⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-02 更新
Adaptively Distilled ControlNet: Accelerated Training and Superior Sampling for Medical Image Synthesis
Authors:Kunpeng Qiu, Zhiying Zhou, Yongxin Guo
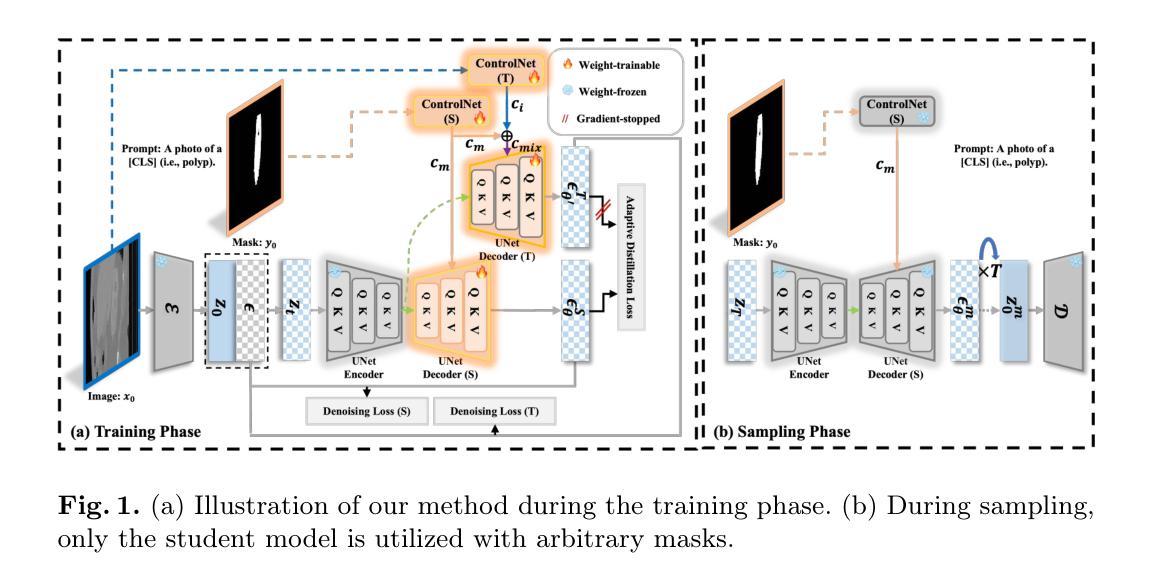
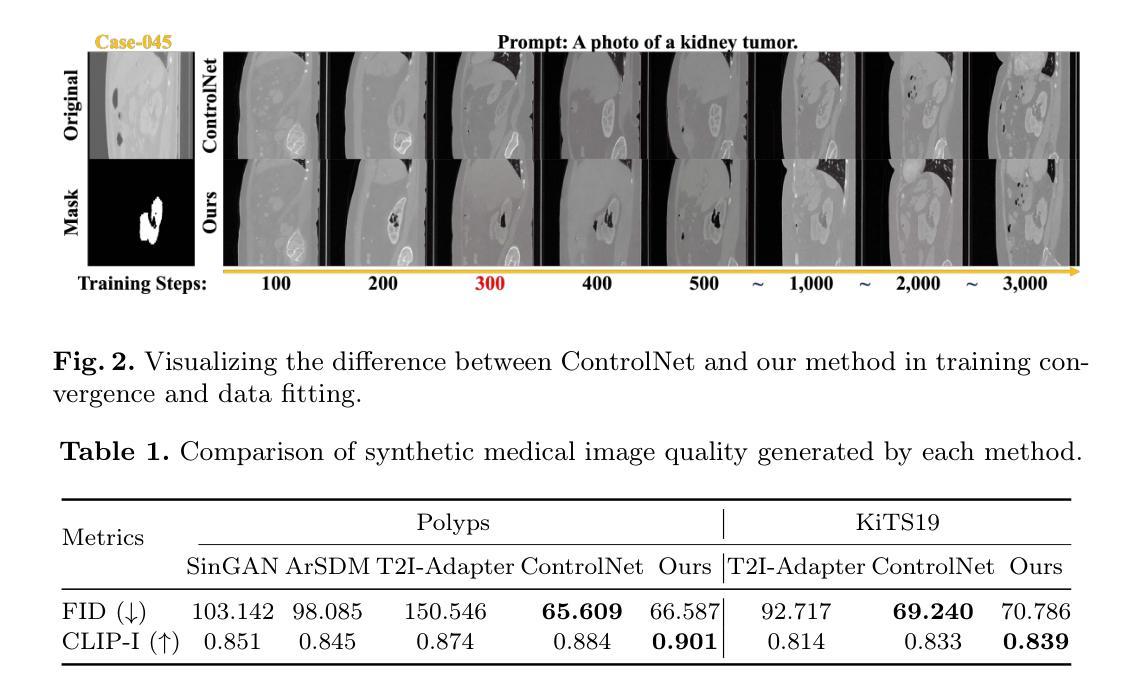
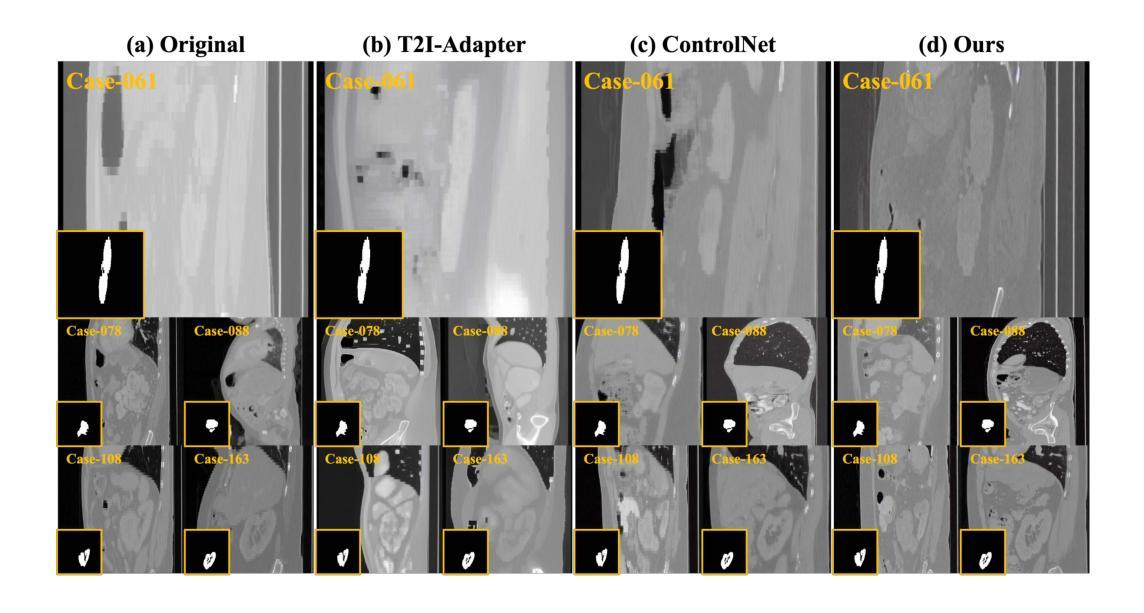
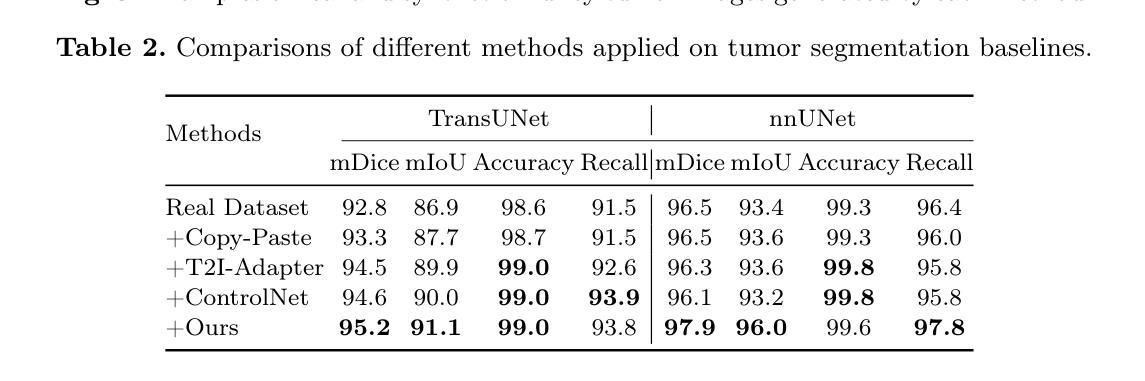
Medical image annotation is constrained by privacy concerns and labor-intensive labeling, significantly limiting the performance and generalization of segmentation models. While mask-controllable diffusion models excel in synthesis, they struggle with precise lesion-mask alignment. We propose \textbf{Adaptively Distilled ControlNet}, a task-agnostic framework that accelerates training and optimization through dual-model distillation. Specifically, during training, a teacher model, conditioned on mask-image pairs, regularizes a mask-only student model via predicted noise alignment in parameter space, further enhanced by adaptive regularization based on lesion-background ratios. During sampling, only the student model is used, enabling privacy-preserving medical image generation. Comprehensive evaluations on two distinct medical datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance: TransUNet improves mDice/mIoU by 2.4%/4.2% on KiTS19, while SANet achieves 2.6%/3.5% gains on Polyps, highlighting its effectiveness and superiority. Code is available at GitHub.
医学图像标注受到隐私担忧和标注工作量大的限制,这显著限制了分割模型的性能和泛化能力。虽然可控制的扩散模型在合成方面表现出色,但在精确病灶掩膜对准方面存在困难。我们提出了自适应蒸馏ControlNet(Adaptively Distilled ControlNet),这是一个任务通用的框架,通过双模型蒸馏加速训练和优化。具体来说,在训练过程中,以教师模型(基于掩膜图像对)通过参数空间的预测噪声对齐来规范仅掩膜的学生模型,并进一步增强基于病灶背景比的自适应正则化。在采样过程中,只使用学生模型,从而实现隐私保护的医学图像生成。在两个不同的医学数据集上的综合评估证明了其卓越性能:TransUNet在KiTS19数据集上提高了mDice/mIoU的得分2.4%/4.2%,而SANet在Polyps数据集上实现了2.6%/3.5%的增益,凸显了其有效性和优越性。代码已在GitHub上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
医学图像标注受限于隐私担忧和繁琐的标注工作,限制了分割模型的性能和泛化能力。提出自适应蒸馏ControlNet,通过双模型蒸馏加速训练和优化。训练期间,以掩膜图像对为条件的教师模型通过参数空间的预测噪声对齐对仅使用掩膜的学生的模型进行正则化,并通过病变背景比率进行自适应增强。采样期间仅使用学生模型,实现隐私保护的医学图像生成。在两种医学数据集上的全面评估表明,其具有卓越的性能,TransUNet在KiTS19上的mDice/mIoU提高了2.4%/4.2%,SANet在Polyps上的增益为2.6%/3.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像标注面临隐私和繁琐标注的挑战,影响模型性能与泛化。
- 自适应蒸馏ControlNet通过双模型蒸馏加速训练和优化。
- 教师模型在训练期间使用掩膜图像对进行正则化,学生模型仅使用掩膜。
- 采样期间仅使用学生模型以实现隐私保护的医学图像生成。
- 该方法在两种医学数据集上表现出卓越性能。
- TransUNet在KiTS19数据集上的mDice/mIoU有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

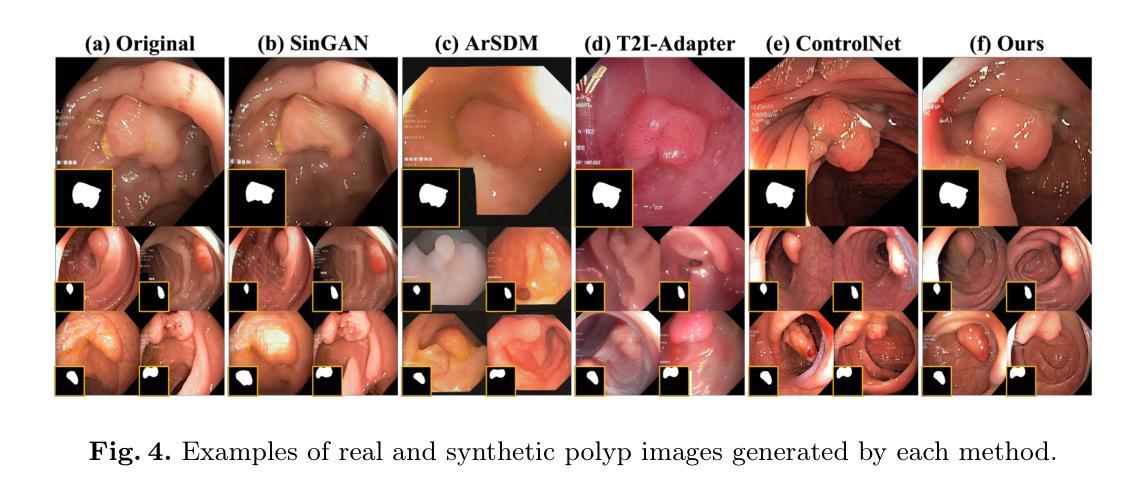
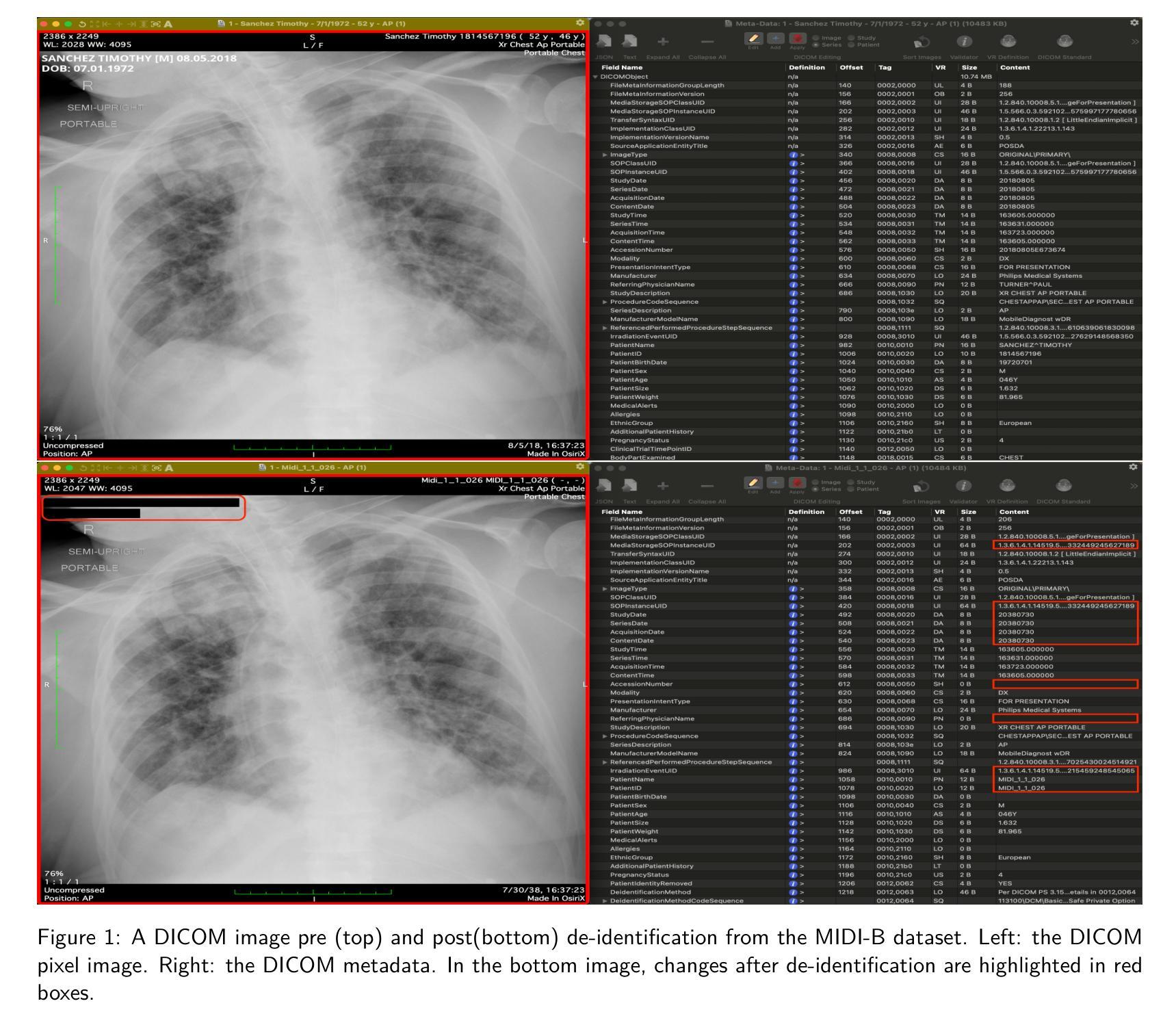
Medical Image De-Identification Benchmark Challenge
Authors:Linmin Pei, Granger Sutton, Michael Rutherford, Ulrike Wagner, Tracy Nolan, Kirk Smith, Phillip Farmer, Peter Gu, Ambar Rana, Kailing Chen, Thomas Ferleman, Brian Park, Ye Wu, Jordan Kojouharov, Gargi Singh, Jon Lemon, Tyler Willis, Milos Vukadinovic, Grant Duffy, Bryan He, David Ouyang, Marco Pereanez, Daniel Samber, Derek A. Smith, Christopher Cannistraci, Zahi Fayad, David S. Mendelson, Michele Bufano, Elmar Kotter, Hamideh Haghiri, Rajesh Baidya, Stefan Dvoretskii, Klaus H. Maier-Hein, Marco Nolden, Christopher Ablett, Silvia Siggillino, Sandeep Kaushik, Hongzhu Jiang, Sihan Xie, Zhiyu Wan, Alex Michie, Simon J Doran, Angeline Aurelia Waly, Felix A. Nathaniel Liang, Humam Arshad Mustagfirin, Michelle Grace Felicia, Kuo Po Chih, Rahul Krish, Ghulam Rasool, Nidhal Bouaynaya, Nikolas Koutsoubis, Kyle Naddeo, Kartik Pandit, Tony O’Sullivan, Raj Krish, Qinyan Pan, Scott Gustafson, Benjamin Kopchick, Laura Opsahl-Ong, Andrea Olvera-Morales, Jonathan Pinney, Kathryn Johnson, Theresa Do, Juergen Klenk, Maria Diaz, Arti Singh, Rong Chai, David A. Clunie, Fred Prior, Keyvan Farahani
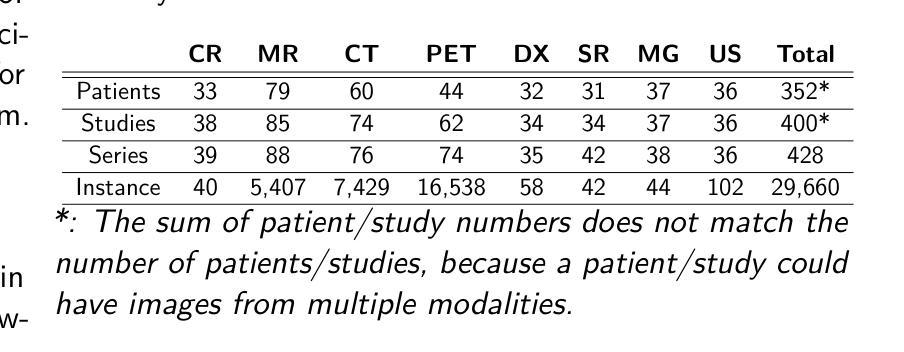
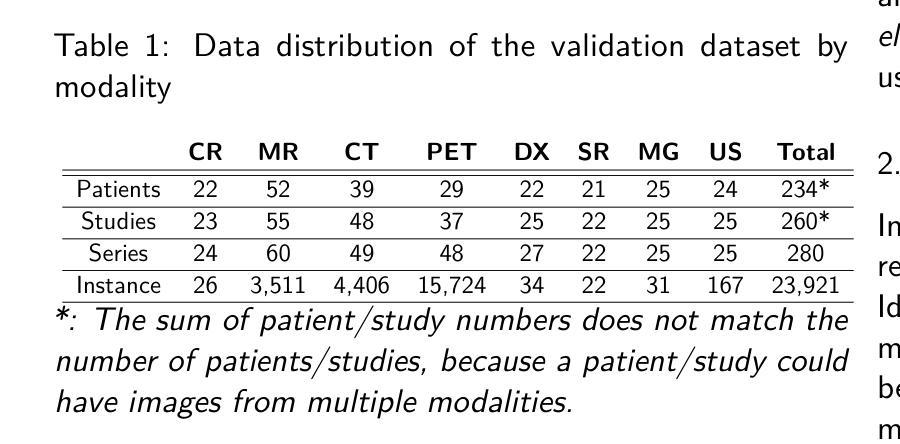
The de-identification (deID) of protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII) is a fundamental requirement for sharing medical images, particularly through public repositories, to ensure compliance with patient privacy laws. In addition, preservation of non-PHI metadata to inform and enable downstream development of imaging artificial intelligence (AI) is an important consideration in biomedical research. The goal of MIDI-B was to provide a standardized platform for benchmarking of DICOM image deID tools based on a set of rules conformant to the HIPAA Safe Harbor regulation, the DICOM Attribute Confidentiality Profiles, and best practices in preservation of research-critical metadata, as defined by The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). The challenge employed a large, diverse, multi-center, and multi-modality set of real de-identified radiology images with synthetic PHI/PII inserted. The MIDI-B Challenge consisted of three phases: training, validation, and test. Eighty individuals registered for the challenge. In the training phase, we encouraged participants to tune their algorithms using their in-house or public data. The validation and test phases utilized the DICOM images containing synthetic identifiers (of 216 and 322 subjects, respectively). Ten teams successfully completed the test phase of the challenge. To measure success of a rule-based approach to image deID, scores were computed as the percentage of correct actions from the total number of required actions. The scores ranged from 97.91% to 99.93%. Participants employed a variety of open-source and proprietary tools with customized configurations, large language models, and optical character recognition (OCR). In this paper we provide a comprehensive report on the MIDI-B Challenge’s design, implementation, results, and lessons learned.
医学图像中受保护的健康信息(PHI)和个人可识别信息(PII)的去标识化是共享医学图像的基本要求,特别是通过公共仓库共享时,以确保符合患者隐私法律。另外,保留非PHI元数据以告知并促进成像人工智能(AI)的下游发展是生物医学研究中的重要考虑因素。MIDI-B的目标是提供一个标准化的平台,以基于一组符合HIPAA安全港法规、DICOM属性保密配置文件以及由癌症成像档案(TCIA)定义的保留研究关键元数据的最佳实践规则,对DICOM图像去标识化工具进行基准测试。该挑战采用了一组大型、多样、多中心、多模式的真实去标识化放射学图像,并插入了合成PHI/PII。MIDI-B挑战包括三个阶段:培训、验证和测试。共有80人注册参加此次挑战。在培训阶段,我们鼓励参与者使用其内部或公开数据调整算法。验证和测试阶段使用了包含合成标识符的DICOM图像(分别为216个和322个主题)。有10支队伍成功完成了挑战的测试阶段。为了衡量基于规则的图像去标识化方法的成功程度,分数是根据正确行动的数量占总行动数量的百分比来计算的。得分范围从97.91%到99.93%。参与者使用了各种开源和专有工具,具有自定义配置、大型语言模型和光学字符识别(OCR)。在本文中,我们提供了关于MIDI-B挑战的设计、实施、结果和经验教训的全面报告。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages
Summary
医学图像共享时,需对保护健康信息(PHI)和个人可识别信息(PII)进行去标识化处理,同时保留非PHI元数据信息以支持下游人工智能成像技术的发展。MIDI-B挑战旨在提供一个标准化平台,基于一组符合HIPAA安全港法规、DICOM属性保密配置文件及最佳实践的研究关键性元数据存储规定的规则,对DICOM图像去标识化工具进行基准测试。挑战使用了大量多中心、多模式的真实去标识化放射图像,并插入了合成PHI/PII。该挑战包括培训、验证和测试三个阶段,共有80人参加。参赛者采用基于规则的方法,成功率在97.91%至99.93%之间。
Key Takeaways
- 去标识化医学图像是共享医学图像的基本要求,以确保符合患者隐私法律。
- MIDI-B挑战旨在提供一个标准化平台,用于基准测试DICOM图像去标识化工具。
- 挑战使用了含有合成PHI/PII的大量多中心、多模式的真实去标识化放射图像。
- 挑战包括培训、验证和测试三个阶段,共有80人参加,有十个团队成功完成测试阶段。
- 基于规则的去标识化方法成功率在97.91%至99.93%之间。
- 参赛者采用了多种开源和专有工具,以及大型语言模型和光学字符识别技术。
点此查看论文截图

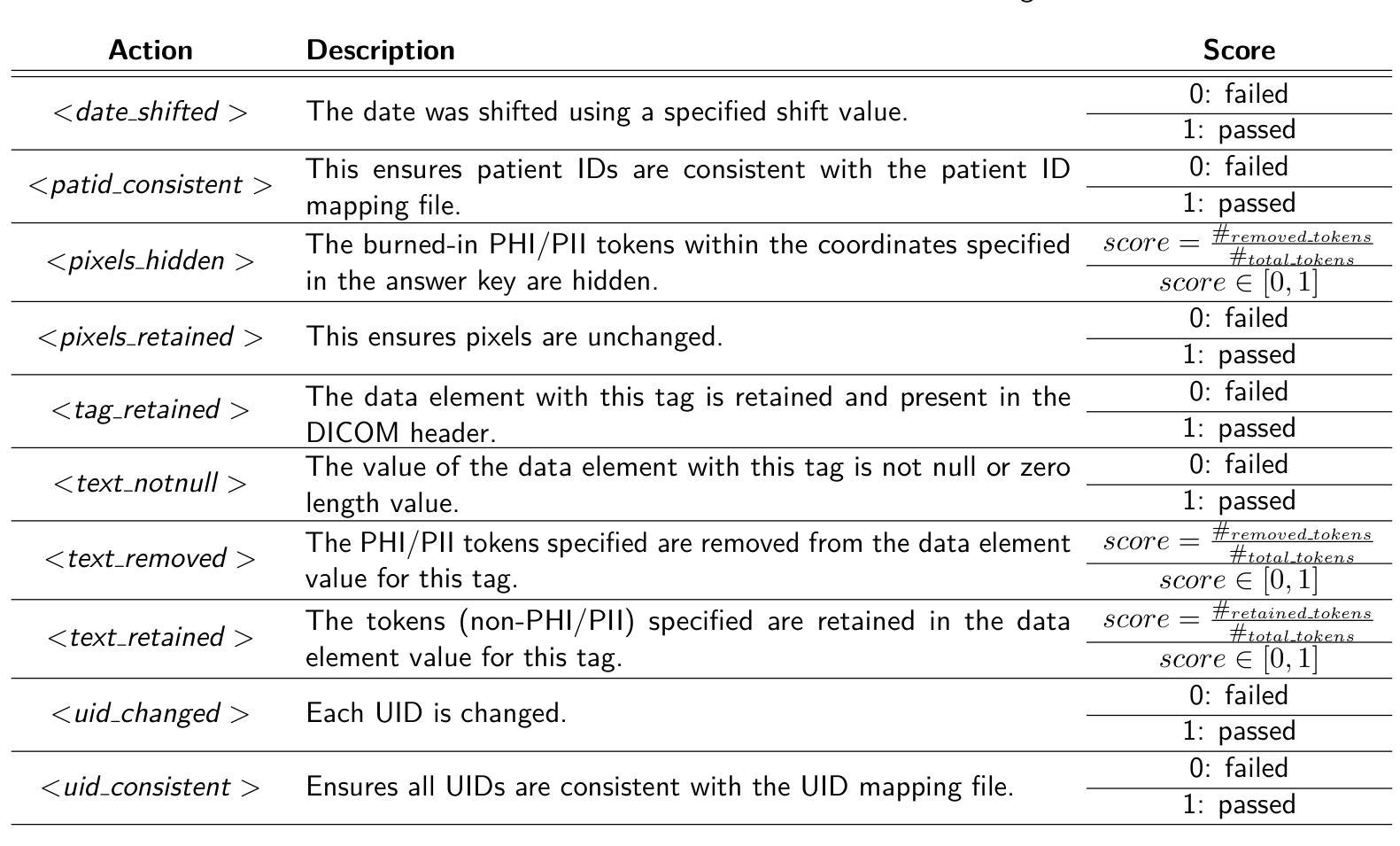
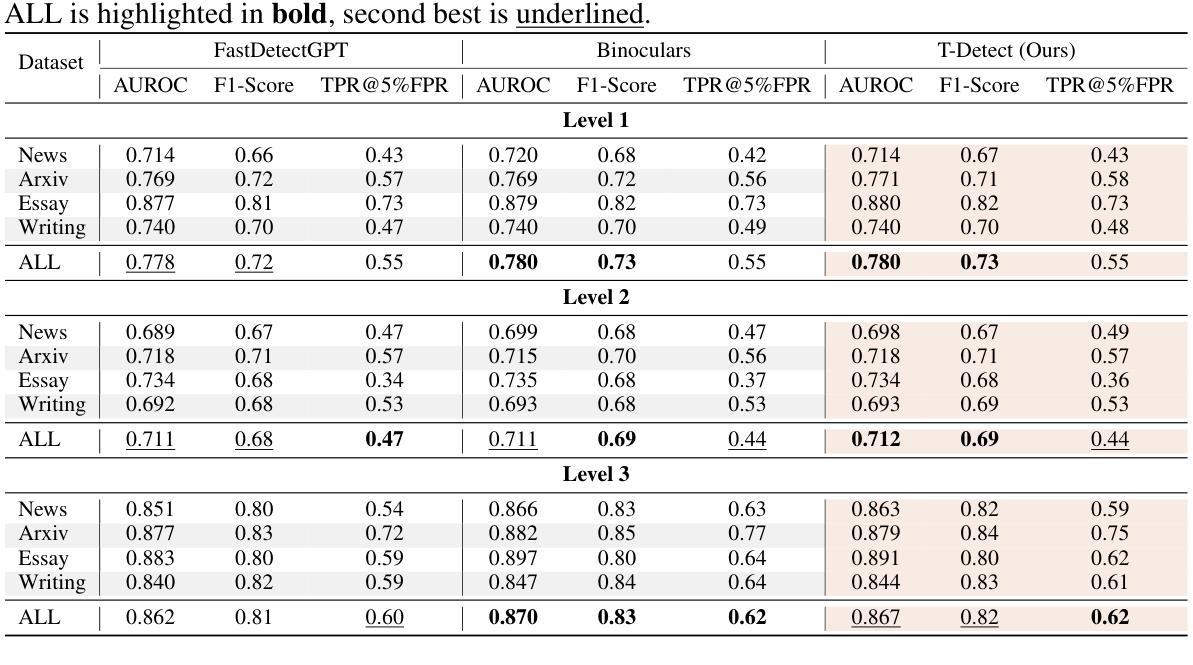
T-Detect: Tail-Aware Statistical Normalization for Robust Detection of Adversarial Machine-Generated Text
Authors:Alva West, Luodan Zhang, Liuliu Zhang, Minjun Zhu, Yixuan Weng, Yue Zhang
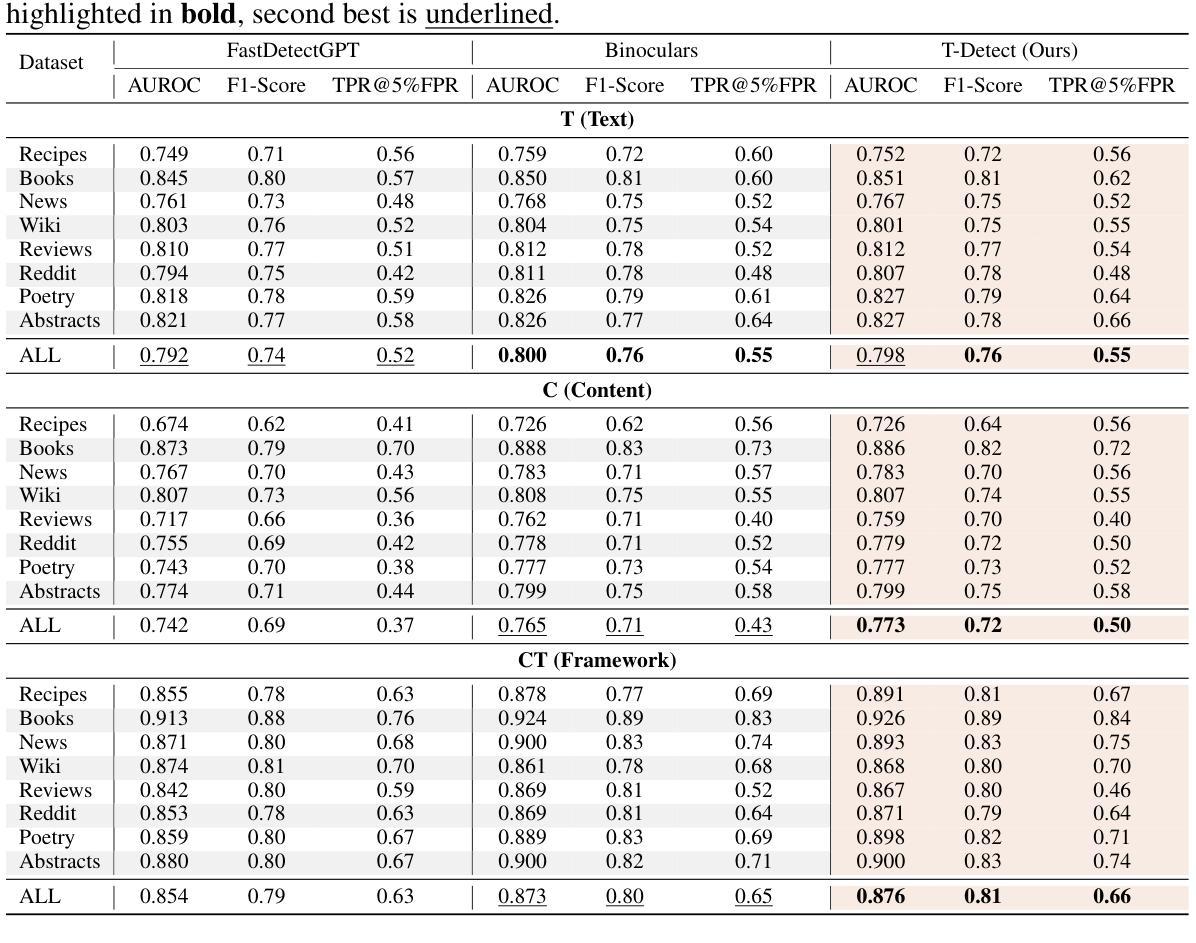
The proliferation of sophisticated text generation models necessitates the development of robust detection methods capable of identifying machine-generated content, particularly text designed to evade detection through adversarial perturbations. Existing zero-shot detectors often rely on statistical measures that implicitly assume Gaussian distributions, a premise that falters when confronted with the heavy-tailed statistical artifacts characteristic of adversarial or non-native English texts. This paper introduces T-Detect, a novel detection method that fundamentally redesigns the statistical core of curvature-based detectors. Our primary innovation is the replacement of standard Gaussian normalization with a heavy-tailed discrepancy score derived from the Student’s t-distribution. This approach is theoretically grounded in the empirical observation that adversarial texts exhibit significant leptokurtosis, rendering traditional statistical assumptions inadequate. T-Detect computes a detection score by normalizing the log-likelihood of a passage against the expected moments of a t-distribution, providing superior resilience to statistical outliers. We validate our approach on the challenging RAID benchmark for adversarial text and the comprehensive HART dataset. Experiments show that T-Detect provides a consistent performance uplift over strong baselines, improving AUROC by up to 3.9% in targeted domains. When integrated into a two-dimensional detection framework (CT), our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, with an AUROC of 0.926 on the Books domain of RAID. Our contributions are a new, theoretically-justified statistical foundation for text detection, an ablation-validated method that demonstrates superior robustness, and a comprehensive analysis of its performance under adversarial conditions. Ours code are released at https://github.com/ResearAI/t-detect.
随着先进的文本生成模型的普及,需要开发能够识别机器生成内容(特别是通过对抗性扰动设计的旨在逃避检测的文本)的稳健检测方法的必要性日益凸显。现有的零样本检测器通常依赖于统计指标,这些指标隐含地假设高斯分布。然而,在面对具有厚尾统计特征的对抗性或非英语原生文本时,这一前提会失效。本文介绍了T-Detect,这是一种新型的检测方法,它从根本上重新设计了基于曲率的检测器的统计核心。我们的主要创新之处在于用基于学生t分布的厚尾偏差得分替换标准的高斯归一化。这一方法从理论上建立在实证观察的基础上,即对抗性文本表现出显著的尖峰度,使得传统的统计假设变得无效。T-Detect通过计算一段文字的对数似然与t分布的期望矩的归一化检测分数,对于统计异常值具有出色的抗干扰能力。我们在具有挑战性的对抗性文本RAID基准测试和全面的HART数据集上验证了我们的方法。实验表明,T-Detect在目标领域上比强大的基线提供了持续的性能提升,在目标领域的曲线下面积(AUROC)提高了高达3.9%。当集成到二维检测框架(CT)中时,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能水平,在RAID的书籍领域的曲线下面积为0.926。我们的贡献在于为文本检测提供了新的理论验证的统计基础,一个经过验证的显示出卓越稳健性的方法,以及对抗条件下其性能的全面分析。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/ResearAI/t-detect。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了T-Detect这一新型的文本检测方法的引入,它专门针对对抗性文本的特点进行改进,对传统高斯正态分布的假设进行优化。使用学生t分布的重尾偏差分数替换标准高斯归一化方法,提升了对抗性文本的识别效果。实验验证了在挑战性和综合性的数据集上,T-Detect方法表现出超越基线方法的稳健性能。其代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- T-Detect是一种新型的文本检测模型,用于识别机器生成的对抗性文本内容。
- 传统基于高斯分布的零样本检测器在面对对抗性或非原生英语文本时存在缺陷。
- T-Detect引入学生t分布的重尾偏差分数替换高斯归一化,应对文本数据集中的重尾统计特性问题。
- 对抗性文本表现出显著的尖峰度,使得传统统计假设失效。
点此查看论文截图

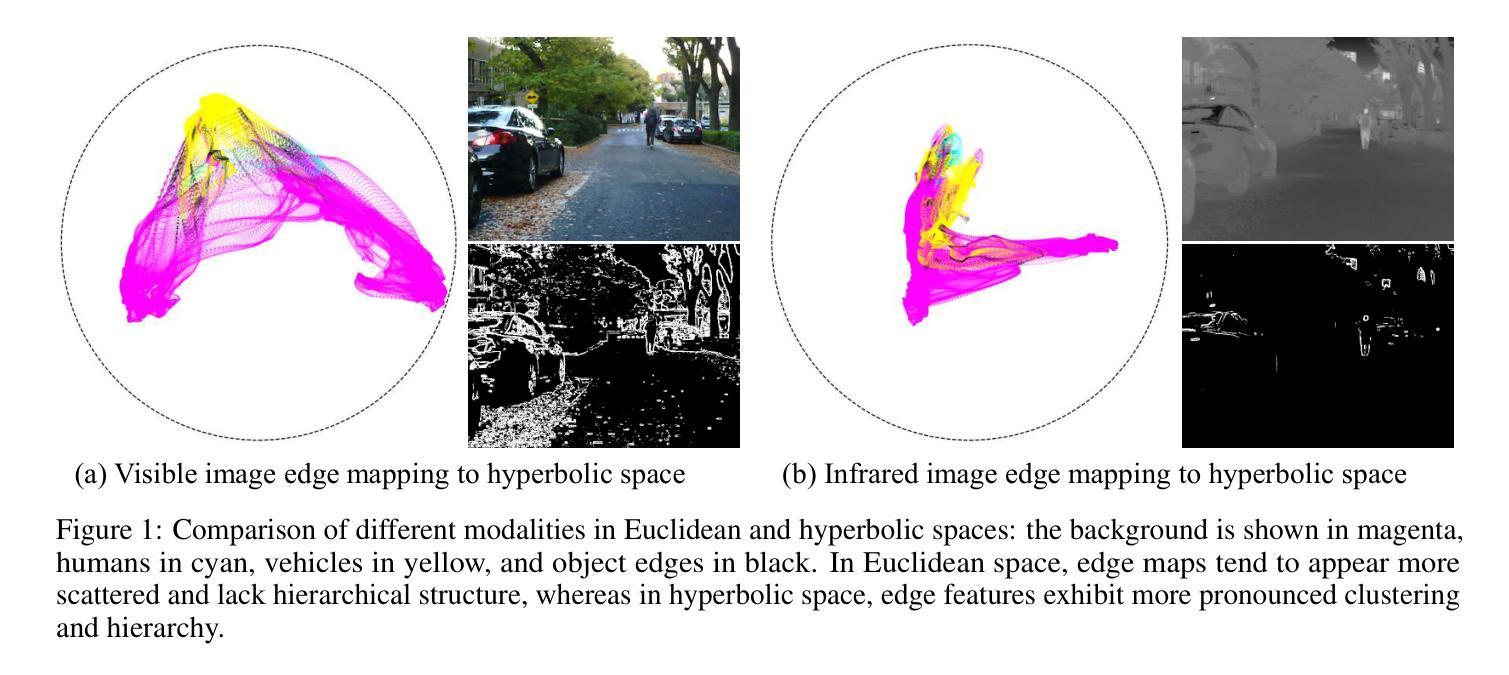
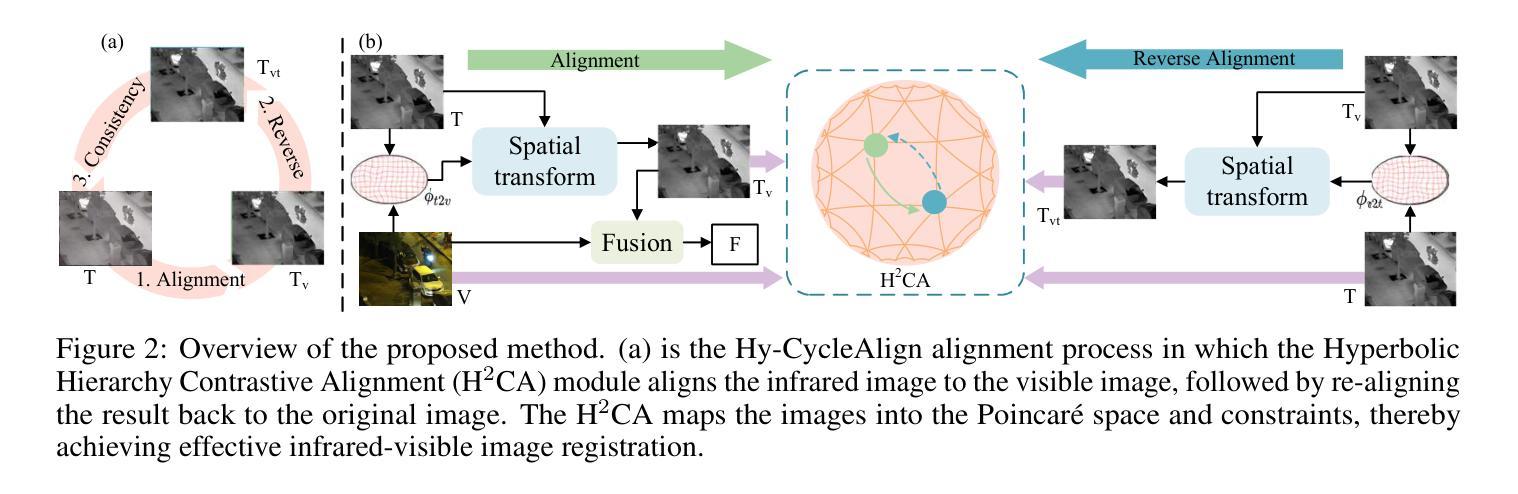
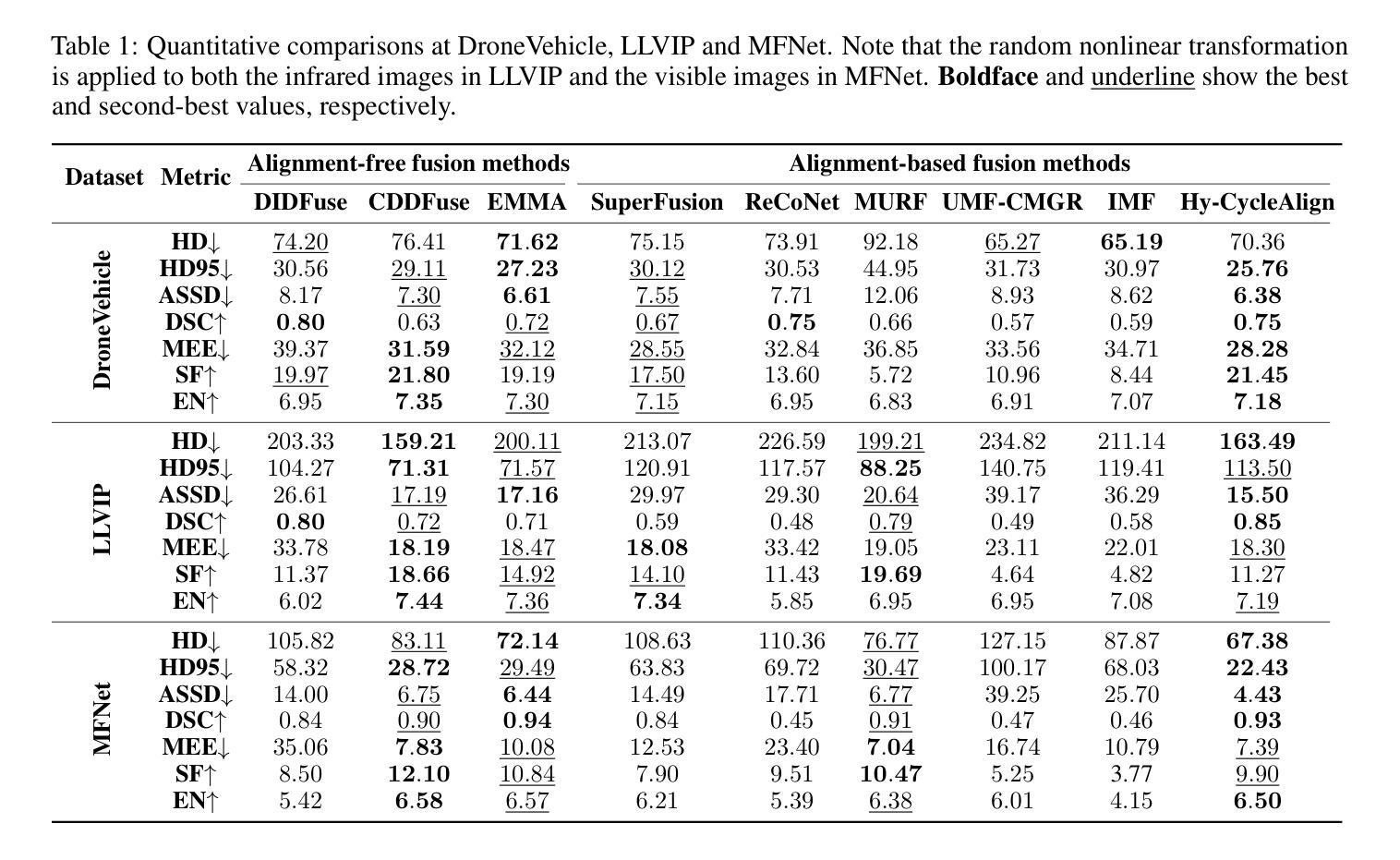
Hyperbolic Cycle Alignment for Infrared-Visible Image Fusion
Authors:Timing Li, Bing Cao, Jiahe Feng, Haifang Cao, Qinghau Hu, Pengfei Zhu
Image fusion synthesizes complementary information from multiple sources, mitigating the inherent limitations of unimodal imaging systems. Accurate image registration is essential for effective multi-source data fusion. However, existing registration methods, often based on image translation in Euclidean space, fail to handle cross-modal misalignment effectively, resulting in suboptimal alignment and fusion quality. To overcome this limitation, we explore image alignment in non-Euclidean space and propose a Hyperbolic Cycle Alignment Network (Hy-CycleAlign). To the best of our knowledge, Hy-CycleAlign is the first image registration method based on hyperbolic space. It introduces a dual-path cross-modal cyclic registration framework, in which a forward registration network aligns cross-modal inputs, while a backward registration network reconstructs the original image, forming a closed-loop registration structure with geometric consistency. Additionally, we design a Hyperbolic Hierarchy Contrastive Alignment (H$^{2}$CA) module, which maps images into hyperbolic space and imposes registration constraints, effectively reducing interference caused by modality discrepancies. We further analyze image registration in both Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces, demonstrating that hyperbolic space enables more sensitive and effective multi-modal image registration. Extensive experiments on misaligned multi-modal images demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in both image alignment and fusion. Our code will be publicly available.
图像融合技术通过融合多个来源的互补信息,缓解了单模态成像系统的固有局限性。准确的图像配准对于有效的多源数据融合至关重要。然而,现有的配准方法通常基于欧几里得空间的图像翻译,无法有效地处理跨模态的错位问题,导致配准和融合质量不佳。为了克服这一局限性,我们探索了非欧几里得空间的图像配准,并提出了一种双路径跨模态循环配准框架——Hyperbolic Cycle Alignment Network(Hy-CycleAlign)。据我们所知,Hy-CycleAlign是基于双曲空间的第一个图像配准方法。它引入了一种双路径跨模态循环配准框架,其中前向配准网络对齐跨模态输入,而后向配准网络重建原始图像,形成具有几何一致性的闭环配准结构。此外,我们设计了一个Hyperbolic Hierarchy Contrastive Alignment(H²CA)模块,它将图像映射到双曲空间并施加配准约束,有效减少了由模态差异引起的干扰。我们进一步分析了欧几里得空间和双曲空间中的图像配准,表明双曲空间能够实现更敏感和有效的多模态图像配准。在错位多模态图像上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在图像配准和融合方面都显著优于现有方法。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像融合能够综合多个来源的互补信息,弥补单模态成像系统的固有局限。准确的图像配准是实现多源数据有效融合的关键。然而,现有的配准方法大多基于欧几里得空间的图像转换,难以有效处理跨模态的错位问题,导致配准和融合质量不佳。为了克服这一局限,本文探索了非欧几里得空间的图像对齐,并首次提出了基于双路径跨模态循环配准框架的Hyperbolic Cycle Alignment Network(Hy-CycleAlign)。此外,还设计了Hyperbolic Hierarchy Contrastive Alignment(H²CA)模块,将图像映射到双曲空间并施加配准约束,有效降低不同模态之间的差异引起的干扰。研究结果显示双曲空间进行多模态图像配准更加精确有效。实验证明,本文方法在图像配准和融合方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图像融合能够综合多个来源的互补信息,有助于克服单模态成像的局限性。
- 准确图像配准是实现多源数据有效融合的关键步骤。
- 现有基于欧几里得空间的图像配准方法难以处理跨模态错位问题。
- 提出了一种新的图像配准方法——Hyperbolic Cycle Alignment Network(Hy-CycleAlign),基于非欧几里得空间进行图像对齐。
- Hy-CycleAlign包括一个前向配准网络和一个后向配准网络,形成闭环注册结构,实现几何一致性。
- 设计的Hyperbolic Hierarchy Contrastive Alignment(H²CA)模块可有效降低不同模态间的干扰。
点此查看论文截图


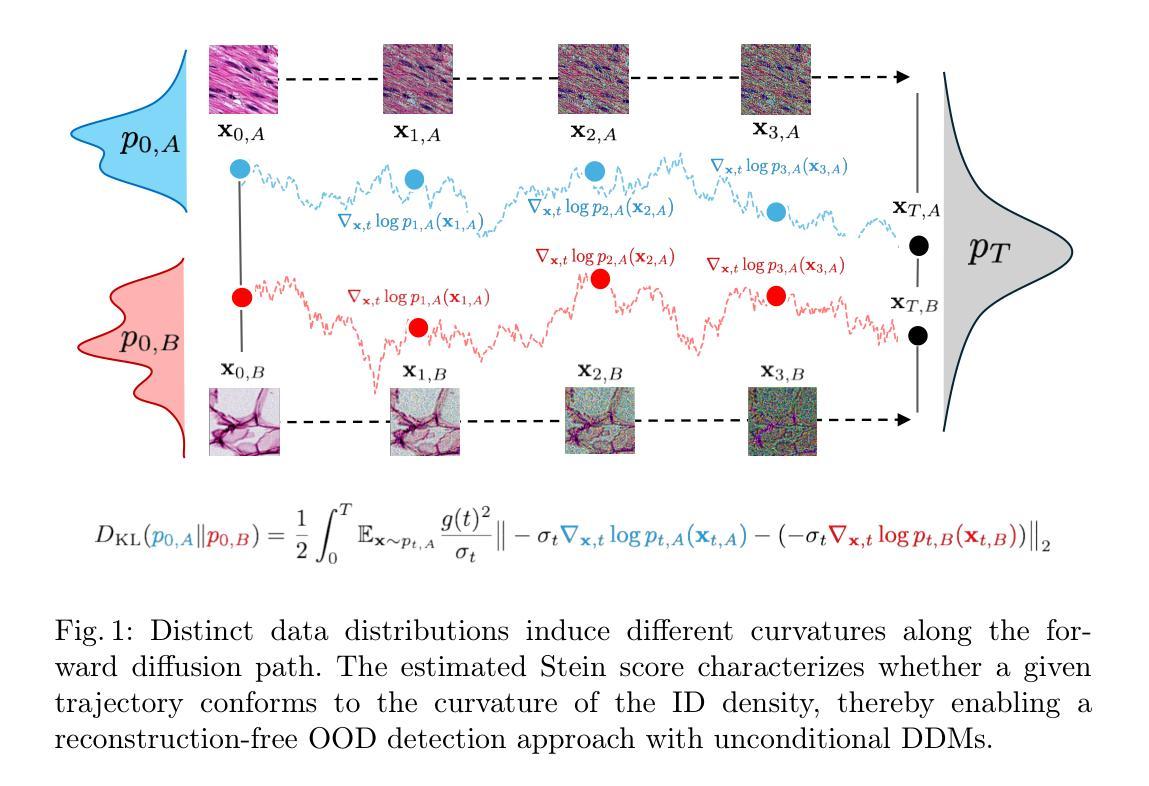
Out-of-Distribution Detection in Medical Imaging via Diffusion Trajectories
Authors:Lemar Abdi, Francisco Caetano, Amaan Valiuddin, Christiaan Viviers, Hamdi Joudeh, Fons van der Sommen
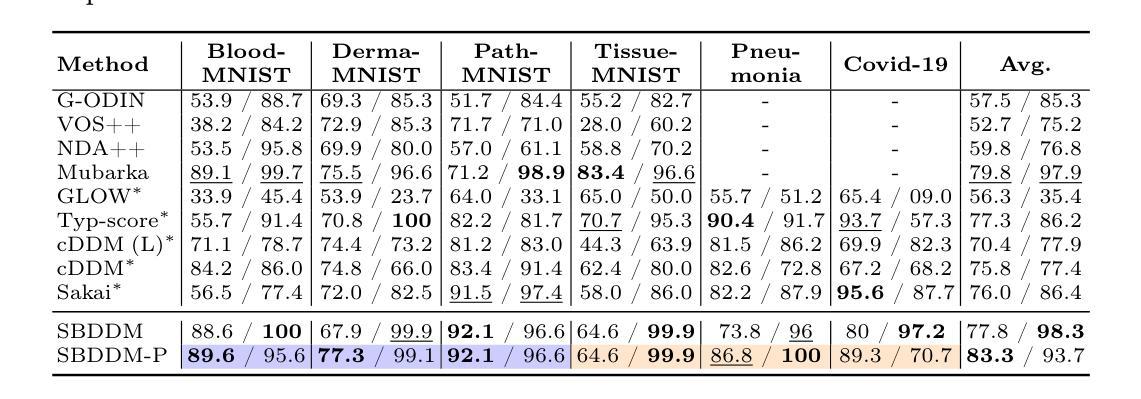
In medical imaging, unsupervised out-of-distribution (OOD) detection offers an attractive approach for identifying pathological cases with extremely low incidence rates. In contrast to supervised methods, OOD-based approaches function without labels and are inherently robust to data imbalances. Current generative approaches often rely on likelihood estimation or reconstruction error, but these methods can be computationally expensive, unreliable, and require retraining if the inlier data changes. These limitations hinder their ability to distinguish nominal from anomalous inputs efficiently, consistently, and robustly. We propose a reconstruction-free OOD detection method that leverages the forward diffusion trajectories of a Stein score-based denoising diffusion model (SBDDM). By capturing trajectory curvature via the estimated Stein score, our approach enables accurate anomaly scoring with only five diffusion steps. A single SBDDM pre-trained on a large, semantically aligned medical dataset generalizes effectively across multiple Near-OOD and Far-OOD benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance while drastically reducing computational cost during inference. Compared to existing methods, SBDDM achieves a relative improvement of up to 10.43% and 18.10% for Near-OOD and Far-OOD detection, making it a practical building block for real-time, reliable computer-aided diagnosis.
在医学成像领域,无监督的离群分布(OOD)检测为识别发病率极低的病理病例提供了一种吸引人的方法。与有监督方法不同,基于OOD的方法无需标签,对数据不平衡具有固有的鲁棒性。当前的生成方法通常依赖于似然估计或重建误差,但这些方法计算量大、不可靠,如果内部数据发生变化,需要重新训练。这些局限性阻碍了它们有效、一致和稳健地区分正常输入与异常输入的能力。我们提出了一种无需重建的OOD检测方法,该方法利用基于Stein得分的降噪扩散模型的正向扩散轨迹(SBDDM)。通过估计的Stein得分捕捉轨迹曲率,我们的方法仅使用五个扩散步骤即可实现精确异常评分。单个SBDDM预训练于大型语义对齐医学数据集上,可有效应用于多个近OOD和远OOD基准测试,实现了最先进的性能,同时大大降低了推理过程中的计算成本。与现有方法相比,SBDDM在近OOD和远OOD检测方面的相对改进率分别高达10.43%和18.10%,使其成为实时可靠计算机辅助诊断的实用构建块。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Uncertainty for Safe Utilization of Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于无监督的离群分布检测,利用Stein评分去噪扩散模型的扩散轨迹进行异常评分,有效实现医学图像中的异常检测。此方法仅需五步扩散,可在多个近离群分布和远离群分布标准上实现良好泛化,显著减少计算成本,具有实际应用于实时可靠的计算机辅助诊断的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 无监督离群分布(OOD)检测在医学图像中用于识别低发病率的病例。
- 与监督方法相比,OOD方法无需标签,能更稳健地应对数据不平衡。
- 当前生成式方法常依赖于可能性估计或重建误差,但存在计算昂贵、不可靠等问题。
- 提出一种基于Stein评分去噪扩散模型的重建式OOD检测方法。
- 通过捕捉扩散轨迹的弯曲度进行异常评分,仅五步扩散即可实现准确异常评分。
- SBDDM模型在多个近离群和远离群标准上实现良好泛化,显著减少推理计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

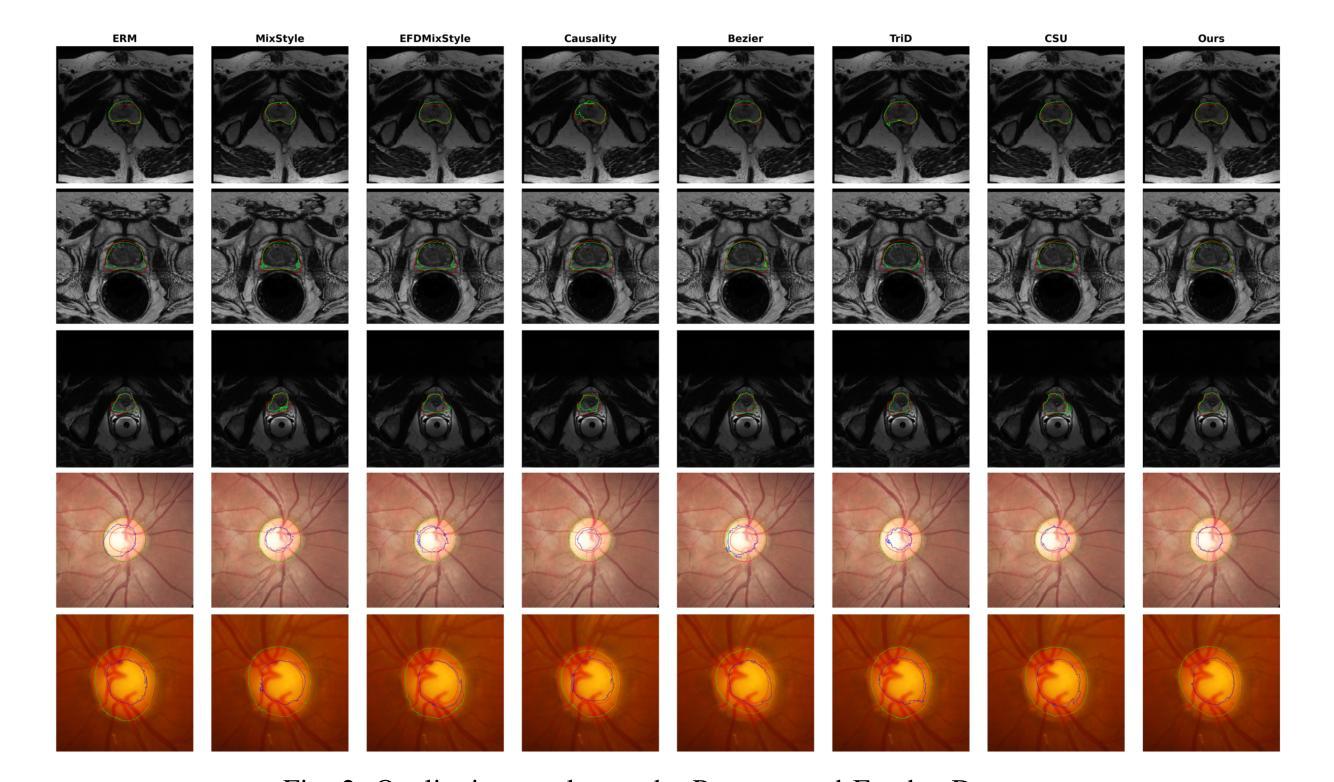
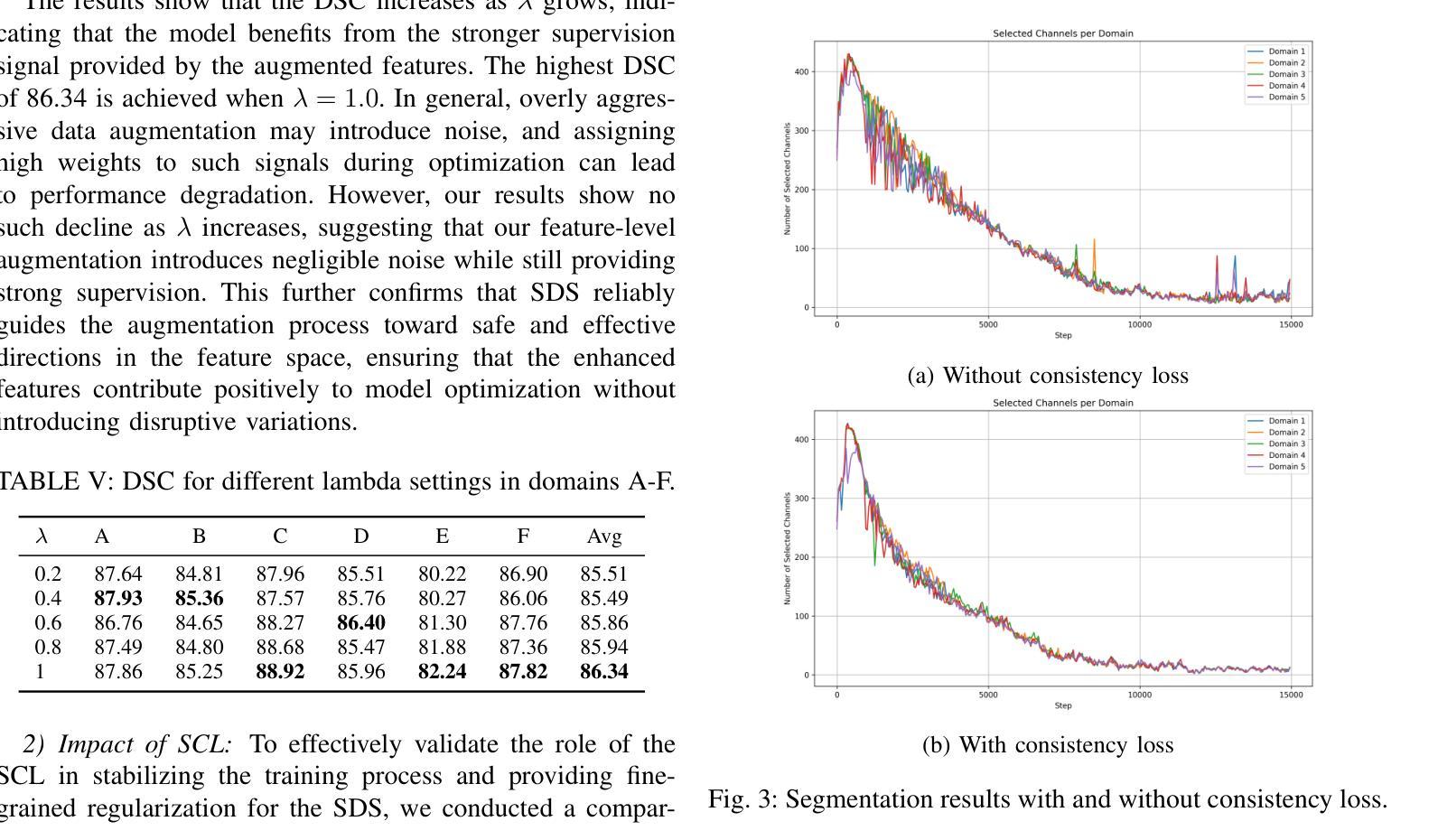
Learning Semantic Directions for Feature Augmentation in Domain-Generalized Medical Segmentation
Authors:Yingkai Wang, Yaoyao Zhu, Xiuding Cai, Yuhao Xiao, Haotian Wu, Yu Yao
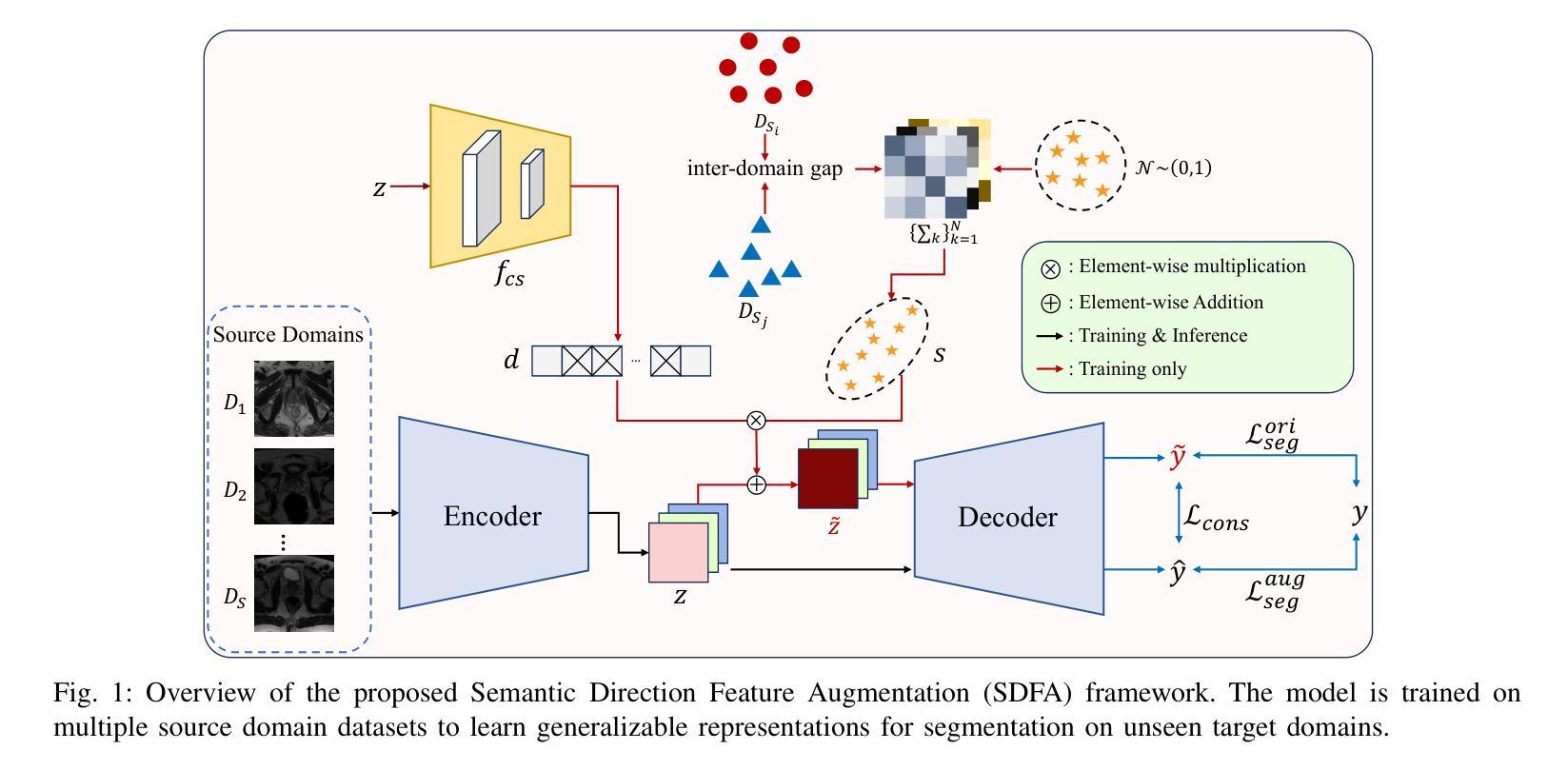
Medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in clinical workflows, but domain shift often leads to performance degradation when models are applied to unseen clinical domains. This challenge arises due to variations in imaging conditions, scanner types, and acquisition protocols, limiting the practical deployment of segmentation models. Unlike natural images, medical images typically exhibit consistent anatomical structures across patients, with domain-specific variations mainly caused by imaging conditions. This unique characteristic makes medical image segmentation particularly challenging. To address this challenge, we propose a domain generalization framework tailored for medical image segmentation. Our approach improves robustness to domain-specific variations by introducing implicit feature perturbations guided by domain statistics. Specifically, we employ a learnable semantic direction selector and a covariance-based semantic intensity sampler to modulate domain-variant features while preserving task-relevant anatomical consistency. Furthermore, we design an adaptive consistency constraint that is selectively applied only when feature adjustment leads to degraded segmentation performance. This constraint encourages the adjusted features to align with the original predictions, thereby stabilizing feature selection and improving the reliability of the segmentation. Extensive experiments on two public multi-center benchmarks show that our framework consistently outperforms existing domain generalization approaches, achieving robust and generalizable segmentation performance across diverse clinical domains.
医学图像分割在临床工作流程中扮演着至关重要的角色,但当模型应用于未见过的临床领域时,领域偏移往往会导致性能下降。这一挑战是由于成像条件、扫描仪类型和采集协议的变化而产生的,限制了分割模型的实际应用。与自然图像不同,医学图像在患者之间通常表现出一致的解剖结构,领域特定的变化主要由成像条件引起。这种独特的特点使得医学图像分割特别具有挑战性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割在临床工作中至关重要,但模型应用于未见领域时,领域偏移会导致性能下降。这一挑战源于成像条件、扫描仪类型和采集协议的变化,限制了分割模型的实用部署。为应对这一挑战,我们提出了针对医学图像分割的领域泛化框架。通过引入由领域统计引导的隐式特征扰动,我们的方法提高了对领域特定变化的稳健性。实验表明,我们的框架在多样化临床领域上表现稳健,优于现有领域泛化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在临床工作中非常重要,但领域偏移会影响模型性能。
- 领域偏移主要由于成像条件、扫描仪类型和采集协议的变化引起。
- 医学图像具有一致的解剖结构特性,这使得医学图像分割更具挑战性。
- 为解决领域偏移问题,提出了针对医学图像分割的领域泛化框架。
- 该框架通过引入隐式特征扰动来提高模型的稳健性,同时保持任务相关的解剖结构一致性。
- 框架中设计了自适应一致性约束,选择性应用特征调整,提高分割的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

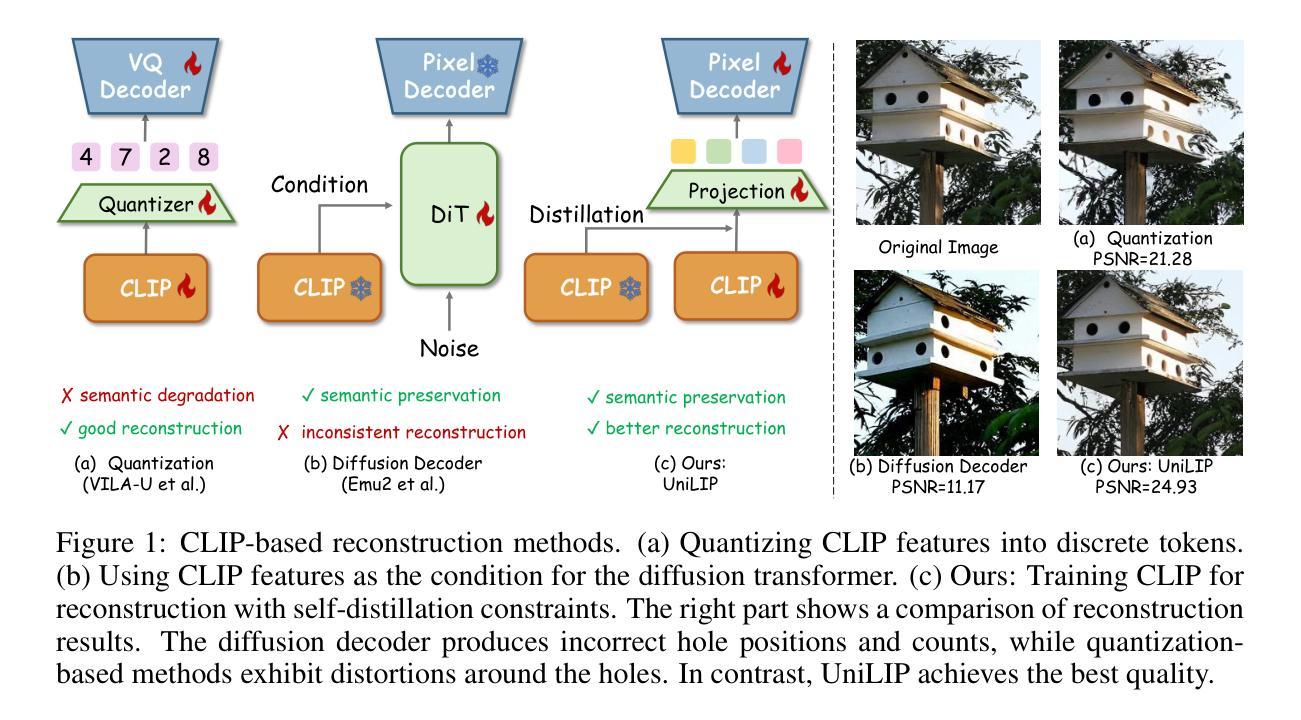
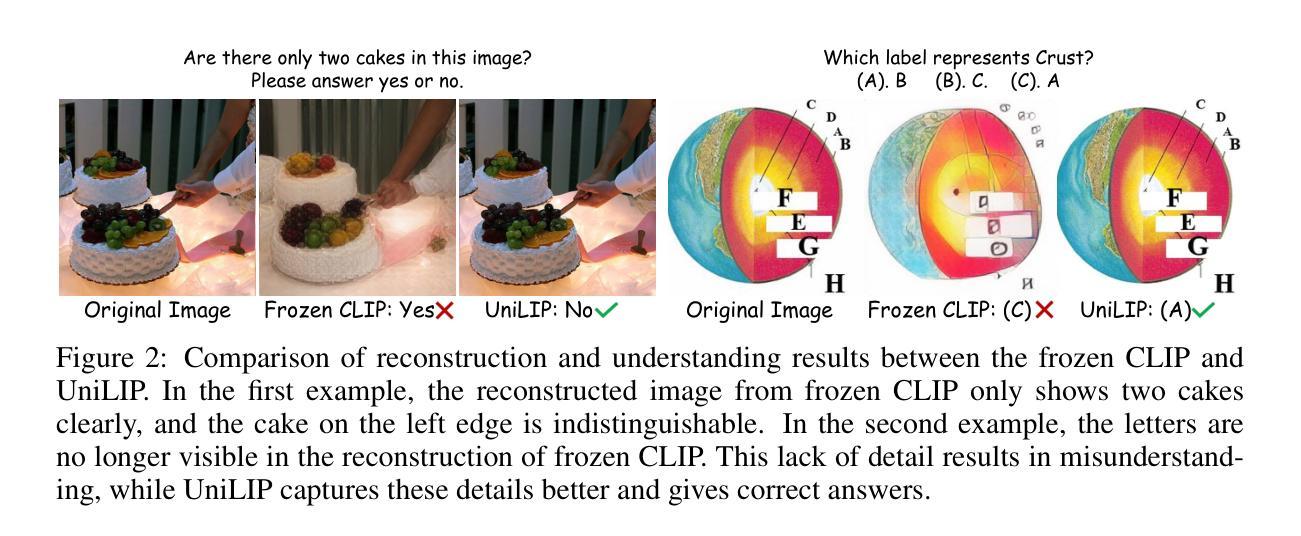
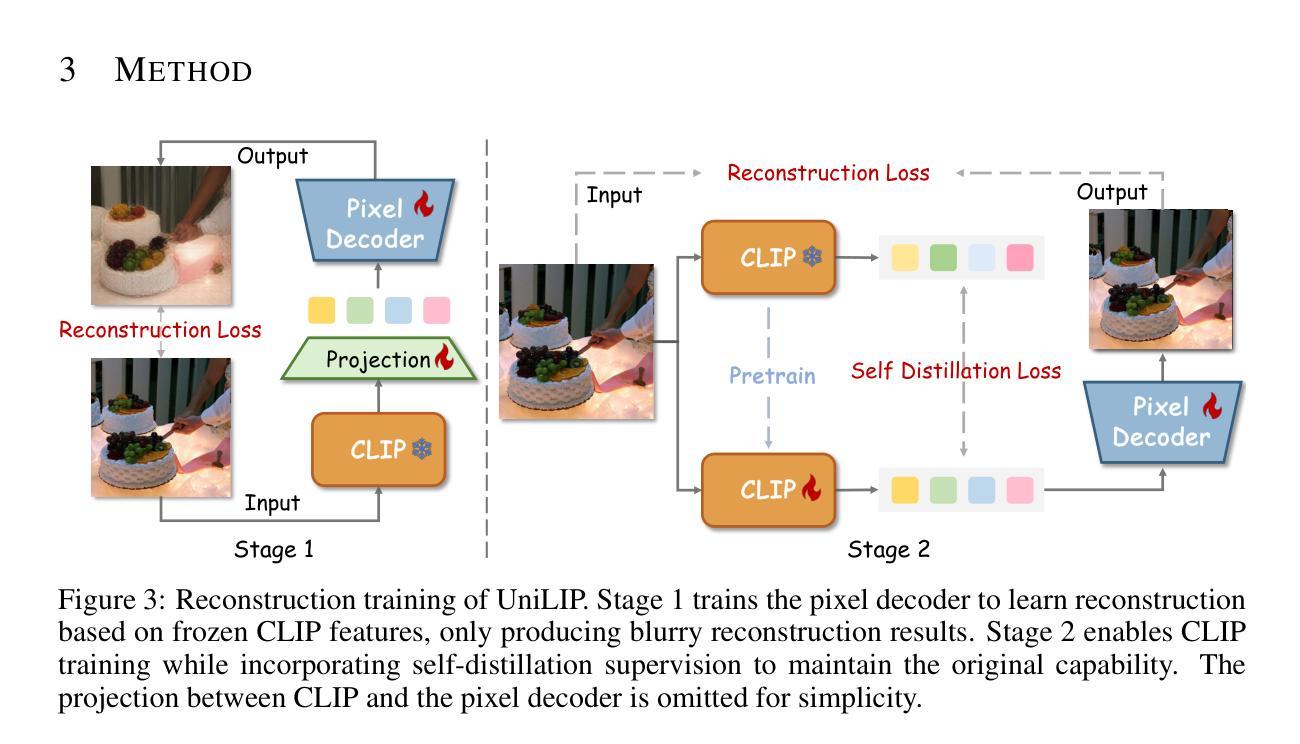
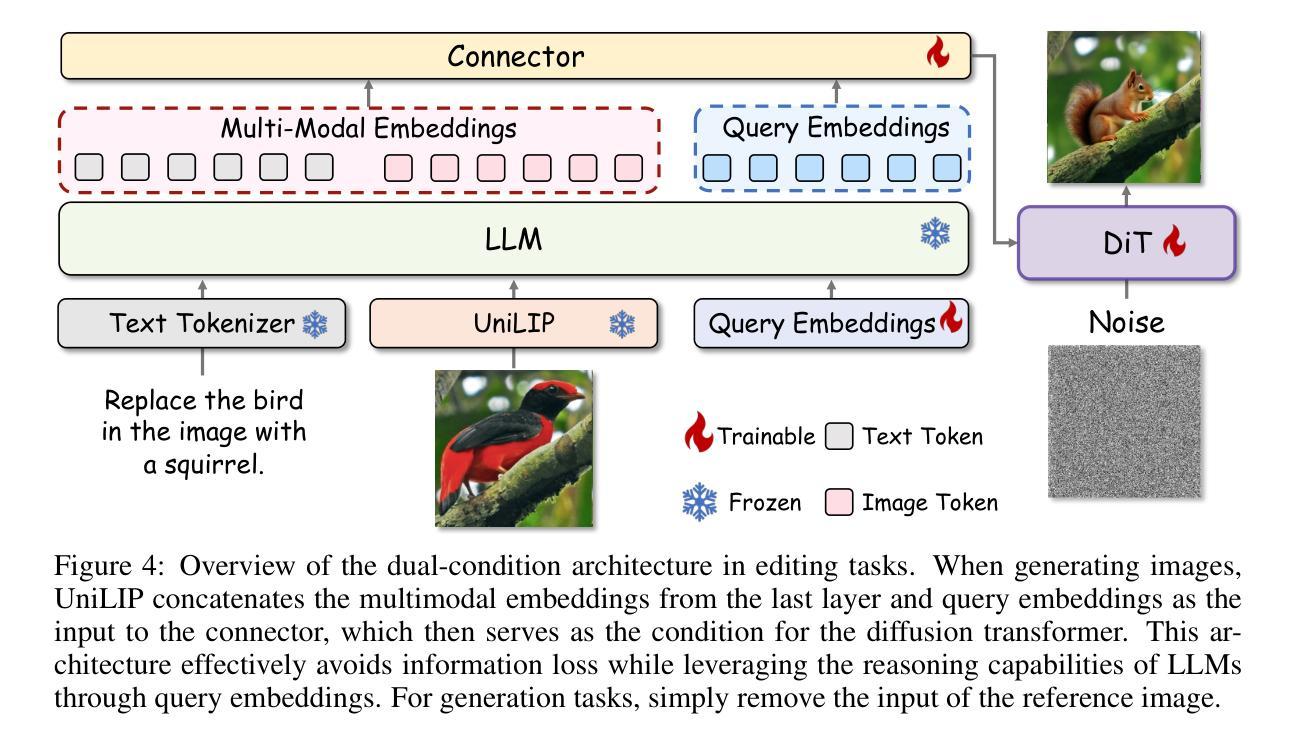
UniLiP: Adapting CLIP for Unified Multimodal Understanding, Generation and Editing
Authors:Hao Tang, Chenwei Xie, Xiaoyi Bao, Tingyu Weng, Pandeng Li, Yun Zheng, Liwei Wang
In this paper, we propose UniLIP, which extends CLIP to reconstruction, generation and editing, thereby building a unified tokenizer upon its exceptional comprehension capabilities. Previous CLIP-based unified methods often require additional diffusion decoders or quantization to support reconstruction and generation tasks, leading to inconsistent reconstruction or degradation of original comprehension performance.In contrast, we introduce a two-stage training scheme and a self-distillation strategy that progressively integrates reconstruction capabilities into CLIP, allowing it to maintain original comprehension performance while achieving effective image reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose a dual-condition architecture to connect the MLLM and diffusion transformer, using both learnable queries and the last layer multimodal hidden states as joint conditions. This method not only enables the utilization of the MLLM’s strong reasoning capabilities in generation tasks, but also maximizes the exploitation of the rich information in UniLIP features during editing tasks. In text-to-image generation tasks, UniLIP obtains scores of 0.87 and 0.53 on GenEval and WISE benchmark respectively, surpassing all previous unified models of similar scale. In image editing, UniLIP also achieves a score of 3.62 on the ImgEdit Benchmark, surpassing recent state-of-the-art models such as BAGEL and UniWorld-V1. UniLIP effectively expand the application scope of CLIP, enabling continuous CLIP features to not only serve as the optimal choice for understanding tasks but also achieve highly competitive performance in generation and editing tasks.
本文中,我们提出了UniLIP,它扩展了CLIP的功能,使其能够进行重建、生成和编辑,从而在其出色的理解能力基础上构建了一个统一的分词器。以前基于CLIP的统一方法通常需要额外的扩散解码器或量化来支持重建和生成任务,这导致重建不一致或原始理解性能下降。相比之下,我们引入了两阶段训练方案和自蒸馏策略,逐步将重建能力集成到CLIP中,使其能够在保持原始理解性能的同时实现有效的图像重建。此外,我们提出了一种双条件架构,将MLLM和扩散变压器连接起来,使用可学习的查询和最后一层多模态隐藏状态作为联合条件。这种方法不仅能使MLLM在生成任务中利用强大的推理能力,而且在编辑任务中最大限度地利用UniLIP特征的丰富信息。在文本到图像生成任务中,UniLIP在GenEval和WISE基准测试上分别获得0.87和0.53的分数,超过了相同规模的所有先前统一模型。在图像编辑方面,UniLIP在ImgEdit基准测试上也取得了3.62的分数,超过了最近的先进模型,如BAGEL和UniWorld-V1。UniLIP有效地扩展了CLIP的应用范围,使CLIP特征不仅能够成为理解任务的最佳选择,而且在生成和编辑任务中也具有高度的竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了UniLIP模型,该模型基于CLIP架构进行扩展,支持重建、生成和编辑功能,构建了一个统一的分词器,并借助其出色的理解能力。通过引入两阶段训练方案和自蒸馏策略,UniLIP能够在保持原有理解能力的同时,实现有效的图像重建。此外,本文还提出了一种双条件架构,连接MLLM和扩散变压器,采用可学习的查询和最后一层多模态隐藏状态作为联合条件。UniLIP在文本到图像生成任务中取得了显著成绩,超越了类似规模的统一模型。在图像编辑方面也表现出强大的性能。总体而言,UniLIP不仅扩大了CLIP的应用范围,而且为生成和编辑任务提供了高度竞争力的性能。
Key Takeaways
- UniLIP扩展了CLIP模型,支持重建、生成和编辑功能,构建了一个统一的分词器。
- 通过两阶段训练方案和自蒸馏策略,UniLIP在保持原有理解能力的同时实现了有效的图像重建。
- 双条件架构连接了MLLM和扩散变压器,结合了强大的推理能力和丰富的特征信息。
- UniLIP在文本到图像生成任务中取得了显著成绩,超越了其他类似规模的统一模型。
- UniLIP在图像编辑方面表现出强大的性能,超过了最近的先进模型。
- UniLIP扩大了CLIP的应用范围,不仅可以用于理解任务,还可以在生成和编辑任务中表现出高度竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Affordable Tumor Segmentation and Visualization for 3D Breast MRI Using SAM2
Authors:Solha Kang, Eugene Kim, Joris Vankerschaver, Utku Ozbulak
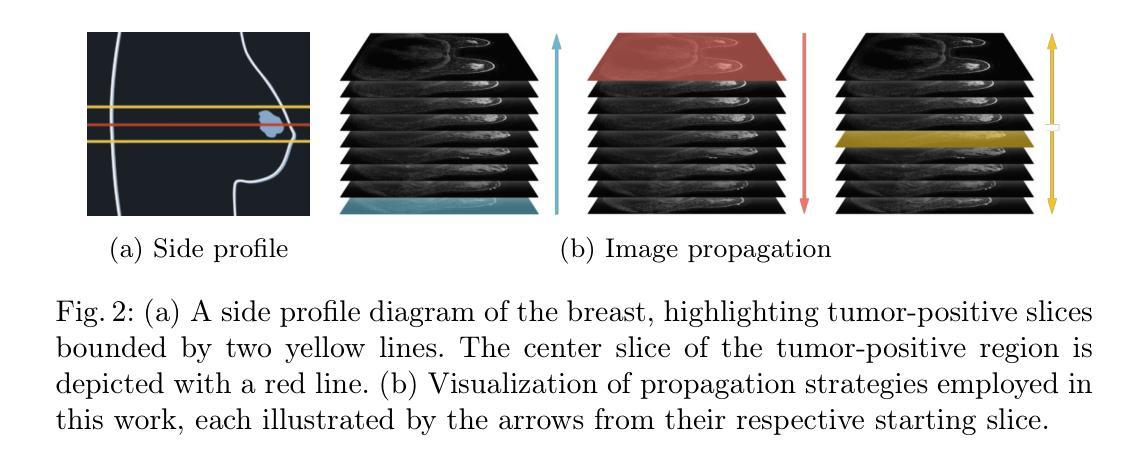
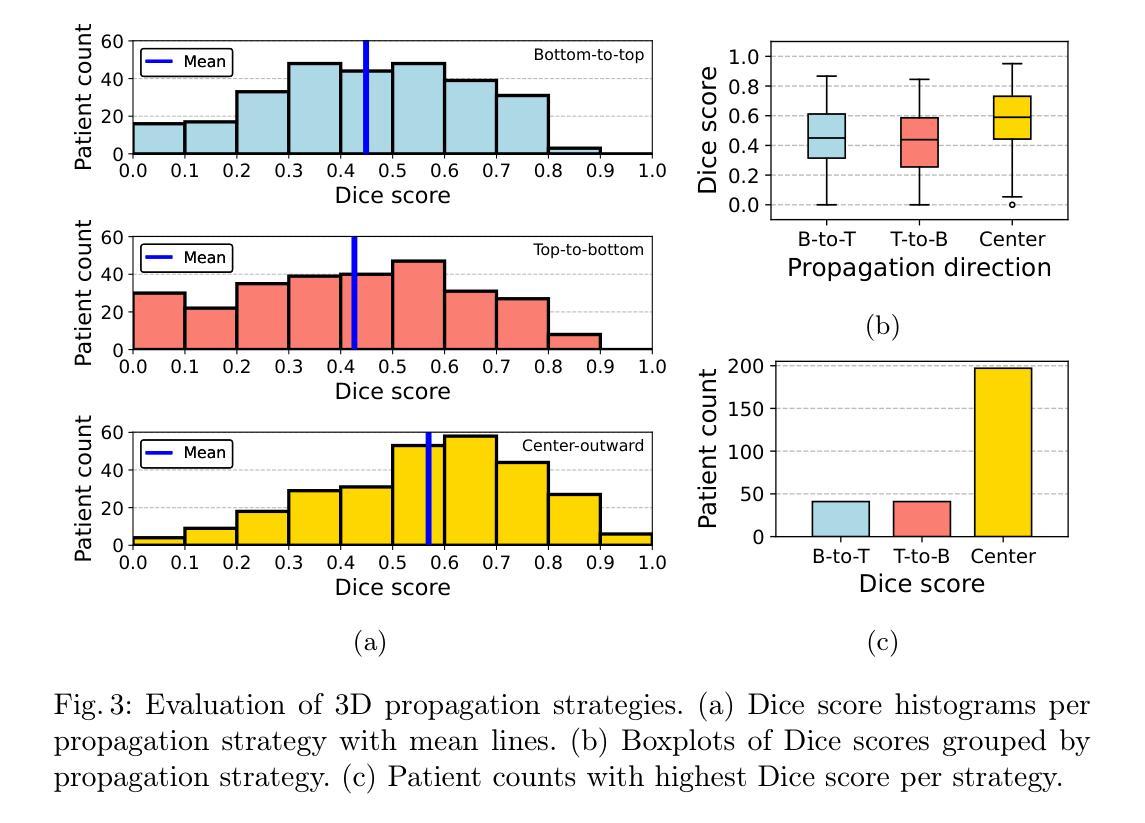
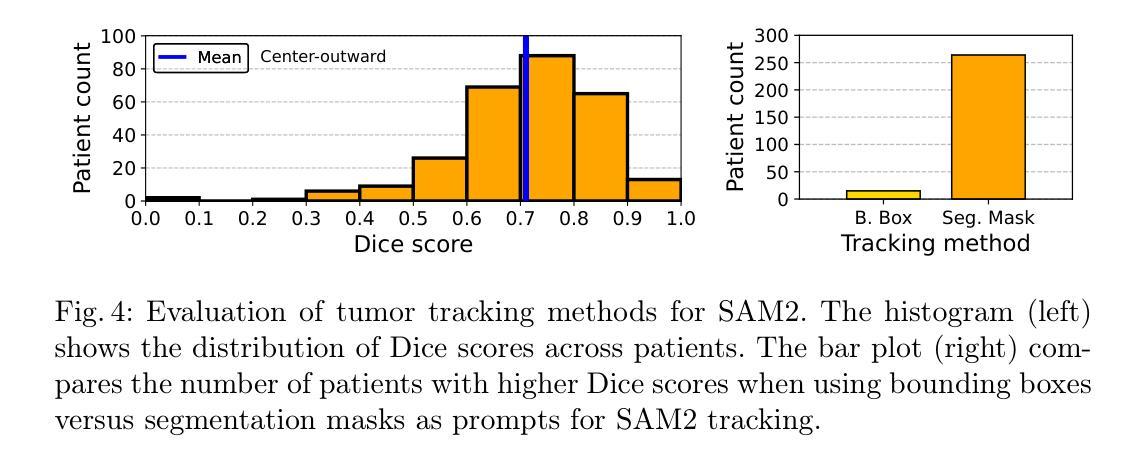
Breast MRI provides high-resolution volumetric imaging critical for tumor assessment and treatment planning, yet manual interpretation of 3D scans remains labor-intensive and subjective. While AI-powered tools hold promise for accelerating medical image analysis, adoption of commercial medical AI products remains limited in low- and middle-income countries due to high license costs, proprietary software, and infrastructure demands. In this work, we investigate whether the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) can be adapted for low-cost, minimal-input 3D tumor segmentation in breast MRI. Using a single bounding box annotation on one slice, we propagate segmentation predictions across the 3D volume using three different slice-wise tracking strategies: top-to-bottom, bottom-to-top, and center-outward. We evaluate these strategies across a large cohort of patients and find that center-outward propagation yields the most consistent and accurate segmentations. Despite being a zero-shot model not trained for volumetric medical data, SAM2 achieves strong segmentation performance under minimal supervision. We further analyze how segmentation performance relates to tumor size, location, and shape, identifying key failure modes. Our results suggest that general-purpose foundation models such as SAM2 can support 3D medical image analysis with minimal supervision, offering an accessible and affordable alternative for resource-constrained settings.
乳腺MRI提供了高分辨率的体积成像,对肿瘤评估和治疗计划至关重要。然而,对3D扫描的手动解读仍然劳动密集且主观。虽然人工智能工具在加速医学图像分析方面显示出潜力,但由于许可证成本高、专有软件和基础设施需求大,商业医疗AI产品在低收入和中收入国家的采用仍然有限。在这项工作中,我们调查Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)是否可适应低成本、最少输入的乳腺MRI 3D肿瘤分割。我们仅对一个切片进行单个边界框注释,然后使用三种不同的切片跟踪策略(从上到下、从下到上、和中心向外)在3D体积上传播分割预测。我们在大批患者中对这些策略进行了评估,发现中心向外传播策略产生了最一致和准确的分割结果。尽管SAM2是一个未针对体积医学数据进行训练的零样本模型,但在极少监督的情况下仍取得了强大的分割性能。我们进一步分析了分割性能与肿瘤大小、位置和形状的关系,确定了关键的失败模式。我们的结果表明,如SAM2等通用基础模型可在极少监督的情况下支持3D医学图像分析,为资源受限的环境提供可负担的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the 28th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), 2nd Deep Breast Workshop on AI and Imaging for Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges in Breast Care (DeepBreath), 2025
Summary
本文探讨了将Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)模型适应于低成本的乳腺癌MRI三维肿瘤分割的可能性。该研究利用单一切片上的边界框标注,通过三种不同的切片跟踪策略进行三维体积内的分割预测传播,最终发现中心向外传播策略最为一致且准确。尽管SAM2是一个未经三维医学数据训练的零样本模型,但在极少监督的情况下仍取得了强大的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺MRI提供高分辨率的体积成像,对肿瘤评估和治疗计划至关重要,但手动解读三维扫描仍然劳动密集且主观。
- AI工具在加速医学图像分析方面具潜力,但在中低收入国家的采用受到限制,主要由于高昂的许可成本、专有软件和基础设施需求。
- 研究者调查了Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)是否可适应低成本、低输入的乳腺MRI三维肿瘤分割。
- 使用单一切片上的边界框标注,研究采用了三种不同的切片跟踪传播策略,发现中心向外传播策略表现最佳。
- 尽管SAM2未经过三维医学数据训练,但在极少监督下仍实现了强大的分割性能。
- 研究进一步分析了分割性能与肿瘤大小、位置和形状的关系,确定了主要的失败模式。
点此查看论文截图

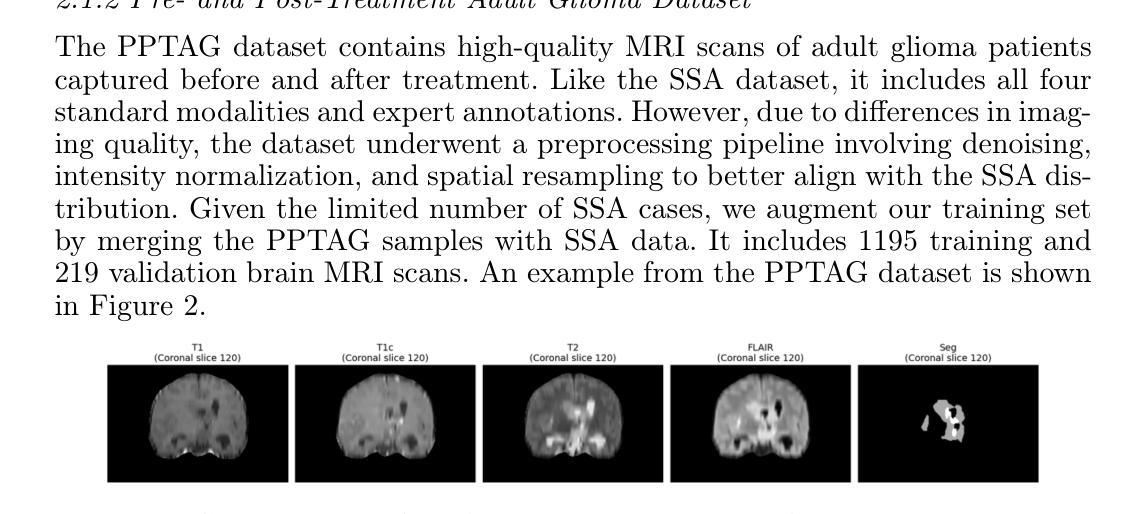
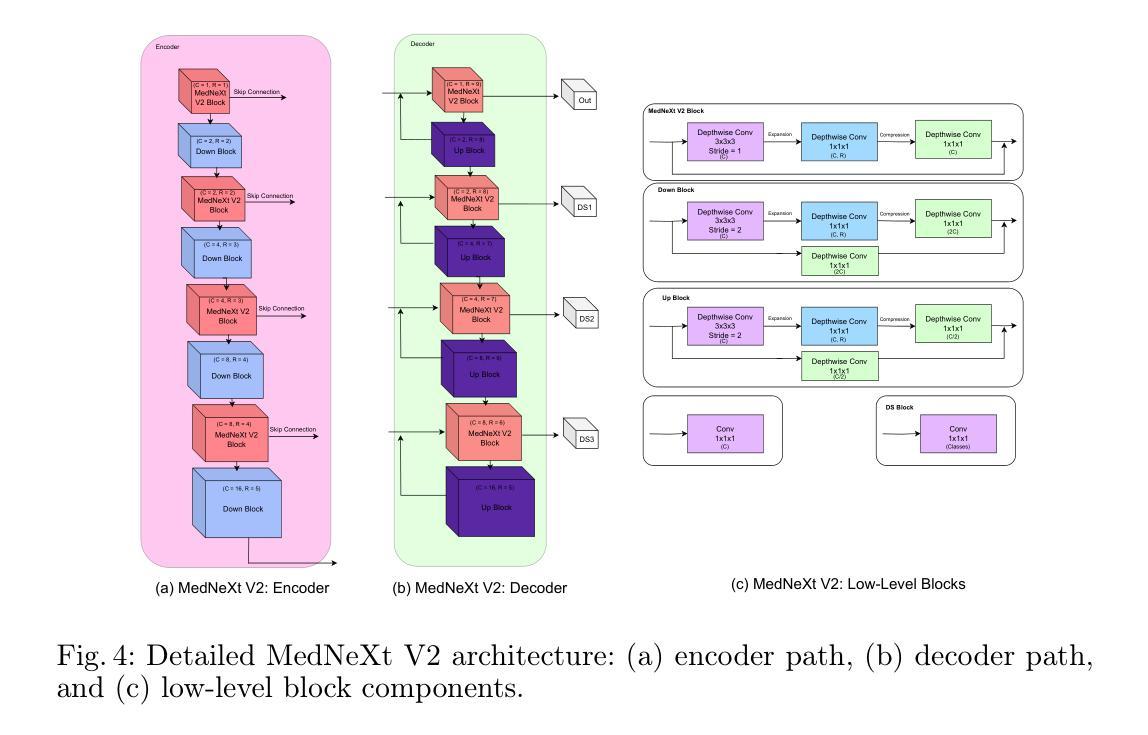
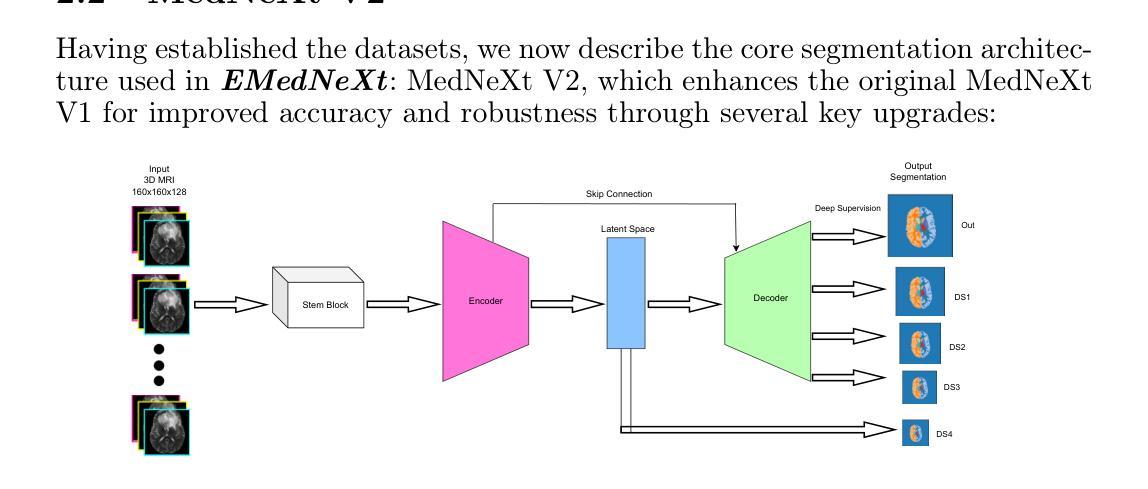
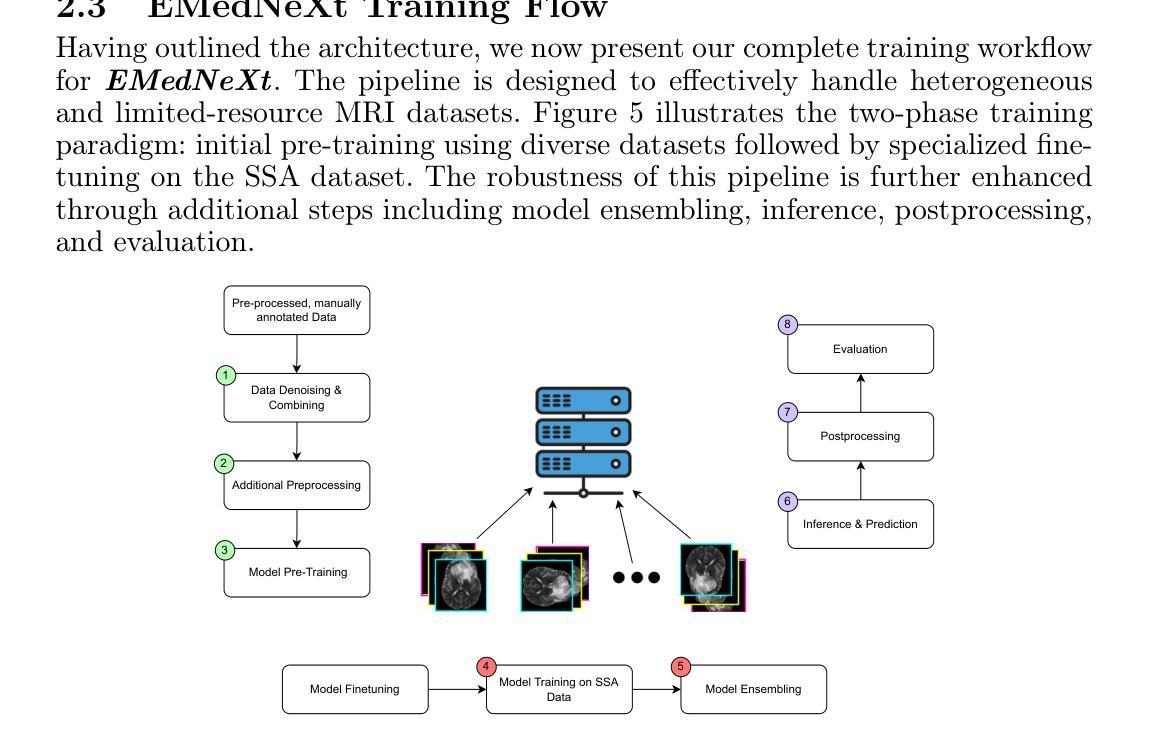
EMedNeXt: An Enhanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Framework for Sub-Saharan Africa using MedNeXt V2 with Deep Supervision
Authors:Ahmed Jaheen, Abdelrahman Elsayed, Damir Kim, Daniil Tikhonov, Matheus Scatolin, Mohor Banerjee, Qiankun Ji, Mostafa Salem, Hu Wang, Sarim Hashmi, Mohammad Yaqub
Brain cancer affects millions worldwide, and in nearly every clinical setting, doctors rely on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose and monitor gliomas. However, the current standard for tumor quantification through manual segmentation of multi-parametric MRI is time-consuming, requires expert radiologists, and is often infeasible in under-resourced healthcare systems. This problem is especially pronounced in low-income regions, where MRI scanners are of lower quality and radiology expertise is scarce, leading to incorrect segmentation and quantification. In addition, the number of acquired MRI scans in Africa is typically small. To address these challenges, the BraTS-Lighthouse 2025 Challenge focuses on robust tumor segmentation in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), where resource constraints and image quality degradation introduce significant shifts. In this study, we present EMedNeXt – an enhanced brain tumor segmentation framework based on MedNeXt V2 with deep supervision and optimized post-processing pipelines tailored for SSA. EMedNeXt introduces three key contributions: a larger region of interest, an improved nnU-Net v2-based architectural skeleton, and a robust model ensembling system. Evaluated on the hidden validation set, our solution achieved an average LesionWise DSC of 0.897 with an average LesionWise NSD of 0.541 and 0.84 at a tolerance of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm, respectively.
脑癌影响全球数百万人,在临床几乎所有场景中,医生都依赖磁共振成像(MRI)来诊断和监测胶质瘤。然而,目前通过多参数MRI手动分割对肿瘤进行量化的标准耗时,需要专家放射科医生,并且在资源不足的卫生系统中通常不可行。这一问题在低收入地区尤为突出,那里的MRI扫描仪质量较差,且缺乏放射学专家,导致分割和量化不准确。此外,非洲获得的MRI扫描数量通常较少。为了应对这些挑战,BraTS-Lighthouse 2025挑战赛的重点是撒哈拉以南非洲(SSA)的稳健肿瘤分割,那里的资源约束和图像质量下降引入了重大变化。在这项研究中,我们提出了EMedNeXt——一种基于MedNeXt V2的增强型脑肿瘤分割框架,具有深度监督和针对SSA优化的后处理管道。EMedNeXt有三个主要贡献:更大的感兴趣区域、改进的nnU-Net v2基础架构,以及稳健的模型集成系统。在隐藏验证集上评估,我们的解决方案平均LesionWise DSC达到0.897,平均LesionWise NSD为0.541和0.84,容忍度分别为0.5毫米和1.0毫米。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the BraTS-Lighthouse 2025 Challenge (MICCAI 2025)
Summary
针对非洲地区医疗资源匮乏、MRI扫描质量不佳等问题,EMedNeXt框架通过深度学习技术实现了对脑胶质瘤的精准分割。该框架基于MedNeXt V2,引入深度监督技术和优化后的后处理流程,用于非洲地区的医学影像分析。其性能在隐藏验证集上表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 脑癌诊断中,MRI是医生依赖的重要工具,尤其在低资源环境下。
- 当前手动分割多参数MRI对肿瘤进行量化存在时间消耗大、依赖专家及在资源匮乏地区难以实施等问题。
- 非洲地区特别是撒哈拉以南非洲面临MRI扫描质量低、资源约束等问题,肿瘤分割挑战更大。
- BraTS-Lighthouse 2025 Challenge旨在针对非洲地区的肿瘤分割难题进行挑战。
- EMedNeXt框架是基于MedNeXt V2开发,加入了深度监督技术和改进的后处理流程。
- EMedNeXt在隐藏验证集上的表现优秀,平均LesionWise DSC达到0.897,LesionWise NSD分别达到0.541和0.84。
- 该研究为非洲地区及其他资源受限地区的医学影像分析提供了可行方案。
点此查看论文截图

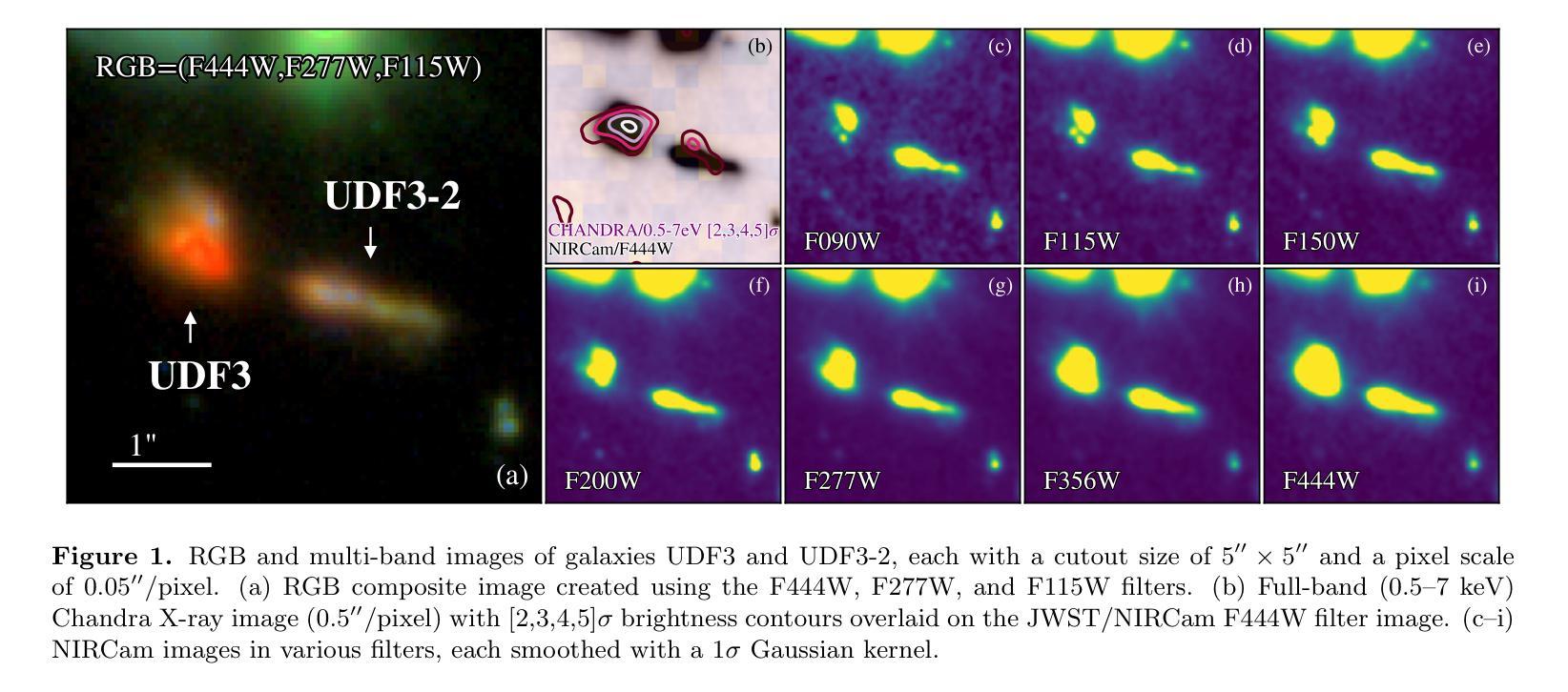
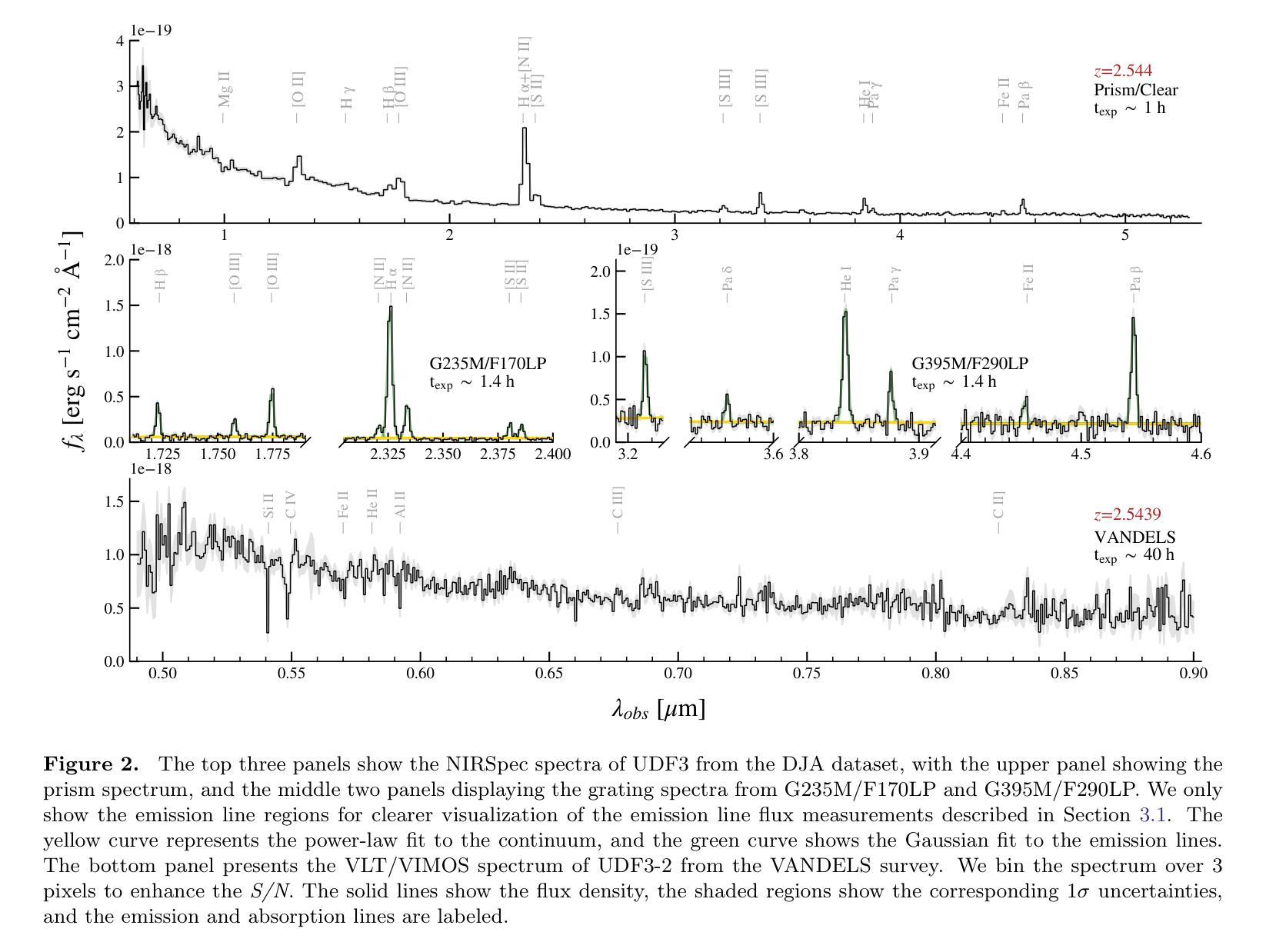
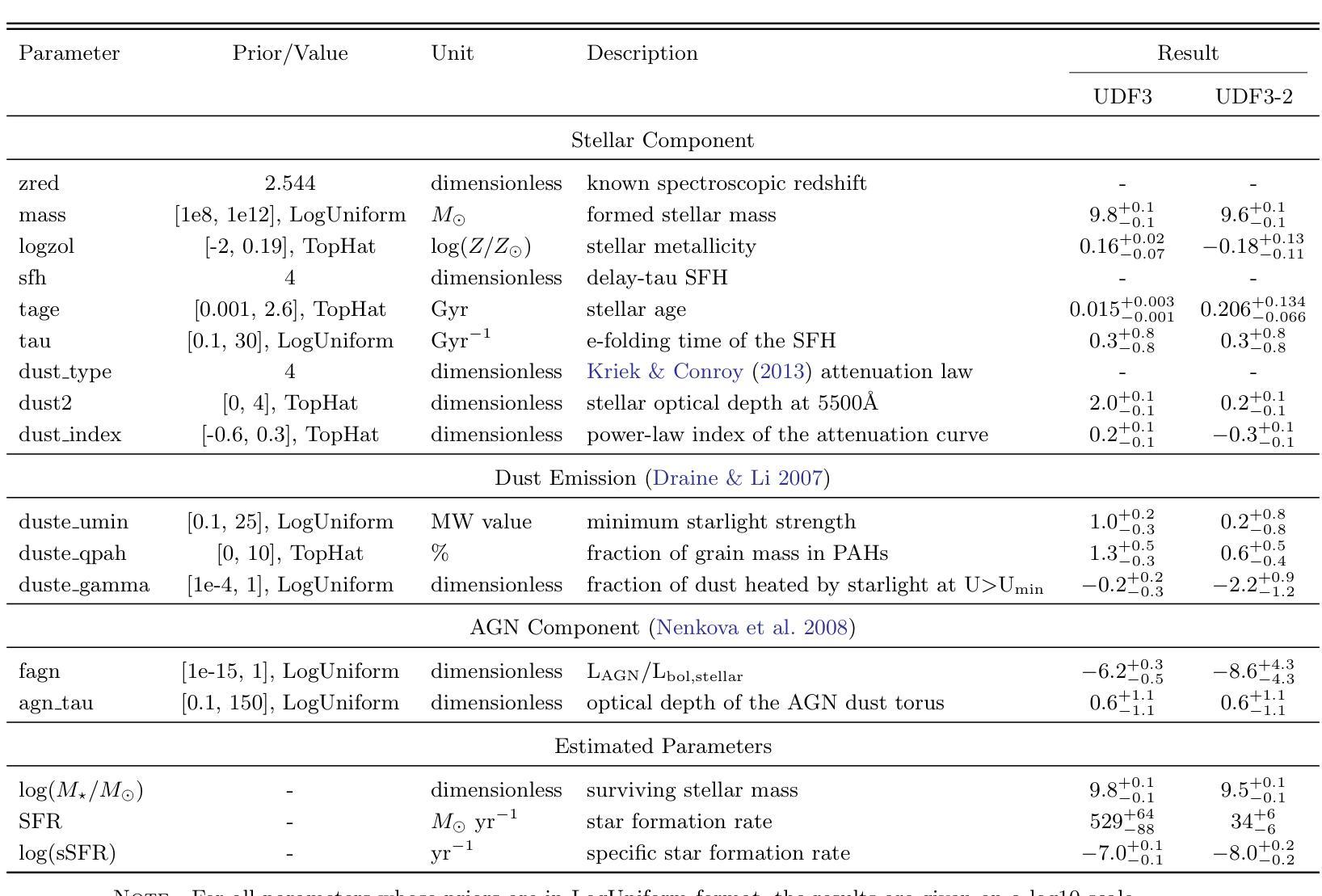
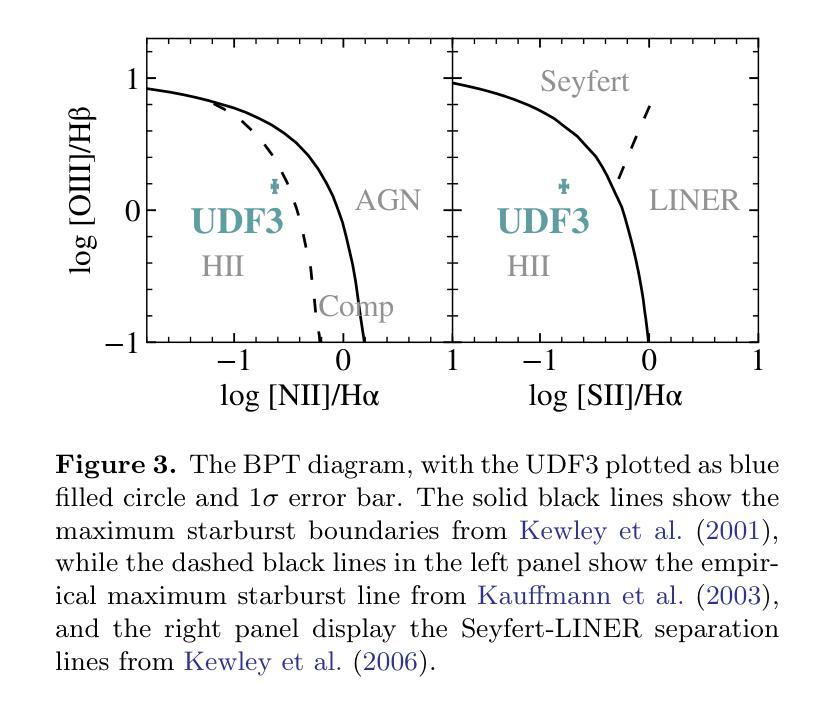
Discovery of a Pair of Galaxies with Both Hosting X-ray Binary Candidates at $z=2.544$
Authors:Sijia Cai, Zheng Cai, Jianwei Lyu, Yunjing Wu, Xiaojing Lin, Mingyu Li, Junjie Mao, Jiayi Chen, Pengjun Lu
Among high-redshift galaxies, aside from active galactic nuclei (AGNs), X-ray binaries (XRBs) can be significant sources of X-ray emission. XRBs play a crucial role in galaxy evolution, reflecting the stellar populations of galaxies and regulating star formation through feedback, thereby shaping galaxy structure. In this study, we report a spectroscopically confirmed X-ray emitting galaxy pair (UDF3 and UDF3-2) at $z = 2.544$. By combining multi-wavelength observations from JWST/NIRSpec MSA spectra, JWST/NIRCam and MIRI imaging, Chandra, HST, VLT, ALMA, and VLA, we analyze the ionized emission lines, which are primarily driven by H II region-like processes. Additionally, we find that the mid-infrared radiation can be fully attributed to dust emission from galaxy themselves. Our results indicate that the X-ray emission from these two galaxies is dominated by high-mass XRBs, with luminosities of $L_X= (1.43\pm0.40) \times 10^{42} , \text{erg} , \text{s}^{-1}$ for UDF3, and $(0.40\pm0.12) \times 10^{42} , \text{erg} , \text{s}^{-1}$ for UDF3-2. Furthermore, we measure the star formation rate (SFR) of $529_{-88}^{+64}$ $M_\odot$ yr$^{-1}$ for UDF3, placing it $\approx$ 0.5 dex below the $L_X$/SFR-$z$ relation. This offset reflects the redshift-dependent enhancement of $L_X$/SFR-$z$ relation, which is influenced by metallicity and serves as a key observable for XRB evolution. In contrast, UDF3-2, with the SFR of $34_{-6}^{+6}$ $M_\odot$ yr$^{-1}$, aligns well with the $L_X$/SFR-$z$ relation. This galaxy pair represents the highest-redshift non-AGN-dominated galaxies with individual X-ray detections reported to date. This finding suggests that the contribution of XRBs to galaxy X-ray emission at high redshift may be underestimated.
在高红移星系中,除了活动星系核(AGNs)外,X射线双星(XRBs)也可能是X射线发射的重要来源。XRBs在星系演化中起着至关重要的作用,反映了星系的恒星种群,并通过反馈调节恒星形成,从而塑造星系结构。在这项研究中,我们报告了一个光谱证实的高红移X射线发射星系对(UDF3和UDF3-2),红移z=2.544。我们通过结合JWST/NIRSpec MSA光谱、JWST/NIRCam和MIRI成像、钱德拉、哈勃望远镜、甚大望远镜、ALMA和VLA的多波长观测数据,分析了电离发射线,这些发射线主要由H II区域过程驱动。此外,我们发现中红外辐射可以完全归因于星系自身的尘埃发射。我们的结果表明,这两个星系的X射线发射主要由高质量XRBs主导,UDF3的X射线光度为(1.43±0.40)×10^42 erg s^-1,(UDF3-2为(0.4±0.1)×10^42 erg s^-1)。此外,我们还测量了UDF3的恒星形成率(SFR)为529_{-88}^{+64} M_odot年^-1,它位于LX/SFR-z关系的下方约0.5 dex。这种偏移反映了LX/SFR与红移之间的关系的红移依赖性增强,这受到金属丰度的影响,并成为XRB演化的关键观测指标。相比之下,UDF3-2的恒星形成率为(每百年有几十亿恒星形成率),符合LX/SFR-z关系。这对星系代表了迄今为止报道的最高红移非活动星系核主导且个体X射线检测到的星系。这一发现表明,对高红移时XRB对星系X射线发射的贡献可能被低估了。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 5 figures. Accepted for publication in ApJL
Summary
高紅移星系中,除了活动星系核(AGNs)外,X射线双星(XRBs)也是重要的X射线发射源。本研究报告了一对光谱证实的X射线发射星系UDF3和UDF3-2(红移z=2.544)。结合多波段观测数据,我们分析了离子化发射线,并发现中红外辐射可完全归因于星系自身的尘埃发射。结果表明,这两个星系的X射线发射主要由高质量XRBs主导,其中UDF3的X射线光度为(1.43±0.40)×10^42 erg s^-1,而UDF3-2的光度为(0.40±0.12)×10^42 erg s^-1。此外,我们还测量了UDF3的恒星形成率为529±152 M⊙ yr^-1,低于L_X/SFR-z关系约0.5 dex。这一偏移反映了L_X/SFR-z关系的红移依赖性增强,受到金属丰度的影响,是XRB演化的关键观测指标。而UDF3-2与L_X/SFR-z关系相符。这一星系对代表了迄今为止报道的最高红移非AGN主导且具备个体X射线检测的星系,这表明高红移时XRBs对星系X射线发射的贡献可能被低估。
Key Takeaways
- X-ray binaries (XRBs) are significant sources of X-ray emission in high-redshift galaxies, apart from active galactic nuclei (AGNs).
- XRBs play a crucial role in galaxy evolution, reflecting stellar populations and regulating star formation through feedback.
- A spectroscopically confirmed X-ray emitting galaxy pair (UDF3 and UDF3-2) at $z = 2.544$ was reported, representing the highest-redshift non-AGN-dominated galaxies with individual X-ray detections.
- The X-ray emission from UDF3 and UDF3-2 is primarily driven by high-mass XRBs, with specific X-ray luminosities measured.
- UDF3的恒星形成率(SFR)低于L_X/SFR-z关系,反映了L_X/SFR-z关系的红移依赖性增强,受到金属丰度的影响。
- UDF3-2的SFR与L_X/SFR-z关系相符,这为我们理解XRB演化提供了关键观测数据。
点此查看论文截图


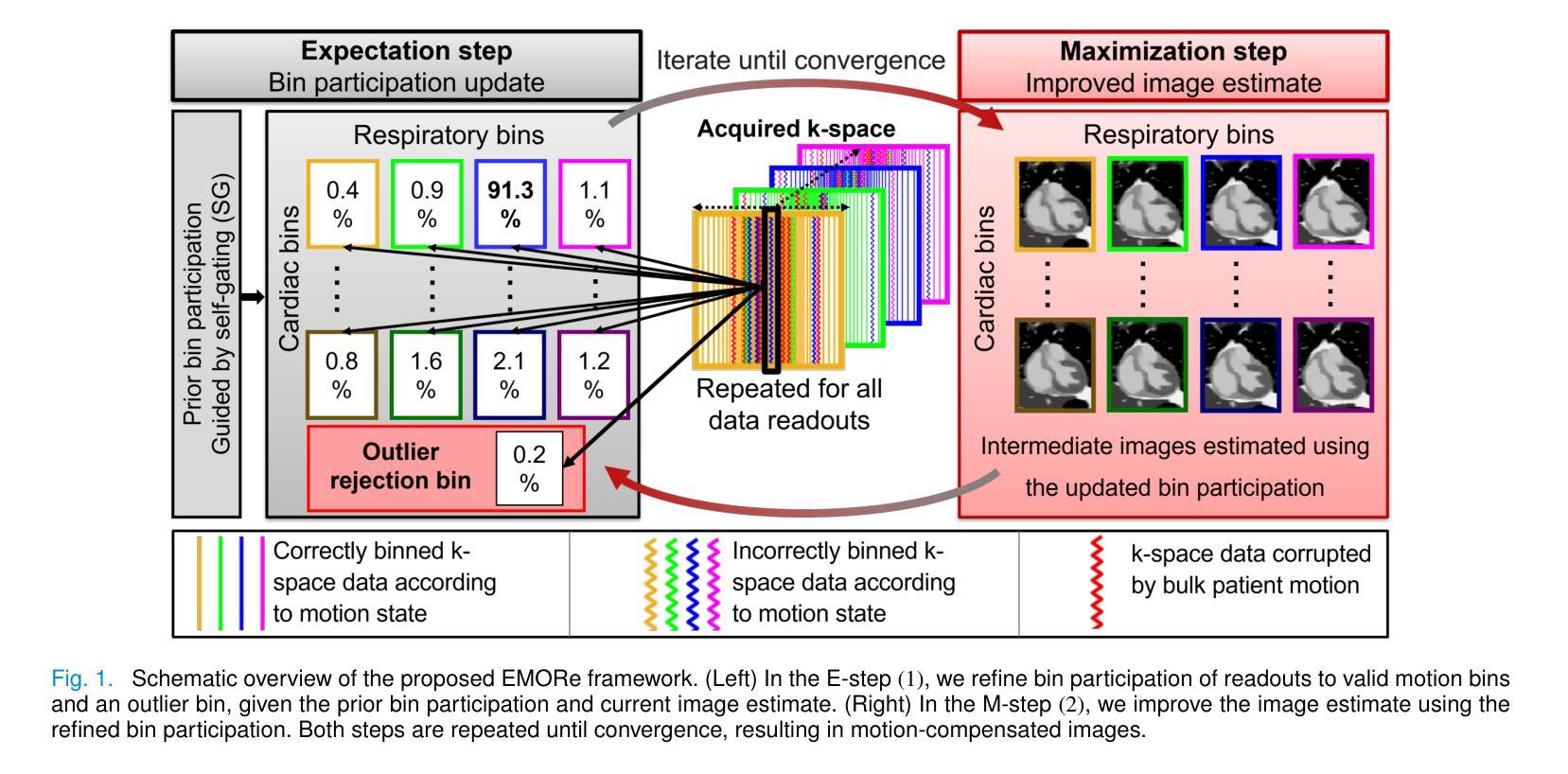
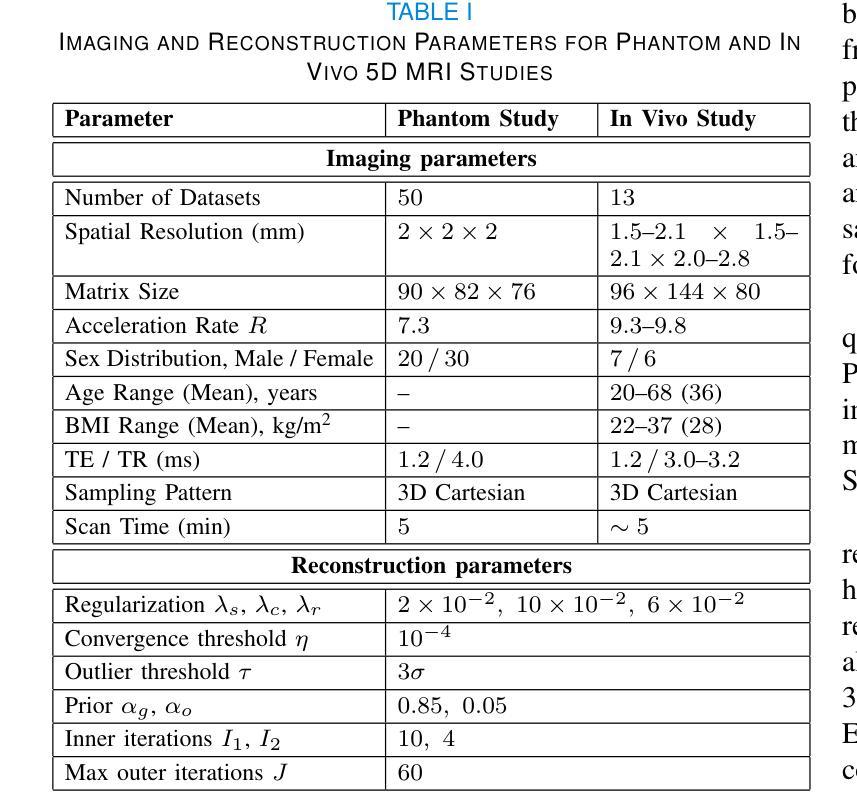
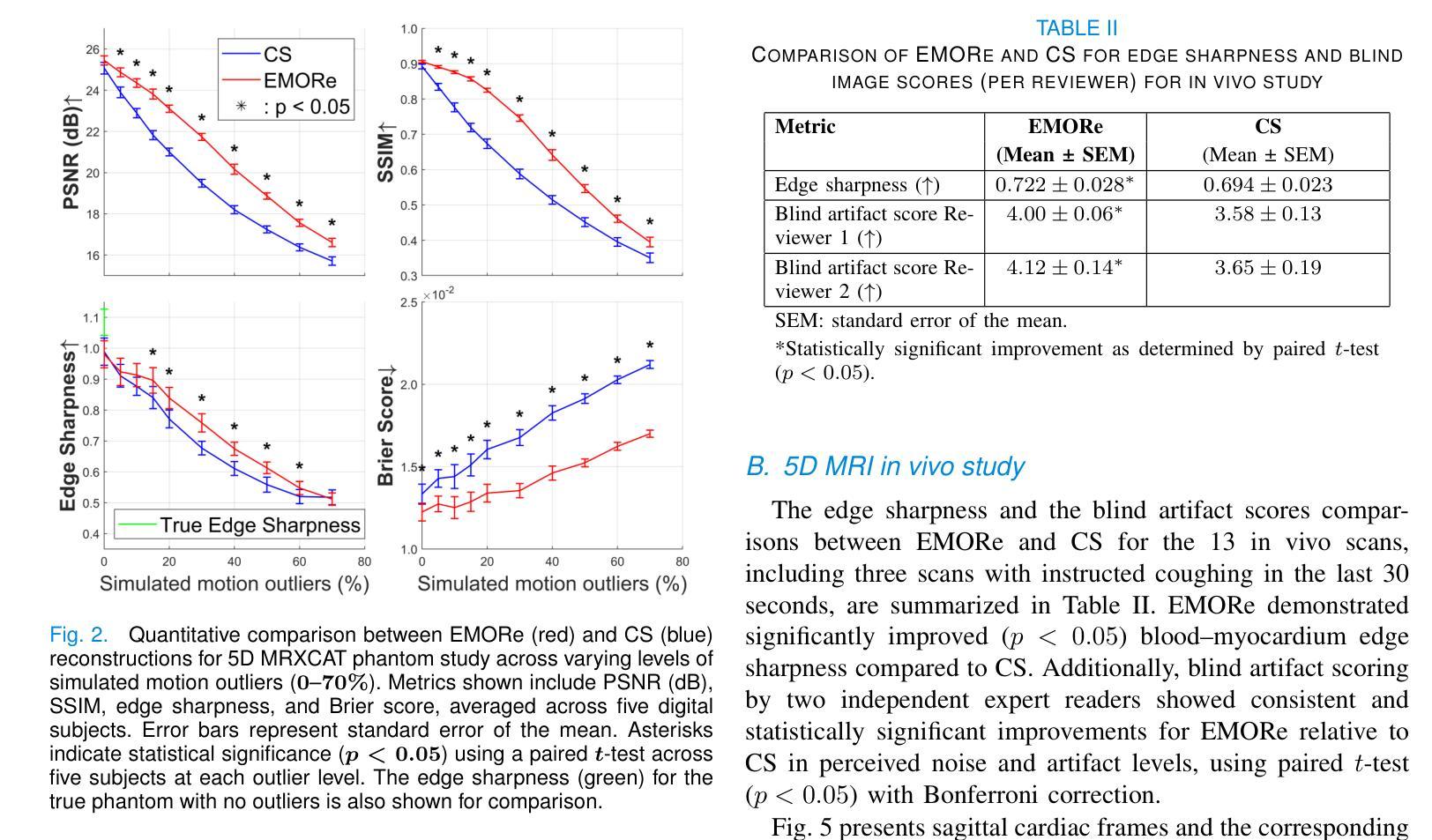
EMORe: Motion-Robust 5D MRI Reconstruction via Expectation-Maximization-Guided Binning Correction and Outlier Rejection
Authors:Syed M. Arshad, Lee C. Potter, Yingmin Liu, Christopher Crabtree, Matthew S. Tong, Rizwan Ahmad
We propose EMORe, an adaptive reconstruction method designed to enhance motion robustness in free-running, free-breathing self-gated 5D cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Traditional self-gating-based motion binning for 5D MRI often results in residual motion artifacts due to inaccuracies in cardiac and respiratory signal extraction and sporadic bulk motion, compromising clinical utility. EMORe addresses these issues by integrating adaptive inter-bin correction and explicit outlier rejection within an expectation-maximization (EM) framework, whereby the E-step and M-step are executed alternately until convergence. In the E-step, probabilistic (soft) bin assignments are refined by correcting misassignment of valid data and rejecting motion-corrupted data to a dedicated outlier bin. In the M-step, the image estimate is improved using the refined soft bin assignments. Validation in a simulated 5D MRXCAT phantom demonstrated EMORe’s superior performance compared to standard compressed sensing reconstruction, showing significant improvements in peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity index, edge sharpness, and bin assignment accuracy across varying levels of simulated bulk motion. In vivo validation in 13 volunteers further confirmed EMORe’s robustness, significantly enhancing blood-myocardium edge sharpness and reducing motion artifacts compared to compressed sensing, particularly in scenarios with controlled coughing-induced motion. Although EMORe incurs a modest increase in computational complexity, its adaptability and robust handling of bulk motion artifacts significantly enhance the clinical applicability and diagnostic confidence of 5D cardiac MRI.
我们提出一种名为EMORe的自适应重建方法,旨在提高自由奔跑、自由呼吸的自门控5D心脏磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动稳健性。基于自门控的5D MRI的传统运动分箱常常由于心脏和呼吸信号提取的不准确以及偶发的整体运动而导致残留运动伪影,从而影响其临床应用价值。EMORe通过期望最大化(EM)框架内的自适应跨箱校正和显式异常值拒绝来解决这些问题,其中E步和M步交替执行直至收敛。在E步中,通过修正有效数据的误分配并拒绝将运动损坏的数据分配给专用的异常值箱来优化概率(软)箱分配。在M步中,使用改进后的软箱分配来改善图像估计。在模拟的5DMRXCAT幽灵中的验证表明,EMORe相对于标准压缩感知重建表现出卓越的性能,在模拟的不同程度的整体运动下,峰值信噪比、结构相似性指数、边缘锐度和箱分配精度均得到显着提高。在13名志愿者中的体内验证进一步证实了EMORe的稳健性,特别是在可控的咳嗽引起的运动场景中,与压缩感知相比,它显著提高了血液心肌边缘的清晰度并减少了运动伪影。尽管EMORe的计算复杂度略有增加,但其对整体运动伪影的适应性和稳健处理显着提高了5D心脏MRI的临床适用性和诊断信心。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为EMORe的自适应重建方法,旨在提高自由运行、自由呼吸的自门控5D心脏磁共振成像中的运动稳健性。EMORe通过整合自适应的跨箱校正和明确的异常值拒绝在期望最大化框架内解决传统自门控为基础的5D MRI中的残留运动伪影问题。模拟验证表明,与标准压缩感知重建相比,EMORe在峰值信噪比、结构相似性指数、边缘锐度和装箱分配准确性方面表现出卓越性能。在志愿者中的实验进一步证实了EMORe的稳健性,特别是在咳嗽引起的运动中,与压缩感知相比,EMORe显著提高了血液心肌边缘的锐度并减少了运动伪影。虽然EMORe的计算复杂度略有增加,但其对批量运动伪影的适应性处理显著提高了其在临床诊断和治疗信心方面的适用性。
Key Takeaways
- EMORe是一种旨在提高自由运行、自由呼吸的自门控5D心脏磁共振成像中运动稳健性的自适应重建方法。
- 传统自门控方法常常因心脏和呼吸信号提取的不准确以及突发性大量运动而导致残留运动伪影。
- EMORe通过期望最大化框架中的自适应跨箱校正和异常值拒绝来解决这些问题。
- 模拟验证显示,与标准压缩感知重建相比,EMORe在多个指标上表现优越。
- 在志愿者中的实验进一步证实了EMORe在减少运动伪影和提高图像质量方面的稳健性。
- EMORe对批量运动伪影的适应性处理显著提高了其在临床诊断和治疗信心方面的适用性。
点此查看论文截图


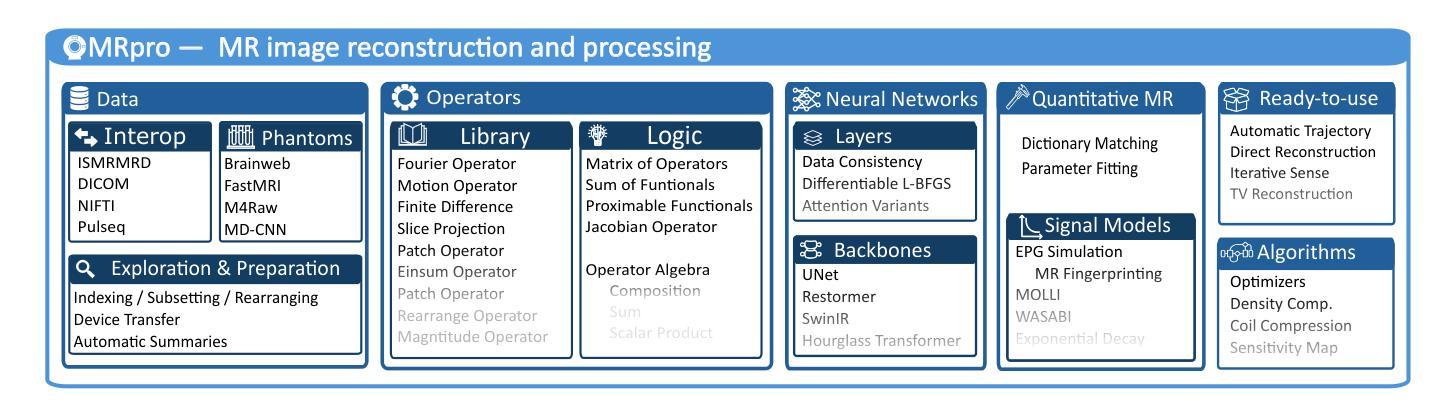
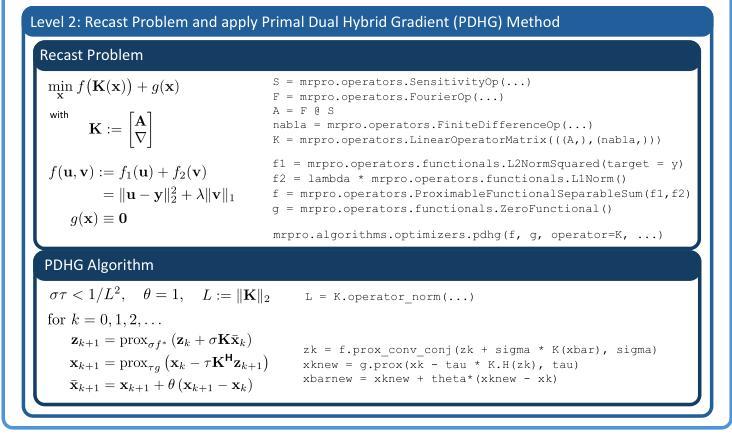
MRpro - open PyTorch-based MR reconstruction and processing package
Authors:Felix Frederik Zimmermann, Patrick Schuenke, Christoph S. Aigner, Bill A. Bernhardt, Mara Guastini, Johannes Hammacher, Noah Jaitner, Andreas Kofler, Leonid Lunin, Stefan Martin, Catarina Redshaw Kranich, Jakob Schattenfroh, David Schote, Yanglei Wu, Christoph Kolbitsch
We introduce MRpro, an open-source image reconstruction package built upon PyTorch and open data formats. The framework comprises three main areas. First, it provides unified data structures for the consistent manipulation of MR datasets and their associated metadata (e.g., k-space trajectories). Second, it offers a library of composable operators, proximable functionals, and optimization algorithms, including a unified Fourier operator for all common trajectories and an extended phase graph simulation for quantitative MR. These components are used to create ready-to-use implementations of key reconstruction algorithms. Third, for deep learning, MRpro includes essential building blocks such as data consistency layers, differentiable optimization layers, and state-of-the-art backbone networks and integrates public datasets to facilitate reproducibility. MRpro is developed as a collaborative project supported by automated quality control. We demonstrate the versatility of MRpro across multiple applications, including Cartesian, radial, and spiral acquisitions; motion-corrected reconstruction; cardiac MR fingerprinting; learned spatially adaptive regularization weights; model-based learned image reconstruction and quantitative parameter estimation. MRpro offers an extensible framework for MR image reconstruction. With reproducibility and maintainability at its core, it facilitates collaborative development and provides a foundation for future MR imaging research.
我们介绍了MRpro,这是一个基于PyTorch和开放数据格式的开源图像重建软件包。该框架主要包括三个领域。首先,它为MR数据集及其相关元数据(例如k空间轨迹)提供统一的数据结构,以便进行一致的操作。其次,它提供了一个可组合的运算符库,包括可用于所有常见轨迹的统一傅里叶运算符和用于定量MR的扩展相位图模拟等可接近的功能和优化算法。这些组件用于创建即插即用的关键重建算法的实现。第三,对于深度学习,MRpro包括必要的基本组件,如数据一致性层、可优化层以及最先进的骨干网络,并整合公共数据集以促进可重复性。MRpro是一个协作项目,受到自动控制质量支持。我们展示了MRpro在多个应用中的通用性,包括笛卡尔、径向和螺旋采集;运动校正重建;心脏MR指纹;学习空间自适应正则化权重;基于模型的图像重建和定量参数估计等。MRpro为MR图像重建提供了一个可扩展的框架。以可重复性和可维护性为核心,它促进了协作开发并为未来的MR成像研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Summary
MRpro是一个开源的磁共振图像重建软件包,基于PyTorch和开放数据格式构建。它主要包含三个部分:统一的数据结构、可组合的运算符库和优化算法,以及用于深度学习的关键构建模块。MRpro在多个应用中表现出其通用性,包括笛卡尔、径向和螺旋采集、运动校正重建、心脏磁共振指纹、学习空间自适应正则化权重以及基于模型的图像重建和定量参数估计。MRpro为磁共振图像重建提供了一个可扩展的框架,注重可重复性和可维护性,促进了协作开发并为未来的磁共振成像研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- MRpro是一个基于PyTorch和开放数据格式的开源磁共振图像重建软件包。
- 它提供了统一的数据结构,用于操作MR数据集及其相关元数据。
- MRpro包含可组合的运算符库、邻近功能函数和优化算法。
- 提供了用于深度学习的关键构建模块,如数据一致性层、可优化差分层以及最新骨干网络。
- MRpro集成了公共数据集,促进了可重复性。
- MRpro在多种应用中表现出其多功能性,包括不同采集方式、运动校正重建、心脏磁共振指纹等。
点此查看论文截图

Rethink Domain Generalization in Heterogeneous Sequence MRI Segmentation
Authors:Zheyuan Zhang, Linkai Peng, Wanying Dou, Cuiling Sun, Halil Ertugrul Aktas, Andrea M. Bejar, Elif Keles, Gorkem Durak, Ulas Bagci
Clinical magnetic-resonance (MR) protocols generate many T1 and T2 sequences whose appearance differs more than the acquisition sites that produce them. Existing domain-generalization benchmarks focus almost on cross-center shifts and overlook this dominant source of variability. Pancreas segmentation remains a major challenge in abdominal imaging: the gland is small, irregularly, surrounded by organs and fat, and often suffers from low T1 contrast. State-of-the-art deep networks that already achieve >90% Dice on the liver or kidneys still miss 20-30% of the pancreas. The organ is also systematically under-represented in public cross-domain benchmarks, despite its clinical importance in early cancer detection, surgery, and diabetes research. To close this gap, we present PancreasDG, a large-scale multi-center 3D MRI pancreas segmentation dataset for investigating domain generalization in medical imaging. The dataset comprises 563 MRI scans from six institutions, spanning both venous phase and out-of-phase sequences, enabling study of both cross-center and cross-sequence variations with pixel-accurate pancreas masks created by a double-blind, two-pass protocol. Through comprehensive analysis, we reveal three insights: (i) limited sampling introduces significant variance that may be mistaken for distribution shifts, (ii) cross-center performance correlates with source domain performance for identical sequences, and (iii) cross-sequence shifts require specialized solutions. We also propose a semi-supervised approach that leverages anatomical invariances, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art domain generalization techniques with 61.63% Dice score improvements and 87.00% on two test centers for cross-sequence segmentation. PancreasDG sets a new benchmark for domain generalization in medical imaging. Dataset, code, and models will be available at https://pancreasdg.netlify.app.
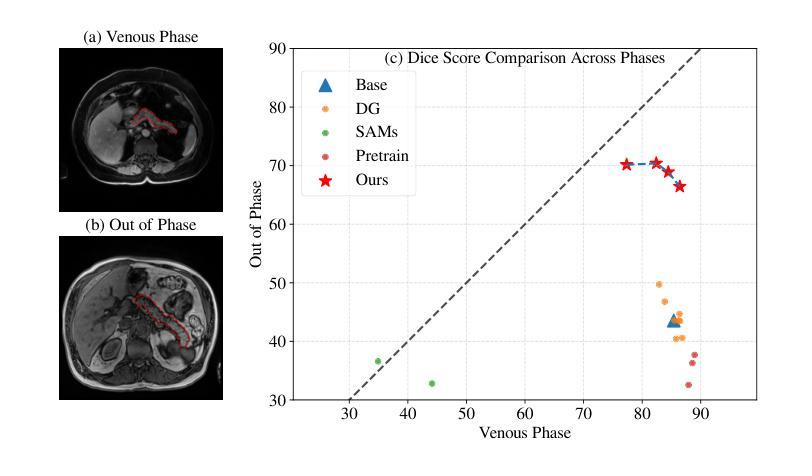
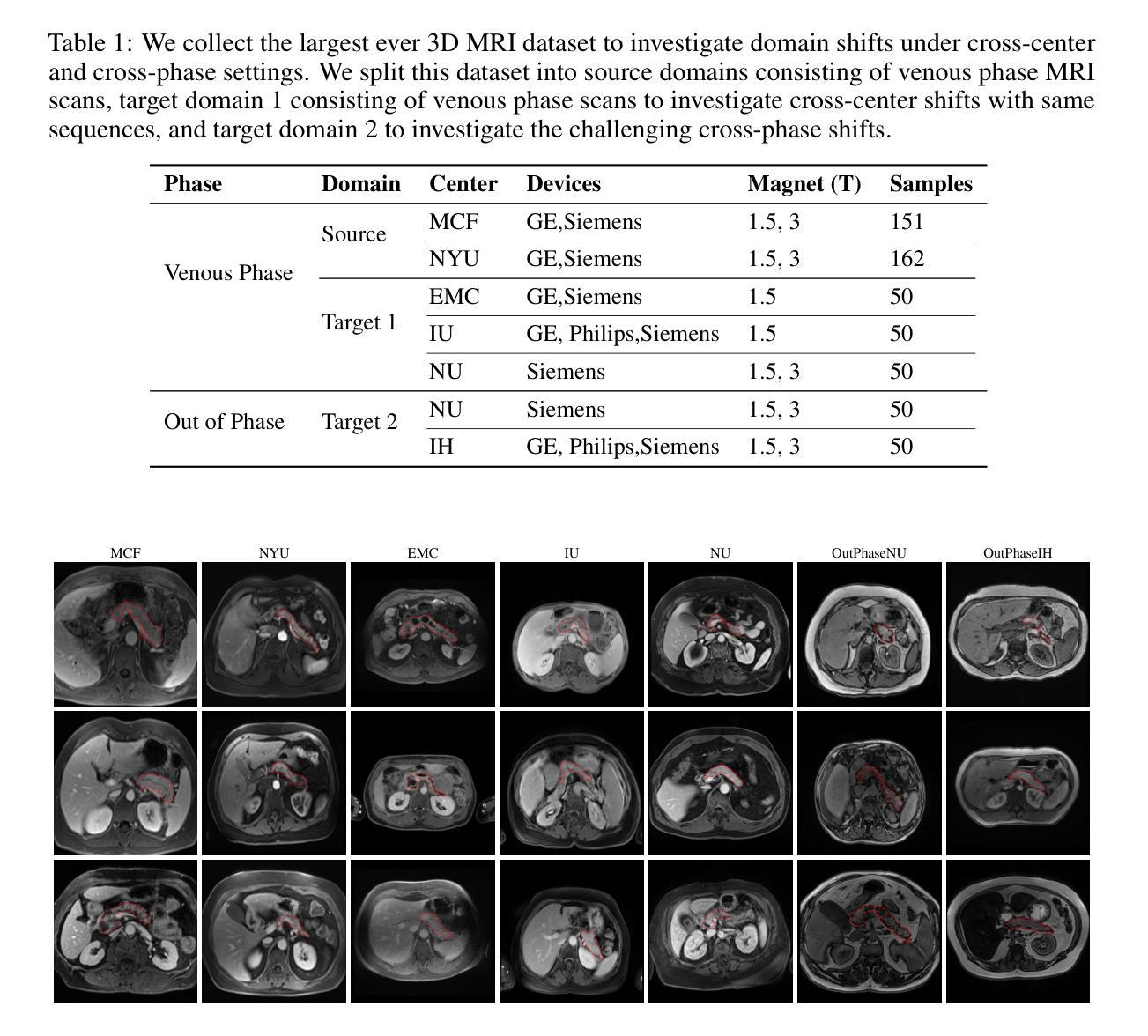
临床磁共振(MR)协议会产生许多T1和T2序列,这些序列的表现在产生它们的采集部位之间有着巨大差异。现有的域泛化基准测试几乎集中在跨中心转移上,而忽略了这一主要的变量来源。胰腺分割在腹部成像中仍然是一个主要挑战:胰腺体积小、形态不规则、被器官和脂肪包围,并且T1对比度通常较低。最先进的深度网络在肝脏或肾脏上已经达到>90%的Dice系数,但仍然会错过20-30%的胰腺。尽管其在早期癌症检测、手术和糖尿病研究中具有重要的临床意义,但该器官在公共跨域基准测试中却被系统性地低估了。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了PancreasDG,这是一个用于研究医学成像领域域泛化的大规模多中心3D MRI胰腺分割数据集。数据集包含来自六个机构的563个MRI扫描,既包括静脉相位也包括异位序列,能够研究跨中心和跨序列变化,通过双重盲法的两阶段协议创建像素精确的胰腺掩膜。通过综合分析,我们揭示了三个见解:(i)有限采样引入的重大变化可能被误认为分布转移;(ii)跨中心性能与相同序列的源域性能相关;(iii)跨序列转移需要专门的解决方案。我们还提出了一种利用解剖不变性的半监督方法,在跨序列分割方面显著优于最先进的域泛化技术,Dice得分提高了61.63%,在两个测试中心的得分达到了87.00%。PancreasDG为医学成像领域中的域泛化设定了一个新的基准。数据集、代码和模型将在https://pancreasdg.netlify.app上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了临床磁共振(MR)协议产生的T1和T2序列在采集位点上的差异被忽略的问题。胰腺分割在腹部成像中仍然是一个主要挑战,因为胰腺较小、形态不规则,并且与器官和脂肪相邻,在T1对比下经常不明显。尽管在肝脏或肾脏上已经达到>90%的Dice系数,但最先进的深度网络仍然会错过20-30%的胰腺。为了弥补这一差距,提出了PancreasDG数据集,用于研究医学成像中的领域泛化问题。该数据集包含来自六个机构的563个MRI扫描,涵盖了静脉相和异相序列,可通过双重盲测、两阶段协议创建像素精确的胰腺掩膜,用于研究跨中心和跨序列变化。综合分析揭示了三个见解,并提出了利用半监督方法的一种新方法,该方法利用解剖不变性,显著优于最先进的领域泛化技术。PancreasDG为医学成像领域泛化设定了一个新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 临床MR协议产生的T1和T2序列在外观上的差异大于采集位点差异,被忽视为主要的变量来源。
- 胰腺分割是腹部成像的主要挑战,因为胰腺较小、形态不规则并且周围有许多器官和脂肪。
- 最先进的深度网络在胰腺分割上仍有很大提升空间,相较于肝脏或肾脏的分割,性能下降明显。
- PancreasDG数据集是一个用于研究医学成像领域泛化的大型多中心3DMRI胰腺分割数据集。
- PancreasDG包含多种MRI扫描序列和来自多个机构的数据,能够研究跨中心和跨序列的变化。
- 通过对数据的综合分析,揭示了采样限制对研究结果的影响、跨中心与跨序列的性能差异及特定解决方案的必要性。
点此查看论文截图
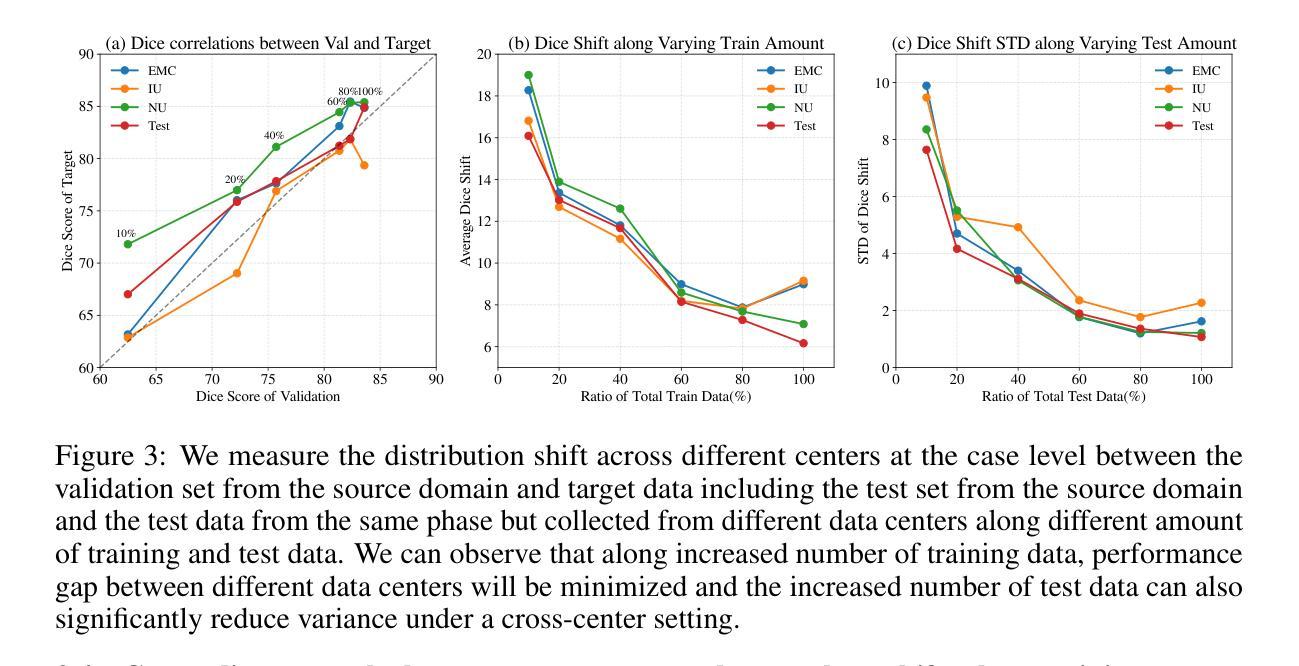
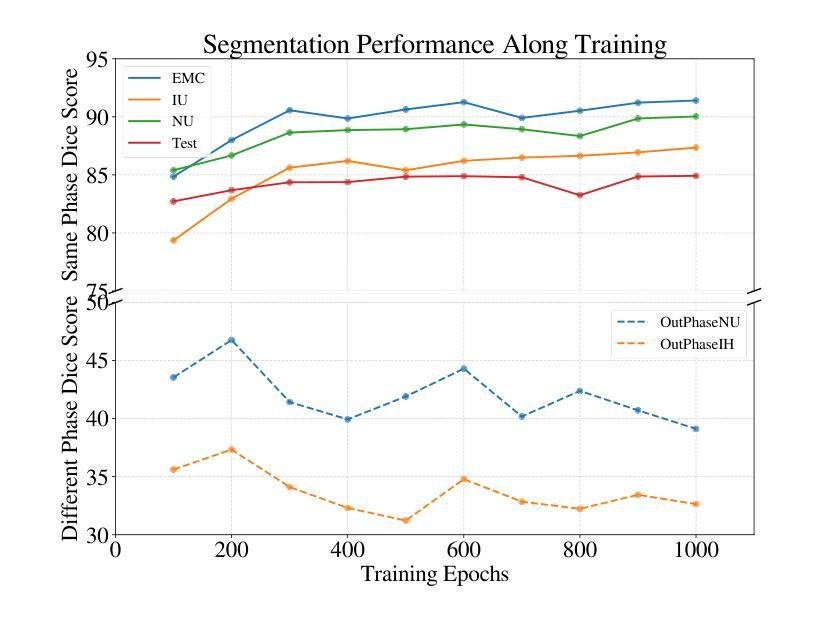
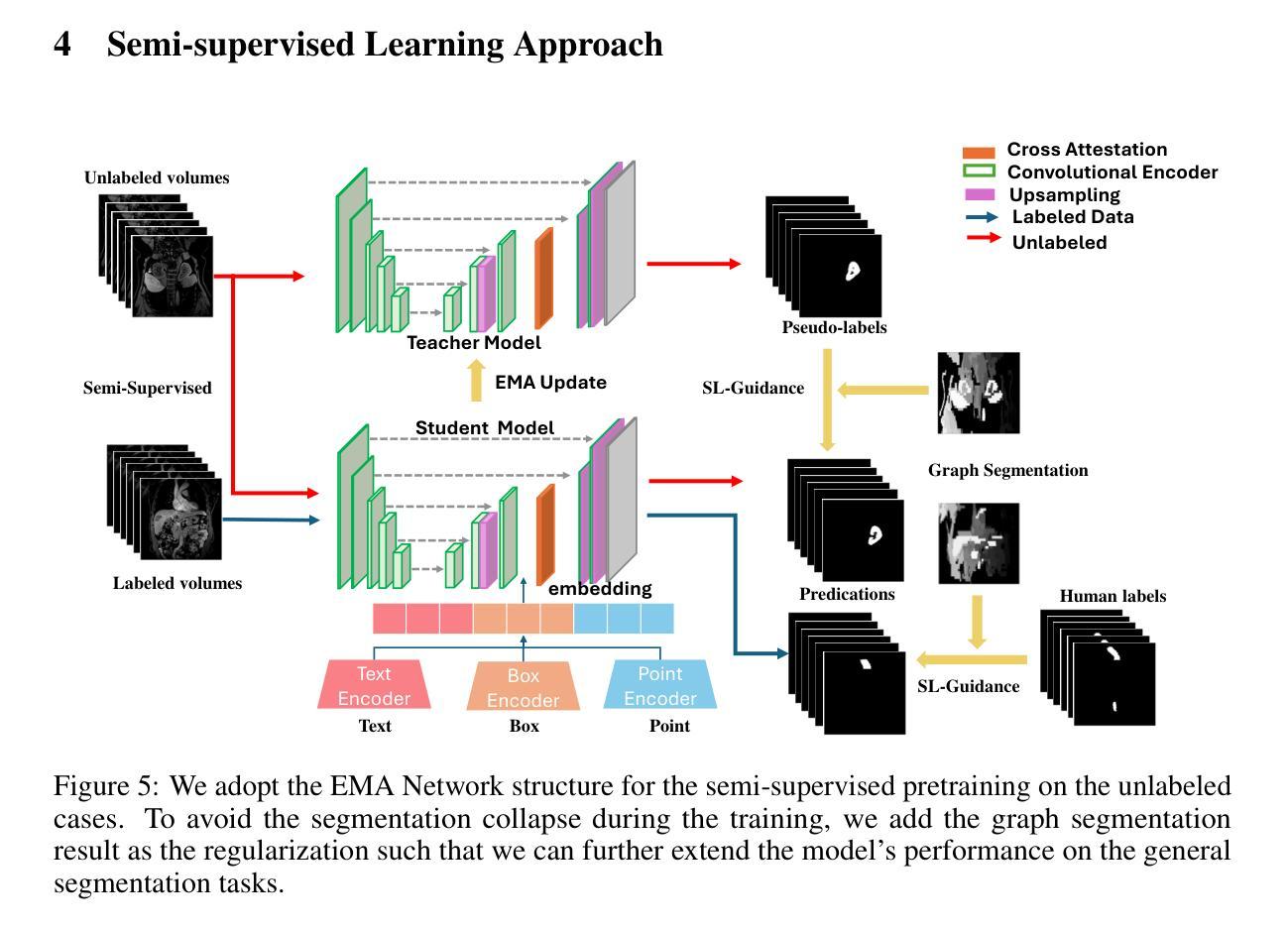
Viscoelastic Profiling of Rare Pediatric Extracranial Tumors using Multifrequency MR Elastography: A Pilot Study
Authors:C. Metz, S. Veldhoen, H. E. Deubzer, F. Mollica, T. Meyer, K. Hauptmann, A. H. Hagemann, A. Eggert, I. Sack, M. S. Anders
Objectives: Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is a noninvasive technique for assessing the viscoelastic properties of soft biological tissues in vivo, with potential relevance for pediatric tumor evaluation. This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of multifrequency MRE in children with solid tumors and to report initial findings on stiffness and fluidity across rare pediatric tumor entities. Additionally, the potential of viscoelastic properties as biomarkers of tumor malignancy was explored. Materials and Methods: Ten pediatric patients (mean age, 5.7 +/- 4.8 years; four female) with extracranial solid tumors underwent multifrequency MRE. Shear waves at 30 - 70 Hz were subsequently generated and measured with a phase-sensitive single-shot spin-echo planar imaging sequence. The obtained shear wave fields were processed by wavenumber (k-)based multi-frequency inversion to reconstruct tumor stiffness and fluidity. The viscoelastic properties within the tumors were quantified and correlated with the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). In addition, differences in stiffness and fluidity were assessed across the histopathologically confirmed tumor entities, which were stratified into malignancy-based groups. Results: MRE was successfully performed in all patients in under five minutes. Differences in viscoelastic properties were observed among tumor entities: Stiffness, fluidity, and their spatial variability increased significantly with tumor malignancy. Furthermore, a significant inverse correlation was observed between stiffness and tumor ADC values. Conclusion: Multifrequency MRE was feasible in pediatric MRI and provided insight into tumor biomechanics. Preliminary data revealed differences in stiffness and fluidity across pediatric solid tumors correlating with malignancy. MRE holds promise for diagnosis and classification of pediatric tumor entities and their malignancy.
目的:磁共振弹性成像(MRE)是一种非侵入性的体内评估软生物组织粘弹性质的技术,对儿科肿瘤评估具有潜在意义。本研究旨在评估在儿童实体瘤患者中应用多频MRE的可行性,并报告关于不同罕见儿科肿瘤实体的僵硬度及流动性的初步发现。此外,还探讨了粘弹性质作为肿瘤恶性生物标志物的潜力。材料与方法:10名(平均年龄5.7±4.8岁,4名女性)患有颅外实体瘤的儿科患者接受了多频MRE检查。随后生成并测量了30-70 Hz的剪切波,采用相位敏感的单脉冲自旋回波平面成像序列进行测量。所获得的剪切波场通过基于波数(k)的多频反演进行处理,以重建肿瘤僵硬度和流动性。对肿瘤内部的粘弹性质进行定量,并与表观扩散系数(ADC)相关。此外,还根据病理组织学确认的肿瘤实体,将其分层到基于恶性的组别中,评估僵硬度和流动性的差异。结果:所有患者均在五分钟内成功完成MRE检查。在肿瘤实体之间观察到粘弹性质的不同:僵硬度、流动性及其空间变化率随肿瘤的恶性程度增加而显著增加。此外,僵硬度和肿瘤ADC值之间存在显著的负相关。结论:多频MRE在儿科MRI中是可行的,为肿瘤的生物力学提供了见解。初步数据显示,儿科实体瘤的僵硬度和流动性与恶性程度相关。MRE在诊断和分类儿科肿瘤实体及其恶性程度方面显示出潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究旨在评估在儿童实体瘤患者中应用多频磁共振弹性成像(MRE)的可行性,并报告不同罕见儿童肿瘤实体的初步刚度与流动性发现。此外,还探讨了粘弹性特性作为肿瘤恶性生物标志物的潜力。对所有患者进行MRE检查均成功,检查时间不到五分钟。不同肿瘤实体的粘弹性特性存在差异,且随着肿瘤恶性程度增高,刚度和流动性及其空间变化显著增加。同时,肿瘤刚度与表观扩散系数(ADC)之间呈显著负相关。多频MRE在儿童磁共振成像中是可行的,为肿瘤生物力学提供了见解。初步数据显示,儿童实体瘤的刚度和流动性与恶性程度相关。MRE在诊断和分类儿童肿瘤实体及其恶性程度方面显示出潜力。
关键见解
- 多频磁共振弹性成像(MRE)是一种非侵入性技术,可用于评估体内软生物组织的粘弹性特性,对儿科肿瘤评估具有潜在意义。
- MRE在儿童实体瘤患者中应用具有可行性,且检查时间短。
- 不同儿科实体肿瘤的粘弹性特性存在差异。
- 肿瘤的刚度和流动性与恶性程度呈正相关。
- 肿瘤刚度与表观扩散系数(ADC)之间呈负相关。
- MRE技术为理解肿瘤生物力学提供了有价值的信息。
点此查看论文截图

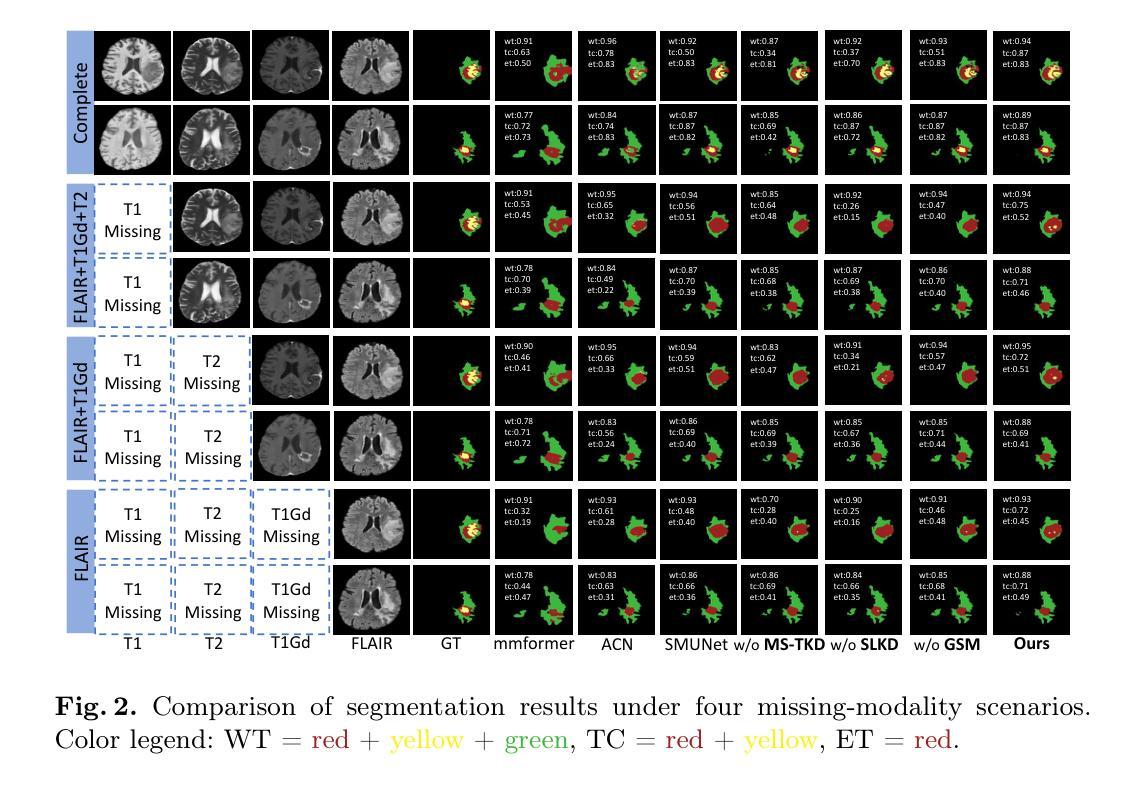
Bridging the Gap in Missing Modalities: Leveraging Knowledge Distillation and Style Matching for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Shenghao Zhu, Yifei Chen, Weihong Chen, Yuanhan Wang, Chang Liu, Shuo Jiang, Feiwei Qin, Changmiao Wang
Accurate and reliable brain tumor segmentation, particularly when dealing with missing modalities, remains a critical challenge in medical image analysis. Previous studies have not fully resolved the challenges of tumor boundary segmentation insensitivity and feature transfer in the absence of key imaging modalities. In this study, we introduce MST-KDNet, aimed at addressing these critical issues. Our model features Multi-Scale Transformer Knowledge Distillation to effectively capture attention weights at various resolutions, Dual-Mode Logit Distillation to improve the transfer of knowledge, and a Global Style Matching Module that integrates feature matching with adversarial learning. Comprehensive experiments conducted on the BraTS and FeTS 2024 datasets demonstrate that MST-KDNet surpasses current leading methods in both Dice and HD95 scores, particularly in conditions with substantial modality loss. Our approach shows exceptional robustness and generalization potential, making it a promising candidate for real-world clinical applications. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/MST-KDNet.
在医学图像分析中,准确可靠的脑肿瘤分割,特别是在处理缺失模态时,仍然是一个关键挑战。之前的研究尚未完全解决肿瘤边界分割敏感性和在缺少关键成像模态时的特征转移的挑战。在这项研究中,我们引入了MST-KDNet,旨在解决这些关键问题。我们的模型具有多尺度转换器知识蒸馏,可有效捕获各种分辨率的注意力权重;双模式逻辑蒸馏,以提高知识的转移;以及全局风格匹配模块,该模块将特征匹配与对抗性学习相结合。在BraTS和FeTS 2024数据集上进行的综合实验表明,MST-KDNet在Dice和HD95得分上均超越了当前领先的方法,特别是在模态损失较大的情况下。我们的方法表现出卓越的鲁棒性和通用性潜力,成为真实世界临床应用的有前途的候选者。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/Quanato607/MST-KDNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为MST-KDNet的医学图像分割模型,用于解决肿瘤边界分割不准确和缺少关键成像模态下的特征转移问题。该模型采用多尺度转换器知识蒸馏、双模式逻辑蒸馏和全局风格匹配模块等技术,在BraTS和FeTS 2024数据集上的实验表明,MST-KDNet在Dice和HD95得分上超越了当前领先的方法,特别是在模态丢失较大的情况下。该模型具有出色的鲁棒性和通用性,有望应用于实际的临床场景。
Key Takeaways
- MST-KDNet模型旨在解决医学图像分析中肿瘤边界分割不准确和缺少关键成像模态下的特征转移问题。
- 该模型采用多尺度转换器知识蒸馏技术,能够在不同分辨率下有效捕捉注意力权重。
- 双模式逻辑蒸馏技术提高了知识转移的效果。
- 全局风格匹配模块结合了特征匹配和对抗学习。
- 在BraTS和FeTS 2024数据集上的实验表明,MST-KDNet在Dice和HD95得分上表现优异,尤其是模态丢失较大的情况下。
- 该模型具有出色的鲁棒性和通用性,有望应用于实际的临床场景。
点此查看论文截图

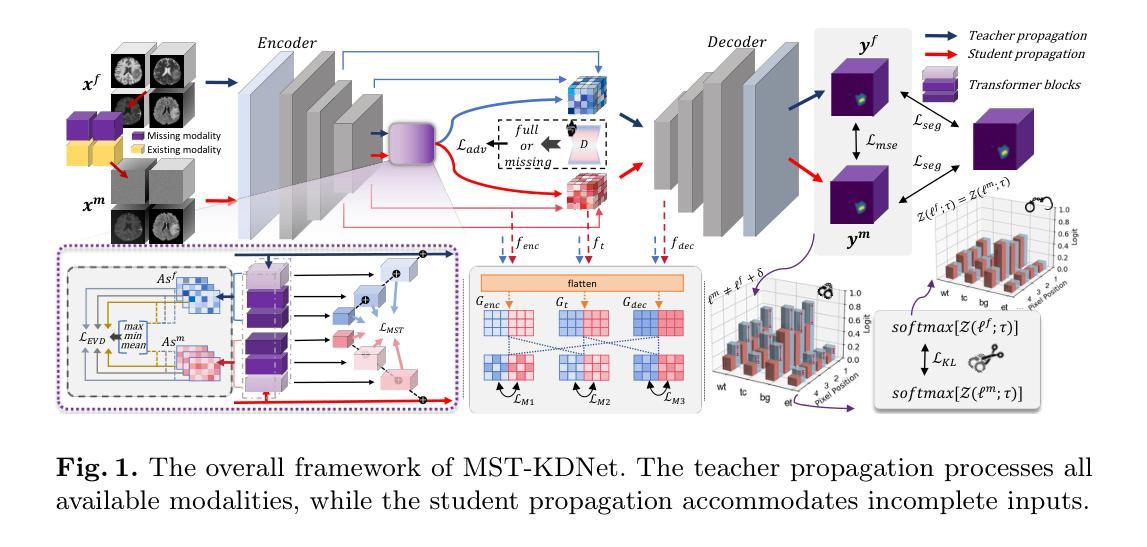
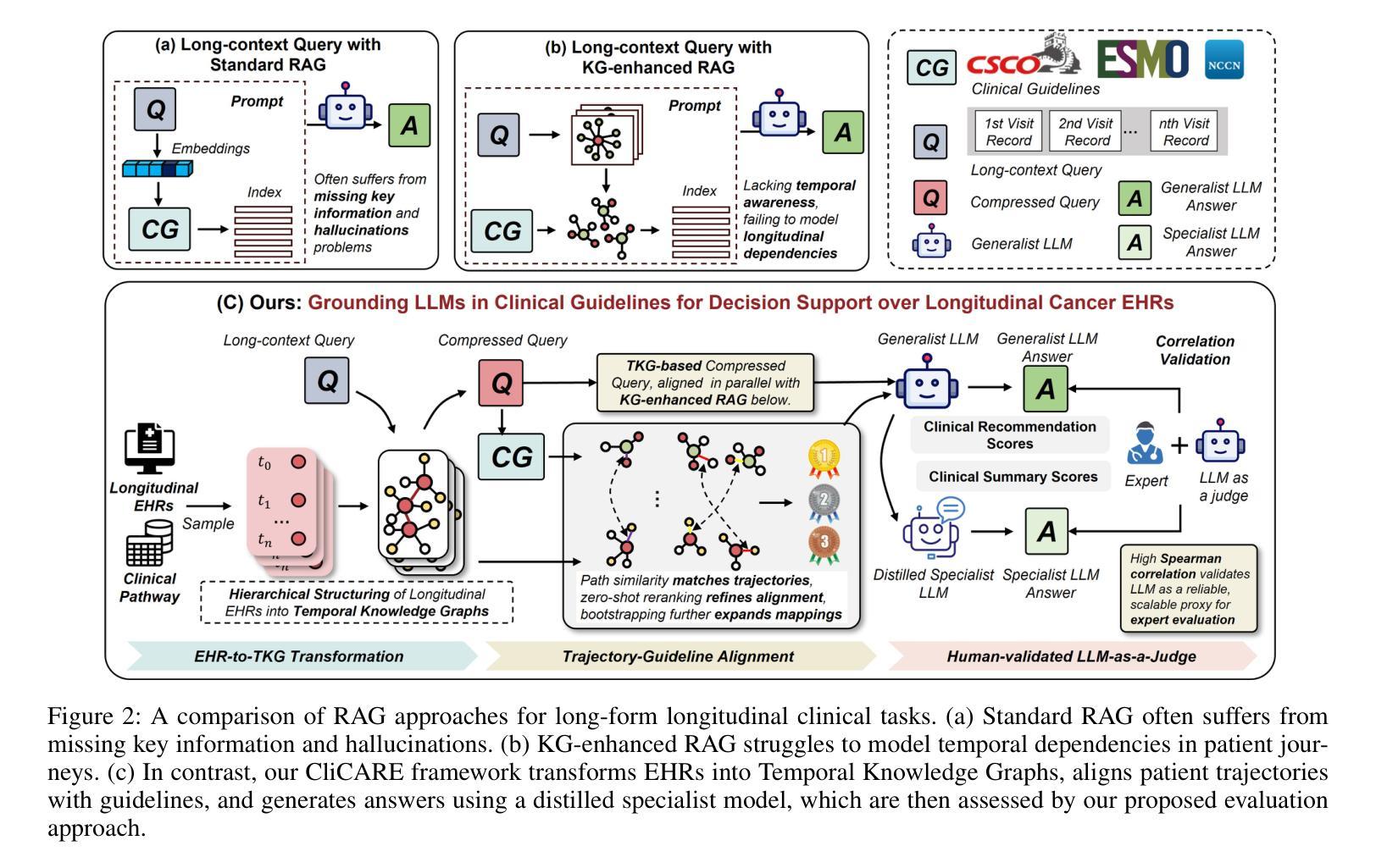
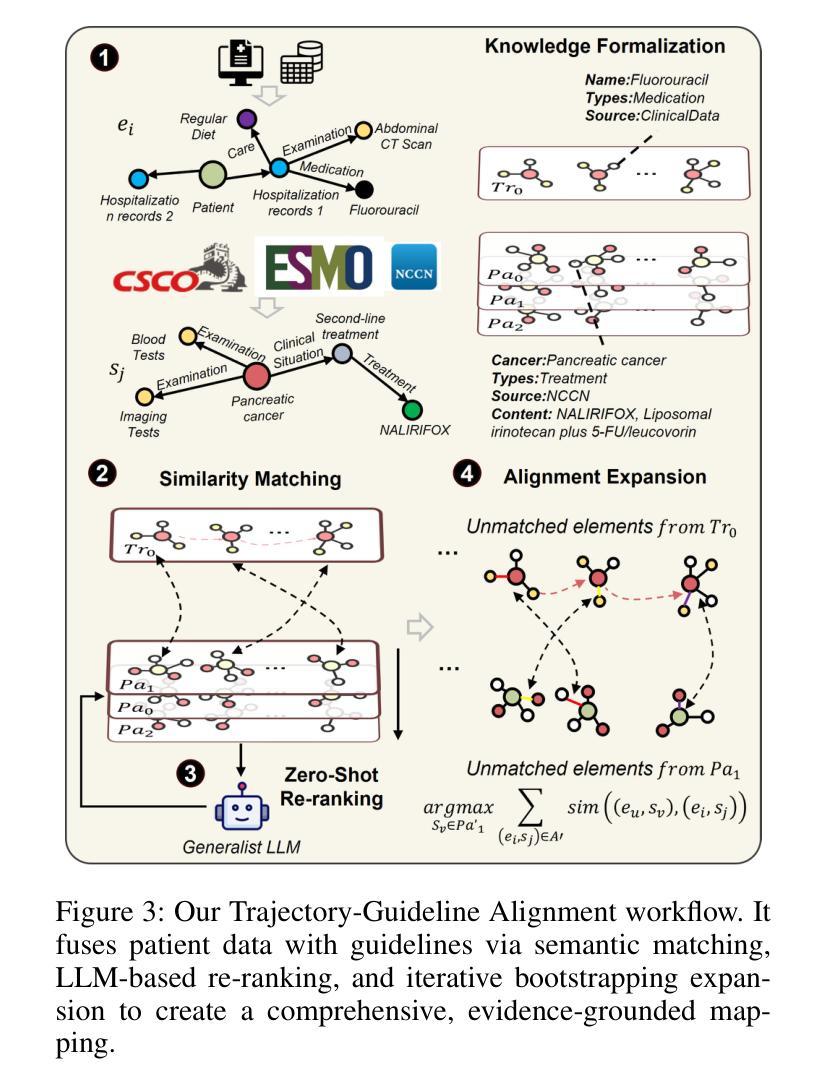
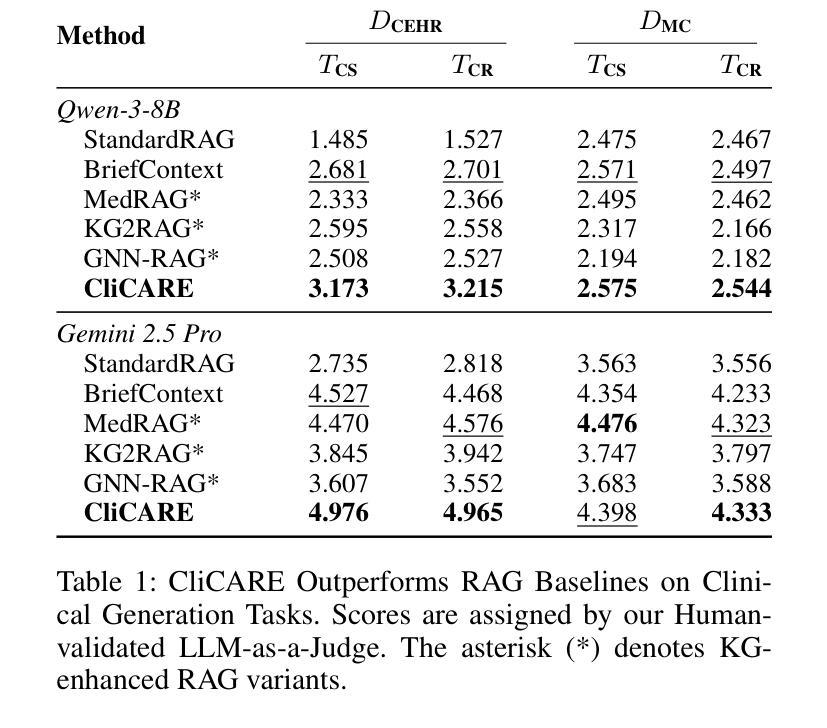
CliCARE: Grounding Large Language Models in Clinical Guidelines for Decision Support over Longitudinal Cancer Electronic Health Records
Authors:Dongchen Li, Jitao Liang, Wei Li, Xiaoyu Wang, Longbing Cao, Kun Yu
Large Language Models (LLMs) hold significant promise for improving clinical decision support and reducing physician burnout by synthesizing complex, longitudinal cancer Electronic Health Records (EHRs). However, their implementation in this critical field faces three primary challenges: the inability to effectively process the extensive length and multilingual nature of patient records for accurate temporal analysis; a heightened risk of clinical hallucination, as conventional grounding techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) do not adequately incorporate process-oriented clinical guidelines; and unreliable evaluation metrics that hinder the validation of AI systems in oncology. To address these issues, we propose CliCARE, a framework for Grounding Large Language Models in Clinical Guidelines for Decision Support over Longitudinal Cancer Electronic Health Records. The framework operates by transforming unstructured, longitudinal EHRs into patient-specific Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKGs) to capture long-range dependencies, and then grounding the decision support process by aligning these real-world patient trajectories with a normative guideline knowledge graph. This approach provides oncologists with evidence-grounded decision support by generating a high-fidelity clinical summary and an actionable recommendation. We validated our framework using large-scale, longitudinal data from a private Chinese cancer dataset and the public English MIMIC-IV dataset. In these diverse settings, CliCARE significantly outperforms strong baselines, including leading long-context LLMs and Knowledge Graph-enhanced RAG methods. The clinical validity of our results is supported by a robust evaluation protocol, which demonstrates a high correlation with assessments made by expert oncologists.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过综合复杂的纵向癌症电子健康记录(EHRs),在改善临床决策支持和减轻医生疲劳方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,其在该关键领域的实施面临三大挑战:无法有效处理患者记录的广泛长度和多语言能力,以进行准确的时间分析;由于传统的接地技术(如增强检索生成(RAG))未能充分融入面向过程的临床指南,导致出现更高的临床幻觉风险;以及不可靠的评估指标,阻碍了肿瘤学领域人工智能系统的验证。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CliCARE框架,该框架旨在通过临床指南支持纵向癌症电子健康记录的决策支持来接地大型语言模型。该框架通过将以非结构化形式存在的纵向EHR转换为针对患者的时序知识图谱(TKGs)来捕获长期依赖关系,然后通过将这些现实世界的患者轨迹与规范性指南知识图谱对齐来支持决策过程。这种方法为肿瘤学家提供了基于证据的支持决策依据,生成了高保真度的临床摘要和可行的建议。我们使用来自私人中文癌症数据集和公共英文MIMIC-IV数据集的大规模纵向数据验证了我们的框架。在这些不同的环境中,CliCARE显著优于强大的基线,包括领先的长文上下文LLM和知识图谱增强的RAG方法。我们的结果的临床有效性得到了稳健的评估协议的支持,该协议与专家肿瘤学家的评估结果高度相关。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在癌症电子健康记录(EHRs)的综合处理方面具有改善临床决策支持和缓解医生疲劳的潜力。然而,其实施面临三大挑战:无法有效处理患者记录的扩展长度和多语言能力,导致准确的时间分析困难;存在临床幻觉的风险,传统接地技术如检索增强生成(RAG)未能充分融入面向过程的临床指南;以及缺乏可靠的评估指标,阻碍了肿瘤学人工智能系统的验证。为解决这些问题,我们提出了CliCARE框架,该框架用于在纵向癌症电子健康记录中进行决策支持的接地大型语言模型。它通过将非结构化的纵向EHR转换为患者特定的时间知识图谱(TKG)来捕捉长期依赖关系,然后通过将这些现实世界的患者轨迹与规范性的指南知识图谱对齐来接地决策支持过程。这种方法为肿瘤学家提供了以证据为基础的决策支持,生成了高保真度的临床摘要和可行的建议。我们的框架在大型纵向数据集上得到了验证,包括来自中国癌症数据库的私有数据集和公共英文MIMIC-IV数据集。在这些不同的环境中,CliCARE显著优于强大的基线,包括领先的长文上下文LLM和知识图谱增强的RAG方法。我们的结果得到了稳健评估协议的支持,该协议与专家肿瘤学家的评估结果高度相关。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在癌症电子健康记录应用中具有改善临床决策和缓解医生疲劳的潜力。
- 实施大型语言模型于临床决策支持面临三大挑战:处理患者记录的扩展长度和多语言能力、临床幻觉风险、缺乏可靠的评估指标。
- CliCARE框架通过创建时间知识图谱来解决这些问题,以捕捉长期依赖关系,并与临床指南对齐以提供接地决策支持。
- CliCARE框架在多个数据集上进行了验证,包括来自中国癌症数据库的私有数据集和公共MIMIC-IV数据集。
- CliCARE框架性能优于其他方法,包括长文上下文的大型语言模型和知识图谱增强的RAG方法。
- CliCARE框架的临床有效性得到了专家评估的支撑。
点此查看论文截图

Aleatoric Uncertainty Medical Image Segmentation Estimation via Flow Matching
Authors:Phi Van Nguyen, Ngoc Huynh Trinh, Duy Minh Lam Nguyen, Phu Loc Nguyen, Quoc Long Tran
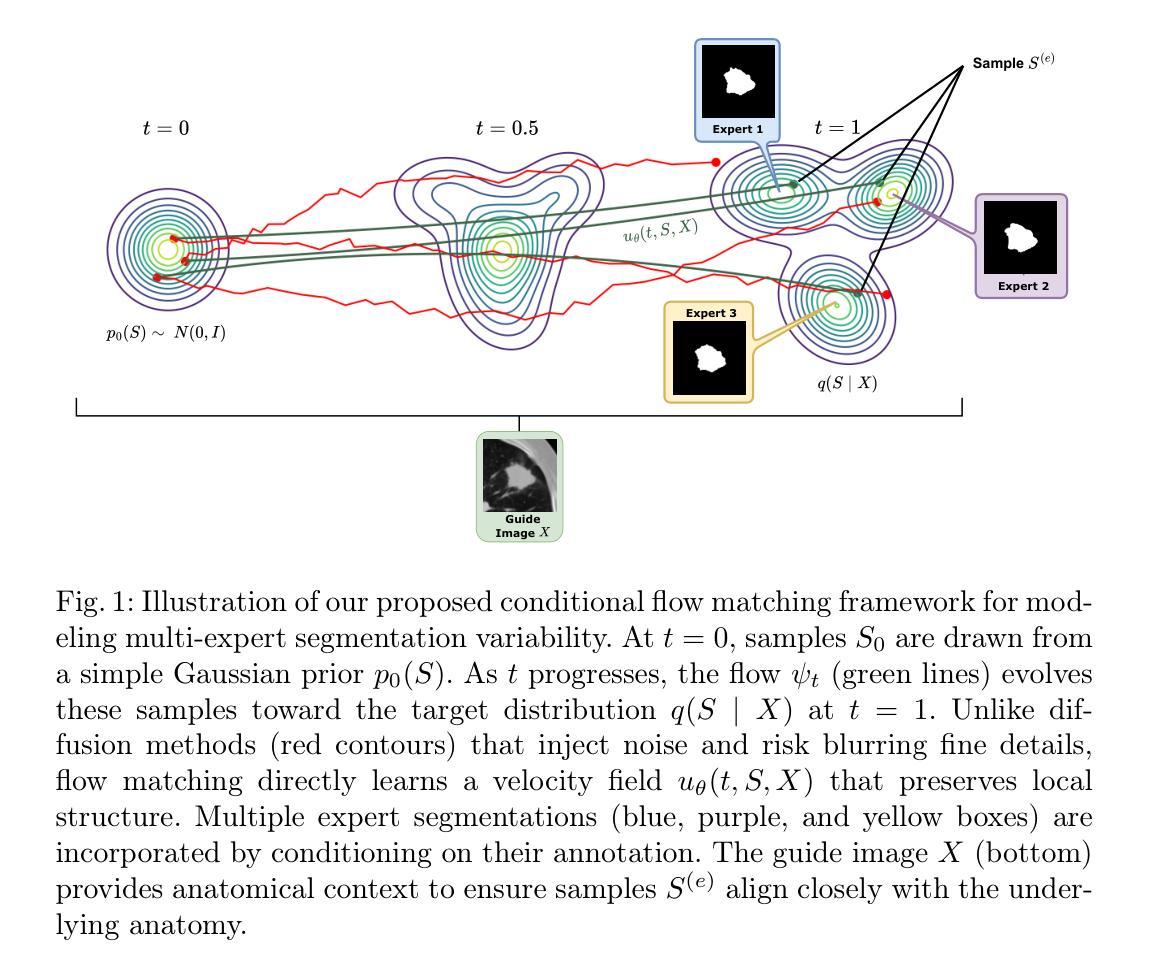
Quantifying aleatoric uncertainty in medical image segmentation is critical since it is a reflection of the natural variability observed among expert annotators. A conventional approach is to model the segmentation distribution using the generative model, but current methods limit the expression ability of generative models. While current diffusion-based approaches have demonstrated impressive performance in approximating the data distribution, their inherent stochastic sampling process and inability to model exact densities limit their effectiveness in accurately capturing uncertainty. In contrast, our proposed method leverages conditional flow matching, a simulation-free flow-based generative model that learns an exact density, to produce highly accurate segmentation results. By guiding the flow model on the input image and sampling multiple data points, our approach synthesizes segmentation samples whose pixel-wise variance reliably reflects the underlying data distribution. This sampling strategy captures uncertainties in regions with ambiguous boundaries, offering robust quantification that mirrors inter-annotator differences. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only achieves competitive segmentation accuracy but also generates uncertainty maps that provide deeper insights into the reliability of the segmentation outcomes. The code for this paper is freely available at https://github.com/huynhspm/Data-Uncertainty
量化医学图像分割中的偶然不确定性至关重要,因为它反映了专家标注者之间观察到的自然变异性。一种常规方法是使用生成模型对分割分布进行建模,但当前的方法限制了生成模型的表达能力。虽然基于扩散的当前方法已经显示出在逼近数据分布方面的令人印象深刻的性能,但其固有的随机采样过程以及无法对确切密度进行建模的限制,使其难以准确捕获不确定性。相比之下,我们提出的方法利用条件流匹配,这是一种无模拟的基于流的生成模型,学习精确密度,以产生高度准确的分割结果。通过在输入图像上引导流模型并采样多个数据点,我们的方法合成分割样本,其像素级方差可靠地反映了底层数据分布。这种采样策略捕获了边界模糊区域的不确定性,提供了稳健的量化,反映了标注者之间的差异。实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅实现了具有竞争力的分割精度,还生成了不确定性地图,为分割结果的可靠性提供了更深入的了解。本论文的代码可免费访问:https://github.com/huynhspm/Data-Uncertainty
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于条件流匹配的无仿真流生成模型的方法,用于量化医学图像分割中的随机不确定性。该方法能够在像素级别准确反映数据分布,通过指导输入图像和采样多个数据点,合成可靠的分割样本,从而捕捉模糊边界区域的不确定性,反映专家标注者之间的差异。实验结果表明,该方法不仅实现了竞争的分割精度,还生成了不确定性地图,为分割结果的可靠性提供了更深入的了解。
Key Takeaways
- 量化医学图像分割中的随机不确定性对于反映专家标注者之间的差异至关重要。
- 传统方法使用生成模型模拟分割分布,但现有方法限制了生成模型的表达能力。
- 扩散方法虽然在逼近数据分布方面表现出色,但其固有的随机采样过程和无法精确建模密度限制了其在捕捉不确定性方面的准确性。
- 本文提出的基于条件流匹配的方法是一种无仿真流生成模型,能够学习精确密度,产生高度准确的分割结果。
- 通过指导流模型在输入图像上并采样多个数据点,该方法能够合成反映底层数据分布的分割样本,其像素级方差能够可靠地反映不确定性。
- 该方法能够在区域边界模糊的情况下捕捉不确定性,提供稳健的量化,反映不同专家标注者之间的差异。
点此查看论文截图

MINR: Implicit Neural Representations with Masked Image Modelling
Authors:Sua Lee, Joonhun Lee, Myungjoo Kang
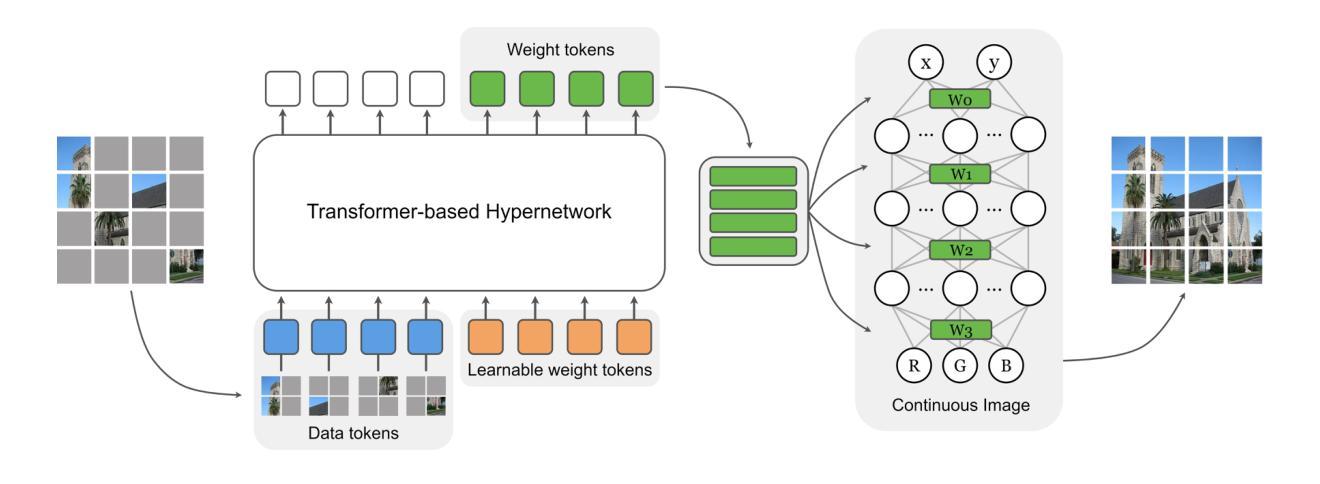
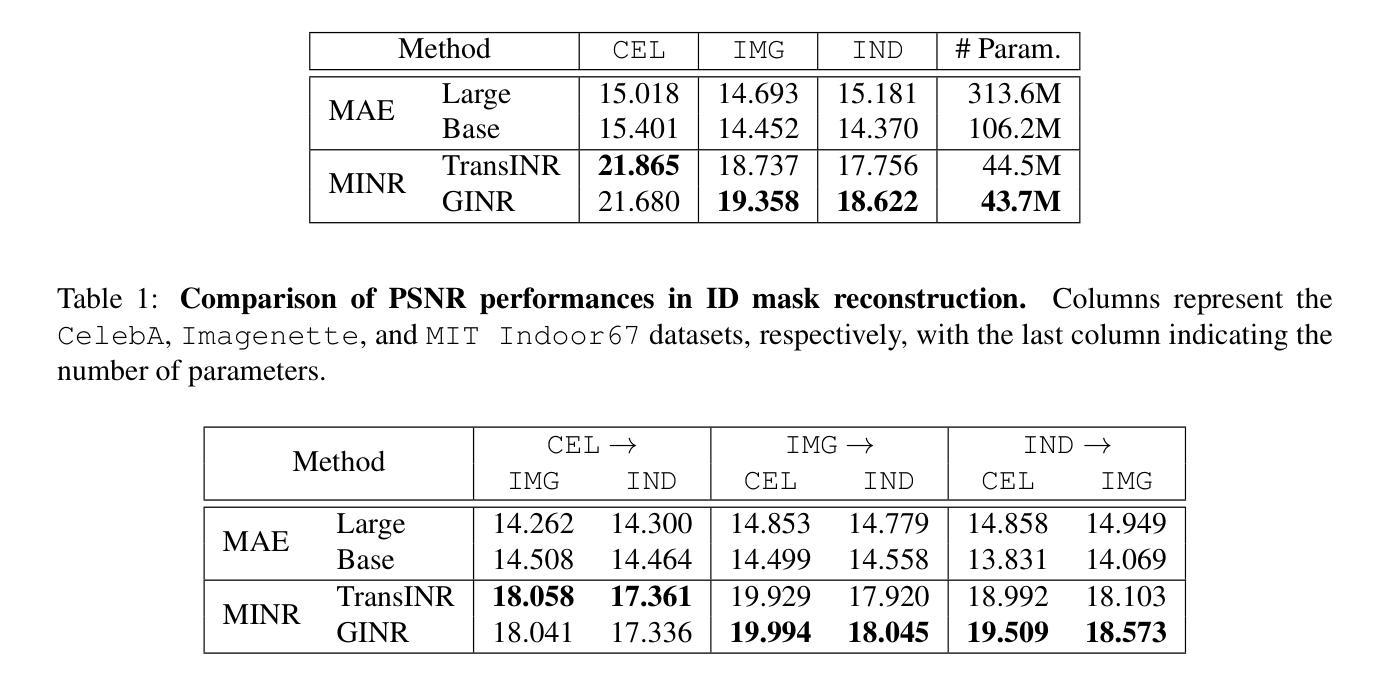
Self-supervised learning methods like masked autoencoders (MAE) have shown significant promise in learning robust feature representations, particularly in image reconstruction-based pretraining task. However, their performance is often strongly dependent on the masking strategies used during training and can degrade when applied to out-of-distribution data. To address these limitations, we introduce the masked implicit neural representations (MINR) framework that synergizes implicit neural representations with masked image modeling. MINR learns a continuous function to represent images, enabling more robust and generalizable reconstructions irrespective of masking strategies. Our experiments demonstrate that MINR not only outperforms MAE in in-domain scenarios but also in out-of-distribution settings, while reducing model complexity. The versatility of MINR extends to various self-supervised learning applications, confirming its utility as a robust and efficient alternative to existing frameworks.
自监督学习方法,如掩码自动编码器(MAE)在学习稳健的特征表示方面显示出巨大潜力,特别是在基于图像重建的预训练任务中。然而,它们的性能往往强烈依赖于训练过程中使用的掩码策略,当应用于离群数据时性能可能会下降。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了掩码隐式神经表示(MINR)框架,它将隐式神经表示与掩码图像建模相结合。MINR学习一种连续函数来表示图像,使得无论采用何种掩码策略,都能进行更稳健和通用的重建。我们的实验表明,MINR不仅在域内场景中优于MAE,而且在离群数据环境中也表现更好,同时降低了模型复杂性。MINR的通用性可应用于各种自监督学习任务,证实其作为现有框架的稳健高效替代方案的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICCV 2023 workshop on Out-of-Distribution Generalization in Computer Vision
Summary
基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的自我监督学习方法在图像重建预训练任务中展现出强大的特征学习能力。然而,其性能依赖于训练中的掩码策略,并且在面对分布外数据时性能可能下降。为解决这些问题,我们引入了掩码隐式神经网络表示(MINR)框架,该框架结合了隐式神经网络表示与掩码图像建模。MINR学习一种连续函数来表示图像,无论掩码策略如何,都能实现更稳健和可泛化的重建。实验证明,无论是在域内场景还是分布外设置中,MINR都优于MAE,同时降低了模型复杂性。MINR的通用性可广泛应用于各种自我监督学习任务,证明其作为现有框架的稳健、高效替代方案的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 掩码自编码器(MAE)在图像重建预训练任务中显示出强大的特征学习能力。
- 掩码策略对MAE性能具有重要影响。
- MINR框架结合了隐式神经网络表示与掩码图像建模。
- MINR通过学习连续函数表示图像,实现更稳健和可泛化的重建。
- MINR在域内场景和分布外场景中均优于MAE。
- MINR降低了模型复杂性。
点此查看论文截图