⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
3D-MOOD: Lifting 2D to 3D for Monocular Open-Set Object Detection
Authors:Yung-Hsu Yang, Luigi Piccinelli, Mattia Segu, Siyuan Li, Rui Huang, Yuqian Fu, Marc Pollefeys, Hermann Blum, Zuria Bauer
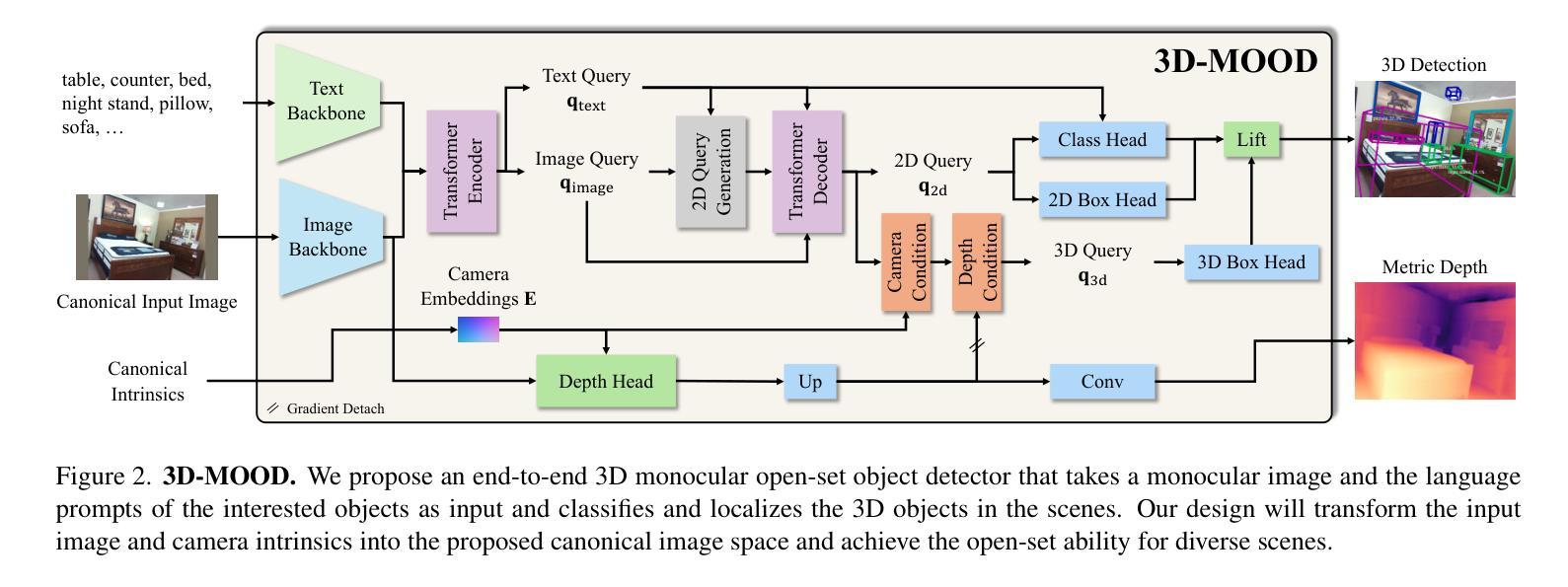
Monocular 3D object detection is valuable for various applications such as robotics and AR/VR. Existing methods are confined to closed-set settings, where the training and testing sets consist of the same scenes and/or object categories. However, real-world applications often introduce new environments and novel object categories, posing a challenge to these methods. In this paper, we address monocular 3D object detection in an open-set setting and introduce the first end-to-end 3D Monocular Open-set Object Detector (3D-MOOD). We propose to lift the open-set 2D detection into 3D space through our designed 3D bounding box head, enabling end-to-end joint training for both 2D and 3D tasks to yield better overall performance. We condition the object queries with geometry prior and overcome the generalization for 3D estimation across diverse scenes. To further improve performance, we design the canonical image space for more efficient cross-dataset training. We evaluate 3D-MOOD on both closed-set settings (Omni3D) and open-set settings (Omni3D to Argoverse 2, ScanNet), and achieve new state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at royyang0714.github.io/3D-MOOD.
单目3D目标检测在机器人和AR/VR等应用中具有价值。现有方法仅限于封闭集场景,即训练和测试集包含相同的场景和/或目标类别。然而,现实世界的应用通常会引入新的环境和新型目标类别,对这些方法构成了挑战。在本文中,我们解决了单目3D目标检测的开放集设置问题,并引入了首个端到端的3D单目开放集目标检测器(3D-MOOD)。我们提出通过设计的3D边界框头将开放集2D检测提升到3D空间,使2D和3D任务的端到端联合训练能够实现更好的整体性能。我们以几何先验条件对目标查询进行约束,并克服了在各种场景中的3D估计的泛化问题。为了进一步提高性能,我们设计了规范图像空间以进行更有效的跨数据集训练。我们在封闭集(Omni3D)和开放集(Omni3D到Argoverse 2,ScanNet)上对3D-MOOD进行了评估,取得了新的最新结果。代码和模型可以在royyang0714.github.io/3D-MOOD上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了单目三维物体检测在开放集场景下的挑战,并提出了首个端到端的三维单目开放集物体检测器(3D-MOOD)。该检测器通过将开放集二维检测提升到三维空间,利用设计的三维边界框头实现端到端的联合训练,以提高整体性能。此外,通过几何先验条件化物体查询,并设计规范化图像空间以进行更有效的跨数据集训练,提高了泛化能力。在封闭集和开放集环境中对3D-MOOD进行了评估,取得了最新成果。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文研究的是单目三维物体检测的开放集设置问题,具有实用价值在机器人、AR/VR等应用领域中。
- 提出首个端到端的单目三维开放集物体检测器(3D-MOOD),突破现有方法的局限。
- 通过将开放集二维检测提升到三维空间,利用设计的三维边界框头进行端到端的联合训练,实现二维和三维任务的整体性能提升。
- 结合几何先验条件化物体查询,改善在多种场景下的三维估计泛化能力。
- 设计规范化图像空间以进行更有效的跨数据集训练,提高性能。
点此查看论文截图


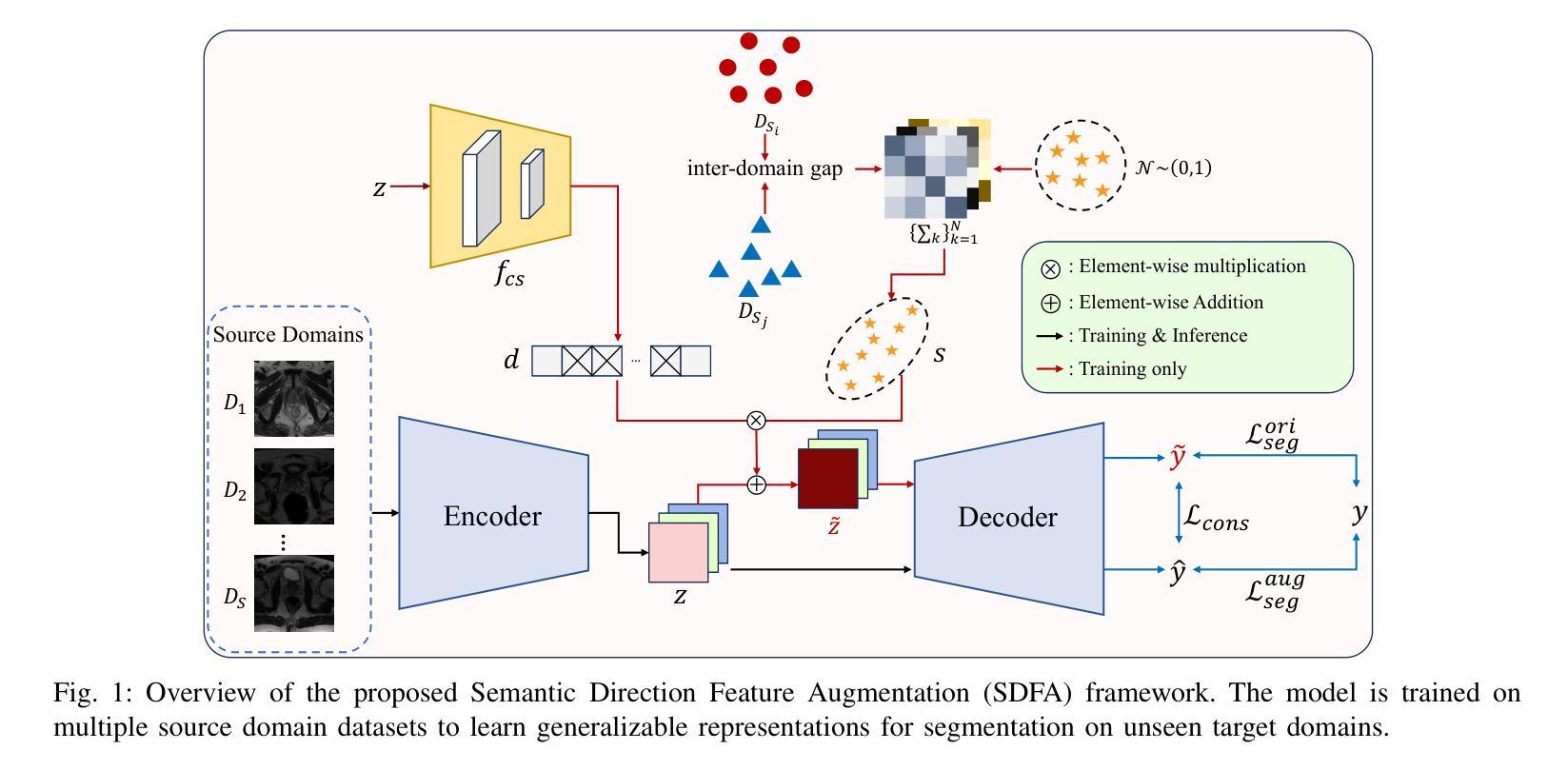
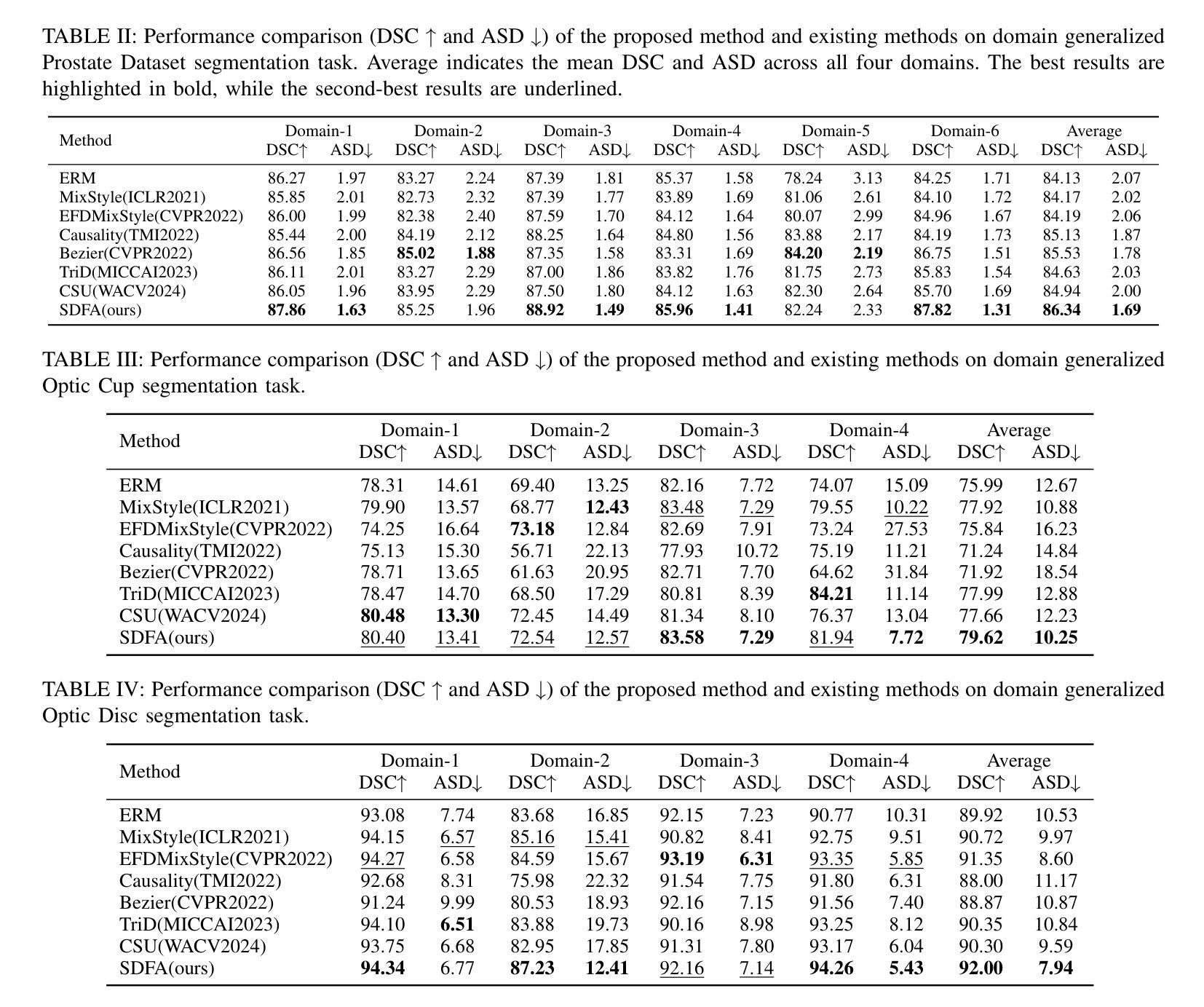
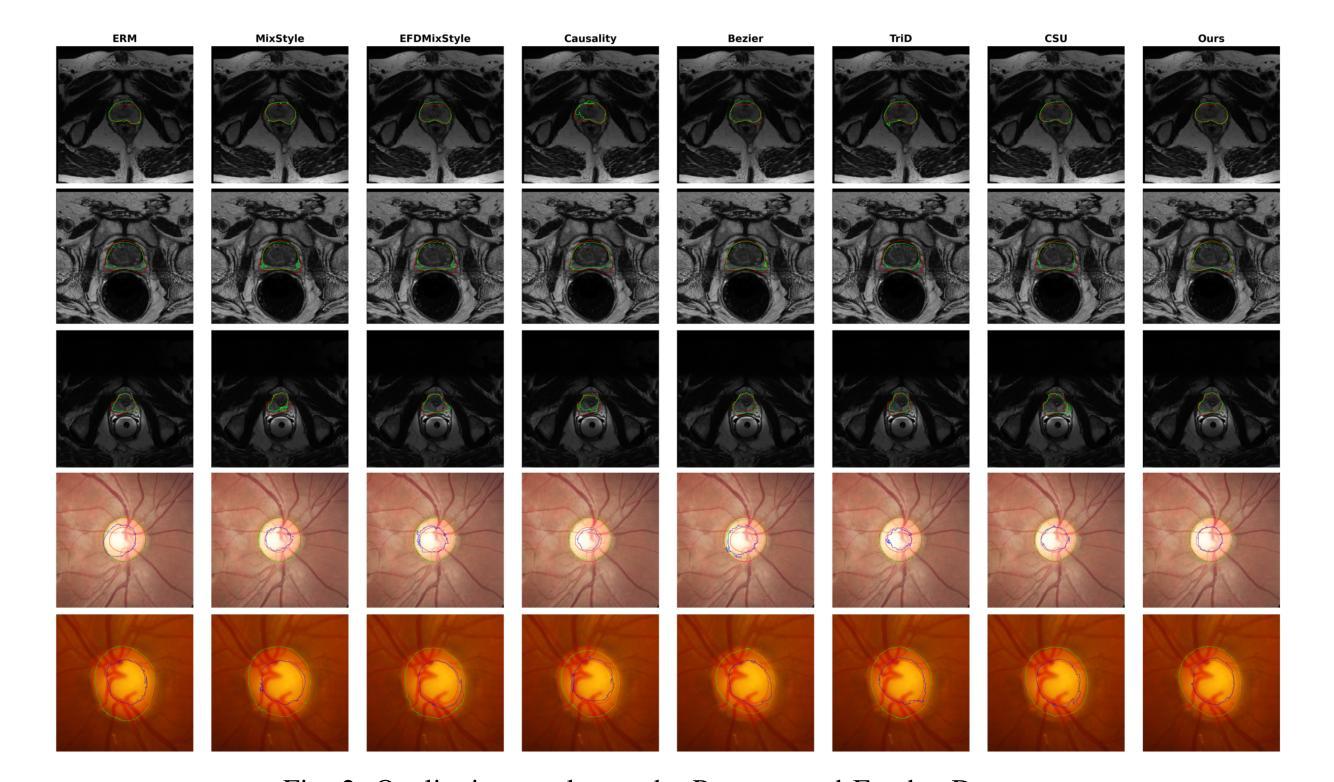
Learning Semantic Directions for Feature Augmentation in Domain-Generalized Medical Segmentation
Authors:Yingkai Wang, Yaoyao Zhu, Xiuding Cai, Yuhao Xiao, Haotian Wu, Yu Yao
Medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in clinical workflows, but domain shift often leads to performance degradation when models are applied to unseen clinical domains. This challenge arises due to variations in imaging conditions, scanner types, and acquisition protocols, limiting the practical deployment of segmentation models. Unlike natural images, medical images typically exhibit consistent anatomical structures across patients, with domain-specific variations mainly caused by imaging conditions. This unique characteristic makes medical image segmentation particularly challenging. To address this challenge, we propose a domain generalization framework tailored for medical image segmentation. Our approach improves robustness to domain-specific variations by introducing implicit feature perturbations guided by domain statistics. Specifically, we employ a learnable semantic direction selector and a covariance-based semantic intensity sampler to modulate domain-variant features while preserving task-relevant anatomical consistency. Furthermore, we design an adaptive consistency constraint that is selectively applied only when feature adjustment leads to degraded segmentation performance. This constraint encourages the adjusted features to align with the original predictions, thereby stabilizing feature selection and improving the reliability of the segmentation. Extensive experiments on two public multi-center benchmarks show that our framework consistently outperforms existing domain generalization approaches, achieving robust and generalizable segmentation performance across diverse clinical domains.
医学图像分割在临床工作流程中起着至关重要的作用,但当模型应用于未见过的临床领域时,领域差异通常会导致性能下降。这一挑战是由于成像条件、扫描仪类型和采集协议的变化所导致的,限制了分割模型的实际部署。与自然图像不同,医学图像在患者之间通常表现出一致的解剖结构,领域特定的变化主要由成像条件引起。这一独特特征使得医学图像分割特别具有挑战性。
为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了针对医学图像分割的领域泛化框架。我们的方法通过引入由领域统计引导的隐式特征扰动来提高对领域特定变化的鲁棒性。具体来说,我们采用可学习的语义方向选择器和基于协方差的语义强度采样器来调节领域变量特征,同时保留与任务相关的解剖结构一致性。此外,我们设计了一种自适应一致性约束,仅在特征调整导致分割性能下降时选择性应用。这种约束鼓励调整后的特征与原始预测对齐,从而稳定特征选择,提高分割的可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像分割在临床工作流程中扮演着至关重要的角色,然而,当模型应用于未见过的临床领域时,领域差异往往会导致性能下降。这一挑战是由于成像条件、扫描仪类型和采集协议的变化而产生的,限制了分割模型的实用部署。医学图像通常展现出跨患者的一致解剖结构,其特有的领域差异主要由成像条件引起,这使得医学图像分割尤为具有挑战性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种针对医学图像分割的领域泛化框架。我们的方法通过引入由领域统计引导的隐式特征扰动,提高了对领域特定变化的稳健性。具体来说,我们采用可学习的语义方向选择器和基于协方差的语义强度采样器来调节领域变体特征,同时保留任务相关的解剖结构一致性。此外,我们设计了一种自适应一致性约束,仅在特征调整导致分割性能下降时选择性应用。这一约束促使调整后的特征与原始预测结果对齐,从而稳定特征选择并提高了分割的可靠性。在公共多中心基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的框架始终优于现有的领域泛化方法,在多样化的临床领域中实现了稳健且可推广的分割性能。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割在临床应用中至关重要,但领域差异导致的模型性能下降是一个挑战。
- 医学图像领域差异主要由成像条件变化引起,具有一致的解剖结构特点。
- 提出了一种新的领域泛化框架,用于医学图像分割,通过引入隐式特征扰动提高模型稳健性。
- 采用可学习的语义方向选择器和基于协方差的语义强度采样器来调节领域变体特征。
- 设计了自适应一致性约束,以稳定特征选择并改善分割结果的可靠性。
- 在公共多中心基准测试上表现出卓越性能,优于现有的领域泛化方法。
点此查看论文截图

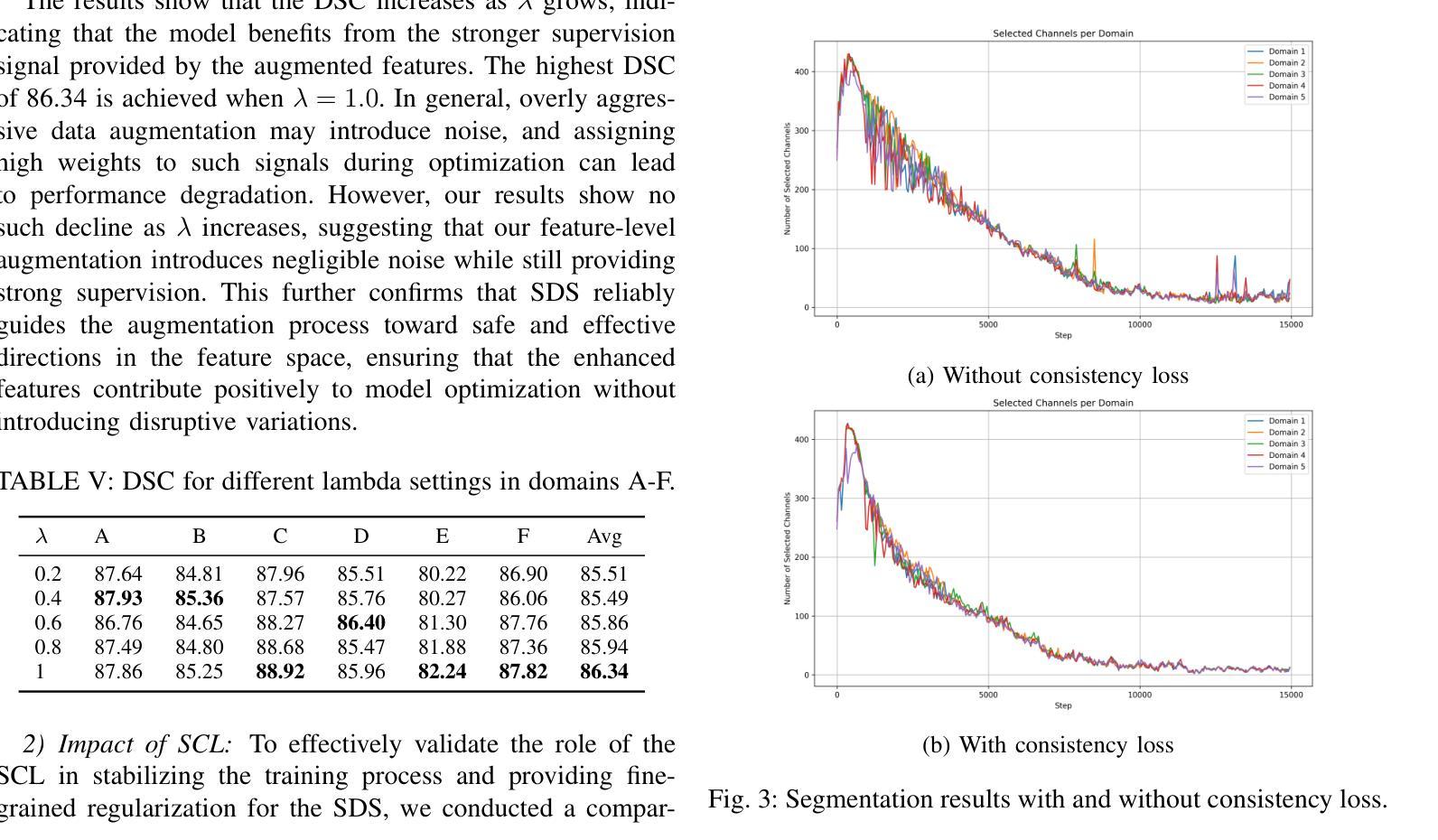
EIFNet: Leveraging Event-Image Fusion for Robust Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhijiang Li, Haoran He
Event-based semantic segmentation explores the potential of event cameras, which offer high dynamic range and fine temporal resolution, to achieve robust scene understanding in challenging environments. Despite these advantages, the task remains difficult due to two main challenges: extracting reliable features from sparse and noisy event streams, and effectively fusing them with dense, semantically rich image data that differ in structure and representation. To address these issues, we propose EIFNet, a multi-modal fusion network that combines the strengths of both event and frame-based inputs. The network includes an Adaptive Event Feature Refinement Module (AEFRM), which improves event representations through multi-scale activity modeling and spatial attention. In addition, we introduce a Modality-Adaptive Recalibration Module (MARM) and a Multi-Head Attention Gated Fusion Module (MGFM), which align and integrate features across modalities using attention mechanisms and gated fusion strategies. Experiments on DDD17-Semantic and DSEC-Semantic datasets show that EIFNet achieves state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating its effectiveness in event-based semantic segmentation.
基于事件的语义分割探索了事件相机的潜力,事件相机具有高动态范围和精细的时间分辨率,可在具有挑战性的环境中实现稳健的场景理解。尽管具有这些优势,但由于从稀疏和嘈杂的事件流中提取可靠特征以及将它们与结构不同且语义丰富的图像数据有效地融合这两个主要挑战,该任务仍然面临困难。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了EIFNet,这是一个结合事件和帧输入优势的多模态融合网络。网络包括自适应事件特征细化模块(AEFRM),它通过多尺度活动建模和空间注意力改进事件表示。此外,我们引入了模态自适应校准模块(MARM)和多头注意力门控融合模块(MGFM),它们使用注意力和门控融合策略来对齐和整合跨模态的特征。在DDD17-Semantic和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的实验表明,EIFNet达到了最先进的性能水平,证明了其在基于事件的语义分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
事件驱动语义分割探索了事件相机在场景理解中的潜力。虽然存在提取可靠特征和跨模态融合的挑战,但EIFNet多模态融合网络通过自适应事件特征细化模块、模态自适应校准模块和多头注意力门控融合模块,实现了事件和帧数据的优化结合,在DDD17-Semantic和DSEC-Semantic数据集上取得了最新技术性能。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机具有高的动态范围和精细的时间分辨率,为场景理解带来了潜力。
- 事件驱动语义分割面临两大挑战:从稀疏和嘈杂的事件流中提取可靠特征,以及与结构丰富的图像数据有效融合。
- EIFNet是一个多模态融合网络,结合了事件和帧数据的优势。
- AEFRM模块通过多尺度活动建模和空间注意力提高了事件表示。
- MARM模块和MGFM模块使用注意力机制和门控融合策略来跨模态对齐和集成特征。
- 在DDD17-Semantic和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的实验表明,EIFNet实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

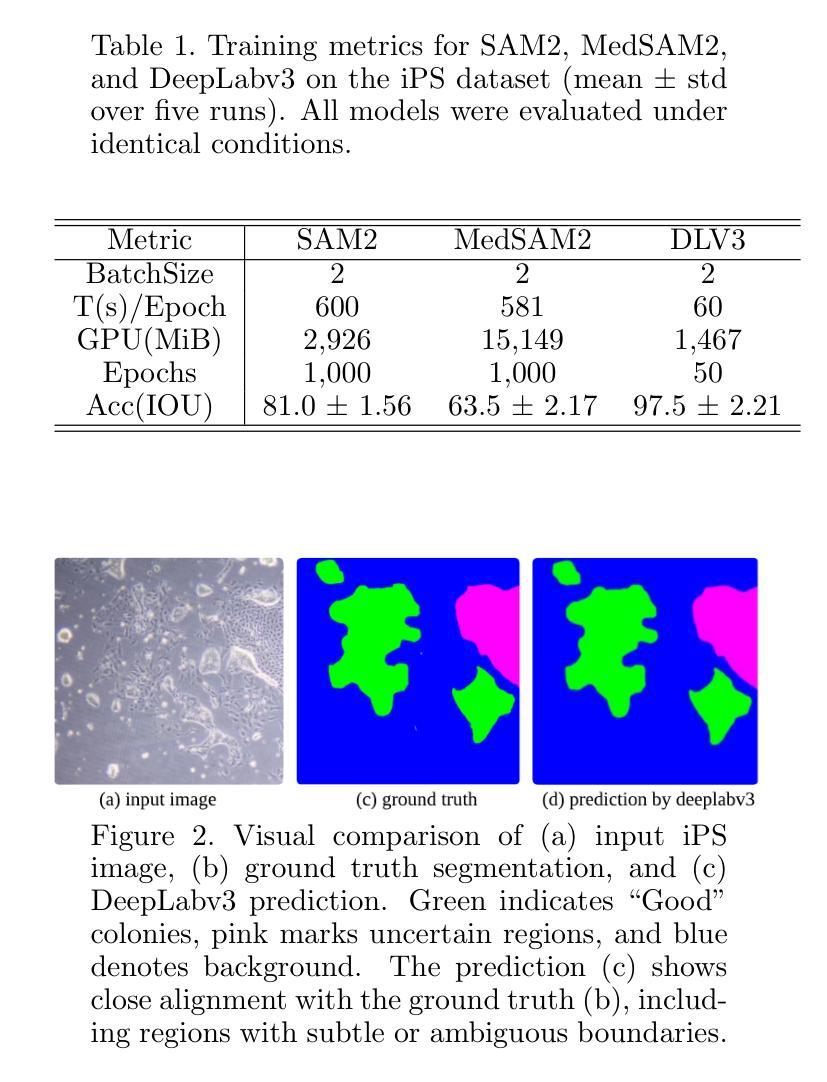
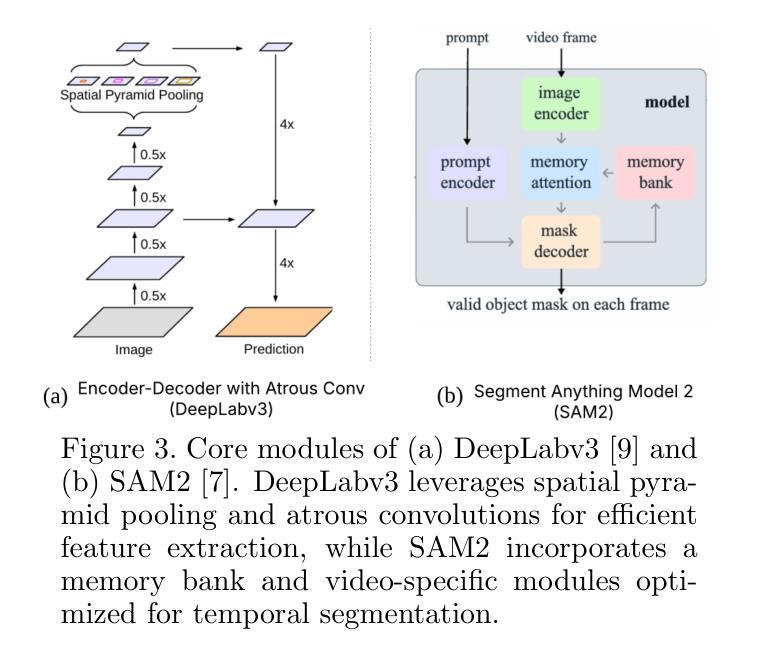
Semantic Segmentation of iPS Cells: Case Study on Model Complexity in Biomedical Imaging
Authors:Maoquan Zhang, Bisser Raytchev, Xiujuan Sun
Medical image segmentation requires not only accuracy but also robustness under challenging imaging conditions. In this study, we show that a carefully configured DeepLabv3 model can achieve high performance in segmenting induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell colonies, and, under our experimental conditions, outperforms large-scale foundation models such as SAM2 and its medical variant MedSAM2 without structural modifications. These results suggest that, for specialized tasks characterized by subtle, low-contrast boundaries, increased model complexity does not necessarily translate to better performance. Our work revisits the assumption that ever-larger and more generalized architectures are always preferable, and provides evidence that appropriately adapted, simpler models may offer strong accuracy and practical reliability in domain-specific biomedical applications. We also offer an open-source implementation that includes strategies for small datasets and domain-specific encoding, with the aim of supporting further advances in semantic segmentation for regenerative medicine and related fields.
医疗图像分割不仅需要准确性,还需要在具有挑战性的成像条件下保持稳健性。本研究表明,经过精心配置的DeepLabv3模型在分割诱导多能干细胞(iPS)细胞菌落方面可以实现高性能,并在我们的实验条件下,在无需结构修改的情况下,优于大规模基础模型,如SAM2及其医学变体MedSAM2。这些结果表明,对于具有细微、低对比度边界特征的专项任务,增加模型复杂性并不一定意味着性能更好。我们的工作重新审视了更大的、更通用的架构始终更可取这一假设,并提供了证据,证明适当简化并适应的模型在特定领域的生物医学应用中可能提供强大的准确性和实际可靠性。我们还提供了一个开源实现,包括针对小数据集和特定领域编码的策略,旨在支持再生医学和相关领域的语义分割的进一步进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications MVA2025
Summary
本研究展示了精心配置的DeepLabv3模型在分割诱导多能干细胞(iPS)细胞菌落方面的高性能表现。相较于大规模的基础模型如SAM2及其医学变体MedSAM2,该模型在特定实验条件下无需结构性修改便展现出优越性。研究结果表明,对于特征细微、低对比度的专业领域任务,增加模型复杂性并不一定意味着性能提升。研究重新考量了大规模通用架构总是首选的假设,并提供证据表明适当简化的模型在特定生物医学应用中可能具有强大的准确性和实用性。此外,本研究还提供包含针对小数据集和特定领域编码策略的开源实现,旨在支持再生医学和相关领域的语义分割的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- DeepLabv3模型在分割诱导多能干细胞(iPS)细胞菌落方面表现出高性能。
- 在特定实验条件下,DeepLabv3模型优于大规模的基础模型,如SAM2和MedSAM2。
- 对于具有细微、低对比度的专业领域任务,增加模型复杂性并不一定带来更好的性能。
- 研究重新评估了大规模通用架构的必要性,强调适当简化的模型在特定生物医学应用中的优势。
- 研究提供了一个包含针对小数据集和特定领域编码策略的开源实现。
- 该研究支持再生医学和相关领域的语义分割的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

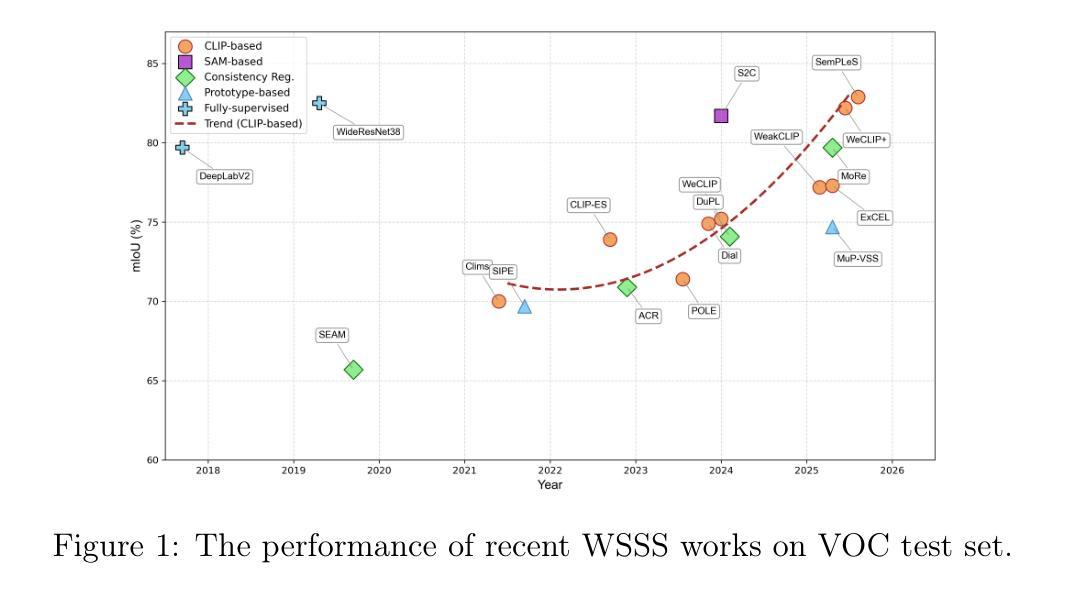
Emerging Trends in Pseudo-Label Refinement for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation with Image-Level Supervision
Authors:Zheyuan Zhang, Wang Zhang
Unlike fully supervised semantic segmentation, weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) relies on weaker forms of supervision to perform dense prediction tasks. Among the various types of weak supervision, WSSS with image level annotations is considered both the most challenging and the most practical, attracting significant research attention. Therefore, in this review, we focus on WSSS with image level annotations. Additionally, this review concentrates on mainstream research directions, deliberately omitting less influential branches. Given the rapid development of new methods and the limitations of existing surveys in capturing recent trends, there is a pressing need for an updated and comprehensive review. Our goal is to fill this gap by synthesizing the latest advancements and state-of-the-art techniques in WSSS with image level labels. Basically, we provide a comprehensive review of recent advancements in WSSS with image level labels, categorizing existing methods based on the types and levels of additional supervision involved. We also examine the challenges of applying advanced methods to domain specific datasets in WSSS,a topic that remains underexplored. Finally, we discuss the current challenges, evaluate the limitations of existing approaches, and outline several promising directions for future research. This review is intended for researchers who are already familiar with the fundamental concepts of WSSS and are seeking to deepen their understanding of current advances and methodological innovations.
与完全监督语义分割不同,弱监督语义分割(WSSS)依赖于较弱的监督形式来执行密集预测任务。在多种类型的弱监督中,使用图像级别注释的WSSS被认为是最具挑战性和最实用的,引起了研究人员的广泛关注。因此,在本次综述中,我们专注于使用图像级别注释的WSSS。此外,本次综述集中在主要研究方向上,故意省略了影响较小的分支。鉴于新方法的快速发展以及现有调查在捕捉最新趋势方面的局限性,迫切需要进行更新和全面的综述。我们的目标是通过综合最新的发展情况和最先进的图像级标签WSSS技术来填补这一空白。基本上,我们全面回顾了使用图像级标签的WSSS的最新发展,根据所涉及的其他监督和级别对现有方法进行分类。我们还探讨了将高级方法应用于特定领域数据集的WSSS的挑战,这是一个尚未被充分探索的主题。最后,我们讨论了当前面临的挑战,评估了现有方法的局限性,并概述了未来研究的几个有前途的方向。本综述旨在帮助已经熟悉WSSS基本概念的研究人员加深对当前进展和方法创新的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文综述了基于图像级别标注的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的最新进展和前沿技术,重点介绍了现有方法的分类、面临的挑战以及未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways:
- WSSS依赖于弱形式的监督来执行密集预测任务,其中基于图像级别标注的WSSS最具挑战性和实用性。
- 现有文献中对WSSS的研究多集中在通用数据集上,但对特定数据集的应用仍缺乏深入研究。
- 当前的WSSS方法基于额外监督的类型和程度进行分类。
- 应用先进方法到特定领域的WSSS数据集存在挑战。
- 当前方法的局限性包括难以精确标注和模型泛化能力有限等。
- 未来研究方向包括改进模型架构以提高性能、探索更有效的弱监督策略等。
点此查看论文截图

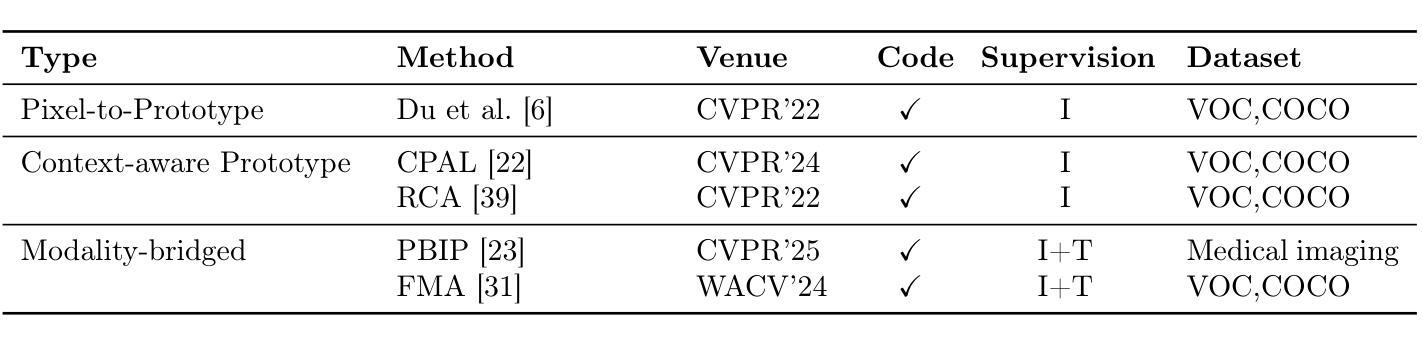
An Angular-Temporal Interaction Network for Light Field Object Tracking in Low-Light Scenes
Authors:Mianzhao Wang, Fan Shi, Xu Cheng, Feifei Zhang, Shengyong Chen
High-quality 4D light field representation with efficient angular feature modeling is crucial for scene perception, as it can provide discriminative spatial-angular cues to identify moving targets. However, recent developments still struggle to deliver reliable angular modeling in the temporal domain, particularly in complex low-light scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel light field epipolar-plane structure image (ESI) representation that explicitly defines the geometric structure within the light field. By capitalizing on the abrupt changes in the angles of light rays within the epipolar plane, this representation can enhance visual expression in low-light scenes and reduce redundancy in high-dimensional light fields. We further propose an angular-temporal interaction network (ATINet) for light field object tracking that learns angular-aware representations from the geometric structural cues and angular-temporal interaction cues of light fields. Furthermore, ATINet can also be optimized in a self-supervised manner to enhance the geometric feature interaction across the temporal domain. Finally, we introduce a large-scale light field low-light dataset for object tracking. Extensive experimentation demonstrates that ATINet achieves state-of-the-art performance in single object tracking. Furthermore, we extend the proposed method to multiple object tracking, which also shows the effectiveness of high-quality light field angular-temporal modeling.
高质量的四维光场表示与有效的角度特征建模对于场景感知至关重要,因为它可以提供用于识别移动目标的空间角度线索。然而,最近的进展在时间上可靠的角度建模方面仍然面临困难,特别是在复杂的低光场景中。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的光场极平面结构图像(ESI)表示,它明确地定义了光场内的几何结构。通过利用极平面内光线角度的急剧变化,这种表示形式可以提高低光场景中的视觉表达效果,并减少高维光场的冗余信息。我们进一步提出了一种用于光场对象跟踪的角度时间交互网络(ATINet),该网络从光场的几何结构线索和角度时间交互线索中学习角度感知表示。此外,ATINet还可以采用自监督的方式进行优化,以增强时间域上的几何特征交互。最后,我们引入了一个用于对象跟踪的大规模光场低光数据集。大量实验表明,ATINet在单目标跟踪方面达到了最新技术水平。此外,我们将所提出的方法扩展到多目标跟踪,这也表明了高质量光场角度时间建模的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于高效角特征建模的高质量四维光场表示对场景感知至关重要,可为移动目标识别提供辨别性空间角线索。然而,近期发展在复杂低光场景中的时间域角建模仍存在挑战。本文提出一种新型光场极平面结构图像(ESI)表示方法,明确定义了光场内的几何结构。通过利用极平面内光线角度的突变,该表示方法可提高低光场景的视觉表达效果,并减少高维光场的冗余信息。此外,还提出了一种用于光场目标跟踪的角时间交互网络(ATINet),从光场的几何结构线索和角时间交互线索中学习角感知表示。值得一提的是,ATINet还可以通过自监督方式进行优化,增强时间域内的几何特征交互。最后,我们引入了一个大型光场低光数据集用于目标跟踪。实验表明,ATINet在单目标跟踪方面达到了最新技术水平,并将此方法扩展到多目标跟踪也显示了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量四维光场表示对于场景感知至关重要,能够提供识别移动目标的辨别性空间角线索。
- 极平面结构图像(ESI)表示方法提高了低光场景的视觉表达效果并减少了高维光场的冗余信息。
- 角时间交互网络(ATINet)能从光场的几何结构和角时间交互线索中学习角感知表示。
- ATINet通过自监督优化方式提高了时间域内的几何特征交互能力。
- 引入的大型光场低光数据集用于目标跟踪研究。
- 实验显示ATINet在单目标跟踪方面达到了最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图


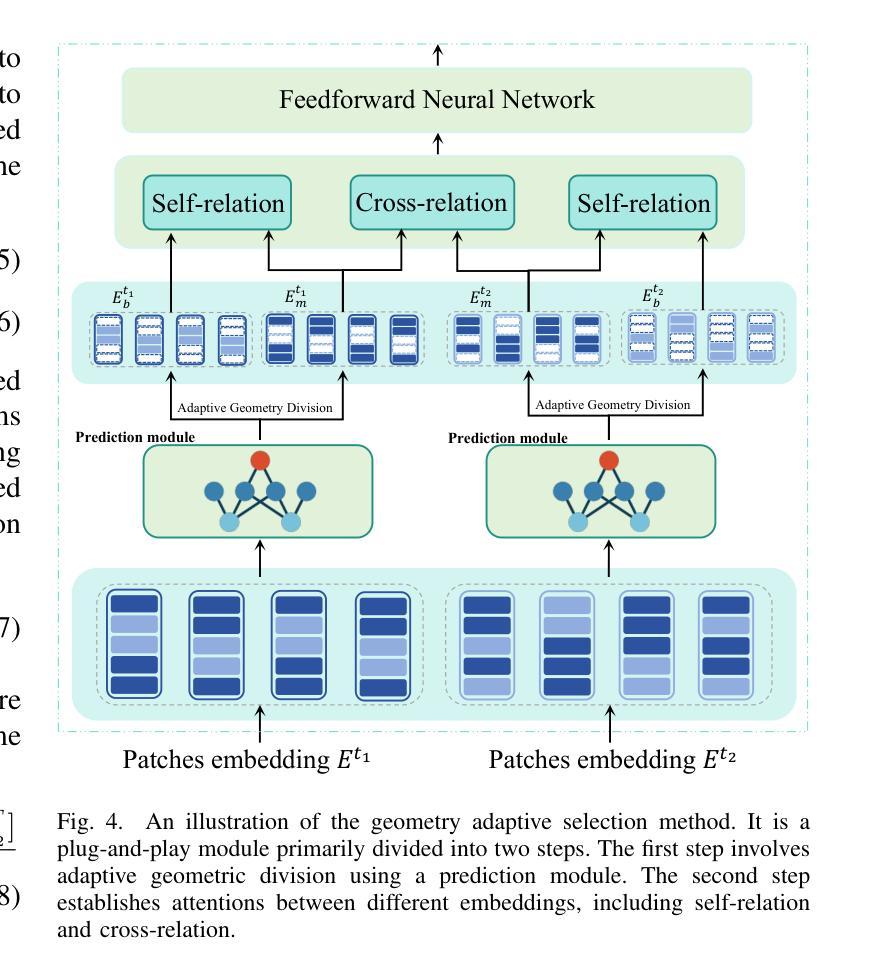

Dual Cross-image Semantic Consistency with Self-aware Pseudo Labeling for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Han Wu, Chong Wang, Zhiming Cui
Semi-supervised learning has proven highly effective in tackling the challenge of limited labeled training data in medical image segmentation. In general, current approaches, which rely on intra-image pixel-wise consistency training via pseudo-labeling, overlook the consistency at more comprehensive semantic levels (e.g., object region) and suffer from severe discrepancy of extracted features resulting from an imbalanced number of labeled and unlabeled data. To overcome these limitations, we present a new \underline{Du}al \underline{C}ross-\underline{i}mage \underline{S}emantic \underline{C}onsistency (DuCiSC) learning framework, for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Concretely, beyond enforcing pixel-wise semantic consistency, DuCiSC proposes dual paradigms to encourage region-level semantic consistency across: 1) labeled and unlabeled images; and 2) labeled and fused images, by explicitly aligning their prototypes. Relying on the dual paradigms, DuCiSC can effectively establish consistent cross-image semantics via prototype representations, thereby addressing the feature discrepancy issue. Moreover, we devise a novel self-aware confidence estimation strategy to accurately select reliable pseudo labels, allowing for exploiting the training dynamics of unlabeled data. Our DuCiSC method is extensively validated on four datasets, including two popular binary benchmarks in segmenting the left atrium and pancreas, a multi-class Automatic Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge dataset, and a challenging scenario of segmenting the inferior alveolar nerve that features complicated anatomical structures, showing superior segmentation results over previous state-of-the-art approaches. Our code is publicly available at \href{https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC}{https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC}.
在半监督学习在处理医学图像分割中有限的标记训练数据挑战方面取得了显著成效。通常,当前的方法依赖于通过伪标签进行图像内像素级的一致性训练,而忽视了更全面的语义级别的一致性(例如,对象区域),并因标记和无标记数据数量不平衡而遭受特征提取差异的问题。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的半监督医学图像分割方法——双重交叉图像语义一致性(DuCiSC)学习框架。具体来说,除了强制像素级的语义一致性外,DuCiSC还提出了双重范式来鼓励区域级别的语义一致性跨越:1)标记和无标记图像;以及2)标记和融合图像,通过明确地对其原型进行对齐。依靠双重范式,DuCiSC可以有效地建立一致的跨图像语义通过原型表示,从而解决特征差异问题。此外,我们设计了一种新型的自感知置信度估计策略,以准确选择可靠的伪标签,从而能够利用无标签数据的训练动态。我们的DuCiSC方法在四个数据集上进行了广泛验证,包括两个流行的左心房和胰腺分割二元基准测试、多类别的自动心脏诊断挑战赛数据集以及一个复杂的下牙槽神经分割场景,该场景具有复杂的解剖结构,显示出优于以前最先进的分割方法。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE TMI
Summary
半监督学习在处理医学图像分割中有限标记训练数据的问题时表现出高度有效性。当前方法主要依赖伪标签进行图像内像素级一致性训练,但忽略了更全面的语义级别的一致性,并受到特征提取不平衡导致的特征差异问题的困扰。针对这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的双跨图像语义一致性(DuCiSC)半监督医学图像分割学习框架。除了强制像素级语义一致性外,DuCiSC还提出了两种范式来鼓励跨标记图像和无标记图像以及标记图像和融合图像的区域级语义一致性。此外,我们设计了一种新型的自感知置信度估计策略,以准确选择可靠的伪标签,从而利用无标签数据的训练动态。DuCiSC方法在四个数据集上的验证结果均优于先前最先进的方法,包括两个流行的左心房和胰腺分割二元基准测试、多类自动心脏诊断挑战数据集以及复杂的下颌神经分割场景。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在医学图像分割中能有效解决标记数据有限的问题。
- 当前方法主要依赖伪标签进行像素级一致性训练,但忽略了更全面语义级别的一致性。
- DuCiSC学习框架通过双重范式鼓励区域级语义一致性,提高特征提取的平衡性。
- DuCiSC采用新型自感知置信度估计策略,选择可靠的伪标签以利用无标签数据的训练动态。
- DuCiSC在四个数据集上的表现均优于其他方法,包括左心房和胰腺分割、自动心脏诊断挑战和下颌神经分割等场景。
- DuCiSC方法已公开可用,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

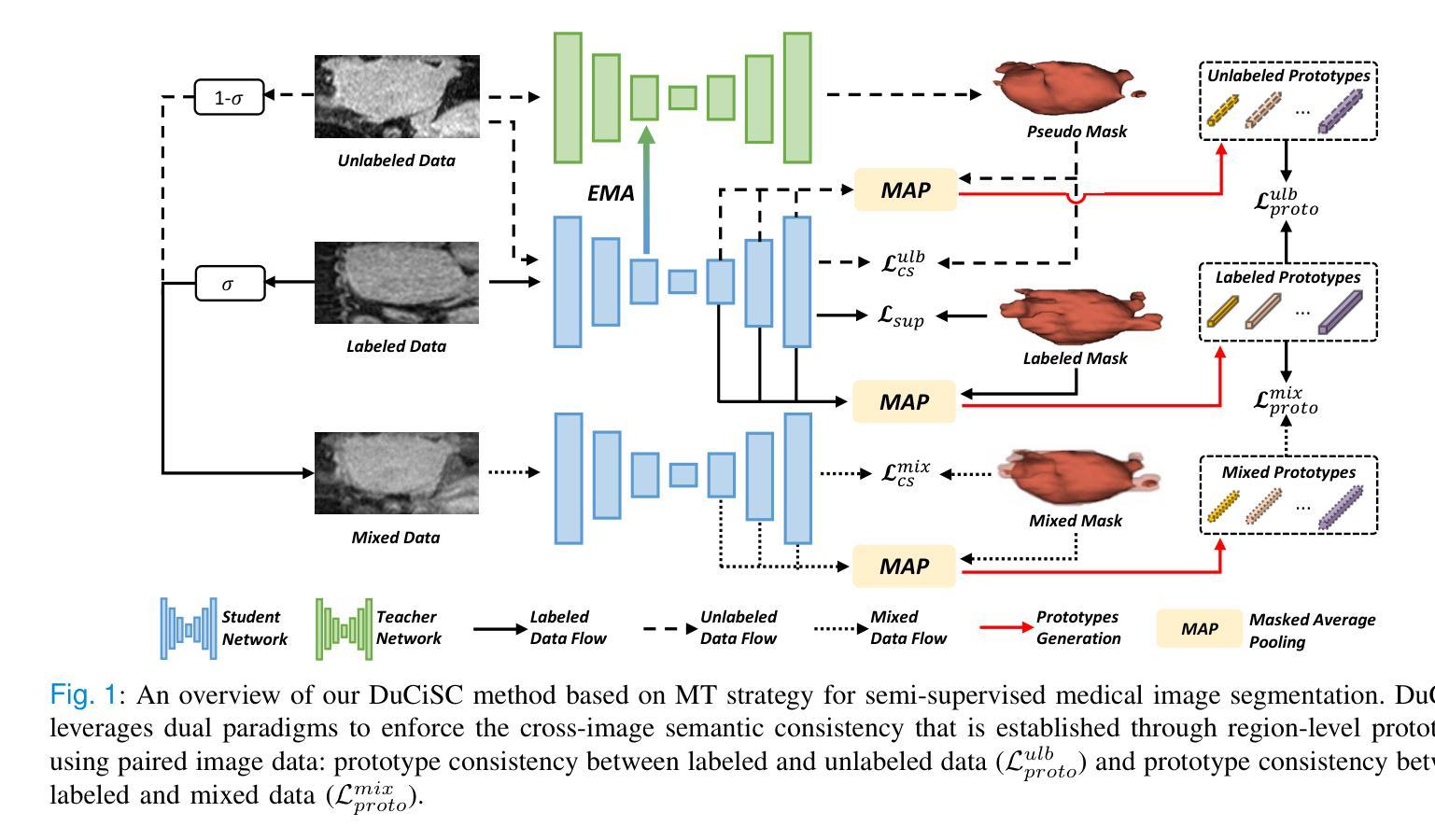
Exploring Probabilistic Modeling Beyond Domain Generalization for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:I-Hsiang Chen, Hua-En Chang, Wei-Ting Chen, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Sy-Yen Kuo
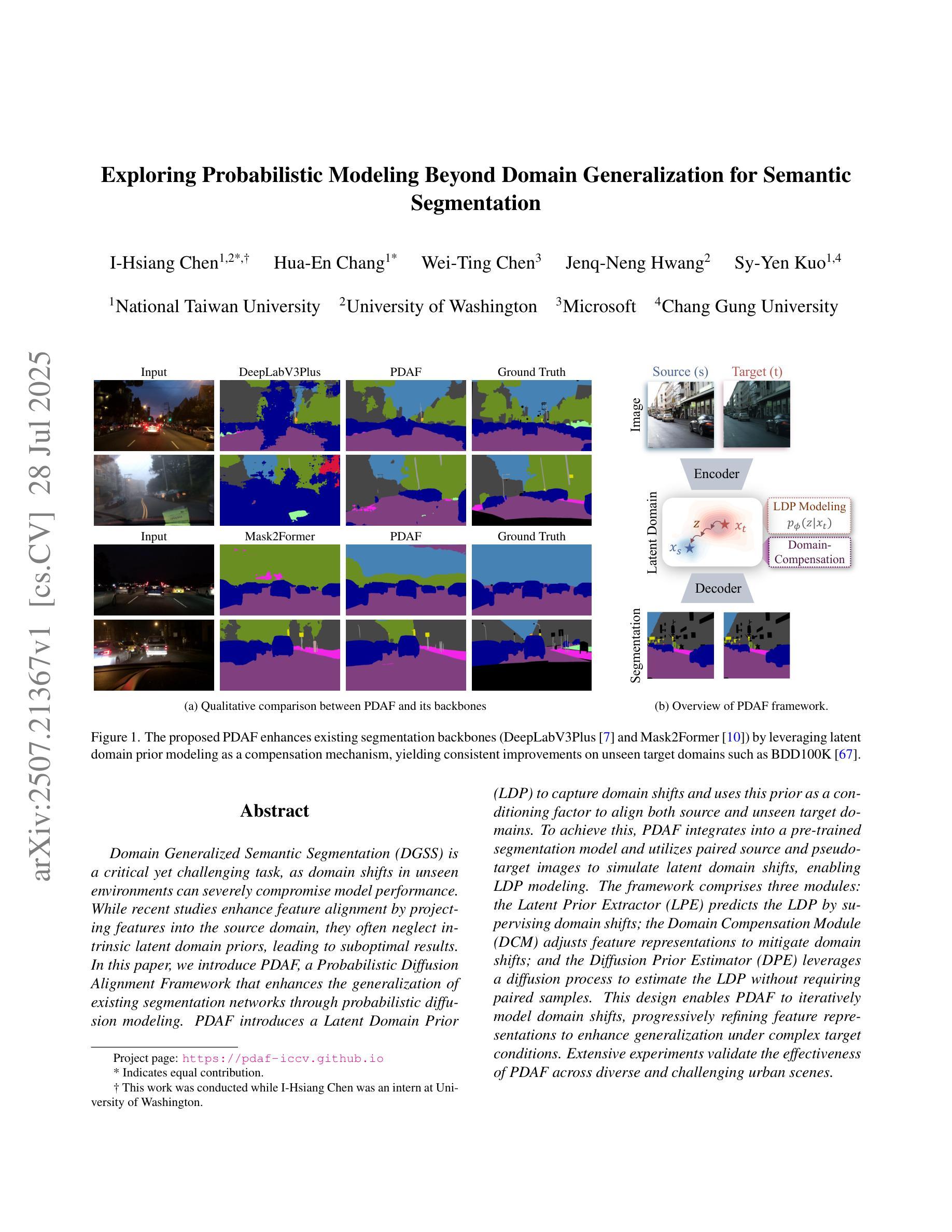
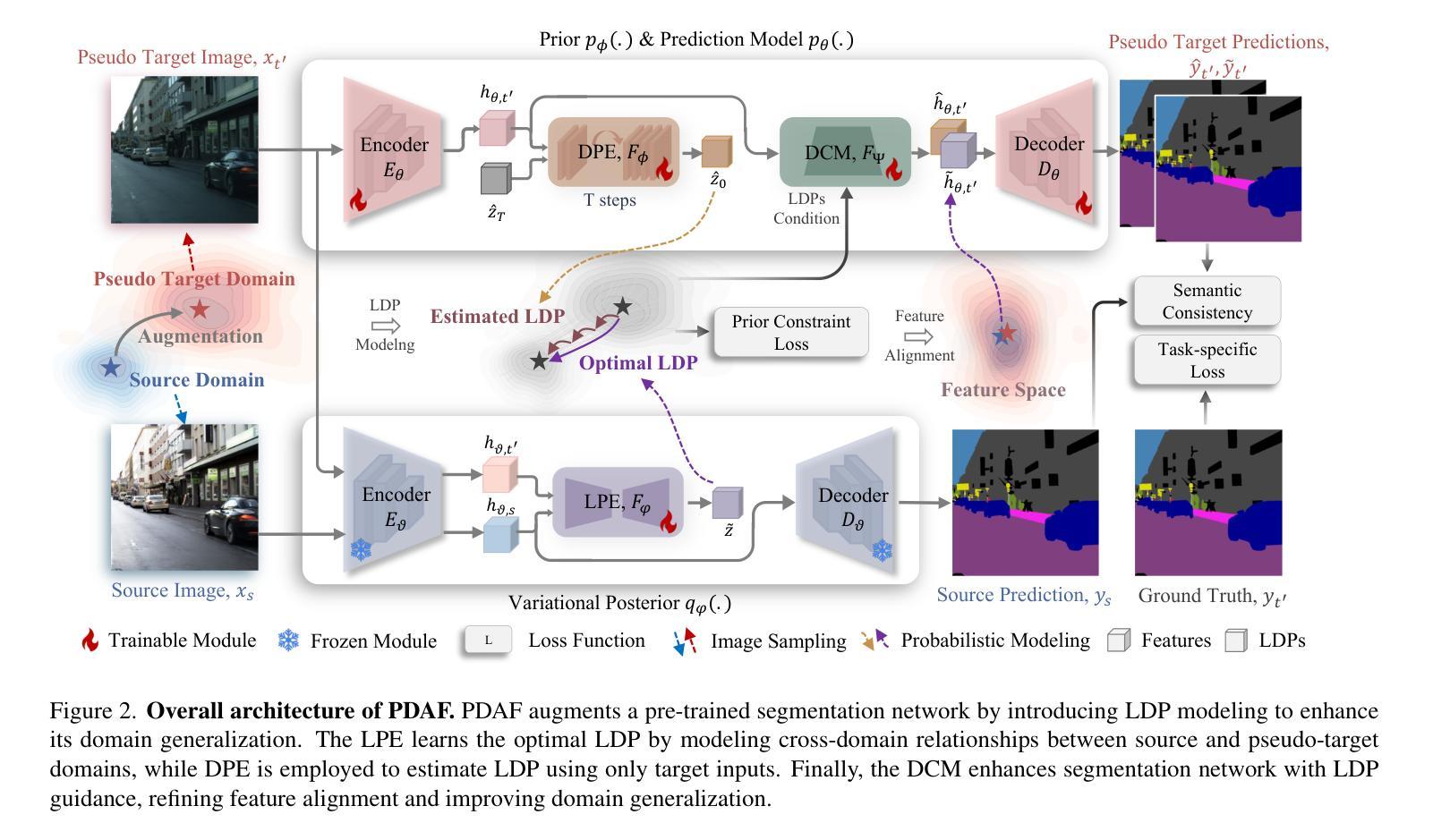
Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS) is a critical yet challenging task, as domain shifts in unseen environments can severely compromise model performance. While recent studies enhance feature alignment by projecting features into the source domain, they often neglect intrinsic latent domain priors, leading to suboptimal results. In this paper, we introduce PDAF, a Probabilistic Diffusion Alignment Framework that enhances the generalization of existing segmentation networks through probabilistic diffusion modeling. PDAF introduces a Latent Domain Prior (LDP) to capture domain shifts and uses this prior as a conditioning factor to align both source and unseen target domains. To achieve this, PDAF integrates into a pre-trained segmentation model and utilizes paired source and pseudo-target images to simulate latent domain shifts, enabling LDP modeling. The framework comprises three modules: the Latent Prior Extractor (LPE) predicts the LDP by supervising domain shifts; the Domain Compensation Module (DCM) adjusts feature representations to mitigate domain shifts; and the Diffusion Prior Estimator (DPE) leverages a diffusion process to estimate the LDP without requiring paired samples. This design enables PDAF to iteratively model domain shifts, progressively refining feature representations to enhance generalization under complex target conditions. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of PDAF across diverse and challenging urban scenes.
领域泛化语义分割(DGSS)是一项至关重要的且具有挑战性的任务,因为未知环境中的领域偏移可能会严重损害模型性能。虽然最近的研究通过将特征投影到源域来增强特征对齐,但它们往往忽略了内在的潜在领域先验,从而导致结果不佳。在本文中,我们介绍了PDAF,即概率扩散对齐框架,它通过概率扩散建模增强现有分割网络的泛化能力。PDAF引入潜在领域先验(LDP)来捕获领域偏移,并将此先验作为条件因素来对齐源域和未见过的目标域。为了实现这一点,PDAF集成到预训练的分割模型中,并利用成对的源和伪目标图像来模拟潜在领域偏移,从而实现LDP建模。该框架包含三个模块:潜在先验提取器(LPE)通过监督领域偏移来预测LDP;领域补偿模块(DCM)调整特征表示以减轻领域偏移;扩散先验估计器(DPE)利用扩散过程来估计LDP,无需配对样本。这种设计使PDAF能够迭代地模拟领域偏移,逐渐优化特征表示,在复杂的目标条件下提高泛化能力。大量实验验证了PDAF在多样且具挑战性的城市场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为PDAF的Probabilistic Diffusion Alignment Framework,用于增强现有分割网络的泛化能力。该框架通过概率扩散建模捕捉领域迁移并用作对齐源域和未见目标域的条件因素。它包括三个模块:Latent Prior Extractor(LPE)、Domain Compensation Module(DCM)和Diffusion Prior Estimator(DPE)。通过模拟潜在领域迁移并利用配对的源和伪目标图像进行训练,该框架能够逐步建模领域迁移并优化特征表示,从而提高复杂目标条件下的泛化能力。实验证明,PDAF在多样且复杂的城市场景下具有显著效果。
Key Takeaways
- PDAF是一种增强现有分割网络泛化能力的Probabilistic Diffusion Alignment Framework。
- PDAF通过概率扩散建模捕捉领域迁移,并引入Latent Domain Prior(LDP)作为对齐源域和未见目标域的条件因素。
- PDAF包括三个模块:Latent Prior Extractor(LPE)用于预测LDP并监测领域迁移;Domain Compensation Module(DCM)用于调整特征表示以减轻领域迁移的影响;Diffusion Prior Estimator(DPE)利用扩散过程估计LDP,无需配对样本。
- PDAF通过模拟潜在领域迁移并利用配对的源和伪目标图像进行训练,能够逐步建模领域迁移并优化特征表示。
- PDAF设计用于增强在复杂目标条件下的泛化能力。
- 实验证明,PDAF在多样且复杂的城市场景下具有显著效果。
点此查看论文截图
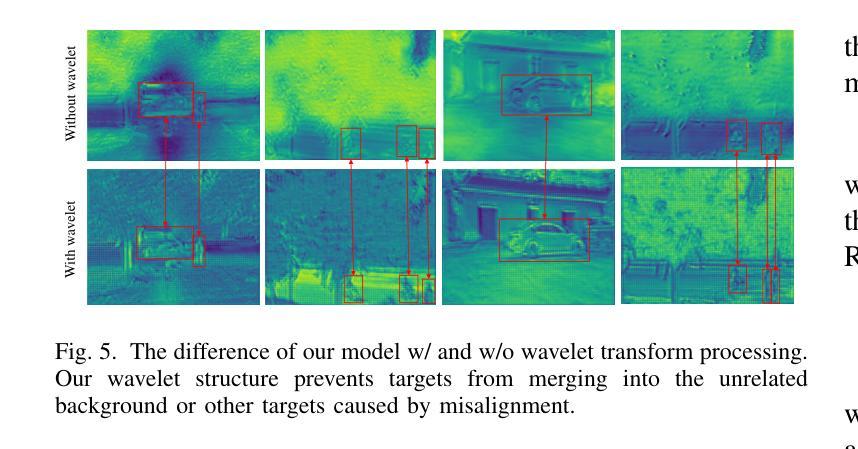
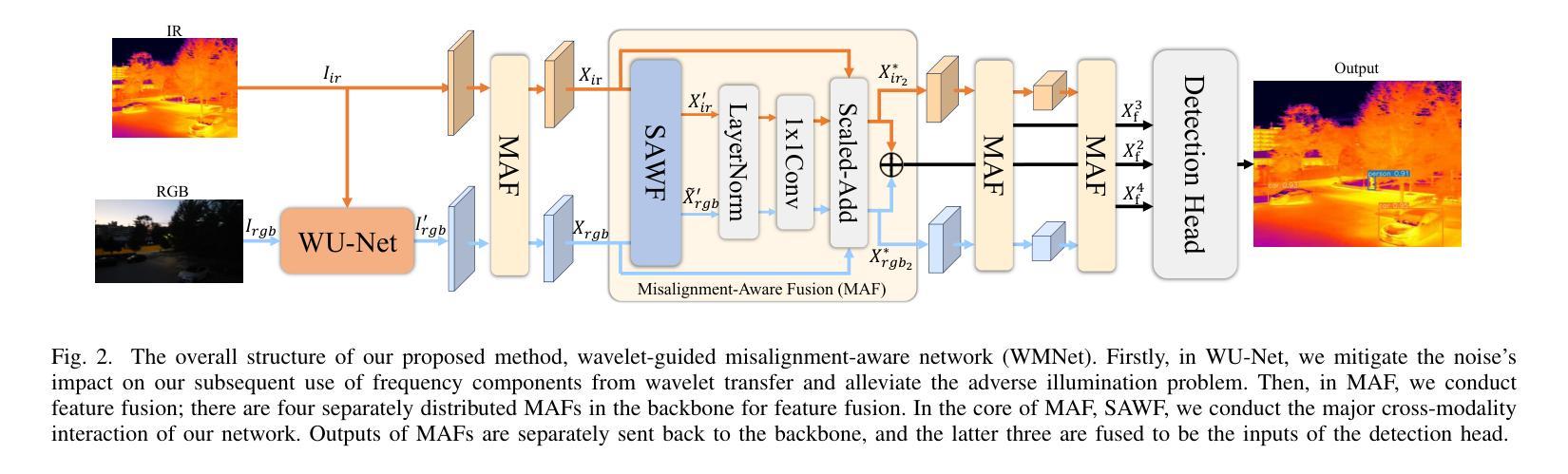
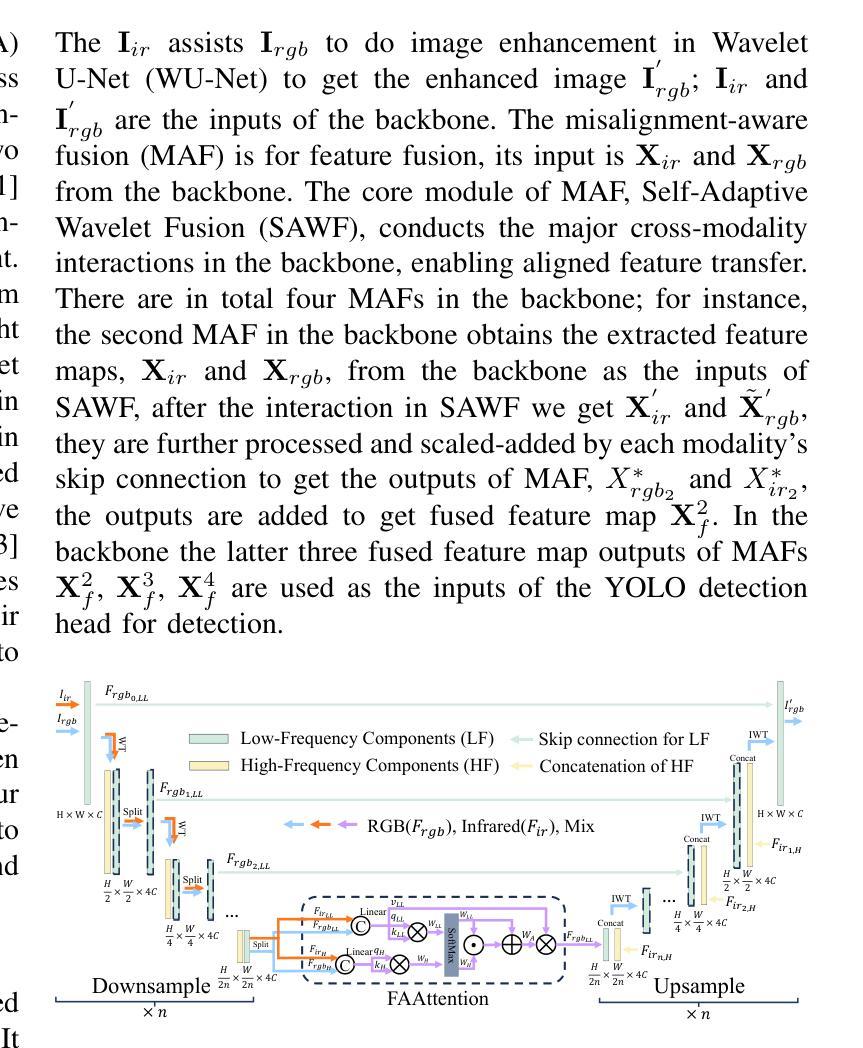
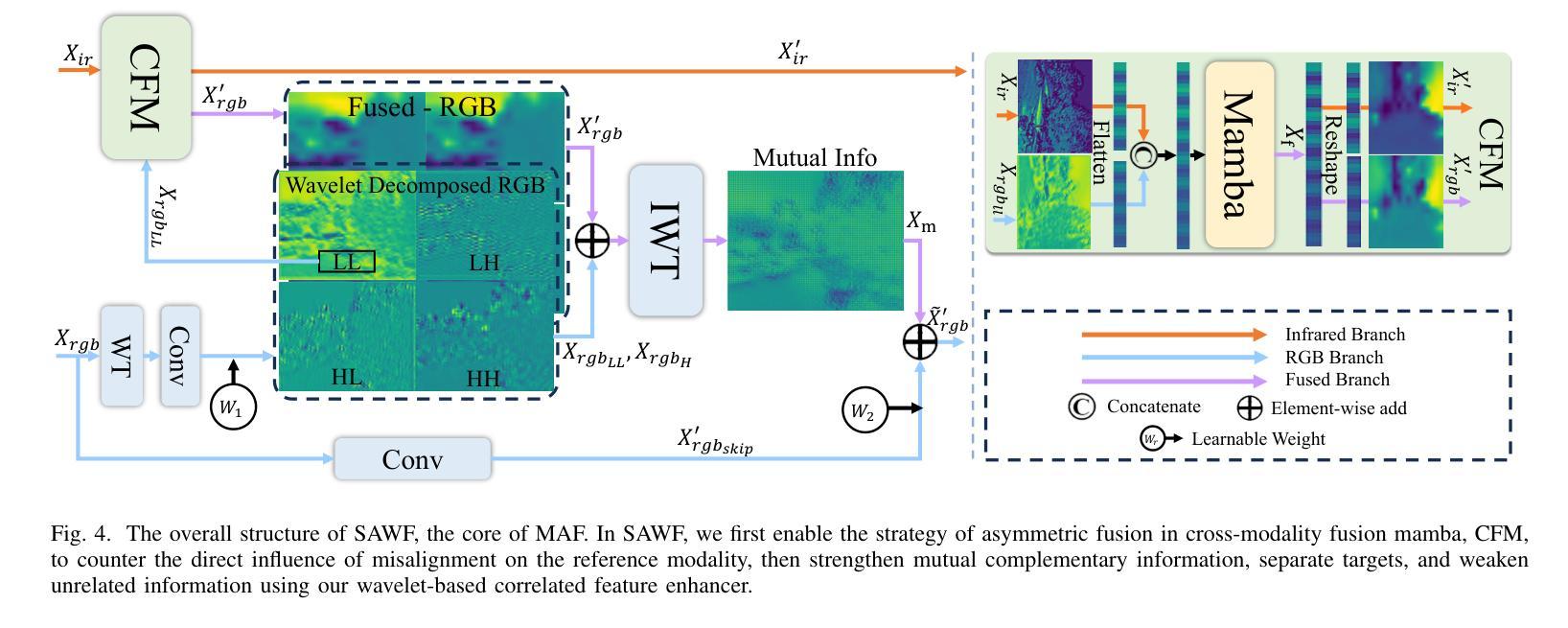
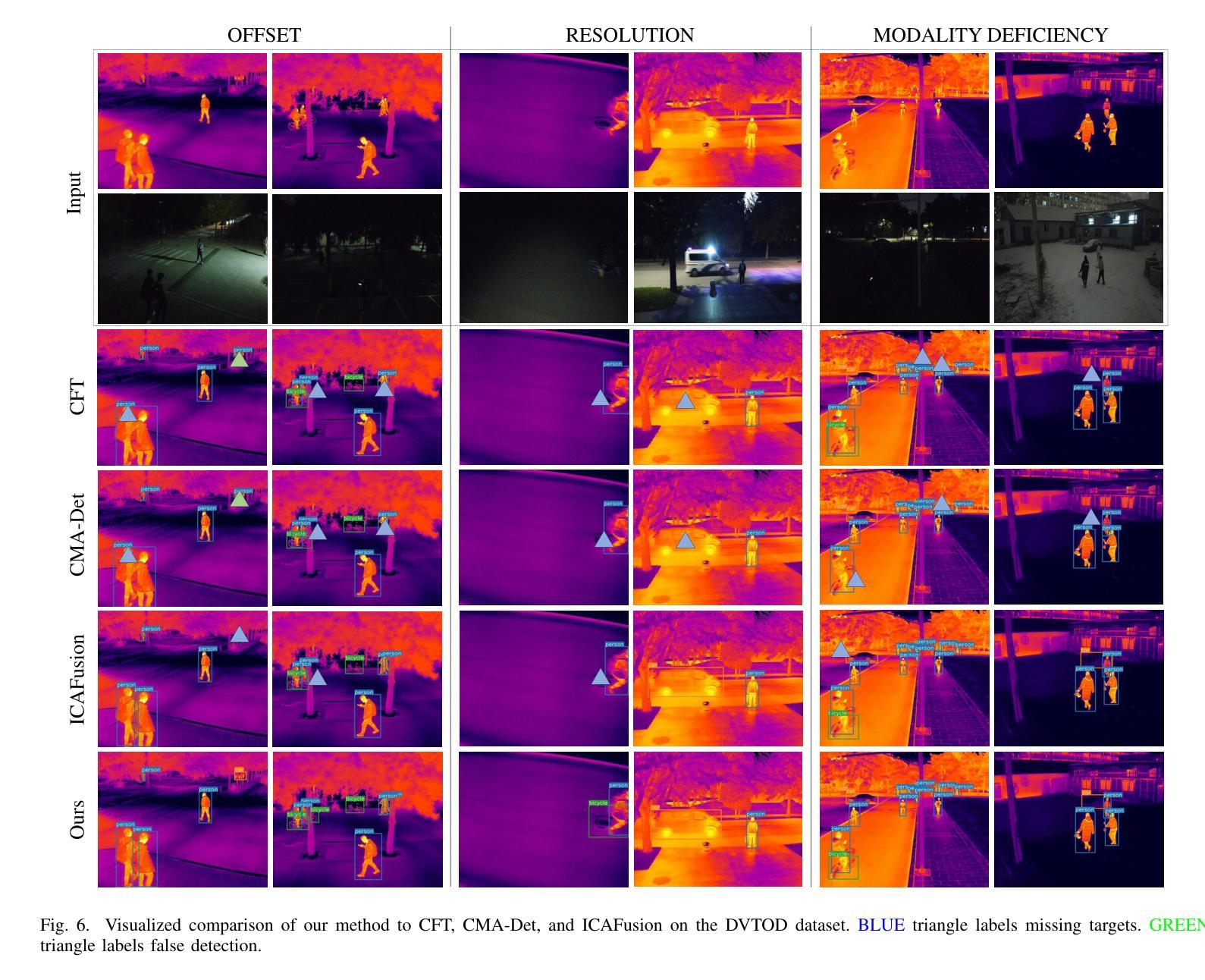
Wavelet-guided Misalignment-aware Network for Visible-Infrared Object Detection
Authors:Haote Zhang, Lipeng Gu, Wuzhou Quan, Fu Lee Wang, Honghui Fan, Jiali Tang, Dingkun Zhu, Haoran Xie, Xiaoping Zhang, Mingqiang Wei
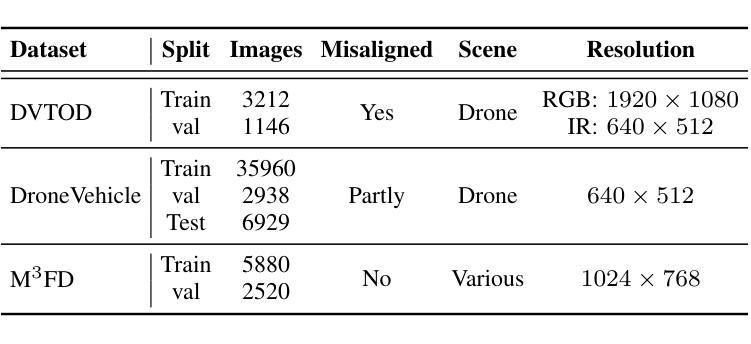
Visible-infrared object detection aims to enhance the detection robustness by exploiting the complementary information of visible and infrared image pairs. However, its performance is often limited by frequent misalignments caused by resolution disparities, spatial displacements, and modality inconsistencies. To address this issue, we propose the Wavelet-guided Misalignment-aware Network (WMNet), a unified framework designed to adaptively address different cross-modal misalignment patterns. WMNet incorporates wavelet-based multi-frequency analysis and modality-aware fusion mechanisms to improve the alignment and integration of cross-modal features. By jointly exploiting low and high-frequency information and introducing adaptive guidance across modalities, WMNet alleviates the adverse effects of noise, illumination variation, and spatial misalignment. Furthermore, it enhances the representation of salient target features while suppressing spurious or misleading information, thereby promoting more accurate and robust detection. Extensive evaluations on the DVTOD, DroneVehicle, and M3FD datasets demonstrate that WMNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on misaligned cross-modal object detection tasks, confirming its effectiveness and practical applicability.
可见光红外目标检测旨在利用可见光和红外图像对的互补信息提高检测稳健性。然而,其性能往往受到由分辨率差异、空间位移和模态不一致引起的频繁错位的影响。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于小波引导的错位感知网络(WMNet),这是一个统一框架,旨在自适应地解决不同的跨模态错位模式。WMNet结合了基于小波的多频分析和模态感知融合机制,以提高跨模态特征的对齐和集成。通过联合利用高低频信息和引入跨模态的自适应指导,WMNet减轻了噪声、光照变化和空间错位的不利影响。此外,它还增强了显著目标特征的表示,同时抑制了虚假或误导信息,从而促进了更准确和稳健的检测。在DVTOD、DroneVehicle和M3FD数据集上的广泛评估表明,WMNet在错位跨模态目标检测任务上达到了最新技术水平,证实了其有效性和实际应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
可见光红外目标检测旨在利用可见光和红外图像对的互补信息提高检测稳健性。然而,性能常受限于跨模态错位导致的频繁误对齐问题。为解决此问题,我们提出Wavelet-guided Misalignment-aware网络(WMNet),一个统一框架,可自适应解决不同的跨模态错位模式。WMNet结合小波多频分析和模态感知融合机制,改善跨模态特征的对齐和集成。通过联合利用高低频信息和引入跨模态自适应指导,WMNet减轻了噪声、光照变化和空间错位的不利影响,提高了目标特征的表示能力,同时抑制了冗余或误导信息,促进了更准确和稳健的检测。在DVTOD、DroneVehicle和M3FD数据集上的广泛评估证明了WMNet在跨模态误对齐目标检测任务上的先进性。
Key Takeaways:
- 可见光红外目标检测追求利用两种图像信息的互补性来提升检测稳健性。
- 跨模态错位问题是影响性能的主要因素之一。
- WMNet被设计为一个统一框架,能够自适应处理不同的跨模态错位模式。
- WMNet结合小波多频分析和模态感知融合来提升跨模态特征的对齐和集成。
- 通过联合高低频信息和跨模态自适应指导,WMNet提高了目标特征的表示能力并抑制了冗余信息。
- WMNet在多个数据集上的评估证明了其在跨模态误对齐目标检测任务上的先进性。
点此查看论文截图


DriveIndia: An Object Detection Dataset for Diverse Indian Traffic Scenes
Authors:Rishav Kumar, D. Santhosh Reddy, P. Rajalakshmi
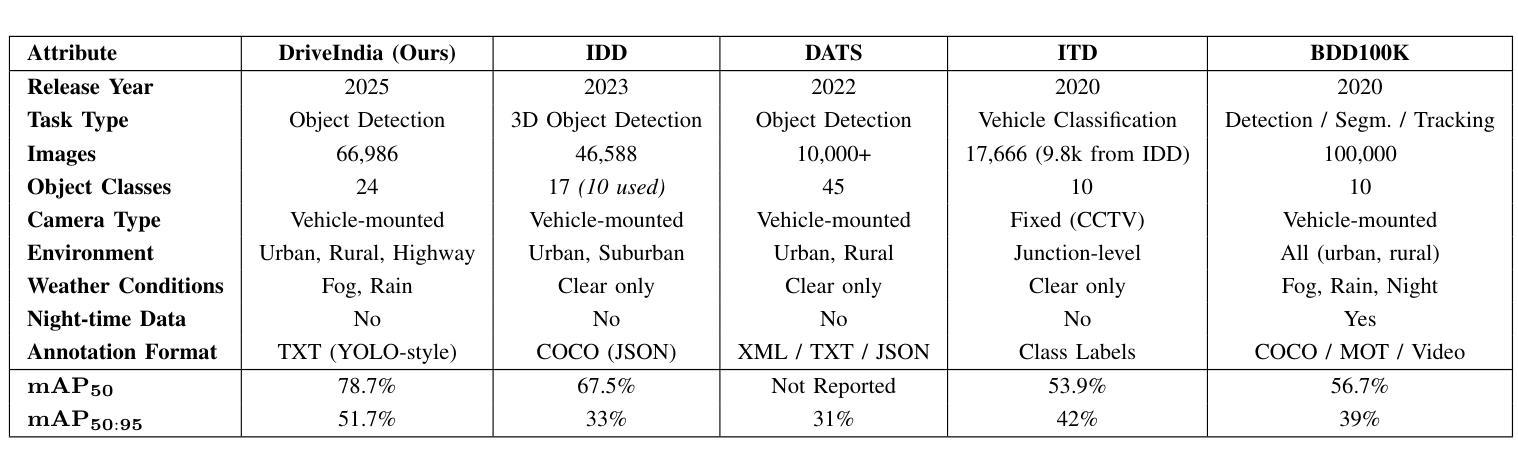
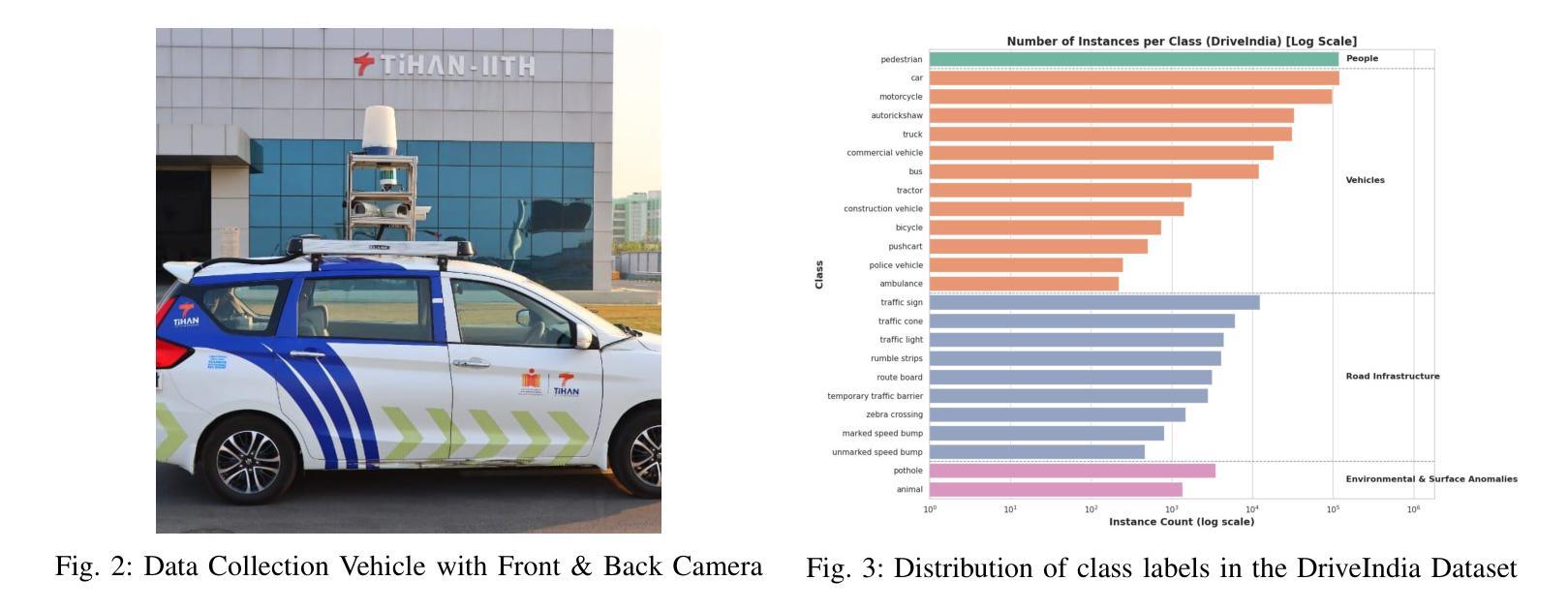
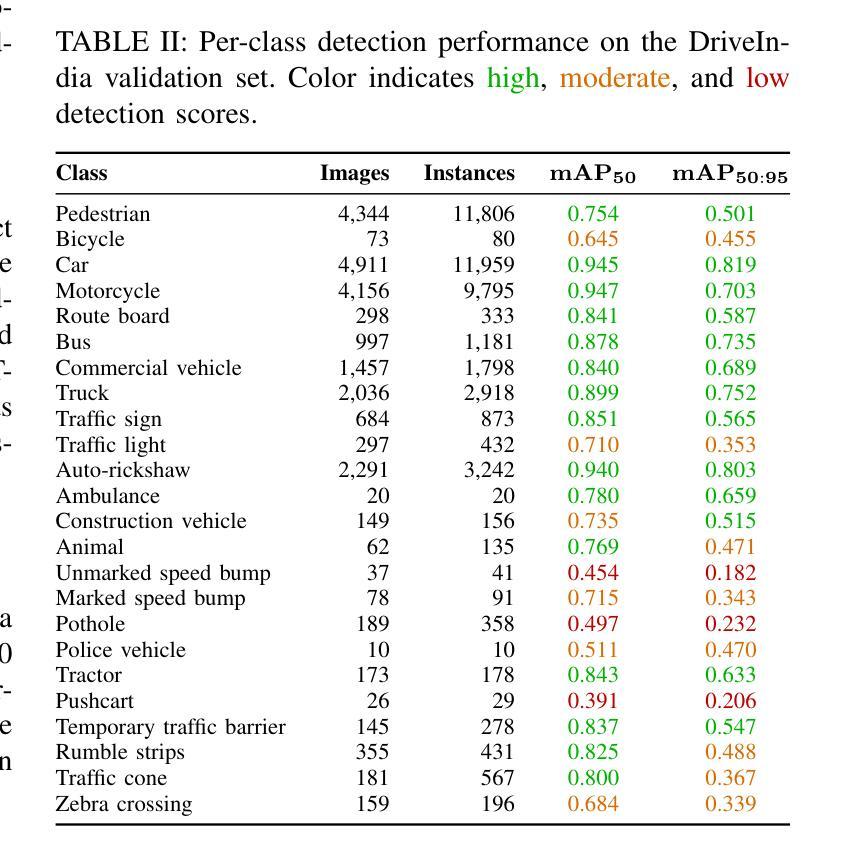
We introduce DriveIndia, a large-scale object detection dataset purpose-built to capture the complexity and unpredictability of Indian traffic environments. The dataset contains 66,986 high-resolution images annotated in YOLO format across 24 traffic-relevant object categories, encompassing diverse conditions such as varied weather (fog, rain), illumination changes, heterogeneous road infrastructure, and dense, mixed traffic patterns and collected over 120+ hours and covering 3,400+ kilometers across urban, rural, and highway routes. DriveIndia offers a comprehensive benchmark for real-world autonomous driving challenges. We provide baseline results using state-of-the-art YOLO family models, with the top-performing variant achieving a mAP50 of 78.7%. Designed to support research in robust, generalizable object detection under uncertain road conditions, DriveIndia will be publicly available via the TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad dataset repository (https://tihan.iith.ac.in/tiand-datasets/).
我们推出DriveIndia数据集,这是一个专门为了捕捉印度交通环境的复杂性和不可预测性而构建的大规模物体检测数据集。该数据集包含以YOLO格式标注的66,986张高分辨率图片,涉及交通相关的24个类别物体。数据集涵盖各种条件下的数据,包括多变的天气(如雾、雨)、光照变化、不同的道路基础设施以及密集且混合的交通模式等。数据收集时间超过120小时,覆盖城市和乡村以及高速公路路线共超过三千四百公里的路段。对于现实世界中自动驾驶挑战提供了全面基准指标评估的数据集,我们可以利用目前前沿的YOLO家族模型给出基线测试结果。性能最优的版本能在YOLO(MAP@0.5 IoU)基准测试中得到78.7%的指标结果。DriveIndia被设计用于支持在不确定道路条件下实现稳健可推广的物体检测研究,并通过TiHAN-印度理工学院海德拉巴数据集仓库公开提供(https://tihan.iith.ac.in/tiand-datasets/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ITSC 2025 Conference
Summary
驱动印度数据集介绍。该数据集包含6万6千多张高分辨率图片,用于捕捉印度复杂的交通环境,可用于自主驾驶真实世界挑战评估。数据涵盖了各种条件如不同天气和照明变化等。使用最先进的YOLO家族模型提供基准结果,最佳模型达到78.7%的mAP50准确率。数据将通过TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad数据集仓库公开访问。
Key Takeaways
- DriveIndia是一个针对印度交通环境构建的大规模对象检测数据集。
- 数据集包含超过6万张高分辨率图片,涵盖多种交通相关对象类别。
- 数据集考虑了多种条件,包括不同天气、照明变化、道路基础设施的多样性和密集混合的交通模式。
- 使用YOLO格式进行标注,并提供了使用最先进YOLO家族模型的基准结果。
- 最佳模型达到78.7%的mAP50准确率。
- 该数据集旨在支持不确定道路条件下的稳健、通用对象检测研究。
点此查看论文截图


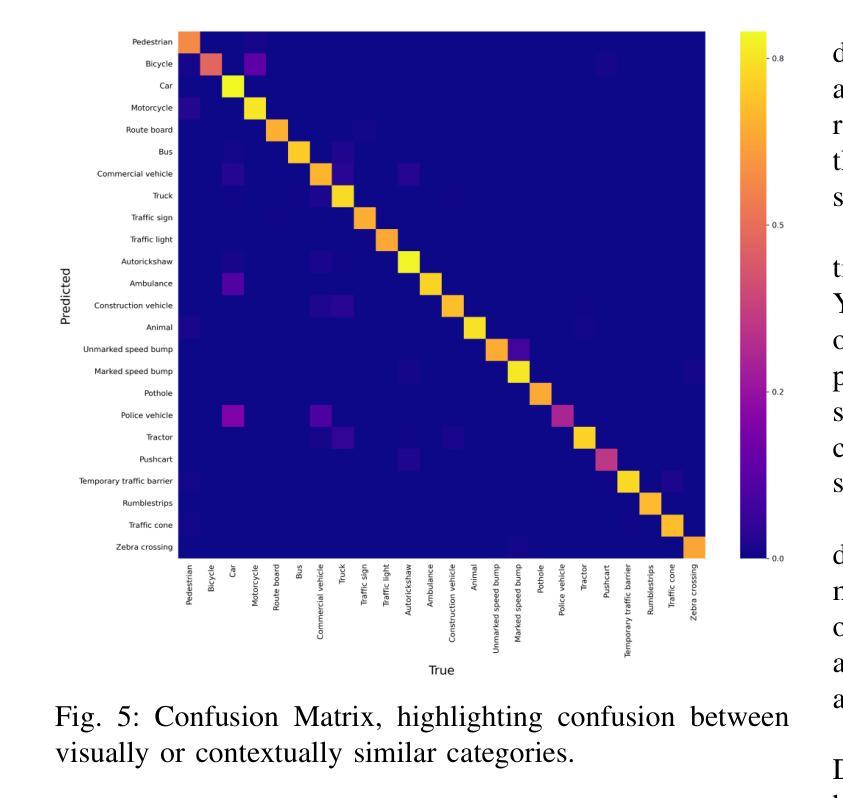
FedS2R: One-Shot Federated Domain Generalization for Synthetic-to-Real Semantic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Tao Lian, Jose L. Gómez, Antonio M. López
Federated domain generalization has shown promising progress in image classification by enabling collaborative training across multiple clients without sharing raw data. However, its potential in the semantic segmentation of autonomous driving remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose FedS2R, the first one-shot federated domain generalization framework for synthetic-to-real semantic segmentation in autonomous driving. FedS2R comprises two components: an inconsistency-driven data augmentation strategy that generates images for unstable classes, and a multi-client knowledge distillation scheme with feature fusion that distills a global model from multiple client models. Experiments on five real-world datasets, Cityscapes, BDD100K, Mapillary, IDD, and ACDC, show that the global model significantly outperforms individual client models and is only 2 mIoU points behind the model trained with simultaneous access to all client data. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of FedS2R in synthetic-to-real semantic segmentation for autonomous driving under federated learning
联邦域泛化(Federated Domain Generalization)在图像分类方面展现出巨大的潜力,通过跨多个客户端进行协同训练,无需共享原始数据。然而,其在自动驾驶语义分割领域的应用仍被较少探索。在本文中,我们提出了FedS2R,这是首个针对自动驾驶合成到真实语义分割的一站式联邦域泛化框架。FedS2R包含两个组件:一种基于不一致性的数据增强策略,用于生成不稳定类的图像;一种多客户端知识蒸馏方案,带有特征融合,从多个客户端模型中提炼出全局模型。在五个真实世界数据集Cityscapes、BDD100K、Mapillary、IDD和ACDC上的实验表明,全局模型显著优于单个客户端模型,并且仅比同时访问所有客户端数据的模型低2 mIoU点。这些结果证明了FedS2R在联邦学习下自动驾驶合成到真实语义分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在图像分类方面,联邦域泛化通过在多个客户端之间进行协作训练且不共享原始数据的方式展现了良好的发展势头。然而,它在自动驾驶语义分割方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。本文提出了FedS2R,这是首个针对自动驾驶中合成到真实场景的语义分割的一次性联邦域泛化框架。FedS2R包含两个组件:一种以不一致性驱动的数据增强策略,用于生成不稳定类的图像;以及一种具有特征融合的多客户端知识蒸馏方案,它从多个客户端模型中提炼出全局模型。在五个真实世界数据集Cityscapes、BDD100K、Mapillary、IDD和ACDC上的实验表明,全局模型的性能显著优于单个客户端模型,并且只比同时访问所有客户端数据的模型落后2 mIoU点。这些结果证明了FedS2R在联邦学习下的自动驾驶合成到真实语义分割中的有效性。
要点
- 联邦域泛化在图像分类中展现出通过跨多个客户端协作训练的优势,但在自动驾驶语义分割方面的应用尚未充分研究。
- 提出了FedS2R框架,它是针对自动驾驶合成到真实场景的语义分割的一次性联邦域泛化框架的首创。
- FedS2R包含两个核心组件:以不一致性驱动的数据增强策略和具有特征融合的多客户端知识蒸馏方案。
- 实验在五个真实世界数据集上进行,证明FedS2R能够显著提升全局模型的性能,与最佳表现模型仅相差2 mIoU点。
- FedS2R框架能有效应用于联邦学习下的自动驾驶语义分割任务。
- 该框架具有潜力在保护数据隐私的同时提高模型性能,为自动驾驶技术的发展开辟新途径。
点此查看论文截图

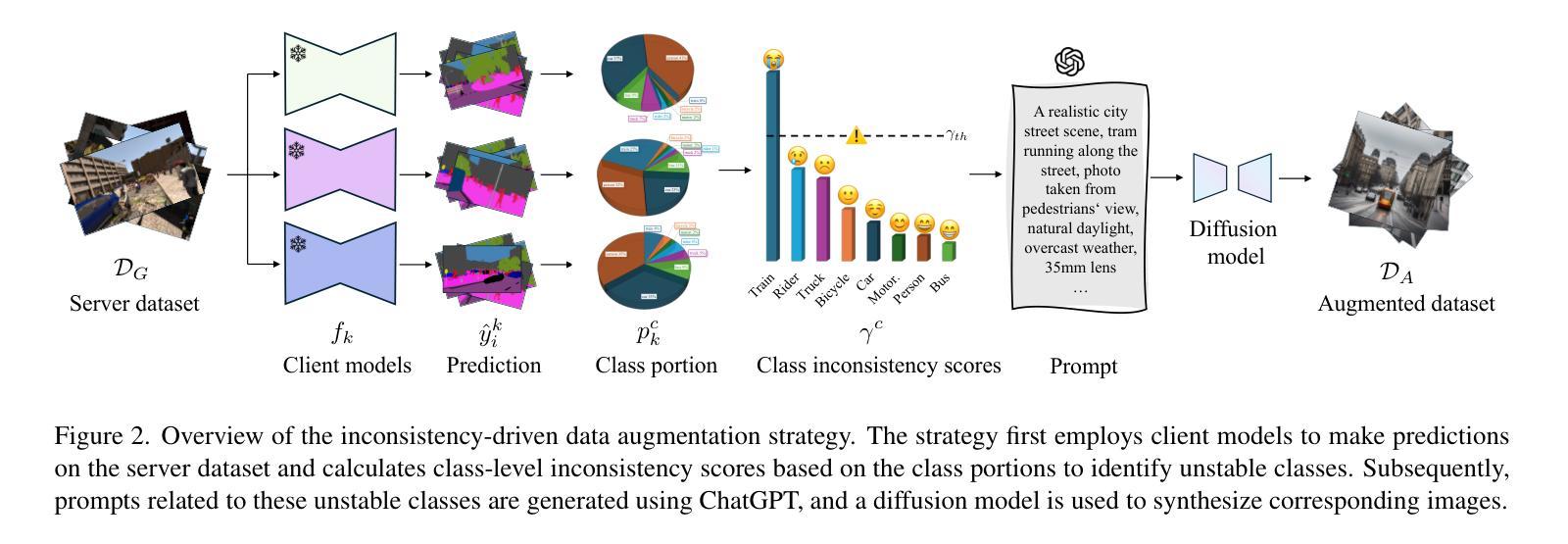

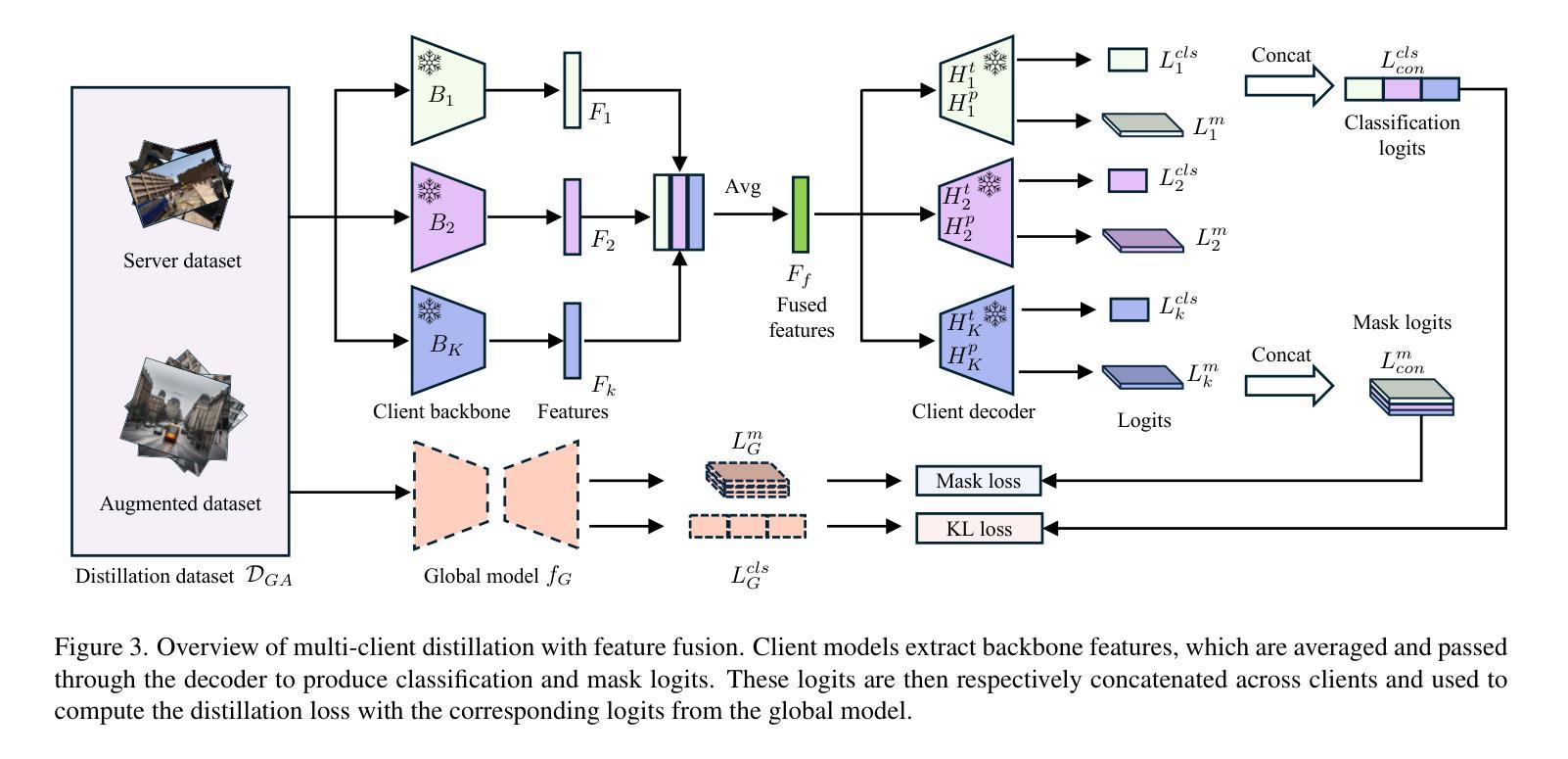
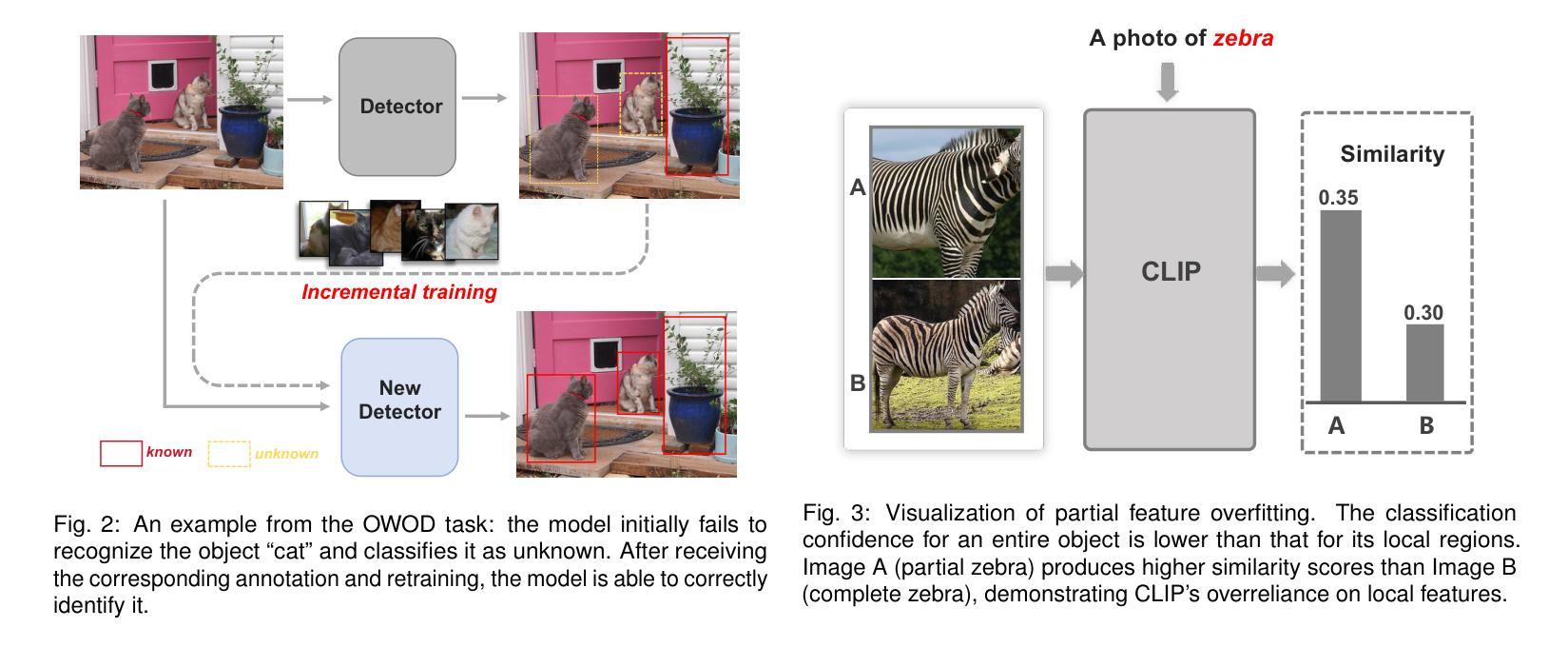
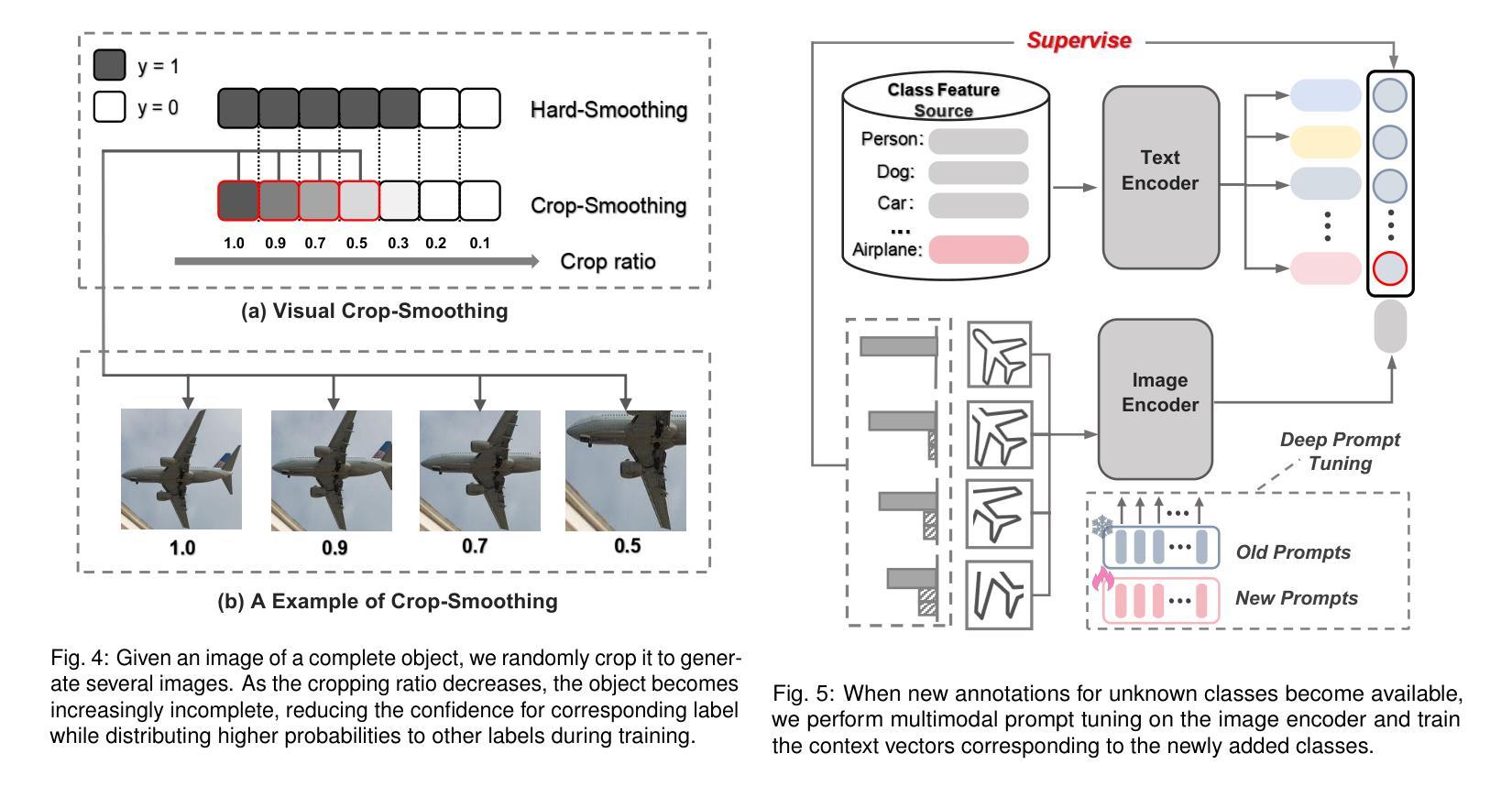
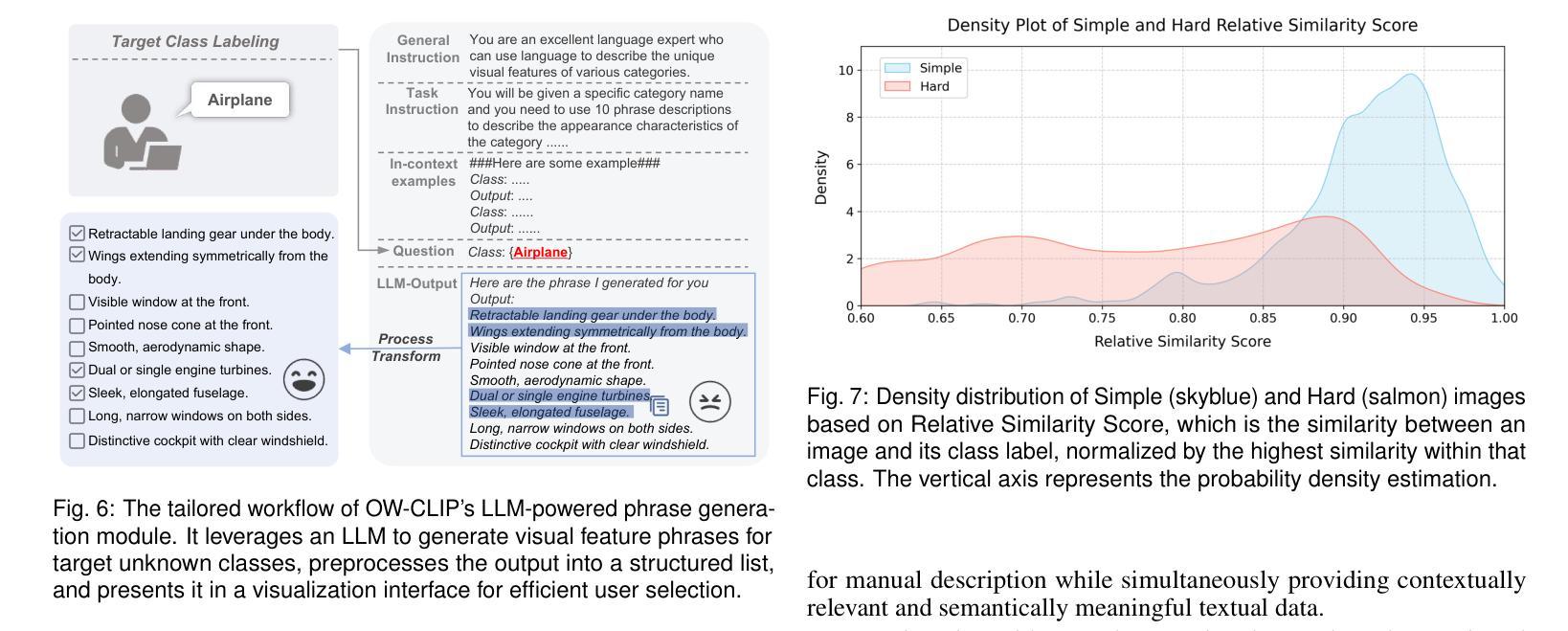
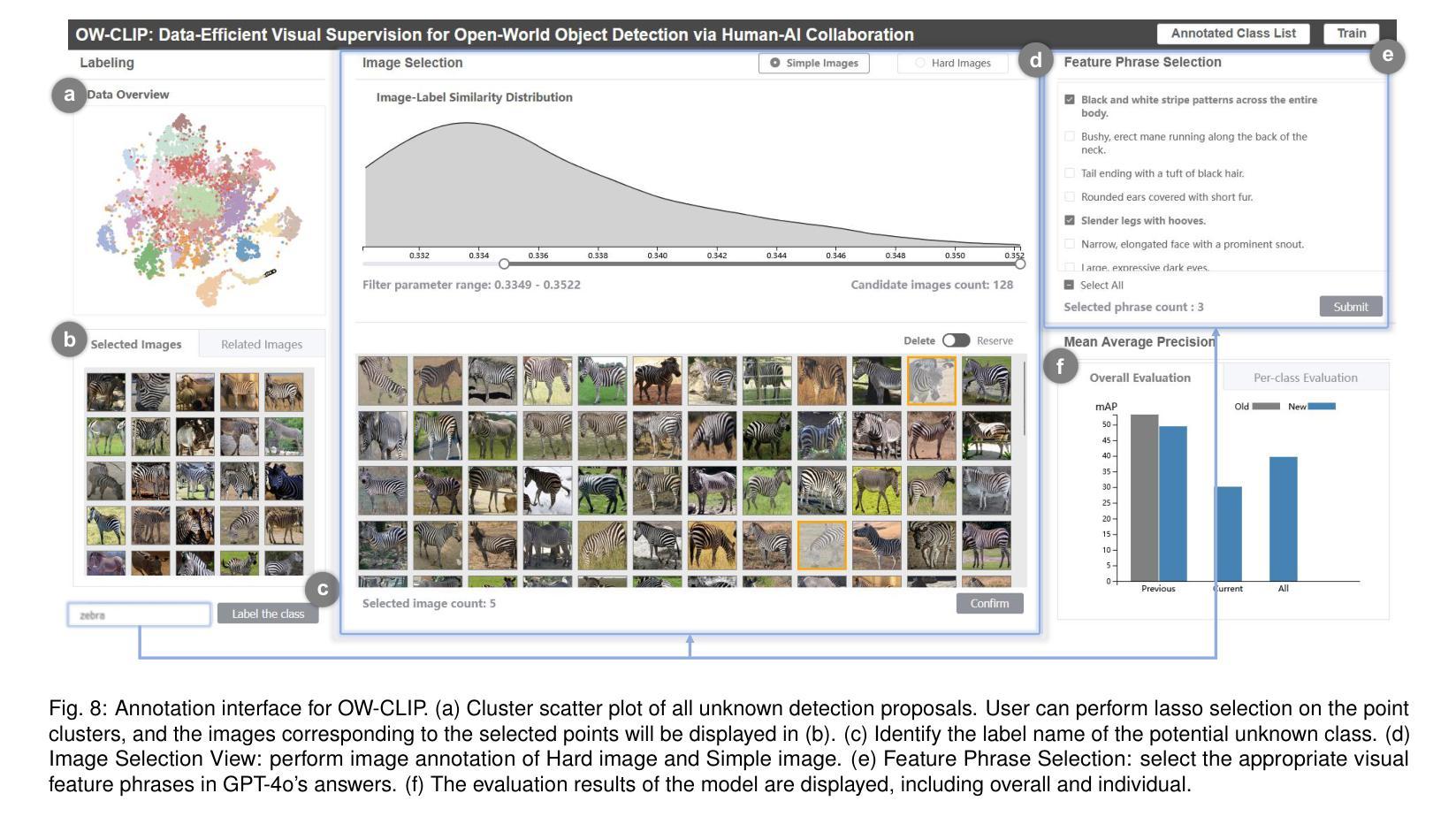
OW-CLIP: Data-Efficient Visual Supervision for Open-World Object Detection via Human-AI Collaboration
Authors:Junwen Duan, Wei Xue, Ziyao Kang, Shixia Liu, Jiazhi Xia
Open-world object detection (OWOD) extends traditional object detection to identifying both known and unknown object, necessitating continuous model adaptation as new annotations emerge. Current approaches face significant limitations: 1) data-hungry training due to reliance on a large number of crowdsourced annotations, 2) susceptibility to “partial feature overfitting,” and 3) limited flexibility due to required model architecture modifications. To tackle these issues, we present OW-CLIP, a visual analytics system that provides curated data and enables data-efficient OWOD model incremental training. OW-CLIP implements plug-and-play multimodal prompt tuning tailored for OWOD settings and introduces a novel “Crop-Smoothing” technique to mitigate partial feature overfitting. To meet the data requirements for the training methodology, we propose dual-modal data refinement methods that leverage large language models and cross-modal similarity for data generation and filtering. Simultaneously, we develope a visualization interface that enables users to explore and deliver high-quality annotations: including class-specific visual feature phrases and fine-grained differentiated images. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates that OW-CLIP achieves competitive performance at 89% of state-of-the-art performance while requiring only 3.8% self-generated data, while outperforming SOTA approach when trained with equivalent data volumes. A case study shows the effectiveness of the developed method and the improved annotation quality of our visualization system.
开放世界目标检测(OWOD)将传统目标检测扩展到识别和未知目标,随着新标注的出现,需要持续模型适应。当前方法面临重大局限性:1)由于依赖大量众包标注,导致数据饥饿型训练;2)容易“局部特征过度拟合”;3)由于需要修改模型架构,导致灵活性有限。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了OW-CLIP,一个视觉分析系统,提供定制数据并启用了数据高效的OWOD模型增量训练。OW-CLIP实现了为OWOD设置量身定制的即插即用多模式提示调整,并引入了一种新颖的“裁剪平滑”技术来缓解局部特征过度拟合问题。为了满足训练方法的数据要求,我们提出了双模态数据精炼方法,利用大型语言模型和跨模态相似性进行数据生成和过滤。同时,我们开发了一个可视化界面,使用户能够探索和提供高质量标注,包括特定类别的视觉特征短语和精细差异图像。定量评估表明,OW-CLIP达到了最新技术的89%性能水平,同时仅需要3.8%的自我生成数据,而在使用等效数据量进行训练时表现优于最新技术方法。案例研究表明所开发方法的有效性以及我们可视化系统改进标注质量的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 11 figures
Summary
OWOD面临数据依赖性强、易局部特征过拟合和模型架构修改灵活性有限等问题。为应对这些问题,提出了OW-CLIP视觉分析系统,实现数据高效的OWOD模型增量训练。采用量身定制的“即插即用”多模态提示调整,引入新颖的“Crop-Smoothing”技术减轻局部特征过拟合问题。利用大型语言模型和跨模态相似性进行双模态数据精炼,满足训练方法论的数据要求。同时开发可视化界面,用户可探索并提供高质量注释。定量评估显示,OW-CLIP在仅使用3.8%自我生成数据的情况下达到最新技术性能的89%,并在等效数据量训练时表现更优。案例研究证明了开发方法的有效性和可视化系统提高的注释质量。
Key Takeaways
- 开放世界目标检测(OWOD)面临多个挑战,包括数据依赖性强、易局部特征过拟合和模型架构灵活性有限。
- 提出OW-CLIP视觉分析系统,实现数据高效的OWOD模型增量训练,解决上述问题。
- OW-CLIP采用量身定制的多模态提示调整,引入Crop-Smoothing技术来减轻局部特征过拟合。
- 利用大型语言模型和跨模态相似性进行双模态数据精炼,满足训练方法论的数据需求。
- 开发可视化界面,便于用户探索并提供高质量注释。
- 定量评估显示,OW-CLIP在数据效率方面表现出竞争力,仅在3.8%的自我生成数据下即达到最新技术的89%性能。在等效数据量训练时表现更出色。
点此查看论文截图
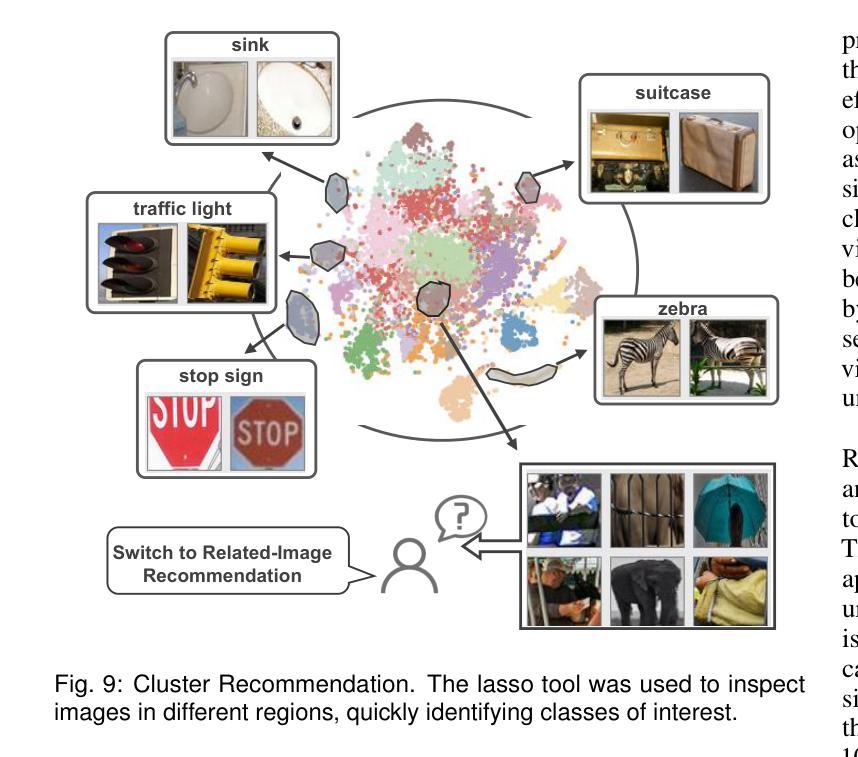
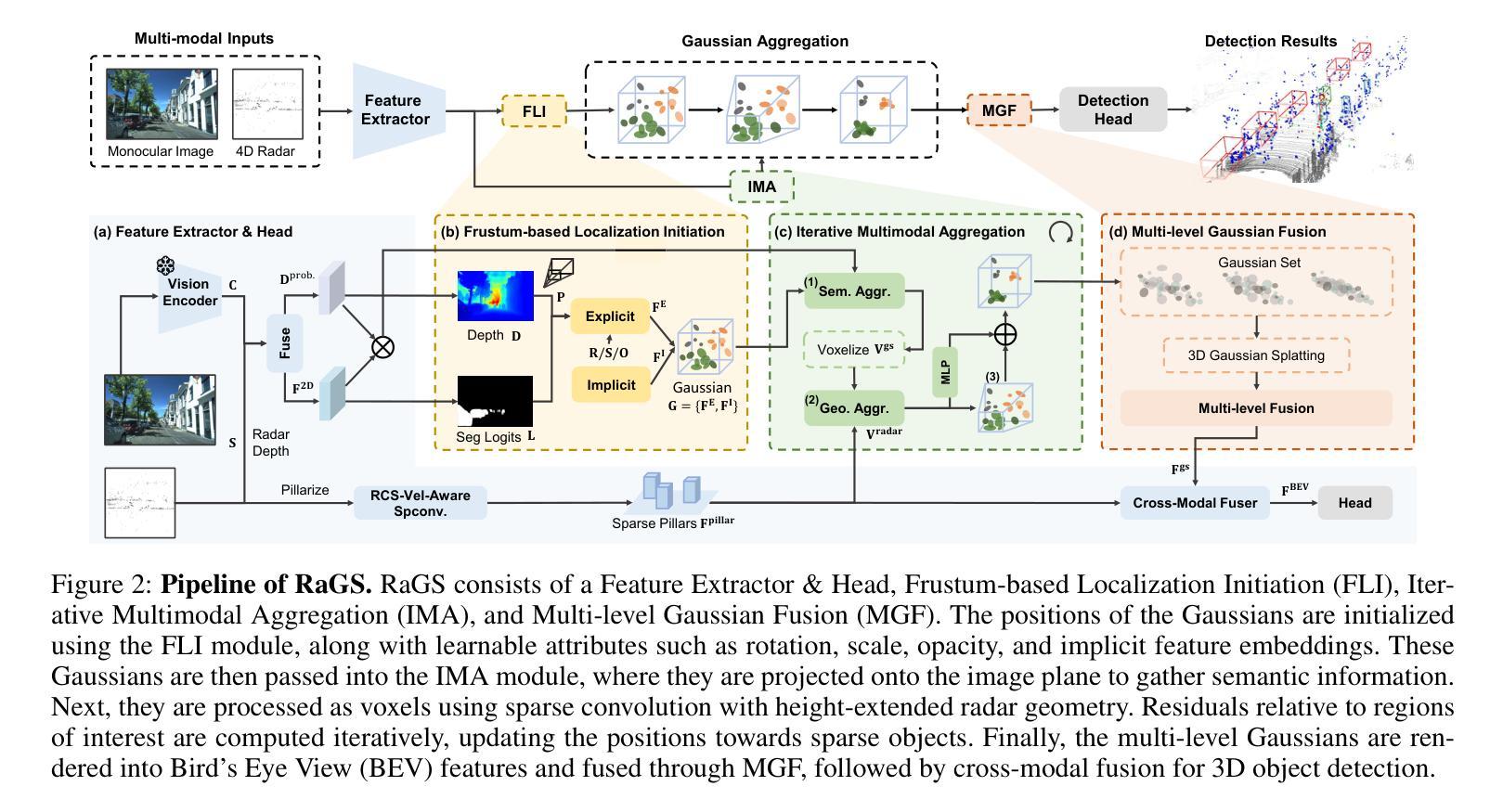
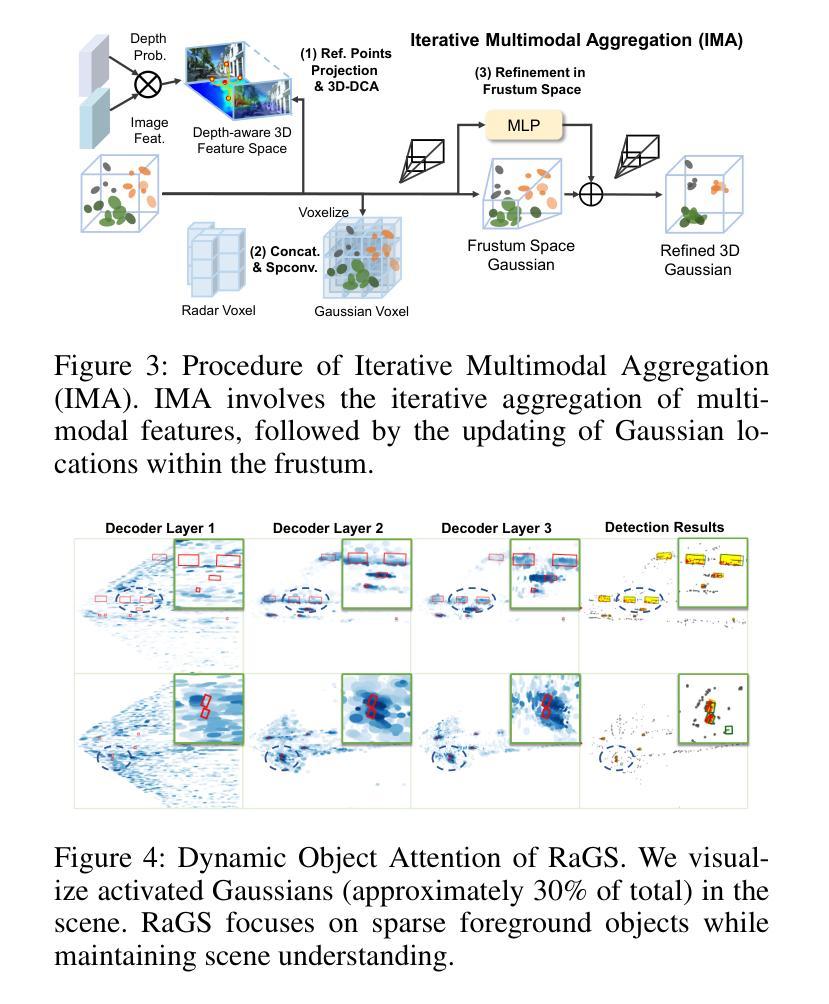
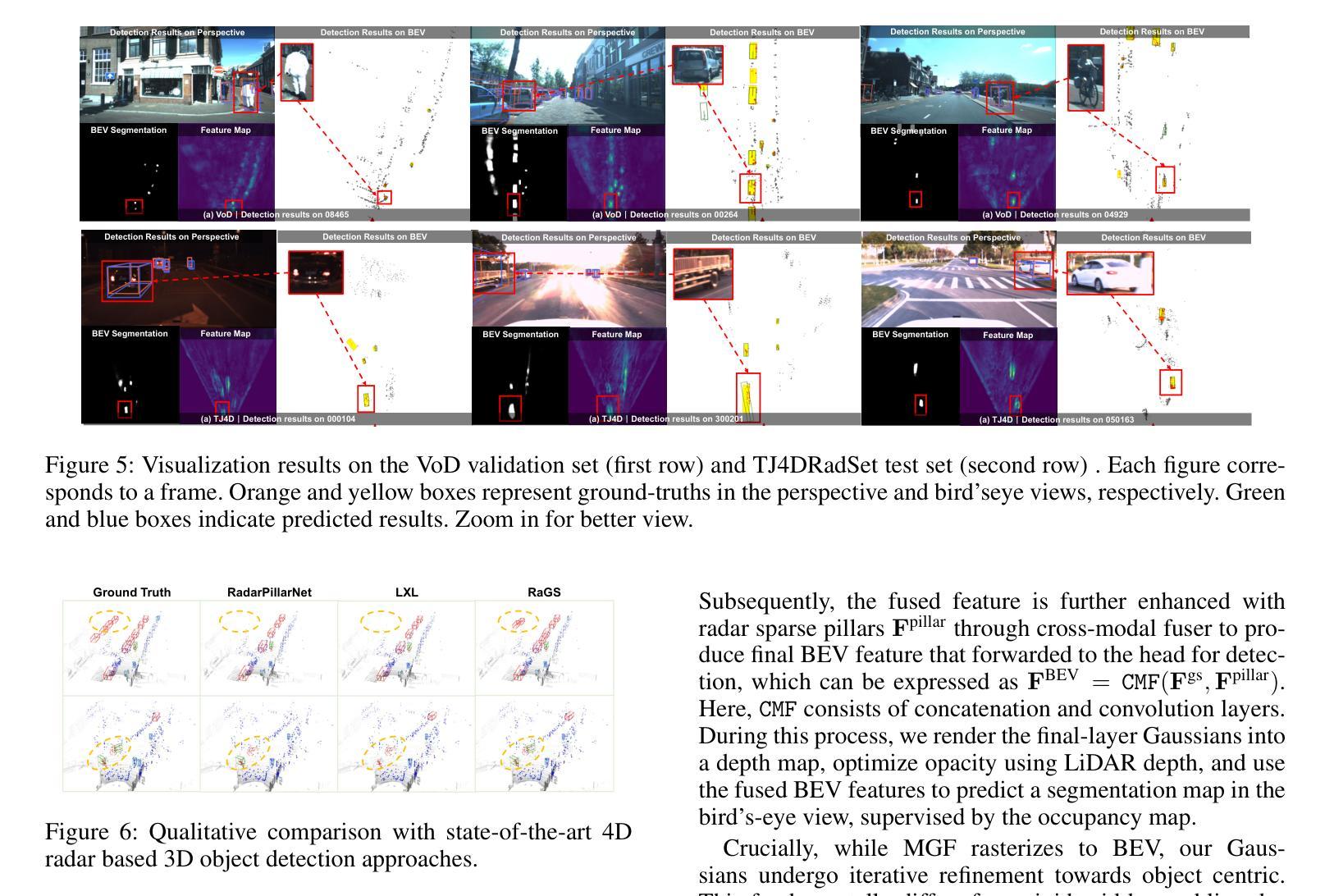
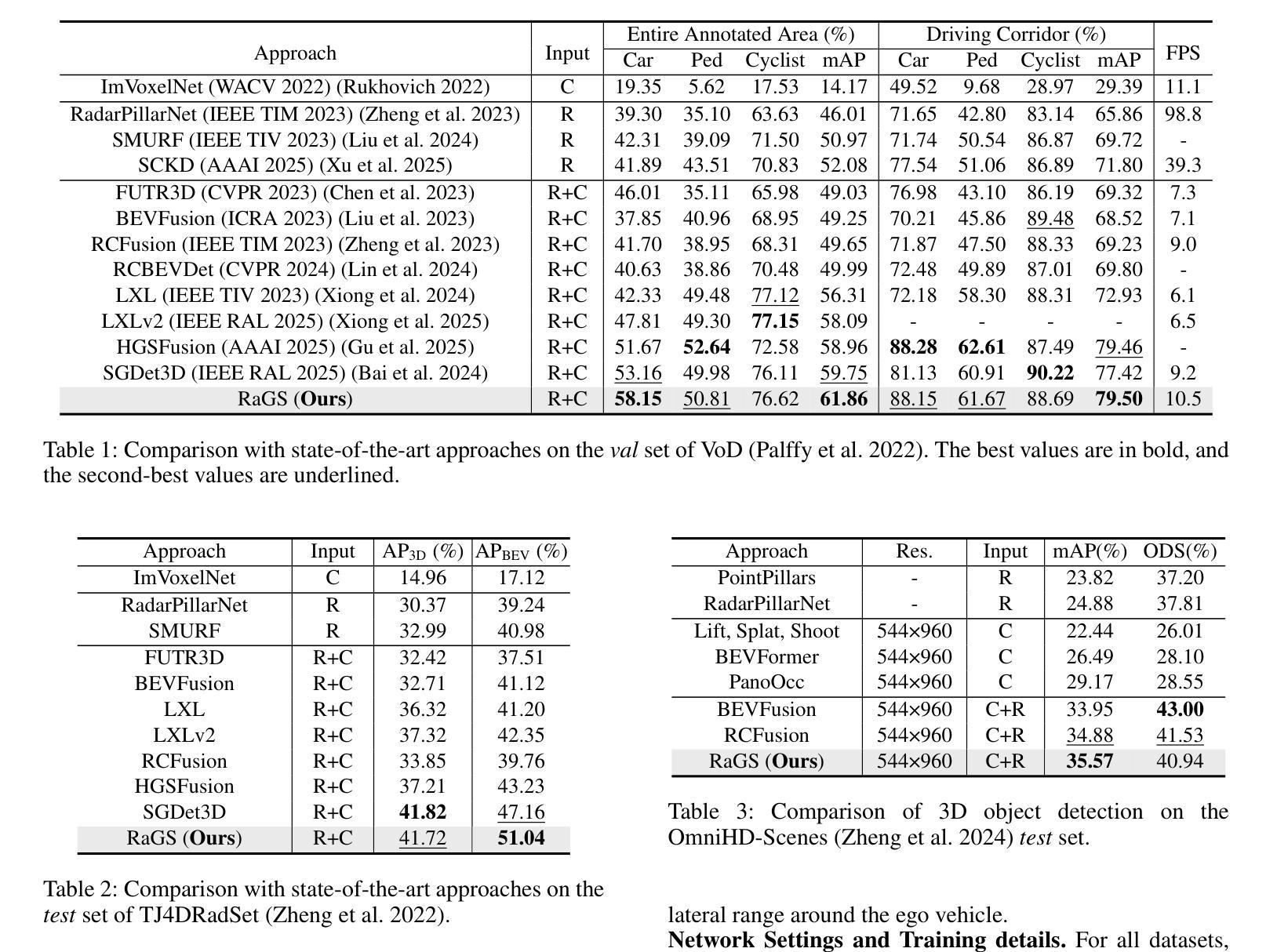
RaGS: Unleashing 3D Gaussian Splatting from 4D Radar and Monocular Cues for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Xiaokai Bai, Chenxu Zhou, Lianqing Zheng, Si-Yuan Cao, Jianan Liu, Xiaohan Zhang, Zhengzhuang Zhang, Hui-liang Shen
4D millimeter-wave radar has emerged as a promising sensor for autonomous driving, but effective 3D object detection from both 4D radar and monocular images remains a challenge. Existing fusion approaches typically rely on either instance-based proposals or dense BEV grids, which either lack holistic scene understanding or are limited by rigid grid structures. To address these, we propose RaGS, the first framework to leverage 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) as representation for fusing 4D radar and monocular cues in 3D object detection. 3D GS naturally suits 3D object detection by modeling the scene as a field of Gaussians, dynamically allocating resources on foreground objects and providing a flexible, resource-efficient solution. RaGS uses a cascaded pipeline to construct and refine the Gaussian field. It starts with the Frustum-based Localization Initiation (FLI), which unprojects foreground pixels to initialize coarse 3D Gaussians positions. Then, the Iterative Multimodal Aggregation (IMA) fuses semantics and geometry, refining the limited Gaussians to the regions of interest. Finally, the Multi-level Gaussian Fusion (MGF) renders the Gaussians into multi-level BEV features for 3D object detection. By dynamically focusing on sparse objects within scenes, RaGS enable object concentrating while offering comprehensive scene perception. Extensive experiments on View-of-Delft, TJ4DRadSet, and OmniHD-Scenes benchmarks demonstrate its state-of-the-art performance. Code will be released.
4D毫米波雷达作为自动驾驶的传感器展现出巨大的潜力,但从4D雷达和单目图像中进行有效的3D目标检测仍然是一个挑战。现有的融合方法通常依赖于基于实例的提案或密集的BEV网格,这些方法要么缺乏整体场景的理解,要么受到刚性网格结构的限制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了RaGS,这是第一个利用3D高斯贴图(GS)作为表示方法,融合4D雷达和单目图像提示进行3D目标检测。3D GS自然地适合进行3D目标检测,通过将场景建模为高斯场,动态分配资源于前景目标并提供灵活且资源高效的解决方案。RaGS使用级联管道来构建和细化高斯场。它开始于基于Frustum的定位初始化(FLI),将前景像素反投影以初始化粗略的3D高斯位置。然后,迭代多模态聚合(IMA)融合了语义和几何信息,对有限的高斯进行精炼以定位感兴趣区域。最后,多层次高斯融合(MGF)将高斯渲染为多层次BEV特征用于3D目标检测。通过动态关注场景中的稀疏目标,RaGS实现了目标集中并提供了全面的场景感知。在View-of-Delft、TJ4DRadSet和OmniHD-Scenes基准测试上的大量实验证明了其卓越的性能。代码将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, conference
摘要
雷达技术与图像技术在自动驾驶领域的融合面临挑战。现有融合方法缺乏全景场景理解或受限于网格结构。本研究提出RaGS框架,首次利用三维高斯映射(GS)技术融合四维雷达与单目图像信息,实现三维物体检测。通过前景对象动态分配资源并构建高斯场,提供灵活、高效的解决方案。实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上表现卓越。
要点掌握
- 4D毫米波雷达在自动驾驶领域具有潜力,但3D物体检测仍是挑战。
- 现有融合方法缺乏全景场景理解或受限于网格结构。
- RaGS框架利用三维高斯映射(GS)技术融合四维雷达与单目图像信息。
- 高斯映射技术通过前景对象动态分配资源,为三维物体检测提供灵活、高效的解决方案。
- RaGS通过级联管道构建和细化高斯场,包括基于视锥的定位启动(FLI)、迭代多模式聚合(IMA)和多级高斯融合(MGF)。
- RaGS方法在多个数据集上表现优秀,将提供开源代码。
点此查看论文截图

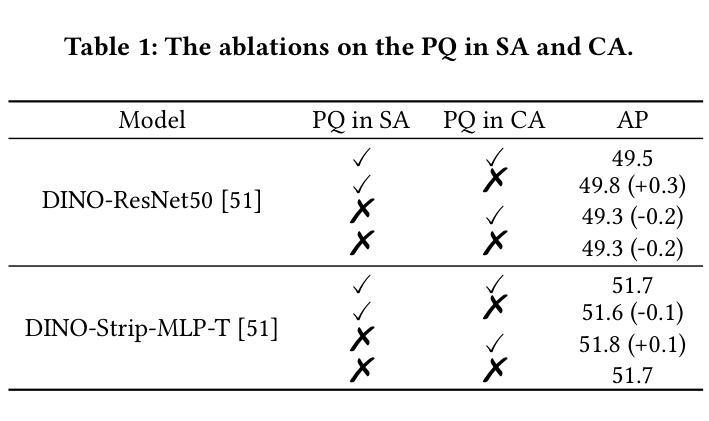
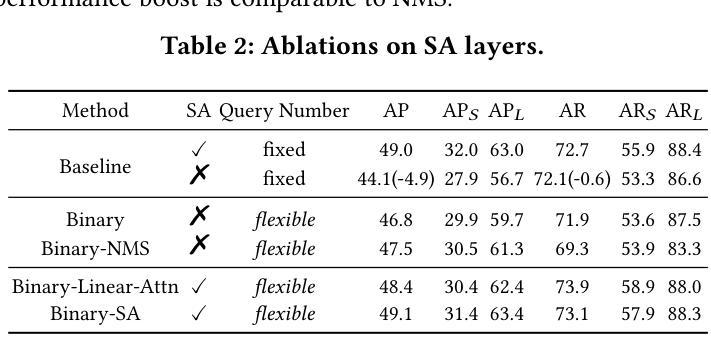
DS-Det: Single-Query Paradigm and Attention Disentangled Learning for Flexible Object Detection
Authors:Guiping Cao, Xiangyuan Lan, Wenjian Huang, Jianguo Zhang, Dongmei Jiang, Yaowei Wang
Popular transformer detectors have achieved promising performance through query-based learning using attention mechanisms. However, the roles of existing decoder query types (e.g., content query and positional query) are still underexplored. These queries are generally predefined with a fixed number (fixed-query), which limits their flexibility. We find that the learning of these fixed-query is impaired by Recurrent Opposing inTeractions (ROT) between two attention operations: Self-Attention (query-to-query) and Cross-Attention (query-to-encoder), thereby degrading decoder efficiency. Furthermore, “query ambiguity” arises when shared-weight decoder layers are processed with both one-to-one and one-to-many label assignments during training, violating DETR’s one-to-one matching principle. To address these challenges, we propose DS-Det, a more efficient detector capable of detecting a flexible number of objects in images. Specifically, we reformulate and introduce a new unified Single-Query paradigm for decoder modeling, transforming the fixed-query into flexible. Furthermore, we propose a simplified decoder framework through attention disentangled learning: locating boxes with Cross-Attention (one-to-many process), deduplicating predictions with Self-Attention (one-to-one process), addressing “query ambiguity” and “ROT” issues directly, and enhancing decoder efficiency. We further introduce a unified PoCoo loss that leverages box size priors to prioritize query learning on hard samples such as small objects. Extensive experiments across five different backbone models on COCO2017 and WiderPerson datasets demonstrate the general effectiveness and superiority of DS-Det. The source codes are available at https://github.com/Med-Process/DS-Det/.
现有的流行的转换器检测器已通过基于注意力的查询学习取得了有前景的性能。然而,现有的解码器查询类型(如内容查询和位置查询)的角色仍然被低估。这些查询通常是预先定义的固定数量(固定查询),这限制了它们的灵活性。我们发现这些固定查询的学习受到两种注意力操作之间的循环相反交互(ROT)的损害:自注意力(查询对查询)和交叉注意力(查询对编码器),从而降低了解码器的效率。此外,当共享权重解码器层在训练过程中进行一对一和一对多标签分配时,“查询歧义”就会出现,这违反了DETR的一对一匹配原则。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DS-Det,这是一种更高效的检测器,能够检测图像中可变数量的对象。具体来说,我们对解码器建模提出了新的统一单查询范式,将固定查询转变为灵活的查询。此外,我们提出了一个简化的解码器框架,通过注意力解耦学习:使用交叉注意力定位盒子(一对多过程),用自注意力去除重复预测(一对一过程),直接解决“查询歧义”和“ROT”问题,提高解码器效率。我们还引入了一个统一的PoCoo损失,它利用框大小先验来优先学习硬样本上的查询,如小对象。在COCO2017和WiderPerson数据集上的五个不同主干模型的大量实验证明了DS-Det的通用有效性和优越性。源代码可在https://github.com/Med-Process/DS-Det/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了现有基于注意力机制的检测器在处理图像检测任务时面临的挑战,包括固定查询数量、查询学习过程中的交互问题以及查询歧义等。针对这些问题,提出了一种名为DS-Det的新检测器,通过引入单一查询范式和注意力解耦学习来增强解码器效率,并通过引入一种优先于盒子大小的先验损失来解决“查询歧义”问题。实验结果证明,DS-Det在多个数据集上的表现优于其他检测器。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于注意力机制的检测器存在固定查询数量的局限性。这些查询数量通常在训练中已经被预设并限制在一定范围内。此外还存在自注意力与跨注意力的相互作用问题和查询歧义问题。为了解决这些问题并提高解码器的效率,研究人员提出了名为DS-Det的新检测器。
点此查看论文截图


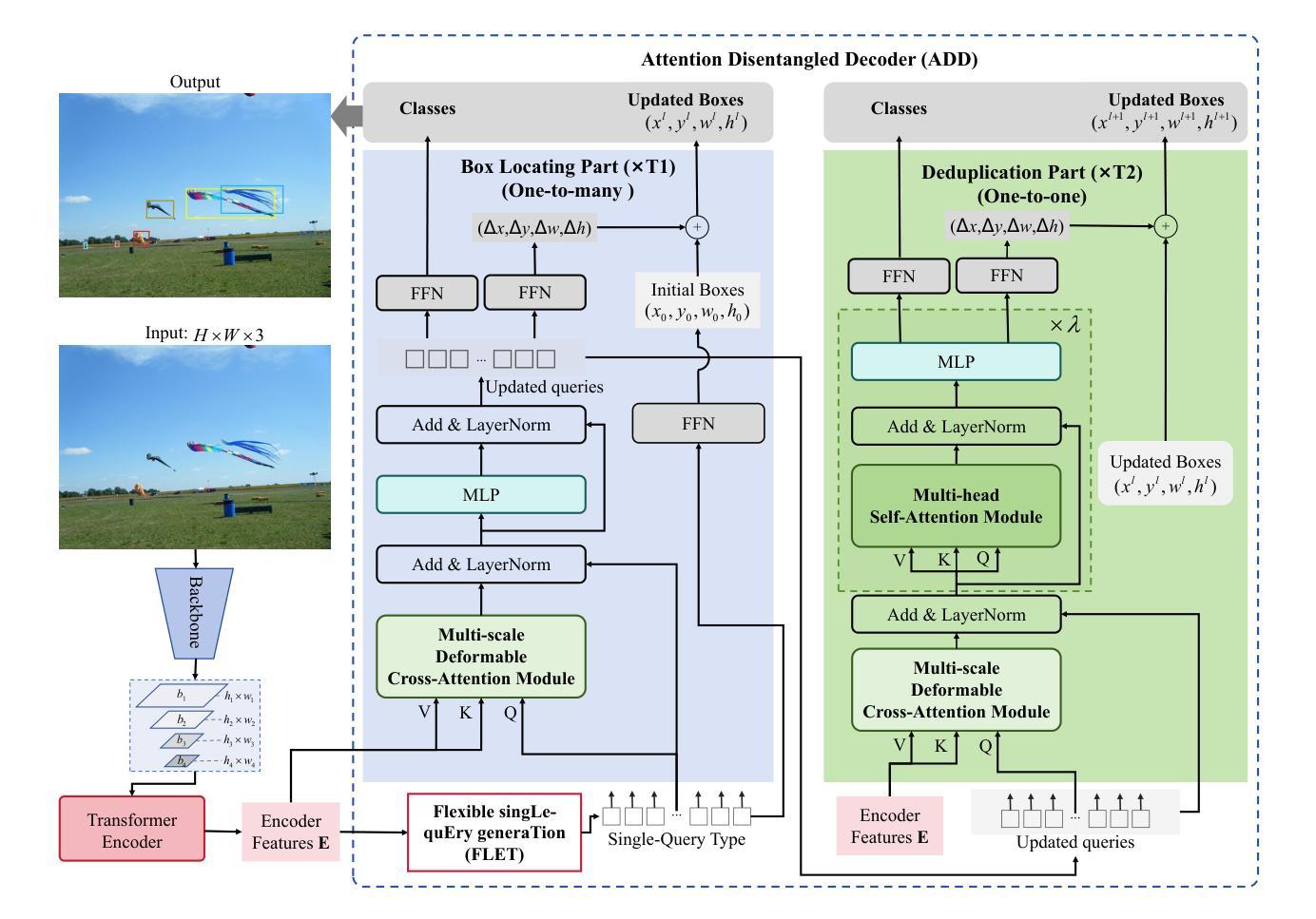
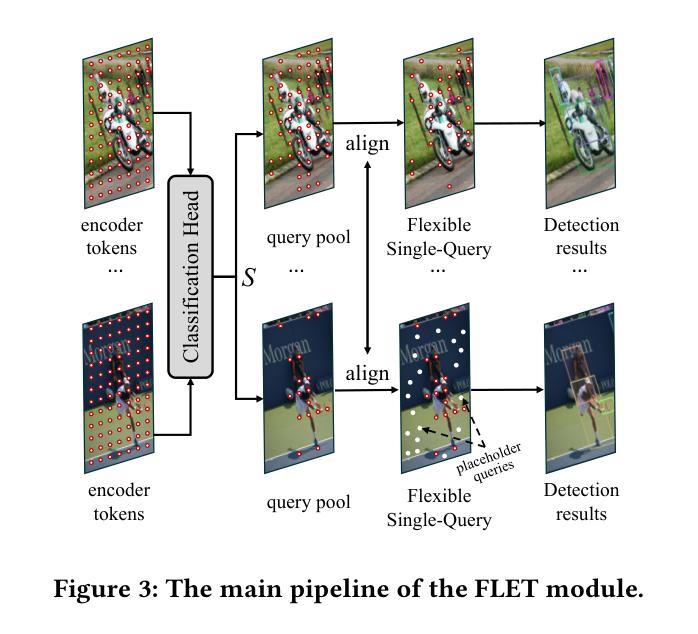
TransFlow: Motion Knowledge Transfer from Video Diffusion Models to Video Salient Object Detection
Authors:Suhwan Cho, Minhyeok Lee, Jungho Lee, Sunghun Yang, Sangyoun Lee
Video salient object detection (SOD) relies on motion cues to distinguish salient objects from backgrounds, but training such models is limited by scarce video datasets compared to abundant image datasets. Existing approaches that use spatial transformations to create video sequences from static images fail for motion-guided tasks, as these transformations produce unrealistic optical flows that lack semantic understanding of motion. We present TransFlow, which transfers motion knowledge from pre-trained video diffusion models to generate realistic training data for video SOD. Video diffusion models have learned rich semantic motion priors from large-scale video data, understanding how different objects naturally move in real scenes. TransFlow leverages this knowledge to generate semantically-aware optical flows from static images, where objects exhibit natural motion patterns while preserving spatial boundaries and temporal coherence. Our method achieves improved performance across multiple benchmarks, demonstrating effective motion knowledge transfer.
视频显著目标检测(SOD)依赖于运动线索来区分显著目标与背景,但与丰富的图像数据集相比,训练此类模型受到稀缺视频数据集的限制。现有方法使用空间变换从静态图像创建视频序列,不适用于运动引导的任务,因为这些变换会产生缺乏运动语义理解的不真实光流。我们提出了TransFlow,它将预训练的视频扩散模型中的运动知识转移,以生成用于视频SOD的现实训练数据。视频扩散模型已经从大规模视频数据中学习了丰富的语义运动先验知识,理解不同对象在真实场景中的自然运动方式。TransFlow利用这些知识从静态图像生成语义感知的光流,其中对象表现出自然运动模式,同时保留空间边界和时间连贯性。我们的方法在多个基准测试上实现了性能提升,证明了有效的运动知识转移。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCVW 2025
Summary
视频显著性目标检测(SOD)依赖运动线索来区分显著目标背景,但由于视频数据集相对于图像数据集较为稀缺,训练此类模型受到限制。现有方法使用空间变换从静态图像创建视频序列,但不适用于运动引导的任务,因为这些变换会产生缺乏语义理解的不真实的光流。本文提出TransFlow,它将预训练的视频扩散模型中的运动知识转移,以生成用于视频SOD的现实训练数据。视频扩散模型从大规模视频数据中学习了丰富的语义运动先验知识,理解不同对象在真实场景中的自然运动方式。TransFlow利用这些知识从静态图像生成语义感知的光流,其中对象表现出自然运动模式,同时保留空间边界和时间连贯性。我们的方法在多基准测试中实现了性能提升,证明了有效的运动知识转移。
Key Takeaways
- 视频显著性目标检测(SOD)依赖运动线索进行背景区分,但训练模型受视频数据集稀缺限制。
- 现有方法使用空间变换从静态图像创建视频序列,但这种方法产生的光流不真实,缺乏语义理解。
- 本文提出TransFlow,利用预训练的视频扩散模型中的运动知识来生成现实训练数据。
- 视频扩散模型能从大规模视频数据中学习丰富的语义运动先验知识。
- TransFlow能生成语义感知的光流,其中对象表现出自然运动模式,同时保留空间边界和时间连贯性。
- TransFlow方法在多基准测试中实现了性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

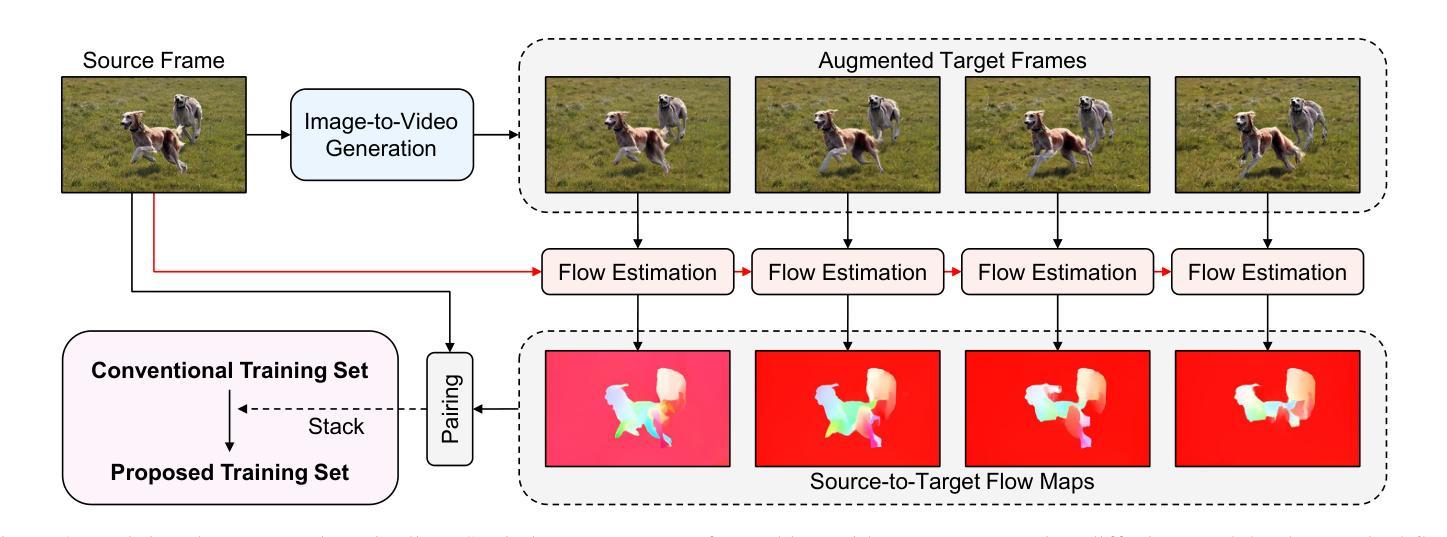
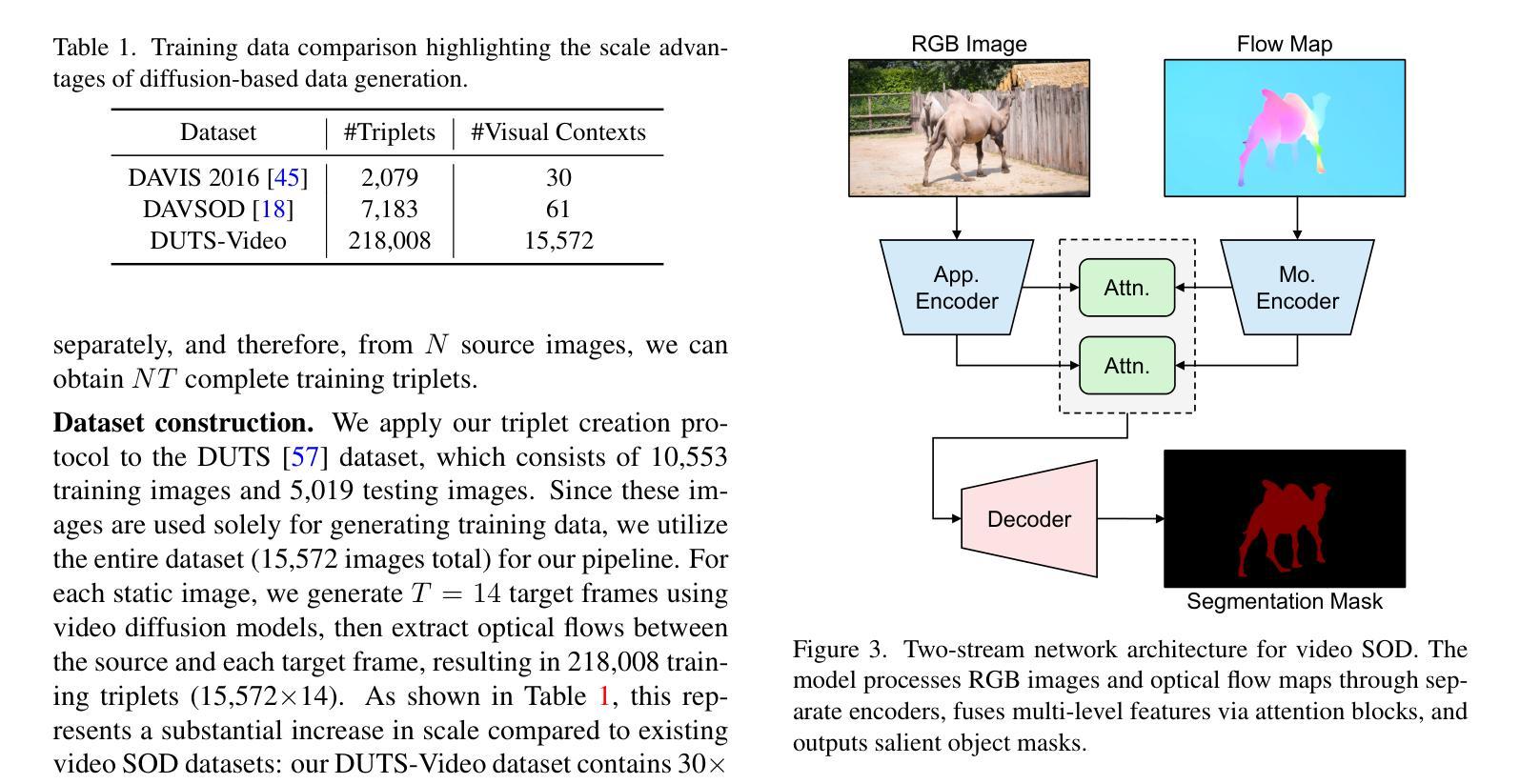
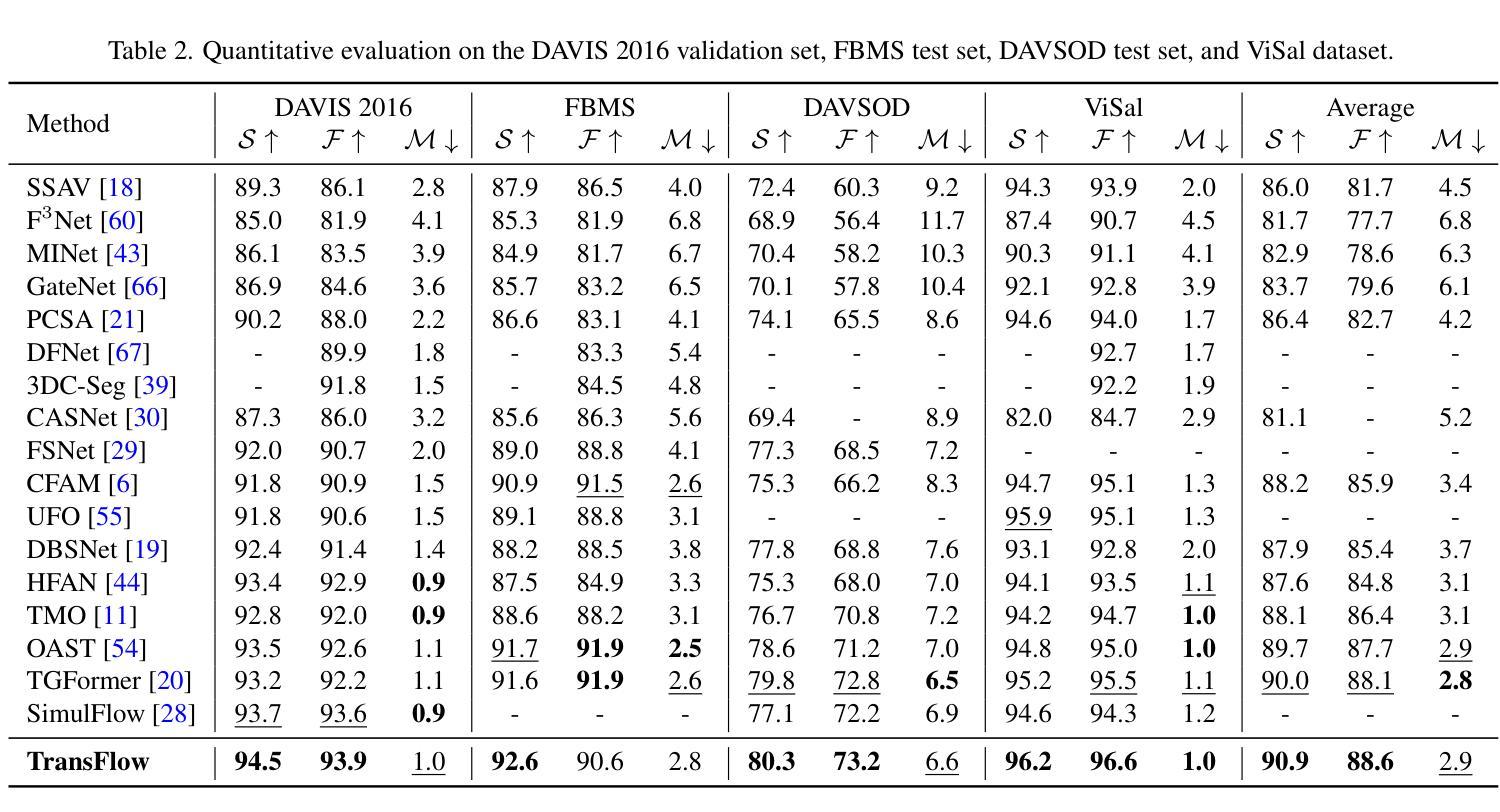

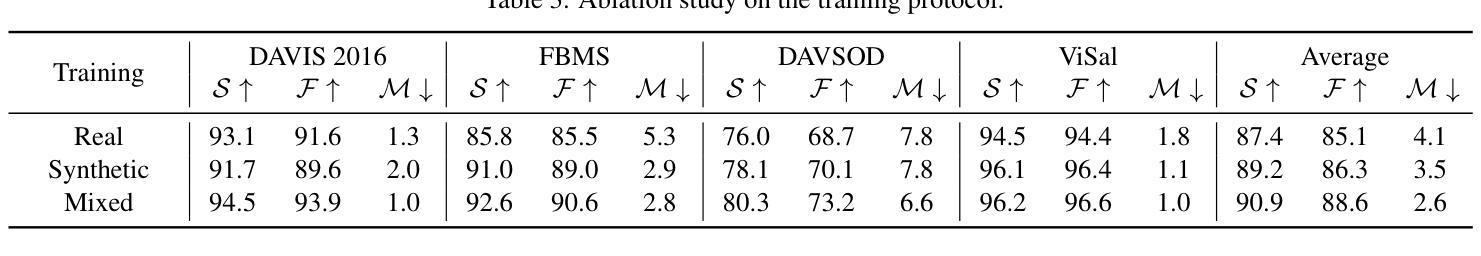
Synthetic-to-Real Camouflaged Object Detection
Authors:Zhihao Luo, Luojun Lin, Zheng Lin
Due to the high cost of collection and labeling, there are relatively few datasets for camouflaged object detection (COD). In particular, for certain specialized categories, the available image dataset is insufficiently populated. Synthetic datasets can be utilized to alleviate the problem of limited data to some extent. However, directly training with synthetic datasets compared to real datasets can lead to a degradation in model performance. To tackle this problem, in this work, we investigate a new task, namely Syn-to-Real Camouflaged Object Detection (S2R-COD). In order to improve the model performance in real world scenarios, a set of annotated synthetic camouflaged images and a limited number of unannotated real images must be utilized. We propose the Cycling Syn-to-Real Domain Adaptation Framework (CSRDA), a method based on the student-teacher model. Specially, CSRDA propagates class information from the labeled source domain to the unlabeled target domain through pseudo labeling combined with consistency regularization. Considering that narrowing the intra-domain gap can improve the quality of pseudo labeling, CSRDA utilizes a recurrent learning framework to build an evolving real domain for bridging the source and target domain. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework, mitigating the problem of limited data and handcraft annotations in COD. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/Muscape/S2R-COD.
由于收集与标记的成本较高,针对隐蔽目标检测(COD)的数据集相对较少。尤其是针对某些特定类别,可用的图像数据集不够丰富。在一定程度上,可以利用合成数据集来缓解数据有限的问题。然而,与真实数据集相比,直接使用合成数据集进行训练可能会导致模型性能下降。为了解决这个问题,我们在本文中研究了一个新的任务,即合成到真实隐蔽目标检测(S2R-COD)。为了提高模型在现实场景中的性能,必须使用一组带注释的合成隐蔽图像和少量未注释的真实图像。我们提出了循环合成到真实域适应框架(CSRDA),这是一种基于师徒模型的方法。特别是,CSRDA通过伪标签与一致性正则化相结合,将类信息从标记的源域传播到未标记的目标域。考虑到缩小域内差距可以提高伪标签的质量,CSRDA利用递归学习框架来构建连接源域和目标域的不断发展的真实域。大量实验证明了我们框架的有效性,缓解了COD中数据有限和手工标注的问题。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/Muscape/S2R-COD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了在伪装目标检测中因数据收集与标注成本高昂导致的数据集稀少问题。特别是一些特定类别的图像数据集严重不足。为缓解这一问题,提出了利用合成数据集的方法。但直接使用合成数据集进行训练会导致模型性能下降。为此,本文研究了一个新的任务,即合成到现实伪装目标检测(S2R-COD)。为提高模型在现实场景中的性能,使用了一批标注过的合成伪装图像和少量未标注的真实图像。提出了基于学生-教师模型的循环合成到现实域适应框架(CSRDA)。CSRDA通过伪标签和一致性正则化将源域的类别信息传递给目标域。同时,缩小源域和目标域之间的内部差距可以提高伪标签的质量,因此CSRDA采用递归学习框架来构建不断演变的真实域以缩小两者之间的差距。实验证明,该框架有效解决了伪装目标检测中的数据有限和手工标注问题。
Key Takeaways
- 伪装目标检测数据集因高成本而相对稀缺,特别是特定类别的图像数据集。
- 合成数据集可以缓解数据有限的问题。
- 直接使用合成数据集训练会导致模型性能下降。
- 提出新的任务:合成到现实伪装目标检测(S2R-COD)。
- 为提高模型在现实场景中的性能,结合标注的合成图像和少量未标注的真实图像。
- 引入基于学生-教师模型的循环合成到现实域适应框架(CSRDA)。
点此查看论文截图

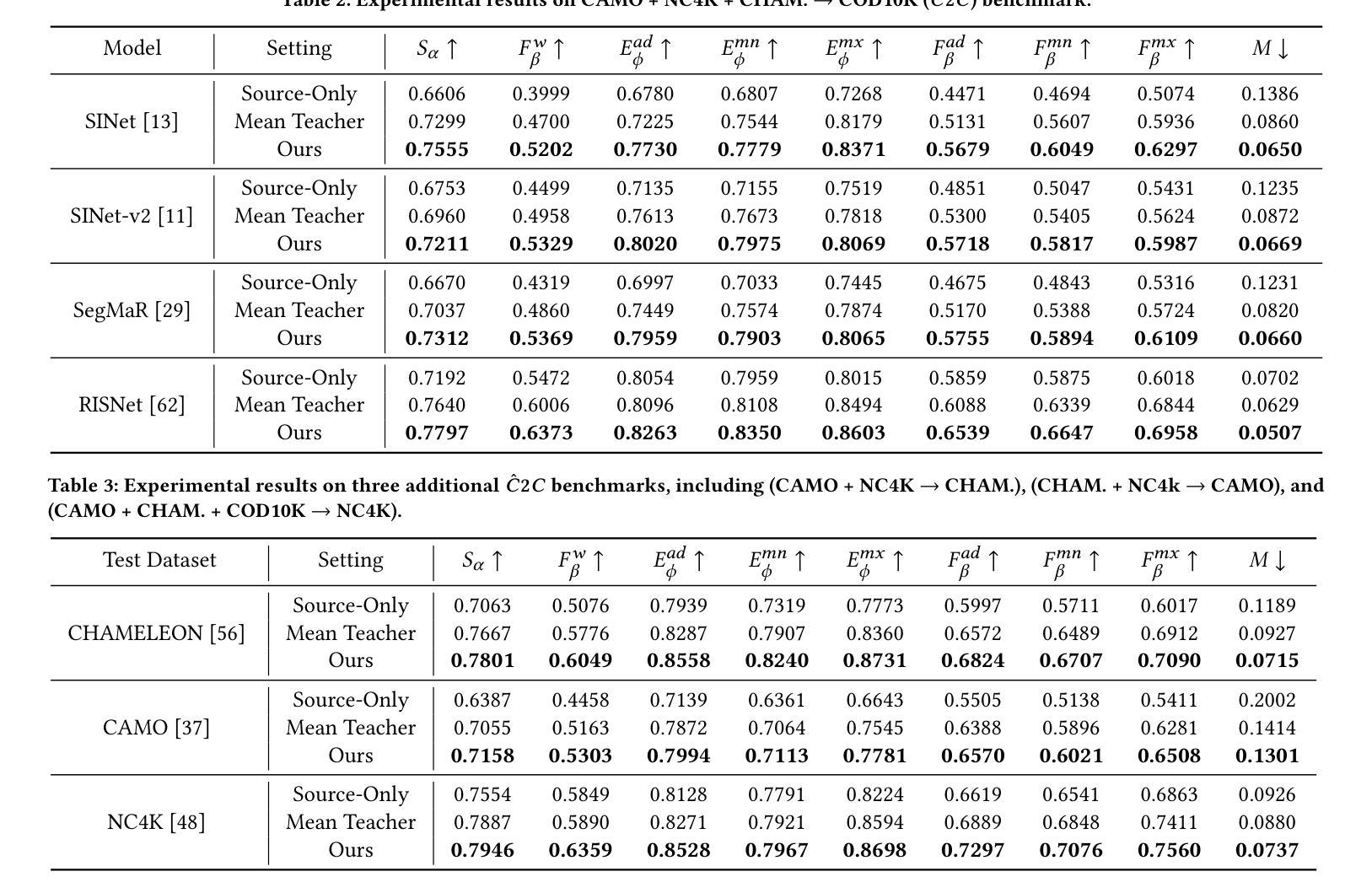
Boosting Multi-View Indoor 3D Object Detection via Adaptive 3D Volume Construction
Authors:Runmin Zhang, Zhu Yu, Si-Yuan Cao, Lingyu Zhu, Guangyi Zhang, Xiaokai Bai, Hui-Liang Shen
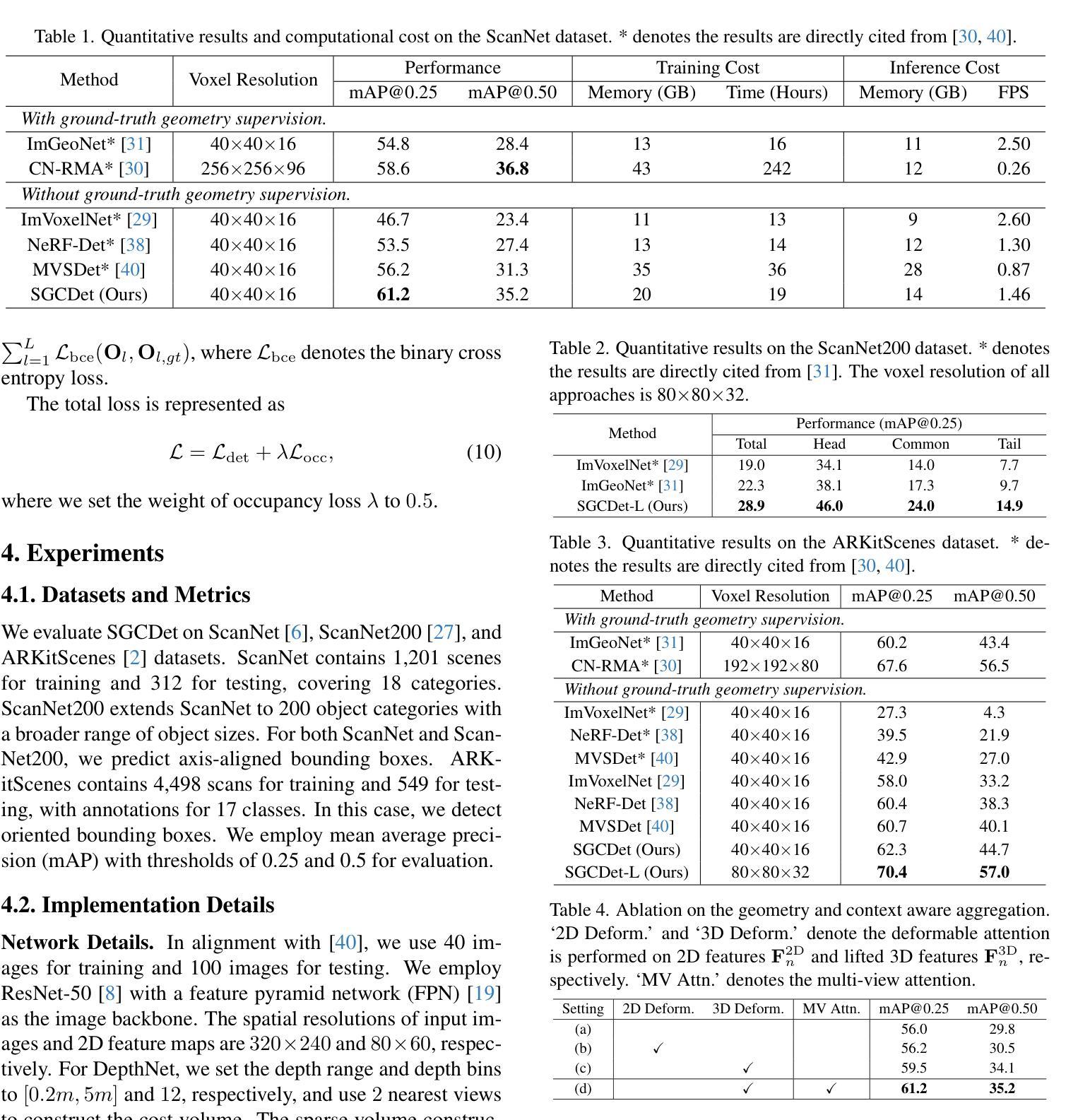
This work presents SGCDet, a novel multi-view indoor 3D object detection framework based on adaptive 3D volume construction. Unlike previous approaches that restrict the receptive field of voxels to fixed locations on images, we introduce a geometry and context aware aggregation module to integrate geometric and contextual information within adaptive regions in each image and dynamically adjust the contributions from different views, enhancing the representation capability of voxel features. Furthermore, we propose a sparse volume construction strategy that adaptively identifies and selects voxels with high occupancy probabilities for feature refinement, minimizing redundant computation in free space. Benefiting from the above designs, our framework achieves effective and efficient volume construction in an adaptive way. Better still, our network can be supervised using only 3D bounding boxes, eliminating the dependence on ground-truth scene geometry. Experimental results demonstrate that SGCDet achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ScanNet, ScanNet200 and ARKitScenes datasets. The source code is available at https://github.com/RM-Zhang/SGCDet.
本文提出了SGCDet,这是一种基于自适应3D体积构建的多视角室内3D目标检测新框架。不同于之前将体素感受野限制在图像固定位置的方法,我们引入了一个融合几何和上下文信息的聚合模块,该模块可以整合每个图像自适应区域内的几何和上下文信息,并动态调整不同视角的贡献,增强了体素特征的表示能力。此外,我们提出了一种稀疏体积构建策略,该策略可以自适应地识别和选择高占用概率的体素进行特征细化,从而最小化空闲空间的冗余计算。得益于上述设计,我们的框架以自适应的方式实现了有效且高效的体积构建。更好的是,我们的网络仅使用3D边界框进行监管,从而消除了对真实场景几何的依赖。实验结果表明,SGCDet在ScanNet、ScanNet200和ARKitScenes数据集上达到了最先进的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/RM-Zhang/SGCDet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了SGCDet,一种基于自适应三维体积构建的多视角室内3D目标检测框架。该框架通过引入几何和上下文感知聚合模块,动态调整不同视角的贡献,增强体积特征的表示能力。同时,提出一种稀疏体积构建策略,自适应识别并选择高占用概率的体素进行特征细化,减少自由空间中的冗余计算。实验结果表明,SGCDet在ScanNet、ScanNet200和ARKitScenes数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SGCDet是一种多视角室内3D目标检测框架,基于自适应三维体积构建。
- 引入几何和上下文感知聚合模块,整合图像中的几何和上下文信息。
- 动态调整不同视角的贡献,增强体积特征的表示能力。
- 提出稀疏体积构建策略,自适应识别并选择高占用概率的体素。
- 框架可在无需地面真实场景几何信息的情况下进行监督训练。
- 实验结果证明SGCDet在多个数据集上达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

LMM-Det: Make Large Multimodal Models Excel in Object Detection
Authors:Jincheng Li, Chunyu Xie, Ji Ao, Dawei Leng, Yuhui Yin
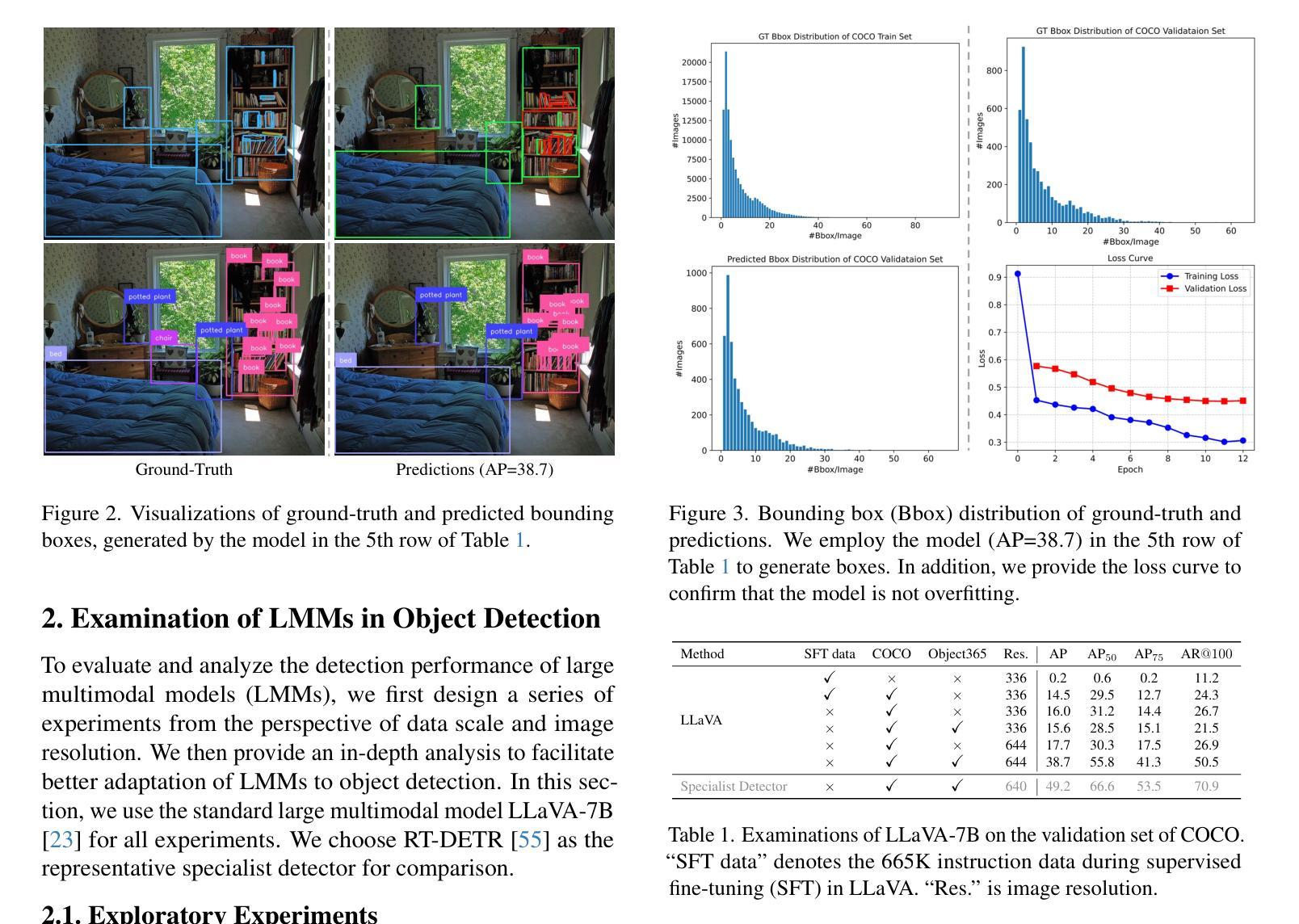
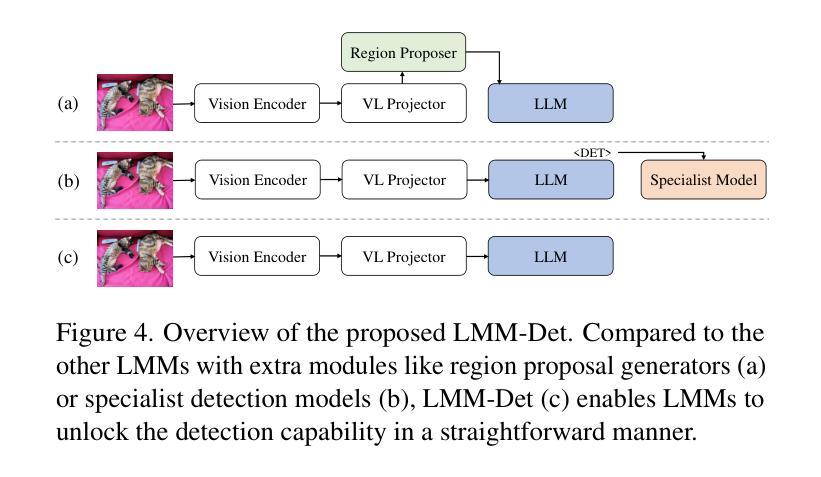
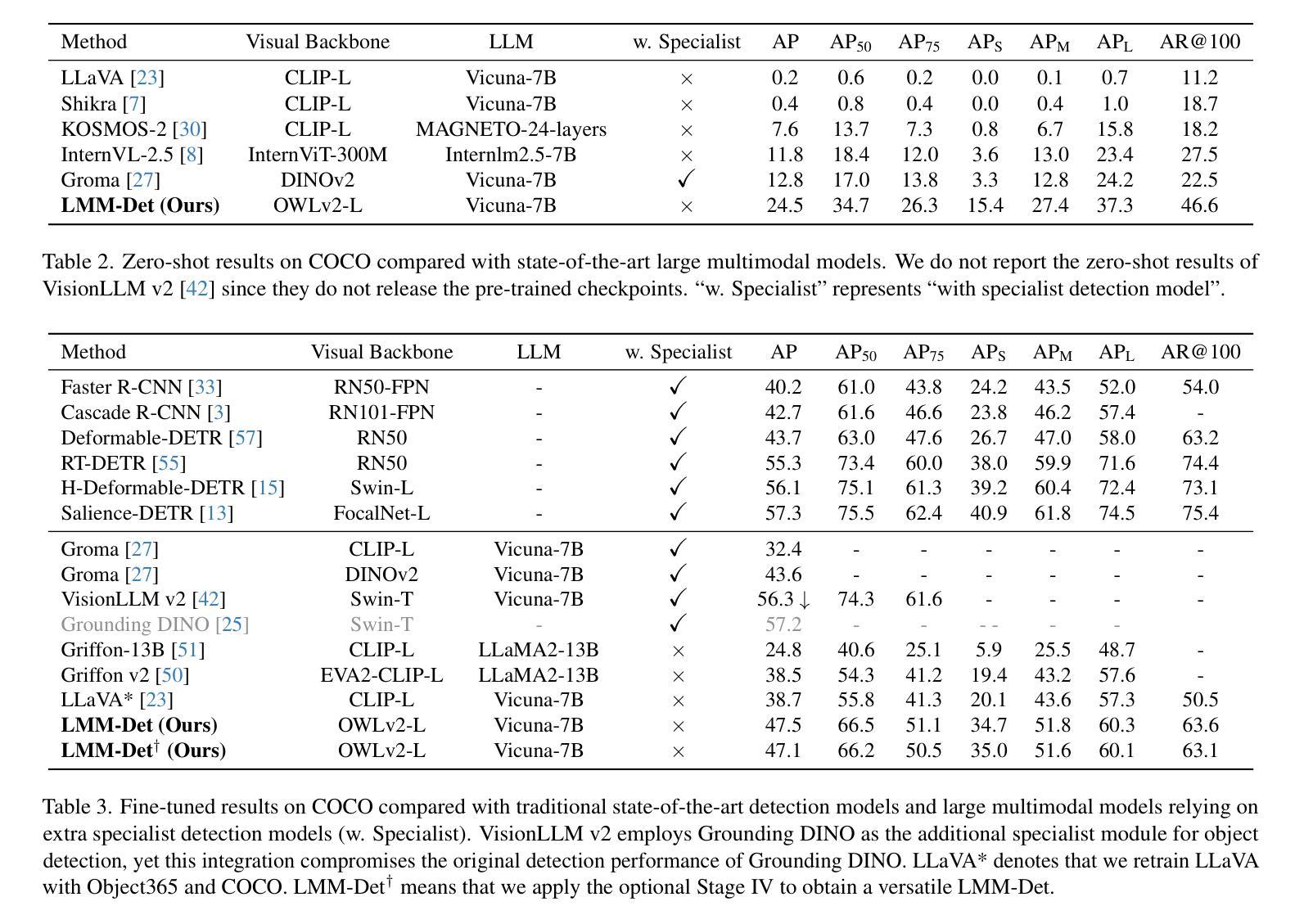
Large multimodal models (LMMs) have garnered wide-spread attention and interest within the artificial intelligence research and industrial communities, owing to their remarkable capability in multimodal understanding, reasoning, and in-context learning, among others. While LMMs have demonstrated promising results in tackling multimodal tasks like image captioning, visual question answering, and visual grounding, the object detection capabilities of LMMs exhibit a significant gap compared to specialist detectors. To bridge the gap, we depart from the conventional methods of integrating heavy detectors with LMMs and propose LMM-Det, a simple yet effective approach that leverages a Large Multimodal Model for vanilla object Detection without relying on specialized detection modules. Specifically, we conduct a comprehensive exploratory analysis when a large multimodal model meets with object detection, revealing that the recall rate degrades significantly compared with specialist detection models. To mitigate this, we propose to increase the recall rate by introducing data distribution adjustment and inference optimization tailored for object detection. We re-organize the instruction conversations to enhance the object detection capabilities of large multimodal models. We claim that a large multimodal model possesses detection capability without any extra detection modules. Extensive experiments support our claim and show the effectiveness of the versatile LMM-Det. The datasets, models, and codes are available at https://github.com/360CVGroup/LMM-Det.
大型多模态模型(LMMs)因其强大的多模态理解、推理和上下文学习能力而引起了人工智能研究和工业界的广泛关注。虽然LMMs在处理图像描述、视觉问答和视觉定位等多模态任务方面展现出了良好的潜力,但在对象检测方面的能力与专业检测器相比仍存在显著差距。为了弥差距,我们放弃了将重型检测器与LMMs集成结合的常规方法,并提出了LMM-Det。这是一种简单而有效的方法,它利用大型多模态模型进行基本对象检测,无需依赖专业检测模块。具体来说,当大型多模态模型遇到对象检测时,我们进行了全面的探索性分析,发现其召回率与专业检测模型相比显著降低。为了缓解这一问题,我们提议通过引入针对对象检测的数据分布调整和推理优化来提高召回率。我们重新组织指令对话,以增强大型多模态模型的对象检测能力。我们认为,大型多模态模型本身就具备检测能力,无需额外的检测模块。大量实验支持我们的观点并证明了LMM-Det的有效性。相关数据集、模型和代码可通过https://github.com/360CVGroup/LMM-Det获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary:大型多模态模型(LMMs)在人工智能研究和工业界引起了广泛关注,因其具有出色的多模态理解、推理和上下文学习能力等优点。虽然LMMs在多模态任务如图像描述、视觉问答和视觉定位等方面表现出色,但在目标检测方面与专业检测器相比存在明显差距。为了缩小这一差距,本文提出了一种简单有效的方法LMM-Det,它利用大型多模态模型进行基本的对象检测,无需依赖专业检测模块。通过引入数据分布调整和针对对象检测的推理优化,提高了召回率。通过重组指令对话,增强了大型多模态模型的目标检测能力。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型多模态模型(LMMs)在人工智能领域受到广泛关注,具有出色的多模态理解和推理能力。
- LMMs在多模态任务(如图像描述、视觉问答和视觉定位)上表现出色。
- LMMs在目标检测方面与专业检测器相比存在差距。
- 提出了一种新的方法LMM-Det,利用大型多模态模型进行对象检测,无需专业检测模块。
- 通过数据分布调整和推理优化,提高了目标检测的召回率。
- 通过重组指令对话,增强了大型多模态模型的目标检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

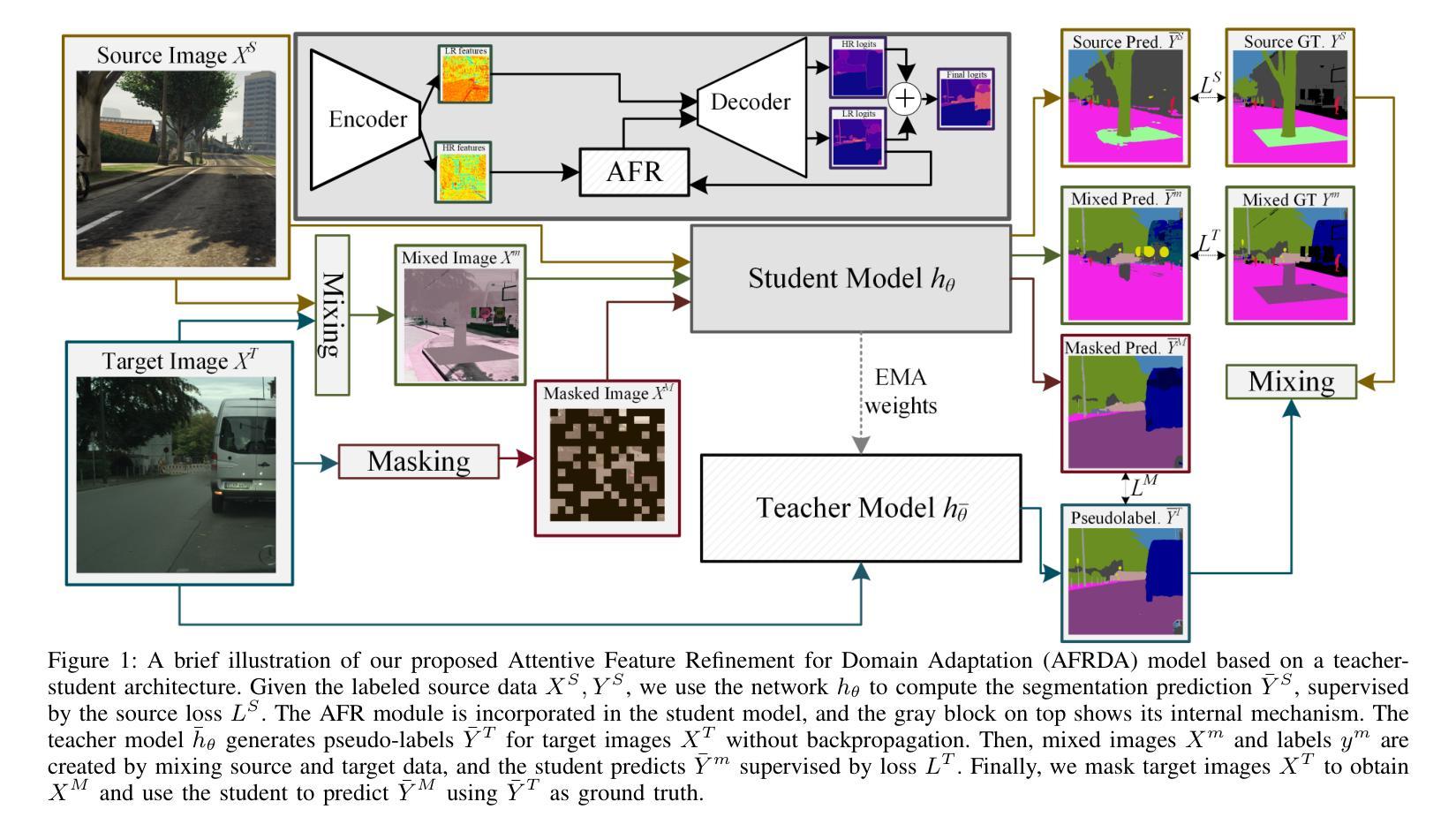
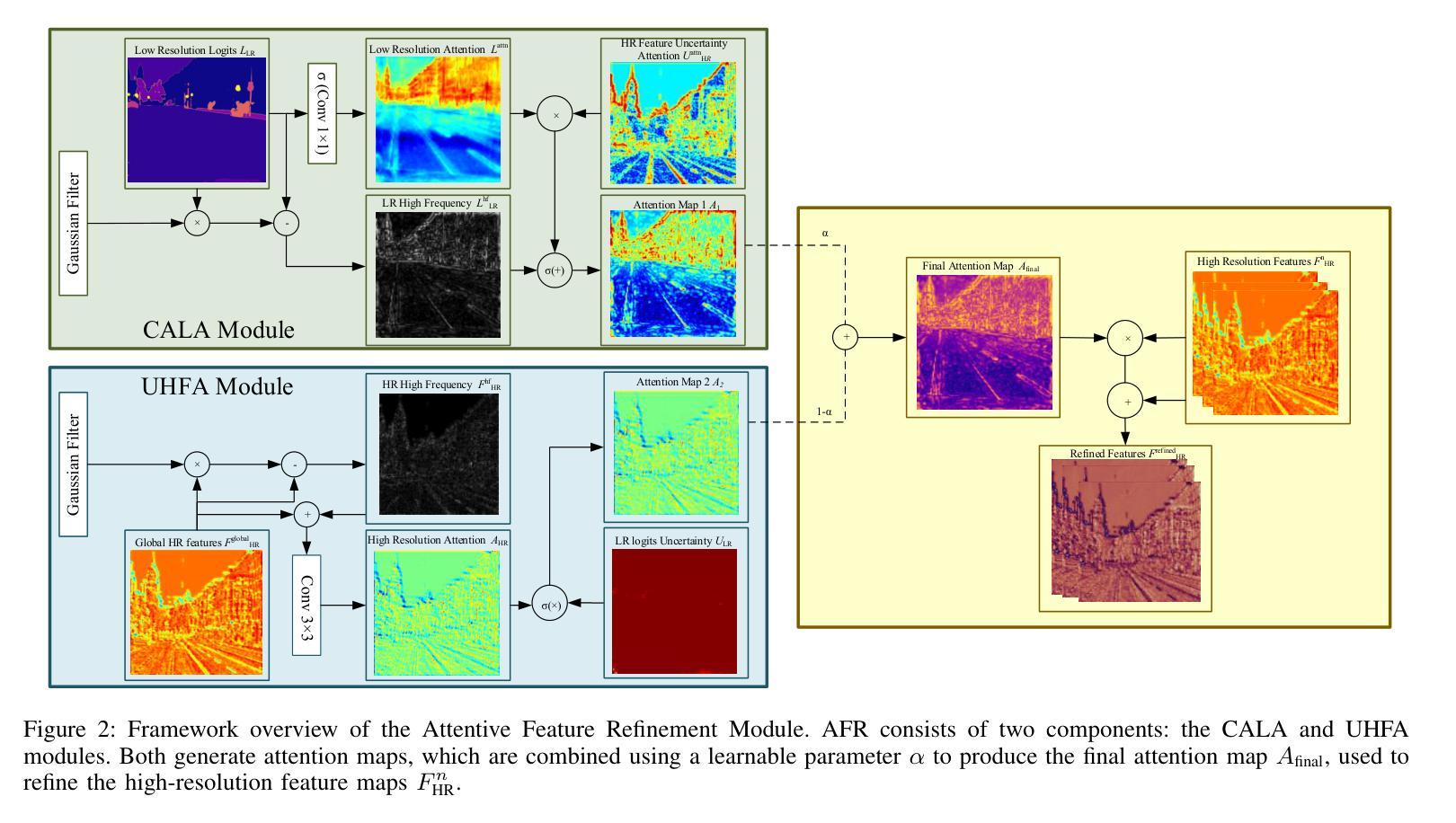
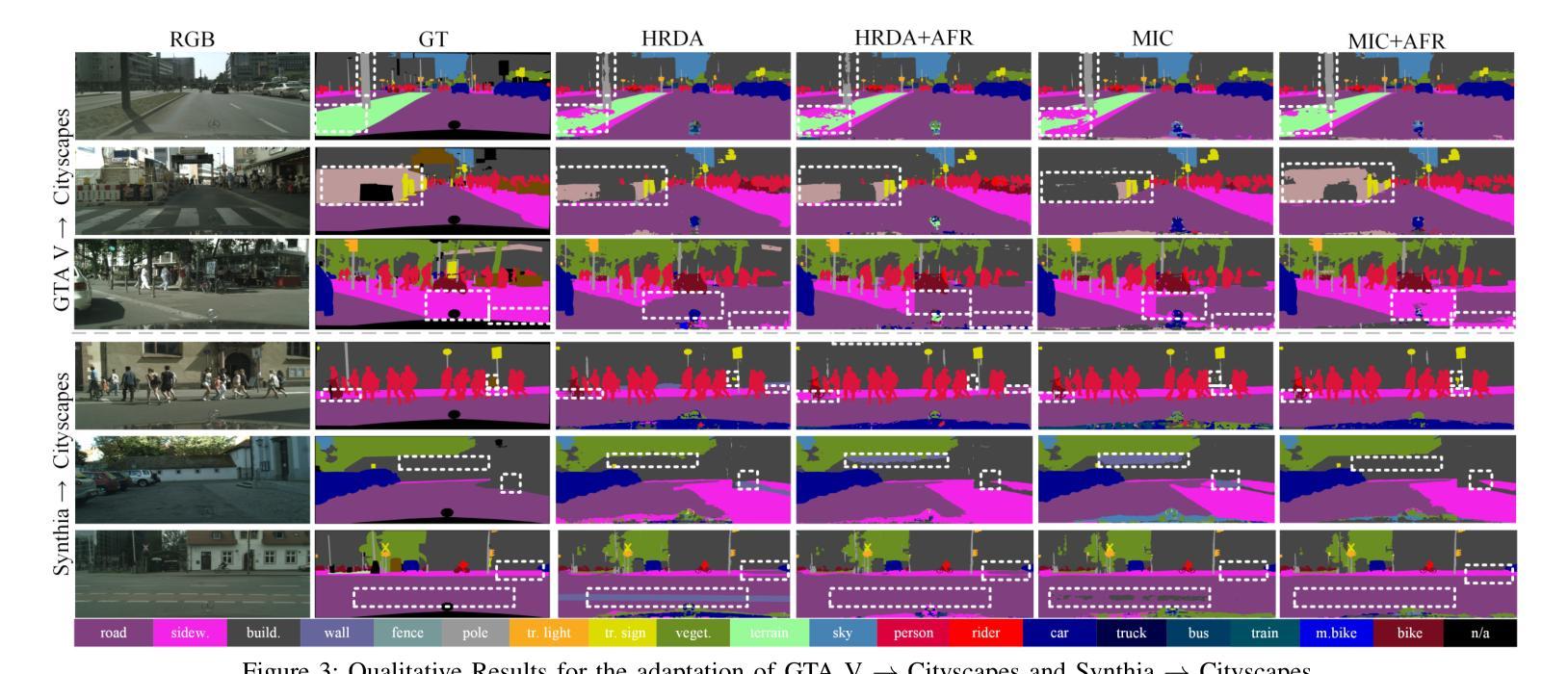
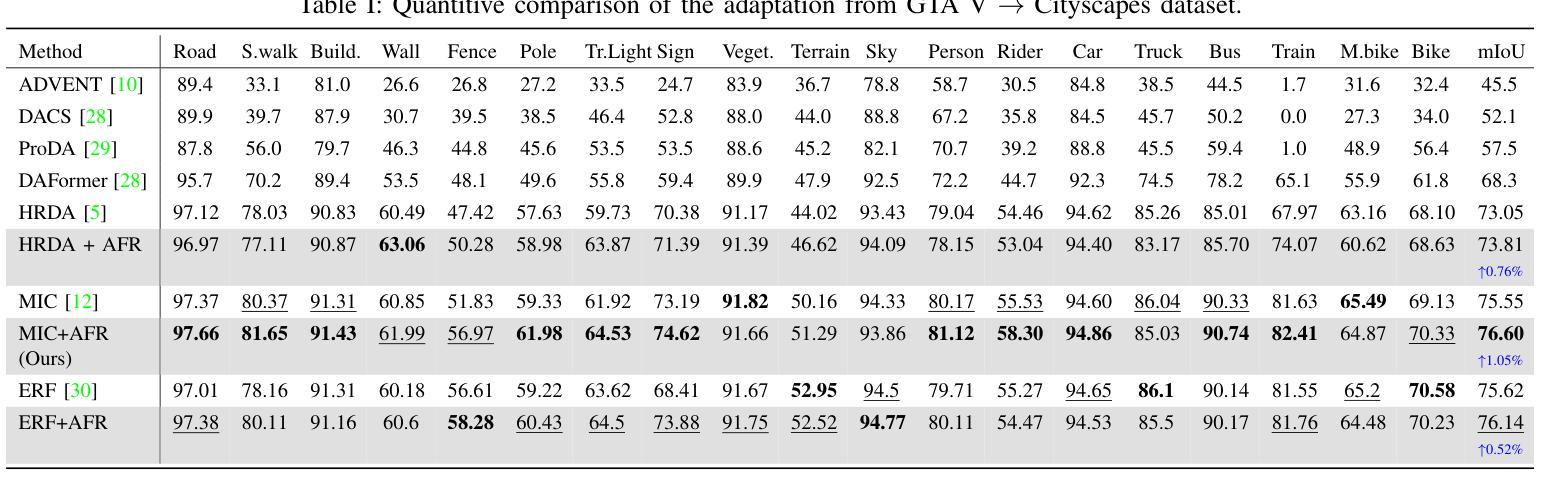
AFRDA: Attentive Feature Refinement for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Md. Al-Masrur Khan, Durgakant Pushp, Lantao Liu
In Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation (UDA-SS), a model is trained on labeled source domain data (e.g., synthetic images) and adapted to an unlabeled target domain (e.g., real-world images) without access to target annotations. Existing UDA-SS methods often struggle to balance fine-grained local details with global contextual information, leading to segmentation errors in complex regions. To address this, we introduce the Adaptive Feature Refinement (AFR) module, which enhances segmentation accuracy by refining highresolution features using semantic priors from low-resolution logits. AFR also integrates high-frequency components, which capture fine-grained structures and provide crucial boundary information, improving object delineation. Additionally, AFR adaptively balances local and global information through uncertaintydriven attention, reducing misclassifications. Its lightweight design allows seamless integration into HRDA-based UDA methods, leading to state-of-the-art segmentation performance. Our approach improves existing UDA-SS methods by 1.05% mIoU on GTA V –> Cityscapes and 1.04% mIoU on Synthia–>Cityscapes. The implementation of our framework is available at: https://github.com/Masrur02/AFRDA
在无需监督的领域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)中,模型会在标注的源域数据(例如,合成图像)上进行训练,并适应未标注的目标域(例如,真实世界图像),而无需访问目标注释。现有的UDA-SS方法往往难以平衡精细的局部细节和全局上下文信息,导致在复杂区域出现分割错误。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了自适应特征细化(AFR)模块,它通过利用低分辨率逻辑中的语义先验来细化高分辨率特征,从而提高分割准确性。AFR还集成了高频组件,这些组件可以捕捉精细结构并提供关键边界信息,从而改善对象轮廓。此外,AFR通过不确定性驱动的关注机制自适应地平衡局部和全局信息,减少误分类。其轻量级的设计可以无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法,达到最先进的分割性能。我们的方法在GTA V到Cityscapes和Synthia到Cityscapes的UDA-SS任务上分别提高了1.05%和1.04%的mIoU。我们框架的实现可以在以下网址找到:https://github.com/Masrur02/AFRDA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了无监督域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)中的一项新技术——自适应特征细化(AFR)模块。该技术能够在无需目标域标注的情况下,训练在源域数据上的模型并适应目标域。通过利用低分辨率逻辑语义先验对高分辨率特征进行细化,并集成高频率组件以捕获精细结构并提供关键边界信息,从而提高了分割精度。此外,它通过不确定性驱动的注意力机制自适应地平衡局部和全局信息,减少了误分类。该设计轻巧,可无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法中,实现了最先进的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- UDA-SS技术面临在复杂区域中平衡局部细节和全局信息的挑战,导致分割错误。
- 新技术AFR模块通过利用低分辨率逻辑语义先验对高分辨率特征进行细化,提高了分割精度。
- AFR模块集成高频率组件,捕获精细结构并提供关键边界信息,改善物体轮廓描绘。
- 通过不确定性驱动的注意力机制,AFR模块自适应平衡局部和全局信息,减少误分类。
- AFR设计轻巧,可无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法中。
- 与现有UDA-SS方法相比,新方法在GTA V到Cityscapes和Synthia到Cityscapes的测试中分别提高了1.05%和1.04%的mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

Dynamic Scoring with Enhanced Semantics for Training-Free Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Francesco Tonini, Lorenzo Vaquero, Alessandro Conti, Cigdem Beyan, Elisa Ricci
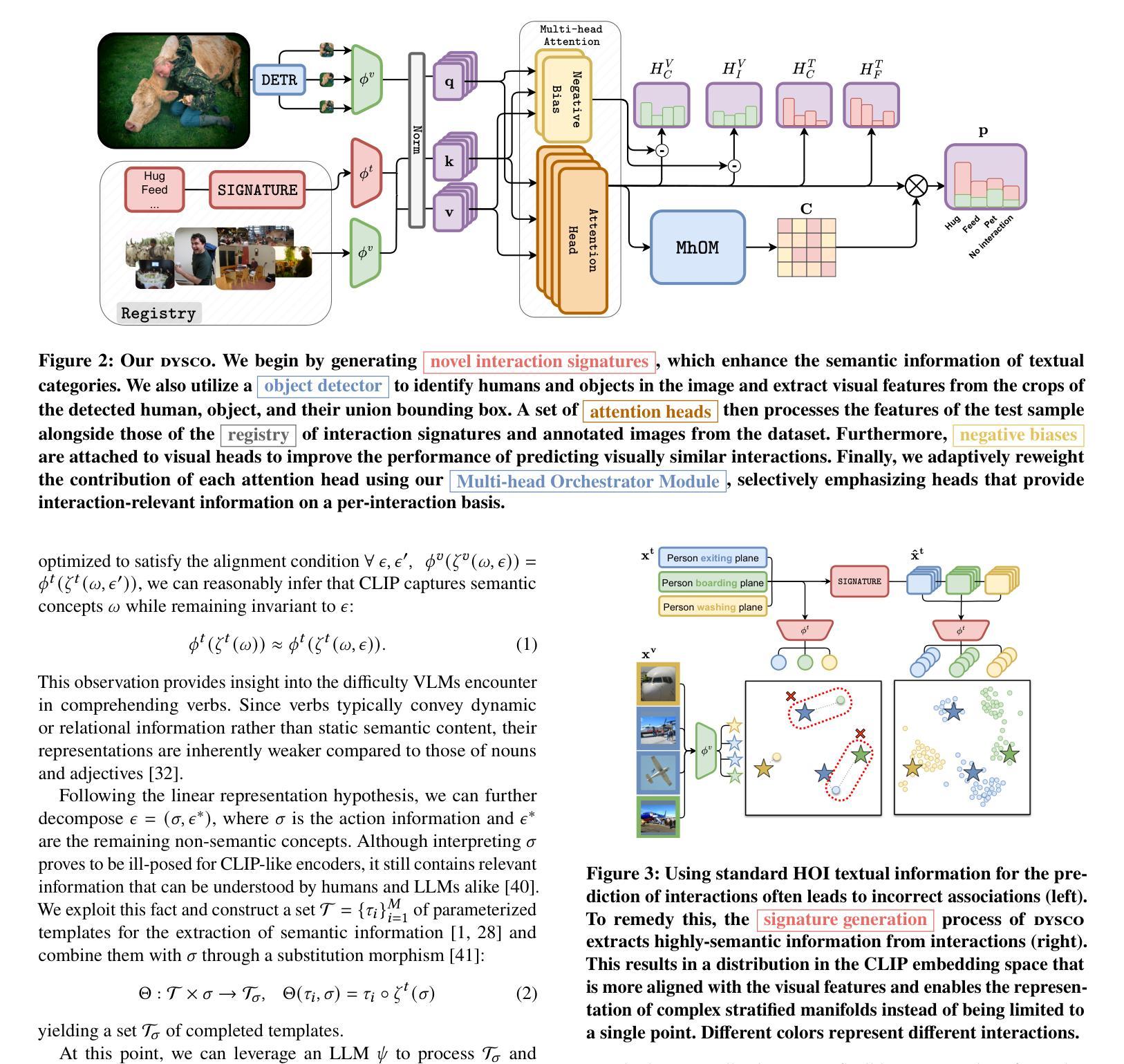
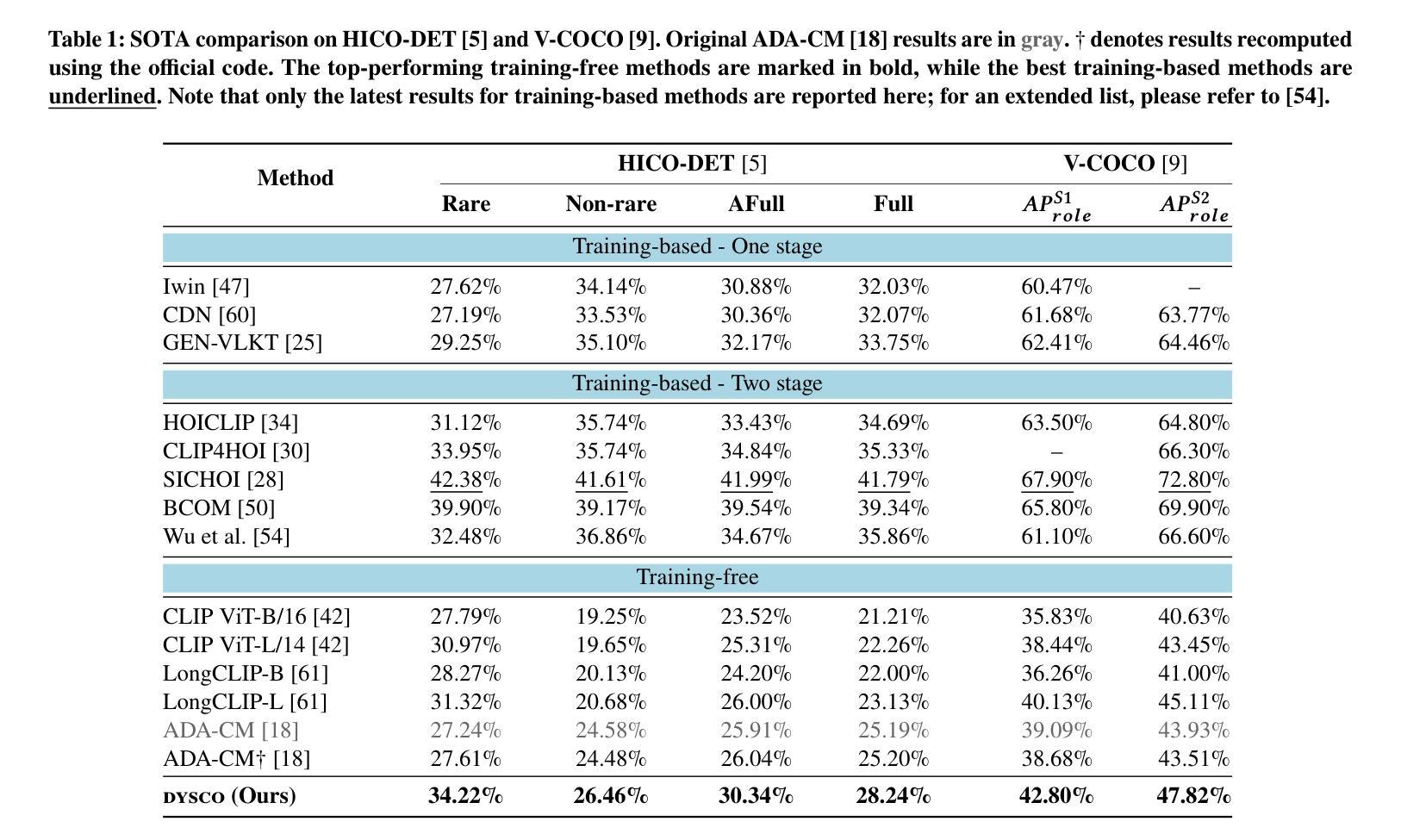
Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection aims to identify humans and objects within images and interpret their interactions. Existing HOI methods rely heavily on large datasets with manual annotations to learn interactions from visual cues. These annotations are labor-intensive to create, prone to inconsistency, and limit scalability to new domains and rare interactions. We argue that recent advances in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer untapped potential, particularly in enhancing interaction representation. While prior work has injected such potential and even proposed training-free methods, there remain key gaps. Consequently, we propose a novel training-free HOI detection framework for Dynamic Scoring with enhanced semantics (DYSCO) that effectively utilizes textual and visual interaction representations within a multimodal registry, enabling robust and nuanced interaction understanding. This registry incorporates a small set of visual cues and uses innovative interaction signatures to improve the semantic alignment of verbs, facilitating effective generalization to rare interactions. Additionally, we propose a unique multi-head attention mechanism that adaptively weights the contributions of the visual and textual features. Experimental results demonstrate that our DYSCO surpasses training-free state-of-the-art models and is competitive with training-based approaches, particularly excelling in rare interactions. Code is available at https://github.com/francescotonini/dysco.
人机交互(HOI)检测旨在识别图像中的人类和物体,并解释其交互。现有的HOI方法严重依赖于带有手动注释的大型数据集来学习视觉线索中的交互。这些注释的创建需要大量劳动力,容易出现不一致,并且在新领域和罕见交互上的可扩展性受到限制。我们认为,视觉语言模型(VLM)的最新进展提供了尚未开发的潜力,特别是在增强交互表示方面。尽管先前的工作已经注入了这种潜力,甚至提出了无训练的方法,但仍存在关键差距。因此,我们提出了一种新型的无训练HOI检测框架动态评分增强语义(DYSCO),该框架有效利用多模式注册表中的文本和视觉交互表示,实现稳健而细微的交互理解。该注册表结合了少量视觉线索,并使用创新的交互签名改进动词的语义对齐,促进了对罕见交互的有效泛化。此外,我们提出了一种独特的多头注意力机制,可以自适应地加权视觉和文本特征的贡献。实验结果表明,我们的DYSCO超越了无训练的最先进模型,并与基于训练的方法相竞争,特别是在罕见交互方面表现出色。代码可在https://github.com/francescotonini/dysco找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了Human-Object Interaction(HOI)检测的任务目标,即识别图像中的人类和物体并解释其交互。现有方法依赖于大量手工标注的数据集来学习视觉线索中的交互,但这些标注创建成本高、易出错且对新领域和罕见交互的可扩展性有限。文章指出,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的近期进展具有巨大潜力,特别是在增强交互表示方面。为此,文章提出了一种新型的无需训练的人机交互检测框架DYSCO,它利用多模式注册中的文本和视觉交互表示,实现稳健和细微的交互理解。该框架采用一小部分视觉线索并创新使用交互签名来改进动词的语义对齐,能很好地泛化到罕见的交互上。此外,它还提出了一种独特的多头注意力机制,可以自适应地加权视觉和文本特征的贡献。实验表明,DYSCO超越了无训练状态下的最新模型,并且与基于训练的方法相比具有竞争力,尤其在罕见交互方面表现突出。
Key Takeaways:
- Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection的目标是识别图像中的的人和物体并解释其交互。
- 现有HOI检测方法依赖于大量手工标注的数据集,存在创建成本高、易出错和泛化能力有限的问题。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在增强交互表示方面具有巨大潜力。
- 提出的DYSCO框架是一种无需训练的人机交互检测框架,利用多模式注册中的文本和视觉交互表示。
- DYSCO采用创新使用交互签名和改进动词的语义对齐来泛化到罕见的交互。
- DYSCO采用多头注意力机制,自适应地加权视觉和文本特征的贡献。
- 实验表明DYSCO在无需训练的情况下表现超越最新模型,并且在罕见交互方面表现尤为出色。
点此查看论文截图