⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
CATVis: Context-Aware Thought Visualization
Authors:Tariq Mehmood, Hamza Ahmad, Muhammad Haroon Shakeel, Murtaza Taj
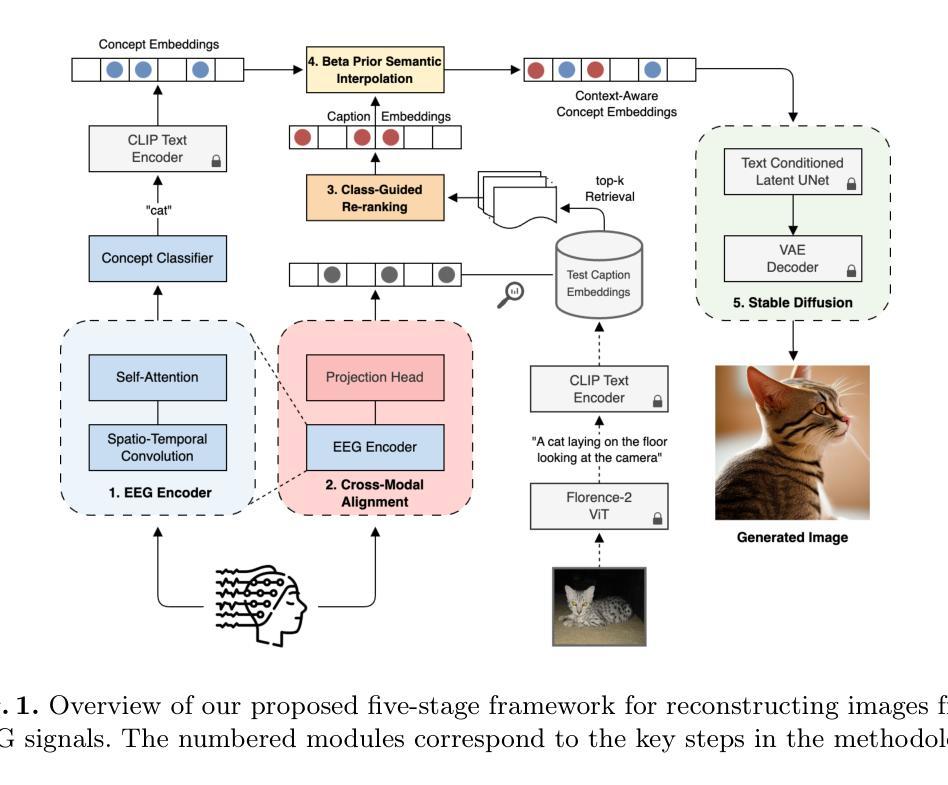
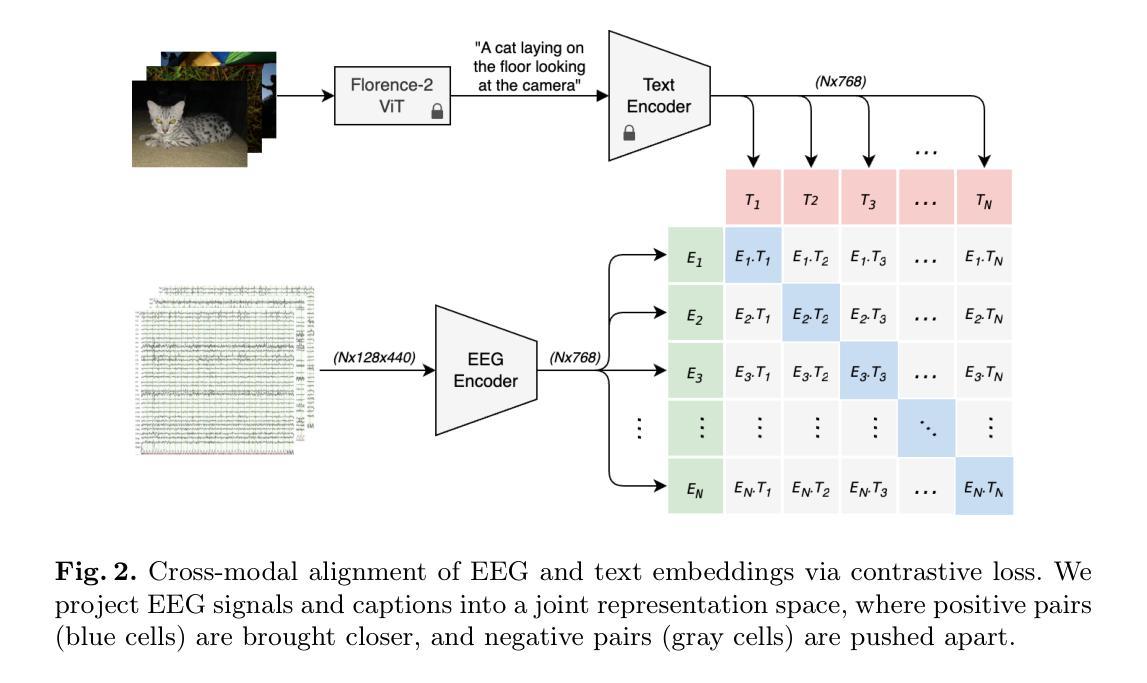
EEG-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have shown promise in various applications, such as motor imagery and cognitive state monitoring. However, decoding visual representations from EEG signals remains a significant challenge due to their complex and noisy nature. We thus propose a novel 5-stage framework for decoding visual representations from EEG signals: (1) an EEG encoder for concept classification, (2) cross-modal alignment of EEG and text embeddings in CLIP feature space, (3) caption refinement via re-ranking, (4) weighted interpolation of concept and caption embeddings for richer semantics, and (5) image generation using a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model. We enable context-aware EEG-to-image generation through cross-modal alignment and re-ranking. Experimental results demonstrate that our method generates high-quality images aligned with visual stimuli, outperforming SOTA approaches by 13.43% in Classification Accuracy, 15.21% in Generation Accuracy and reducing Fr'echet Inception Distance by 36.61%, indicating superior semantic alignment and image quality.
基于脑电图的脑机接口(BCIs)在多种应用中显示出广阔前景,如运动想象和认知状态监测。然而,由于脑电图信号的复杂性和噪声干扰,从脑电图信号中解码视觉表征仍然是一个巨大的挑战。因此,我们提出了一种新颖的解码视觉表征的5阶段框架,从脑电图信号中提取信息:(1)EEG编码器用于概念分类;(2)在CLIP特征空间中实现EEG和文本嵌入的跨模态对齐;(3)通过重新排序进行字幕优化;(4)对概念嵌入和字幕嵌入进行加权插值,以获取更丰富的语义信息;(5)使用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型进行图像生成。我们通过跨模态对齐和重新排序,实现了上下文感知的EEG到图像生成。实验结果表明,我们的方法生成了与视觉刺激对齐的高质量图像,在分类准确率上较当前最佳方法提高了13.43%,生成准确率提高了15.21%,同时减少了Frechet Inception距离(FID)36.61%,这表明了更优秀的语义对齐和图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025. This is the submitted version prior to peer review. The final Version of Record will appear in the MICCAI 2025 proceedings (Springer LNCS)
Summary
本文提出了一种基于EEG的五阶段框架,用于从脑电图信号中解码视觉表征。该方法包括概念分类的EEG编码器、跨模态对齐的EEG和文本嵌入、通过重新排序进行字幕优化、概念与字幕嵌入的加权插值以丰富语义,以及使用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型生成图像。实验结果表明,该方法生成与视觉刺激对齐的高质量图像,在分类准确性上优于现有技术方法达13.43%,在生成准确性上提高15.21%,同时减少了Fréchet Inception距离(FID)达36.61%,表现出优越的语义对齐和图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新颖的基于EEG的五个阶段框架用于解码视觉表征。
- 通过EEG编码器进行概念分类是此框架的第一步。
- 利用CLIP特征空间进行跨模态对齐的EEG和文本嵌入。
- 通过重新排序进行字幕优化,增强语义丰富性。
- 利用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型生成图像。
- 实验结果表明该框架生成高质量、与视觉刺激对齐的图像。
点此查看论文截图
Implementing Adaptations for Vision AutoRegressive Model
Authors:Kaif Shaikh, Antoni Kowalczuk, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
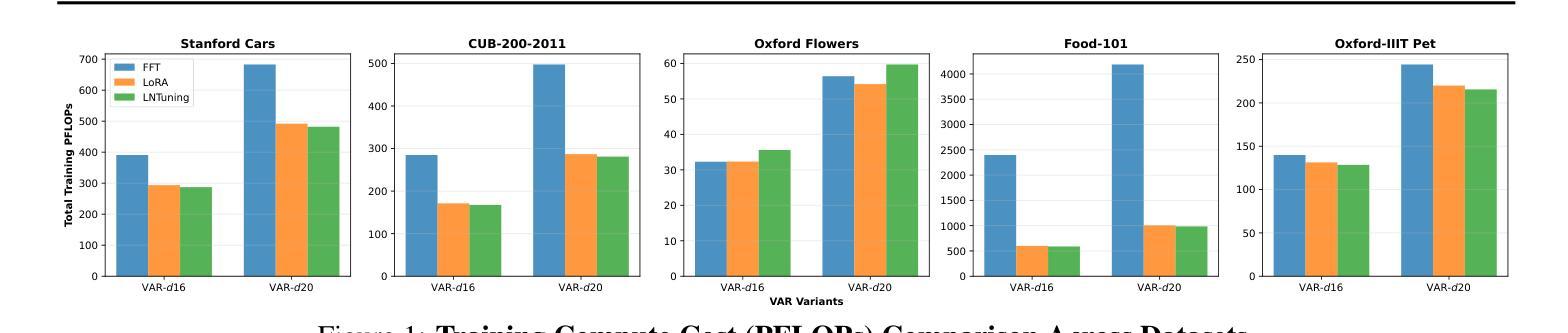
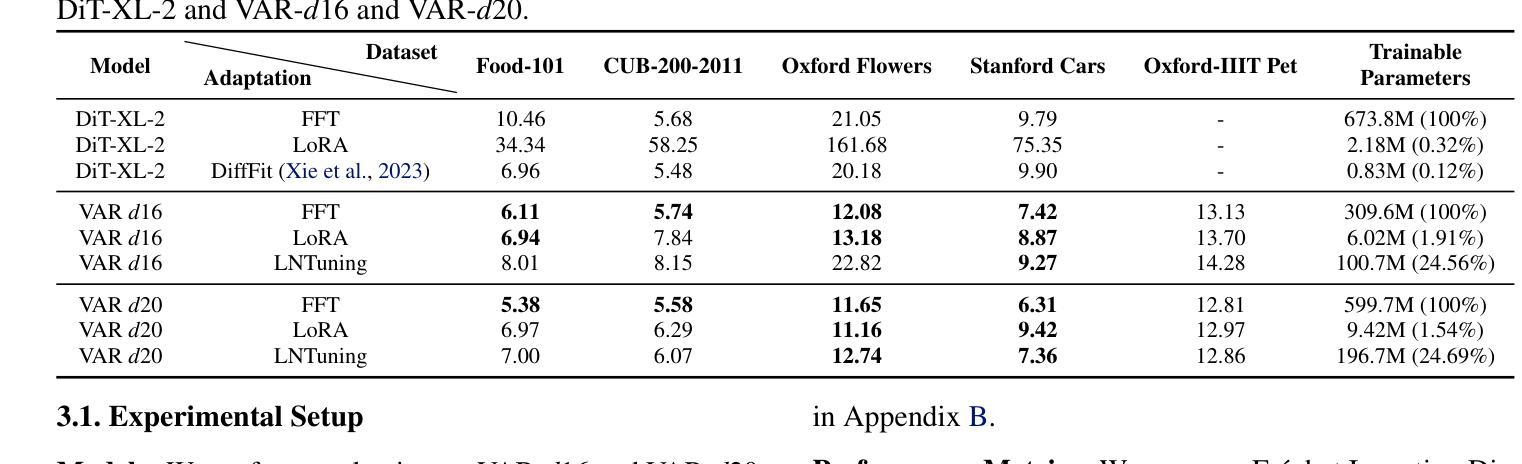
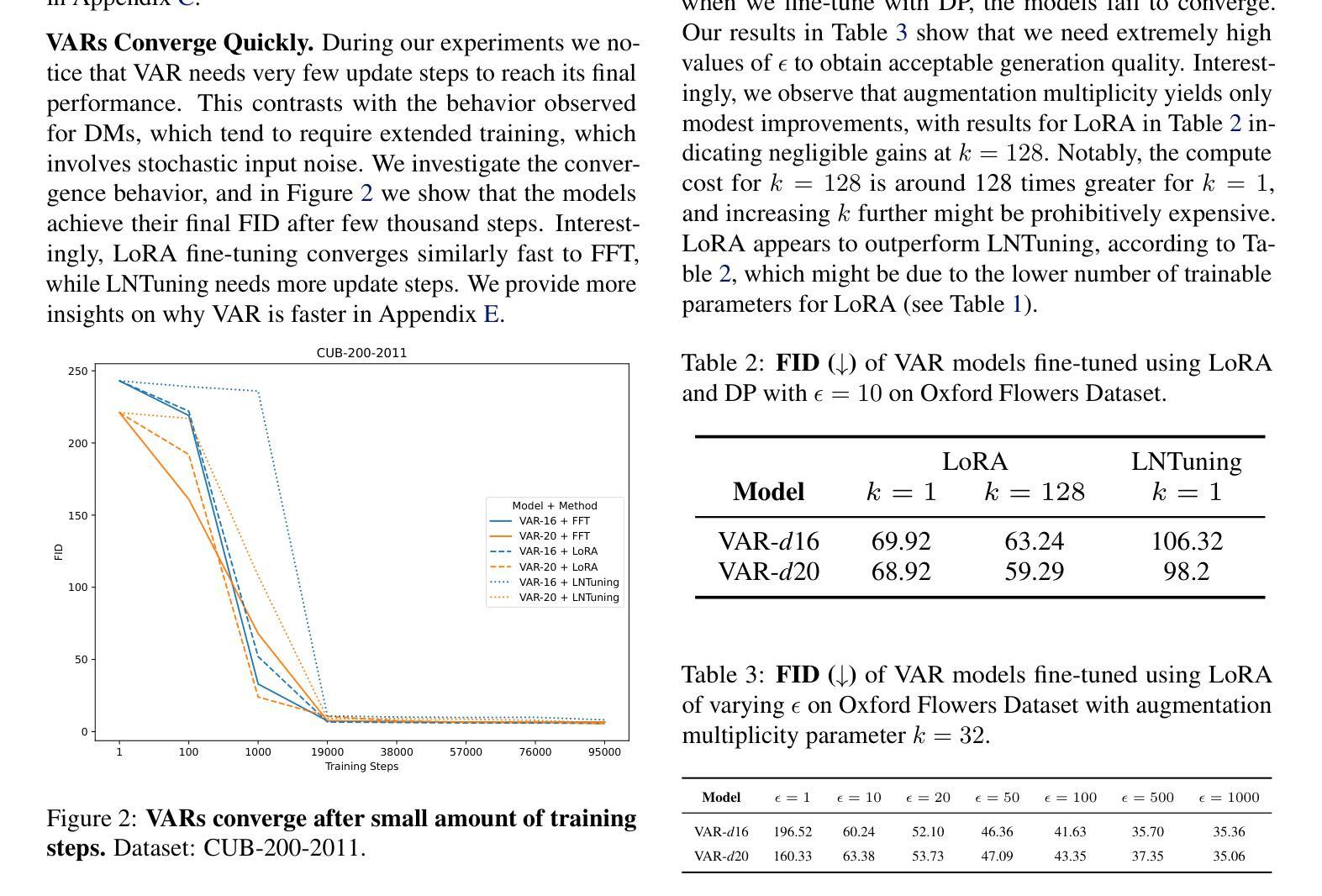
Vision AutoRegressive model (VAR) was recently introduced as an alternative to Diffusion Models (DMs) in image generation domain. In this work we focus on its adaptations, which aim to fine-tune pre-trained models to perform specific downstream tasks, like medical data generation. While for DMs there exist many techniques, adaptations for VAR remain underexplored. Similarly, differentially private (DP) adaptations-ones that aim to preserve privacy of the adaptation data-have been extensively studied for DMs, while VAR lacks such solutions. In our work, we implement and benchmark many strategies for VAR, and compare them to state-of-the-art DM adaptation strategies. We observe that VAR outperforms DMs for non-DP adaptations, however, the performance of DP suffers, which necessitates further research in private adaptations for VAR. Code is available at https://github.com/sprintml/finetuning_var_dp.
最近引入了Vision AutoRegressive模型(VAR)作为图像生成领域中Diffusion Models(DMs)的替代方案。在这项工作中,我们关注其适应性的调整,旨在微调预训练模型以执行特定的下游任务,如医学数据生成。虽然对于DMs存在许多技术,但VAR的适应性调整仍然未被充分探索。类似地,针对DMs的差分私有(DP)适应性调整——旨在保护适应性数据的隐私——已经得到了广泛的研究,而VAR缺乏此类解决方案。在我们的工作中,我们实现了多种VAR的策略并进行了基准测试,并将其与最新的DM适应策略进行了比较。我们发现VAR在非DP适应性方面表现优于DMs,但是DP的性能却有所下降,这需要在VAR的私有适应性方面进行进一步的研究。代码可在[https://github.com/sprintml/finetuning_var_dp找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at DIG-BUGS: Data in Generative Models Workshop @ ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Vision AutoRegressive模型(VAR)在图像生成领域作为Diffusion Models(DMs)的替代方案,并重点探讨了其针对特定下游任务的适应性问题,如医疗数据生成。文章比较了VAR与DM的适应策略,发现VAR在非差分隐私(DP)适应方面表现优于DMs,但在差分隐私适应方面性能有待提高。
Key Takeaways
- Vision AutoRegressive模型(VAR)被引入作为图像生成领域中的Diffusion Models(DMs)的替代方案。
- 文章重点探讨了VAR模型的适应性问题,特别是针对预训练模型的微调以执行特定的下游任务,如医疗数据生成。
- 与DMs的适应策略相比,VAR在非差分隐私(DP)适应方面表现出优势。
- VAR在差分隐私(DP)适应方面的性能有待提高,需要进一步研究。
- 文章提供了多种VAR适应策略的实现和基准测试。
- 代码可通过https://github.com/sprintml/finetuning_var_dp访问。
点此查看论文截图

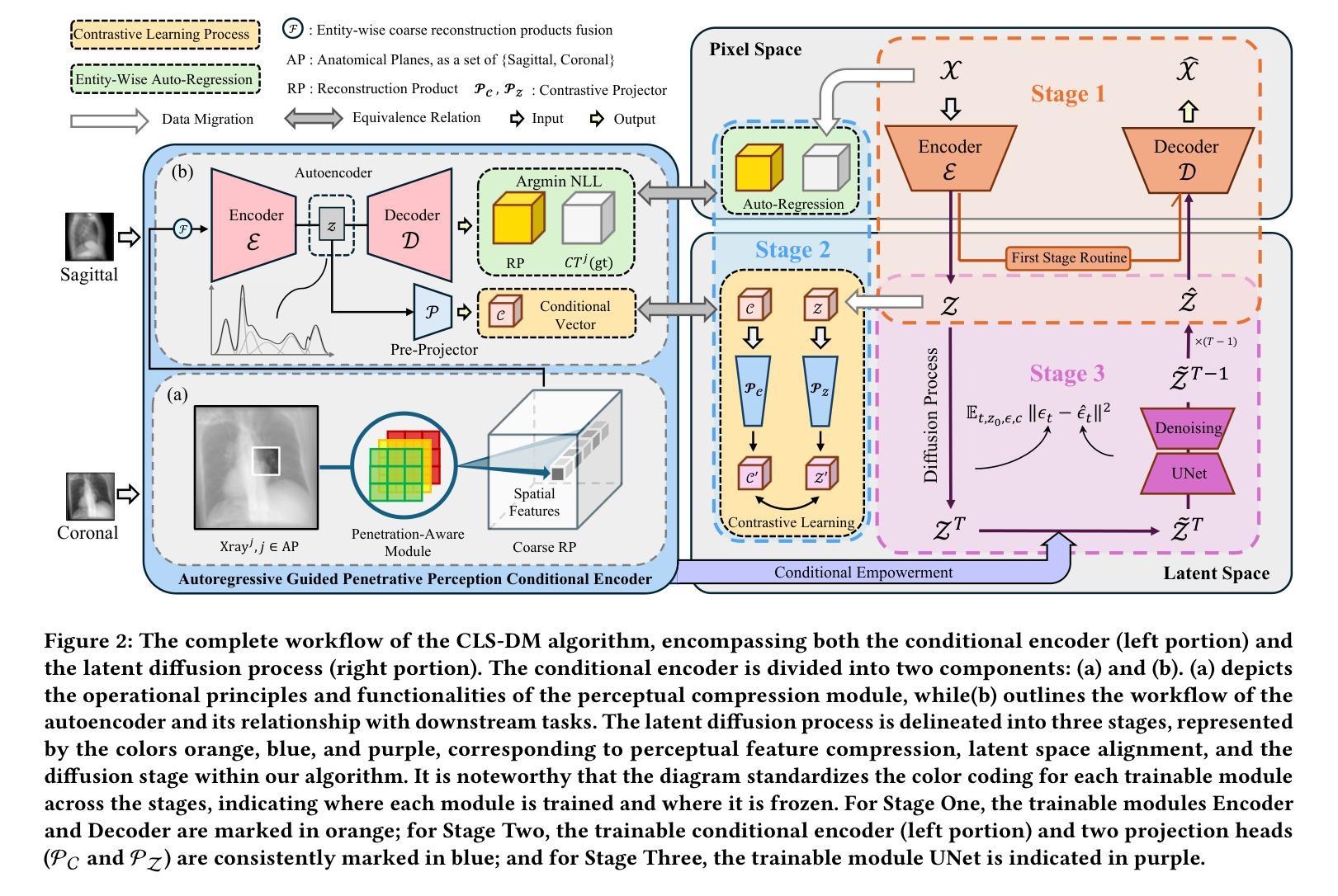
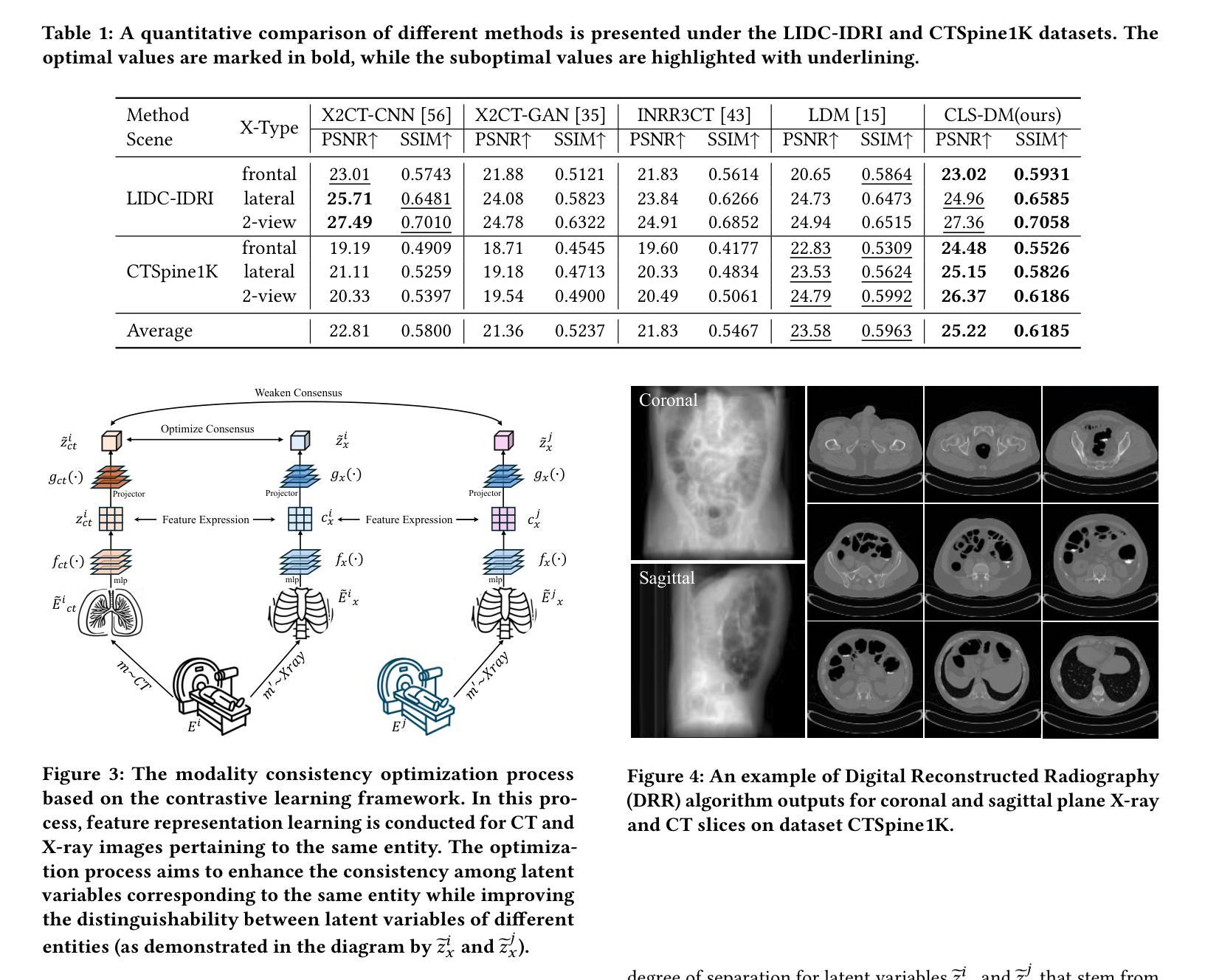
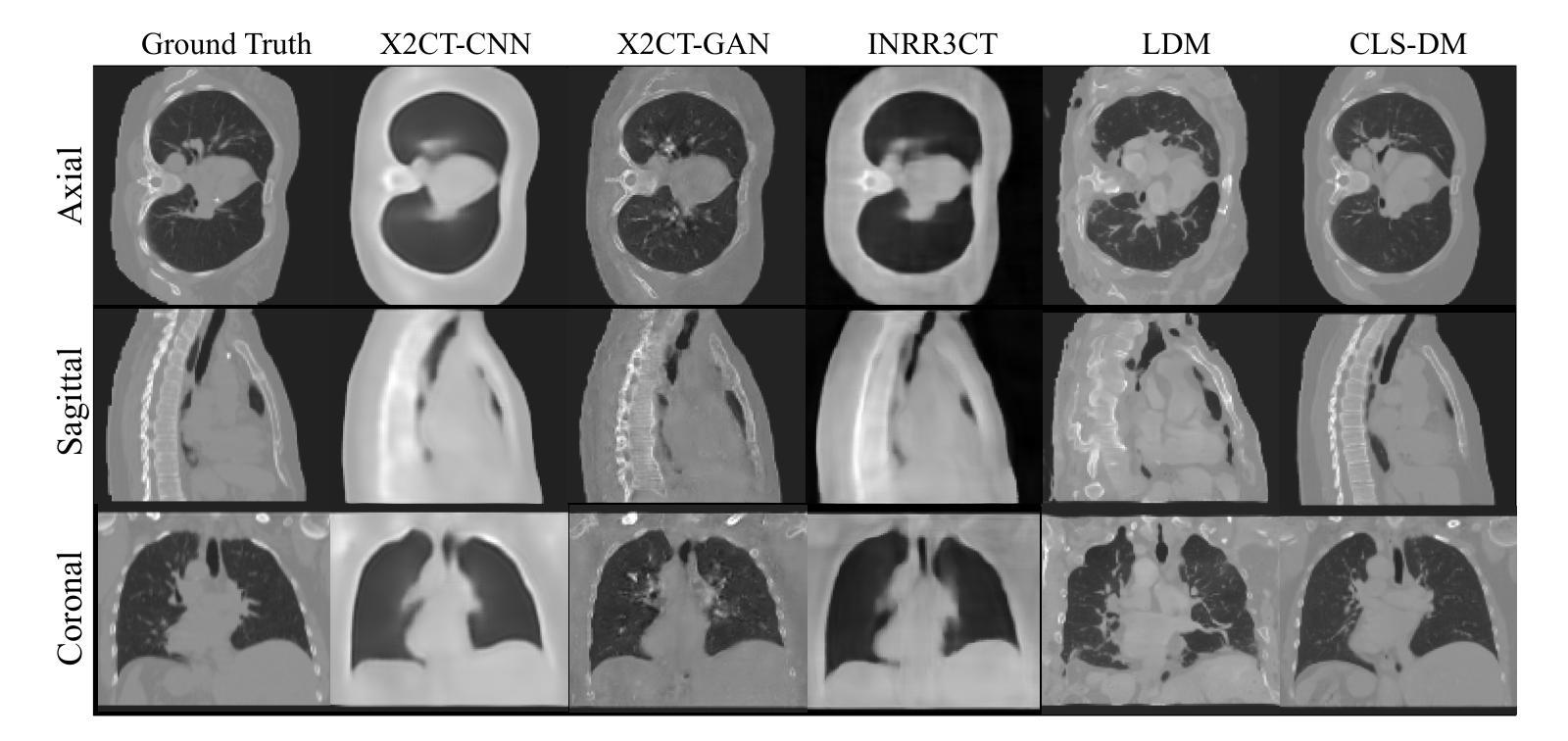
Latent Space Consistency for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Authors:Duoyou Chen, Yunqing Chen, Can Zhang, Zhou Wang, Cheng Chen, Ruoxiu Xiao
Computed Tomography (CT) is a widely utilized imaging modality in clinical settings. Using densely acquired rotational X-ray arrays, CT can capture 3D spatial features. However, it is confronted with challenged such as significant time consumption and high radiation exposure. CT reconstruction methods based on sparse-view X-ray images have garnered substantial attention from researchers as they present a means to mitigate costs and risks. In recent years, diffusion models, particularly the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM), have demonstrated promising potential in the domain of 3D CT reconstruction. Nonetheless, due to the substantial differences between the 2D latent representation of X-ray modalities and the 3D latent representation of CT modalities, the vanilla LDM is incapable of achieving effective alignment within the latent space. To address this issue, we propose the Consistent Latent Space Diffusion Model (CLS-DM), which incorporates cross-modal feature contrastive learning to efficiently extract latent 3D information from 2D X-ray images and achieve latent space alignment between modalities. Experimental results indicate that CLS-DM outperforms classical and state-of-the-art generative models in terms of standard voxel-level metrics (PSNR, SSIM) on the LIDC-IDRI and CTSpine1K datasets. This methodology not only aids in enhancing the effectiveness and economic viability of sparse X-ray reconstructed CT but can also be generalized to other cross-modal transformation tasks, such as text-to-image synthesis. We have made our code publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CLS-DM-50D6/ to facilitate further research and applications in other domains.
计算机断层扫描(CT)是临床环境中广泛应用的成像技术。它使用密集采集的旋转X射线阵列,能够捕捉三维空间特征。然而,它面临着重大挑战,如时间消耗巨大和高辐射暴露。基于稀疏视角X射线图像的CT重建方法已经引起了研究人员的广泛关注,因为它们提供了一种降低成本和风险的方法。近年来,扩散模型,特别是潜在扩散模型(LDM),在三维CT重建领域显示出巨大的潜力。然而,由于X射线模态的二维潜在表示和CT模态的三维潜在表示之间存在巨大差异,标准的LDM无法在潜在空间内进行有效对齐。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了跨模态一致潜在空间扩散模型(CLS-DM),它结合了跨模态特征对比学习,可以有效地从二维X射线图像中提取潜在的三维信息,并在不同模态之间实现潜在空间对齐。实验结果表明,CLS-DM在LIDC-IDRI和CTSpine1K数据集上,在标准体素级指标(PSNR、SSIM)方面优于经典和最新的生成模型。这种方法不仅有助于提高稀疏X射线重建CT的有效性和经济可行性,还可以推广到其他跨模态转换任务,如文本到图像的合成。为了方便其他领域的研究和应用,我们已将代码公开发布在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CLS-DM-50D6/上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACMMM2025 Accepted
摘要
本文主要探讨了计算层析成像(CT)面临的挑战以及基于稀疏视角X射线图像的CT重建方法的发展。由于CT成像需要大量的旋转X射线阵列,因此存在时间长、辐射暴露高等问题。研究人员关注扩散模型在CT重建中的应用,特别是潜在扩散模型(LDM)。然而,由于二维X射线模态的潜在表示与三维CT模态的潜在表示之间存在显著差异,LDM无法有效地对齐潜在空间。为解决这一问题,本文提出了跨模态特征对比学习的一致潜在空间扩散模型(CLS-DM)。CLS-DM可以从二维X射线图像中提取潜在的三维信息,并在不同模态之间实现对齐潜在空间。实验结果表明,CLS-DM在LIDC-IDRI和CTSpine1K数据集上优于经典和最先进的生成模型的标准体素级指标(PSNR、SSIM)。此方法不仅提高了稀疏X射线重建CT的有效性和经济可行性,还可推广到其他跨模态转换任务,如文本到图像合成。我们的代码已公开可用,以促进其他领域的研究和应用。
关键见解
- 计算层析成像(CT)面临时间长和辐射暴露高等挑战。
- 扩散模型,特别是潜在扩散模型(LDM)在CT重建中展现出潜力。
- LDM由于二维X射线与三维CT的潜在表示差异,无法有效对齐潜在空间。
- 提出了基于跨模态特征对比学习的一致潜在空间扩散模型(CLS-DM)。
- CLS-DM可从二维X射线图像中提取潜在的三维信息,实现模态间的潜在空间对齐。
- 实验结果显示CLS-DM在标准体素级指标上优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

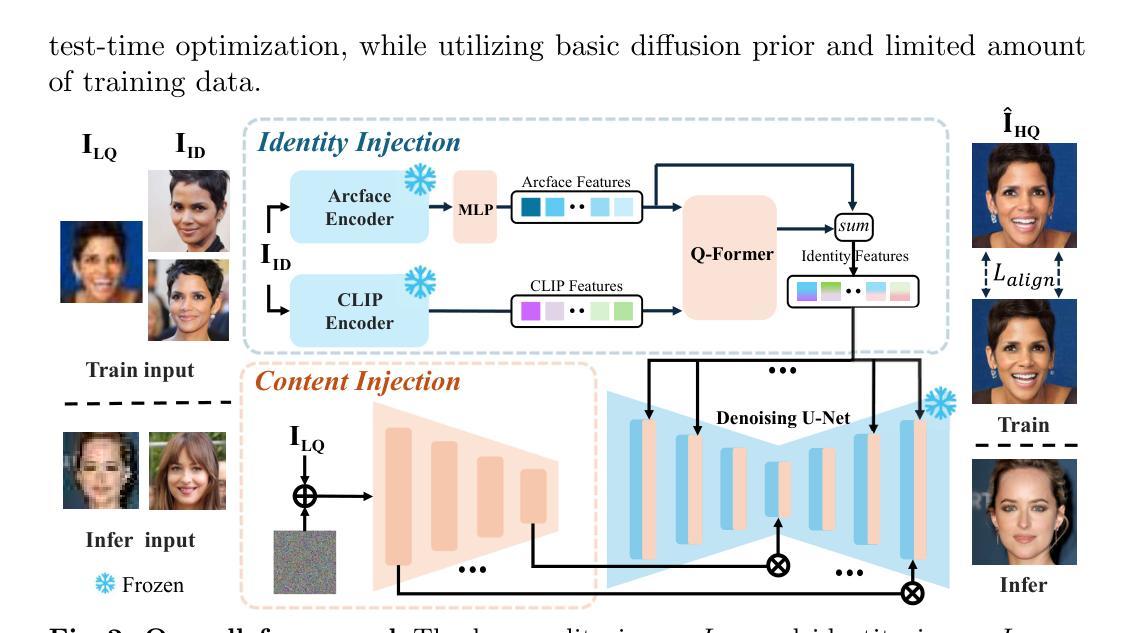
Robust ID-Specific Face Restoration via Alignment Learning
Authors:Yushun Fang, Lu Liu, Xiang Gao, Qiang Hu, Ning Cao, Jianghe Cui, Gang Chen, Xiaoyun Zhang
The latest developments in Face Restoration have yielded significant advancements in visual quality through the utilization of diverse diffusion priors. Nevertheless, the uncertainty of face identity introduced by identity-obscure inputs and stochastic generative processes remains unresolved. To address this challenge, we present Robust ID-Specific Face Restoration (RIDFR), a novel ID-specific face restoration framework based on diffusion models. Specifically, RIDFR leverages a pre-trained diffusion model in conjunction with two parallel conditioning modules. The Content Injection Module inputs the severely degraded image, while the Identity Injection Module integrates the specific identity from a given image. Subsequently, RIDFR incorporates Alignment Learning, which aligns the restoration results from multiple references with the same identity in order to suppress the interference of ID-irrelevant face semantics (e.g. pose, expression, make-up, hair style). Experiments demonstrate that our framework outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, reconstructing high-quality ID-specific results with high identity fidelity and demonstrating strong robustness.
面部修复的最新发展通过利用多种扩散先验知识在视觉质量方面取得了显著进展。然而,由身份模糊输入和随机生成过程引入的身份不确定性仍未解决。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了基于扩散模型的Robust ID-Specific Face Restoration (RIDFR)这一新型身份特定面部修复框架。具体而言,RIDFR利用预训练的扩散模型和两个并行条件模块。内容注入模块输入严重退化的图像,而身份注入模块则整合给定图像中的特定身份。随后,RIDFR结合了对齐学习,通过对齐同一身份的多个参考的修复结果,以抑制身份无关面部语义(如姿势、表情、化妆、发型)的干扰。实验表明,我们的框架优于现有最先进的方法,能够重建高质量的身份特定结果,具有高度的身份保真性和强大的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 8 figures
Summary
基于扩散模型的最新进展,提出了一种名为Robust ID-Specific Face Restoration(RIDFR)的新型面部修复框架,用于解决身份模糊输入和随机生成过程带来的身份不确定性问题。该框架结合预训练的扩散模型与两个并行条件模块,通过内容注入模块和身份注入模块实现面部修复。此外,还引入了对齐学习,通过对齐多个相同身份的参考结果,抑制了与身份无关的面部语义的干扰。实验证明,该框架在身份一致性和稳健性方面表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 最新面部修复技术通过利用多样的扩散先验信息在视觉质量方面取得了显著进展。
- 身份模糊输入和随机生成过程导致的身份不确定性问题仍然有待解决。
- 提出了一种新的面部修复框架RIDFR,基于扩散模型进行ID特定修复。
- RIDFR结合预训练的扩散模型与两个并行条件模块:内容注入模块和身份注入模块。
- RIDFR引入了对齐学习,通过对齐多个相同身份的参考结果来提高稳健性并抑制无关语义的干扰。
- 实验表明,RIDFR框架在身份一致性和稳健性方面超越了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图


Text Embedding Knows How to Quantize Text-Guided Diffusion Models
Authors:Hongjae Lee, Myungjun Son, Dongjea Kang, Seung-Won Jung
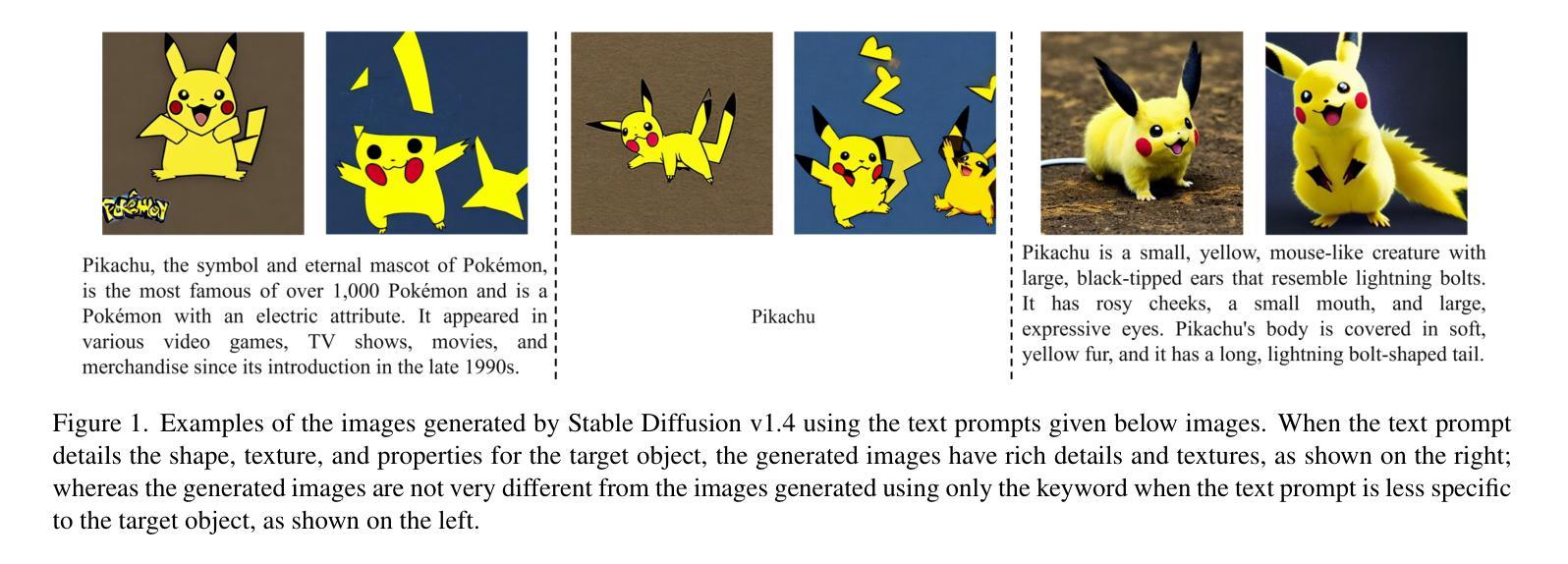
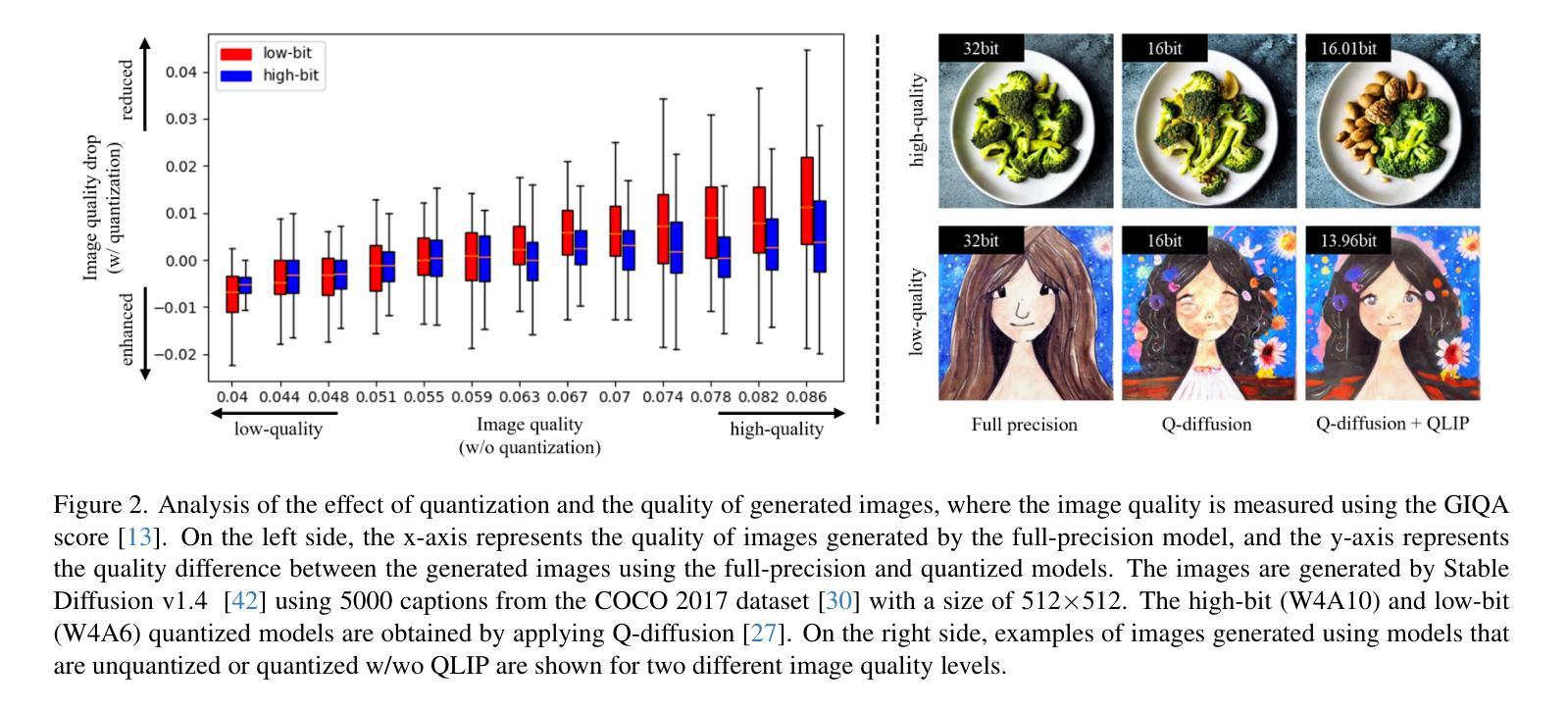
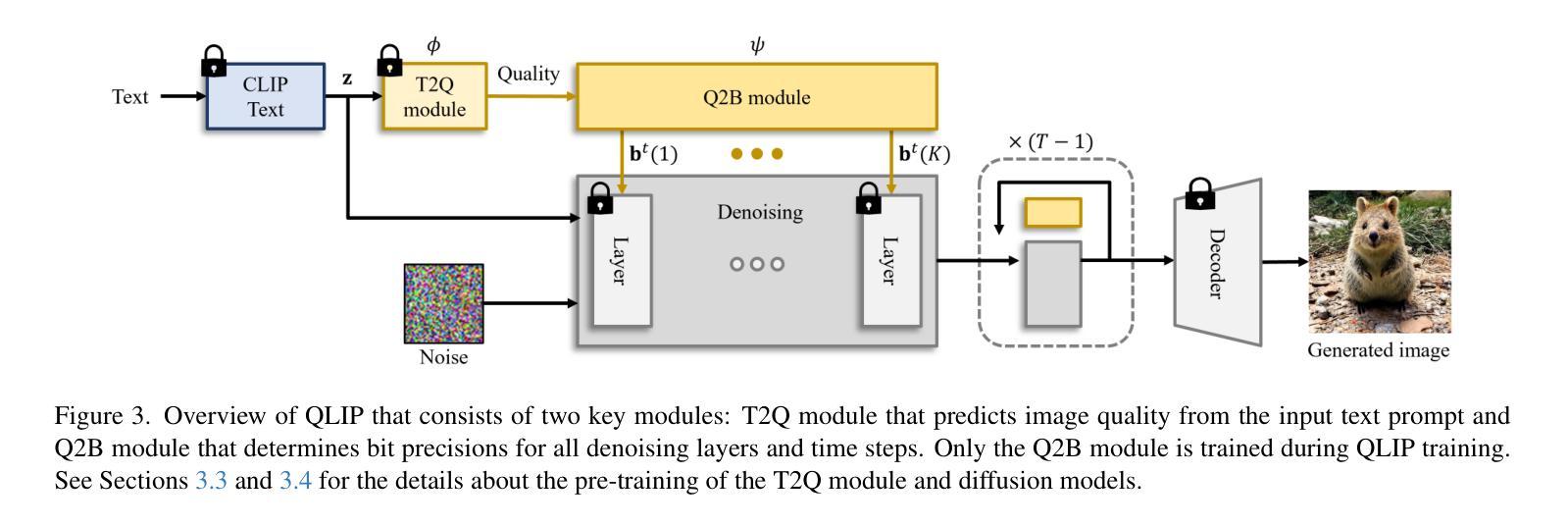
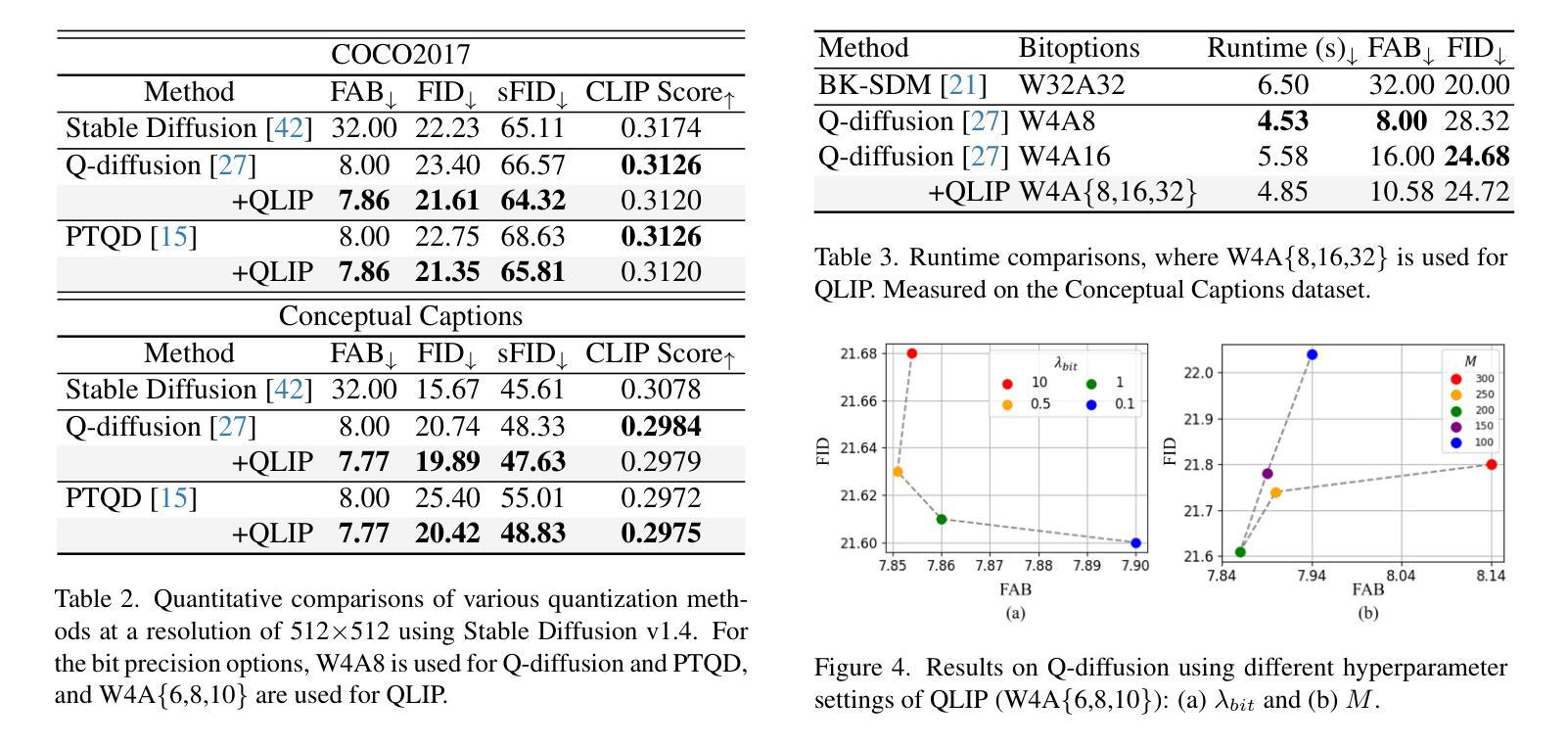
Despite the success of diffusion models in image generation tasks such as text-to-image, the enormous computational complexity of diffusion models limits their use in resource-constrained environments. To address this, network quantization has emerged as a promising solution for designing efficient diffusion models. However, existing diffusion model quantization methods do not consider input conditions, such as text prompts, as an essential source of information for quantization. In this paper, we propose a novel quantization method dubbed Quantization of Language-to-Image diffusion models using text Prompts (QLIP). QLIP leverages text prompts to guide the selection of bit precision for every layer at each time step. In addition, QLIP can be seamlessly integrated into existing quantization methods to enhance quantization efficiency. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of QLIP in reducing computational complexity and improving the quality of the generated images across various datasets.
尽管扩散模型在文本到图像等图像生成任务中取得了成功,但其巨大的计算复杂度限制了其在资源受限环境中的应用。为了解决这一问题,网络量化作为设计高效扩散模型的有前途的解决方案而出现。然而,现有的扩散模型量化方法没有考虑输入条件,如文本提示,作为量化的重要信息来源。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的量化方法,称为使用文本提示的语言到图像扩散模型量化(QLIP)。QLIP利用文本提示来指导每个时间步长每一层的位精度的选择。此外,QLIP可以无缝集成到现有量化方法中,以提高量化的效率。我们的广泛实验表明,QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高各种数据集生成的图像质量方面是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成任务(如文本到图像)中取得了成功,但其巨大的计算复杂性限制了其在资源受限环境中的使用。为解决此问题,网络量化已成为设计高效扩散模型的有前途的解决方案。然而,现有的扩散模型量化方法没有考虑输入条件,如文本提示,作为量化的重要信息来源。本文提出了一种新的量化方法,称为使用文本提示的文本到图像扩散模型的量化(QLIP)。QLIP利用文本提示来指导每个时间步的每一层的位精度选择。此外,QLIP可以无缝集成到现有的量化方法中,以提高量化的效率。实验证明,QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高生成图像质量方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成任务中表现出色,但计算复杂性限制了其在资源受限环境中的应用。
- 网络量化是解决扩散模型计算复杂性的一种有前途的方法。
- 现有扩散模型量化方法未充分利用输入条件(如文本提示)作为量化过程中的重要信息。
- QLIP是一种新的扩散模型量化方法,利用文本提示来指导位精度的选择。
- QLIP可以提高量化效率,并可以无缝集成到现有的量化方法中。
- QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高生成图像质量方面表现出色。
- 广泛实验证明了QLIP的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

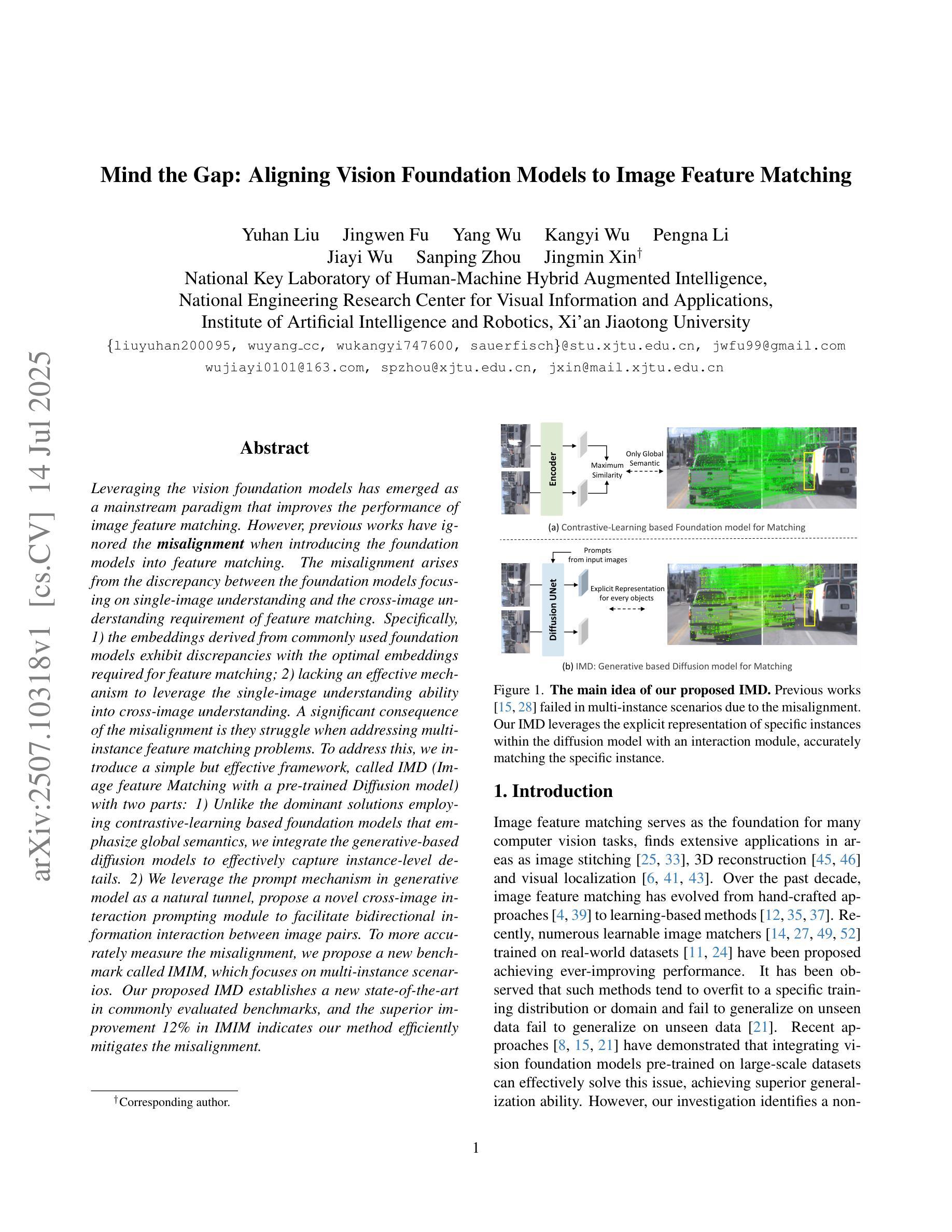
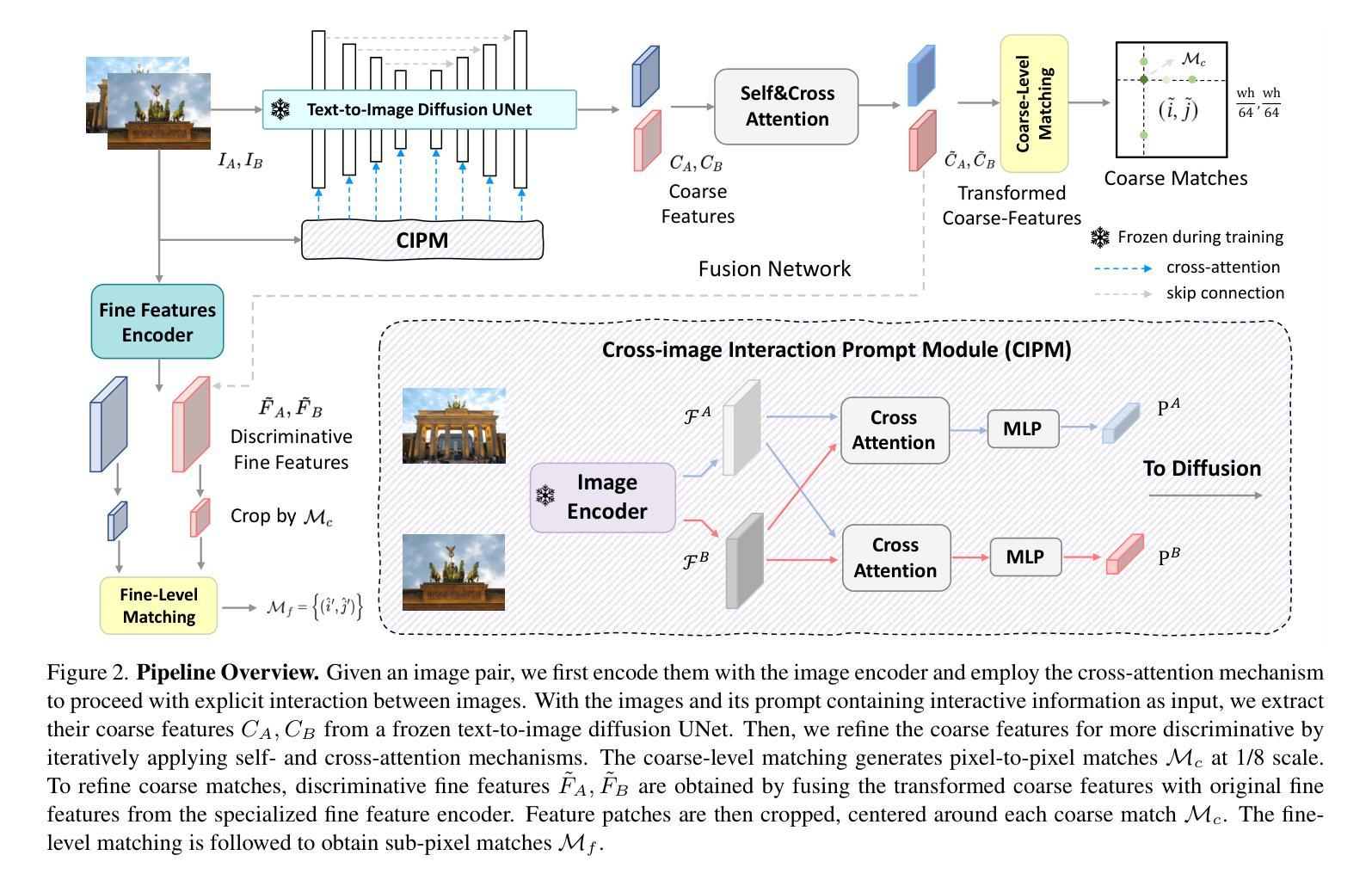
Mind the Gap: Aligning Vision Foundation Models to Image Feature Matching
Authors:Yuhan Liu, Jingwen Fu, Yang Wu, Kangyi Wu, Pengna Li, Jiayi Wu, Sanping Zhou, Jingmin Xin
Leveraging the vision foundation models has emerged as a mainstream paradigm that improves the performance of image feature matching. However, previous works have ignored the misalignment when introducing the foundation models into feature matching. The misalignment arises from the discrepancy between the foundation models focusing on single-image understanding and the cross-image understanding requirement of feature matching. Specifically, 1) the embeddings derived from commonly used foundation models exhibit discrepancies with the optimal embeddings required for feature matching; 2) lacking an effective mechanism to leverage the single-image understanding ability into cross-image understanding. A significant consequence of the misalignment is they struggle when addressing multi-instance feature matching problems. To address this, we introduce a simple but effective framework, called IMD (Image feature Matching with a pre-trained Diffusion model) with two parts: 1) Unlike the dominant solutions employing contrastive-learning based foundation models that emphasize global semantics, we integrate the generative-based diffusion models to effectively capture instance-level details. 2) We leverage the prompt mechanism in generative model as a natural tunnel, propose a novel cross-image interaction prompting module to facilitate bidirectional information interaction between image pairs. To more accurately measure the misalignment, we propose a new benchmark called IMIM, which focuses on multi-instance scenarios. Our proposed IMD establishes a new state-of-the-art in commonly evaluated benchmarks, and the superior improvement 12% in IMIM indicates our method efficiently mitigates the misalignment.
利用视觉基础模型(vision foundation models)作为主流范式来提高图像特征匹配的效能已成为行业主流趋势。然而,之前的工作在将基础模型引入特征匹配时忽略了错配问题。这种错配源于基础模型对单图理解的需求与特征匹配对跨图像理解需求之间的分歧。具体来说,存在的痛点有两点:一是常用的基础模型生成的嵌入特征与为图像特征匹配设计所需要的最优嵌入特征存在偏差;二是缺乏一种有效的机制将单图理解能力转化为跨图理解能力。错配的一个显著后果是它们在处理多实例特征匹配问题时面临困难。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个简单有效的框架,称为IMD(带有预训练扩散模型的图像特征匹配),它包含两部分:首先,不同于采用基于对比学习的主流基础模型强调全局语义的做法,我们整合了基于生成的扩散模型,以有效捕捉实例级细节;其次,我们利用生成模型中的提示机制作为自然通道,提出了一种新颖的跨图像交互提示模块,以促进图像对之间的双向信息交互。为了更准确地测量错配情况,我们提出了一个新的基准测试IMIM,它专注于多实例场景。我们提出的IMD在常用的基准测试中建立了新的最先进的水平,并且在IMIM上的卓越改进提升了12%,这表明我们的方法有效地缓解了错配问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
基于预训练的扩散模型进行图像特征匹配的方法已经崭露头角。然而,现有方法忽视了引入基础模型时的特征不匹配问题。该问题源于基础模型关注单图理解,而特征匹配需要跨图理解。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一个简单有效的框架IMD,融合了生成式的扩散模型来捕捉实例级别的细节,并利用生成模型的提示机制来促进图像对之间的双向信息交流。我们还引入了新的基准测试IMIM来更准确地衡量不匹配问题,而IMD在常规基准测试中建立了新的最高水平,并在IMIM上实现了高达12%的优异改进,表明我们的方法有效地缓解了不匹配问题。
Key Takeaways
- 利用预训练的扩散模型改进图像特征匹配已成为主流范式。
- 现有方法忽视了引入基础模型时的特征不匹配问题。
- 特征不匹配源于基础模型关注单图理解,而特征匹配需要跨图理解。
- 提出了一个新的图像特征匹配框架IMD,融合了生成式的扩散模型并引入了跨图交互提示模块。
- 为更准确地衡量不匹配问题,引入了新的基准测试IMIM。
点此查看论文截图
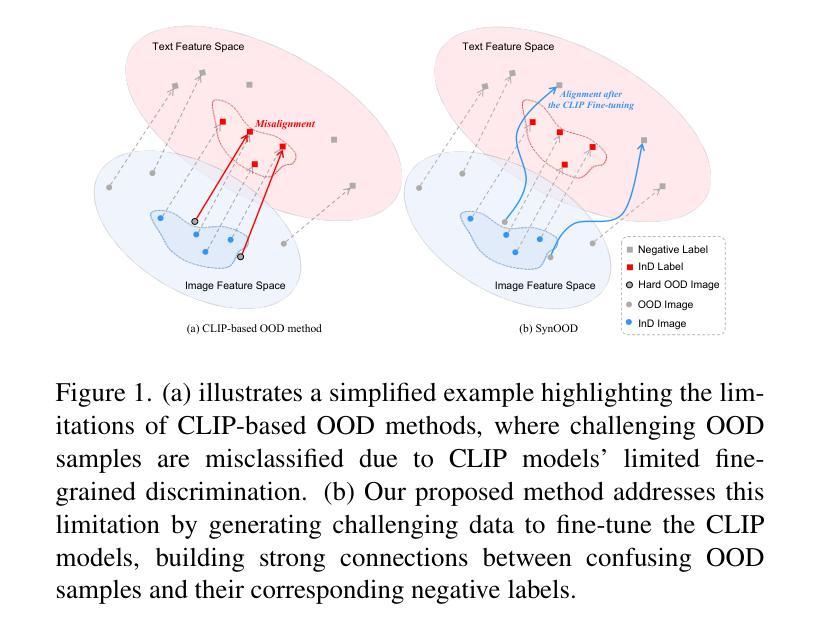
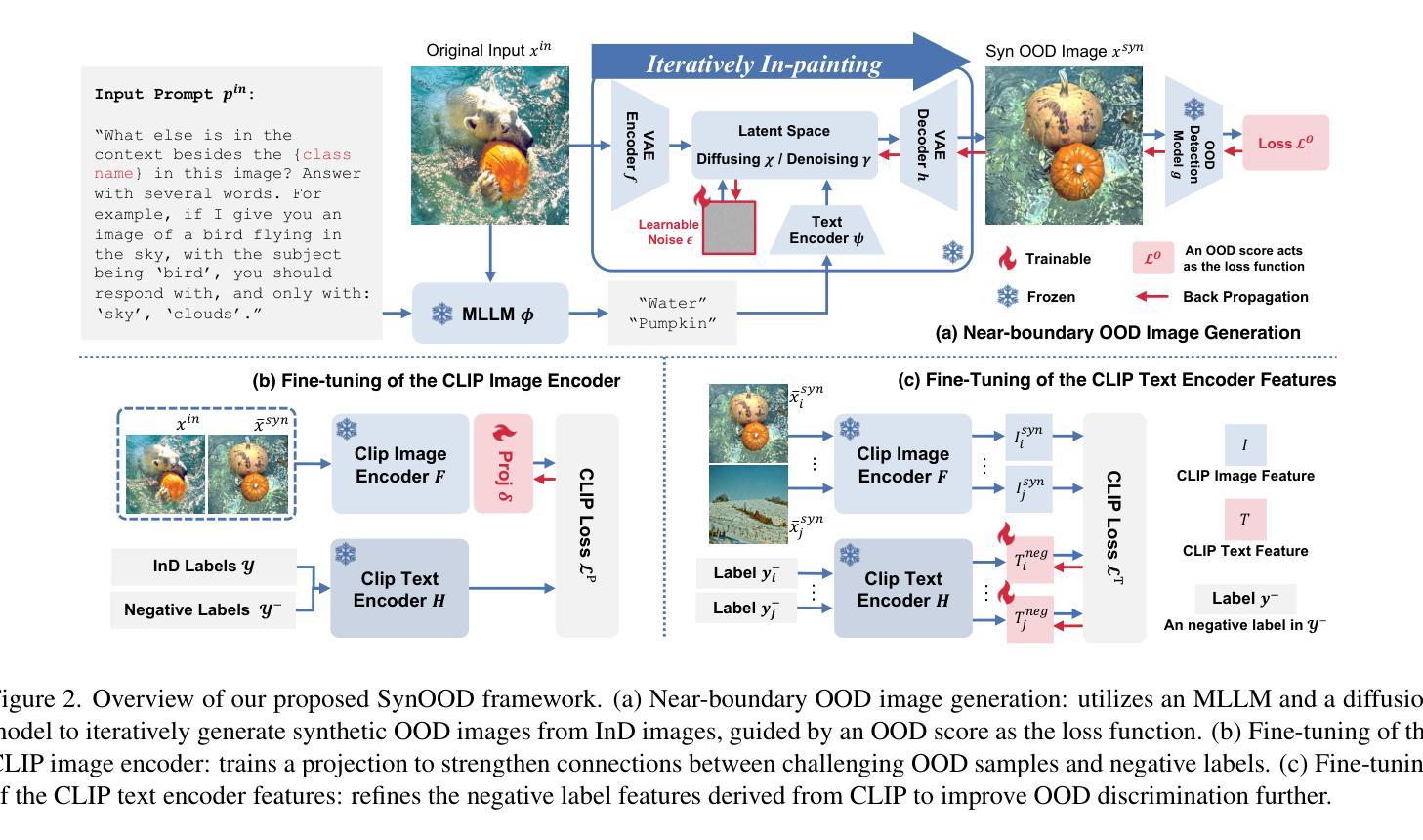
Synthesizing Near-Boundary OOD Samples for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Jinglun Li, Kaixun Jiang, Zhaoyu Chen, Bo Lin, Yao Tang, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
Pre-trained vision-language models have exhibited remarkable abilities in detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. However, some challenging OOD samples, which lie close to in-distribution (InD) data in image feature space, can still lead to misclassification. The emergence of foundation models like diffusion models and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) offers a potential solution to this issue. In this work, we propose SynOOD, a novel approach that harnesses foundation models to generate synthetic, challenging OOD data for fine-tuning CLIP models, thereby enhancing boundary-level discrimination between InD and OOD samples. Our method uses an iterative in-painting process guided by contextual prompts from MLLMs to produce nuanced, boundary-aligned OOD samples. These samples are refined through noise adjustments based on gradients from OOD scores like the energy score, effectively sampling from the InD/OOD boundary. With these carefully synthesized images, we fine-tune the CLIP image encoder and negative label features derived from the text encoder to strengthen connections between near-boundary OOD samples and a set of negative labels. Finally, SynOOD achieves state-of-the-art performance on the large-scale ImageNet benchmark, with minimal increases in parameters and runtime. Our approach significantly surpasses existing methods, improving AUROC by 2.80% and reducing FPR95 by 11.13%. Codes are available in https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD.
预训练的语言视觉模型在检测分布外(OOD)样本方面表现出了卓越的能力。然而,一些具有挑战性的OOD样本,在图像特征空间中与分布内(InD)数据相邻,仍可能导致误分类。扩散模型和多媒体语言模型等基础模型的兴起为解决这一问题提供了潜在解决方案。在这项工作中,我们提出了SynOOD,这是一种利用基础模型生成合成、具有挑战性的OOD数据,对CLIP模型进行微调的新方法,从而增强InD和OOD样本之间边界级别的判别能力。我们的方法使用一个由多媒体语言模型提供的上下文提示引导的迭代填充过程来产生微妙的、与边界对齐的OOD样本。这些样本通过基于OOD分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整来细化处理,有效地从InD/OOD边界进行采样。使用这些精心合成的图像,我们微调CLIP图像编码器和从文本编码器派生的负标签特征,以加强近边界OOD样本与一组负标签之间的联系。最后,SynOOD在大规模ImageNet基准测试中达到了最先进的性能水平,在参数和运行时增加最小的情况下实现了显著超越现有方法的性能提升。我们的方法将AUROC提高了2.80%,将FPR95降低了11.13%。相关代码可通过链接https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型在检测分布外(OOD)样本方面表现出卓越的能力,但对于与分布内(InD)数据在图像特征空间相近的具有挑战性的OOD样本,仍可能导致误分类。本研究提出一种利用基础模型如扩散模型和多媒体大型语言模型(MLLMs)生成合成、具有挑战性的OOD数据,以微调CLIP模型的方法,从而提高InD和OOD样本之间的边界级别判别能力。该方法通过迭代填充过程,结合MLLMs的上下文提示,生成微妙的、与边界对齐的OOD样本。这些样本通过基于OOD分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整,有效地从InD/OOD边界进行采样。使用这些精心合成的图像,我们微调CLIP图像编码器和来自文本编码器的负标签特征,以加强近边界OOD样本与一组负标签之间的联系。最终,SynOOD在大型ImageNet基准测试上实现了最佳性能,参数和运行时略有增加。我们的方法显著优于现有方法,提高了AUROC值2.80%,并降低了FPR95值11.13%。相关代码已发布在GitHub上供公众参考和应用。详情请访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型在检测某些OOD样本时存在误分类风险,特别是对于与InD数据相近的样本。
- 提出了一种利用基础模型(如扩散模型和MLLMs)生成合成OOD数据的方法,以改进模型的判别能力。
- 通过迭代填充过程和上下文提示生成微妙的、与边界对齐的OOD样本。
- 使用OOD分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整,有效采样InD/OOD边界。
- 通过微调CLIP模型的图像和文本编码器,增强近边界OOD样本与负标签的联系。
- SynOOD方法在ImageNet基准测试上实现了卓越性能,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

From Wardrobe to Canvas: Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA for Part-level Controllable Human Image Generation
Authors:Jeongho Kim, Sunghyun Park, Hyoungwoo Park, Sungrack Yun, Jaegul Choo, Seokeon Cho
Recent diffusion models achieve personalization by learning specific subjects, allowing learned attributes to be integrated into generated images. However, personalized human image generation remains challenging due to the need for precise and consistent attribute preservation (e.g., identity, clothing details). Existing subject-driven image generation methods often require either (1) inference-time fine-tuning with few images for each new subject or (2) large-scale dataset training for generalization. Both approaches are computationally expensive and impractical for real-time applications. To address these limitations, we present Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA, a novel part-level controllable model for personalized human image generation. By training only LoRA layers, our method removes the computational burden at inference while ensuring high-fidelity synthesis of unseen subjects. Our key idea is to condition the generation on the subject’s wardrobe and leverage spatial references to reduce information loss, thereby improving fidelity and consistency. Additionally, we introduce a selective subject region loss, which encourages the model to disregard some of reference images during training. Our loss ensures that generated images better align with text prompts while maintaining subject integrity. Notably, our Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA requires no additional parameters at the inference stage and performs generation using a single model trained on a few training samples. We construct a new dataset and benchmark tailored for personalized human image generation. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms existing techniques in fidelity and consistency, enabling realistic and identity-preserving full-body synthesis.
最近的扩散模型通过学习特定主题来实现个性化,使得学习到的属性可以集成到生成的图像中。然而,由于需要精确且一致地保留属性(例如身份、服装细节),个性化的人物图像生成仍然具有挑战性。现有的主题驱动图像生成方法通常需要(1)针对每个新主题的少量图像进行推理时间微调,或(2)大规模数据集训练以实现通用性。这两种方法计算成本高昂,不适用于实时应用程序。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA,这是一种用于个性化人物图像生成的新型局部可控模型。通过仅训练LoRA层,我们的方法在推理时去除了计算负担,同时确保了未见主体的高保真合成。我们的核心思想是根据主体的衣橱进行生成,并利用空间参考来减少信息损失,从而提高保真度和一致性。此外,我们引入了一种选择性主题区域损失,鼓励模型在训练过程中忽略部分参考图像。我们的损失确保生成图像与文本提示更好地对齐,同时保持主题完整性。值得注意的是,我们的Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA在推理阶段不需要添加任何额外参数,并使用单个模型在少量训练样本上进行生成。我们构建了一个针对个性化人物图像生成的新数据集和基准测试。大量实验表明,我们的方法在保真度和一致性方面显著优于现有技术,能够实现真实且身份保留的全身合成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA的新型部分可控模型,用于个性化人类图像生成。该模型通过仅训练LoRA层,在推理时去除计算负担,确保对未见过的主体进行高保真合成。通过条件生成主体的衣柜并利用空间参考,减少了信息损失,提高了保真度和一致性。此外,引入了选择性主体区域损失,鼓励模型在训练过程中忽略部分参考图像,使生成的图像更符合文本提示,同时保持主体完整性。该模型无需在推理阶段添加额外参数,使用少量训练样本即可进行生成。
Key Takeaways
- Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA模型通过训练特定的LoRA层,能够在推理时实现高效计算,同时确保高保真度的个性化人类图像生成。
- 该模型通过条件生成主体的衣柜并利用空间参考,提高了图像生成的保真度和一致性。
- 引入选择性主体区域损失,使模型在训练过程中能够忽略部分参考图像,使生成的图像更符合文本提示。
- Wardrobe Polyptych LoRA模型在推理阶段无需额外参数,且能用单个模型在少量训练样本上进行生成。
- 模型在新构建的数据集上进行训练并评估,该数据集专为个性化人类图像生成而设计。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在保真度和一致性方面显著优于现有技术,能够实现真实且身份保全的全身合成。
点此查看论文截图



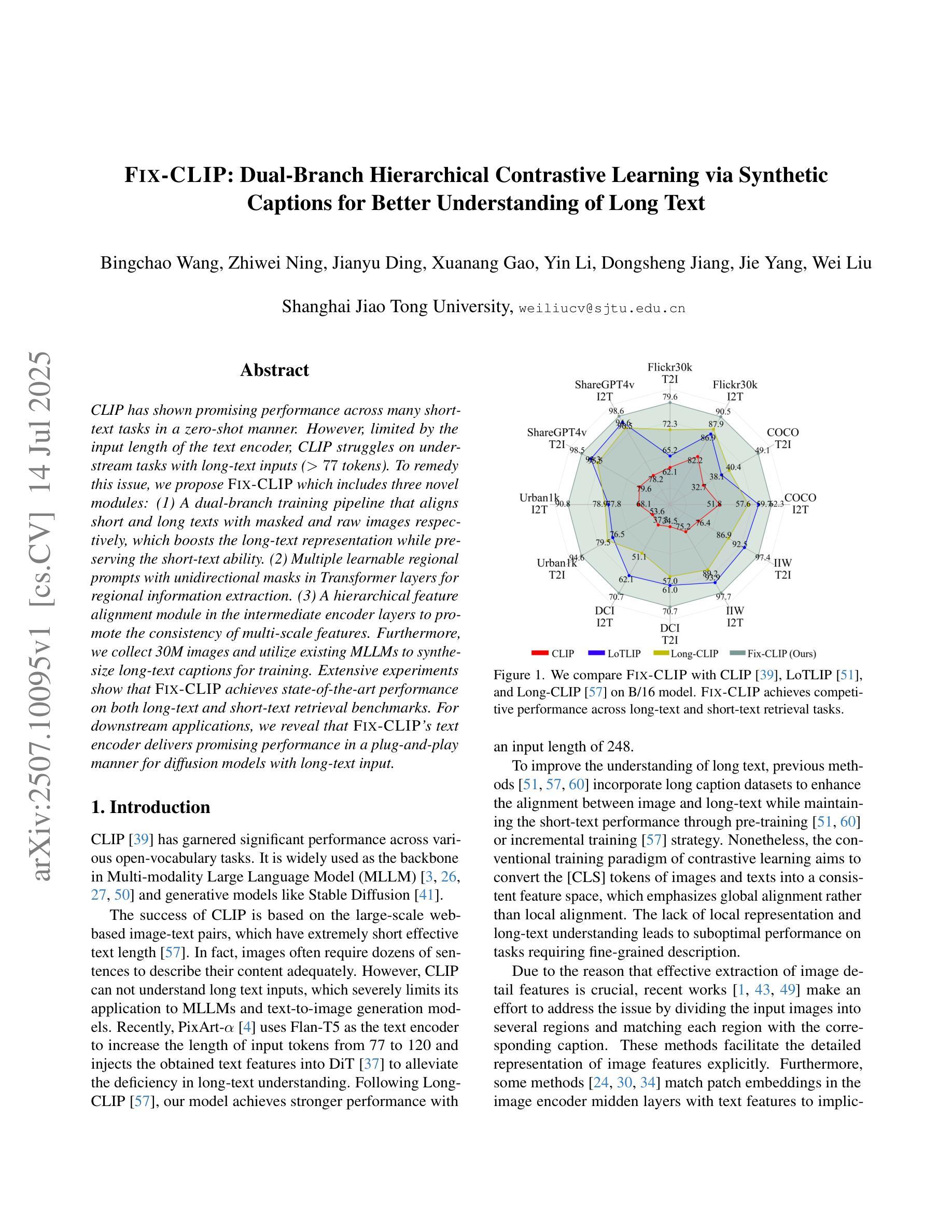
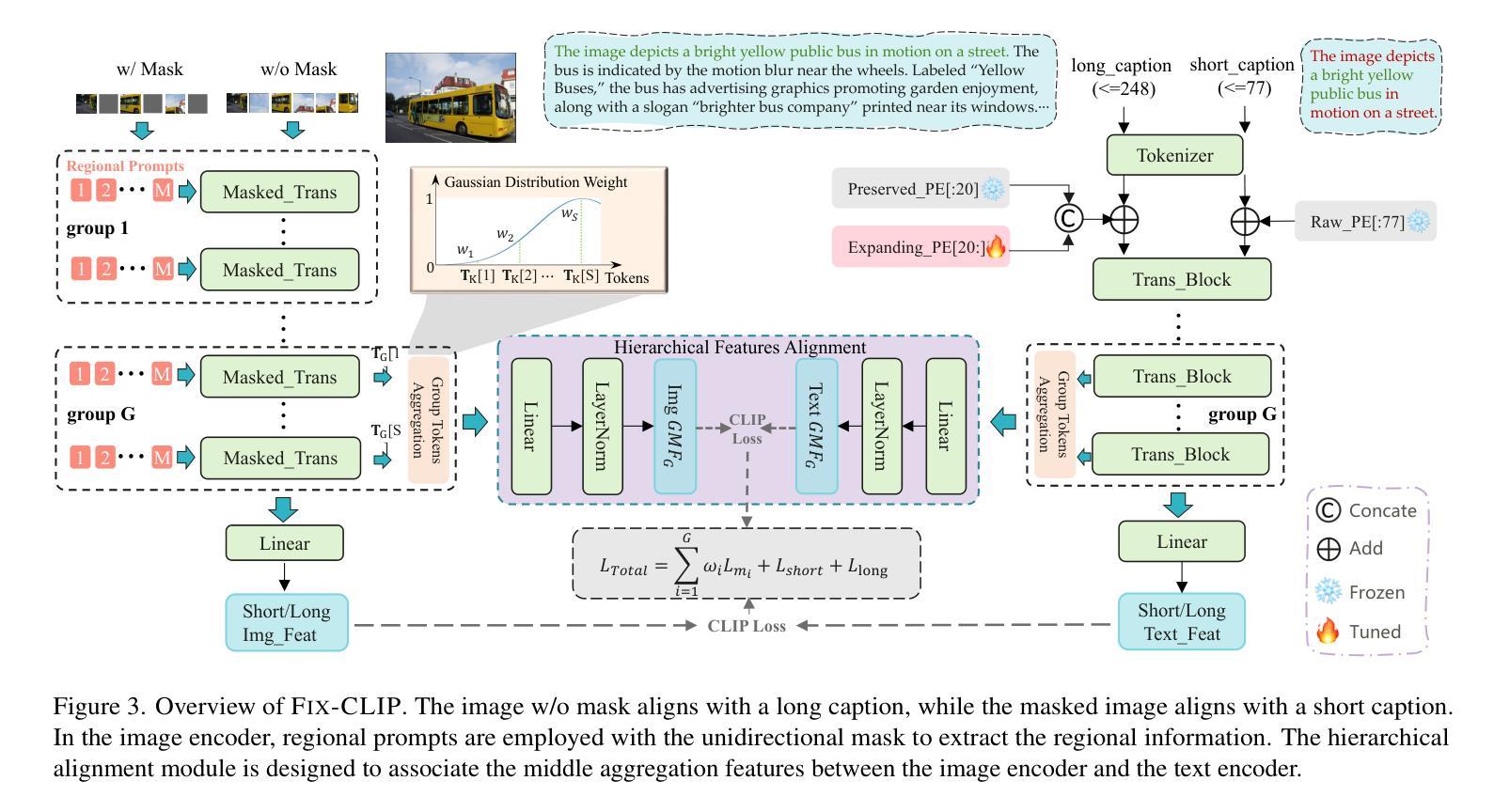
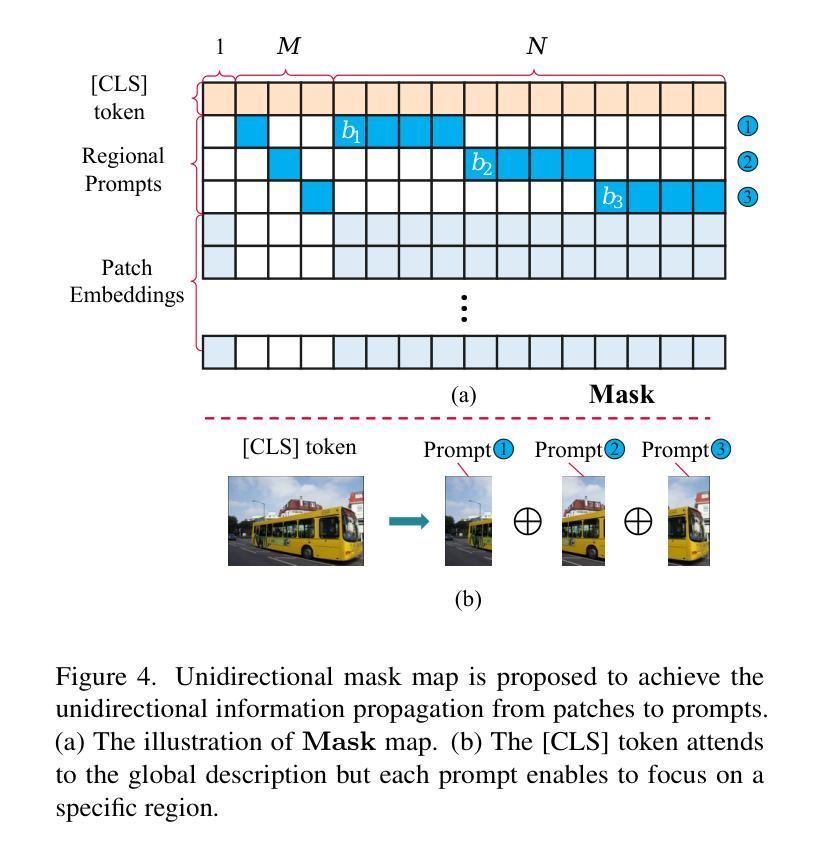
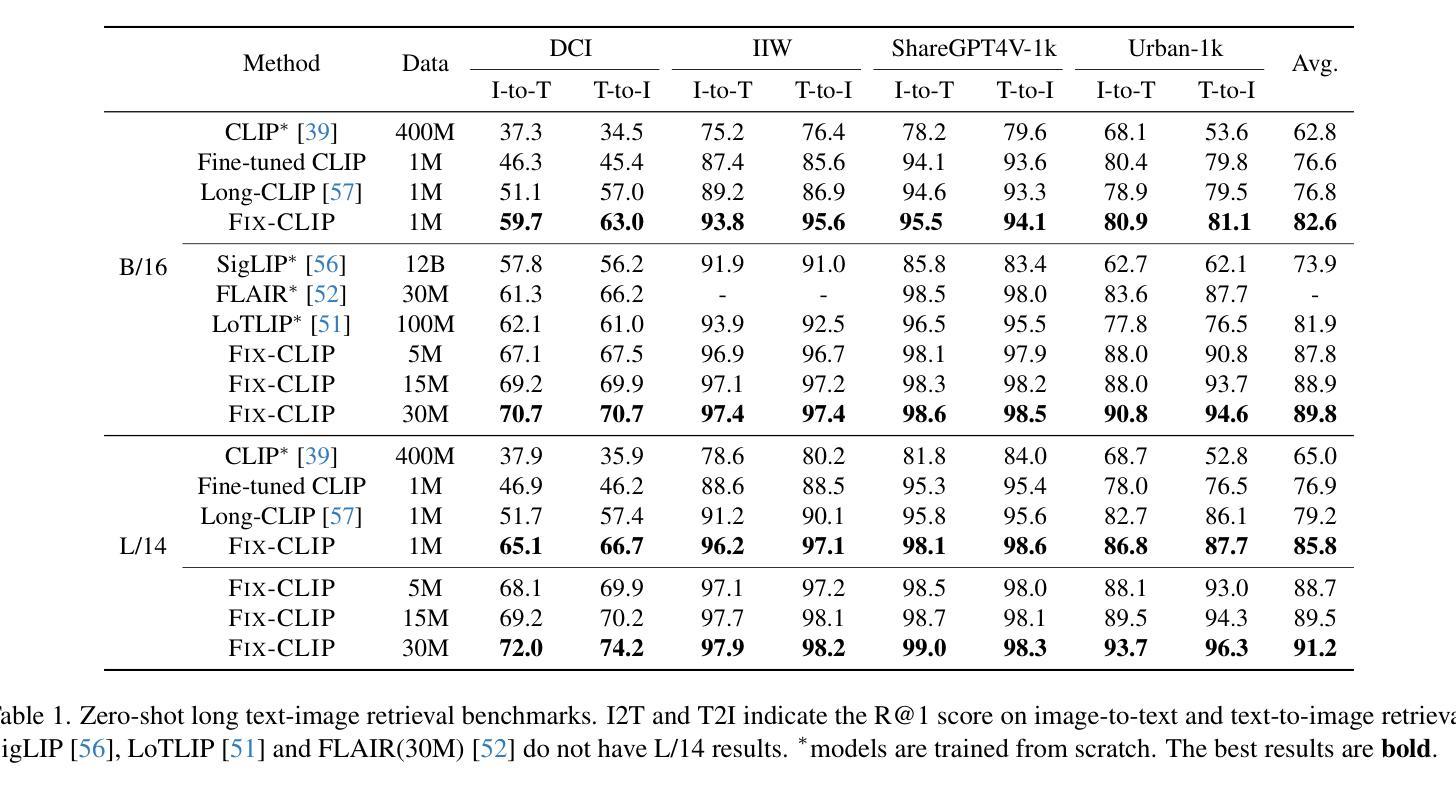
FIX-CLIP: Dual-Branch Hierarchical Contrastive Learning via Synthetic Captions for Better Understanding of Long Text
Authors:Bingchao Wang, Zhiwei Ning, Jianyu Ding, Xuanang Gao, Yin Li, Dongsheng Jiang, Jie Yang, Wei Liu
CLIP has shown promising performance across many short-text tasks in a zero-shot manner. However, limited by the input length of the text encoder, CLIP struggles on under-stream tasks with long-text inputs (>77 tokens). To remedy this issue, we propose FIX-CLIP which includes three novel modules: (1) A dual-branch training pipeline that aligns short and long texts with masked and raw images respectively, which boosts the long-text representation while preserving the short-text ability. (2) Multiple learnable regional prompts with unidirectional masks in Transformer layers for regional information extraction. (3) A hierarchical feature alignment module in the intermediate encoder layers to promote the consistency of multi-scale features. Furthermore, we collect 30M images and utilize existing MLLMs to synthesize long-text captions for training. Extensive experiments show that FIX-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on both long-text and short-text retrieval benchmarks. For downstream applications, we reveal that FIX-CLIP’s text encoder delivers promising performance in a plug-and-play manner for diffusion models with long-text input.
CLIP在许多短文本任务中表现出了零样本方式下的良好性能。然而,由于文本编码器的输入长度限制,CLIP在处理长文本输入(>77个令牌)的下游任务时遇到了困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP,它包括三个新模块:(1)双分支训练管道,分别用带掩码和原始图像对齐短文本和长文本,这提高了长文本的表示能力,同时保留了短文本的能力。(2)在Transformer层中使用带有单向掩码的可学习区域提示,用于区域信息提取。(3)在中间编码器层中的分层特征对齐模块,以促进多尺度特征的一致性。此外,我们收集了3000万张图像,并利用现有的大型语言模型来合成长文本描述符进行训练。大量实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长文本和短文本检索基准测试上均达到了最新技术水平。对于下游应用,我们发现FIX-CLIP的文本编码器在以即插即用方式应用于具有长文本输入的扩散模型时表现出良好性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP在短文本任务上表现优异,但在处理长文本输入时因文本编码器的输入长度限制而表现不佳。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP,包括三个新颖模块:1)双分支训练管道,分别对齐短文本和长文本与掩码和原始图像,提升长文本表征能力同时保留短文本能力;2)在Transformer层使用多个可学习区域提示和单向掩码进行区域信息提取;3)在中间编码器层中引入层次特征对齐模块,促进多尺度特征的一致性。此外,我们收集了3亿张图像并利用现有的MLLMs合成长文本描述进行训练。实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长文本和短文本检索基准测试中实现了最佳性能,并在下游应用中展现了其在扩散模型中的优异表现。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在短文本任务上表现良好,但在处理长文本输入时存在限制。
- FIX-CLIP包含三个新颖模块:双分支训练管道、区域信息提取模块和层次特征对齐模块。
- 双分支训练管道能够提升长文本表征能力并保留短文本处理能力。
- FIX-CLIP采用多个可学习区域提示和单向掩码以增强区域信息提取。
- 层次特征对齐模块有助于促进多尺度特征的一致性。
- 收集大量图像并利用MLLMs合成长文本描述进行训练。
- FIX-CLIP在长文本和短文本检索基准测试中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

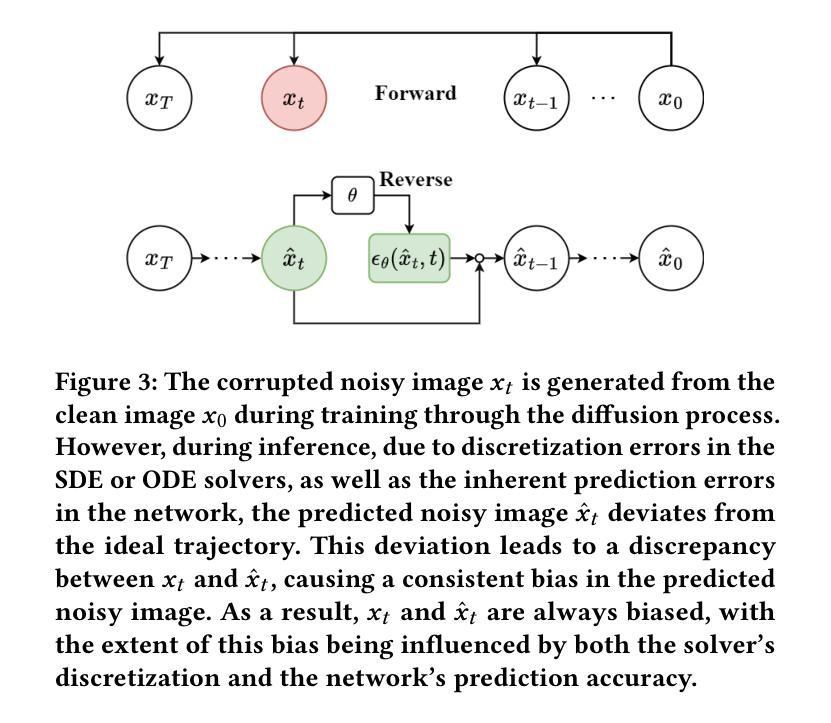
Frequency Regulation for Exposure Bias Mitigation in Diffusion Models
Authors:Meng Yu, Kun Zhan
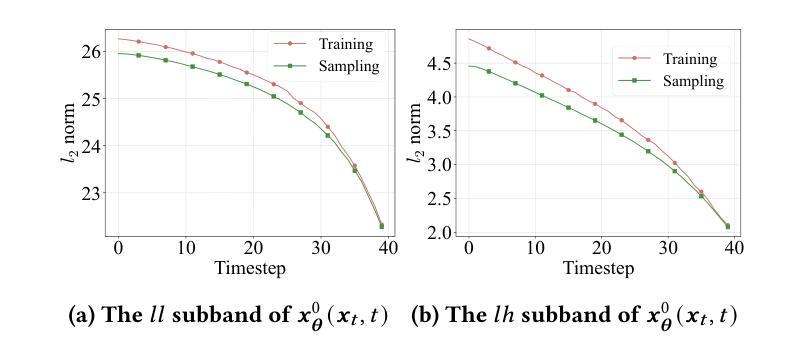
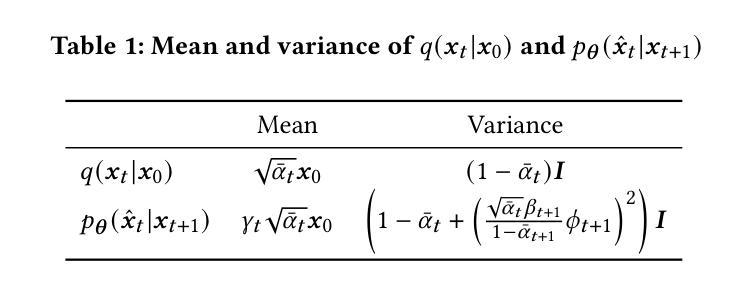
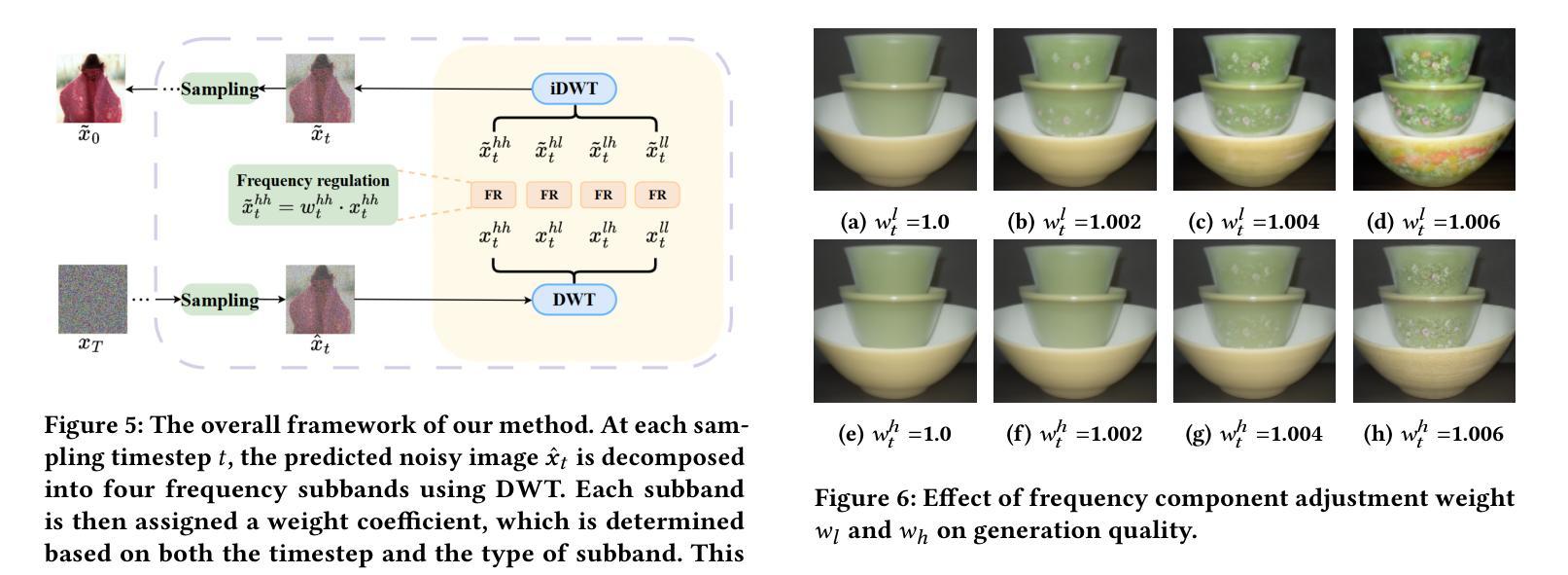
Diffusion models exhibit impressive generative capabilities but are significantly impacted by exposure bias. In this paper, we make a key observation: the energy of the predicted noisy images decreases during the diffusion process. Building on this, we identify two important findings: 1) The reduction in energy follows distinct patterns in the low-frequency and high-frequency subbands; 2) This energy reduction results in amplitude variations between the network-reconstructed clean data and the real clean data. Based on the first finding, we introduce a frequency-domain regulation mechanism utilizing wavelet transforms, which separately adjusts the low- and high-frequency subbands. Leveraging the second insight, we provide a more accurate analysis of exposure bias in the two subbands. Our method is training-free and plug-and-play, significantly improving the generative quality of various diffusion models and providing a robust solution to exposure bias across different model architectures. The source code is available at https://github.com/kunzhan/wpp.
扩散模型展现出令人印象深刻的生成能力,但受到暴露偏差的显著影响。在本文中,我们有一个关键发现:在扩散过程中,预测噪声图像的能量会减少。在此基础上,我们发现了两个重要观点:1)能量减少在低频频带和高频频带中遵循不同的模式;2)这种能量减少导致网络重建的清洁数据与真实清洁数据之间的振幅变化。基于第一个发现,我们引入了一种利用小波变换的频率域调节机制,该机制可以分别调整低频频带和高频频带。利用第二个见解,我们对两个子频带的暴露偏差进行了更准确的分析。我们的方法无需训练,即插即用,可显著提高各种扩散模型的生成质量,并为不同模型架构提供稳健的解决暴露偏差的方案。源代码可在https://github.com/kunzhan/wpp找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM Multimedia 2025 accepted!
Summary
本文观察到扩散模型在扩散过程中预测噪声图像的能量会下降,并发现这一现象在低频频带和高频频带表现出不同的模式。基于此,引入利用小波变换的频率域调节机制,对低频和高频子带进行单独调整。该方法无需训练,即插即用,显著提高了扩散模型的生成质量,为不同模型结构中的曝光偏差提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在扩散过程中预测噪声图像的能量会下降。
- 能量下降在低频频带和高频频带表现出不同的模式。
- 能量下降导致网络重建的清洁数据与真实清洁数据之间的幅度变化。
- 引入频率域调节机制,利用小波变换对低频和高频子带进行单独调整。
- 方法无需训练,即插即用,提高了扩散模型的生成质量。
- 该方法为解决不同模型结构中的曝光偏差提供了稳健的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


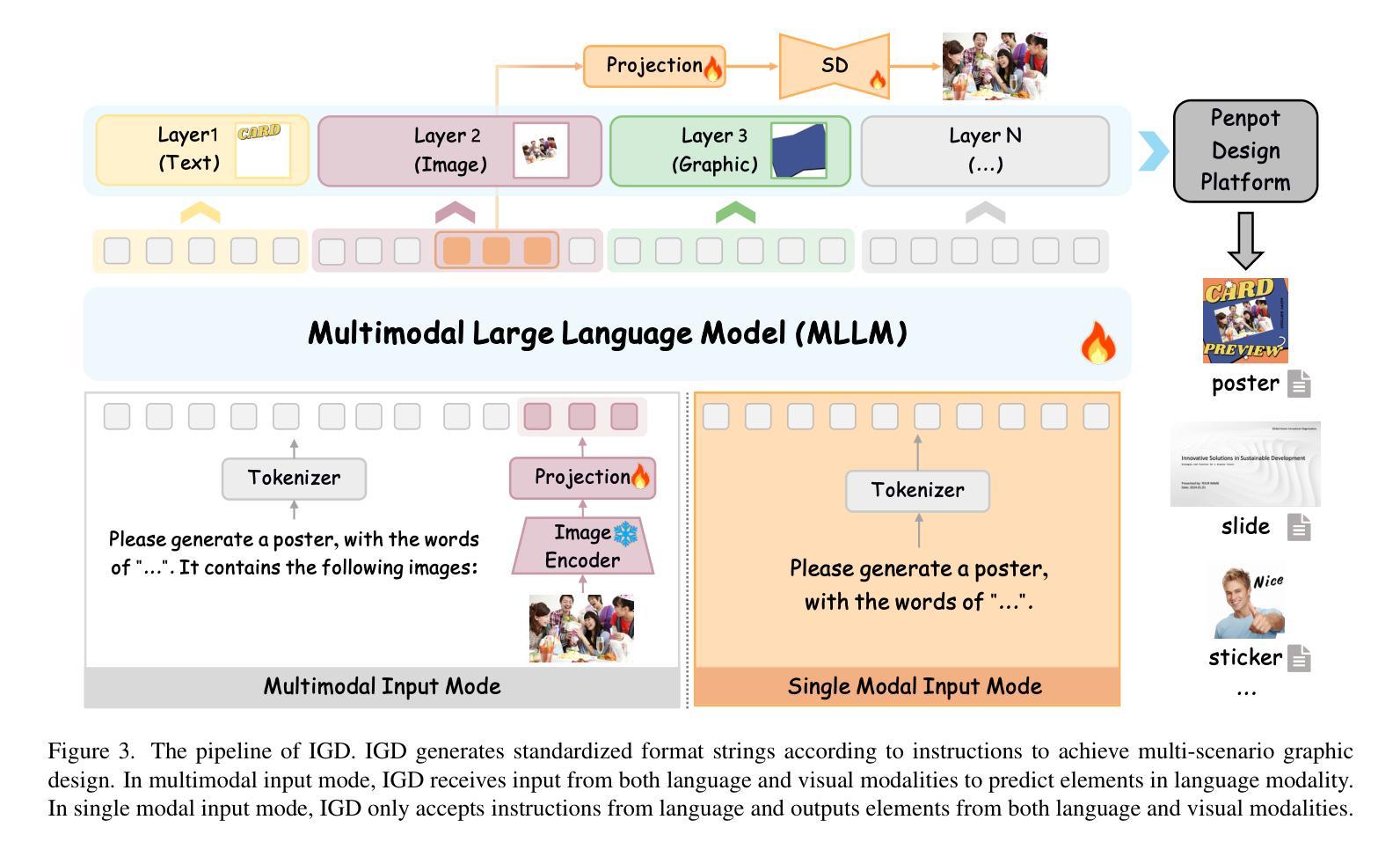
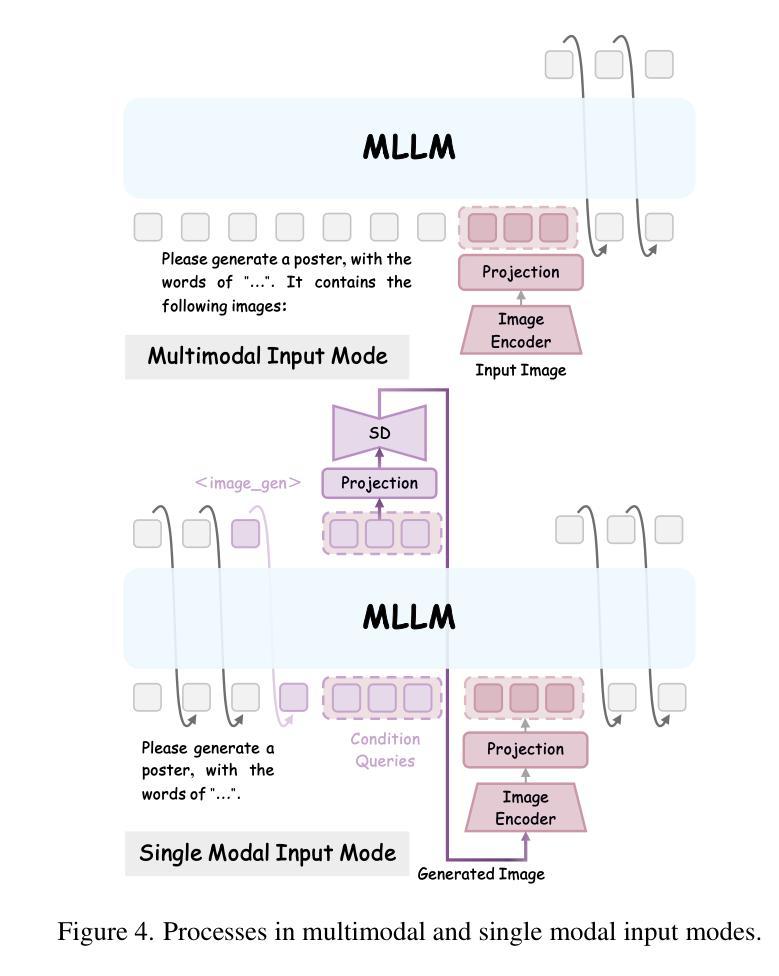
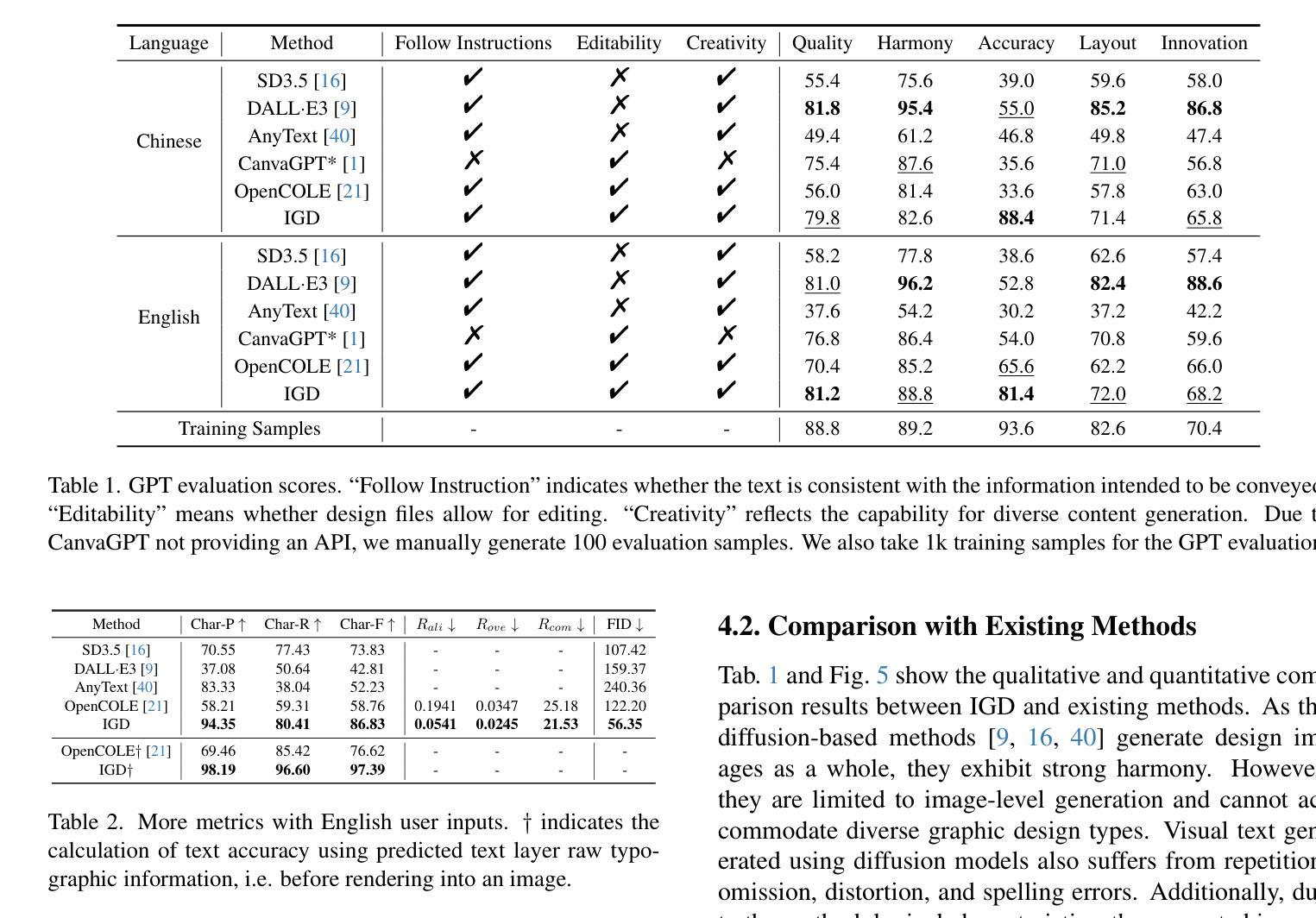
IGD: Instructional Graphic Design with Multimodal Layer Generation
Authors:Yadong Qu, Shancheng Fang, Yuxin Wang, Xiaorui Wang, Zhineng Chen, Hongtao Xie, Yongdong Zhang
Graphic design visually conveys information and data by creating and combining text, images and graphics. Two-stage methods that rely primarily on layout generation lack creativity and intelligence, making graphic design still labor-intensive. Existing diffusion-based methods generate non-editable graphic design files at image level with poor legibility in visual text rendering, which prevents them from achieving satisfactory and practical automated graphic design. In this paper, we propose Instructional Graphic Designer (IGD) to swiftly generate multimodal layers with editable flexibility with only natural language instructions. IGD adopts a new paradigm that leverages parametric rendering and image asset generation. First, we develop a design platform and establish a standardized format for multi-scenario design files, thus laying the foundation for scaling up data. Second, IGD utilizes the multimodal understanding and reasoning capabilities of MLLM to accomplish attribute prediction, sequencing and layout of layers. It also employs a diffusion model to generate image content for assets. By enabling end-to-end training, IGD architecturally supports scalability and extensibility in complex graphic design tasks. The superior experimental results demonstrate that IGD offers a new solution for graphic design.
平面设计通过创建和组合文本、图像和图形来视觉传达信息和数据。现有的两阶段方法主要依赖于布局生成,缺乏创造力和智能,导致平面设计仍然是劳动密集型的。现有的基于扩散的方法生成非编辑的平面设计文件,仅在图像层面具有良好的清晰度,这在视觉文本渲染方面表现较差,阻碍了它们实现令人满意和实用的自动化平面设计。在本文中,我们提出指令性平面设计师(IGD)来快速生成仅通过自然语言指令即可进行灵活编辑的多模式图层。IGD采用了一种新的范式,利用参数渲染和图像资产生成。首先,我们开发了一个设计平台,建立了多场景设计文件的标准化格式,从而为扩大数据规模奠定了基础。其次,IGD利用MLLM的多模式理解和推理能力来完成属性预测、图层排序和布局。它还采用扩散模型来生成资产图像内容。通过支持端到端训练,IGD在复杂的平面设计任务中支持可伸缩性和可扩展性。优异的实验结果证明了IGD在平面设计领域提供了新的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型图形设计系统——Instructional Graphic Designer(IGD)。该系统通过自然语言指令快速生成具有可编辑灵活性的多模式层,并采用参数渲染和图像资产生成的新范式。通过开发设计平台和建立多场景设计文件的标准化格式,IGD实现了数据规模化扩展的基础。同时,利用多模态理解和推理能力完成属性预测、层序和布局,并采用扩散模型生成图像内容资产。实验结果表明,IGD在复杂图形设计任务中具有可扩展性和可伸缩性,为图形设计提供了新的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- IGD系统通过自然语言指令快速生成多模式层,具有可编辑灵活性。
- IGD采用参数渲染和图像资产生成的新范式。
- 设计平台和多场景设计文件的标准化格式为实现数据规模化扩展奠定基础。
- IGD利用多模态理解和推理能力完成属性预测、层序和布局。
- IGD采用扩散模型生成图像内容资产,支持端到端的训练。
- IGD在复杂图形设计任务中具有可扩展性和可伸缩性。
点此查看论文截图


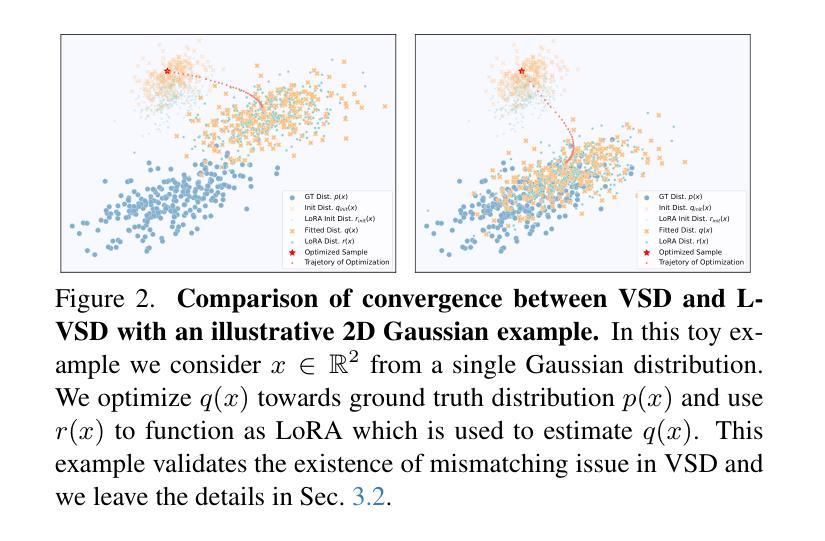
Advancing Text-to-3D Generation with Linearized Lookahead Variational Score Distillation
Authors:Yu Lei, Bingde Liu, Qingsong Xie, Haonan Lu, Zhijie Deng
Text-to-3D generation based on score distillation of pre-trained 2D diffusion models has gained increasing interest, with variational score distillation (VSD) as a remarkable example. VSD proves that vanilla score distillation can be improved by introducing an extra score-based model, which characterizes the distribution of images rendered from 3D models, to correct the distillation gradient. Despite the theoretical foundations, VSD, in practice, is likely to suffer from slow and sometimes ill-posed convergence. In this paper, we perform an in-depth investigation of the interplay between the introduced score model and the 3D model, and find that there exists a mismatching problem between LoRA and 3D distributions in practical implementation. We can simply adjust their optimization order to improve the generation quality. By doing so, the score model looks ahead to the current 3D state and hence yields more reasonable corrections. Nevertheless, naive lookahead VSD may suffer from unstable training in practice due to the potential over-fitting. To address this, we propose to use a linearized variant of the model for score distillation, giving rise to the Linearized Lookahead Variational Score Distillation ($L^2$-VSD). $L^2$-VSD can be realized efficiently with forward-mode autodiff functionalities of existing deep learning libraries. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of $L^2$-VSD, revealing its clear superiority over prior score distillation-based methods. We also show that our method can be seamlessly incorporated into any other VSD-based text-to-3D framework.
基于预训练的2D扩散模型的分数蒸馏进行文本到3D生成已经引起了广泛关注,变分分数蒸馏(VSD)就是一个显著的例子。VSD证明,通过引入额外的基于分数的模型来改善普通分数蒸馏是可行的,该模型能够描述从3D模型呈现的图像分布,以校正蒸馏梯度。尽管有理论上的基础,但VSD在实践中可能会遇到收敛缓慢或有时不适定的问题。
在本文中,我们深入研究了引入的分数模型与3D模型之间的相互作用,并发现在实际实施中存在LoRA与3D分布不匹配的问题。我们可以通过调整其优化顺序来改进生成质量。这样做的话,分数模型会前瞻当前的3D状态,从而提供更合理的校正。然而,简单的前瞻VSD在实践中可能会因潜在过拟合而导致训练不稳定。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
基于预训练的二维扩散模型的分数蒸馏进行文本到三维生成越来越受到关注,其中的变分分数蒸馏(VSD)是一个显著示例。本文通过深入研究新引入的分数模型与三维模型之间的相互作用,发现实际应用中存在LoRA与三维分布不匹配的问题。通过调整优化顺序,可以提高生成质量。然而,简单的向前查看VSD在实践中可能会因过拟合而导致训练不稳定。为此,本文提出了线性化变体模型用于分数蒸馏,即Linearized Lookahead 变分分数蒸馏($L^2$-VSD)。$L^2$-VSD可利用现有深度学习库的向前模式自动微分功能高效实现。大量实验验证了$L^2$-VSD的有效性,表明其在基于分数蒸馏的文本到三维生成框架中明显优于其他方法,并且能无缝地融入任何其他基于VSD的文本到三维框架。
Key Takeaways
- 变分分数蒸馏(VSD)改进了传统的分数蒸馏方法,通过引入额外的基于分数的模型来纠正蒸馏梯度。
- 在实践中,VSD可能会遭遇缓慢和不合预期的收敛问题。
- 分数模型与三维模型之间存在不匹配问题,通过调整优化顺序可以提高生成质量。
- 简单的向前查看VSD可能会因过拟合而导致训练不稳定。
- 提出了Linearized Lookahead 变分分数蒸馏($L^2$-VSD),它是一个高效的解决方案,能够利用现有深度学习库的自动微分功能。
- 实验证明$L^2$-VSD在基于分数蒸馏的文本到三维生成框架中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图



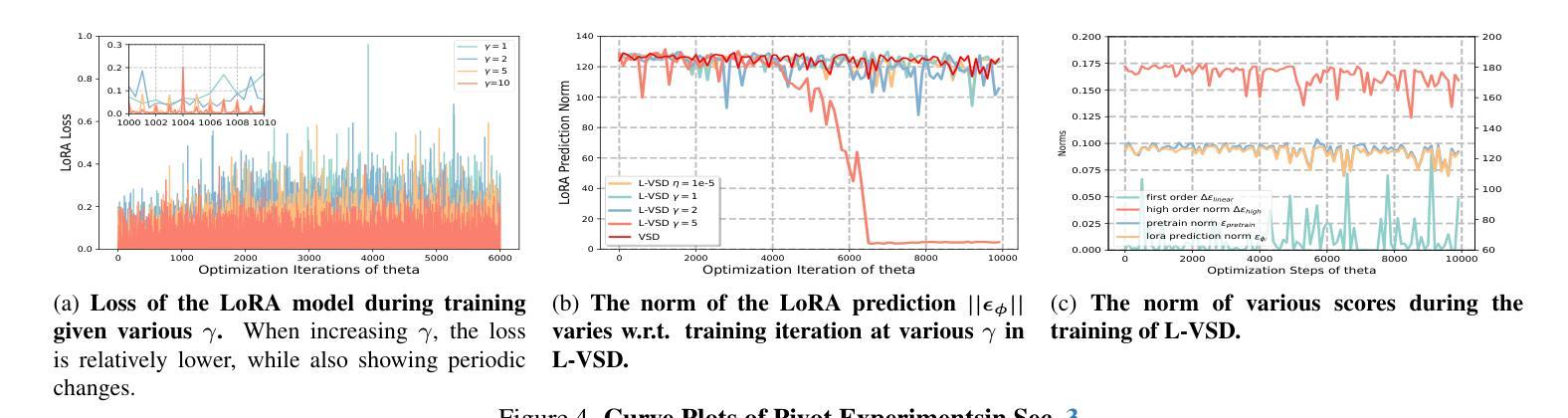

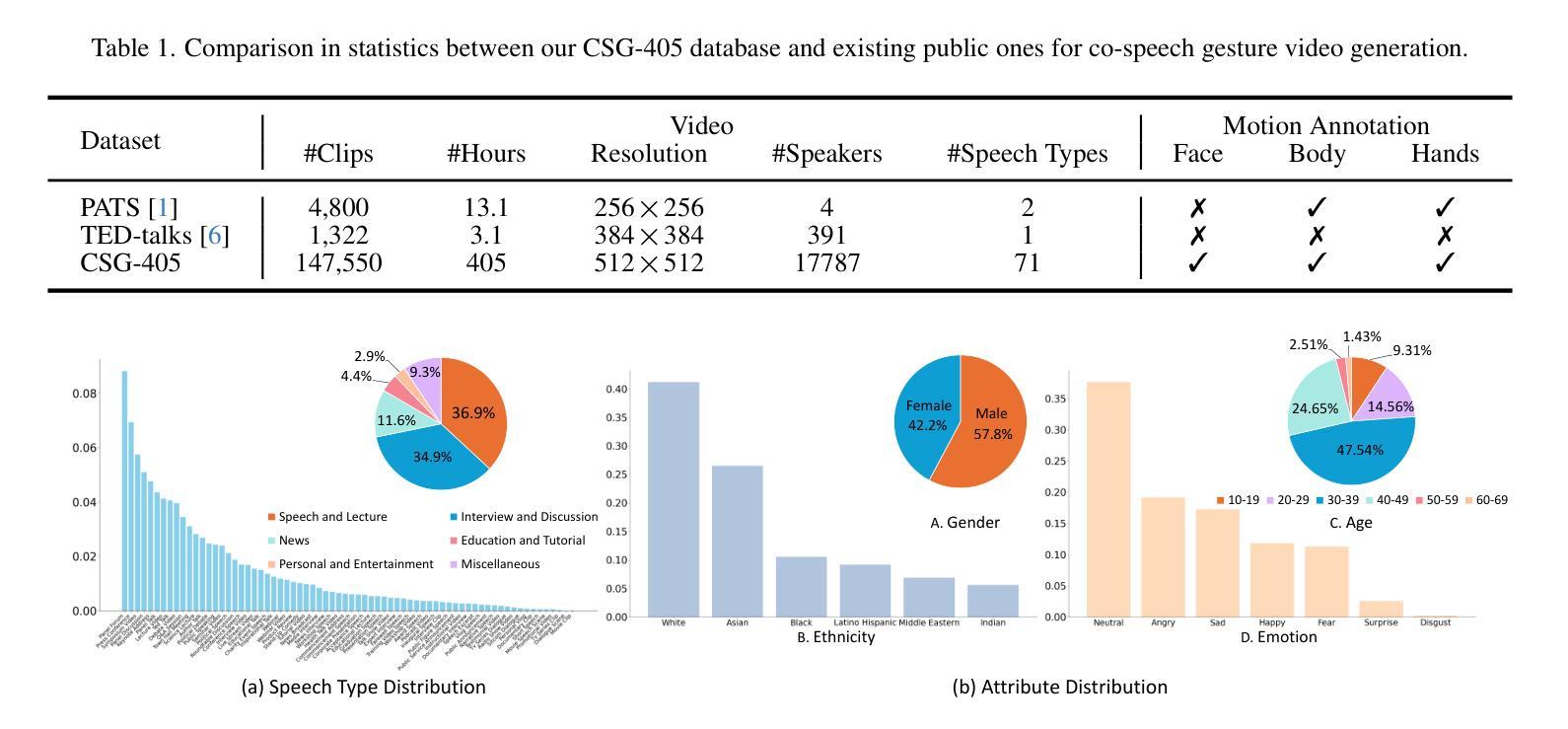
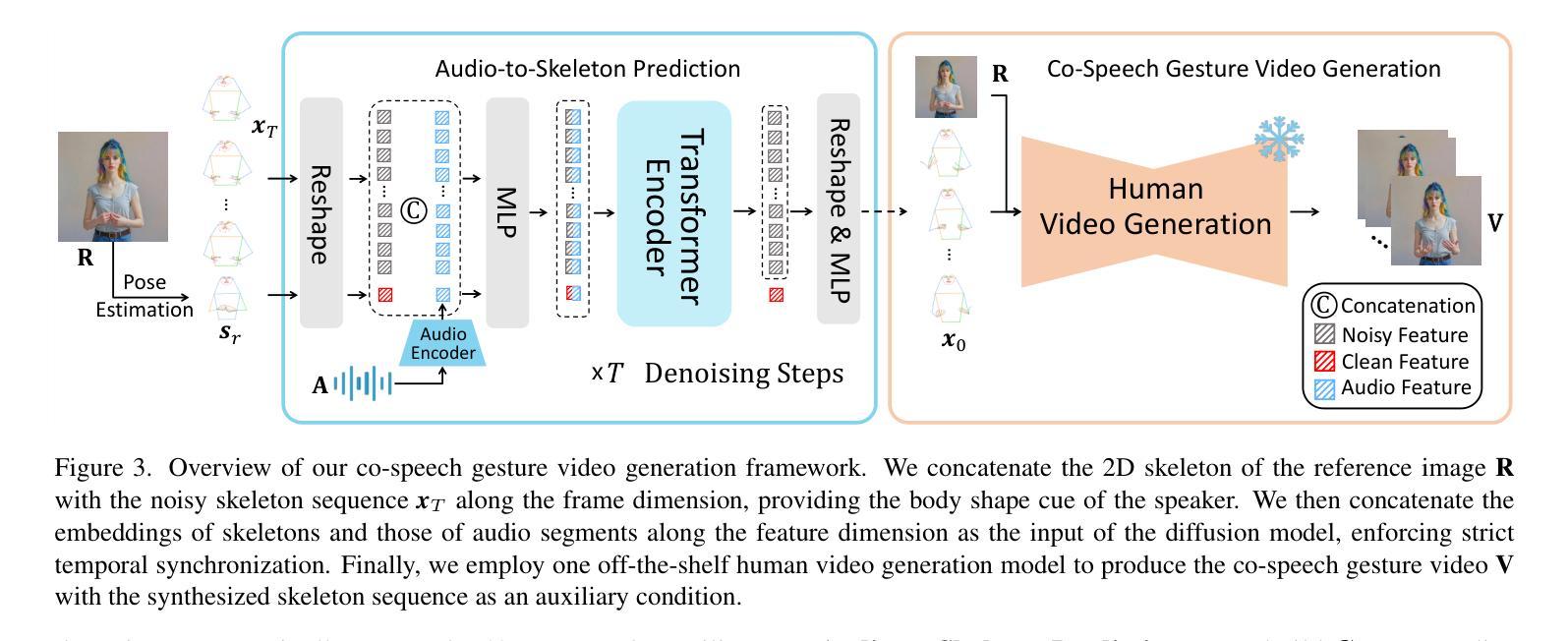
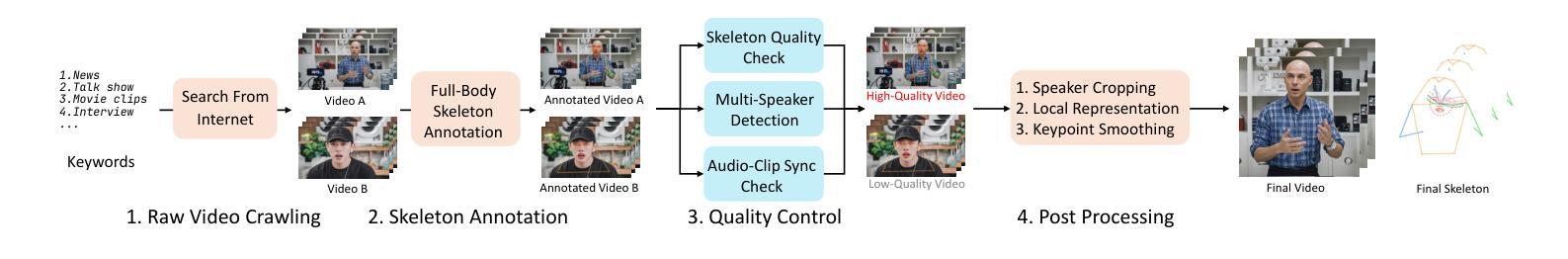
Democratizing High-Fidelity Co-Speech Gesture Video Generation
Authors:Xu Yang, Shaoli Huang, Shenbo Xie, Xuelin Chen, Yifei Liu, Changxing Ding
Co-speech gesture video generation aims to synthesize realistic, audio-aligned videos of speakers, complete with synchronized facial expressions and body gestures. This task presents challenges due to the significant one-to-many mapping between audio and visual content, further complicated by the scarcity of large-scale public datasets and high computational demands. We propose a lightweight framework that utilizes 2D full-body skeletons as an efficient auxiliary condition to bridge audio signals with visual outputs. Our approach introduces a diffusion model conditioned on fine-grained audio segments and a skeleton extracted from the speaker’s reference image, predicting skeletal motions through skeleton-audio feature fusion to ensure strict audio coordination and body shape consistency. The generated skeletons are then fed into an off-the-shelf human video generation model with the speaker’s reference image to synthesize high-fidelity videos. To democratize research, we present CSG-405-the first public dataset with 405 hours of high-resolution videos across 71 speech types, annotated with 2D skeletons and diverse speaker demographics. Experiments show that our method exceeds state-of-the-art approaches in visual quality and synchronization while generalizing across speakers and contexts. Code, models, and CSG-405 are publicly released at https://mpi-lab.github.io/Democratizing-CSG/
协同语音手势视频生成旨在合成与音频对齐的、逼真的发言人视频,包括同步的面部表情和体态。由于音频和视觉内容之间的一到多映射关系显著,再加上大规模公共数据集的稀缺和高计算需求,此任务面临挑战。我们提出了一种轻量级的框架,利用二维全身骨架作为连接音频信号和视觉输出的高效辅助条件。我们的方法引入了一个扩散模型,该模型根据精细的音频片段和从发言人参考图像中提取的骨架进行条件设置,通过骨架音频特征融合来预测骨架运动,以确保严格的音频协调和体态一致性。生成的骨架然后输入到带有发言人参考图像的商品人物视频生成模型中,以合成高保真视频。为了普及研究,我们推出了CSG-405数据集——第一个公共数据集,包含71种语音类型的405小时高分辨率视频,标注了二维骨架和多样的发言人人口统计数据。实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量和同步方面超过了最先进的方法,并且在跨发言人和上下文方面具有很强的通用性。代码、模型和CSG-405数据集可在https://mpi-lab.github.io/Democratizing-CSG/公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于二维全身骨骼的高效轻量级框架,用于合成与音频信号同步的说话人手势视频。该框架利用精细的音频片段和从参考图像中提取的骨骼信息,通过骨骼音频特征融合预测骨骼运动,确保严格的音频协调和身体形状一致性。生成的骨骼信息将输入到现成的视频生成模型中,结合参考图像合成高质量视频。此外,还发布了首个公共数据集CSG-405,包含405小时的高分辨率视频,跨越71种语音类型,并附有二维骨骼和多样的说话者人口统计信息。实验表明,该方法在视觉质量和同步方面超过了现有技术,并在跨说话者和上下文方面具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个基于二维全身骨骼的轻量级框架进行音频对齐的视频生成。
- 通过骨骼音频特征融合预测骨骼运动,确保音频与视觉输出同步。
- 利用现有的视频生成模型和参考图像合成高质量视频。
- 介绍了首个公共数据集CSG-405,包含多种语音类型和丰富的二维骨骼信息。
- 该方法提高了视觉质量和同步性能,超越了现有技术。
- 方法具有良好的跨说话者和上下文泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

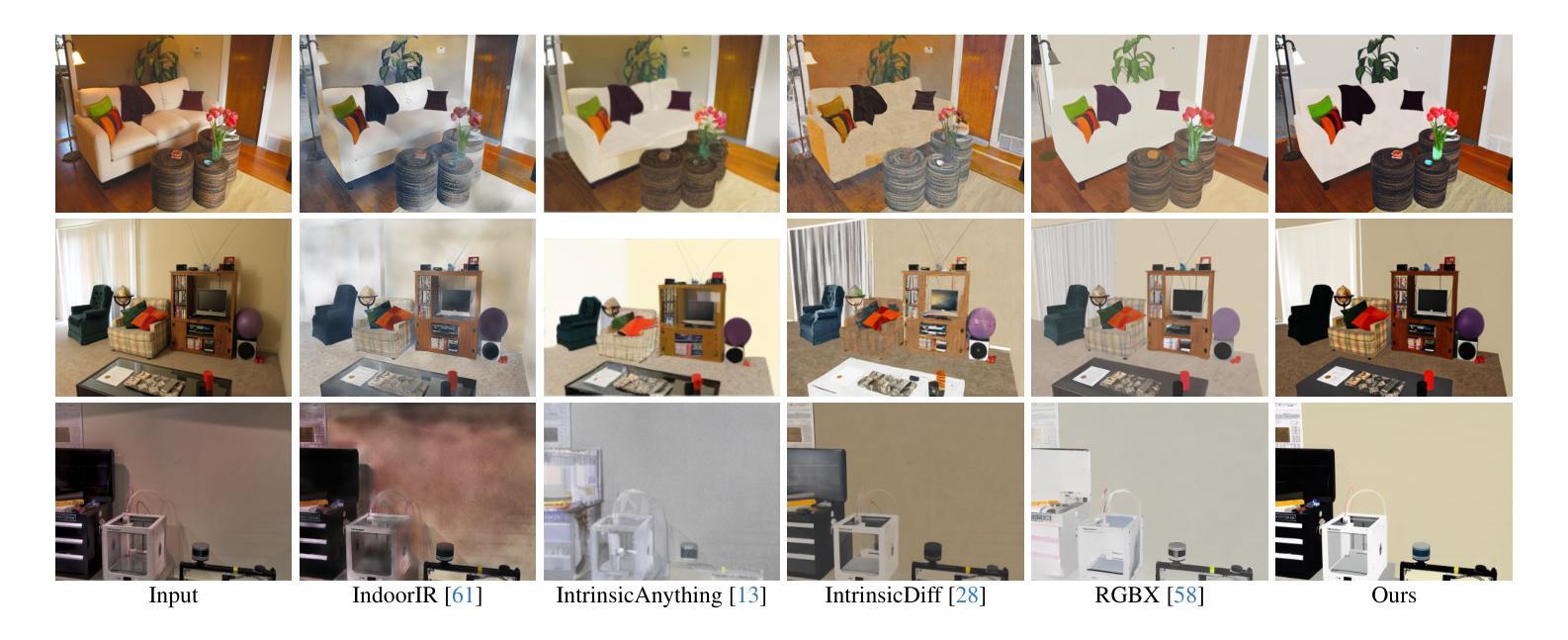
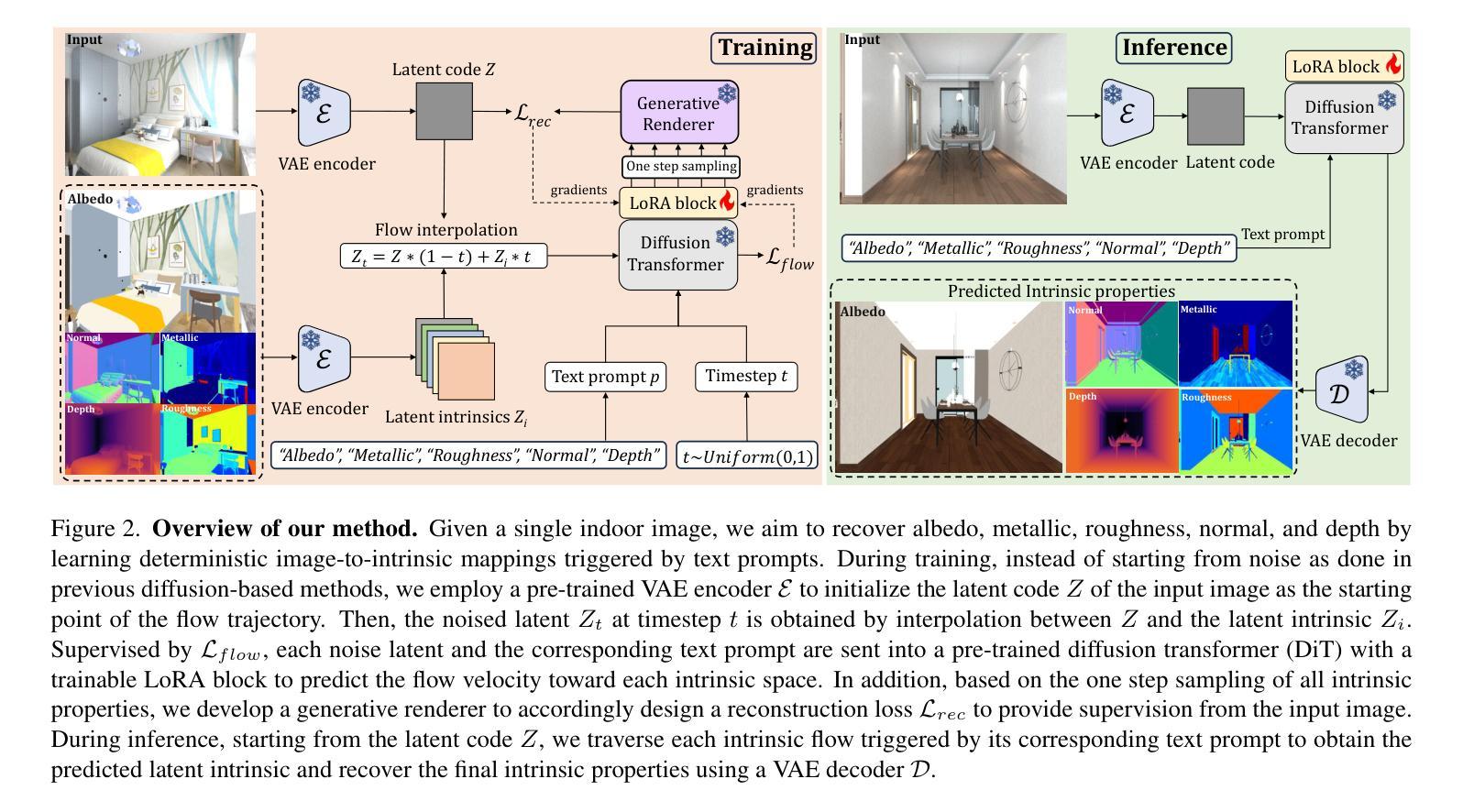
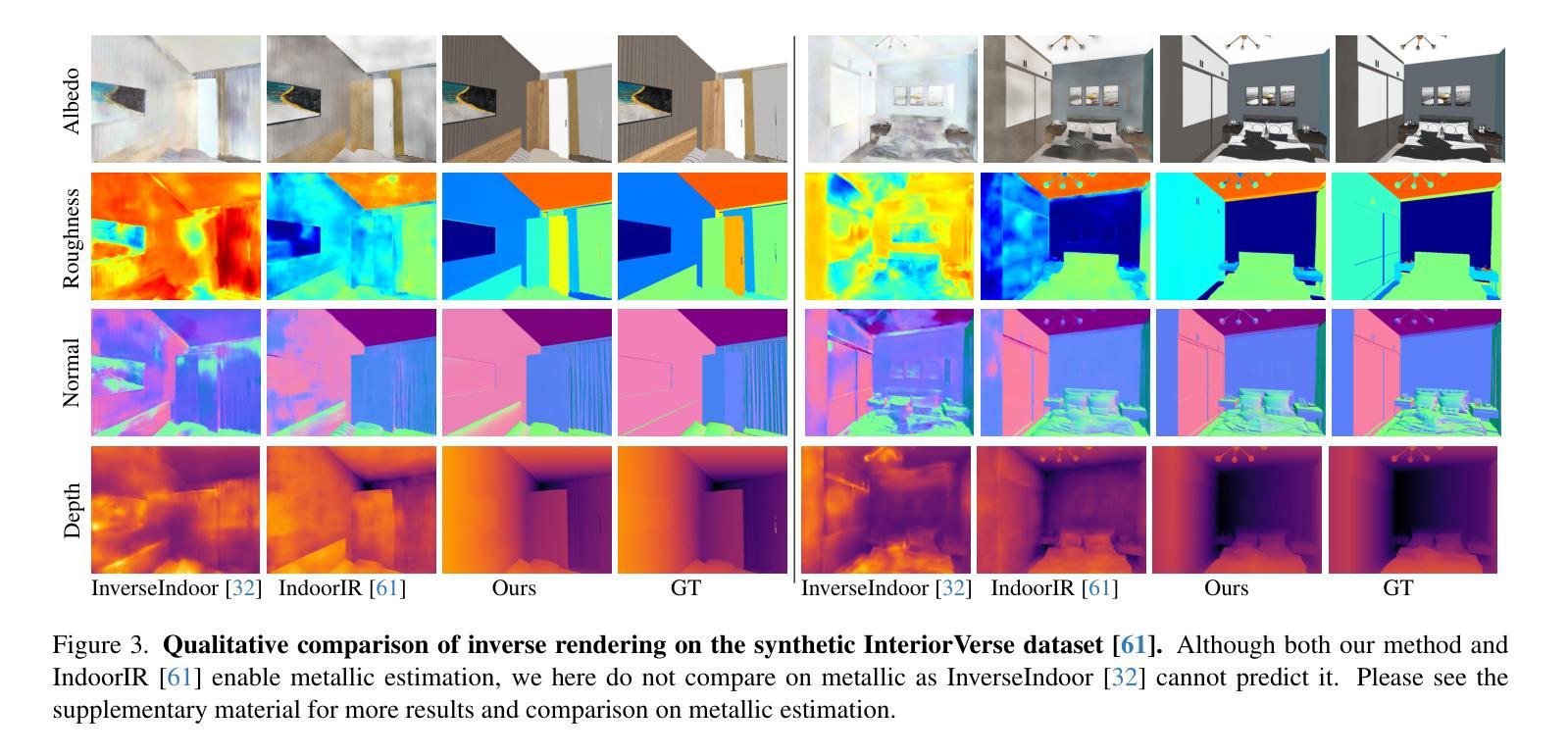
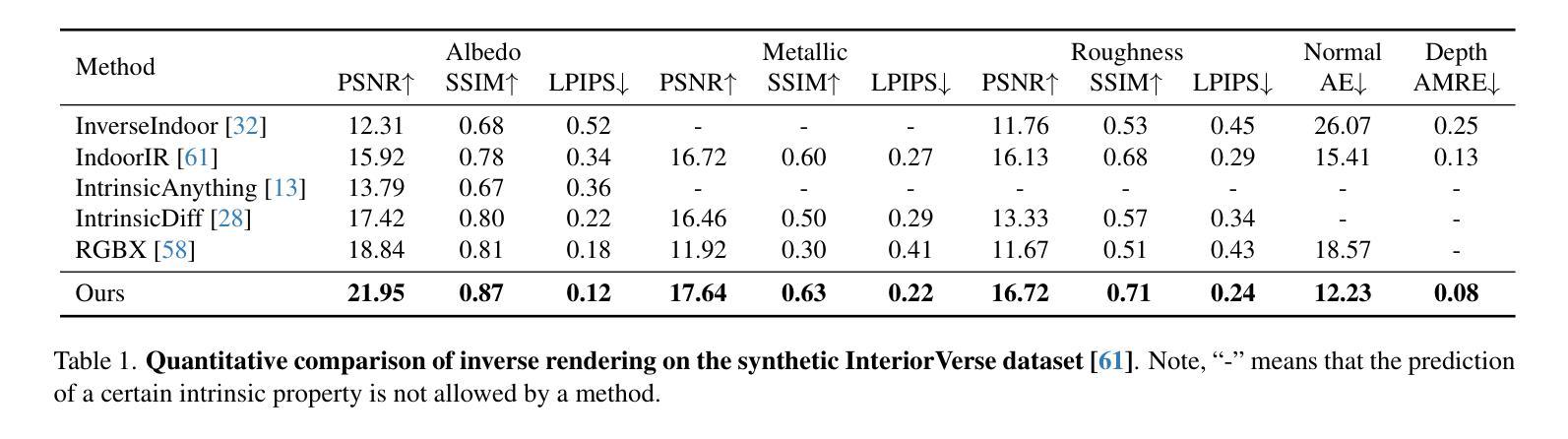
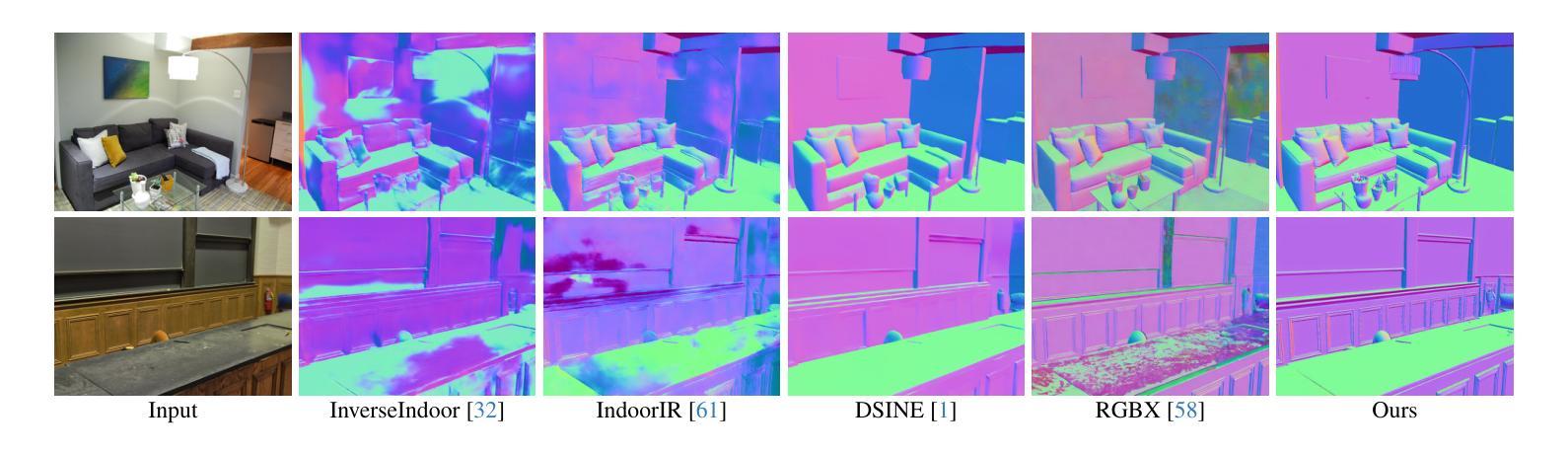
DNF-Intrinsic: Deterministic Noise-Free Diffusion for Indoor Inverse Rendering
Authors:Rongjia Zheng, Qing Zhang, Chengjiang Long, Wei-Shi Zheng
Recent methods have shown that pre-trained diffusion models can be fine-tuned to enable generative inverse rendering by learning image-conditioned noise-to-intrinsic mapping. Despite their remarkable progress, they struggle to robustly produce high-quality results as the noise-to-intrinsic paradigm essentially utilizes noisy images with deteriorated structure and appearance for intrinsic prediction, while it is common knowledge that structure and appearance information in an image are crucial for inverse rendering. To address this issue, we present DNF-Intrinsic, a robust yet efficient inverse rendering approach fine-tuned from a pre-trained diffusion model, where we propose to take the source image rather than Gaussian noise as input to directly predict deterministic intrinsic properties via flow matching. Moreover, we design a generative renderer to constrain that the predicted intrinsic properties are physically faithful to the source image. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that our method clearly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
最新方法已经表明,通过对预训练的扩散模型进行微调,可以通过学习图像条件下的噪声到内在映射来实现生成式逆向渲染。尽管取得了显著的进步,它们在稳定地产生高质量结果方面仍然面临挑战,因为噪声到内在的模式本质上利用的是结构恶化和外观退化的噪声图像来进行内在预测,而众所周知,图像中的结构和外观信息对于逆向渲染至关重要。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了DNF-Intrinsic,这是一种从预训练的扩散模型进行微调的稳健而高效的逆向渲染方法,我们建议以源图像而非高斯噪声为输入,通过流匹配直接预测确定性内在属性。此外,我们设计了一个生成式渲染器来约束预测的内在属性在物理上忠于源图像。在合成数据集和真实世界数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法明显优于现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV2025
Summary:预训练扩散模型可以通过学习图像条件噪声到内在映射进行微调,以实现生成式逆向渲染。但它们在产生高质量结果方面存在困难,因为噪声到内在范式本质上利用的是结构退化的噪声图像进行内在预测。为解决此问题,我们提出DNF-Intrinsic方法,使用源图像而非高斯噪声作为输入,通过流匹配直接预测确定性内在属性,并设计生成渲染器约束预测的内在属性在物理上忠于源图像。实验表明,我们的方法明显优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型可以通过微调实现生成式逆向渲染。
- 现有方法利用结构退化的噪声图像进行内在预测,影响结果质量。
- DNF-Intrinsic方法以源图像为输入,通过流匹配直接预测确定性内在属性。
- 引入生成渲染器以约束预测的内在属性与源图像的物理一致性。
- DNF-Intrinsic在合成和真实数据集上的表现均优于现有先进技术。
- 方法具有鲁棒性和高效性。
点此查看论文截图


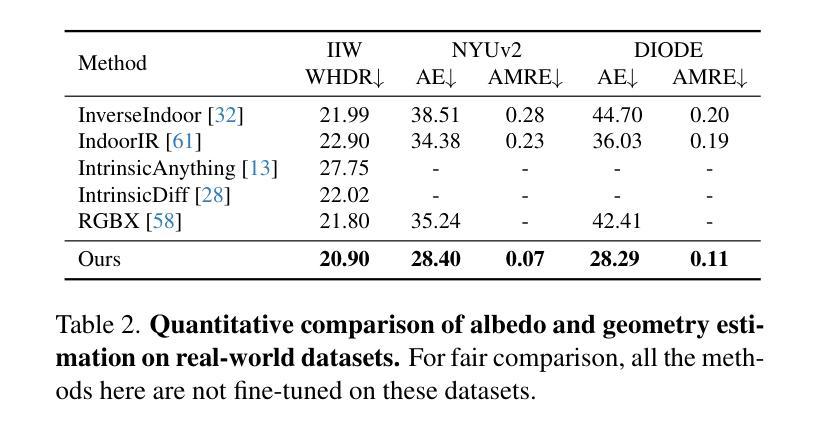
Imagine for Me: Creative Conceptual Blending of Real Images and Text via Blended Attention
Authors:Wonwoong Cho, Yanxia Zhang, Yan-Ying Chen, David I. Inouye
Blending visual and textual concepts into a new visual concept is a unique and powerful trait of human beings that can fuel creativity. However, in practice, cross-modal conceptual blending for humans is prone to cognitive biases, like design fixation, which leads to local minima in the design space. In this paper, we propose a T2I diffusion adapter “IT-Blender” that can automate the blending process to enhance human creativity. Prior works related to cross-modal conceptual blending are limited in encoding a real image without loss of details or in disentangling the image and text inputs. To address these gaps, IT-Blender leverages pretrained diffusion models (SD and FLUX) to blend the latent representations of a clean reference image with those of the noisy generated image. Combined with our novel blended attention, IT-Blender encodes the real reference image without loss of details and blends the visual concept with the object specified by the text in a disentangled way. Our experiment results show that IT-Blender outperforms the baselines by a large margin in blending visual and textual concepts, shedding light on the new application of image generative models to augment human creativity.
将视觉和文本概念融合为一个新的视觉概念是人类独特且强大的特质,能够激发创造力。然而,在实践中,人类的跨模态概念融合容易受到认知偏见的影响,如设计僵化,这会导致设计空间中的局部最小值。在本文中,我们提出了一种T2I扩散适配器“IT-Blender”,它可以自动化融合过程以增强人类的创造力。以往与跨模态概念融合相关的工作在编码真实图像时存在细节损失或在分离图像和文本输入方面的局限性。为了解决这些问题,IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型(SD和FLUX)来融合干净参考图像的潜在表示与噪声生成图像的潜在表示。结合我们新颖的融合注意力机制,IT-Blender能够编码真实参考图像而不损失细节,并以分离的方式将视觉概念与文本指定的对象融合在一起。我们的实验结果表明,在融合视觉和文本概念方面,IT-Blender大大优于基线,为图像生成模型在人类创造力增强方面的新应用提供了启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website is available at https://imagineforme.github.io/
摘要
人类能够融合视觉和文本概念以形成新的视觉概念,这是人类独特且强大的创造力体现。然而,在实践中,人类的跨模态概念融合易受到认知偏见的影响,如设计僵化,这会导致设计空间中的局部最小值。本文提出了一种T2I扩散适配器IT-Blender,可以自动化融合过程以增强人类的创造力。先前关于跨模态概念融合的研究受限于无法对真实图像进行无损编码或无法将图像和文本输入分开。为了解决这些问题,IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型(SD和FLUX)将干净参考图像和噪声生成图像的潜在表示融合在一起。结合我们新颖的融合注意力机制,IT-Blender能够对真实参考图像进行无损编码,并以分离的方式将视觉概念与文本指定的对象融合在一起。实验结果表明,IT-Blender在融合视觉和文本概念方面远超基线方法,为图像生成模型在人类创造力提升方面的应用提供了新的启示。
关键见解
- 人类能够融合视觉和文本概念以创造新的视觉概念,但这一过程易受到认知偏见的影响。
- IT-Blender是一种T2I扩散适配器,旨在自动化融合过程以增强人类创造力。
- 以往的跨模态概念融合研究在图像编码和图像与文本输入的分离方面存在局限。
- IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型和融合注意力机制进行视觉与文本概念的融合。
- IT-Blender能够对真实参考图像进行无损编码,并以分离的方式处理视觉概念和文本指定的对象。
- 实验结果表明,IT-Blender在融合视觉和文本概念方面效果显著,远超基线方法。
- IT-Blender的应用为图像生成模型在人类创造力提升方面的作用提供了新的视角。
点此查看论文截图

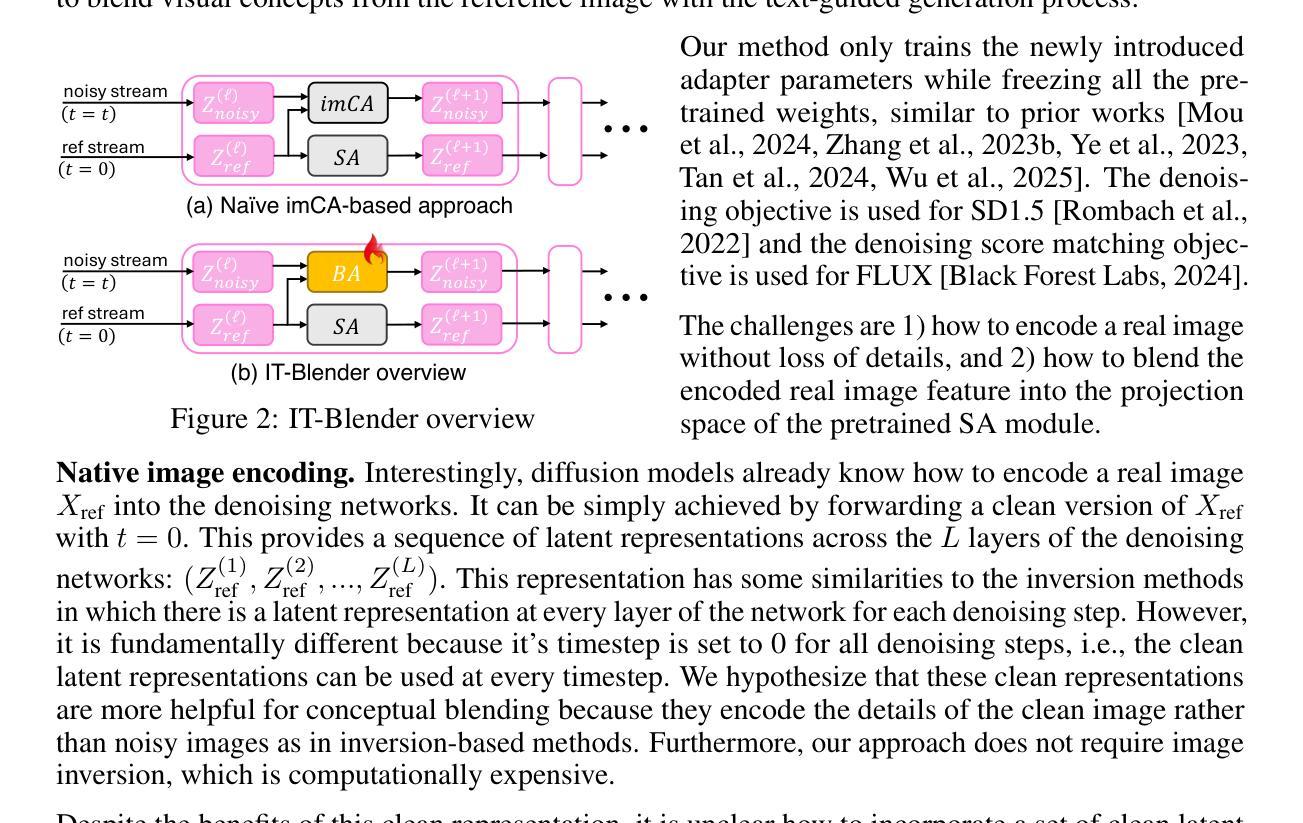
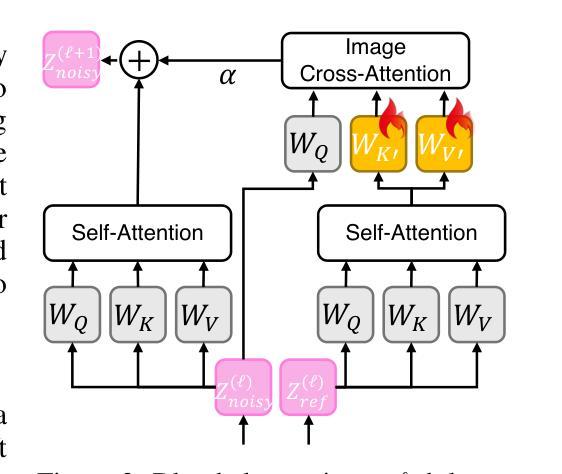
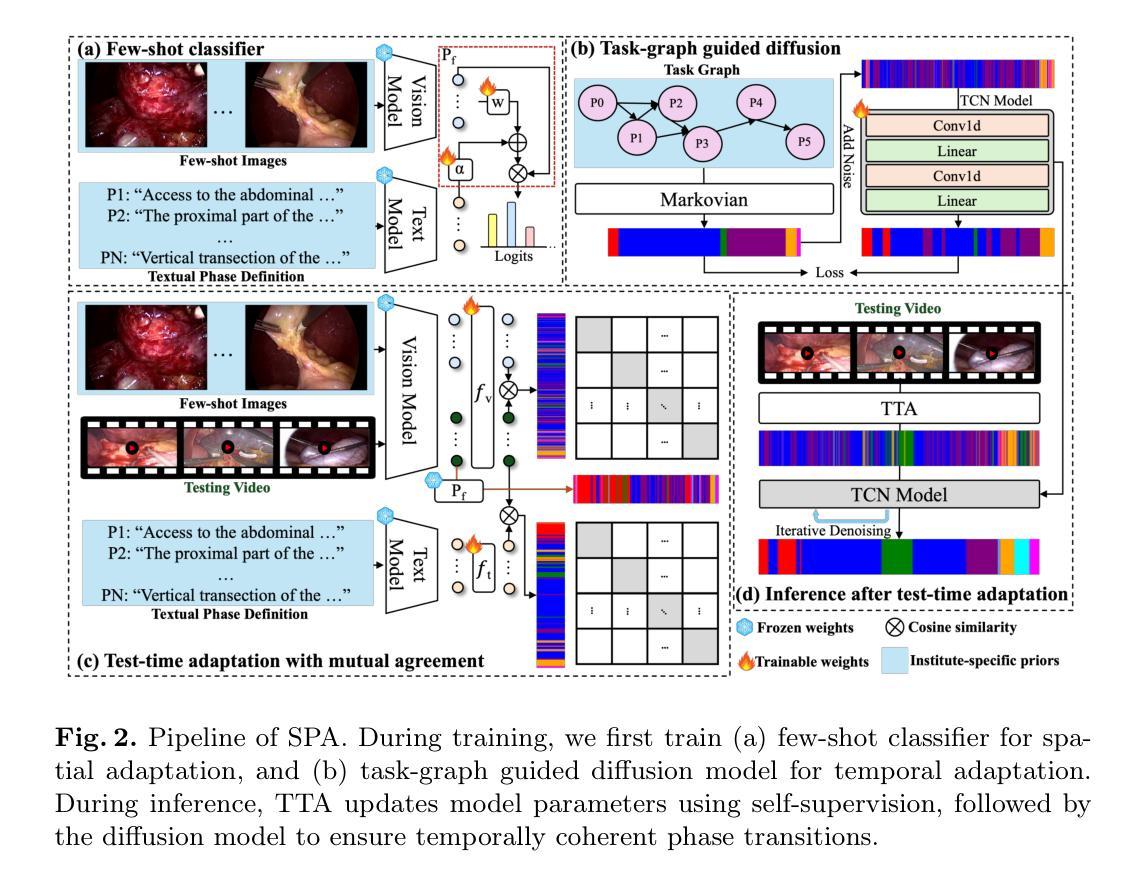
Recognizing Surgical Phases Anywhere: Few-Shot Test-time Adaptation and Task-graph Guided Refinement
Authors:Kun Yuan, Tingxuan Chen, Shi Li, Joel L. Lavanchy, Christian Heiliger, Ege Özsoy, Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Nassir Navab, Vinkle Srivastav, Hongliang Ren, Nicolas Padoy
The complexity and diversity of surgical workflows, driven by heterogeneous operating room settings, institutional protocols, and anatomical variability, present a significant challenge in developing generalizable models for cross-institutional and cross-procedural surgical understanding. While recent surgical foundation models pretrained on large-scale vision-language data offer promising transferability, their zero-shot performance remains constrained by domain shifts, limiting their utility in unseen surgical environments. To address this, we introduce Surgical Phase Anywhere (SPA), a lightweight framework for versatile surgical workflow understanding that adapts foundation models to institutional settings with minimal annotation. SPA leverages few-shot spatial adaptation to align multi-modal embeddings with institution-specific surgical scenes and phases. It also ensures temporal consistency through diffusion modeling, which encodes task-graph priors derived from institutional procedure protocols. Finally, SPA employs dynamic test-time adaptation, exploiting the mutual agreement between multi-modal phase prediction streams to adapt the model to a given test video in a self-supervised manner, enhancing the reliability under test-time distribution shifts. SPA is a lightweight adaptation framework, allowing hospitals to rapidly customize phase recognition models by defining phases in natural language text, annotating a few images with the phase labels, and providing a task graph defining phase transitions. The experimental results show that the SPA framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot surgical phase recognition across multiple institutions and procedures, even outperforming full-shot models with 32-shot labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA
手术流程的复杂性和多样性,受到手术室设置、机构协议和解剖结构差异的影响,为跨机构和跨程序的手术理解开发通用模型带来了巨大的挑战。虽然最近基于大规模视觉语言数据的预训练手术基础模型展现出有前景的迁移性,但它们的零样本性能仍然受到领域偏移的限制,在未见过的手术环境中效用有限。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了Surgical Phase Anywhere(SPA),这是一个轻量级的通用手术流程理解框架,能够适应机构设置,并最大限度地减少标注工作。SPA利用少样本空间自适应来对齐多模态嵌入和机构特定的手术场景和阶段。它还通过扩散模型确保时间一致性,该模型编码来自机构程序协议的任务图先验信息。最后,SPA采用动态测试时间自适应,利用多模态阶段预测流之间的相互一致性,以自我监督的方式适应给定的测试视频,在测试时间分布变化的情况下提高可靠性。SPA是一个轻量级的适应框架,允许医院通过用自然语言文本定义阶段、对少数图像进行阶段标签标注以及提供定义阶段转换的任务图来快速定制阶段识别模型。实验结果表明,SPA框架在多个机构和程序中的少样本手术阶段识别中达到最新性能水平,即使在拥有32个带标签样本的全样本模型中也能取得优势。相关代码可在 https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对手术流程理解的跨机构模型开发所面临的挑战。针对这一问题,提出了一种轻量级的手术流程理解框架——Surgical Phase Anywhere(SPA)。SPA能够利用少量的样本数据进行空间适应,以与特定机构的手术场景和阶段对齐。通过扩散建模确保时间一致性,并编码机构手术协议的任务图先验。此外,SPA采用动态测试时间适应,利用多模态阶段预测流的相互一致性,以自我监督的方式适应给定的测试视频,提高测试时分布变化的可靠性。实验结果证明,SPA框架在多个机构和程序中的小样本手术阶段识别中实现了最佳性能,甚至在标注数据只有32次全镜头的情况下也表现出优势。
Key Takeaways
- 手术工作流的复杂性和多样性对开发可跨机构和跨手术理解的通用模型提出了重大挑战。
- Surgical Phase Anywhere(SPA)框架被引入为解决这一问题,它允许利用少量的样本数据进行空间适应。
- SPA通过扩散建模确保时间一致性,并编码任务图先验,反映机构特定的手术协议。
- SPA采用动态测试时间适应,以提高模型在测试时面对分布变化的可靠性。
- SPA框架允许医院通过自然语言文本定义阶段、对少数图像进行阶段标签注释以及提供定义阶段转换的任务图,来快速定制阶段识别模型。
- 实验结果表明,SPA框架在少样本手术阶段识别中实现了最佳性能,甚至在标注数据量较小的情况下也表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

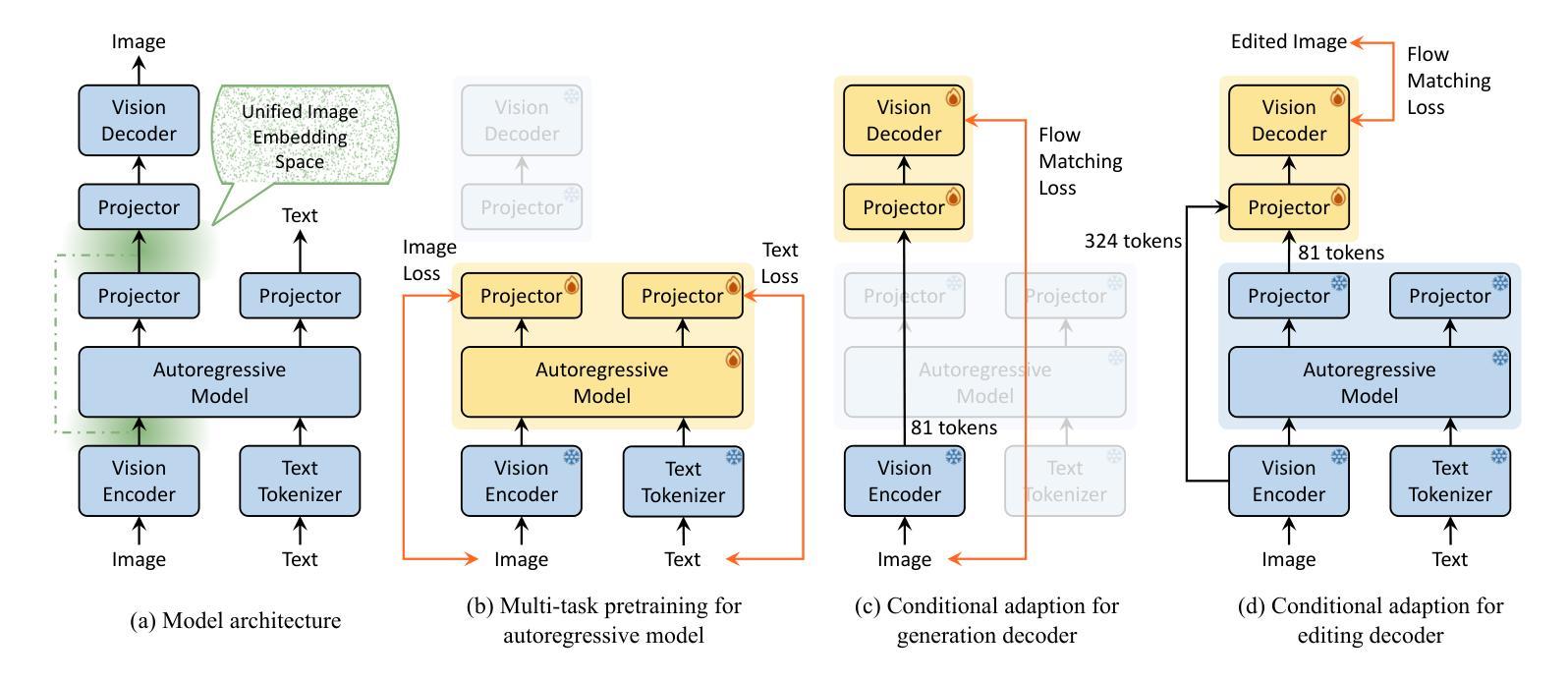
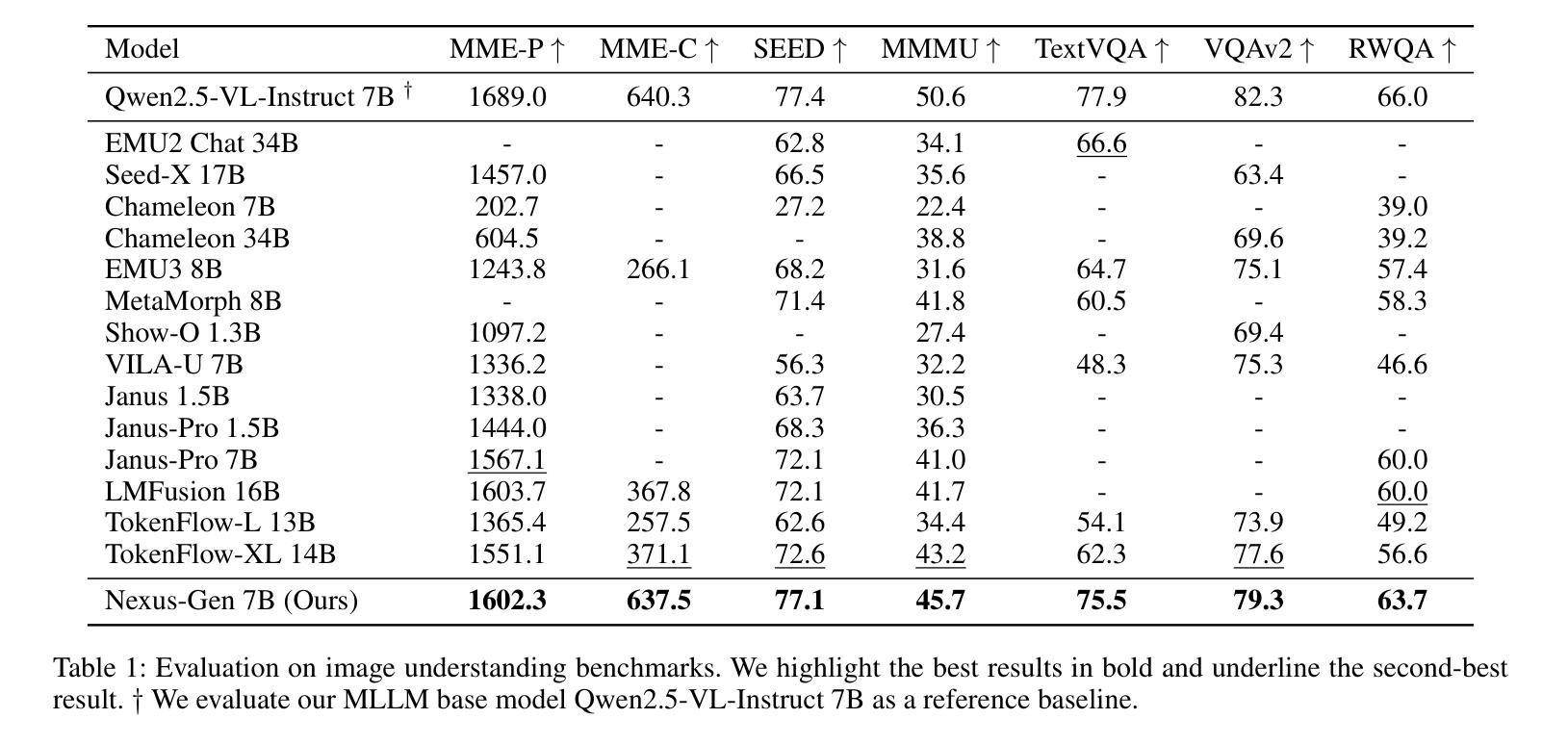
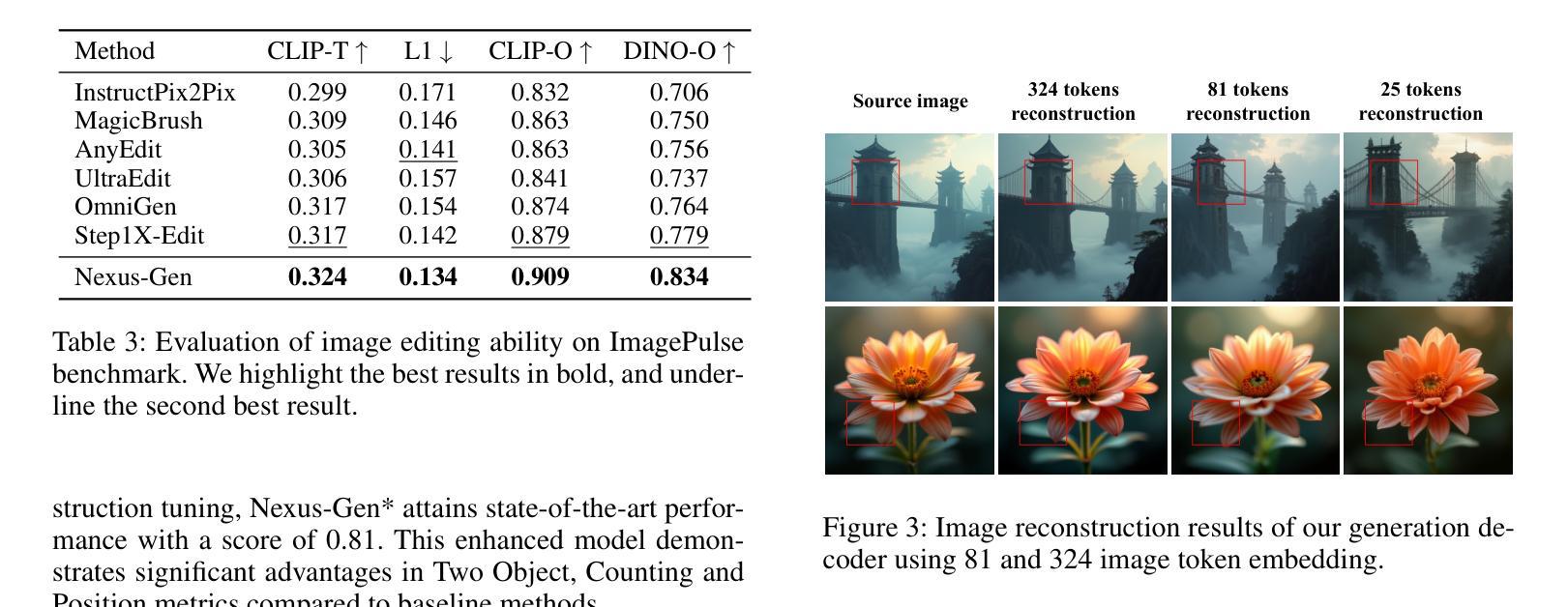
Nexus-Gen: Unified Image Understanding, Generation, and Editing via Prefilled Autoregression in Shared Embedding Space
Authors:Hong Zhang, Zhongjie Duan, Xingjun Wang, Yuze Zhao, Weiyi Lu, Zhipeng Di, Yixuan Xu, Yingda Chen, Yu Zhang
Unified multimodal generative models aim to integrate image understanding and generation abilities, offering significant advantages in harnessing multimodal corpora, particularly interleaved text-image data. However, existing unified models exhibit limitations in image synthesis quality, autoregressive error accumulation, and image editing capability. In this work, we propose Nexus-Gen, a novel architecture that unifies image understanding, generation, and editing tasks in a shared image embedding space. This shared space serves as a bridge for the autoregressive and diffusion models, which seamlessly integrates their complementary strengths in cross-modal modeling. To mitigate the severe error accumulation during autoregressive embedding prediction, we propose a novel prefilled autoregression strategy that aligns training-inference dynamics by prefilling input sequences with learnable embeddings. After multi-stage and multi-task training on our constructed large-scale dataset with 26.3 million samples, Nexus-Gen achieves state-of-the-art performance on the evaluation benchmarks spanning image understanding, generation and editing tasks. All models, datasets, and source codes are released in https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen to facilitate further advancements across the field.
统一多模态生成模型旨在整合图像理解和生成能力,在利用多模态语料库方面,特别是交织的文本图像数据方面,具有显著优势。然而,现有的统一模型在图像合成质量、自回归误差累积和图像编辑能力方面存在局限性。在这项工作中,我们提出了Nexus-Gen,这是一种新型架构,在共享的图像嵌入空间中统一了图像理解、生成和编辑任务。这个共享空间作为自回归和扩散模型的桥梁,无缝集成了它们在跨模态建模中的互补优势。为了减轻自回归嵌入预测过程中的严重误差累积,我们提出了一种新的预填充自回归策略,通过预填充可学习嵌入来对齐训练推理动态。在我们构建的大规模数据集(包含2630万样本)上进行多阶段多任务训练后,Nexus-Gen在涵盖图像理解、生成和编辑任务的评估基准上达到了最新技术水平。所有模型、数据集和源代码均已发布在https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen,以促进该领域的进一步进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Nexus-Gen的统一多模态生成模型,旨在在一个共享的图像嵌入空间中统一图像理解、生成和编辑任务。该模型通过桥接自回归模型和扩散模型,实现了跨模态建模的互补优势。为解决自回归嵌入预测中的误差累积问题,提出了一种预填充自回归策略,通过预填充学习嵌入来对齐训练和推理动态。经过在构建的大规模数据集上的多阶段多任务训练,Nexus-Gen在图像理解、生成和编辑任务的评价指标上均达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- Nexus-Gen是一个统一的多模态生成模型,旨在在一个共享的图像嵌入空间中完成图像理解、生成和编辑任务。
- 该模型通过桥接自回归模型和扩散模型,实现了跨模态建模的互补优势。
- Nexus-Gen采用预填充自回归策略,解决自回归嵌入预测中的误差累积问题。
- 该模型在大规模数据集上进行多阶段多任务训练,展示了在图像理解、生成和编辑任务上的优越性。
- Nexus-Gen的性能在评价基准测试中达到了最新技术水平。
- 所有模型、数据集和源代码都已公开发布,以便促进该领域的进一步发展。
- 该研究为统一多模态生成模型的发展提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图



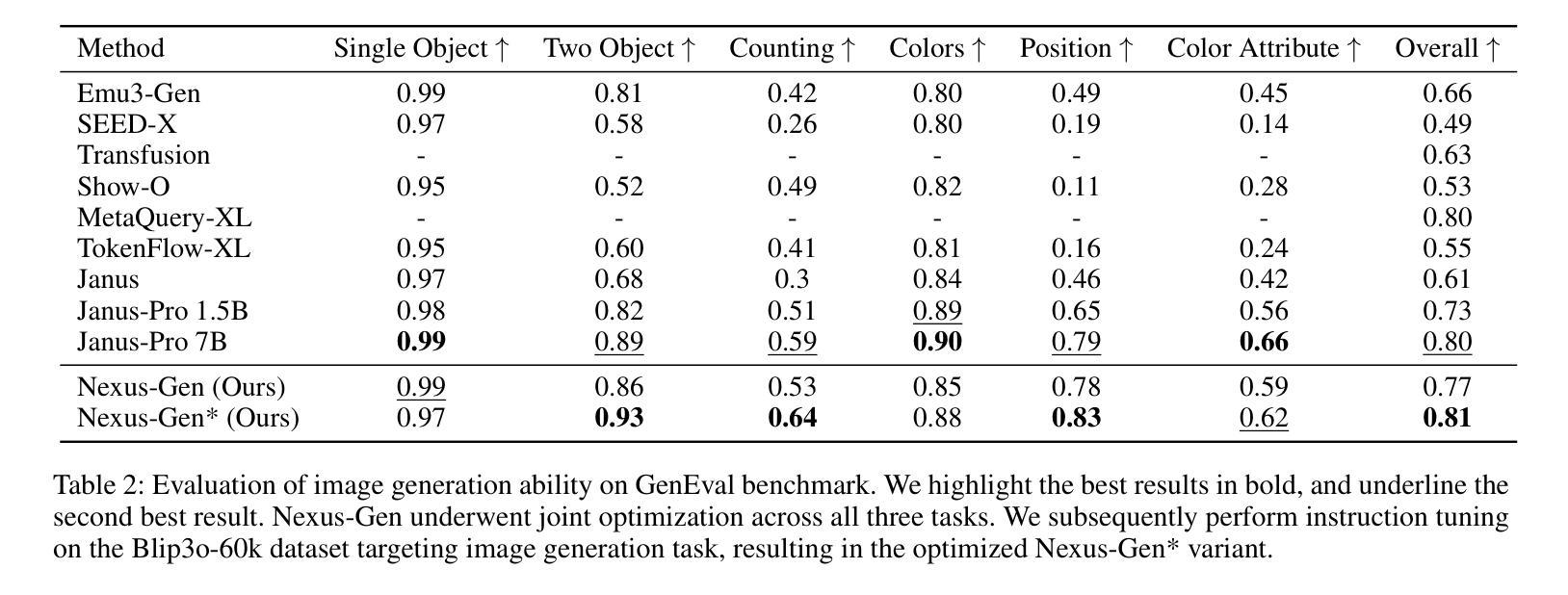
Diffusion Models for Robotic Manipulation: A Survey
Authors:Rosa Wolf, Yitian Shi, Sheng Liu, Rania Rayyes
Diffusion generative models have demonstrated remarkable success in visual domains such as image and video generation. They have also recently emerged as a promising approach in robotics, especially in robot manipulations. Diffusion models leverage a probabilistic framework, and they stand out with their ability to model multi-modal distributions and their robustness to high-dimensional input and output spaces. This survey provides a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art diffusion models in robotic manipulation, including grasp learning, trajectory planning, and data augmentation. Diffusion models for scene and image augmentation lie at the intersection of robotics and computer vision for vision-based tasks to enhance generalizability and data scarcity. This paper also presents the two main frameworks of diffusion models and their integration with imitation learning and reinforcement learning. In addition, it discusses the common architectures and benchmarks and points out the challenges and advantages of current state-of-the-art diffusion-based methods.
扩散生成模型在图像和视频生成等视觉领域取得了显著的成功。它们最近也出现在机器人技术中,尤其是机器人操控方面,展现出了巨大的潜力。扩散模型采用概率框架,它们的特点在于能够模拟多模态分布,并且对高维输入和输出空间具有很强的稳健性。这篇综述对机器人操控中的最新扩散模型进行了全面回顾,包括抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强。场景和图像增强的扩散模型位于机器人技术和计算机视觉的交叉点,用于基于视觉的任务,以提高通用性和解决数据稀缺问题。本文还介绍了扩散模型的两个主要框架及其与模仿学习和强化学习的融合。此外,它还讨论了常见的架构和基准测试,并指出了当前最新扩散方法的优势和挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 2 figure, 9 tables
Summary
扩散生成模型在图像和视频生成等领域取得了显著的成功,最近在机器人领域,特别是在机器人操作方面展现出巨大的潜力。本文全面综述了机器人操作中的扩散模型,包括抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强等。扩散模型结合了计算机视觉和机器人技术,用于基于视觉的任务,以提高通用性和解决数据稀缺问题。本文还介绍了扩散模型的两个主要框架及其与模仿学习和强化学习的结合,讨论了常见的架构和基准测试,并指出了当前先进扩散方法面临的挑战和优势。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在视觉领域如图像和视频生成取得了显著成功。
- 扩散模型在机器人操作领域展现出巨大潜力。
- 扩散模型用于机器人操作的多个方面,包括抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强。
- 扩散模型结合了计算机视觉和机器人技术,用于基于视觉的任务。
- 扩散模型的两个主要框架包括与模仿学习和强化学习的结合。
- 当前扩散模型面临一些挑战,但也具有优势。
- 文章讨论了常见的架构和基准测试来衡量扩散模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Conditional Data Synthesis Augmentation
Authors:Xinyu Tian, Xiaotong Shen
Reliable machine learning and statistical analysis rely on diverse, well-distributed training data. However, real-world datasets are often limited in size and exhibit underrepresentation across key subpopulations, leading to biased predictions and reduced performance, particularly in supervised tasks such as classification. To address these challenges, we propose Conditional Data Synthesis Augmentation (CoDSA), a novel framework that leverages generative models, such as diffusion models, to synthesize high-fidelity data for improving model performance across multimodal domains including tabular, textual, and image data. CoDSA generates synthetic samples that faithfully capture the conditional distributions of the original data, with a focus on under-sampled or high-interest regions. Through transfer learning, CoDSA fine-tunes pre-trained generative models to enhance the realism of synthetic data and increase sample density in sparse areas. This process preserves inter-modal relationships, mitigates data imbalance, improves domain adaptation, and boosts generalization. We also introduce a theoretical framework that quantifies the statistical accuracy improvements enabled by CoDSA as a function of synthetic sample volume and targeted region allocation, providing formal guarantees of its effectiveness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoDSA consistently outperforms non-adaptive augmentation strategies and state-of-the-art baselines in both supervised and unsupervised settings.
可靠机器学习和统计分析依赖于多样且分布良好的训练数据。然而,现实世界的数据集通常规模有限,并且在关键子群体中表现代表性不足,从而导致预测偏差和性能下降,特别是在分类等监督任务中。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了条件数据合成增强(CoDSA)这一新型框架,它利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高质量数据,以改善跨多模式域(包括表格、文本和图像数据)的模型性能。CoDSA生成合成样本,忠实捕捉原始数据的条件分布,重点关注欠采样或高兴趣区域。通过迁移学习,CoDSA对预训练的生成模型进行微调,以增强合成数据的真实性和稀疏区域的样本密度。这一过程保留了跨模式的关系,缓解了数据不平衡问题,改善了域适应性和提高了泛化能力。我们还引入了一个理论框架,以量化合成样本量和目标区域分配所实现的CoDSA的统计精度改进,从而为其提供有效的正式保证。大量实验表明,无论是在监督还是非监督环境中,CoDSA始终优于非自适应增强策略和最新基线技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为条件数据合成增强(CoDSA)的新型框架,它利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高质量数据,以提高包括表格、文本和图像数据等多模式领域的模型性能。CoDSA关注于欠采样或高兴趣区域的合成样本,通过迁移学习对预训练的生成模型进行微调,提高合成数据的真实性和稀疏区域的样本密度。此框架能够保留跨模态关系,缓解数据不平衡问题,改善领域适应性和提高泛化能力。实验证明,CoDSA在监督和无监督设置中均优于非自适应增强策略和最新基线。
Key Takeaways
- CoDSA利用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成高质量数据,旨在提高机器学习和统计分析的可靠性。
- 该框架关注于欠采样或高兴趣区域的合成样本,以改善模型在关键子人群中的表现。
- 通过迁移学习,CoDSA对预训练的生成模型进行微调,提高合成数据的真实性和稀疏区域的样本密度。
- CoDSA能够保留跨模态关系,缓解数据不平衡问题。
- 该框架提高了领域适应性和模型的泛化能力。
- 文中提供了理论框架,量化CoDSA在统计准确性方面的改进,并给出其有效性的正式保证。
点此查看论文截图

Compression-Aware One-Step Diffusion Model for JPEG Artifact Removal
Authors:Jinpei Guo, Zheng Chen, Wenbo Li, Yong Guo, Yulun Zhang
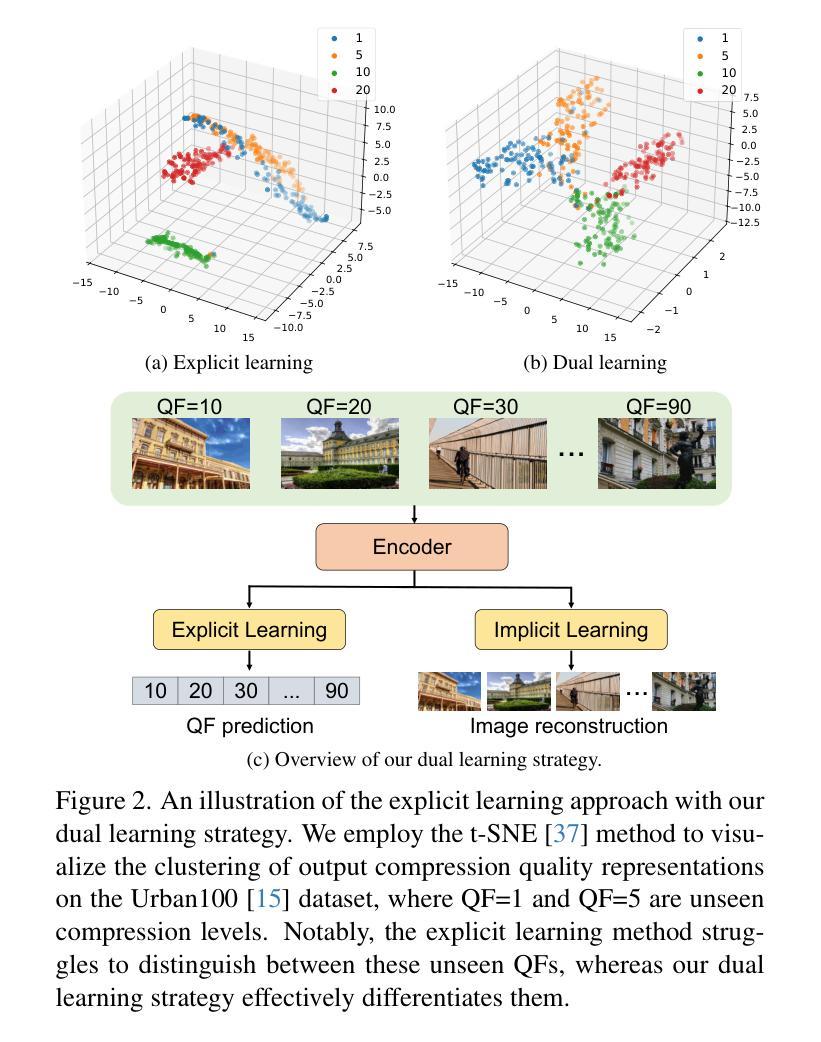
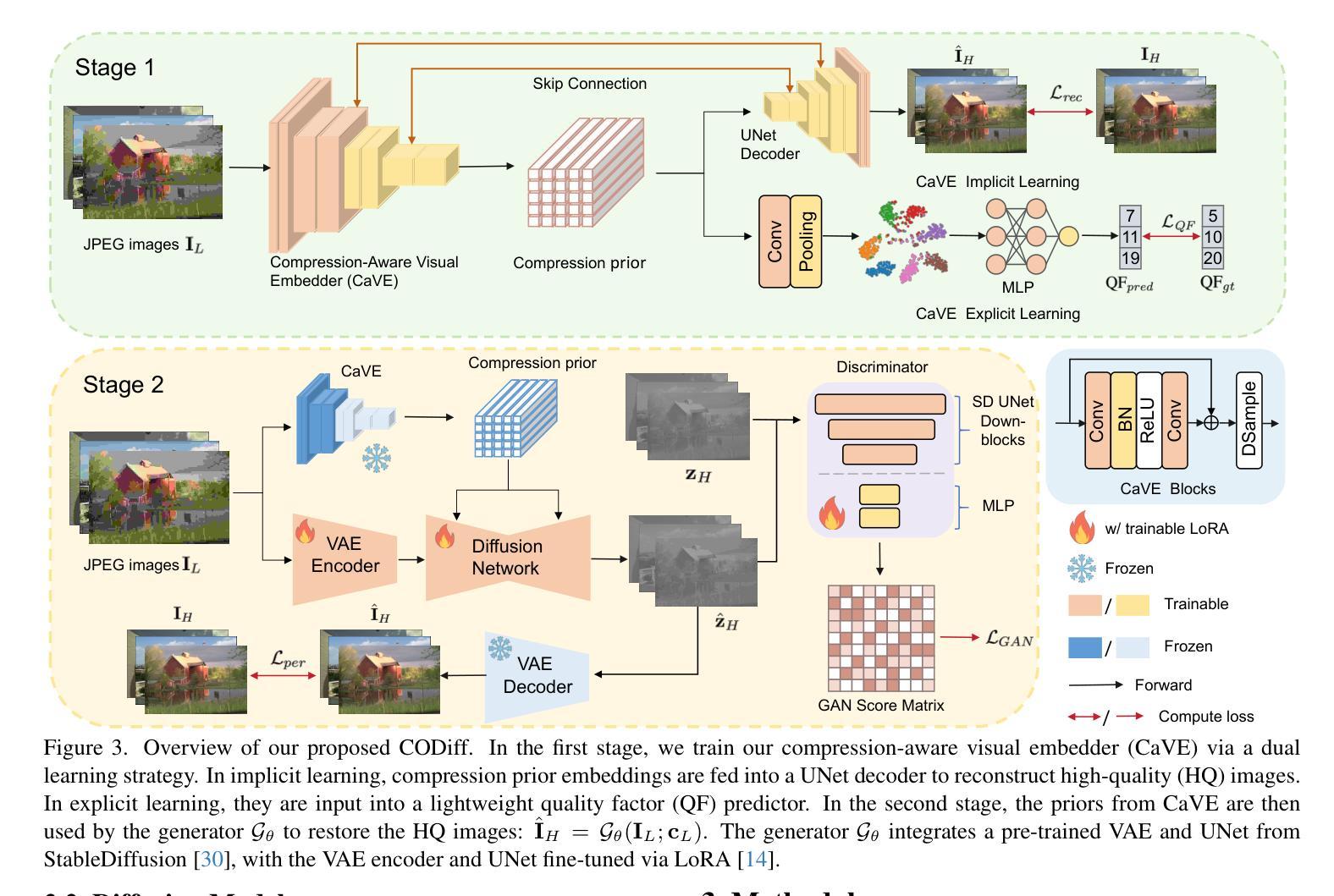
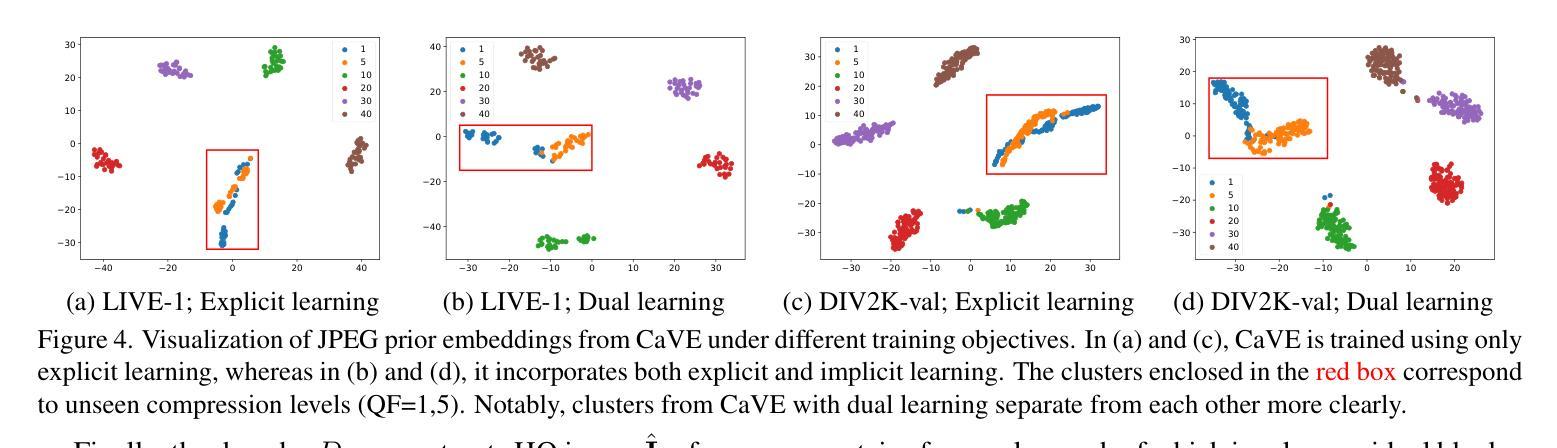
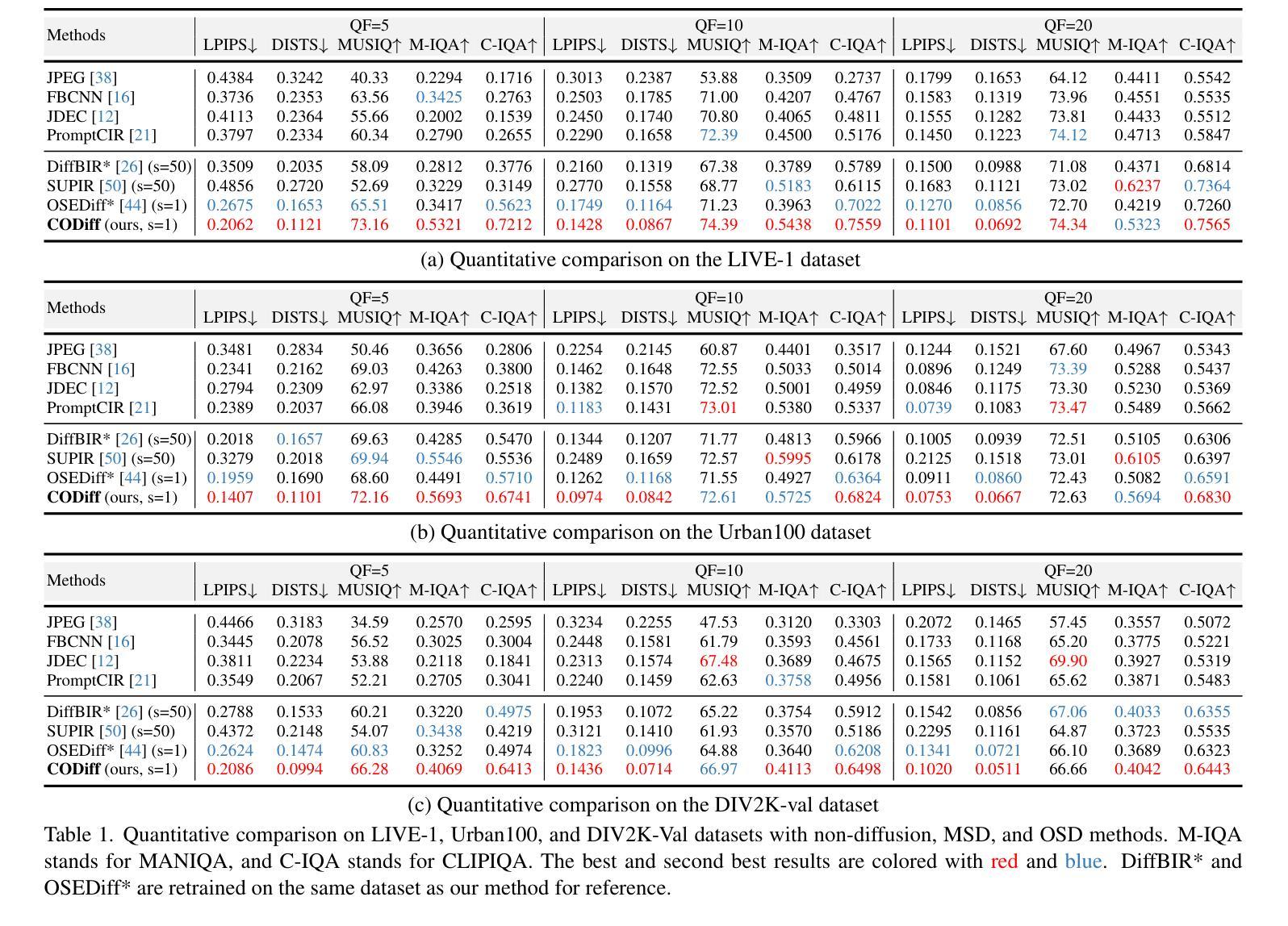
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in image restoration tasks. However, their multi-step denoising process introduces significant computational overhead, limiting their practical deployment. Furthermore, existing methods struggle to effectively remove severe JPEG artifact, especially in highly compressed images. To address these challenges, we propose CODiff, a compression-aware one-step diffusion model for JPEG artifact removal. The core of CODiff is the compression-aware visual embedder (CaVE), which extracts and leverages JPEG compression priors to guide the diffusion model. We propose a dual learning strategy that combines explicit and implicit learning. Specifically, explicit learning enforces a quality prediction objective to differentiate low-quality images with different compression levels. Implicit learning employs a reconstruction objective that enhances the model’s generalization. This dual learning allows for a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of JPEG compression. Experimental results demonstrate that CODiff surpasses recent leading methods in both quantitative and visual quality metrics. The code is released at https://github.com/jp-guo/CODiff.
扩散模型在图像恢复任务中取得了显著的成功。然而,其多步骤去噪过程产生了大量的计算开销,限制了其实际部署的应用。此外,现有方法在去除严重的JPEG伪影方面存在困难,特别是在高度压缩的图像中。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CODiff,这是一种用于JPEG伪影去除的压缩感知一步扩散模型。CODiff的核心是压缩感知视觉嵌入器(CaVE),它提取并利用JPEG压缩先验来指导扩散模型。我们提出了一种结合显式学习和隐式学习的双重学习策略。具体来说,显式学习通过强制实施质量预测目标来区分不同压缩级别的低质量图像。隐式学习采用重建目标,提高了模型的泛化能力。这种双重学习可以更深入、更全面地理解JPEG压缩。实验结果表明,CODiff在定量和视觉质量指标上均超越了最新的先进方法。代码已发布在https://github.com/jp-guo/CODiff。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为CODiff的压缩感知一步扩散模型,用于JPEG图像去伪。该模型的核心是压缩感知视觉嵌入器(CaVE),能够提取和利用JPEG压缩先验来指导扩散模型。通过结合显式学习和隐式学习的双重学习策略,CODiff实现了对JPEG压缩的深入和全面理解,并在定量和视觉质量指标上超越了现有领先方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像恢复任务中取得了显著成功,但在多步去噪过程中存在计算开销大的问题。
- 现有方法难以有效去除高度压缩图像中的JPEG伪影。
- CODiff模型被提出以解决这些挑战,它是一个压缩感知的一步扩散模型,用于JPEG伪影去除。
- CODiff模型的核心是压缩感知视觉嵌入器(CaVE),它能提取和利用JPEG压缩先验。
- CODiff采用双重学习策略,结合显式学习和隐式学习,实现对JPEG压缩的深入和全面理解。
- 显式学习通过质量预测目标来区分不同压缩级别的低质量图像。
点此查看论文截图