⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-02 更新
Robust Deepfake Detection for Electronic Know Your Customer Systems Using Registered Images
Authors:Takuma Amada, Kazuya Kakizaki, Taiki Miyagawa, Akinori F. Ebihara, Kaede Shiohara, Toshihiko Yamasaki
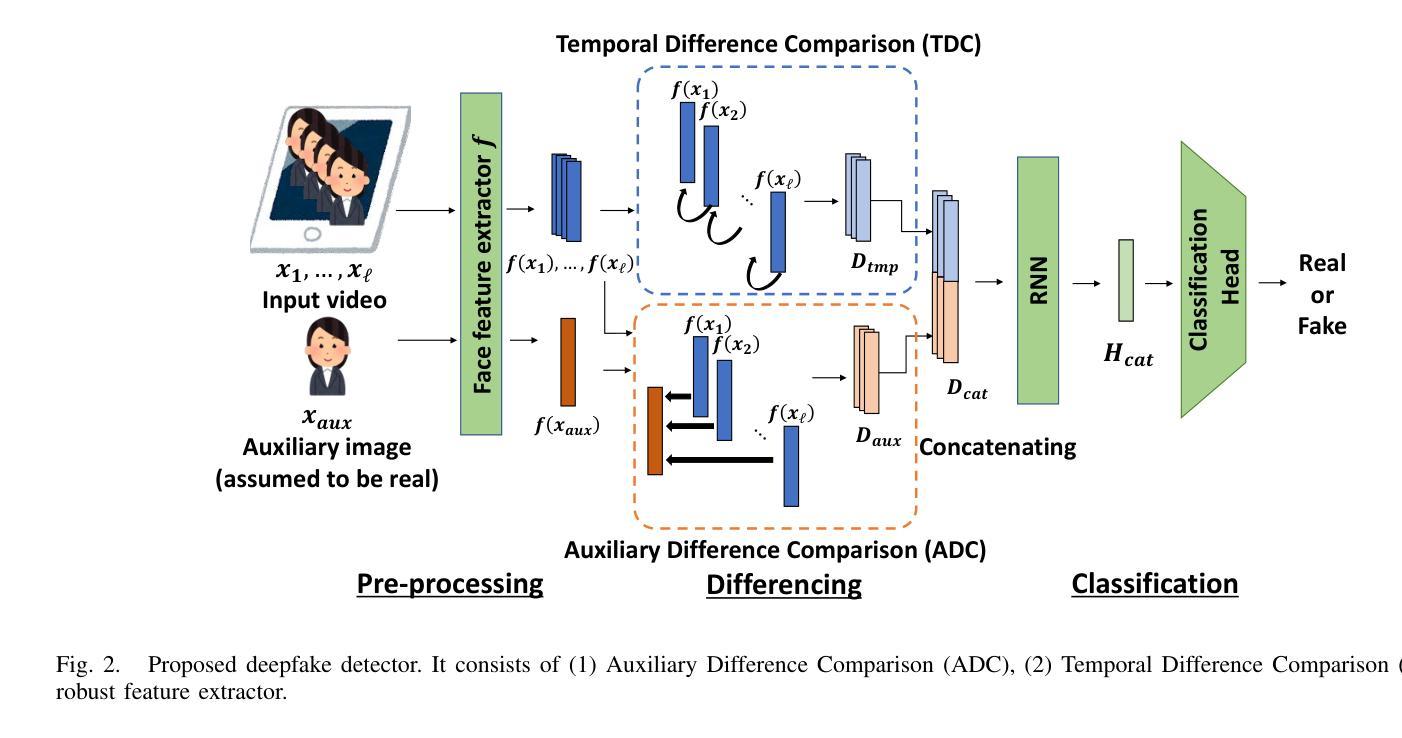
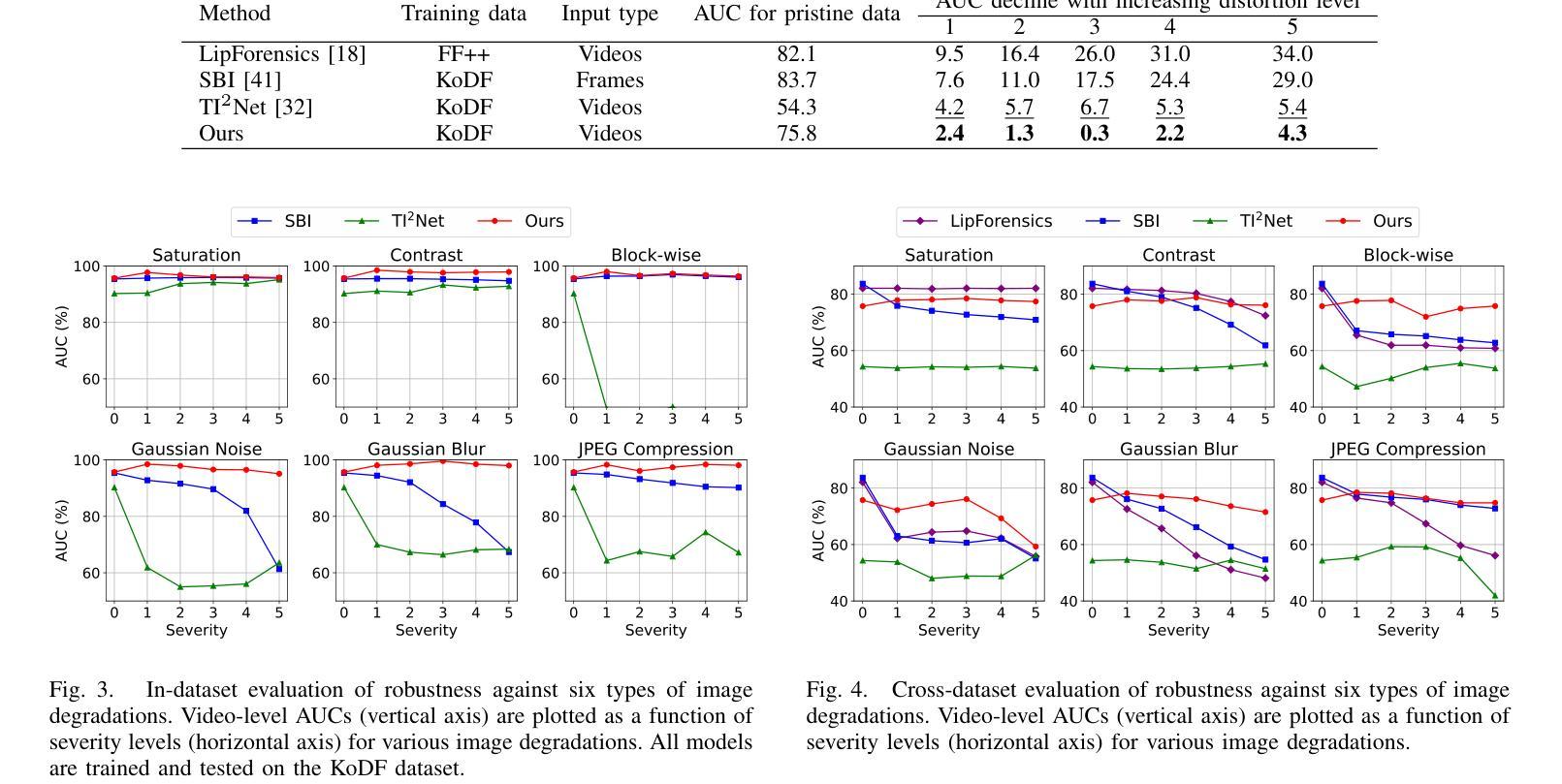
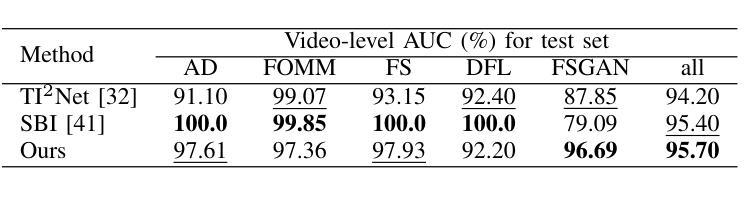
In this paper, we present a deepfake detection algorithm specifically designed for electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) systems. To ensure the reliability of eKYC systems against deepfake attacks, it is essential to develop a robust deepfake detector capable of identifying both face swapping and face reenactment, while also being robust to image degradation. We address these challenges through three key contributions: (1)Our approach evaluates the video’s authenticity by detecting temporal inconsistencies in identity vectors extracted by face recognition models, leading to comprehensive detection of both face swapping and face reenactment. (2)In addition to processing video input, the algorithm utilizes a registered image (assumed to be genuine) to calculate identity discrepancies between the input video and the registered image, significantly improving detection accuracy. (3)~We find that employing a face feature extractor trained on a larger dataset enhances both detection performance and robustness against image degradation. Our experimental results show that our proposed method accurately detects both face swapping and face reenactment comprehensively and is robust against various forms of unseen image degradation. Our source code is publicly available https://github.com/TaikiMiyagawa/DeepfakeDetection4eKYC.
本文提出了一种专门针对电子了解你的客户(eKYC)系统的深度伪造检测算法。为了确保eKYC系统对抗深度伪造攻击的可靠性,开发一个强大的深度伪造检测器至关重要,该检测器能够识别面部替换和面部再扮演,同时对图像退化具有稳健性。我们通过三个关键贡献来解决这些挑战:(1)我们的方法通过检测面部识别模型提取的身份向量中的时间不一致性来评估视频的真实性,从而实现对面部替换和面部再扮演的全面检测。(2)除了处理视频输入外,该算法还利用注册图像(假定为真实的)来计算输入视频与注册图像之间的身份差异,从而显著提高检测精度。(3)我们发现,在较大数据集上训练的面部特征提取器的使用提高了检测性能和对抗图像退化的稳健性。我们的实验结果表明,我们提出的方法能够全面、准确地检测面部替换和面部再扮演,并对各种未见过的图像退化具有稳健性。我们的源代码公开可用:https://github.com/TaikiMiyagawa/DeepfakeDetection4eKYC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to 19th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对电子客户识别系统(eKYC)的深度伪造检测算法。该算法通过检测身份向量中的时间不一致性来评估视频的真实性,从而全面检测面部替换和面部重演。此外,该算法还利用注册图像(假设为真实图像)计算输入视频与注册图像之间的身份差异,从而提高检测准确性。使用大型数据集训练的面部特征提取器可增强检测性能和对抗图像降质的稳健性。实验结果表明,该方法能够全面准确地检测面部替换和面部重演,对各种未见过的图像降质具有稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种针对eKYC系统的深度伪造检测算法,能够全面检测面部替换和面部重演。
- 算法通过检测身份向量中的时间不一致性来评估视频真实性。
- 算法利用注册图像提高检测准确性,计算输入视频与注册图像之间的身份差异。
- 使用大型数据集训练的面部特征提取器可增强检测性能和稳健性。
- 该方法对各种形式的未见图像降质具有稳健性。
- 论文提供的源代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

Visual Language Models as Zero-Shot Deepfake Detectors
Authors:Viacheslav Pirogov
The contemporary phenomenon of deepfakes, utilizing GAN or diffusion models for face swapping, presents a substantial and evolving threat in digital media, identity verification, and a multitude of other systems. The majority of existing methods for detecting deepfakes rely on training specialized classifiers to distinguish between genuine and manipulated images, focusing only on the image domain without incorporating any auxiliary tasks that could enhance robustness. In this paper, inspired by the zero-shot capabilities of Vision Language Models, we propose a novel VLM-based approach to image classification and then evaluate it for deepfake detection. Specifically, we utilize a new high-quality deepfake dataset comprising 60,000 images, on which our zero-shot models demonstrate superior performance to almost all existing methods. Subsequently, we compare the performance of the best-performing architecture, InstructBLIP, on the popular deepfake dataset DFDC-P against traditional methods in two scenarios: zero-shot and in-domain fine-tuning. Our results demonstrate the superiority of VLMs over traditional classifiers.
现代深度伪造现象,利用生成对抗网络(GAN)或扩散模型进行面部替换,对数字媒体、身份验证和其他多种系统构成了重大且不断发展的威胁。大多数现有的检测深度伪造的方法依赖于训练专门的分类器来区分真实和操纵的图像,只专注于图像领域,而没有纳入可以增强稳健性的任何辅助任务。本文受视觉语言模型的零射击能力的启发,我们提出了一种基于视觉语言模型的新颖图像分类方法,并对其在深伪检测方面的性能进行了评估。具体来说,我们利用包含6万张图像的高质量深度伪造数据集,零射击模型表现出几乎超越所有现有方法的性能。随后,我们在流行的深度伪造数据集DFDC-P上对比了表现最佳的架构InstructBLIP与传统方法在零射击和域内微调两种场景下的性能。我们的结果证明了视觉语言模型在性能上优于传统分类器。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICML 2025 Workshop on Reliable and Responsible Foundation Models
Summary
本文介绍了利用GAN或扩散模型进行人脸替换的深假现象,对数字媒体、身份验证等多个系统造成了重大且不断发展的威胁。现有的大多数检测深假的方法都依赖于训练专门的分类器来区分真实和操纵过的图像,只关注图像域,没有融入任何可以增强稳健性的辅助任务。本文受视觉语言模型的零射击能力的启发,提出了一种新的基于VLM的图像分类方法,并对其进行评估用于深假检测。利用新的高质量深假数据集进行试验,证明零射击模型表现优异,远超现有大多数方法。随后,在流行的深假数据集DFDC-P上对比了表现最佳的架构InstructBLIP与传统方法在不同场景下的性能表现,证明VLMs相较于传统分类器的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 深假现象已成为数字媒体等领域的重大威胁,利用GAN或扩散模型进行人脸替换。
- 现有检测深假的方法主要依赖专门的分类器来区分真实和操纵过的图像,但缺乏辅助任务的融入,限制了检测的稳健性。
- 本文受视觉语言模型的零射击能力的启发,提出了基于VLM的图像分类新方法。
- 使用高质量深假数据集进行实验,结果表明零射击模型性能优越。
- 对比了最佳模型InstructBLIP与传统方法在深假检测数据集DFDC-P上的表现,验证了VLMs的优越性。
- 零射击模型能在无需额外训练的情况下识别深假图像,显示出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


HairCUP: Hair Compositional Universal Prior for 3D Gaussian Avatars
Authors:Byungjun Kim, Shunsuke Saito, Giljoo Nam, Tomas Simon, Jason Saragih, Hanbyul Joo, Junxuan Li
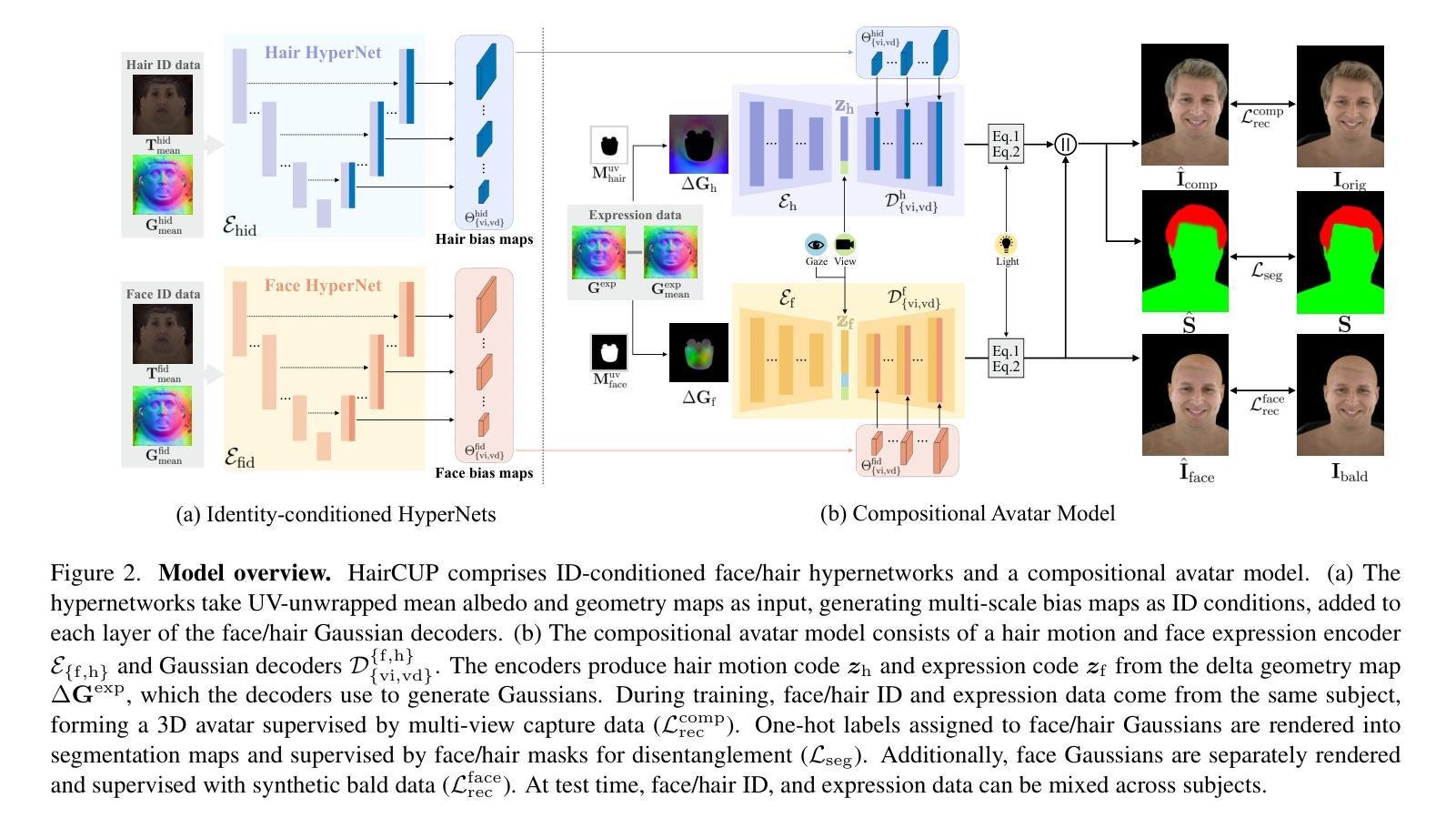
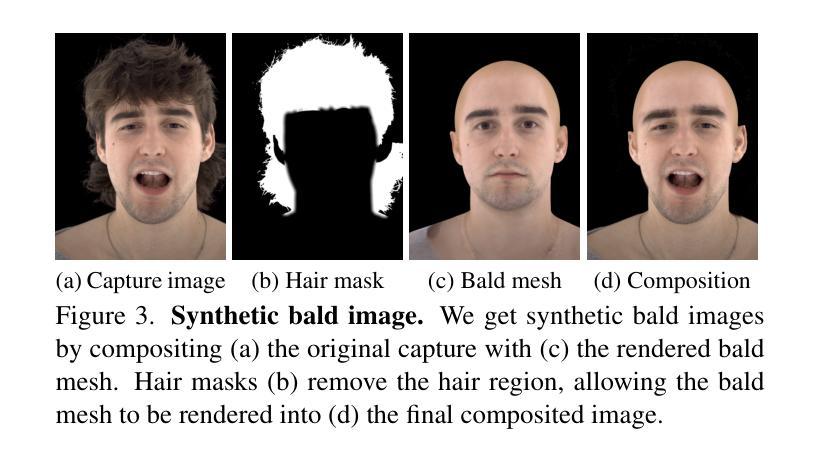
We present a universal prior model for 3D head avatars with explicit hair compositionality. Existing approaches to build generalizable priors for 3D head avatars often adopt a holistic modeling approach, treating the face and hair as an inseparable entity. This overlooks the inherent compositionality of the human head, making it difficult for the model to naturally disentangle face and hair representations, especially when the dataset is limited. Furthermore, such holistic models struggle to support applications like 3D face and hairstyle swapping in a flexible and controllable manner. To address these challenges, we introduce a prior model that explicitly accounts for the compositionality of face and hair, learning their latent spaces separately. A key enabler of this approach is our synthetic hairless data creation pipeline, which removes hair from studio-captured datasets using estimated hairless geometry and texture derived from a diffusion prior. By leveraging a paired dataset of hair and hairless captures, we train disentangled prior models for face and hair, incorporating compositionality as an inductive bias to facilitate effective separation. Our model’s inherent compositionality enables seamless transfer of face and hair components between avatars while preserving identity. Additionally, we demonstrate that our model can be fine-tuned in a few-shot manner using monocular captures to create high-fidelity, hair-compositional 3D head avatars for unseen subjects. These capabilities highlight the practical applicability of our approach in real-world scenarios, paving the way for flexible and expressive 3D avatar generation.
我们为带有明确头发组成性的3D头部化身提供了一个通用先验模型。现有的为3D头部化身构建通用先验的方法通常采用整体建模方法,将脸和头发视为一个不可分割的实体。这忽略了人类头部的固有组成性,使得模型难以自然地分离面部和头发表示,尤其是在数据集有限的情况下。此外,这种整体模型很难以灵活可控的方式支持像3D面部和发型交换这样的应用。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了一个先验模型,该模型显式地考虑了面部和头发的组成性,分别学习它们的潜在空间。此方法的关键是我们合成无发数据创建管道,该管道使用估计的无发几何和纹理从扩散先验中派生出工作室捕获的数据集来移除头发。通过利用带有头发和无发捕获的配对数据集,我们对面部和头发进行了分离训练先验模型,并将组成性作为归纳偏置以促进有效分离。我们模型的固有组成性能够在化身之间无缝转移面部和头发组件,同时保留身份。此外,我们证明我们的模型可以使用单目捕获以少量拍摄的方式进行微调,以创建用于未见主体的高保真度、头发组成的3D头部化身。这些功能突出了我们的方法在现实世界场景中的实际适用性,为灵活和富有表现力的3D化身生成铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://bjkim95.github.io/haircup/
摘要
本文提出了一种用于3D头像的通用先验模型,该模型具有明确的头发组成。现有方法对3D头像进行通用先验建模时通常采用整体建模方法,将面部和头发视为不可分割的实体。这忽略了头部本身的组成性,使得模型在面临有限数据集时难以自然地区分面部和头发表示。此外,这种整体模型在支持3D面部和发型替换等应用时,难以实现灵活可控的方式。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种先验模型,该模型显式考虑面部和头发的组成性,并分别学习它们的潜在空间。这一方法的关键在于我们的无发合成数据创建管道,它通过估计的无发几何和纹理从扩散先验中去除数据集中的头发。通过利用头发和无发捕获的配对数据集,我们对面部和头发进行了分离先验建模,并将组成性作为归纳偏见以促进有效的分离。我们模型的内在组成性使得不同头像之间的面部和头发组件无缝转移成为可能,同时保留身份特征。此外,我们证明我们的模型可以通过使用单目捕获进行少量微调来创建高保真、具有头发组成的3D头像来呈现未见过的主体。这些功能展示了我们的方法在现实世界场景中的实际适用性,为灵活和生动的3D头像生成铺平了道路。
关键见解
- 提出了一种用于3D头像的通用先验模型,考虑了头部各部分的组成性。
- 通过合成数据创建管道去除头发信息,为面部和头发建模提供清晰的数据集。
- 采用分离先验模型对面部和头发进行建模,实现其潜在空间的独立学习。
- 模型具有内在组成性,可实现无缝转移面部和头发组件,同时保留身份特征。
- 模型可适应少量样本微调,利用单目捕获创建高保真度的个性化3D头像。
- 方法为灵活和生动的3D头像生成提供了可能,具有广泛的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

WaveMamba: Wavelet-Driven Mamba Fusion for RGB-Infrared Object Detection
Authors:Haodong Zhu, Wenhao Dong, Linlin Yang, Hong Li, Yuguang Yang, Yangyang Ren, Qingcheng Zhu, Zichao Feng, Changbai Li, Shaohui Lin, Runqi Wang, Xiaoyan Luo, Baochang Zhang
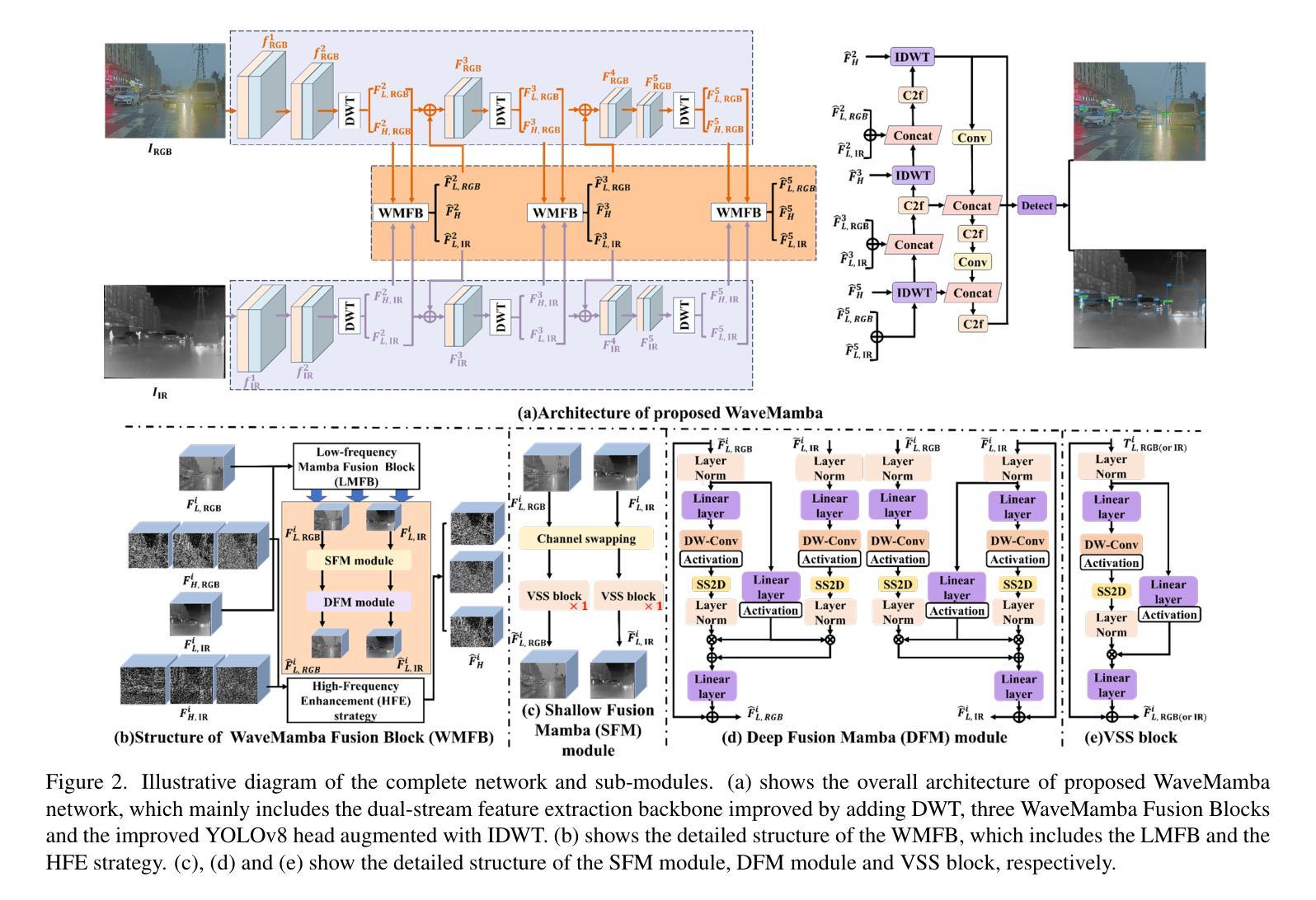
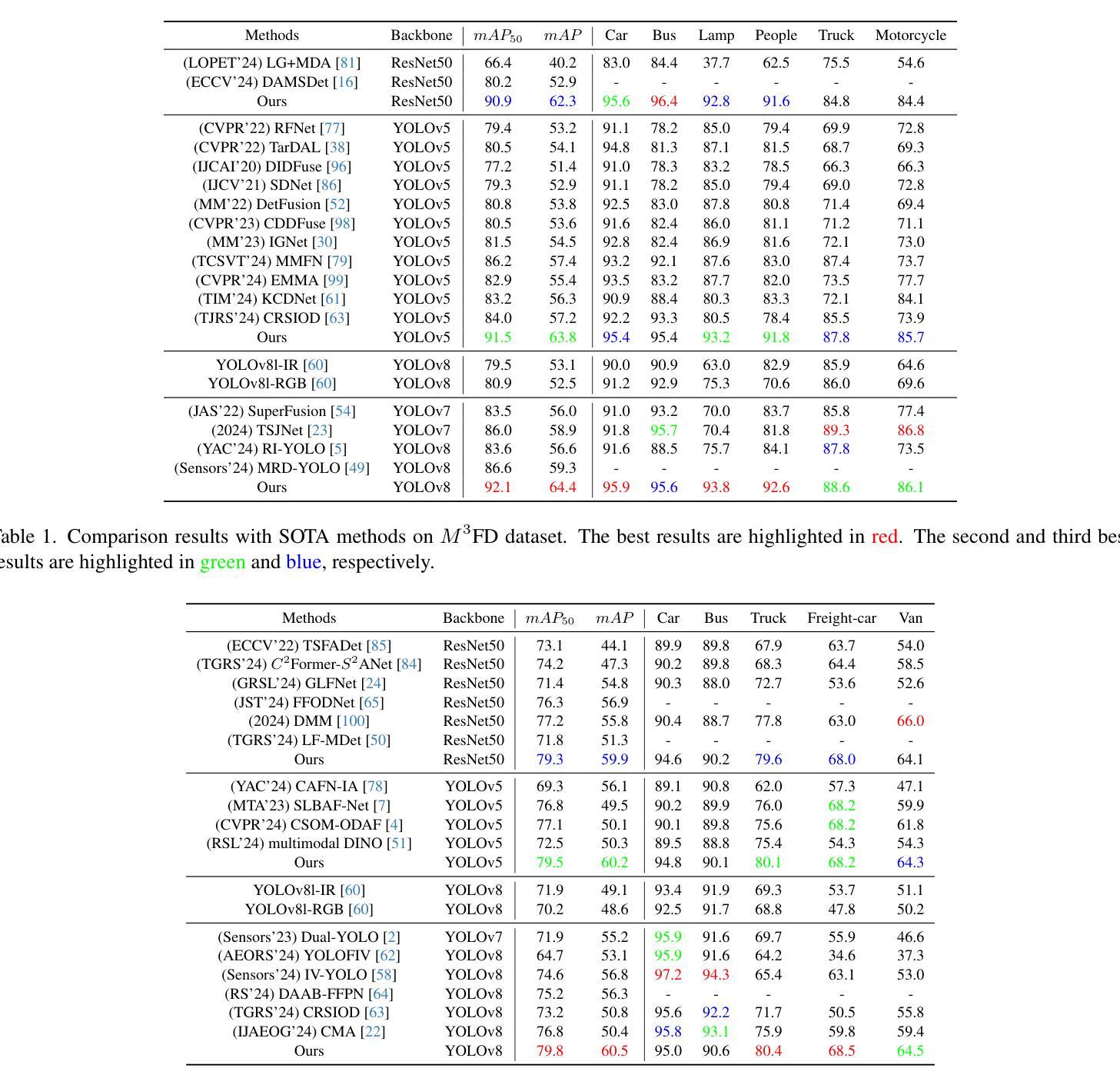
Leveraging the complementary characteristics of visible (RGB) and infrared (IR) imagery offers significant potential for improving object detection. In this paper, we propose WaveMamba, a cross-modality fusion method that efficiently integrates the unique and complementary frequency features of RGB and IR decomposed by Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). An improved detection head incorporating the Inverse Discrete Wavelet Transform (IDWT) is also proposed to reduce information loss and produce the final detection results. The core of our approach is the introduction of WaveMamba Fusion Block (WMFB), which facilitates comprehensive fusion across low-/high-frequency sub-bands. Within WMFB, the Low-frequency Mamba Fusion Block (LMFB), built upon the Mamba framework, first performs initial low-frequency feature fusion with channel swapping, followed by deep fusion with an advanced gated attention mechanism for enhanced integration. High-frequency features are enhanced using a strategy that applies an ``absolute maximum” fusion approach. These advancements lead to significant performance gains, with our method surpassing state-of-the-art approaches and achieving average mAP improvements of 4.5% on four benchmarks.
利用可见光(RGB)和红外(IR)图像的互补特性,为改进目标检测提供了巨大潜力。在本文中,我们提出了WaveMamba,这是一种跨模态融合方法,它有效地集成了通过离散小波变换(DWT)分解的RGB和IR的独特且互补的频率特征。我们还提出了一种改进的检测头,它结合了逆离散小波变换(IDWT)来减少信息损失并产生最终检测结果。我们的方法的核心是WaveMamba融合块(WMFB)的引入,它促进了低/高频子带之间的全面融合。WMFB中的低频Mamba融合块(LMFB)建立在Mamba框架上,首先通过通道交换执行初始低频特征融合,然后通过先进的门控注意机制进行深度融合,以实现增强的集成。高频特征通过使用一种采用“绝对最大值”融合方法的策略来增强。这些进步带来了显著的性能提升,我们的方法在四个基准测试上平均mAP提高了4.5%,超越了最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用可见光(RGB)和红外(IR)影像的互补特性,对于提升物体检测具有显著潜力。本文提出WaveMamba,一种跨模态融合方法,通过离散小波变换(DWT)有效融合RGB和IR影像的独特且互补的频率特征。还提出了一种改进的检测头,结合逆离散小波变换(IDWT)以减少信息损失并产生最终检测结果。本方法的核心是WaveMamba融合块(WMFB)的引入,它促进了低/高频子带之间的全面融合。通过基于Mamba框架的低频Mamba融合块(LMFB)进行初步的低频特征融合,随后通过先进的门控注意力机制进行深度融合以实现增强的集成。高频特征则采用“绝对最大值”融合策略进行增强。该方法显著提高了性能,在四个基准测试中平均mAP提升了4.5%,超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 利用RGB和IR影像的互补特性可提升物体检测性能。
- WaveMamba是一种跨模态融合方法,通过DWT融合RGB和IR的频率特征。
- 改进的检测头结合IDWT以减少信息损失并产生最终检测结果。
- WaveMamba融合块(WMFB)是方法的核心,实现了低/高频子带的全面融合。
- 低频Mamba融合块(LMFB)基于Mamba框架进行低频特征融合,采用通道交换和先进的门控注意力机制。
- 高频特征采用“绝对最大值”融合策略进行增强。
点此查看论文截图
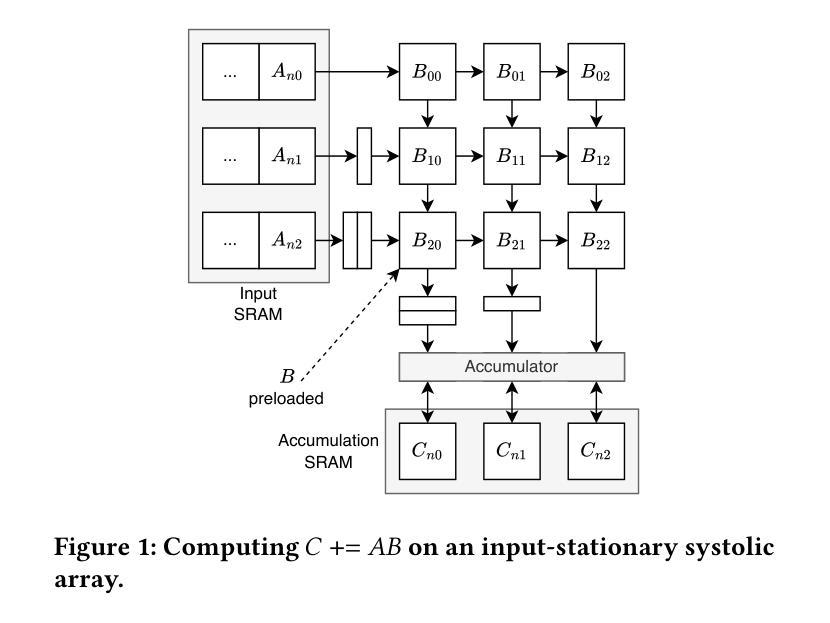
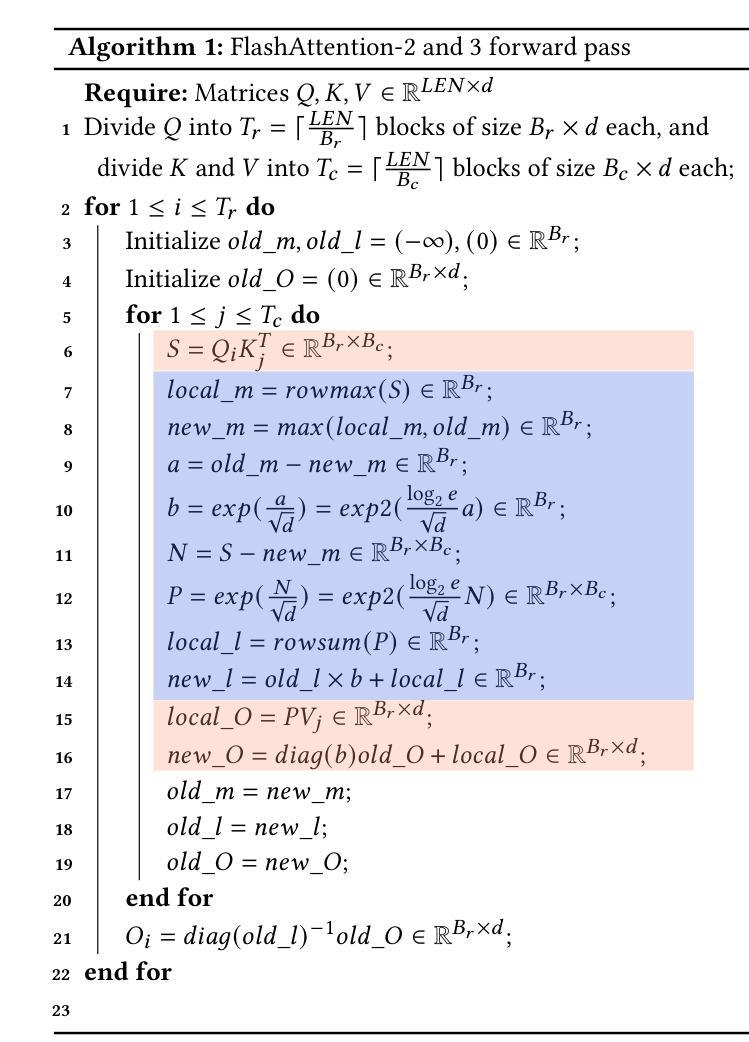
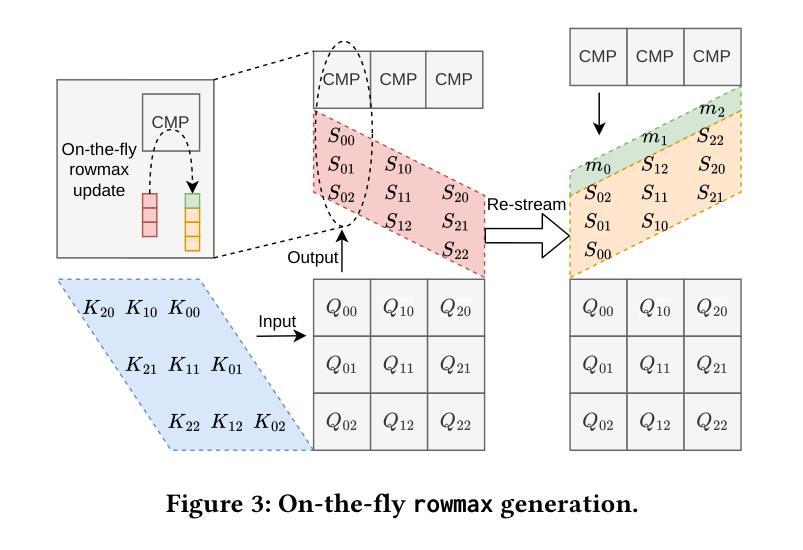
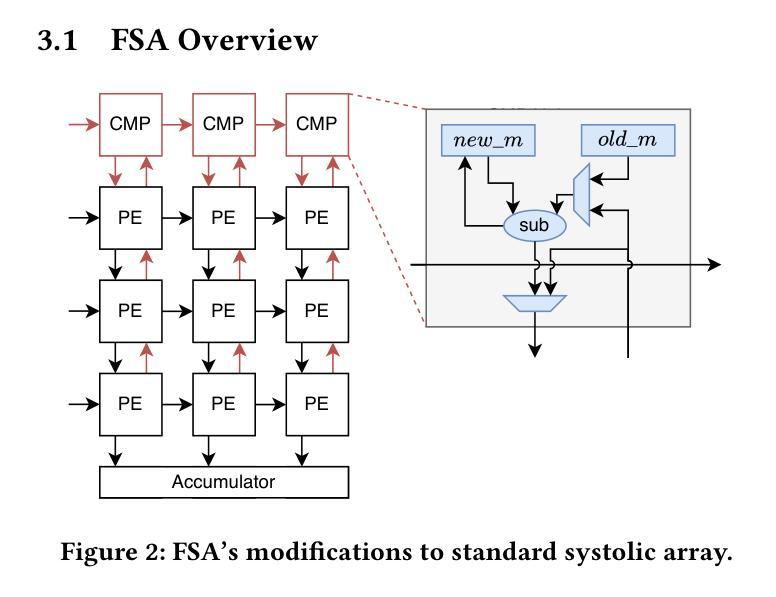
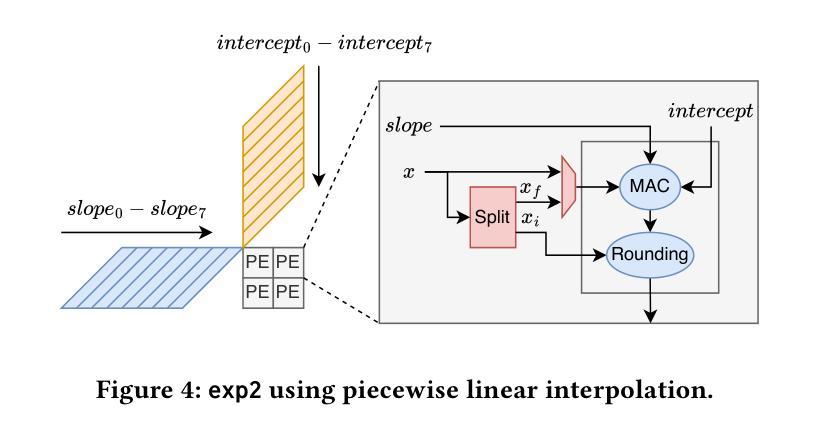
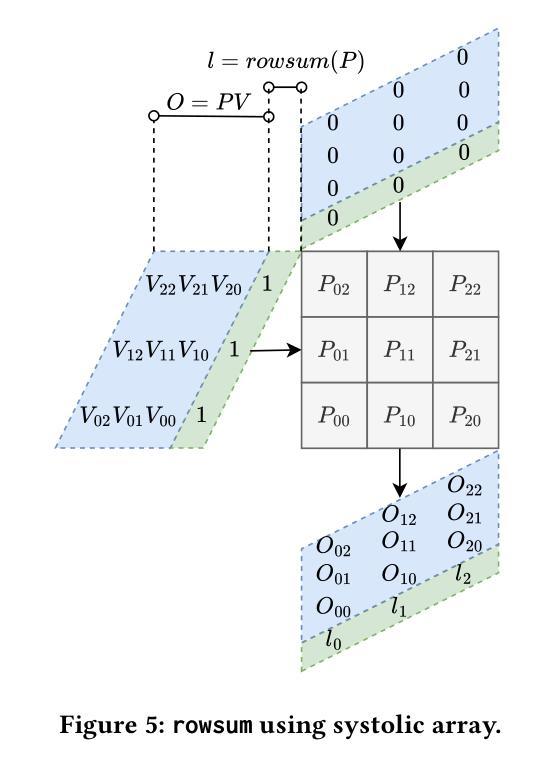
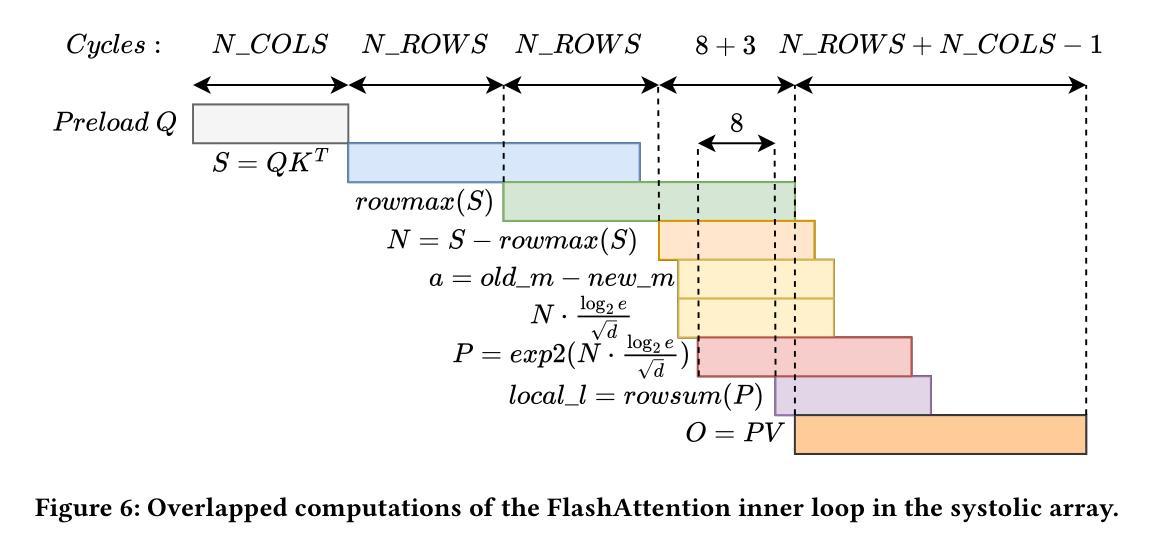
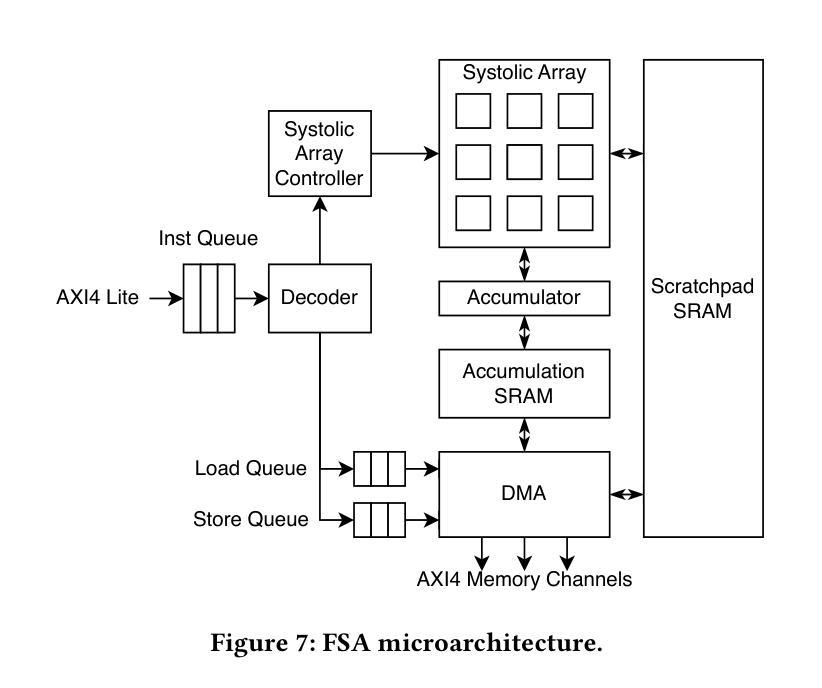
SystolicAttention: Fusing FlashAttention within a Single Systolic Array
Authors:Jiawei Lin, Guokai Chen, Yuanlong Li, Thomas Bourgeat
Transformer models rely heavily on scaled dot-product attention (SDPA), typically implemented using the FlashAttention algorithm. However, current systolic-array-based accelerators face significant challenges when executing FlashAttention. Systolic arrays can only achieve high utilization for consecutive and large matrix multiplications. In contrast, FlashAttention requires frequently interleaved matrix multiplications and softmax operations. The frequent data swaps between the systolic array and external vector units result in low systolic array utilization. This is further exacerbated by the fact that softmax involves numerous non-matrix operations, which are not well-suited for systolic arrays. Moreover, the concurrent execution of matrix multiplication on systolic arrays and softmax on vector units leads to register file and SRAM port contention, further degrading performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose FSA, an enhanced systolic array architecture that enables the entire FlashAttention algorithm to run entirely within a single systolic array, eliminating the need for external vector units. At the core of FSA is SystolicAttention, a novel scheduling algorithm that maps FlashAttention operations onto systolic arrays with fine-grained, element-wise overlap. This significantly improves array utilization while preserving the original floating-point operation order to maintain numerical stability. We implement FSA in synthesizable RTL and evaluate its performance against state-of-the-art commercial accelerators. Our results show that FSA achieves 1.77x and 4.83x higher attention FLOPs/s utilization compared to AWS NeuronCore-v2 and Google TPUv5e, respectively, with only about 10% area overhead.
Transformer模型严重依赖于缩放点积注意力(SDPA),通常使用FlashAttention算法实现。然而,当前的基于收缩阵列的加速器在执行FlashAttention时面临重大挑战。收缩阵列只能对连续且大规模的矩阵乘法实现高利用率。相比之下,FlashAttention需要频繁交替的矩阵乘法和softmax操作。收缩阵列与外部向量单元之间的频繁数据交换导致收缩阵列利用率低。softmax涉及众多非矩阵操作,不适合收缩阵列,这进一步加剧了问题。此外,在收缩阵列上执行矩阵乘法和在向量单元上执行softmax导致寄存器文件和SRAM端口竞争,进一步降低性能。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了FSA,这是一种增强的收缩阵列架构,它使整个FlashAttention算法能够在单个收缩阵列内运行,无需外部向量单元。FSA的核心是SystolicAttention,这是一种新型调度算法,它以细粒度、元素级重叠的方式将FlashAttention操作映射到收缩阵列上。这显著提高了阵列利用率,同时保持原始浮点操作顺序,以维持数值稳定性。我们在可综合的RTL中实现了FSA,并评估了其与最新商业加速器的性能。结果表明,FSA与AWS NeuronCore-v2和Google TPUv5e相比,注意力FLOPs/s利用率分别提高了1.77倍和4.83倍,且仅增加了约10%的面积开销。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该文介绍了Transformer模型在采用FlashAttention算法实现时面临的挑战,特别是面向sysatic阵列加速器的问题。现有sysatic阵列难以执行频繁交织的矩阵乘法和softmax操作,导致低效率。为此,本文提出了一种改进的sysatic阵列架构FSA,通过全新的调度算法SystolicAttention,实现了FlashAttention算法在单一sysatic阵列内的完全运行。相较于当前主流的商业加速器,FSA在面积仅增加约10%的情况下,实现了更高的注意力FLOPs/s利用率。
Key Takeaways:
- Transformer模型依赖FlashAttention算法实现缩放点积注意力(SDPA)。
- 现有sysatic阵列加速器在执行FlashAttention时面临挑战,主要问题在于其难以实现频繁交织的矩阵乘法和softmax操作。
- Softmax涉及的非矩阵操作不适合sysatic阵列,导致数据交换频繁,降低效率。
- FSA是一种改进的sysatic阵列架构,能在单一阵列内执行整个FlashAttention算法。
- SystolicAttention是FSA的核心调度算法,以精细粒度的元素级重叠方式映射FlashAttention操作到sysatic阵列。
- FSA提高了sysatic阵列的利用率,同时保持了浮点操作的顺序,保证了数值稳定性。
点此查看论文截图