⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
AI-Enhanced Pediatric Pneumonia Detection: A CNN-Based Approach Using Data Augmentation and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Authors:Abdul Manaf, Nimra Mughal
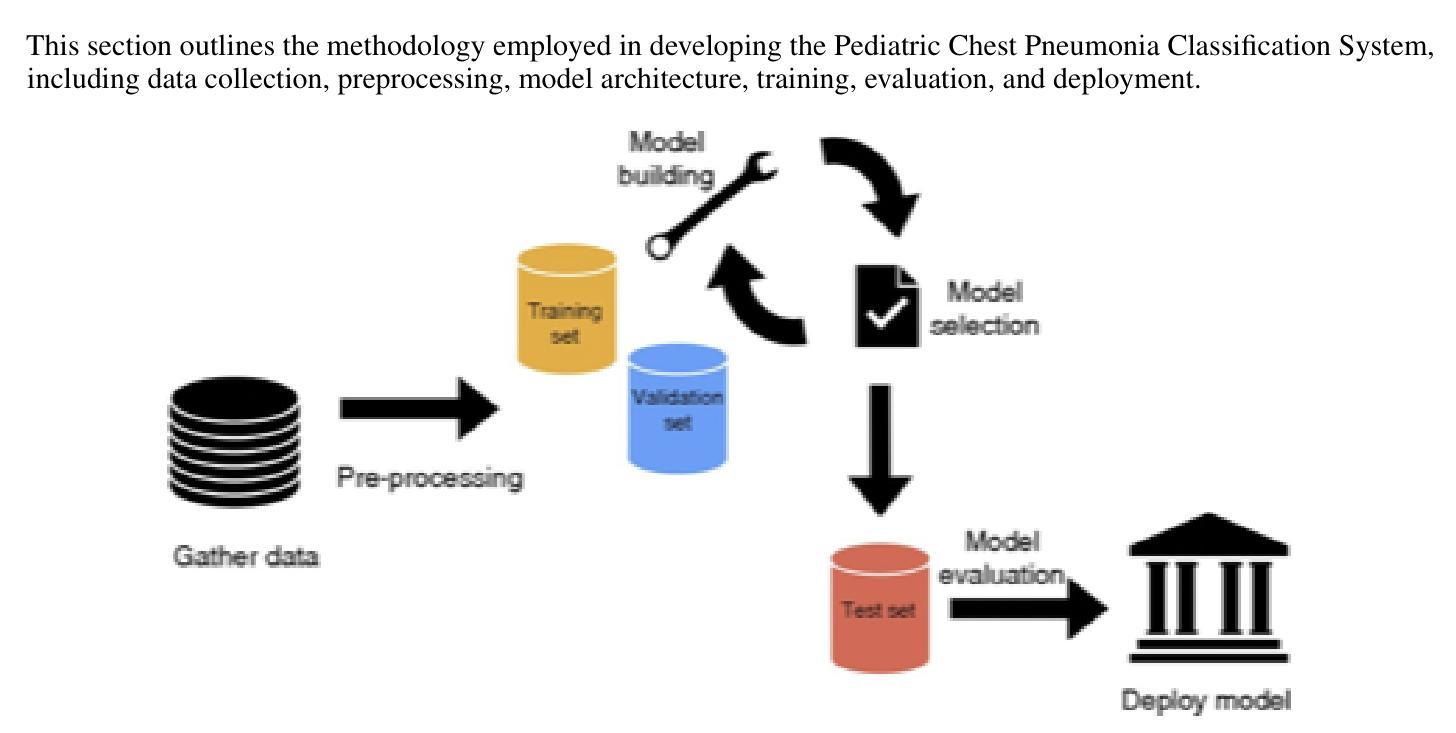
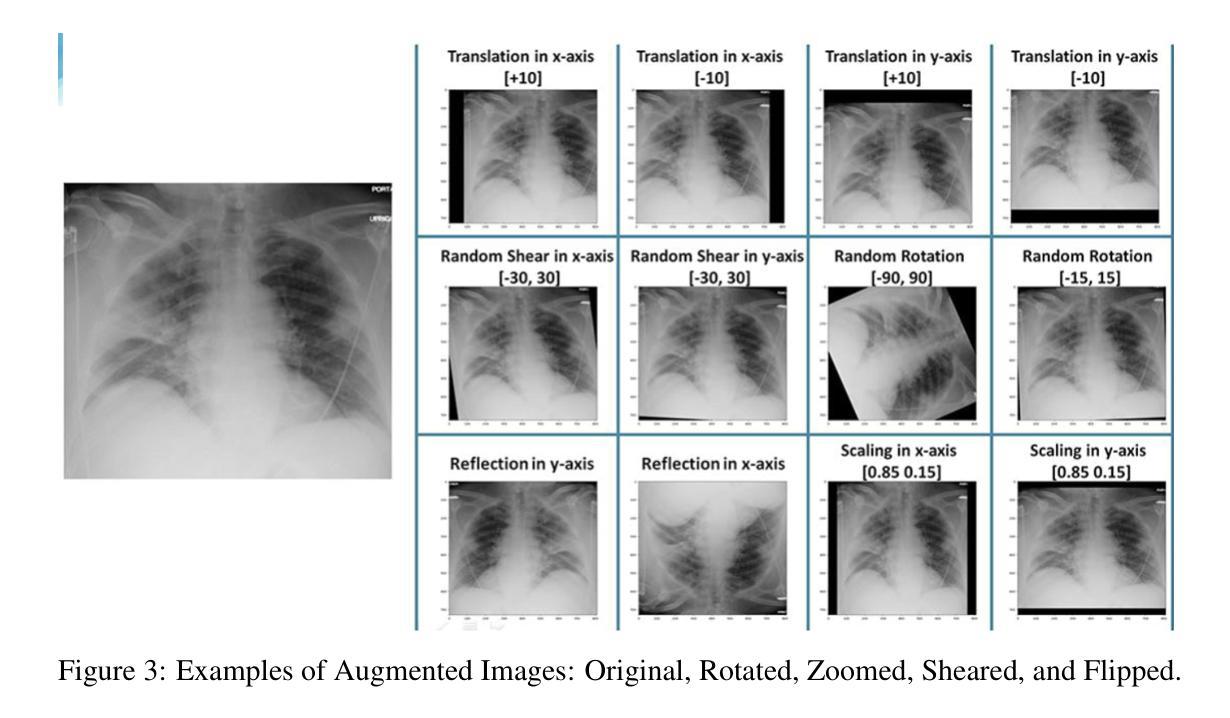
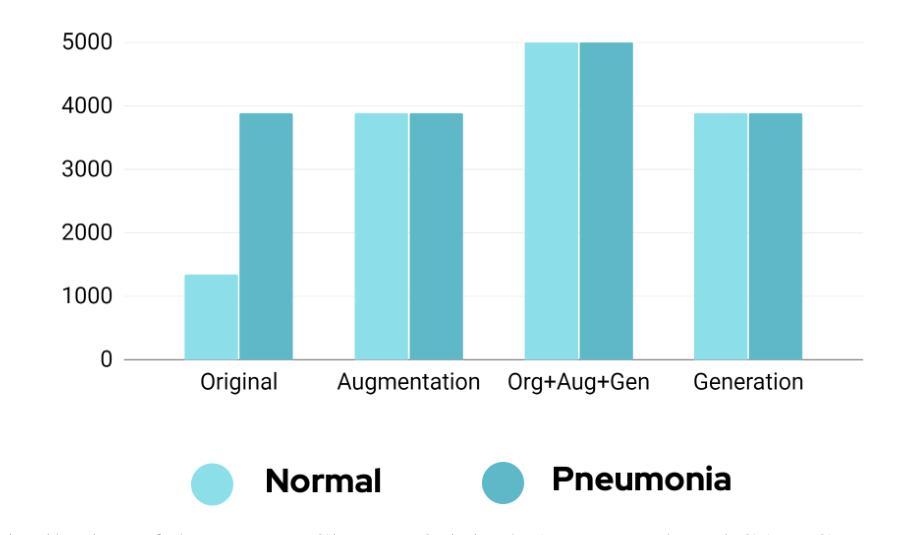
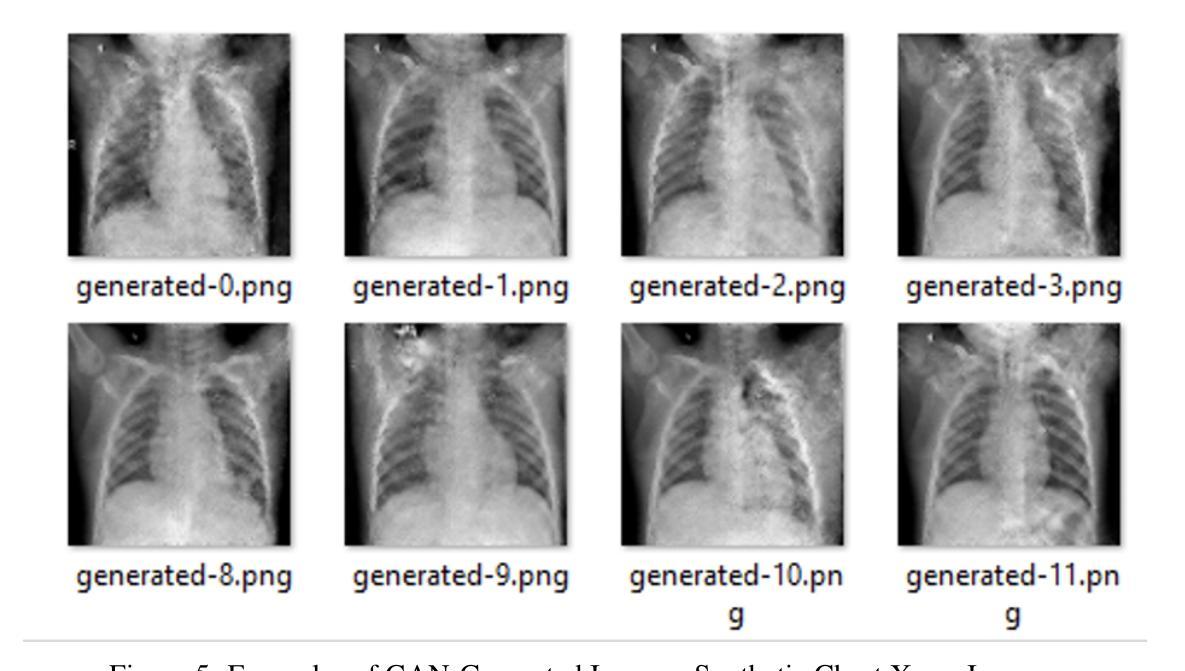
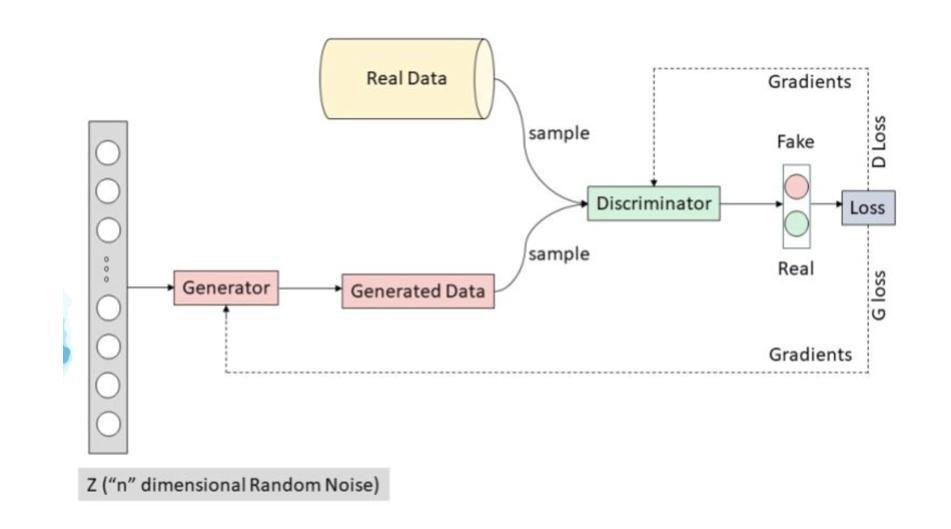
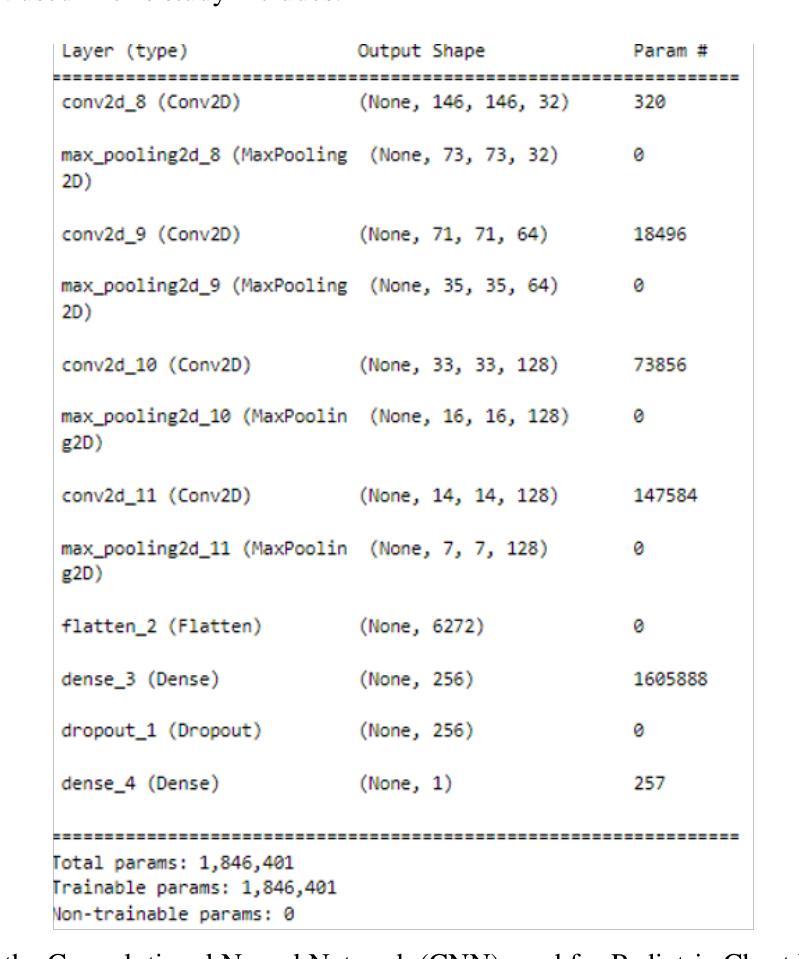
Pneumonia is a leading cause of mortality in children under five, requiring accurate chest X-ray diagnosis. This study presents a machine learning-based Pediatric Chest Pneumonia Classification System to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing pneumonia from chest X-ray images. The CNN-based model was trained on 5,863 labeled chest X-ray images from children aged 0-5 years from the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center. To address limited data, we applied augmentation techniques (rotation, zooming, shear, horizontal flipping) and employed GANs to generate synthetic images, addressing class imbalance. The system achieved optimal performance using combined original, augmented, and GAN-generated data, evaluated through accuracy and F1 score metrics. The final model was deployed via a Flask web application, enabling real-time classification with probability estimates. Results demonstrate the potential of deep learning and GANs in improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency for pediatric pneumonia classification, particularly valuable in resource-limited clinical settings https://github.com/AbdulManaf12/Pediatric-Chest-Pneumonia-Classification
肺炎是5岁以下儿童的主要致死原因,需要准确的胸部X射线诊断。本研究提出了一种基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,旨在帮助医疗专业人员根据胸部X射线图像诊断肺炎。该模型基于卷积神经网络(CNN),在广州妇女儿童医疗中心收集的5863张标记的胸部X射线图像上进行训练,图像来源于年龄在0-5岁的儿童。为了解决数据有限的问题,我们应用了增强技术(旋转、缩放、剪切、水平翻转),并采用了生成对抗网络(GANs)来生成合成图像,以解决类别不平衡的问题。该系统通过使用原始、增强和GAN生成的组合数据实现了最佳性能,通过准确度和F1分数指标进行了评估。最终模型通过Flask web应用程序部署,可实现带有概率估计的实时分类。结果表明,深度学习和GAN在提高儿童肺炎诊断的准确性和效率方面具有潜力,特别是在资源有限的临床环境中具有很高的价值。项目详情可通过以下链接访问:https://github.com/AbdulManaf12/Pediatric-Chest-Pneumonia-Classification
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,用于辅助医疗专业人员通过胸部X光图像诊断肺炎。研究使用卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,在广州妇女儿童医疗中心采集的5863张0-5岁儿童标记的胸部X光图像上进行训练。为解决数据有限和类别不平衡问题,研究应用了图像增强技术和生成对抗网络(GANs)生成合成图像。系统使用原始、增强和GAN生成的数据取得了最佳性能,通过准确率和F1分数进行评估。最后,模型通过Flask web应用程序部署,可实现实时分类与概率估计。研究证明了深度学习和GAN在提高儿童肺炎分类的诊断准确性和效率方面的潜力,尤其在资源有限的临床环境中价值显著。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究开发了一个基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,旨在提高医疗专业人员对肺炎的X光图像诊断能力。
- 使用卷积神经网络(CNN)模型进行训练,数据来源于广州妇女儿童医疗中心。
- 面对数据有限和类别不平衡问题,采用了图像增强技术和生成对抗网络(GANs)生成合成图像。
- 系统性能通过准确率和F1分数进行评估,使用原始、增强和GAN生成的数据达到最佳效果。
- 模型通过Flask web应用程序部署,支持实时分类,并提供概率估计。
- 研究表明,深度学习和GAN技术在提高儿童肺炎诊断的准确性和效率方面具有潜力。
- 该系统特别适用于资源有限的临床环境。
点此查看论文截图

Hybrid Quantum-Classical Generative Adversarial Networks with Transfer Learning
Authors:Asma Al-Othni, Saif Al-Kuwari, Mohammad Mahdi Nasiri Fatmehsari, Kamila Zaman, Ebrahim Ardeshir Larijani
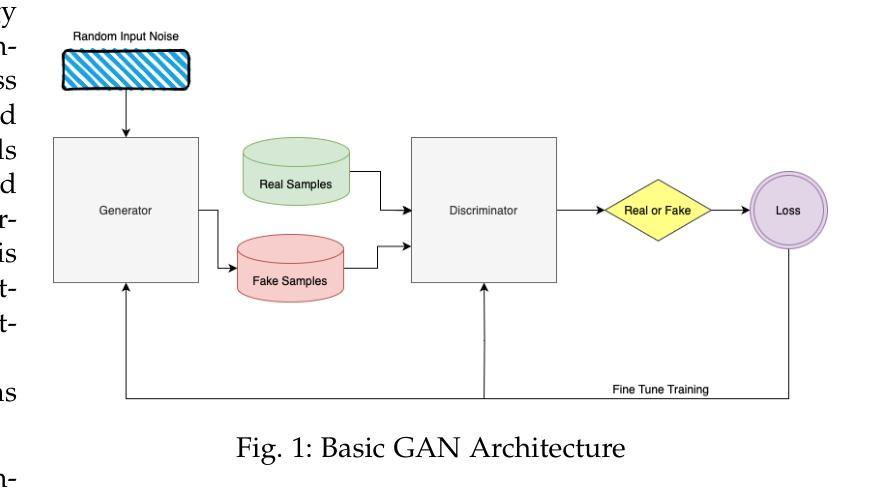
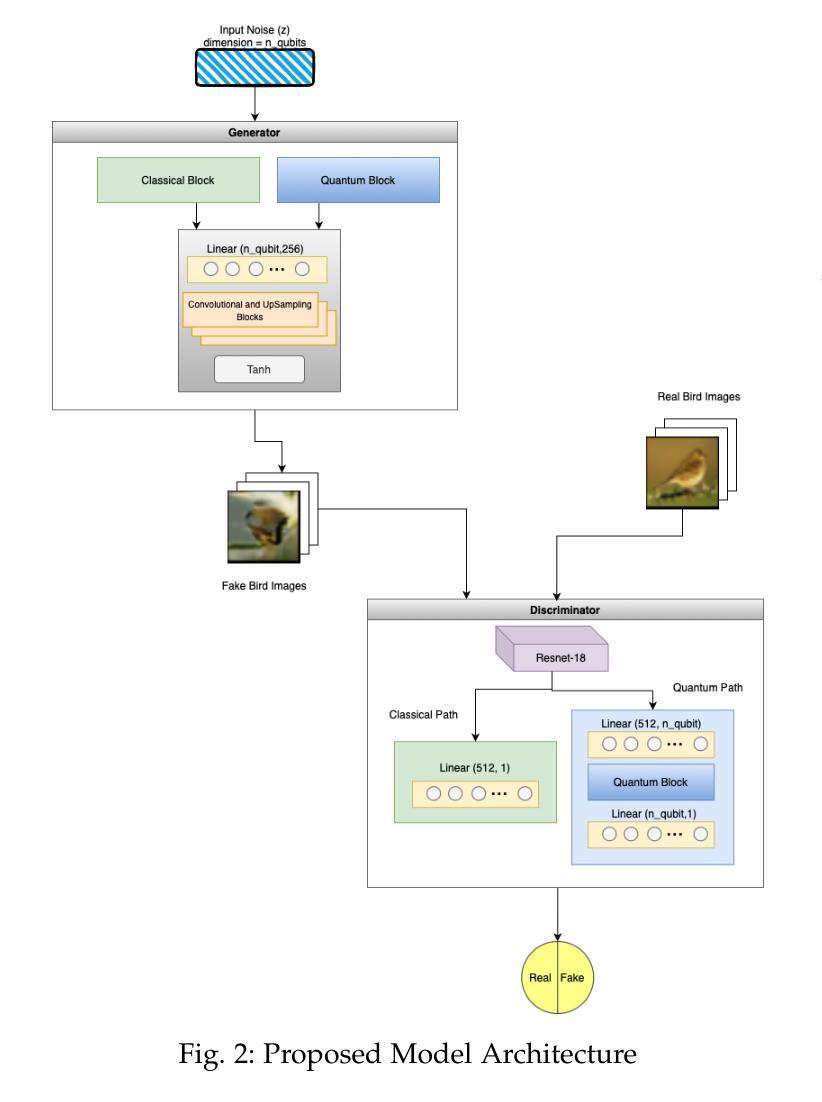
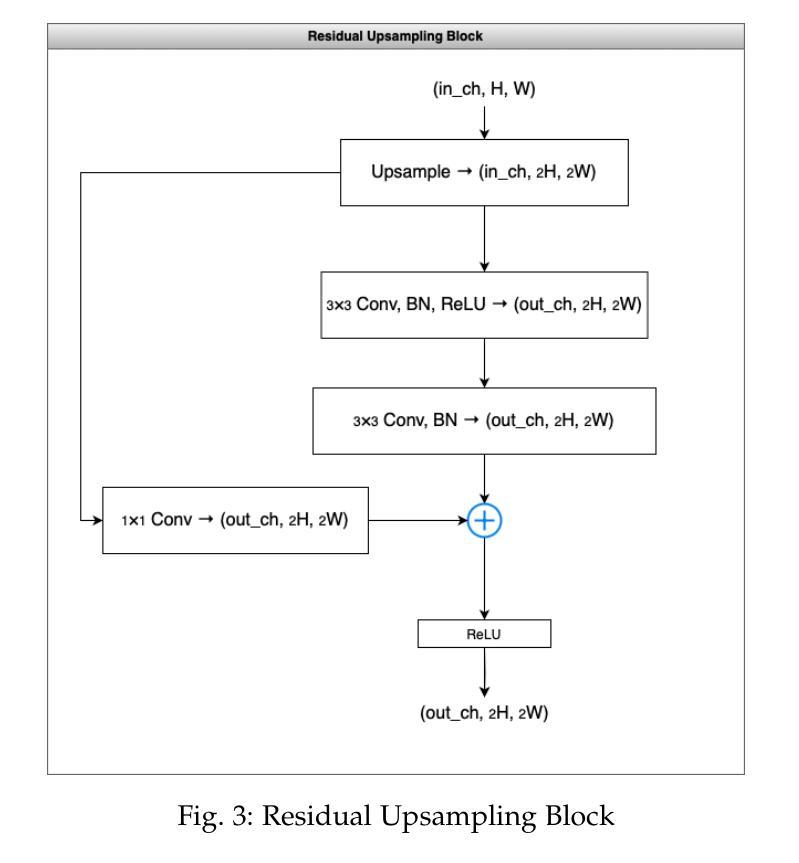
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have demonstrated immense potential in synthesizing diverse and high-fidelity images. However, critical questions remain unanswered regarding how quantum principles might best enhance their representational and computational capacity. In this paper, we investigate hybrid quantum-classical GAN architectures supplemented by transfer learning to systematically examine whether incorporating Variational Quantum Circuits (VQCs) into the generator, the discriminator, or both improves performance over a fully classical baseline. Our findings indicate that fully hybrid models, which incorporate VQCs in both the generator and the discriminator, consistently produce images of higher visual quality and achieve more favorable quantitative metrics compared to their fully classical counterparts. In particular, VQCs in the generator accelerate early feature learning, whereas those in the discriminator, despite exhibiting slower initial convergence, ultimately facilitate more refined synthetic outputs. Moreover, the model sustains near-comparable performance even when the dataset size is drastically reduced, suggesting that transfer learning and quantum enhancements mitigate the problem of data scarcity. Overall, the results underscore that carefully integrating quantum computing with classical adversarial training and pretrained feature extraction can considerably enrich GAN-based image synthesis. These insights open avenues for future work on higher-resolution tasks, alternative quantum circuit designs, and experimentation with emerging quantum hardware.
生成对抗网络(GANs)在合成多样化和高保真图像方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,关于如何利用量子原理最佳地增强其表征和计算能力的关键问题仍未得到解答。在本文中,我们研究了混合量子经典GAN架构,并结合迁移学习,以系统地检查将变分量子电路(VQCs)融入生成器、判别器或两者中是否能在完全经典的基线之上提高性能。我们的研究结果表明,完全混合模型(在生成器和判别器中均融入VQCs)始终能产生更高视觉质量的图像,并且在定量指标上表现出比其完全经典对应物更好的性能。特别是,生成器中的VQCs加速了早期特征学习,而尽管判别器中的VQCs初始收敛较慢,但最终产生了更精细的合成输出。此外,即使数据集大小大幅减少,该模型仍能保持相近的性能,这表明迁移学习和量子增强缓解了数据稀缺的问题。总体而言,结果强调,将量子计算与经典对抗训练和预先训练的特征提取相结合,可以极大地丰富基于GAN的图像合成。这些见解为未来的高分辨率任务、替代量子电路设计以及与新兴量子硬件的实验研究打开了途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 24 figures
Summary
本文探讨了如何将量子计算与生成对抗网络(GANs)结合,以提升图像合成的质量。研究通过混合量子经典GAN架构与迁移学习,系统研究了在生成器、判别器或两者中融入变分量子电路(VQCs)的效果。研究发现,完全混合模型(即在生成器和判别器中均融入VQCs)生成的图像视觉质量更高,定量指标更优越。VQCs在生成器中加速早期特征学习,而在判别器中的虽然初始收敛较慢,但最终有助于更精细的合成输出。此外,当数据集大小大幅减少时,该模型仍能保持相近的性能,表明迁移学习和量子增强缓解了数据稀缺的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了将量子计算与生成对抗网络(GANs)结合以提升图像合成的质量。
- 通过混合量子经典GAN架构与迁移学习,发现完全混合模型生成的图像质量更高。
- VQCs在生成器中能加速早期特征学习。
- VQCs在判别器中尽管初始收敛较慢,但最终有助于更精细的合成输出。
- 模型在数据集大小减少时仍能保持性能,表明量子增强和迁移学习有助于缓解数据稀缺问题。
- 整合量子计算与经典对抗训练及预训练特征提取能极大地丰富GAN的图像合成。
点此查看论文截图

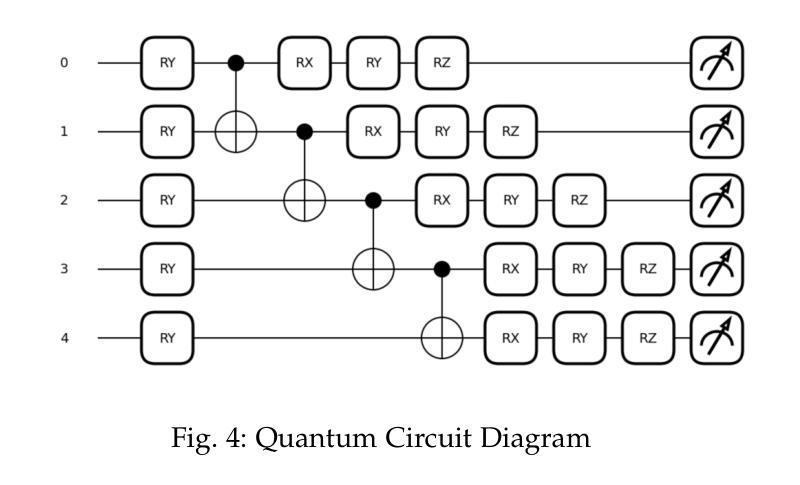
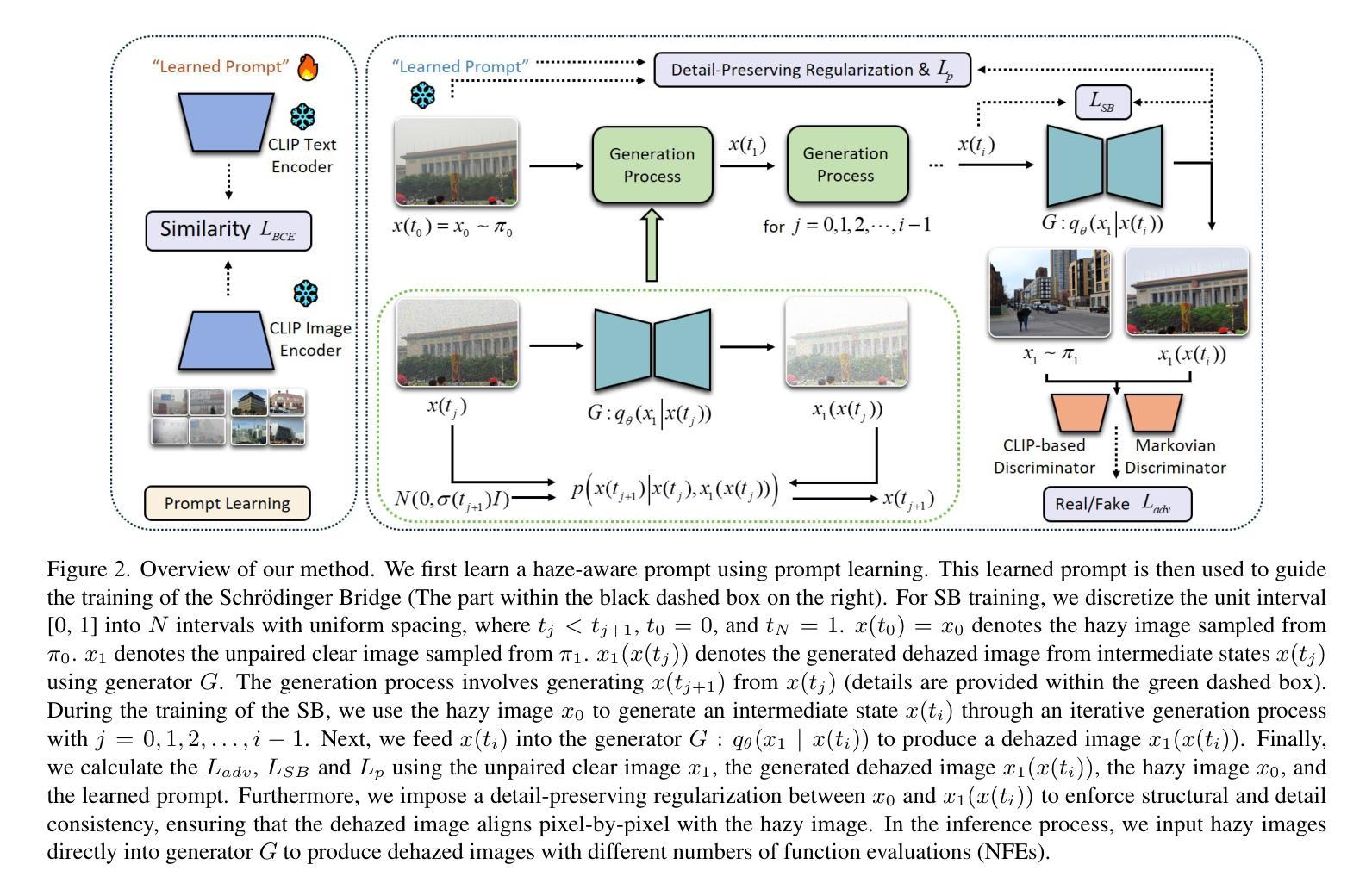
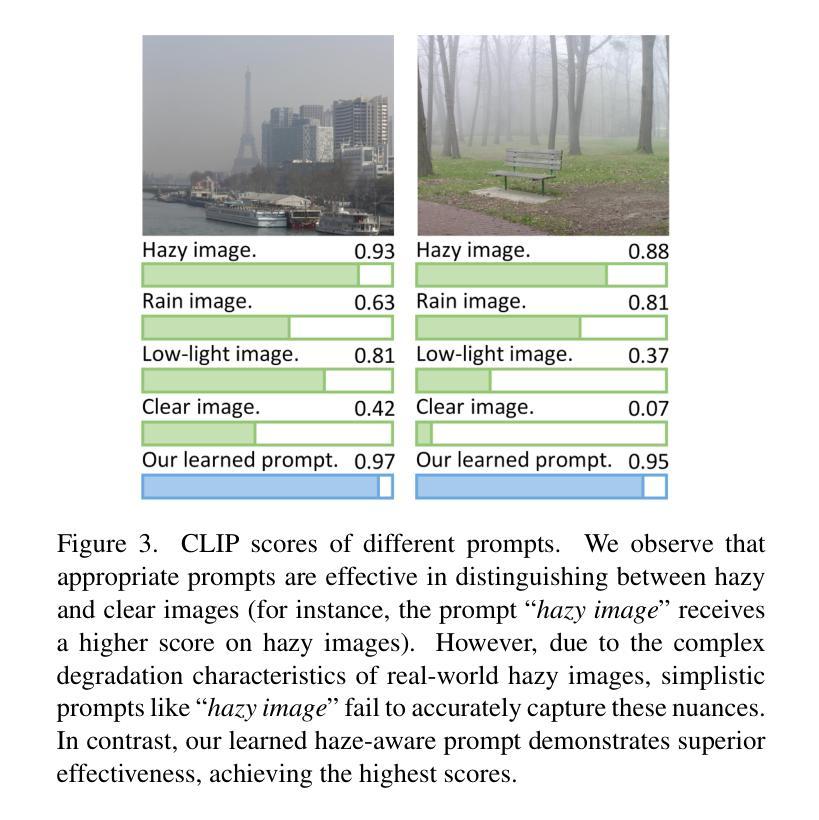
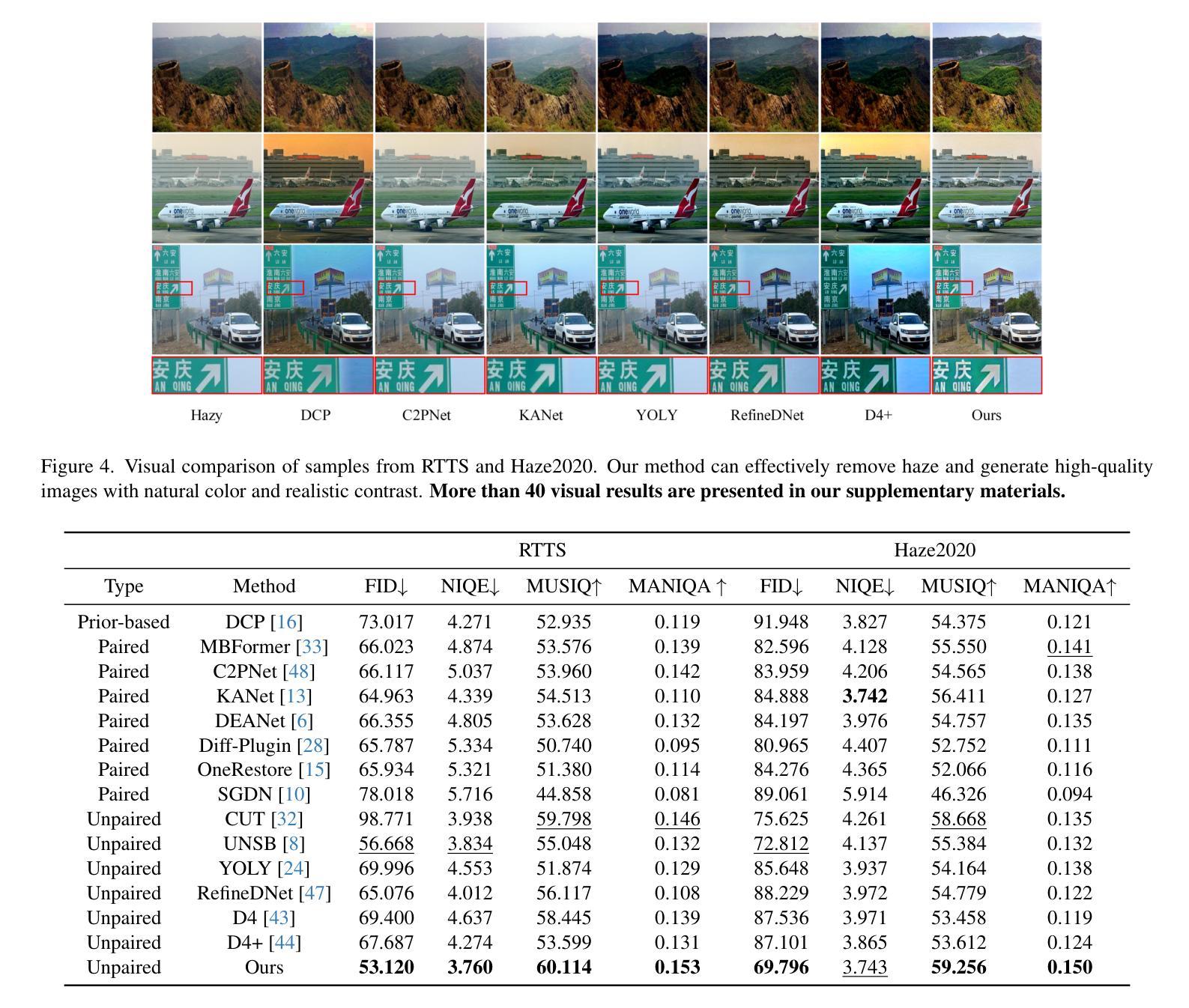
When Schrödinger Bridge Meets Real-World Image Dehazing with Unpaired Training
Authors:Yunwei Lan, Zhigao Cui, Xin Luo, Chang Liu, Nian Wang, Menglin Zhang, Yanzhao Su, Dong Liu
Recent advancements in unpaired dehazing, particularly those using GANs, show promising performance in processing real-world hazy images. However, these methods tend to face limitations due to the generator’s limited transport mapping capability, which hinders the full exploitation of their effectiveness in unpaired training paradigms. To address these challenges, we propose DehazeSB, a novel unpaired dehazing framework based on the Schr"odinger Bridge. By leveraging optimal transport (OT) theory, DehazeSB directly bridges the distributions between hazy and clear images. This enables optimal transport mappings from hazy to clear images in fewer steps, thereby generating high-quality results. To ensure the consistency of structural information and details in the restored images, we introduce detail-preserving regularization, which enforces pixel-level alignment between hazy inputs and dehazed outputs. Furthermore, we propose a novel prompt learning to leverage pre-trained CLIP models in distinguishing hazy images and clear ones, by learning a haze-aware vision-language alignment. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate our method’s superiority. Code: https://github.com/ywxjm/DehazeSB.
近期在无配对去雾技术的最新进展,特别是使用生成对抗网络(GANs)的方法,在处理真实世界中的雾霾图像时表现出有前景的性能。然而,这些方法往往面临由于生成器的有限传输映射能力而导致的局限性,这阻碍了它们在无配对训练范式中的充分有效性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于薛定谔桥的全新无配对去雾框架DehazeSB。通过利用最优传输(OT)理论,DehazeSB直接连接雾霾图像和清晰图像之间的分布。这能够实现从雾霾图像到清晰图像的最优传输映射,从而减少步骤,生成高质量的结果。为了确保恢复图像的结构信息和细节的一致性,我们引入了细节保留正则化,这强制要求在雾霾输入和去雾输出之间进行像素级对齐。此外,我们提出了一种新的提示学习,利用预训练的CLIP模型来区分雾霾图像和清晰的图像,通过学习对雾霾感知的视觉语言对齐。在多个真实世界数据集上的广泛实验证明了我们方法的优越性。代码地址:https://github.com/ywxjm/DehazeSB。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
GAN在配对去雾方面的最新进展展示了处理现实世界模糊图像的良好潜力,但仍面临生成器传输映射能力有限的挑战。我们提出一种基于Schrödinger Bridge的去雾框架DehazeSB,利用最优传输理论,在配对模糊的图像与清晰的图像之间直接建立桥梁,生成高质量的映射结果。我们还引入了一种细节保持的正则化方法,确保恢复图像的结构信息一致性。此外,我们提出了一种新的提示学习方法,利用预训练的CLIP模型区分模糊和清晰的图像,学习一个能识别雾的视觉语言对齐方法。在多真实世界数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法更加优秀。代码在GitHub上有提供。
Key Takeaways
- GAN在去雾领域展示潜力,但面临生成器传输映射能力有限的问题。
- DehazeSB基于Schrödinger Bridge去雾框架解决了上述问题,实现高质量的映射结果。
- 通过细节保持的正则化方法确保恢复图像的结构信息一致性。
- 利用预训练的CLIP模型进行提示学习,区分模糊和清晰的图像。
- 学习一个能识别雾的视觉语言对齐方法。
- 在多个真实世界数据集上的实验证明了该方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

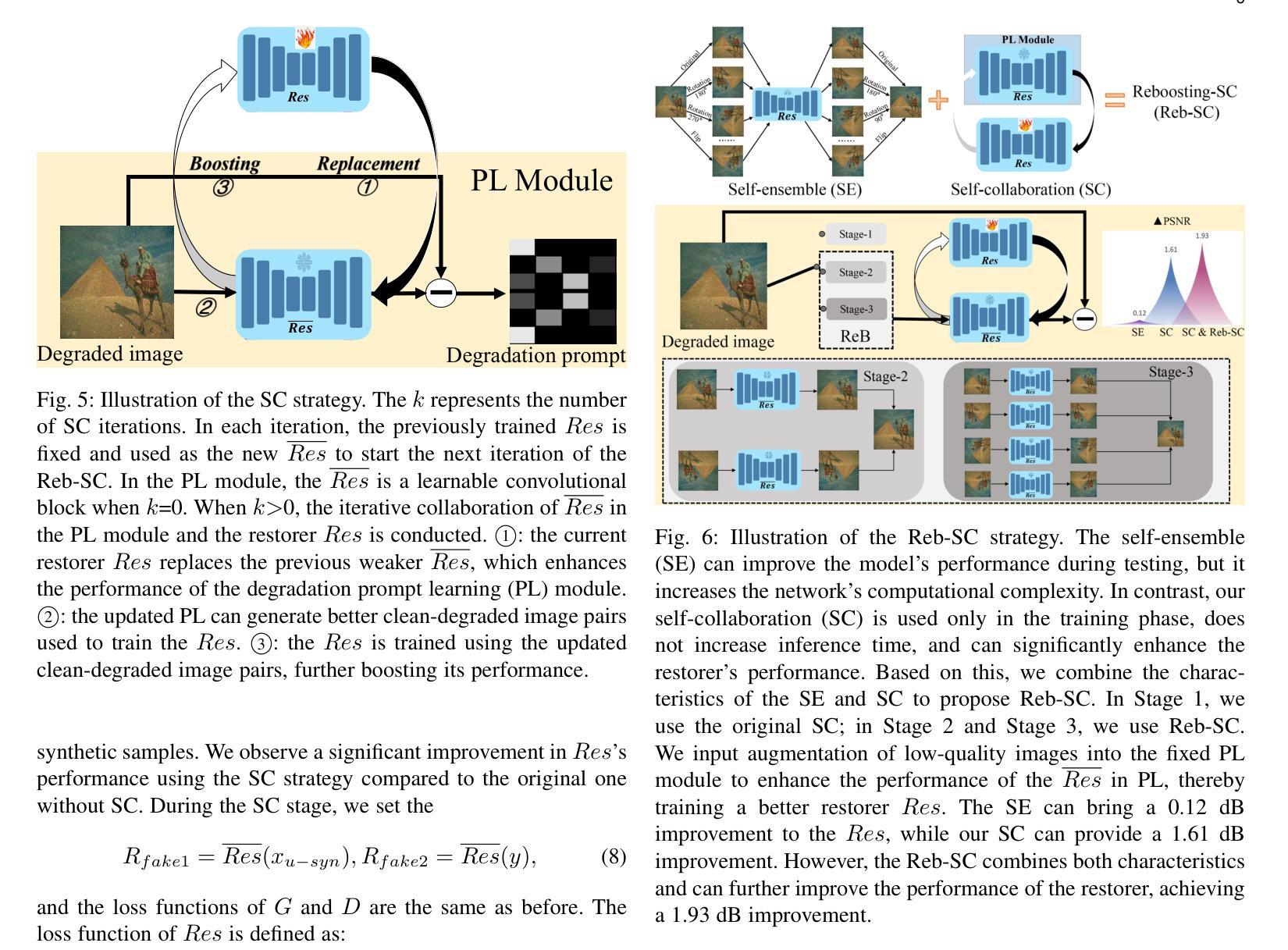
Re-boosting Self-Collaboration Parallel Prompt GAN for Unsupervised Image Restoration
Authors:Xin Lin, Yuyan Zhou, Jingtong Yue, Chao Ren, Kelvin C. K. Chan, Lu Qi, Ming-Hsuan Yang
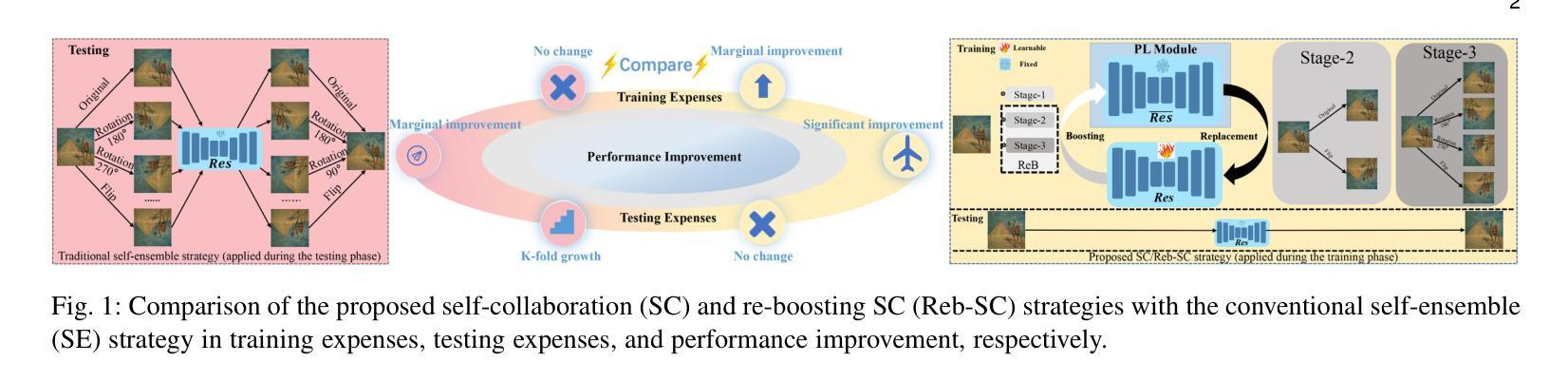
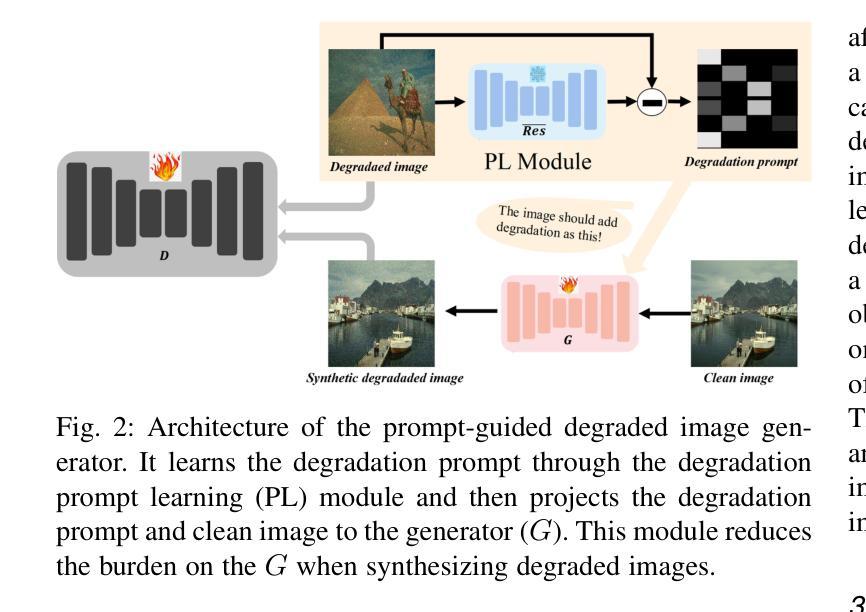
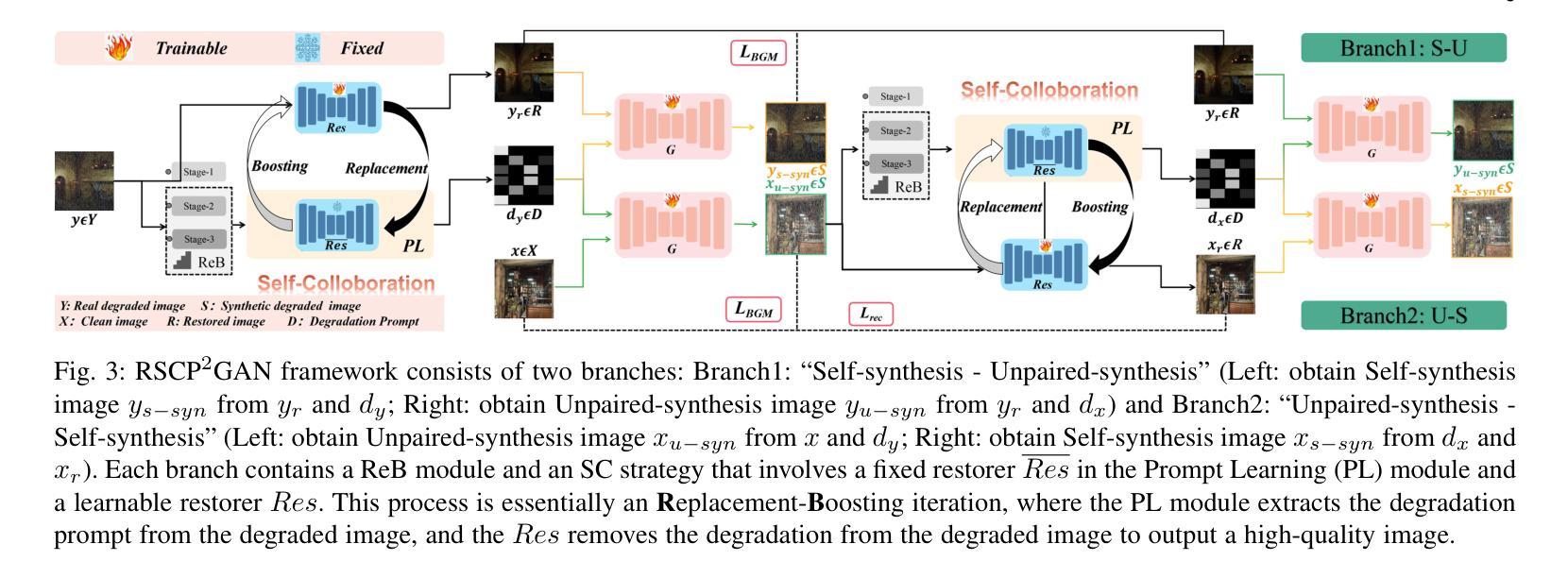
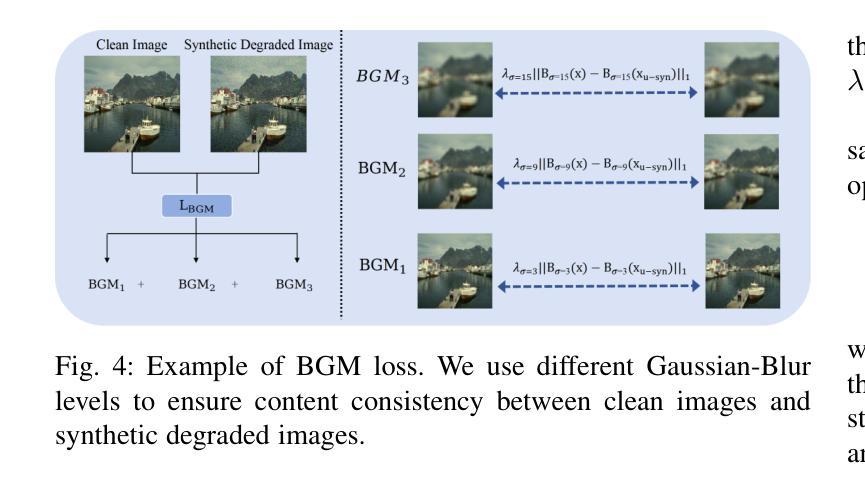
Unsupervised restoration approaches based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) offer a promising solution without requiring paired datasets. Yet, these GAN-based approaches struggle to surpass the performance of conventional unsupervised GAN-based frameworks without significantly modifying model structures or increasing the computational complexity. To address these issues, we propose a self-collaboration (SC) strategy for existing restoration models. This strategy utilizes information from the previous stage as feedback to guide subsequent stages, achieving significant performance improvement without increasing the framework’s inference complexity. The SC strategy comprises a prompt learning (PL) module and a restorer ($Res$). It iteratively replaces the previous less powerful fixed restorer $\overline{Res}$ in the PL module with a more powerful $Res$. The enhanced PL module generates better pseudo-degraded/clean image pairs, leading to a more powerful $Res$ for the next iteration. Our SC can significantly improve the $Res$’s performance by over 1.5 dB without adding extra parameters or computational complexity during inference. Meanwhile, existing self-ensemble (SE) and our SC strategies enhance the performance of pre-trained restorers from different perspectives. As SE increases computational complexity during inference, we propose a re-boosting module to the SC (Reb-SC) to improve the SC strategy further by incorporating SE into SC without increasing inference time. This approach further enhances the restorer’s performance by approximately 0.3 dB. Extensive experimental results on restoration tasks demonstrate that the proposed model performs favorably against existing state-of-the-art unsupervised restoration methods. Source code and trained models are publicly available at: https://github.com/linxin0/RSCP2GAN.
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的无监督修复方法提供了一种很有前景的解决方案,而无需配对数据集。然而,这些基于GAN的方法很难在不显著改变模型结构或增加计算复杂性的情况下超越传统基于GAN的无监督框架的性能。为了解决这些问题,我们为现有的修复模型提出了一种自协作(SC)策略。该策略利用前一阶段的信息作为反馈来指导后续阶段,在不影响框架推理复杂性的情况下实现了显著的性能提升。SC策略包括一个提示学习(PL)模块和一个修复器(Res)。它迭代地用更强大的Res替换PL模块中之前较弱的固定修复器Res。增强的PL模块生成更好的伪退化/清洁图像对,从而为下一次迭代产生更强大的Res。我们的SC可以在推理过程中不添加额外参数或计算复杂性的情况下,将Res的性能提高超过1.5分贝。同时,现有的自集成(SE)和我们的SC策略从不同角度提高了预训练修复器的性能。由于SE在推理过程中增加了计算复杂性,我们提出了对SC进行再增强(Reb-SC)的模块,通过将SE融入SC而无需增加推理时间,进一步改进了SC策略。这种方法将修复器的性能提高了大约0.3分贝。在修复任务上的大量实验结果证明,该模型的表现优于现有的先进无监督修复方法。源代码和训练模型可在以下网址公开获取:https://github.com/linxin0/RSCP2GAN。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE T-PAMI
Summary
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的无人监督修复方法在没有配对数据集的情况下提供了一种有前途的解决方案。为解决现有GAN方法性能不足的问题,本文提出了一种针对现有修复模型的自我协作(SC)策略。该策略利用前一阶段的信息作为反馈来引导后续阶段,在提高性能的同时,不增加框架的推理复杂性。通过迭代更新修复器,实现了显著的性能提升。此外,本文还提出了结合自我协作和自训练策略的Reb-SC方法,进一步提升了修复器的性能。实验结果证明了该模型在修复任务上的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 基于GAN的无人监督修复方法无需配对数据集,具有潜力。
- 现有GAN方法面临性能瓶颈,需改进模型结构或增加计算复杂性。
- 自我协作(SC)策略利用前一阶段信息来提高修复模型的性能,且不会增加推理复杂性。
- SC策略通过迭代更新修复器,实现了显著的性能提升。
- Reb-SC方法结合了SC和自训练策略,进一步提升了修复器的性能。
- 广泛实验结果表明,该模型在修复任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图