⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
CharaConsist: Fine-Grained Consistent Character Generation
Authors:Mengyu Wang, Henghui Ding, Jianing Peng, Yao Zhao, Yunpeng Chen, Yunchao Wei
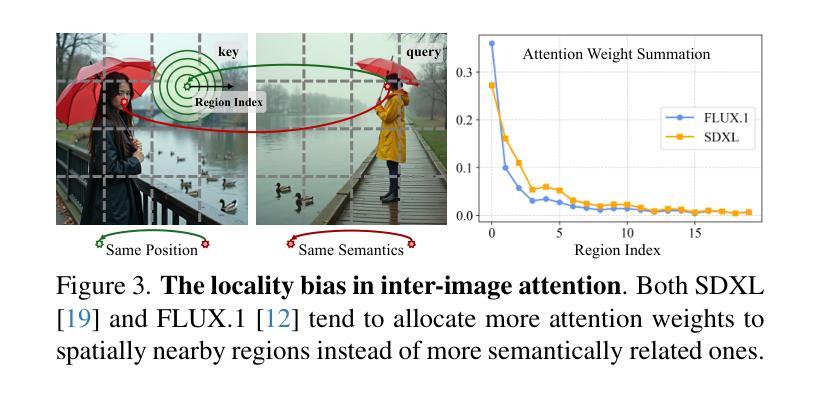
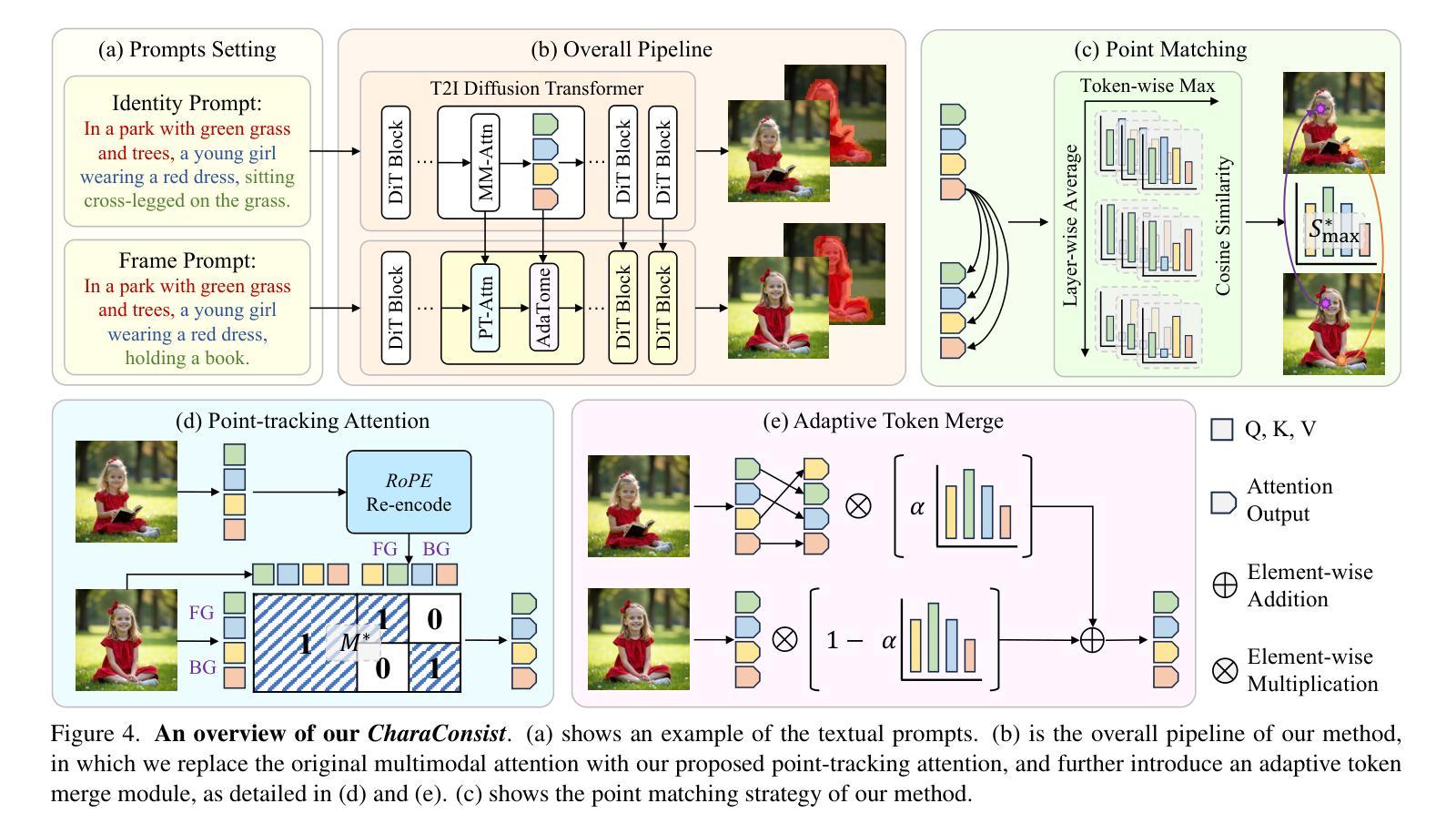
In text-to-image generation, producing a series of consistent contents that preserve the same identity is highly valuable for real-world applications. Although a few works have explored training-free methods to enhance the consistency of generated subjects, we observe that they suffer from the following problems. First, they fail to maintain consistent background details, which limits their applicability. Furthermore, when the foreground character undergoes large motion variations, inconsistencies in identity and clothing details become evident. To address these problems, we propose CharaConsist, which employs point-tracking attention and adaptive token merge along with decoupled control of the foreground and background. CharaConsist enables fine-grained consistency for both foreground and background, supporting the generation of one character in continuous shots within a fixed scene or in discrete shots across different scenes. Moreover, CharaConsist is the first consistent generation method tailored for text-to-image DiT model. Its ability to maintain fine-grained consistency, combined with the larger capacity of latest base model, enables it to produce high-quality visual outputs, broadening its applicability to a wider range of real-world scenarios. The source code has been released at https://github.com/Murray-Wang/CharaConsist
在文本到图像生成过程中,生成一系列保持一致的内容并保留相同的身份对于实际应用而言具有极高的价值。尽管已有一些作品探讨了无训练方法来提高生成主题的一致性,但我们观察到它们存在以下问题。首先,它们无法保持背景细节的连贯性,这限制了其适用性。此外,当前景角色经历较大的动作变化时,身份和服装细节的不一致性变得明显。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CharactConsistency(简称为CharaConsist),它采用点跟踪注意力、自适应令牌合并以及前景和背景的解耦控制。CharaConsist能够实现前景和背景的精细一致性,支持在固定场景内的连续镜头中生成一个角色或在不同场景中的离散镜头中生成角色。此外,CharaConsist是针对文本到图像DiT模型的定制一致性生成方法。其保持精细一致性的能力,结合最新基础模型的更大容量,使其能够产生高质量的视觉输出,扩大了其在更广泛的现实场景中的应用范围。源代码已发布在https://github.com/Murray-Wang/CharaConsist。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 accepted paper, project page: https://murray-wang.github.io/CharaConsist/
Summary
文本中介绍了一种用于解决文本转图像生成中一致性问题的新方法——CharaConsist。该方法通过点跟踪注意力、自适应令牌合并以及前景和背景的独立控制,提高了前景和背景的一致性。它能够生成连续镜头中的单个角色或不同场景中的离散镜头,同时保持高一致性和高质量视觉输出。适用于更广泛的真实世界场景应用。
Key Takeaways
- CharaConsist旨在解决文本转图像生成中的一致性问题。
- 通过点跟踪注意力机制维持背景细节的一致性。
- 自适应令牌合并解决了前景角色大动作变化时的一致性问题。
- 通过前景和背景的独立控制,提高了生成内容的精细一致性。
- CharaConsist是专为文本转图像DiT模型设计的首个一致性生成方法。
- 该方法结合了最新基础模型的更大容量,可产生高质量视觉输出。
点此查看论文截图


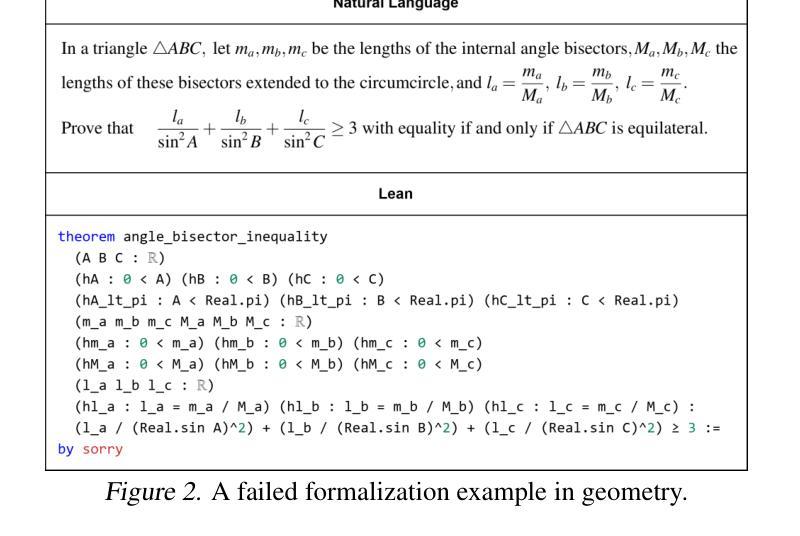
FMC: Formalization of Natural Language Mathematical Competition Problems
Authors:Jiaxuan Xie, Chengwu Liu, Ye Yuan, Siqi Li, Zhiping Xiao, Ming Zhang
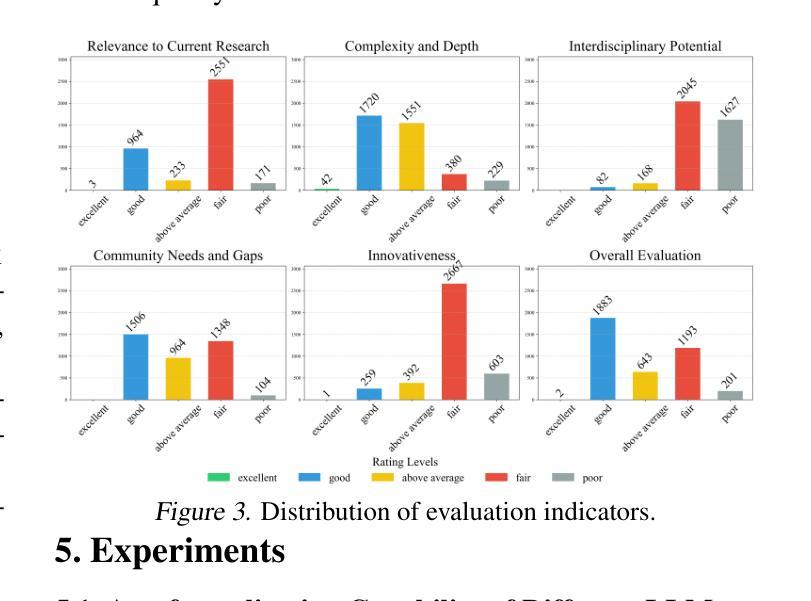
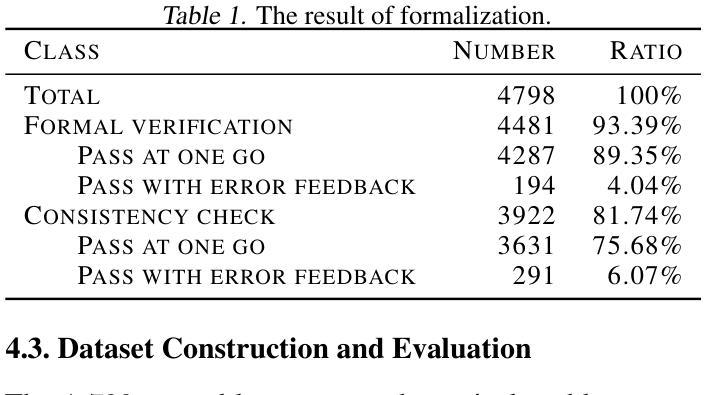
Efficient and accurate autoformalization methods, which leverage large-scale datasets of extensive natural language mathematical problems to construct formal language datasets, are key to advancing formal mathematical reasoning. In this paper, we propose an autoformalization pipeline based on large language models with error feedback, achieving a fully automatic and training-free formalization approach. Using this pipeline, we curate an Olympiad-level dataset aligning natural language problems with Lean formalizations. The dataset comprises $3,922$ mathematical problems in natural language and $9,787$ in Lean, of which $64.46%$ were assessed as at least above-average quality, making it suitable as a benchmark for automated theorem provers. Additionally, we investigate the formalization and reasoning capabilities of various LLMs and empirically demonstrate that few-shot learning, error feedback, and increasing sampling numbers enhance the autoformalization process. Experiments of three automated theorem provers on the \dataset\ dataset also highlight its challenging nature and its value as a benchmark for formal reasoning tasks.
高效且准确的自动形式化方法,是利用大规模的自然语言数学问题数据集来构建形式化语言数据集的关键,是推动数学形式推理发展的核心。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于大型语言模型的自动形式化流水线,该流水线具有错误反馈功能,实现了全自动且无需训练的形式化方法。使用该流水线,我们整理了一个与Lean形式化对齐的奥林匹亚级别数据集。该数据集包含以自然语言表述的3922个数学问题和以Lean表述的9787个数学问题,其中经过评估,有64.46%至少达到了平均质量以上,适合作为自动化定理证明者的基准测试。此外,我们还探讨了各种大型语言模型的形式化推理能力,并通过实证发现,小样学习、错误反馈和增加采样数量都可以增强自动形式化过程。在特定数据集上进行的三个自动化定理证明器的实验也突显了它的挑战性以及作为基准测试的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICML 2025 AI4MATH Workshop
Summary
大规模自然语言数学问题的数据集对于构建形式语言数据集至关重要,推动了形式化数学推理的发展。本文提出了基于大型语言模型的自动形式化管道,采用错误反馈实现全自动、无需训练的形式化方法。使用该管道,我们整理了一个与Lean形式化对齐的奥赛级别数据集,包含自然语言数学问题3922个,Lean形式化问题9787个,其中64.46%被评为至少中等质量水平以上,适合作为自动化定理证明器的基准测试。此外,本文还探讨了不同大型语言模型的形式化和推理能力,并实证表明少样本学习、错误反馈和增加采样数量可提升自动形式化过程的效果。在\dataset\数据集上进行的三个自动化定理证明器的实验突显了其挑战性,并验证了其作为形式推理任务基准测试的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模数据集在构建形式语言数据集中的作用至关重要,推动了形式化数学推理的进步。
- 提出了基于大型语言模型的自动形式化管道,实现全自动、无需训练的形式化方法。
- 整理了一个奥赛级别的数据集,包含自然语言与Lean形式化的数学问题,多数问题质量较高,适合作为自动化定理证明器的基准测试。
- 探讨并实证了少样本学习、错误反馈和增加采样数量在提升自动形式化过程中的应用效果。
- \dataset\数据集具有挑战性,可作为形式推理任务的基准测试。
- 文中展示了该管道及数据集在自动定理证明任务中的潜力与应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

MSA at ImageCLEF 2025 Multimodal Reasoning: Multilingual Multimodal Reasoning With Ensemble Vision Language Models
Authors:Seif Ahmed, Mohamed T. Younes, Abdelrahman Moustafa, Abdelrahman Allam, Hamza Moustafa
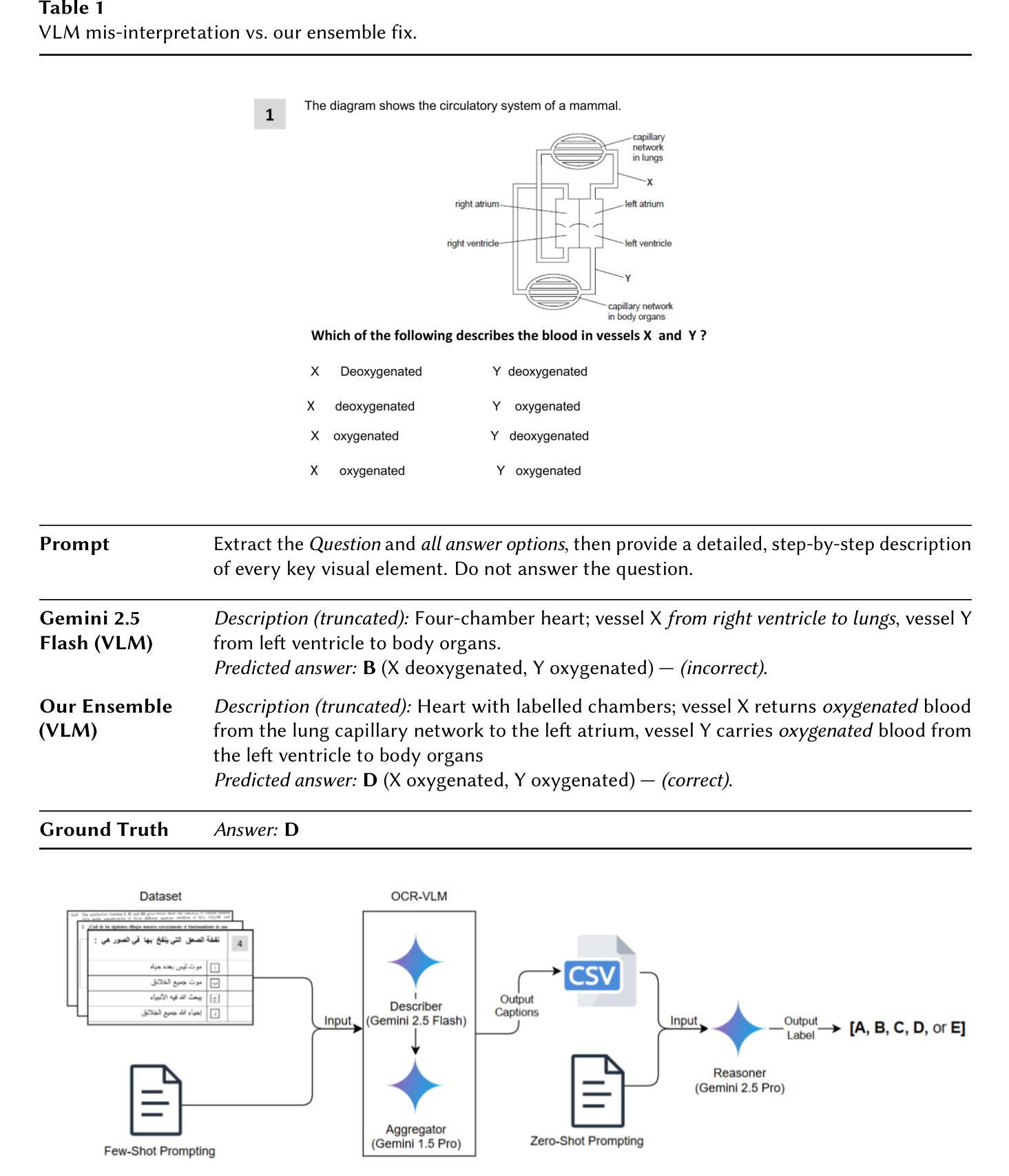
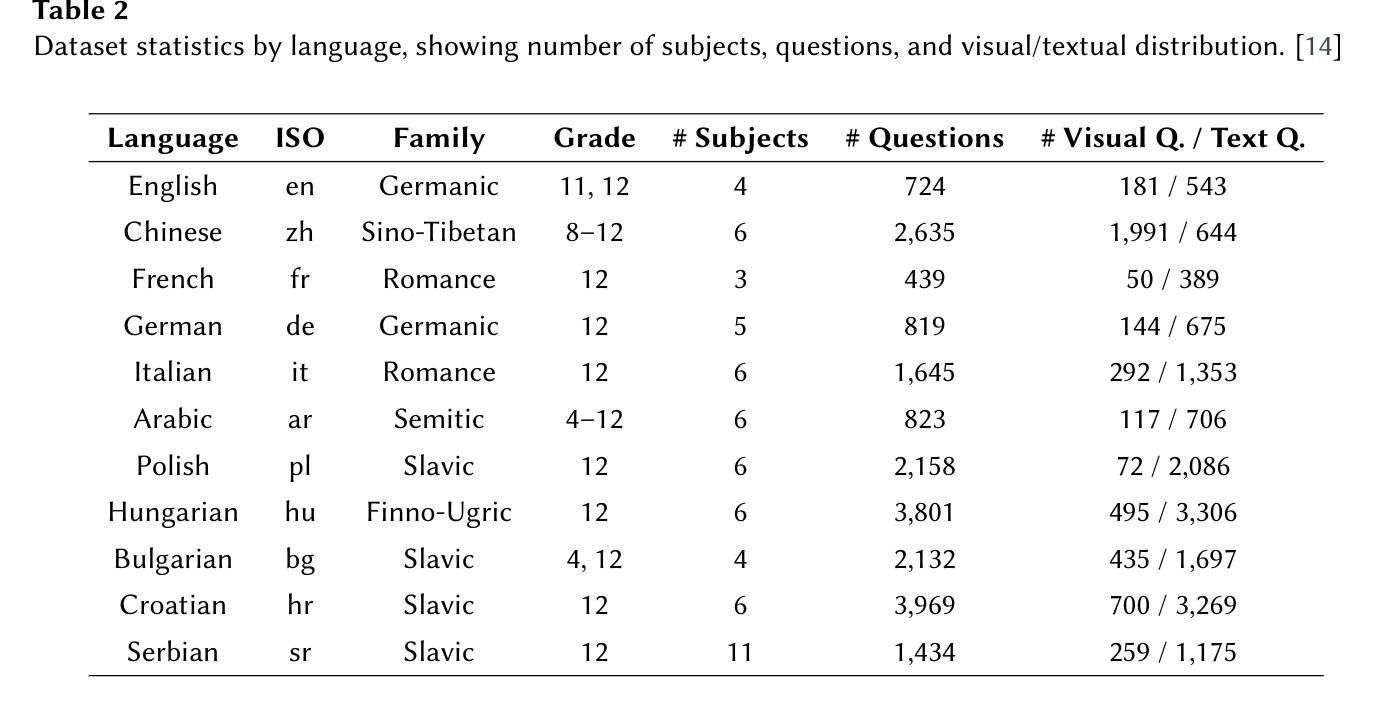
We present a robust ensemble-based system for multilingual multimodal reasoning, designed for the ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V challenge. Our approach integrates Gemini 2.5 Flash for visual description, Gemini 1.5 Pro for caption refinement and consistency checks, and Gemini 2.5 Pro as a reasoner which handles final answer selection, all coordinated through carefully engineered few-shot and zero-shot prompts. We conducted an extensive ablation study, training several large language models (Gemini 2.5 Flash, Phi 4, Gemma 3, Mistral) on an English dataset and its multilingual augmented version. Additionally, we evaluated Gemini 2.5 Flash in a zero-shot setting for comparison and found it to substantially outperform the trained models. Prompt design also proved critical: enforcing concise, language-normalized formats and prohibiting explanatory text boosted model accuracy on the English validation set from 55.9% to 61.7%. On the official leaderboard, our system (Team MSA) achieved first place overall in the multilingual track with 81.4% accuracy, and led 11 out of 13 individual language tracks, with top results such as 95.07% for Croatian and 92.12% for Italian. These findings highlight that lightweight OCR-VLM ensembles, when paired with precise prompt strategies and cross-lingual augmentation, can outperform heavier end-to-end models in high-stakes, multilingual educational settings.
我们针对ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战,设计了一个稳健的基于集成系统的多语言多模态推理系统。我们的方法融合了Gemini 2.5 Flash进行视觉描述、Gemini 1.5 Pro进行字幕优化和一致性检查,以及Gemini 2.5 Pro作为推理器进行最终答案选择,所有这些功能都通过精心设计的少量和零样本提示进行协调。我们对多个大型语言模型(Gemini 2.5 Flash、Phi 4、Gemma 3、Mistral)进行了广泛的消融研究训练,训练数据集包括英语数据集及其多语言增强版本。此外,我们还对Gemini 2.5 Flash进行了零样本设置下的比较评估,发现其性能远超训练模型。提示设计也证明是关键:采用简洁、语言规范化的格式,禁止解释性文本,将模型在英语验证集上的准确率从55.9%提高到61.7%。在官方排行榜上,我们的系统(MSA团队)在多语言赛道上总体排名第一,准确率为81.4%,并在13个语言赛道中的11个赛道上领先,如在克罗地亚语赛道上的95.07%和意大利语赛道的92.12%。这些发现表明,当轻量级的OCR-VLM集成系统与精确的提示策略和跨语言增强相结合时,可以在高风险、多语言的教育环境中表现优于更重的端到端模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一个为ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战设计的稳健的基于集成系统的多语言多模态推理系统。该系统通过整合Gemini 2.5 Flash进行视觉描述、Gemini 1.5 Pro进行标题优化和一致性检查、以及Gemini 2.5 Pro作为推理机进行最终答案选择,并通过精心设计的少样本和零样本提示进行协调。研究进行了广泛的消融研究,训练了多个大型语言模型,并在英语数据集及其多语言增强版本上进行了评估。结果显示,在零样本设置下,Gemini 2.5 Flash的表现优于训练模型。提示设计也至关重要:采用简洁、语言规范化的格式,禁止解释性文本,提高了模型在英语验证集上的准确率。该系统在多元语言轨道上获得第一名,准确率高达81.4%,并在13个语言轨道中的11个轨道上领先,如克罗地亚语的95.07%和意大利语的92.12%。这表明在关键的多语言教育环境中,轻量级的OCR-VLM集成系统配合精确的提示策略和跨语言增强技术,可以超越更重的端到端模型。
Key Takeaways
- 团队MSA提出一种针对ImageCLEF 2025 EXAMS V挑战的多语言多模态推理系统。
- 系统集成了多个组件,包括用于视觉描述的Gemini 2.5 Flash、用于标题优化的Gemini 1.5 Pro和作为推理机的Gemini 2.5 Pro。
- 通过精心设计的少样本和零样本提示进行协调各组件。
- 研究进行了广泛的消融研究,训练了多个大型语言模型,并在英语数据集及其多语言增强版本上评估了系统性能。
- Gemini 2.5 Flash在零样本设置下的表现优于训练模型。
- 提示设计对模型性能有重要影响,采用简洁、语言规范化的格式,禁止解释性文本可以提高模型准确率。
点此查看论文截图


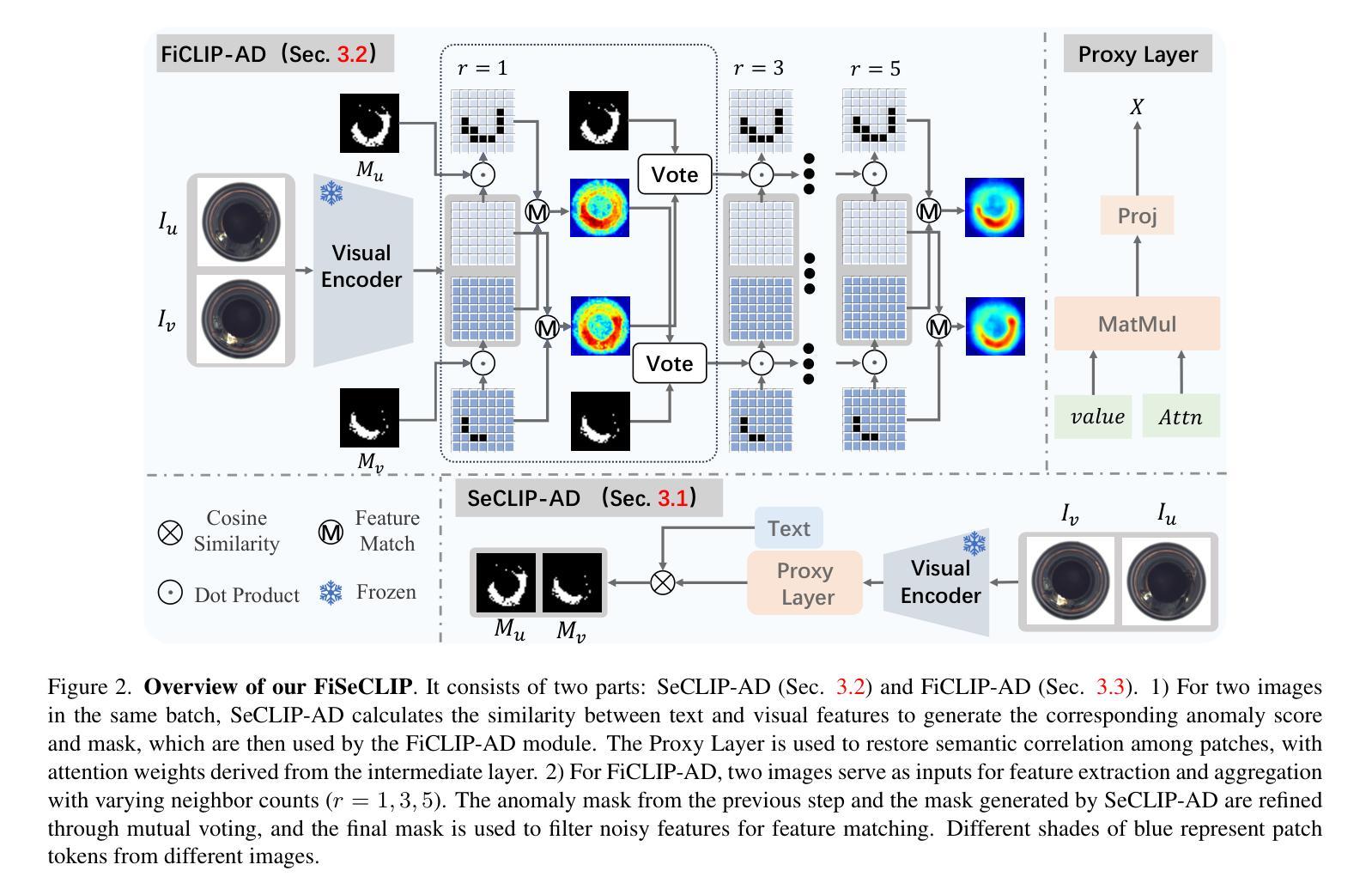
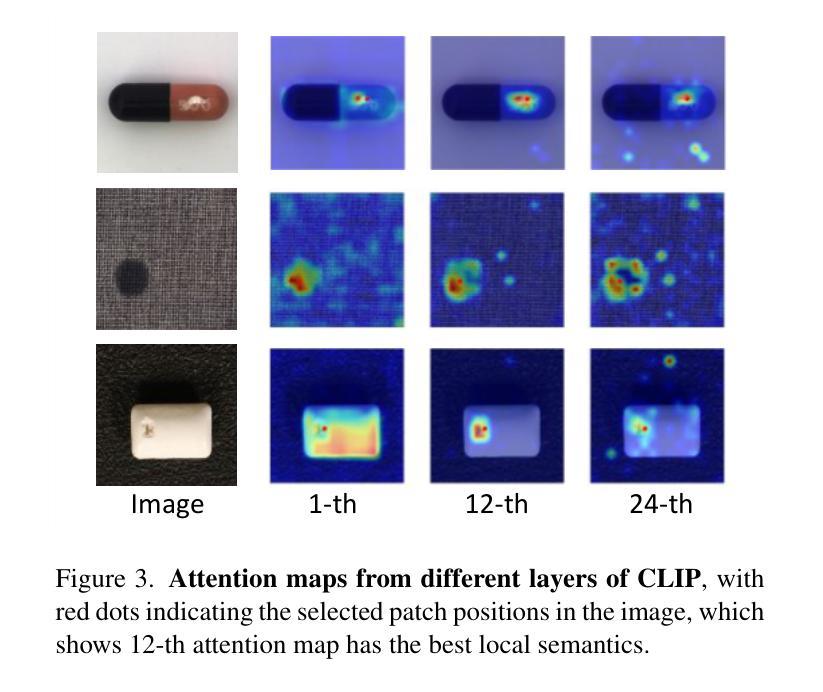
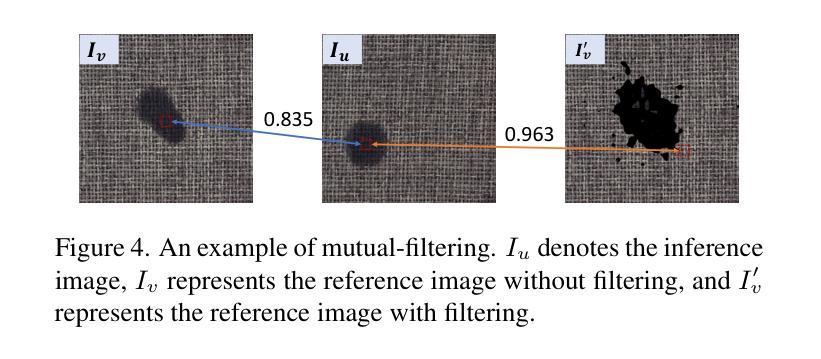
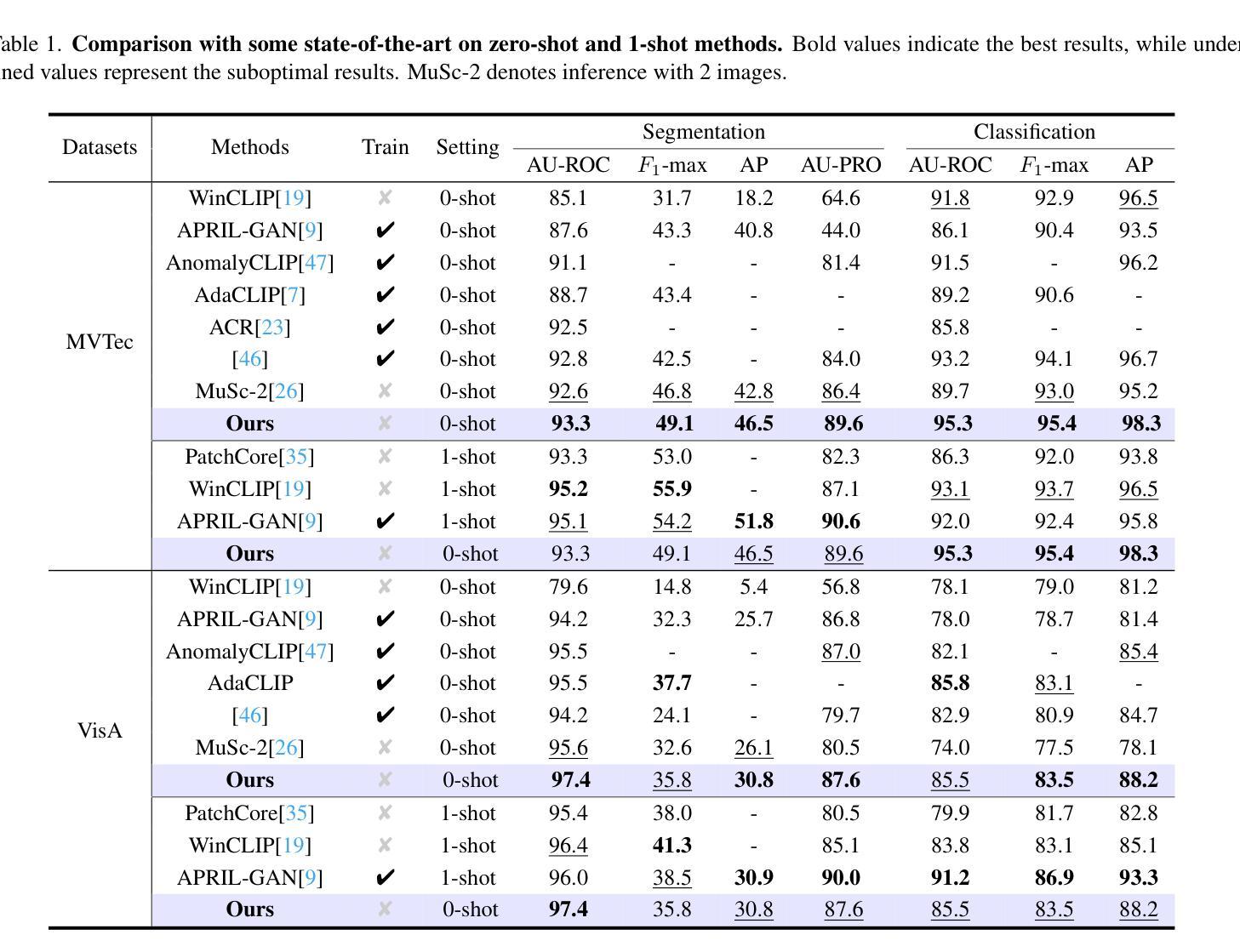
Bridge Feature Matching and Cross-Modal Alignment with Mutual-filtering for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Yuhu Bai, Jiangning Zhang, Yunkang Cao, Guangyuan Lu, Qingdong He, Xiangtai Li, Guanzhong Tian
With the advent of vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) in zero- and few-shot settings, CLIP has been widely applied to zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) in recent research, where the rare classes are essential and expected in many applications. This study introduces \textbf{FiSeCLIP} for ZSAD with training-free \textbf{CLIP}, combining the feature matching with the cross-modal alignment. Testing with the entire dataset is impractical, while batch-based testing better aligns with real industrial needs, and images within a batch can serve as mutual reference points. Accordingly, FiSeCLIP utilizes other images in the same batch as reference information for the current image. However, the lack of labels for these references can introduce ambiguity, we apply text information to \textbf{fi}lter out noisy features. In addition, we further explore CLIP’s inherent potential to restore its local \textbf{se}mantic correlation, adapting it for fine-grained anomaly detection tasks to enable a more accurate filtering process. Our approach exhibits superior performance for both anomaly classification and segmentation on anomaly detection benchmarks, building a stronger baseline for the direction, e.g., on MVTec-AD, FiSeCLIP outperforms the SOTA AdaCLIP by +4.6%$\uparrow$/+5.7%$\uparrow$ in segmentation metrics AU-ROC/$F_1$-max.
随着视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在零样本和少样本场景的出现,CLIP已被广泛应用于最近的零样本异常检测(ZSAD)研究中,其中稀有类别在许多应用中都是关键和预期的。本研究介绍了一种用于ZSAD的FiSeCLIP,它结合了特征匹配和跨模态对齐,使用无需训练的CLIP。对整个数据集进行测试并不实际,而基于批次的测试更符合实际的工业需求,批次内的图像可以作为相互的参考点。因此,FiSeCLIP利用同一批次中的其他图像作为当前图像的参考信息。然而,这些参考缺乏标签可能会引入模糊性,我们应用文本信息来过滤掉嘈杂的特征。此外,我们进一步探索CLIP的内在潜力来恢复其局部语义相关性,将其适应于精细粒度的异常检测任务,以实现更精确过滤过程。我们的方法在异常检测基准测试上表现出卓越的性能,无论是异常分类还是分割,为这一方向建立了更强的基准。例如,在MVTec-AD上,FiSeCLIP在分割指标AU-ROC/F1-max上的表现优于最新技术AdaCLIP,分别提高了+4.6%↑/+5.7%↑。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在零样本和少样本场景的应用,CLIP已被广泛用于零样本异常检测(ZSAD)。本研究提出了FiSeCLIP方法用于ZSAD,采用无需训练的CLIP,结合特征匹配和跨模态对齐。本研究利用同一批次的其他图像作为当前图像的参考信息,并采用文本信息过滤掉噪声特征。此外,研究还探索了CLIP的固有潜力来恢复其局部语义相关性,以适应精细粒度异常检测任务,以实现更准确的过滤过程。此方法在异常检测基准测试中表现出卓越的性能,为未来的研究建立了更强的基线。
Key Takeaways
- FiSeCLIP被提出用于零样本异常检测(ZSAD),结合了特征匹配和跨模态对齐。
- 研究利用同一批次的其他图像作为参考信息来检测当前图像中的异常。
- 文本信息被用来过滤掉由于使用图像参考而产生的噪声特征。
- 研究探索了CLIP的潜力来恢复其局部语义相关性,以提高异常检测的准确性。
- FiSeCLIP在异常分类和分段方面表现出卓越性能,建立了该方向研究的新基线。
- 在MVTec-AD基准测试中,FiSeCLIP在分割指标AU-ROC和$F_1$-max上超过了现有最佳方法AdaCLIP。
点此查看论文截图


Evaluating Generated Commit Messages with Large Language Models
Authors:Qunhong Zeng, Yuxia Zhang, Zexiong Ma, Bo Jiang, Ningyuan Sun, Klaas-Jan Stol, Xingyu Mou, Hui Liu
Commit messages are essential in software development as they serve to document and explain code changes. Yet, their quality often falls short in practice, with studies showing significant proportions of empty or inadequate messages. While automated commit message generation has advanced significantly, particularly with Large Language Models (LLMs), the evaluation of generated messages remains challenging. Traditional reference-based automatic metrics like BLEU, ROUGE-L, and METEOR have notable limitations in assessing commit message quality, as they assume a one-to-one mapping between code changes and commit messages, leading researchers to rely on resource-intensive human evaluation. This study investigates the potential of LLMs as automated evaluators for commit message quality. Through systematic experimentation with various prompt strategies and state-of-the-art LLMs, we demonstrate that LLMs combining Chain-of-Thought reasoning with few-shot demonstrations achieve near human-level evaluation proficiency. Our LLM-based evaluator significantly outperforms traditional metrics while maintaining acceptable reproducibility, robustness, and fairness levels despite some inherent variability. This work conducts a comprehensive preliminary study on using LLMs for commit message evaluation, offering a scalable alternative to human assessment while maintaining high-quality evaluation.
代码提交信息是软件开发中的关键组成部分,它们用于记录和解释代码更改。然而,在实践中,它们的品质往往不尽如人意,研究表明有很大比例的信息为空或不足。尽管自动生成的提交消息已经有了很大的进步,特别是借助大型语言模型(LLM),但对生成信息的评估仍然具有挑战性。传统的基于参考的自动度量方法,如BLEU、ROUGE-L和METEOR,在评估提交消息质量方面存在明显的局限性,因为它们假设代码更改和提交消息之间存在一一对应关系,导致研究人员不得不依赖资源密集型的人类评估方法。本研究探讨了将大型语言模型作为提交消息质量自动评估器的潜力。通过系统地尝试各种提示策略和最先进的LLM,我们证明了结合“思维链”推理和少量示例的大型语言模型能够实现接近人类水平的评估能力。我们的基于LLM的评估器在保持可接受的再现性、稳健性和公平性的同时,显著优于传统度量标准。尽管存在一些固有的变化性,但这项工作进行了关于使用LLM进行提交信息评估的全面初步研究,提供了一种可扩展的替代人类评估的方法,同时保持了高质量的评价。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇文章探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)作为自动化评估提交消息质量的潜力。通过系统的实验和提示策略,研究表明结合Chain-of-Thought推理和少量演示的LLMs能够达到接近人类水平的评估能力,显著优于传统指标,同时保持可接受的重复性、稳健性和公平性水平。这为使用LLMs进行提交消息评估提供了可扩展的替代方案,同时保持了高质量的评估。
Key Takeaways
- 提交消息在软件开发中具有重要性和作用,但实际执行中其质量常常不足或缺失。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动提交消息生成方面取得了进展。
- 传统自动评估指标(如BLEU、ROUGE-L和METEOR)在评估提交消息质量方面存在局限性。
- 这项研究探索了使用LLMs作为自动化评估提交消息质量的潜力。
- 结合Chain-of-Thought推理和少量提示策略的LLMs可以接近人类水平的评估能力。
- LLMs的评估器在性能上显著优于传统指标,同时保持了可接受的重复性、稳健性和公平性。
点此查看论文截图

BioScore: A Foundational Scoring Function For Diverse Biomolecular Complexes
Authors:Yuchen Zhu, Jihong Chen, Yitong Li, Xiaomin Fang, Xianbin Ye, Jingzhou He, Xujun Zhang, Jingxuan Ge, Chao Shen, Xiaonan Zhang, Tingjun Hou, Chang-Yu Hsieh
Structural assessment of biomolecular complexes is vital for translating molecular models into functional insights, shaping our understanding of biology and aiding drug discovery. However, current structure-based scoring functions often lack generalizability across diverse biomolecular systems. We present BioScore, a foundational scoring function that addresses key challenges – data sparsity, cross-system representation, and task compatibility – through a dual-scale geometric graph learning framework with tailored modules for structure assessment and affinity prediction. BioScore supports a wide range of tasks, including affinity prediction, conformation ranking, and structure-based virtual screening. Evaluated on 16 benchmarks spanning proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, and carbohydrates, BioScore consistently outperforms or matches 70 traditional and deep learning methods. Our newly proposed PPI Benchmark further enables comprehensive evaluation of protein-protein complex scoring. BioScore demonstrates broad applicability: (1) pretraining on mixed-structure data boosts protein-protein affinity prediction by up to 40% and antigen-antibody binding correlation by over 90%; (2) cross-system generalizability enables zero- and few-shot prediction with up to 71% correlation gain; and (3) its unified representation captures chemically challenging systems such as cyclic peptides, improving affinity prediction by over 60%. BioScore establishes a robust and generalizable framework for structural assessment across complex biomolecular landscapes.
生物分子复合物的结构评估对于将分子模型转化为功能见解、塑造我们对生物学的理解以及辅助药物发现至关重要。然而,当前基于结构的评分函数通常在跨不同生物分子系统时缺乏通用性。我们提出了BioScore,这是一个基础评分函数,通过双尺度几何图学习框架和针对结构评估和亲和力预测的定制模块,解决了数据稀疏性、跨系统表示和任务兼容性等关键挑战。BioScore支持各种任务,包括亲和力预测、构象排序和基于结构的虚拟筛选。在涵盖蛋白质、核酸、小分子和碳水化合物的16个基准测试上,BioScore持续优于或与传统深度学习方法的匹配度达到70种以上。我们新提出的PPI基准测试进一步实现了蛋白质-蛋白质复合物评分的全面评估。BioScore展示了广泛的应用性:(1)在混合结构数据上进行预训练,蛋白质-蛋白质亲和力预测提高了高达40%,抗原-抗体结合相关性提高了超过90%;(2)跨系统的通用性实现了零样本和少样本预测,相关性增益高达71%;(3)其统一表示能够捕捉化学上复杂的系统,如环状肽,亲和力预测提高了超过60%。BioScore为跨复杂生物分子景观的结构评估建立了稳健且通用的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:生物分子复合物的结构评估对于将分子模型转化为功能见解、塑造我们对生物学的理解以及辅助药物发现至关重要。然而,当前的结构评分函数在跨不同生物分子系统时缺乏通用性。本研究提出了BioScore,一个基础评分函数,通过双尺度几何图学习框架和针对结构评估和亲和力预测的定制模块,解决了数据稀疏性、跨系统表示和任务兼容性等关键挑战。BioScore支持多种任务,包括亲和力预测、构象排名和结构基础上的虚拟筛选。在跨越蛋白质、核酸、小分子和碳水化合物的16个基准测试上,BioScore的表现始终优于或相当于70种传统和深度学习方法。此外,新提出的PPI基准测试进一步实现了蛋白质-蛋白质复合物评分的全面评估。BioScore展示了广泛的应用性:预训练混合结构数据可提高蛋白质-蛋白质亲和力预测达40%,抗原-抗体结合相关性提高超过90%;跨系统通用性可实现零样本和少样本预测,相关性提高达71%;其统一表示可捕获化学上具有挑战性的系统,如环状肽,亲和力预测提高超过60%。BioScore为跨复杂生物分子景观的结构评估建立了稳健和通用的框架。
Key Takeaways:
- BioScore解决了生物分子复合物结构评估中的关键挑战,包括数据稀疏性、跨系统表示和任务兼容性。
- BioScore支持多种任务,如亲和力预测、构象排名和结构基础上的虚拟筛选。
- 在多个基准测试中,BioScore表现优异,优于或相当于大多数传统和深度学习方法。
- PPI基准测试的实现为蛋白质-蛋白质复合物评分提供了全面评估。
- BioScore具有广泛的应用性,预训练混合结构数据可显著提高预测性能。
- BioScore实现了零样本和少样本预测,显示出其跨系统的通用性。
- BioScore的统一表示可处理化学上挑战性的系统,如环状肽,提高了亲和力预测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Automated Thematic Analyses Using LLMs: Xylazine Wound Management Social Media Chatter Use Case
Authors:JaMor Hairston, Ritvik Ranjan, Sahithi Lakamana, Anthony Spadaro, Selen Bozkurt, Jeanmarie Perrone, Abeed Sarker
Background Large language models (LLMs) face challenges in inductive thematic analysis, a task requiring deep interpretive and domain-specific expertise. We evaluated the feasibility of using LLMs to replicate expert-driven thematic analysis of social media data. Methods Using two temporally non-intersecting Reddit datasets on xylazine (n=286 and n=686, for model optimization and validation, respectively) with twelve expert-derived themes, we evaluated five LLMs against expert coding. We modeled the task as a series of binary classifications, rather than a single, multi-label classification, employing zero-, single-, and few-shot prompting strategies and measuring performance via accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Results On the validation set, GPT-4o with two-shot prompting performed best (accuracy: 90.9%; F1-score: 0.71). For high-prevalence themes, model-derived thematic distributions closely mirrored expert classifications (e.g., xylazine use: 13.6% vs. 17.8%; MOUD use: 16.5% vs. 17.8%). Conclusions Our findings suggest that few-shot LLM-based approaches can automate thematic analyses, offering a scalable supplement for qualitative research. Keywords: thematic analysis, large language models, natural language processing, qualitative analysis, social media, prompt engineering, public health
背景:大型语言模型(LLMs)在归纳主题分析方面面临挑战,这是一项需要深度解读和特定领域专业知识的任务。我们评估了使用LLMs复制基于专家的社交媒体数据主题分析的可行性。方法:我们使用了两组时间上没有重叠的关于安定剂(xylazine)的Reddit数据集(分别为286个和686个帖子,用于模型优化和验证),并包含专家得出的十二个主题。我们评估了五种LLMs与专家编码的对比效果。我们将任务建模为一系列二元分类,而不是单一的多标签分类,采用零样本、单样本和少样本提示策略,并通过准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数来衡量性能。结果:在验证集上,GPT-4o的二次提示表现最佳(准确率:90.9%;F1分数:0.71)。对于高发病率主题,模型衍生的主题分布与专家分类结果非常接近(例如,安定剂使用:模型为13.6% vs 专家为17.8%;MOUD使用:模型为16.5% vs 专家为17.8%)。结论:我们的研究结果表明,基于少样本的LLM方法能够自动化主题分析,为定性研究提供了可扩展的补充。关键词:主题分析、大型语言模型、自然语言处理、定性分析、社交媒体、提示工程、公共卫生。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pages: 19, Abstract word count: 151 words, Manuscript word count: 2185 words, References: 14, Figures: 3, Tables: 2
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在归纳主题分析方面存在挑战,需要深度解读和特定领域的专业知识。研究评估了使用LLMs复制专家驱动的社会媒体数据主题分析的可行性。通过两个关于安定剂Reddit数据集,评估了五个LLMs与专家编码的性能。任务被建模为一系列二元分类,而非单一多元标签分类。采用零、单、少镜头提示策略,并通过准确度、精确度、召回率和F1分数衡量性能。结果显示,GPT-4o在两次提示下的性能最佳(准确度:90.9%;F1分数:0.71)。对于高发病率主题,模型衍生的主题分布与专家分类基本一致。研究结果表明,基于少镜头LLM的方法可以自动进行主题分析,为定性研究提供可扩展的补充。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型面临归纳主题分析的挑战,需要深度解读和特定领域的专业知识。
- 研究使用LLMs进行社会媒体数据的主题分析,并评估了其可行性。
- 通过两个关于安定剂的Reddit数据集进行模型评估。
- 任务被建模为一系列二元分类。
- 尝试了多种提示策略并评估了性能。
- GPT-4o在两次提示下表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

Integrating Biological Knowledge for Robust Microscopy Image Profiling on De Novo Cell Lines
Authors:Jiayuan Chen, Thai-Hoang Pham, Yuanlong Wang, Ping Zhang
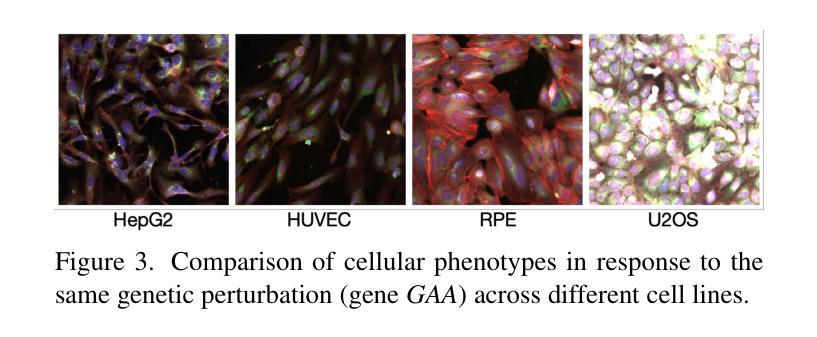
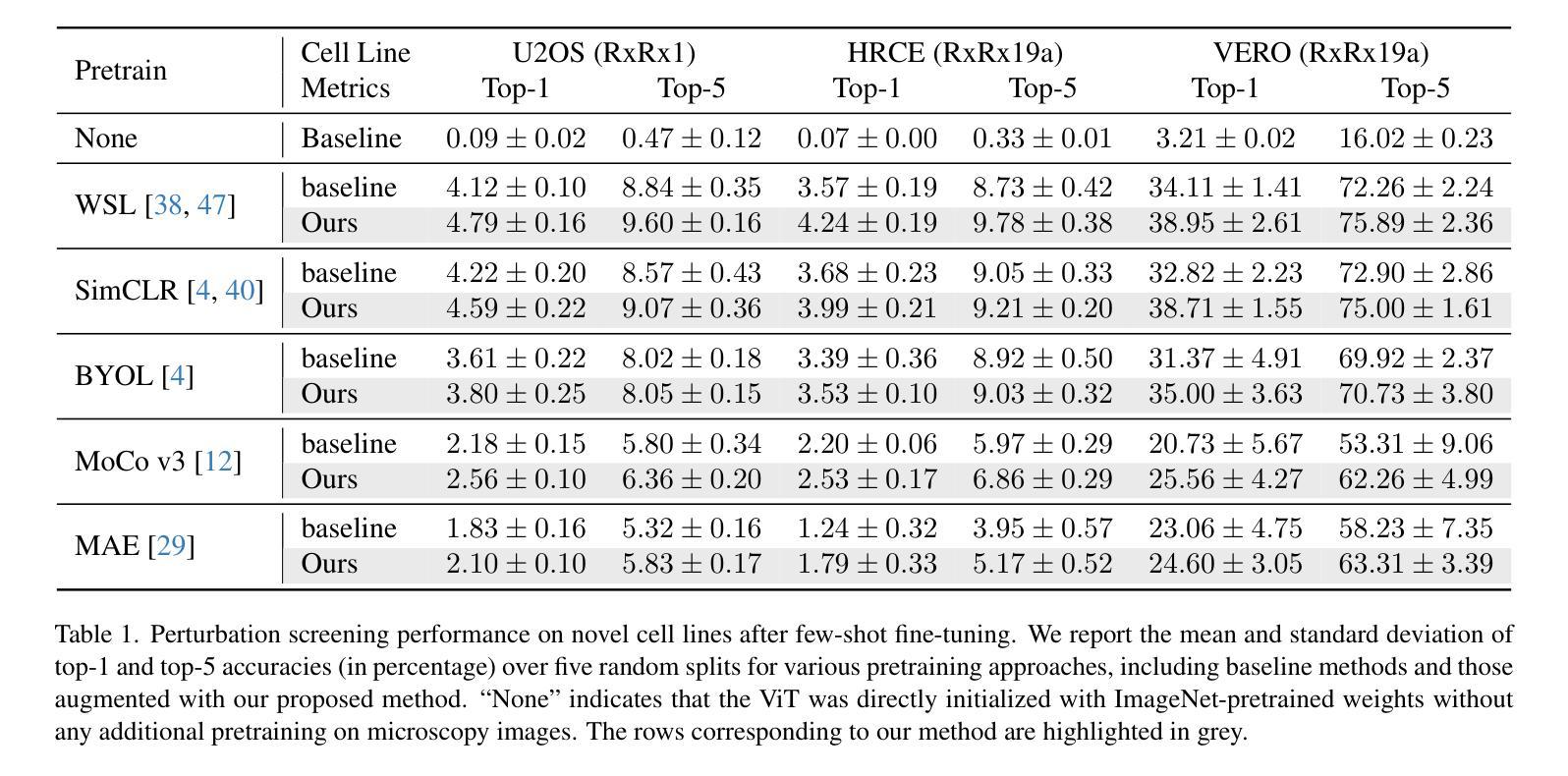
High-throughput screening techniques, such as microscopy imaging of cellular responses to genetic and chemical perturbations, play a crucial role in drug discovery and biomedical research. However, robust perturbation screening for \textit{de novo} cell lines remains challenging due to the significant morphological and biological heterogeneity across cell lines. To address this, we propose a novel framework that integrates external biological knowledge into existing pretraining strategies to enhance microscopy image profiling models. Our approach explicitly disentangles perturbation-specific and cell line-specific representations using external biological information. Specifically, we construct a knowledge graph leveraging protein interaction data from STRING and Hetionet databases to guide models toward perturbation-specific features during pretraining. Additionally, we incorporate transcriptomic features from single-cell foundation models to capture cell line-specific representations. By learning these disentangled features, our method improves the generalization of imaging models to \textit{de novo} cell lines. We evaluate our framework on the RxRx database through one-shot fine-tuning on an RxRx1 cell line and few-shot fine-tuning on cell lines from the RxRx19a dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our method enhances microscopy image profiling for \textit{de novo} cell lines, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world phenotype-based drug discovery applications.
高通量筛选技术,如通过显微镜成像观察细胞对遗传和化学干扰的响应,在药物发现和生物医学研究中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,由于细胞系之间存在显著的形态和生物异质性,对新型细胞系的稳健干扰筛选仍然是一个挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的框架,它将外部生物学知识整合到现有的预训练策略中,以增强显微镜图像分析模型。我们的方法利用外部生物学信息显式地分解干扰特异性和细胞系特异性表示。具体来说,我们构建了一个知识图谱,利用STRING和Hetionet数据库中的蛋白质相互作用数据来指导模型在预训练过程中关注干扰特异性特征。此外,我们还结合了单细胞基础模型的转录组特征来捕捉细胞系特异性表示。通过学习这些分离的特征,我们的方法提高了成像模型对新型细胞系的泛化能力。我们在RxRx数据库上评估了我们的框架,通过一次微调(RxRx的一个细胞系)和几次微调(RxRx十九甲基的数据集中的细胞系)进行了评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法提高了新型细胞系的显微镜图像分析效果,突显其在基于表型的药物发现应用中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
在药物发现和生物医学研究中,高通量筛选技术,如利用显微镜成像观察细胞对遗传和化学干扰的响应,发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,对于新型细胞系的稳健性干扰筛选仍具有挑战性。为此,研究团队提出了一种新型框架,该框架将外部生物学知识融入现有的预训练策略中,以提升显微镜图像分析模型的性能。该研究通过明确区分干扰特异性和细胞系特异性表征来解决这一问题,并利用蛋白质相互作用数据和单细胞转录组特征构建知识图谱来指导模型学习。实验结果表明,该方法能提高对新型细胞系的成像模型泛化能力,在基于表型的药物发现应用中具有实际应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 高通量筛选技术在药物发现和生物医学研究中具有关键作用。
- 对新型细胞系的稳健性干扰筛选存在挑战,因为细胞系之间存在显著的形态学和生物学异质性。
- 研究团队提出了一种结合外部生物学知识的新型框架,以提高显微镜图像分析模型的性能。
- 该框架通过明确区分干扰特异性和细胞系特异性表征来解决挑战。
- 研究利用蛋白质相互作用数据和单细胞转录组特征构建知识图谱来指导模型学习。
- 方法提高了对新型细胞系的成像模型泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


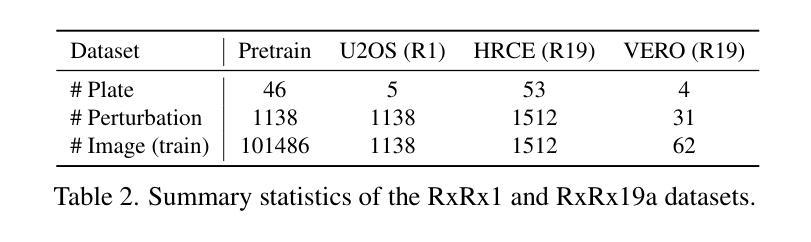
Machine-learning inference of stellar properties using integrated photometric and spectroscopic data
Authors:Ilay Kamai, Alex M. Bronstein, Hagai B. Perets
Stellar astrophysics relies on diverse observational modalities-primarily photometric light curves and spectroscopic data-from which fundamental stellar properties are inferred. While machine learning (ML) has advanced analysis within individual modalities, the complementary information encoded across modalities remains largely underexploited. We present DESA (Dual Embedding model for Stellar Astrophysics), a novel multi-modal foundation model that integrates light curves and spectra to learn a unified, physically meaningful latent space for stars. DESA first trains separate modality-specific encoders using a hybrid supervised/self-supervised scheme, and then aligns them through DualFormer, a transformer-based cross-modal integration module tailored for astrophysical data. DualFormer combines cross- and self-attention, a novel dual-projection alignment loss, and a projection-space eigendecomposition that yields physically structured embeddings. We demonstrate that DESA significantly outperforms leading unimodal and self-supervised baselines across a range of tasks. In zero- and few-shot settings, DESA’s learned representations recover stellar color-magnitude and Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams with high fidelity ($R^2 = 0.92$ for photometric regressions). In full fine-tuning, DESA achieves state-of-the-art accuracy for binary star detection (AUC = $0.99$, AP = $1.00$) and stellar age prediction (RMSE = $0.94$ Gyr). As a compelling case, DESA naturally separates synchronized binaries from young stars, two populations with nearly identical light curves, purely from their embedded positions in UMAP space, without requiring external kinematic or luminosity information. DESA thus offers a powerful new framework for multimodal, data-driven stellar population analysis, enabling both accurate prediction and novel discovery.
恒星天文学依赖于多种观测方式,主要是光度光变曲线和光谱数据,从中可以推断出恒星的基本属性。虽然机器学习(ML)已经在单一模式分析方面取得了进展,但跨模式的互补信息仍然在很大程度上被忽视。我们提出了DESA(用于恒星天文学的双重嵌入模型),这是一种新型的多模式基础模型,它结合了光变曲线和光谱数据,学习一个统一、具有物理意义的恒星潜在空间。DESA首先使用混合的监督/自监督方案训练特定的模态编码器,然后通过针对天文数据定制的基于变压器的跨模态集成模块DualFormer进行对齐。DualFormer结合了跨注意力和自注意力、新颖的双投影对齐损失以及投影空间特征分解,从而产生具有物理结构的嵌入。我们证明,DESA在一系列任务上显著优于领先的单模态和自我监督的基线。在零样本和少样本情况下,DESA学习的表示能够高度保真地恢复恒星的颜色幅度和赫罗图($R^2 = 0.92$用于光度回归)。在完全微调的情况下,DESA在二元恒星检测(AUC = $0.99$,AP = $1.00$)和恒星年龄预测(RMSE = $0.94$吉年)方面达到了最先进水平。作为一个引人注目的案例,DESA能够自然地分离同步双星和年轻恒星这两个几乎具有相同光变曲线的群体,仅仅基于它们在UMAP空间中的嵌入位置,无需额外的运动学或光度信息。因此,DESA提供了一个强大的新框架,用于多模态、数据驱动的恒星群体分析,能够实现准确的预测和新颖的发现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to ApJ
Summary
本文介绍了DESA模型,这是一种用于恒星天文学的多模态基础模型。DESA通过整合光曲线和光谱数据,学习了一个统一的、具有物理意义的恒星潜在空间。该模型通过混合监督/自监督方案训练特定模态的编码器,然后通过基于变压器的跨模态集成模块DualFormer进行对齐。DESA在多种任务上显著优于领先的单模态和自我监督基线。在零样本和少样本情况下,DESA能够恢复高保真度的恒星色标图和赫罗图。在完全微调的情况下,DESA实现了二进制恒星检测和恒星年龄预测的最新准确性。DESA为多元数据驱动恒星群体分析提供了强大的新框架,既可用于准确预测,也可用于新颖发现。
Key Takeaways
- DESA是一个多模态模型,用于恒星天文学,整合了光曲线和光谱数据。
- DESA通过混合监督/自监督方案训练特定模态的编码器。
- DESA使用基于变压器的跨模态集成模块DualFormer进行模态对齐。
- DESA在各种任务上表现出显著性能,包括回归和分类任务。
- 在零样本和少样本情况下,DESA能够恢复高保真度的恒星色标图和赫罗图。
- DESA实现了二进制恒星检测和恒星年龄预测的最新准确性。
点此查看论文截图

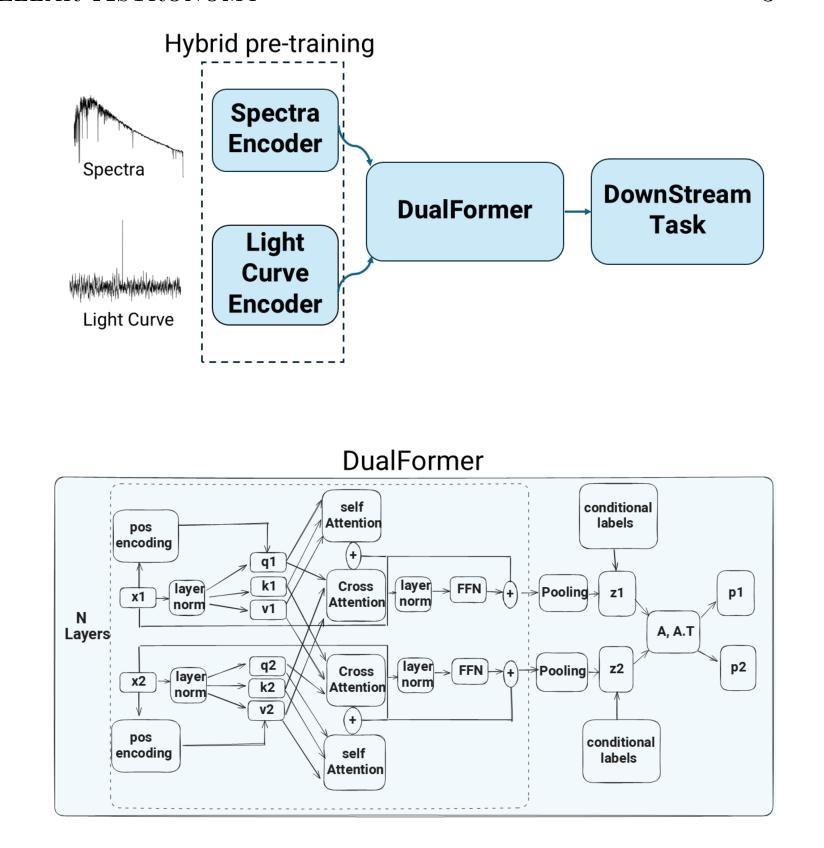
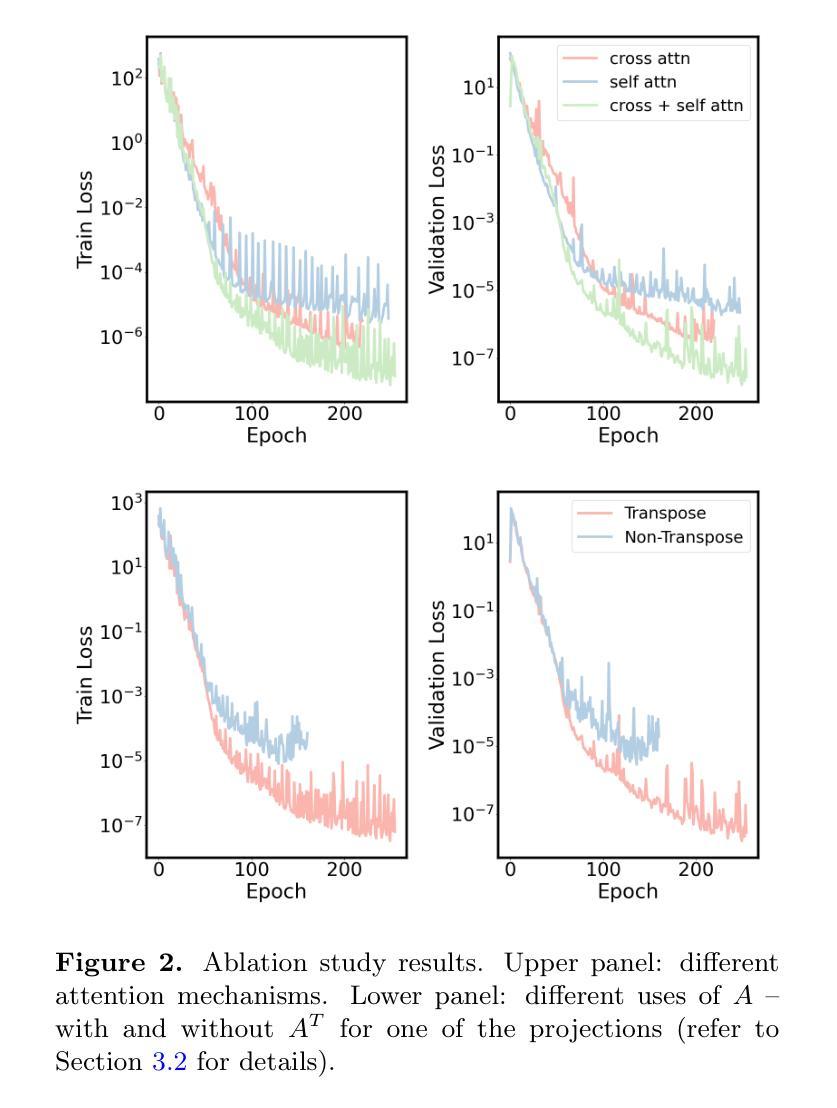
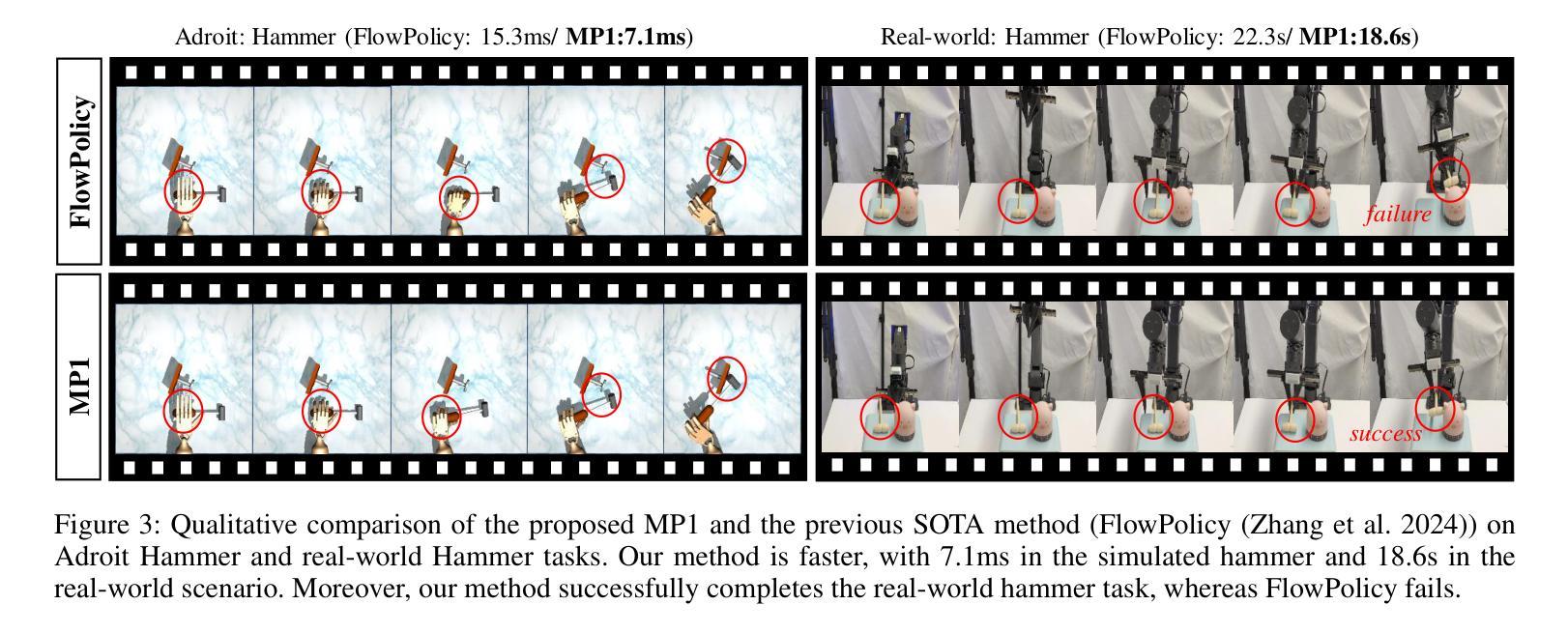
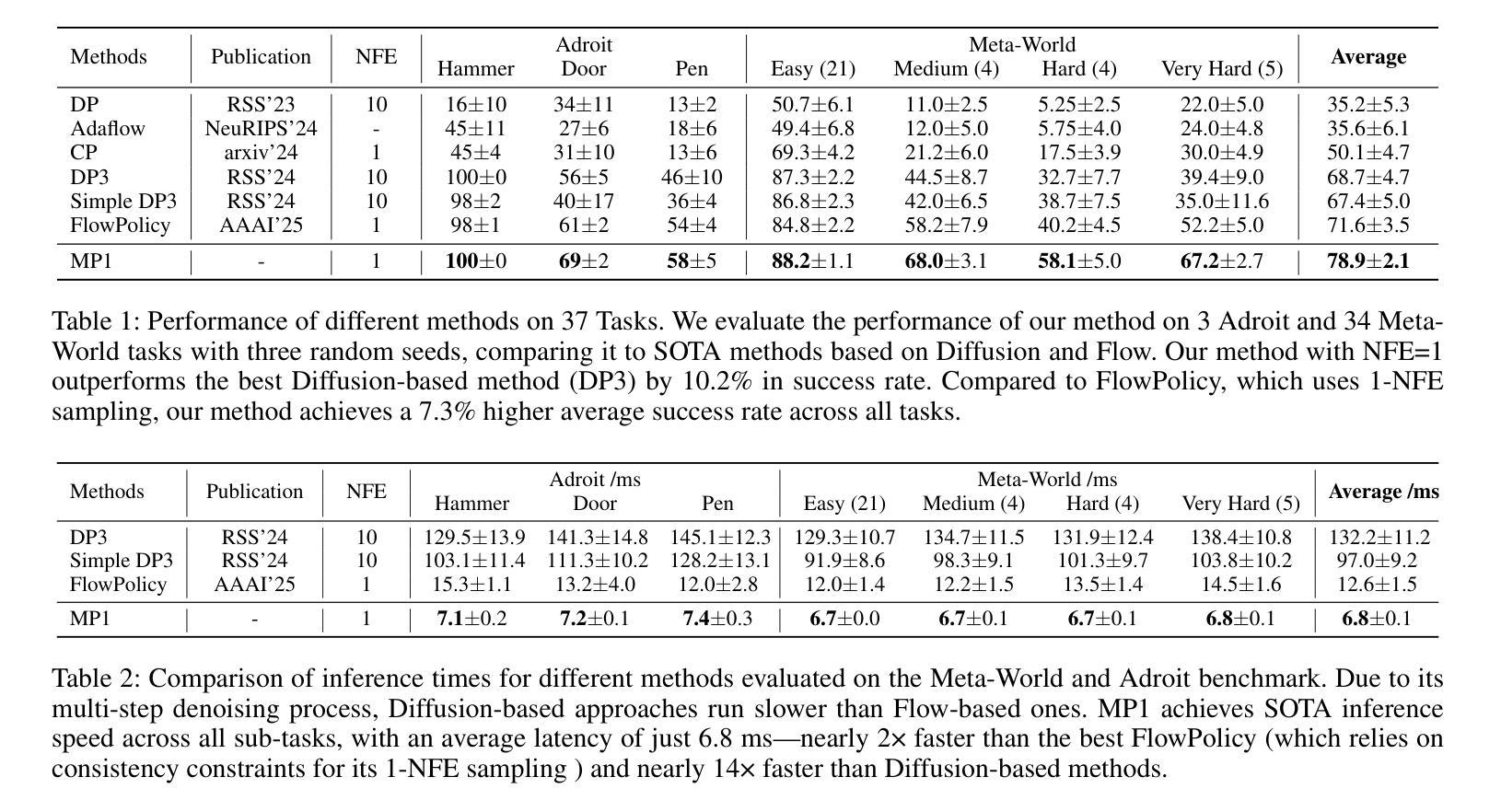
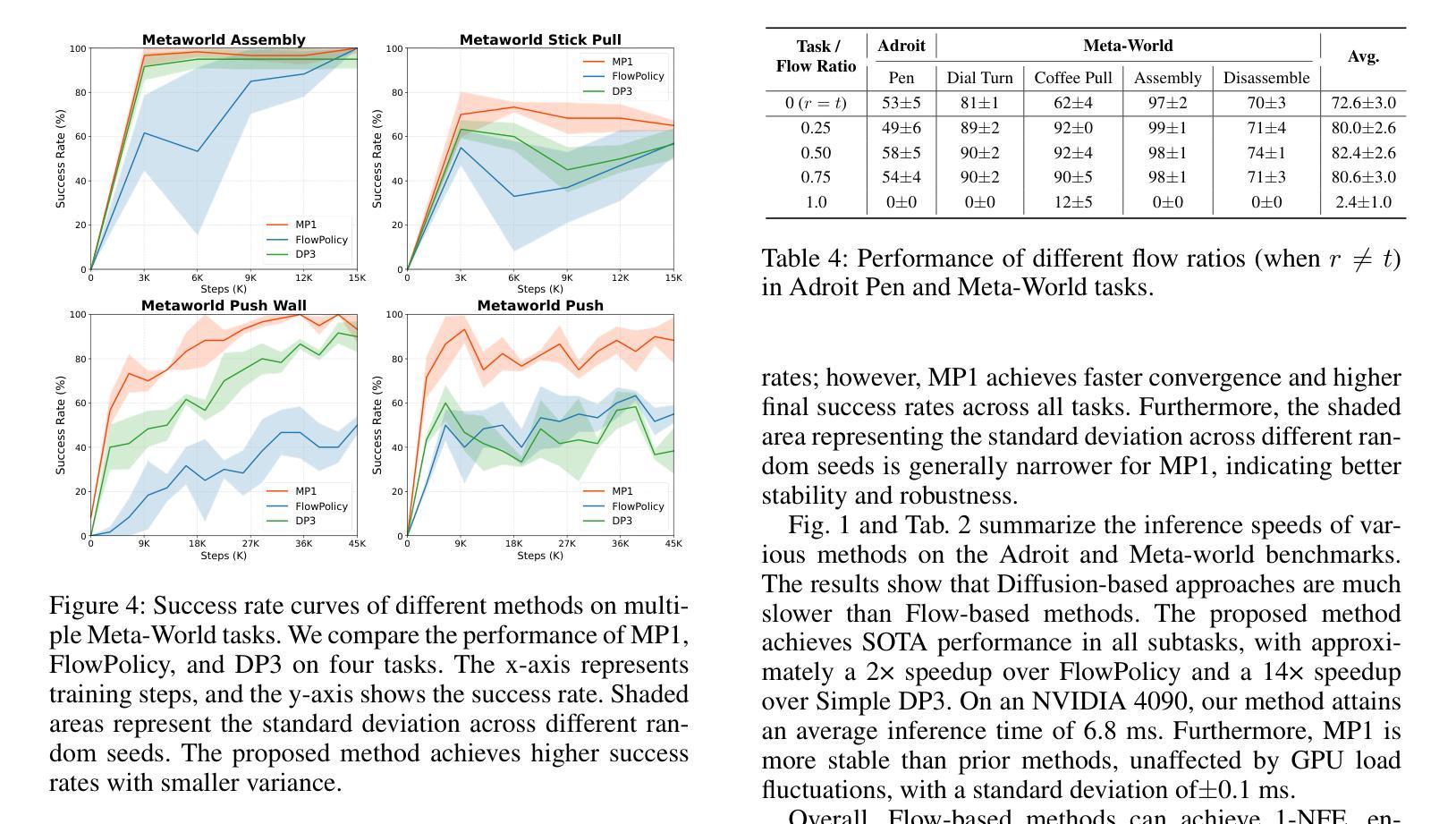
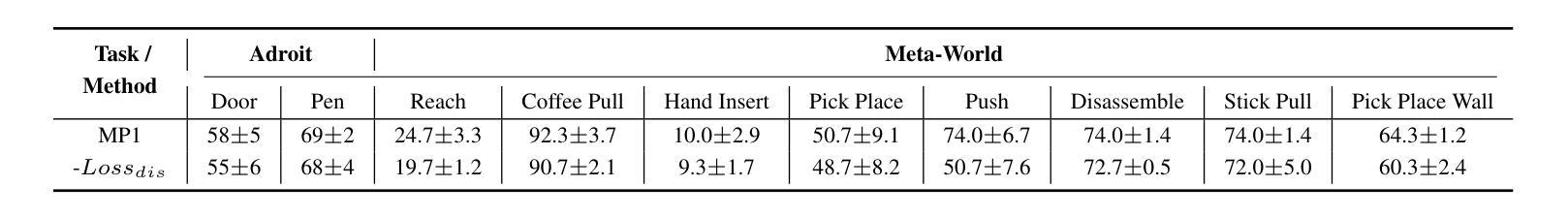
MP1: Mean Flow Tames Policy Learning in 1-step for Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Juyi Sheng, Ziyi Wang, Peiming Li, Mengyuan Liu
In robot manipulation, robot learning has become a prevailing approach. However, generative models within this field face a fundamental trade-off between the slow, iterative sampling of diffusion models and the architectural constraints of faster Flow-based methods, which often rely on explicit consistency losses. To address these limitations, we introduce MP1, which pairs 3D point-cloud inputs with the MeanFlow paradigm to generate action trajectories in one network function evaluation (1-NFE). By directly learning the interval-averaged velocity via the MeanFlow Identity, our policy avoids any additional consistency constraints. This formulation eliminates numerical ODE-solver errors during inference, yielding more precise trajectories. MP1 further incorporates CFG for improved trajectory controllability while retaining 1-NFE inference without reintroducing structural constraints. Because subtle scene-context variations are critical for robot learning, especially in few-shot learning, we introduce a lightweight Dispersive Loss that repels state embeddings during training, boosting generalization without slowing inference. We validate our method on the Adroit and Meta-World benchmarks, as well as in real-world scenarios. Experimental results show MP1 achieves superior average task success rates, outperforming DP3 by 10.2% and FlowPolicy by 7.3%. Its average inference time is only 6.8 ms-19x faster than DP3 and nearly 2x faster than FlowPolicy. Our code is available at https://mp1-2254.github.io/.
在机器人操作领域,机器人学习已经成为一种流行的方法。然而,该领域中的生成模型面临着扩散模型的缓慢迭代采样和基于流的快速方法的结构约束之间的基本权衡,后者通常依赖于明确的一致性损失。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了MP1,它将3D点云输入与MeanFlow范式相结合,在一个网络功能评估(1-NFE)中生成行动轨迹。通过直接学习MeanFlow Identity的间隔平均速度,我们的策略避免了任何额外的一致性约束。这种公式消除了推理过程中的数值ODE求解器错误,产生了更精确的轨迹。MP1还结合了CFG,以提高轨迹的可控性,同时保持1-NFE推理,而没有重新引入结构约束。由于微妙的场景上下文变化对机器人学习至关重要,特别是在小样本学习中,我们引入了一个轻量级的分散损失,在训练期间排斥状态嵌入,提高泛化能力而不会减慢推理速度。我们在Adroit和Meta-World基准测试以及真实世界场景中验证了我们的方法。实验结果表明,MP1达到了更高的平均任务成功率,比DP3高出10.2%,比FlowPolicy高出7.3%。其平均推理时间仅为6.8毫秒,比DP3快19倍,比FlowPolicy快近2倍。我们的代码可在网站链接找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了机器人操控领域中的机器人学习成为主流方法的情况。为解决生成模型中的扩散模型迭代采样慢与流式方法架构约束之间的权衡问题,提出了MP1方法。它通过结合3D点云输入和MeanFlow范式,在一次网络功能评估中生成动作轨迹,避免了额外的一致性约束,消除了数值ODE求解器在推理过程中的误差,从而生成更精确的轨迹。此外,MP1还结合了CFG,提高了轨迹的可控性,同时保持了1-NFE推理速度,未重新引入结构性约束。为解决机器人学习中场景上下文变化的重要性,特别是few-shot学习中的关键问题,引入了分散损失,在训练期间排斥状态嵌入,提高了泛化能力而不会减慢推理速度。实验结果表明,MP1在Adroit和Meta-World基准测试中取得了更高的任务成功率,平均推理时间也很快。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人学习在操控领域中被广泛采用,但生成模型面临扩散模型迭代采样慢和流式方法架构约束之间的权衡问题。
- MP1方法通过结合3D点云输入和MeanFlow范式在一次网络功能评估中生成动作轨迹,避免了额外的一致性约束。
- MP1消除了数值ODE求解器在推理过程中的误差,生成更精确的轨迹。
- MP1结合了CFG以提高轨迹可控性,同时保持快速推理速度,未引入新的结构性约束。
- 场景上下文变化对机器人学习至关重要,特别是few-shot学习中。
- MP1引入了分散损失,以提高在训练期间的状态嵌入泛化能力,同时不增加推理时间。
点此查看论文截图

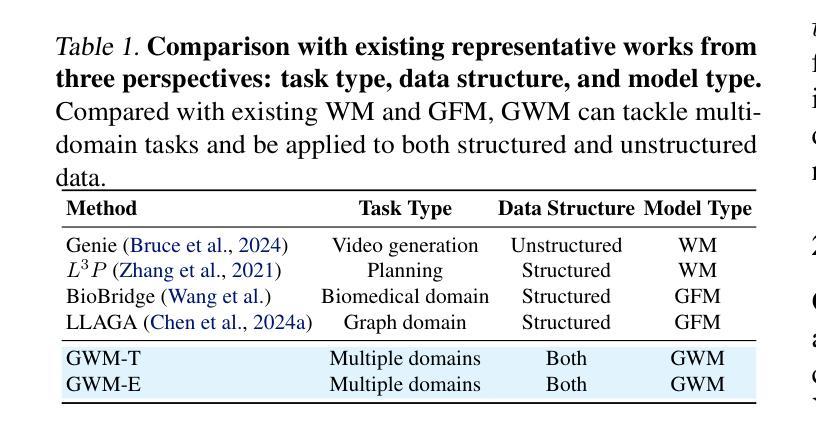
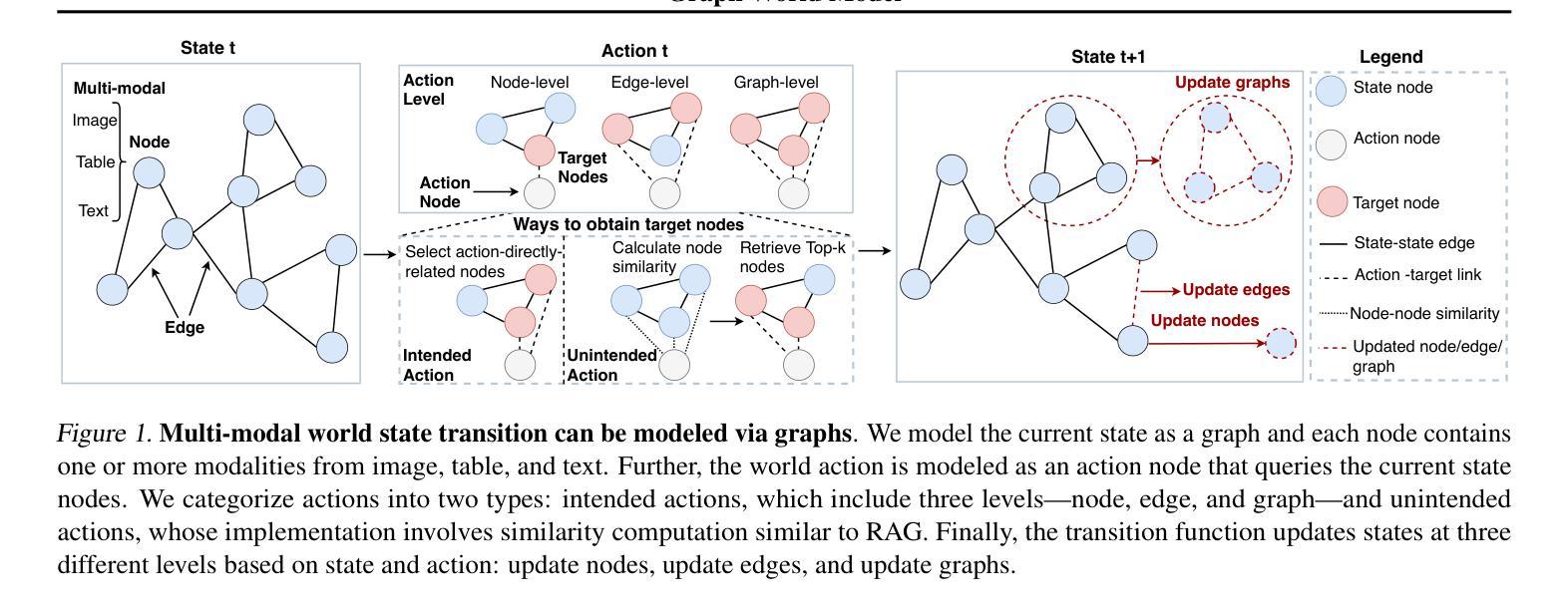
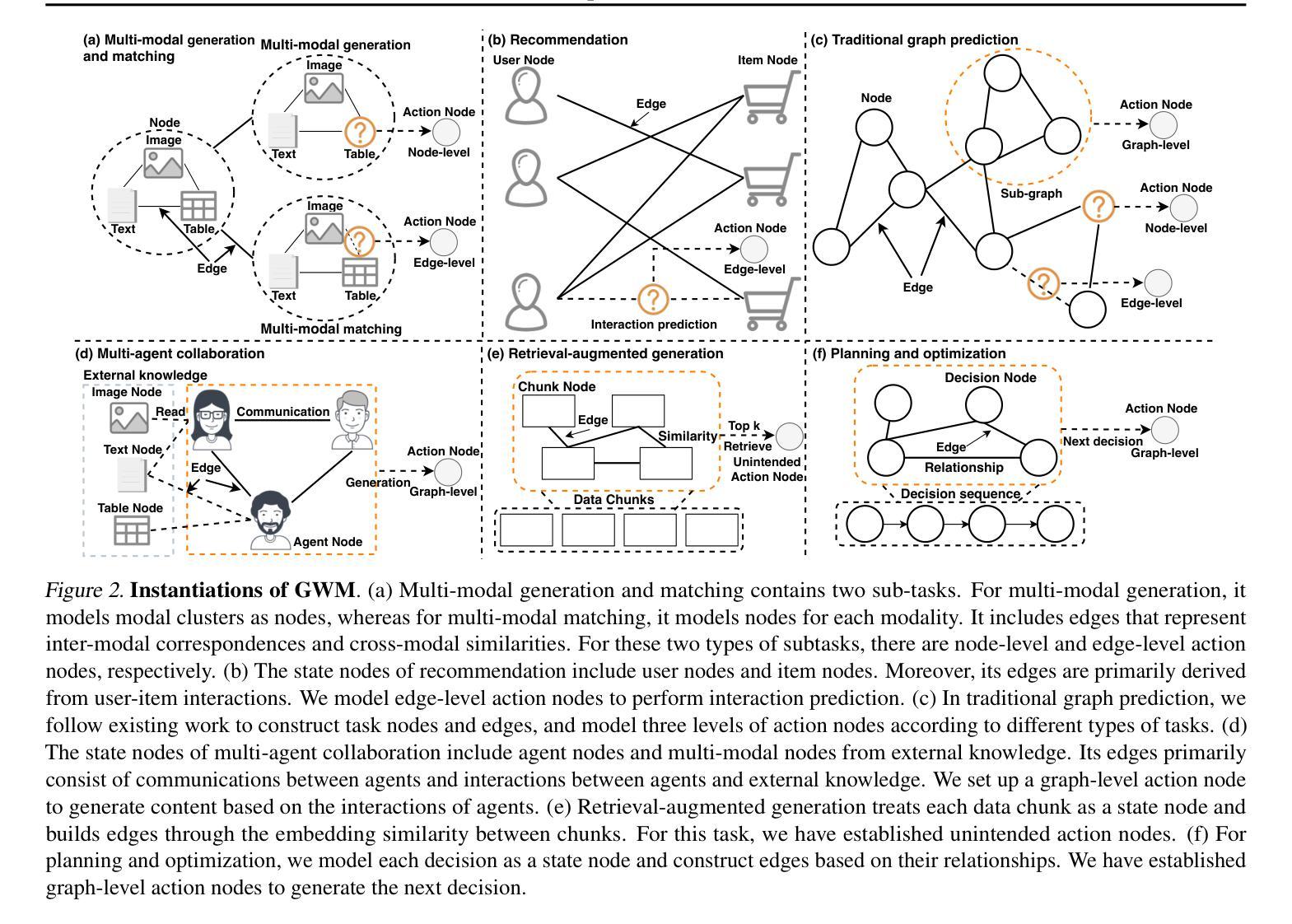
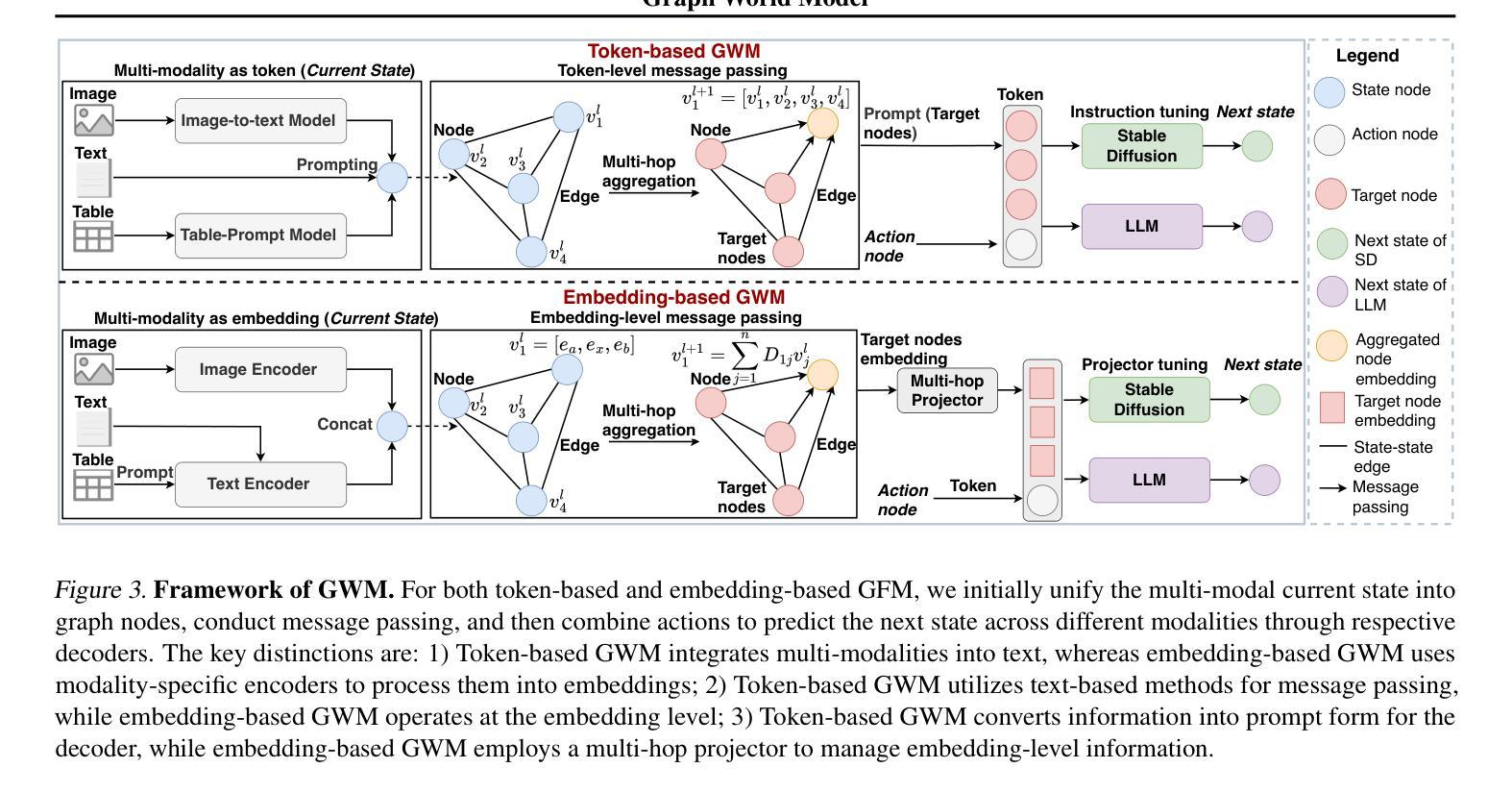
Graph World Model
Authors:Tao Feng, Yexin Wu, Guanyu Lin, Jiaxuan You
World models (WMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in prediction, generation, and planning tasks. Existing WMs primarily focus on unstructured data and cannot leverage the ubiquitous structured data, often represented as graphs, in the digital world. While multiple graph foundation models have been proposed, they focus on graph learning tasks and cannot extend to diverse multi-modal data and interdisciplinary tasks. To address these challenges, we propose the Graph World Model (GWM), a world model that supports both unstructured and graph-structured states with multi-modal information and represents diverse tasks as actions. The core of a GWM is a generic message-passing algorithm to aggregate structured information, either over a unified multi-modal token space by converting multi-modal data into text (GWM-T) or a unified multi-modal embedding space by modality-specific encoders (GWM-E). Notably, GWM introduces action nodes to support diverse tasks, where action nodes are linked to other nodes via direct reference or similarity computation. Extensive experiments on six tasks from diverse domains, including multi-modal generation and matching, recommendation, graph prediction, multi-agent, retrieval-augmented generation, and planning and optimization, show that the same GWM outperforms or matches domain-specific baselines’ performance, benefits from multi-hop structures, and demonstrates strong zero-shot/few-shot capabilities on unseen new tasks. Our code for GWM is released at https://github.com/ulab-uiuc/GWM.
世界模型(WMs)在预测、生成和规划任务中展现出强大的能力。现有的WMs主要关注非结构化数据,无法利用普遍存在的结构化数据(通常表示为图)在数字世界中的价值。虽然已提出多个图基础模型,但它们主要关注图学习任务,无法扩展到多样化的多模态数据和跨学科任务。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了图世界模型(GWM),这是一种支持非结构化图和结构化状态的多模态信息的世界模型,它将各种任务表示为动作。GWM的核心是一个通用消息传递算法,用于聚合结构化信息,无论是在统一的多模态符号空间(通过将多模态数据转换为文本)还是统一的多模态嵌入空间(通过特定模态的编码器)。值得注意的是,GWM引入了动作节点来支持各种任务,动作节点通过直接引用或相似性计算与其他节点链接。在来自不同领域的六个任务上的大量实验表明,同一GWM超越了或匹配了领域特定的基线性能,受益于多跳结构,并在未见的新任务上表现出强大的零样本/小样本能力。我们的GWM代码已发布在https://github.com/ulab-uiuc/GWM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
世界模型(WMs)在预测、生成和规划任务中表现出强大的能力,但它们主要关注于非结构化数据,无法利用普遍存在的结构化数据(通常以图形表示)。为解决此挑战,提出了图世界模型(GWM),它支持非结构化与图形结构化状态,具备多模式信息,并将各种任务表示为行动。GWM的核心是通用消息传递算法,该算法可通过将多模式数据转换为文本(GWM-T)或在模态特定编码器上的统一多模式嵌入空间(GWM-E)来聚合结构化信息。GWM引入行动节点以支持各种任务,行动节点通过直接引用或相似性计算与其他节点链接。在来自不同领域的六个任务上的实验表明,同一GWM优于或匹配领域特定基准线的性能,受益于多跳结构,并在未见的新任务上表现出强大的零样本/小样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- 世界模型(WMs)具有强大的预测、生成和规划能力,但主要处理非结构化数据。
- 图世界模型(GWM)支持非结构化和图形结构化数据,并处理多模式信息。
- GWM通过通用消息传递算法聚合结构化信息,提供两种实现方式:GWM-T(通过文本转换)和GWM-E(通过模态特定编码器)。
- GWM引入行动节点以支持多种任务,这些行动节点与其他节点通过直接引用或相似性计算链接。
- GWM在多个领域任务上表现出强大的性能,包括多模式生成与匹配、推荐、图形预测、多智能体、检索增强生成、规划和优化。
- GWM具有强大的零样本/小样本学习能力,能够在未见的新任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

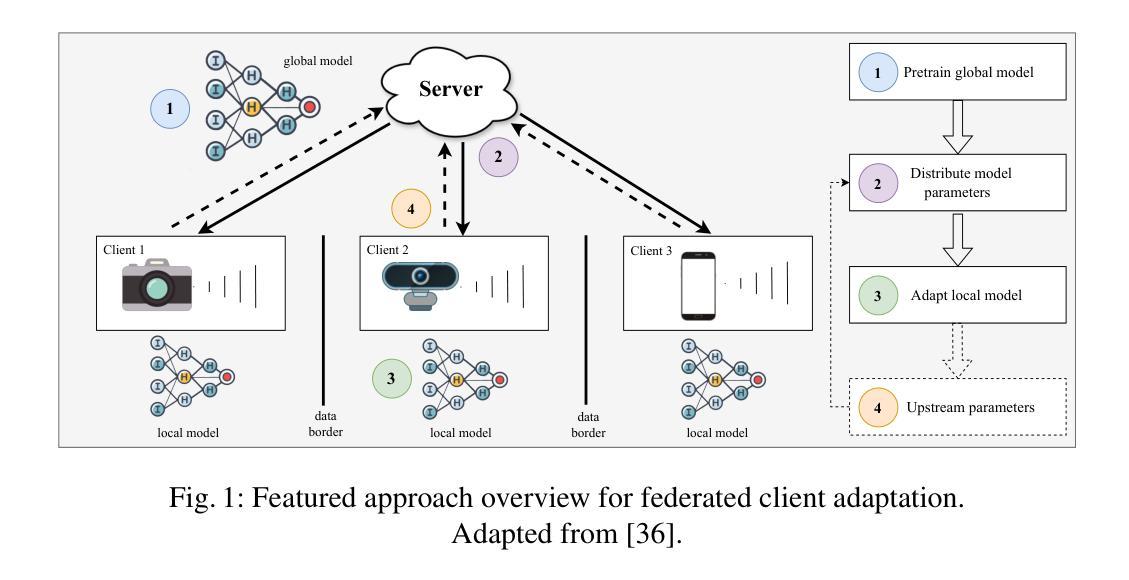
Domain Borders Are There to Be Crossed With Federated Few-Shot Adaptation
Authors:Manuel Röder, Christoph Raab, Frank-Michael Schleif
Federated Learning has emerged as a leading paradigm for decentralized, privacy-preserving learning, particularly relevant in the era of interconnected edge devices equipped with sensors. However, the practical implementation of Federated Learning faces three primary challenges: the need for human involvement in costly data labelling processes for target adaptation, covariate shift in client device data collection due to environmental factors affecting sensors, leading to discrepancies between source and target samples, and the impracticality of continuous or regular model updates in resource-constrained environments due to limited data transmission capabilities and technical constraints on channel availability and energy efficiency. To tackle these issues, we expand upon an efficient and scalable Federated Learning framework tailored for real-world client adaptation in industrial settings. This framework leverages a pre-trained source model comprising a deep backbone, an adaptation module, and a classifier running on a powerful server. By freezing the backbone and classifier during client adaptation on resource-constrained devices, we allow the domain adaptive linear layer to handle target domain adaptation, thus minimizing overall computational overhead. Furthermore, this setup, designated as FedAcross+, is extended to encompass the processing of streaming data, thereby rendering the solution suitable for non-stationary environments. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of FedAcross+ in achieving competitive adaptation on low-end client devices with limited target samples, successfully addressing the challenge of domain shift. Moreover, our framework accommodates sporadic model updates within resource-constrained environments, ensuring practical and seamless deployment.
联邦学习已成为去中心化、保护隐私的学习的主要范式,特别是在配备传感器的互联边缘设备时代。然而,联邦学习的实际应用面临三大挑战:需要人类参与昂贵的数据标记过程以适应目标,由于影响传感器的环境因素导致客户端设备数据收集中的协变量偏移,从而导致源样本和目标样本之间的差异,以及由于数据传输能力有限和通道可用性和能效方面的技术约束,资源受限环境中连续或定期模型更新的不切实际性。为了解决这些问题,我们扩展了一个高效且可扩展的联邦学习框架,该框架旨在适应工业环境中的真实世界客户端。该框架利用预训练的源模型,包括深度主干、适配模块和分类器,在功能强大的服务器上运行。通过在客户端适应资源受限的设备时冻结主干和分类器,我们允许域自适应线性层处理目标域适应,从而最小化总体计算开销。此外,这个被称为FedAcross+的设置被扩展以涵盖流式数据的处理,从而使解决方案适合非静止环境。大量的实验结果表明,FedAcross+在低端客户端设备上实现具有竞争力的适应目标样本方面非常有效,成功解决了领域偏移的挑战。而且,我们的框架能够在资源受限的环境中容纳间歇性模型更新,确保实用且无缝的部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extension of http://dx.doi.org/10.5220/0012351900003654
Summary
联邦学习已成为去中心化、保护隐私的学习主流范式,尤其在配备传感器的互联边缘设备时代具有重要意义。然而,其实践面临三大挑战。为应对这些挑战,我们扩展了一个高效、可扩展的联邦学习框架,用于工业环境中的真实客户端适应。该框架利用预训练源模型,包括深度主干、适配模块和分类器在强大服务器上运行。通过冻结主干和分类器,在资源受限的设备上进行客户端适配,允许领域自适应线性层处理目标领域适配,从而最小化整体计算开销。此外,FedAcross+ 框架能够处理流式数据,使其适用于非静态环境。实验结果证明了 FedAcross+ 在具有有限目标样本的低端客户端设备上实现竞争适配的有效性,成功解决了领域偏移的挑战。同时,该框架支持资源受限环境中偶尔的模型更新,确保实际部署的实用性和无缝性。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习已成为去中心化、隐私保护的主流学习范式,尤其在边缘设备时代具有重要意义。
- 联邦学习的实际应用面临三大挑战:目标适应的数据标注成本、源与靶样本之间的环境差异导致的协变量偏移以及资源受限环境中的连续或定期模型更新的不实用性。
- 提出了一个针对工业环境中真实客户端适应的高效联邦学习框架——FedAcross+,该框架利用预训练源模型并冻结主干和分类器,以降低计算开销,并实现目标领域适配。
- FedAcross+ 能够处理流式数据,适应非静态环境。
- 实验结果表明,FedAcross+ 在具有有限目标样本的低端客户端设备上实现有效的竞争适配,成功解决领域偏移挑战。
- FedAcross+ 框架支持资源受限环境中的偶尔模型更新,确保实际部署的实用性和无缝性。
点此查看论文截图


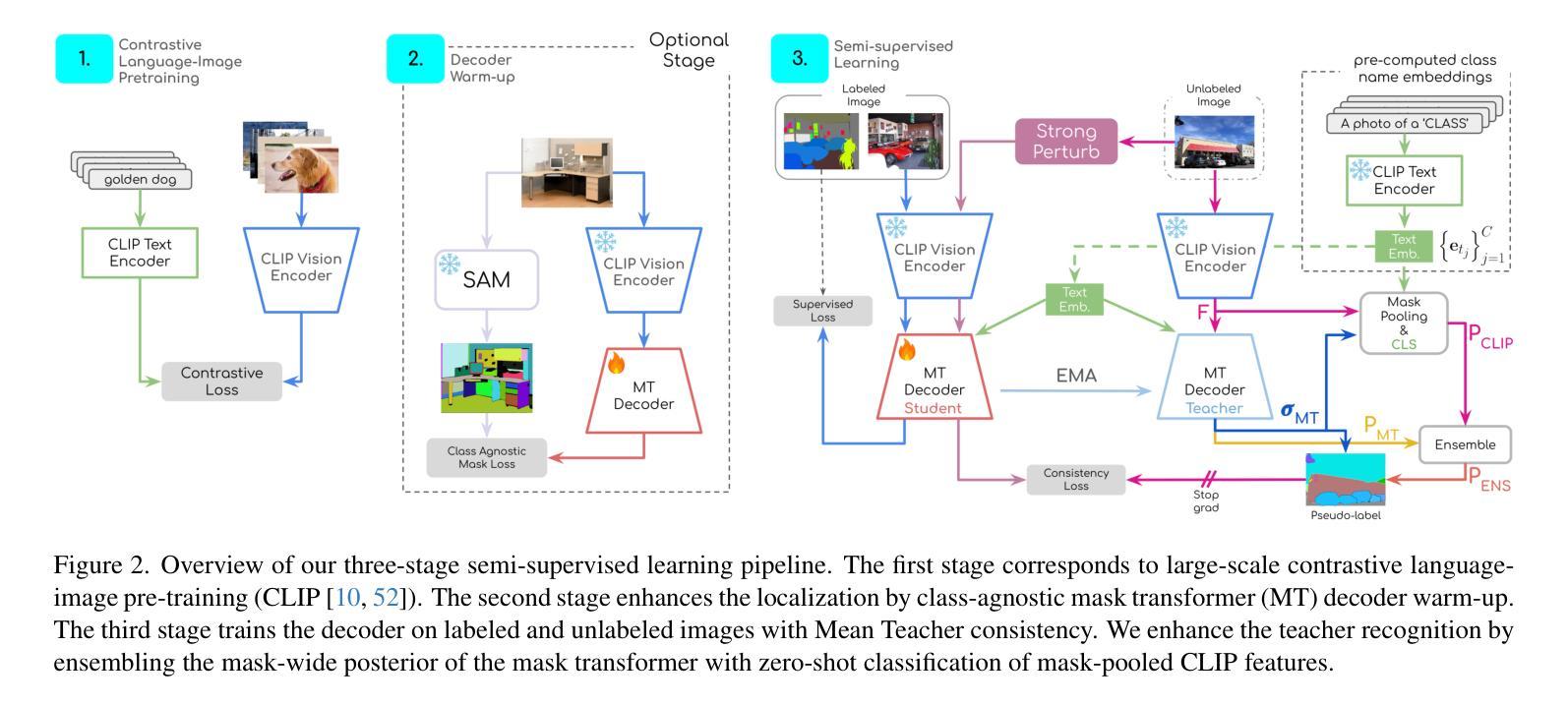
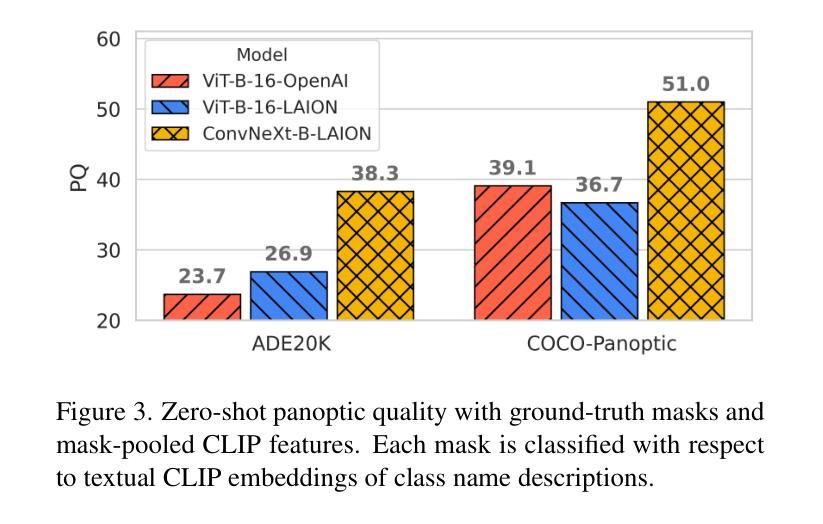
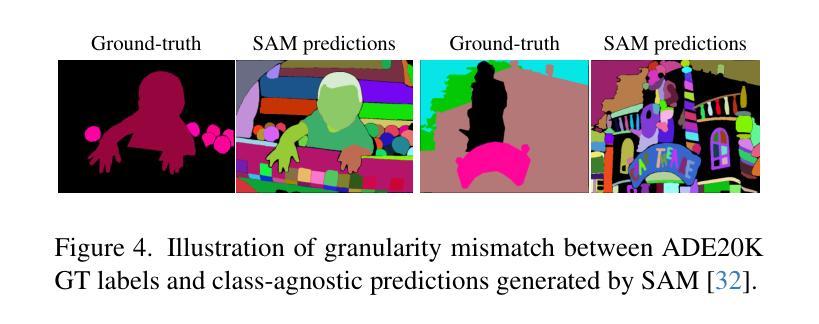
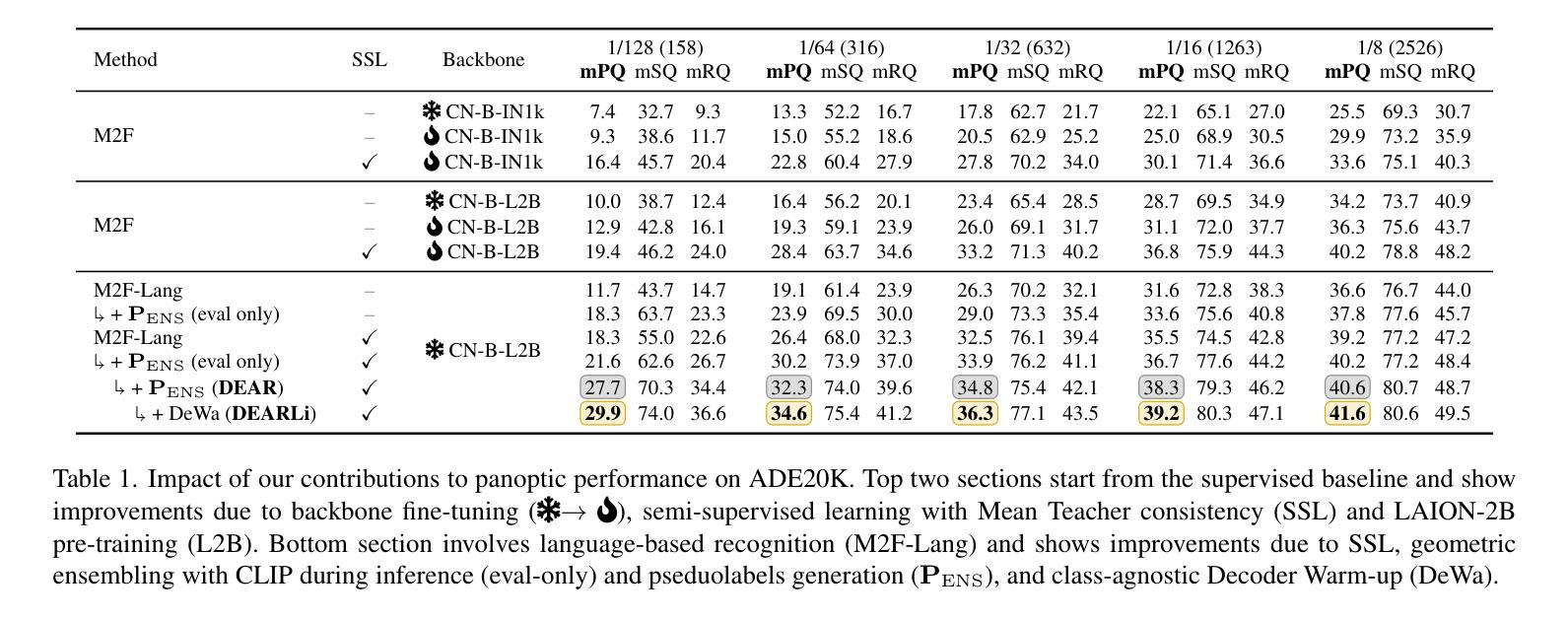
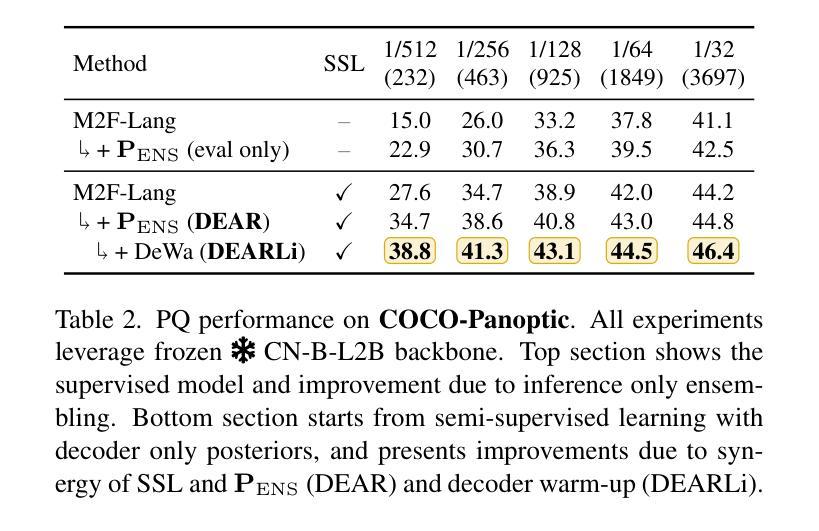
DEARLi: Decoupled Enhancement of Recognition and Localization for Semi-supervised Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Ivan Martinović, Josip Šarić, Marin Oršić, Matej Kristan, Siniša Šegvić
Pixel-level annotation is expensive and time-consuming. Semi-supervised segmentation methods address this challenge by learning models on few labeled images alongside a large corpus of unlabeled images. Although foundation models could further account for label scarcity, effective mechanisms for their exploitation remain underexplored. We address this by devising a novel semi-supervised panoptic approach fueled by two dedicated foundation models. We enhance recognition by complementing unsupervised mask-transformer consistency with zero-shot classification of CLIP features. We enhance localization by class-agnostic decoder warm-up with respect to SAM pseudo-labels. The resulting decoupled enhancement of recognition and localization (DEARLi) particularly excels in the most challenging semi-supervised scenarios with large taxonomies and limited labeled data. Moreover, DEARLi outperforms the state of the art in semi-supervised semantic segmentation by a large margin while requiring 8x less GPU memory, in spite of being trained only for the panoptic objective. We observe 29.9 PQ and 38.9 mIoU on ADE20K with only 158 labeled images. The source code is available at https://github.com/helen1c/DEARLi.
像素级标注既昂贵又耗时。半监督分割方法通过少数标注图像和大量未标注图像数据集上的模型学习来解决这一挑战。虽然基础模型可以进一步解决标签稀缺问题,但对其利用的有效机制仍被忽视。我们通过开发一种新的半监督泛全景方法来解决这个问题,该方法由两个专用的基础模型推动。我们通过将无监督掩膜转换器的一致性补充与CLIP特征的零样本分类相结合,提高识别能力。通过关于SAM伪标签的类别无关解码器预热来提高定位能力。这种去耦的识别和定位增强(DEARLi)技术在标签数据有限的大型分类学中面临最具挑战性的半监督场景时尤其表现出色。此外,尽管DEARLi仅针对全景目标进行训练,但在半监督语义分割方面仍大大优于现有技术,同时需要使用的GPU内存减少了8倍。在ADE20K上,仅使用158个标注图像就实现了29.9的PQ和38.9的mIoU。源代码可在https://github.com/helen1c/DEARLi找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Findings Workshop
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于半监督学习方法的像素级标注问题解决方案。该方法结合了两种专门的模型进行训练,使用半监督全景分析技术和一系列特定增强手段提高识别与定位能力。该方法在具有大量分类和有限标签数据的挑战性半监督场景中表现优异,显著优于现有技术,同时减少了GPU内存需求。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法采用半监督学习方法解决了像素级标注的昂贵和耗时问题。
- 通过结合两种专门的模型进行训练,提高了模型的性能。
- 使用半监督全景分析技术增强了识别能力。
- 通过特定增强手段提高模型的定位能力。
- 该方法在具有挑战性的半监督场景中表现优异,尤其是那些涉及大量分类和有限标签数据的场景。
点此查看论文截图
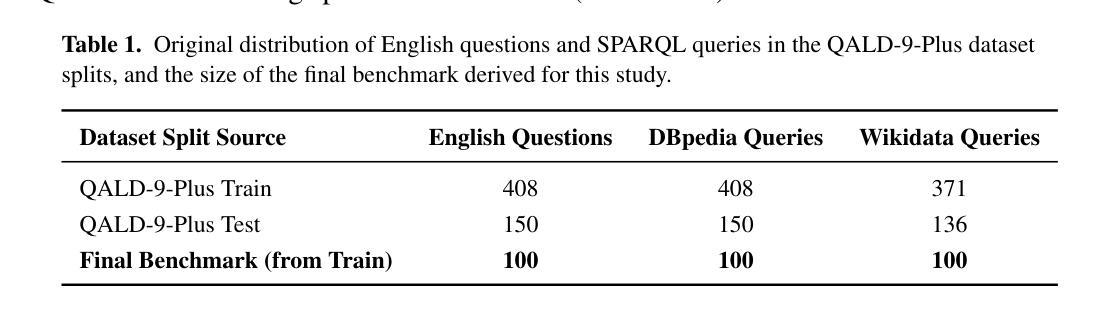
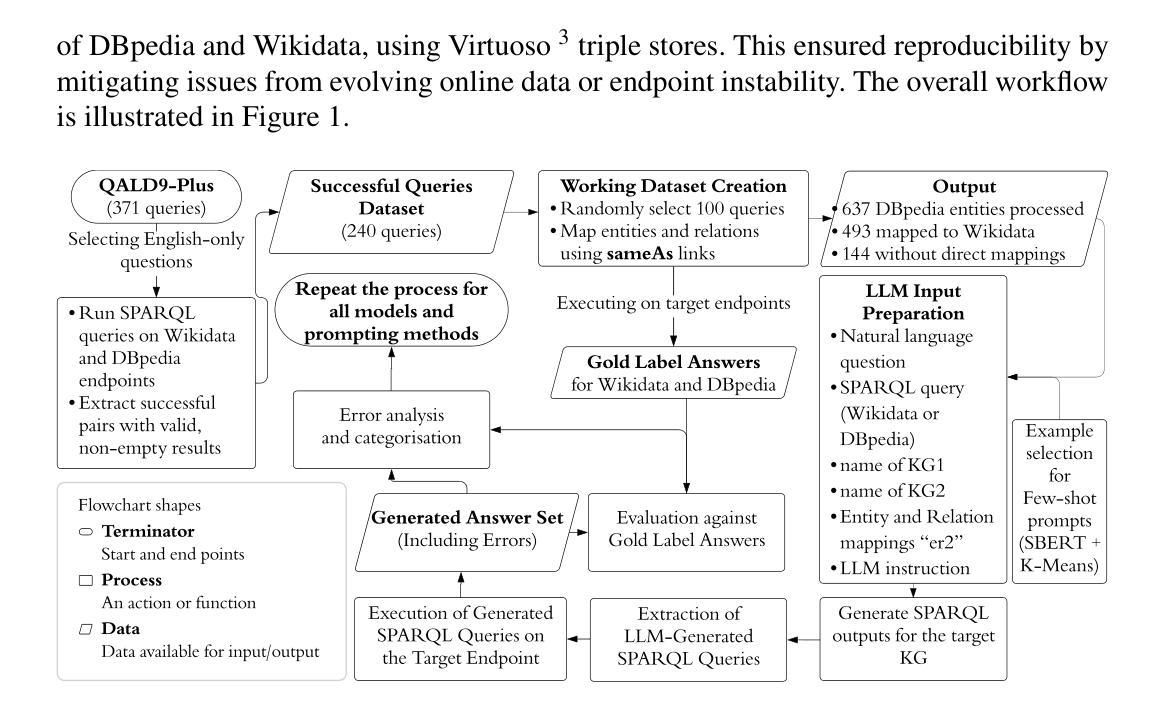
Automating SPARQL Query Translations between DBpedia and Wikidata
Authors:Malte Christian Bartels, Debayan Banerjee, Ricardo Usbeck
This paper investigates whether state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) can automatically translate SPARQL between popular Knowledge Graph (KG) schemas. We focus on translations between the DBpedia and Wikidata KG, and later on DBLP and OpenAlex KG. This study addresses a notable gap in KG interoperability research by rigorously evaluating LLM performance on SPARQL-to-SPARQL translation. Two benchmarks are assembled, where the first align 100 DBpedia-Wikidata queries from QALD-9-Plus; the second contains 100 DBLP queries aligned to OpenAlex, testing generalizability beyond encyclopaedic KGs. Three open LLMs: Llama-3-8B, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B, and Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 are selected based on their sizes and architectures and tested with zero-shot, few-shot, and two chain-of-thought variants. Outputs were compared with gold answers, and resulting errors were categorized. We find that the performance varies markedly across models and prompting strategies, and that translations for Wikidata to DBpedia work far better than translations for DBpedia to Wikidata.
本文旨在研究最先进的自然语言大模型是否能够自动翻译知识图谱(KG)之间流行的SPARQL查询。我们重点关注DBpedia和Wikidata KG之间的翻译,后续研究还包括DBLP和OpenAlex KG之间的翻译。本研究通过严格评估LLM在SPARQL-to-SPARQL翻译方面的性能,解决了知识图谱互操作性研究中的一个显著空白。我们构建了两个基准测试集,第一个基准测试集对齐QALD-9-Plus中的100个DBpedia-Wikidata查询;第二个基准测试集包含对齐到OpenAlex的100个DBLP查询,以测试其在百科全书知识图谱之外的泛化能力。基于规模与架构,我们选择三个开源的大型语言模型:Llama-3-8B、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B以及Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407进行试验。试验包括零样本、少样本以及两种思维链方法。输出答案与标准答案进行比较,并对产生的错误进行分类。我们发现不同模型和提示策略之间的性能差异很大,并且从Wikidata到DBpedia的翻译效果远胜于从DBpedia到Wikidata的翻译。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 2 figues. Paper accepted at SEMANTiCS 2025 conference happening on September 2025
Summary
这篇论文探讨了最先进的自然语言大模型(LLM)是否能自动翻译知识图谱(KG)中的SPARQL查询语句。研究聚焦于DBpedia和Wikidata以及DBLp和OpenAlex两大知识图谱之间的翻译,填补了知识图谱互操作性研究的空白。论文构建了两个基准测试集,评估了三个开源大模型在不同翻译场景下的性能,并发现性能在不同模型和提示策略之间有很大差异,且从Wikidata到DBpedia的翻译效果优于从DBpedia到Wikidata的翻译。
Key Takeaways
- 论文探讨了使用大语言模型(LLM)自动翻译SPARQL查询语句的可行性。
- 研究聚焦于DBpedia和Wikidata以及DBLp和OpenAlex两大知识图谱之间的翻译。
- 论文构建了两个基准测试集,用于评估LLM在SPARQL-to-SPARQL翻译方面的性能。
- 评估了三个开源大模型,包括Llama-3-8B、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B和Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407。
- 论文采用了零样本、小样例以及两种思维链方法进行了测试。
- 性能在不同模型和提示策略之间有很大差异。
点此查看论文截图

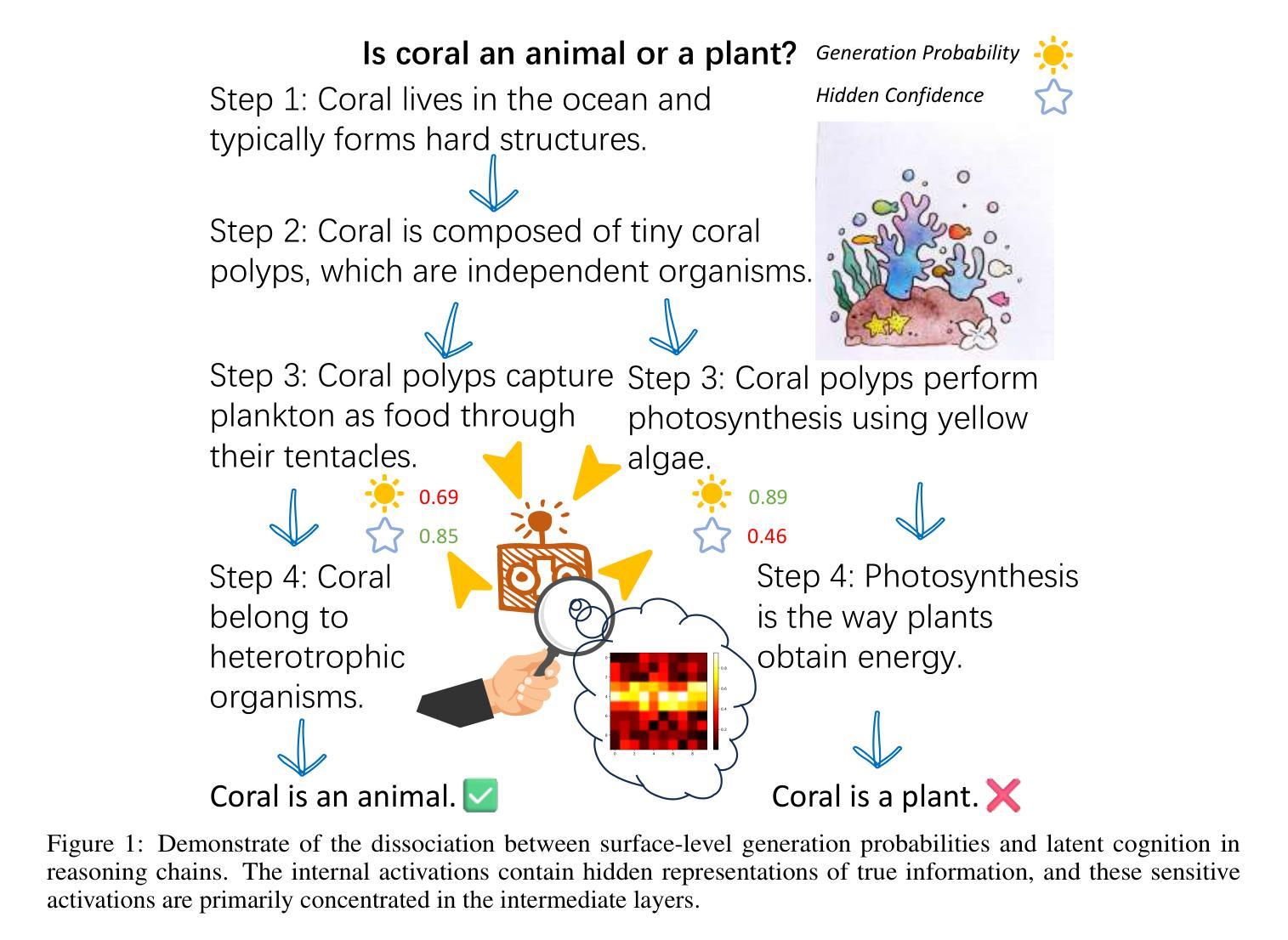
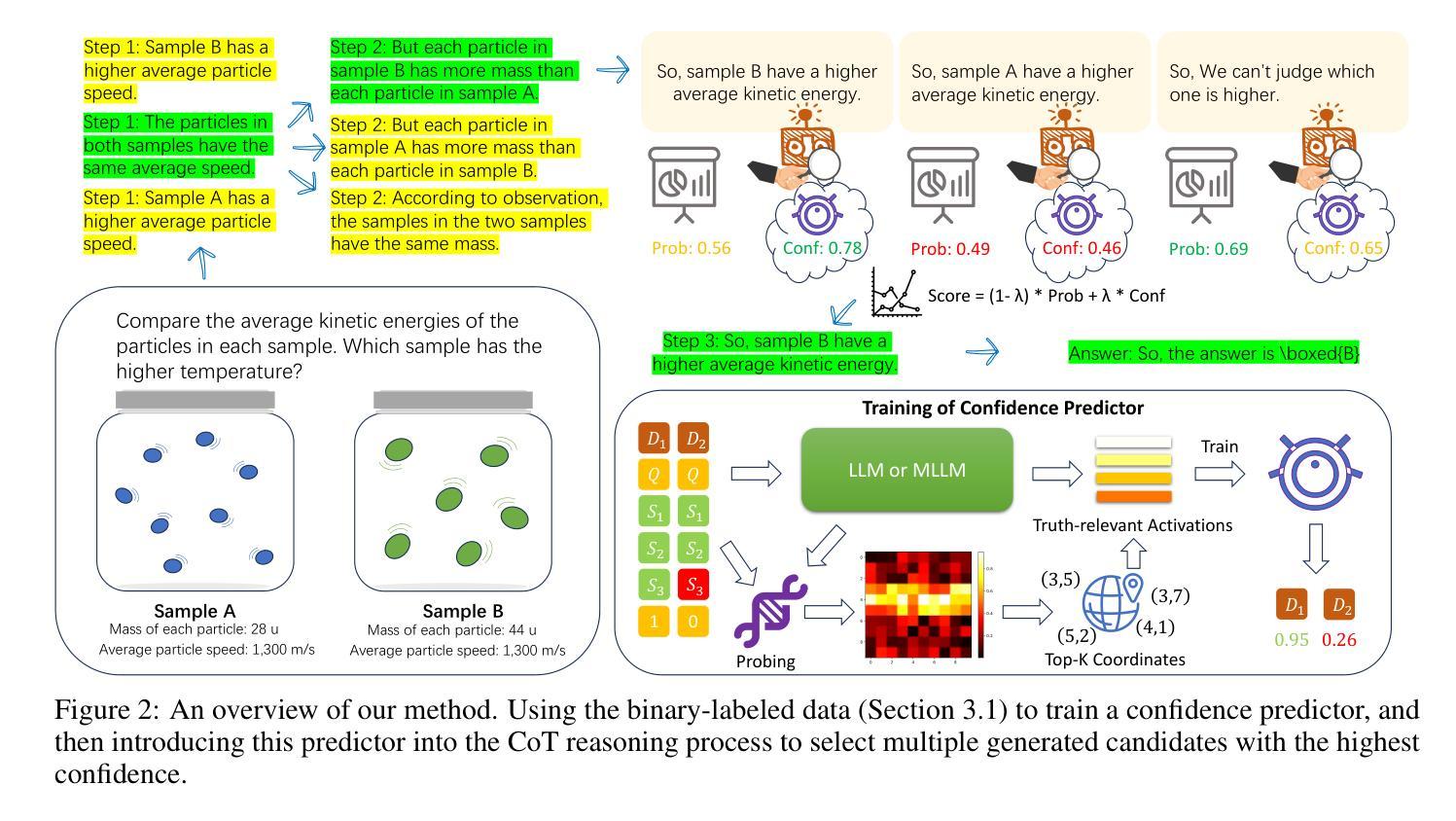
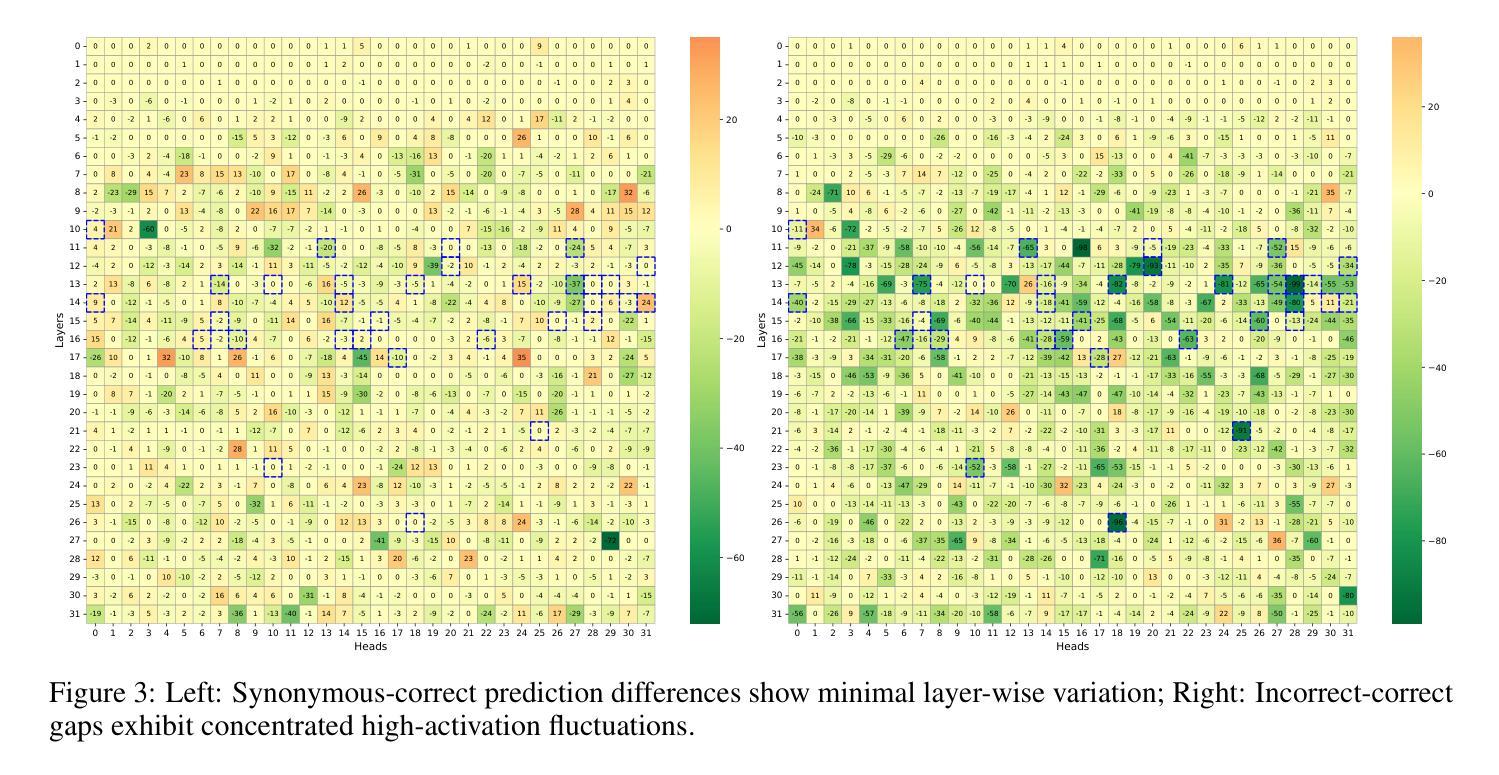
Deep Hidden Cognition Facilitates Reliable Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Zijun Chen, Wenbo Hu, Richang Hong
Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning has demonstrated remarkable deep reasoning capabilities in both large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, its reliability is often undermined by the accumulation of errors in intermediate steps. This paper introduces an novel approach to calibrate the CoT reasoning accuracy by leveraging the model’s intrinsic veracity encoding. We discover that specific attention head activations reliably reflect the truthfulness of reasoning steps in CoT. Based on this insight, we train a confidence predictor to evaluate the correctness of each reasoning step using these truthfulness-sensitive activations, dynamically selecting the most plausible reasoning path via beam search. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines (e.g., Few-Shot CoT, Self-Consistency, and Self-Evaluation Guided Beam Search) across the mathematical, symbolic, and commonsense reasoning tasks, exhibiting superior accuracy and reliability in both unimodal and multimodal settings. We further validate the approach on large reasoning models, confirming its applicability to specialized reasoning models. Additionally, we explore the role of the model’s self-correction ability in CoT reasoning. This work provides a novel reliability improvement path for CoT reasoning with broad application potential.
链式思维(Chain of Thought,简称CoT)推理在大规模语言模型(LLM)和多模态大规模语言模型(MLLM)中都表现出了显著的深度推理能力。然而,其可靠性往往受到中间步骤误差累积的影响。本文介绍了一种利用模型内在真实性编码来校准CoT推理精度的新方法。我们发现特定的注意力头激活能够可靠地反映CoT中推理步骤的真实性。基于这一发现,我们训练了一个置信度预测器,利用这些真实性敏感的激活来评估每个推理步骤的正确性,并通过集束搜索动态选择最合理的推理路径。实验结果表明,我们的方法在数学、符号和常识推理任务上显著优于最先进的基线方法(如少样本CoT、自我一致性、自我评估引导集束搜索等),在单模态和多模态环境中表现出更高的准确性和可靠性。我们在大型推理模型上进一步验证了该方法,证明了它在专业推理模型中的适用性。此外,我们还探索了模型中自我校正能力在CoT推理中的作用。这项工作为CoT推理提供了一种新的可靠性提升路径,具有广泛的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用模型内在真实性编码来提升Chain of Thought(CoT)推理准确性的新方法。研究发现了特定注意力头激活能可靠反映CoT推理步骤的真实性,并基于这一发现训练了信心预测器来评估每个推理步骤的正确性。该方法通过动态选择最合理的推理路径,显著提高了数学、符号和常识推理任务的性能,并在单模态和多模态环境中表现出卓越准确性和可靠性。同时,文章还探讨了模型在CoT推理中的自我校正能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新方法校准CoT推理准确性,通过模型内在真实性编码提升性能。
- 发现特定注意力头激活能反映CoT推理步骤的真实性。
- 训练信心预测器评估每个推理步骤的正确性。
- 方法在多种推理任务上显著优于现有技术,适用于单模态和多模态环境。
- 方法提高了数学、符号和常识推理的准确性和可靠性。
- 探索了模型在CoT推理中的自我校正能力。
点此查看论文截图

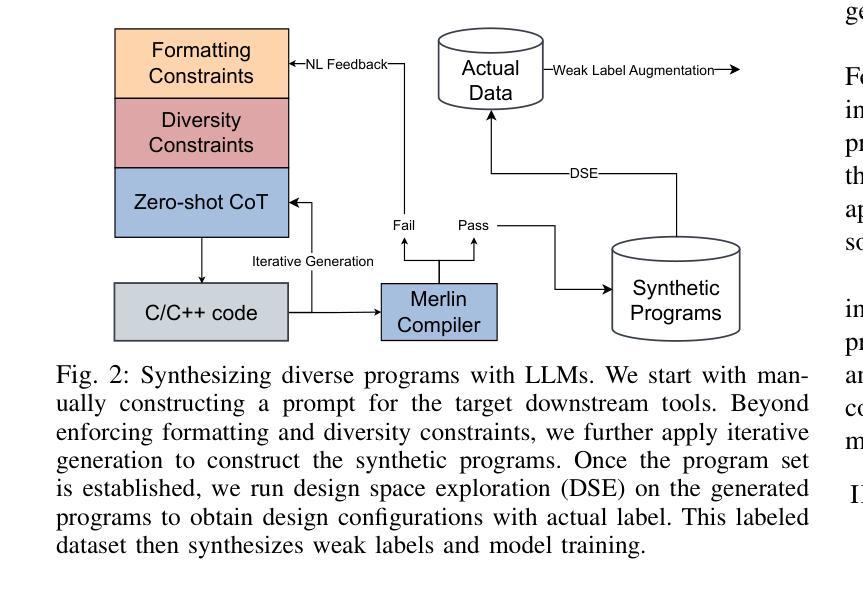
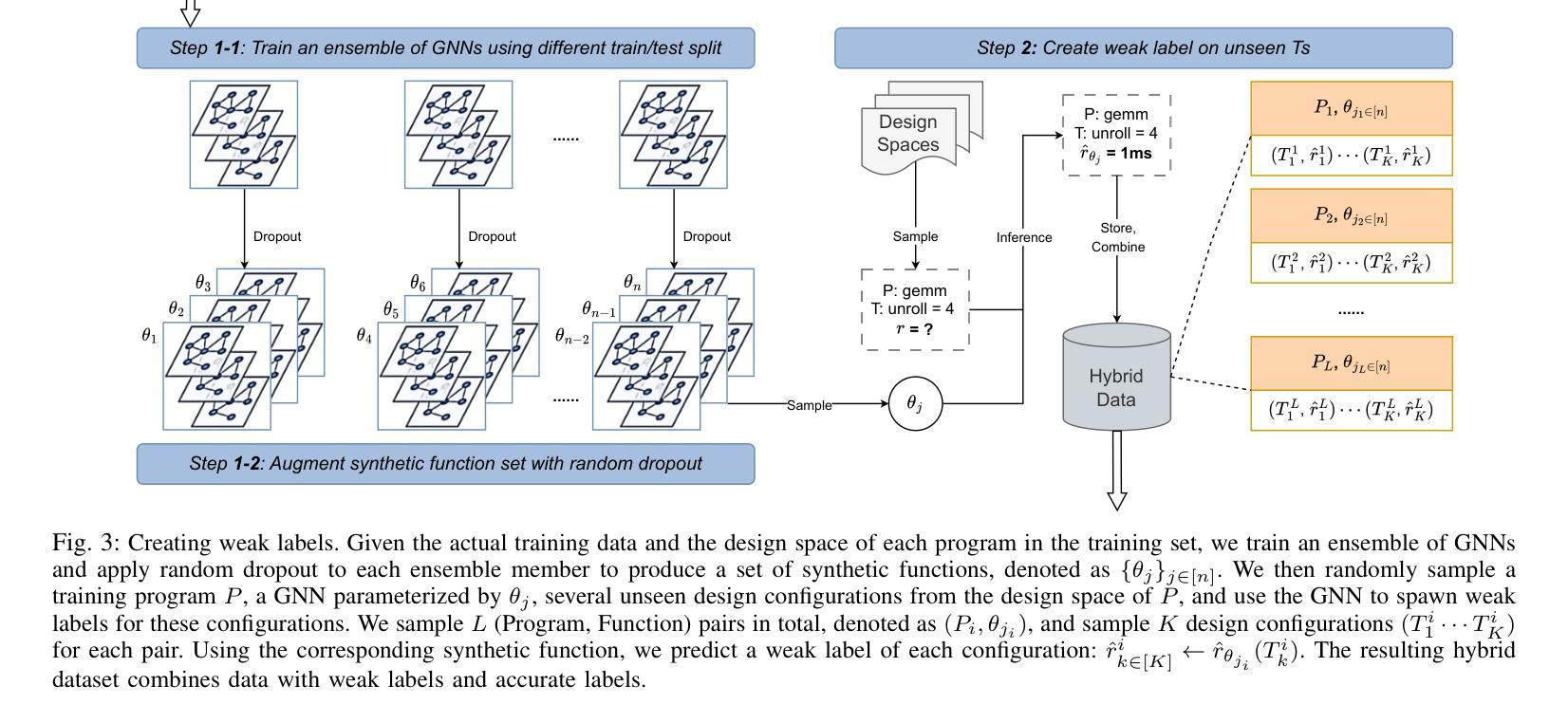
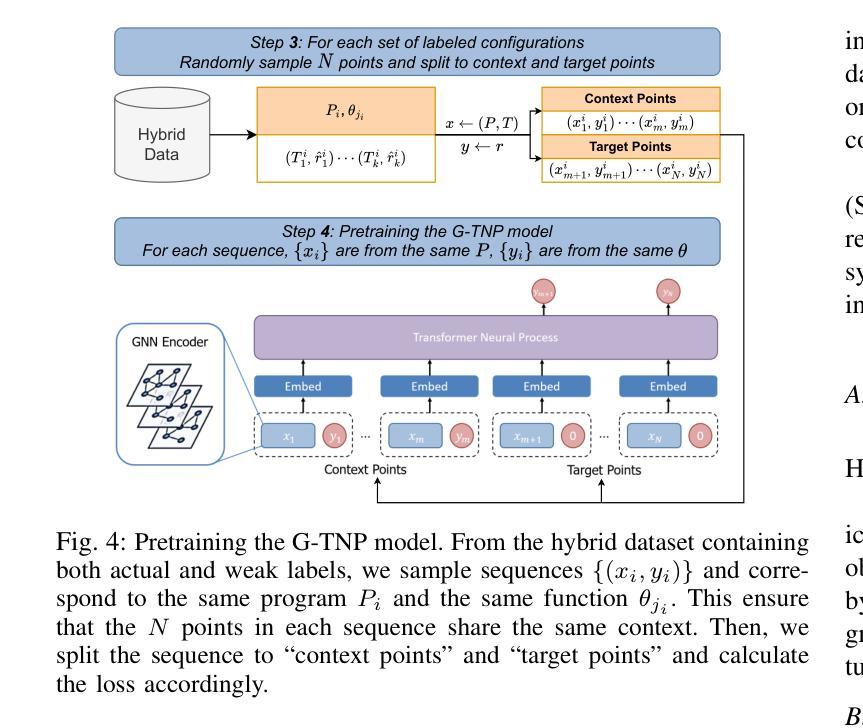
Iceberg: Enhancing HLS Modeling with Synthetic Data
Authors:Zijian Ding, Tung Nguyen, Weikai Li, Aditya Grover, Yizhou Sun, Jason Cong
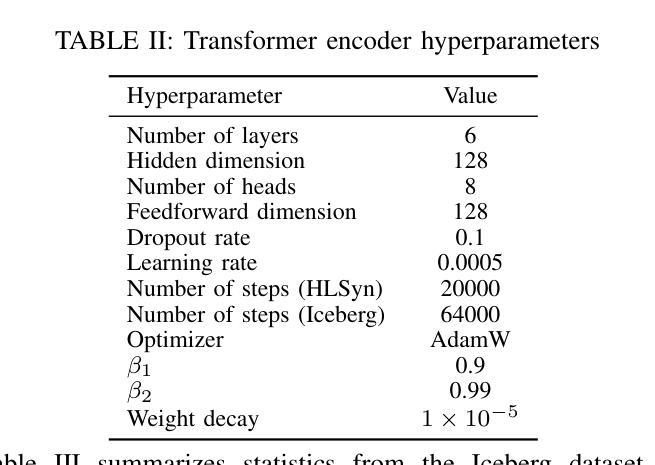
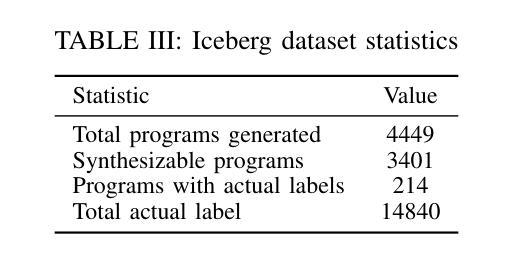
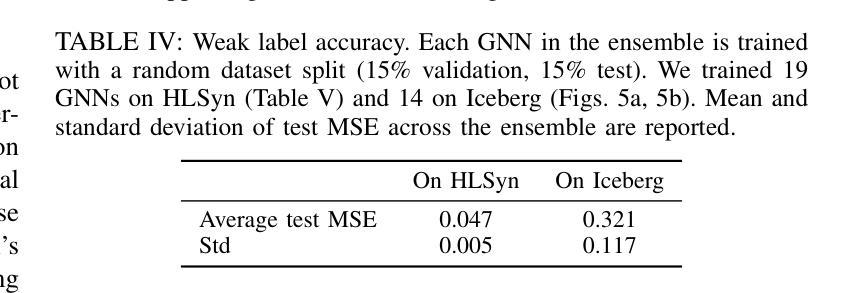
Deep learning-based prediction models for High-Level Synthesis (HLS) of hardware designs often struggle to generalize. In this paper, we study how to close the generalizability gap of these models through pretraining on synthetic data and introduce Iceberg, a synthetic data augmentation approach that expands both large language model (LLM)-generated programs and weak labels of unseen design configurations. Our weak label generation method is integrated with an in-context model architecture, enabling meta-learning from actual and proximate labels. Iceberg improves the geometric mean modeling accuracy by $86.4%$ when adapt to six real-world applications with few-shot examples and achieves a $2.47\times$ and a $1.12\times$ better offline DSE performance when adapting to two different test datasets. Our open-sourced code is here: \href{https://github.com/UCLA-VAST/iceberg}{https://github.com/UCLA-VAST/iceberg}
针对硬件设计的高级综合(HLS)深度学习的预测模型通常面临难以泛化的问题。在本文中,我们研究了如何通过合成数据的预训练来缩小这些模型的泛化差距,并引入了Iceberg,这是一种合成数据增强方法,它扩展了大规模语言模型(LLM)生成的程序和未见设计配置的弱标签。我们的弱标签生成方法与上下文模型架构相结合,实现了从实际和近似标签的元学习。Iceberg在适应六个具有少量示例的实际应用时,提高了几何平均建模精度达86.4%,在适应两个不同的测试数据集时,离线DSE性能分别提高了2.47倍和1.12倍。我们的开源代码在此:https://github.com/UCLA-VAST/iceberg。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages. accepted to ICLAD’25
Summary
深度学习在硬件设计高级综合(HLS)的预测模型通常存在泛化问题。本研究通过预训练合成数据来缩小模型泛化差距,并引入Iceberg方法,扩展了大型语言模型生成的程序和未见设计配置的弱标签。集成弱标签生成方法与上下文模型架构,实现元学习从实际和近似标签中学习。Iceberg在适应少数实例的真实世界应用时,建模精度提高了86.4%,在适应两个不同的测试数据集时,离线DSE性能分别提高了2.47倍和1.12倍。代码已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在硬件设计高级综合的预测模型存在泛化问题。
- 通过预训练合成数据来提高模型的泛化能力。
- 引入Iceberg方法,扩展大型语言模型生成的程序和未见设计配置的弱标签。
- 集成弱标签生成方法与上下文模型架构,实现元学习。
- Iceberg方法在适应少数实例的真实世界应用时,建模精度显著提高。
- Iceberg方法提高了离线DSE性能。
点此查看论文截图

ViT-ProtoNet for Few-Shot Image Classification: A Multi-Benchmark Evaluation
Authors:Abdulvahap Mutlu, Şengül Doğan, Türker Tuncer
The remarkable representational power of Vision Transformers (ViTs) remains underutilized in few-shot image classification. In this work, we introduce ViT-ProtoNet, which integrates a ViT-Small backbone into the Prototypical Network framework. By averaging class conditional token embeddings from a handful of support examples, ViT-ProtoNet constructs robust prototypes that generalize to novel categories under 5-shot settings. We conduct an extensive empirical evaluation on four standard benchmarks: Mini-ImageNet, FC100, CUB-200, and CIFAR-FS, including overlapped support variants to assess robustness. Across all splits, ViT-ProtoNet consistently outperforms CNN-based prototypical counterparts, achieving up to a 3.2% improvement in 5-shot accuracy and demonstrating superior feature separability in latent space. Furthermore, it outperforms or is competitive with transformer-based competitors using a more lightweight backbone. Comprehensive ablations examine the impact of transformer depth, patch size, and fine-tuning strategy. To foster reproducibility, we release code and pretrained weights. Our results establish ViT-ProtoNet as a powerful, flexible approach for few-shot classification and set a new baseline for transformer-based meta-learners.
视觉Transformer(ViT)的表示能力在少样本图像分类中尚未得到充分利用。在这项工作中,我们引入了ViT-ProtoNet,它将ViT-Small骨干网集成到原型网络框架中。通过平均少量支持样本的类别条件令牌嵌入,ViT-ProtoNet构建了在5个样本设置下能够推广到新型类别的稳健原型。我们在四个标准数据集上进行了广泛的实证评估:Mini-ImageNet、FC100、CUB-200和CIFAR-FS,包括重叠的支持变体以评估稳健性。在所有分割中,ViT-ProtoNet始终优于基于CNN的原型对应模型,在5次射击的准确性上最多提高了3.2%,并在潜在空间中显示出卓越的特征可分离性。此外,使用更轻量级骨干网的情况下,它与基于Transformer的竞争对手相比具有优势或竞争力。全面的研究考察了Transformer深度、补丁大小和微调策略的影响。为促进可重复性,我们发布了代码和预训练权重。我们的结果确立了ViT-ProtoNet在少样本分类中的强大和灵活方法,并为基于Transformer的元学习者设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF All codes are available at https://github.com/abdulvahapmutlu/vit-protonet
Summary
本文介绍了将Vision Transformer(ViT)与Prototypical Network框架相结合的ViT-ProtoNet模型,用于小样本图像分类。通过平均少量支持样本的类别条件令牌嵌入来构建稳健原型,ViT-ProtoNet在5个样本的情况下可推广到新型类别。在四个标准数据集上的实验结果表明,ViT-ProtoNet在基于CNN的原型模型上实现了高达3.2%的改进,并在潜在空间中表现出卓越的特征可分离性。此外,使用更轻量级骨干的基于Transformer的竞争对手相比,ViT-ProtoNet具有出色的性能。代码和预训练权重已发布,以促进可重复性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer(ViT)在小样本图像分类中的代表性能力尚未得到充分利用。
- ViT-ProtoNet结合了ViT-Small骨干网络和Prototypical Network框架,用于小样本图像分类。
- 通过平均少量支持样本的类别条件令牌嵌入,ViT-ProtoNet构建了稳健的原型。
- 在四个标准数据集上的实验表明,ViT-ProtoNet在5个样本的情况下表现优异,且在潜在空间中具有卓越的特征可分离性。
- ViT-ProtoNet在基于CNN的原型模型上实现了显著改进,最高达到3.2%。
- 与其他基于Transformer的竞争对手相比,使用更轻量级骨干的ViT-ProtoNet表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图

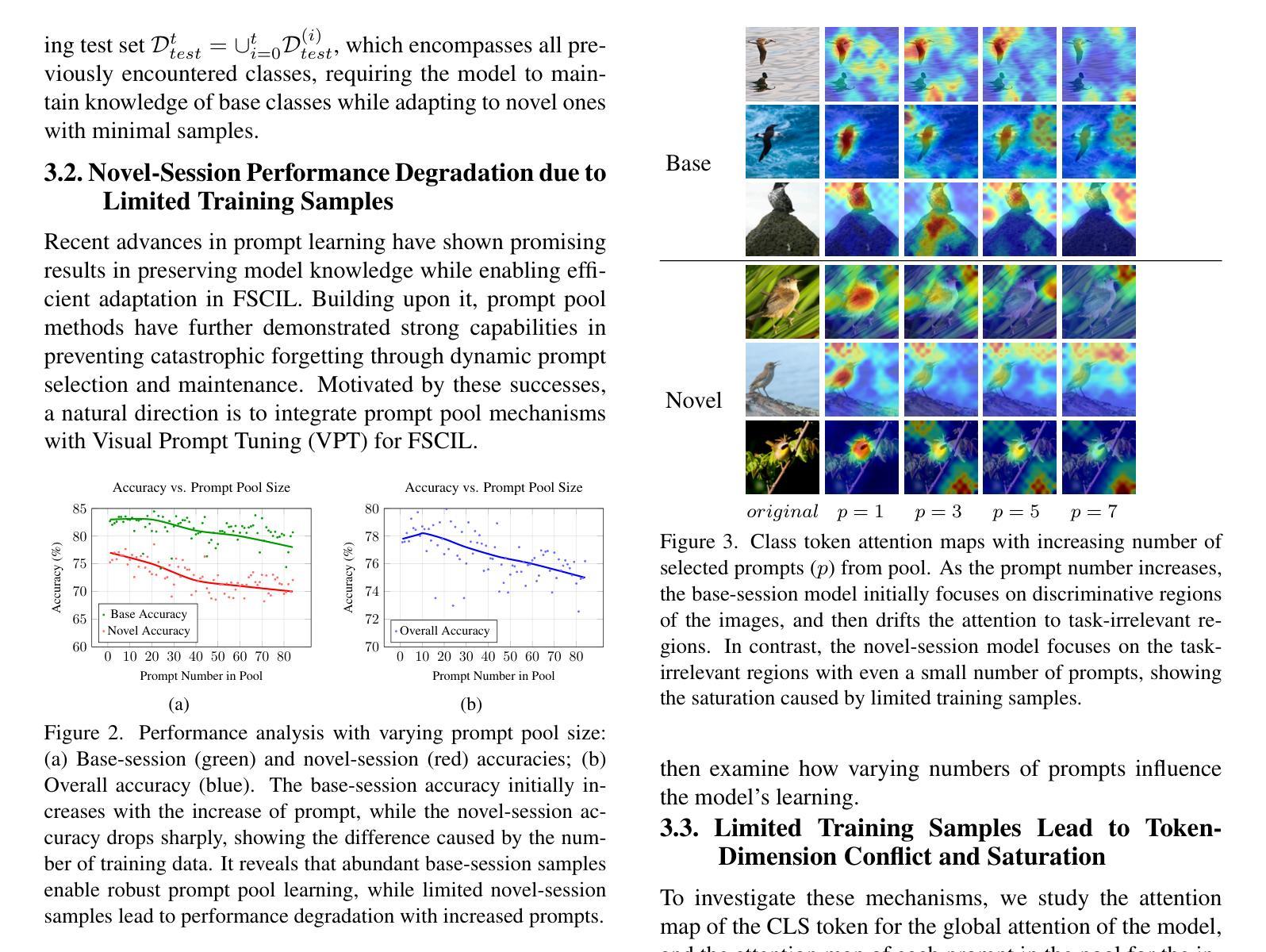
Revisiting Pool-based Prompt Learning for Few-shot Class-incremental Learning
Authors:Yongwei Jiang, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
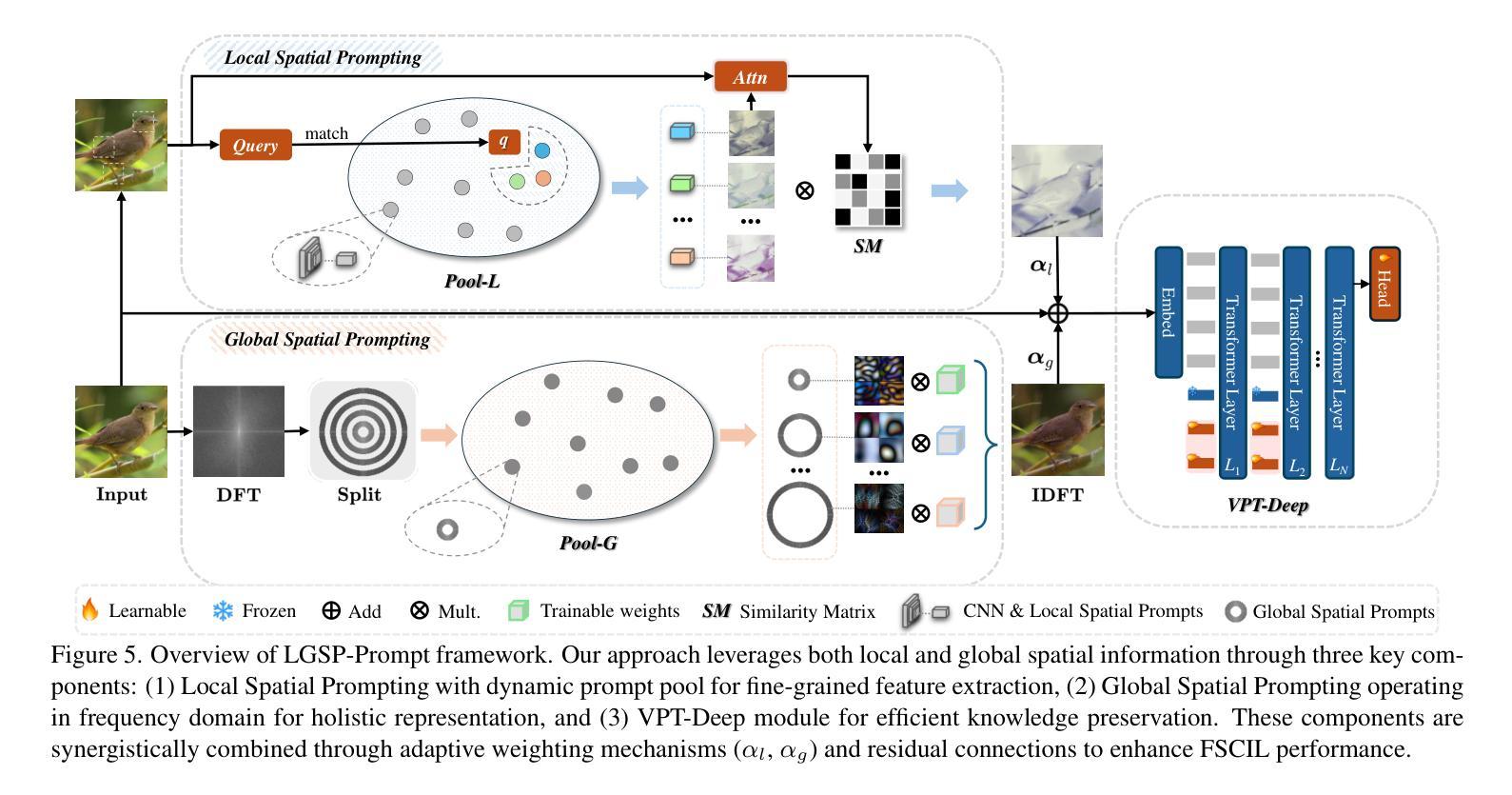
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) faces dual challenges of data scarcity and incremental learning in real-world scenarios. While pool-based prompting methods have demonstrated success in traditional incremental learning, their effectiveness in FSCIL settings remains unexplored. This paper presents the first study of current prompt pool methods in FSCIL tasks, revealing an unanticipated performance degradation in incremental sessions. Through comprehensive analysis, we identify that this phenomenon stems from token-dimension saturation: with limited data, excessive prompts compete for task-relevant information, leading to model overfitting. Based on this finding, we propose LGSP-Prompt (Local-Global Spatial Prompting), which innovatively shifts pool-based prompt learning from the token dimension to the spatial dimension. LGSP-Prompt generates spatial prompts by synergistically combining local spatial features and global frequency-domain representations to highlight key patterns in input images. We construct two spatial prompt pools enabling dynamic prompt selection to maintain acquired knowledge while effectively learning novel sessions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple FSCIL benchmarks, showing significant advantages in both base knowledge preservation and incremental learning. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/Jywsuperman/LGSP.
在真实场景中,Few-Shot 类增量学习(FSCIL)面临着数据稀缺和增量学习的双重挑战。虽然基于池体的提示方法在传统的增量学习中已经取得了成功,但它们在FSCIL设置中的有效性尚未被探索。本文首次研究了当前提示池方法在FSCIL任务中的应用,揭示了增量会话中预期之外的性能下降。通过综合分析,我们发现这一现象源于token维度的饱和:在有限的数据下,过多的提示会争夺任务相关信息,导致模型过度拟合。基于这一发现,我们提出了LGSP-Prompt(局部-全局空间提示),它创新地将基于池体的提示学习从token维度转移到空间维度。LGSP-Prompt通过协同结合局部空间特征和全局频域表示来生成空间提示,以突出输入图像中的关键模式。我们构建了两个空间提示池,以支持动态提示选择,以维持已获取的知识并有效地学习新的会话。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个FSCIL基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,在基础知识的保留和增量学习方面都显示出显著的优势。我们的实现可在https://github.com/Jywsuperman/LGSP中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025, 11 pages
摘要
该论文针对小样本类别增量学习(FSCIL)领域数据稀缺和增量学习双重挑战进行研究。虽然基于提示池的方法在传统增量学习中取得了成功,但在FSCIL场景中的有效性尚未得到探索。本文首次研究了当前提示池方法在FSCIL任务中的表现,发现增量会话中存在意外的性能下降现象。经过综合分析,我们确定这是由于标记维度饱和导致的:在有限数据下,过多的提示会争夺任务相关信息,导致模型过拟合。基于此发现,我们提出了LGSP-Prompt(局部全局空间提示),创新地将基于提示池的学习从标记维度转向空间维度。LGSP-Prompt通过协同结合局部空间特征和全局频域表示来生成空间提示,从而突出输入图像中的关键模式。我们构建了两个空间提示池,以实现动态提示选择,既保持已获得的知识,又能有效学习新的会话。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个FSCIL基准测试中达到了最新性能水平,在基础知识保留和增量学习方面都显示出显著优势。
关键见解
- FSCIL面临数据稀缺和增量学习的双重挑战。
- 基于提示池的方法在FSCIL任务中表现出意外的性能下降现象。
- 现象的原因在于标记维度饱和,过量提示导致模型过拟合。
- 引入LGSP-Prompt方法,将基于提示池的学习从标记维度转向空间维度。
- LGSP-Prompt结合局部空间特征和全局频域表示生成空间提示。
- 构建了两个空间提示池以实现动态提示选择,同时保持知识和学习新会话。
- 实验表明,该方法在多个FSCIL基准测试中表现最佳,具有显著的保留和增量学习优势。
点此查看论文截图

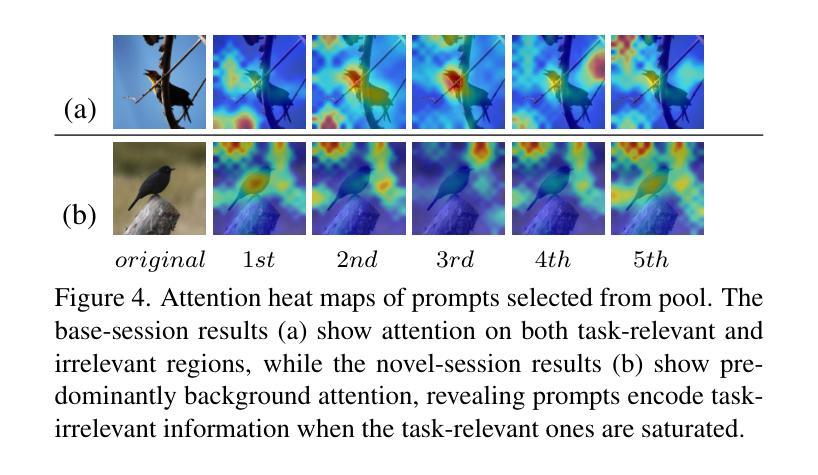
Beyond Scale: Small Language Models are Comparable to GPT-4 in Mental Health Understanding
Authors:Hong Jia, Shiya Fu, Feng Xia, Vassilis Kostakos, Ting Dang
The emergence of Small Language Models (SLMs) as privacy-preserving alternatives for sensitive applications raises a fundamental question about their inherent understanding capabilities compared to Large Language Models (LLMs). This paper investigates the mental health understanding capabilities of current SLMs through systematic evaluation across diverse classification tasks. Employing zero-shot and few-shot learning paradigms, we benchmark their performance against established LLM baselines to elucidate their relative strengths and limitations in this critical domain. We assess five state-of-the-art SLMs (Phi-3, Phi-3.5, Qwen2.5, Llama-3.2, Gemma2) against three LLMs (GPT-4, FLAN-T5-XXL, Alpaca-7B) on six mental health understanding tasks. Our findings reveal that SLMs achieve mean performance within 2% of LLMs on binary classification tasks (F1 scores of 0.64 vs 0.66 in zero-shot settings), demonstrating notable competence despite orders of magnitude fewer parameters. Both model categories experience similar degradation on multi-class severity tasks (a drop of over 30%), suggesting that nuanced clinical understanding challenges transcend model scale. Few-shot prompting provides substantial improvements for SLMs (up to 14.6%), while LLM gains are more variable. Our work highlights the potential of SLMs in mental health understanding, showing they can be effective privacy-preserving tools for analyzing sensitive online text data. In particular, their ability to quickly adapt and specialize with minimal data through few-shot learning positions them as promising candidates for scalable mental health screening tools.
随着小型语言模型(SLMs)作为敏感应用的隐私保护替代方案的出现,关于它们与大型语言模型(LLMs)的内在理解能力的比较,引发了一个根本性的问题。本文通过系统评估各种分类任务,研究当前SLM在心理健康理解方面的能力。我们采用零样本学习和小样本学习范式,将它们的性能与现有的LLM基准进行测试,以阐明这一关键领域中的相对优势和局限性。我们对五个最先进的大型语言模型进行评估,分别是Phi-3、Phi-3.5、Qwen2.5、Llama-3.2和Gemma2等,以及三个大型语言模型GPT-4、FLAN-T5-XXL和Alpaca-7B等六个心理健康理解任务。我们的研究发现,在二元分类任务上,SLM的均值与LLM在短短两个百分点以内达到相对水平(零样本设置中F1分数为0.64对0.66),虽然参数相差多个数量级,但也表现出相当的可信能力。两种模型在多类严重性任务上的性能均出现类似下降(降幅超过百分之三十),这表明细微的临床理解挑战已超越了模型的规模范围。小样本提示(即让机器学习系统的操作显示一些小量样例的能力)可为SLM带来巨大改善(高达百分之十四点六),而大型语言模型的收益则更为不稳定。我们的工作重点突出了SLM在心理健康理解方面的潜力,显示出它们可以成为分析敏感在线文本数据的有效隐私保护工具。特别是它们通过小样本学习快速适应和专门化的能力,使它们成为心理健康筛查工具的可选方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
当前文本探讨了小型语言模型(SLMs)在心理健康理解方面的能力,通过与大型语言模型(LLMs)的对比实验,展示了SLMs在此领域的潜力和优势。研究发现,SLMs在二元分类任务上的表现与LLMs相近,少数镜头学习技术的引入为SLMs带来了显著的性能提升。尽管存在多类别严重程度任务上的挑战,但SLMs展现了在心理健康理解领域的有效性和潜力。总体来说,SLMs可以作为隐私保护工具应用于敏感文本数据的分析,尤其在快速适应和专业化方面展现出巨大潜力,有望用于可扩展的心理健康筛查工具。
Key Takeaways
- SLMs作为隐私保护替代方案在敏感应用中的兴起,引发了对它们与LLMs在理解能力方面的比较。
- 通过多种分类任务的系统评估,发现SLMs在心理健康理解方面表现出竞争力。
- 在二元分类任务上,SLMs的性能与LLMs相近,少数镜头学习技术显著提升SLMs性能。
- 在多类别严重程度任务上,两种模型均面临挑战,显示微妙的临床理解难度超越模型规模。
- SLMs在心理健康理解领域具有潜力和有效性。
- SLMs可作为隐私保护工具用于分析敏感文本数据。
点此查看论文截图

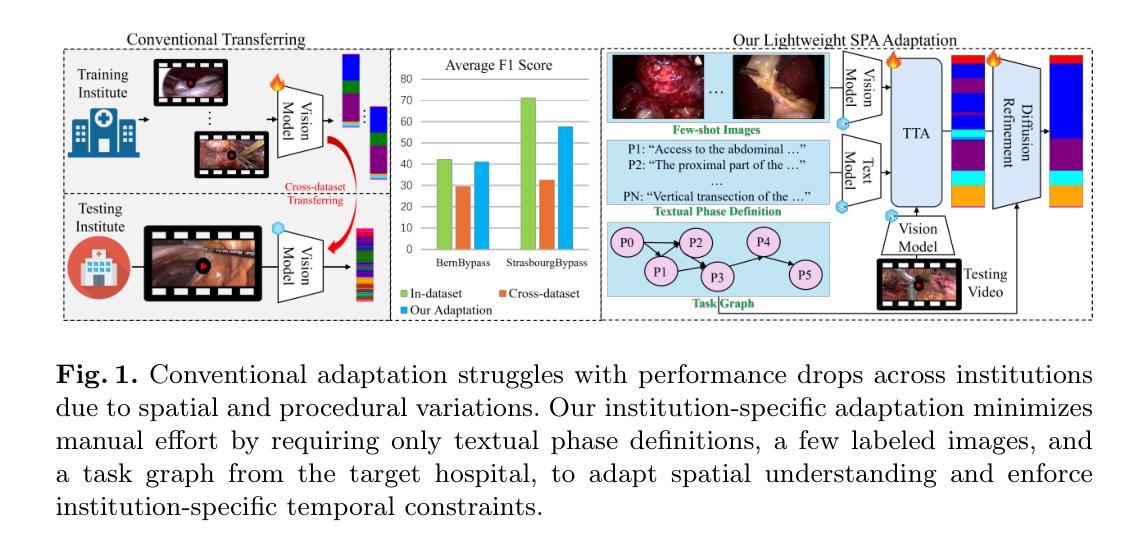
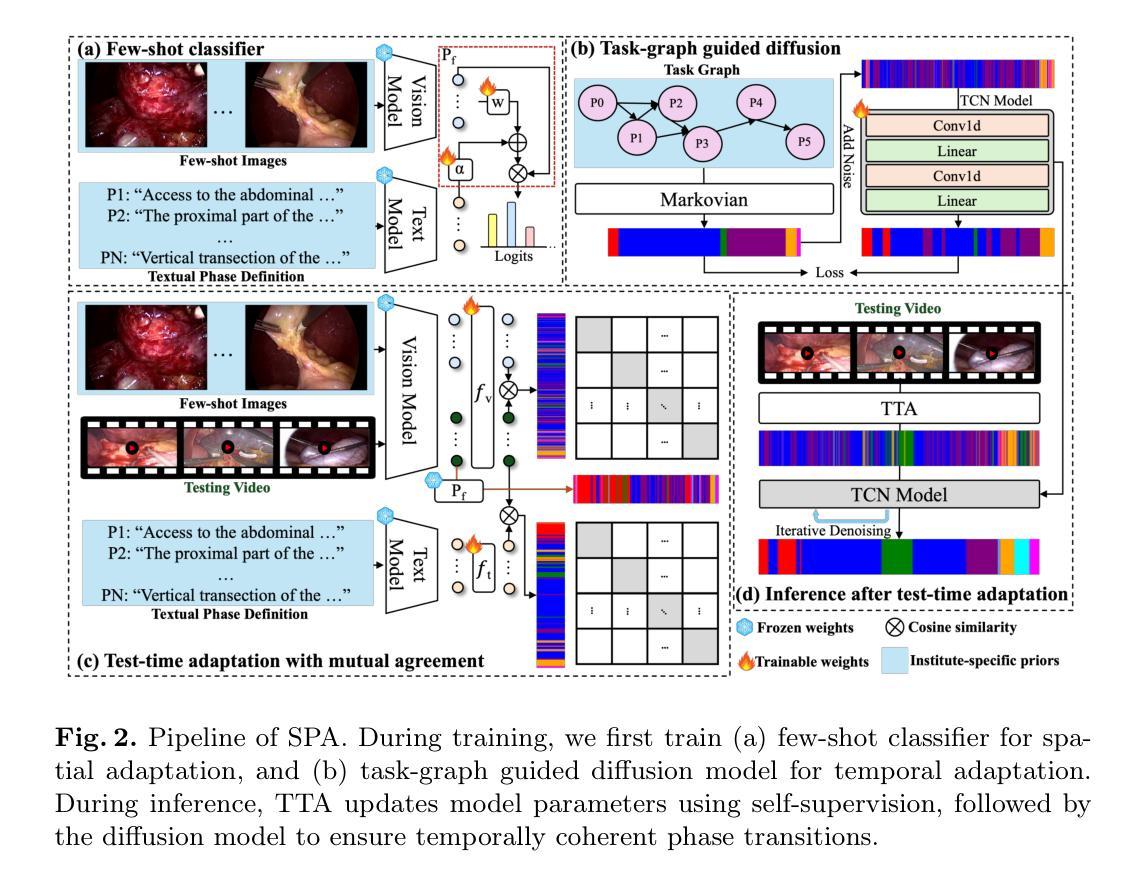
Recognizing Surgical Phases Anywhere: Few-Shot Test-time Adaptation and Task-graph Guided Refinement
Authors:Kun Yuan, Tingxuan Chen, Shi Li, Joel L. Lavanchy, Christian Heiliger, Ege Özsoy, Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Nassir Navab, Vinkle Srivastav, Hongliang Ren, Nicolas Padoy
The complexity and diversity of surgical workflows, driven by heterogeneous operating room settings, institutional protocols, and anatomical variability, present a significant challenge in developing generalizable models for cross-institutional and cross-procedural surgical understanding. While recent surgical foundation models pretrained on large-scale vision-language data offer promising transferability, their zero-shot performance remains constrained by domain shifts, limiting their utility in unseen surgical environments. To address this, we introduce Surgical Phase Anywhere (SPA), a lightweight framework for versatile surgical workflow understanding that adapts foundation models to institutional settings with minimal annotation. SPA leverages few-shot spatial adaptation to align multi-modal embeddings with institution-specific surgical scenes and phases. It also ensures temporal consistency through diffusion modeling, which encodes task-graph priors derived from institutional procedure protocols. Finally, SPA employs dynamic test-time adaptation, exploiting the mutual agreement between multi-modal phase prediction streams to adapt the model to a given test video in a self-supervised manner, enhancing the reliability under test-time distribution shifts. SPA is a lightweight adaptation framework, allowing hospitals to rapidly customize phase recognition models by defining phases in natural language text, annotating a few images with the phase labels, and providing a task graph defining phase transitions. The experimental results show that the SPA framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot surgical phase recognition across multiple institutions and procedures, even outperforming full-shot models with 32-shot labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA
手术流程的复杂性和多样性,受到手术室设置、机构协议和解剖结构差异的影响,在为跨机构和跨手术程序手术理解开发可推广模型时面临重大挑战。虽然最近基于大规模视觉语言数据的预训练手术基础模型表现出有希望的迁移能力,但它们的零样本性能仍受到领域差异的限制,在未见过的手术环境中效用有限。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了Surgical Phase Anywhere(SPA),这是一个用于通用手术流程理解的轻便框架,能够借助最少的标注来适应机构环境。SPA利用小样本空间适应,使多模式嵌入与特定机构的手术场景和阶段保持一致。它还通过扩散建模确保时间一致性,根据机构程序协议衍生任务图先验编码。此外,SPA采用动态测试时间自适应,利用多模式阶段预测流之间的相互协议,以自我监督的方式将模型适应给定的测试视频,在测试时间分布变化下提高可靠性。SPA是一个轻量级的适应框架,允许医院通过用自然语言文本定义阶段、对少数图像进行阶段标签注释以及提供定义阶段转换的任务图来快速定制阶段识别模型。实验结果表明,SPA框架在多个机构和程序中的小样本手术阶段识别中达到了最先进的性能,甚至在32个样本标记数据的情况下超过了全样本模型。代码可在https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对手术流程理解的一个新型框架——Surgical Phase Anywhere(SPA)。该框架旨在解决手术流程复杂性及多样性带来的挑战,通过少量标注数据,适应不同机构的手术环境。SPA利用少样本空间适应、扩散建模以及动态测试时间适应等技术,实现了机构特定手术场景和阶段的对齐、任务图先验的编码以及模型的自适应调整。实验结果显示,SPA框架在跨机构和跨手术程序的少样本手术阶段识别中实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Surgical workflows的复杂性和多样性给跨机构和跨手术程序的理解带来了挑战。
- 现有的预训练模型在未见过的手术环境中表现受限。
- SPA框架通过少样本空间适应,适应不同机构的手术环境。
- SPA利用扩散建模实现任务图先验的编码,确保时间一致性。
- SPA采用动态测试时间适应,提高模型在测试时分布变化下的可靠性。
- SPA框架允许医院通过自然语言文本定义阶段,通过少量图像标注,提供任务图定义阶段转换,实现快速定制阶段识别模型。
点此查看论文截图