⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-17 更新
FasTUSS: Faster Task-Aware Unified Source Separation
Authors:Francesco Paissan, Gordon Wichern, Yoshiki Masuyama, Ryo Aihara, François G. Germain, Kohei Saijo, Jonathan Le Roux
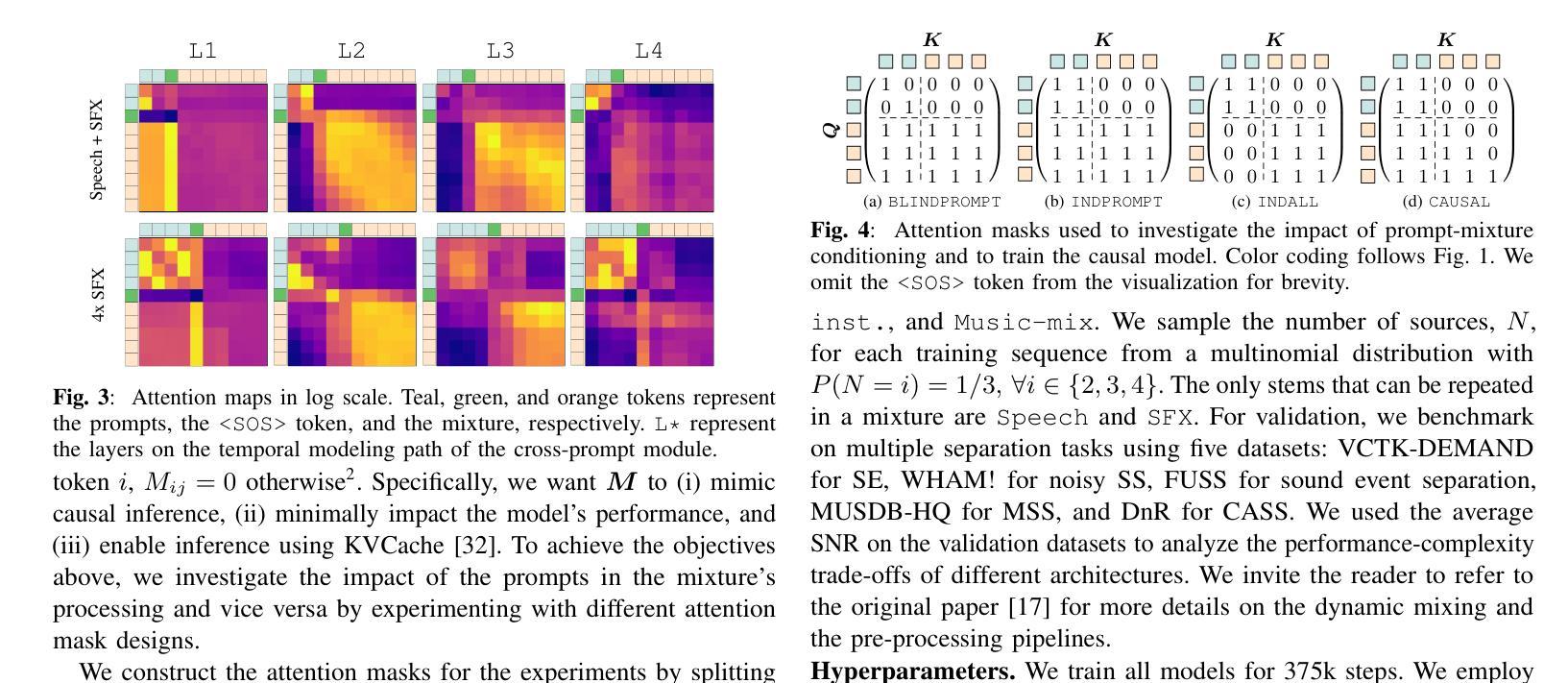
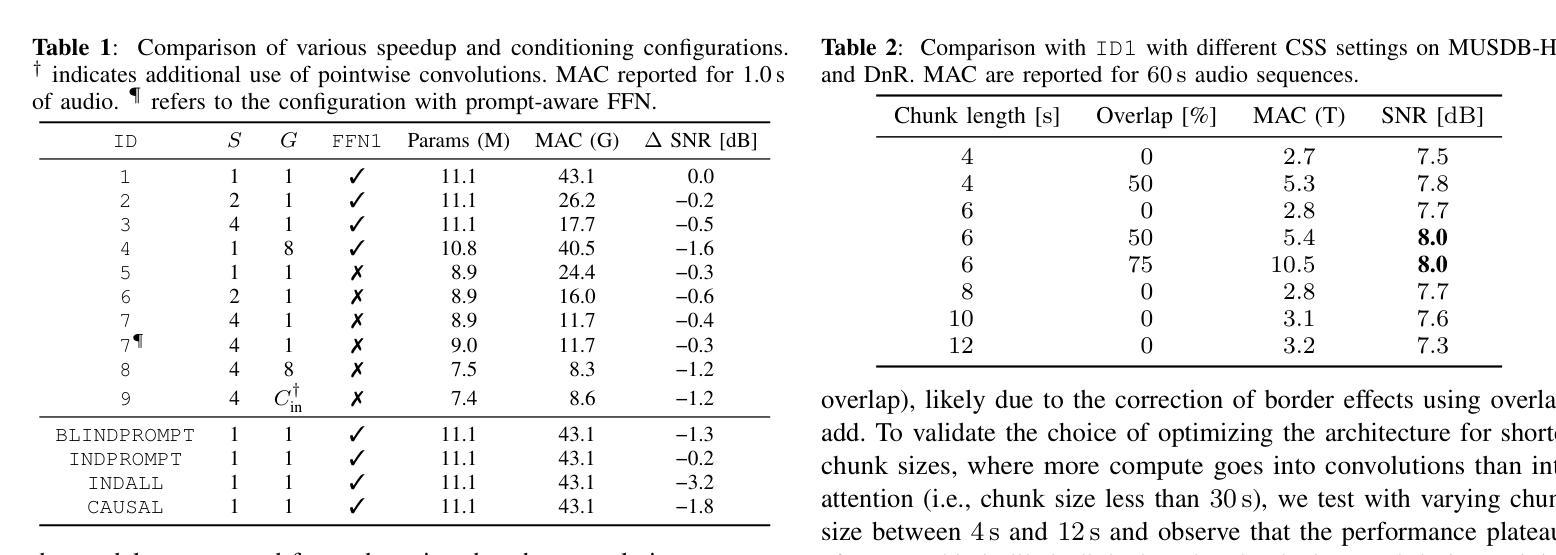
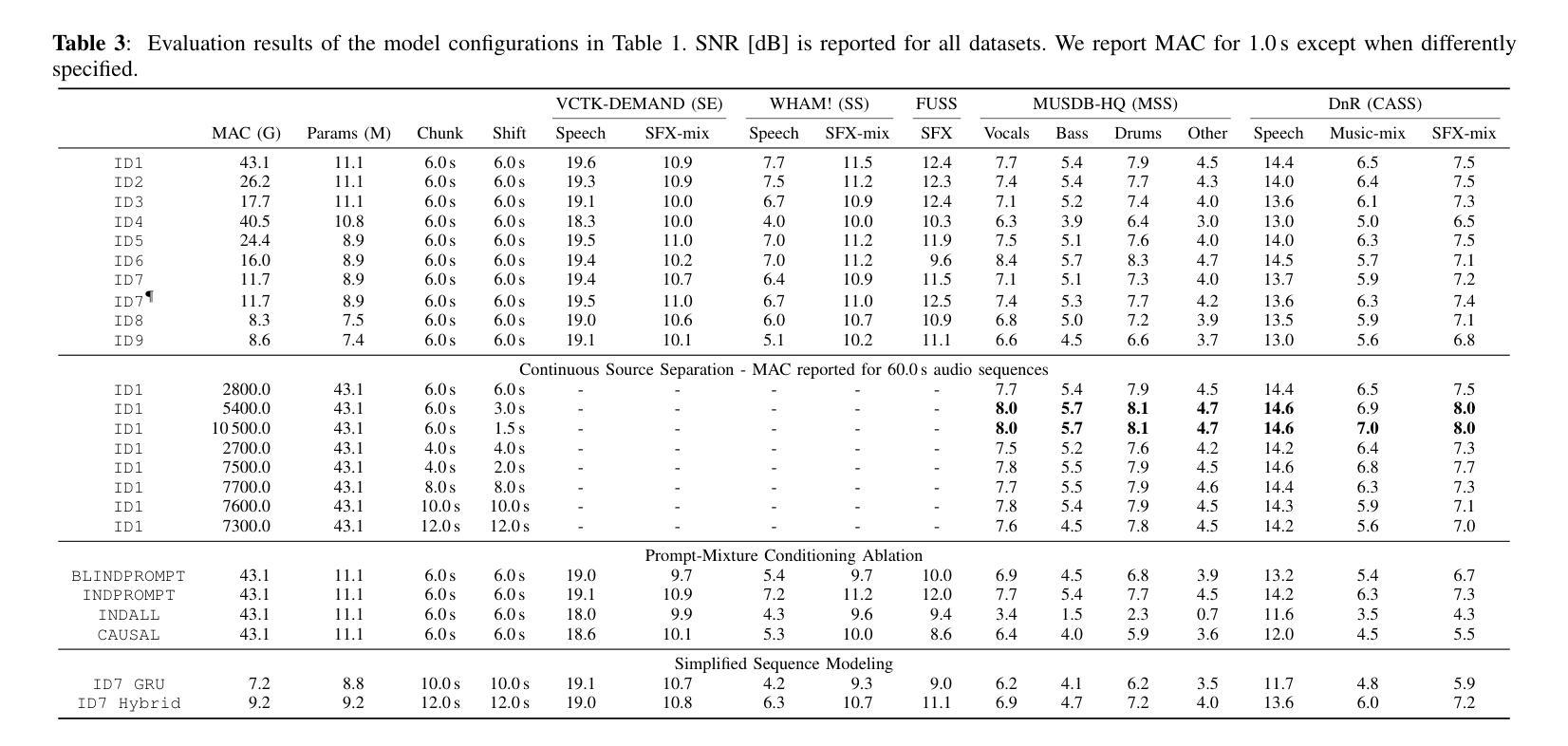
Time-Frequency (TF) dual-path models are currently among the best performing audio source separation network architectures, achieving state-of-the-art performance in speech enhancement, music source separation, and cinematic audio source separation. While they are characterized by a relatively low parameter count, they still require a considerable number of operations, implying a higher execution time. This problem is exacerbated by the trend towards bigger models trained on large amounts of data to solve more general tasks, such as the recently introduced task-aware unified source separation (TUSS) model. TUSS, which aims to solve audio source separation tasks using a single, conditional model, is built upon TF-Locoformer, a TF dual-path model combining convolution and attention layers. The task definition comes in the form of a sequence of prompts that specify the number and type of sources to be extracted. In this paper, we analyze the design choices of TUSS with the goal of optimizing its performance-complexity trade-off. We derive two more efficient models, FasTUSS-8.3G and FasTUSS-11.7G that reduce the original model’s operations by 81% and 73% with minor performance drops of 1.2dB and 0.4dB averaged over all benchmarks, respectively. Additionally, we investigate the impact of prompt conditioning to derive a causal TUSS model.
时间频率(TF)双路径模型是目前表现最好的音频源分离网络架构之一,在语音增强、音乐源分离和电影音频源分离等领域达到了最新技术性能水平。虽然这些模型参数相对较少,但它们仍然需要大量的运算,导致执行时间较高。随着在大量数据上训练更大模型以解决更一般任务的趋势,这一问题进一步加剧,例如最近推出的任务感知统一源分离(TUSS)模型。TUSS旨在使用一个条件模型解决音频源分离任务,它建立在TF-Locoformer的基础上,这是一个结合了卷积和注意力层的TF双路径模型。任务定义的形式是一系列提示,指定要提取的源的数量和类型。在本文中,我们分析了TUSS的设计选择,旨在优化其性能复杂性权衡。我们推出了两个更有效的模型FasTUSS-8.3G和FasTUSS-11.7G,它们将原始模型的运算量分别减少了81%和73%,在所有基准测试上的性能平均分别下降了1.2dB和0.4dB。此外,我们还研究了提示条件的影响,以推导出因果TUSS模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WASPAA 2025
Summary
时序双路径模型是目前表现最佳的音频源分离网络架构之一,广泛应用于语音增强、音乐源分离和电影音频源分离等领域。针对此架构运算量大、执行时间长的问题,本文分析了TUSS模型的设计选择,并优化其性能复杂度权衡,推出更加高效的FasTUSS-8.3G和FasTUSS-11.7G模型,分别将原始模型运算量降低了81%和73%,在各项基准测试中的性能下降分别为1.2dB和0.4dB。此外,本文还探讨了基于提示条件的因果TUSS模型的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 时序双路径模型是目前音频源分离领域的最佳网络架构之一。
- TUSS模型旨在使用单一条件模型解决音频源分离任务。
- TUSS模型基于TF-Locoformer架构,结合了卷积和注意力层。
- 本文分析了TUSS模型的设计选择,旨在优化其性能复杂度之间的权衡。
- 推出更高效的FasTUSS-8.3G和FasTUSS-11.7G模型,降低了运算量并保持了较好的性能。
- FasTUSS模型性能下降程度分别为1.2dB和0.4dB。
点此查看论文截图

WhisperKit: On-device Real-time ASR with Billion-Scale Transformers
Authors:Atila Orhon, Arda Okan, Berkin Durmus, Zach Nagengast, Eduardo Pacheco
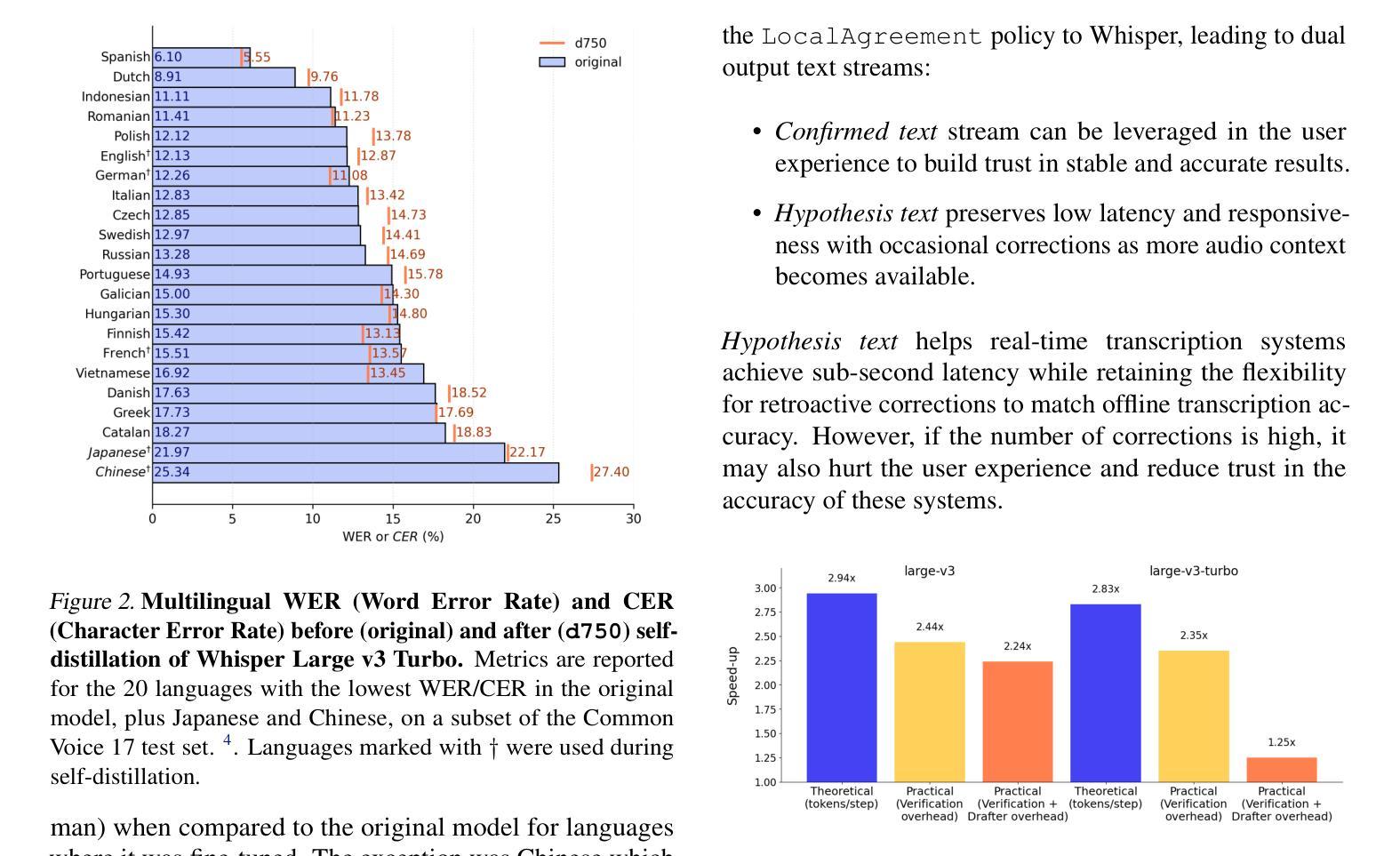
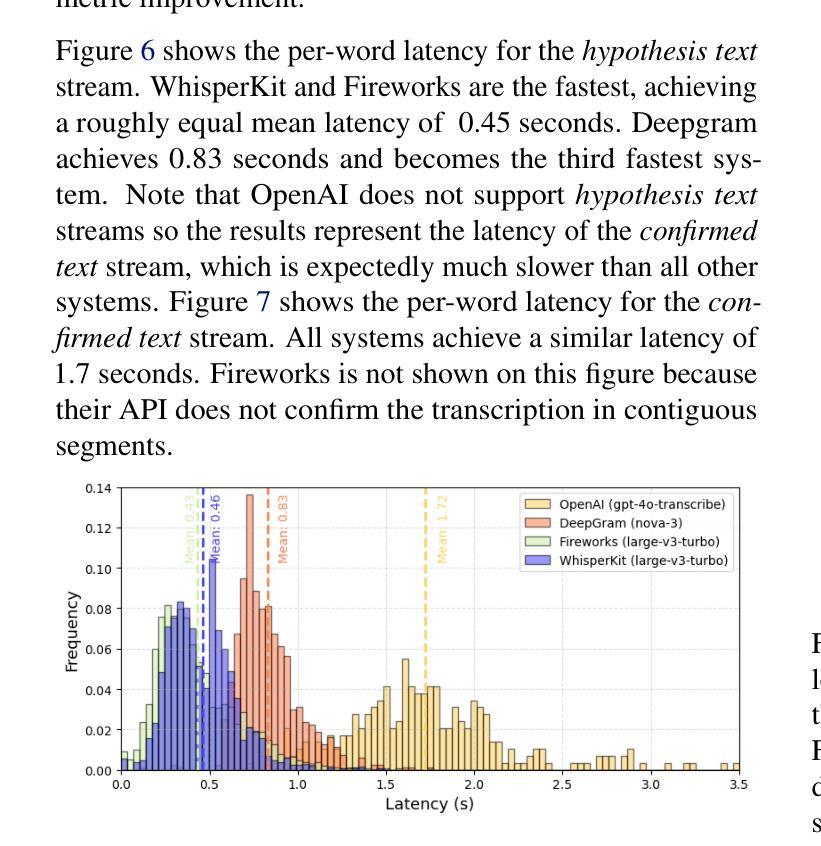
Real-time Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is a fundamental building block for many commercial applications of ML, including live captioning, dictation, meeting transcriptions, and medical scribes. Accuracy and latency are the most important factors when companies select a system to deploy. We present WhisperKit, an optimized on-device inference system for real-time ASR that significantly outperforms leading cloud-based systems. We benchmark against server-side systems that deploy a diverse set of models, including a frontier model (OpenAI gpt-4o-transcribe), a proprietary model (Deepgram nova-3), and an open-source model (Fireworks large-v3-turbo).Our results show that WhisperKit matches the lowest latency at 0.46s while achieving the highest accuracy 2.2% WER. The optimizations behind the WhisperKit system are described in detail in this paper.
实时自动语音识别(ASR)是机器学习许多商业应用的基础构件,包括实时字幕、听写、会议记录和医疗记录等。公司在选择部署系统时,准确性和延迟是最重要的因素。我们推出了WhisperKit,这是一个优化的实时ASR设备端推理系统,它显著优于领先的云系统。我们以服务器端系统为基准进行测试,这些系统部署了多种模型,包括前沿模型(OpenAI gpt-4o-transcribe)、专有模型(Deepgram nova-3)和开源模型(Fireworks large-v3-turbo)。我们的结果表明,WhisperKit在达到最低延迟0.46秒的同时,实现了最高的准确性,词错误率为2.2%。WhisperKit系统背后的优化细节都详细描述在这篇论文中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 - On-Device Learning for Foundational Models Workshop
摘要
实时语音识别(ASR)是机器学习许多商业应用的基础构件,包括实时字幕、听写、会议转录和医疗记录等。公司在选择部署系统时,准确性和延迟是最重要的因素。本文介绍了WhisperKit,这是一种优化的实时ASR设备端推理系统,显著优于领先的云系统。我们以部署了各种模型的服务器端系统为基准进行了评估,包括前沿模型(OpenAI gpt-4o-transcribe)、专有模型(Deepgram nova-3)和开源模型(Fireworks large-v3-turbo)。结果表明,WhisperKit在达到最低延迟0.46秒的同时实现了最高的准确性,字错误率为2.2%。本文详细描述了WhisperKit系统的优化过程。
要点
- 实时语音识别(ASR)在许多商业应用中具有关键作用,如实时字幕、听写等。
- 准确性与延迟是选择语音识别系统最重要的两个因素。
- WhisperKit是一个优化的实时ASR手机端推理系统,表现显著优于多数云系统。
- WhisperKit的基准测试包括与多种服务器端系统对比,包括前沿模型如OpenAI gpt-4o-transcribe。
- WhisperKit在延迟和准确性方面表现优异,延迟达到最低的0.46秒,字错误率为2.2%。
- WhisperKit的优化过程在论文中有详细描述。
- 该系统可为商业应用提供高效、准确的实时语音识别服务。
点此查看论文截图

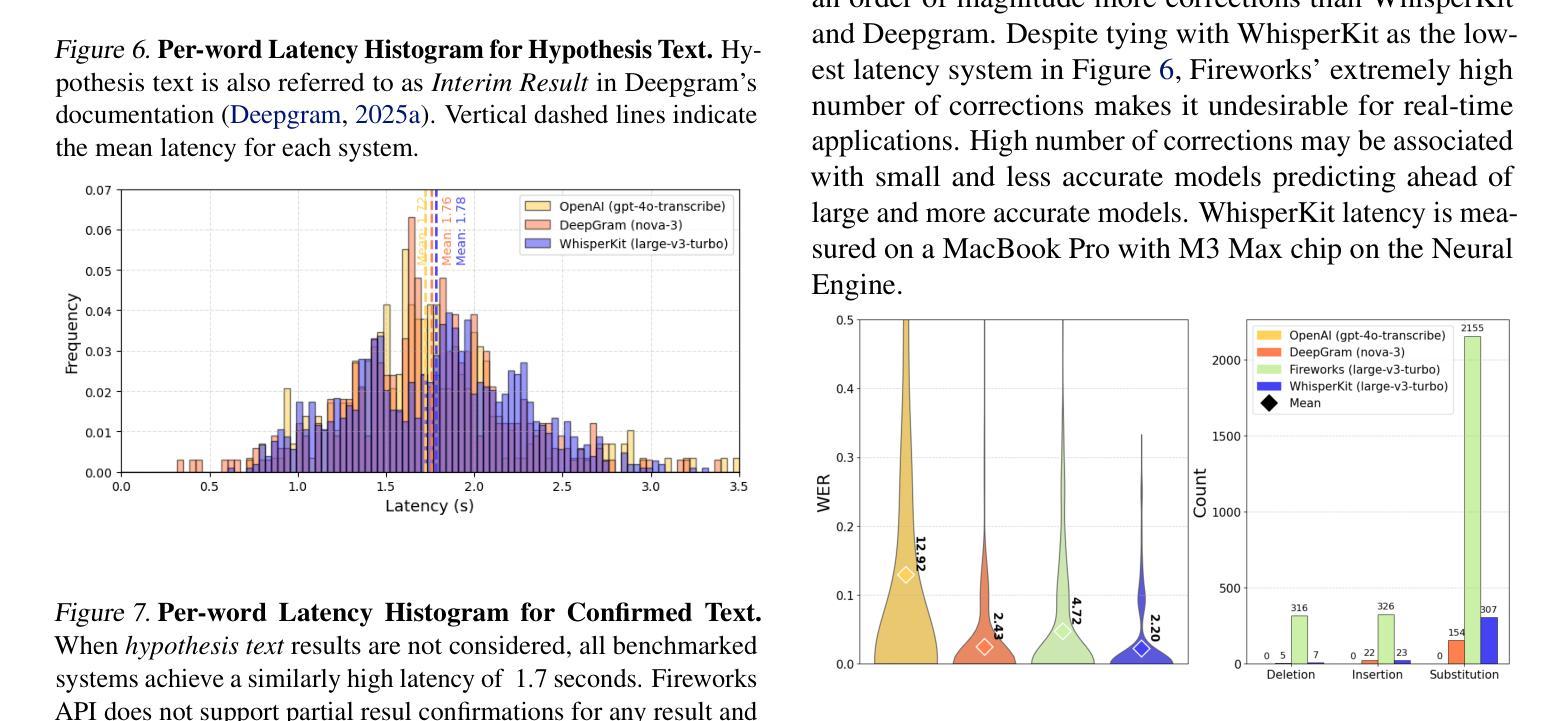
Supporting SENĆOTEN Language Documentation Efforts with Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Mengzhe Geng, Patrick Littell, Aidan Pine, PENÁĆ, Marc Tessier, Roland Kuhn
The SEN'{C}OTEN language, spoken on the Saanich peninsula of southern Vancouver Island, is in the midst of vigorous language revitalization efforts to turn the tide of language loss as a result of colonial language policies. To support these on-the-ground efforts, the community is turning to digital technology. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) technology holds great promise for accelerating language documentation and the creation of educational resources. However, developing ASR systems for SEN'{C}OTEN is challenging due to limited data and significant vocabulary variation from its polysynthetic structure and stress-driven metathesis. To address these challenges, we propose an ASR-driven documentation pipeline that leverages augmented speech data from a text-to-speech (TTS) system and cross-lingual transfer learning with Speech Foundation Models (SFMs). An n-gram language model is also incorporated via shallow fusion or n-best restoring to maximize the use of available data. Experiments on the SEN'{C}OTEN dataset show a word error rate (WER) of 19.34% and a character error rate (CER) of 5.09% on the test set with a 57.02% out-of-vocabulary (OOV) rate. After filtering minor cedilla-related errors, WER improves to 14.32% (26.48% on unseen words) and CER to 3.45%, demonstrating the potential of our ASR-driven pipeline to support SEN'{C}OTEN language documentation.
SEN’C’OTEN语言是讲于温哥华岛南部的塞尼切半岛的一种语言。由于殖民语言政策导致语言流失的形势严峻,该语言正在经历着一场激烈的振兴努力。为了支持这些地面上的努力,该社区正转向数字技术。自动语音识别(ASR)技术对于加速语言文献的记载和教育资源的创造方面有很大潜力。然而,由于数据有限以及由聚合结构和压力驱动的换词导致的显著词汇变化,开发适用于SEN’C’OTEN的ASR系统是一个挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种ASR驱动的文献记录管道,该管道利用文本到语音(TTS)系统的增强语音数据以及基于语音基础模型的跨语言迁移学习。通过浅融合或n-best恢复方法融入n元语言模型,以充分利用可用数据。在SEN’C’OTEN数据集上的实验显示,测试集上的单词错误率(WER)为19.34%,字符错误率(CER)为5.09%,词汇表外(OOV)的比率为57.02%。过滤掉与cedilla相关的轻微错误后,WER提高至14.32%(未见过词汇的比率为26.48%),CER降至3.45%,这证明了我们的ASR驱动管道在支持SEN’C’OTEN语言文献记录方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ComputEL-8
Summary
本文介绍了位于温哥华岛南部萨尼奇半岛的森科特恩语言(SEN’C{O}TEN)正处于激烈的复兴阶段,以扭转因殖民语言政策导致的语言流失。社区正在借助数字技术来支持这一复兴工作,自动语音识别(ASR)技术有望加速语言记录和创建教育资源。然而,由于数据有限和词汇量的巨大变化(来自其综合结构和压力驱动的元音变化),开发ASR系统对森科特恩语言具有挑战性。为此,本文提出了一种基于ASR的语言记录管道,利用文本到语音(TTS)系统的增强语音数据和跨语言的迁移学习与语音基础模型(SFMs)。实验结果显示,该管道在森科特恩数据集上的词错误率(WER)为14.32%(未见词的错误率为26.48%),字符错误率(CER)为3.45%,证明了该管道支持森科特恩语言记录的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- SEN’C{O}TEN语言正在经历复兴,以应对殖民语言政策导致的语言流失。
- 社区正在借助数字技术和自动语音识别(ASR)技术来支持这一复兴工作。
- 开发针对SEN’C{O}TEN语言的ASR系统面临数据有限和词汇变化大的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于ASR的语言记录管道,结合增强语音数据、跨语言迁移学习和语音基础模型(SFMs)。
- 实验结果展示了该管道在森科特恩数据集上的性能,词错误率(WER)和字符错误率(CER)有所降低。
- 管道具有潜力支持森科特恩语言的记录工作。
点此查看论文截图

AudioMAE++: learning better masked audio representations with SwiGLU FFNs
Authors:Sarthak Yadav, Sergios Theodoridis, Zheng-Hua Tan
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) trained on audio spectrogram patches have emerged as a prominent approach for learning self-supervised audio representations. While several recent papers have evaluated key aspects of training MAEs on audio data, the majority of these approaches still leverage vanilla transformer building blocks, whereas the transformer community has seen steady integration of newer architectural advancements. In this work, we propose AudioMAE++, a revamped audio masked autoencoder with two such enhancements, namely macaron-style transformer blocks with gated linear units. When pretrained on the AudioSet dataset, the proposed AudioMAE++ models outperform existing MAE based approaches on 10 diverse downstream tasks, demonstrating excellent performance on audio classification and speech-based benchmarks. The proposed AudioMAE++ models also demonstrate excellent scaling characteristics, outperforming directly comparable standard MAE baselines with up to 4x more parameters.
基于音频频谱图块训练的Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)已成为学习自监督音频表示的一种突出方法。虽然最近的几篇论文已经评估了训练MAEs在音频数据上的关键方面,但大多数方法仍然使用普通的变压器构建块,而变压器社区已经看到了新的架构进步的稳定集成。在这项工作中,我们提出了AudioMAE++,这是一个翻新的音频掩码自动编码器,具有两个这样的增强功能,即带有门控线性单元的夹心饼干式变压器块。在AudioSet数据集上进行预训练时,所提出的AudioMAE++模型在10个不同的下游任务上优于现有的基于MAE的方法,在音频分类和基于语音的基准测试中表现出卓越的性能。此外,所提出的AudioMAE++模型还表现出卓越的可扩展性特征,在参数最多达四倍的可直接比较的标准MAE基线之上表现良好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TO APPEAR AT IEEE MLSP 2025
Summary
基于音频频谱图块的Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)已成为学习自监督音频表示的主流方法。本文提出AudioMAE++模型,其引入了两项改进,包括使用具有门控线性单元的夹心饼干风格的变压器块。在AudioSet数据集上进行预训练后,AudioMAE++模型在多个下游任务上的性能优于现有的MAE方法,展现了出色的音频分类和语音基准测试性能。此外,AudioMAE++模型还展现出卓越的可扩展性,使用多达四倍参数的常规MAE基线模型也能实现出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Autoencoders (MAEs)成为自监督音频表示学习的主要方法。
- AudioMAE++模型引入了两项改进:采用夹心饼干风格的变压器块和门控线性单元。
- AudioMAE++在多个下游任务上的性能优于现有MAE方法。
- AudioMAE++模型在音频分类和语音基准测试上展现出卓越性能。
- AudioMAE++模型具有良好的可扩展性,使用更多的参数也能实现出色的性能。
点此查看论文截图


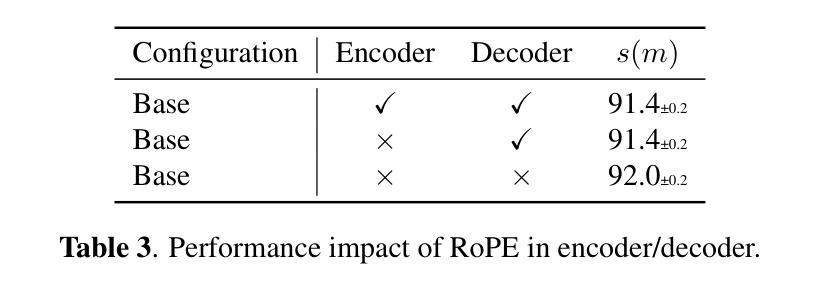
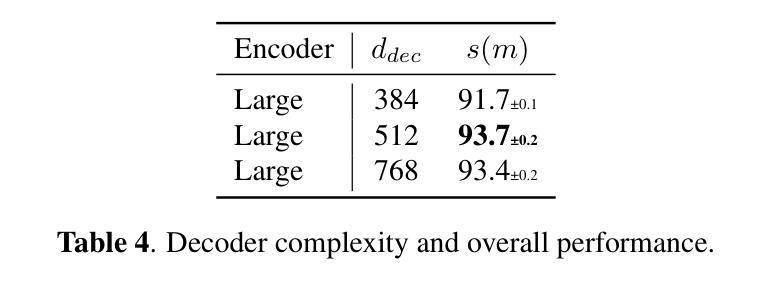
Knowing When to Quit: Probabilistic Early Exits for Speech Separation
Authors:Kenny Falkær Olsen. Mads Østergaard, Karl Ulbæk, Søren Føns Nielsen, Rasmus Malik Høegh Lindrup, Bjørn Sand Jensen, Morten Mørup
In recent years, deep learning-based single-channel speech separation has improved considerably, in large part driven by increasingly compute- and parameter-efficient neural network architectures. Most such architectures are, however, designed with a fixed compute and parameter budget, and consequently cannot scale to varying compute demands or resources, which limits their use in embedded and heterogeneous devices such as mobile phones and hearables. To enable such use-cases we design a neural network architecture for speech separation capable of early-exit, and we propose an uncertainty-aware probabilistic framework to jointly model the clean speech signal and error variance which we use to derive probabilistic early-exit conditions in terms of desired signal-to-noise ratios. We evaluate our methods on both speech separation and enhancement tasks, and we show that a single early-exit model can be competitive with state-of-the-art models trained at many compute and parameter budgets. Our framework enables fine-grained dynamic compute-scaling of speech separation networks while achieving state-of-the-art performance and interpretable exit conditions.
近年来,基于深度学习的单通道语音分离技术有了显著的改进,这在很大程度上是由于神经网络架构的计算和参数效率不断提高。然而,大多数这样的架构都是根据固定的计算和参数预算设计的,因此无法适应变化的计算需求或资源,这限制了它们在嵌入式和异构设备(如手机和可穿戴设备)中的应用。为了支持这些用例,我们设计了一种用于语音分离的神经网络架构,该架构具备提前退出功能。我们提出了一种基于不确定性的概率框架,以联合建模干净语音信号和误差方差,并利用其推导概率提前退出条件,以达到所需的信噪比。我们在语音分离和增强任务上评估了我们的方法,并证明单个提前退出模型可以与在许多计算和参数预算上训练的最新模型相竞争。我们的框架能够在实现最先进的性能的同时,实现对语音分离网络的精细动态计算缩放,并提供可解释的退出条件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着深度学习在单通道语音分离领域的不断发展,近年来神经网络架构的效率和性能不断提升。然而,大多数架构都是针对固定计算和参数预算设计的,无法适应不同的计算需求或资源限制,这在嵌入式和异构设备(如手机和可佩戴设备)中的应用受到限制。为此,我们设计了一种具备早期退出功能的语音分离神经网络架构,并提出一种不确定性感知的概率框架,以联合建模干净语音信号和误差方差,从而推导出基于所需信噪比的概率早期退出条件。我们的方法在语音分离和增强任务上表现出竞争力,单个早期退出模型即可与在多种计算和参数预算下训练的最新模型相抗衡。我们的框架实现了语音分离网络的精细动态计算缩放,同时达到了最新性能并提供了可解释的早期退出条件。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在单通道语音分离领域取得显著进步,归功于更高效的神经网络架构。
- 现有架构大多针对固定计算和参数预算设计,无法适应不同计算需求或资源限制。
- 提出一种具备早期退出功能的语音分离神经网络架构,适用于嵌入式和异构设备。
- 引入不确定性感知的概率框架,联合建模干净语音信号和误差方差。
- 基于信噪比推导概率早期退出条件,实现更精细的动态计算缩放。
- 方法在语音分离和增强任务上表现竞争力,与最新模型相当。
点此查看论文截图

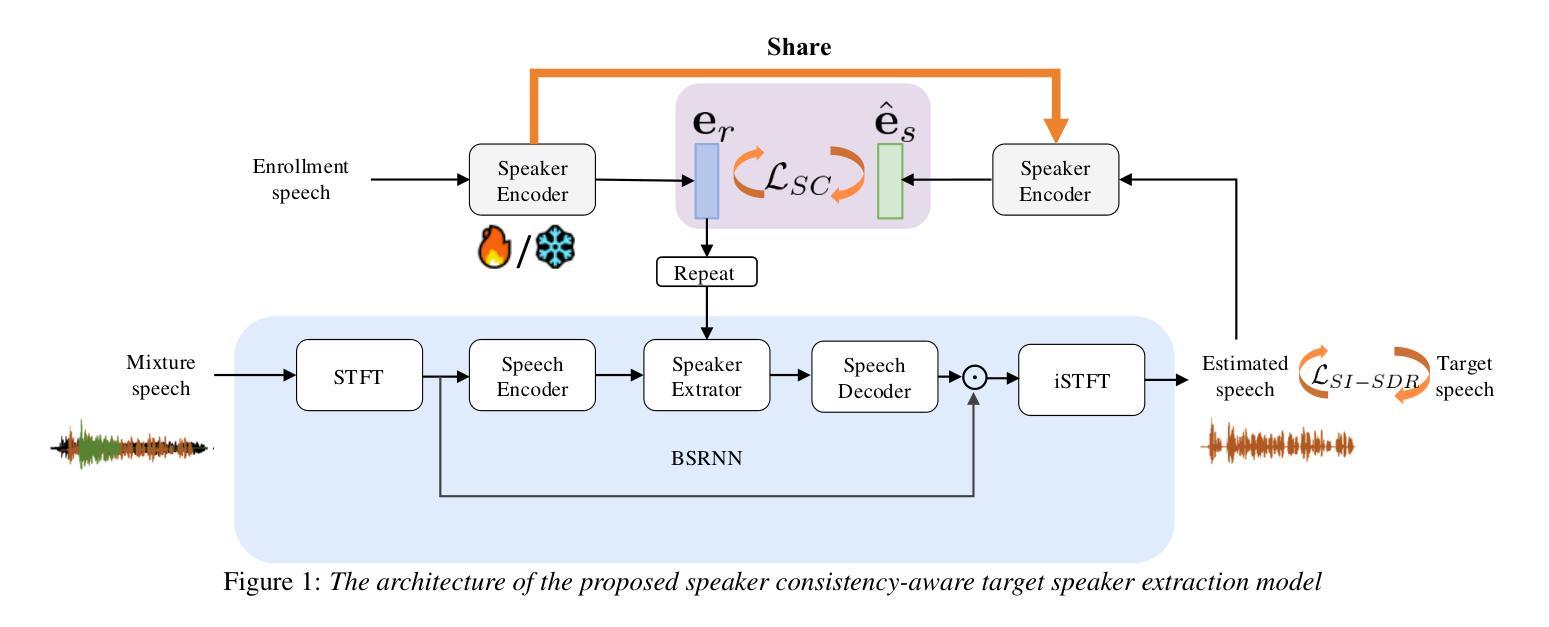
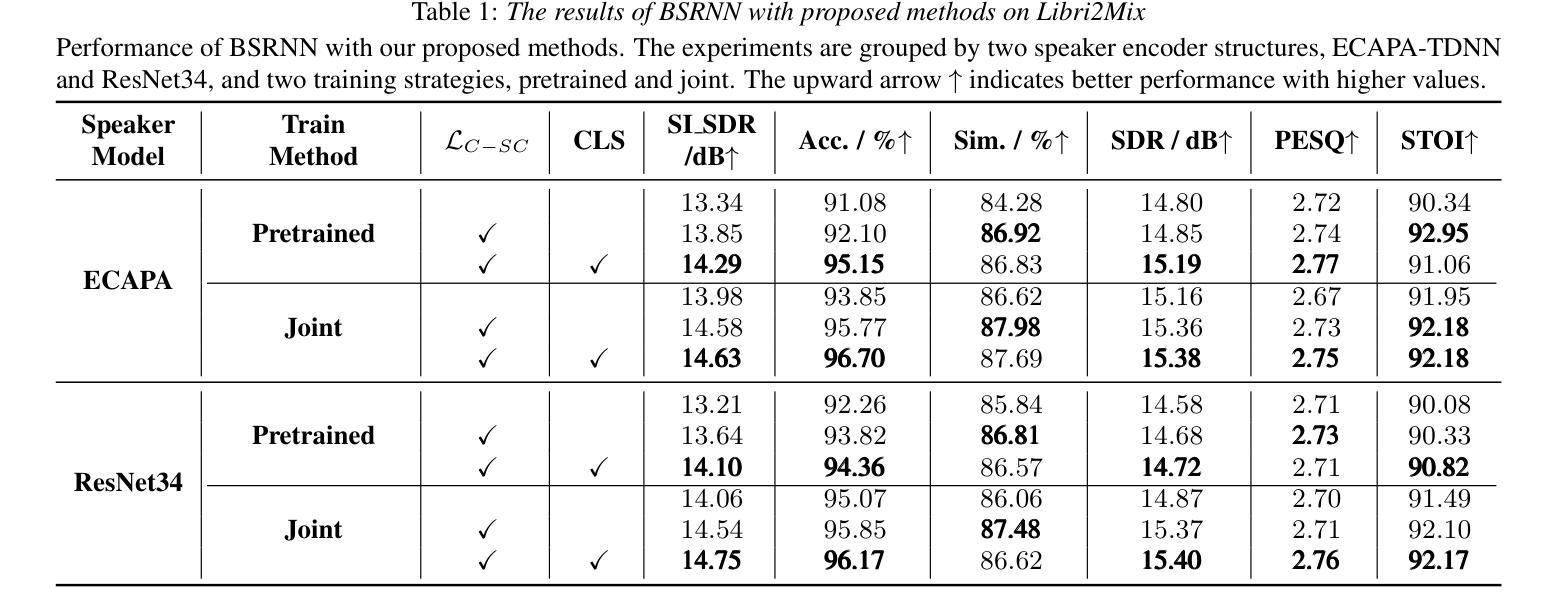
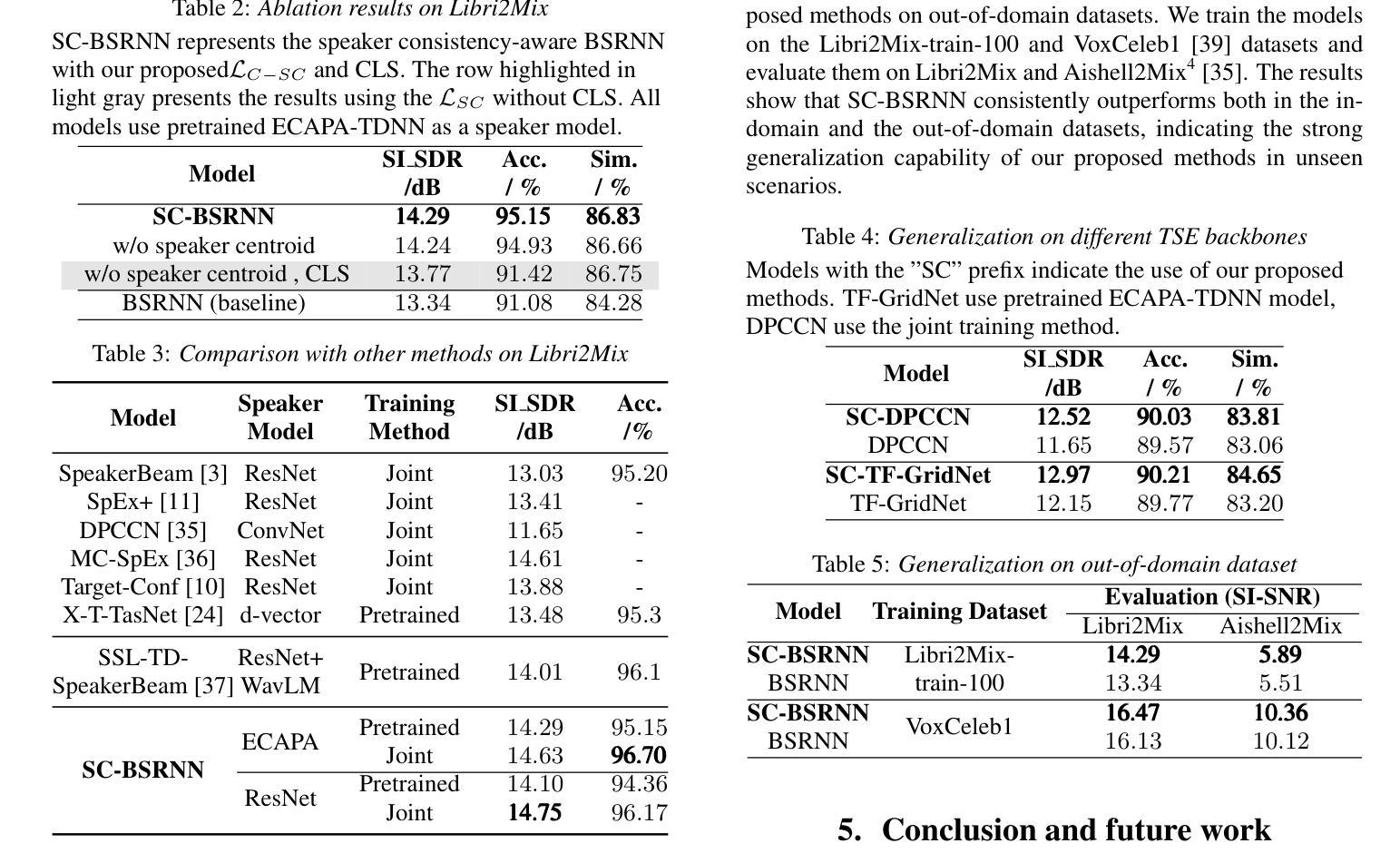
SC-TSE: Speaker Consistency-Aware Target Speaker Extraction
Authors:Shu Wu, Anbin Qi, Yanzhang Xie, Xiang Xie
Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) uses a reference cue to extract the target speech from a mixture. In TSE systems relying on audio cues, the speaker embedding from the enrolled speech is crucial to performance. However, these embeddings may suffer from speaker identity confusion. Unlike previous studies that focus on improving speaker embedding extraction, we improve TSE performance from the perspective of speaker consistency. In this paper, we propose a speaker consistency-aware target speaker extraction method that incorporates a centroid-based speaker consistency loss. This approach enhances TSE performance by ensuring speaker consistency between the enrolled and extracted speech. In addition, we integrate conditional loss suppression into the training process. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of our proposed methods in advancing the TSE performance. A speech demo is available online.\footnote{https://sc-tse.netlify.app/
目标说话人提取(TSE)使用参考线索从混合语音中提取目标语音。在依赖音频线索的TSE系统中,注册语音的说话人嵌入对性能至关重要。然而,这些嵌入可能会受到说话人身份混淆的影响。与以往专注于提高说话人嵌入提取的研究不同,我们从说话人一致性的角度提高TSE的性能。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于质心的说话人一致性感知目标说话人提取方法,该方法结合了基于质心的说话人一致性损失。这种方法通过确保注册语音和提取语音之间的说话人一致性,提高了TSE的性能。此外,我们将条件损失抑制集成到训练过程中。实验结果验证了我们的方法在提高TSE性能方面的有效性。在线提供语音演示。注:https://sc-tse.netlify.app/(在线演示链接)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept to Interspeech2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于音频提示的目标语音提取系统(Target Speaker Extraction,简称TSE)。该系统使用基于质心的说话人一致性损失方法提高说话人一致性,进而提高已注册语音和目标提取语音之间的性能。此外,还结合了条件损失抑制进行训练。本文提出的两种方法提高了TSE的性能。可通过在线语音演示展示相关内容。具体网址已在文中给出。
Key Takeaways
- TSE系统利用参考线索从混合语音中提取目标语音。
- 音频提示下的TSE系统中,已注册语音的说话人嵌入对性能至关重要。
- 说话人嵌入可能受到说话人身份混淆的影响。
- 本文从提高说话人一致性的角度改进了TSE性能。
- 提出了一种基于质心的说话人一致性损失方法,确保已注册和提取的语音之间的说话人一致性。
- 结合条件损失抑制进行训练,进一步提高TSE性能。
点此查看论文截图

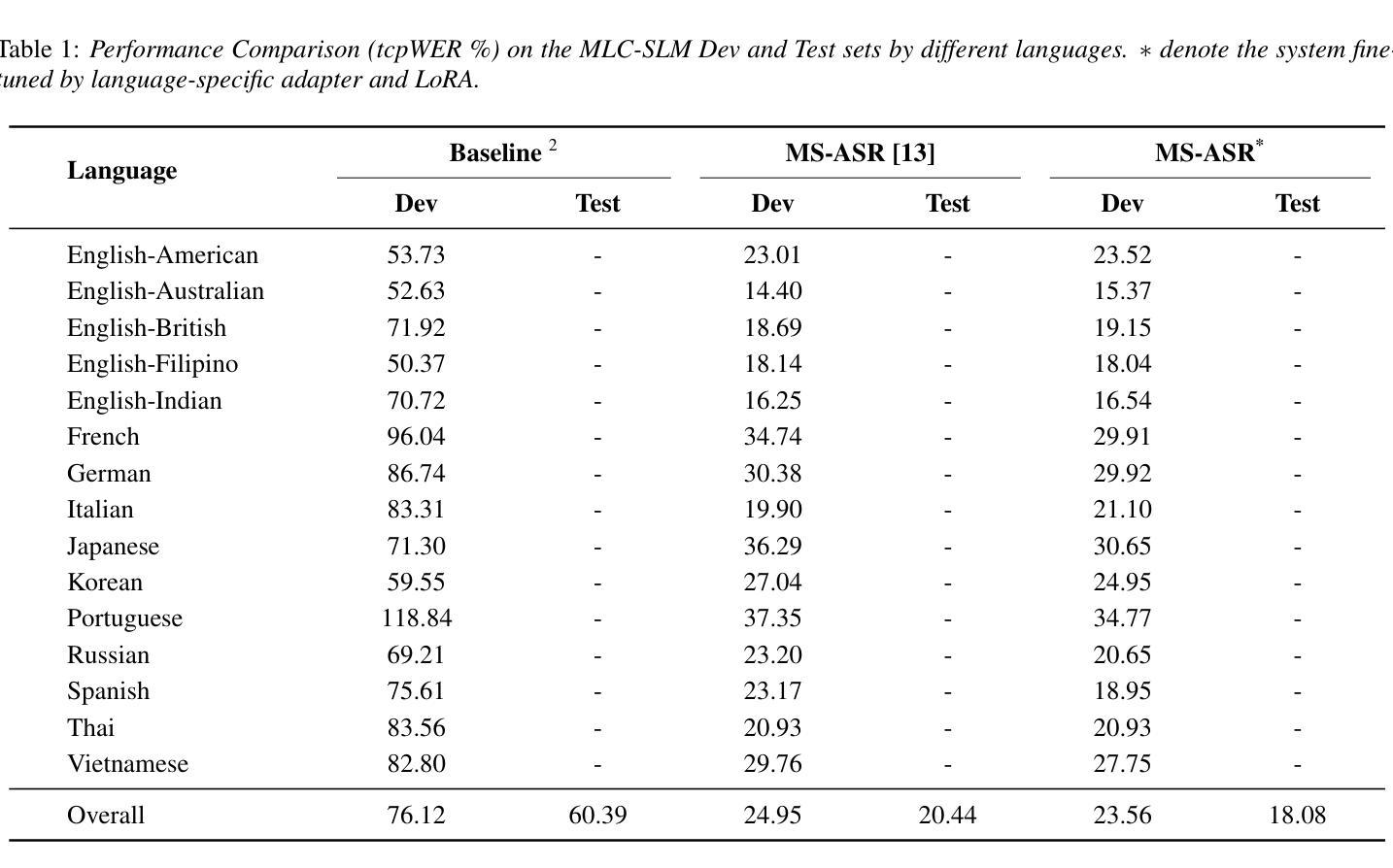
The DKU System for Multi-Speaker Automatic Speech Recognition in MLC-SLM Challenge
Authors:Yuke Lin, Ming Cheng, Ze Li, Ming Li
We present the DKU system for Task 2 of the MLC-SLM Challenge, which aims to perform multi-speaker automatic speech recognition directly from raw audio without Oracle speaker labels or time boundaries. Our approach builds upon a diarization-aware framework integrating speaker embeddings and temporal utterance boundaries into a Qwen2.5-based large language model (LLM). Then, we enhance the system’s multilingual performance by fine-tuning language-specific adapters and LoRA modules within the LLM decoder. Finally, our system achieves the tcpWER of 23.56% and 18.08% on the development and test sets of the MLC-SLM dataset, substantially outperforming the official baseline.
我们为MLC-SLM挑战的Task 2提出了DKU系统,旨在直接从原始音频执行多发言人自动语音识别,无需Oracle发言人标签或时间边界。我们的方法基于一个融合发言人嵌入和时序话语边界的识辨化框架,该框架以基于Qwen2.5的大型语言模型(LLM)为基础。然后,我们通过微调LLM解码器中的语言特定适配器和LoRA模块,增强系统的多语言能力。最后,我们的系统在MLC-SLM数据集的开发集和测试集上实现了tcpWER分别为23.56%和18.08%,大幅超越了官方基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report for MLC-SLM Challenge in Interspeech2025
Summary
本研究提出了DKU系统,用于MLC-SLM挑战任务2,旨在直接从原始音频进行多说话者自动语音识别,无需Oracle说话者标签或时间边界。研究采用基于语音识别模型的结合说话者嵌入和临时话语边界的基于Qwen2.5的大型语言模型(LLM)。通过微调语言特定适配器和LoRA模块,增强了系统的多语言能力。最终,在MLC-SLM数据集的开发和测试集上,该系统实现了tcpWER分别为23.56%和18.08%,明显优于官方基线。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出DKU系统,针对MLC-SLM挑战任务2的多说话者自动语音识别任务。
- 系统无需Oracle说话者标签或时间边界信息。
- 系统采用基于Qwen2.5的大型语言模型(LLM),集成说话者嵌入和临时话语边界。
- 通过微调语言特定适配器和LoRA模块,增强了系统的多语言能力。
- 系统在MLC-SLM数据集的开发集上实现了tcpWER为23.56%。
- 系统在MLC-SLM数据集的测试集上实现了tcpWER为18.08%,优于官方基线。
点此查看论文截图

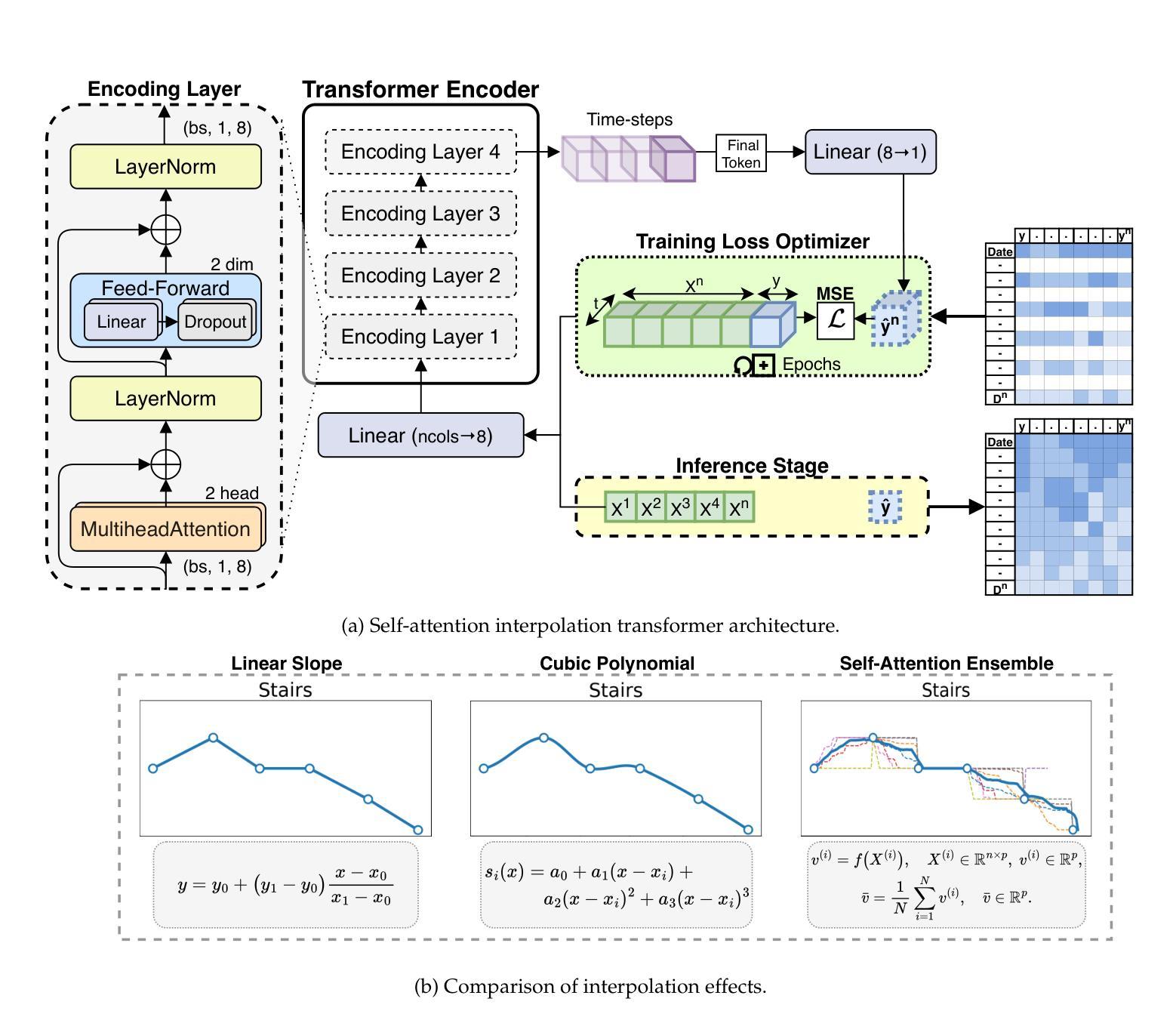
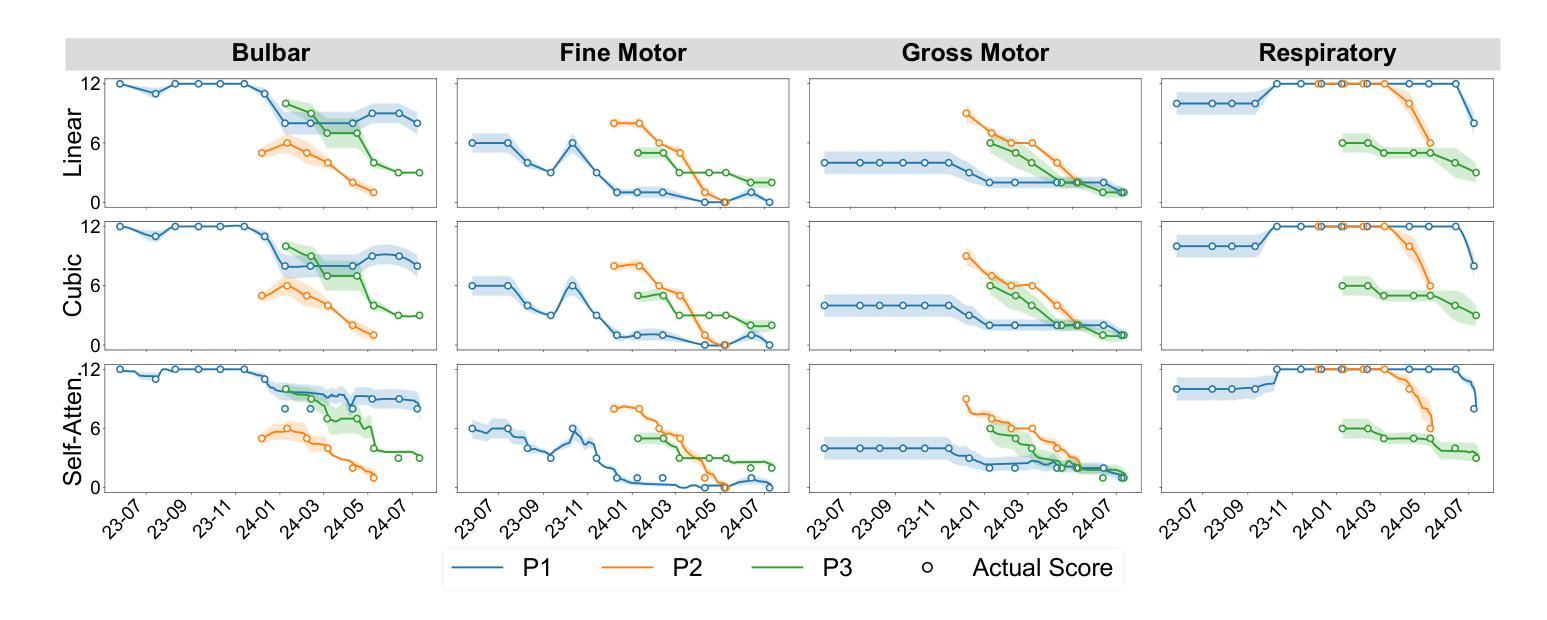
Enhancing ALS Progression Tracking with Semi-Supervised ALSFRS-R Scores Estimated from Ambient Home Health Monitoring
Authors:Noah Marchal, William E. Janes, Mihail Popescu, Xing Song
Clinical monitoring of functional decline in ALS relies on periodic assessments that may miss critical changes occurring between visits. To address this gap, semi-supervised regression models were developed to estimate rates of decline in a case series cohort by targeting ALSFRS- R scale trajectories with continuous in-home sensor monitoring data. Our analysis compared three model paradigms (individual batch learning and cohort-level batch versus incremental fine-tuned transfer learning) across linear slope, cubic polynomial, and ensembled self-attention pseudo-label interpolations. Results revealed cohort homogeneity across functional domains responding to learning methods, with transfer learning improving prediction error for ALSFRS-R subscales in 28 of 32 contrasts (mean RMSE=0.20(0.04)), and individual batch learning for predicting the composite scale (mean RMSE=3.15(1.25)) in 2 of 3. Self-attention interpolation achieved the lowest prediction error for subscale-level models (mean RMSE=0.19(0.06)), capturing complex nonlinear progression patterns, outperforming linear and cubic interpolations in 20 of 32 contrasts, though linear interpolation proved more stable in all ALSFRS-R composite scale models (mean RMSE=0.23(0.10)). We identified distinct homogeneity-heterogeneity profiles across functional domains with respiratory and speech exhibiting patient-specific patterns benefiting from personalized incremental adaptation, while swallowing and dressing functions followed cohort-level trajectories suitable for transfer models. These findings suggest that matching learning and pseudo-labeling techniques to functional domain-specific homogeneity-heterogeneity profiles enhances predictive accuracy in ALS progression tracking. Integrating adaptive model selection within sensor monitoring platforms could enable timely interventions and scalable deployment in future multi-center studies.
临床监测肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)的功能衰退依赖于定期评估,可能会错过就诊期间发生的重大变化。为了解决这一空白,开发了半监督回归模型,通过针对ALSFRS-R量表轨迹与连续居家传感器监测数据,估计系列病例的衰退率。我们的分析比较了三种模型范式(个体批量学习、群体层面批量学习与增量精细调整迁移学习)在线性斜率、三次多项式以及集成自注意力伪标签插值方面的应用。结果显示,群体在各功能领域对学习方法有同质性反应,迁移学习在ALSFRS-R子量表预测误差的对比中改善了28项中的23项(平均RMSE=0.20(0.04)),个体批量学习在预测综合指标方面仅在两项对比中的一项表现出色(平均RMSE=3.15(1.25))。自注意力插值在子量表级别模型中实现了最低的预测误差(平均RMSE=0.19(0.06)),能够捕捉复杂的非线性进展模式,在32项对比中优于线性插值和三次插值20项,尽管线性插值在所有ALSFRS-R综合指标模型中表现更稳定(平均RMSE=0.23(0.10))。我们确定了不同功能领域的同质性-异质性分布特征,其中呼吸和言语具有特定的患者模式,受益于个性化增量适应,而吞咽和穿衣功能遵循群体层面轨迹,适合迁移模型。这些发现表明,将学习与伪标签技术与功能域特定的同质性-异质性分布特征相匹配,可提高ALS进展跟踪的预测准确性。在传感器监测平台中整合自适应模型选择可为未来多中心研究提供及时的干预和可规模化部署的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 8 Figures
摘要
本文开发半监督回归模型,以针对渐冻人症(ALS)的功能衰退进行临床监测。研究采用连续居家传感器监测数据,通过三种模型范式(个体批量学习、群体水平批量学习与增量精细调整转移学习)分析ALS功能衰退速率。研究结果显示,转移学习在预测ALS功能性量表(ALSFRS-R)子量表方面的预测误差有所改进,在32次对比中的28次表现出更佳的均方根误差(RMSE)。自我注意插值在子量表级别模型中实现最低预测误差,并捕获复杂的非线性进展模式。然而,线性插值在ALSFRS-R综合量表模型中表现更稳定。研究还发现,不同功能领域的同质性和异质性特征影响模型效果,如呼吸和言语功能受益于个性化增量适应,而吞咽和穿衣功能适合使用转移模型。总之,该研究建议匹配学习与伪标签技术至特定功能领域的同质性和异质性特征,以提高ALS进展跟踪的预测准确性。整合自适应模型选择进入传感器监测平台可实现及时干预和大规模部署。
关键见解
- 半监督回归模型用于估计ALS的功能衰退速率,使用连续居家传感器监测数据。
- 比较了三种模型范式,包括个体批量学习、群体水平批量学习与增量精细调整转移学习。
- 转移学习在预测ALSFRS-R子量表的预测误差方面表现出较好的效果。
- 自我注意插值在子量表级别模型中实现最低预测误差,捕捉复杂的非线性进展模式。
- 不同功能领域(如呼吸、言语、吞咽和穿衣)的同质性和异质性特征影响模型效果。
- 研究建议根据功能领域的同质性和异质性特征匹配学习和伪标签技术,以提高预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图

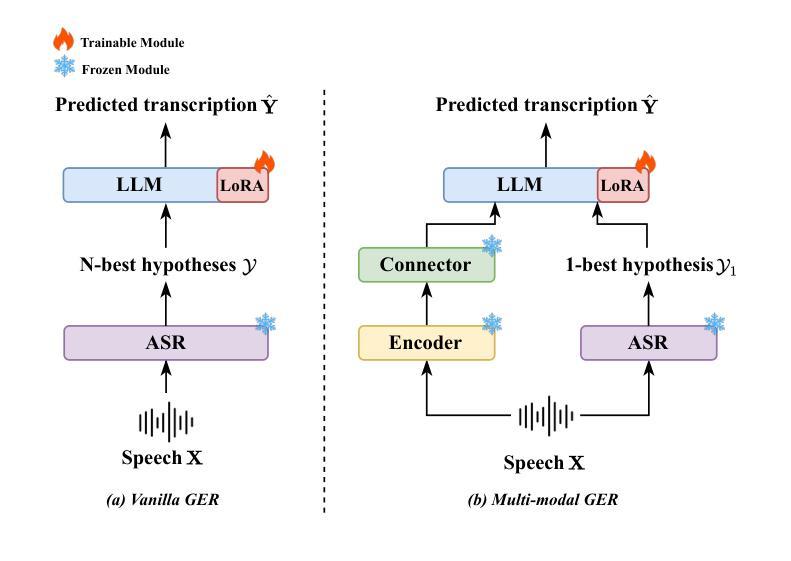
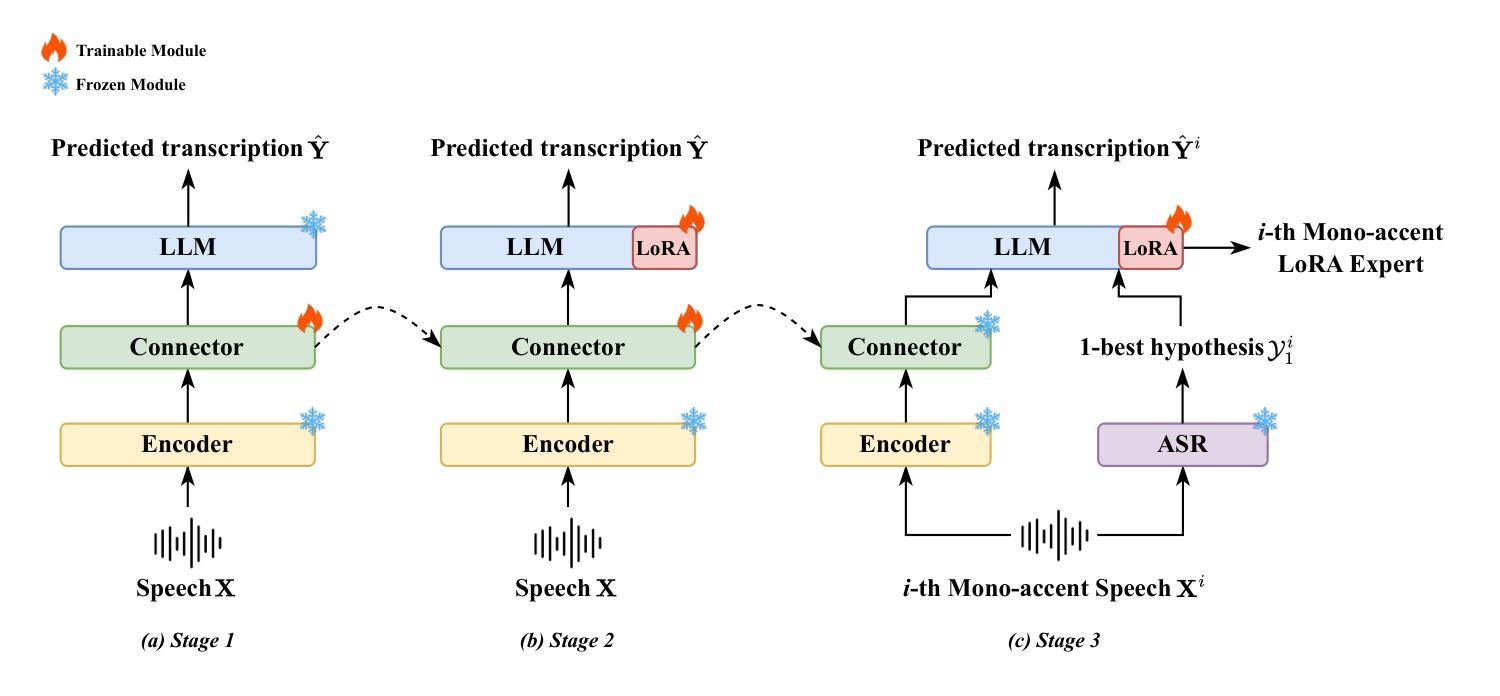
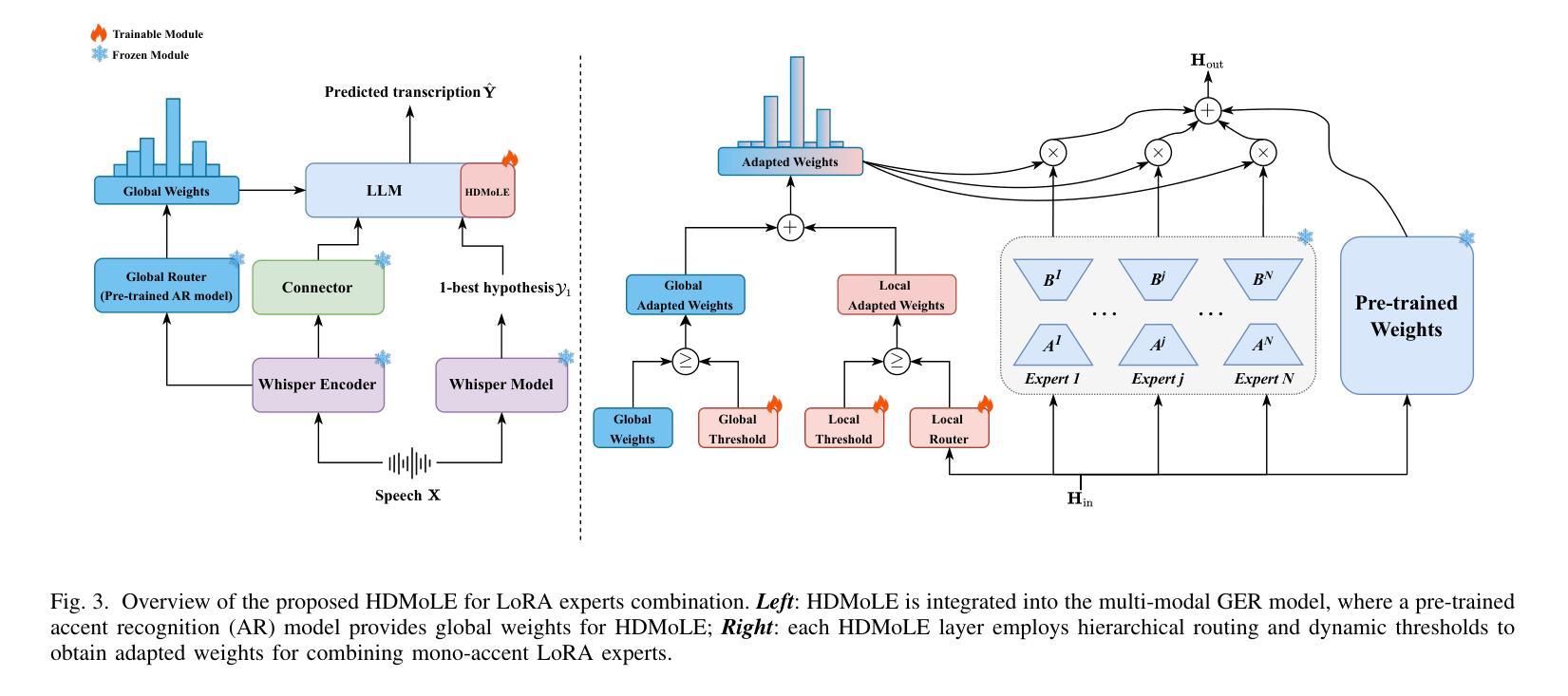
Mixture of LoRA Experts with Multi-Modal and Multi-Granularity LLM Generative Error Correction for Accented Speech Recognition
Authors:Bingshen Mu, Kun Wei, Pengcheng Guo, Lei Xie
Despite substantial improvements in ASR, performance tends to degrade when faced with adverse conditions such as speaker accents. Generative error correction (GER) leverages the rich linguistic knowledge and exceptional reasoning ability of LLMs, significantly outperforming typical LM methods. However, it lacks specificity in accented speech scenarios. In this study, we leverage GER to improve the accuracy of transcription predictions by addressing the two primary features of accented speech recognition. To fully leverage pronunciation information, we propose the multi-modal GER, which integrates pronunciation information from the speech modality, and the multi-granularity GER, which incorporates fine-grained phoneme-level information related to pronunciation. These two methods enable the LLM to utilize the pronunciation information of accented speech and the semantic information from word-level hypotheses for accurate transcription predictions through LoRA fine-tuning. On the one hand, we employ a three-stage training strategy to train separate multi-modal GER models for each accent to obtain mono-accent LoRA experts. By adopting our proposed HDMoLE method, which incorporates hierarchical routing and dynamic thresholds within the mixture of LoRA experts, we effectively merge multiple mono-accent LoRA experts within a single multi-modal GER to overcome the challenges posed by accent diversity. On the other hand, multi-granularity GER leverages the N-best word-level and phoneme-level hypotheses generated by the HDMoLE model to predict the final accented speech transcriptions. Experimental results on the multi-accent English dataset demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed methods. Our methods achieve a remarkable relative WER reduction of 67.35% compared to the Whisper-large-v3 baseline.
尽管语音识别技术(ASR)有了实质性的改进,但在面对如说话者口音等不利条件时,性能往往会有所下降。生成错误校正(GER)能够利用大型语言模型(LLM)丰富的语言知识和出色的推理能力,显著优于典型的语言模型方法。然而,它在带有口音的语音场景上缺乏特异性。本研究中,我们利用GER来提高转录预测的准确性,通过解决带口音语音识别的两个主要特征来实现这一目标。为了充分利用发音信息,我们提出了多模态GER,它结合了语音模态的发音信息,以及多粒度GER,它结合了与发音相关的精细音素级信息。这两种方法使LLM能够通过LoRA微调利用带口音语音的发音信息和词级假设的语义信息进行准确的转录预测。一方面,我们采用三阶段训练策略,针对每种口音训练单独的多模态GER模型,以获得单口音LoRA专家。通过采用我们提出的HDMoLE方法,该方法结合了层次路由和动态阈值在LoRA专家混合体中,我们有效地将多个单口音LoRA专家合并到一个单一的多模态GER中,以克服口音多样性带来的挑战。另一方面,多粒度GER利用HDMoLE模型生成的N个最佳词级和音素级假设来预测最终的带口音语音转录。在多口音英语数据集上的实验结果表明了我们提出的方法的有效性。我们的方法相较于Whisper-large-v3基线实现了相对的字错误率(WER)降低了67.35%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing
Summary
本研究针对带有口音的语音识别问题,提出了多模态生成式错误修正(GER)方法和多粒度GER方法,以提高发音信息的准确性和转录预测的字级语义信息的利用。通过LoRA微调技术,结合口音的发音信息和字级假设信息,对带口音的语音进行精准转录。采用三阶段训练策略,为每种口音训练单独的多模态GER模型,并利用HDMoLE方法有效合并多个单口音LoRA专家,以应对口音多样性带来的挑战。同时,多粒度GER利用N-best的字级和音素级假设进行最终带口音语音转录预测。在多项英语口音数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法相比基准模型实现了67.35%的相对WER减少。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式错误修正(GER)在处理带有口音的语音识别时表现突出,相较于传统的LM方法具有显著优势。
- 多模态GER方法融合了语音模态的发音信息,提高了发音的准确性。
- 多粒度GER方法结合了音素级的精细信息和字级的语义信息,用于准确转录带口音的语音。
- 采用三阶段训练策略,针对每种口音训练单独的多模态GER模型,以应对口音多样性。
- HDMoLE方法有效合并多个单口音LoRA专家模型,提高了模型处理多种口音的能力。
- 多粒度GER利用N-best假设进行最终转录预测,提高了预测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

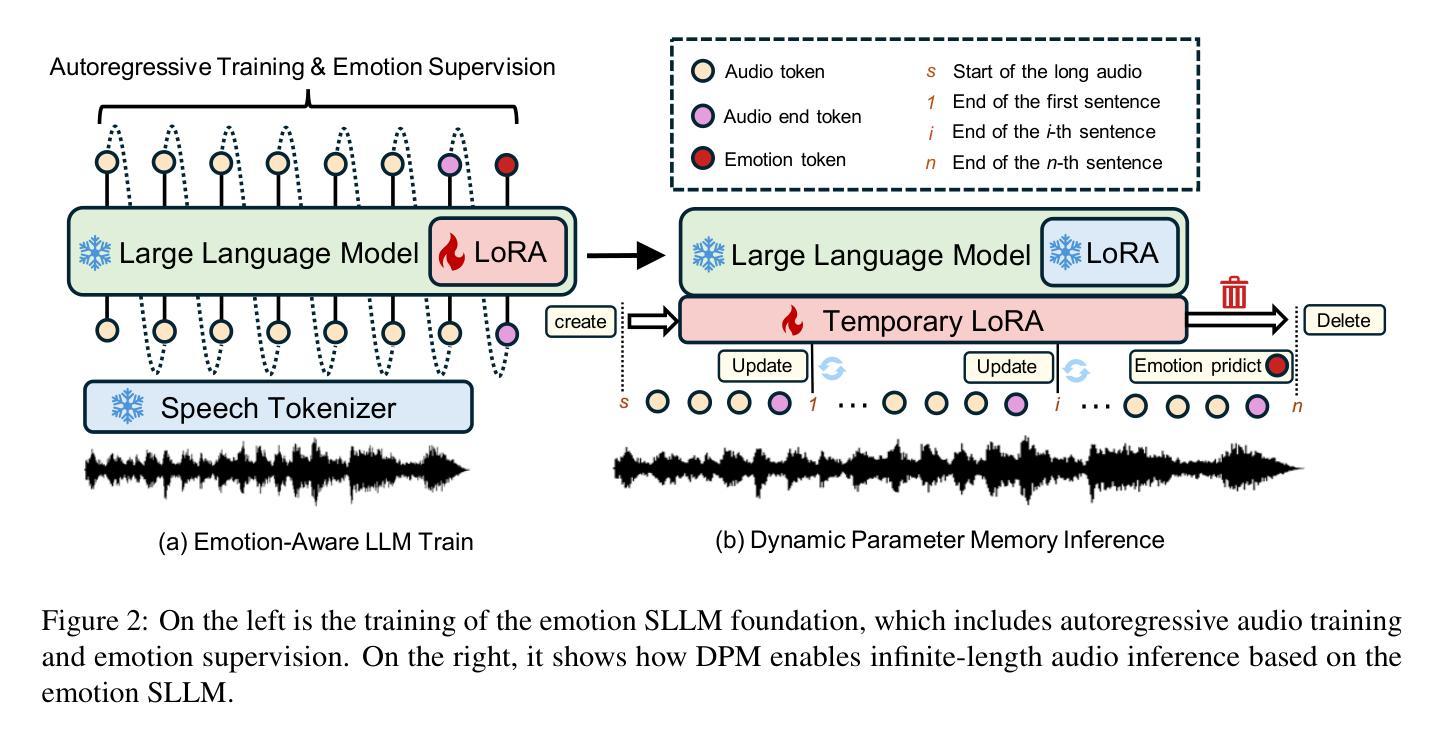
Dynamic Parameter Memory: Temporary LoRA-Enhanced LLM for Long-Sequence Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Authors:Jialong Mai, Xiaofen Xing, Yawei Li, Zhipeng Li, Jingyuan Xing, Xiangmin Xu
Recent research has focused on applying speech large language model (SLLM) to improve speech emotion recognition (SER). However, the inherently high frame rate in speech modality severely limits the signal processing and understanding capabilities of SLLM. For example, a SLLM with a 4K context window can only process 80 seconds of audio at 50Hz feature sampling rate before reaching its capacity limit. Input token compression methods used in SLLM overlook the continuity and inertia of emotions across multiple conversation turns. This paper proposes a Dynamic Parameter Memory (DPM) mechanism with contextual semantics and sentence-level emotion encoding, enabling processing of unlimited-length audio with limited context windows in SLLM. Specifically, DPM progressively encodes sentence-level information and emotions into a temporary LoRA module during inference to effectively “memorize” the contextual information. We trained an emotion SLLM as a backbone and incorporated our DPM into inference for emotion recognition in conversation (ERC). Experimental results on the IEMOCAP dataset show that DPM significantly improves the emotion recognition capabilities of SLLM when processing long audio sequences, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
最近的研究集中在将语音大语言模型(SLLM)应用于提高语音情感识别(SER)上。然而,语音模态本身的高帧率严重限制了SLLM的信号处理和理解能力。例如,一个具有4K上下文窗口的SLLM在50Hz的特征采样率下只能处理80秒的音频,然后就会达到其容量限制。SLLM中使用的输入令牌压缩方法忽略了情感在多轮对话中的连续性和惯性。本文提出了一种具有上下文语义和句子级情感编码的动态参数内存(DPM)机制,能够在SLLM中的有限上下文窗口中处理无限长度的音频。具体来说,DPM在推理过程中将句子级信息和情感逐步编码到临时的LoRA模块中,以有效地“记忆”上下文信息。我们训练了一个情感SLLM作为主干,并将我们的DPM用于对话情感识别(ERC)的推理。在IEMOCAP数据集上的实验结果表明,在处理长音频序列时,DPM显著提高了SLLM的情感识别能力,达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to EMNLP 2025
Summary
近期研究将语音大语言模型(SLLM)应用于语音情感识别(SER)的改进。然而,语音模态的高帧率严重限制了SLLM的信号处理和理解能力。本文提出一种动态参数记忆(DPM)机制,结合上下文语义和句子级情感编码,在有限的语境窗口中处理无限长度的音频。DPM能够逐步将句子级信息和情感编码到临时LoRA模块中,有效“记忆”上下文信息。在IEMOCAP数据集上的实验结果表明,DPM在处理长音频序列时显著提高了SLLM的情感识别能力,达到了先进性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- SLLM在语音情感识别中的局限性:高帧率导致的信号处理和理解能力受限。
- DPM机制介绍:结合上下文语义和句子级情感编码,处理无限长度音频。
- DPM的工作原理:在推理过程中逐步编码句子级信息和情感到临时LoRA模块中。
- 实验结果:在IEMOCAP数据集上,DPM显著提高SLLM处理长音频序列时的情感识别能力。
- DPM达到先进性能水平。
- 输入令牌压缩方法的不足:忽略情感的连续性和惯性。
点此查看论文截图


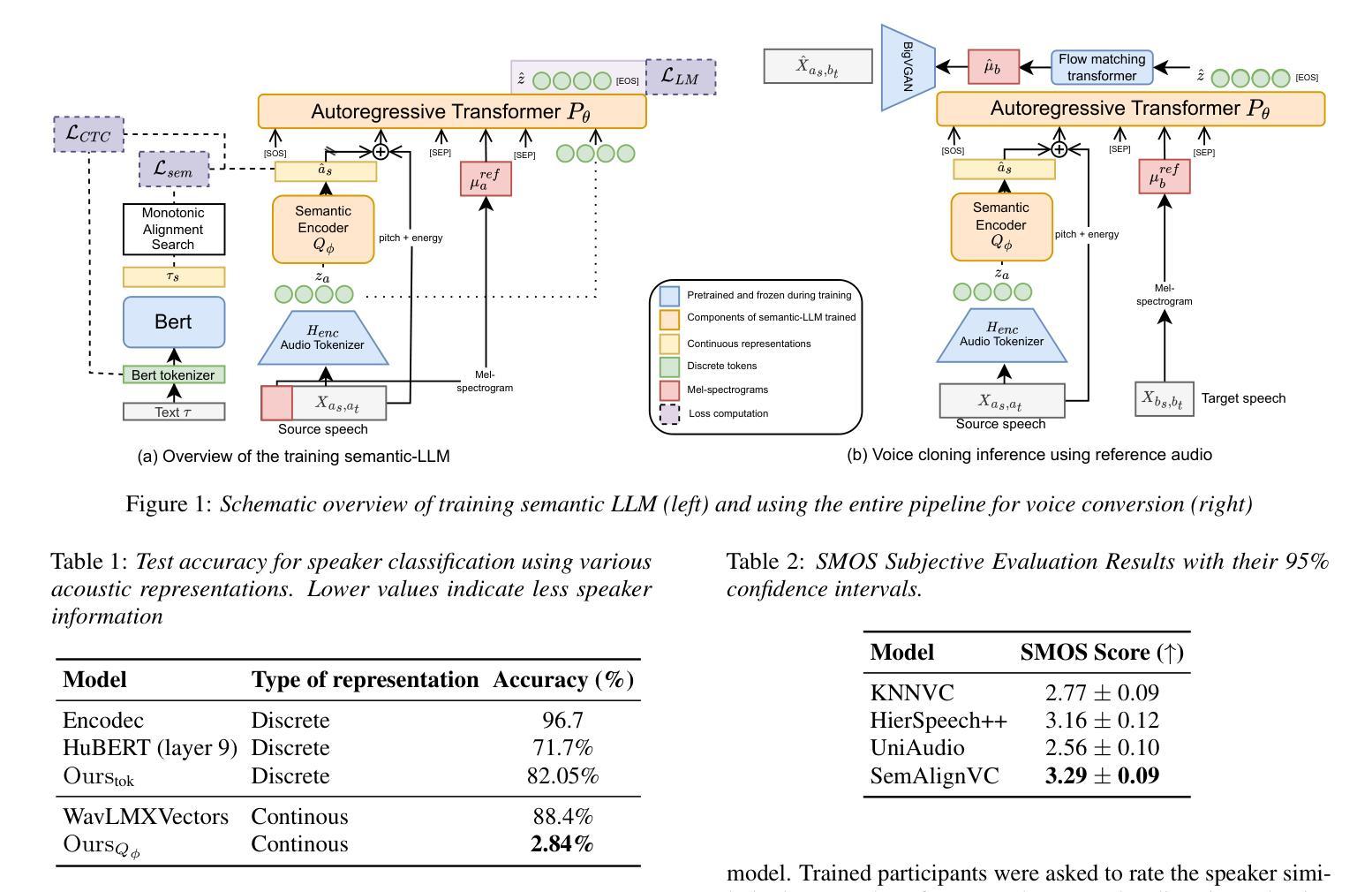
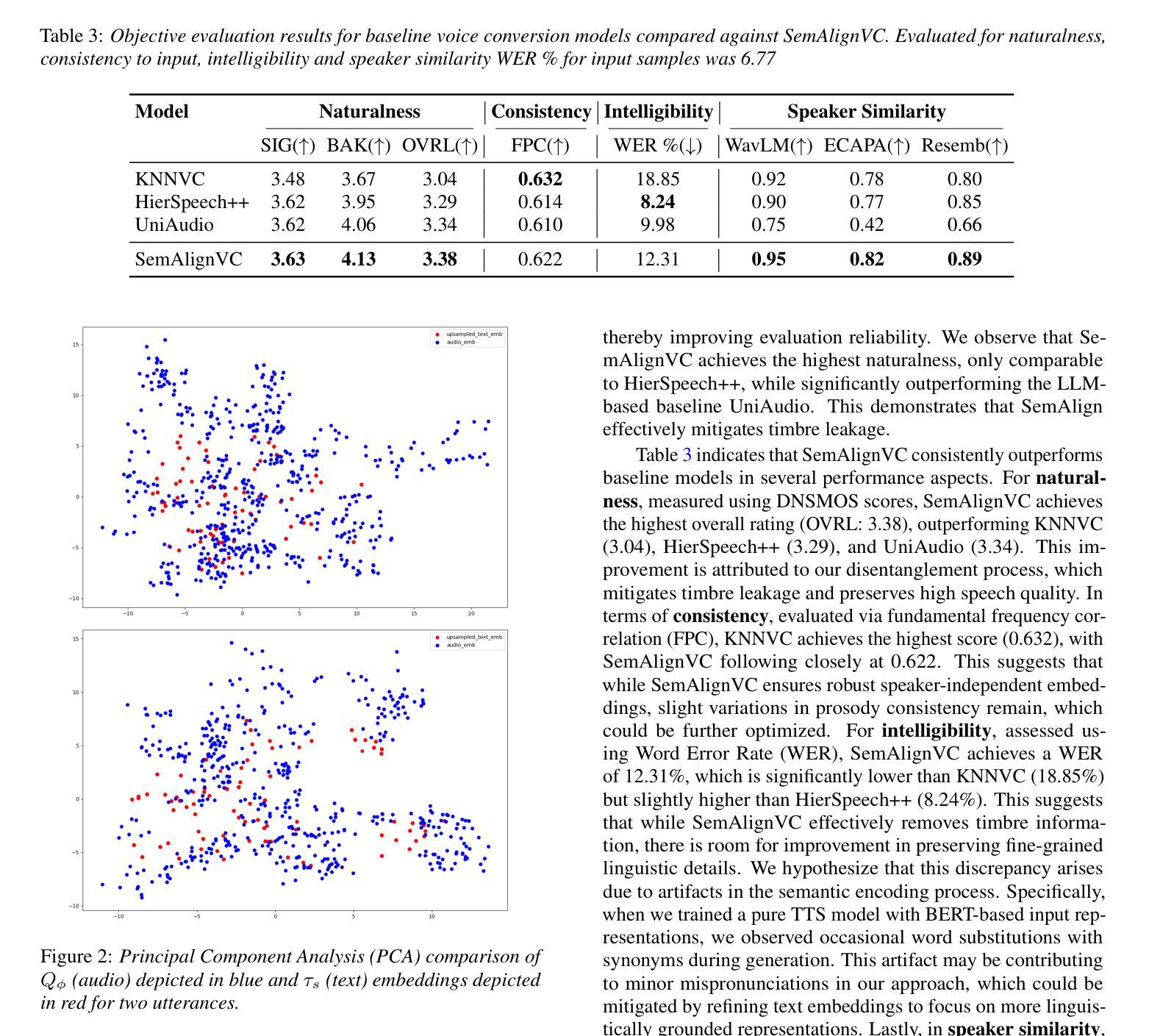
SemAlignVC: Enhancing zero-shot timbre conversion using semantic alignment
Authors:Shivam Mehta, Yingru Liu, Zhenyu Tang, Kainan Peng, Vimal Manohar, Shun Zhang, Mike Seltzer, Qing He, Mingbo Ma
Zero-shot voice conversion (VC) synthesizes speech in a target speaker’s voice while preserving linguistic and paralinguistic content. However, timbre leakage-where source speaker traits persist-remains a challenge, especially in neural codec and LLM-based VC, where quantized representations entangle speaker identity with content. We introduce SemAlignVC, an architecture designed to prevent timbre leakage using SemAlign, a novel method that aligns text and audio representations to ensure speaker-independent semantic encoding. This disentangled representation conditions an autoregressive transformer for high-fidelity conversion without explicit speaker embeddings. Experiments show SemAlignVC significantly reduces timbre leakage, outperforming baselines in speaker timbre similarity, intelligibility, and naturalness, making it a robust, privacy-preserving, and generalizable VC solution. Audio samples can be accessed at https://shivammehta25.github.io/SemAlignVC/
零样本语音转换(VC)技术能够在目标说话者的声音中合成语音,同时保留语言和副语言内容。然而,声纹泄露(即源说话者的特征持续存在)仍然是一个挑战,特别是在基于神经网络编解码器和大型语言模型(LLM)的VC中,其中量化表示将说话人身份与内容纠缠在一起。我们引入了SemAlignVC,这是一种旨在防止声纹泄露的架构,它使用了SemAlign这一新方法,通过文本和音频表示的对齐来确保与说话人无关的语义编码。这种解纠缠的表示为一个自回归变压器提供条件,以实现高保真转换,无需明确的说话人嵌入。实验表明,SemAlignVC能显著降低声纹泄露,在说话人声纹相似性、清晰度和自然度方面超越基线,成为了一种稳健、保护隐私且可推广的VC解决方案。音频样本可通过https://shivammehta25.github.io/SemAlignVC/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 2 figures, Accepted at the ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop (SSW) 2025
Summary:零样本语音转换技术旨在合成目标说话人的语音,同时保留语言和副语言内容。然而,声纹泄露(即源说话人的特征持续存在)仍然是一个挑战,特别是在神经网络编码器和大型语言模型(LLM)的语音转换中,量化表示将说话人身份与内容纠缠在一起。为解决这一问题,我们提出了SemAlignVC架构和其中的SemAlign新方法,该方法通过对文本和音频表示进行对齐来防止声纹泄露,确保独立于说话人的语义编码。这种分离表示条件自回归变压器可实现高保真转换,无需明确的说话人嵌入。实验表明,SemAlignVC在声纹泄露方面表现出显著降低,在说话人声纹相似性、清晰度和自然度方面优于基线方法,成为了一种稳健、保护隐私和通用的语音转换解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 零样本语音转换旨在合成目标说话人的语音并保留语言和副语言内容。
- 声纹泄露是语音转换技术中的一个挑战,特别是在神经网络编码器和大型语言模型的应用中。
- SemAlignVC架构通过SemAlign方法解决声纹泄露问题,通过对文本和音频表示进行对齐来确保独立于说话人的语义编码。
- 实验证明SemAlignVC在声纹泄露、说话人声纹相似性、清晰度和自然度方面优于基线方法。
- SemAlignVC不需要明确的说话人嵌入,可实现高保真转换。
- 音频样本可通过特定链接访问。
点此查看论文截图

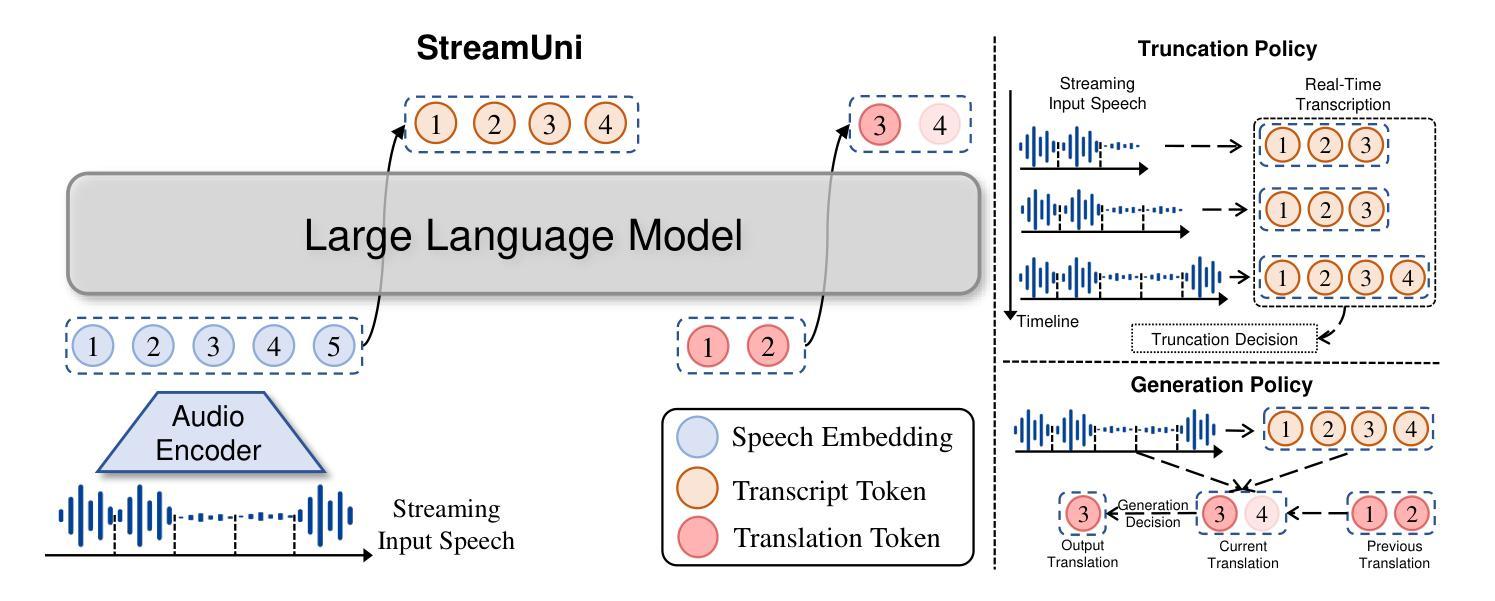
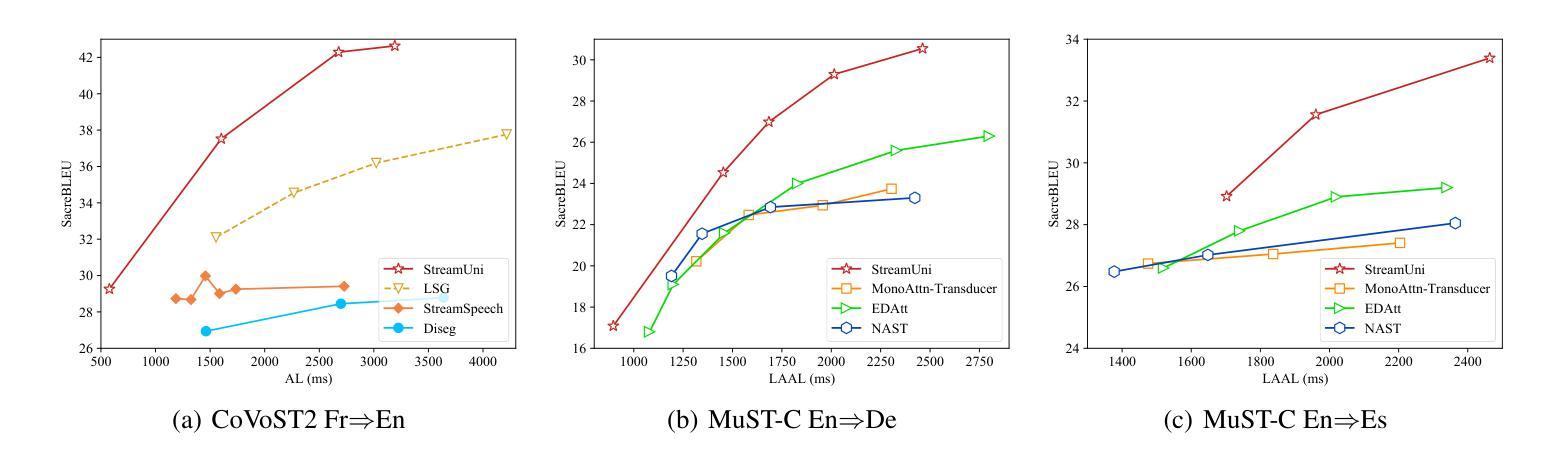
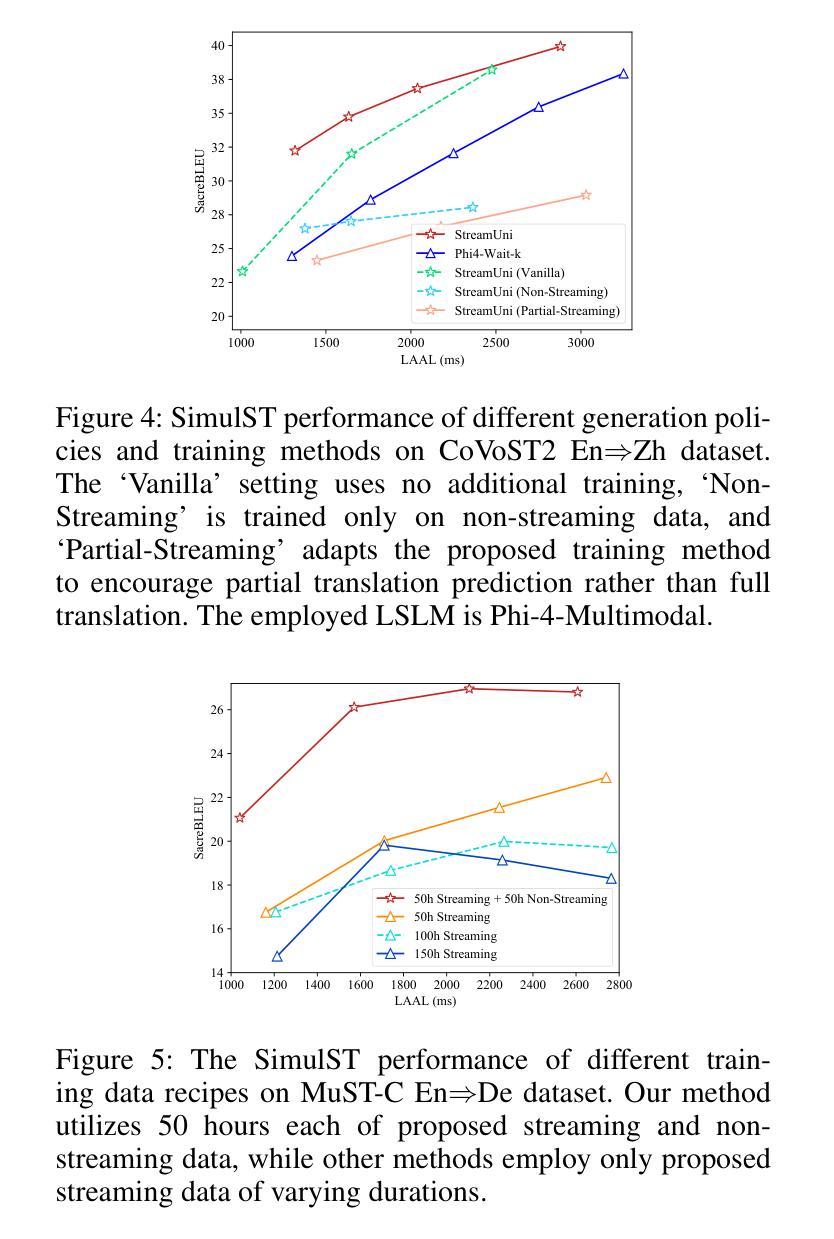
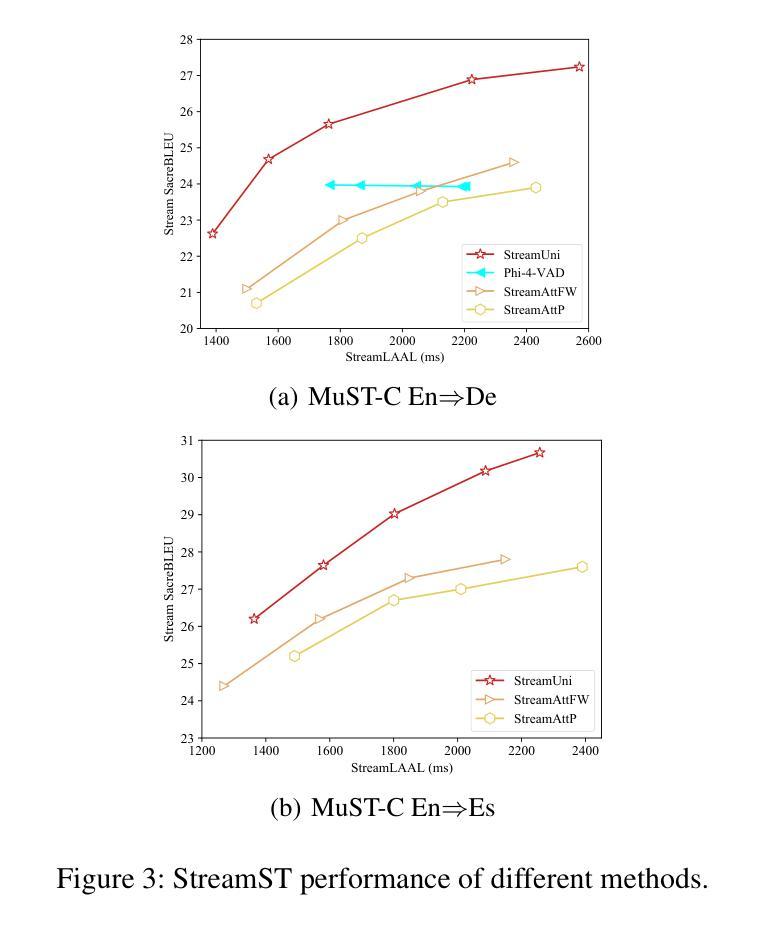
StreamUni: Achieving Streaming Speech Translation with a Unified Large Speech-Language Model
Authors:Shoutao Guo, Xiang Li, Mengge Liu, Wei Chen, Yang Feng
Streaming speech translation (StreamST) requires determining appropriate timing, known as policy, to generate translations while continuously receiving source speech inputs, balancing low latency with high translation quality. However, existing StreamST methods typically operate on sentence-level speech segments, referred to as simultaneous speech translation (SimulST). In practice, they require collaboration with segmentation models to accomplish StreamST, where the truncated speech segments constrain SimulST models to make policy decisions and generate translations based on limited contextual information. Moreover, SimulST models struggle to learn effective policies due to the complexity of speech inputs and cross-lingual generation. To address these challenges, we propose StreamUni, which achieves StreamST through a unified Large Speech-Language Model (LSLM). Specifically, StreamUni incorporates speech Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in guiding the LSLM to generate multi-stage outputs. Leveraging these multi-stage outputs, StreamUni simultaneously accomplishes speech segmentation, policy decision, and translation generation, completing StreamST without requiring massive policy-specific training. Additionally, we propose a streaming CoT training method that enhances low-latency policy decisions and generation capabilities using limited CoT data. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on StreamST tasks.
流式语音翻译(StreamST)要求在连续接收源语音输入的过程中确定适当的翻译生成时机,这种时机被称为策略,需要在低延迟和高翻译质量之间取得平衡。然而,现有的StreamST方法通常运行在句子级别的语音段上,称为同步语音翻译(SimulST)。在实践中,它们需要与分割模型协作来完成StreamST,截断的语音段限制SimulST模型在有限的上下文信息基础上做出策略决策并生成翻译。而且,由于语音输入的复杂性和跨语言生成,SimulST模型在学习有效策略方面面临困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了StreamUni,它通过统一的大规模语音识别语言模型(LSLM)实现StreamST。具体来说,StreamUni将语音思维链(CoT)融入LSLM,以指导生成多阶段输出。利用这些多阶段输出,StreamUni可以同时完成语音分割、策略决策和翻译生成,无需大量的特定策略训练即可完成StreamST。此外,我们还提出了一种流式CoT训练方法,使用有限的CoT数据增强低延迟的策略决策和生成能力。实验表明,我们的方法在StreamST任务上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code is at https://github.com/ictnlp/StreamUni; The model is at https://huggingface.co/ICTNLP/StreamUni-Phi4
Summary
本文提出一种基于统一大规模语言模型的流式语音识别翻译方法StreamUni,通过融入语音链式思维(CoT)生成多阶段输出,实现了无需大规模政策特定训练的流式语音识别翻译。此方法可同时进行语音分段、政策决策和翻译生成,解决了现有方法中需要协作分段模型、基于有限语境信息做出决策和生成翻译的问题。此外,还提出了一种增强低延迟政策决策和生成能力的流式CoT训练方法。实验证明,该方法在流式语音识别翻译任务上取得了最新技术水平的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 现有流式语音识别翻译(StreamST)方法通常基于句子级别的语音段进行,称为同步语音识别翻译(SimulST)。
- SimulST方法需要与分段模型协作,受截断语音段的限制,基于有限语境信息做出决策和生成翻译。
- StreamUni通过统一大规模语言模型(LSLM)实现StreamST,融入语音链式思维(CoT)生成多阶段输出,可同时完成语音分段、政策决策和翻译生成。
- StreamUni方法无需大规模政策特定训练,解决了SimulST模型在复杂语音输入和跨语言生成方面学习有效政策的困难。
- 提出了一种增强低延迟政策决策和生成能力的流式CoT训练方法,使用有限的CoT数据。
- 实验证明,StreamUni方法在流式语音识别翻译任务上取得了最新技术水平的性能。
点此查看论文截图

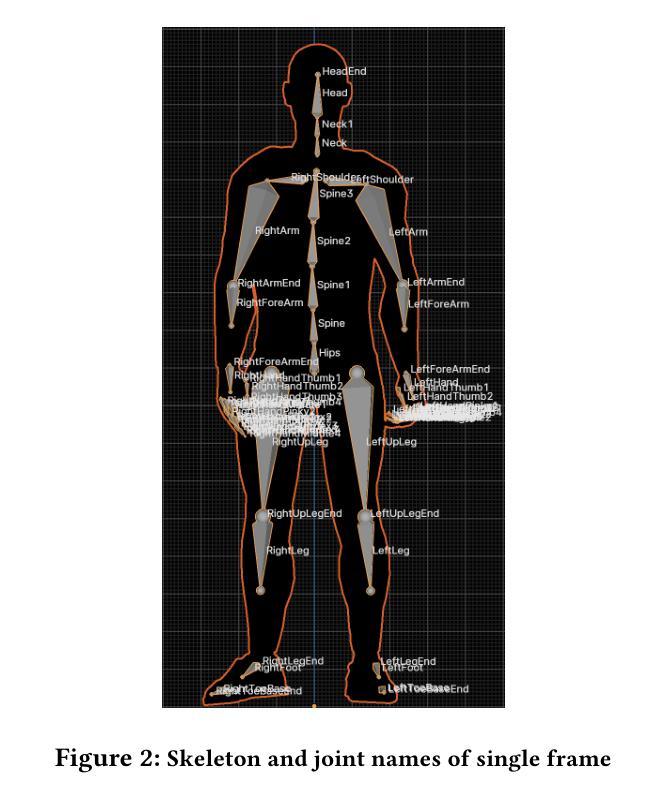
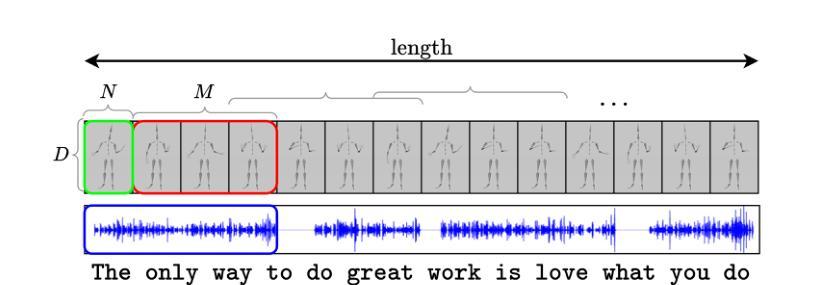
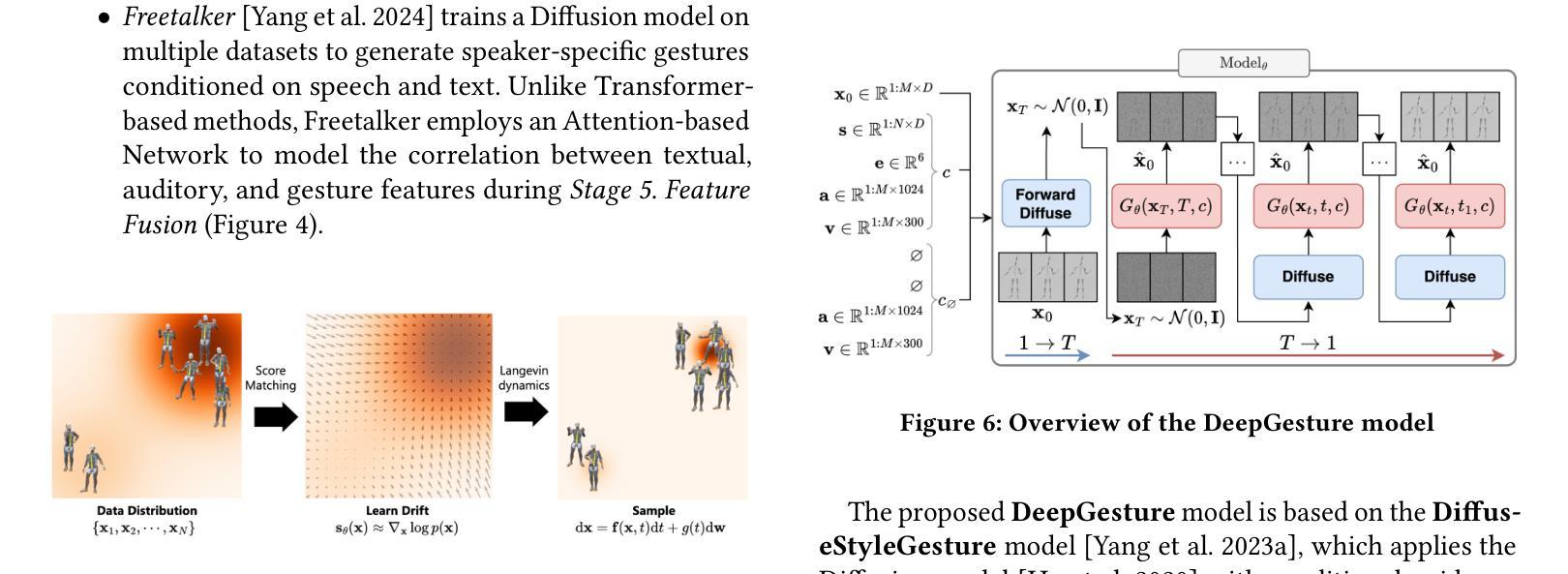
DeepGesture: A conversational gesture synthesis system based on emotions and semantics
Authors:Thanh Hoang-Minh
Along with the explosion of large language models, improvements in speech synthesis, advancements in hardware, and the evolution of computer graphics, the current bottleneck in creating digital humans lies in generating character movements that correspond naturally to text or speech inputs. In this work, we present DeepGesture, a diffusion-based gesture synthesis framework for generating expressive co-speech gestures conditioned on multimodal signals - text, speech, emotion, and seed motion. Built upon the DiffuseStyleGesture model, DeepGesture introduces novel architectural enhancements that improve semantic alignment and emotional expressiveness in generated gestures. Specifically, we integrate fast text transcriptions as semantic conditioning and implement emotion-guided classifier-free diffusion to support controllable gesture generation across affective states. To visualize results, we implement a full rendering pipeline in Unity based on BVH output from the model. Evaluation on the ZeroEGGS dataset shows that DeepGesture produces gestures with improved human-likeness and contextual appropriateness. Our system supports interpolation between emotional states and demonstrates generalization to out-of-distribution speech, including synthetic voices - marking a step forward toward fully multimodal, emotionally aware digital humans. Project page: https://deepgesture.github.io
随着大型语言模型的爆发,语音合成的改进,硬件的进步以及计算机图形的演变,当前创建数字人的瓶颈在于生成与文本或语音输入相对应的自然动作。在这项工作中,我们提出了DeepGesture,这是一个基于扩散的手势合成框架,能够根据文本、语音、情感和种子动作等多模态信号生成富有表现力的协同语音手势。DeepGesture建立在DiffuseStyleGesture模型的基础上,引入了新型架构改进,提高了语义对齐和生成手势的情感表现力。具体来说,我们将快速文本转录作为语义条件,并实现了情感引导的无分类扩散,以支持情感状态下的可控手势生成。为了可视化结果,我们在Unity中实现了基于模型BVH输出的完整渲染管道。在ZeroEGGS数据集上的评估表明,DeepGesture产生的手势在人性化和上下文恰当性方面有所改进。我们的系统支持情感状态之间的插值,并展示了对分布外语音的泛化能力,包括对合成声音的泛化——标志着朝着完全多模态、情感感知的数字人方向迈出了一步。项目页面:https://deepgesture.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://deepgesture.github.io
Summary
文本描述了DeepGesture系统及其优势。随着大型语言模型的爆炸式发展,以及语音合成、硬件进步和计算机图形技术的提升,当前创建数字人类的瓶颈在于生成自然对应文本或语音输入的角色动作。DeepGesture是一个基于扩散的手势合成框架,能够根据文本、语音、情感和种子动作等多模式信号生成表达性共语手势。它改进了语义对齐和情绪表达,支持跨情感状态的可控手势生成。在Unity中实现的全渲染管道,基于模型的BVH输出可视化结果。在ZeroEGGS数据集上的评估显示,DeepGesture生成的手势更具人类性和上下文适当性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前数字人类的创建瓶颈在于生成自然对应文本或语音输入的角色动作。
- DeepGesture是一个基于扩散的手势合成框架,旨在解决这一问题。
- DeepGesture集成了多模式信号,如文本、语音、情感和种子动作,用于生成表达性共语手势。
- 它通过改进语义对齐和情绪表达来提高生成手势的自然度和表达力。
- DeepGesture支持跨情感状态的可控手势生成。
- 在Unity中实现的全渲染管道可以可视化生成的手势。
- 在ZeroEGGS数据集上的评估显示,DeepGesture生成的手势更具人类性和上下文适当性。
点此查看论文截图

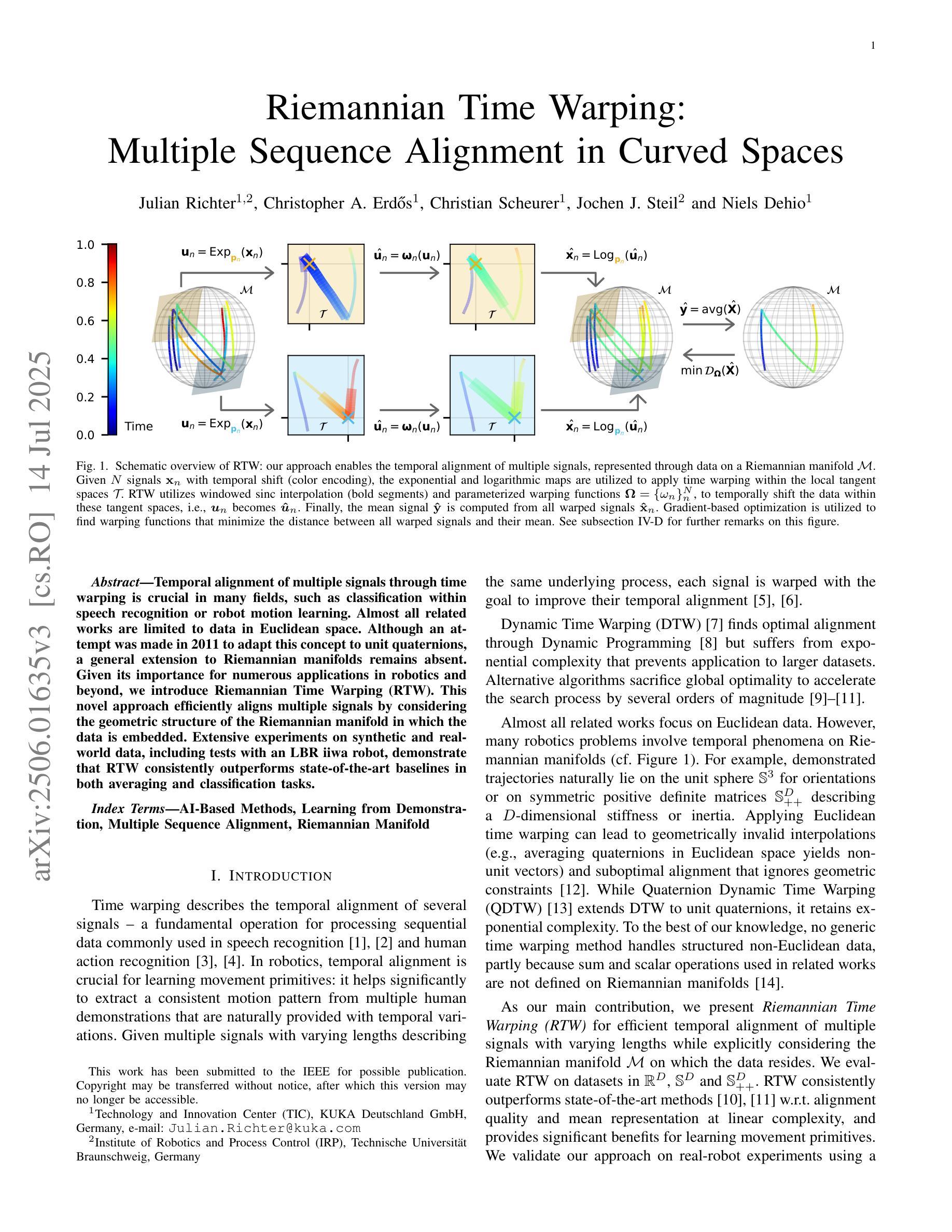
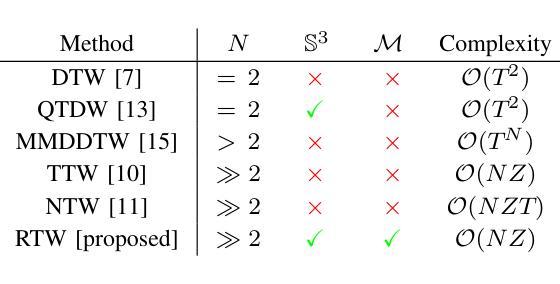
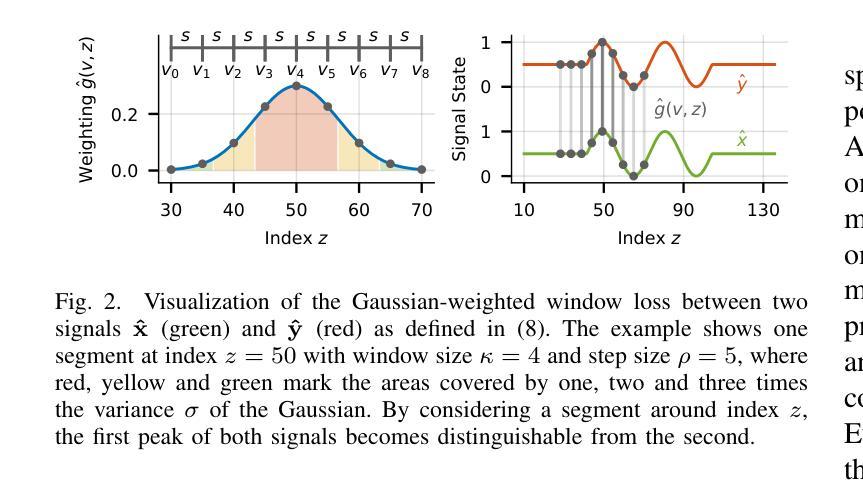
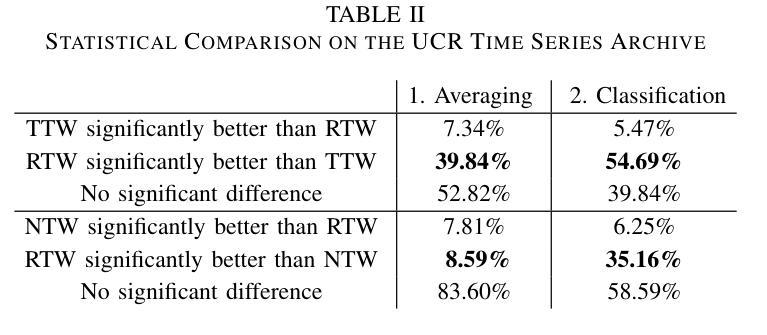
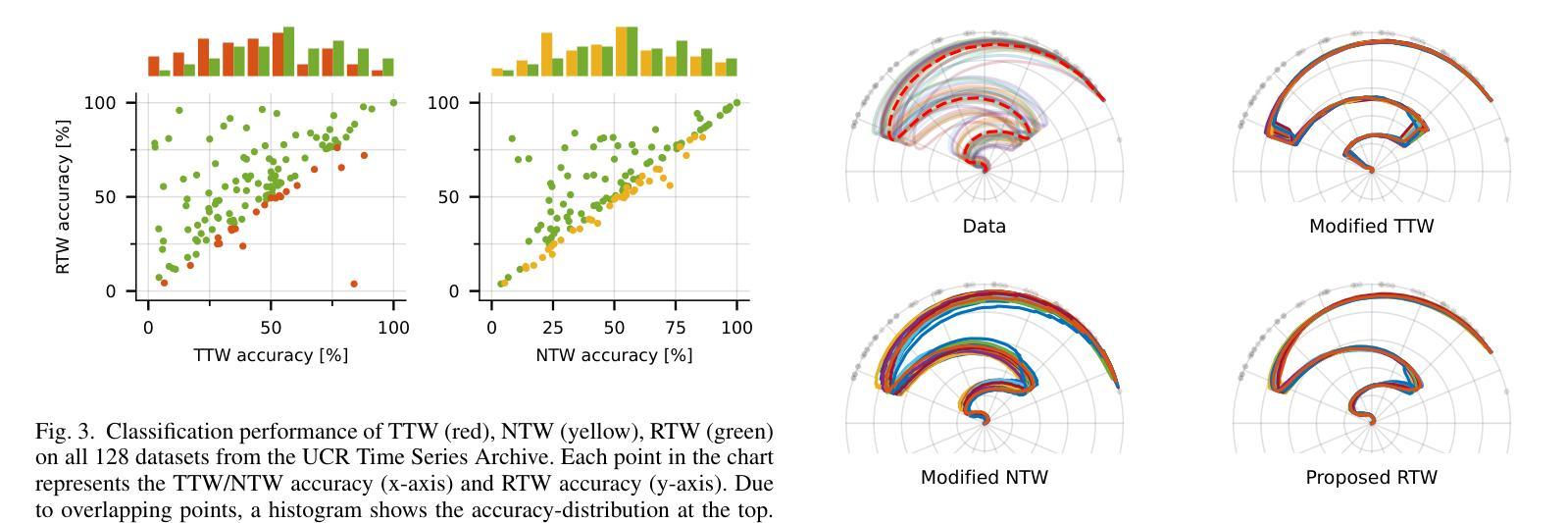
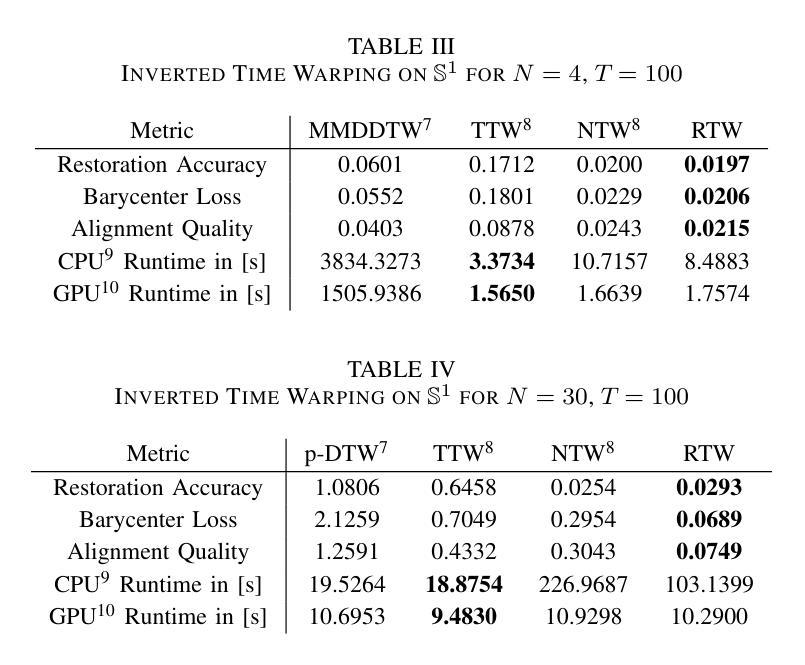
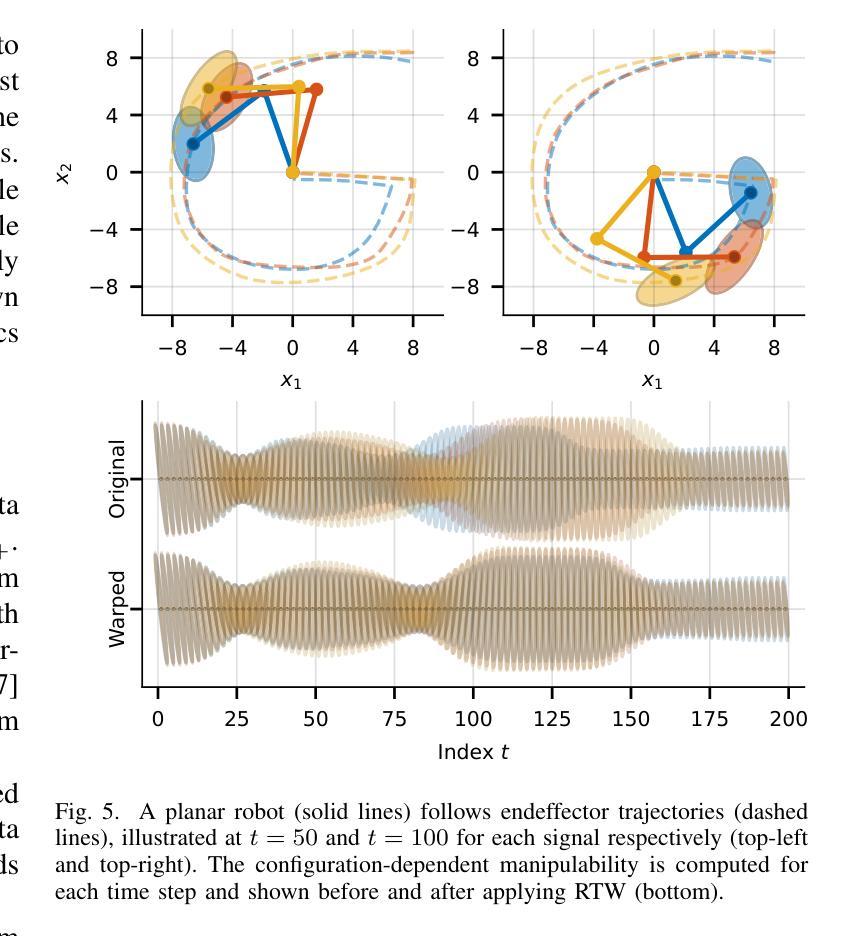
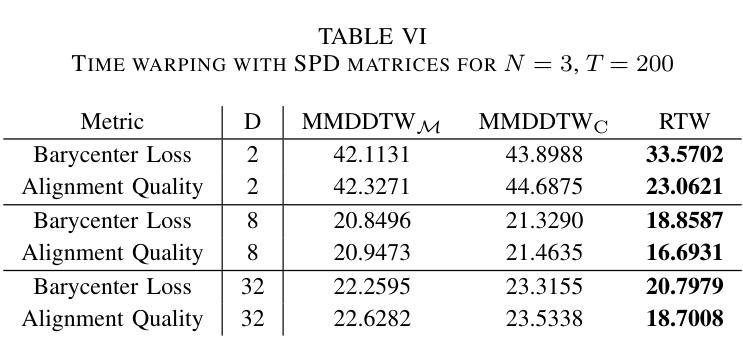
Riemannian Time Warping: Multiple Sequence Alignment in Curved Spaces
Authors:Julian Richter, Christopher A. Erdös, Christian Scheurer, Jochen J. Steil, Niels Dehio
Temporal alignment of multiple signals through time warping is crucial in many fields, such as classification within speech recognition or robot motion learning. Almost all related works are limited to data in Euclidean space. Although an attempt was made in 2011 to adapt this concept to unit quaternions, a general extension to Riemannian manifolds remains absent. Given its importance for numerous applications in robotics and beyond, we introduce Riemannian Time Warping (RTW). This novel approach efficiently aligns multiple signals by considering the geometric structure of the Riemannian manifold in which the data is embedded. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world data, including tests with an LBR iiwa robot, demonstrate that RTW consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both averaging and classification tasks.
多个信号通过时间扭曲的时间对齐在多个领域都至关重要,如在语音识别或机器人运动学习中的分类。几乎所有相关工作都局限于欧几里得空间中的数据。尽管在2011年有人试图将这一概念适应于单位四元数,但到黎曼流形的通用扩展仍然缺失。考虑到其在机器人技术及其以外的众多应用中的重要性,我们引入了黎曼时间扭曲(RTW)。这种方法通过考虑数据嵌入的黎曼流形的几何结构,可以有效地对齐多个信号。在合成数据和真实世界数据上的大量实验,包括对LBR iiwa机器人的测试,证明无论是在平均任务还是分类任务中,RTW始终优于最新的基线技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时空弯曲技术对于许多领域如语音识别或机器人运动学习中的分类至关重要。尽管已有尝试将概念扩展到单位四元数,但目前还缺乏将其扩展到黎曼流形的一般方法。我们引入黎曼时间弯曲(RTW),该方法考虑数据嵌入的黎曼流形的几何结构,有效对齐多个信号。在合成数据和真实世界数据上的广泛实验以及对LBR iiwa机器人的测试表明,RTW在平均和分类任务上均优于最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- 时空弯曲技术在多个领域(如语音识别和机器人运动学习)中的分类任务中起到关键作用。
- 目前大多数相关研究仅限于欧几里得空间内的数据。
- 尽管已有尝试将概念扩展到单位四元数,但将其一般扩展到黎曼流形的方法仍然缺失。
- 引入了一种新的方法——黎曼时间弯曲(RTW),该方法考虑数据嵌入的几何结构,实现对多个信号的有效对齐。
- 与现有技术相比,黎曼时间弯曲在平均和分类任务上的性能表现更优。
- 黎曼时间弯曲技术的广泛应用可能推动机器人技术等多个领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图
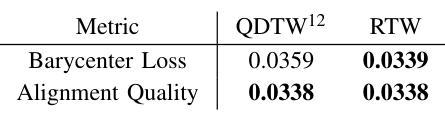
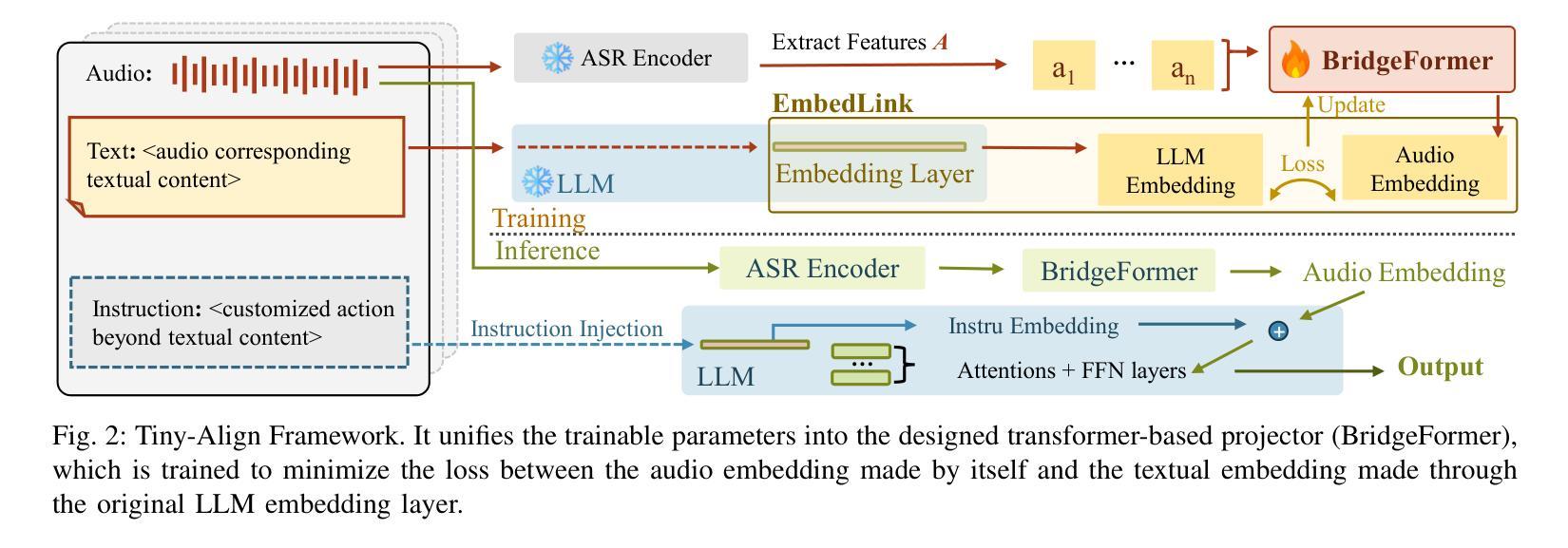
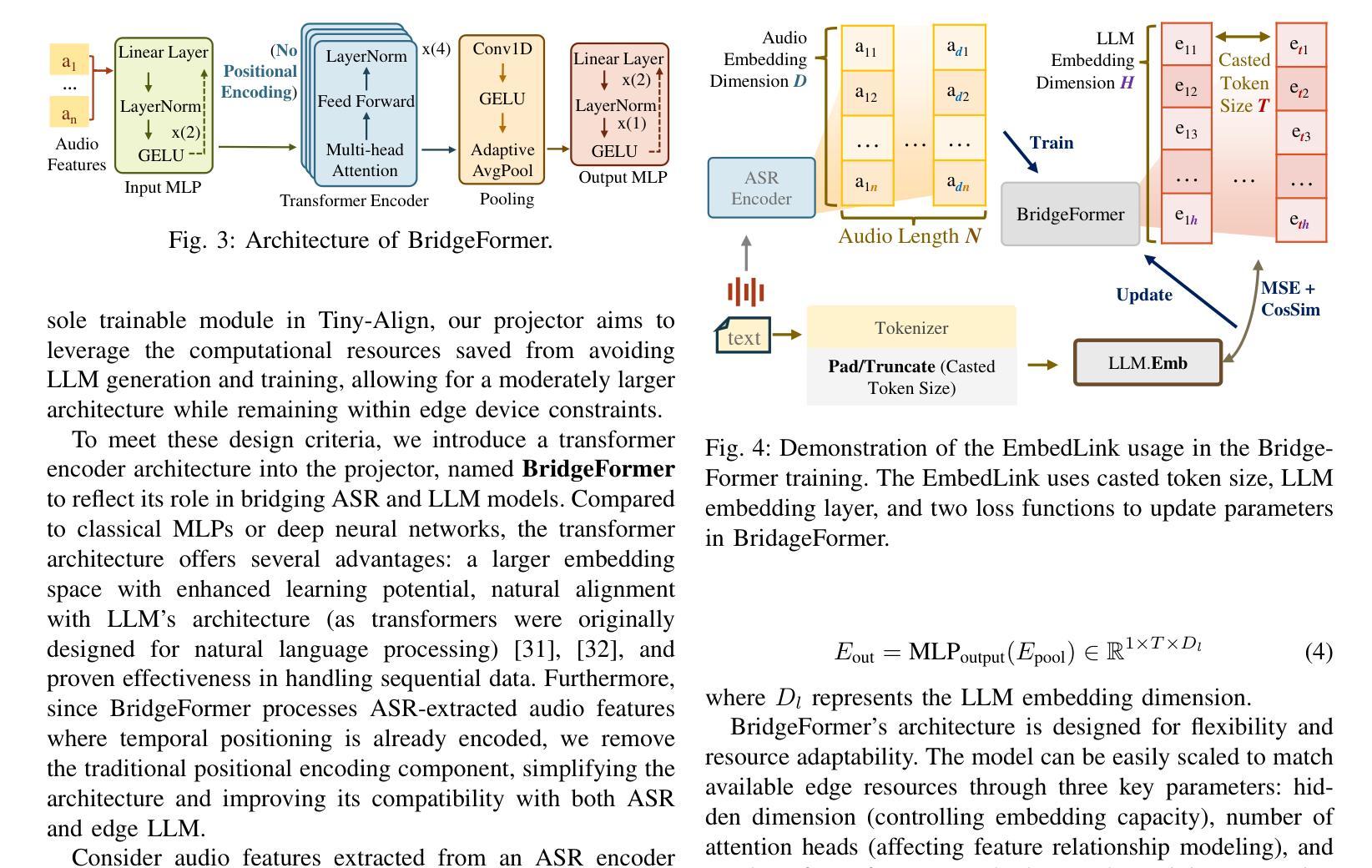
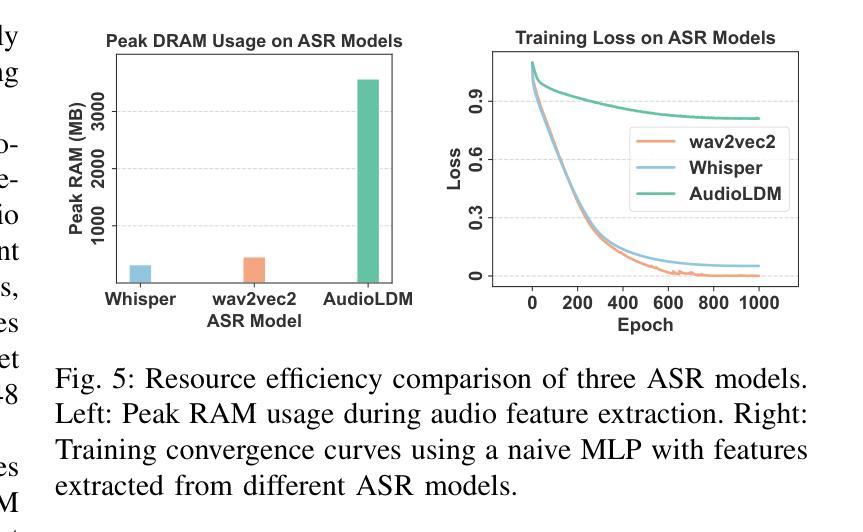
Tiny-Align: Bridging Automatic Speech Recognition and Large Language Model on the Edge
Authors:Ruiyang Qin, Dancheng Liu, Gelei Xu, Zheyu Yan, Chenhui Xu, Yuting Hu, Shaocong Wang, X. Sharon Hu, Jinjun Xiong, Yiyu Shi
The combination of Large Language Models (LLM) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), when deployed on edge devices (called edge ASR-LLM), can serve as a powerful personalized assistant to enable audio-based interaction for users. Compared to text-based interaction, edge ASR-LLM allows accessible and natural audio interactions. Unfortunately, existing ASR-LLM models are mainly trained in high-performance computing environments and produce substantial model weights, making them difficult to deploy on edge devices. More importantly, to better serve users’ personalized needs, the ASR-LLM must be able to learn from each distinct user, given that audio input often contains highly personalized characteristics that necessitate personalized on-device training. Since individually fine-tuning the ASR or LLM often leads to suboptimal results due to modality-specific limitations, end-to-end training ensures seamless integration of audio features and language understanding (cross-modal alignment), ultimately enabling a more personalized and efficient adaptation on edge devices. However, due to the complex training requirements and substantial computational demands of existing approaches, cross-modal alignment between ASR audio and LLM can be challenging on edge devices. In this work, we propose a resource-efficient cross-modal alignment framework that bridges ASR and LLMs on edge devices to handle personalized audio input. Our framework enables efficient ASR-LLM alignment on resource-constrained devices like NVIDIA Jetson Orin (8GB RAM), achieving 50x training time speedup while improving the alignment quality by more than 50%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to study efficient ASR-LLM alignment on resource-constrained edge devices.
大型语言模型(LLM)与自动语音识别(ASR)的结合,在边缘设备上部署(称为边缘ASR-LLM)时,可作为强大的个性化助手,使用户能够基于音频进行交互。与基于文本的交互相比,边缘ASR-LLM允许可访问和自然的音频交互。然而,现有的ASR-LLM模型主要在高性能计算环境中进行训练,产生大量的模型权重,使得它们难以在边缘设备上部署。更重要的是,为了更好地满足用户的个性化需求,ASR-LLM必须能够从每个不同的用户身上学习,因为音频输入通常包含高度个性化的特征,需要进行个性化的设备端训练。由于单独微调ASR或LLM往往会导致次优结果,端到端训练确保音频特征和语言理解的无缝集成(跨模态对齐),最终在边缘设备上实现更个性化和高效的适应。然而,由于现有方法的复杂训练要求和巨大的计算需求,ASR音频和LLM之间的跨模态对齐在边缘设备上可能具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个资源高效的跨模态对齐框架,该框架可在边缘设备上实现ASR和LLM的衔接,以处理个性化的音频输入。我们的框架能够在像NVIDIA Jetson Orin(8GB RAM)这样的资源受限设备上实现高效的ASR-LLM对齐,实现50倍的培训时间加速,同时提高对齐质量超过50%。据我们所知,这是第一项在资源受限的边缘设备上研究高效ASR-LLM对齐的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCAD’25
摘要
在边缘设备上部署大型语言模型(LLM)与自动语音识别(ASR)的组合(称为边缘ASR-LLM),可作为强大的个性化助手,实现基于音频的用户交互。相较于文本交互,边缘ASR-LLM允许更便捷、更自然的音频交互。然而,现有的ASR-LLM模型主要在高性能计算环境中训练,模型体积庞大,难以部署在边缘设备上。更重要的是,为了更好地服务用户的个性化需求,ASR-LLM必须具备从每个独立用户身上学习的能力,因为音频输入往往包含高度个性化的特征,需要进行个性化的设备端训练。由于单独微调ASR或LLM往往因模态特定限制而导致结果不佳,端到端训练可确保音频特征与语言理解的无缝集成(跨模态对齐),最终在边缘设备上实现更个性化和高效的适应。然而,由于现有方法的复杂训练要求和巨大的计算需求,在边缘设备上实现ASR音频和LLM之间的跨模态对齐具有挑战性。本研究提出一种资源高效的跨模态对齐框架,该框架可在边缘设备上桥接ASR和LLM,处理个性化音频输入。我们的框架可在资源受限的设备上实现高效的ASR-LLM对齐,如8GB RAM的NVIDIA Jetson Orin,实现50倍的培训时间加速,同时提高对齐质量超过50%。据我们所知,这是第一项在资源受限的边缘设备上研究高效ASR-LLM对齐的工作。
关键见解
- 边缘设备上的大型语言模型(LLM)与自动语音识别(ASR)结合可提供强大的个性化助手功能,支持音频交互。
- 现有ASR-LLM模型主要在高性能环境中训练,难以部署在资源有限的边缘设备上。
- 个性化音频输入需要个性化设备训练,因为音频包含高度个性化的特征。
- 单独微调ASR或LLM因模态特定限制可能效果不佳,端到端训练可实现跨模态无缝集成(跨模态对齐)。
- 现有方法在边缘设备上实现跨模态对齐具有挑战,因为复杂的训练要求和计算需求。
- 提出的资源高效跨模态对齐框架可在边缘设备上桥接ASR和LLM,实现个性化音频输入的高效处理。
点此查看论文截图

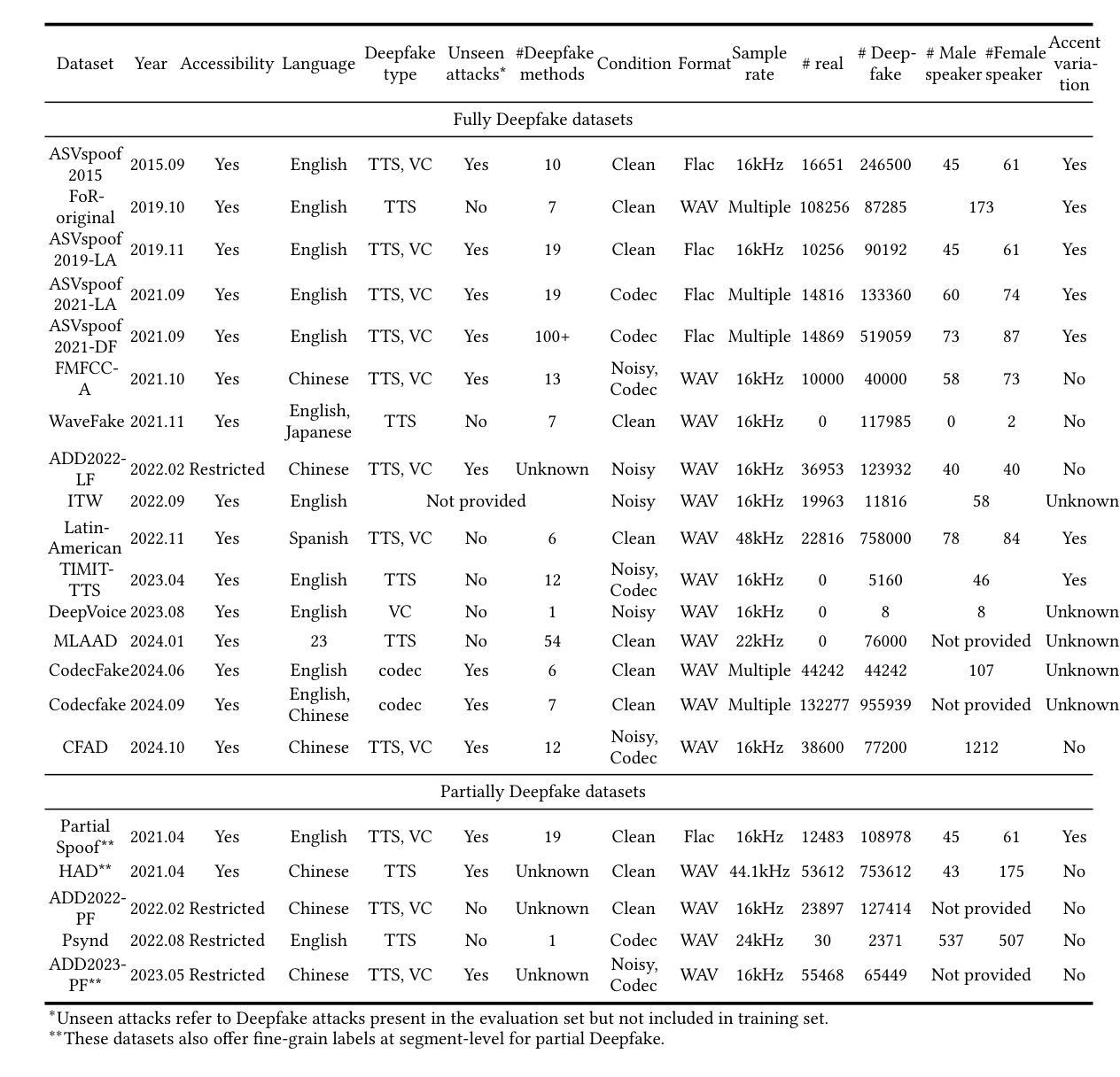
A Survey on Speech Deepfake Detection
Authors:Menglu Li, Yasaman Ahmadiadli, Xiao-Ping Zhang
The availability of smart devices leads to an exponential increase in multimedia content. However, advancements in deep learning have also enabled the creation of highly sophisticated Deepfake content, including speech Deepfakes, which pose a serious threat by generating realistic voices and spreading misinformation. To combat this, numerous challenges have been organized to advance speech Deepfake detection techniques. In this survey, we systematically analyze more than 200 papers published up to March 2024. We provide a comprehensive review of each component in the detection pipeline, including model architectures, optimization techniques, generalizability, evaluation metrics, performance comparisons, available datasets, and open source availability. For each aspect, we assess recent progress and discuss ongoing challenges. In addition, we explore emerging topics such as partial Deepfake detection, cross-dataset evaluation, and defences against adversarial attacks, while suggesting promising research directions. This survey not only identifies the current state of the art to establish strong baselines for future experiments but also offers clear guidance for researchers aiming to enhance speech Deepfake detection systems.
智能设备的普及导致多媒体内容呈指数级增长。然而,深度学习的发展也催生了高度复杂的深度伪造内容(Deepfake)的生成,其中包括语音深度伪造(Speech Deepfakes),它能生成逼真的声音并传播错误信息,构成严重威胁。为了应对这一问题,已经组织了多次挑战来推进语音深度伪造检测技术的发展。在这篇综述中,我们系统地分析了截至2024年3月发表的超过200篇论文。我们对检测流程中的每个组件进行了全面的回顾,包括模型架构、优化技术、通用性、评价指标、性能比较、可用数据集和开源可用性。对于每个方面,我们都评估了最新的进展并讨论了持续存在的挑战。此外,我们还探讨了新兴话题,如局部深度伪造检测、跨数据集评估和对抗攻击的防御策略,同时提出了有前景的研究方向。这篇综述不仅确定了当前的研究现状,为未来的实验建立了强大的基准线,而且也为旨在提高语音深度伪造检测系统的研究者提供了明确的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages. This paper has been accepted by ACM Computing Surveys
Summary
智能设备的发展导致多媒体内容呈指数级增长,深度学习技术的进步也催生了高度复杂化的Deepfake内容,包括语音Deepfakes。它们通过生成真实声音和扩散错误信息构成严重威胁。为应对此挑战,已组织多次竞赛推动语音Deepfake检测技术的发展。本文系统分析了超过200篇至2024年3月发表的论文,全面评述检测流程中的每个组件,包括模型架构、优化技术、通用性、评估指标、性能对比、可用数据集和开源可用性。同时探讨新兴话题如部分Deepfake检测、跨数据集评估和对抗攻击的防御策略,并为未来研究指明方向。本文不仅确定了当前研究的顶尖水平,还为希望提高语音Deepfake检测系统的研究人员提供了清晰的指导。
Key Takeaways
- 智能设备普及导致多媒体内容激增,包括高度复杂的Deepfake内容。
- 语音Deepfakes通过生成真实声音和扩散错误信息构成严重威胁。
- 为应对语音Deepfake的挑战,已组织多次竞赛推动检测技术发展。
- 本文系统分析了超过200篇关于语音Deepfake检测的论文,全面评述检测流程中的各个组件。
- 文章探讨了新兴话题,如部分Deepfake检测、跨数据集评价和对抗攻击的防御策略。
- 本文确定了当前研究的顶尖水平,为建立未来实验提供了强基准线。
点此查看论文截图