⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
AI-Enhanced Pediatric Pneumonia Detection: A CNN-Based Approach Using Data Augmentation and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Authors:Abdul Manaf, Nimra Mughal
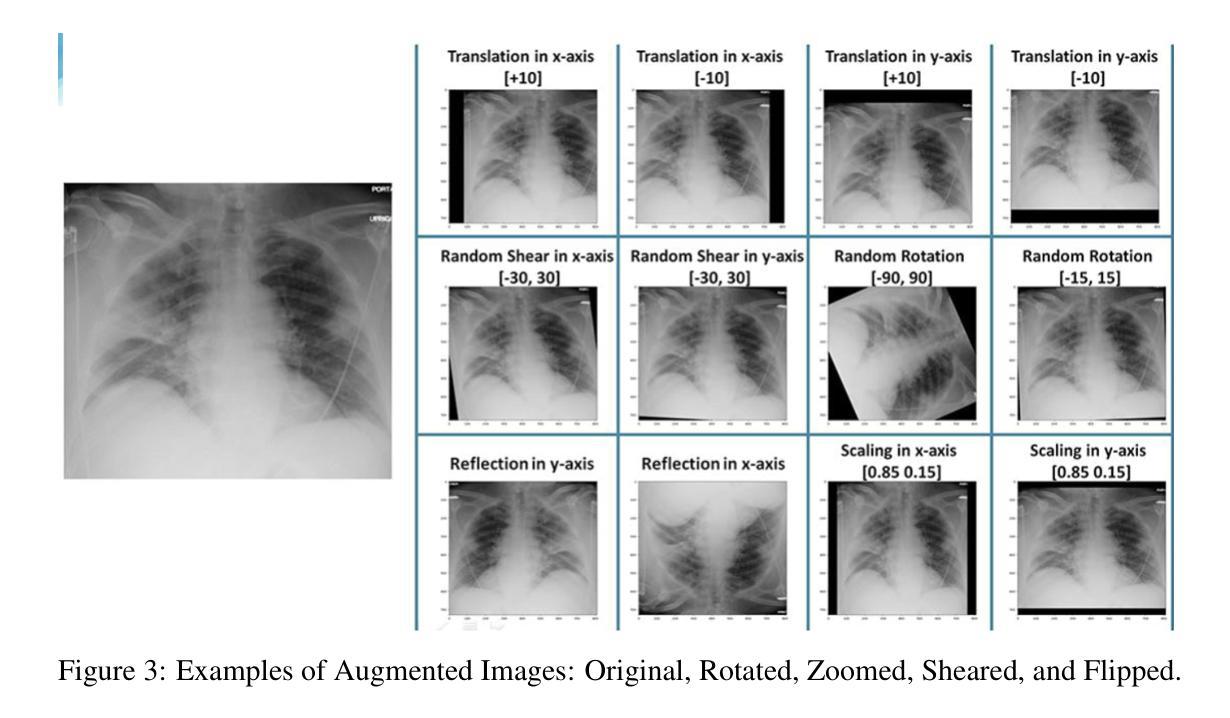
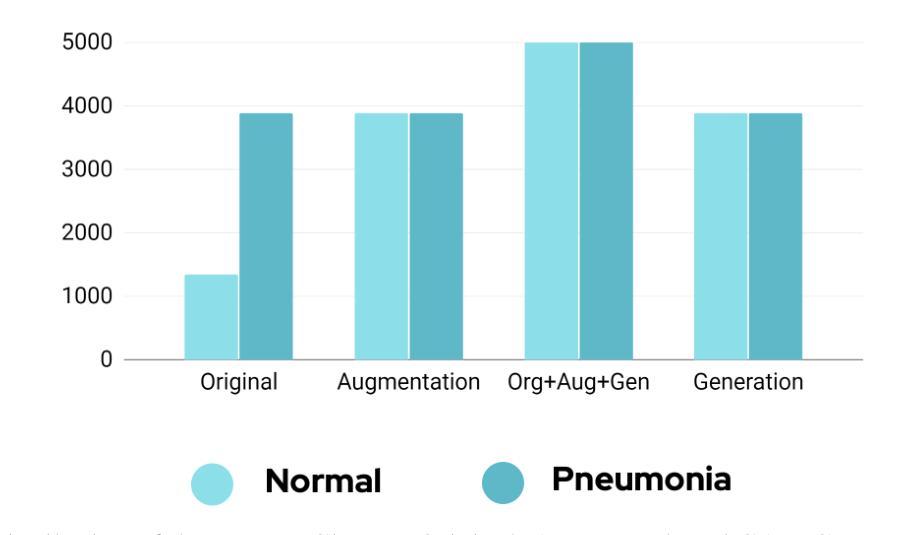
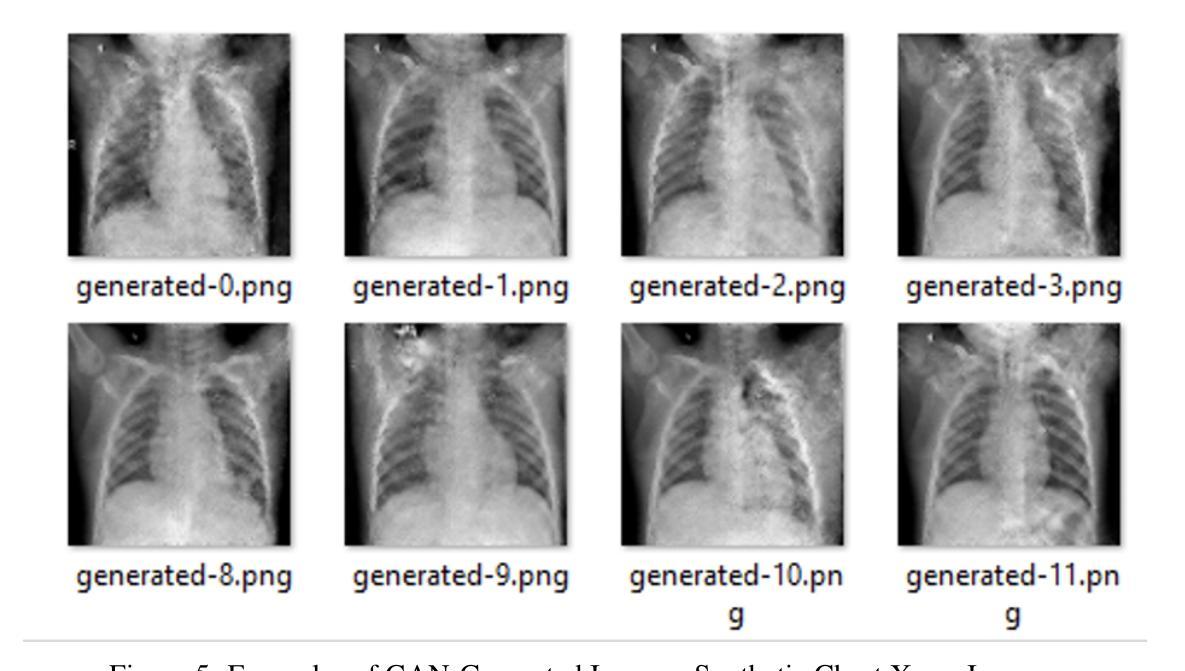
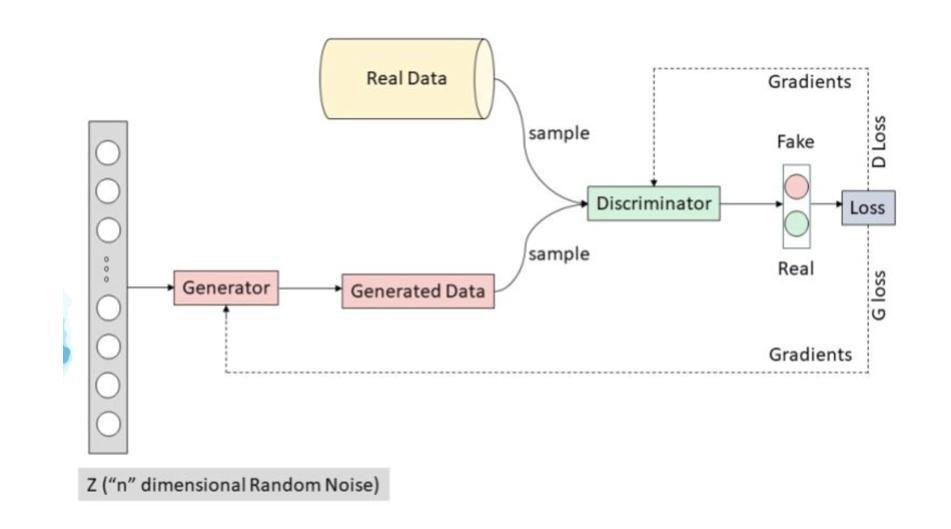
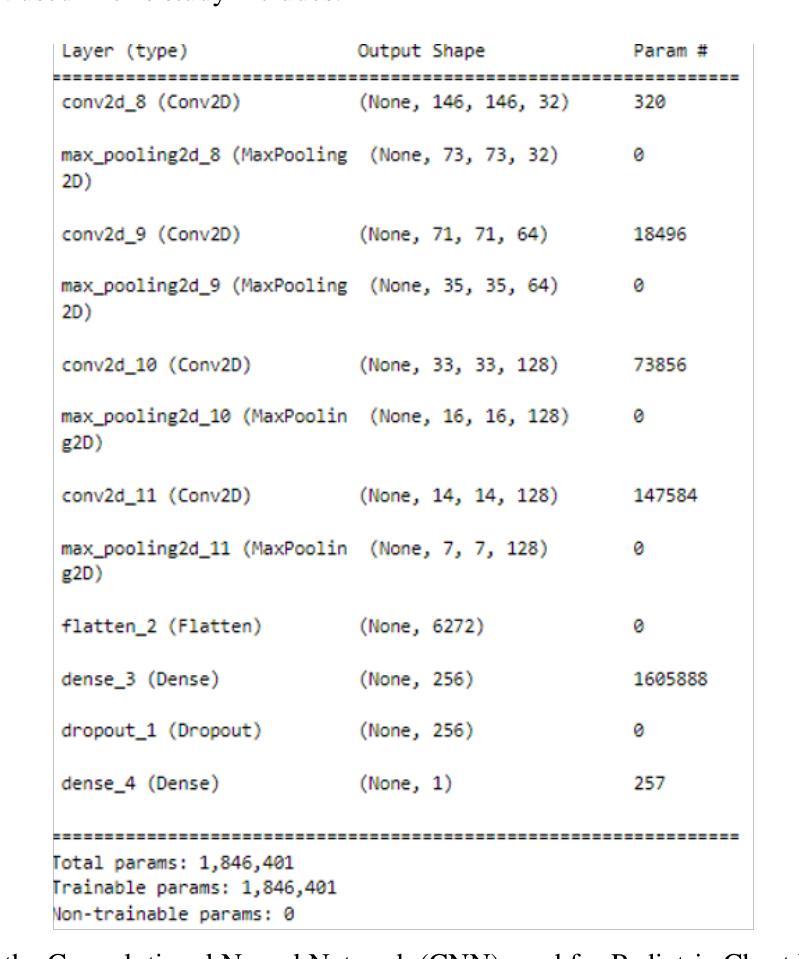
Pneumonia is a leading cause of mortality in children under five, requiring accurate chest X-ray diagnosis. This study presents a machine learning-based Pediatric Chest Pneumonia Classification System to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing pneumonia from chest X-ray images. The CNN-based model was trained on 5,863 labeled chest X-ray images from children aged 0-5 years from the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center. To address limited data, we applied augmentation techniques (rotation, zooming, shear, horizontal flipping) and employed GANs to generate synthetic images, addressing class imbalance. The system achieved optimal performance using combined original, augmented, and GAN-generated data, evaluated through accuracy and F1 score metrics. The final model was deployed via a Flask web application, enabling real-time classification with probability estimates. Results demonstrate the potential of deep learning and GANs in improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency for pediatric pneumonia classification, particularly valuable in resource-limited clinical settings https://github.com/AbdulManaf12/Pediatric-Chest-Pneumonia-Classification
肺炎是5岁以下儿童的主要致死原因,需要准确的胸部X射线诊断。本研究提出了一种基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,旨在帮助医疗专业人员根据胸部X射线图像诊断肺炎。该CNN模型在来自广州妇女儿童医疗中心的5863张0-5岁儿童胸部X射线图像上进行训练。为解决数据有限的问题,我们采用了增强技术(旋转、缩放、剪切、水平翻转),并采用了生成对抗网络(GANs)生成合成图像,以解决类别不平衡的问题。该系统通过使用原始、增强和GAN生成的组合数据实现了最佳性能,并通过准确率和F1分数指标进行了评估。最终模型通过Flask web应用程序进行部署,可实现实时分类并给出概率估计。结果证明了深度学习和生成对抗网络在提高儿童肺炎诊断的准确性和效率方面的潜力,特别是在资源有限的临床环境中具有特别的价值。相关代码地址:https://github.com/AbdulManaf12/Pediatric-Chest-Pneumonia-Classification
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究开发了一个基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,用于辅助医疗专业人员通过胸部X光片诊断肺炎。该系统采用基于CNN的模型,训练数据来自广州妇女儿童医疗中心的5863张0-5岁儿童胸部X光片。为解决数据有限问题,研究采用了图像增强技术和生成对抗网络(GANs)生成合成图像,以解决类别不平衡问题。系统通过使用原始、增强和GAN生成的组合数据,以精确度和F1分数评估,实现了最佳性能。最终模型通过Flask web应用程序部署,可实现实时分类与概率估计。研究结果证明了深度学习和GAN在提高儿童肺炎分类的诊断准确性和效率方面的潜力,特别是在资源有限的临床环境中具有特别价值。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究开发了一个基于机器学习的儿童胸部肺炎分类系统,旨在通过胸部X光片辅助诊断肺炎。
- 采用CNN模型,并在广州妇女儿童医疗中心的X光图像数据集上进行训练。
- 面对数据有限的问题,研究采用了图像增强技术和GANs生成合成图像,以解决类别不平衡的挑战。
- 系统使用组合数据(原始、增强和GAN生成的数据)进行训练,并通过精确度和F1分数评估性能。
- 最终模型通过Flask web应用程序部署,实现实时分类,提供概率估计。
- 研究结果表明深度学习和GAN在提高儿童肺炎诊断的准确性和效率方面有很大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

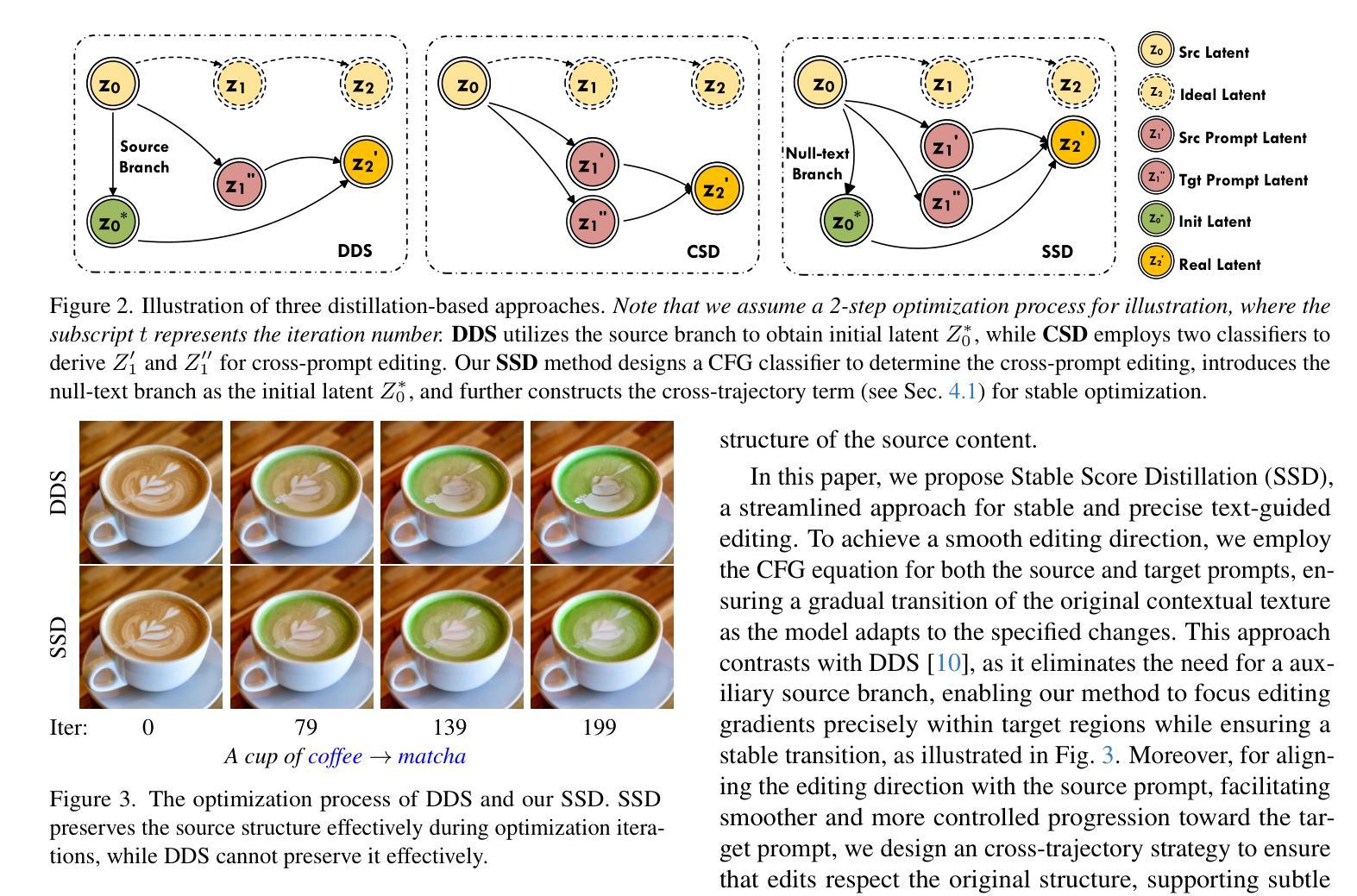
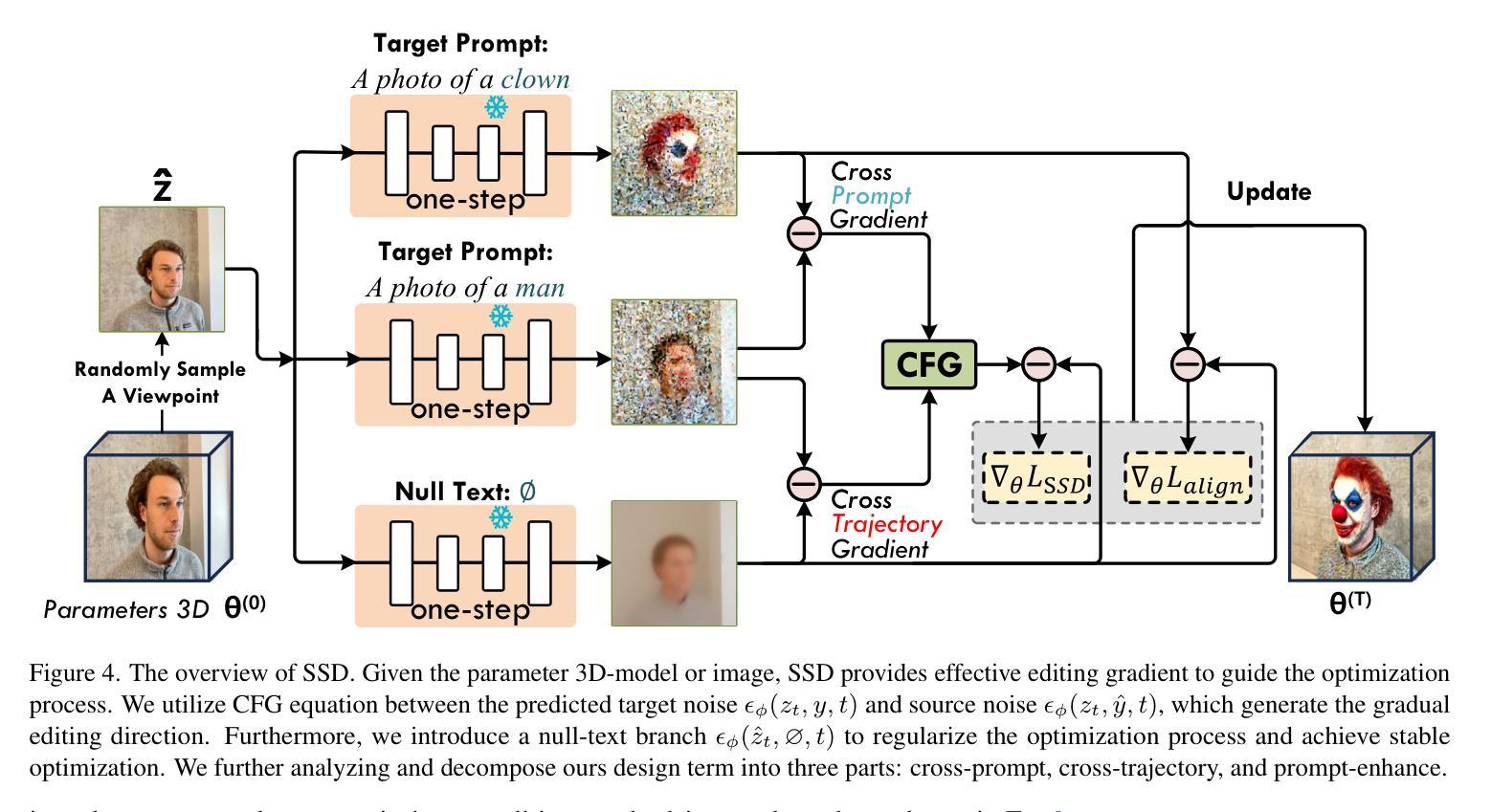
Stable Score Distillation
Authors:Haiming Zhu, Yangyang Xu, Chenshu Xu, Tingrui Shen, Wenxi Liu, Yong Du, Jun Yu, Shengfeng He
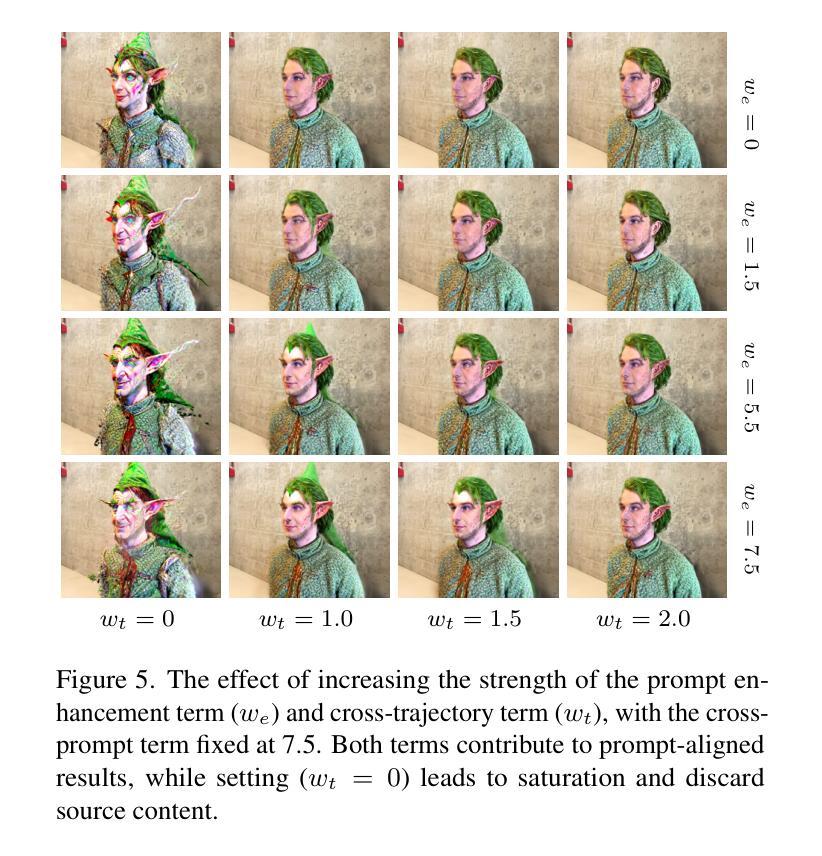
Text-guided image and 3D editing have advanced with diffusion-based models, yet methods like Delta Denoising Score often struggle with stability, spatial control, and editing strength. These limitations stem from reliance on complex auxiliary structures, which introduce conflicting optimization signals and restrict precise, localized edits. We introduce Stable Score Distillation (SSD), a streamlined framework that enhances stability and alignment in the editing process by anchoring a single classifier to the source prompt. Specifically, SSD utilizes Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) equation to achieves cross-prompt alignment, and introduces a constant term null-text branch to stabilize the optimization process. This approach preserves the original content’s structure and ensures that editing trajectories are closely aligned with the source prompt, enabling smooth, prompt-specific modifications while maintaining coherence in surrounding regions. Additionally, SSD incorporates a prompt enhancement branch to boost editing strength, particularly for style transformations. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results in 2D and 3D editing tasks, including NeRF and text-driven style edits, with faster convergence and reduced complexity, providing a robust and efficient solution for text-guided editing.
文本引导的图像和3D编辑已经随着基于扩散的模型而发展,然而Delta Denoising Score等方法经常在稳定性、空间控制和编辑强度方面遇到困难。这些限制源于对复杂辅助结构的依赖,这些结构引入了冲突的优化信号并限制了精确、局部化的编辑。我们引入了Stable Score Distillation(SSD)这一简化框架,通过锚定单个分类器到源提示来增强编辑过程中的稳定性和对齐性。具体来说,SSD利用无分类器引导(CFG)方程实现跨提示对齐,并引入恒定项空文本分支来稳定优化过程。这种方法保留了原始内容的结构,并确保编辑轨迹与源提示紧密对齐,从而实现平滑、特定提示的修改,同时保持周围区域的连贯性。此外,SSD还结合了提示增强分支以增强编辑强度,尤其是风格转换。我们的方法在2D和3D编辑任务上取得了最新成果,包括NeRF和文本驱动的风格编辑。我们的方法具有更快的收敛速度和较低的复杂性,为文本引导编辑提供了稳健而高效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的文本引导图像和3D编辑技术取得进展,但仍存在稳定性、空间控制和编辑强度等问题。现有方法如Delta Denoising Score存在依赖复杂辅助结构的问题,引入冲突的优化信号并限制精确局部编辑。我们提出Stable Score Distillation(SSD)框架,通过锚定源提示的单分类器增强编辑过程的稳定性和对齐性。SSD利用无分类器引导(CFG)方程实现跨提示对齐,并引入恒定项空文本分支来稳定优化过程。该方法保留原始内容的结构并确保编辑轨迹与源提示紧密对齐,可实现流畅、提示特定的修改,同时保持周围区域的连贯性。此外,SSD还加入了提示增强分支以提升编辑强度,特别是在风格转换方面。我们的方法在2D和3D编辑任务中实现领先结果,包括NeRF和文本驱动风格编辑,具有更快的收敛速度和降低的复杂性,为文本引导编辑提供了稳健高效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导图像和3D编辑技术利用扩散模型取得进展。
- 当前方法如Delta Denoising Score存在稳定性、空间控制和编辑强度问题。
- SSD框架通过锚定源提示的单分类器增强编辑过程的稳定性和对齐。
- SSD利用无分类器引导(CFG)方程实现跨提示对齐。
- SSD引入恒定项空文本分支以稳定优化过程并保留原始内容结构。
- SSD可实现流畅、提示特定的修改,并维持周围区域的连贯性。
点此查看论文截图


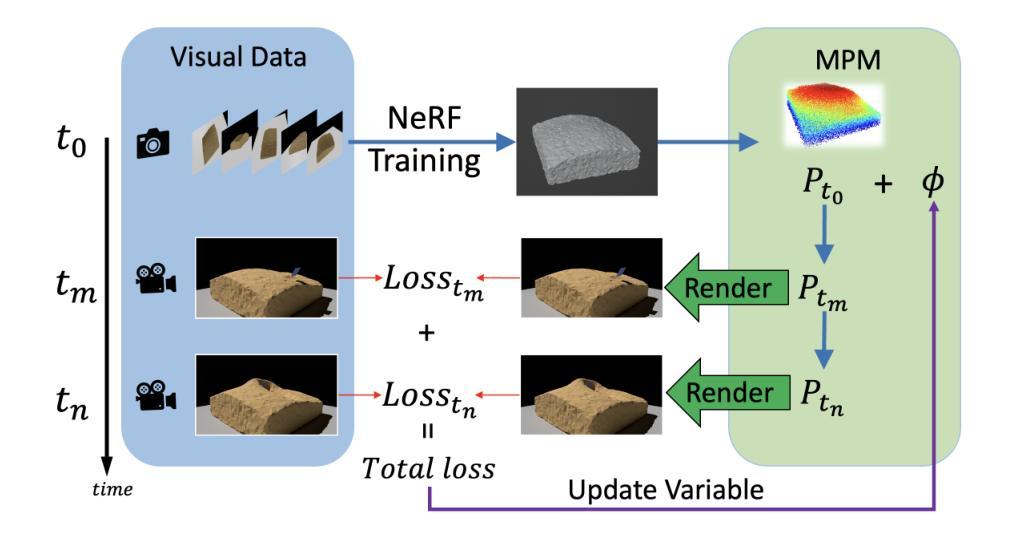
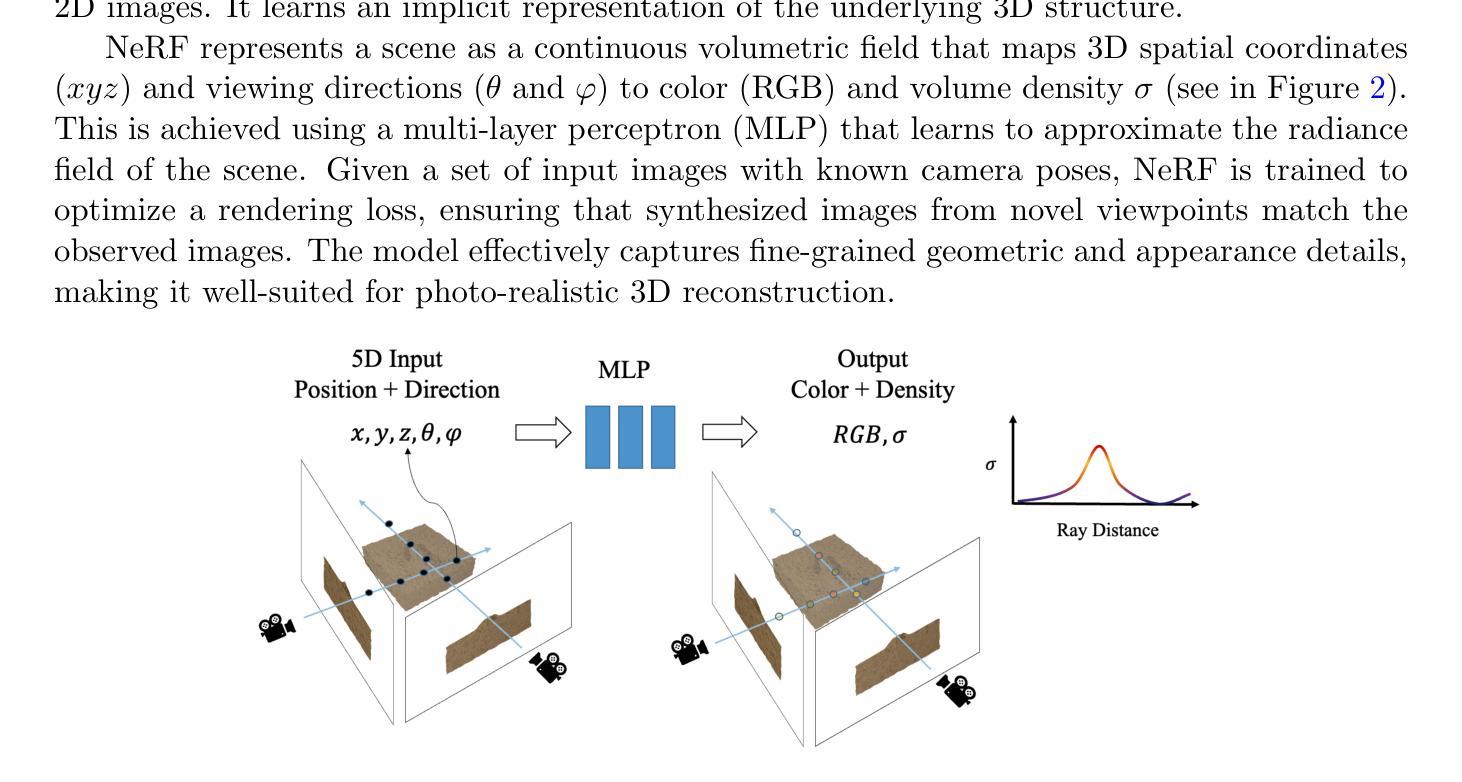
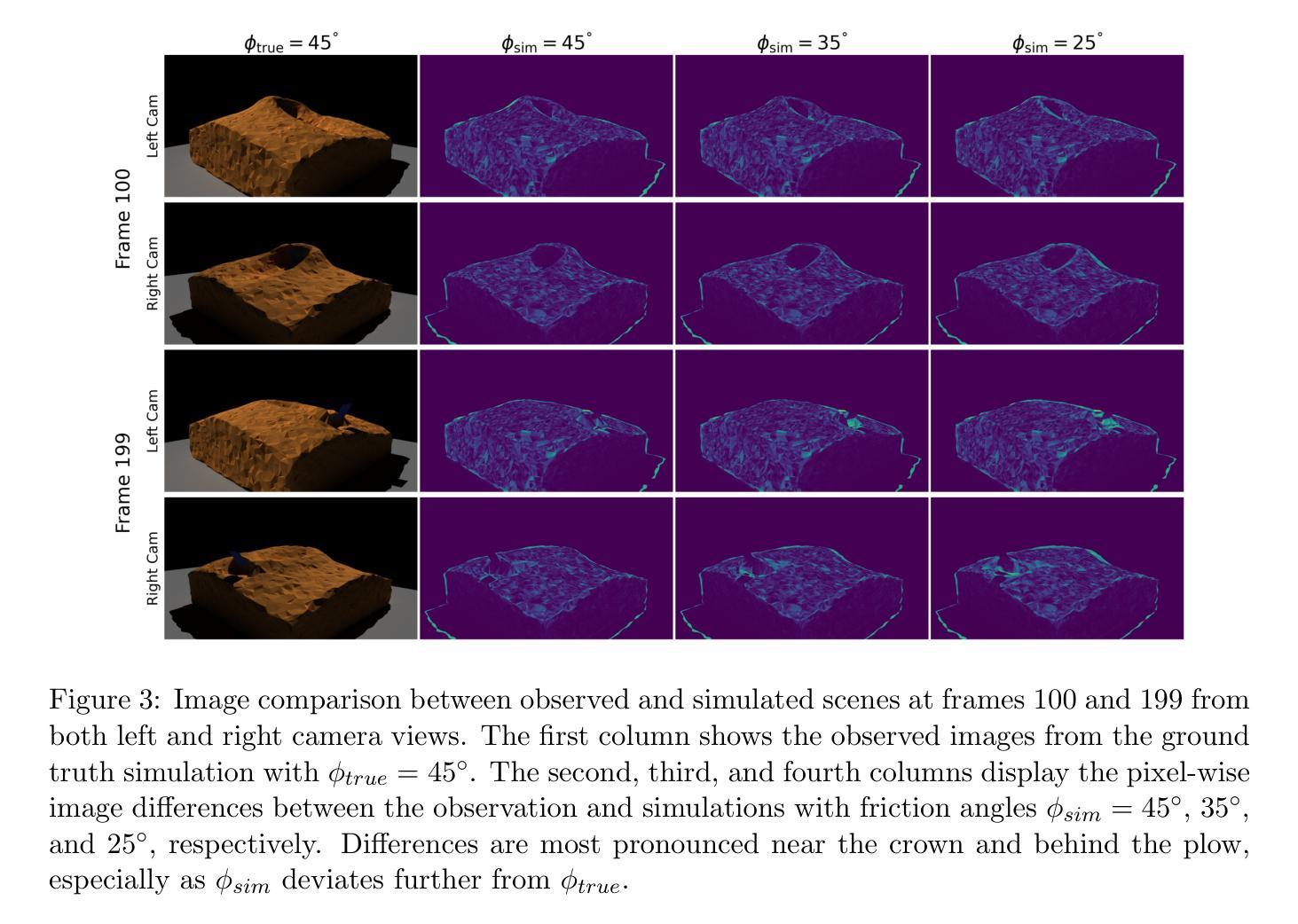
From images to properties: a NeRF-driven framework for granular material parameter inversion
Authors:Cheng-Hsi Hsiao, Krishna Kumar
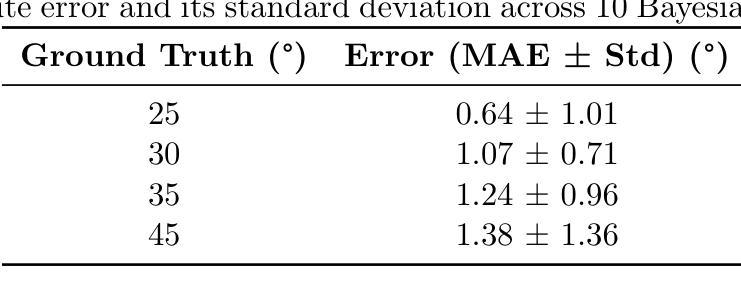
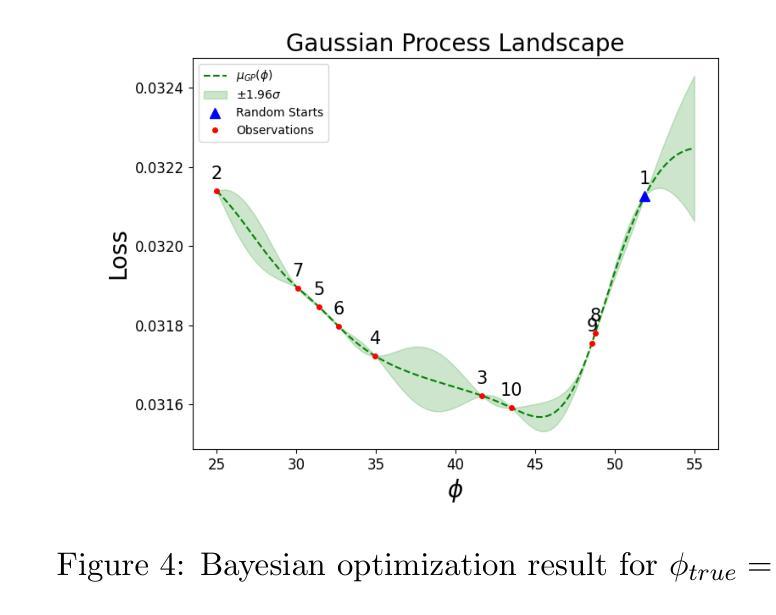
We introduce a novel framework that integrates Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) with Material Point Method (MPM) simulation to infer granular material properties from visual observations. Our approach begins by generating synthetic experimental data, simulating an plow interacting with sand. The experiment is rendered into realistic images as the photographic observations. These observations include multi-view images of the experiment’s initial state and time-sequenced images from two fixed cameras. Using NeRF, we reconstruct the 3D geometry from the initial multi-view images, leveraging its capability to synthesize novel viewpoints and capture intricate surface details. The reconstructed geometry is then used to initialize material point positions for the MPM simulation, where the friction angle remains unknown. We render images of the simulation under the same camera setup and compare them to the observed images. By employing Bayesian optimization, we minimize the image loss to estimate the best-fitting friction angle. Our results demonstrate that friction angle can be estimated with an error within 2 degrees, highlighting the effectiveness of inverse analysis through purely visual observations. This approach offers a promising solution for characterizing granular materials in real-world scenarios where direct measurement is impractical or impossible.
我们介绍了一个新型框架,该框架将神经辐射场(NeRF)与物质点法(MPM)模拟相结合,从视觉观察推断颗粒材料属性。我们的方法首先从生成合成实验数据开始,模拟犁与沙子的相互作用。该实验被渲染成逼真的图像作为照片观察。这些观察包括实验初始状态的多视角图像和来自两个固定摄像头的时序图像。我们使用NeRF,从初始的多视角图像重建3D几何结构,利用其合成新视角和捕捉复杂表面细节的能力。重建的几何结构用于初始化物质点的位置进行MPM模拟,其中摩擦角仍然是未知的。我们在相同的相机设置下呈现模拟图像,并与观察到的图像进行比较。通过采用贝叶斯优化,我们最小化图像损失以估计最佳拟合的摩擦角。我们的结果表明,摩擦角的估计误差在2度以内,突显了通过纯视觉观察进行逆向分析的有效性。这种方法为在现实世界场景中表征颗粒材料提供了有前景的解决方案,尤其是在直接测量不实用或不可能的情况下。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型框架,结合了神经辐射场(NeRF)和材料点方法(MPM)模拟,从视觉观察推断颗粒材料属性。通过生成合成实验数据,模拟犁与沙子的相互作用,并渲染成逼真图像作为观察。利用NeRF从初始多视角图像重建3D几何结构,然后用其初始化MPM模拟的材料点位置。通过渲染模拟图像并与观察图像进行比较,采用贝叶斯优化最小化图像损失来估计最佳拟合的摩擦角。研究结果表明,摩擦角的估计误差在2度以内,突显了通过纯视觉观察进行反分析的有效性。此方法为在直接测量不实际或不可能的现实场景中表征颗粒材料提供了有前途的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 结合了神经辐射场(NeRF)和材料点方法(MPM)模拟,创新性地用于从视觉观察推断颗粒材料属性。
- 通过生成合成实验数据,模拟犁与沙子的相互作用。
- 利用NeRF重建3D几何结构,并初始化MPM模拟的材料点位置。
- 通过比较模拟和观察图像,采用贝叶斯优化估计摩擦角。
- 摩擦角的估计误差在2度以内,显示了反分析的有效性。
- 该方法对于直接测量不实际或不可能的场合,如真实场景中的颗粒材料表征,具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

BayesSDF: Surface-Based Laplacian Uncertainty Estimation for 3D Geometry with Neural Signed Distance Fields
Authors:Rushil Desai
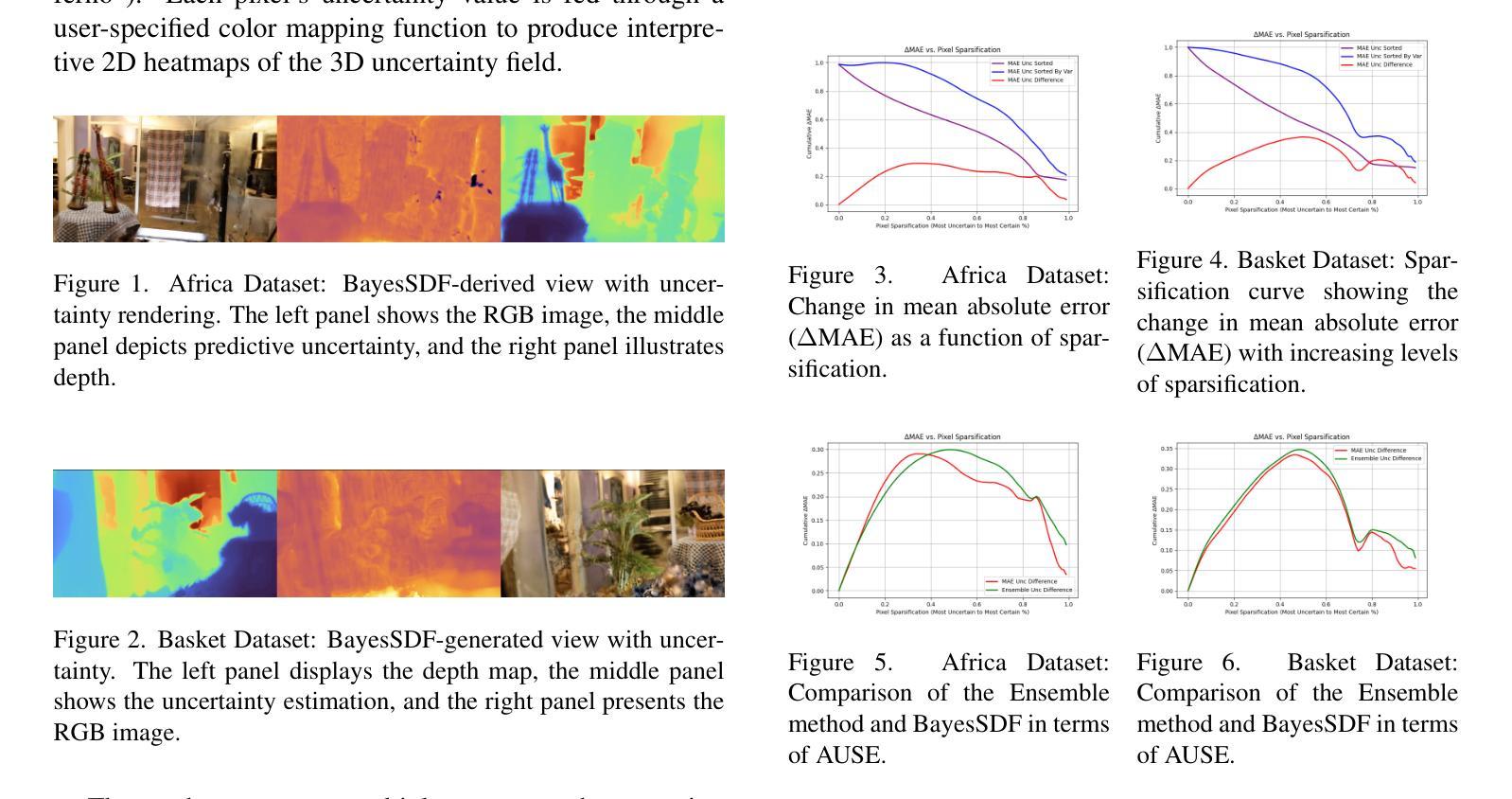
Quantifying uncertainty in neural implicit 3D representations, particularly those utilizing Signed Distance Functions (SDFs), remains a substantial challenge due to computational inefficiencies, scalability issues, and geometric inconsistencies. Existing methods typically neglect direct geometric integration, leading to poorly calibrated uncertainty maps. We introduce BayesSDF, a novel probabilistic framework for uncertainty quantification in neural implicit SDF models, motivated by scientific simulation applications with 3D environments (e.g., forests) such as modeling fluid flow through forests, where precise surface geometry and reliable uncertainty estimates are essential. Unlike radiance-based models such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian splatting, which lack explicit surface formulations, Signed Distance Functions (SDFs) define continuous and differentiable geometry, making them better suited for physical modeling and analysis. BayesSDF leverages a Laplace approximation to quantify local surface instability using Hessian-based metrics, enabling efficient, surfaceaware uncertainty estimation. Our method shows that uncertainty predictions correspond closely with poorly reconstructed geometry, providing actionable confidence measures for downstream use. Extensive evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that BayesSDF outperforms existing methods in both calibration and geometric consistency, establishing a strong foundation for uncertainty-aware 3D scene reconstruction, simulation, and robotic decision-making.
对神经隐式三维表示中的不确定性进行量化,特别是那些利用有向距离函数(SDFs)的表示,仍然是一个巨大的挑战,主要由于计算效率低下、可扩展性问题以及几何不一致性。现有方法通常忽略直接几何集成,导致校准不良的不确定性图。我们介绍了BayesSDF,这是一种用于神经隐式SDF模型中的不确定性量化的新型概率框架,该框架受三维环境科学模拟应用程序(例如森林模型,如森林中的水流)的启发,在这些应用中,精确的曲面几何和可靠的不确定性估计是必不可少的。与基于辐射率的模型(例如神经辐射场(NeRF)或三维高斯涂抹)不同,这些模型没有明确的表面公式,而有向距离函数(SDFs)定义了连续和可区分的几何形状,使它们更适合物理建模和分析。BayesSDF利用Laplace近似来量化局部表面不稳定性,使用基于Hessian的指标,从而实现高效、面向表面的不确定性估计。我们的方法表明,不确定性预测与重建不良的几何形状紧密对应,为下游使用提供了可行的置信度度量。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛评估表明,BayesSDF在校准和几何一致性方面优于现有方法,为不确定性感知的3D场景重建、模拟和机器人决策制定奠定了坚实基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Workshops (8 Pages, 6 Figures, 2 Tables)
Summary
神经网络隐式三维表示中的不确定性量化,特别是使用带符号距离函数(SDFs)的方法,面临着计算效率低下、可扩展性问题和几何不一致性等多重挑战。现有方法往往忽略了直接的几何集成,导致不确定性映射校准不佳。本文介绍了一种新型的贝叶斯框架BayesSDF,用于神经隐式SDF模型中的不确定性量化。不同于基于辐射率的模型(如NeRF或三维高斯涂片),BayesSDF使用Laplace近似法,利用Hessian度量衡量局部表面稳定性,实现高效、感知表面的不确定性估计。该方法在合成和真实数据集上的评估表明,BayesSDF在校准和几何一致性方面优于现有方法,为不确定性的三维场景重建、模拟和机器人决策奠定了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- BayesSDF是一种用于神经隐式SDF模型中不确定性量化的新型贝叶斯框架。
- 现有方法在计算效率和不确定性映射校准方面存在缺陷。
- BayesSDF解决了现有方法的缺点,通过利用Laplace近似和Hessian度量提高了计算效率和不确定性映射的准确性。
- BayesSDF适用于物理建模和分析,因为它使用连续的、可微分的几何定义。
- 该方法在合成和真实数据集上的表现优于现有方法,为不确定性的三维场景重建、模拟和机器人决策提供了可靠的基础。
点此查看论文截图

HGSLoc: 3DGS-based Heuristic Camera Pose Refinement
Authors:Zhongyan Niu, Zhen Tan, Jinpu Zhang, Xueliang Yang, Dewen Hu
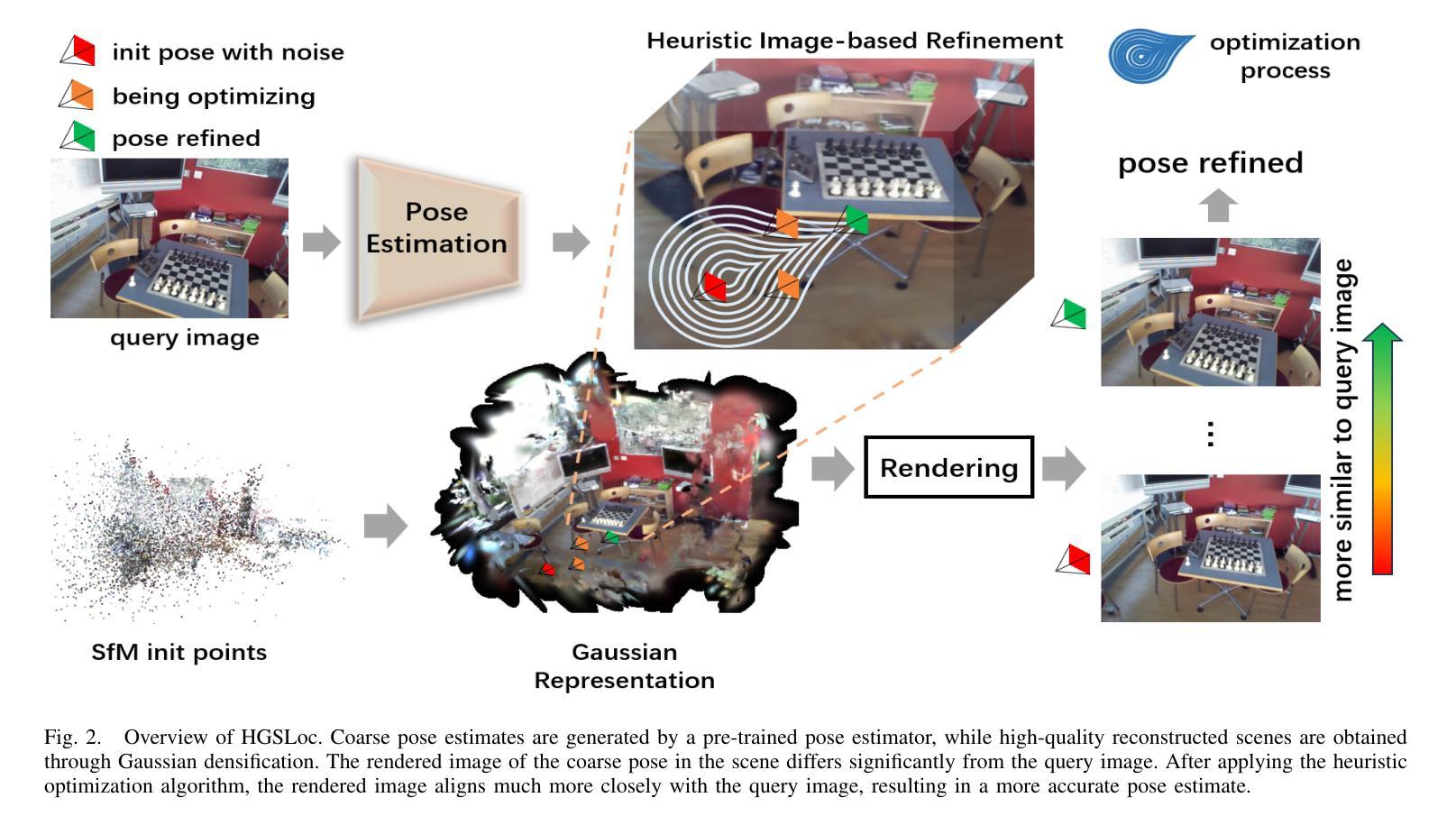
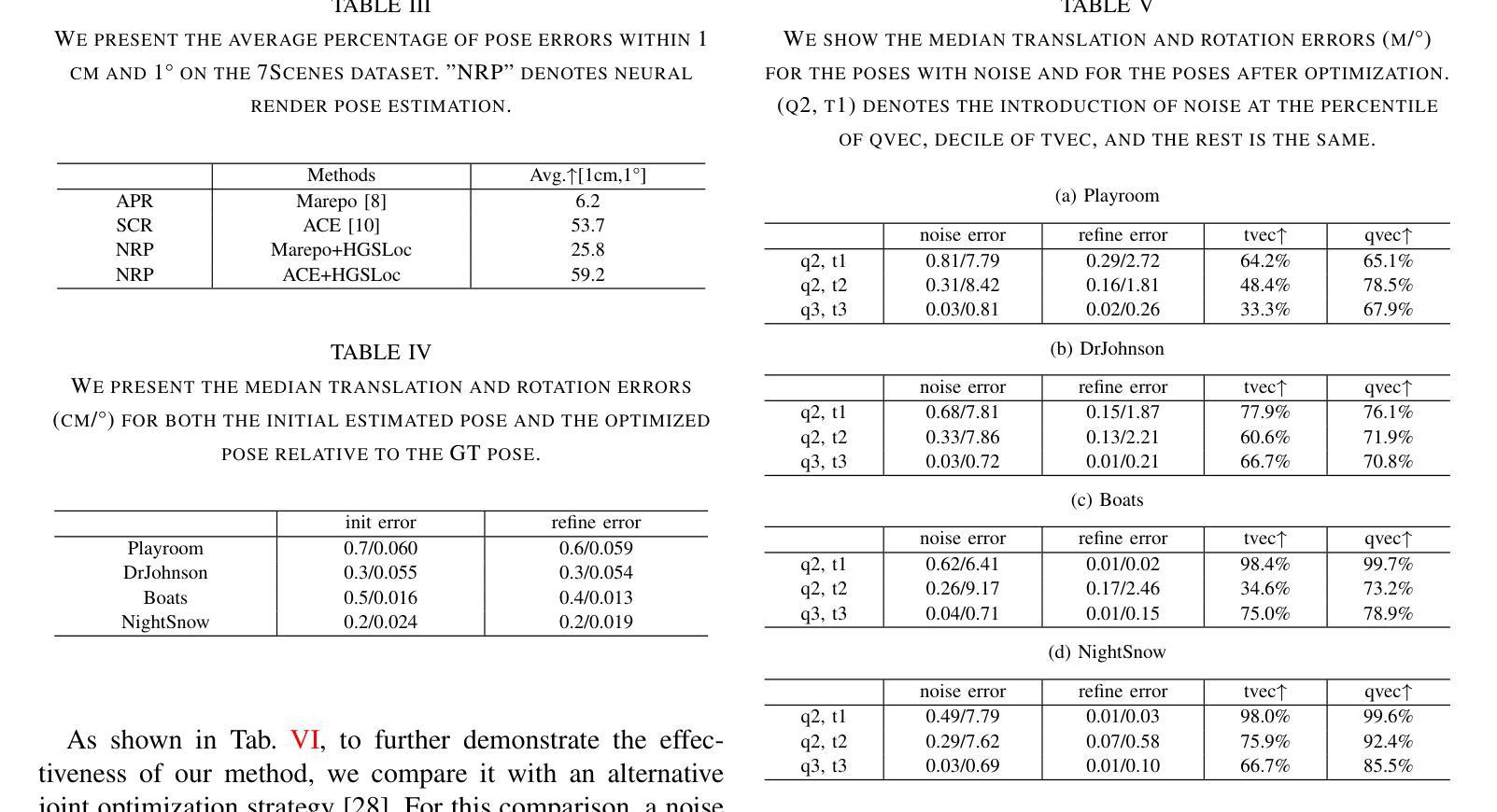
Visual localization refers to the process of determining camera poses and orientation within a known scene representation. This task is often complicated by factors such as changes in illumination and variations in viewing angles. In this paper, we propose HGSLoc, a novel lightweight plug-and-play pose optimization framework, which integrates 3D reconstruction with a heuristic refinement strategy to achieve higher pose estimation accuracy. Specifically, we introduce an explicit geometric map for 3D representation and high-fidelity rendering, allowing the generation of high-quality synthesized views to support accurate visual localization. Our method demonstrates higher localization accuracy compared to NeRF-based neural rendering localization approaches. We introduce a heuristic refinement strategy, its efficient optimization capability can quickly locate the target node, while we set the step level optimization step to enhance the pose accuracy in the scenarios with small errors. With carefully designed heuristic functions, it offers efficient optimization capabilities, enabling rapid error reduction in rough localization estimations. Our method mitigates the dependence on complex neural network models while demonstrating improved robustness against noise and higher localization accuracy in challenging environments, as compared to neural network joint optimization strategies. The optimization framework proposed in this paper introduces novel approaches to visual localization by integrating the advantages of 3D reconstruction and the heuristic refinement strategy, which demonstrates strong performance across multiple benchmark datasets, including 7Scenes and Deep Blending dataset. The implementation of our method has been released at https://github.com/anchang699/HGSLoc.
视觉定位是指确定相机在已知场景表示中的姿态和方向的过程。此任务通常受到光照变化和观看角度变化等因素的影响而变得复杂。在本文中,我们提出了HGSLoc,这是一种新型的轻量级即插即用姿态优化框架,它将3D重建与启发式细化策略相结合,以实现更高的姿态估计精度。具体来说,我们引入了用于3D表示和高保真渲染的显式几何地图,以生成高质量合成视图,从而支持精确视觉定位。我们的方法展示了比基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法更高的定位精度。我们引入了启发式细化策略,其高效的优化能力可以快速定位目标节点,同时我们设置了步骤级优化步骤,以提高在小错误场景中的姿态精度。通过精心设计的启发式函数,它提供了高效的优化能力,能够在粗略的定位估计中迅速减少误差。我们的方法减轻了对复杂的神经网络模型的依赖,同时展示了对噪声的改进鲁棒性和在具有挑战的环境中更高的定位精度,这与神经网络联合优化策略相比。本文提出的优化框架通过整合3D重建和启发式细化策略的优势,为视觉定位引入了新颖的方法,并在多个基准数据集(包括7Scenes和Deep Blending数据集)上展示了强大的性能。我们的方法的实现已发布在https://github.com/anchang699/HGSLoc。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种名为HGSLoc的新型轻量级即插即用姿态优化框架,用于视觉定位任务。该框架结合3D重建和启发式优化策略,以实现更高的姿态估计精度。通过引入明确的几何地图进行3D表示和高保真渲染,支持准确视觉定位。与基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法相比,HGSLoc具有更高的定位精度。此外,其启发式优化策略能快速定位目标节点,并在存在小误差的场景中通过步骤级优化进一步提高姿态精度。本文方法降低了对复杂神经网络模型的依赖,在噪声环境下表现出更强的鲁棒性,并在具有挑战性的环境中实现了更高的定位精度。该优化框架结合了3D重建和启发式优化策略的优点,在多个基准数据集上表现出卓越性能。
关键见解
- 引入HGSLoc姿态优化框架,结合3D重建和启发式细化策略,提高姿态估计精度。
- 采用明确的几何地图进行3D表示和高保真渲染,支持高质量合成视图生成,从而准确实现视觉定位。
- 与基于NeRF的神经渲染定位方法相比,HGSLoc具有更高的定位精度。
- 引入启发式细化策略,具备快速定位目标节点和增强姿态精度的能力。
- 启发式函数的设计使优化过程更加高效,减少粗略定位估计中的误差。
- 方法降低了对复杂神经网络模型的依赖,同时在噪声环境下表现出更强的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图




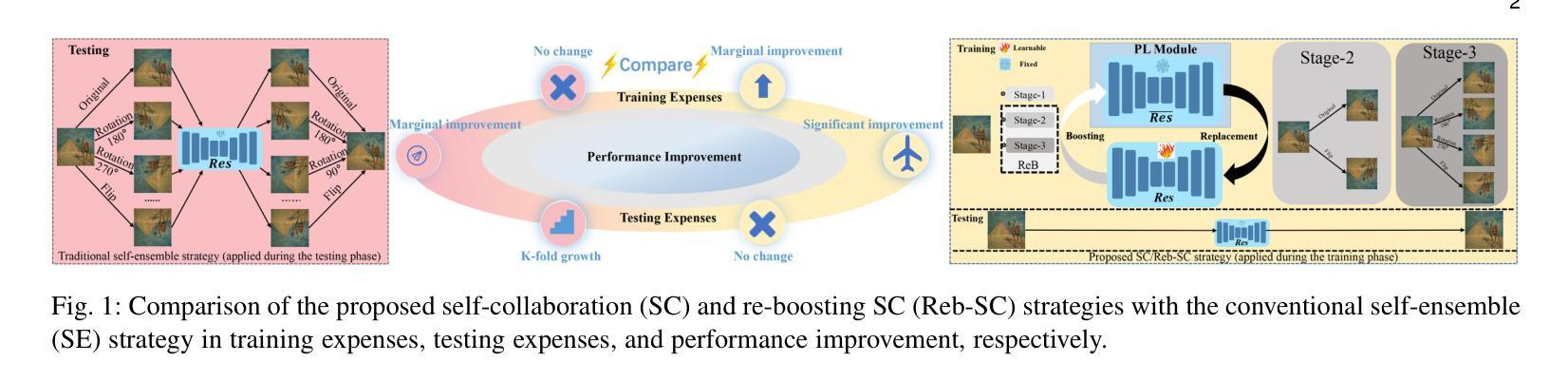
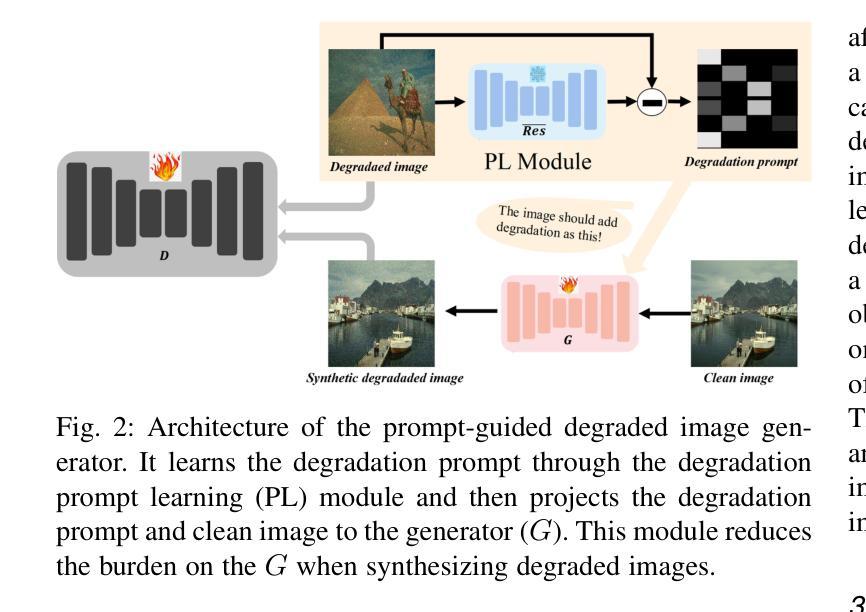
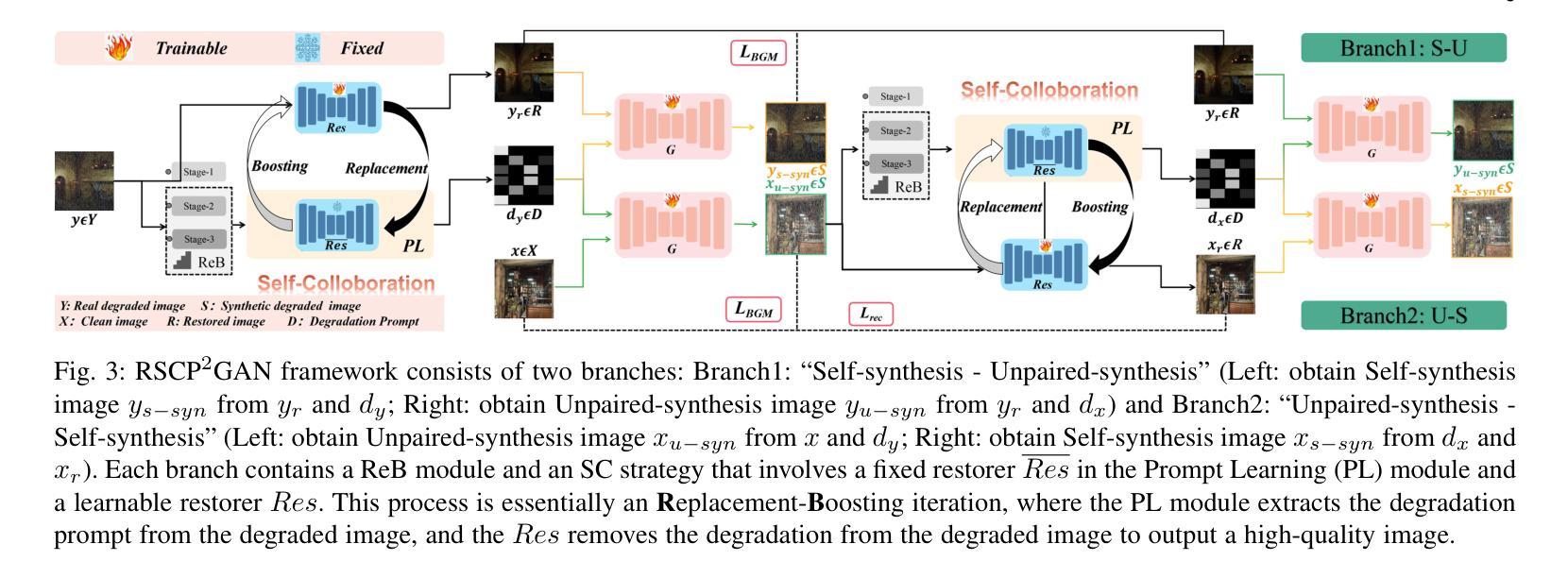
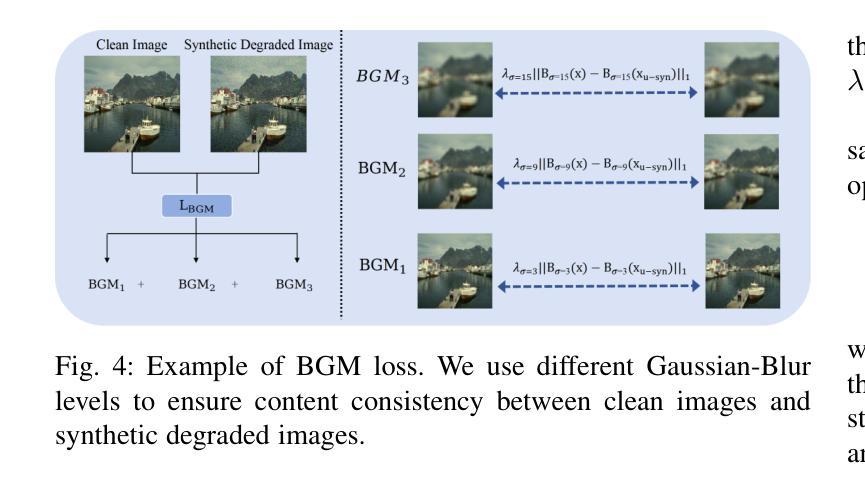
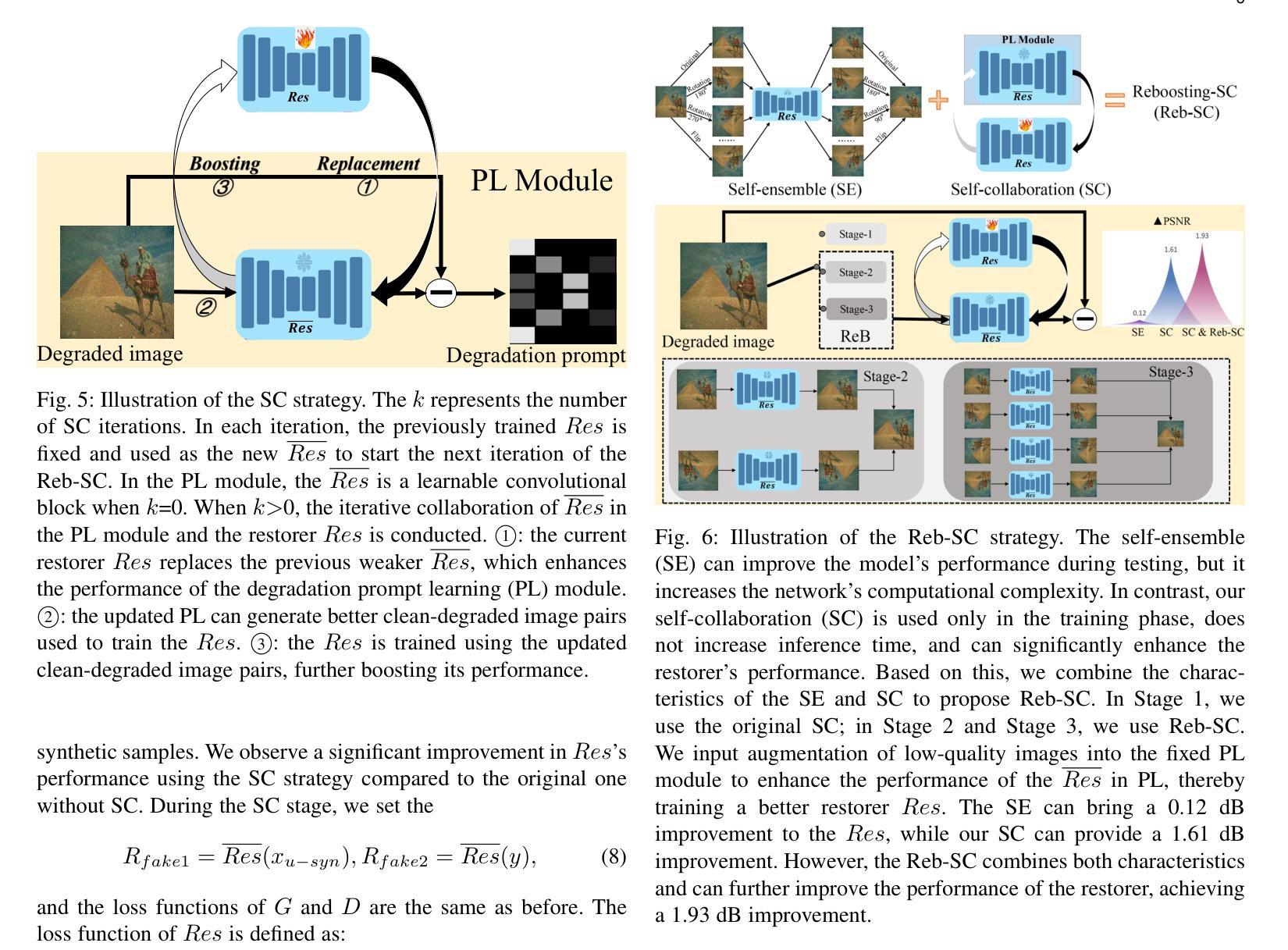
Re-boosting Self-Collaboration Parallel Prompt GAN for Unsupervised Image Restoration
Authors:Xin Lin, Yuyan Zhou, Jingtong Yue, Chao Ren, Kelvin C. K. Chan, Lu Qi, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Unsupervised restoration approaches based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) offer a promising solution without requiring paired datasets. Yet, these GAN-based approaches struggle to surpass the performance of conventional unsupervised GAN-based frameworks without significantly modifying model structures or increasing the computational complexity. To address these issues, we propose a self-collaboration (SC) strategy for existing restoration models. This strategy utilizes information from the previous stage as feedback to guide subsequent stages, achieving significant performance improvement without increasing the framework’s inference complexity. The SC strategy comprises a prompt learning (PL) module and a restorer ($Res$). It iteratively replaces the previous less powerful fixed restorer $\overline{Res}$ in the PL module with a more powerful $Res$. The enhanced PL module generates better pseudo-degraded/clean image pairs, leading to a more powerful $Res$ for the next iteration. Our SC can significantly improve the $Res$’s performance by over 1.5 dB without adding extra parameters or computational complexity during inference. Meanwhile, existing self-ensemble (SE) and our SC strategies enhance the performance of pre-trained restorers from different perspectives. As SE increases computational complexity during inference, we propose a re-boosting module to the SC (Reb-SC) to improve the SC strategy further by incorporating SE into SC without increasing inference time. This approach further enhances the restorer’s performance by approximately 0.3 dB. Extensive experimental results on restoration tasks demonstrate that the proposed model performs favorably against existing state-of-the-art unsupervised restoration methods. Source code and trained models are publicly available at: https://github.com/linxin0/RSCP2GAN.
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的无监督修复方法提供了一种有前途的解决方案,无需配对数据集。然而,这些基于GAN的方法在模型结构改动较小或计算复杂度不增加的情况下难以超越传统基于GAN的无监督框架的性能。为了解决这些问题,我们为现有的修复模型提出了一种自协作(SC)策略。该策略利用前一阶段的信息作为反馈来指导后续阶段,在不影响框架推理复杂度的情况下实现了显著的性能提升。SC策略包括一个提示学习(PL)模块和一个修复器(Res)。它迭代地将PL模块中之前较弱的固定修复器$\overline{Res}$替换为更强大的Res。增强的PL模块生成更好的伪退化/清洁图像对,从而为下一次迭代产生更强大的Res。我们的SC可以在推理过程中不增加额外参数或计算复杂度的情况下,提高Res的性能超过1.5分贝。同时,现有的自集成(SE)和我们的SC策略从不同角度提高了预训练修复器的性能。由于SE在推理过程中增加了计算复杂度,我们为SC增加了一个重增强模块(Reb-SC),通过将SE融入SC而不增加推理时间,进一步改进了SC策略。这种方法进一步提高了修复器的性能约0.3分贝。在修复任务上的大量实验结果证明,该模型与现有的最先进的无监督修复方法相比表现良好。源代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/linxin0/RSCP2GAN公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE T-PAMI
摘要
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的无监督修复方法在不依赖配对数据集的情况下展现出巨大的潜力。然而,这些方法往往难以超越传统无监督GAN框架的性能,且需要大幅度改变模型结构或增加计算复杂性。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种针对现有修复模型的自协作(SC)策略。该策略利用前一阶段的信息作为反馈来引导后续阶段,可在不增加框架推理复杂性的情况下显著提高性能。SC策略包括一个提示学习(PL)模块和一个修复器(Res)。它通过迭代方式用更强大的Res替换PL模块中较弱的固定修复器Res,从而生成更好的伪退化/清洁图像对,为下一次迭代提供更强大的Res。我们的SC可以在不增加推理阶段的额外参数或计算复杂性的情况下,显著提高Res的性能超过1.5分贝。同时,现有的自集成(SE)和我们的SC策略从不同角度提高了预训练修复器的性能。由于SE在推理过程中会增加计算复杂性,我们提出了对SC进行再提升模块(Reb-SC),通过融入SE而无需增加推理时间,进一步改进SC策略。此方法可将修复器的性能再提高大约0.3分贝。大量修复任务实验结果表明,所提出的模型在现有的先进无监督修复方法中表现优异。源代码和训练模型可在https://github.com/linxin0/RSCP2GAN获取。
关键见解
- 提出了一种自协作(SC)策略,针对现有基于GAN的修复模型性能不足的问题。
- SC策略通过利用前一阶段的信息作为反馈来引导后续阶段,提高了修复模型的性能。
- SC策略包括提示学习(PL)模块和修复器(Res),通过迭代方式优化性能。
- 与传统无监督GAN框架相比,SC策略在不增加推理复杂性的情况下,能显著提高性能超过1.5分贝。
- 引入再提升模块(Reb-SC),在融入自集成(SE)策略的同时,不增加推理时间,进一步提高模型性能。
- 提出的模型在大量修复任务上表现优越,超越现有先进无监督修复方法。
点此查看论文截图