⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
Style-Aware Blending and Prototype-Based Cross-Contrast Consistency for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chaowei Chen, Xiang Zhang, Honglie Guo, Shunfang Wang
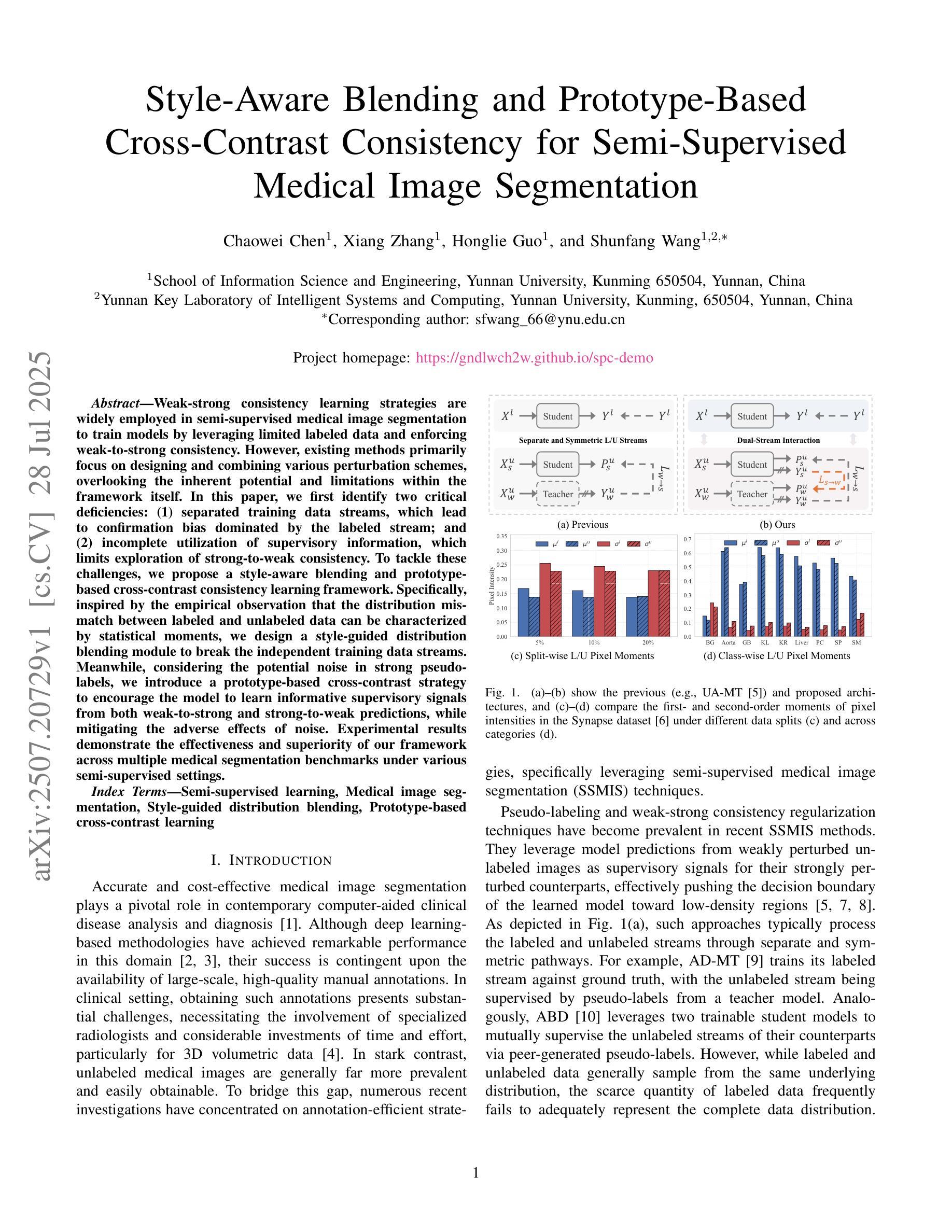
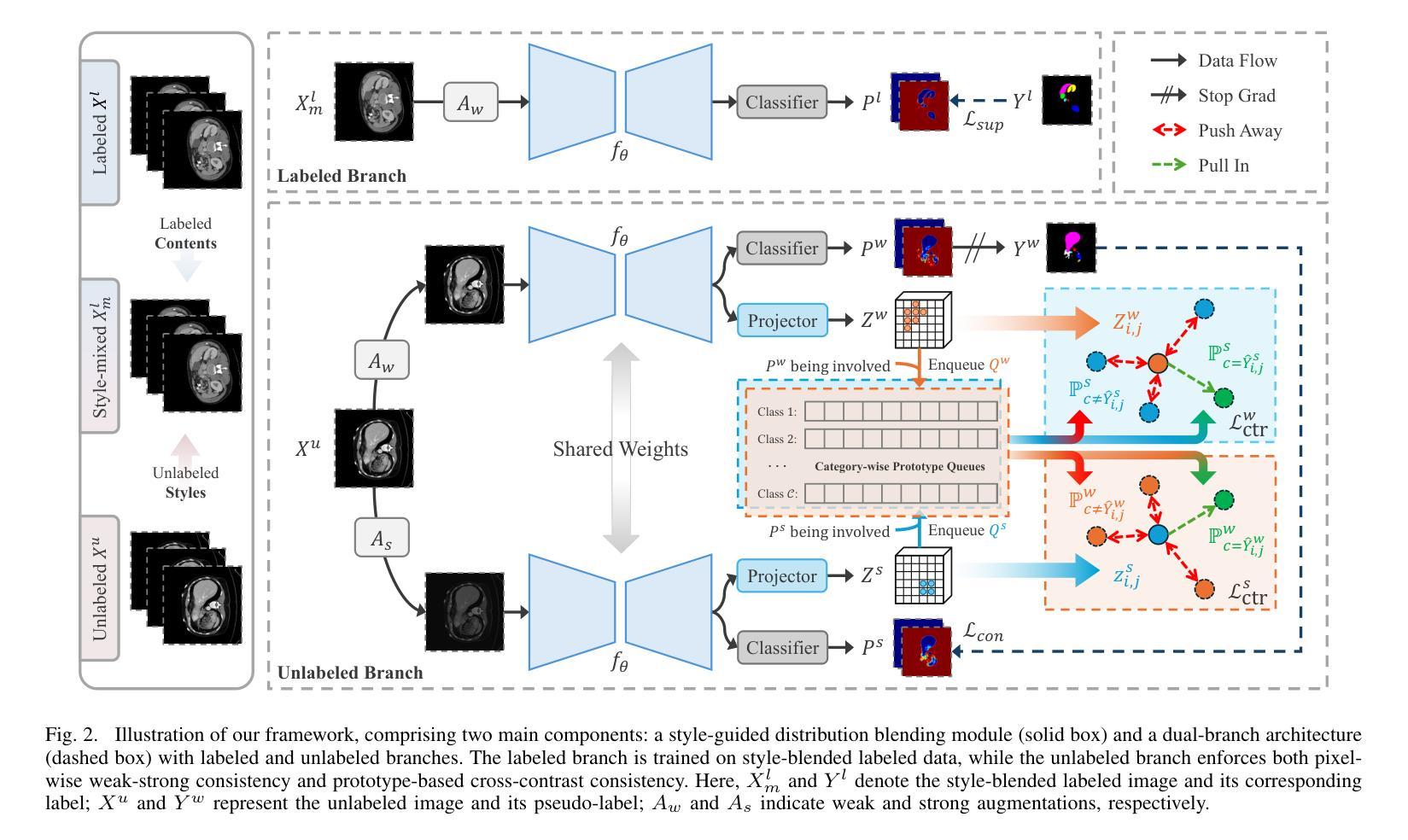
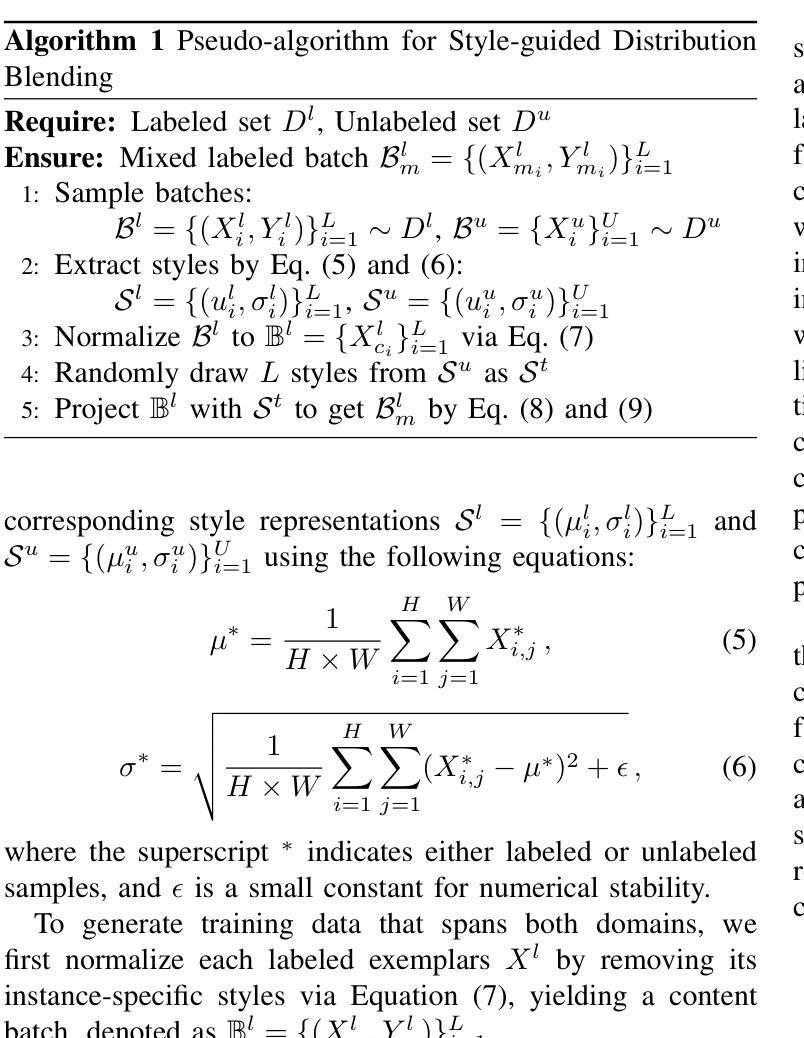
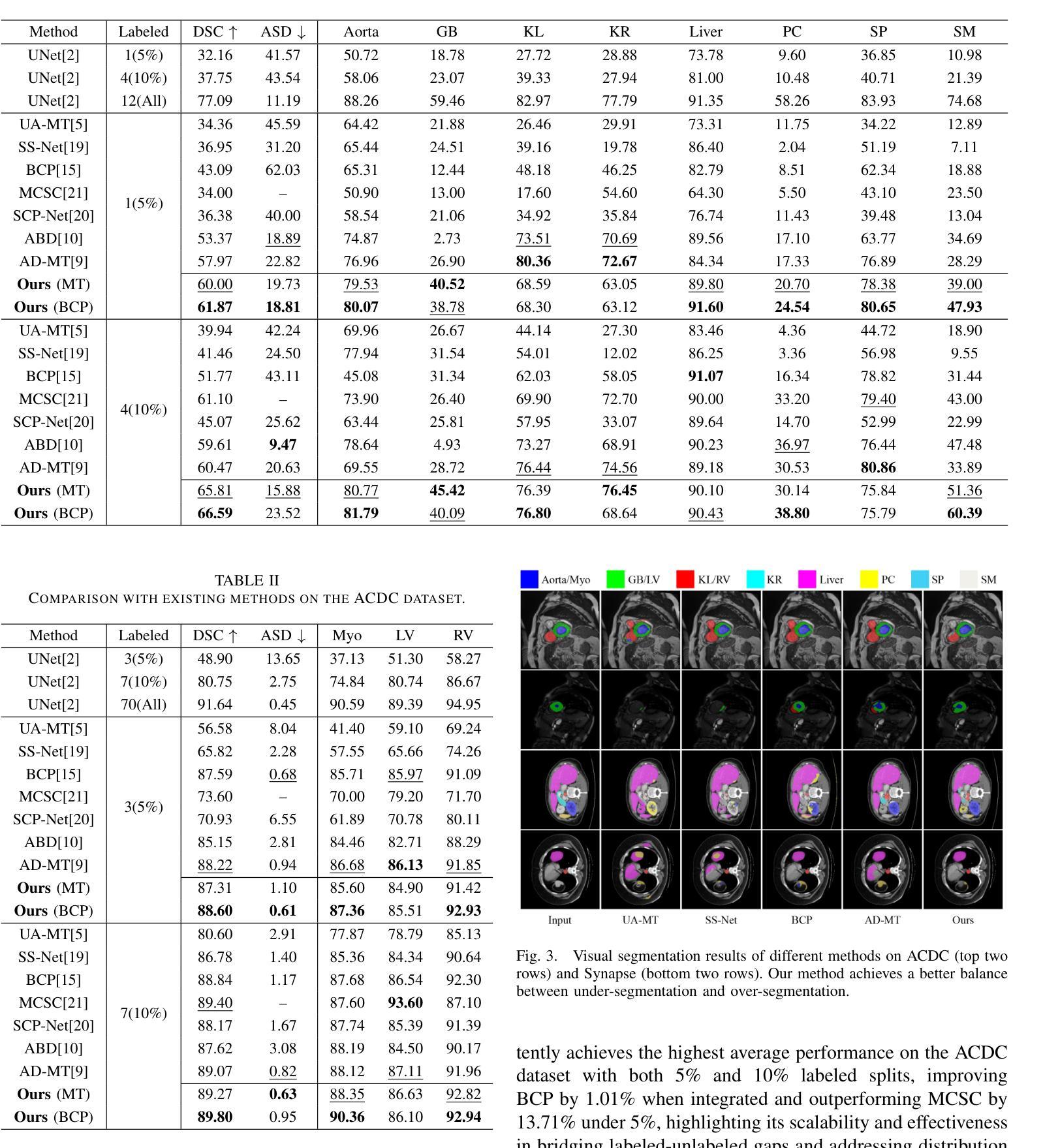
Weak-strong consistency learning strategies are widely employed in semi-supervised medical image segmentation to train models by leveraging limited labeled data and enforcing weak-to-strong consistency. However, existing methods primarily focus on designing and combining various perturbation schemes, overlooking the inherent potential and limitations within the framework itself. In this paper, we first identify two critical deficiencies: (1) separated training data streams, which lead to confirmation bias dominated by the labeled stream; and (2) incomplete utilization of supervisory information, which limits exploration of strong-to-weak consistency. To tackle these challenges, we propose a style-aware blending and prototype-based cross-contrast consistency learning framework. Specifically, inspired by the empirical observation that the distribution mismatch between labeled and unlabeled data can be characterized by statistical moments, we design a style-guided distribution blending module to break the independent training data streams. Meanwhile, considering the potential noise in strong pseudo-labels, we introduce a prototype-based cross-contrast strategy to encourage the model to learn informative supervisory signals from both weak-to-strong and strong-to-weak predictions, while mitigating the adverse effects of noise. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our framework across multiple medical segmentation benchmarks under various semi-supervised settings.
弱强一致性学习策略在半监督医学图像分割中得到了广泛应用,通过利用有限的标记数据并强制执行弱到强的一致性来训练模型。然而,现有方法主要集中在设计和组合各种扰动方案,而忽略了框架本身的内在潜力和局限性。在本文中,我们首先识别出两个关键缺陷:(1)训练数据流分离,导致以标记流为主的确认偏见;(2)监督信息利用不完整,限制了从强到弱的一致性的探索。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个风格感知的混合和基于原型的交叉对比一致性学习框架。具体来说,受经验观察启发,即标记数据和无标记数据之间的分布不匹配可以通过统计矩来表征,我们设计了一个风格引导的分布混合模块来打破独立的训练数据流。同时,考虑到强伪标签中的潜在噪声,我们引入了一种基于原型的交叉对比策略,以鼓励模型从弱到强和强到弱的预测中学习有用的监督信号,同时减轻噪声的不利影响。实验结果表明,我们的框架在多个医学分割基准测试下具有有效性和优越性。在各种半监督设置下都表现出了出色的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无监督半监督对比学习中的弱强一致性学习策略广泛应用于医学图像分割的深度学习模型中,通过使用有限标记数据执行训练和维持弱到强的一致性来提高模型性能。然而,现有方法主要关注设计不同的扰动方案进行组合,忽略了框架本身的潜在能力和局限性。针对现有研究的缺陷,我们提出了一种基于风格感知混合和原型交叉对比的一致性学习框架,打破独立训练数据流的问题并充分利用监督信息学习更准确的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 现有弱强一致性学习方法主要关注设计扰动方案组合,忽略了框架本身的潜在能力和局限性。
- 提出两种关键缺陷:分离的训练数据流导致确认偏见主要局限于标记流;监督信息利用不完整限制了从强到弱的一致性的探索。
- 为解决挑战,提出了一种基于风格感知混合的分布融合模块,打破独立训练数据流的问题。
- 考虑到强伪标签的潜在噪声,引入了基于原型的交叉对比策略,鼓励模型从弱到强和强到弱的预测中学习有用的监督信号,同时减轻噪声的不利影响。
- 实验结果表明,在多种医学分割基准测试下,该框架在各种半监督设置中的有效性和优越性。
- 通过风格感知混合和原型交叉对比策略的结合,提高了模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图
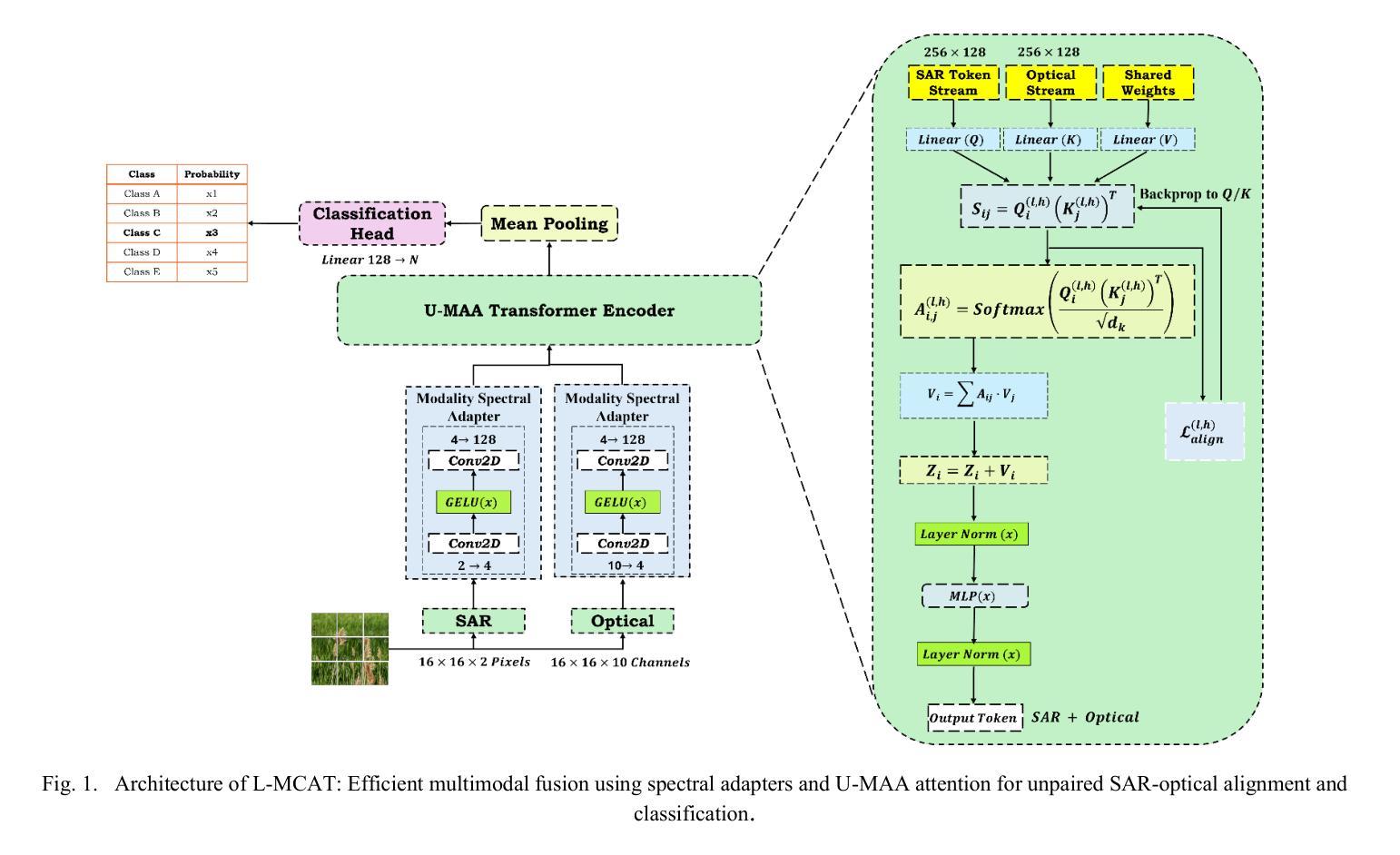
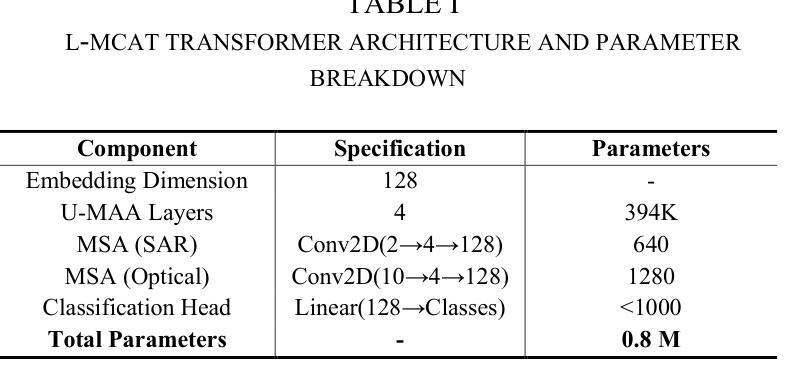
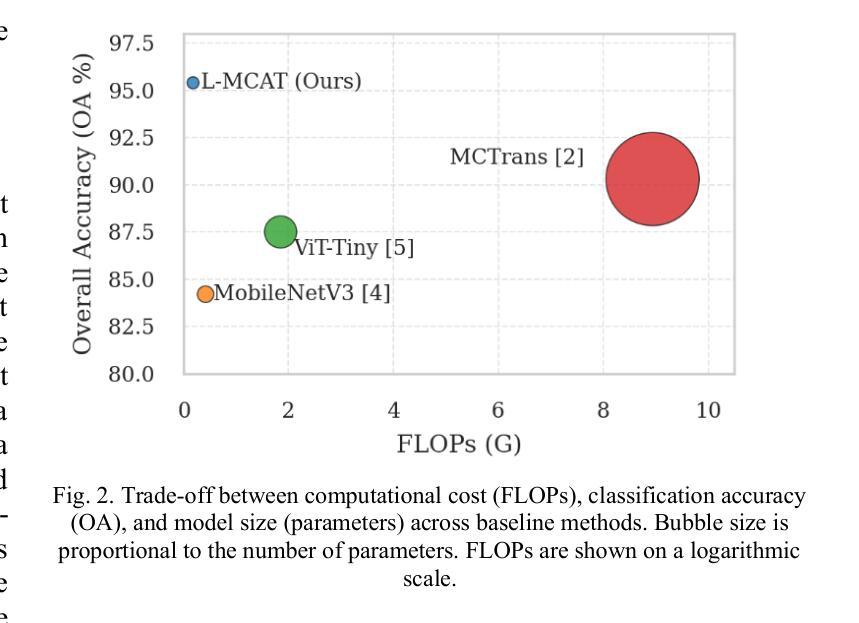
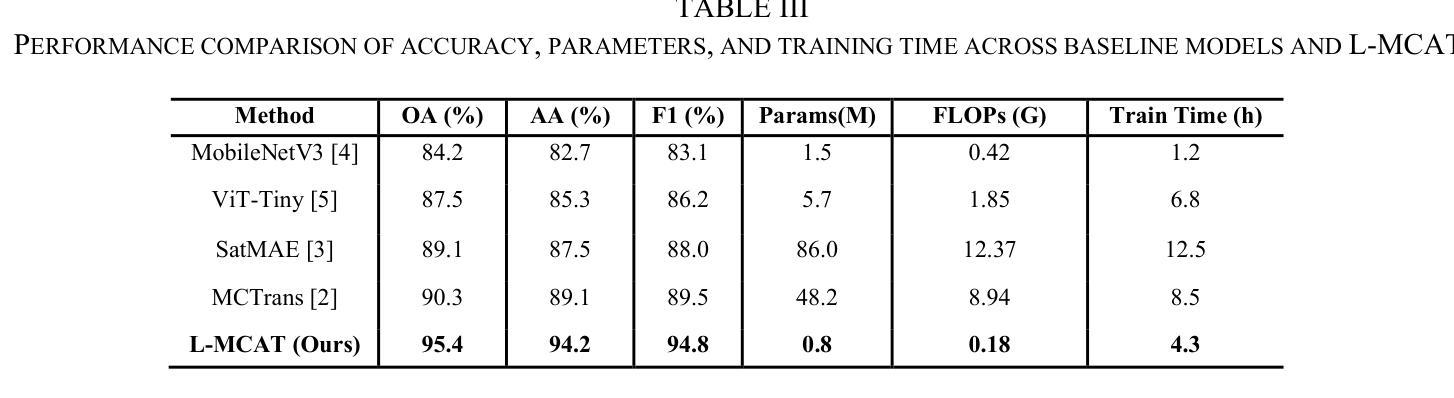
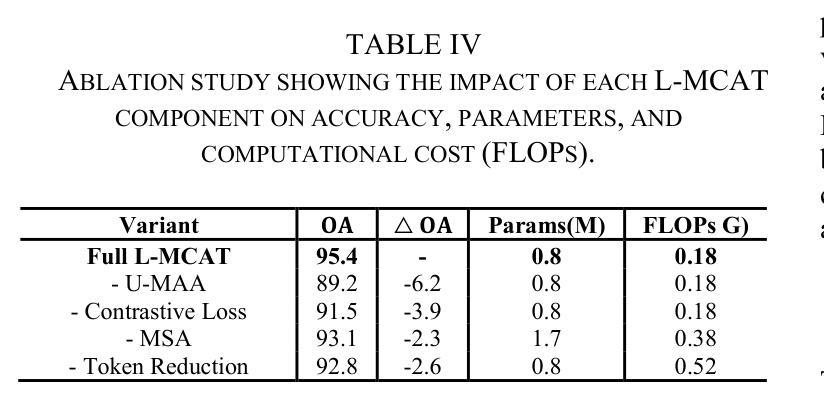
L-MCAT: Unpaired Multimodal Transformer with Contrastive Attention for Label-Efficient Satellite Image Classification
Authors:Mitul Goswami, Mrinal Goswami
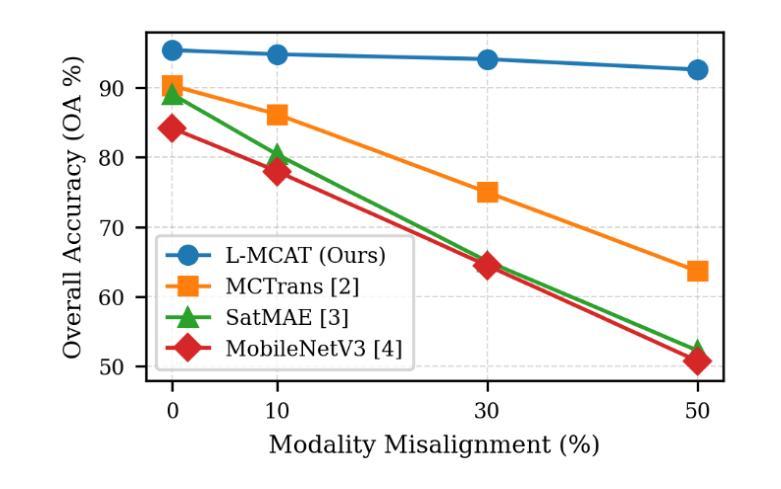
We propose the Lightweight Multimodal Contrastive Attention Transformer (L-MCAT), a novel transformer-based framework for label-efficient remote sensing image classification using unpaired multimodal satellite data. L-MCAT introduces two core innovations: (1) Modality-Spectral Adapters (MSA) that compress high-dimensional sensor inputs into a unified embedding space, and (2) Unpaired Multimodal Attention Alignment (U-MAA), a contrastive self-supervised mechanism integrated into the attention layers to align heterogeneous modalities without pixel-level correspondence or labels. L-MCAT achieves 95.4% overall accuracy on the SEN12MS dataset using only 20 labels per class, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines while using 47x fewer parameters and 23x fewer FLOPs than MCTrans. It maintains over 92% accuracy even under 50% spatial misalignment, demonstrating robustness for real-world deployment. The model trains end-to-end in under 5 hours on a single consumer GPU.
我们提出了轻量级多模态对比注意力转换器(L-MCAT),这是一个基于转换器的新型框架,用于使用非配对的多模态卫星数据进行标签效率高的遥感图像分类。L-MCAT引入了两个核心创新点:(1)模态光谱适配器(MSA),它将高维传感器输入压缩到统一的嵌入空间;(2)非配对多模态注意力对齐(U-MAA),这是一种集成到注意力层中的对比自监督机制,用于对齐不同模式,无需像素级的对应或标签。L-MCAT在SEN12MS数据集上仅使用每类20个标签就实现了95.4%的总体准确率,优于最新基线技术,同时使用MCTrans的47倍更少的参数和23倍更少的FLOPs。即使在50%的空间错位情况下,也能保持超过92%的准确率,证明了其在现实世界部署中的稳健性。该模型在单个消费级GPU上可以在不到5小时内进行端到端的训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了轻量级多模态对比注意力转换器(L-MCAT),这是一种基于转换器的、利用无配对多模态卫星数据进行标签效率高的遥感图像分类的新框架。L-MCAT有两个核心创新点:一是模态光谱适配器(MSA),能将高维传感器输入压缩到统一嵌入空间;二是无配对多模态注意力对齐(U-MAA),这是一种对比自监督机制,集成到注意力层中,无需像素级对应或标签即可对齐不同模态。L-MCAT在SEN12MS数据集上仅使用每类20个标签就达到了95.4%的整体准确率,且比MCTrans使用更少的参数和FLOPs。在50%的空间错位下,它仍能保持超过92%的准确率,证明了其在现实世界的部署中的稳健性。该模型可在单个消费者GPU上在不到5小时内进行端到端的训练。
Key Takeaways
- L-MCAT是一个基于转换器的框架,用于遥感图像分类。
- L-MCAT利用无配对多模态卫星数据,实现标签效率高的分类。
- 模态光谱适配器(MSA)将高维传感器输入压缩到统一嵌入空间。
- 无配对多模态注意力对齐(U-MAA)机制用于对齐不同模态,无需像素级对应或标签。
- L-MCAT在SEN12MS数据集上实现了高准确率,且使用较少的参数和计算量。
- L-MCAT具有在50%空间错位下的稳健性,适合现实世界的部署。
点此查看论文截图

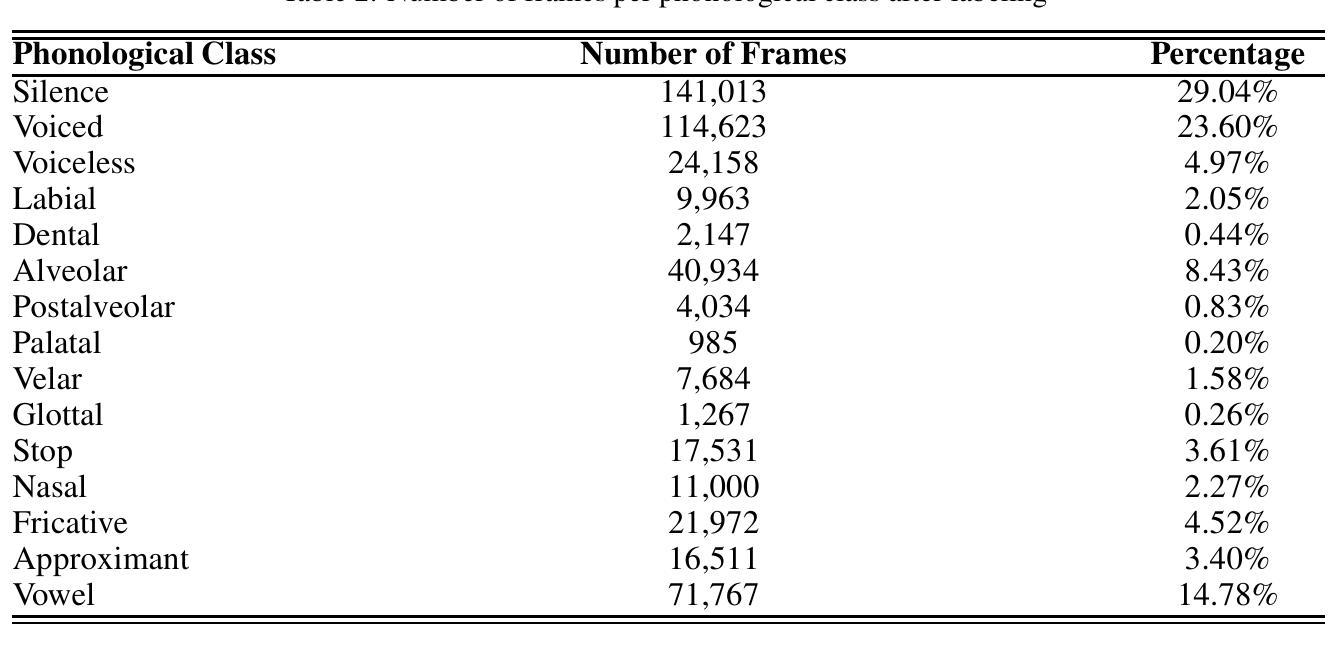
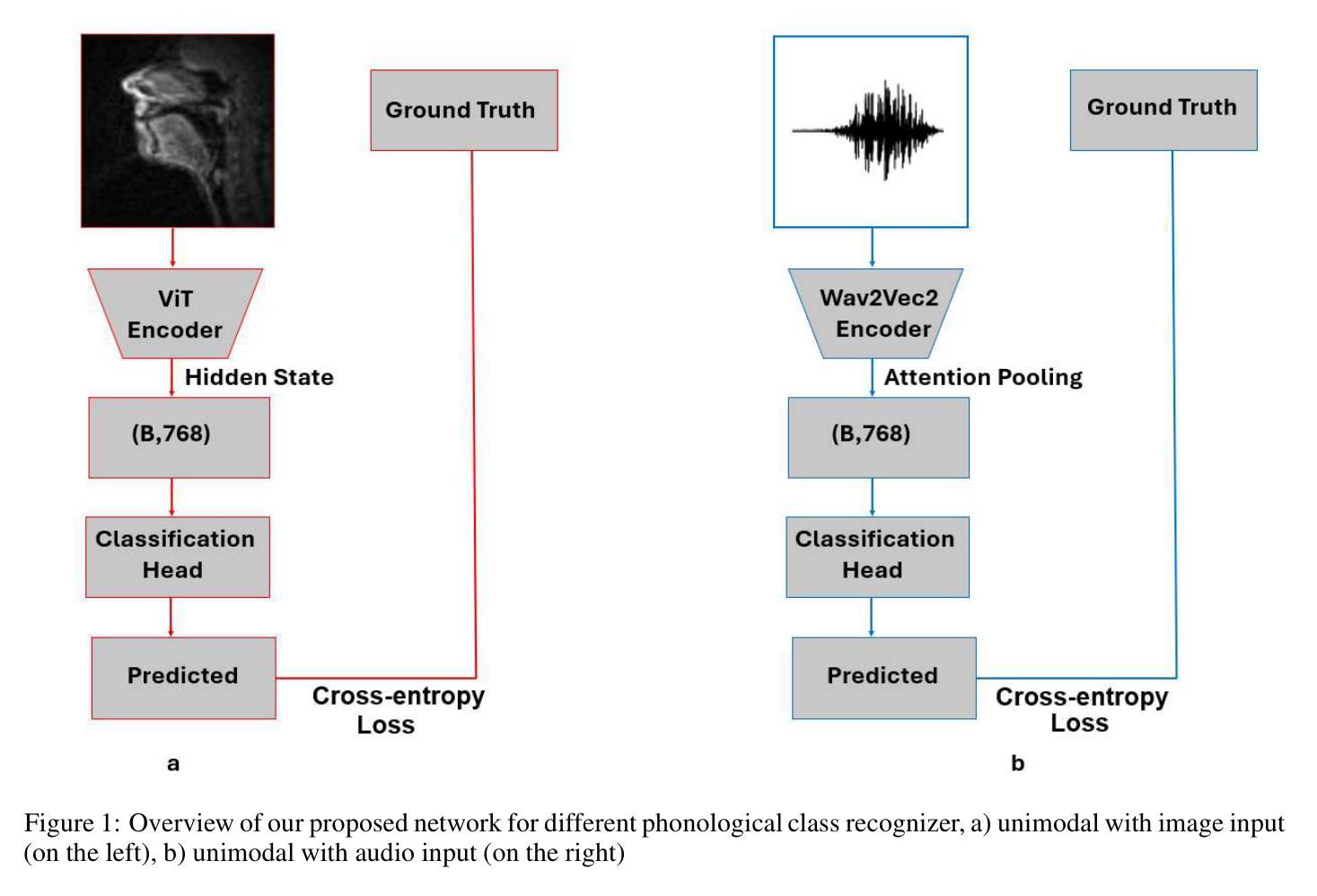
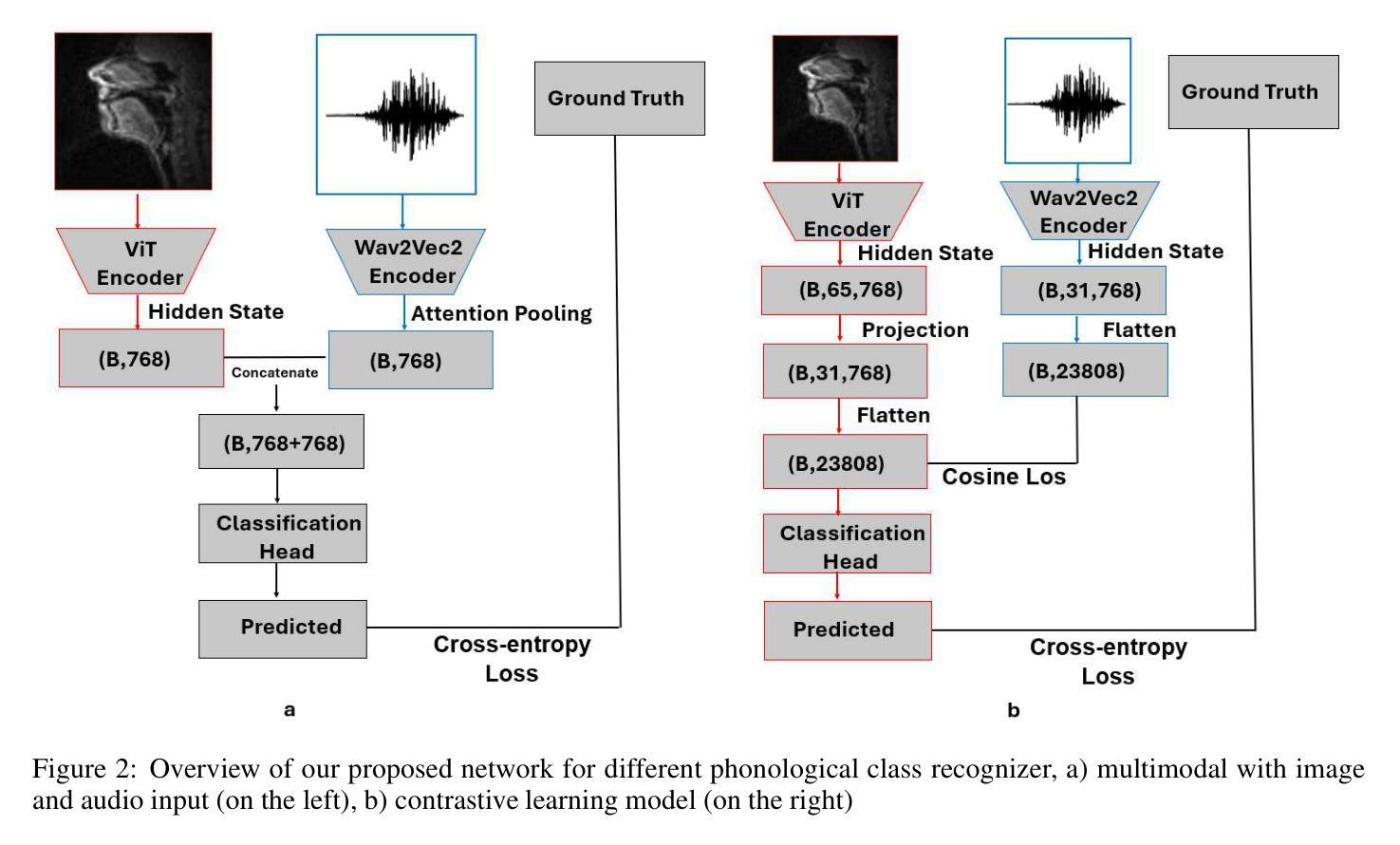
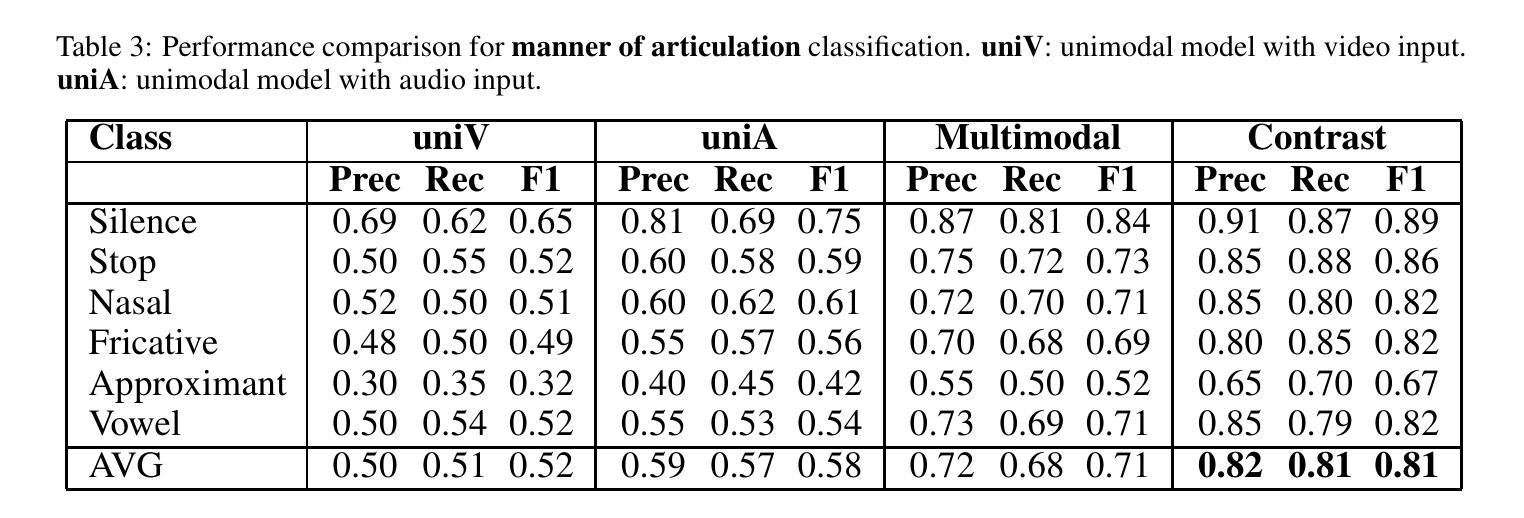
Audio-Vision Contrastive Learning for Phonological Class Recognition
Authors:Daiqi Liu, Tomás Arias-Vergara, Jana Hutter, Andreas Maier, Paula Andrea Pérez-Toro
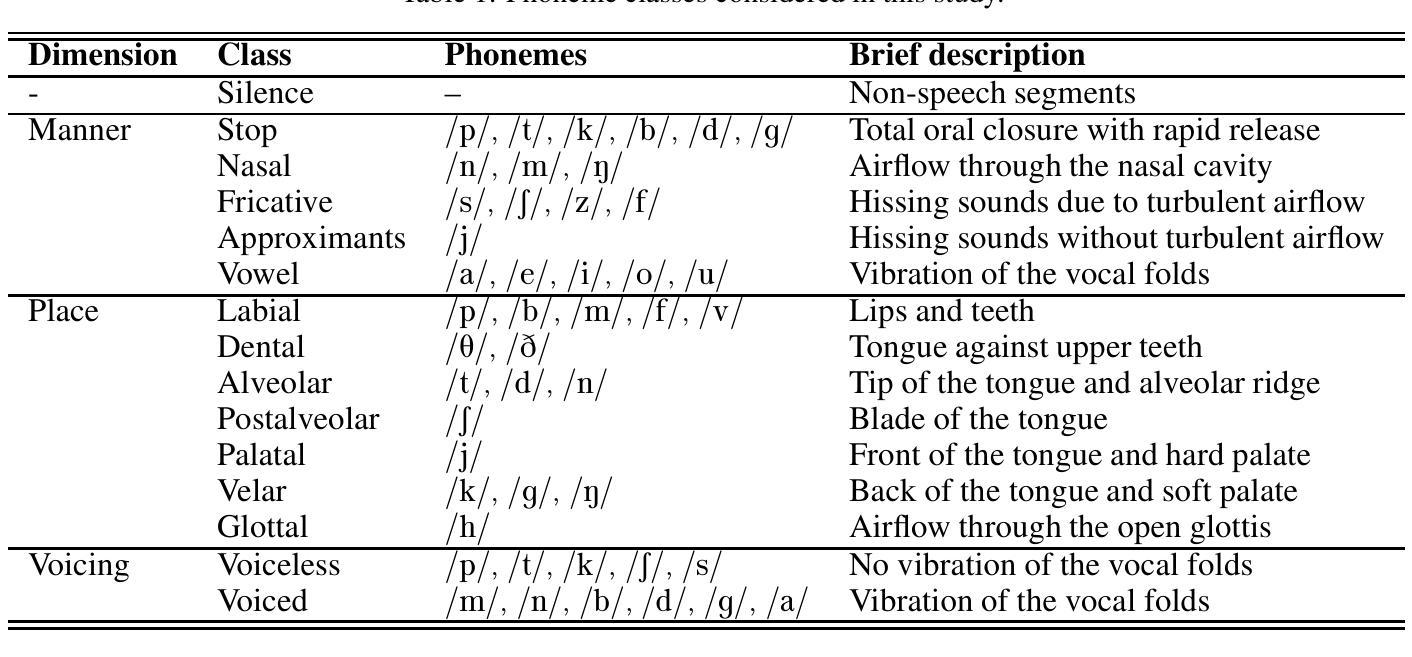
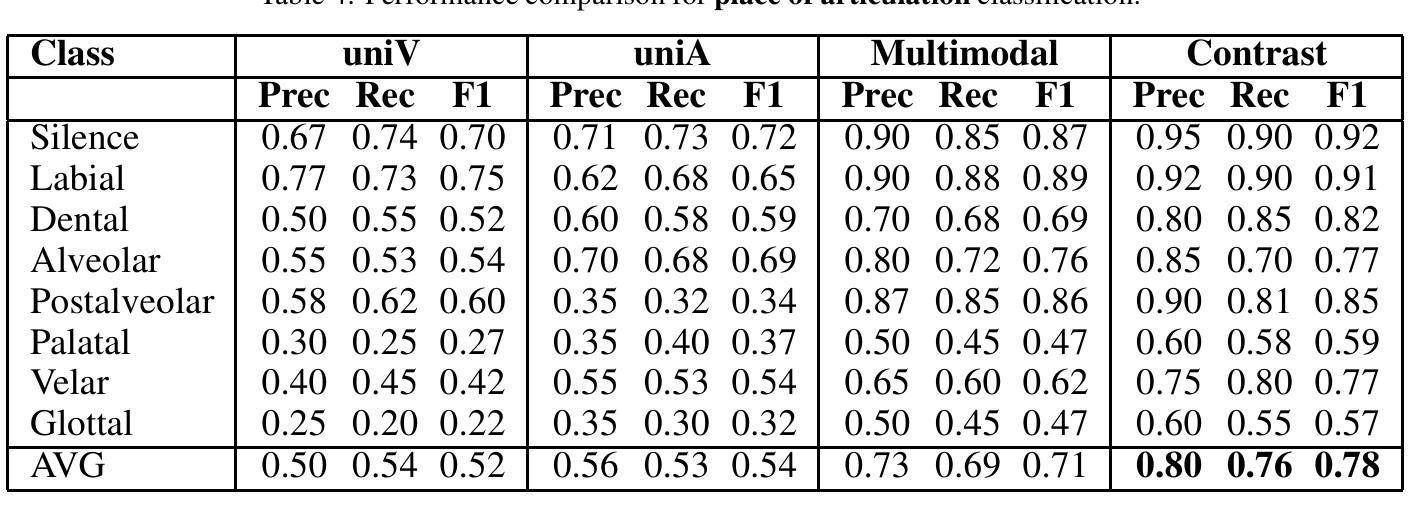
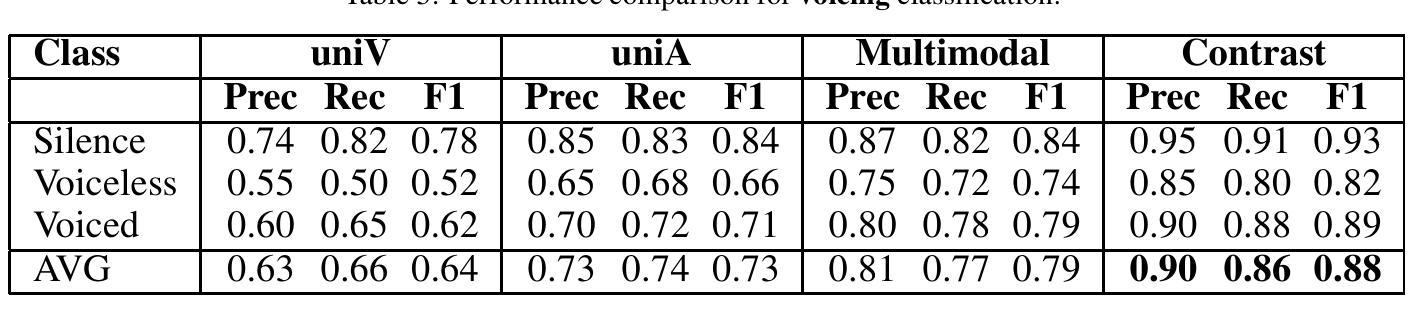
Accurate classification of articulatory-phonological features plays a vital role in understanding human speech production and developing robust speech technologies, particularly in clinical contexts where targeted phonemic analysis and therapy can improve disease diagnosis accuracy and personalized rehabilitation. In this work, we propose a multimodal deep learning framework that combines real-time magnetic resonance imaging (rtMRI) and speech signals to classify three key articulatory dimensions: manner of articulation, place of articulation, and voicing. We perform classification on 15 phonological classes derived from the aforementioned articulatory dimensions and evaluate the system with four audio/vision configurations: unimodal rtMRI, unimodal audio signals, multimodal middle fusion, and contrastive learning-based audio-vision fusion. Experimental results on the USC-TIMIT dataset show that our contrastive learning-based approach achieves state-of-the-art performance, with an average F1-score of 0.81, representing an absolute increase of 0.23 over the unimodal baseline. The results confirm the effectiveness of contrastive representation learning for multimodal articulatory analysis. Our code and processed dataset will be made publicly available at https://github.com/DaE-plz/AC_Contrastive_Phonology to support future research.
准确分类发音-音系特征对于理解人类言语产生和发展稳健的语音技术起着至关重要的作用,特别是在临床环境中,有针对性的音系分析和治疗可以提高疾病诊断的准确性和个性化的康复效果。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种多模态深度学习框架,结合了实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)和语音信号,对三个关键的发音维度进行分类:发音方式、发音部位和发声。我们对从上述发音维度派生的15个音系类别进行分类,并使用四种音频/视觉配置对系统进行评估:单模态rtMRI、单模态音频信号、多模态中间融合和基于对比学习的视听融合。在USC-TIMIT数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的基于对比学习的方法达到了最新性能,平均F1分数为0.81,比单模态基线提高了0.23。结果证实了对比表示学习在多模态发音分析中的有效性。我们的代码和处理后的数据集将在https://github.com/DaE-plz/AC_Contrastive_Phonology上公开,以支持未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF conference to TSD 2025
Summary
本文提出一种多模态深度学习框架,结合实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)和语音信号,对发音方式、发音部位和发音声音三个关键发音维度进行分类。在USC-TIMIT数据集上的实验结果表明,基于对比学习的多模态融合方法达到了最新的性能水平,平均F1分数为0.81,相对于单模态基线绝对提高了0.23。这证实了对比表示学习在模态发音分析中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 准确分类发音的三大维度:发音方式、发音部位和发音声音对于理解人类言语产生和研发稳健的语音技术至关重要,特别是在临床环境中。
- 提出了一种多模态深度学习框架,结合了实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)和语音信号进行分类。
- 对比学习在发音分析中的应用取得了显著成果,平均F1分数达到了0.81,相较于单模态基线有显著的提升。
- 对比表示学习在模态发音分析中的有效性得到了证实。
- 该研究公开了代码和处理过的数据集,以便支持未来的研究。
- 该方法在实际应用中可能有助于提高语音相关疾病的诊断准确性和个性化康复效果。
点此查看论文截图

CLAMP: Contrastive Learning with Adaptive Multi-loss and Progressive Fusion for Multimodal Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Authors:Xiaoqiang He
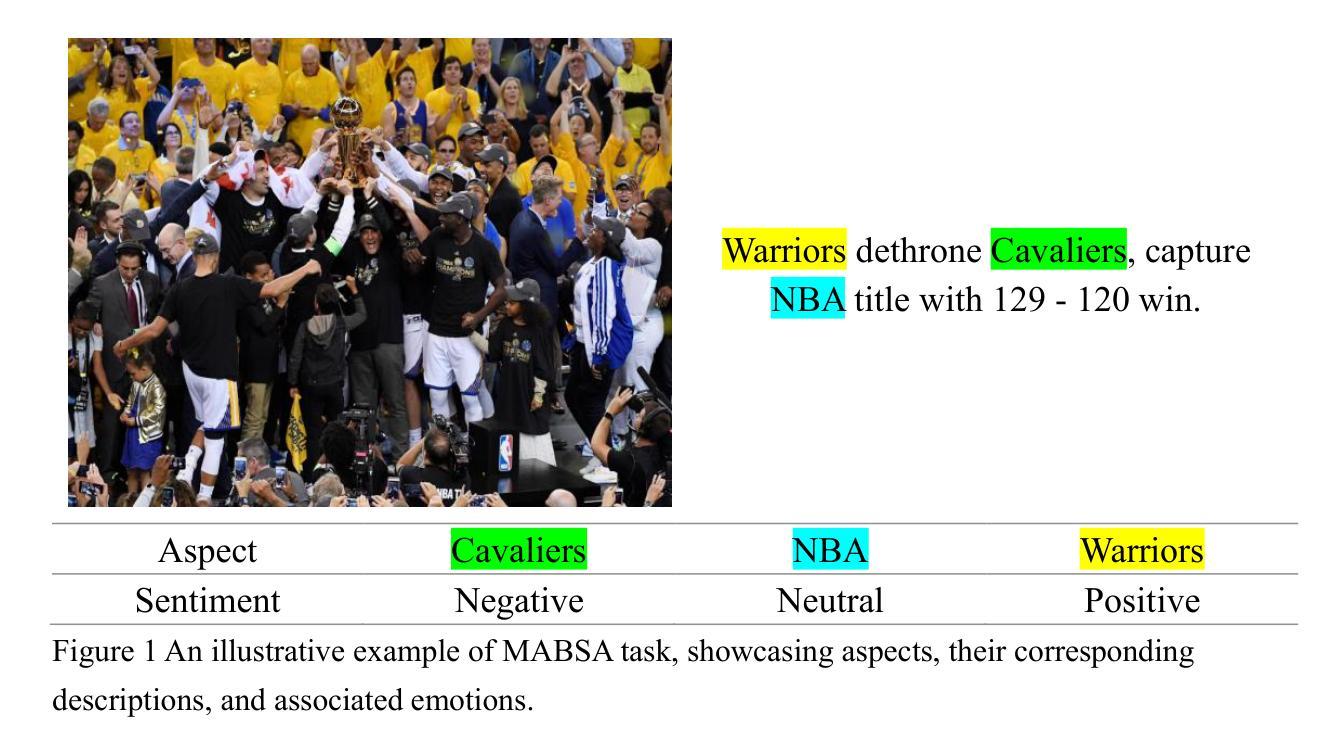
Multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis(MABSA) seeks to identify aspect terms within paired image-text data and determine their fine grained sentiment polarities, representing a fundamental task for improving the effectiveness of applications such as product review systems and public opinion monitoring. Existing methods face challenges such as cross modal alignment noise and insufficient consistency in fine-grained representations. While global modality alignment methods often overlook the connection between aspect terms and their corresponding local visual regions, bridging the representation gap between text and images remains a challenge. To address these limitations, this paper introduces an end to end Contrastive Learning framework with Adaptive Multi-loss and Progressive Attention Fusion(CLAMP). The framework is composed of three novel modules: Progressive Attention Fusion network, Multi-task Contrastive Learning, and Adaptive Multi-loss Aggregation. The Progressive Attention Fusion network enhances fine-grained alignment between textual features and image regions via hierarchical, multi-stage cross modal interactions, effectively suppressing irrelevant visual noise. Secondly, multi-task contrastive learning combines global modal contrast and local granularity alignment to enhance cross modal representation consistency. Adaptive Multi-loss Aggregation employs a dynamic uncertainty based weighting mechanism to calibrate loss contributions according to each task’s uncertainty, thereby mitigating gradient interference. Evaluation on standard public benchmarks demonstrates that CLAMP consistently outperforms the vast majority of existing state of the art methods.
多模态基于方面的情感分析(MABSA)旨在识别配对图像文本数据中的方面术语,并确定其细粒度情感极性,是改进产品评论系统和舆情监测等应用效果的基础任务。现有方法面临跨模态对齐噪声和细粒度表示一致性不足等挑战。虽然全局模态对齐方法往往忽略了方面术语与其对应的局部视觉区域之间的联系,但弥合文本和图像之间的表示差距仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这些局限性,本文引入了一种端到端的对比学习框架,该框架具有自适应多损失和渐进式注意力融合(CLAMP)。该框架由三个新颖模块组成:渐进式注意力融合网络、多任务对比学习和自适应多损失聚合。渐进式注意力融合网络通过分层多阶段跨模态交互,提高了文本特征和图像区域之间的精细对齐,有效地抑制了无关的视觉噪声。其次,多任务对比学习结合了全局模态对比和局部粒度对齐,以提高跨模态表示的一致性。自适应多损失聚合采用基于动态不确定性的加权机制,根据每项任务的不确定性来校准损失的贡献,从而减轻梯度干扰。在标准公共基准测试上的评估表明,CLAMP始终在绝大多数现有最先进的方法中表现优越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于对比学习的多模态面向方面的情感分析(MABSA)方法,旨在识别图像文本数据中的方面术语并确定其精细粒度的情感极性。针对现有方法的跨模态对齐噪声和精细粒度表示不一致等挑战,本文提出了一个端到端的对比学习框架CLAMP,包含渐进注意力融合网络、多任务对比学习和自适应多损失聚合三个模块。该框架能够更有效地进行文本与图像之间的跨模态对齐,从而在产品评论系统、公众意见监测等应用中实现更准确的情感分析。
Key Takeaways
- MABSA的目标是识别图像文本数据中的方面术语并确定其精细粒度的情感极性,对于产品评论系统和公众意见监测等应用至关重要。
- 现有方法在多模态面向方面的情感分析上面临跨模态对齐噪声和精细粒度表示不一致等挑战。
- CLAMP框架通过渐进注意力融合网络实现文本与图像之间的精细粒度对齐,通过多层次、多阶段的跨模态交互有效抑制无关的视觉噪声。
- 多任务对比学习结合了全局模态对比和局部粒度对齐,增强了跨模态表示的的一致性。
- 自适应多损失聚合根据任务的不确定性动态调整损失贡献的权重,减轻了梯度干扰的问题。
- 在公共标准基准上的评估表明,CLAMP框架在性能上持续超越了大多数现有最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

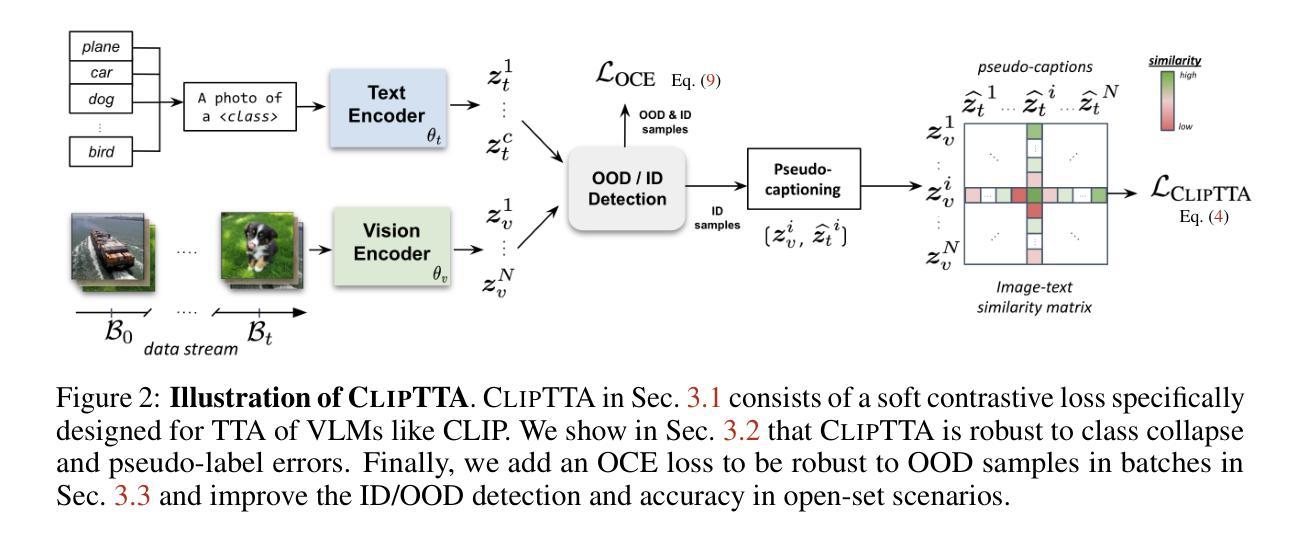
CLIPTTA: Robust Contrastive Vision-Language Test-Time Adaptation
Authors:Marc Lafon, Gustavo Adolfo Vargas Hakim, Clément Rambour, Christian Desrosier, Nicolas Thome
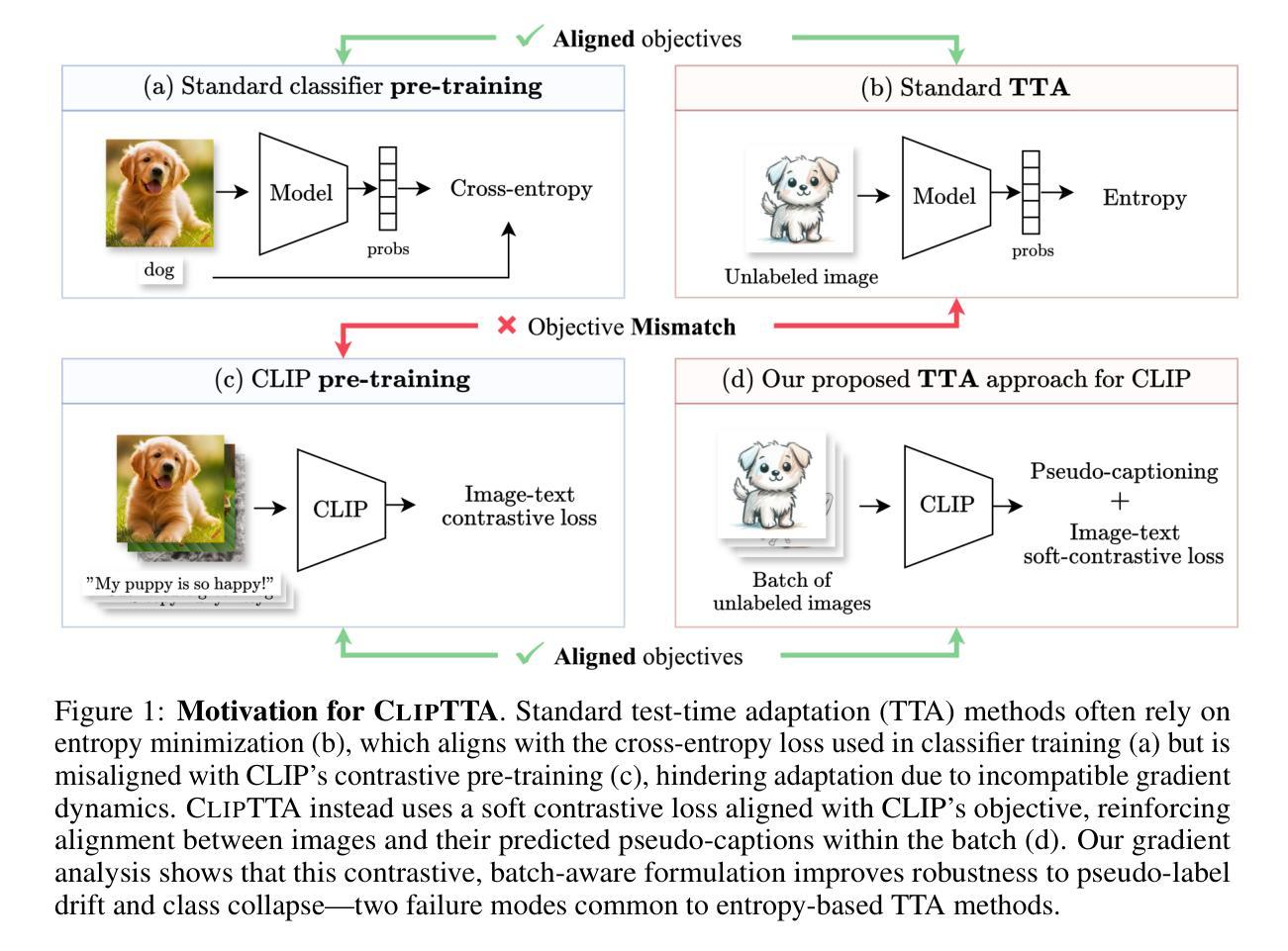
Vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP exhibit strong zero-shot capabilities but often fail to generalize under distribution shifts. Test-time adaptation (TTA) allows models to update at inference time without labeled data, typically via entropy minimization. However, this objective is fundamentally misaligned with the contrastive image-text training of VLMs, limiting adaptation performance and introducing failure modes such as pseudo-label drift and class collapse. We propose CLIPTTA, a new gradient-based TTA method for vision-language models that leverages a soft contrastive loss aligned with CLIP’s pre-training objective. We provide a theoretical analysis of CLIPTTA’s gradients, showing how its batch-aware design mitigates the risk of collapse. We further extend CLIPTTA to the open-set setting, where both in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) samples are encountered, using an Outlier Contrastive Exposure (OCE) loss to improve OOD detection. Evaluated on 75 datasets spanning diverse distribution shifts, CLIPTTA consistently outperforms entropy-based objectives and is highly competitive with state-of-the-art TTA methods, outperforming them on a large number of datasets and exhibiting more stable performance across diverse shifts.
视觉语言模型(如CLIP)表现出强大的零样本能力,但在分布变化时往往无法泛化。测试时适应(TTA)允许模型在推理时间无需标记数据进行更新,通常通过熵最小化实现。然而,这一目标与视觉语言模型的对比图像文本训练存在根本上的不一致,限制了适应性能,并引入了失败模式,如伪标签漂移和类别崩溃。我们提出了CLIPTTA,这是一种基于梯度的新TTA方法,用于视觉语言模型,它利用与CLIP预训练目标对齐的软对比损失。我们对CLIPTTA的梯度进行了理论分析,展示了其批处理感知设计如何缓解崩溃的风险。我们进一步将CLIPTTA扩展到开放集环境,在该环境中遇到既有的内部分布(ID)和未知的外部分布(OOD)样本,使用异常值对比曝光(OCE)损失来改善OOD检测。在涵盖多种分布变化的75个数据集上评估,CLIPTTA始终优于基于熵的目标,并与最先进的TTA方法竞争,在大多数数据集上表现优于它们,并在各种变化中表现出更稳定的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的测试时间自适应(TTA)新方法CLIPTTA。该方法利用与CLIP预训练目标对齐的软对比损失,通过梯度更新模型在推理时的性能。CLIPTTA具有缓解伪标签漂移和类别崩溃等问题的功能,并通过理论分析和实验验证其有效性。此外,CLIPTTA还扩展到开放集设置,使用异常值对比曝光(OCE)损失改进了检测未知样本的能力。在多个数据集上的评估表明,CLIPTTA在多种分布转移上表现稳定且优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways:
- CLIPTTA是一种针对视觉语言模型的测试时间自适应(TTA)方法,用于在推理时更新模型性能。
- CLIPTTA使用软对比损失,与CLIP的预训练目标对齐,以提高模型的泛化能力。
- CLIPTTA通过理论分析和实验验证具有缓解伪标签漂移和类别崩溃等问题的功能。
- CLIPTTA扩展到开放集设置,利用异常值对比曝光(OCE)损失提高检测未知样本的能力。
- CLIPTTA在多种分布转移上表现稳定,优于基于熵的目标和其他先进的TTA方法。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,CLIPTTA在大多数情况下都能取得良好的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

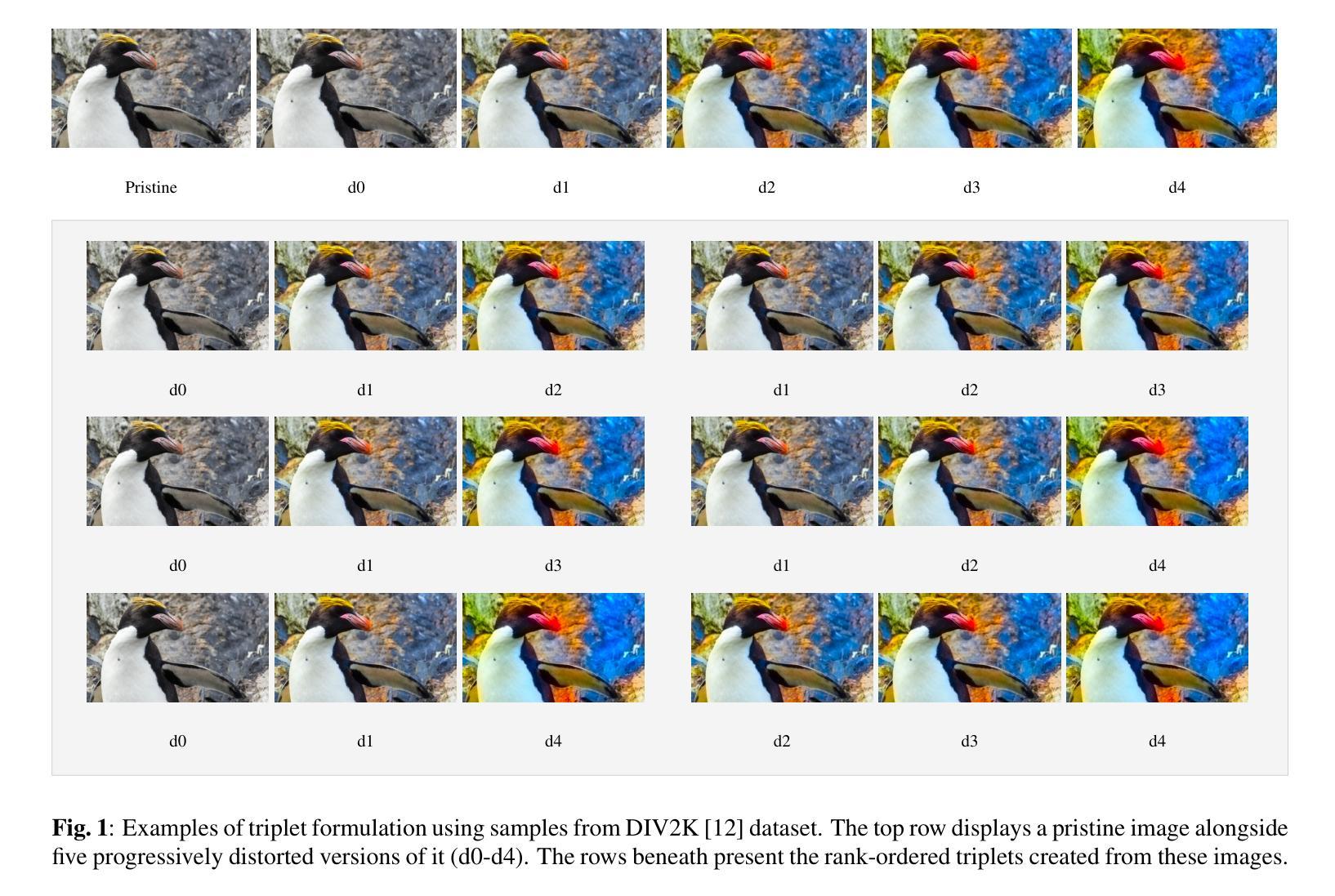
TRIQA: Image Quality Assessment by Contrastive Pretraining on Ordered Distortion Triplets
Authors:Rajesh Sureddi, Saman Zadtootaghaj, Nabajeet Barman, Alan C. Bovik
Image Quality Assessment (IQA) models aim to predict perceptual image quality in alignment with human judgments. No-Reference (NR) IQA remains particularly challenging due to the absence of a reference image. While deep learning has significantly advanced this field, a major hurdle in developing NR-IQA models is the limited availability of subjectively labeled data. Most existing deep learning-based NR-IQA approaches rely on pre-training on large-scale datasets before fine-tuning for IQA tasks. To further advance progress in this area, we propose a novel approach that constructs a custom dataset using a limited number of reference content images and introduces a no-reference IQA model that incorporates both content and quality features for perceptual quality prediction. Specifically, we train a quality-aware model using contrastive triplet-based learning, enabling efficient training with fewer samples while achieving strong generalization performance across publicly available datasets. Our repository is available at https://github.com/rajeshsureddi/triqa.
图像质量评估(IQA)模型旨在根据人类判断预测感知图像质量。无参考(NR)IQA仍然特别具有挑战性,因为缺少参考图像。虽然深度学习已经大大推动了这一领域的发展,但开发NR-IQA模型的主要障碍是主观标签数据的有限可用性。大多数现有的基于深度学习的NR-IQA方法依赖于在大型数据集上进行预训练,然后再对IQA任务进行微调。为了在这个领域进一步取得进展,我们提出了一种新的方法,使用有限数量的参考内容图像构建自定义数据集,并引入了一种无参考IQA模型,该模型结合了内容和质量特征进行感知质量预测。具体来说,我们使用基于对比三元组的学习方法来训练一个质量感知模型,可以在较少的样本上进行高效训练,同时在公开可用的数据集上实现强大的泛化性能。我们的仓库可在https://github.com/rajeshsureddi/triqa访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种新的无参考图像质量评估(NR-IQA)方法。该方法利用有限数量的参考内容图像构建自定义数据集,并引入一个结合内容和质量特征的NR-IQA模型进行感知质量预测。通过采用基于对比三元组学习的方法,该模型在有限样本训练下表现出强大的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于深度学习的无参考图像质量评估(NR-IQA)新方法。
- 构建自定义数据集,利用有限数量的参考内容图像进行训练。
- 引入了结合内容和质量特征的NR-IQA模型。
- 采用基于对比三元组学习的方法,提高模型泛化性能。
- 模型在公开数据集上表现出色。
- 提供了模型仓库链接,便于公众访问和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图

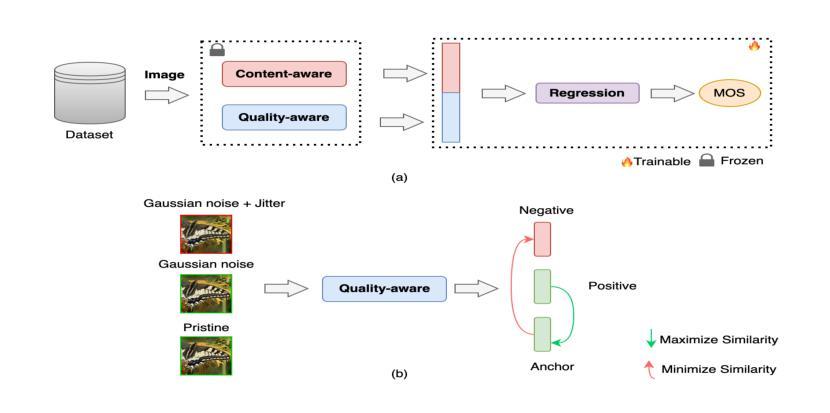
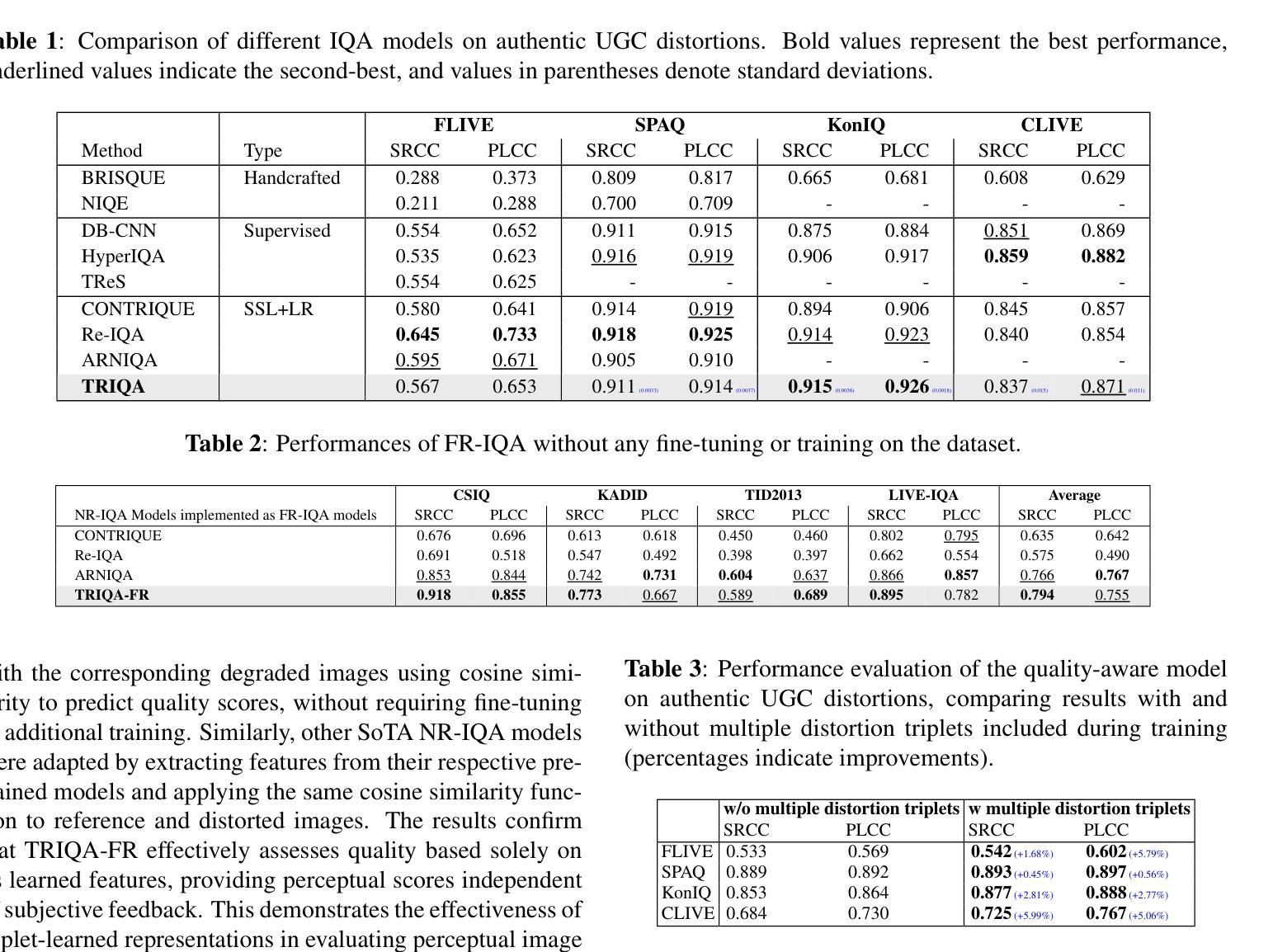
Language-Guided Contrastive Audio-Visual Masked Autoencoder with Automatically Generated Audio-Visual-Text Triplets from Videos
Authors:Yuchi Ishikawa, Shota Nakada, Hokuto Munakata, Kazuhiro Saito, Tatsuya Komatsu, Yoshimitsu Aoki
In this paper, we propose Language-Guided Contrastive Audio-Visual Masked Autoencoders (LG-CAV-MAE) to improve audio-visual representation learning. LG-CAV-MAE integrates a pretrained text encoder into contrastive audio-visual masked autoencoders, enabling the model to learn across audio, visual and text modalities. To train LG-CAV-MAE, we introduce an automatic method to generate audio-visual-text triplets from unlabeled videos. We first generate frame-level captions using an image captioning model and then apply CLAP-based filtering to ensure strong alignment between audio and captions. This approach yields high-quality audio-visual-text triplets without requiring manual annotations. We evaluate LG-CAV-MAE on audio-visual retrieval tasks, as well as an audio-visual classification task. Our method significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving up to a 5.6% improvement in recall@10 for retrieval tasks and a 3.2% improvement for the classification task.
本文提出了语言引导对比视听掩码自编码器(LG-CAV-MAE)以改进视听表示学习。LG-CAV-MAE将预训练的文本编码器集成到对比视听掩码自编码器中,使模型能够在音频、视觉和文本模式之间进行学习。为了训练LG-CAV-MAE,我们引入了一种自动生成未标注视频中的视听文本三元组的方法。首先,我们使用图像描述模型生成帧级别描述,然后应用基于CLAP的过滤技术以确保音频和描述之间的强对齐。这种方法能够在无需手动标注的情况下生成高质量的视听文本三元组。我们在视听检索任务和视听分类任务上评估了LG-CAV-MAE的性能。我们的方法显著优于现有方法,在检索任务上提高了高达5.6%的recall@10指标,在分类任务上提高了3.2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了Language-Guided Contrastive Audio-Visual Masked Autoencoders(LG-CAV-MAE)以改进音频视觉表示学习。LG-CAV-MAE结合了预训练的文本编码器,使得模型能够在音频、视觉和文本模式之间学习。训练过程中引入了自动从非标记视频中生成音频视觉文本三元组的方法。通过图像描述模型生成帧级描述,并采用CLAP基础过滤技术确保音频与描述之间的强对齐。此方法无需手动注释即可生成高质量的音频视觉文本三元组。在音频视觉检索任务和音频视觉分类任务上评估LG-CAV-MAE,该方法显著优于现有方法,检索任务提高了高达5.6%的recall@10,分类任务提高了3.2%。
Key Takeaways
- LG-CAV-MAE结合了预训练的文本编码器,实现跨音频、视觉和文本模式的学习。
- 训练LG-CAV-MAE时,引入了从非标记视频中自动生成音频视觉文本三元组的方法。
- 通过图像描述模型生成帧级描述,确保音频与描述之间的强对齐。
- 该方法无需手动注释即可生成高质量的音频视觉文本三元组。
- LG-CAV-MAE在音频视觉检索任务上表现优异,提高了召回率。
- LG-CAV-MAE在音频视觉分类任务上也有显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图

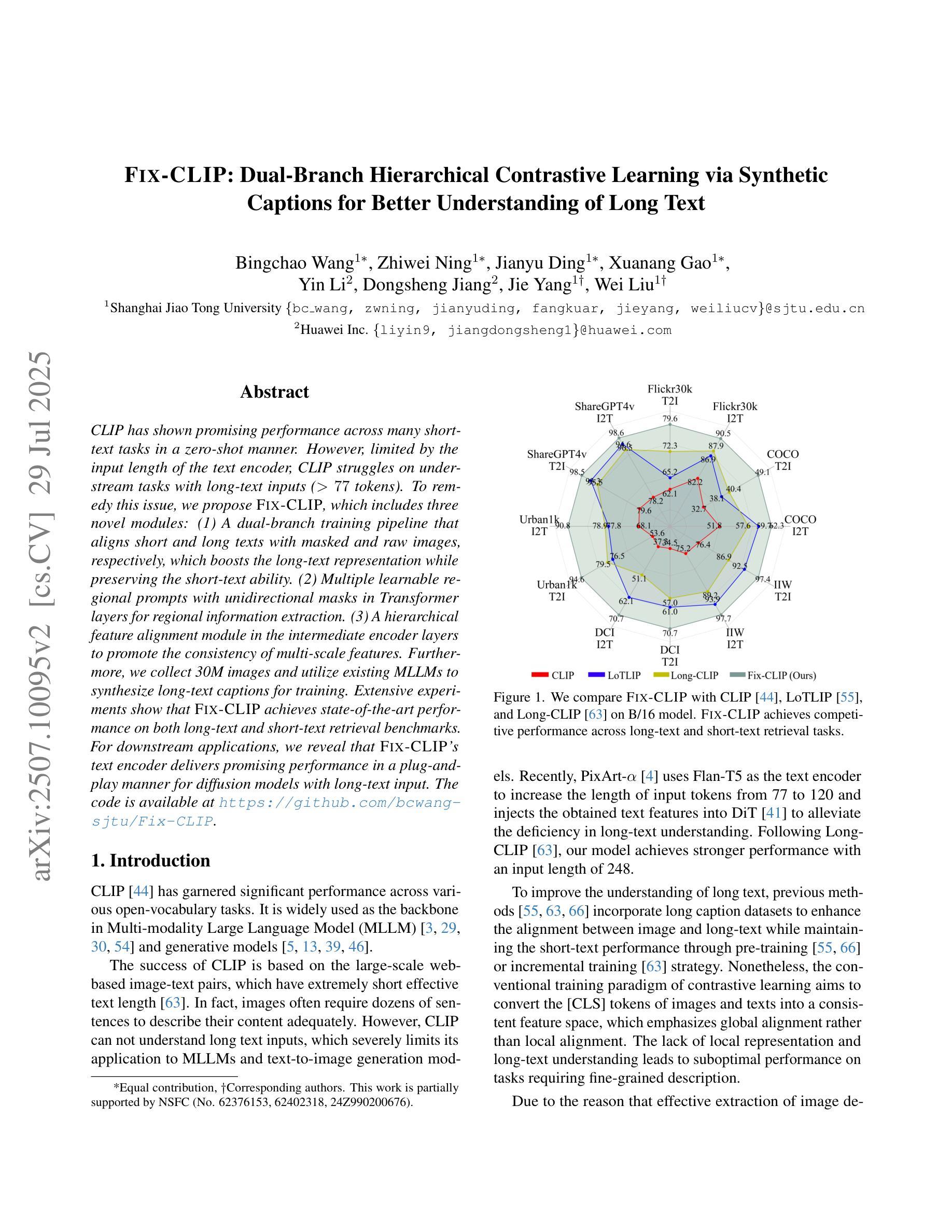
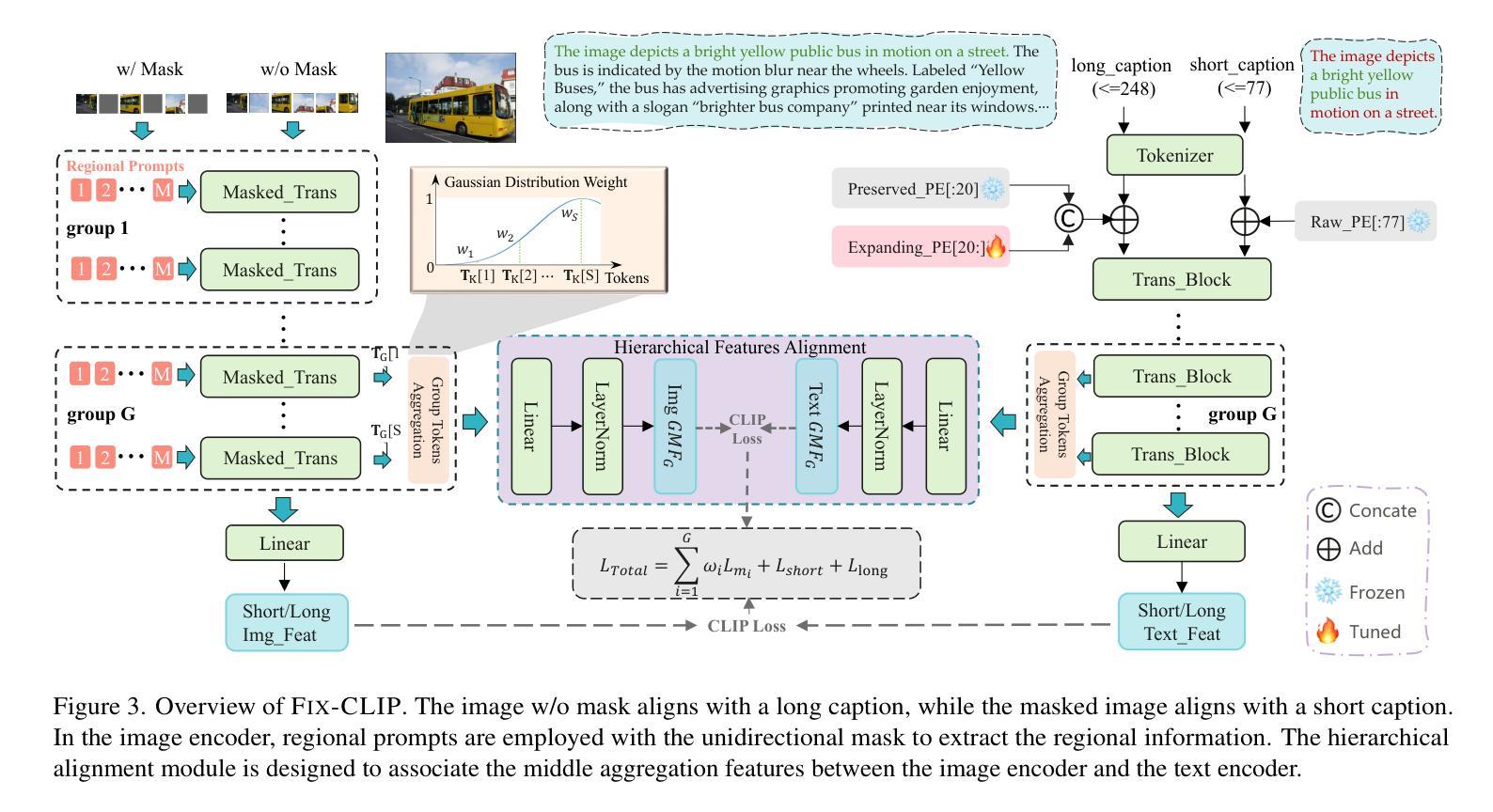
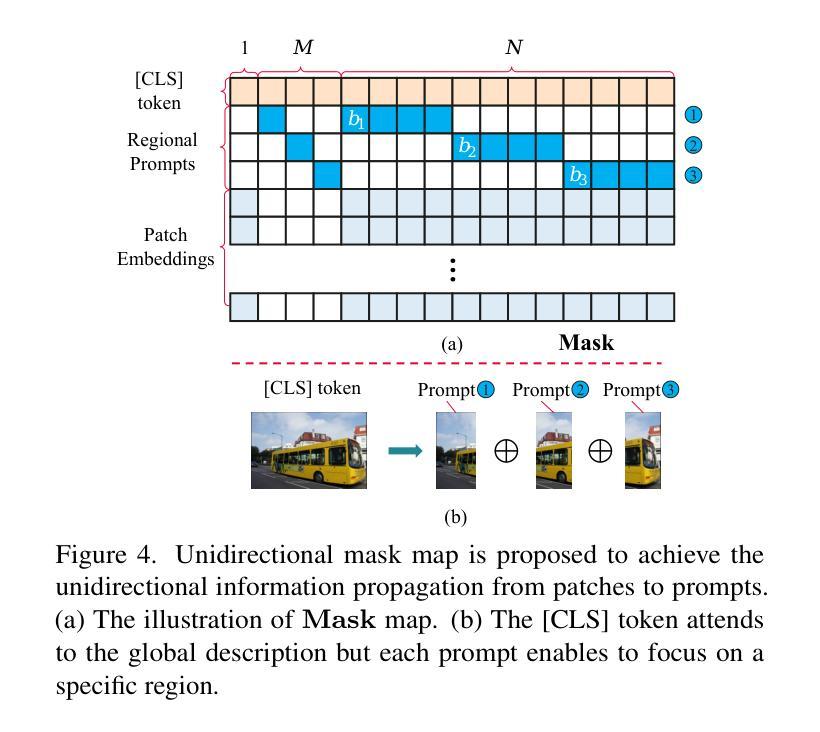
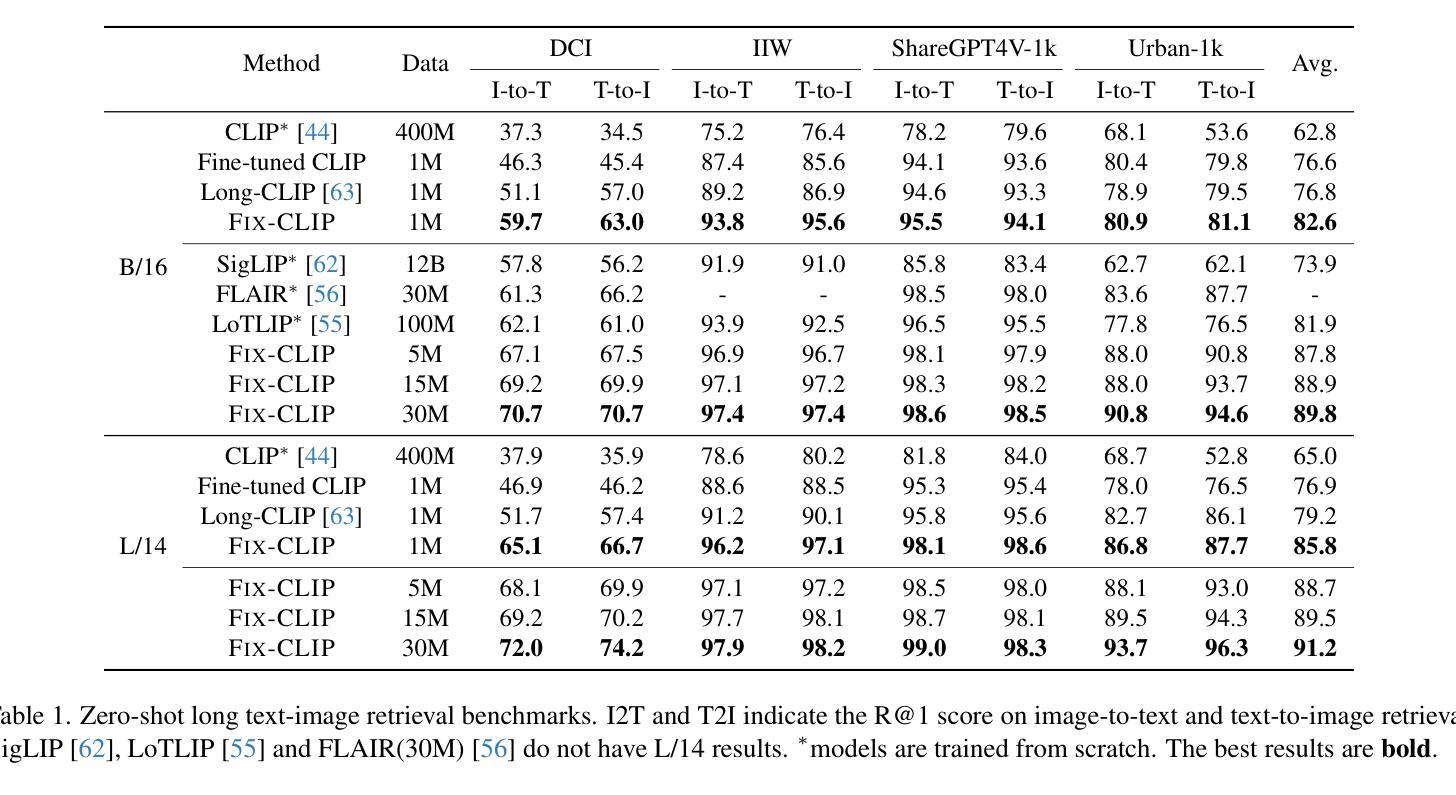
FIX-CLIP: Dual-Branch Hierarchical Contrastive Learning via Synthetic Captions for Better Understanding of Long Text
Authors:Bingchao Wang, Zhiwei Ning, Jianyu Ding, Xuanang Gao, Yin Li, Dongsheng Jiang, Jie Yang, Wei Liu
CLIP has shown promising performance across many short-text tasks in a zero-shot manner. However, limited by the input length of the text encoder, CLIP struggles on under-stream tasks with long-text inputs ($>77$ tokens). To remedy this issue, we propose FIX-CLIP, which includes three novel modules: (1) A dual-branch training pipeline that aligns short and long texts with masked and raw images, respectively, which boosts the long-text representation while preserving the short-text ability. (2) Multiple learnable regional prompts with unidirectional masks in Transformer layers for regional information extraction. (3) A hierarchical feature alignment module in the intermediate encoder layers to promote the consistency of multi-scale features. Furthermore, we collect 30M images and utilize existing MLLMs to synthesize long-text captions for training. Extensive experiments show that FIX-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on both long-text and short-text retrieval benchmarks. For downstream applications, we reveal that FIX-CLIP’s text encoder delivers promising performance in a plug-and-play manner for diffusion models with long-text input. The code is available at https://github.com/bcwang-sjtu/Fix-CLIP.
CLIP在许多短文本任务中表现出了零样本方式下的良好性能。然而,由于文本编码器的输入长度限制,CLIP在处理长文本输入(>77个标记)的流式任务时面临困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP,它包括三个新颖模块:(1)双分支训练管道,分别用掩码和原始图像对齐短文本和长文本,这提高了长文本表示能力的同时保留了短文本的能力。(2)在Transformer层中使用带有单向掩码的可学习多个区域提示来进行区域信息提取。(3)在中间编码器层中的分层特征对齐模块,以促进多尺度特征的一致性。此外,我们收集了3000万张图像,并利用现有的大型语言模型来合成长文本描述进行训练。大量实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长文本和短文本检索基准测试上均达到了最先进的性能。对于下游应用,我们揭示了FIX-CLIP的文本编码器在具有长文本输入的扩散模型中即插即用方式下具有良好的性能。代码可在https://github.com/bcwang-sjtu/Fix-CLIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
CLIP模型在许多短文本任务中表现出色,但在处理长文本输入时存在局限性。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FIX-CLIP模型,包含三个新模块:双分支训练管道、带有单向掩码的多区域提示和中间编码器层中的分层特征对齐模块。我们还收集了30M图像,并利用现有大型语言模型合成长文本描述进行训练。实验表明,FIX-CLIP在长短文本检索基准测试中均达到领先水平,并在下游应用中表现出良好的即插即用性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在处理长文本输入时存在局限性。
- FIX-CLIP通过三个新模块解决CLIP在长文本处理上的问题:双分支训练管道、多区域提示和分层特征对齐。
- FIX-CLIP模型通过收集30M图像和现有大型语言模型合成长文本描述进行训练。
- FIX-CLIP在长短文本检索基准测试中表现优秀。
- FIX-CLIP的文本编码器在下游应用中具有即插即用的性能优势。
- FIX-CLIP的代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

CL-Polyp: A Contrastive Learning-Enhanced Network for Accurate Polyp Segmentation
Authors:Desheng Li, Chaoliang Liu, Zhiyong Xiao
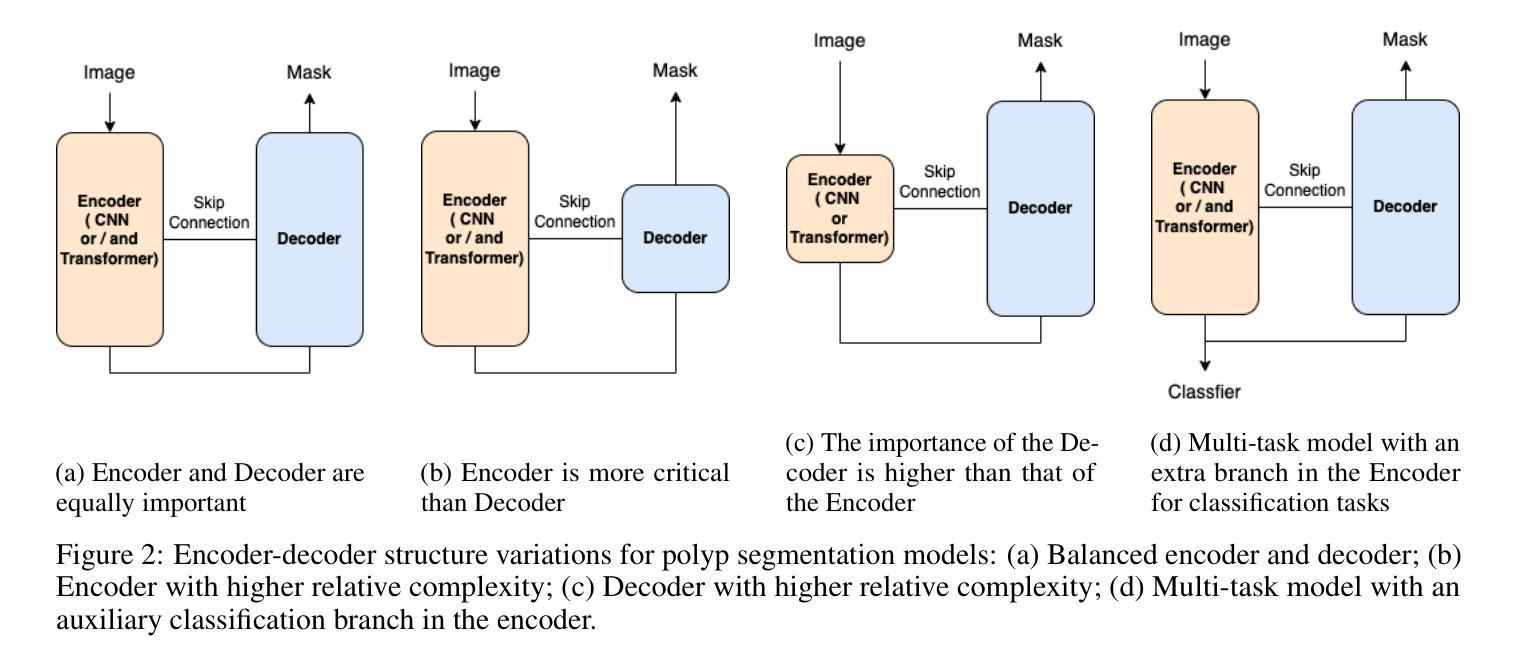
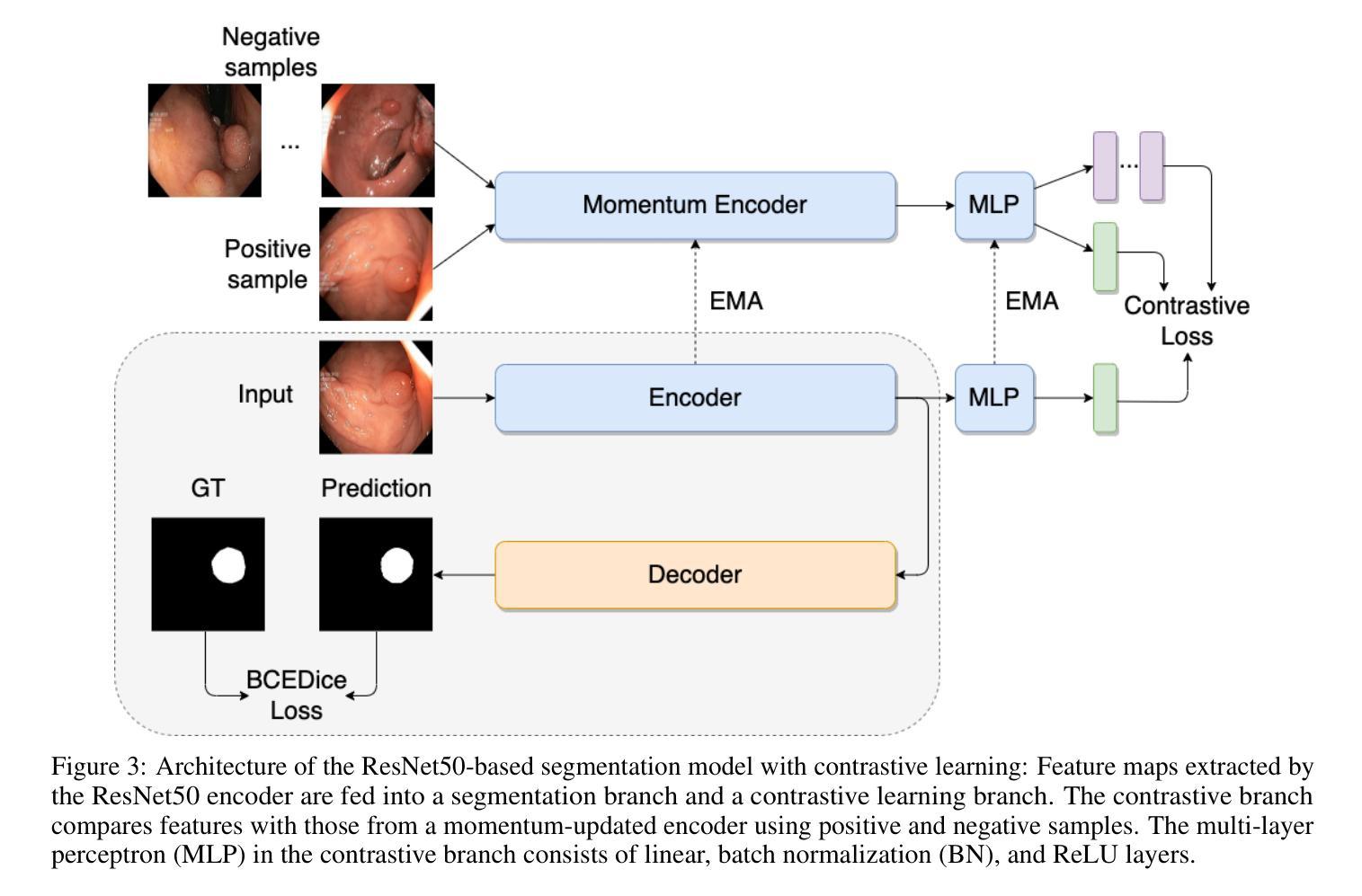
Accurate segmentation of polyps from colonoscopy images is crucial for the early diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Most existing deep learning-based polyp segmentation methods adopt an Encoder-Decoder architecture, and some utilize multi-task frameworks that incorporate auxiliary tasks like classification to improve segmentation. However, these methods often need more labeled data and depend on task similarity, potentially limiting generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose CL-Polyp, a contrastive learning-enhanced polyp segmentation network. Our method uses contrastive learning to enhance the encoder’s extraction of discriminative features by contrasting positive and negative sample pairs from polyp images. This self-supervised strategy improves visual representation without needing additional annotations. We also introduce two efficient, lightweight modules: the Modified Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (MASPP) module for improved multi-scale feature fusion, and the Channel Concatenate and Element Add (CA) module to merge low-level and upsampled features for {enhanced} boundary reconstruction. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets-Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ClinicDB, CVC-ColonDB, CVC-300, and ETIS-show that CL-Polyp consistently surpasses state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, it enhances the IoU metric by 0.011 and 0.020 on the Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB datasets, respectively, demonstrating its effectiveness in clinical polyp segmentation.
在结肠镜图像中对息肉进行精确分割对于结直肠癌的早期诊断和治疗至关重要。现有的大多数基于深度学习的息肉分割方法采用编码器-解码器架构,一些方法还利用多任务框架,结合分类等辅助任务来提高分割效果。然而,这些方法通常需要更多的标记数据,并依赖于任务相似性,从而可能限制了其泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CL-Polyp,一种增强对比学习的息肉分割网络。我们的方法使用对比学习来增强编码器提取判别特征的能力,通过对比息肉图像中的正负样本对。这种自监督策略在不需要额外注释的情况下提高了视觉表示。我们还引入了两个高效、轻量级的模块:用于改进多尺度特征融合的改进型空洞空间金字塔池化(MASPP)模块,以及用于合并低级和上采样特征的通道合并和元素添加(CA)模块,以增强边界重建。在Kvasir-SEG、CVC-ClinicDB、CVC-ColonDB、CVC 结直肠数据库和ETIS等五个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,CL-Polyp始终超越了最先进的方法。具体而言,它在Kvasir-SEG和CVC-ClinicDB数据集上分别将IoU指标提高了0.011和0.020,证明了其在临床息肉分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于对比学习的结肠息肉分割网络CL-Polyp,采用对比学习增强编码器提取判别特征的能力,通过对比结肠息肉图像中的正负样本对,提高视觉表征能力,而无需额外的标注。同时引入两个高效轻量级模块——改进的膨胀空间金字塔池化(MASPP)模块和通道合并与元素添加(CA)模块,分别用于改进多尺度特征融合和合并低级别与上采样特征以增强边界重建。在五个基准数据集上的实验表明,CL-Polyp的性能优于现有技术,特别是在Kvasir-SEG和CVC-ClinicDB数据集上,交并比(IoU)指标分别提高了0.011和0.020。
Key Takeaways
- 结肠息肉的准确分割对早期结肠癌诊断和治疗至关重要。
- 现有基于深度学习的结肠息肉分割方法通常采用Encoder-Decoder架构,并借助多任务框架提高分割性能。
- 提出了一种基于对比学习的结肠息肉分割网络CL-Polyp,利用对比学习提高编码器提取判别特征的能力。
- CL-Polyp通过对比结肠息肉图像中的正负样本对进行自监督学习,提高视觉表征能力且无需额外标注。
- CL-Polyp引入两个轻量级模块,用于改进多尺度特征融合和边界重建。
- 在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,CL-Polyp性能优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

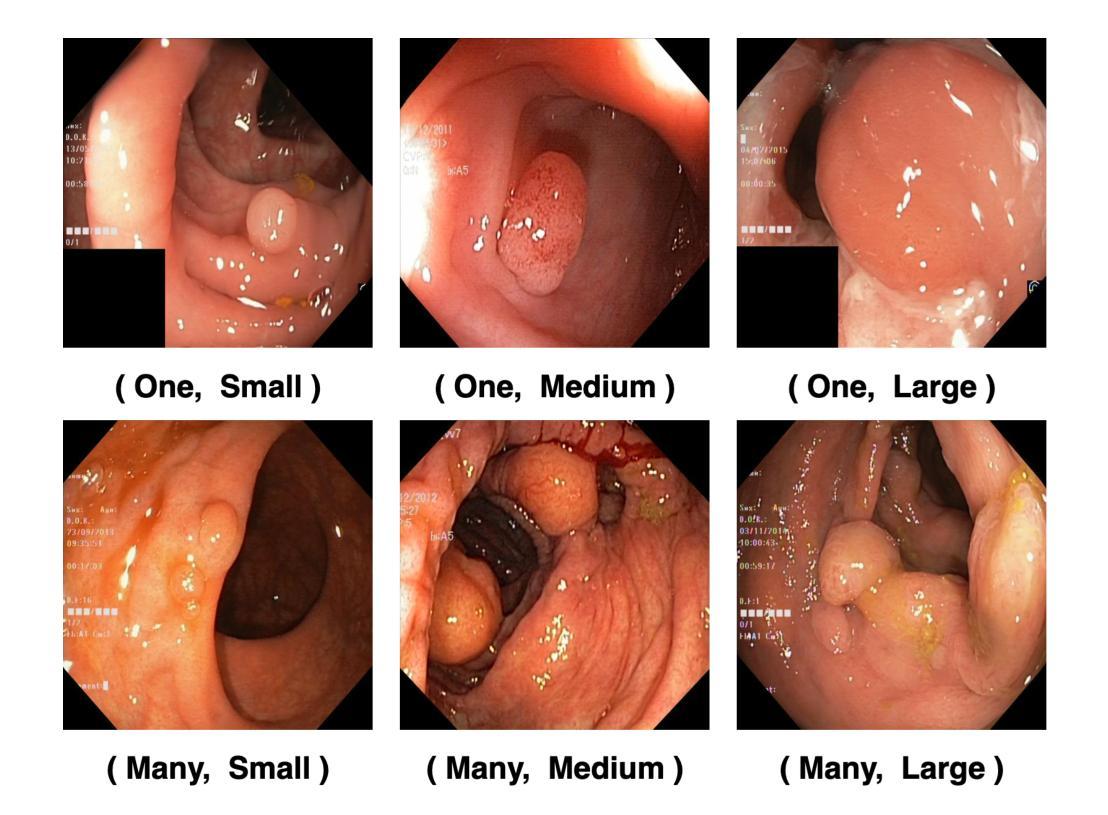
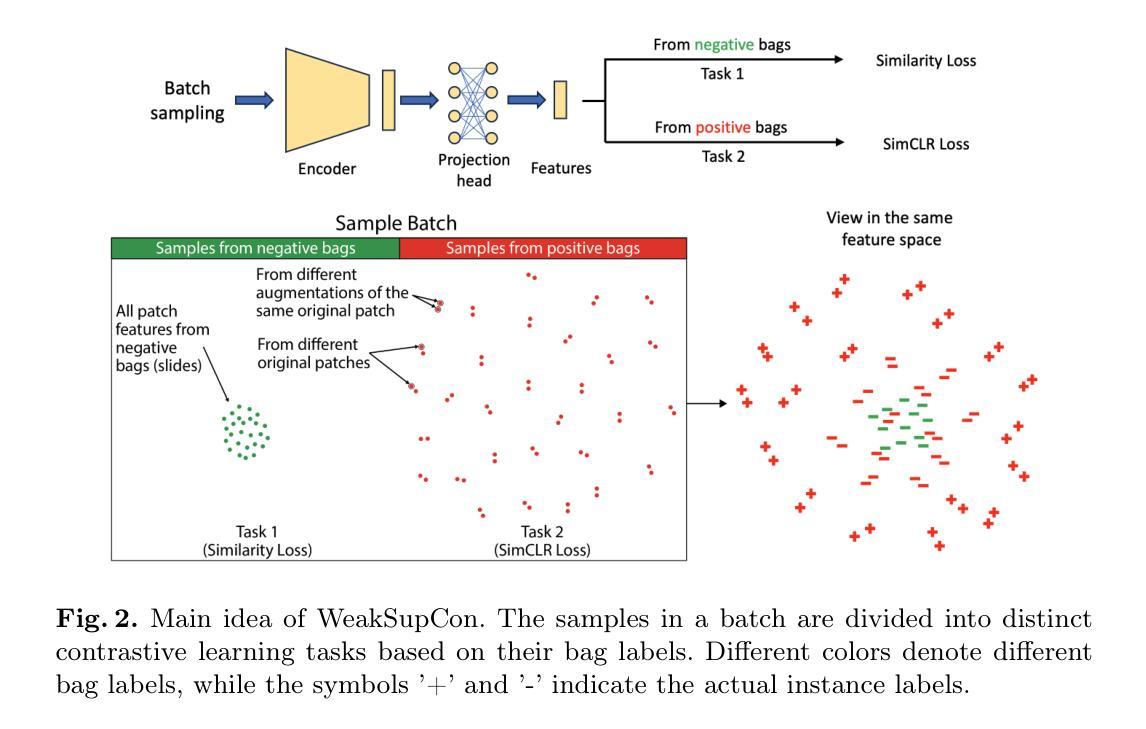
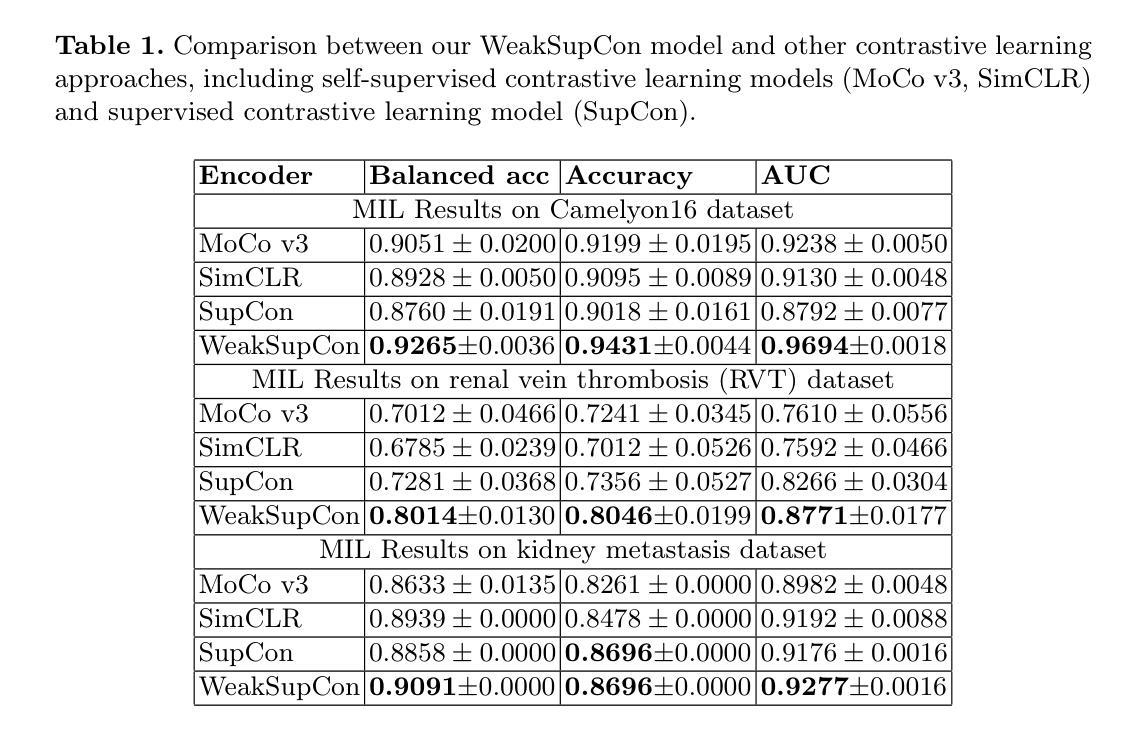
WeakSupCon: Weakly Supervised Contrastive Learning for Encoder Pre-training
Authors:Bodong Zhang, Hamid Manoochehri, Xiwen Li, Beatrice S. Knudsen, Tolga Tasdizen
Weakly supervised multiple instance learning (MIL) is a challenging task given that only bag-level labels are provided, while each bag typically contains multiple instances. This topic has been extensively studied in histopathological image analysis, where labels are usually available only at the whole slide image (WSI) level, while each WSI could be divided into thousands of small image patches for training. The dominant MIL approaches focus on feature aggregation and take fixed patch features as inputs. However, weakly supervised feature representation learning in MIL settings is always neglected. Those features used to be generated by self-supervised learning methods that do not utilize weak labels, or by foundation encoders pre-trained on other large datasets. In this paper, we propose a novel weakly supervised feature representation learning method called Weakly Supervised Contrastive Learning (WeakSupCon) that utilizes bag-level labels. In our method, we employ multi-task learning and define distinct contrastive losses for samples with different bag labels. Our experiments demonstrate that the features generated using WeakSupCon with limited computing resources significantly enhance MIL classification performance compared to self-supervised approaches across three datasets. Our WeakSupCon code is available at github.com/BzhangURU/Paper_WeakSupCon
弱监督多实例学习(MIL)是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为只提供袋级标签,而每个袋中通常包含多个实例。这一话题在病理图像分析中得到广泛研究,通常整个幻灯片图像(WSI)级别的标签可用,而每个WSI可以被划分为数千个小图像块用于训练。主流的MIL方法侧重于特征聚合,并以固定的补丁特征作为输入。然而,在MIL设置中,弱监督特征表示学习一直被忽视。这些特征通常是通过不利用弱标签的自我监督学习方法生成,或者由在其他大型数据集上预训练的基础编码器生成。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的弱监督特征表示学习方法,称为Weakly Supervised Contrastive Learning(WeakSupCon),该方法利用袋级标签。在我们的方法中,我们采用多任务学习,并为具有不同袋标签的样本定义不同的对比损失。我们的实验表明,使用有限的计算资源,通过WeakSupCon生成的特征显著提高了与三个数据集中的自我监督方法相比的MIL分类性能。我们的WeakSupCon代码可在github.com/BzhangURU/Paper_WeakSupCon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2025 workshop on Efficient Medical AI
Summary
弱监督多实例学习(MIL)是一个挑战任务,仅提供袋级标签,而每个袋中通常包含多个实例。本文提出一种名为WeakSupCon的弱监督对比学习新方法,利用袋级标签进行特征表示学习。该方法采用多任务学习,为不同袋标签的样本定义不同的对比损失。实验表明,使用WeakSupCon生成的特征在有限的计算资源下,相较于自监督方法,能显著提高MIL分类性能。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督多实例学习(MIL)在仅提供袋级标签的情况下是一个挑战,特别是在病理图像分析领域。
- 现有的MIL方法主要关注特征聚合,而忽略了在弱监督环境下的特征表示学习。
- 本文提出了一种新的弱监督对比学习方法WeakSupCon,该方法利用袋级标签。
- WeakSupCon采用多任务学习,并为不同袋标签的样本定义特定的对比损失。
- 实验表明,WeakSupCon在有限的计算资源下,能显著提高MIL分类性能,优于自监督方法。
- WeakSupCon代码已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

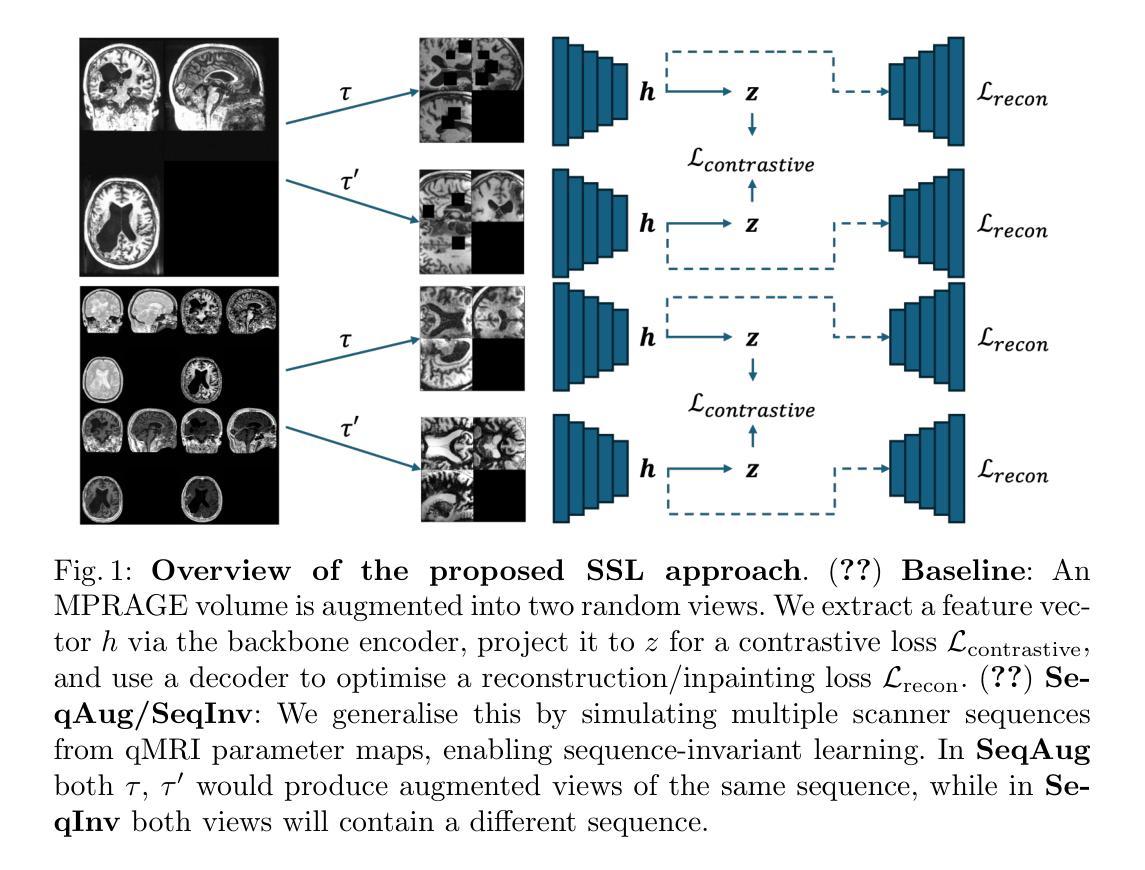
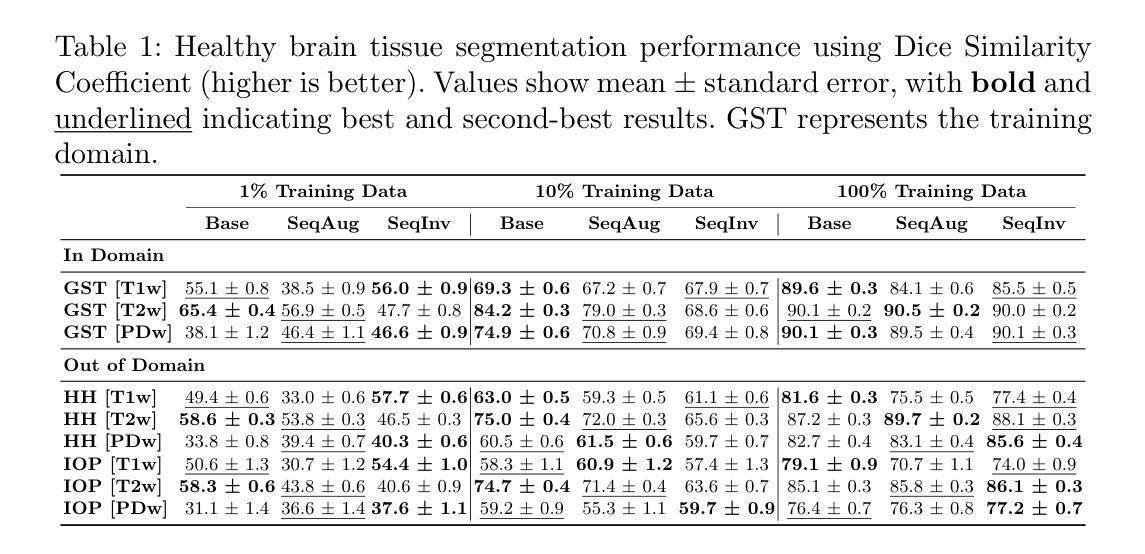
Unified 3D MRI Representations via Sequence-Invariant Contrastive Learning
Authors:Liam Chalcroft, Jenny Crinion, Cathy J. Price, John Ashburner
Self-supervised deep learning has accelerated 2D natural image analysis but remains difficult to translate into 3D MRI, where data are scarce and pre-trained 2D backbones cannot capture volumetric context. We present a \emph{sequence-invariant} self-supervised framework leveraging quantitative MRI (qMRI). By simulating multiple MRI contrasts from a single 3D qMRI scan and enforcing consistent representations across these contrasts, we learn anatomy-centric rather than sequence-specific features. The result is a single 3D encoder that excels across tasks and protocols. Experiments on healthy brain segmentation (IXI), stroke lesion segmentation (ARC), and MRI denoising show significant gains over baseline SSL approaches, especially in low-data settings (up to +8.3% Dice, +4.2 dB PSNR). It also generalises to unseen sites, supporting scalable clinical use. Code and trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/liamchalcroft/contrast-squared
自监督深度学习已经加速了2D自然图像分析,但将其转化为3D MRI仍然很困难,因为MRI数据稀缺,预训练的2D主结构无法捕捉体积上下文信息。我们提出了一种利用定量MRI(qMRI)的序列不变自监督框架。通过模拟从单个3D qMRI扫描中获得的多重MRI对比度,并强制这些对比度之间保持一致的表示,我们学习到的是以解剖为中心而非特定序列的特征。结果是一个单一的3D编码器,它在各种任务和协议中都表现出色。在健康大脑分割(IXI)、中风病灶分割(ARC)和MRI去噪实验上,与传统的自监督学习方法相比,我们的方法取得了显著的改进,特别是在数据较少的情况下(最高可达+8.3%的Dice系数,+4.2 dB的PSNR)。它还适用于未见过的站点,支持可扩展的临床使用。相关代码和训练模型已在https://github.com/liamchalcroft/contrast-squared公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用定量MRI(qMRI)的序列不变性自监督框架,通过模拟单一3D qMRI扫描的多种MRI对比并强制这些对比之间保持一致的表示,学习以解剖为中心而非特定序列的特征。该框架实现了跨任务和协议的单一3D编码器,在健康大脑分割(IXI)、中风病灶分割(ARC)和MRI去噪方面表现出显著的优势,特别是在低数据设置下。此外,它还能够推广到未见过的站点,支持可扩展的临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- 利用定量MRI(qMRI)进行序列不变性自监督学习。
- 通过模拟多种MRI对比来增强自监督学习效果。
- 框架实现了跨任务和协议的单一3D编码器。
- 在不同实验(如健康大脑分割、中风病灶分割和MRI去噪)中相比基础SSL方法取得了显著优势。
- 在低数据设置下表现优异,提升了达+8.3%的Dice系数和+4.2 dB的PSNR。
- 模型能够推广到未见过的站点,支持可扩展的临床应用。
点此查看论文截图

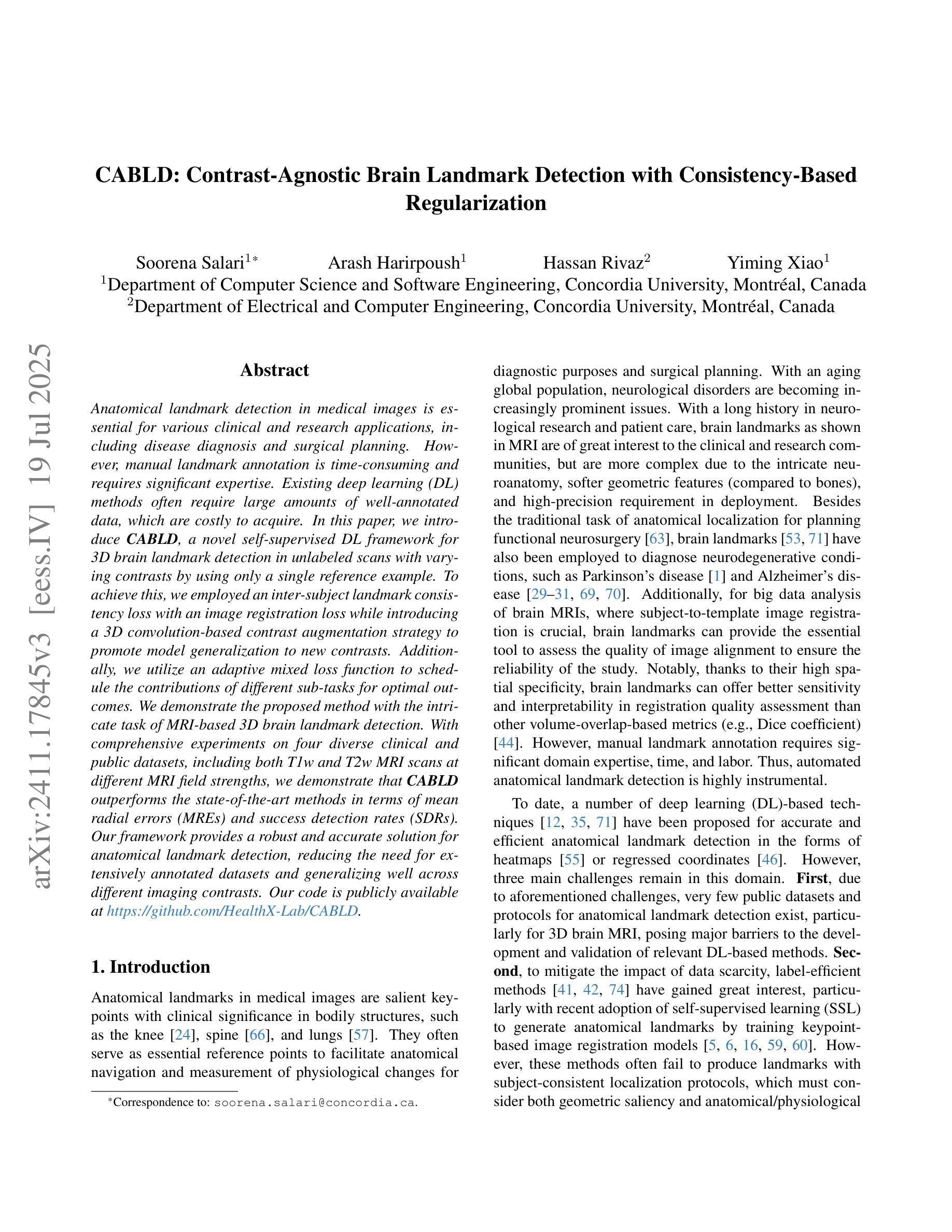
CABLD: Contrast-Agnostic Brain Landmark Detection with Consistency-Based Regularization
Authors:Soorena Salari, Arash Harirpoush, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Anatomical landmark detection in medical images is essential for various clinical and research applications, including disease diagnosis and surgical planning. However, manual landmark annotation is time-consuming and requires significant expertise. Existing deep learning (DL) methods often require large amounts of well-annotated data, which are costly to acquire. In this paper, we introduce CABLD, a novel self-supervised DL framework for 3D brain landmark detection in unlabeled scans with varying contrasts by using only a single reference example. To achieve this, we employed an inter-subject landmark consistency loss with an image registration loss while introducing a 3D convolution-based contrast augmentation strategy to promote model generalization to new contrasts. Additionally, we utilize an adaptive mixed loss function to schedule the contributions of different sub-tasks for optimal outcomes. We demonstrate the proposed method with the intricate task of MRI-based 3D brain landmark detection. With comprehensive experiments on four diverse clinical and public datasets, including both T1w and T2w MRI scans at different MRI field strengths, we demonstrate that CABLD outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of mean radial errors (MREs) and success detection rates (SDRs). Our framework provides a robust and accurate solution for anatomical landmark detection, reducing the need for extensively annotated datasets and generalizing well across different imaging contrasts. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CABLD.
医学图像中的解剖标志点检测对于各种临床和研究应用至关重要,包括疾病诊断和手术规划。然而,手动标注标志点既耗时又需要丰富的专业知识。现有的深度学习(DL)方法通常需要大量标注好的数据,而这些数据的获取成本高昂。在本文中,我们介绍了CABLD,这是一种新型的自监督深度学习框架,可用于在未标记的扫描图像中对3D脑标志点进行检测,通过使用仅一个参考样本即可应对不同对比度的图像。为实现这一点,我们采用了主体间标志点一致性损失和图像配准损失,同时引入了一种基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,以促进模型对新对比度图像的泛化能力。此外,我们还采用了一种自适应混合损失函数,以调度不同子任务的贡献以获取最佳结果。我们通过基于MRI的3D脑标志点检测这一复杂任务来展示所提出的方法。我们在四个不同的临床和公共数据集上进行了全面的实验,包括不同MRI场强的T1w和T -论文工作中有很多医学专有名词的表达不太明确或不存在直接对应的中文表达,在翻译过程中可能需要结合专业背景进行一定的解释或再表述。尽管如此,我会尽力提供一个准确的翻译。如有需要,请咨询医学领域的专业人士以获取更准确的解释和翻译。以下是基于您提供的文本进行的翻译:
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的半监督深度学习框架CABLD,用于在无需大量标注数据的情况下,进行3D脑地标检测。通过采用跨主体地标一致性损失、图像注册损失和基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,CABLD能够在不同的MRI对比度扫描中准确检测地标。实验证明,CABLD在多个临床和公共数据集上的表现均优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- CABLD是一种新型的半监督深度学习框架,用于在无需大量标注数据的情况下进行3D脑地标检测。
- 通过采用跨主体地标一致性损失和图像注册损失,提高了模型的准确性。
- 引入基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,提高了模型在不同MRI对比度下的泛化能力。
- 采用自适应混合损失函数,优化不同子任务的贡献。
- 在四个不同的临床和公共数据集上进行了实验验证,包括不同MRI场强的T1w和T2w MRI扫描。
- 实验结果显示,CABLD在平均径向误差(MREs)和成功检测率(SDRs)方面均优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
Positive-Augmented Contrastive Learning for Vision-and-Language Evaluation and Training
Authors:Sara Sarto, Nicholas Moratelli, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara
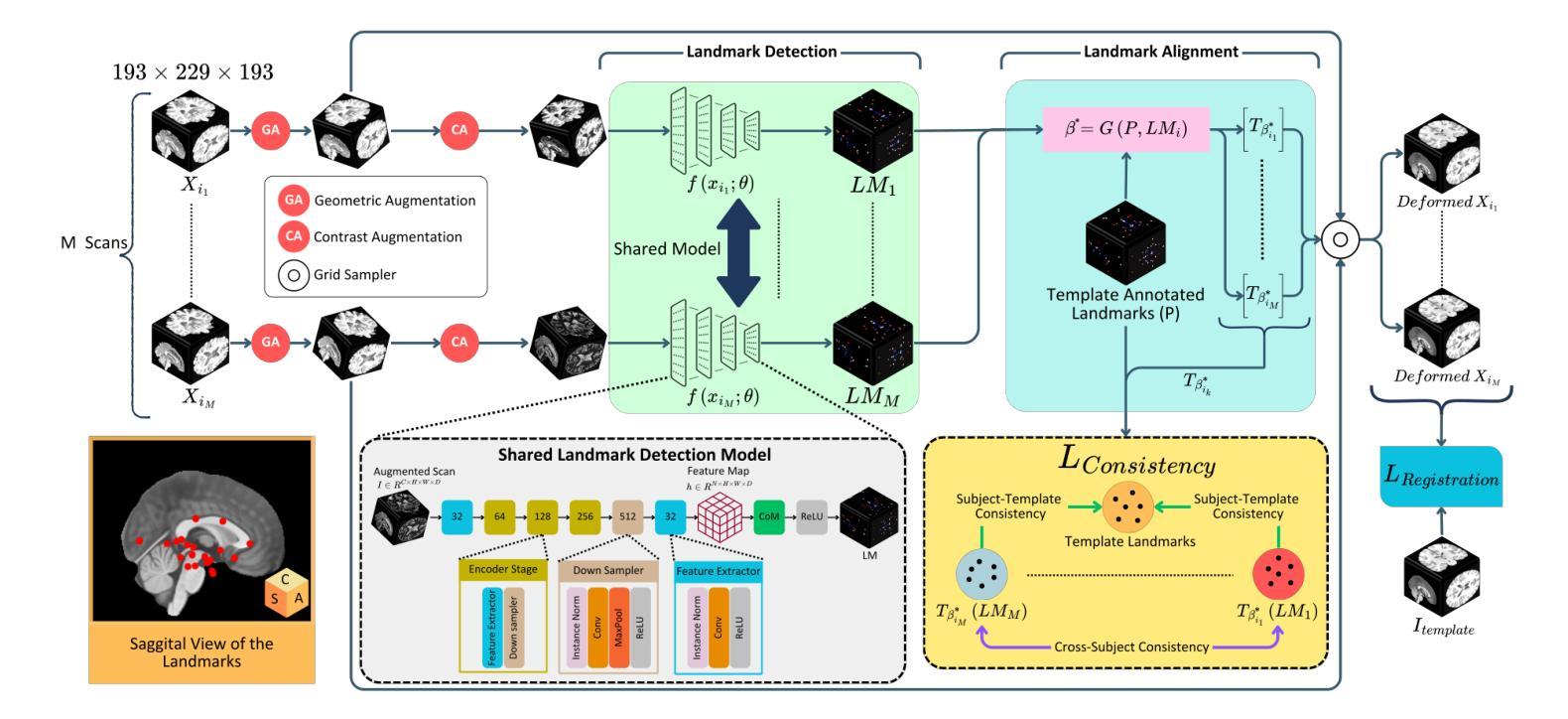
Despite significant advancements in caption generation, existing evaluation metrics often fail to capture the full quality or fine-grained details of captions. This is mainly due to their reliance on non-specific human-written references or noisy pre-training data. Still, finding an effective metric is crucial not only for captions evaluation but also for the generation phase. Metrics can indeed play a key role in the fine-tuning stage of captioning models, ultimately enhancing the quality of the generated captions. In this paper, we propose PAC-S++, a learnable metric that leverages the CLIP model, pre-trained on both web-collected and cleaned data and regularized through additional pairs of generated visual and textual positive samples. Exploiting this stronger and curated pre-training, we also apply PAC-S++ as a reward in the Self-Critical Sequence Training (SCST) stage typically employed to fine-tune captioning models. Extensive experiments on different image and video datasets highlight the effectiveness of PAC-S++ compared to popular metrics for the task, including its sensitivity to object hallucinations. Furthermore, we show that integrating PAC-S++ into the fine-tuning stage of a captioning model results in semantically richer captions with fewer repetitions and grammatical errors. Evaluations on out-of-domain benchmarks further demonstrate the efficacy of our fine-tuning approach in enhancing model capabilities. Source code and trained models are publicly available at: https://github.com/aimagelab/pacscore.
尽管字幕生成领域已经取得了重大进展,但现有的评估指标通常无法捕捉字幕的完整质量或精细细节。这主要是因为它们依赖于非特定的人类编写参考或嘈杂的预训练数据。然而,找到有效的评估指标不仅对字幕评估至关重要,对生成阶段也至关重要。实际上,评估指标在字幕模型的微调阶段可以起到关键作用,最终提高生成字幕的质量。在本文中,我们提出了PAC-S++这一可学习的评估指标,它利用CLIP模型,该模型在收集和清理的网页数据上进行预训练,并通过生成的视觉和文本正样本对进行正则化。利用这种强大且精选的预训练,我们还将在通常用于微调字幕模型的自我批判序列训练(SCST)阶段应用PAC-S++作为奖励。在不同图像和视频数据集上的大量实验表明,与任务中流行的评估指标相比,PAC-S++更为有效,其对对象幻觉也很敏感。此外,我们展示将PAC-S++集成到字幕模型的微调阶段,可以生成语义更丰富、重复更少、语法错误更少的字幕。在域外基准测试上的评估进一步证明了我们微调方法在提高模型能力方面的有效性。源代码和训练好的模型可在:https://github.com/aimagelab/pacscore公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Journal of Computer Vision (2025)
摘要
本文提出一种新的图像和视频字幕生成评估方法PAC-S++。该方法利用CLIP模型,采用网页采集的清洁数据以及生成的视觉和文本正样本对进行预训练,强化评估准确性。同时,将PAC-S++作为奖励函数应用于序列自训练(SCST)阶段,提高字幕生成模型的微调效果。实验证明,PAC-S++相较于其他流行评价指标更为敏感,能有效识别物体幻觉现象。集成到字幕模型的微调阶段后,能生成语义更丰富、重复和语法错误较少的字幕。该方法的源代码和训练模型已公开于GitHub上。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的图像和视频字幕生成评估方法PAC-S++。
- 利用CLIP模型预训练,提高评估准确性。
- PAC-S++被应用于序列自训练(SCST)阶段作为奖励函数,增强字幕生成模型的微调效果。
- 实验证明PAC-S++相较于其他评价指标更为敏感,能有效识别物体幻觉现象。
- 集成到字幕模型的微调阶段后,能生成语义更丰富、重复和语法错误较少的字幕。
- 公开了源代码和训练模型在GitHub上,便于他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图

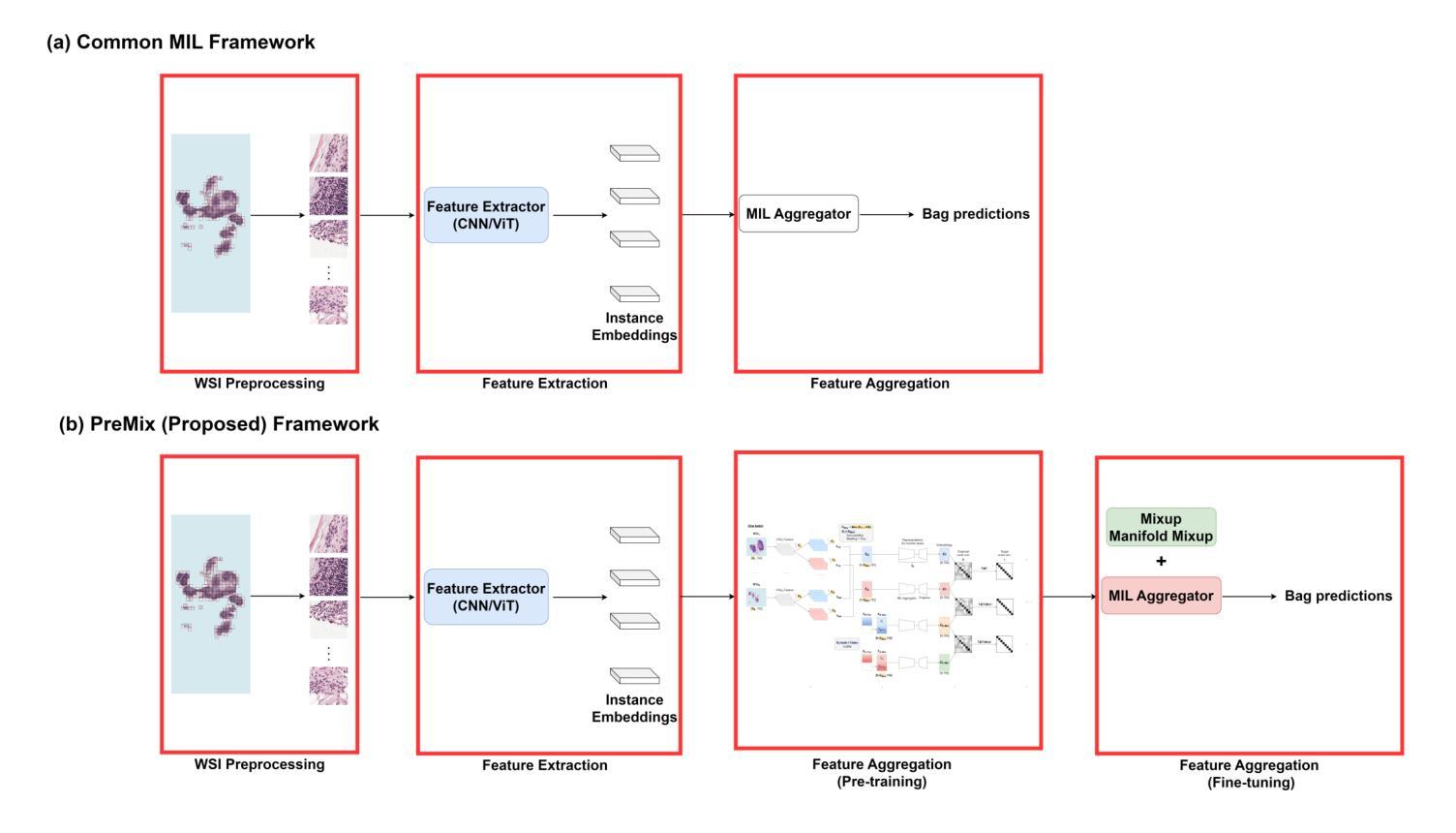
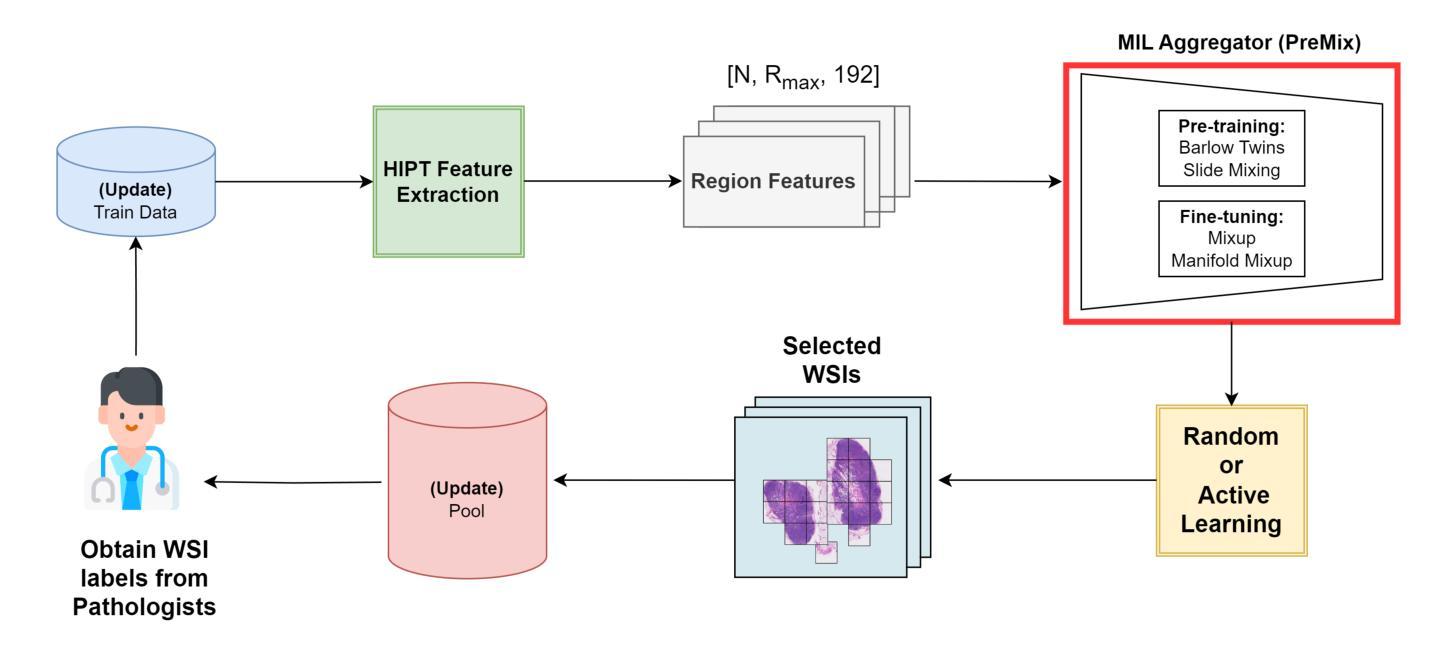
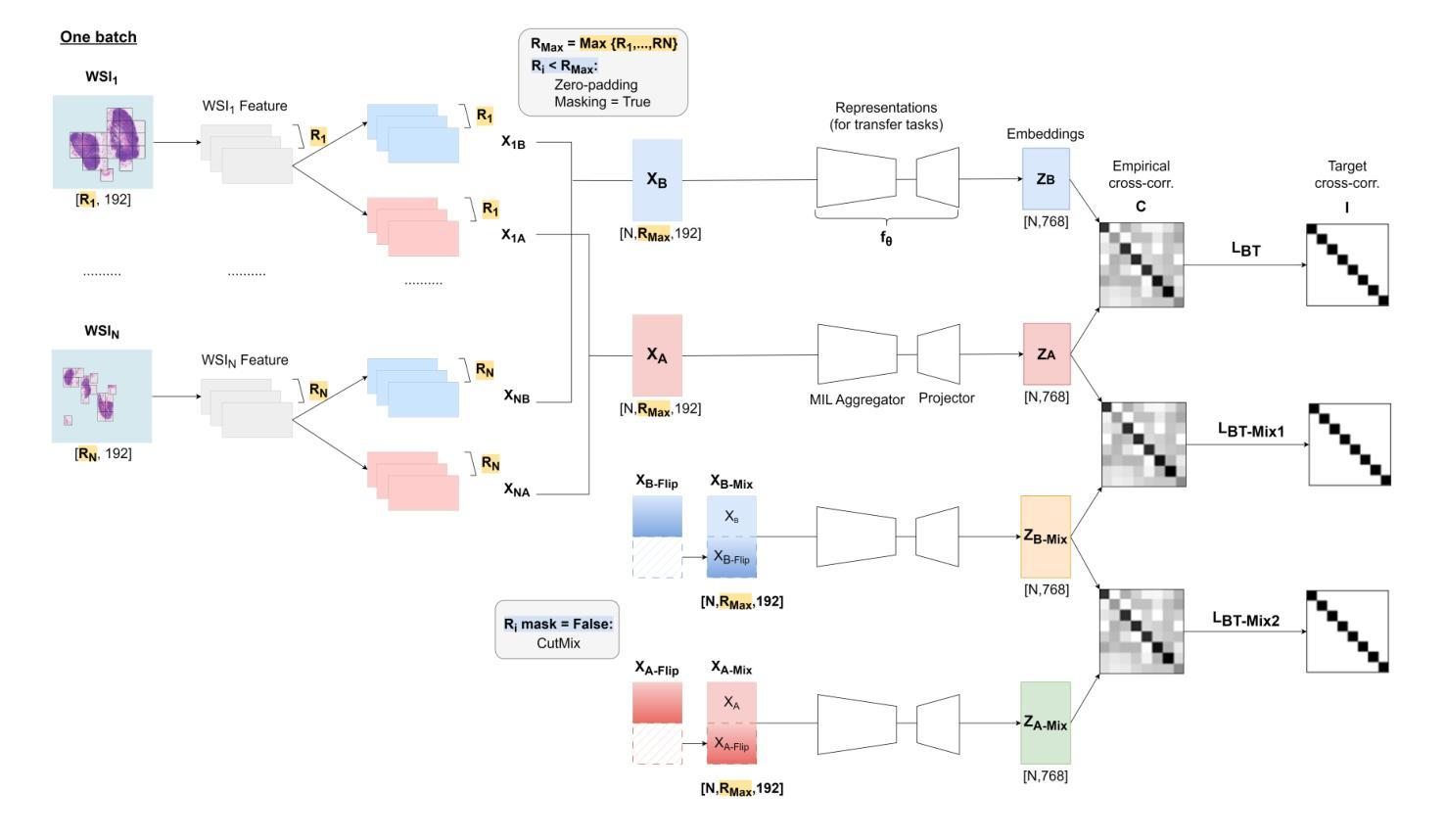
PreMix: Label-Efficient Multiple Instance Learning via Non-Contrastive Pre-training and Feature Mixing
Authors:Bryan Wong, Mun Yong Yi
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has emerged as a powerful framework for weakly supervised whole slide image (WSI) classification, enabling slide-level predictions without requiring detailed patch-level annotations. Despite its success, a critical limitation of current MIL methods lies in the underutilization of pre-training for the MIL aggregator. Most existing approaches initialize the aggregator randomly and train it from scratch, making performance highly sensitive to the quantity of labeled WSIs and ignoring the abundance of unlabeled WSIs commonly available in clinical settings. To address this, we propose PreMix, a novel framework that leverages a non-contrastive pre-training method, Barlow Twins, augmented with the Slide Mixing approach to generate additional positive pairs and enhance feature learning, particularly under limited labeled WSI conditions. Fine-tuning with Mixup and Manifold Mixup further enhances robustness by effectively handling the diverse sizes of gigapixel WSIs. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating PreMix as a plug-in module into HIPT yields an average F1 improvement of 4.7% over the baseline HIPT across various WSI training sizes and datasets. These findings underscore its potential to advance WSI classification with limited labeled data and its applicability to real-world histopathology practices. The code is available at https://github.com/bryanwong17/PreMix
多实例学习(MIL)已成为弱监督全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的强大框架,能够在无需详细补丁级别注释的情况下进行幻灯片级别的预测。尽管取得了成功,但当前MIL方法的一个关键局限性在于未能充分利用MIL聚合器的预训练。大多数现有方法都会随机初始化聚合器并从头开始训练,这使得性能高度依赖于标记的WSI数量,并忽略了临床环境中通常大量存在的未标记的WSI。针对这一问题,我们提出了PreMix这一新型框架,它利用非对比预训练方法Barlow Twins,辅以幻灯片混合(Slide Mixing)方法生成额外的正向对并增强特征学习,特别是在有限的标记WSI条件下。通过Mixup和流形Mixup进行微调,可以有效处理吉像素WSI的多样大小,进一步提高稳健性。实验结果表明,将PreMix作为插件模块集成到HIPT中,在各种WSI训练规模和数据集上较基线HIPT平均F1得分提高了4.7%。这些发现突显了其在有限标记数据下推进WSI分类的潜力,以及其在实际病理实践中的适用性。代码可在https://github.com/bryanwong17/PreMix找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了基于多重实例学习(MIL)的弱监督全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的新框架PreMix。PreMix通过利用非对比预训练方法Barlow Twins和幻灯片混合技术,解决了现有MIL方法在利用预训练模型方面的不足。实验结果显示,PreMix作为HIPT的插件模块,在有限的标记WSI条件下,平均F1得分提高了4.7%。这突显了PreMix在有限标记数据下推进WSI分类的潜力及其在现实世界病理学实践中的应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 多重实例学习(MIL)在弱监督全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类中展现出强大的潜力,可在无需详细补丁级别注释的情况下进行幻灯片级别的预测。
- 现有MIL方法的一个关键局限性在于未能充分利用预训练模型,大多数现有方法随机初始化聚合器并从头开始训练。
- PreMix框架通过结合非对比预训练方法和幻灯片混合技术来解决这一问题,生成额外的正对并增强特征学习。
- 在有限的标记WSI条件下,PreMix增强了模型的稳健性,特别是在处理千兆像素大小的WSI时。
- 实验结果表明,将PreMix集成到HIPT中,在各种WSI训练大小和数据集上平均F1得分提高了4.7%。
- PreMix具有在有限标记数据条件下推进WSI分类的潜力,并适用于现实世界的病理学实践。
点此查看论文截图