⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
Hierarchical Message-Passing Policies for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Tommaso Marzi, Cesare Alippi, Andrea Cini
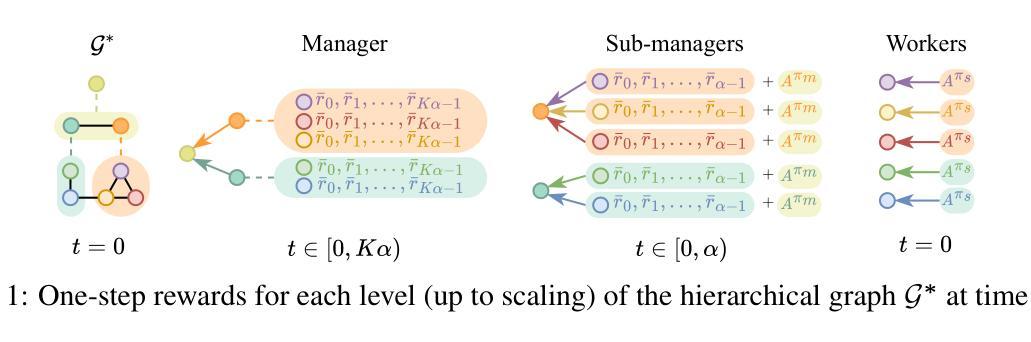
Decentralized Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) methods allow for learning scalable multi-agent policies, but suffer from partial observability and induced non-stationarity. These challenges can be addressed by introducing mechanisms that facilitate coordination and high-level planning. Specifically, coordination and temporal abstraction can be achieved through communication (e.g., message passing) and Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL) approaches to decision-making. However, optimization issues limit the applicability of hierarchical policies to multi-agent systems. As such, the combination of these approaches has not been fully explored. To fill this void, we propose a novel and effective methodology for learning multi-agent hierarchies of message-passing policies. We adopt the feudal HRL framework and rely on a hierarchical graph structure for planning and coordination among agents. Agents at lower levels in the hierarchy receive goals from the upper levels and exchange messages with neighboring agents at the same level. To learn hierarchical multi-agent policies, we design a novel reward-assignment method based on training the lower-level policies to maximize the advantage function associated with the upper levels. Results on relevant benchmarks show that our method performs favorably compared to the state of the art.
去中心化的多智能体强化学习(MARL)方法允许学习可扩展的多智能体策略,但受到部分可观察性和诱导的非平稳性的困扰。这些挑战可以通过引入促进协调和高级规划的机制来解决。具体来说,协调和临时抽象可以通过通信(例如,信息传递)和分层强化学习(HRL)的决策方法来实现。然而,优化问题限制了分层策略在多智能体系统中的应用。因此,这些方法的结合尚未得到充分探索。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了一种用于学习多智能体层级传递消息策略的新型有效方法。我们采用封建的HRL框架,并依赖分层图形结构进行智能体之间的规划和协调。层级结构中的较低级别的智能体从上级接收目标,并与同级相邻的智能体交换消息。为了学习分层多智能体策略,我们设计了一种基于训练下级策略以最大化与上级相关的优势函数的新型奖励分配方法。在相关基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法与最新技术相比表现良好。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多代理强化学习(MARL)的方法能够实现可伸缩的多代理政策学习,但面临部分可观察性和诱导的非平稳性问题。通过引入协调机制和高级规划,可以解决这个问题。协调和临时抽象可以通过通信(如消息传递)和分层强化学习(HRL)决策方法来实现。然而,优化问题限制了分层政策在多代理系统中的应用。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新的有效的多代理层次消息传递政策学习方法。我们采用封建HRL框架,并依赖于分层图结构进行规划和协调代理之间的交互。层次结构中的较低级别的代理接收来自上级的目标,并与同级的其他代理交换消息。为了学习分层多代理政策,我们设计了一种新的奖励分配方法,基于训练低级政策以最大化与上级相关的优势函数。在相关基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法与当前最佳实践相比表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理强化学习(MARL)面临部分可观察性和非平稳性的挑战。
- 协调和临时抽象是解决这些问题的关键。
- 通信和分层强化学习(HRL)方法可实现协调和高级规划。
- 分层政策在多代理系统中的应用受到优化问题的限制。
- 提出了一种新的多代理层次消息传递政策学习方法。
- 采用封建HRL框架和分层图结构进行规划和协调。
点此查看论文截图

Trae Agent: An LLM-based Agent for Software Engineering with Test-time Scaling
Authors: Trae Research Team, Pengfei Gao, Zhao Tian, Xiangxin Meng, Xinchen Wang, Ruida Hu, Yuanan Xiao, Yizhou Liu, Zhao Zhang, Junjie Chen, Cuiyun Gao, Yun Lin, Yingfei Xiong, Chao Peng, Xia Liu
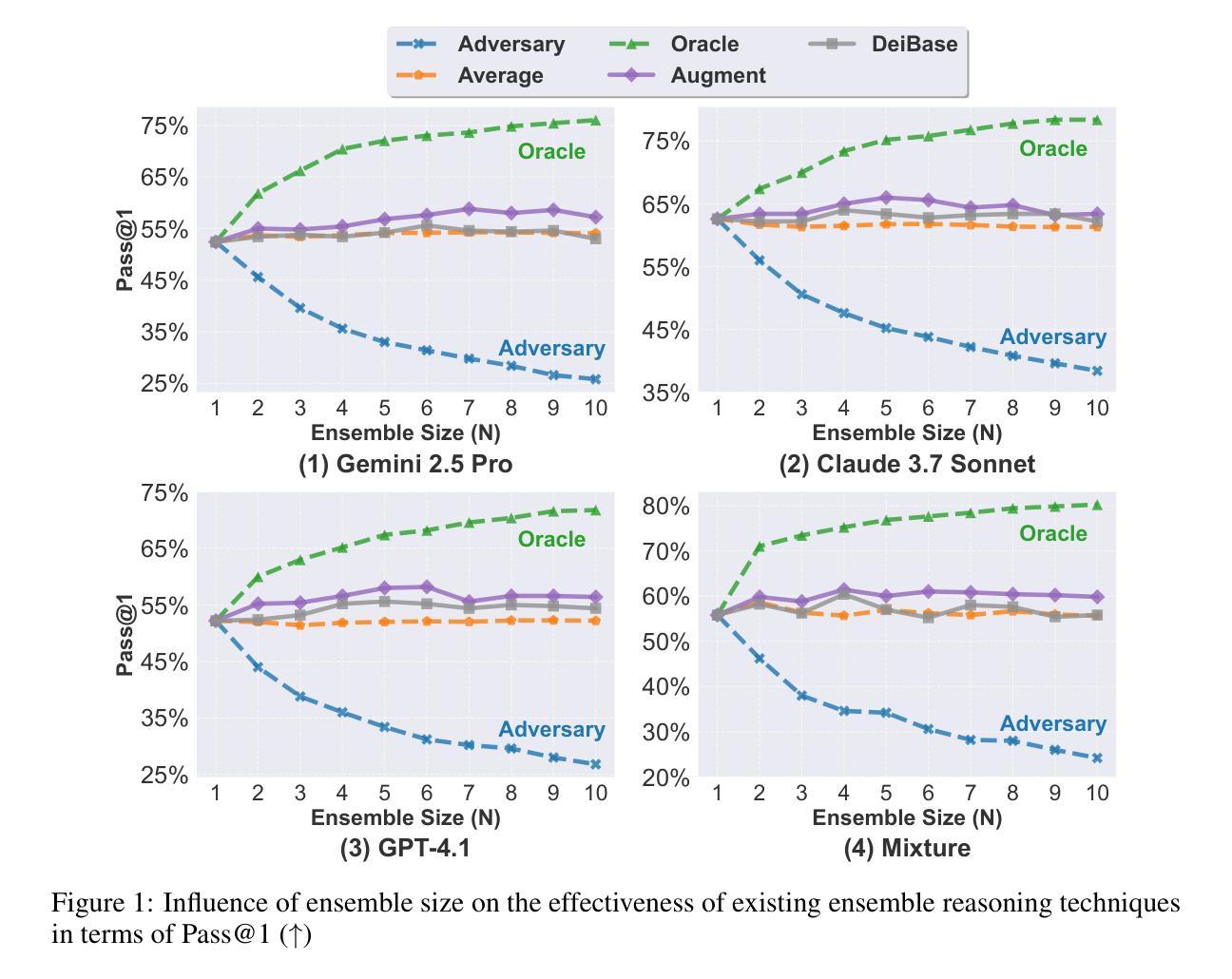
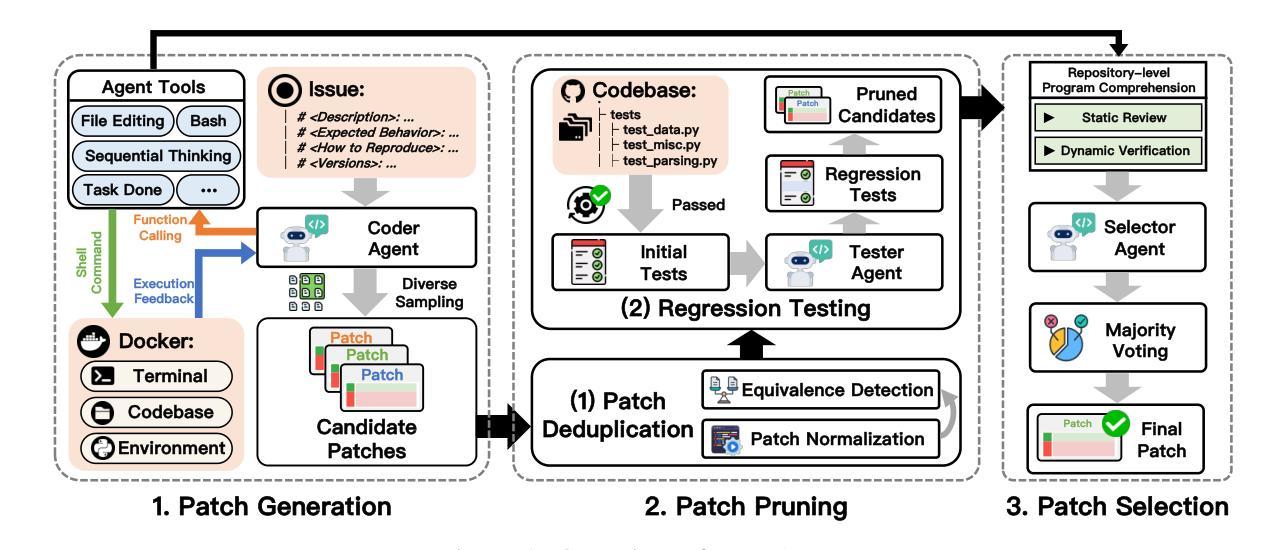
Software issue resolution is a critical challenge in software engineering and has garnered increasing attention in recent years. With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), substantial progress has been made in addressing real-world software engineering tasks. Recent studies have introduced ensemble reasoning techniques to enhance the performance of LLM-based issue resolution. However, existing prompting-based methods still face limitations in effectively exploring large ensemble spaces and lack the capacity for repository-level understanding, both of which constrain their overall effectiveness. In this paper, we propose Trae Agent, the first agent-based ensemble reasoning approach for repository-level issue resolution. Trae Agent formulates our goal as an optimal solution search problem and addresses two key challenges, i.e., large ensemble spaces and repository-level understanding, through modular agents for generation, pruning, and selection. We conduct extensive experiments using three leading LLMs on the widely-adopted SWE-bench benchmark, comparing Trae Agent against four state-of-the-art ensemble reasoning techniques. Experimental results demonstrate that Trae Agent consistently achieves superior performance, with an average improvement of 10.22% over all baselines in terms of Pass@1. Trae Agent has achieved first place on the SWE-bench Verified leaderboard, with a notable Pass@1 score of 75.20%. We are pleased to release Trae Agent as an open-source project to support the research community, with all resources available at https://github.com/bytedance/trae-agent.
软件问题解答在软件工程中是一项关键挑战,近年来也获得了越来越多的关注。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,解决现实世界软件工程任务方面取得了实质性进展。最近的研究引入了集成推理技术,以提高基于LLM的问题解答性能。然而,现有的基于提示的方法在有效探索大型集成空间和仓库级理解方面仍存在局限性,这两方面都限制了它们的整体有效性。在本文中,我们提出了Trae Agent,这是基于仓库级别问题解答的第一个基于代理的集成推理方法。Trae Agent将我们的目标制定为寻找最优解决方案的问题,并通过用于生成、修剪和选择的模块化代理来解决两个关键挑战,即大型集成空间和仓库级理解。我们使用三个领先的大型语言模型在广泛采用的SWE-bench基准测试上进行了大量实验,将Trae Agent与四种最先进的集成推理技术进行了比较。实验结果表明,Trae Agent的性能一直较为优越,在Pass@1方面的平均改进率为10.22%。Trae Agent在SWE-bench验证排行榜上获得第一名,Pass@1分数达到了75.20%。我们很高兴将Trae Agent作为开源项目发布,以支持研究界,所有资源均可在https://github.com/bytedance/trae-agent获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pengfei Gao and Zhao Tian contributed equally to this technical report
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的软件问题解决方案已成为软件工程领域的重要挑战。近期研究引入了基于代理的集成推理方法Trae Agent,解决了仓库级别的问题解决难题。Trae Agent通过模块化代理进行生成、修剪和选择,解决了大规模集成空间和仓库级别理解两大难题。实验结果表明,Trae Agent在SWE-bench基准测试上的性能优于其他四种先进的集成推理技术,平均提高了10.22%,并在SWE-bench验证排行榜上获得第一名,Pass@1得分为75.20%。目前,Trae Agent已作为支持研究人员的开源项目发布。
Key Takeaways
- 软件问题解决方案在软件工程中至关重要,大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为这一问题提供了新思路。
- 现有基于提示的方法在探索大规模集成空间和仓库级别理解方面存在局限性。
- Trae Agent是首个基于代理的仓库级别问题解决的集成推理方法。
- Trae Agent通过模块化代理解决大规模集成空间和仓库级别理解的挑战。
- Trae Agent在SWE-bench基准测试上的性能优于其他先进的集成推理技术,平均提高10.22%。
- Trae Agent在SWE-bench验证排行榜上获得第一名,Pass@1得分为75.20%。
点此查看论文截图

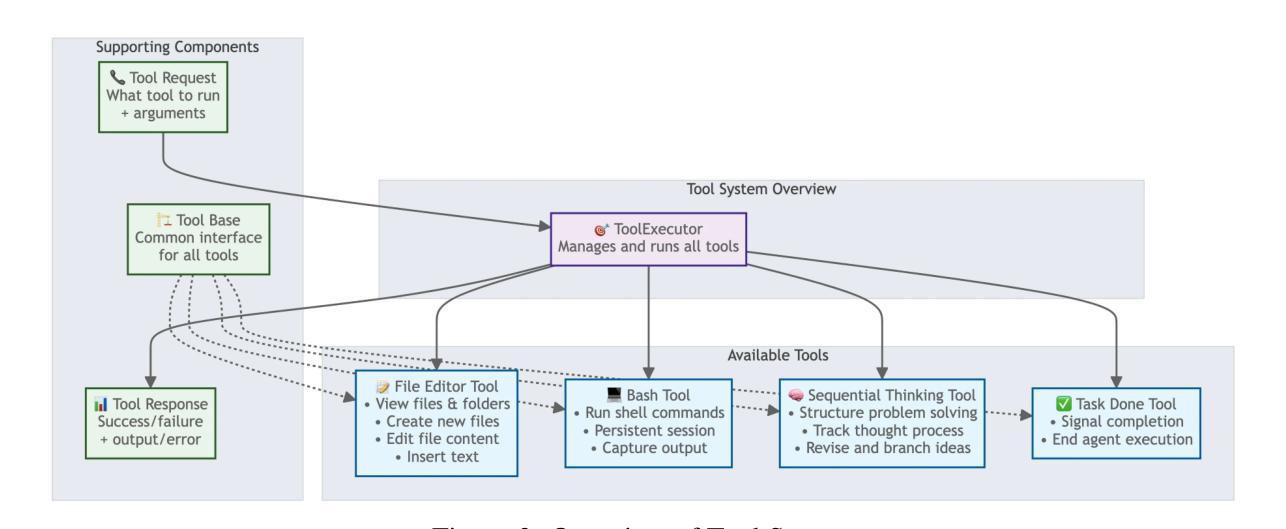
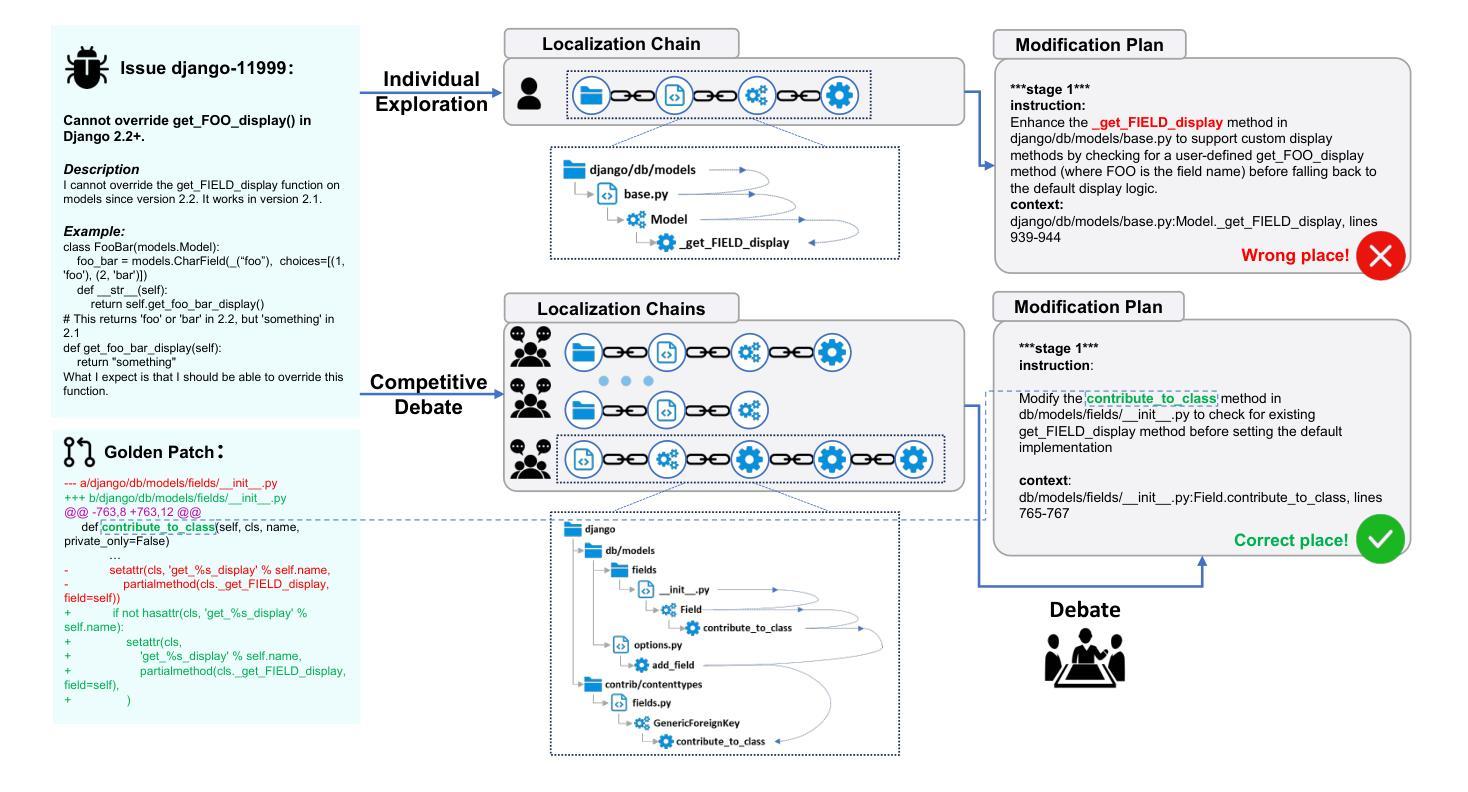
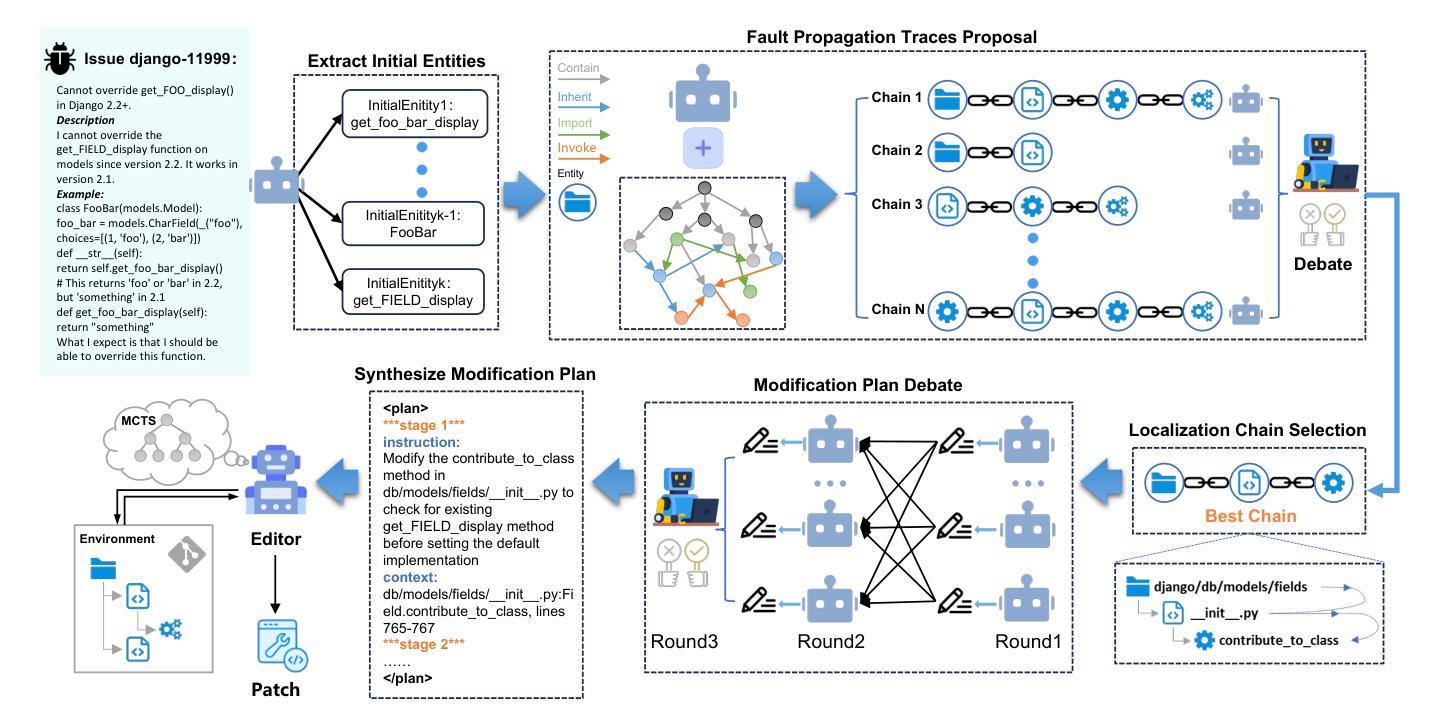
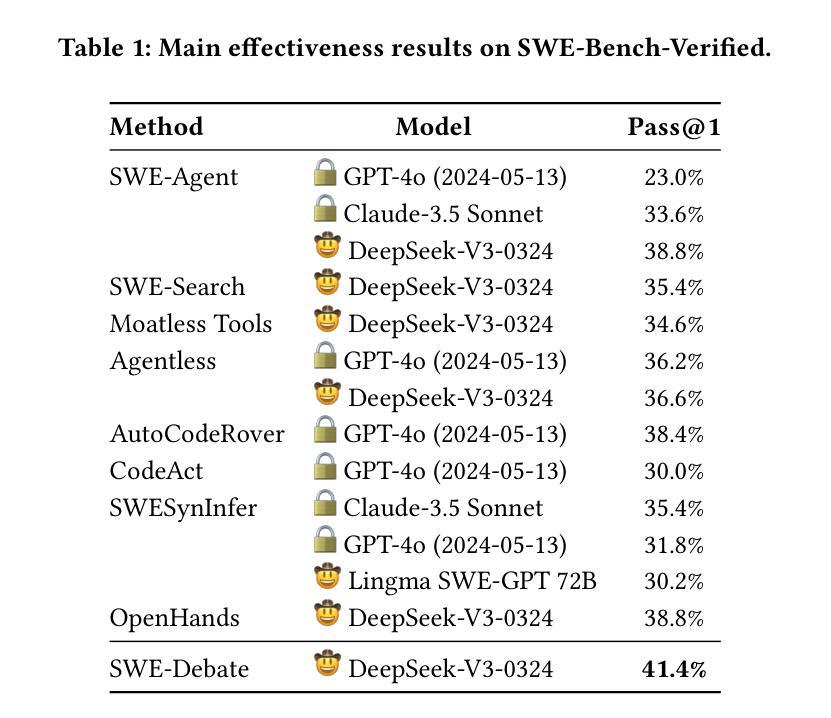
SWE-Debate: Competitive Multi-Agent Debate for Software Issue Resolution
Authors:Han Li, Yuling Shi, Shaoxin Lin, Xiaodong Gu, Heng Lian, Xin Wang, Yantao Jia, Tao Huang, Qianxiang Wang
Issue resolution has made remarkable progress thanks to the advanced reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Recently, agent-based frameworks such as SWE-agent have further advanced this progress by enabling autonomous, tool-using agents to tackle complex software engineering tasks. While existing agent-based issue resolution approaches are primarily based on agents’ independent explorations, they often get stuck in local solutions and fail to identify issue patterns that span across different parts of the codebase. To address this limitation, we propose SWE-Debate, a competitive multi-agent debate framework that encourages diverse reasoning paths and achieves more consolidated issue localization. SWE-Debate first creates multiple fault propagation traces as localization proposals by traversing a code dependency graph. Then, it organizes a three-round debate among specialized agents, each embodying distinct reasoning perspectives along the fault propagation trace. This structured competition enables agents to collaboratively converge on a consolidated fix plan. Finally, this consolidated fix plan is integrated into an MCTS-based code modification agent for patch generation. Experiments on the SWE-bench benchmark show that SWE-Debate achieves new state-of-the-art results in open-source agent frameworks and outperforms baselines by a large margin.
得益于大型语言模型(LLM)的先进推理能力,问题解决的进展已经取得了显著成果。最近,基于代理的框架(如SWE-agent)通过使能够自主使用工具代理来处理复杂的软件工程任务,进一步推动了这一进展。虽然现有的基于代理的问题解决方式主要基于代理的独立探索,但它们经常陷入局部解决方案中,并且无法识别跨越代码库不同部分的跨问题模式。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SWE-Debate,这是一个竞争性的多代理辩论框架,它鼓励不同的推理路径并实现了更巩固的问题定位。SWE-Debate首先通过遍历代码依赖图来创建多个故障传播轨迹作为定位建议。然后,它在专业代理之间组织了一个三轮辩论,每个代理在故障传播轨迹上体现了不同的推理角度。这种结构化竞争使代理能够协同收敛到一个统一的修复计划上。最后,这个统一的修复计划被整合到基于MCTS的代码修改代理中进行补丁生成。在SWE-bench基准测试上的实验表明,SWE-Debate在开源代理框架上取得了最新成果,并在很大程度上优于基线水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code and data are available at https://github.com/YerbaPage/SWE-Debate
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的先进推理能力为问题解决带来了显著进展。最近,基于代理的框架(如SWE-agent)进一步推动了这一进展,使自主工具使用代理能够完成复杂的软件工程任务。针对现有基于代理的问题解决策略主要基于代理的独立探索,但往往陷入局部解决方案并无法识别跨越代码库不同部分的问题模式,提出了SWE-Debate。这是一种竞争性的多代理辩论框架,鼓励多样化的推理路径并实现更巩固的问题定位。SWE-Debate通过遍历代码依赖图创建多个故障传播轨迹作为定位建议。然后,它在专业代理之间进行三轮辩论,每个代理在故障传播轨迹上体现不同的推理角度。这种结构化的竞争使代理能够协作制定一个统一的修复计划。最终,此计划被整合到基于MCTS的代码修改代理中进行补丁生成。在SWE-bench基准测试上的实验表明,SWE-Debate在开源代理框架中取得了最新最先进的成果,并大幅度超越了基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力在问题解决方案中起到了重要作用。
- 基于代理的框架(如SWE-agent)已经使代理能够自主完成复杂的软件工程任务。
- 现有问题解决方案经常陷入局部解决方案,无法识别跨越代码库不同部分的问题模式。
- SWE-Debate是一个多代理辩论框架,旨在通过鼓励多样化的推理路径来解决此问题并实现更巩固的问题定位。
- SWE-Debate通过创建故障传播轨迹和进行专业代理之间的辩论来定位问题。
- 通过结构化竞争,SWE-Debate使代理能够协作制定统一的修复计划。
点此查看论文截图

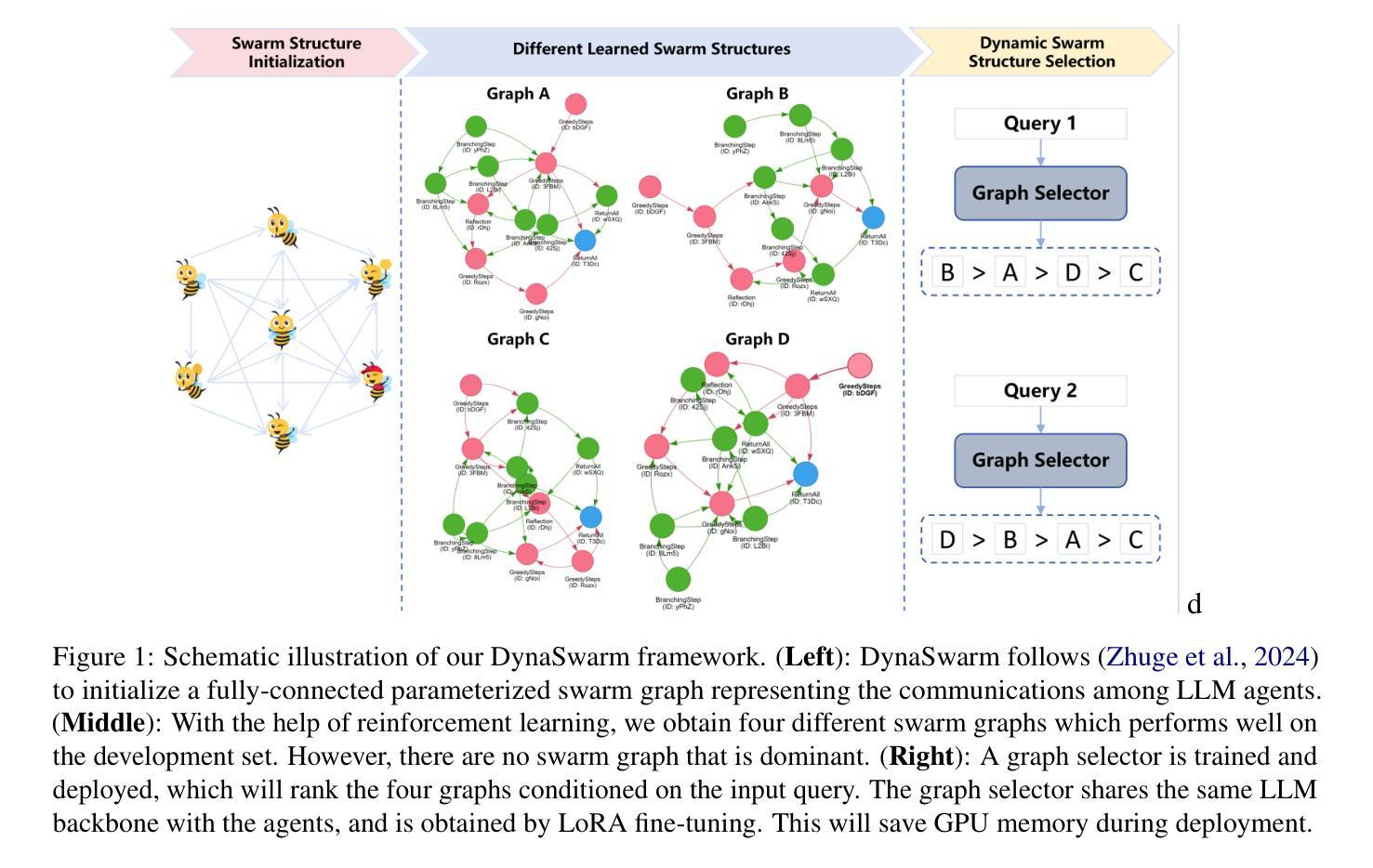
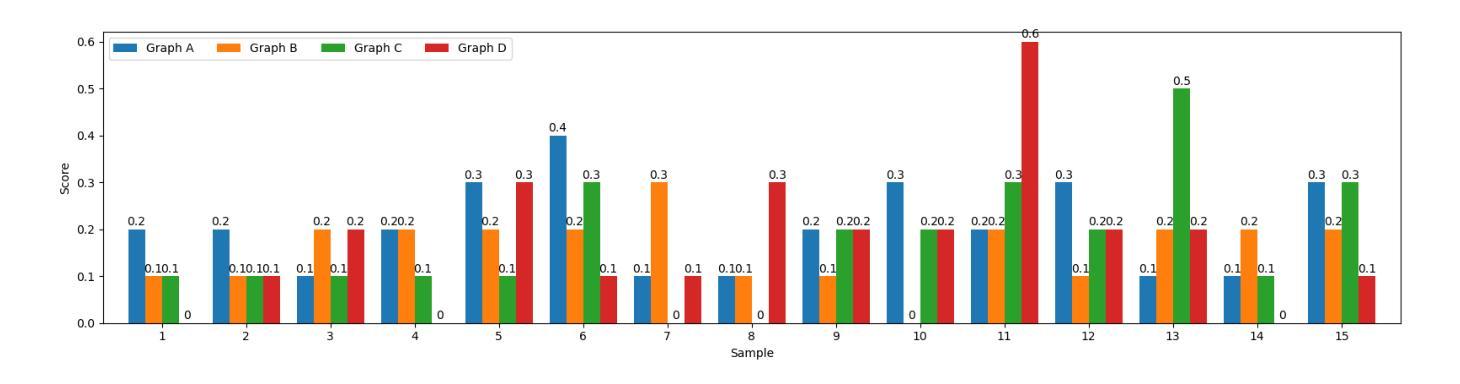
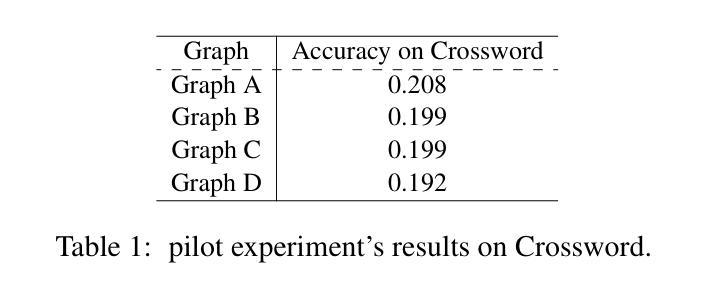
DynaSwarm: Dynamically Graph Structure Selection for LLM-based Multi-agent System
Authors:Hui Yi Leong, Yuqing Wu
Current multi-agent systems (MAS) frameworks often rely on manually designed and static collaboration graph structures, limiting adaptability and performance. To address these limitations, we propose DynaSwarm, a dynamic framework that enhances LLM-based MAS through two key innovations: (1) an actor-critic reinforcement learning (A2C) mechanism to optimize graph structures with improved stability over prior RL methods, and (2) a dynamic graph selector that adaptively chooses the optimal graph structure for each input sample via parameter-efficient LLM fine-tuning. DynaSwarm eliminates the need for rigid, one-fits-all graph architectures, instead leveraging sample-specific idiosyncrasies to dynamically route queries through specialized agent networks. (c) We propose to fine-tune the demonstration retriever to fully exploit the power of in-context learning (ICL). Extensive experiments on question answering, mathematical reasoning, and coding tasks demonstrate that DynaSwarm consistently outperforms state-of-the-art single-agent and MAS baselines across multiple LLM backbones. Our findings highlight the importance of sample-aware structural flexibility in LLM MAS designs.
当前的多智能体系统(MAS)框架通常依赖于手动设计和静态的协作图结构,这限制了其适应性和性能。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了DynaSwarm,这是一个动态框架,通过两个关键创新点增强了基于大型语言模型(LLM)的MAS:(1)一种基于行动者评论家强化学习(A2C)的机制,以优化图结构,提高相对于之前的强化学习方法的稳定性;(2)一个动态图选择器,通过参数高效的大型语言模型微调,自适应地为每个输入样本选择最佳图结构。DynaSwarm消除了对僵化、一刀切图形架构的需求,而是利用样本特定的特性来动态地通过专用代理网络路由查询。©我们提出对演示检索器进行微调,以充分利用上下文学习(ICL)的力量。在问答、数学推理和编码任务方面的大量实验表明,DynaSwarm在多个大型语言模型主干上始终优于最新的单智能体和多智能体基准测试。我们的研究结果表明,在大型语言模型多智能体设计中,样本感知的结构灵活性非常重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多智能体系统(MAS)框架通常采用手动设计和静态协作图结构,限制了其适应性和性能。针对这些局限性,我们提出了DynaSwarm动态框架,它通过两个关键创新点增强了基于大型语言模型(LLM)的MAS:(1)采用行动者评论家强化学习(A2C)机制优化图结构,提高了相对于之前的强化学习方法的稳定性;(2)通过参数高效的大型语言模型微调,动态选择针对每个输入样本的最佳图结构。DynaSwarm不需要固定的通用图架构,而是利用样本特定的特性通过专门的智能体网络动态路由查询。实验表明,DynaSwarm在问答、数学推理和编码任务上均优于最新的单智能体和多智能体基准测试,突显了样本感知的结构灵活性在大型语言模型多智能体系统设计中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统(MAS)当前依赖于手动设计和静态协作图结构,具有局限性。
- DynaSwarm框架通过两个关键创新点增强LLM-based的MAS:使用A2C机制优化图结构和通过参数高效的大型语言模型微调来选择最佳图结构。
- DynaSwarm框架能够动态地根据每个输入样本的特性选择图结构,不需要固定的通用图架构。
- DynaSwarm在问答、数学推理和编码任务上的性能表现优于现有的单智能体和多智能体基准测试。
- 样本感知的结构灵活性在大型语言模型多智能体系统设计中至关重要。
- DynaSwarm通过强化学习优化图结构,提高了系统的稳定性和性能。
点此查看论文截图

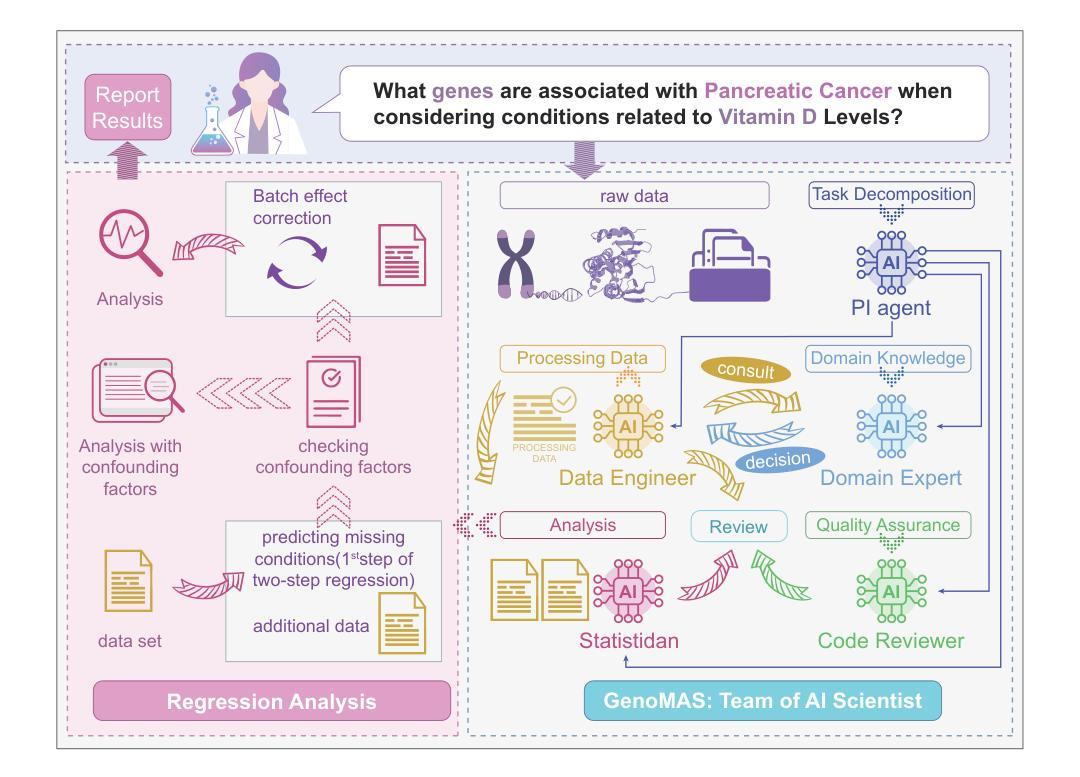
GenoMAS: A Multi-Agent Framework for Scientific Discovery via Code-Driven Gene Expression Analysis
Authors:Haoyang Liu, Yijiang Li, Haohan Wang
Gene expression analysis holds the key to many biomedical discoveries, yet extracting insights from raw transcriptomic data remains formidable due to the complexity of multiple large, semi-structured files and the need for extensive domain expertise. Current automation approaches are often limited by either inflexible workflows that break down in edge cases or by fully autonomous agents that lack the necessary precision for rigorous scientific inquiry. GenoMAS charts a different course by presenting a team of LLM-based scientists that integrates the reliability of structured workflows with the adaptability of autonomous agents. GenoMAS orchestrates six specialized LLM agents through typed message-passing protocols, each contributing complementary strengths to a shared analytic canvas. At the heart of GenoMAS lies a guided-planning framework: programming agents unfold high-level task guidelines into Action Units and, at each juncture, elect to advance, revise, bypass, or backtrack, thereby maintaining logical coherence while bending gracefully to the idiosyncrasies of genomic data. On the GenoTEX benchmark, GenoMAS reaches a Composite Similarity Correlation of 89.13% for data preprocessing and an F$_1$ of 60.48% for gene identification, surpassing the best prior art by 10.61% and 16.85% respectively. Beyond metrics, GenoMAS surfaces biologically plausible gene-phenotype associations corroborated by the literature, all while adjusting for latent confounders. Code is available at https://github.com/Liu-Hy/GenoMAS.
基因表达分析在许多生物医学发现中起着关键作用,然而,从原始转录组数据中提取洞察仍然是一项艰巨的任务,这主要是由于多个大型半结构化文件的复杂性以及需要广泛的专业知识。当前的自动化方法常常受到僵化工作流程的限制,在特殊情况下会失效,或者由于缺乏精确性而无法满足严格科学探索的全自主代理的需求。GenoMAS通过提出一个由大型语言模型(LLM)科学家组成的团队,开辟了不同的路径,该团队将结构化工作流程的可靠性与自主代理的适应性相结合。GenoMAS通过类型化消息传递协议协调六个专业的LLM代理,每个代理都在共享的分析画布上发挥互补优势。GenoMAS的核心是一个引导规划框架:编程代理将高级任务指南展开为行动单元,并在每个路口选择前进、修订、绕过或回溯,从而在保持逻辑连贯性的同时,优雅地适应基因组数据的特性。在GenoTEX基准测试中,GenoMAS在数据预处理方面达到89.13%的组合相似性相关性,在基因识别方面达到60.48%的F1分数,分别比现有最佳技术高出10.61%和16.85%。除了度量指标外,GenoMAS还根据文献证实了生物学上合理的基因-表型关联,同时调整潜在混杂因素。代码可在https://github.com/Liu-Hy/GenoMAS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 51 pages (13 pages for the main text, 9 pages for references, and 29 pages for the appendix)
Summary
基因表达分析是生物医学发现的关键,但处理原始转录组数据仍然是一项艰巨的任务。当前自动化方法存在局限性,无法兼顾灵活性和精确度。GenoMAS项目通过整合结构化工作流和自主代理的优势,提出一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的解决方案。它通过消息传递协议协调六个专业LLM代理,在基因识别和数据预处理方面实现了高性能。GenoMAS不仅提高了效率,还能发现生物上合理的基因-表型关联,并调整潜在混杂因素。
Key Takeaways
- 基因表达分析是生物医学研究的核心,但处理转录组数据具有挑战性,需要强大的自动化工具。
- 当前自动化方法在灵活性和精确度方面存在局限。
- GenoMAS项目利用大型语言模型(LLM)技术,整合结构化工作流和自主代理的优势。
- GenoMAS通过消息传递协议协调多个LLM代理,实现高效基因识别和数据预处理。
- GenoMAS在GenoTEX基准测试上实现了高性能,达到了89.13%的复合相似性关联和60.48%的F1得分。
- GenoMAS能够发现生物上合理的基因-表型关联,并调整潜在混杂因素。
- GenoMAS代码已公开,可供研究人使用。
点此查看论文截图
Decentralized Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Agent Collision Avoidance with Model Predictive Path Integral
Authors:Stepan Dergachev, Konstantin Yakovlev
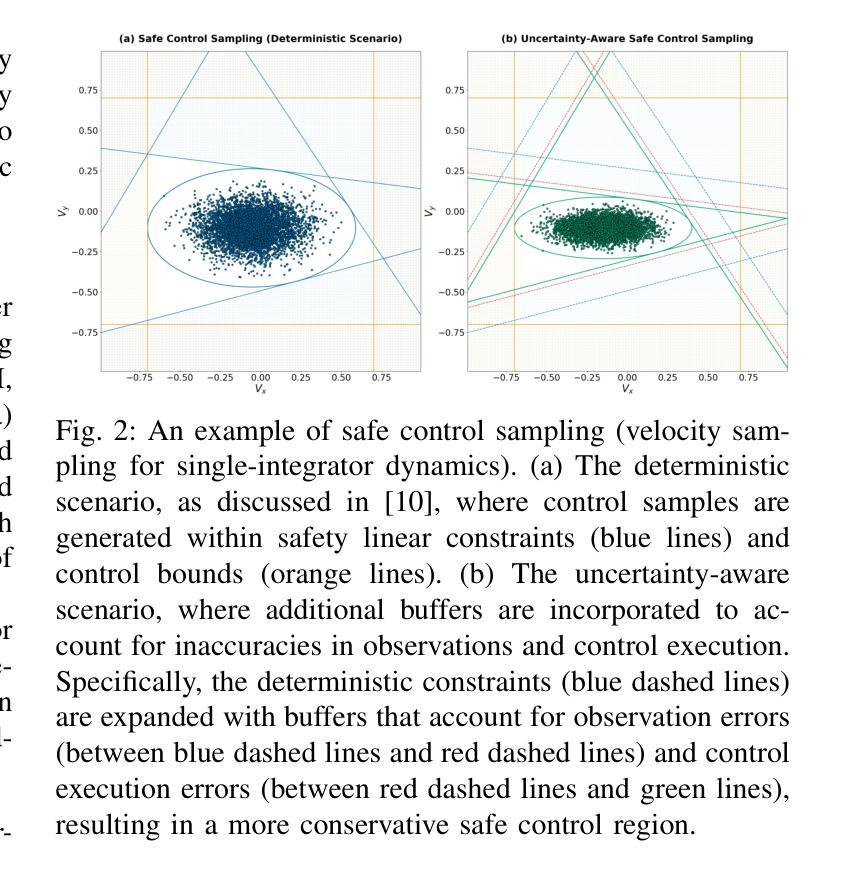
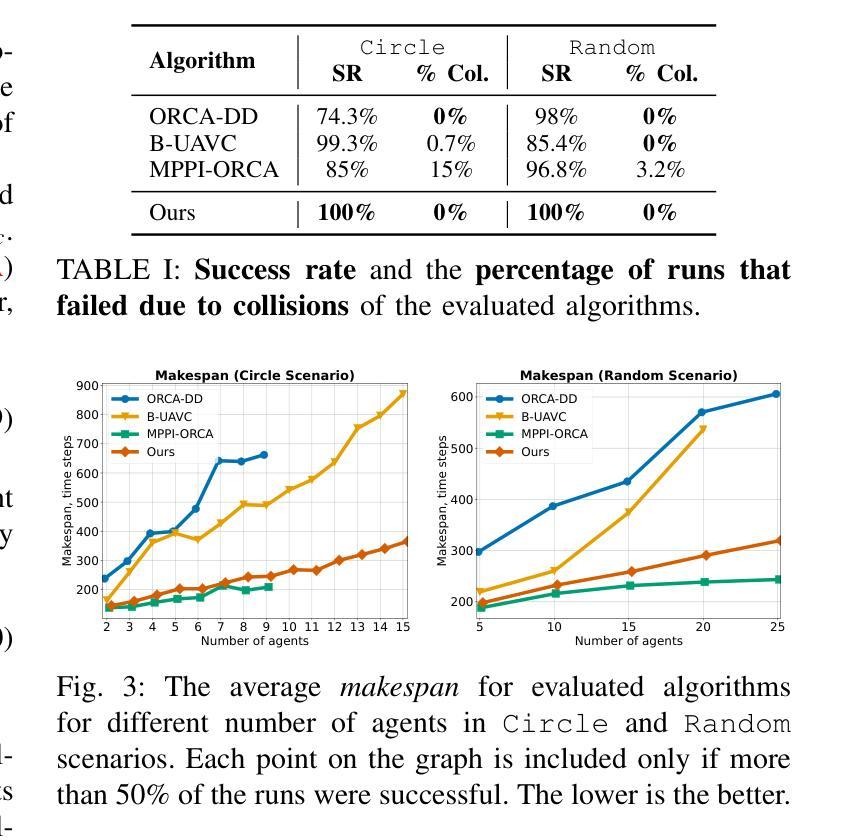
Decentralized multi-agent navigation under uncertainty is a complex task that arises in numerous robotic applications. It requires collision avoidance strategies that account for both kinematic constraints, sensing and action execution noise. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that integrates the Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI) with a probabilistic adaptation of Optimal Reciprocal Collision Avoidance. Our method ensures safe and efficient multi-agent navigation by incorporating probabilistic safety constraints directly into the MPPI sampling process via a Second-Order Cone Programming formulation. This approach enables agents to operate independently using local noisy observations while maintaining safety guarantees. We validate our algorithm through extensive simulations with differential-drive robots and benchmark it against state-of-the-art methods, including ORCA-DD and B-UAVC. Results demonstrate that our approach outperforms them while achieving high success rates, even in densely populated environments. Additionally, validation in the Gazebo simulator confirms its practical applicability to robotic platforms. A source code is available at http://github.com/PathPlanning/MPPI-Collision-Avoidance.
在不确定条件下的分布式多智能体导航是众多机器人应用中出现的一项复杂任务。这需要避撞策略,该策略要考虑到运动学约束、感知和执行动作的噪声。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型方法,它将模型预测路径积分(MPPI)与最优相互避撞(Optimal Reciprocal Collision Avoidance)的概率适应相结合。我们的方法通过二阶锥程序(Second-Order Cone Programming)公式将概率安全约束直接纳入MPPI采样过程,确保安全高效的多智能体导航。这种方法使得智能体能够利用局部噪声观测进行独立操作,同时保持安全保证。我们通过差速驱动机器人的大量模拟验证了我们的算法,并将其与包括ORCA-DD和B-UAVC在内的最新技术进行了比较。结果表明,我们的方法表现优于它们,即使在人口稠密的环境中也能实现较高的成功率。此外,在Gazebo模拟器中的验证证实了其在机器人平台上的实际应用能力。源代码可在http://github.com/PathPlanning/MPPI-Collision-Avoidance获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a pre-print of the paper accepted to IROS2025. The manuscript includes 8 pages, 4 figures, and 1 table. A supplementary video is available at https://youtu.be/_D4zDYJ4KCk Updated version: added link to source code in the abstract; updated experimental results description in Section VI.A; updated author affiliation and funding information; minor typo corrections
Summary
本文提出了一种将模型预测路径积分(MPPI)与最优相互碰撞避免算法的概率适应相结合的新方法,用于解决去中心化多智能体在不确定环境下的导航问题。该方法通过二阶锥编程的形式将概率安全约束直接纳入MPPI采样过程,确保智能体在独立使用局部噪声观测的同时保持安全保证。通过广泛的模拟验证,该方法在差分驱动机器人上表现出优异性能,与ORCA-DD和B-UAVC等现有先进方法相比具有更高的成功率。同时,在Gazebo模拟器中的验证也证明了其在实际机器人平台上的适用性。相关源代码已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的多智能体导航方法,结合了模型预测路径积分(MPPI)和概率适应的最优相互碰撞避免算法。
- 通过二阶锥编程将概率安全约束纳入MPPI采样过程。
- 智能体在独立使用局部噪声观测的同时能确保安全。
- 通过广泛的模拟验证,该方法在差分驱动机器人上表现出优异性能。
- 与现有先进方法相比,该方法具有更高的成功率,尤其在密集环境中。
- 在Gazebo模拟器中的验证证明了其在实际机器人平台上的适用性。
点此查看论文截图
Think, Act, Learn: A Framework for Autonomous Robotic Agents using Closed-Loop Large Language Models
Authors:Anjali R. Menon, Rohit K. Sharma, Priya Singh, Chengyu Wang, Aurora M. Ferreira, Mateja Novak
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into robotics has unlocked unprecedented capabilities in high-level task planning. However, most current systems operate in an open-loop fashion, where LLMs act as one-shot planners, rendering them brittle and unable to adapt to unforeseen circumstances in dynamic physical environments. To overcome this limitation, this paper introduces the “Think, Act, Learn” (T-A-L) framework, a novel architecture that enables an embodied agent to autonomously learn and refine its policies through continuous interaction. Our framework establishes a closed-loop cycle where an LLM first “thinks” by decomposing high-level commands into actionable plans. The robot then “acts” by executing these plans while gathering rich, multimodal sensory feedback. Critically, the “learn” module processes this feedback to facilitate LLM-driven self-reflection, allowing the agent to perform causal analysis on its failures and generate corrective strategies. These insights are stored in an experiential memory to guide future planning cycles. We demonstrate through extensive experiments in both simulation and the real world that our T-A-L agent significantly outperforms baseline methods, including open-loop LLMs, Behavioral Cloning, and traditional Reinforcement Learning. Our framework achieves over a 97% success rate on complex, long-horizon tasks, converges to a stable policy in an average of just 9 trials, and exhibits remarkable generalization to unseen tasks. This work presents a significant step towards developing more robust, adaptive, and truly autonomous robotic agents.
将大型语言模型(LLM)整合到机器人技术中,已经实现了前所未有的高级任务规划能力。然而,目前大多数系统都采取开放式循环的方式运行,LLM充当一次性规划器,这使得它们脆弱且无法适应动态物理环境中无法预见的情况。为了克服这一局限性,本文介绍了“思考-行动-学习”(T-A-L)框架,这是一种新型架构,能够使实体代理人通过持续的交互自主学习和完善其政策。我们的框架建立了一个闭环周期,其中LLM首先“思考”将高级命令分解为可操作的计划。然后机器人“行动”通过执行这些计划同时收集丰富的多模式感官反馈。关键的是,“学习”模块处理这些反馈来推动LLM驱动的自我反思,使代理人能够对失败进行因果分析并产生纠正策略。这些见解存储在经验记忆中,以指导未来的规划周期。我们通过模拟和真实世界的广泛实验证明,我们的T-A-L代理人显著优于基线方法,包括开放式循环LLM、行为克隆和传统强化学习。我们的框架在复杂、长期的任务上成功率超过97%,平均只需9次试验就能稳定政策,并且对未见的任务表现出惊人的泛化能力。这项工作朝着开发更稳健、更适应和真正自主的机器人代理人迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 7 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)与机器人技术的融合为高层次的任务规划带来了前所未有的能力。然而,当前大多数系统采用开放式循环模式,使LLM作为一次性规划器,无法适应动态物理环境中的意外情况。为克服这一局限,本文提出了“思考-行动-学习”(T-A-L)框架,这是一种新型架构,能够让实体代理人通过持续互动自主学习和优化其策略。我们的框架建立了闭环循环,其中LLM首先“思考”将高层次指令分解为可操作的计划。机器人接着“行动”执行这些计划,同时收集丰富的多模式感官反馈。关键的是,“学习”模块处理这些反馈信息,促进LLM驱动的自我反思,使代理人能够对失败进行因果分析并产生纠正策略。这些见解储存在经验记忆中,以指导未来的规划循环。我们在模拟和现实世界的大量实验中证明,我们的T-A-L代理人在复杂、长期的任务上成功率超过97%,平均只需9次试验就能稳定策略,并且在未见的任务中展现出显著的泛化能力。本研究是朝着开发更稳健、适应性强和真正自主的机器人代理人迈出的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)与机器人融合带来高层次任务规划的新能力。
- 当前LLM在机器人应用中主要采取开放式循环模式,限制了其适应动态环境的能力。
- “思考-行动-学习”(T-A-L)框架被提出,建立闭环循环,增强机器人自主性。
- T-A-L框架允许LLM进行反思和自我调整策略,以适应环境变化。
- 通过实验验证,T-A-L框架在复杂任务上的成功率超过97%,并且能快速收敛到稳定策略。
- T-A-L框架展现出良好的泛化能力,在未见任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

FinGAIA: A Chinese Benchmark for AI Agents in Real-World Financial Domain
Authors:Lingfeng Zeng, Fangqi Lou, Zixuan Wang, Jiajie Xu, Jinyi Niu, Mengping Li, Yifan Dong, Qi Qi, Wei Zhang, Ziwei Yang, Jun Han, Ruilun Feng, Ruiqi Hu, Lejie Zhang, Zhengbo Feng, Yicheng Ren, Xin Guo, Zhaowei Liu, Dongpo Cheng, Weige Cai, Liwen Zhang
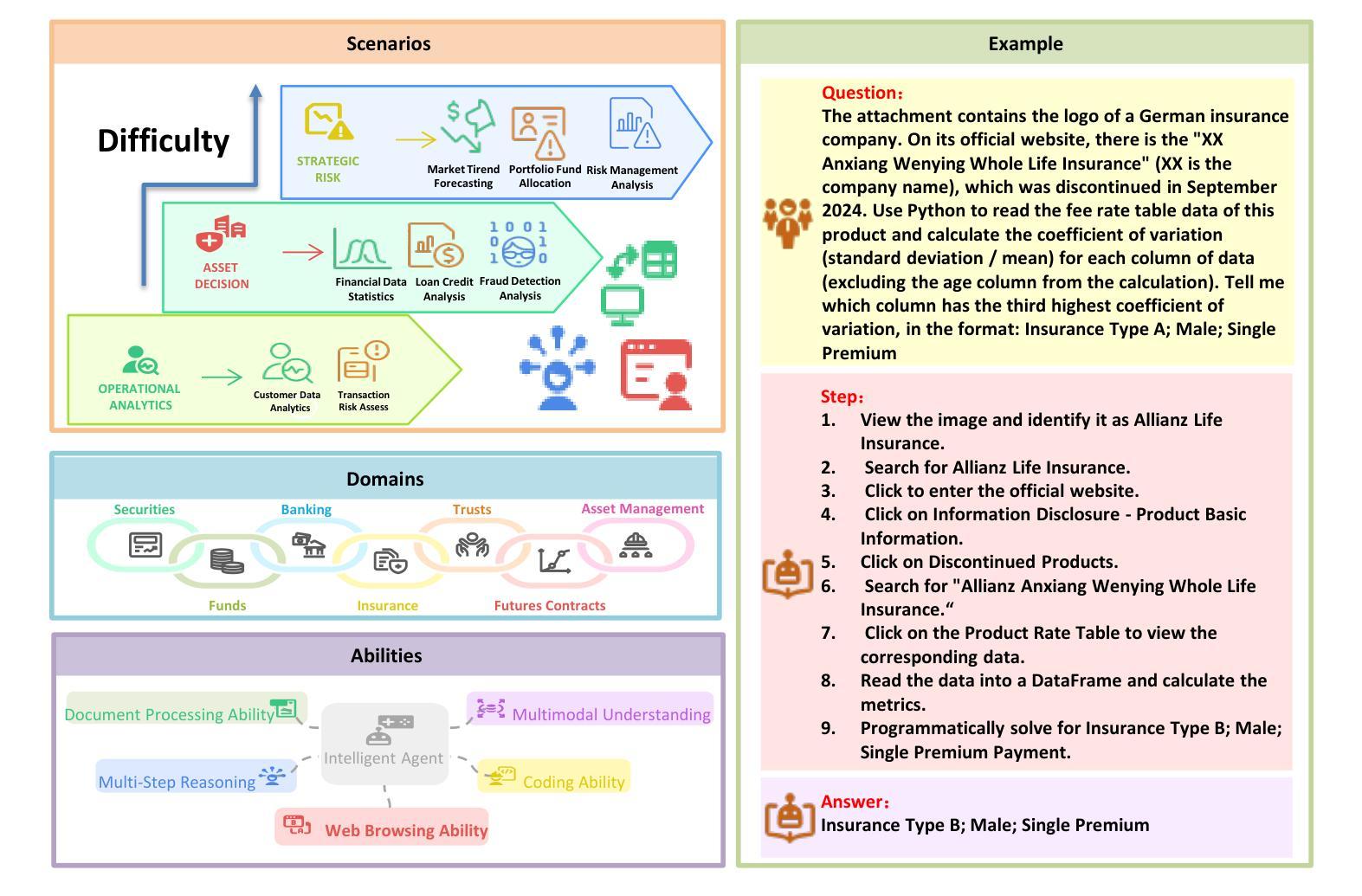
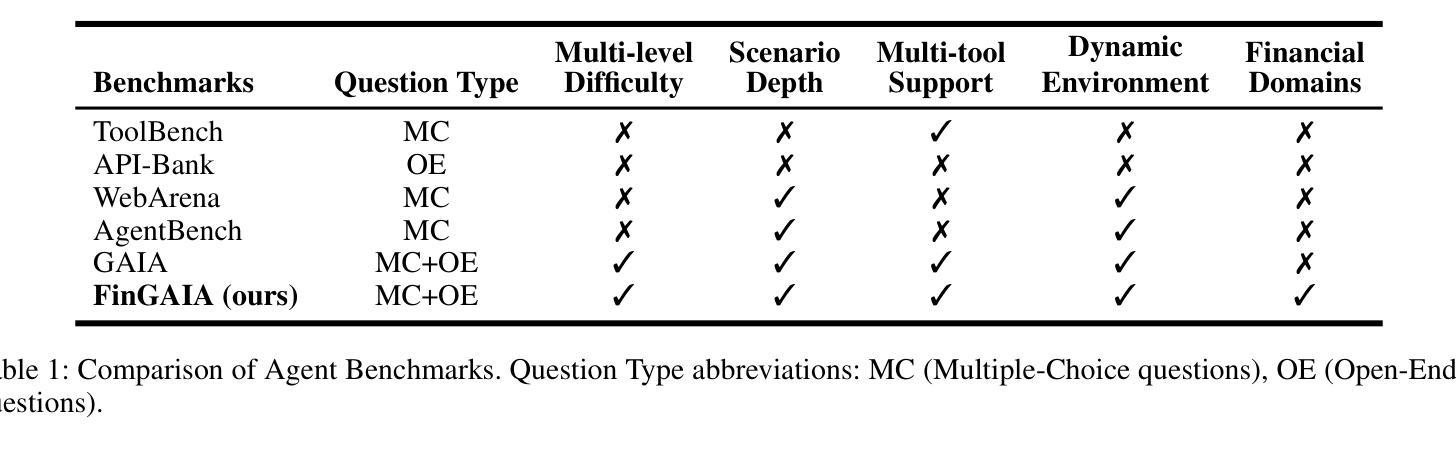
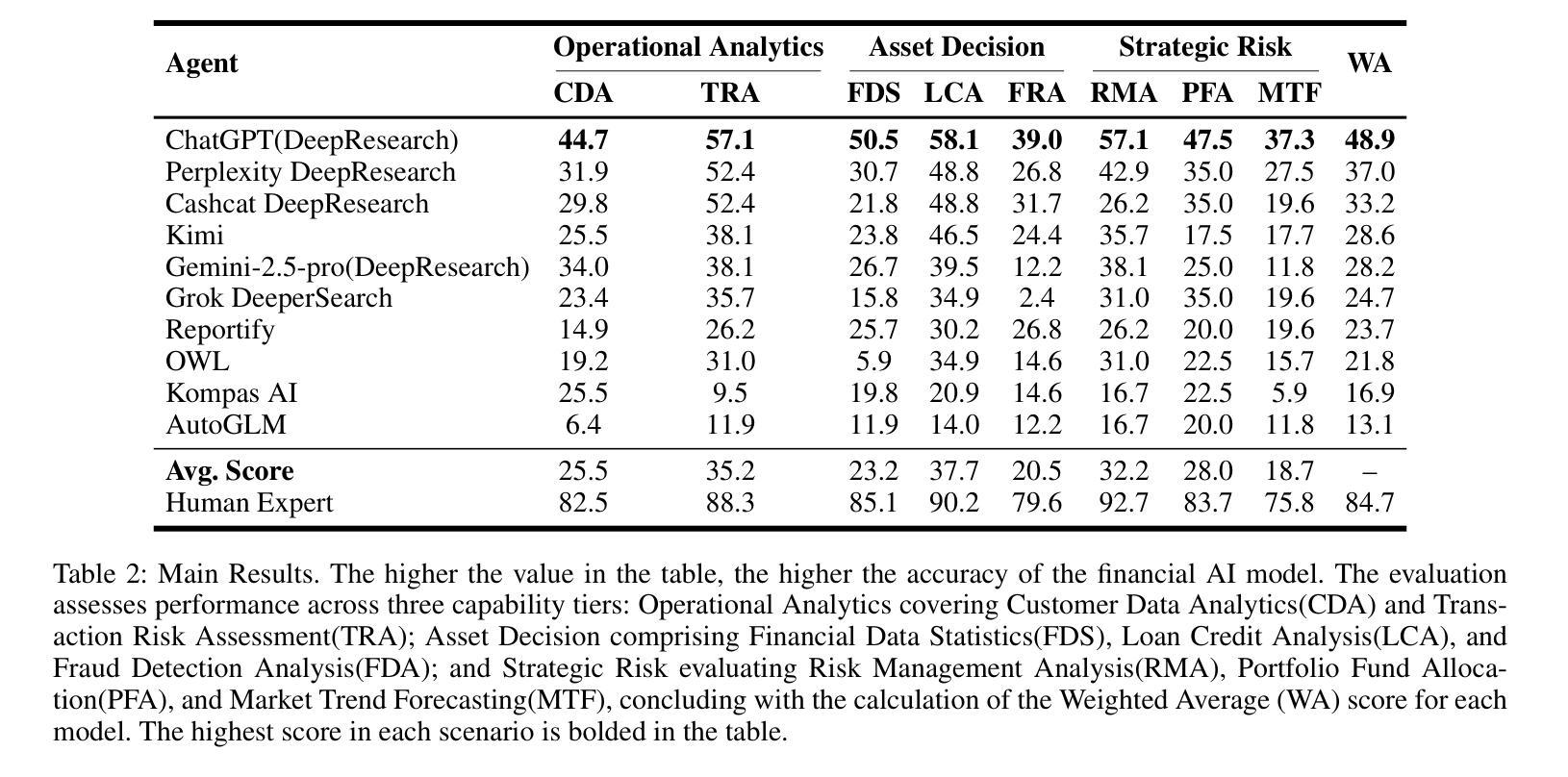
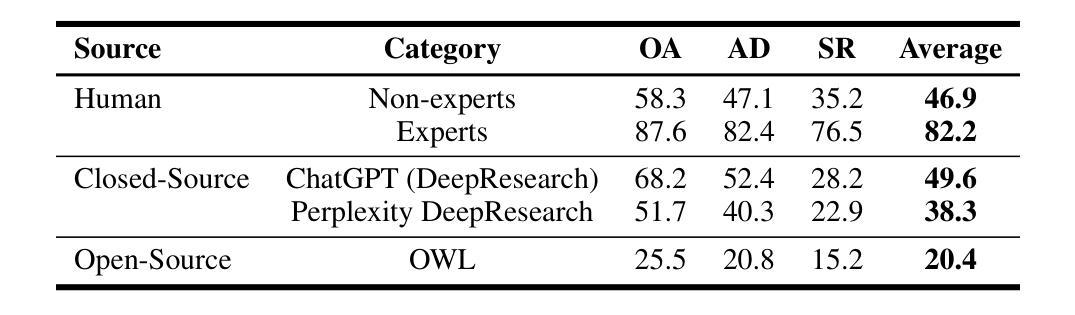
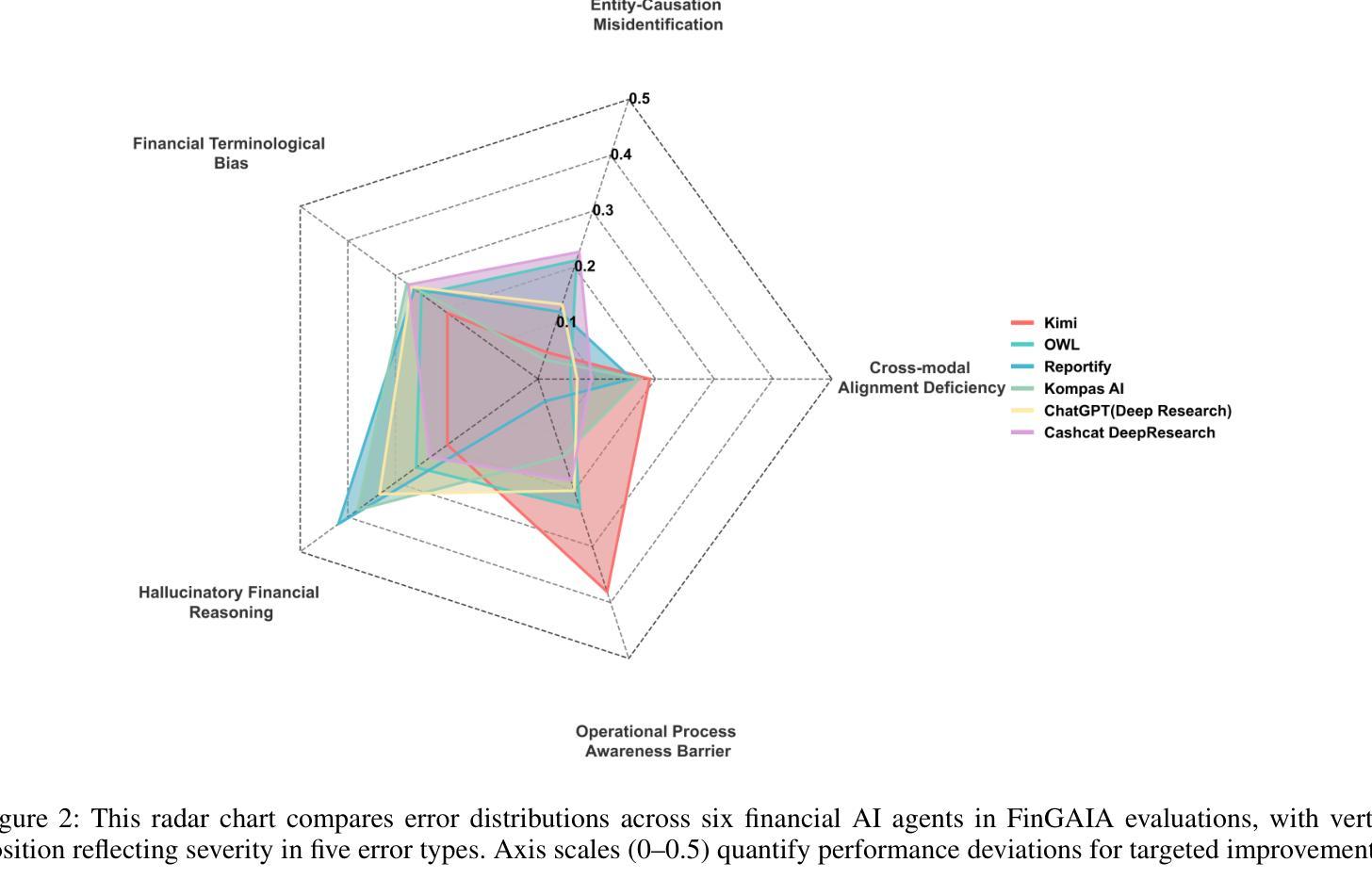
The booming development of AI agents presents unprecedented opportunities for automating complex tasks across various domains. However, their multi-step, multi-tool collaboration capabilities in the financial sector remain underexplored. This paper introduces FinGAIA, an end-to-end benchmark designed to evaluate the practical abilities of AI agents in the financial domain. FinGAIA comprises 407 meticulously crafted tasks, spanning seven major financial sub-domains: securities, funds, banking, insurance, futures, trusts, and asset management. These tasks are organized into three hierarchical levels of scenario depth: basic business analysis, asset decision support, and strategic risk management. We evaluated 10 mainstream AI agents in a zero-shot setting. The best-performing agent, ChatGPT, achieved an overall accuracy of 48.9%, which, while superior to non-professionals, still lags financial experts by over 35 percentage points. Error analysis has revealed five recurring failure patterns: Cross-modal Alignment Deficiency, Financial Terminological Bias, Operational Process Awareness Barrier, among others. These patterns point to crucial directions for future research. Our work provides the first agent benchmark closely related to the financial domain, aiming to objectively assess and promote the development of agents in this crucial field. Partial data is available at https://github.com/SUFE-AIFLM-Lab/FinGAIA.
随着人工智能代理的蓬勃发展,为跨不同领域的复杂任务自动化提供了前所未有的机会。然而,它们在金融领域的多步骤、多工具协作能力仍被忽视。本文介绍了FinGAIA,这是一个旨在评估人工智能代理在金融领域实际应用能力的端到端基准测试。FinGAIA包含407个精心设计的任务,涵盖七大金融子域:证券、基金、银行、保险、期货、信托和资产管理。这些任务被组织成三个层次递进的场景深度:基本业务分析、资产决策支持和战略风险管理。我们在零射击环境中评估了10种主流的人工智能代理。表现最佳的代理是ChatGPT,总体准确率为48.9%,虽然比非专业人士更优秀,但仍比金融专家落后超过35个百分点。错误分析揭示了五种常见的失败模式:跨模态对齐不足、金融术语偏差、操作流程意识障碍等。这些模式为未来研究指出了关键方向。我们的工作提供了与金融领域密切相关的首个代理基准测试,旨在客观地评估和推动该领域代理的发展。部分数据可在https://github.com/SUFE-AIFLM-Lab/FinGAIA获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了AI代理在金融领域的应用和发展。文章提出了FinGAIA这一金融领域的端到端评估基准,旨在评估AI代理在金融领域的实际操作能力。通过对10款主流AI代理的评估,发现ChatGPT表现最佳,但其准确率仅为48.9%,仍落后于金融专家超过35个百分点。文章还指出了AI代理在金融领域的五大失败模式,为未来研究提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- AI代理在金融领域具有巨大的发展潜力,但多步骤、多工具协作能力尚未得到充分探索。
- FinGAIA是一个针对金融领域的AI代理评估基准,包含407个精心设计的任务,覆盖七个主要金融子域。
- 评估的AI代理中,ChatGPT表现最佳,但准确率仅为48.9%,仍需提高。
- AI代理在金融领域的失败模式包括跨模态对齐缺陷、金融术语偏差、操作流程意识障碍等。
- 这些失败模式为未来的AI代理研究提供了关键方向。
- FinGAIA的基准评估为客观评估和促进金融领域AI代理的发展提供了有力支持。
点此查看论文截图

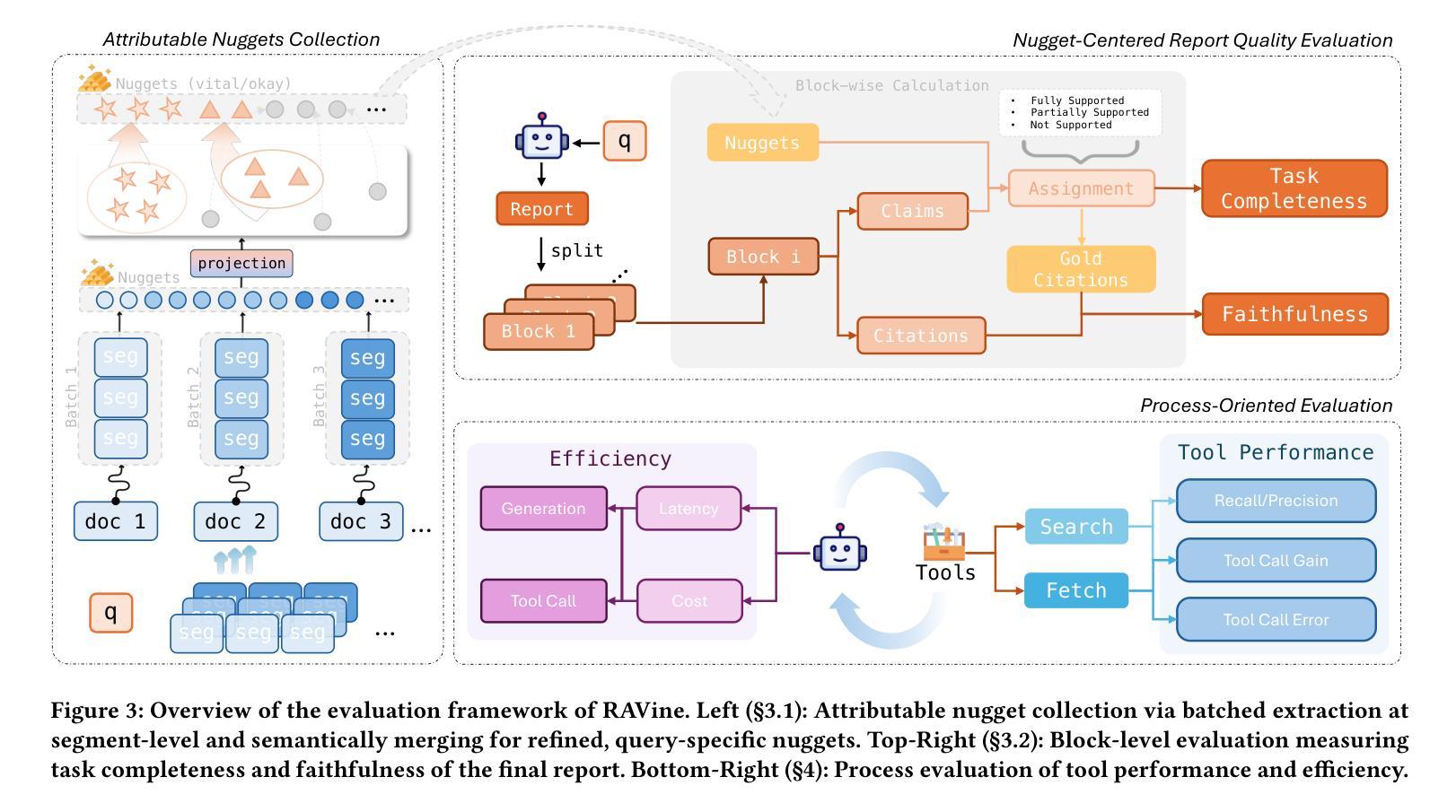
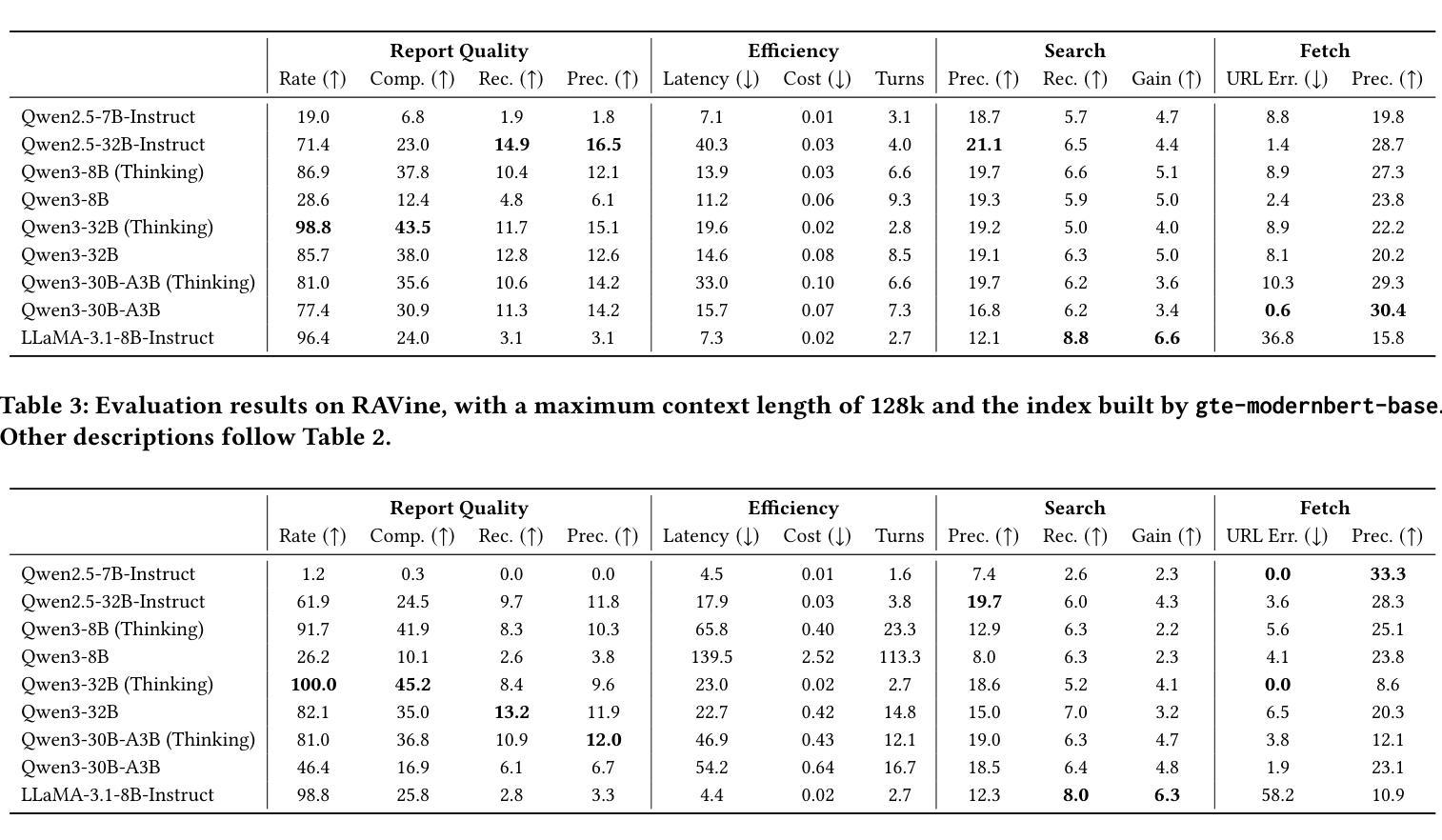
RAVine: Reality-Aligned Evaluation for Agentic Search
Authors:Yilong Xu, Xiang Long, Zhi Zheng, Jinhua Gao
Agentic search, as a more autonomous and adaptive paradigm of retrieval augmentation, is driving the evolution of intelligent search systems. However, existing evaluation frameworks fail to align well with the goals of agentic search. First, the complex queries commonly used in current benchmarks often deviate from realistic user search scenarios. Second, prior approaches tend to introduce noise when extracting ground truth for end-to-end evaluations, leading to distorted assessments at a fine-grained level. Third, most current frameworks focus solely on the quality of final answers, neglecting the evaluation of the iterative process inherent to agentic search. To address these limitations, we propose RAVine – a Reality-Aligned eValuation framework for agentic LLMs with search. RAVine targets multi-point queries and long-form answers that better reflect user intents, and introduces an attributable ground truth construction strategy to enhance the accuracy of fine-grained evaluation. Moreover, RAVine examines model’s interaction with search tools throughout the iterative process, and accounts for factors of efficiency. We benchmark a series of models using RAVine and derive several insights, which we hope will contribute to advancing the development of agentic search systems. The code and datasets are available at https://github.com/SwordFaith/RAVine.
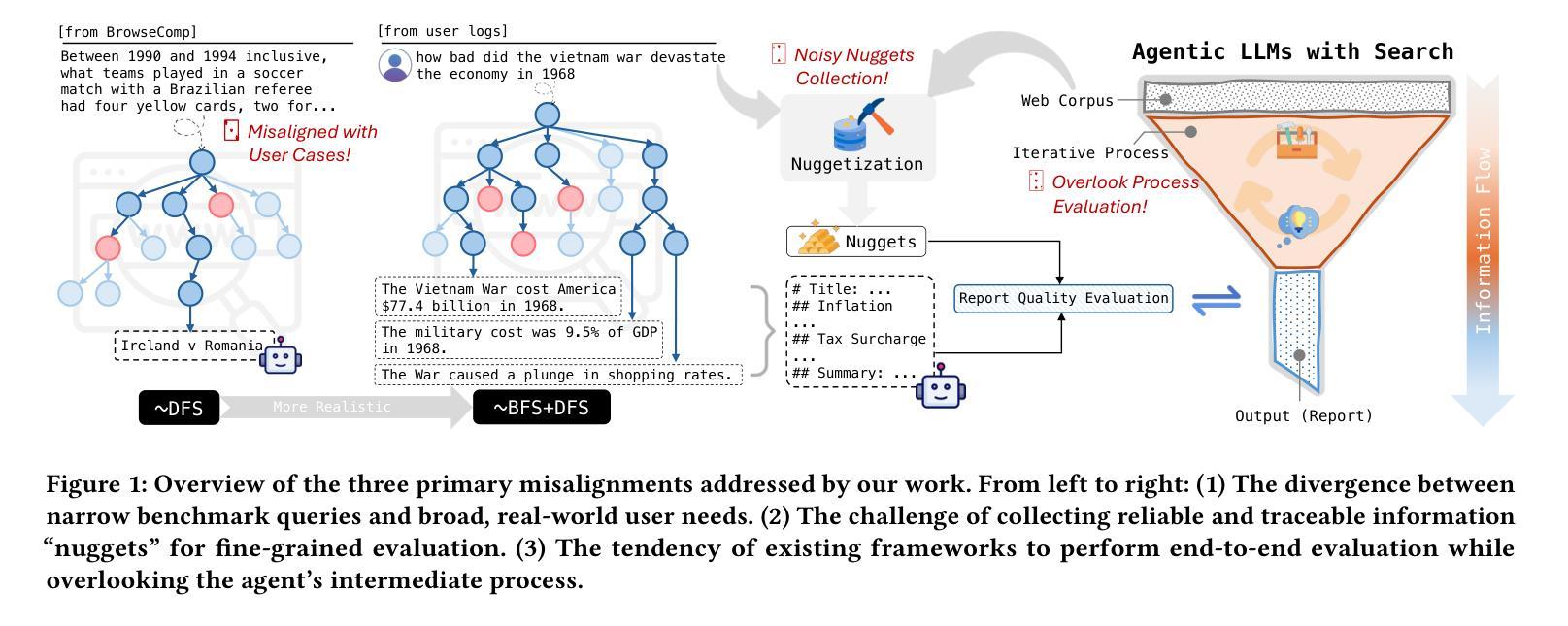
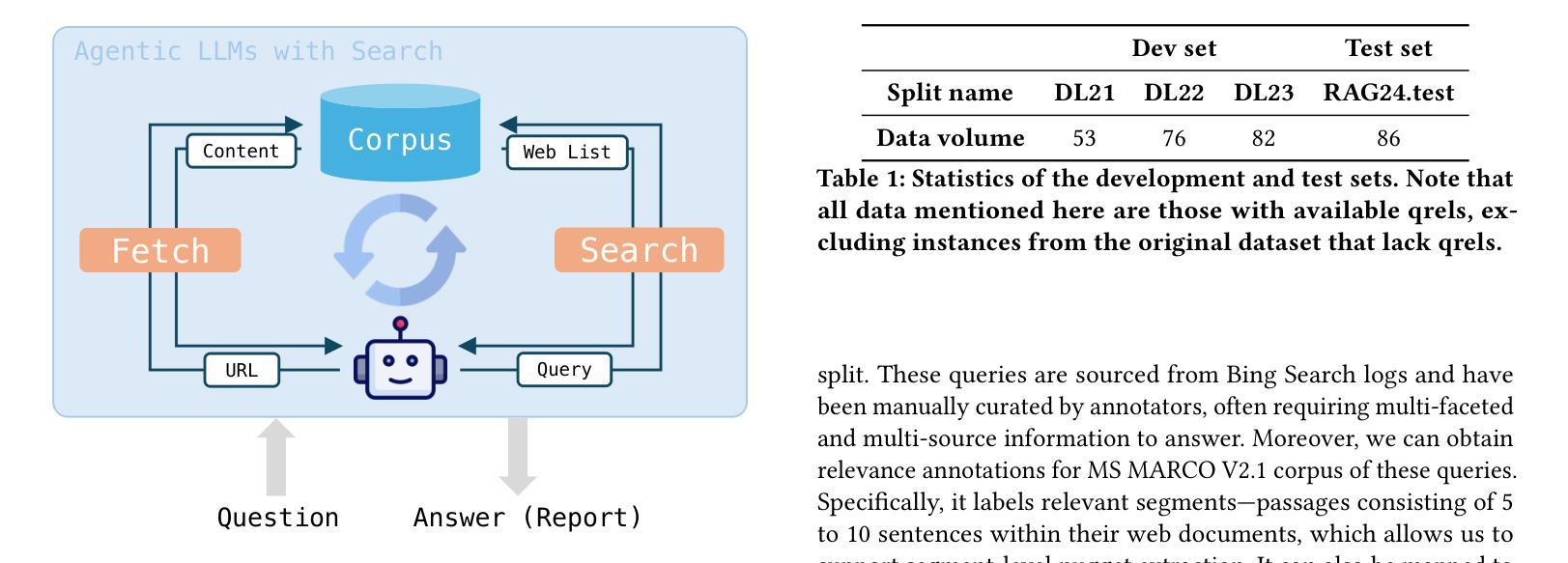
智能检索增强(Agentic Search)作为一种更自主和适应性更强的检索增强范式,正在推动智能搜索系统的进化。然而,现有的评估框架与智能检索的目标并不完全契合。首先,当前基准测试中常用的复杂查询常常偏离现实用户搜索场景。其次,先前的方法在提取端到端评估的地面真实数据时往往会引入噪声,导致精细级别的评估失真。再次,大多数当前框架只关注最终答案的质量,忽视了智能检索中固有的迭代过程的评估。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了RAVine——一个面向智能检索大模型的现实性评估框架。RAVine针对多点查询和长答案的需求进行设计,以更好地反映用户意图,并引入可归属的地面真实数据构建策略,以提高精细级别评估的准确性。此外,RAVine还考察了模型在搜索工具使用过程中的交互以及效率因素。我们使用RAVine对一系列模型进行了基准测试,并获得了一些见解,我们希望这些见解能对推动智能检索系统的发展做出贡献。相关代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/SwordFaith/RAVine获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Agentic搜索作为更自主和适应性的检索增强范式,正在推动智能搜索系统的进化。然而,现有的评估框架与agentic搜索的目标并不对齐。为此,我们提出了RAVine评估框架,针对多要点查询和长答案反映用户意图,引入可归属的地面真实构建策略提高精细评估的准确性。同时,RAVine关注模型在迭代过程中的搜索工具交互并考虑效率因素。我们通过对一系列模型的基准测试获得了一些见解,有望推动agentic搜索系统的发展。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic搜索正推动智能搜索系统的进化,需求更自主和适应性的检索方式。
- 当前评估框架与agentic搜索目标存在不匹配问题。
- 复杂查询常常偏离现实用户搜索场景。
- 现有评估方法提取地面真实数据时易引入噪声,导致精细评估失真。
- 现有框架过于关注答案质量,忽略agentic搜索的迭代过程评估。
- RAVine评估框架针对多要点查询和长答案设计,旨在提高评估准确性并反映用户意图。
点此查看论文截图

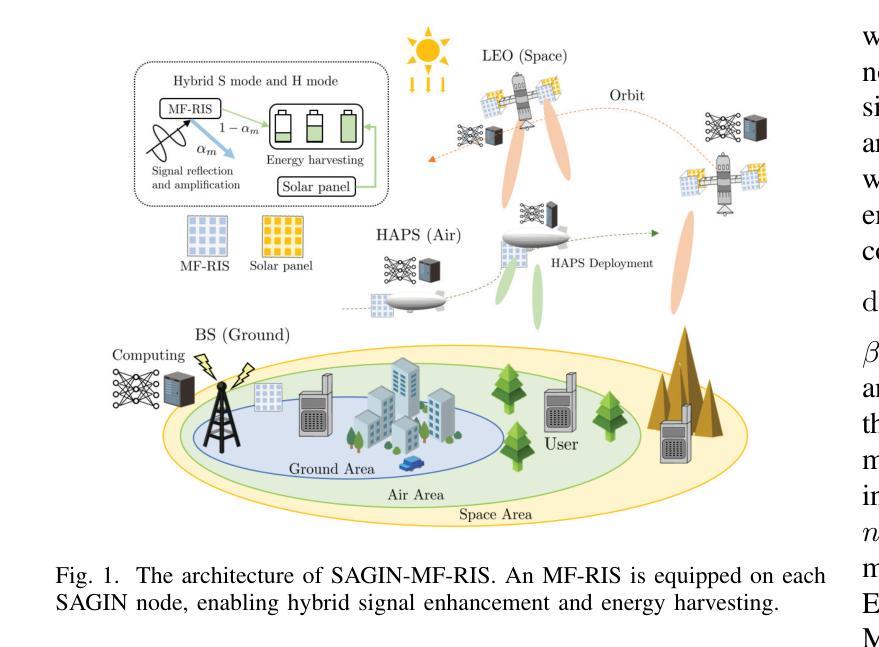
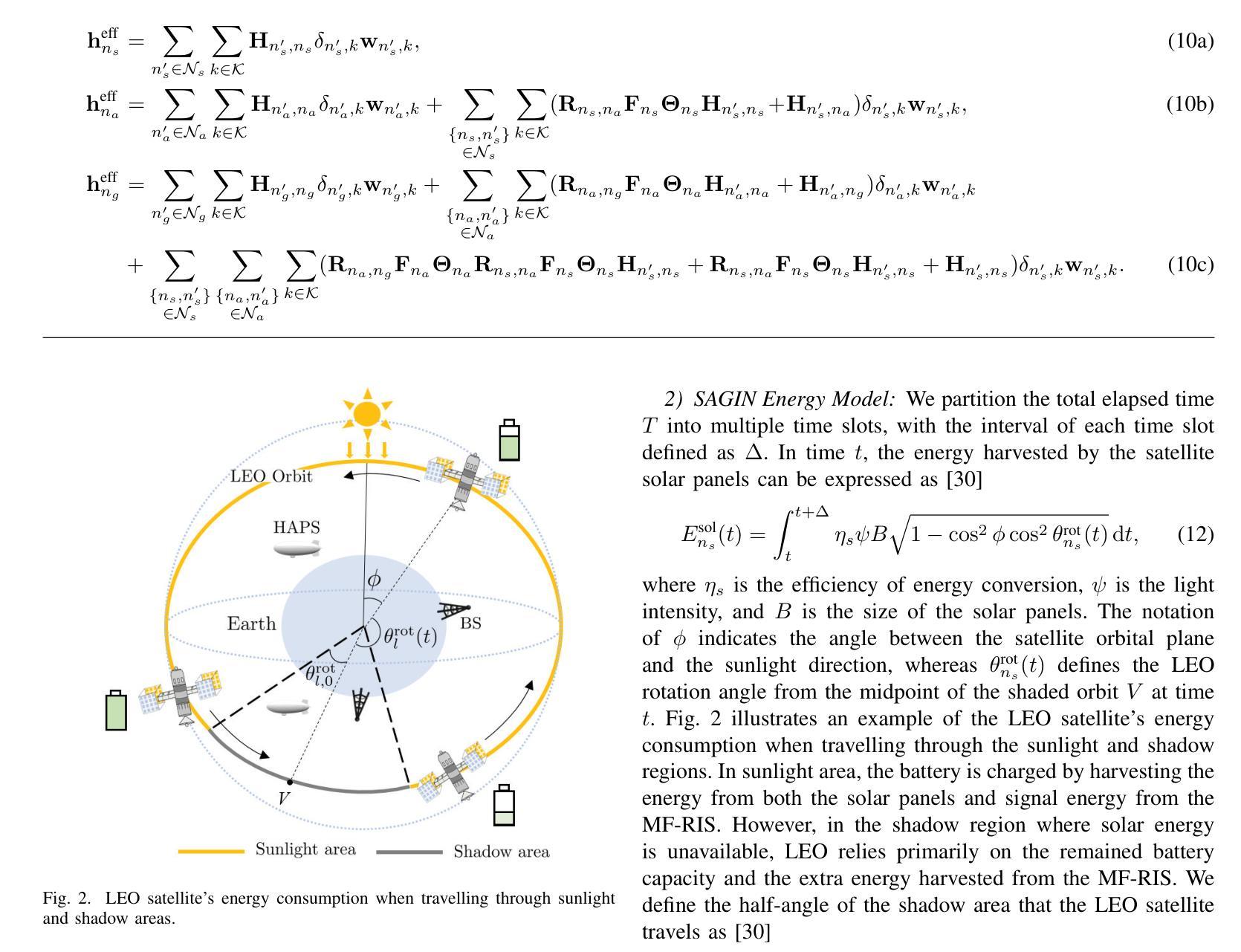
CHIMERA: Compressed Hybrid Intelligence for Twin-Model Enhanced Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Functional RIS-Assisted Space-Air-Ground Integrated Networks
Authors:Li-Hsiang Shen, Jyun-Jhe Huang
A space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) architecture is proposed, empowered by multi-functional reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (MF-RIS) capable of simultaneously reflecting, amplifying, and harvesting wireless energy. The MF-RIS plays a pivotal role in addressing the energy shortages of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites operating in shadowed regions, while explicitly accounting for both communication and computing energy consumption across the SAGIN nodes. To maximize the long-term energy efficiency (EE), we formulate a joint optimization problem over the MF-RIS parameters, including signal amplification, phase-shifts, energy harvesting ratio, and active element selection as well as the SAGIN parameters of beamforming vectors, high-altitude platform station (HAPS) deployment, user association, and computing capability. The formulated problem is highly non-convex and non-linear and contains mixed discrete-continuous parameters. To tackle this, we conceive a compressed hybrid intelligence for twin-model enhanced multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (CHIMERA) framework, which integrates semantic state-action compression and parametrized sharing under hybrid reinforcement learning to efficiently explore suitable complex actions. The simulation results have demonstrated that the proposed CHIMERA scheme substantially outperforms the conventional benchmarks, including fixed-configuration or non-harvesting MF-RIS, traditional RIS, and no-RIS cases, as well as centralized and multi-agent deep reinforcement learning baselines in terms of the highest EE. Moreover, the proposed SAGIN-MF-RIS architecture achieves superior EE performance due to its complementary coverage, offering notable advantages over either standalone satellite, aerial, or ground-only deployments.
提出了一种由多功能可重构智能表面(MF-RIS)赋能的空天地一体化网络(SAGIN)架构。MF-RIS能够同时反射、放大和采集无线能量。MF-RIS在解决低地球轨道(LEO)卫星在阴影区域的能源短缺问题中起着至关重要的作用,同时明确考虑了SAGIN节点中通信和计算能耗。为了最大化长期能效(EE),我们对MF-RIS参数进行了联合优化,包括信号放大、相位偏移、能量采集比、活动元素选择以及SAGIN的波束形成向量参数、高空平台站(HAPS)部署、用户关联和计算能力等。所形成的问题具有高度非凸、非线性以及混合离散连续参数的特点。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于增强型多智能体深度强化学习的压缩混合智能(CHIMERA)框架,该框架集成了语义状态-动作压缩和参数化共享下的混合强化学习,以有效地探索合适的复杂动作。仿真结果表明,所提出的CHIMERA方案在能效方面大大超过了传统基准测试,包括固定配置或非采集MF-RIS、传统RIS和无RIS情况,以及集中式和分布式深度强化学习基线。此外,所提出的SAGIN-MF-RIS架构由于具有互补覆盖性而实现了卓越的能效性能,相对于单独的卫星、空中或地面部署具有明显优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多功能可重构智能表面(MF-RIS)的空间-空中-地面一体化网络(SAGIN)架构,通过反射、放大和采集无线能量等技术,解决了低轨道卫星在阴影区域的能源短缺问题,同时考虑了通信和计算能耗。针对长期能效最大化问题,对MF-RIS参数和SAGIN参数进行了联合优化,包括信号放大、相位偏移、能量采集比例、活动元素选择以及波束形成向量、高空平台站部署、用户关联和计算能力等。采用压缩混合智能双模型增强多智能体深度强化学习(CHIMERA)框架来解决这一高度非凸非线性问题。模拟结果表明,CHIMERA方案在能效方面显著优于传统基准测试,表现出优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SAGIN架构结合了空间、空中和地面网络,利用MF-RIS技术实现无线能量的反射、放大和采集。
- MF-RIS技术解决了低轨道卫星在阴影区域的能源短缺问题。
- 长期能效最大化需要对MF-RIS参数和SAGIN参数进行联合优化。
- 优化问题包括信号放大、相位偏移、能量采集比例等连续参数和波束形成向量等离散参数。
- CHIMERA框架结合了语义状态动作压缩和参数化共享,通过混合强化学习高效探索复杂动作。
- 模拟结果表明CHIMERA方案在能效方面显著优于传统基准测试和多种深度学习方案。
点此查看论文截图

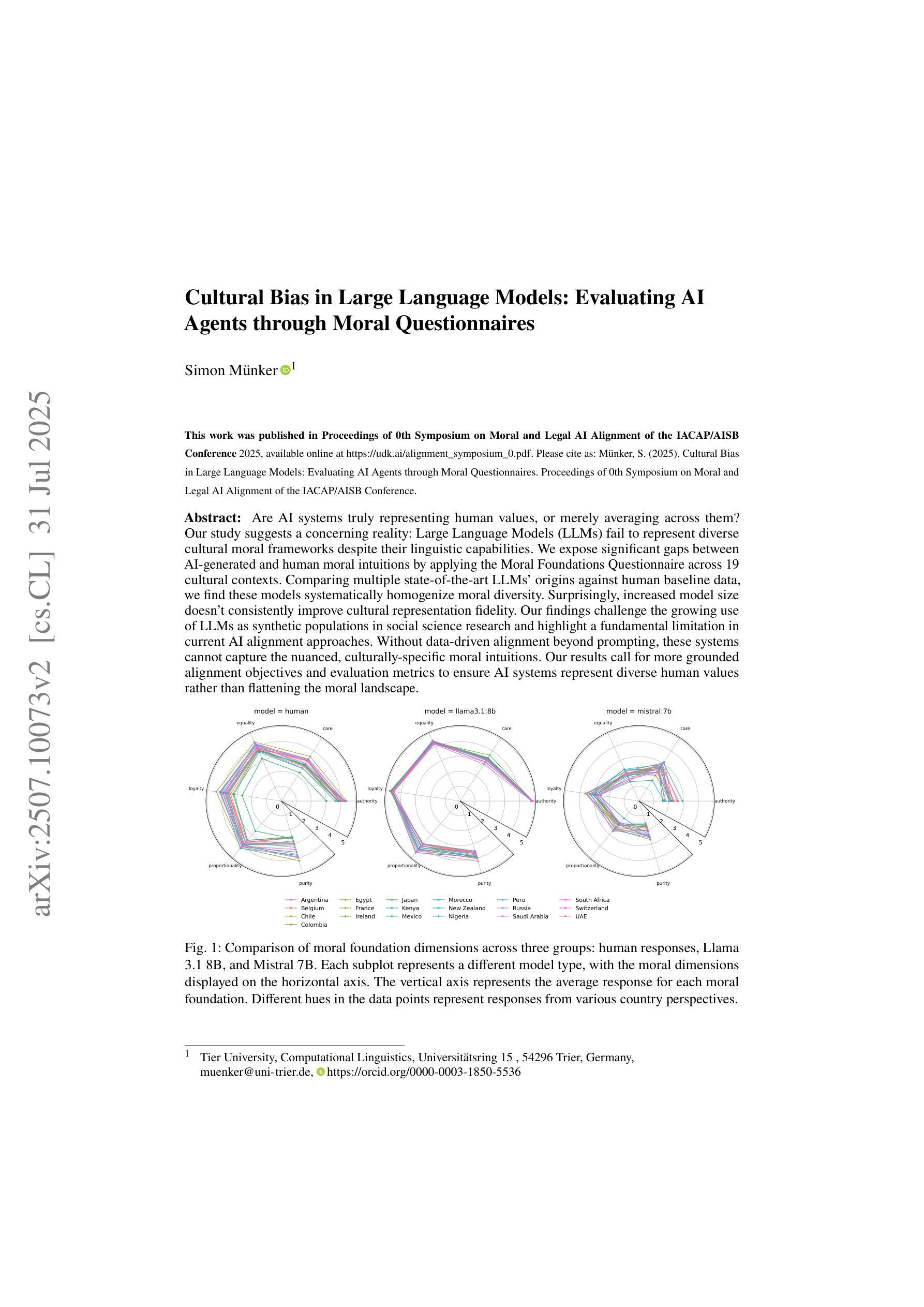
Cultural Bias in Large Language Models: Evaluating AI Agents through Moral Questionnaires
Authors:Simon Münker
Are AI systems truly representing human values, or merely averaging across them? Our study suggests a concerning reality: Large Language Models (LLMs) fail to represent diverse cultural moral frameworks despite their linguistic capabilities. We expose significant gaps between AI-generated and human moral intuitions by applying the Moral Foundations Questionnaire across 19 cultural contexts. Comparing multiple state-of-the-art LLMs’ origins against human baseline data, we find these models systematically homogenize moral diversity. Surprisingly, increased model size doesn’t consistently improve cultural representation fidelity. Our findings challenge the growing use of LLMs as synthetic populations in social science research and highlight a fundamental limitation in current AI alignment approaches. Without data-driven alignment beyond prompting, these systems cannot capture the nuanced, culturally-specific moral intuitions. Our results call for more grounded alignment objectives and evaluation metrics to ensure AI systems represent diverse human values rather than flattening the moral landscape.
人工智能系统是否真的代表人类价值观,还只是平均反映它们?我们的研究表明了一个令人担忧的现实:尽管大型语言模型具有语言能力,但它们无法代表多样化的文化道德框架。我们通过应用道德基础问卷,在19个文化背景下揭示了人工智能生成和人类道德直觉之间的巨大差距。通过将多个最新大型语言模型的起源与人类基准数据进行比较,我们发现这些模型系统地简化了道德的多样性。令人惊讶的是,增加模型大小并不总能提高文化代表性。我们的研究质疑了大型语言模型在社会科学研究中的作为合成人口不断增长的使用情况,并强调了当前人工智能对齐方法的基本局限性。如果不通过数据驱动的对齐方式超出提示范围,这些系统就无法捕捉到微妙且文化特定的道德直觉。我们的研究结果呼吁建立更具体的对齐目标和评估指标,以确保人工智能系统代表多样化的人类价值观,而不是简化道德景观。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15pages, 1 figure, 2 tables
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在文化道德框架方面的表现令人担忧,尽管拥有语言处理能力,却无法体现多样化的文化道德观念。通过跨十九种文化背景的问卷调查发现,人工智能与人类道德直觉之间存在显著差距。对比多个顶尖LLM与人类基线数据,发现这些模型系统地将道德多样性同质化。模型规模的增加并不一定能提高文化代表性。这一发现对LLM在社会科学研究中作为合成人口的使用提出了挑战,并指出了当前人工智能对齐方法的基本局限性。没有数据驱动的超越提示的对齐,这些系统无法捕捉微妙的、具有文化特色的道德直觉。这要求更基于现实的对齐目标和评估指标,以确保人工智能系统能够代表多样化的人类价值观,而不是抹平道德层面的差异。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)无法充分展现多样的文化道德框架。
- AI与人类的道德直觉存在显著差距。
- 顶尖LLM在处理道德多样性时存在系统化同质化现象。
- 模型规模的增加并不总是能提高对文化多样性的代表性。
- LLM在社会科学研究中的使用存在挑战,尤其在代表多样化人口方面。
- 当前的人工智能对齐方法存在局限性,需要进一步发展和完善。
点此查看论文截图
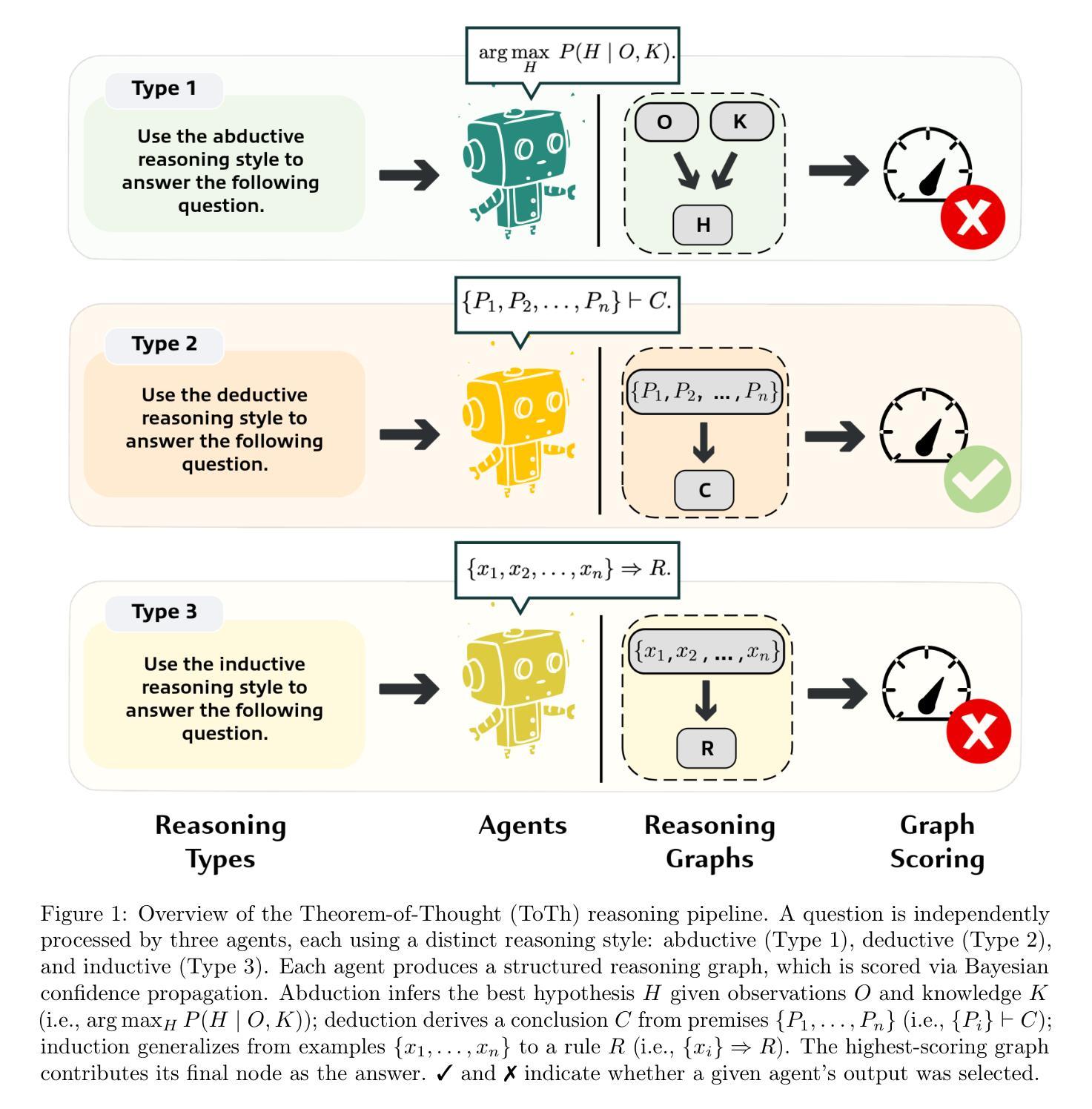
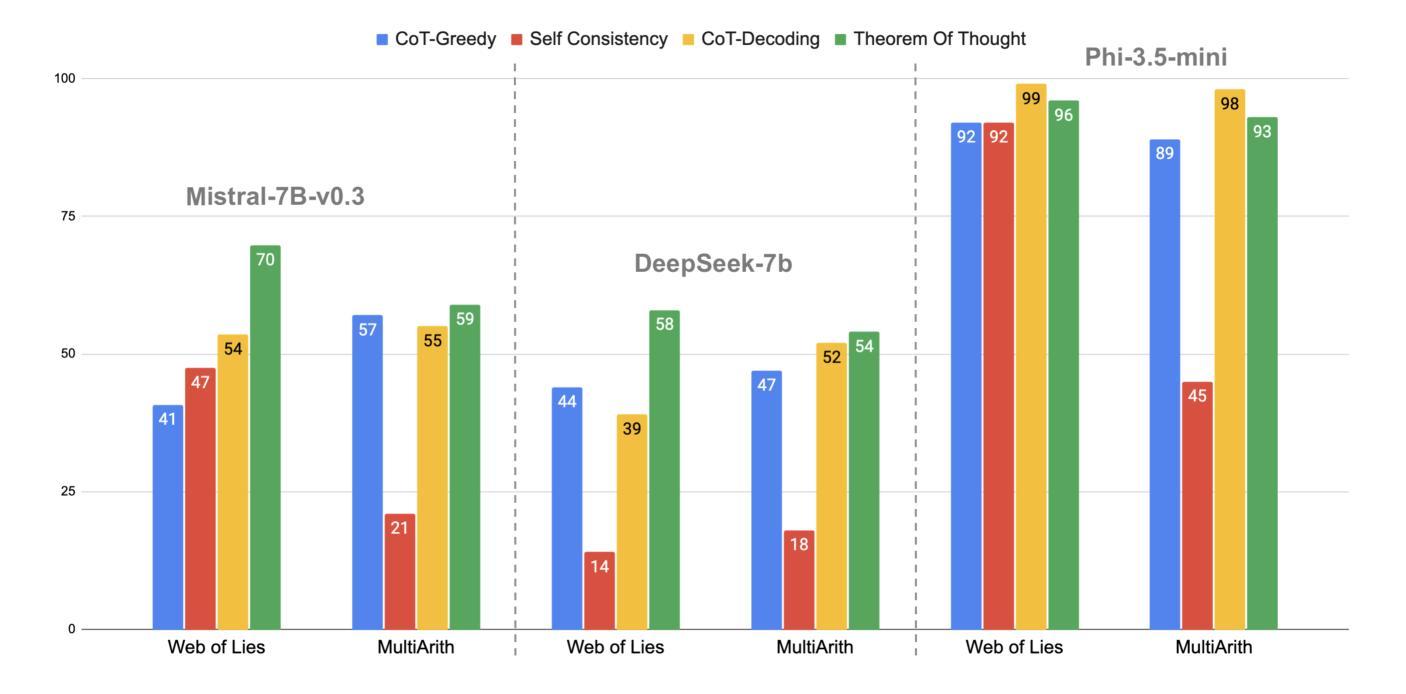
Theorem-of-Thought: A Multi-Agent Framework for Abductive, Deductive, and Inductive Reasoning in Language Models
Authors:Samir Abdaljalil, Hasan Kurban, Khalid Qaraqe, Erchin Serpedin
Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong performance across natural language reasoning tasks, yet their reasoning processes remain brittle and difficult to interpret. Prompting techniques like Chain-of-Thought (CoT) enhance reliability by eliciting intermediate reasoning steps or aggregating multiple outputs. However, they lack mechanisms for enforcing logical structure and assessing internal coherence. We introduce Theorem-of-Thought (ToTh), a novel framework that models reasoning as collaboration among three parallel agents, each simulating a distinct mode of inference: abductive, deductive, and inductive. Each agent produces a reasoning trace, which is structured into a formal reasoning graph. To evaluate consistency, we apply Bayesian belief propagation guided by natural language inference (NLI), assigning confidence scores to each step. The most coherent graph is selected to derive the final answer. Experiments on symbolic (WebOfLies) and numerical (MultiArith) reasoning benchmarks show that ToTh consistently outperforms CoT, Self-Consistency, and CoT-Decoding across multiple LLMs, while producing interpretable and logically grounded reasoning chains. Our findings suggest a promising direction for building more robust and cognitively inspired LLM reasoning. The implementation is available at https://github.com/KurbanIntelligenceLab/theorem-of-thought.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言推理任务中表现出强大的性能,但它们的推理过程仍然脆弱且难以解释。Chain-of-Thought(CoT)等提示技术通过激发中间推理步骤或聚合多个输出来提高可靠性。然而,它们缺乏执行逻辑结构的机制和评估内部连贯性的能力。我们引入了Theorem-of-Thought(ToTh)这一新型框架,它将推理建模为三个并行代理之间的协作,每个代理模拟一种独特的推理模式:溯因推理、演绎推理和归纳推理。每个代理产生一条推理轨迹,结构化为正正式推理图。为了评估一致性,我们应用受自然语言推理(NLI)指导的贝叶斯信念传播,为每一步分配置信度分数。选择最连贯的图来得出最终答案。在符号(WebOfLies)和数值(MultiArith)推理基准测试上的实验表明,ToTh在多个LLM中始终优于CoT、自我一致性(Self-Consistency)和CoT-Decoding,同时产生可解释且逻辑上合理的推理链。我们的研究为构建更强大、更具认知启发性的LLM推理提供了有前景的方向。实现细节可在https://github.com/KurbanIntelligenceLab/theorem-of-thought找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 KnowFM
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言推理任务中表现出强大的性能,但其推理过程脆弱且难以解释。本文提出一种新型框架——定理思维(ToTh),将推理过程模拟为三个并行代理之间的协作,每个代理模拟不同的推理模式:归纳推理、演绎推理和溯因推理。每个代理生成结构化为正式推理图的推理轨迹。通过贝叶斯信念传播和自然语言推断(NLI)评估一致性,为每一步分配置信分数,并选择最连贯的图来得出最终答案。实验表明,ToTh在符号和数值推理基准测试上均优于思维链(CoT),自我一致性以及CoT解码,同时产生可解释且逻辑严密的推理链。这为构建更强大和认知启发式的LLM推理提供了希望的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然语言推理任务中表现出良好的性能,但存在推理过程脆弱和难以解释的问题。
- 提出了定理思维(ToTh)框架来解决这一问题,模拟人类推理过程,通过三个并行代理的协作进行推理。
- ToTh框架中的每个代理分别模拟归纳、演绎和溯因三种不同的推理模式,生成结构化的推理轨迹。
- ToTh使用贝叶斯信念传播和自然语言推断来评估推理过程中的一致性,并为每一步分配置信分数。
- 实验结果显示,ToTh在符号和数值推理基准测试上的表现优于现有的方法,如思维链(CoT)。
- ToTh框架产生的推理链是可解释且逻辑严密的。
点此查看论文截图

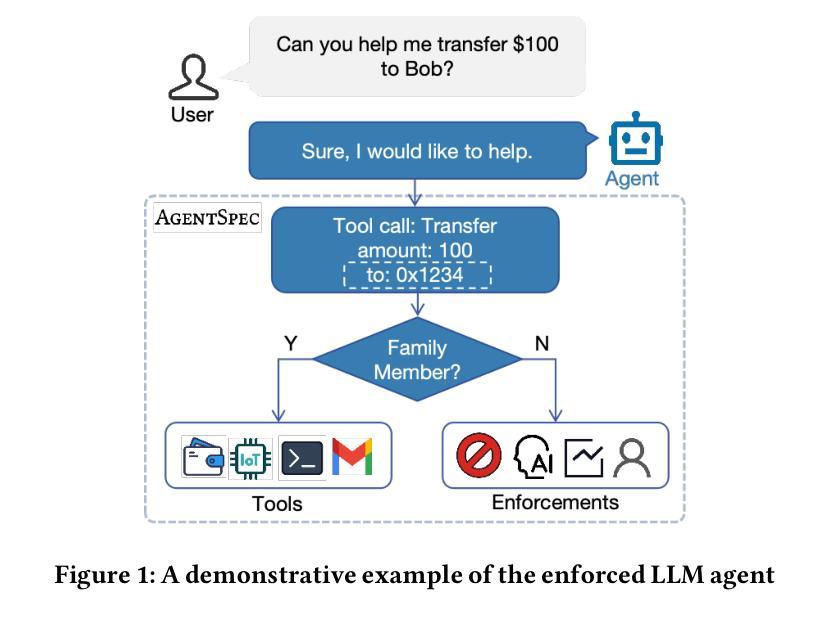
AgentSpec: Customizable Runtime Enforcement for Safe and Reliable LLM Agents
Authors:Haoyu Wang, Christopher M. Poskitt, Jun Sun
Agents built on LLMs are increasingly deployed across diverse domains, automating complex decision-making and task execution. However, their autonomy introduces safety risks, including security vulnerabilities, legal violations, and unintended harmful actions. Existing mitigation methods, such as model-based safeguards and early enforcement strategies, fall short in robustness, interpretability, and adaptability. To address these challenges, we propose AgentSpec, a lightweight domain-specific language for specifying and enforcing runtime constraints on LLM agents. With AgentSpec, users define structured rules that incorporate triggers, predicates, and enforcement mechanisms, ensuring agents operate within predefined safety boundaries. We implement AgentSpec across multiple domains, including code execution, embodied agents, and autonomous driving, demonstrating its adaptability and effectiveness. Our evaluation shows that AgentSpec successfully prevents unsafe executions in over 90% of code agent cases, eliminates all hazardous actions in embodied agent tasks, and enforces 100% compliance by autonomous vehicles (AVs). Despite its strong safety guarantees, AgentSpec remains computationally lightweight, with overheads in milliseconds. By combining interpretability, modularity, and efficiency, AgentSpec provides a practical and scalable solution for enforcing LLM agent safety across diverse applications. We also automate the generation of rules using LLMs and assess their effectiveness. Our evaluation shows that the rules generated by OpenAI o1 achieve a precision of 95.56% and recall of 70.96% for embodied agents, successfully identify 87.26% of the risky code, and prevent AVs from breaking laws in 5 out of 8 scenarios.
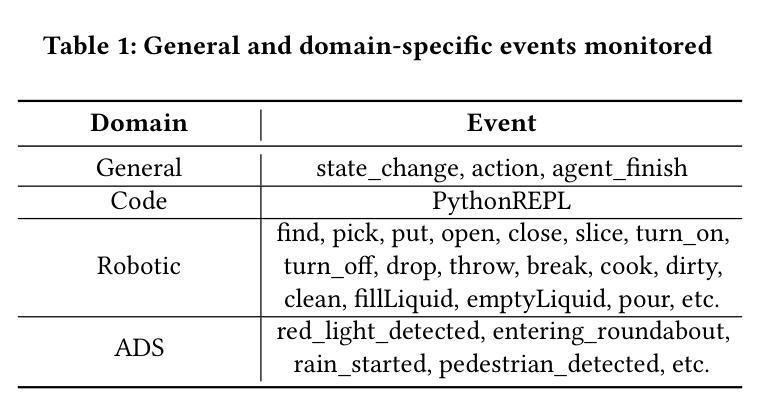
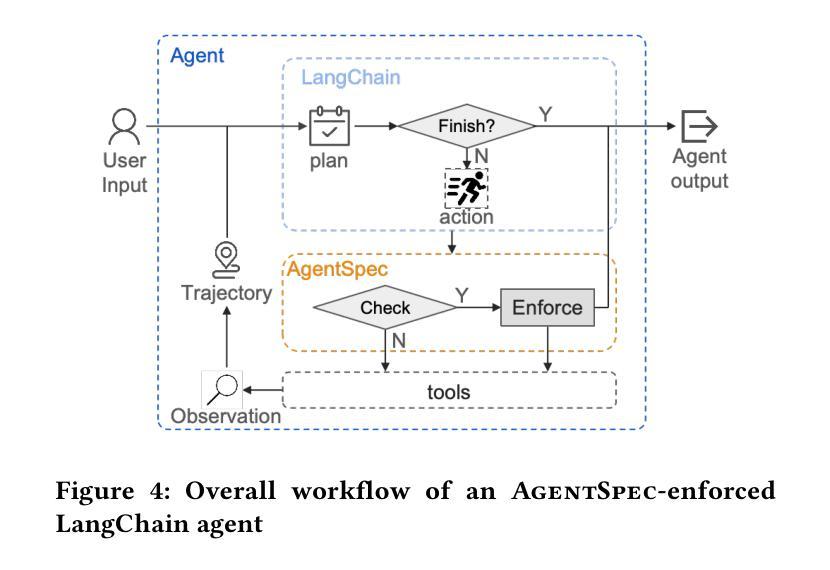
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的智能代理已越来越多地部署于各个领域,实现复杂的决策制定和任务执行自动化。然而,它们的自主性也带来了安全风险,包括安全漏洞、法律违规和意外的有害行为。现有的缓解方法,如基于模型的保障和早期执行策略,在稳健性、可解释性和适应性方面存在不足。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AgentSpec,这是一种为LLM代理指定和执行运行时约束的轻量级特定领域语言。通过AgentSpec,用户定义包含触发器、谓词和执行机制的结构化规则,确保代理在预定的安全边界内运行。我们在多个领域实现了AgentSpec,包括代码执行、实体代理和自动驾驶,展示了其适应性和有效性。我们的评估显示,AgentSpec成功阻止了90%以上的代码代理不安全执行,消除了实体代理任务中的所有危险行为,并实现了自动驾驶车辆100%的合规性。尽管AgentSpec具有强大的安全保证,但其计算仍然轻量级,开销仅为毫秒级。通过结合可解释性、模块化和效率,AgentSpec为在不同应用中强制执行LLM代理安全提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。我们还使用LLM自动生成规则并评估了其有效性。我们的评估结果显示,OpenAI o1生成的规则对实体代理的精确度为95.56%,召回率为70.96%,成功识别出87.26%的风险代码,并在8个场景中的5个中防止自动驾驶车辆违法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 48th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2026)
Summary
LLM构建的代理已广泛应用于多个领域,但在自主决策和执行任务时存在安全风险。现有方法存在稳健性、可解释性和适应性的不足。为此,我们提出了AgentSpec,一种轻量级的领域特定语言,用于指定和执行LLM代理的运行时约束。AgentSpec确保代理在预设的安全边界内运行,并在代码执行、实体代理和自动驾驶等多个领域得到实施。评估显示,AgentSpec在代码代理案例中成功防止了90%以上的不安全执行,消除了实体代理任务中的所有危险行为,并使自动驾驶车辆达到100%的合规性。尽管具有强大的安全保证,但AgentSpec的计算开销仍然很小,仅为毫秒级。其结合可解释性、模块化和效率,为跨多种应用的LLM代理安全提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。我们还使用LLM自动化生成规则并评估了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM构建的代理广泛应用于多个领域,自主决策存在安全风险。
- 现有安全方法存在稳健性、可解释性和适应性问题。
- AgentSpec是一种轻量级领域特定语言,用于指定和执行LLM代理的运行时约束。
- AgentSpec确保代理在预设的安全边界内运行,适应多个领域。
- AgentSpec成功防止不安全执行,消除危险行为,提高合规性。
- AgentSpec计算开销小,具有毫秒级性能。
- AgentSpec结合可解释性、模块化和效率,提供实用且可扩展的LLM代理安全解决方案。使用LLM自动化生成规则的方法有效。
点此查看论文截图



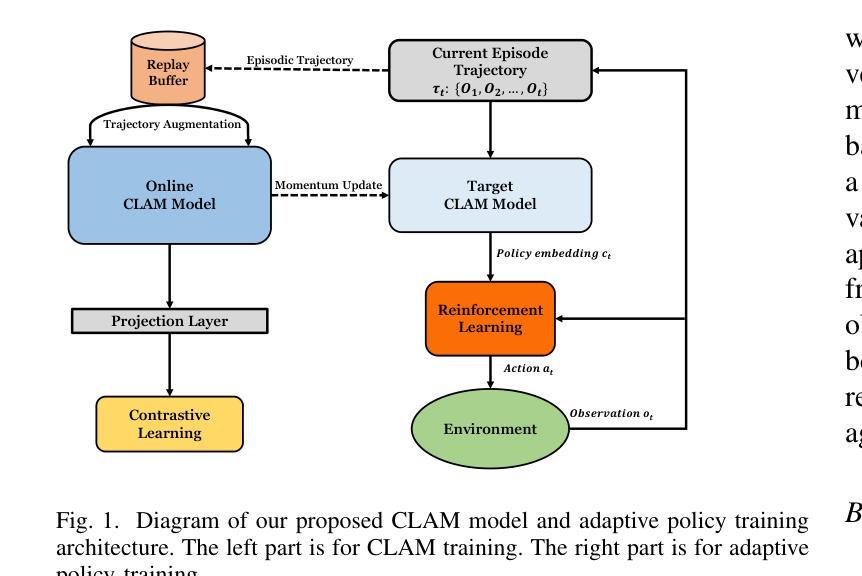
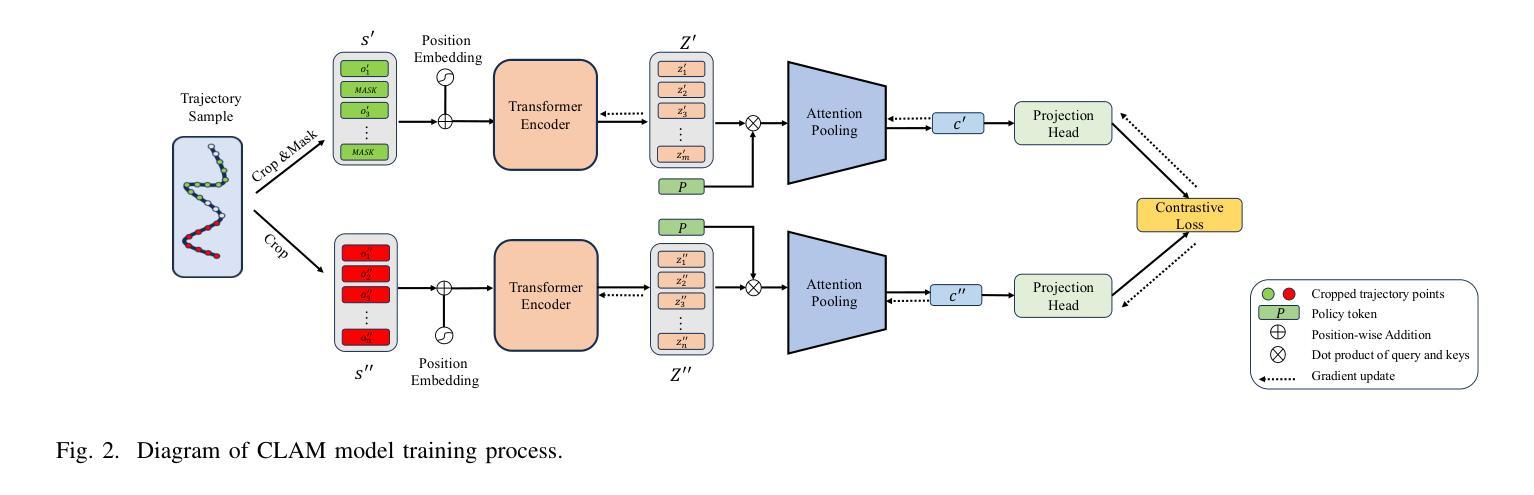
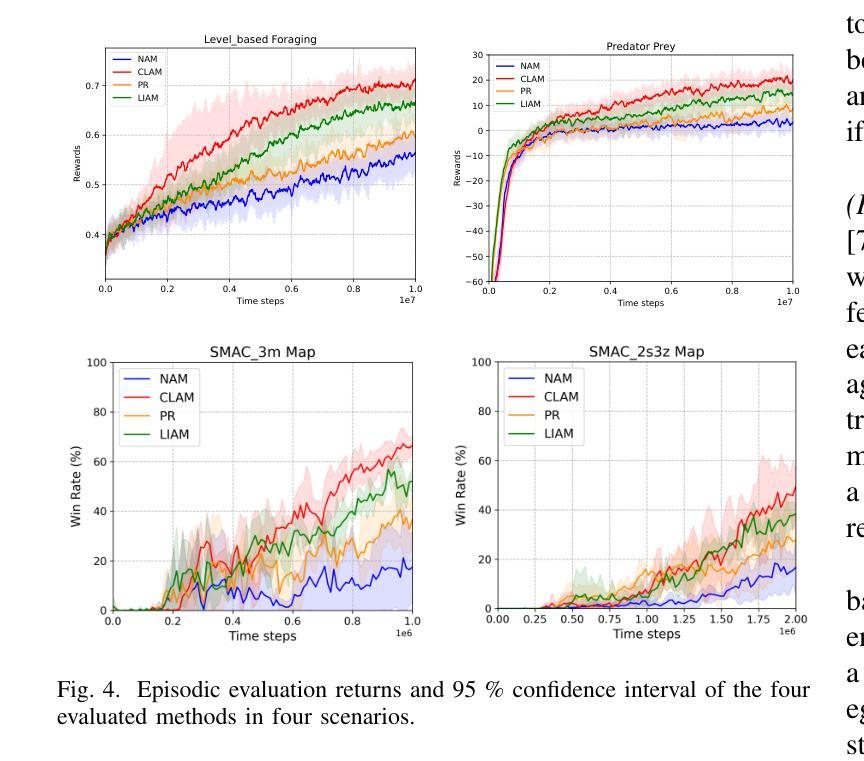
Contrastive learning-based agent modeling for deep reinforcement learning
Authors:Wenhao Ma, Yu-Cheng Chang, Jie Yang, Yu-Kai Wang, Chin-Teng Lin
Multi-agent systems often require agents to collaborate with or compete against other agents with diverse goals, behaviors, or strategies. Agent modeling is essential when designing adaptive policies for intelligent machine agents in multiagent systems, as this is the means by which the ego agent understands other agents’ behavior and extracts their meaningful policy representations. These representations can be used to enhance the ego agent’s adaptive policy which is trained by reinforcement learning. However, existing agent modeling approaches typically assume the availability of local observations from other agents (modeled agents) during training or a long observation trajectory for policy adaption. To remove these constrictive assumptions and improve agent modeling performance, we devised a Contrastive Learning-based Agent Modeling (CLAM) method that relies only on the local observations from the ego agent during training and execution. With these observations, CLAM is capable of generating consistent high-quality policy representations in real-time right from the beginning of each episode. We evaluated the efficacy of our approach in both cooperative and competitive multi-agent environments. Our experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art on both cooperative and competitive tasks, highlighting the potential of contrastive learning-based agent modeling for enhancing reinforcement learning.
在多智能体系统中,智能体通常需要与其他具有不同目标、行为或策略的智能体进行协作或竞争。在设计多智能体系统中智能机器智能体的自适应策略时,智能体建模至关重要。这是自我智能体理解其他智能体行为并提取其有意义策略表示的手段。这些表示可用于增强由强化学习训练的自适应策略。然而,现有的智能体建模方法通常假设在训练过程中或策略适应时需要其他智能体的局部观察。为了消除这些限制性假设并提高智能体建模性能,我们设计了一种基于对比学习的智能体建模(CLAM)方法,该方法仅依赖于训练和执行过程中的自我智能体的局部观察。通过这些观察,CLAM能够实时生成一致的高质量策略表示,从每集的开始阶段开始。我们在合作和竞争的多智能体环境中评估了我们的方法的有效性。实验表明,我们的方法在合作和竞争任务上均达到了最新水平,凸显了基于对比学习的智能体建模在强化学习中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了多智能体系统中智能机器代理的建模重要性。在合作和竞争场景中,代理需要理解其他代理的行为并提取有意义的策略表示,以改善自我代理的适应性策略。为了消除现有代理建模方法的局限性,本文提出了一种基于对比学习的代理建模(CLAM)方法,仅依赖于自我代理在训练和运行期间的本地观察来生成实时一致的高质量策略表示。实验证明,该方法在合作和竞争的多智能体环境中均取得了最佳效果,展示了对比学习在增强强化学习潜力方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键要点摘要:
- 在多智能体系统中,智能机器代理的建模至关重要,特别是在合作和竞争场景中。
- 代理需要理解其他代理的行为并提取有意义的策略表示来改善自我代理的适应性策略。
- 基于对比学习的代理建模(CLAM)方法仅依赖于自我代理的本地观察。
- CLAM能够在实时中生成一致的高质量策略表示。
- 实验证明CLAM在合作和竞争的多智能体环境中均取得了最佳效果。
- 对比学习在增强强化学习潜力方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图