⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-02 更新
Subtyping Breast Lesions via Generative Augmentation based Long-tailed Recognition in Ultrasound
Authors:Shijing Chen, Xinrui Zhou, Yuhao Wang, Yuhao Huang, Ao Chang, Dong Ni, Ruobing Huang
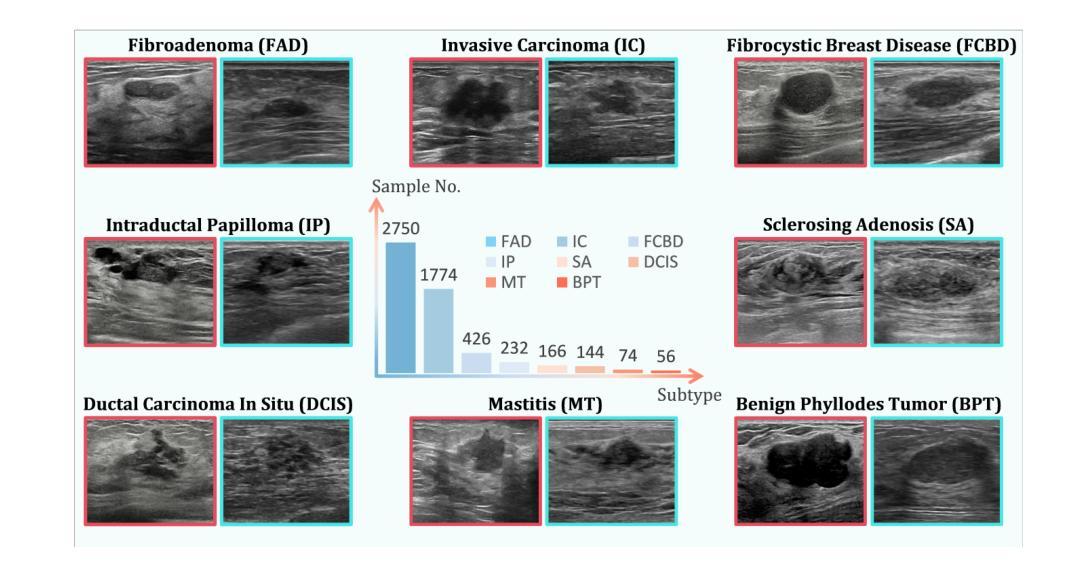
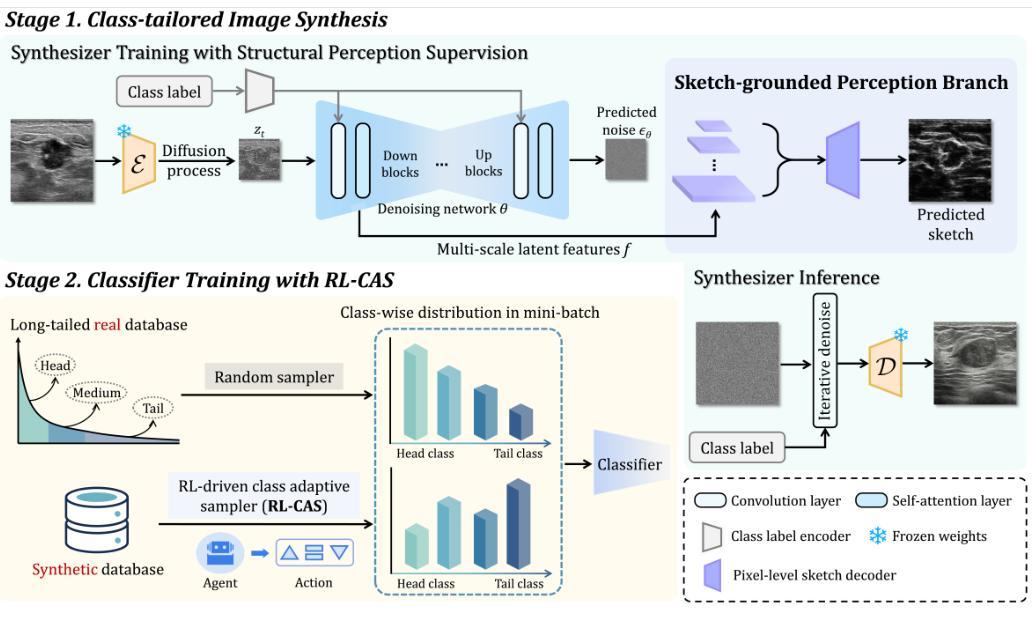
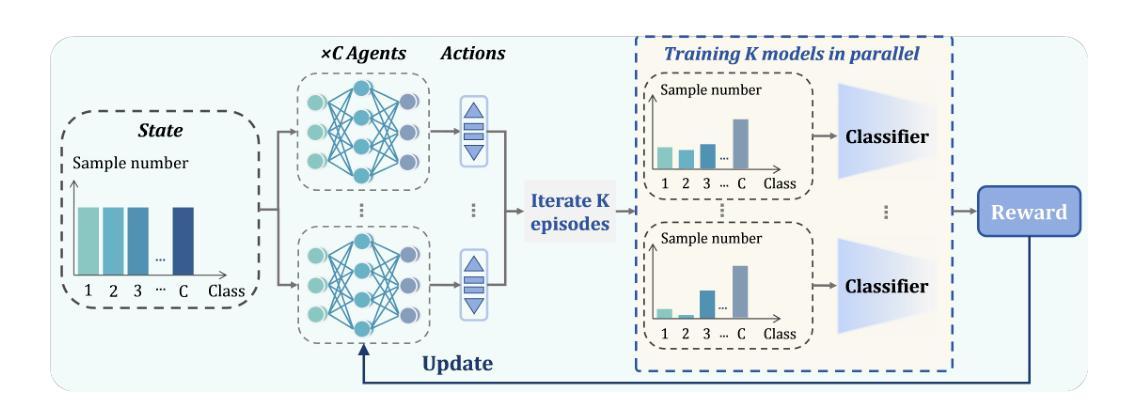
Accurate identification of breast lesion subtypes can facilitate personalized treatment and interventions. Ultrasound (US), as a safe and accessible imaging modality, is extensively employed in breast abnormality screening and diagnosis. However, the incidence of different subtypes exhibits a skewed long-tailed distribution, posing significant challenges for automated recognition. Generative augmentation provides a promising solution to rectify data distribution. Inspired by this, we propose a dual-phase framework for long-tailed classification that mitigates distributional bias through high-fidelity data synthesis while avoiding overuse that corrupts holistic performance. The framework incorporates a reinforcement learning-driven adaptive sampler, dynamically calibrating synthetic-real data ratios by training a strategic multi-agent to compensate for scarcities of real data while ensuring stable discriminative capability. Furthermore, our class-controllable synthetic network integrates a sketch-grounded perception branch that harnesses anatomical priors to maintain distinctive class features while enabling annotation-free inference. Extensive experiments on an in-house long-tailed and a public imbalanced breast US datasets demonstrate that our method achieves promising performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches. More synthetic images can be found at https://github.com/Stinalalala/Breast-LT-GenAug.
准确识别乳腺病变亚型有助于个性化治疗和干预。超声(US)作为一种安全且可及的成像模式,广泛应用于乳腺异常筛查和诊断。然而,不同亚型的发病率呈现出偏态长尾分布,给自动识别带来了巨大挑战。生成增强技术提供了一个有前景的解决方案来纠正数据分布。在此基础上,我们提出了一个用于长尾分类的双阶段框架,通过高保真数据合成来缓解分布偏见,同时避免过度使用破坏整体性能。该框架采用强化学习驱动的自适应采样器,通过训练战略多智能体来动态校准合成与现实数据的比例,以弥补真实数据的稀缺,同时确保稳定的辨别能力。此外,我们的类可控合成网络集成了基于草图的感知分支,利用解剖先验知识来保持独特的类特征,同时实现无注解推理。在内部长尾和公共不平衡乳腺超声数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法与最先进的方法相比取得了有前景的性能。更多的合成图像可在 https://github.com/Stinalalala/Breast-LT-GenAug 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI2025 Early Accept. 11 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文提出一种用于处理长尾分类问题的双阶段框架,通过高保真数据合成解决数据分布不均的问题,同时避免过度使用合成数据对整体性能的影响。该框架结合强化学习驱动的自适应采样器,动态调整合成数据与真实数据的比例,通过训练战略多智能体来补偿真实数据的稀缺性,同时确保稳定的鉴别能力。此外,其类可控的合成网络结合了基于草图的感知分支,利用解剖先验信息来保持各类特征的同时实现无标注推理。实验证明,该方法在内部长尾和公共不平衡乳腺超声数据集上取得了良好的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺病变亚型的准确识别有助于个性化治疗和干预。
- 超声作为一种安全可及的成像模式,广泛应用于乳腺异常筛查和诊断。
- 不同乳腺病变亚型的发生率呈长尾分布,给自动化识别带来挑战。
- 生成增强技术提供了纠正数据分布的有前途的解决方案。
- 提出的双阶段框架通过高保真数据合成解决分布偏差问题,避免合成数据过度使用。
- 框架结合强化学习驱动的自适应采样器,动态调整合成与真实数据的比例。
点此查看论文截图

VidFuncta: Towards Generalizable Neural Representations for Ultrasound Videos
Authors:Julia Wolleb, Florentin Bieder, Paul Friedrich, Hemant D. Tagare, Xenophon Papademetris
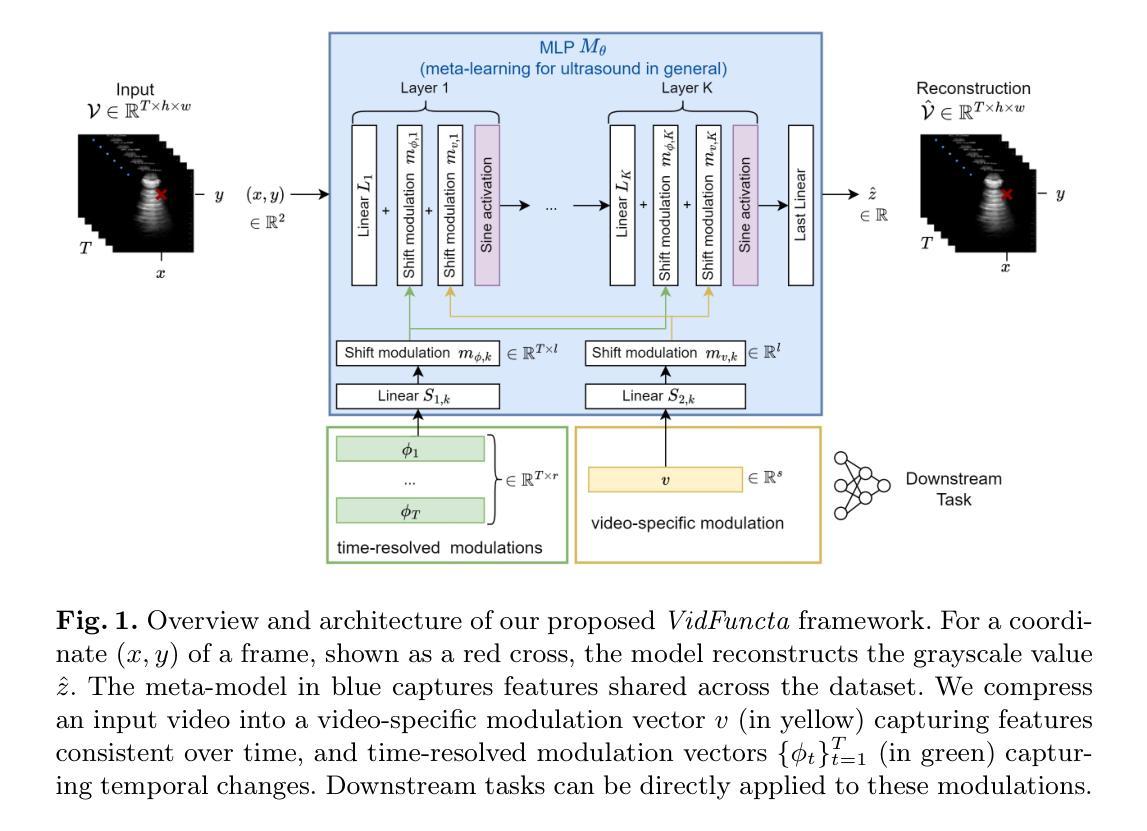
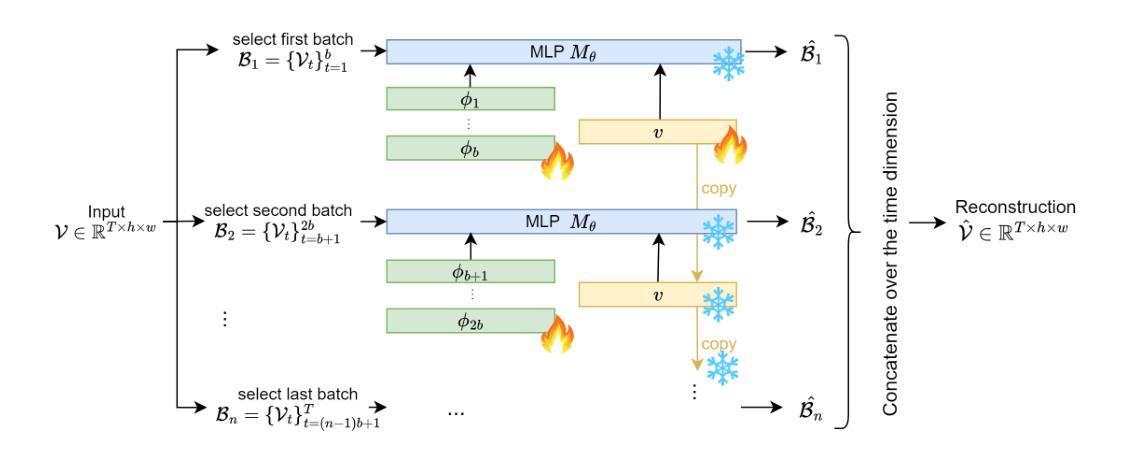
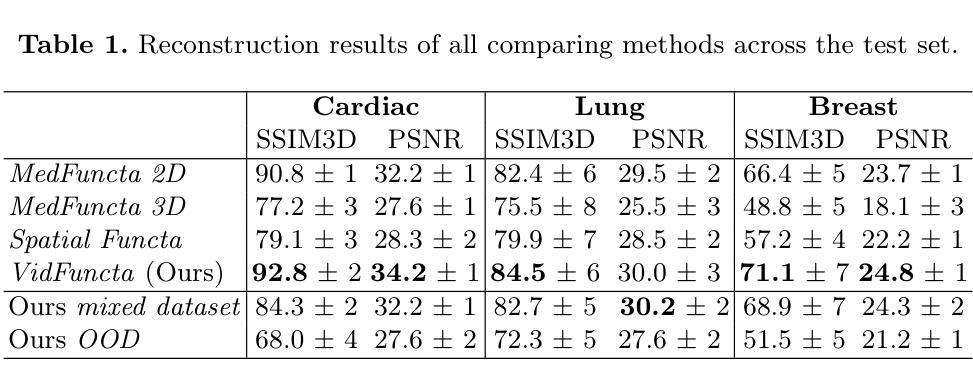
Ultrasound is widely used in clinical care, yet standard deep learning methods often struggle with full video analysis due to non-standardized acquisition and operator bias. We offer a new perspective on ultrasound video analysis through implicit neural representations (INRs). We build on Functa, an INR framework in which each image is represented by a modulation vector that conditions a shared neural network. However, its extension to the temporal domain of medical videos remains unexplored. To address this gap, we propose VidFuncta, a novel framework that leverages Functa to encode variable-length ultrasound videos into compact, time-resolved representations. VidFuncta disentangles each video into a static video-specific vector and a sequence of time-dependent modulation vectors, capturing both temporal dynamics and dataset-level redundancies. Our method outperforms 2D and 3D baselines on video reconstruction and enables downstream tasks to directly operate on the learned 1D modulation vectors. We validate VidFuncta on three public ultrasound video datasets – cardiac, lung, and breast – and evaluate its downstream performance on ejection fraction prediction, B-line detection, and breast lesion classification. These results highlight the potential of VidFuncta as a generalizable and efficient representation framework for ultrasound videos. Our code is publicly available under https://github.com/JuliaWolleb/VidFuncta_public.
超声波在临床护理中得到了广泛应用,但传统的深度学习方法由于非标准化采集和操作者偏见,通常在完整视频分析中面临挑战。我们通过隐式神经表示(INR)为超声波视频分析提供了新的视角。我们基于Functa,这是一个INR框架,其中每张图像由调制向量表示,该向量调节共享神经网络。然而,它在医疗视频的时态领域的应用仍然未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了VidFuncta,这是一个利用Functa将可变长度超声波视频编码为紧凑、时间解析表示的新框架。VidFuncta将每个视频分解为静态的视频特定向量和一系列时间相关的调制向量,捕捉时序动态和数据集级别的冗余。我们的方法在视频重建方面超越了2D和3D基准线,并使下游任务能够直接在学到的1D调制向量上进行操作。我们在三个公共超声波视频数据集(心脏、肺部和乳房)上验证了VidFuncta,并对其在下游任务(射血分数预测、B线检测和乳腺病变分类)上的性能进行了评估。这些结果突显了VidFuncta作为超声波视频通用和高效表示框架的潜力。我们的代码公开可访问于https://github.com/JuliaWolleb/VidFuncta_public。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted 6th International Workshop of Advances in Simplifying Medical UltraSound (ASMUS) to be held at MICCAI 2025
摘要
本文提出一种基于隐神经表示(INR)的超声视频分析新方法——VidFuncta。该方法利用Functa框架将可变长度的超声视频编码为紧凑、时间解析的表示形式,将视频分解为静态视频特定向量和时间依赖调制向量序列,捕捉视频的时间动态和数据集级别的冗余信息。该方法在视频重建任务上优于2D和3D基线,并能直接对学习的1D调制向量进行下游操作。在心脏、肺部和乳房的公共超声视频数据集上的验证及其在下游任务(如射血分数预测、B线检测和乳房病变分类)上的表现证明了VidFuncta作为超声视频通用和高效表示框架的潜力。
关键见解
- 本文介绍了超声视频分析的新视角,即通过隐神经表示(INR)。
- 提出了一种新的框架VidFuncta,利用Functa处理超声视频,将其编码为紧凑且时间解析的表示形式。
- VidFuncta能将视频分解为静态和动态的组成部分,捕捉视频的时空特性。
- 该方法在视频重建任务上表现出优异的性能,优于传统的2D和3D方法。
- VidFuncta支持下游任务直接操作学习到的1D调制向量。
- 在心脏、肺部和乳房的超声视频数据集上的实验结果证明了VidFuncta的通用性和效率。
- 该研究的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图