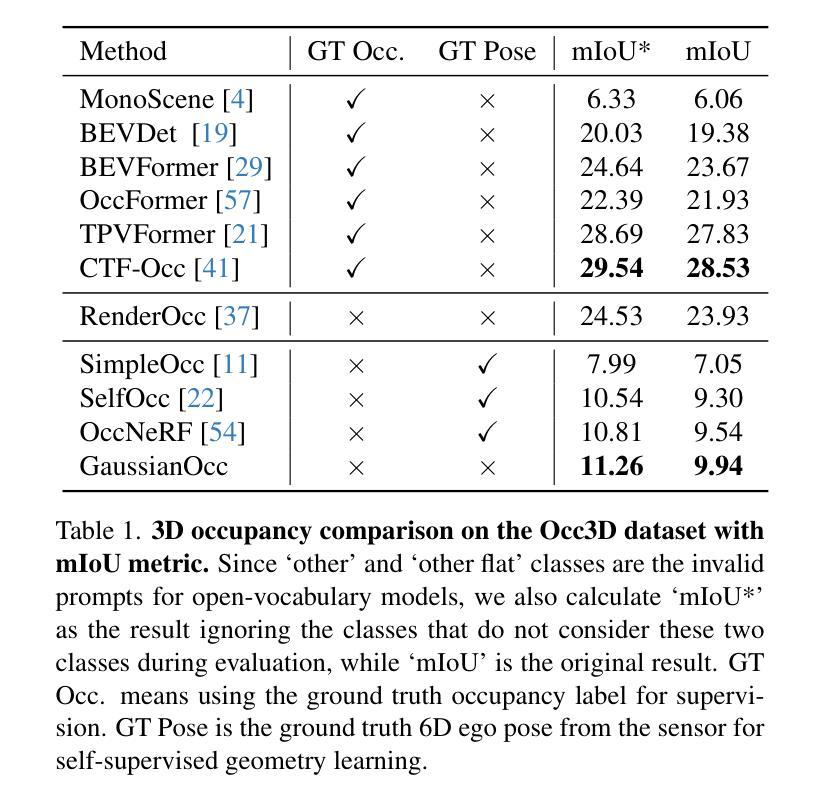
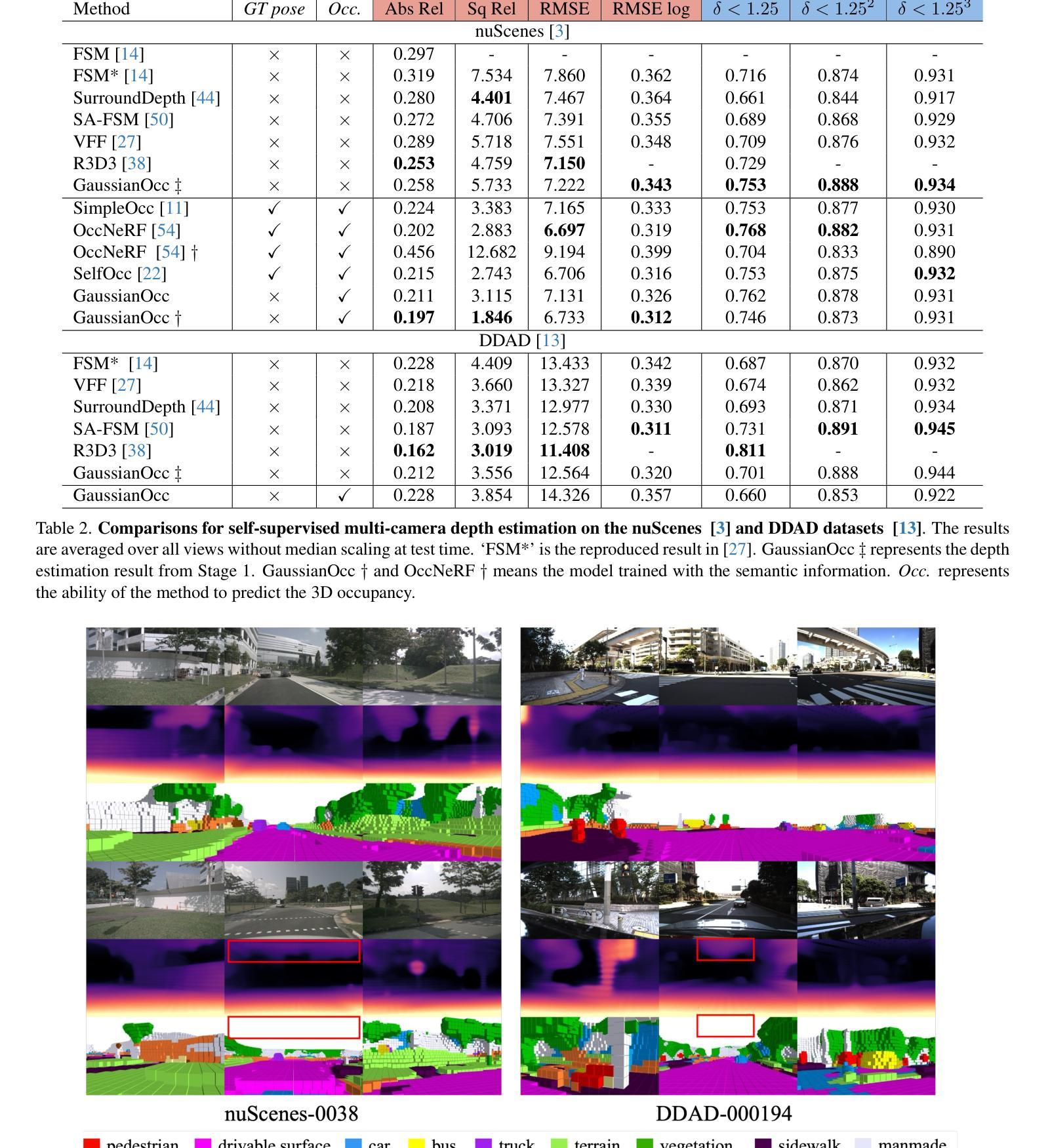
GaussianOcc: Fully Self-supervised and Efficient 3D Occupancy Estimation with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Wanshui Gan, Fang Liu, Hongbin Xu, Ningkai Mo, Naoto Yokoya
We introduce GaussianOcc, a systematic method that investigates the two usages of Gaussian splatting for fully self-supervised and efficient 3D occupancy estimation in surround views. First, traditional methods for self-supervised 3D occupancy estimation still require ground truth 6D poses from sensors during training. To address this limitation, we propose Gaussian Splatting for Projection (GSP) module to provide accurate scale information for fully self-supervised training from adjacent view projection. Additionally, existing methods rely on volume rendering for final 3D voxel representation learning using 2D signals (depth maps, semantic maps), which is both time-consuming and less effective. We propose Gaussian Splatting from Voxel space (GSV) to leverage the fast rendering properties of Gaussian splatting. As a result, the proposed GaussianOcc method enables fully self-supervised (no ground truth pose) 3D occupancy estimation in competitive performance with low computational cost (2.7 times faster in training and 5 times faster in rendering). The relevant code is available in https://github.com/GANWANSHUI/GaussianOcc.git.
我们介绍了GaussianOcc,这是一种系统性方法,研究了高斯展布(Gaussian Splatting)的两种应用,以在周围视图中实现全自监督和高效率的3D占用估计。首先,现有的自监督3D占用估计方法仍然需要在训练过程中使用来自传感器的真实6D姿态。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了用于投影的高斯展布(Gaussian Splatting for Projection,GSP)模块,通过相邻视图投影提供准确的尺度信息以实现全自监督训练。此外,现有方法依赖于体积渲染来利用二维信号(深度图、语义图)进行最终的三维体素表示学习,这既耗时又效率较低。我们提出了基于体素空间的高斯展布(Gaussian Splatting from Voxel space,GSV),利用高斯展布的快速渲染属性。因此,提出的GaussianOcc方法能够在无需真实姿态的情况下实现全自监督的3D占用估计,具有竞争力且计算成本低(训练速度提高了2.7倍,渲染速度提高了5倍)。相关代码可在https://github.com/GANWANSHUI/GaussianOcc.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ganwanshui.github.io/GaussianOcc/
Summary
本文介绍了GaussianOcc方法,该方法通过高斯摊铺技术实现了全自我监督的3D占用空间估计。为解决现有方法需要传感器提供的地面真实6D姿态数据进行训练的问题,提出了高斯摊铺投影(GSP)模块,用于从相邻视图投影提供准确的尺度信息以实现全自我监督训练。此外,现有方法依赖体积渲染来通过二维信号(深度图、语义图)学习最终的3D体素表示,这既耗时又效果不佳。因此提出从体素空间进行高斯摊铺(GSV),利用高斯摊铺的快速渲染属性。这使得GaussianOcc方法能够在无需地面真实姿态数据的情况下实现自我监督的3D占用空间估计,具有竞争性的性能且计算成本低(训练速度提高2.7倍,渲染速度提高5倍)。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianOcc通过高斯摊铺技术实现了全自我监督的3D占用空间估计。
- 提出了高斯摊铺投影(GSP)模块,为全自我监督训练提供准确尺度信息。
- 现有的方法依赖体积渲染来学习最终的3D体素表示,但这一过程既耗时又效果不佳。
- 提出了从体素空间进行高斯摊铺(GSV),利用高斯摊铺的快速渲染属性。
- GaussianOcc方法提高了训练速度和渲染速度。
- 该方法的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图