⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
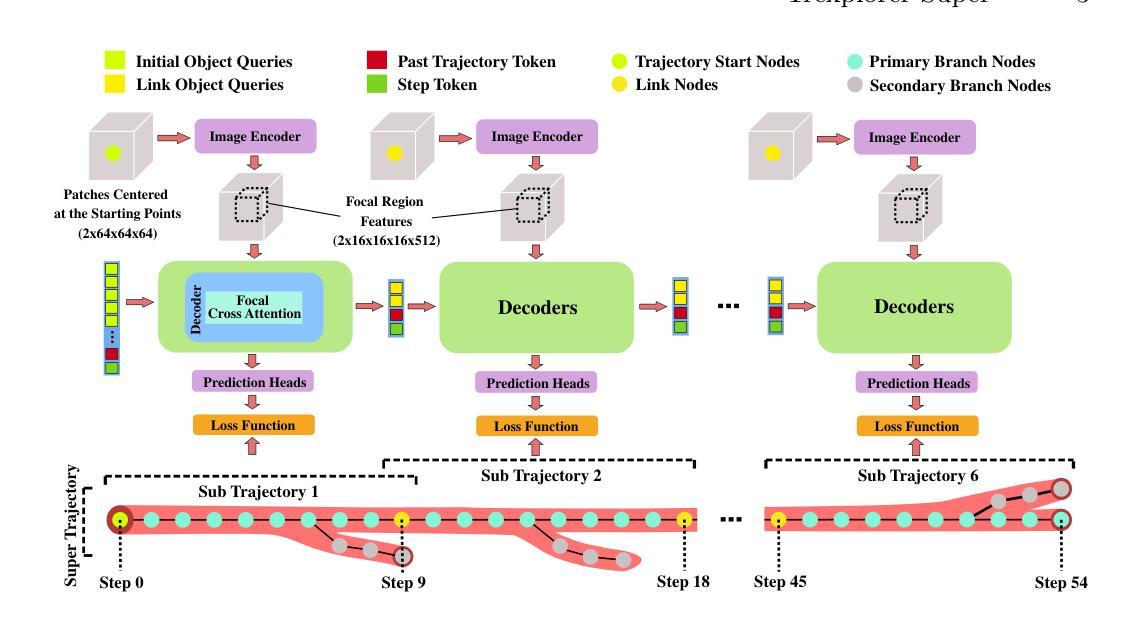
Trexplorer Super: Topologically Correct Centerline Tree Tracking of Tubular Objects in CT Volumes
Authors:Roman Naeem, David Hagerman, Jennifer Alvén, Lennart Svensson, Fredrik Kahl
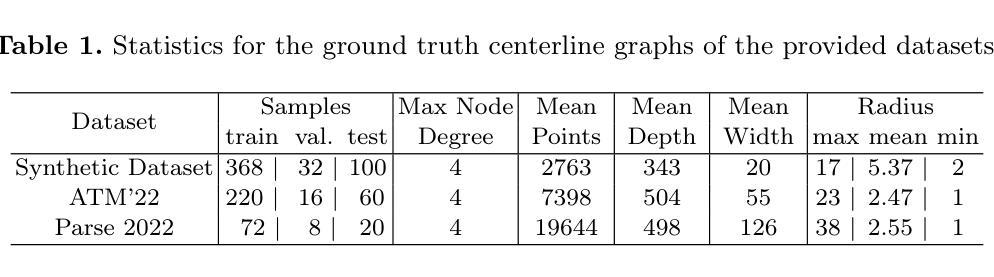
Tubular tree structures, such as blood vessels and airways, are essential in human anatomy and accurately tracking them while preserving their topology is crucial for various downstream tasks. Trexplorer is a recurrent model designed for centerline tracking in 3D medical images but it struggles with predicting duplicate branches and terminating tracking prematurely. To address these issues, we present Trexplorer Super, an enhanced version that notably improves performance through novel advancements. However, evaluating centerline tracking models is challenging due to the lack of public datasets. To enable thorough evaluation, we develop three centerline datasets, one synthetic and two real, each with increasing difficulty. Using these datasets, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) models and compare them with our approach. Trexplorer Super outperforms previous SOTA models on every dataset. Our results also highlight that strong performance on synthetic data does not necessarily translate to real datasets. The code and datasets are available at https://github.com/RomStriker/Trexplorer-Super.
管状树状结构,如血管和气道,在人类解剖学中至关重要,而准确追踪它们同时保持其拓扑结构对于各种下游任务至关重要。Trexplorer是一款为3D医学图像中心线追踪而设计的递归模型,但在预测重复分支以及过早终止追踪方面存在困难。为了解决这些问题,我们推出了Trexplorer Super,这是一个通过新颖的进步显著提高了性能的更高级版本。然而,由于缺少公共数据集,评估中心线追踪模型具有挑战性。为了实现全面评估,我们开发了三个中心线数据集,一个合成数据集和两个真实数据集,每个数据集的难度都在增加。使用这些数据集,我们对现有的最新(SOTA)模型进行了全面评估,并将它们与我们的方法进行了比较。Trexplorer Super在每个数据集上的表现都超过了之前的最新模型。我们的结果还强调,在合成数据上的出色表现并不一定适用于真实数据集。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/RomStriker/Trexplorer-Super找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted Version. Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Trexplorer Super,一个用于3D医学图像中心线追踪的递归模型。该模型解决了预测重复分支和过早终止追踪的问题,并在多个数据集上表现优异。为评估模型性能,本文开发了三组中心线数据集,并比较了最新模型与现有技术前沿模型的性能。结果表明,在真实数据集上,Trexplorer Super表现优于其他前沿模型,但在合成数据与真实数据之间的性能表现存在差异。
Key Takeaways
- Tubular tree structures在人体解剖学中占据重要地位,精确追踪这些结构并保持其拓扑结构对于下游任务至关重要。
- Trexplorer Super是专为3D医学图像中心线追踪设计的递归模型,解决了预测重复分支和过早终止追踪的问题。
- 评估中心线追踪模型具有挑战性,因为缺乏公共数据集。为此,研究团队开发了三个中心线数据集,包括一个合成数据集和两个真实数据集,难度逐渐增加。
- Trexplorer Super在所有数据集上的表现均优于现有最前沿模型。
- 研究结果显示,在合成数据上的良好表现并不一定能在真实数据集上取得同样效果。
- 公开的代码和数据集有助于促进对该领域的进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图

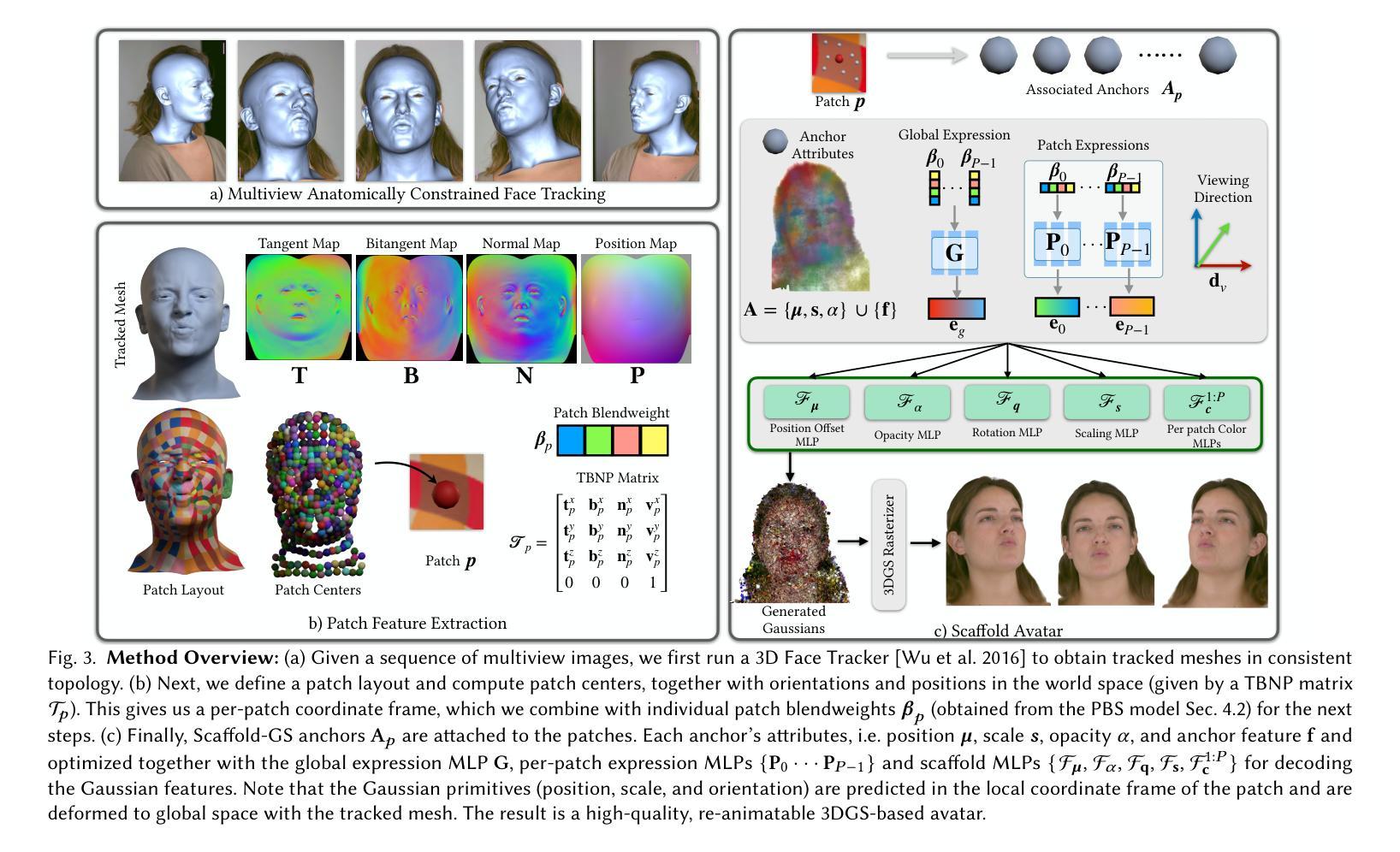
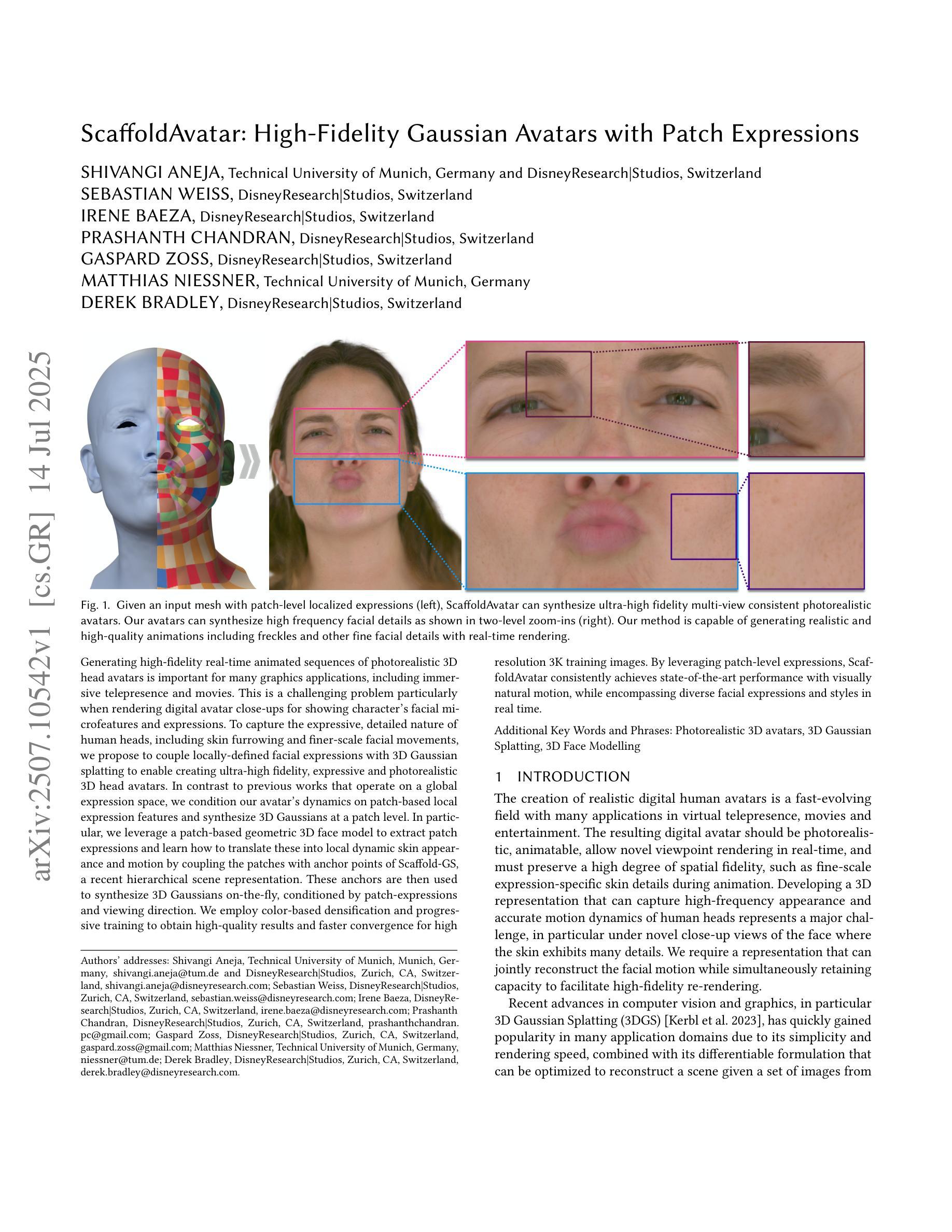
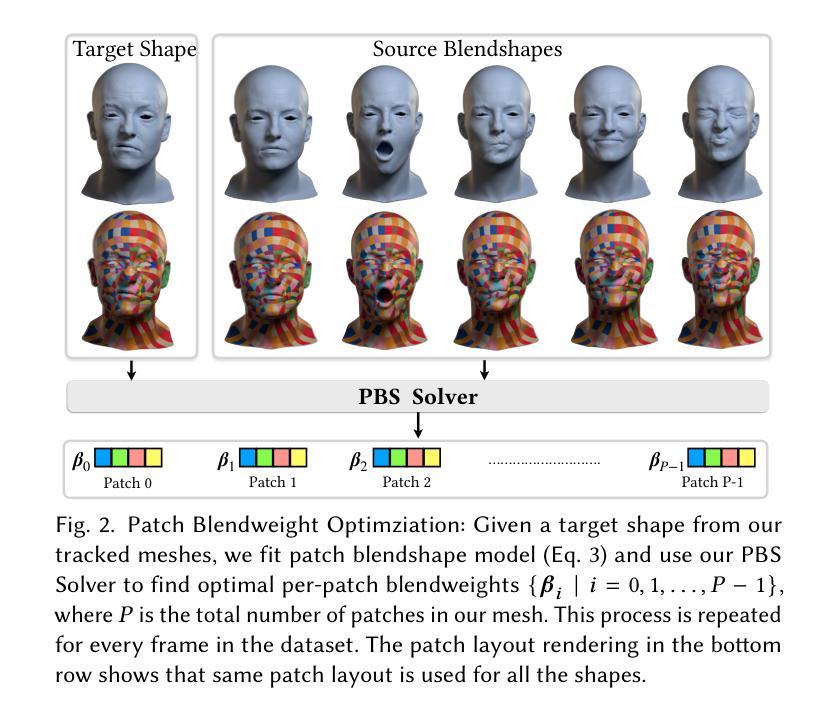
ScaffoldAvatar: High-Fidelity Gaussian Avatars with Patch Expressions
Authors:Shivangi Aneja, Sebastian Weiss, Irene Baeza, Prashanth Chandran, Gaspard Zoss, Matthias Nießner, Derek Bradley
Generating high-fidelity real-time animated sequences of photorealistic 3D head avatars is important for many graphics applications, including immersive telepresence and movies. This is a challenging problem particularly when rendering digital avatar close-ups for showing character’s facial microfeatures and expressions. To capture the expressive, detailed nature of human heads, including skin furrowing and finer-scale facial movements, we propose to couple locally-defined facial expressions with 3D Gaussian splatting to enable creating ultra-high fidelity, expressive and photorealistic 3D head avatars. In contrast to previous works that operate on a global expression space, we condition our avatar’s dynamics on patch-based local expression features and synthesize 3D Gaussians at a patch level. In particular, we leverage a patch-based geometric 3D face model to extract patch expressions and learn how to translate these into local dynamic skin appearance and motion by coupling the patches with anchor points of Scaffold-GS, a recent hierarchical scene representation. These anchors are then used to synthesize 3D Gaussians on-the-fly, conditioned by patch-expressions and viewing direction. We employ color-based densification and progressive training to obtain high-quality results and faster convergence for high resolution 3K training images. By leveraging patch-level expressions, ScaffoldAvatar consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance with visually natural motion, while encompassing diverse facial expressions and styles in real time.
生成高保真实时动画序列的光照真实三维头像对许多图形应用(包括沉浸式遥在和电影)至关重要。当渲染数字头像特写以显示角色的面部微观特征和表情时,这是一个特别具有挑战性的问题。为了捕捉人类头部的表情和细节特征,包括皮肤皱纹和更精细的面部动作,我们提议将局部定义的面部表情与三维高斯贴片技术相结合,以创建超高保真、表情丰富和光照真实的三维头像。与之前在全局表情空间上操作的工作不同,我们将头像的动态特性建立在基于补丁的局部表情特征上,并在补丁级别上合成三维高斯分布。特别是,我们利用基于补丁的三维几何面部模型来提取补丁表情,并学习如何将它们转化为局部动态皮肤外观和运动,通过将补丁与Scaffold-GS的锚点相结合,这是一种最新的层次场景表示。然后,这些锚点被用来根据补丁表情和观看方向实时合成三维高斯分布。我们采用基于颜色的稠密化和渐进式训练,以获得高质量的结果和更快的收敛速度,适用于高分辨率的3K训练图像。通过利用补丁级别的表情,ScaffoldAvatar始终实现最先进的性能,具有视觉上的自然运动,同时实时包含各种面部表情和风格。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF (SIGGRAPH 2025) Paper Video: https://youtu.be/VyWkgsGdbkk Project Page: https://shivangi-aneja.github.io/projects/scaffoldavatar/
Summary
本文提出一种基于局部定义面部表情与3D高斯喷绘技术的方法,用于生成高保真、实时、逼真的3D头像动画序列。该方法以斑块为基础,通过斑块表情特征控制头像动态,合成3D高斯分布。该方法实现了高保真、生动的头像动画,并支持实时渲染多种面部表情和风格。
Key Takeaways
- 生成高保真实时动画的3D头像序列对于图形应用至关重要,尤其是在展示角色的面部细微特征和表情时。
- 局部定义的面部表情与3D高斯喷绘技术的结合,使创建超高保真、生动逼真的3D头像成为可能。
- 与全局表情空间的工作不同,该方法的头像动态是基于斑块局部表情特征进行控制的。
- 利用基于斑块的几何3D面部模型提取斑块表情,并学习如何将这些表情翻译为局部动态皮肤外观和运动。
- 通过与Scaffold-GS的锚点结合,合成3D高斯分布,由斑块表情和观看方向决定。
- 采用基于颜色的加密和渐进训练,获得高质量结果,加快高分辨率3K训练图像的收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图

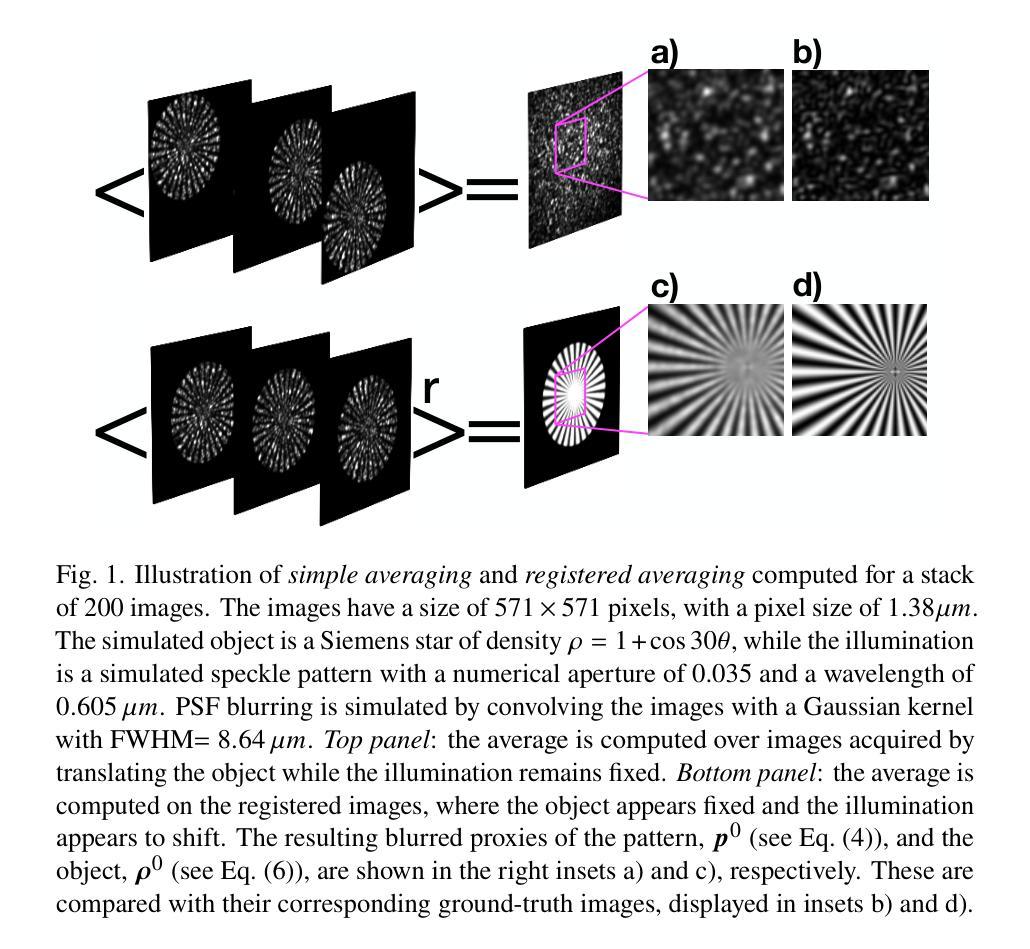
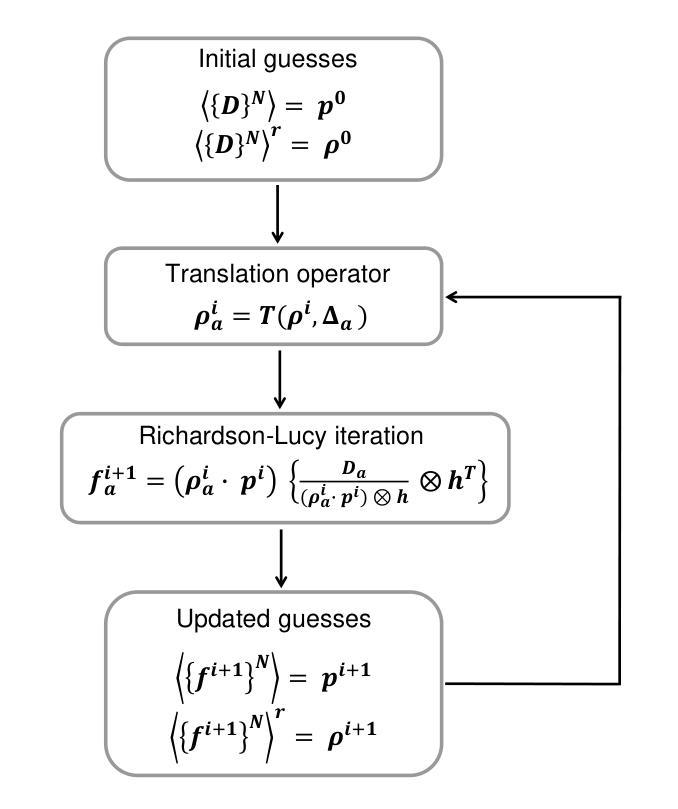
Translation-based structured illumination microscopy via generalized Richardson-Lucy method
Authors:Valentina Capalbo, Damiana Battaglini, Marialaura Petroni, Giancarlo Ruocco, Marco Leonetti
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) can achieve a $2\times$ resolution enhancement beyond the classical diffraction limit by employing illumination translations with respect to the object. This method has also been successfully implemented in a blind'' configuration, i.e., with unknown illumination patterns, allowing for more relaxed constraints on the control of illumination delivery. Here, we present a similar approach using a novel super-resolution algorithm that employs a generalized version of the popular Richardson-Lucy algorithm, alongside an optimized and customized optical setup. Both numerical and experimental validations demonstrate that our technique exhibits high noise resilience. Moreover, by implementing random translations instead of ordered’’ ones, noise-related artifacts are reduced. These advancements enable wide-field super-resolved imaging with significantly reduced optical complexity.
结构照明显微镜(SIM)通过相对于物体的照明转换实现了超过经典衍射极限的$2\times$分辨率增强。此方法还成功地在“盲”配置中实现,即具有未知的照明模式,使得对照明传递的控制更加宽松。在这里,我们提出了一种类似的方法,使用一种新型超分辨率算法,该算法结合了流行的Richardson-Lucy算法的通用版本以及优化和定制的光学装置。数值和实验验证均表明我们的技术具有很高的抗噪声性。此外,通过实施随机转换而不是“有序”转换,减少了与噪声相关的伪影。这些进步实现了具有显著降低光学复杂性的宽场超分辨率成像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, including Appendix A and B
Summary
结构化照明显微镜(SIM)通过相对于物体进行照明转换,实现了超越经典衍射极限的2倍分辨率提升。此方法已成功应用于“盲”配置,即未知照明模式,对照明传递的控制要求较为宽松。本文介绍了一种采用通用Richardson-Lucy算法的新超分辨率算法,并搭配优化定制的光学装置。数值和实验验证均显示,该技术具有良好的抗噪性。通过实施随机转换而非“有序”转换,减少了与噪声相关的伪影。这些进步使得具有显著降低光学复杂性的宽场超分辨率成像成为可能。
Key Takeaways
- 结构化照明显微镜(SIM)能通过照明转换实现超越衍射极限的2倍分辨率提升。
- SIM方法已成功在“盲”配置下实施,即使用未知照明模式,降低对照明传递控制的要求。
- 介绍了一种新的超分辨率算法,该算法基于通用的Richardson-Lucy算法,并进行了优化。
- 搭配优化定制的光学装置,该算法实现了宽场超分辨率成像。
- 技术具有良好的抗噪性,并通过实施随机转换来减少噪声相关的伪影。
- 与传统方法相比,该技术在光学复杂性方面有明显的降低。
点此查看论文截图

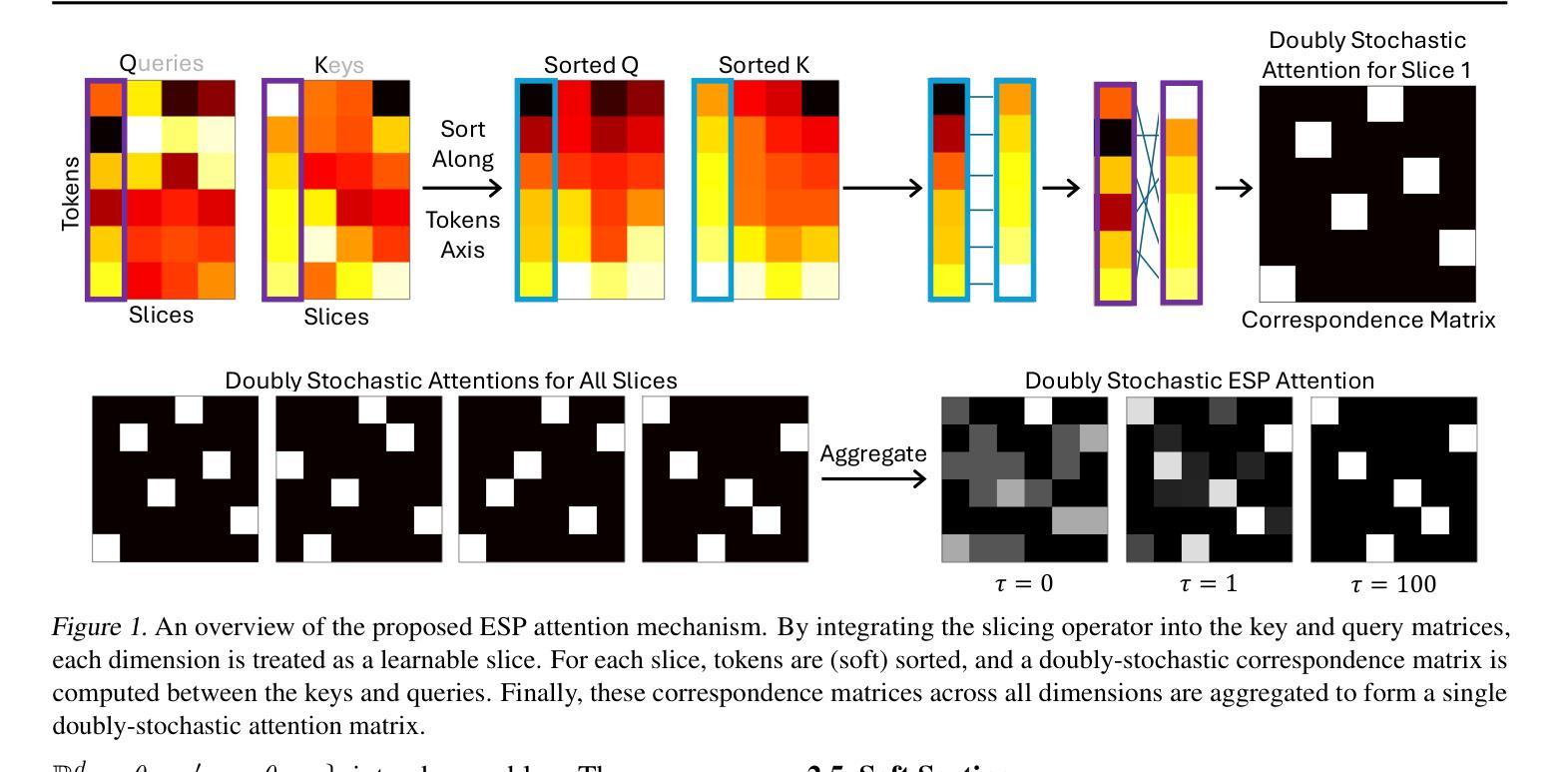
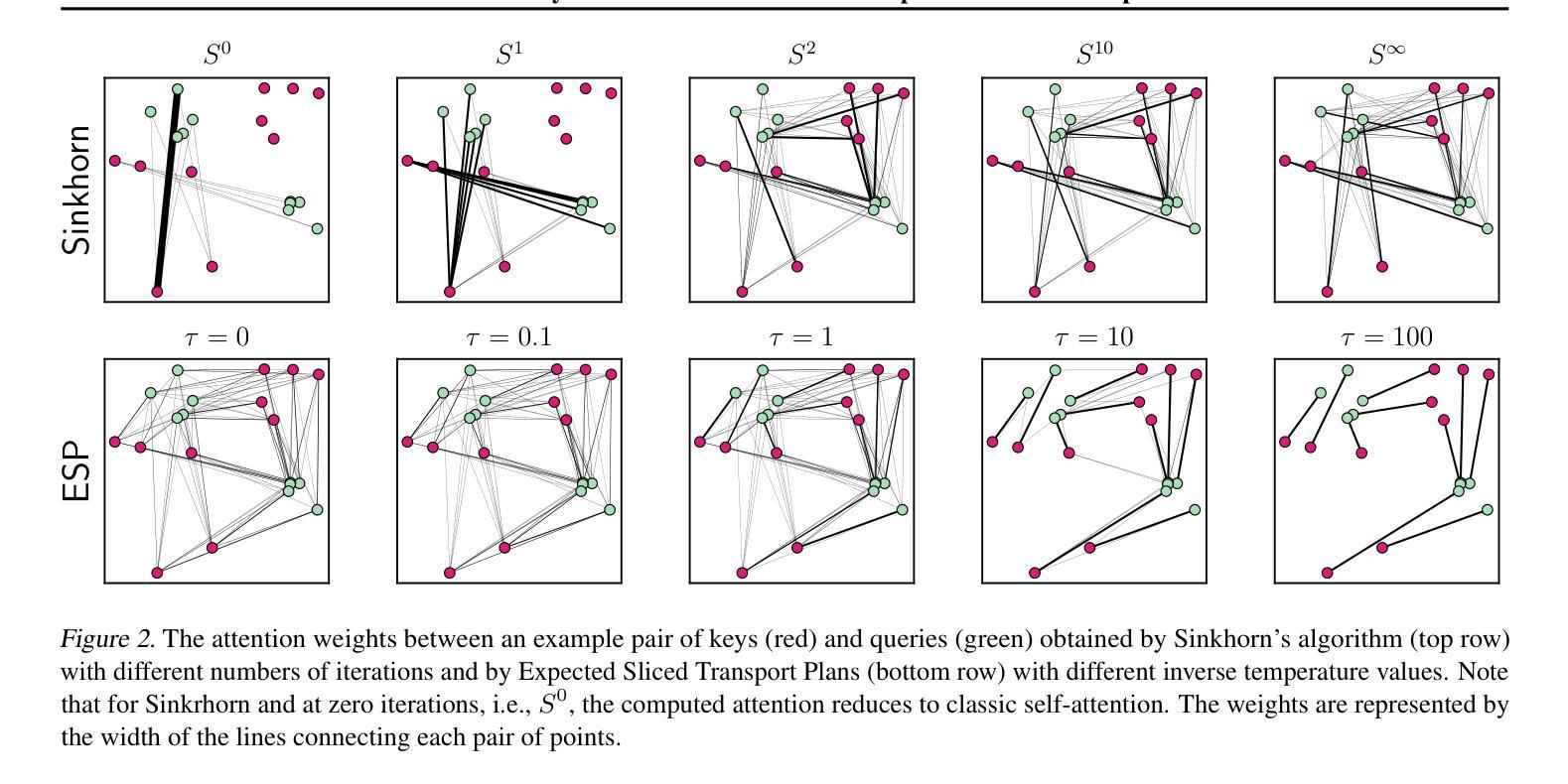
ESPFormer: Doubly-Stochastic Attention with Expected Sliced Transport Plans
Authors:Ashkan Shahbazi, Elaheh Akbari, Darian Salehi, Xinran Liu, Navid Naderializadeh, Soheil Kolouri
While self-attention has been instrumental in the success of Transformers, it can lead to over-concentration on a few tokens during training, resulting in suboptimal information flow. Enforcing doubly-stochastic constraints in attention matrices has been shown to improve structure and balance in attention distributions. However, existing methods rely on iterative Sinkhorn normalization, which is computationally costly. In this paper, we introduce a novel, fully parallelizable doubly-stochastic attention mechanism based on sliced optimal transport, leveraging Expected Sliced Transport Plans (ESP). Unlike prior approaches, our method enforces doubly stochasticity without iterative Sinkhorn normalization, significantly enhancing efficiency. To ensure differentiability, we incorporate a temperature-based soft sorting technique, enabling seamless integration into deep learning models. Experiments across multiple benchmark datasets, including image classification, point cloud classification, sentiment analysis, and neural machine translation, demonstrate that our enhanced attention regularization consistently improves performance across diverse applications. Our implementation code can be found at https://github.com/dariansal/ESPFormer.
虽然自注意力机制在Transformer的成功中发挥了关键作用,但它也可能导致训练过程中对某些令牌的过度集中,从而导致信息流动不佳。在注意力矩阵中实施双重随机约束已被证明可以改善结构和平衡注意力分布。然而,现有方法依赖于迭代式的Sinkhorn归一化,这计算成本高昂。在本文中,我们介绍了一种基于切片最优传输的新型全并行化双重随机注意力机制,利用预期切片传输计划(ESP)。与以前的方法不同,我们的方法在不进行迭代Sinkhorn归一化的情况下强制执行双重随机性,从而大大提高了效率。为了确保可微性,我们采用基于温度的软排序技术,能够无缝地集成到深度学习模型中。在多个基准数据集上的实验,包括图像分类、点云分类、情感分析和神经机器翻译,表明我们增强的注意力正则化在多种应用中始终提高了性能。我们的实现代码可在https://github.com/dariansal/ESPFormer中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于切片最优传输计划的全新并行化双随机注意力机制,该方法利用期望切片传输计划(ESP),在不使用迭代Sinkhorn归一化的前提下,实现了注意力分布的双随机性强化,显著提升了效率。同时,通过温度排序技术确保可微性,并能无缝融入深度学习模型。实验证明,该方法在不同应用领域的性能提升显著。
Key Takeaways
- 自注意力机制虽对Transformer的成功至关重要,但可能导致训练时过度关注某些标记,影响信息流的优化。
- 双随机约束在注意力矩阵中的应用已被证明能改善结构和平衡。
- 现有方法依赖计算成本较高的迭代Sinkhorn归一化。
- 本文提出了一种基于切片最优传输的全新双随机注意力机制,无需迭代Sinkhorn归一化,显著提升效率。
- 通过温度排序技术确保方法的可微性,能无缝融入深度学习模型。
- 实验证明该方法在图像分类、点云分类、情感分析和神经机器翻译等多个基准数据集上的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

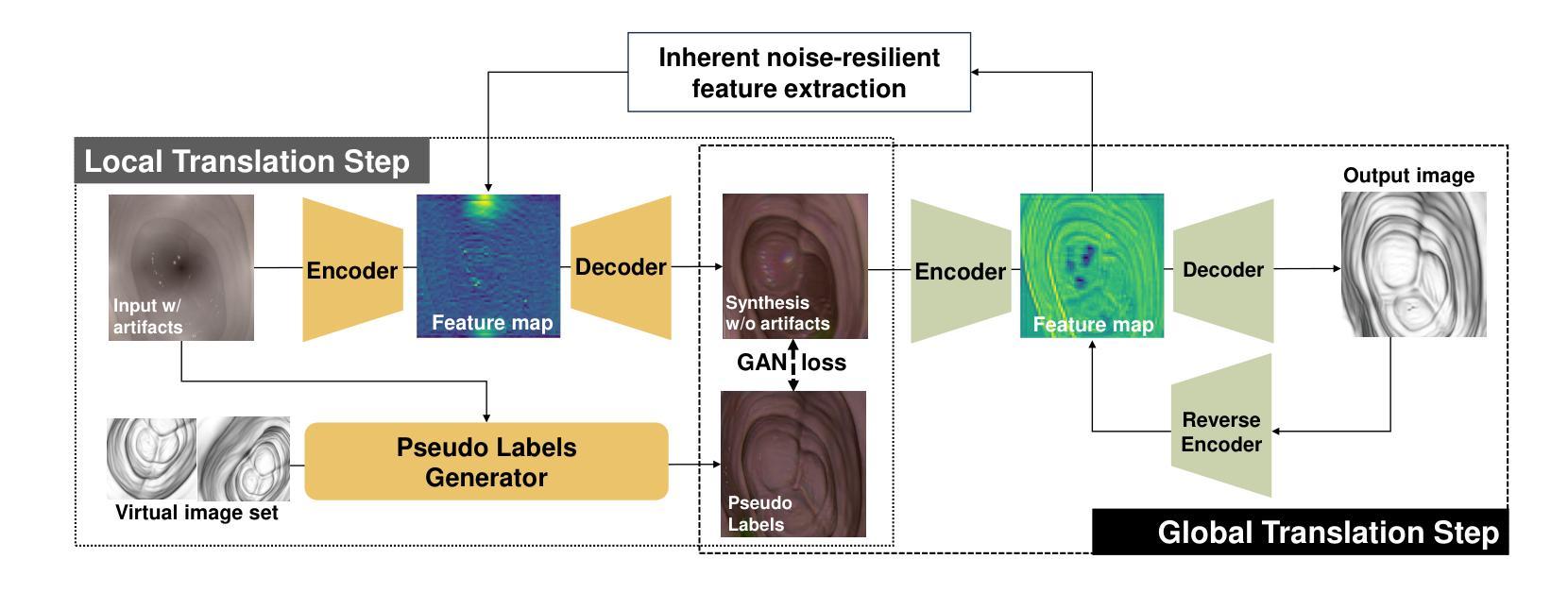
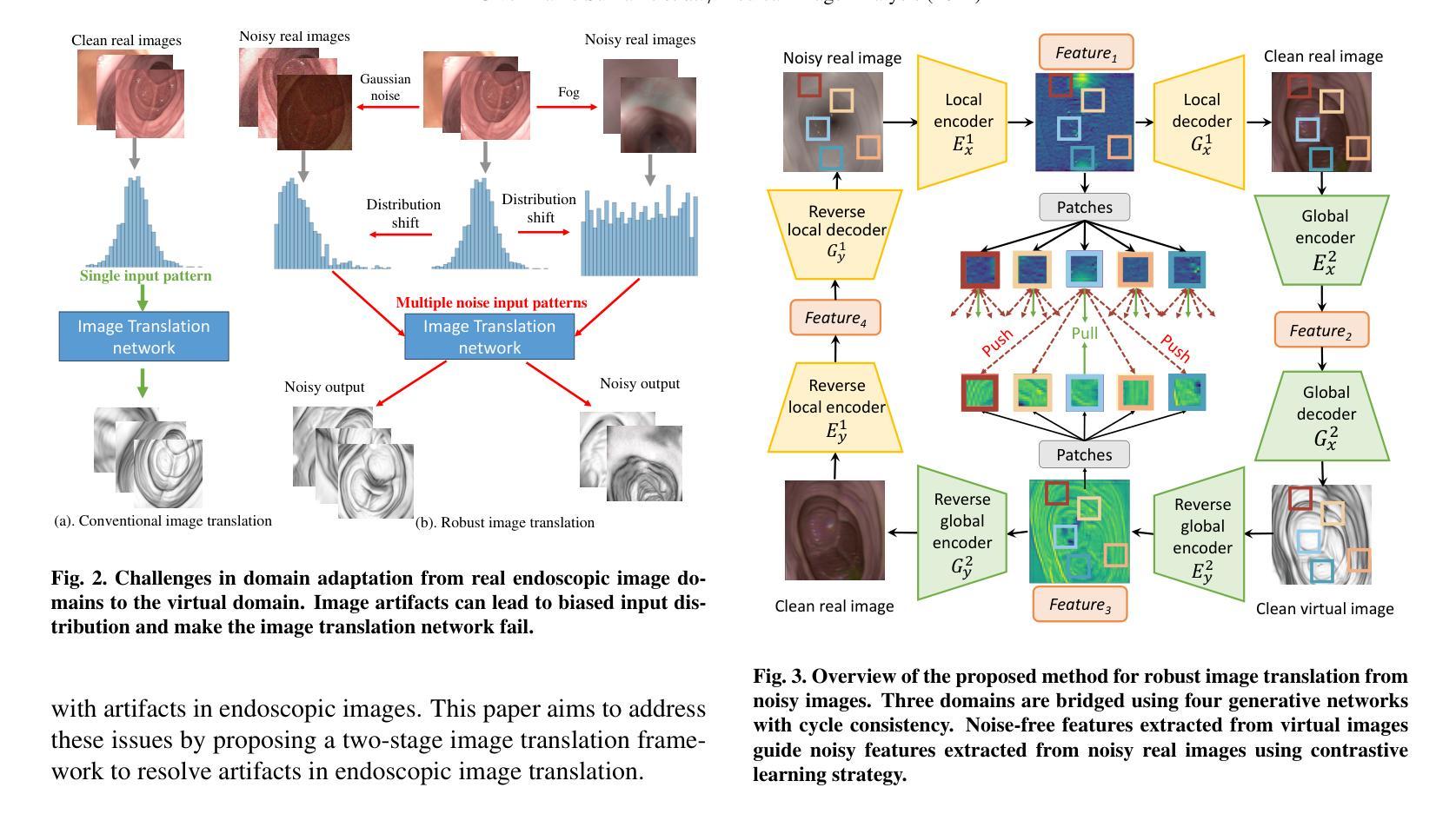
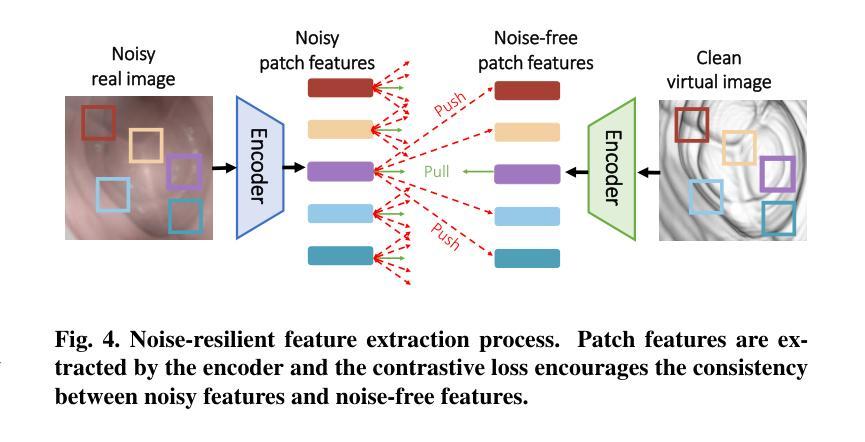
From Real Artifacts to Virtual Reference: A Robust Framework for Translating Endoscopic Images
Authors:Junyang Wu, Fangfang Xie, Jiayuan Sun, Yun Gu, Guang-Zhong Yang
Domain adaptation, which bridges the distributions across different modalities, plays a crucial role in multimodal medical image analysis. In endoscopic imaging, combining pre-operative data with intra-operative imaging is important for surgical planning and navigation. However, existing domain adaptation methods are hampered by distribution shift caused by in vivo artifacts, necessitating robust techniques for aligning noisy and artifact abundant patient endoscopic videos with clean virtual images reconstructed from pre-operative tomographic data for pose estimation during intraoperative guidance. This paper presents an artifact-resilient image translation method and an associated benchmark for this purpose. The method incorporates a novel ``local-global’’ translation framework and a noise-resilient feature extraction strategy. For the former, it decouples the image translation process into a local step for feature denoising, and a global step for global style transfer. For feature extraction, a new contrastive learning strategy is proposed, which can extract noise-resilient features for establishing robust correspondence across domains. Detailed validation on both public and in-house clinical datasets has been conducted, demonstrating significantly improved performance compared to the current state-of-the-art.
领域适应(domain adaptation)在多模态医疗图像分析中扮演着重要角色,它架起了不同分布之间的桥梁。在内窥成像中,将术前数据与术中成像相结合对于手术规划和导航至关重要。然而,现有的领域适应方法受到体内伪影引起的分布变化的影响。因此,需要可靠的技术来对齐带有噪声和丰富伪影的患者内窥镜视频与通过术前断层扫描数据重建的干净虚拟图像,以用于术中指导的姿势估计。本文提出了一种用于此目的的伪影弹性图像翻译方法和相关基准测试。该方法结合了一种新型的“局部-全局”翻译框架和一种抗噪声特性提取策略。对于前者,它将图像翻译过程分解为局部特征去噪和全局风格转换两个步骤。对于特性提取,提出了一种新的对比学习策略,可以提取出稳健的跨域对应特性。在公共和内部临床数据集上的详细验证表明,与当前最新技术相比,其性能得到了显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The conclusions of the paper has error. It requires substantial re-evaluation, and I plan to resubmit an updated version in the future
Summary
多模态医学图像分析中,域适应技术起着关键作用,尤其在跨不同模态的数据分布之间搭建桥梁。在内窥镜成像领域,结合术前数据与术中影像对手术规划与导航至关重要。然而,现有域适应方法受到体内伪影引起的分布偏移的制约。本文提出了一种耐伪影的图像翻译方法和相应的基准测试。该方法引入了一种新颖的“局部-全局”翻译框架和一种耐噪声的特征提取策略。前者将图像翻译过程分解为局部特征去噪和全局风格转换。对于特征提取,提出了一种新的对比学习策略,能够提取出耐噪声的特征,为跨域建立稳健对应关系打下基础。在公共和内部临床数据集上的详细验证显示,与当前最新技术相比,该方法性能显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 域适应在多模态医学图像分析中很重要,尤其在桥接不同模态数据分布方面。
- 内窥镜成像中结合术前与术中数据对手术规划和导航至关重要。
- 现有域适应方法受到体内伪影导致的分布偏移的制约。
- 本文提出了一种耐伪影的图像翻译方法和相应的基准测试。
- 引入的“局部-全局”翻译框架旨在分解图像翻译过程。
- 采用新的对比学习策略提取耐噪声特征,以建立跨域的稳健对应关系。
- 在多个数据集上的验证显示,该方法性能优于当前最新技术。
点此查看论文截图

Average Calibration Error: A Differentiable Loss for Improved Reliability in Image Segmentation
Authors:Theodore Barfoot, Luis Garcia-Peraza-Herrera, Ben Glocker, Tom Vercauteren
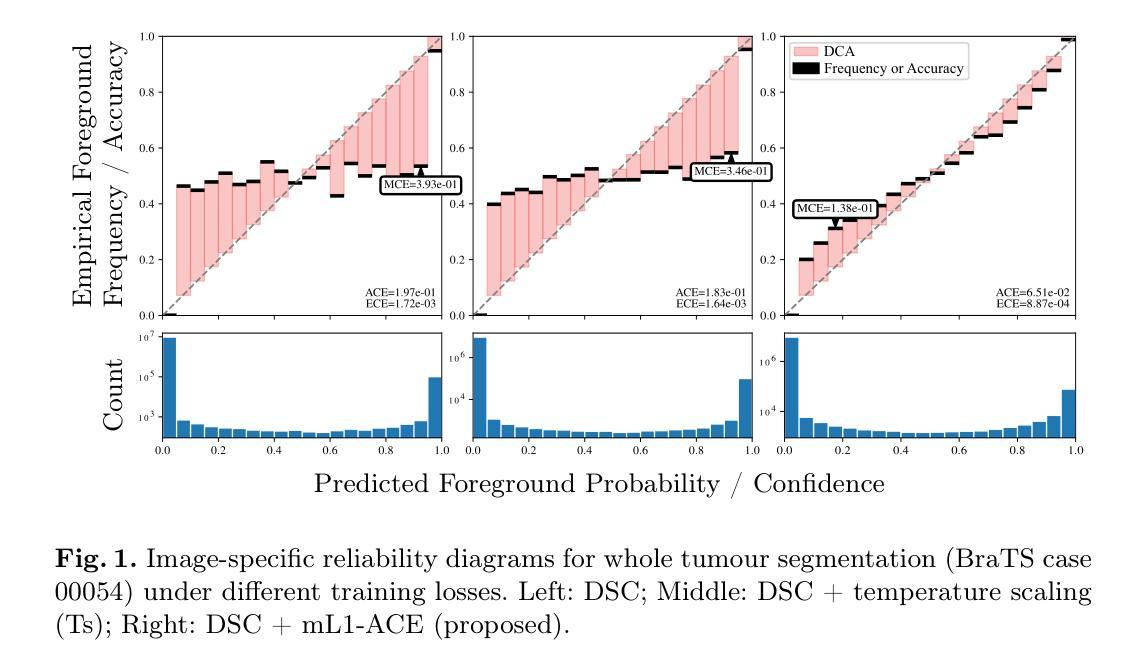
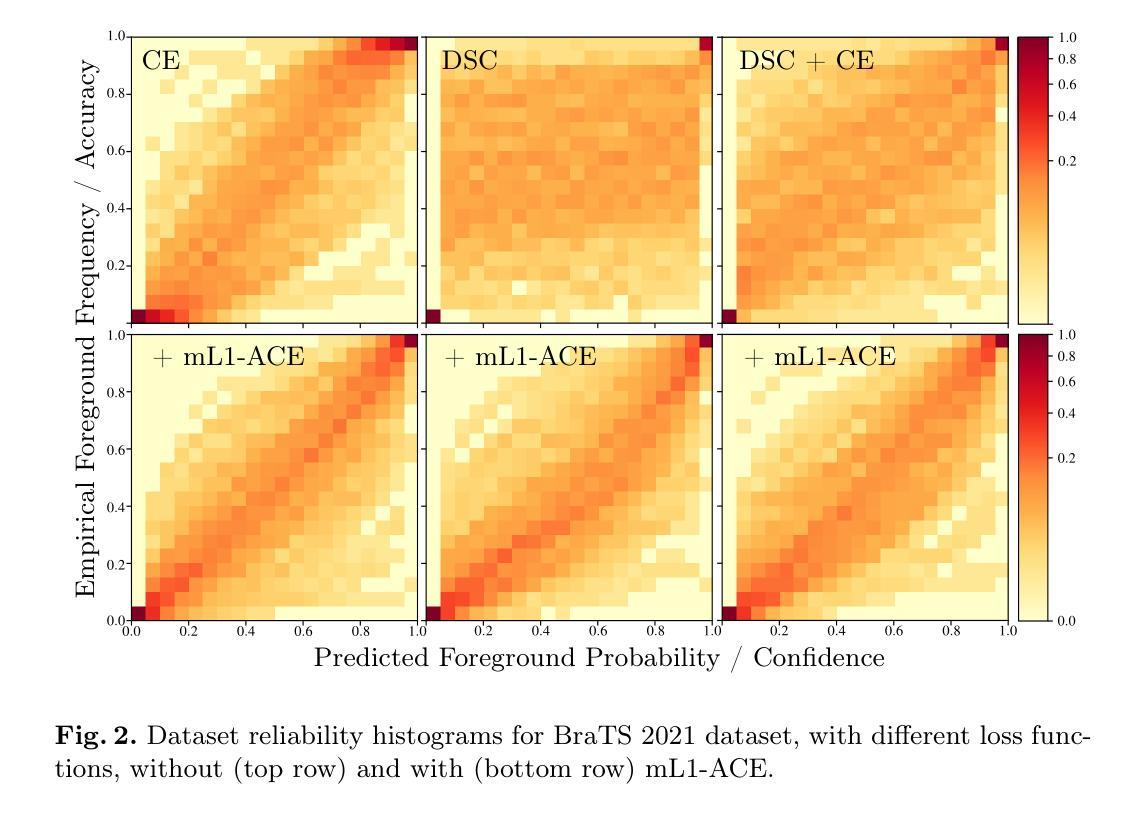
Deep neural networks for medical image segmentation often produce overconfident results misaligned with empirical observations. Such miscalibration, challenges their clinical translation. We propose to use marginal L1 average calibration error (mL1-ACE) as a novel auxiliary loss function to improve pixel-wise calibration without compromising segmentation quality. We show that this loss, despite using hard binning, is directly differentiable, bypassing the need for approximate but differentiable surrogate or soft binning approaches. Our work also introduces the concept of dataset reliability histograms which generalises standard reliability diagrams for refined visual assessment of calibration in semantic segmentation aggregated at the dataset level. Using mL1-ACE, we reduce average and maximum calibration error by 45% and 55% respectively, maintaining a Dice score of 87% on the BraTS 2021 dataset. We share our code here: https://github.com/cai4cai/ACE-DLIRIS
针对医学图像分割的深度神经网络经常产生过于自信的结果,与经验观察不符。这种误校准对其临床翻译提出了挑战。我们建议使用边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为一种新型辅助损失函数,以提高像素级校准,而不损害分割质量。我们证明,尽管使用了硬分箱,但这种损失是直接可微分的,从而绕过了对近似但可微分的替代或软分箱方法的需求。我们的工作还引入了数据集可靠性直方图的概念,该概念将标准可靠性图推广到数据集级别的校准的精细视觉评估的语义分割。使用mL1-ACE,我们在BraTS 2021数据集上将平均和最大校准误差分别降低了45%和55%,同时保持Dice得分为87%。我们在以下链接分享我们的代码:https://github.com/cai4cai/ACE-DLIRIS
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera ready version as in 10.1007/978-3-031-72114-4_14
Summary:
神经网络模型用于医学图像分割时可能过于自信,造成与实际观察结果不符的误校准问题。本文提出使用边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为新的辅助损失函数,以改善像素级的校准问题,且不影响分割质量。此方法即使采用硬分栏也直接可微分,无需近似但可微分的替代或软分栏方法。同时引入数据集可靠性直方图概念,便于更精细地可视化评估语义分割的校准情况。使用mL1-ACE在BraTS 2021数据集上平均和最大校准误差分别降低了45%和55%,同时Dice得分保持为87%。代码已共享。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度神经网络在医学图像分割中的过度自信问题导致实际应用中的挑战。
- 边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为一种新的辅助损失函数,可以改善像素级的校准问题。
- mL1-ACE可以在不损害分割质量的前提下应用。
- mL1-ACE在硬分栏情况下具有直接可微分的特性。
- 引入数据集可靠性直方图以更精细地可视化评估语义分割的校准情况。
- 使用mL1-ACE在BraTS 2021数据集上取得了显著的校准误差降低效果。
点此查看论文截图