⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
Journalism-Guided Agentic In-Context Learning for News Stance Detection
Authors:Dahyun Lee, Jonghyeon Choi, Jiyoung Han, Kunwoo Park
As online news consumption grows, personalized recommendation systems have become integral to digital journalism. However, these systems risk reinforcing filter bubbles and political polarization by failing to incorporate diverse perspectives. Stance detection – identifying a text’s position on a target – can help mitigate this by enabling viewpoint-aware recommendations and data-driven analyses of media bias. Yet, existing stance detection research remains largely limited to short texts and high-resource languages. To address these gaps, we introduce \textsc{K-News-Stance}, the first Korean dataset for article-level stance detection, comprising 2,000 news articles with article-level and 19,650 segment-level stance annotations across 47 societal issues. We also propose \textsc{JoA-ICL}, a \textbf{Jo}urnalism-guided \textbf{A}gentic \textbf{I}n-\textbf{C}ontext \textbf{L}earning framework that employs a language model agent to predict the stances of key structural segments (e.g., leads, quotes), which are then aggregated to infer the overall article stance. Experiments show that \textsc{JoA-ICL} outperforms existing stance detection methods, highlighting the benefits of segment-level agency in capturing the overall position of long-form news articles. Two case studies further demonstrate its broader utility in promoting viewpoint diversity in news recommendations and uncovering patterns of media bias.
随着在线新闻消费的增长,个性化推荐系统已成为数字新闻不可或缺的一部分。然而,这些系统因未能融入多元化的观点,存在强化信息茧房和政治极化的风险。立场检测——识别文本对目标的立场——可以通过实现观点感知推荐和媒体偏见的数据驱动分析来帮助缓解这一问题。然而,现有的立场检测研究大多局限于短文本和高资源语言。为了弥补这些不足,我们引入了\textsc{K-News-Stance},这是首个用于文章级别立场检测的韩语数据集,包含2000篇新闻文章,跨越47个社会问题的文章级别和19650个段落级别的立场注释。我们还提出了\textsc{JoA-ICL}框架,这是一个以新闻为导向的语境学习框架,它采用语言模型代理来预测关键结构段落(如导语、引语)的立场,然后聚合这些立场来推断整篇文章的立场。实验表明,\textsc{JoA-ICL}优于现有的立场检测方法,突显了分段级别的机构在捕捉长篇新闻文章整体立场方面的优势。两个案例研究进一步证明了其在促进新闻推荐中的观点多样性和揭示媒体偏见模式方面的更广泛的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. 24 pages
Summary
随着在线新闻消费的增长,个性化推荐系统在数字新闻中愈发重要,但同时也存在风险,如忽略不同视角可能会加剧资讯茧房和政治极化。立场检测能缓解这些问题,通过对文章或段落进行立场分析识别文章目标立场,进而促进观点感知的推荐和媒体偏见的数据驱动分析。然而现有的立场检测研究多局限于短文本和高资源语言。为填补这些空白,推出首个用于韩国文章级别立场检测的数据集K-News-Stance。同时提出了基于新闻报道指导的JoA-ICL框架,利用语言模型预测关键结构段落的立场,进而推断整体文章立场。实验显示JoA-ICL优于现有立场检测方法,展示了其在捕捉长新闻整体立场方面的优势。在促进新闻推荐的观点多样性和揭示媒体偏见方面也有广泛应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 在线新闻消费的增长推动了个性化推荐系统在数字新闻中的重要性。
- 个性化推荐系统若忽略不同视角可能加剧资讯茧房和政治极化问题。
- 立场检测可识别文本对目标的立场,有助于促进观点感知的推荐和媒体偏见分析。
- 现有立场检测研究多局限于短文本和高资源语言,存在研究空白。
- 推出首个韩国文章级别立场检测数据集K-News-Stance,包括2000篇新闻文章和相应立场标注。
- 提出JoA-ICL框架,通过预测关键结构段落的立场来推断整体文章立场,表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

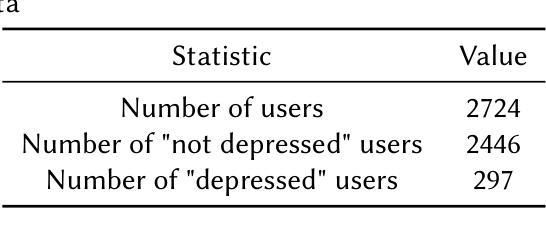
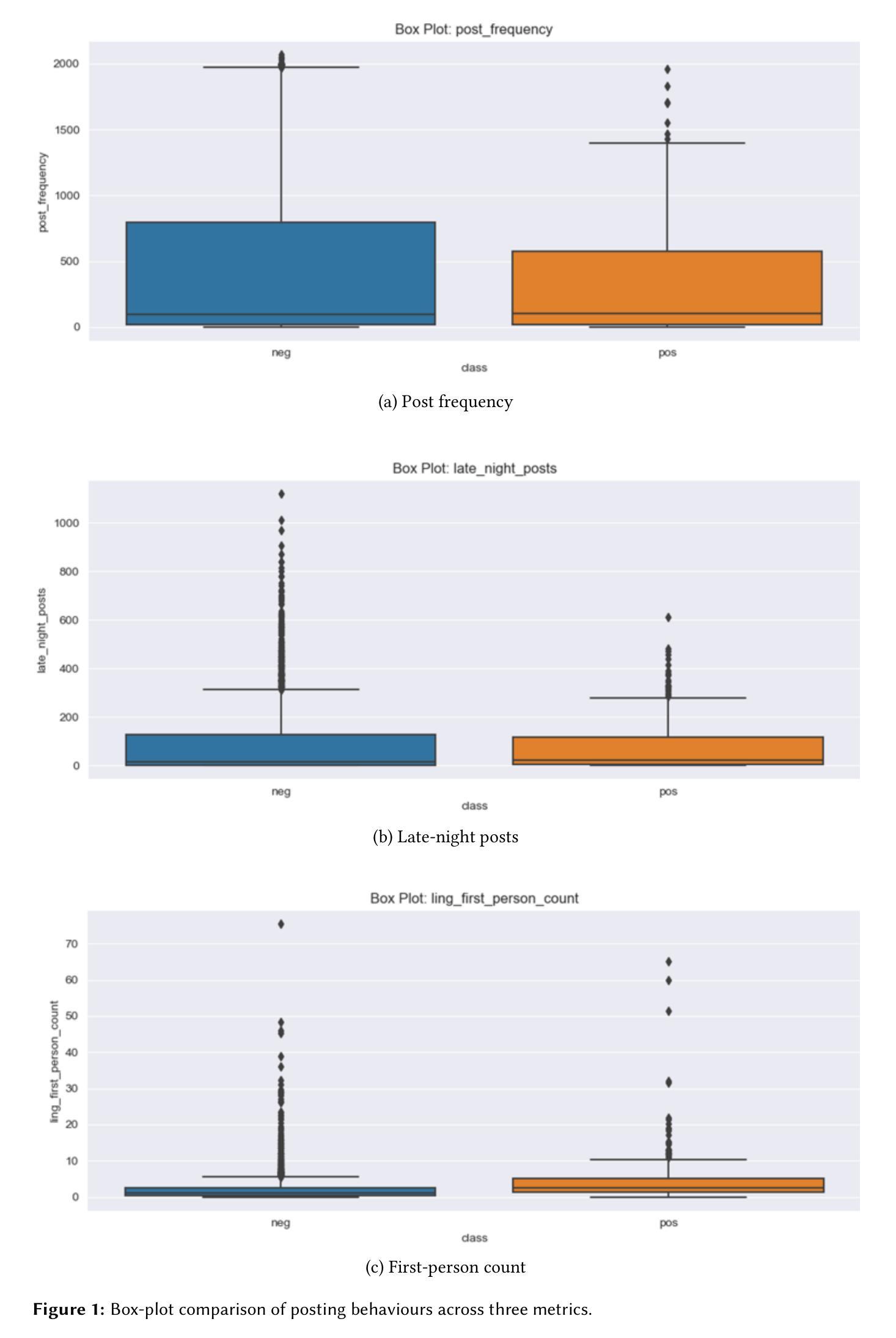
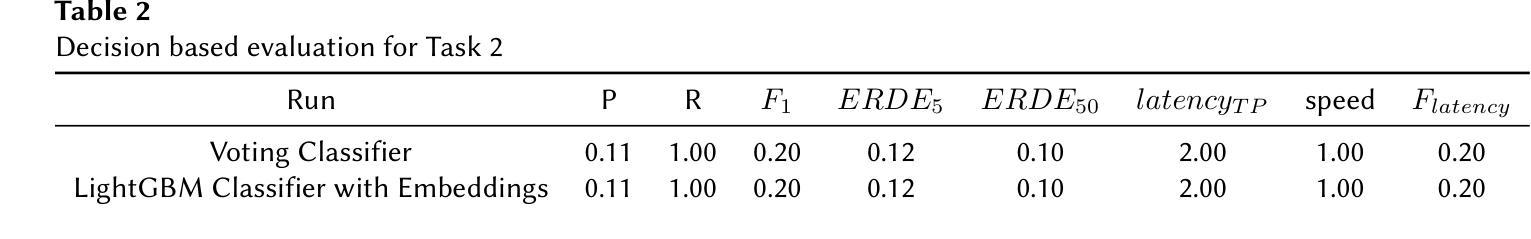
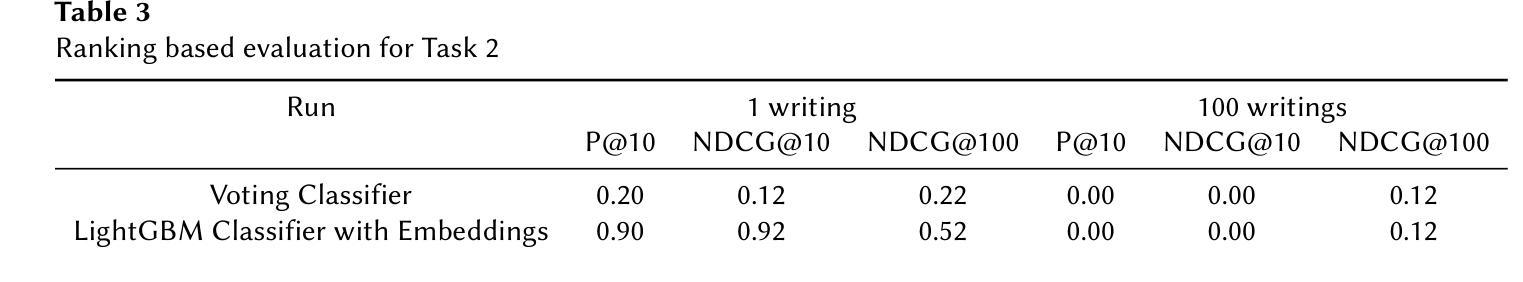
DS@GT at eRisk 2025: From prompts to predictions, benchmarking early depression detection with conversational agent based assessments and temporal attention models
Authors:Anthony Miyaguchi, David Guecha, Yuwen Chiu, Sidharth Gaur
This Working Note summarizes the participation of the DS@GT team in two eRisk 2025 challenges. For the Pilot Task on conversational depression detection with large language-models (LLMs), we adopted a prompt-engineering strategy in which diverse LLMs conducted BDI-II-based assessments and produced structured JSON outputs. Because ground-truth labels were unavailable, we evaluated cross-model agreement and internal consistency. Our prompt design methodology aligned model outputs with BDI-II criteria and enabled the analysis of conversational cues that influenced the prediction of symptoms. Our best submission, second on the official leaderboard, achieved DCHR = 0.50, ADODL = 0.89, and ASHR = 0.27.
本工作笔记总结了DS@GT团队参与两项eRisk 2025挑战的情况。在基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的对话式抑郁症检测试点任务中,我们采用了提示工程策略,让多种LLMs进行基于BDI-II的评估,并生成结构化JSON输出。由于无法获取真实标签,我们评估了跨模型的一致性和内部一致性。我们的提示设计方法使模型输出与BDI-II标准相符,并能分析影响症状预测的对话线索。我们的最佳提交成绩在官方排行榜上排名第二,达到DCHR=0.50,ADODL=0.89和ASHR=0.27。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DS@GT团队参与了两个eRisk 2025挑战项目的工作笔记总结。在基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的对话式抑郁症检测试点任务中,我们采用了提示工程策略,通过多样的LLMs进行BDI-II基准评估并生成结构化JSON输出。由于缺少真实标签,我们评估了跨模型的一致性和内部一致性。我们的提示设计方法使模型输出与BDI-II标准相符,并能分析影响症状预测的对话线索。我们的最佳提交在官方排行榜上排名第二,达到了DCHR=0.50,ADODL=0.89和ASHR=0.27的成效。
Key Takeaways
- DS@GT团队参与了eRisk 2025挑战中的两个任务。
- 在对话式抑郁症检测任务中,团队采用了基于大型语言模型的提示工程策略。
- 通过多种LLMs进行BDI-II基准评估并生成结构化输出。
- 缺乏真实标签的情况下,团队通过评估跨模型的一致性和内部一致性来进行评价。
- 提示设计使模型输出与BDI-II标准相符,并分析了对话中的线索对症状预测的影响。
- 最佳提交在官方排行榜上获得第二名。
点此查看论文截图

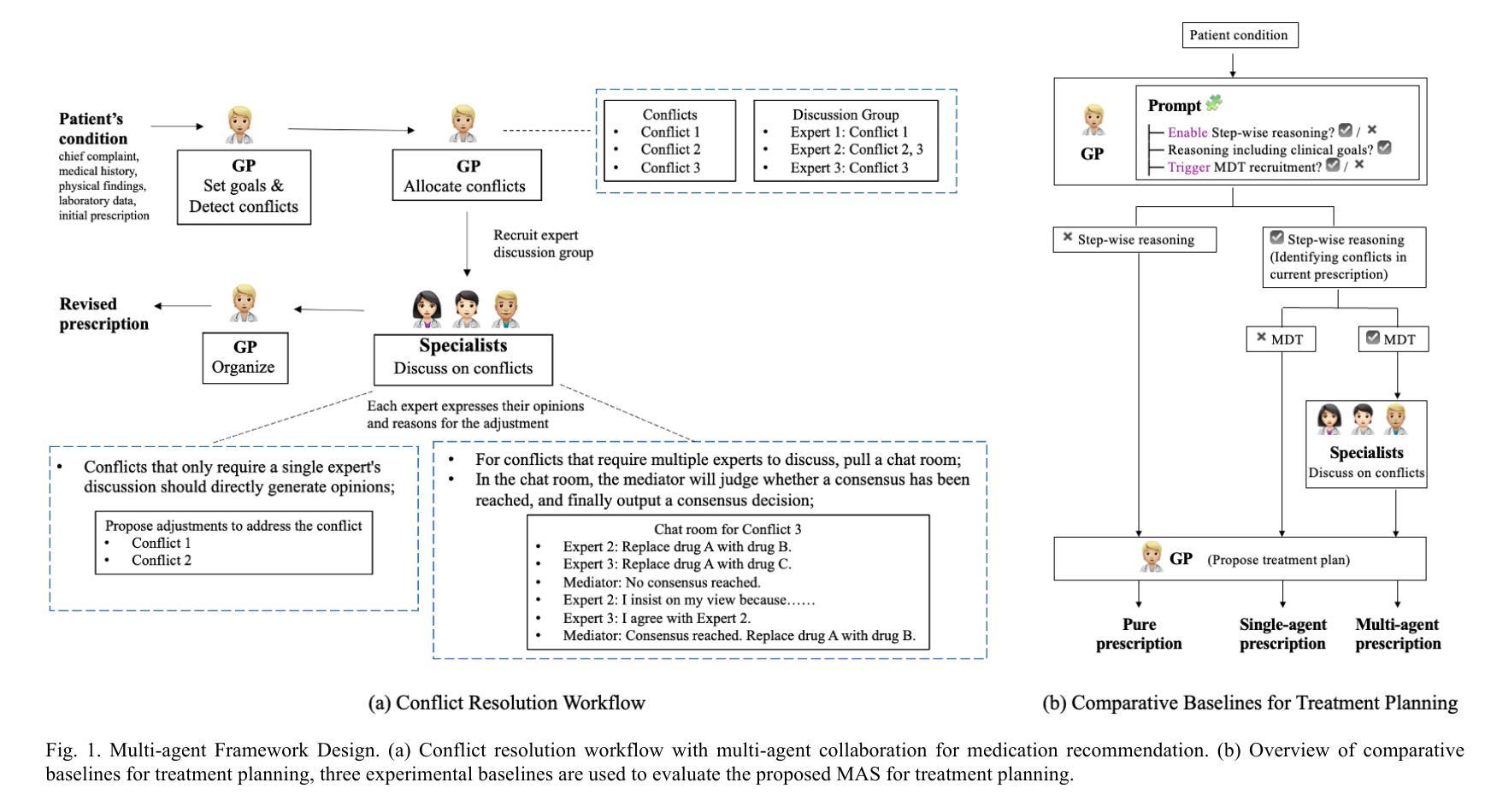
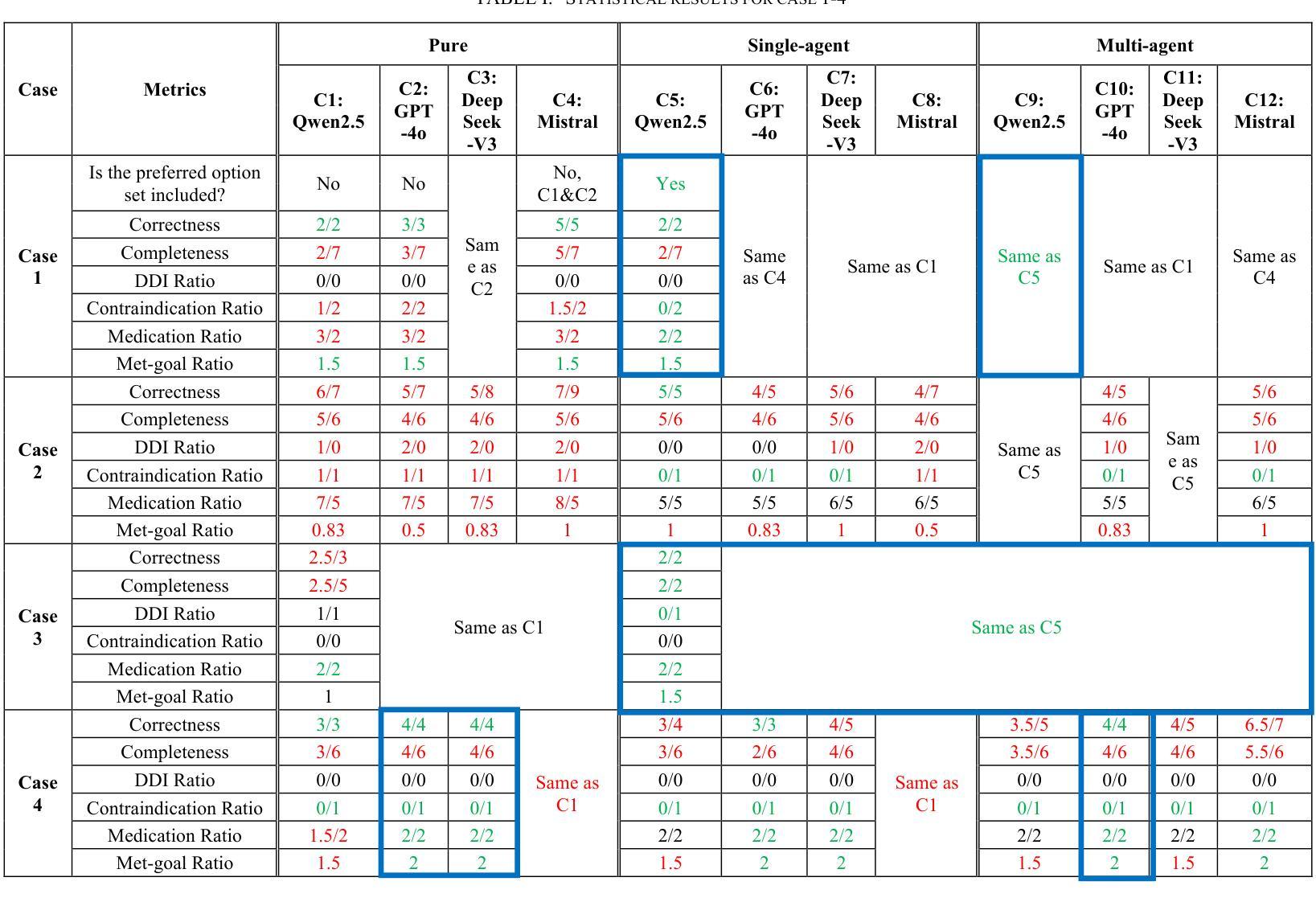
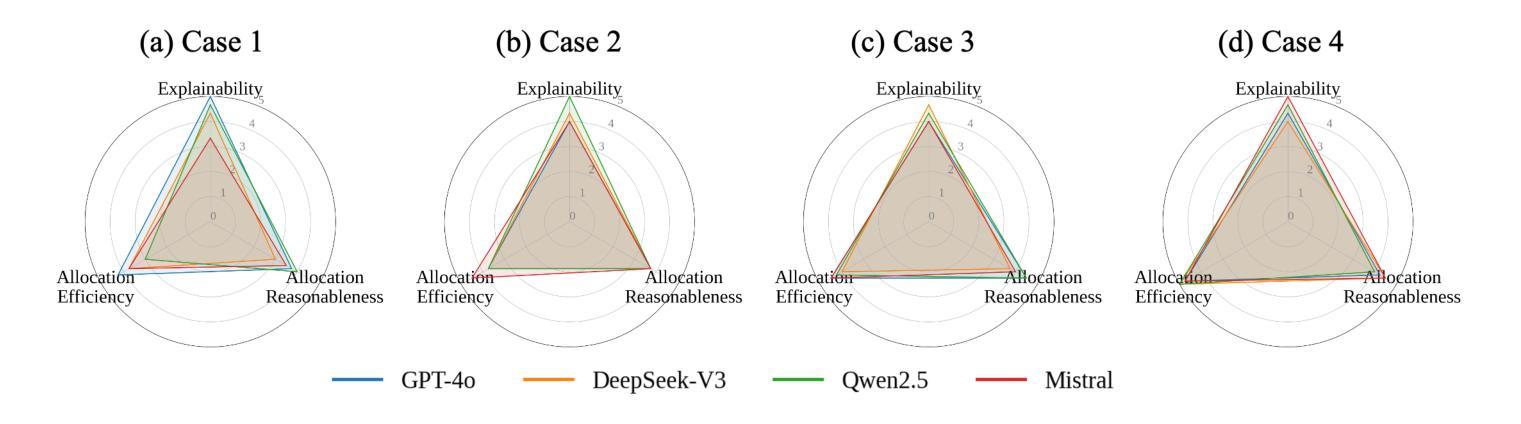
Lessons Learned from Evaluation of LLM based Multi-agents in Safer Therapy Recommendation
Authors:Yicong Wu, Ting Chen, Irit Hochberg, Zhoujian Sun, Ruth Edry, Zhengxing Huang, Mor Peleg
Therapy recommendation for chronic patients with multimorbidity is challenging due to risks of treatment conflicts. Existing decision support systems face scalability limitations. Inspired by the way in which general practitioners (GP) manage multimorbidity patients, occasionally convening multidisciplinary team (MDT) collaboration, this study investigated the feasibility and value of using a Large Language Model (LLM)-based multi-agent system (MAS) for safer therapy recommendations. We designed a single agent and a MAS framework simulating MDT decision-making by enabling discussion among LLM agents to resolve medical conflicts. The systems were evaluated on therapy planning tasks for multimorbidity patients using benchmark cases. We compared MAS performance with single-agent approaches and real-world benchmarks. An important contribution of our study is the definition of evaluation metrics that go beyond the technical precision and recall and allow the inspection of clinical goals met and medication burden of the proposed advices to a gold standard benchmark. Our results show that with current LLMs, a single agent GP performs as well as MDTs. The best-scoring models provide correct recommendations that address all clinical goals, yet the advices are incomplete. Some models also present unnecessary medications, resulting in unnecessary conflicts between medication and conditions or drug-drug interactions.
对于患有多种慢性疾病的患者的治疗建议具有挑战性,因为存在治疗冲突的风险。现有的决策支持系统面临可扩展性限制。本研究受到全科医师(GP)管理多病因患者的方式的启发,后者会偶尔召集多学科团队(MDT)进行合作。本研究调查了使用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多代理系统(MAS)进行更安全治疗建议的可行性和价值。我们设计了一个单一代理和MAS框架,通过模拟LLM代理之间的讨论来解决医学冲突,从而模拟多学科团队的决策制定。我们使用基准病例对用于多病因患者的治疗规划任务的系统进行了评估。我们将MAS的性能与单代理方法和真实世界基准进行了比较。本研究的一个重要贡献是定义了评估指标,这些指标超越了技术上的精确性和召回率,并允许检查所提建议的临床目标达成情况和药物负担与金标准基准的比较。我们的结果表明,使用当前的大型语言模型,单一代理的全科医师的表现与多学科团队相当。得分最高的模型提供了正确的建议,解决了所有临床目标,但建议并不完整。一些模型还提出了不必要的药物,导致药物与条件之间或药物之间的不必要冲突。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用大型语言模型(LLM)构建的多智能体系统(MAS)在针对多病共存患者的治疗推荐方面具有可行性及价值。该研究通过模拟多学科团队(MDT)决策讨论,设计单一智能体和MAS框架解决医疗冲突。评估系统对多病共存患者的治疗规划任务时,与单一智能体方法和真实世界基准进行比较。研究定义的评价指标不仅限于技术精度和召回率,还允许检查临床目标的达成情况和建议的药物负担与黄金标准基准的比较。结果显示,当前LLM的单一智能体表现与MDT相当,最佳模型能提出满足所有临床目标的正确建议,但建议尚不完整,部分模型存在不必要用药,导致药物与条件或药物之间的不必要冲突。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)构建的多智能体系统(MAS)在处理慢性多病共存患者的治疗推荐时具有挑战性和价值。
- 多学科团队(MDT)的合作方式被模拟用于解决医疗冲突。
- 系统评估包括技术精度和召回率,同时考虑临床目标的达成情况和建议的药物负担。
- 单一智能体的表现与多学科团队相当。
- 最佳模型能提出正确的建议,满足所有临床目标,但建议尚不完整。
- 部分模型存在不必要用药的问题。
点此查看论文截图

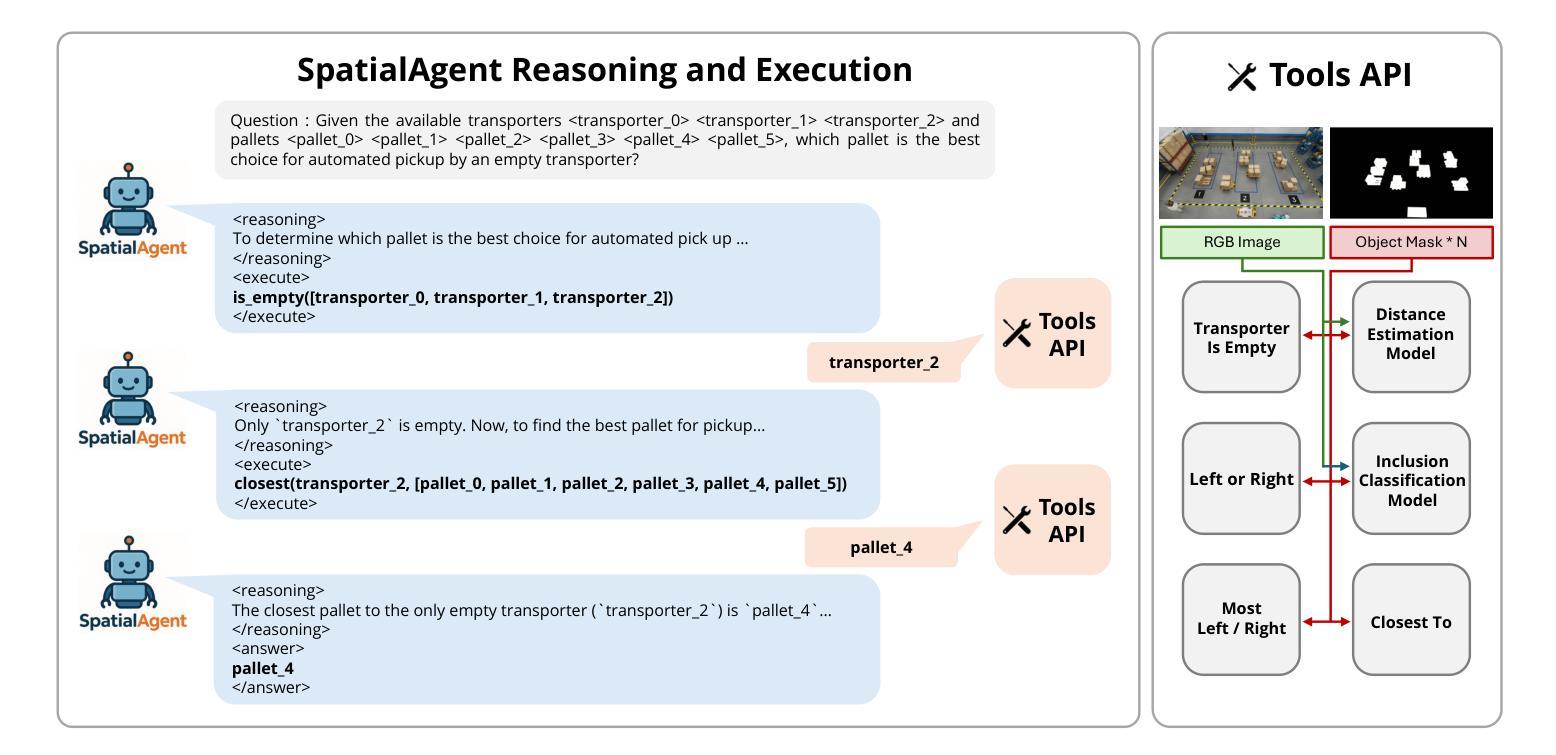
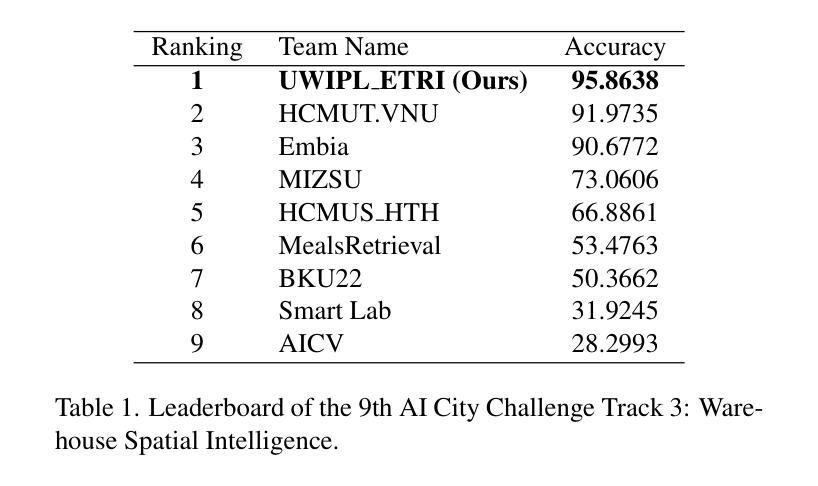
Warehouse Spatial Question Answering with LLM Agent
Authors:Hsiang-Wei Huang, Jen-Hao Cheng, Kuang-Ming Chen, Cheng-Yen Yang, Bahaa Alattar, Yi-Ru Lin, Pyongkun Kim, Sangwon Kim, Kwangju Kim, Chung-I Huang, Jenq-Neng Hwang
Spatial understanding has been a challenging task for existing Multi-modal Large Language Models~(MLLMs). Previous methods leverage large-scale MLLM finetuning to enhance MLLM’s spatial understanding ability. In this paper, we present a data-efficient approach. We propose a LLM agent system with strong and advanced spatial reasoning ability, which can be used to solve the challenging spatial question answering task in complex indoor warehouse scenarios. Our system integrates multiple tools that allow the LLM agent to conduct spatial reasoning and API tools interaction to answer the given complicated spatial question. Extensive evaluations on the 2025 AI City Challenge Physical AI Spatial Intelligence Warehouse dataset demonstrate that our system achieves high accuracy and efficiency in tasks such as object retrieval, counting, and distance estimation. The code is available at: https://github.com/hsiangwei0903/SpatialAgent
空间理解对于现有的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来说一直是一项具有挑战性的任务。之前的方法利用大规模MLLM微调技术来提升MLLM的空间理解能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种数据高效的方法。我们提出了一个具有强大和先进空间推理能力的LLM代理系统,可用于解决复杂室内仓库场景中具有挑战性的空间问答任务。我们的系统集成了多种工具,允许LLM代理进行空间推理和API工具交互,以回答给定的复杂空间问题。在2025年AI城市挑战赛物理AI空间智能仓库数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的系统在对象检索、计数和距离估计等任务上实现了高准确性和高效率。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/hsiangwei0903/SpatialAgent
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 1st Place Solution of the 9th AI City Challenge Track 3
Summary
文本主要描述了一种具有强大空间推理能力的大型语言模型代理系统。该系统采用数据高效的方法解决复杂的室内仓库场景中的空间问答任务,并通过多个工具和API进行空间推理和交互。在AI城市挑战赛物理AI空间智能仓库数据集上的评估表明,该系统在目标检索、计数和距离估计等任务中具有高精度和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在空间理解方面存在挑战。
- 提出了一种具有强大空间推理能力的大型语言模型代理系统。
- 系统通过整合多种工具进行空间推理和API交互以解答复杂的空间问题。
- 在AI城市挑战赛的物理AI空间智能仓库数据集上进行了广泛评估。
- 系统在目标检索、计数和距离估计等任务上表现出高准确性和高效率。
- 该系统可用于复杂的室内仓库场景中的空间问答任务。
点此查看论文截图

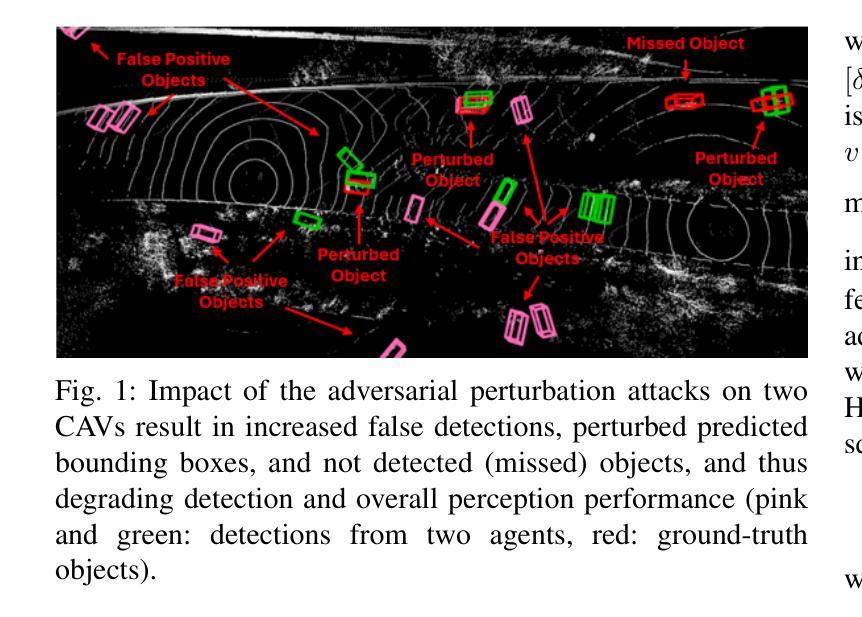
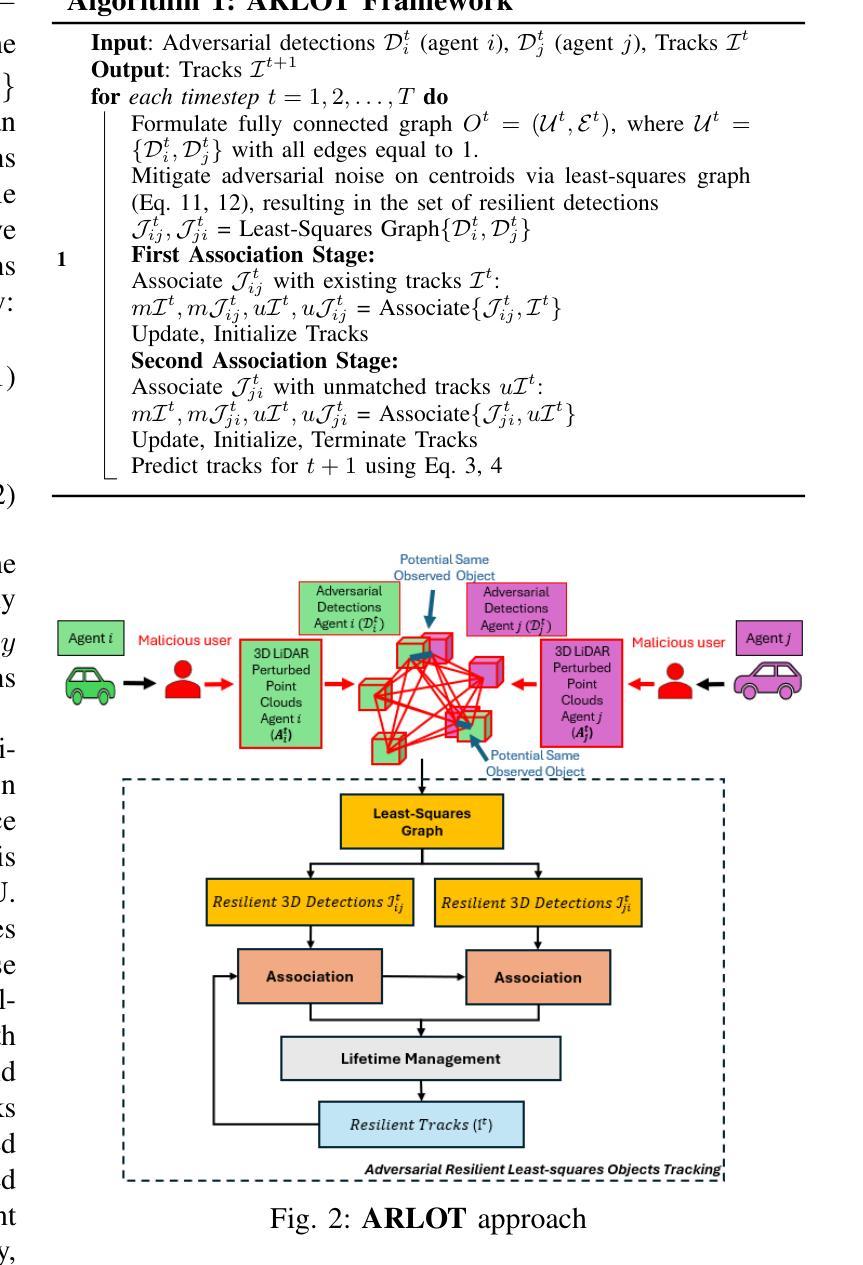
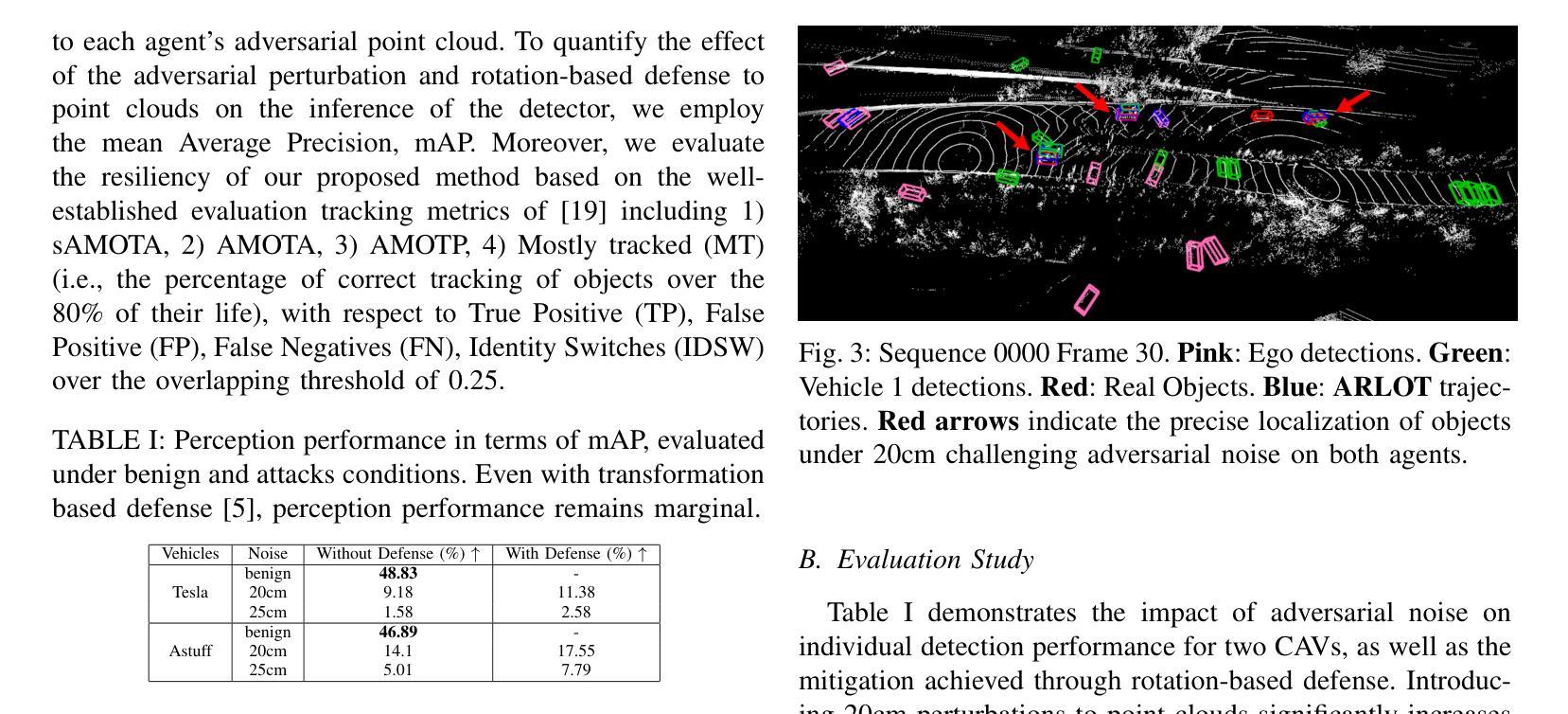
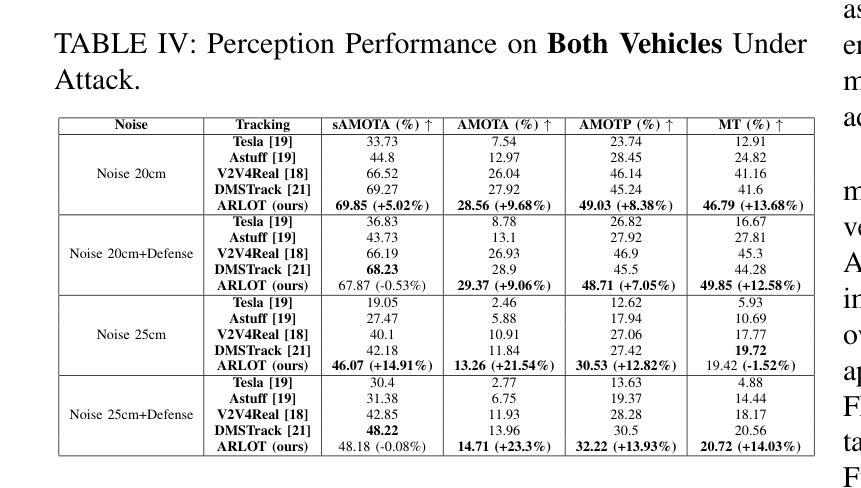
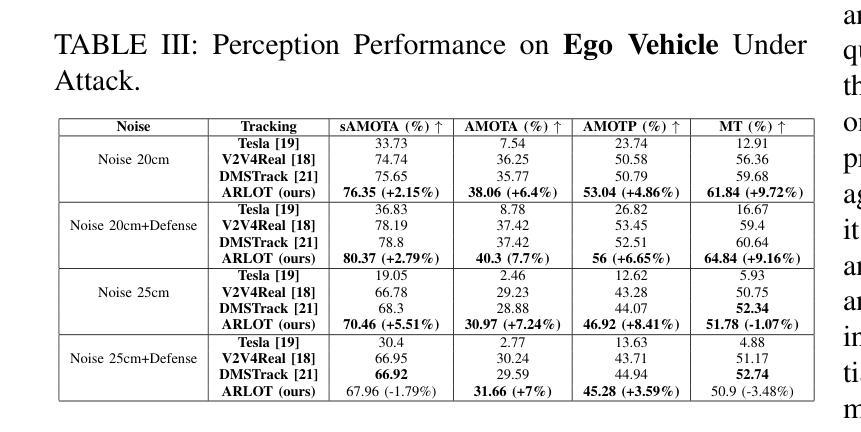
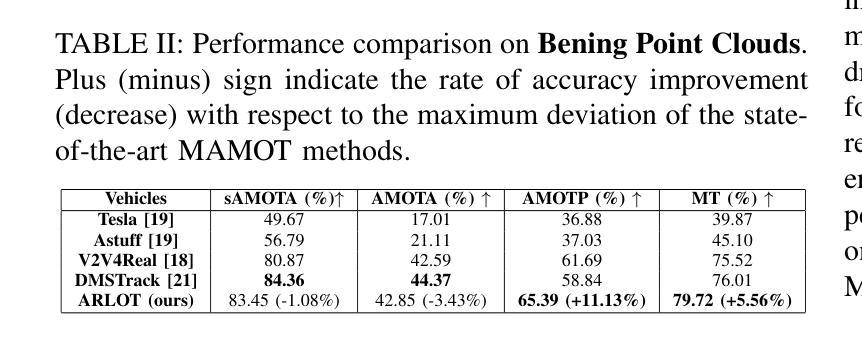
Robustifying 3D Perception via Least-Squares Graphs for Multi-Agent Object Tracking
Authors:Maria Damanaki, Ioulia Kapsali, Nikos Piperigkos, Alexandros Gkillas, Aris S. Lalos
The critical perception capabilities of EdgeAI systems, such as autonomous vehicles, are required to be resilient against adversarial threats, by enabling accurate identification and localization of multiple objects in the scene over time, mitigating their impact. Single-agent tracking offers resilience to adversarial attacks but lacks situational awareness, underscoring the need for multi-agent cooperation to enhance context understanding and robustness. This paper proposes a novel mitigation framework on 3D LiDAR scene against adversarial noise by tracking objects based on least-squares graph on multi-agent adversarial bounding boxes. Specifically, we employ the least-squares graph tool to reduce the induced positional error of each detection’s centroid utilizing overlapped bounding boxes on a fully connected graph via differential coordinates and anchor points. Hence, the multi-vehicle detections are fused and refined mitigating the adversarial impact, and associated with existing tracks in two stages performing tracking to further suppress the adversarial threat. An extensive evaluation study on the real-world V2V4Real dataset demonstrates that the proposed method significantly outperforms both state-of-the-art single and multi-agent tracking frameworks by up to 23.3% under challenging adversarial conditions, operating as a resilient approach without relying on additional defense mechanisms.
边缘人工智能系统(如自动驾驶汽车)的关键感知能力需要对抗恶意威胁具有韧性。这要求系统能够随着时间的推移,准确识别和定位场景中的多个物体,并减轻其影响。单智能体跟踪虽然可以抵御恶意攻击,但缺乏态势感知能力,这强调了多智能体合作以增强上下文理解和稳健性的必要性。本文提出了一种基于最小二乘图的多智能体对抗边界框跟踪对象的新型缓解框架,以对抗激光雷达场景中的对抗噪声。具体来说,我们利用最小二乘图工具来减少每个检测中心点的感应位置误差,通过在完全连接的图上使用差分坐标和锚点,在重叠的边界框中进行操作。因此,多车辆检测被融合和细化,减轻了对抗影响,并与现有轨迹相结合,分为两个阶段进行追踪,进一步抑制了对抗威胁。在真实世界的V2V4Real数据集上的广泛评估研究表明,在具有挑战性的对抗条件下,该方法明显优于最新的单智能体和多智能体跟踪框架,提升率高达23.3%,作为一种具有韧性的方法,无需依赖额外的防御机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures, 4 tables
Summary
边缘智能系统(如自动驾驶汽车)需要具备对抗恶意攻击时的恢复能力,这需要实现对场景中多个物体的准确识别和定位。单智能体追踪虽然可以抵御攻击,但缺乏环境意识,因此需要多智能体合作以增强上下文理解和稳健性。本文提出一种基于最小二乘图和多智能体对抗性边界框的新对抗噪声追踪方法。在连接图中利用重叠的边界框并利用差异坐标和锚点,实现降低对象检测的引入位置误差。通过融合和细化多车辆检测,对抗恶意影响并与现有轨迹关联,进一步抑制恶意威胁。在现实世界V2V4Real数据集上的评估显示,该方法在具有挑战性的对抗条件下显著优于最先进的单智能体和多智能体追踪框架,作为一种不依赖额外防御机制的有恢复力方法。
Key Takeaways
- EdgeAI系统需要对抗恶意攻击时的恢复能力,以实现对场景中物体的准确识别和定位。
- 单智能体追踪虽可抵御攻击但缺乏环境意识,强调多智能体合作的必要性以增强稳健性。
- 论文提出了一种基于最小二乘图和多智能体边界框的追踪方法以抵御恶意噪声攻击。
- 该方法利用最小二乘图工具减少对象检测引入的位置误差。
- 多车辆检测融合和细化有助于对抗恶意影响并与现有轨迹关联。
- 该方法在现实世界数据集上的评估表现优于其他追踪框架。
点此查看论文截图

MATE: LLM-Powered Multi-Agent Translation Environment for Accessibility Applications
Authors:Aleksandr Algazinov, Matt Laing, Paul Laban
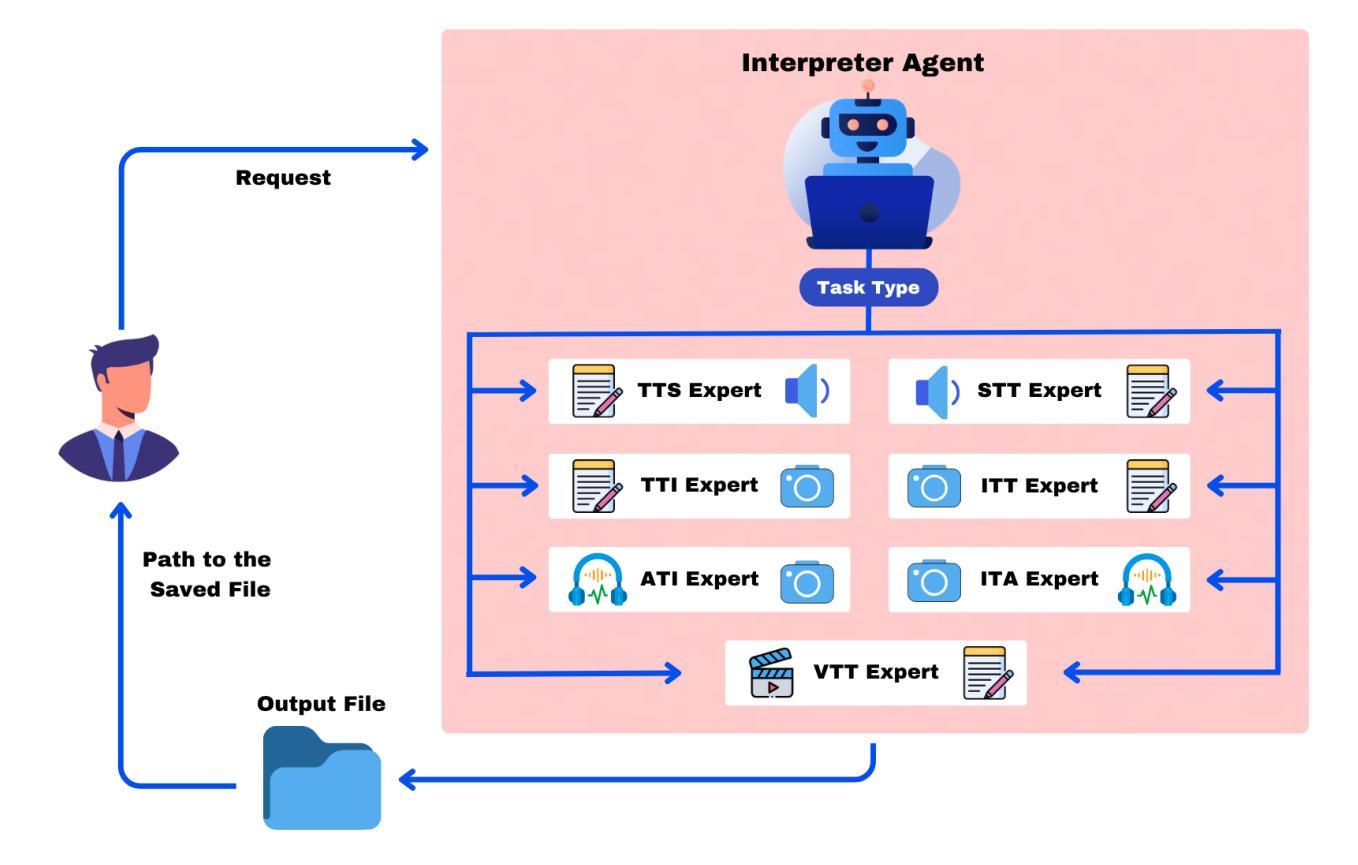
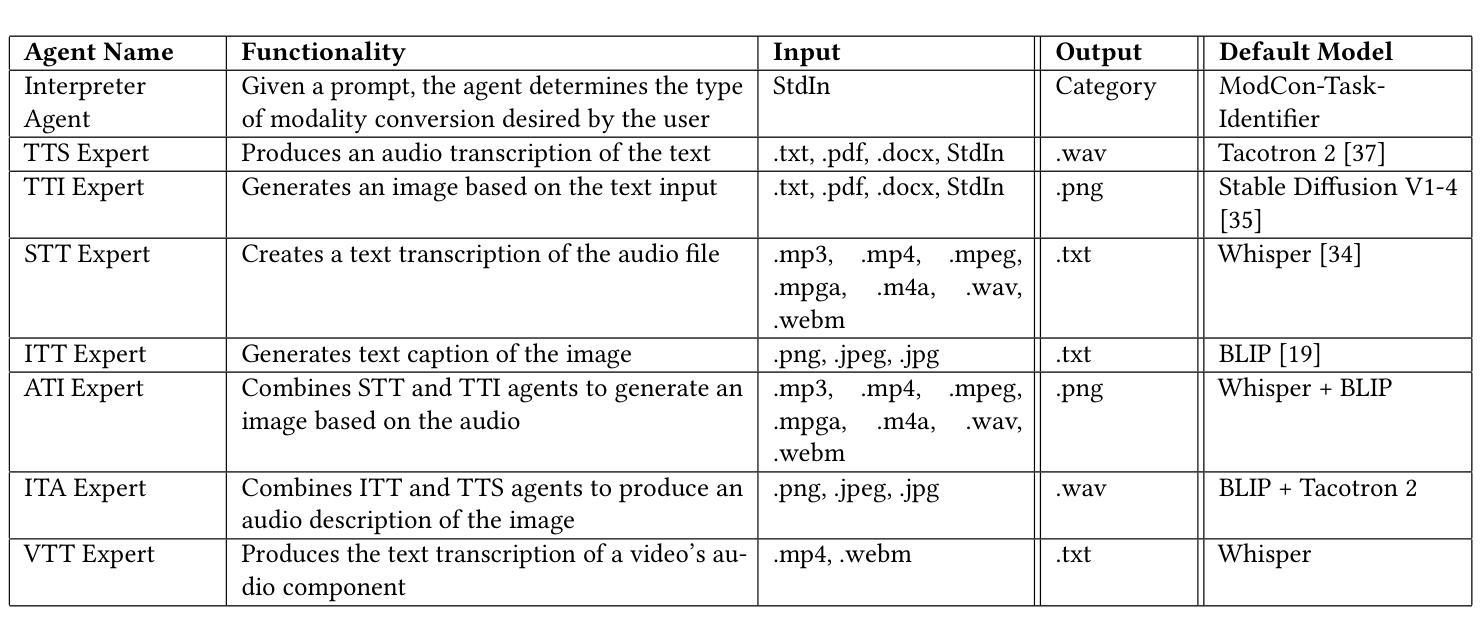
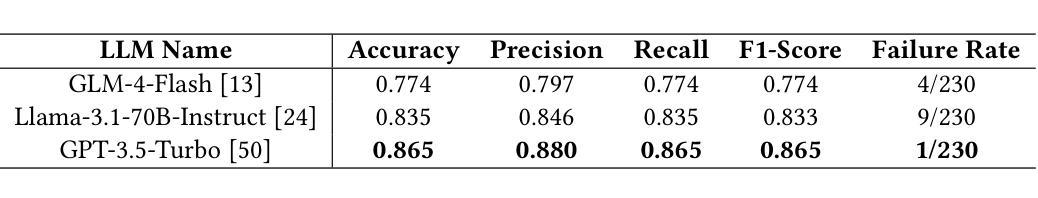
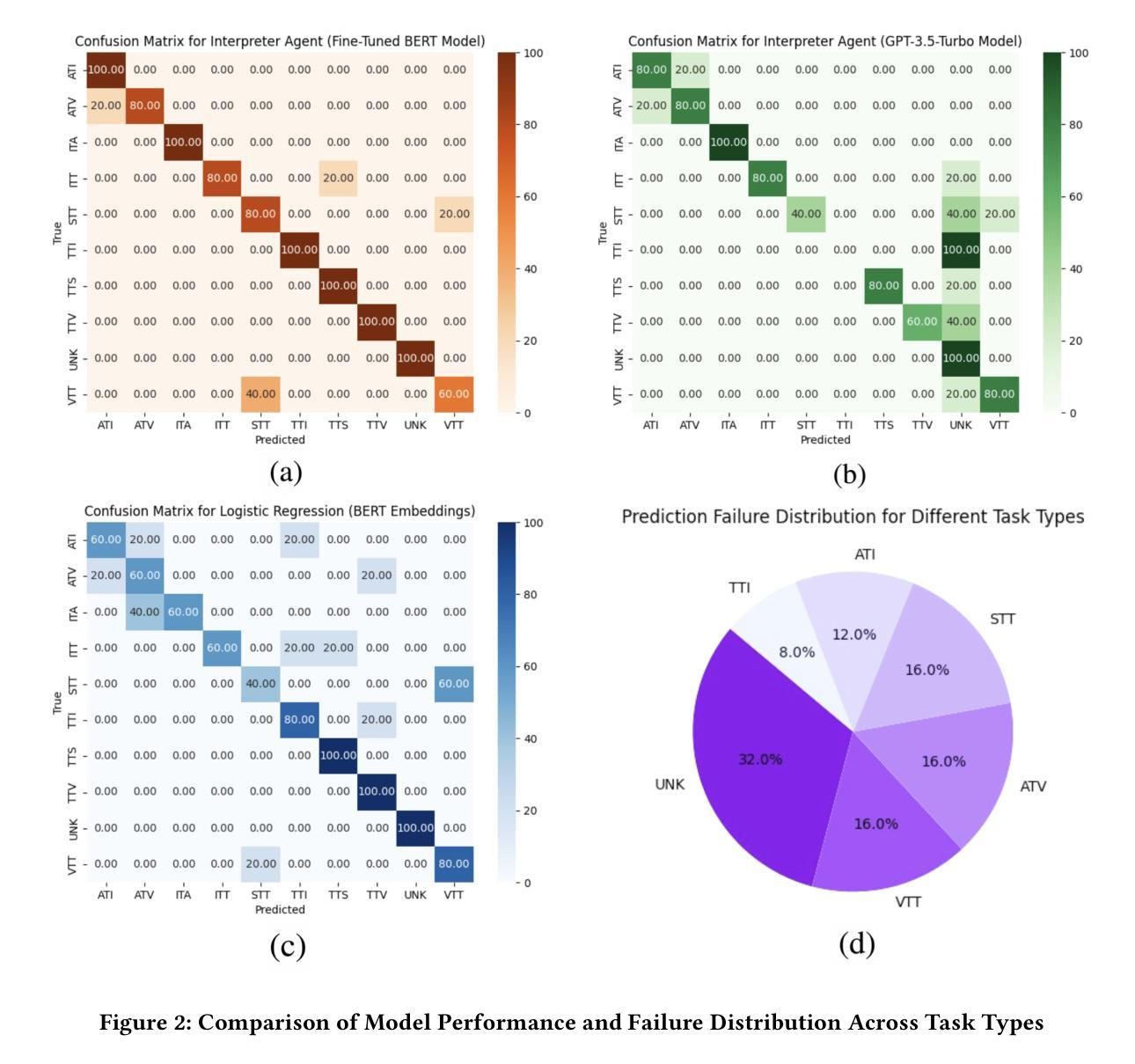
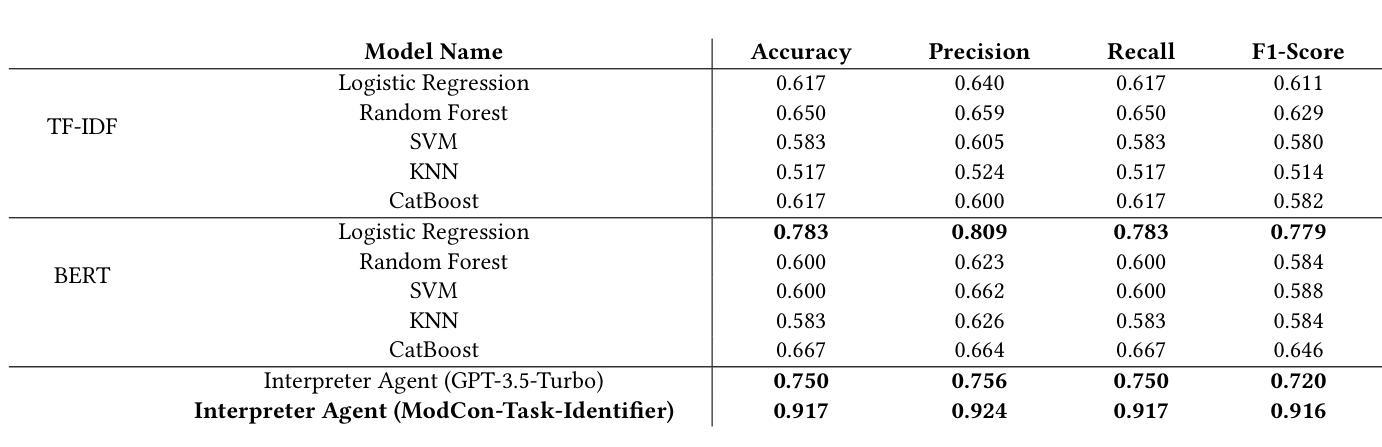
Accessibility remains a critical concern in today’s society, as many technologies are not developed to support the full range of user needs. Existing multi-agent systems (MAS) often cannot provide comprehensive assistance for users in need due to the lack of customization stemming from closed-source designs. Consequently, individuals with disabilities frequently encounter significant barriers when attempting to interact with digital environments. We introduce MATE, a multimodal accessibility MAS, which performs the modality conversions based on the user’s needs. The system is useful for assisting people with disabilities by ensuring that data will be converted to an understandable format. For instance, if the user cannot see well and receives an image, the system converts this image to its audio description. MATE can be applied to a wide range of domains, industries, and areas, such as healthcare, and can become a useful assistant for various groups of users. The system supports multiple types of models, ranging from LLM API calling to using custom machine learning (ML) classifiers. This flexibility ensures that the system can be adapted to various needs and is compatible with a wide variety of hardware. Since the system is expected to run locally, it ensures the privacy and security of sensitive information. In addition, the framework can be effectively integrated with institutional technologies (e.g., digital healthcare service) for real-time user assistance. Furthermore, we introduce ModCon-Task-Identifier, a model that is capable of extracting the precise modality conversion task from the user input. Numerous experiments show that ModCon-Task-Identifier consistently outperforms other LLMs and statistical models on our custom data. Our code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/AlgazinovAleksandr/Multi-Agent-MATE.
在当今社会,无障碍性仍然是一个关键问题,因为许多技术并非为了支持各种用户需求而开发。现有的多智能体系统(MAS)往往由于封闭式设计的缺乏定制化而无法为用户提供全面的帮助。因此,残疾人在尝试与数字环境交互时经常遇到重大障碍。我们介绍了MATE,这是一个多模式访问MAS,它可以根据用户的需求进行模式转换。该系统通过确保数据转换为可理解格式,对于帮助残疾人非常有用。例如,如果用户视力不佳并收到图像,系统会将该图像转换为音频描述。MATE可广泛应用于各种领域、行业和地区,如医疗保健,可以成为各种用户的实用助手。该系统支持多种类型的模型,从调用大型语言模型API到使用自定义机器学习(ML)分类器。这种灵活性确保系统可以根据各种需求进行适应,并且与各种硬件兼容。由于系统预期在本地运行,因此确保敏感信息的隐私和安全。此外,该框架可以有效地与机构技术(例如数字医疗服务)集成,以进行实时用户协助。此外,我们引入了ModCon-Task-Identifier模型,它能够精确地从用户输入中提取模式转换任务。大量实验表明,ModCon-Task-Identifier在我们的自定义数据上始终优于其他大型语言模型和统计模型。我们的代码和数据公开可用在https://github.com/AlgazinovAleksandr/Multi-Agent-MATE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态访问MAS系统(MATE)能根据用户需求进行模态转换,为残疾人提供全面的帮助。MATE适用于各种领域、行业和用户群体,支持多种类型的模型,可灵活适应各种需求。此外,MATE可本地运行以确保敏感信息的隐私和安全,并能有效地与机构技术集成以实现实时用户协助。我们引入了ModCon-Task-Identifier模型,能够从用户输入中提取精确模态转换任务,并在自定义数据上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- MATE系统采用多模态访问MAS技术,可为用户根据需要提供模态转换。
- MATE对于支持残疾人使用数字技术至关重要,可将数据转换为易于理解的形式。
- MATE具有广泛的应用范围,适用于多个领域、行业和用户群体。
- MATE系统支持多种类型的模型,包括LLM API和自定义机器学习分类器,具有灵活性。
- MATE可在本地运行以确保敏感信息的隐私和安全。
- MATE能有效集成到机构技术中,提供实时用户协助。
点此查看论文截图

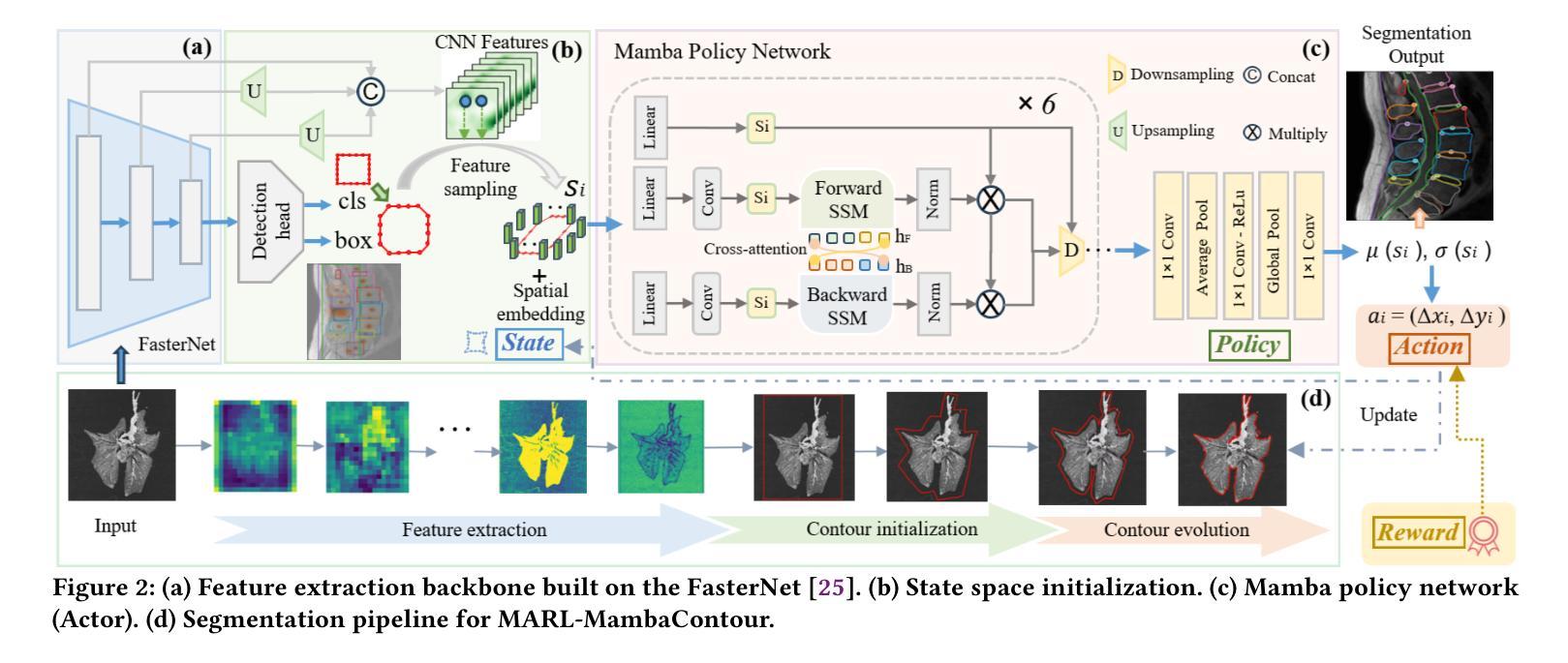
MARL-MambaContour: Unleashing Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Active Contour Optimization in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ruicheng Zhang, Yu Sun, Zeyu Zhang, Jinai Li, Xiaofan Liu, Au Hoi Fan, Haowei Guo, Puxin Yan
We introduce MARL-MambaContour, the first contour-based medical image segmentation framework based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). Our approach reframes segmentation as a multi-agent cooperation task focused on generate topologically consistent object-level contours, addressing the limitations of traditional pixel-based methods which could lack topological constraints and holistic structural awareness of anatomical regions. Each contour point is modeled as an autonomous agent that iteratively adjusts its position to align precisely with the target boundary, enabling adaptation to blurred edges and intricate morphologies common in medical images. This iterative adjustment process is optimized by a contour-specific Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm, further enhanced with the Entropy Regularization Adjustment Mechanism (ERAM) which dynamically balance agent exploration with contour smoothness. Furthermore, the framework incorporates a Mamba-based policy network featuring a novel Bidirectional Cross-attention Hidden-state Fusion Mechanism (BCHFM). This mechanism mitigates potential memory confusion limitations associated with long-range modeling in state space models, thereby facilitating more accurate inter-agent information exchange and informed decision-making. Extensive experiments on five diverse medical imaging datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of MARL-MambaContour, highlighting its potential as an accurate and robust clinical application.
我们引入了基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的首个轮廓基医疗图像分割框架MARL-MambaContour。我们的方法将分割重新构建为一个多智能体合作任务,专注于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法可能缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知解剖区域的局限性。每个轮廓点都被建模为一个自主智能体,可以迭代调整其位置以精确地与目标边界对齐,从而适应医学图像中常见的模糊边缘和复杂形态。这种迭代调整过程通过轮廓特定的柔软演员评论家(SAC)算法优化,进一步通过熵正则化调整机制(ERAM)增强,该机制动态平衡智能体探索与轮廓平滑。此外,该框架采用基于Mamba的策略网络,并引入了一种新颖的双向交叉注意力隐藏状态融合机制(BCHFM)。该机制缓解了状态空间模型中长程建模可能带来的潜在内存混淆限制,从而促进了更准确的跨智能体信息交换和决策。在五个不同的医学成像数据集上的广泛实验证明了MARL-MambaContour的卓越性能,凸显了其在临床应用中作为准确且稳健的潜力的前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的MambaContour轮廓基线医疗图像分割框架。它将分割重新构建为多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法的局限性。通过轮廓特定的Soft Actor-Critic算法和熵正则化调整机制优化迭代调整过程。引入Mamba策略网络及双向交叉注意力隐藏状态融合机制,提高准确性。在五个医疗成像数据集上的实验证明了其卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- MARL-MambaContour是首个基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的轮廓基线医疗图像分割框架。
- 将分割任务重新构建为多智能体合作任务,专注于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓。
- 解决了传统像素级方法的局限性,包括缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知。
- 每个轮廓点被建模为自主智能体,可迭代调整位置以精确对齐目标边界,适应模糊边缘和复杂形态。
- 采用轮廓特定的Soft Actor-Critic算法和熵正则化调整机制优化迭代调整过程。
- 引入Mamba策略网络和双向交叉注意力隐藏状态融合机制,改善信息交换和决策制定。
点此查看论文截图

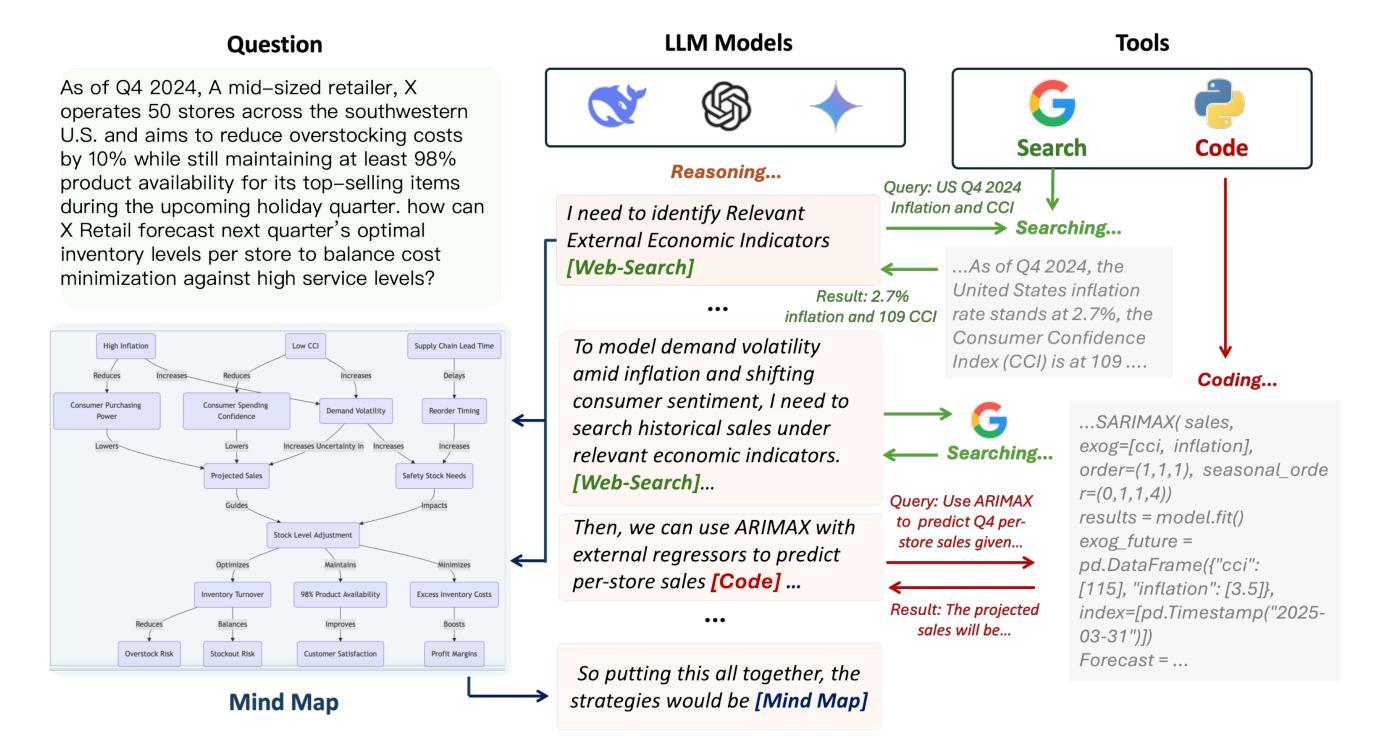
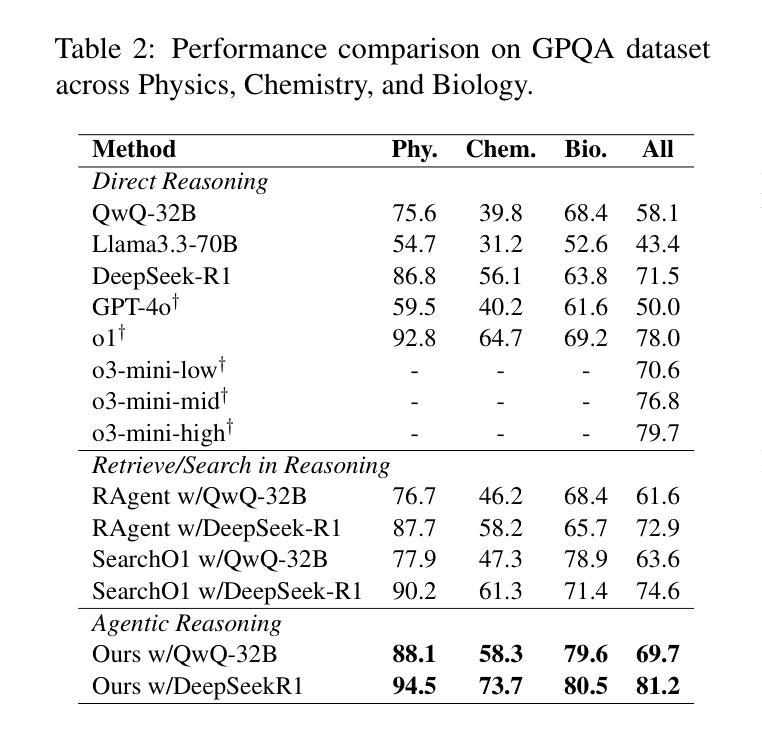
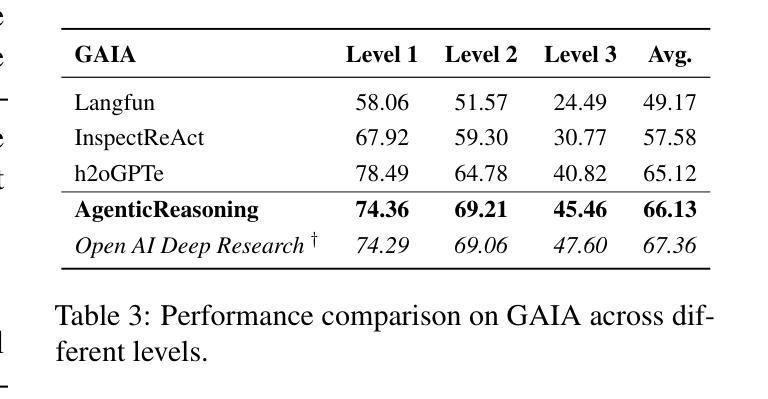
Agentic Reasoning: A Streamlined Framework for Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Agentic Tools
Authors:Junde Wu, Jiayuan Zhu, Yuyuan Liu, Min Xu, Yueming Jin
We introduce Agentic Reasoning, a framework that enhances large language model (LLM) reasoning by integrating external tool-using agents. Agentic Reasoning dynamically leverages web search, code execution, and structured memory to address complex problems requiring deep research. A key innovation in our framework is the Mind-Map agent, which constructs a structured knowledge graph to store reasoning context and track logical relationships, ensuring coherence in long reasoning chains with extensive tool usage. Additionally, we conduct a comprehensive exploration of the Web-Search agent, leading to a highly effective search mechanism that surpasses all prior approaches. When deployed on DeepSeek-R1, our method achieves a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) among public models and delivers performance comparable to OpenAI Deep Research, the leading proprietary model in this domain. Extensive ablation studies validate the optimal selection of agentic tools and confirm the effectiveness of our Mind-Map and Web-Search agents in enhancing LLM reasoning. The code is at: https://github.com/theworldofagents/Agentic-Reasoning
我们引入了Agentic Reasoning,这是一个通过整合外部工具使用代理来增强大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的框架。Agentic Reasoning能够动态利用网页搜索、代码执行和结构化内存来解决需要深入研究的复杂问题。我们框架中的一个关键创新是Mind-Map代理,它构建了一个结构化知识图谱来存储推理上下文并跟踪逻辑关系,确保在长时间使用大量工具的长推理链中保持连贯性。此外,我们对Web-Search代理进行了全面的探索,导致出现了一个高效的搜索机制,超越了所有以前的方法。当部署在DeepSeek-R1上时,我们的方法达到了公共模型中的最新水平,并提供了与此领域领先的专有模型OpenAI Deep Research相当的性能。广泛的消融研究验证了代理工具的优选选择,并证实了我们的Mind-Map和Web-Search代理在提高LLM推理能力方面的有效性。代码位于:https://github.com/theworldofagents/Agentic-Reasoning
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)通过引入Agentic Reasoning框架得到增强,该框架集成了外部工具使用代理。Agentic Reasoning通过动态利用Web搜索、代码执行和结构化内存来解决需要深度研究的复杂问题。框架的关键创新在于Mind-Map代理,能够构建结构化知识图谱来存储推理上下文并跟踪逻辑关系,确保在长时间推理链中使用大量工具时的连贯性。此外,我们对Web-Search代理进行了全面的探索,开发出一种高效的搜索机制,超越了先前所有方法。部署在DeepSeek-R1上时,我们的方法达到了公共模型的新水平,性能与领域领先专有模型OpenAI Deep Research相当。广泛的消融研究验证了代理工具的最佳选择,并证实了我们的Mind-Map和Web-Search代理在提高LLM推理方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic Reasoning框架集成了外部工具使用代理,增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- 该框架通过动态利用Web搜索、代码执行和结构化内存解决复杂问题。
- Mind-Map代理是框架的关键创新,能构建结构化知识图谱以存储推理上下文并跟踪逻辑关系。
- Web-Search代理经过全面探索,开发出高效的搜索机制,超越先前方法。
- 该方法在DeepSeek-R1上部署时表现出卓越性能,达到公共模型的新水平。
- 与领域领先模型OpenAI Deep Research性能相当。
点此查看论文截图


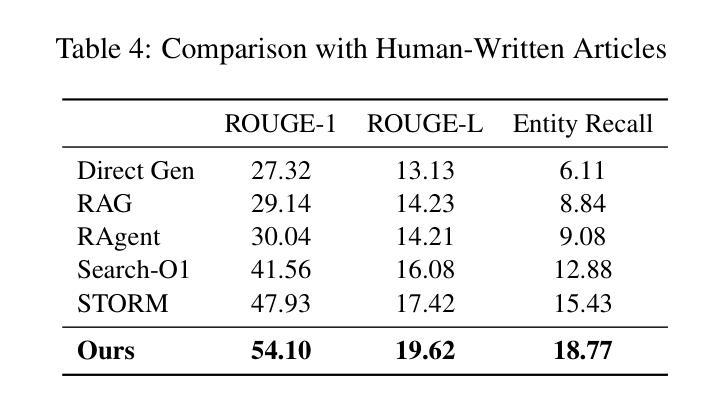
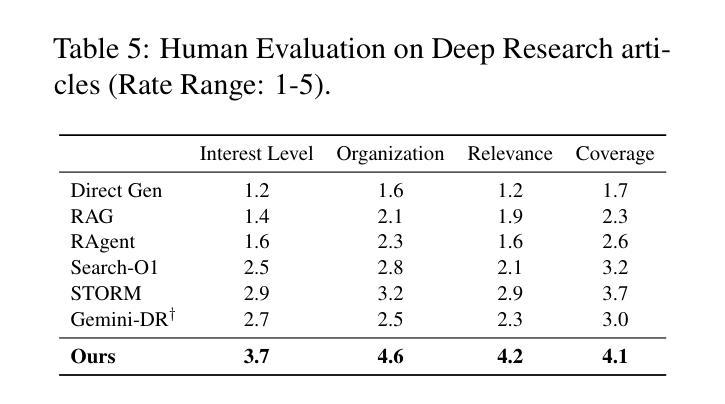
Online Intrinsic Rewards for Decision Making Agents from Large Language Model Feedback
Authors:Qinqing Zheng, Mikael Henaff, Amy Zhang, Aditya Grover, Brandon Amos
Automatically synthesizing dense rewards from natural language descriptions is a promising paradigm in reinforcement learning (RL), with applications to sparse reward problems, open-ended exploration, and hierarchical skill design. Recent works have made promising steps by exploiting the prior knowledge of large language models (LLMs). However, these approaches suffer from important limitations: they are either not scalable to problems requiring billions of environment samples, due to requiring LLM annotations for each observation, or they require a diverse offline dataset, which may not exist or be impossible to collect. In this work, we address these limitations through a combination of algorithmic and systems-level contributions. We propose ONI, a distributed architecture that simultaneously learns an RL policy and an intrinsic reward function using LLM feedback. Our approach annotates the agent’s collected experience via an asynchronous LLM server, which is then distilled into an intrinsic reward model. We explore a range of algorithmic choices for reward modeling with varying complexity, including hashing, classification, and ranking models. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across a range of challenging tasks from the NetHack Learning Environment, while removing the need for large offline datasets required by prior work. We make our code available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/oni .
自动从自然语言描述中合成密集奖励是强化学习(RL)中一个有前途的模式,应用于稀疏奖励问题、开放式探索和分层技能设计。最近的工作通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)的先验知识取得了有希望的进展。然而,这些方法存在重要局限性:它们要么不可扩展至需要数亿环境样本的问题,因为每个观察都需要LLM注释,或者它们需要多样化的离线数据集,这可能不存在或无法收集。在这项工作中,我们通过算法和系统层面的贡献解决了这些局限性。我们提出了ONI,一种分布式架构,可以同时学习RL策略和使用LLM反馈的内在奖励函数。我们的方法通过异步LLM服务器对代理收集的经验进行注释,然后将其蒸馏成内在奖励模型。我们探索了一系列用于奖励建模的算法选择,具有不同的复杂性,包括哈希、分类和排名模型。我们的方法在NetHack学习环境中的一系列具有挑战性的任务上实现了最先进的性能,同时不需要先前工作所需的大量离线数据集。我们在https://github.com/facebookresearch/oni上公开了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合强化学习和大型语言模型反馈的分布式架构ONI,用于从自然语言描述中自动合成密集奖励。针对现有方法存在的可扩展性和离线数据集需求问题,本文提出了相应的算法和系统级贡献。ONI能够同时学习RL策略和内在奖励函数,通过异步LLM服务器对代理收集的经验进行注释,然后蒸馏成内在奖励模型。本文探索了不同复杂度的奖励建模算法选择,包括哈希、分类和排名模型。在NetHack学习环境的一系列挑战性任务上,该方法取得了最新性能,并去除了先前工作所需的大型离线数据集。
Key Takeaways
- ONI是一种结合强化学习和大型语言模型(LLM)反馈的分布式架构。
- ONI能够同时学习RL策略和内在奖励函数。
- 通过异步LLM服务器对代理收集的经验进行注释,然后蒸馏成内在奖励模型。
- 本文解决了现有方法在不要求大量环境样本时存在的可扩展性问题。
- 该方法不需要多样的离线数据集,解决了可能不存在或难以收集的问题。
- 在NetHack学习环境的挑战性任务上取得了最新性能。
点此查看论文截图

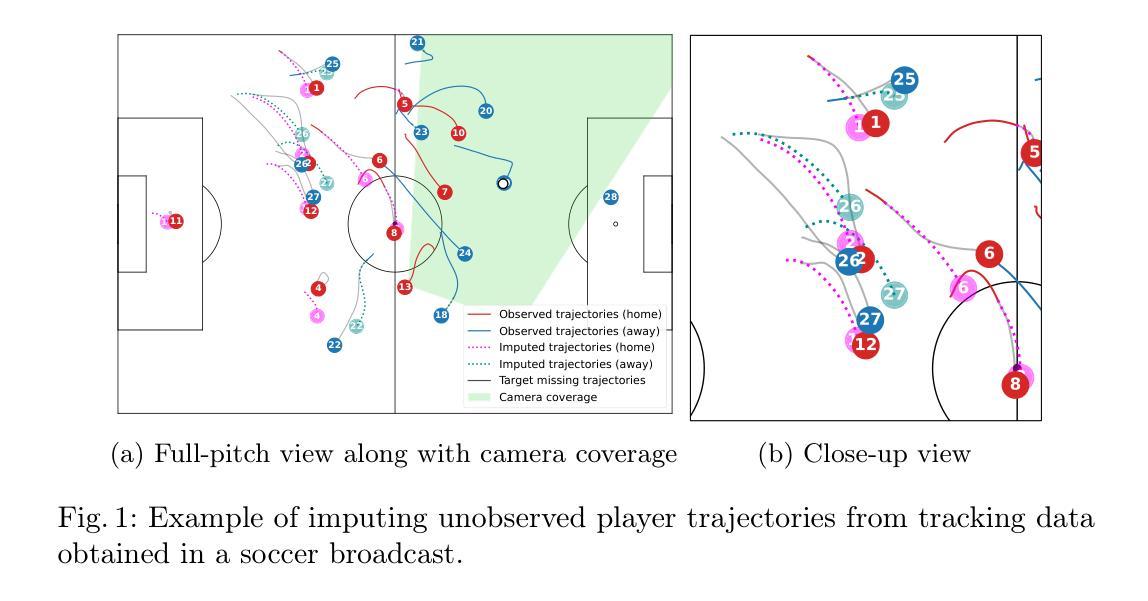
Trajectory Imputation in Multi-Agent Sports with Derivative-Accumulating Self-Ensemble
Authors:Han-Jun Choi, Hyunsung Kim, Minho Lee, Minchul Jeong, Chang-Jo Kim, Jinsung Yoon, Sang-Ki Ko
Multi-agent trajectory data collected from domains such as team sports often suffer from missing values due to various factors. While many imputation methods have been proposed for spatiotemporal data, they are not well-suited for multi-agent sports scenarios where player movements are highly dynamic and inter-agent interactions continuously evolve. To address these challenges, we propose MIDAS (Multi-agent Imputer with Derivative-Accumulating Self-ensemble), a framework that imputes multi-agent trajectories with high accuracy and physical plausibility. It jointly predicts positions, velocities, and accelerations through a Set Transformer-based neural network and generates alternative estimates by recursively accumulating predicted velocity and acceleration values. These predictions are then combined using a learnable weighted ensemble to produce final imputed trajectories. Experiments on three sports datasets demonstrate that MIDAS significantly outperforms existing baselines in both positional accuracy and physical plausibility. Lastly, we showcase use cases of MIDAS, such as approximating total distance and pass success probability, to highlight its applicability to practical downstream tasks that require complete tracking data.
从团队运动等领域收集的多智能体轨迹数据,由于各种因素往往存在缺失值。虽然许多时空数据的插值方法已经被提出,但它们并不适用于多智能体运动场景,因为球员的动作高度动态化,智能体间的互动也在不断变化。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MIDAS(具有导数累积自集成的多智能体插值器),这是一个能够高精度且物理上合理地对多智能体轨迹进行插值的框架。它通过基于集合变换器的神经网络来共同预测位置、速度和加速度,并通过递归累积预测的速度和加速度值来生成替代估计值。然后,这些预测值通过可学习的加权集成组合,生成最终的插值轨迹。在三个体育数据集上的实验表明,MIDAS在位置准确性和物理合理性方面显著优于现有基线。最后,我们展示了MIDAS的应用案例,如估算总距离和传球成功率等,以突出其在需要完整跟踪数据的实际下游任务中的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECML/PKDD 2025
Summary
多源数据缺失是团队运动等领域中常遇到的问题,尤其是在多智能体轨迹数据中。尽管已有许多时空数据插补方法,但它们并不适用于高度动态、交互多变的团队运动场景。本研究提出了MIDAS(基于衍生积累自组织的多智能体插补方法),利用基于集换元神经网络联合预测位置、速度和加速度,通过递归累积预测速度和加速度值生成替代估计值,再采用可学习的加权组合方式生成最终的插补轨迹。在三个运动数据集上的实验表明,MIDAS在位置准确性和物理合理性方面均显著优于现有基线方法。此外,我们还展示了MIDAS在估算总距离和传球成功率等实际应用场景中的应用,突显其在需要完整追踪数据的下游任务中的适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体轨迹数据缺失问题在团队运动等领域中普遍存在。
- 传统时空数据插补方法在多智能体运动场景中表现不佳。
- MIDAS方法通过集换元神经网络联合预测位置、速度和加速度,具有高准确性和物理合理性。
- MIDAS通过递归累积预测值和生成替代估计值来生成最终的插补轨迹。
- 实验结果表明,MIDAS在位置准确性和物理合理性方面优于现有方法。
- MIDAS可应用于估算总距离和传球成功率等实际下游任务。
点此查看论文截图