⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-02 更新
IN45023 Neural Network Design Patterns in Computer Vision Seminar Report, Summer 2025
Authors:Radu-Andrei Bourceanu, Neil De La Fuente, Jan Grimm, Andrei Jardan, Andriy Manucharyan, Cornelius Weiss, Roman Pflugfelder
This report analyzes the evolution of key design patterns in computer vision by examining six influential papers. The analy- sis begins with foundational architectures for image recognition. We review ResNet, which introduced residual connections to overcome the vanishing gradient problem and enable effective training of significantly deeper convolutional networks. Subsequently, we examine the Vision Transformer (ViT), which established a new paradigm by applying the Transformer ar- chitecture to sequences of image patches, demonstrating the efficacy of attention-based models for large-scale image recogni- tion. Building on these visual representation backbones, we investigate generative models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are analyzed for their novel adversarial training process, which challenges a generator against a discriminator to learn complex data distributions. Then, Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) are covered, which improve upon prior generative methods by performing a sequential denoising process in a perceptually compressed latent space. LDMs achieve high-fidelity synthesis with greater computational efficiency, representing the current state-of-the-art for image generation. Finally, we explore self-supervised learning techniques that reduce dependency on labeled data. DINO is a self-distillation framework in which a student network learns to match the output of a momentum-updated teacher, yielding features with strong k-NN classification performance. We conclude with Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which utilize an asymmetric encoder-decoder design to reconstruct heavily masked inputs, providing a highly scalable and effective method for pre-training large-scale vision models.
本报告通过分析六篇有影响力的论文,分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变。分析从图像识别的基本架构开始。我们回顾了ResNet,它引入了残差连接,克服了梯度消失问题,实现了对更深卷积网络的有效训练。之后,我们研究了将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列的Vision Transformer(ViT),这建立了一种新的模式,并证明了注意力模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。基于这些视觉表示骨干网,我们研究了生成模型。分析了生成对抗网络(GANs)的新型对抗训练过程,该过程通过生成器与鉴别器之间的对抗来学习复杂的数据分布。然后介绍了潜在扩散模型(LDMs),通过在感知压缩的潜在空间中进行连续去噪过程,改进了先前的生成方法。LDMs实现了高保真合成,具有更高的计算效率,代表了当前图像生成的最新技术。最后,我们探索了减少对标定数据依赖性的自监督学习技术。DINO是一种自蒸馏框架,学生网络学习匹配动量更新后的教师输出,产生具有强大k-NN分类性能的特征。最后以使用不对称编码器解码器设计重建高度遮挡输入的Masked Autoencoders(MAE)为例,提供了一种高度可扩展和有效的预训练大规模视觉模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇报告分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变,通过考察六篇有影响力的论文进行深入研究。报告从图像识别的基本架构开始,介绍了ResNet和Vision Transformer等关键技术。然后探讨了生成模型,特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)和潜扩散模型(LDMs)的对抗性训练过程和序列降噪技术。最后,报告介绍了自我监督学习技术,如DINO和Masked Autoencoders等,这些技术减少了对于标注数据的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 报告分析了计算机视觉领域关键设计模式的演变,从图像识别的基本架构到生成模型和自我监督学习技术的演进。
- ResNet通过引入残差连接克服了梯度消失问题,使深度卷积网络的有效训练成为可能。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列,展示了注意力模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)的对抗性训练过程挑战了生成器与鉴别器的对抗,从而学习复杂的数据分布。
- 潜扩散模型(LDMs)通过感知压缩的潜在空间中的序列降噪过程改进了先前的生成方法,实现了高保真合成和更高的计算效率。
- DINO是一种自蒸馏框架,学生网络学习匹配动量更新的教师输出,具有强大的k-NN分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

Visual Language Models as Zero-Shot Deepfake Detectors
Authors:Viacheslav Pirogov
The contemporary phenomenon of deepfakes, utilizing GAN or diffusion models for face swapping, presents a substantial and evolving threat in digital media, identity verification, and a multitude of other systems. The majority of existing methods for detecting deepfakes rely on training specialized classifiers to distinguish between genuine and manipulated images, focusing only on the image domain without incorporating any auxiliary tasks that could enhance robustness. In this paper, inspired by the zero-shot capabilities of Vision Language Models, we propose a novel VLM-based approach to image classification and then evaluate it for deepfake detection. Specifically, we utilize a new high-quality deepfake dataset comprising 60,000 images, on which our zero-shot models demonstrate superior performance to almost all existing methods. Subsequently, we compare the performance of the best-performing architecture, InstructBLIP, on the popular deepfake dataset DFDC-P against traditional methods in two scenarios: zero-shot and in-domain fine-tuning. Our results demonstrate the superiority of VLMs over traditional classifiers.
利用生成对抗网络(GAN)或扩散模型进行面部替换的Deepfakes现象已成为数字传媒、身份认证和其他多种系统中一个持续发展的重大威胁。目前大多数检测Deepfakes的方法都依赖于训练专门的分类器来区分真实和操纵过的图像,它们只专注于图像领域,没有引入任何可以提升稳健性的辅助任务。本文受视觉语言模型的零样本能力的启发,提出了一种基于视觉语言模型的新颖的图像分类方法,并评估其在深度伪造检测中的表现。具体来说,我们利用一个新的高质量深度伪造数据集,其中包含6万张图像,我们的零样本模型在数据集上的表现优于几乎所有现有方法。随后,我们在流行的深度伪造数据集DFDC-P上对比了表现最佳的架构InstructBLIP与传统方法在零样本和领域内微调两种场景下的性能。我们的结果证明了视觉语言模型相较于传统分类器的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICML 2025 Workshop on Reliable and Responsible Foundation Models
Summary
基于GAN或扩散模型的面貌换脸技术引发的深度伪造现象,对数字媒体、身份认证等多个系统造成了重大且不断发展的威胁。现有的深度伪造检测主要依赖训练专门的分类器来区分真实和伪造图像,但这种方法缺乏辅助任务的辅助,可能影响其稳健性。本研究受视觉语言模型的零样本能力启发,提出了一种新的基于VLM的图像分类方法,并用于深度伪造检测。研究使用高质量的深度伪造数据集进行验证,结果显示零样本模型性能优于现有大多数方法。此外,对比了最佳架构InstructBLIP在DFDC-P流行深度伪造数据集上的零样本和域内微调两种场景的性能,证明了VLMs相比传统分类器的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度伪造现象已经成为数字媒体领域的重大威胁,现有的检测手段需要改进以增强稳健性。
- 本研究受到视觉语言模型的启发,提出了一种新颖的基于VLM的图像分类方法用于深度伪造检测。
- 使用高质量深度伪造数据集进行验证,零样本模型展现出卓越性能。
- 对比了最佳架构InstructBLIP在流行深度伪造数据集上的表现,包括零样本和域内微调两种场景。
- 研究结果表明,与传统的分类器相比,视觉语言模型在深度伪造检测方面更具优势。
- 通过引入辅助任务,可以提高模型的性能并增强其在实际应用中的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


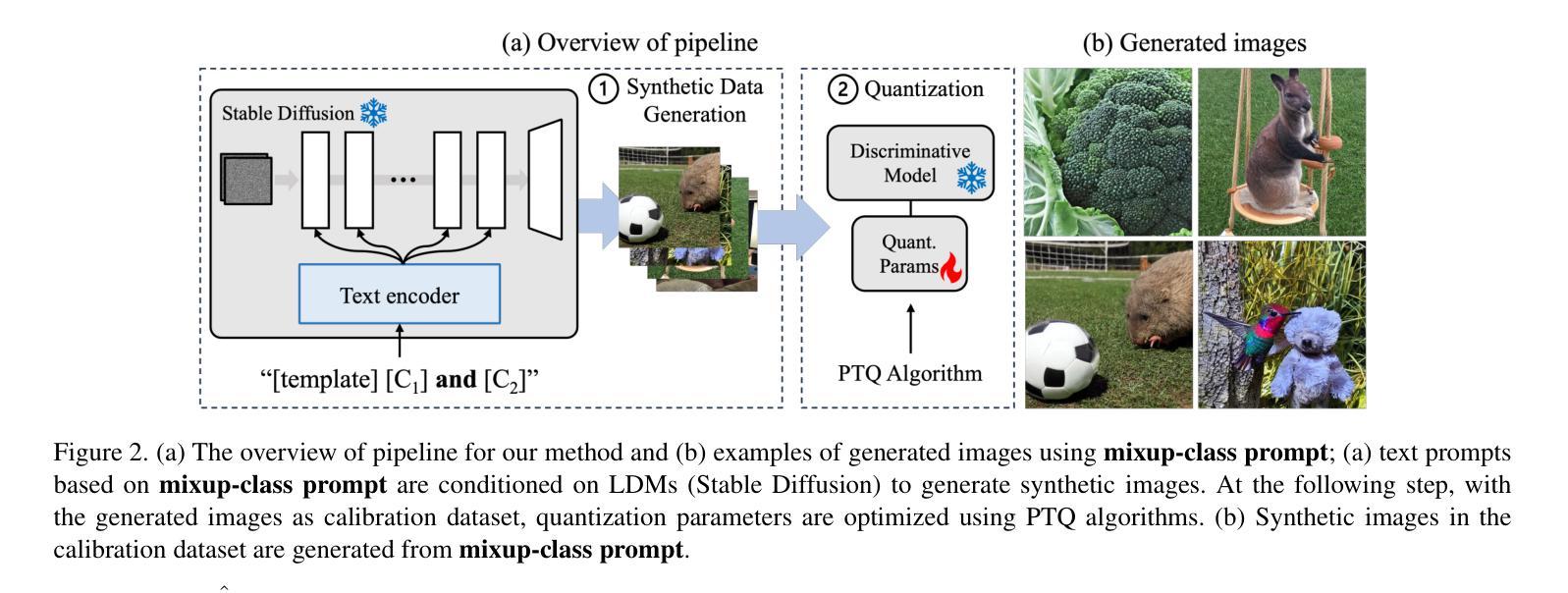
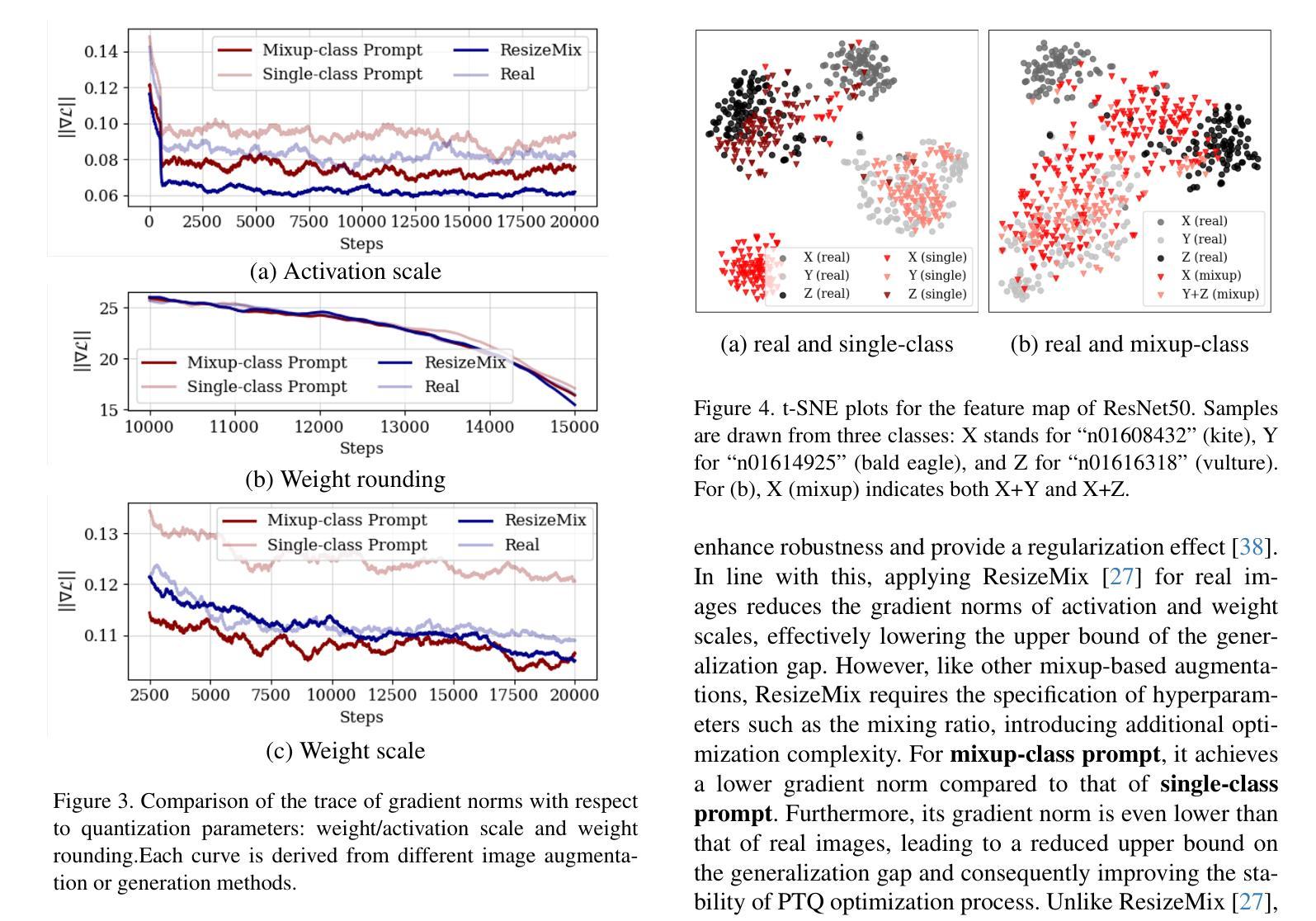
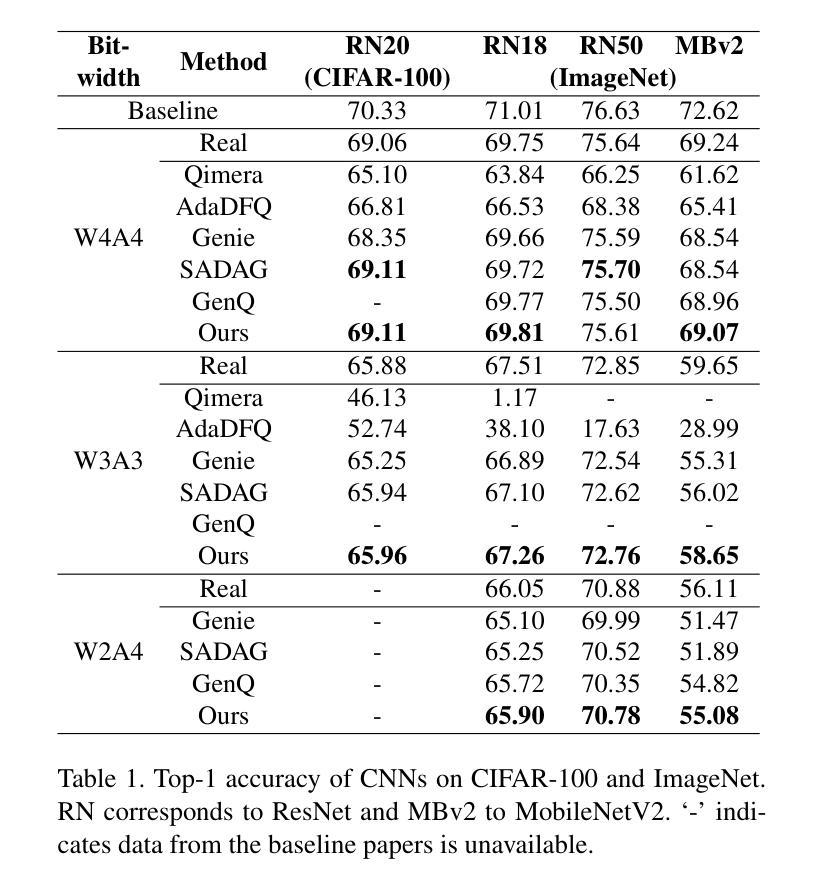
Enhancing Generalization in Data-free Quantization via Mixup-class Prompting
Authors:Jiwoong Park, Chaeun Lee, Yongseok Choi, Sein Park, Deokki Hong, Jungwook Choi
Post-training quantization (PTQ) improves efficiency but struggles with limited calibration data, especially under privacy constraints. Data-free quantization (DFQ) mitigates this by generating synthetic images using generative models such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and text-conditioned latent diffusion models (LDMs), while applying existing PTQ algorithms. However, the relationship between generated synthetic images and the generalizability of the quantized model during PTQ remains underexplored. Without investigating this relationship, synthetic images generated by previous prompt engineering methods based on single-class prompts suffer from issues such as polysemy, leading to performance degradation. We propose \textbf{mixup-class prompt}, a mixup-based text prompting strategy that fuses multiple class labels at the text prompt level to generate diverse, robust synthetic data. This approach enhances generalization, and improves optimization stability in PTQ. We provide quantitative insights through gradient norm and generalization error analysis. Experiments on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art DFQ methods like GenQ. Furthermore, it pushes the performance boundary in extremely low-bit scenarios, achieving new state-of-the-art accuracy in challenging 2-bit weight, 4-bit activation (W2A4) quantization.
后训练量化(PTQ)提高了效率,但在有限的校准数据方面遇到了困难,特别是在隐私约束下。无数据量化(DFQ)通过生成对抗网络(GANs)和文本条件潜在扩散模型(LDMs)等生成模型生成合成图像,并应用现有的PTQ算法,从而缓解了这一问题。然而,在PTQ期间,生成的合成图像与量化模型的泛化能力之间的关系仍未得到充分探索。如果不研究这种关系,以前基于单类提示的提示工程方法生成的合成图像会面临多义性问题,导致性能下降。我们提出混合类提示,这是一种基于混合的文本提示策略,它在文本提示层面融合多个类标签,以生成多样且稳健的合成数据。这种方法增强了泛化能力,并提高了PTQ中的优化稳定性。我们通过梯度范数和泛化误差分析提供了定量见解。在卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最新的DFQ方法,如GenQ。此外,它在极低位场景中推动了性能边界,在具有挑战性的2位权重、4位激活(W2A4)量化中达到了新的最高精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了如何在隐私约束下利用生成对抗网络(GANs)和文本条件潜在扩散模型(LDMs)进行数据无关的量化问题。提出了一种基于混合文本提示策略的合成图像生成方法,增强了模型泛化能力和优化稳定性,在特定场景中性能超过现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 数据无关的量化方法通过生成合成图像解决了校准数据有限的问题。
- 基于生成对抗网络等技术的合成图像应用在PTQ中有良好的表现。但合成图像与模型泛化能力的关系未被充分研究。
- 传统基于单一类别提示的合成图像生成方法存在语义歧义问题,导致性能下降。
- 提出了一种基于混合文本提示策略的“mixup-class prompt”,融合多个类别标签生成多样且稳健的合成数据。
- 该方法增强了模型的泛化能力,提高了优化稳定性,并且在实验上优于现有的DFQ技术。特别是实现了极低位场景(如W2A4)下的最新准确性。这表明在挑战场景下,该策略有显著的优越性。
- 通过梯度范数和泛化误差分析提供了定量见解,证明了该方法的优越性。这些定量数据为理解该策略提供了重要的参考。
点此查看论文截图

Bringing Balance to Hand Shape Classification: Mitigating Data Imbalance Through Generative Models
Authors:Gaston Gustavo Rios, Pedro Dal Bianco, Franco Ronchetti, Facundo Quiroga, Oscar Stanchi, Santiago Ponte Ahón, Waldo Hasperué
Most sign language handshape datasets are severely limited and unbalanced, posing significant challenges to effective model training. In this paper, we explore the effectiveness of augmenting the training data of a handshape classifier by generating synthetic data. We use an EfficientNet classifier trained on the RWTH German sign language handshape dataset, which is small and heavily unbalanced, applying different strategies to combine generated and real images. We compare two Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) architectures for data generation: ReACGAN, which uses label information to condition the data generation process through an auxiliary classifier, and SPADE, which utilizes spatially-adaptive normalization to condition the generation on pose information. ReACGAN allows for the generation of realistic images that align with specific handshape labels, while SPADE focuses on generating images with accurate spatial handshape configurations. Our proposed techniques improve the current state-of-the-art accuracy on the RWTH dataset by 5%, addressing the limitations of small and unbalanced datasets. Additionally, our method demonstrates the capability to generalize across different sign language datasets by leveraging pose-based generation trained on the extensive HaGRID dataset. We achieve comparable performance to single-source trained classifiers without the need for retraining the generator.
大部分手语手势数据集存在严重的限制和不平衡问题,给有效模型训练带来了巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们探索了通过生成合成数据来增强手势分类器训练数据的有效性。我们使用在RWTH德语手语手势数据集上训练的EfficientNet分类器,该数据集小且极度不平衡,应用不同的策略来结合生成图像和真实图像。我们比较了两种用于数据生成的生成对抗网络(GAN)架构:ReACGAN使用标签信息通过辅助分类器对数据生成过程进行条件控制,而SPADE则利用空间自适应归一化对姿势信息进行条件控制以生成图像。ReACGAN能够生成与特定手势标签对齐的真实图像,而SPADE则侧重于生成具有准确空间手势配置的图像。我们提出的技术在RWTH数据集上的准确率提高了5%,解决了数据集小且不平衡的限制。此外,我们的方法通过利用基于姿势的生成器在庞大的HaGRID数据集上进行训练,展示了在不同手语数据集之间进行推广的能力。我们实现了与单源训练分类器相当的性能,且无需重新训练生成器。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 8 figures, to be published in Applied Soft Computing
Summary
本文探索了通过生成合成数据来增强手形分类器训练数据的有效性。研究使用了RWTH德语手语手形数据集训练的EfficientNet分类器,该数据集小且不均衡。通过应用不同的策略来结合生成图像和真实图像,研究比较了两种生成对抗网络(GAN)架构:ReACGAN和SPADE。ReACGAN通过使用标签信息通过辅助分类器对生成过程进行条件控制,生成与特定手形标签对齐的逼真图像,而SPADE则侧重于生成具有准确空间手形配置的图像。所提出的技术提高了RWTH数据集上的最新准确性,解决了数据集小且不均衡的问题。此外,该方法通过利用基于姿态生成的HaGRID数据集进行训练,展示了跨不同手语数据集的泛化能力,无需重新训练生成器即可实现与单源训练分类器相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 手语手形数据集普遍存在限制和不均衡问题,对模型训练构成挑战。
- 研究通过生成合成数据来增强手形分类器的训练数据。
- 采用了EfficientNet分类器,并在RWTH德语手语手形数据集上进行训练。
- 比较了ReACGAN和SPADE两种GAN架构,用于数据生成。
- ReACGAN能够生成与特定手形标签对齐的逼真图像,而SPADE关注生成具有准确空间配置的手形图像。
- 所提出的技术提高了RWTH数据集上的最新准确性,并解决了数据集的限制问题。
点此查看论文截图

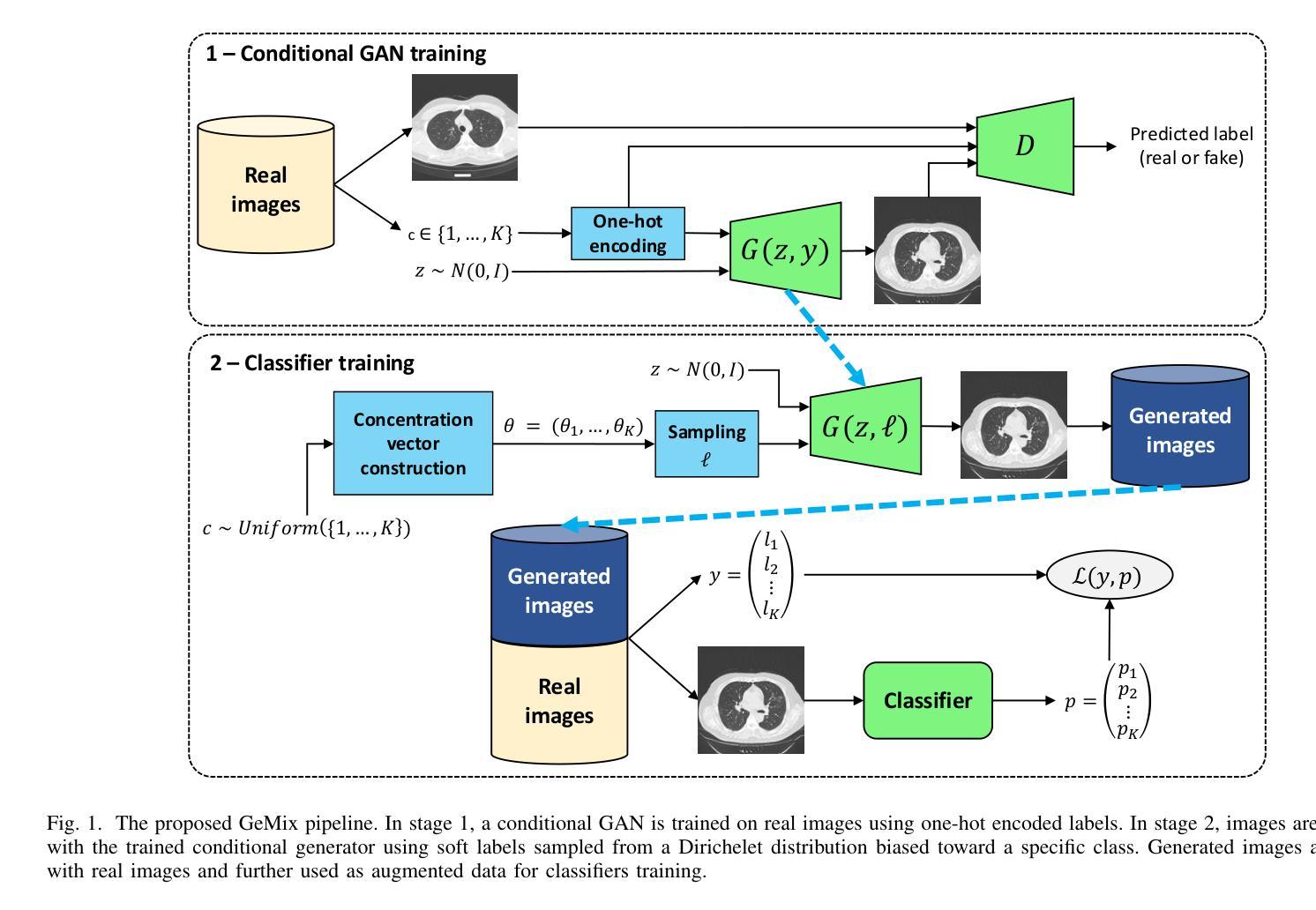
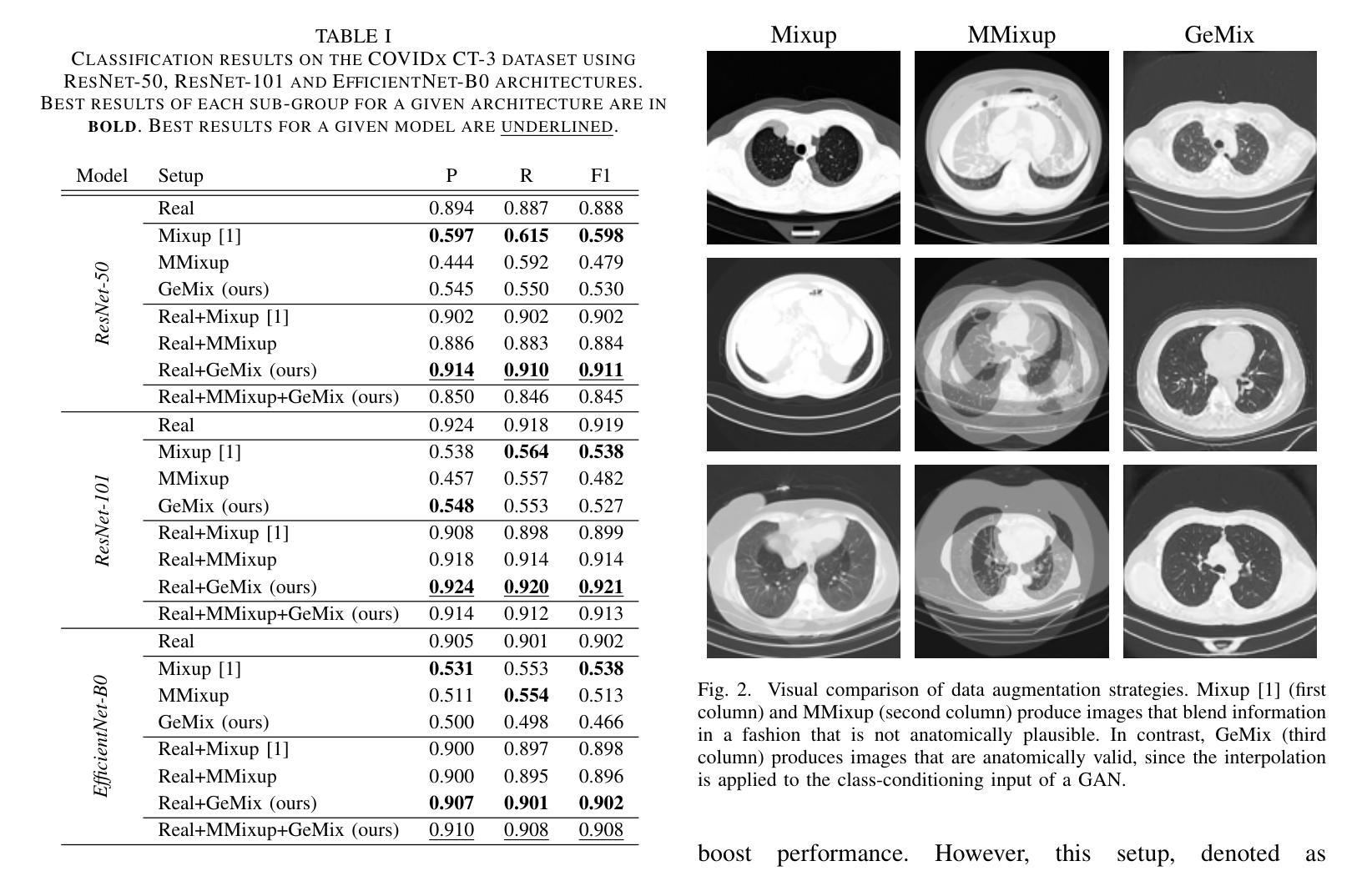
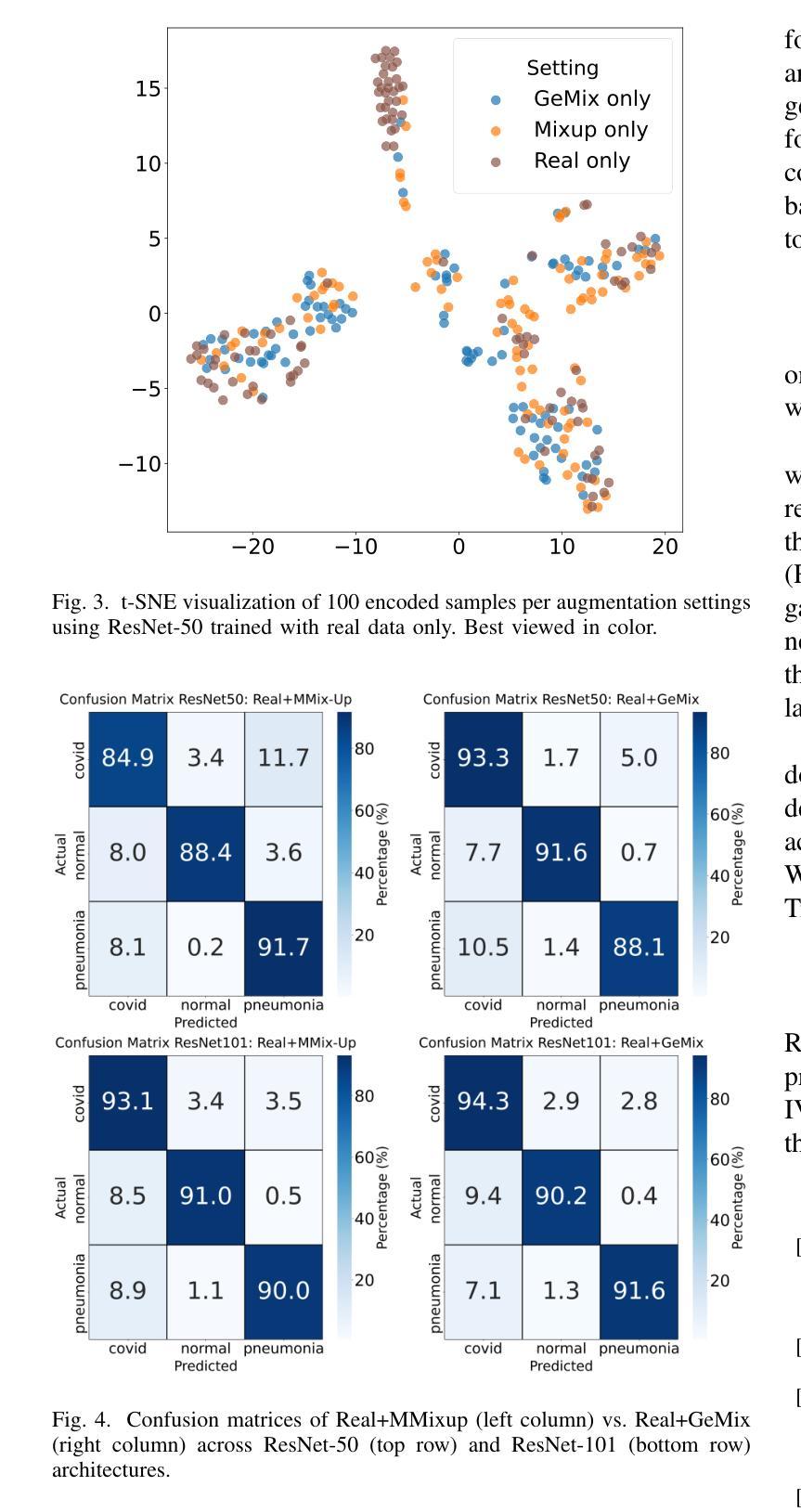
GeMix: Conditional GAN-Based Mixup for Improved Medical Image Augmentation
Authors:Hugo Carlesso, Maria Eliza Patulea, Moncef Garouani, Radu Tudor Ionescu, Josiane Mothe
Mixup has become a popular augmentation strategy for image classification, yet its naive pixel-wise interpolation often produces unrealistic images that can hinder learning, particularly in high-stakes medical applications. We propose GeMix, a two-stage framework that replaces heuristic blending with a learned, label-aware interpolation powered by class-conditional GANs. First, a StyleGAN2-ADA generator is trained on the target dataset. During augmentation, we sample two label vectors from Dirichlet priors biased toward different classes and blend them via a Beta-distributed coefficient. Then, we condition the generator on this soft label to synthesize visually coherent images that lie along a continuous class manifold. We benchmark GeMix on the large-scale COVIDx-CT-3 dataset using three backbones (ResNet-50, ResNet-101, EfficientNet-B0). When combined with real data, our method increases macro-F1 over traditional mixup for all backbones, reducing the false negative rate for COVID-19 detection. GeMix is thus a drop-in replacement for pixel-space mixup, delivering stronger regularization and greater semantic fidelity, without disrupting existing training pipelines. We publicly release our code at https://github.com/hugocarlesso/GeMix to foster reproducibility and further research.
Mixup已成为图像分类中流行的数据增强策略,但其简单的像素级插值常常会产生不真实的图像,从而阻碍学习,特别是在高风险的医疗应用中。我们提出了GeMix,这是一个两阶段的框架,它用基于类别条件生成对抗网络(GANs)的学习感知插值替换了启发式混合方法。首先,在目标数据集上训练StyleGAN2-ADA生成器。在数据增强过程中,我们从偏向不同类别的狄利克雷先验中采样两个标签向量,并通过Beta分布系数将它们混合。然后,我们在这些软标签上设置生成器条件,合成沿连续类别流形的视觉上连贯的图像。我们在大规模的COVIDx-CT-3数据集上采用三种主干网络(ResNet-50、ResNet-101、EfficientNet-B0)对GeMix进行基准测试。当与真实数据结合时,我们的方法在所有主干网络上相对于传统Mixup提高了宏F1分数,并降低了COVID-19检测的误报率。因此,GeMix可以作为像素空间Mixup的替代方案,提供更强大的正则化和更高的语义保真度,同时不会干扰现有的训练管道。我们在https://github.com/hugocarlesso/GeMix公开发布我们的代码,以促进可重复性和进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据增强策略Mixup在图像分类中广泛应用,但其简单的像素级插值在高风险医疗应用中会产生不真实图像,阻碍学习。提出GeMix,一个基于类条件GAN的两阶段框架,用学习到的标签感知插值替换启发式混合。GeMix在大型COVIDx-CT-3数据集上表现良好,能提高宏F1分数,降低COVID-19检测的误报率。GeMix可作为像素空间Mixup的替代品,提供更强大的正则化和更高的语义保真度。
Key Takeaways
- Mixup在图像分类中广泛应用,但在高风险医疗应用中产生不真实图像。
- GeMix是一个基于类条件GAN的两阶段框架,旨在解决Mixup的问题。
- GeMix使用StyleGAN2-ADA生成器进行目标数据集的训练。
- GeMix通过采样两个偏向不同类别的标签向量,并使用Beta分布系数进行混合,实现标签感知插值。
- GeMix合成的图像在连续的类别流形中是视觉连贯的。
- 在大型COVIDx-CT-3数据集上,GeMix提高了宏F1分数,降低了COVID-19检测的误报率。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking GANs, Diffusion Models, and Flow Matching for T1w-to-T2w MRI Translation
Authors:Andrea Moschetto, Lemuel Puglisi, Alec Sargood, Pierluigi Dell’Acqua, Francesco Guarnera, Sebastiano Battiato, Daniele Ravì
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) enables the acquisition of multiple image contrasts, such as T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) scans, each offering distinct diagnostic insights. However, acquiring all desired modalities increases scan time and cost, motivating research into computational methods for cross-modal synthesis. To address this, recent approaches aim to synthesize missing MRI contrasts from those already acquired, reducing acquisition time while preserving diagnostic quality. Image-to-image (I2I) translation provides a promising framework for this task. In this paper, we present a comprehensive benchmark of generative models$\unicode{x2013}$specifically, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), diffusion models, and flow matching (FM) techniques$\unicode{x2013}$for T1w-to-T2w 2D MRI I2I translation. All frameworks are implemented with comparable settings and evaluated on three publicly available MRI datasets of healthy adults. Our quantitative and qualitative analyses show that the GAN-based Pix2Pix model outperforms diffusion and FM-based methods in terms of structural fidelity, image quality, and computational efficiency. Consistent with existing literature, these results suggest that flow-based models are prone to overfitting on small datasets and simpler tasks, and may require more data to match or surpass GAN performance. These findings offer practical guidance for deploying I2I translation techniques in real-world MRI workflows and highlight promising directions for future research in cross-modal medical image synthesis. Code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/AndreaMoschetto/medical-I2I-benchmark.
磁共振成像(MRI)能够获取多种图像对比,如T1加权(T1w)和T2加权(T2w)扫描,每种对比都提供独特的诊断见解。然而,获取所有想要的模态会增加扫描时间和成本,这促使研究人员研究跨模态合成计算的方法。为解决这一问题,近期的方法旨在从已获取的图像中合成缺失的MRI对比,缩短采集时间同时保留诊断质量。图像到图像(I2I)转换为此任务提供了一个有前途的框架。在本文中,我们对生成模型——特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)、扩散模型和流匹配(FM)技术——进行了全面的基准测试,用于T1w到T2w的2DMRI I2I转换。所有框架都在相似的设置下实现,并在三个公开的成人MRI数据集上进行评估。我们的定量和定性分析表明,基于GAN的Pix2Pix模型在结构保真度、图像质量和计算效率方面优于扩散和FM方法。与现有文献一致,这些结果表明基于流的模型易于在小数据集和简单任务上过度拟合,可能需要更多数据才能匹配或超越GAN的性能。这些发现提供了在实际MRI工作流程中部署I2I转换技术的实用指导,并突出了跨模态医学图像合成的未来研究方向。相关代码和模型已公开在:https://github.com/AndreaMoschetto/medical-I2I-benchmark。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的二维磁共振成像(MRI)图像转换技术。研究对三种生成模型(包括GAN、扩散模型和流匹配技术)进行了基准测试评估,用于将T1加权图像转换为T2加权图像。实验结果表明,Pix2Pix模型在结构保真度、图像质量和计算效率方面表现优于其他方法。该研究为在实际MRI工作流程中部署图像到图像(I2I)转换技术提供了实用指导,并指出了未来跨模态医学图像合成研究的前景方向。
Key Takeaways
- 本文对多种生成模型进行了基准测试评估,以研究二维磁共振成像(MRI)中的图像转换技术。
- 研究关注于将T1加权图像转换为T2加权图像,旨在减少扫描时间和成本。
- GAN的Pix2Pix模型在结构保真度、图像质量和计算效率方面表现优越。
- 流匹配模型在小数据集和简单任务上容易出现过拟合问题。
- 研究结果提供了在实际MRI工作流程中部署I2I转换技术的实用指导。
点此查看论文截图

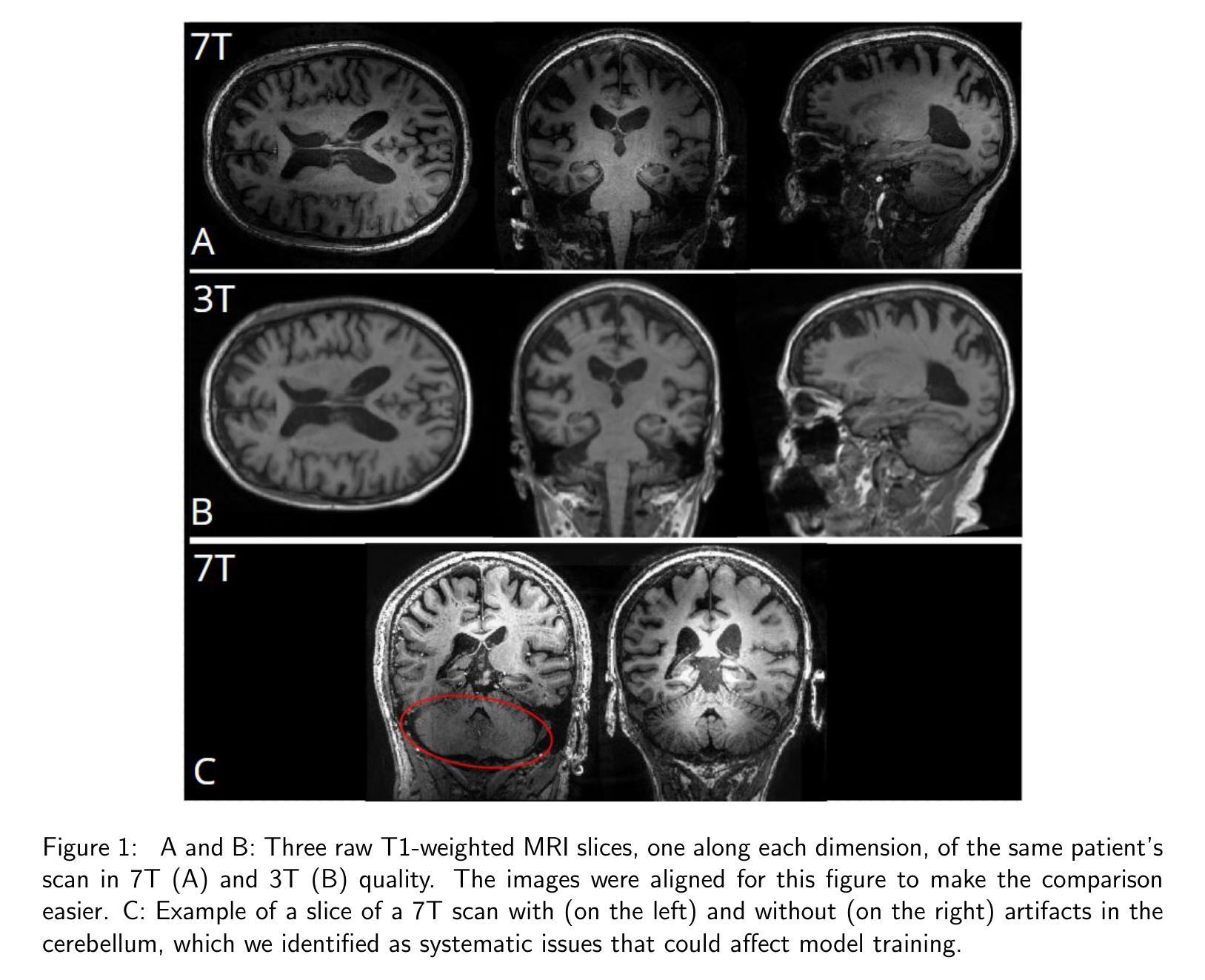
Converting T1-weighted MRI from 3T to 7T quality using deep learning
Authors:Malo Gicquel, Ruoyi Zhao, Anika Wuestefeld, Nicola Spotorno, Olof Strandberg, Kalle Åström, Yu Xiao, Laura EM Wisse, Danielle van Westen, Rik Ossenkoppele, Niklas Mattsson-Carlgren, David Berron, Oskar Hansson, Gabrielle Flood, Jacob Vogel
Ultra-high resolution 7 tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed anatomical views, offering better signal-to-noise ratio, resolution and tissue contrast than 3T MRI, though at the cost of accessibility. We present an advanced deep learning model for synthesizing 7T brain MRI from 3T brain MRI. Paired 7T and 3T T1-weighted images were acquired from 172 participants (124 cognitively unimpaired, 48 impaired) from the Swedish BioFINDER-2 study. To synthesize 7T MRI from 3T images, we trained two models: a specialized U-Net, and a U-Net integrated with a generative adversarial network (GAN U-Net). Our models outperformed two additional state-of-the-art 3T-to-7T models in image-based evaluation metrics. Four blinded MRI professionals judged our synthetic 7T images as comparable in detail to real 7T images, and superior in subjective visual quality to 7T images, apparently due to the reduction of artifacts. Importantly, automated segmentations of the amygdalae of synthetic GAN U-Net 7T images were more similar to manually segmented amygdalae (n=20), than automated segmentations from the 3T images that were used to synthesize the 7T images. Finally, synthetic 7T images showed similar performance to real 3T images in downstream prediction of cognitive status using MRI derivatives (n=3,168). In all, we show that synthetic T1-weighted brain images approaching 7T quality can be generated from 3T images, which may improve image quality and segmentation, without compromising performance in downstream tasks. Future directions, possible clinical use cases, and limitations are discussed.
超高分辨率7特斯拉(7T)磁共振成像(MRI)提供了详细的解剖视图,相较于3T MRI,其拥有更好的信噪比、分辨率和组织对比度。然而,这一切是以可及性作为代价的。我们提出了一种先进的深度学习模型,能够从3T大脑MRI合成7T大脑MRI。我们从瑞典BioFINDER-2研究中获得了配对的7T和3TT1加权图像,共涉及参与者172人(其中认知功能正常者124人,受损者48人)。为了从3T图像合成7T MRI,我们训练了两种模型:一种专用的U-Net模型,以及结合了生成对抗网络(GAN U-Net)的U-Net模型。我们的模型在基于图像的评价指标上表现优于其他两种先进的3T到7T的模型。四名盲态MRI专业人士认为我们的合成7T图像与真实7T图像在细节上具有可比较性,在主观视觉质量上优于真实7T图像,显然是因为伪影的减少。值得注意的是,合成GAN U-Net 7T图像的杏仁核自动化分割与手动分割的杏仁核更为相似(n=20),相较于用于合成7T图像的原始3T图像自动化分割结果更为准确。此外,合成7T图像在利用MRI衍生的下游认知状态预测任务中表现出了与真实3T图像相似的性能(n=3,168)。总之,我们证明了从3T图像可以生成接近7T质量的合成T1加权大脑图像,这可以提高图像质量和分割效果,同时不会损害下游任务的性能。我们还讨论了未来方向、可能的临床应用场景和局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用深度学习模型,特别是结合了生成对抗网络(GAN)的U-Net模型,成功从3T MRI合成7T MRI图像。合成图像在细节和主观视觉质量上表现出优越性,且在下游任务中表现良好,有望改善图像质量和分割效果,同时不损害下游任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- 利用先进的深度学习模型成功合成接近7T分辨率的脑MRI图像。
- 合成图像在细节和主观视觉质量上优于真实7T图像。
- 合成图像减少了伪影,提高了图像质量。
- 合成图像的杏仁核自动化分割结果与手动分割结果更为相似。
- 合成7T图像在下游任务(如认知状态预测)中的表现与真实3T图像相似。
- 该技术可能在不损害下游任务性能的情况下改善图像质量和分割效果。
点此查看论文截图

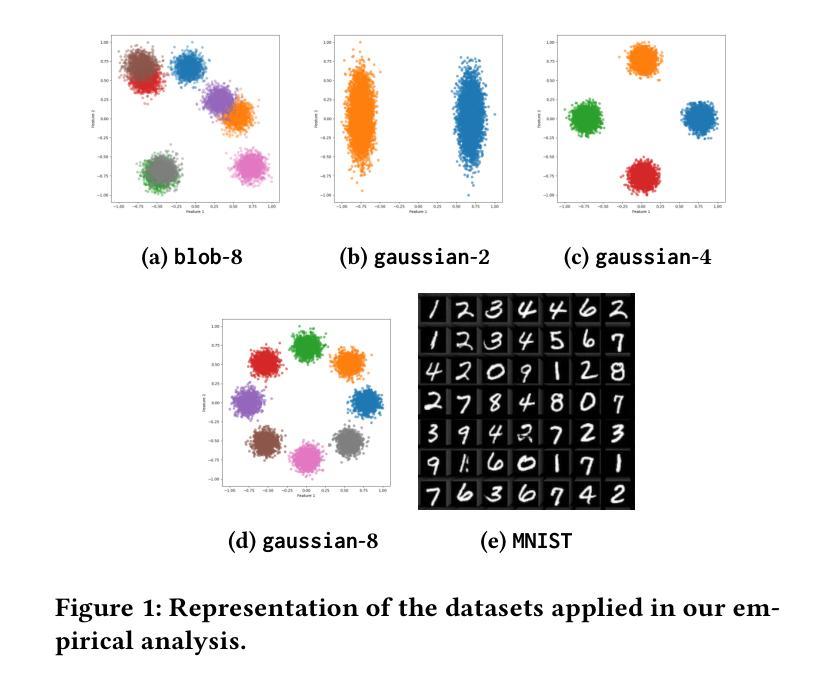
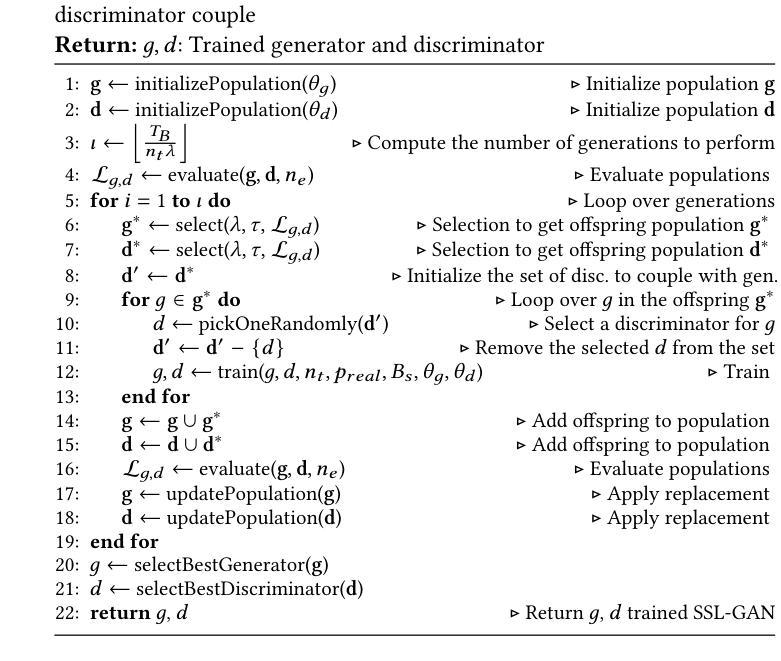
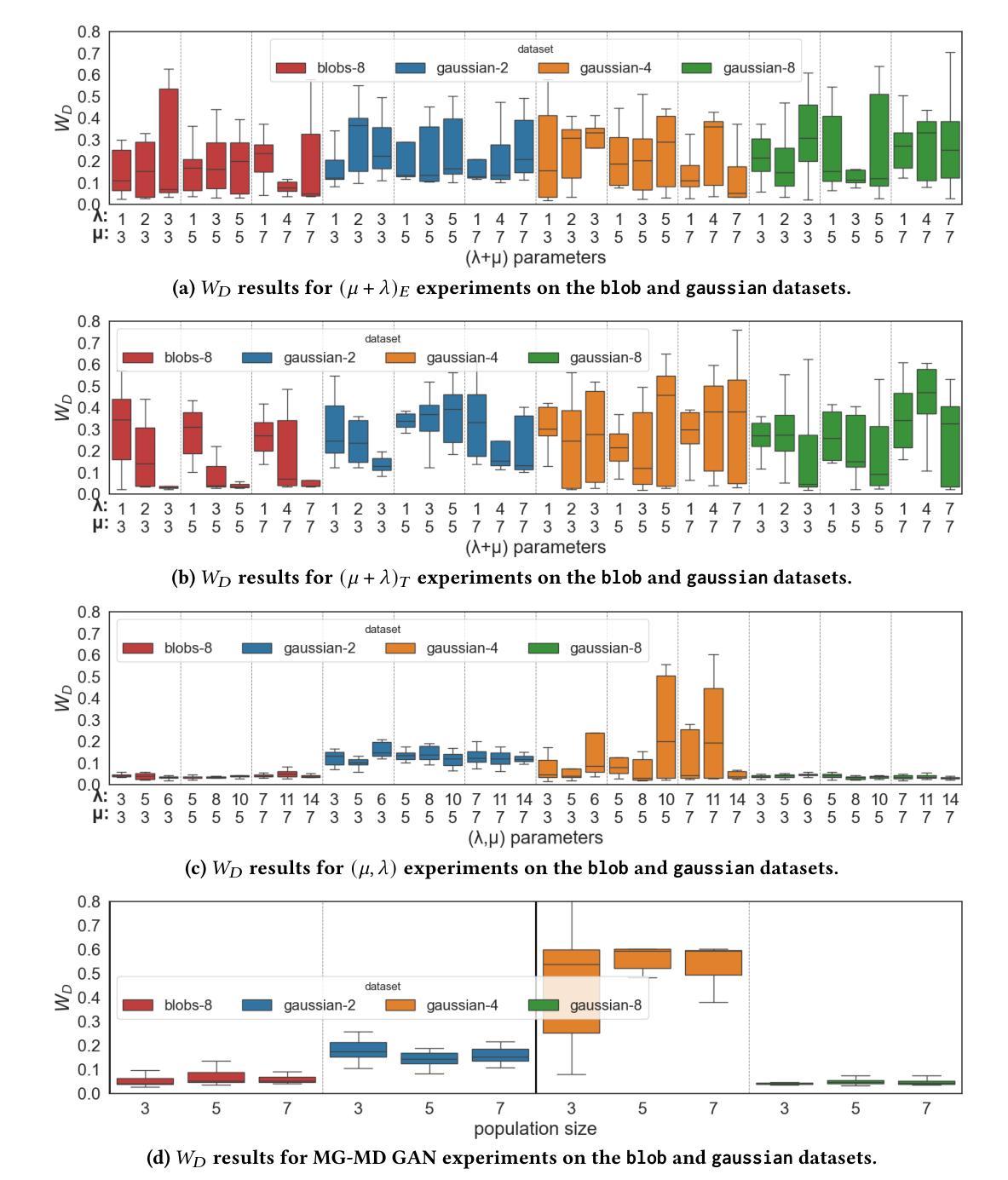
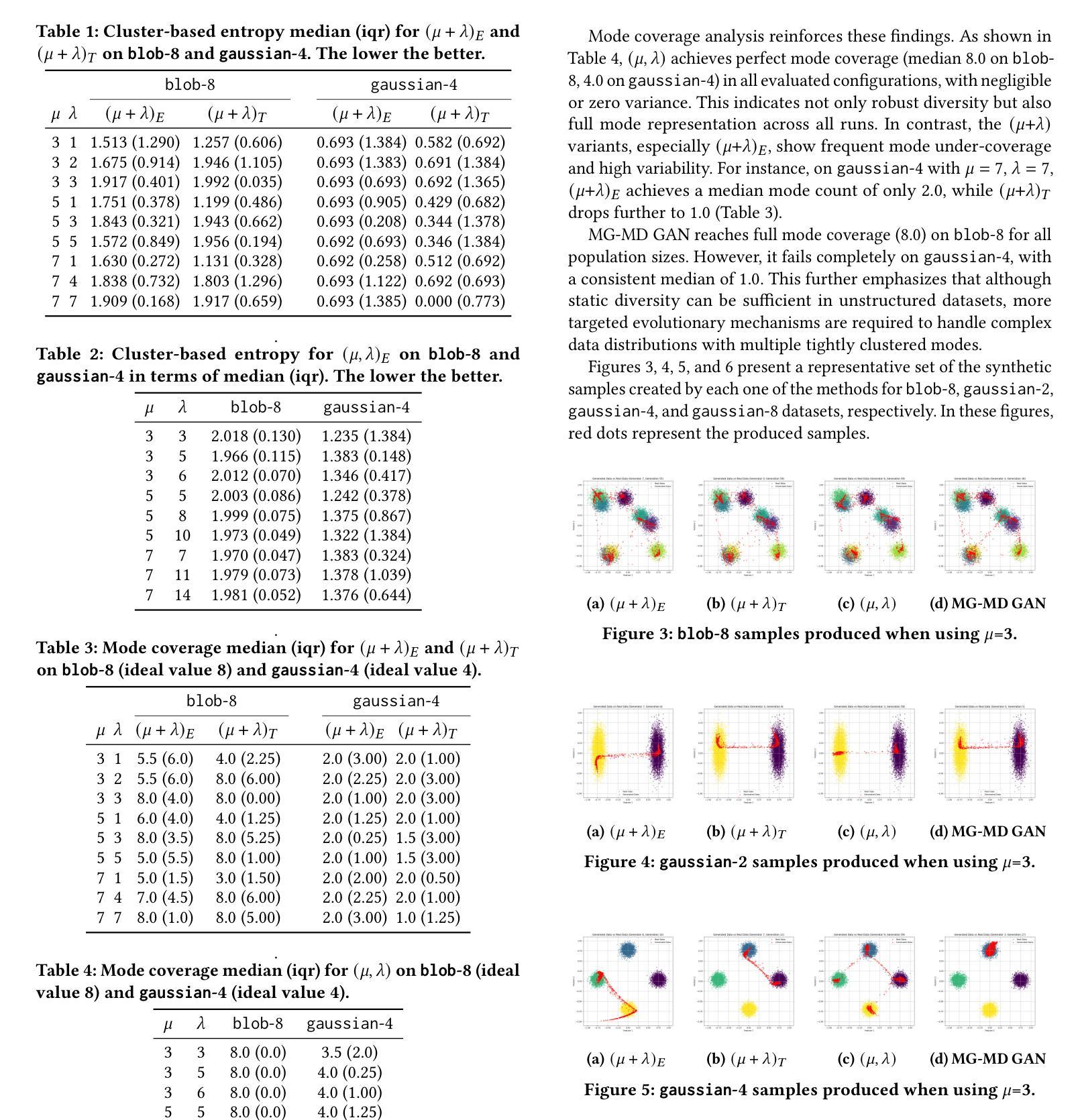
Multi-population GAN Training: Analyzing Co-Evolutionary Algorithms
Authors:Walter P. Casas, Jamal Toutouh
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are powerful generative models but remain challenging to train due to pathologies suchas mode collapse and instability. Recent research has explored co-evolutionary approaches, in which populations of generators and discriminators are evolved, as a promising solution. This paper presents an empirical analysis of different coevolutionary GAN training strategies, focusing on the impact of selection and replacement mechanisms. We compare (mu,lambda), (mu+lambda) with elitism, and (mu+lambda) with tournament selection coevolutionary schemes, along with a non-evolutionary population based multi-generator multi-discriminator GAN baseline, across both synthetic low-dimensional datasets (blob and gaussian mixtures) and an image-based benchmark (MNIST). Results show that full generational replacement, i.e., (mu,lambda), consistently outperforms in terms of both sample quality and diversity, particularly when combined with larger offspring sizes. In contrast, elitist approaches tend to converge prematurely and suffer from reduced diversity. These findings highlight the importance of balancing exploration and exploitation dynamics in coevolutionary GAN training and provide guidance for designing more effective population-based generative models.
生成对抗网络(GANs)是一种强大的生成模型,但由于模式崩溃和不稳定等病理问题,其训练仍然具有挑战性。最近的研究探索了协同进化方法,其中生成器和鉴别器的种群被共同进化,作为一种前景广阔的解决方案。本文对不同协同进化GAN训练策略进行了实证分析,重点研究了选择机制和替换机制的影响。我们比较了(mu,lambda)、(mu+lambda)精英主义和(mu+lambda)锦标赛选拔协同进化方案,以及基于非进化种群的多生成器多鉴别器GAN基线,既包括合成低维数据集(blob和高斯混合)也包括基于图像的基准测试(MNIST)。结果表明,完全的世代更替,即(mu,lambda),在样本质量和多样性方面始终表现更好,尤其是与更大的后代规模相结合时。相比之下,精英主义方法往往过早收敛,且多样性降低。这些发现强调了平衡协同进化GAN训练中的探索和利用动态的重要性,并为设计更有效的基于种群的生成模型提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO ‘25 Companion), July 14–18, 2025, Malaga, Spain
Summary
本文探讨了生成对抗网络(GANs)的训练策略,特别是共进化方法中的选择机制和替代机制对GAN训练的影响。通过对不同共进化GAN训练策略进行实证研究,包括(mu,lambda)、(mu+lambda)精英主义和(mu+lambda)锦标赛选拔等方案,以及基于非进化种群的多生成器多鉴别器GAN基线,在合成低维数据集(blob和高斯混合)和图像基准测试集(MNIST)上的表现。结果显示,完全世代替代策略(即(mu,lambda))在样本质量和多样性方面表现优越,尤其是结合较大的子代规模时表现更好。相比之下,精英策略趋于过早收敛并表现出较低的多样性。这些发现强调了平衡探索和利用动力学在共进化GAN训练中的重要性,并为设计更有效的基于种群的生成模型提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)的训练存在模式崩溃和不稳定等问题。
- 共进化方法是一种有前景的解决策略,涉及生成器和鉴别器的种群演化。
- 实证分析了不同共进化GAN训练策略,重点研究了选择机制和替代机制的影响。
- 完全世代替代策略(mu,lambda)在样本质量和多样性方面表现优越。
- 精英策略可能过早收敛并表现出较低的多样性。
- 平衡探索和利用动力学在共进化GAN训练中至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

fastWDM3D: Fast and Accurate 3D Healthy Tissue Inpainting
Authors:Alicia Durrer, Florentin Bieder, Paul Friedrich, Bjoern Menze, Philippe C. Cattin, Florian Kofler
Healthy tissue inpainting has significant applications, including the generation of pseudo-healthy baselines for tumor growth models and the facilitation of image registration. In previous editions of the BraTS Local Synthesis of Healthy Brain Tissue via Inpainting Challenge, denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) demonstrated qualitatively convincing results but suffered from low sampling speed. To mitigate this limitation, we adapted a 2D image generation approach, combining DDPMs with generative adversarial networks (GANs) and employing a variance-preserving noise schedule, for the task of 3D inpainting. Our experiments showed that the variance-preserving noise schedule and the selected reconstruction losses can be effectively utilized for high-quality 3D inpainting in a few time steps without requiring adversarial training. We applied our findings to a different architecture, a 3D wavelet diffusion model (WDM3D) that does not include a GAN component. The resulting model, denoted as fastWDM3D, obtained a SSIM of 0.8571, a MSE of 0.0079, and a PSNR of 22.26 on the BraTS inpainting test set. Remarkably, it achieved these scores using only two time steps, completing the 3D inpainting process in 1.81 s per image. When compared to other DDPMs used for healthy brain tissue inpainting, our model is up to 800 x faster while still achieving superior performance metrics. Our proposed method, fastWDM3D, represents a promising approach for fast and accurate healthy tissue inpainting. Our code is available at https://github.com/AliciaDurrer/fastWDM3D.
健康组织的补全技术拥有众多重要应用,包括为肿瘤增长模型生成伪健康基准线以及促进图像配准。在之前举办的Brain Tumor Segmentation using GAN(基于GAN的脑肿瘤分割挑战赛)中,降噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)在定性评估上取得了令人信服的结果,但采样速度较慢。为了缓解这一局限性,我们采用了二维图像生成方法,结合了DDPM与生成对抗网络(GAN),并使用保方差噪声调度方案,用于三维补全任务。我们的实验表明,保方差噪声调度方案和所选的重建损失可以在几个时间步骤内有效地用于高质量的三维补全,无需对抗训练。我们将发现应用于不同的架构——三维小波扩散模型(WDM3D),不包括GAN组件。因此得到的模型,被称为fastWDM3D,在BraTS补全测试集上取得了结构相似性度量(SSIM)为0.8571、均方误差(MSE)为0.0079以及峰值信噪比(PSNR)为22.26的成绩。值得注意的是,它仅使用两个时间步骤就取得了这些成绩,完成三维补全过程的每张图像仅需1.81秒。与其他用于健康脑组织补全的DDPM模型相比,我们的模型速度提高了高达800倍,同时仍实现了卓越的性能指标。我们提出的fastWDM3D方法代表着一种快速准确健康组织补全的很有前途的方法。我们的代码位于https://github.com/AliciaDurrer/fastWDM3D。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Philippe C. Cattin and Florian Kofler: equal contribution
Summary
在BraTS健康脑组织合成挑战中,为了加快3D补全速度,研究者结合去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和生成对抗网络(GANs),并运用保方差噪声时间表进行有效改进。实验结果证明了该方法的高效性,同时提出了应用于不含GAN组件的3D小波扩散模型(WDM3D)的新架构。新的模型称为fastWDM3D,使用仅两步时间即可实现高质量3D补全,且在BraTS补全测试集上实现了SSIM 0.8571、MSE 0.0079及PSNR 22.26的得分,每图像仅需1.81秒完成补全。与其他用于健康脑组织补全的DDPMs相比,该模型速度提高了高达800倍,同时性能卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 研究者针对健康组织补全任务,特别是在肿瘤生长模型和图像注册中生成伪健康基线应用的重要性进行了探讨。
- 针对之前DDPMs在补全任务中的低采样速度问题,研究者结合了DDPMs和GANs,并采用保方差噪声时间表进行改进。
- 实验证明保方差噪声时间表及所选重建损失可有效用于高质量3D补全,且仅需要少数时间步骤。
- 研究者将该方法应用于不含GAN组件的3D小波扩散模型(WDM3D),提出名为fastWDM3D的新模型架构。
- fastWDM3D模型在BraTS补全测试集上实现了较高的SSIM、MSE和PSNR得分,显示出其优越性能。
- 与其他DDPMs相比,fastWDM3D模型速度显著提高,达到800倍的速度提升。
点此查看论文截图

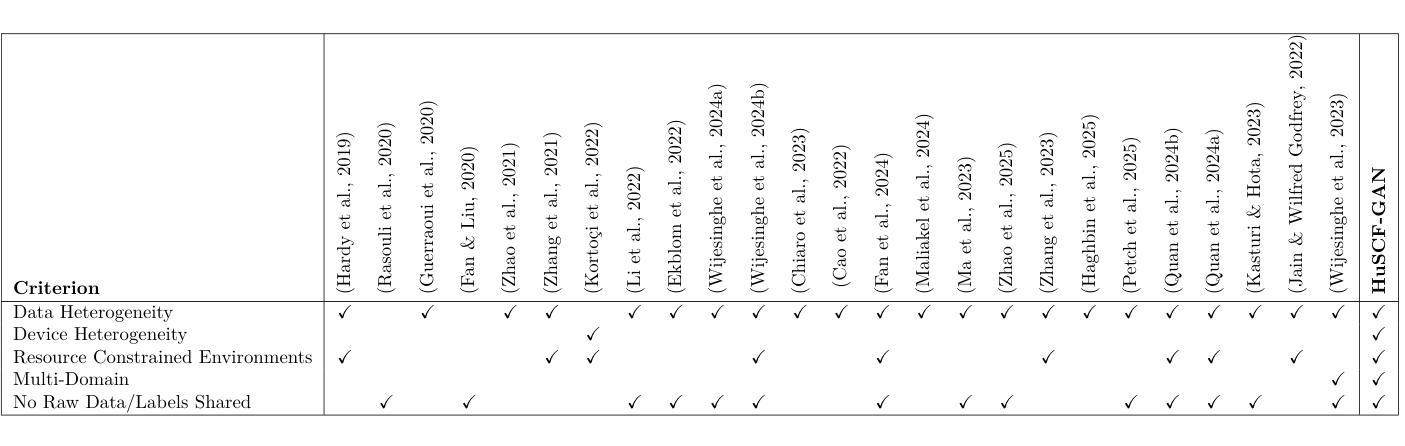
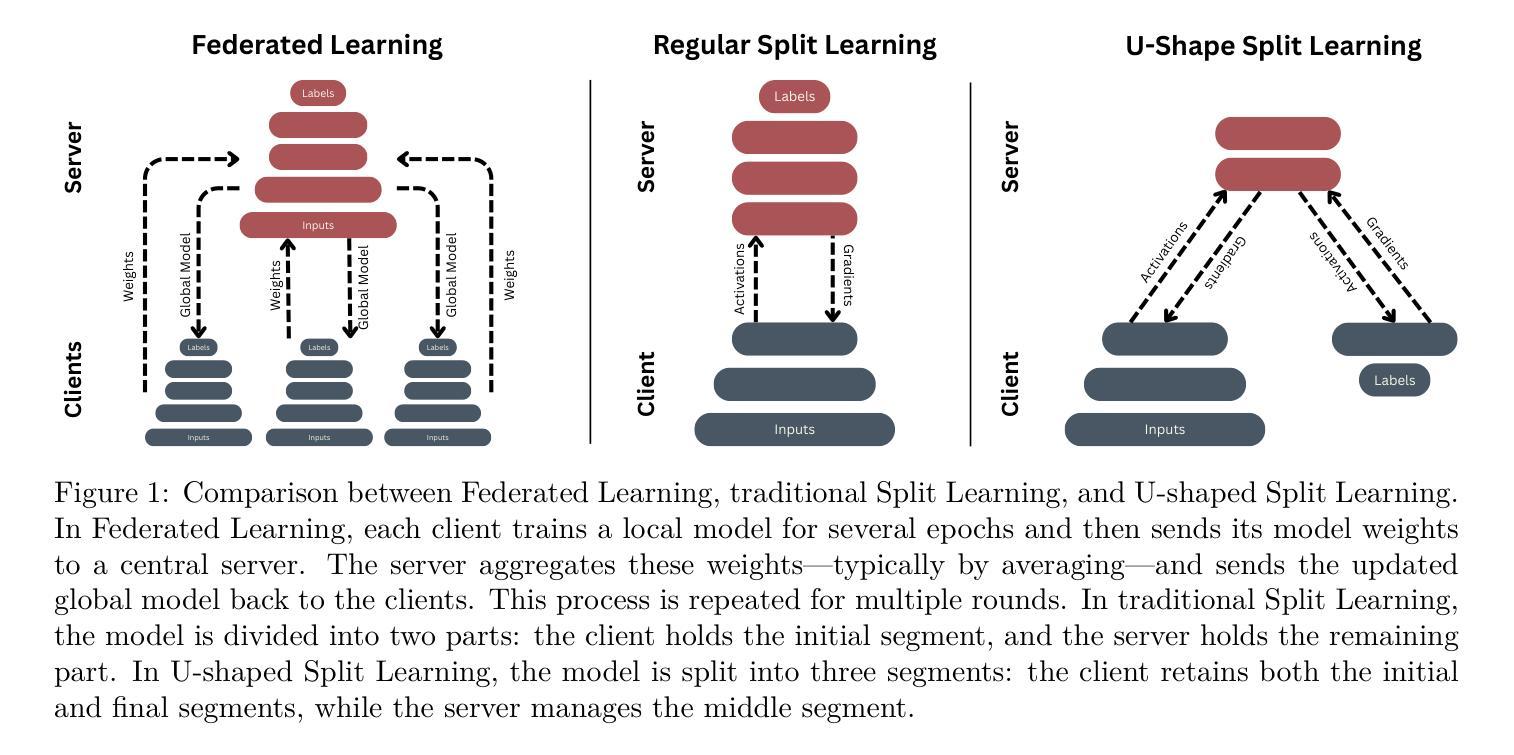
A Distributed Generative AI Approach for Heterogeneous Multi-Domain Environments under Data Sharing constraints
Authors:Youssef Tawfilis, Hossam Amer, Minar El-Aasser, Tallal Elshabrawy
Federated Learning has gained increasing attention for its ability to enable multiple nodes to collaboratively train machine learning models without sharing their raw data. At the same time, Generative AI – particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) – have achieved remarkable success across a wide range of domains, such as healthcare, security, and Image Generation. However, training generative models typically requires large datasets and significant computational resources, which are often unavailable in real-world settings. Acquiring such resources can be costly and inefficient, especially when many underutilized devices – such as IoT devices and edge devices – with varying capabilities remain idle. Moreover, obtaining large datasets is challenging due to privacy concerns and copyright restrictions, as most devices are unwilling to share their data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach for decentralized GAN training that enables the utilization of distributed data and underutilized, low-capability devices while not sharing data in its raw form. Our approach is designed to tackle key challenges in decentralized environments, combining KLD-weighted Clustered Federated Learning to address the issues of data heterogeneity and multi-domain datasets, with Heterogeneous U-Shaped split learning to tackle the challenge of device heterogeneity under strict data sharing constraints – ensuring that no labels or raw data, whether real or synthetic, are ever shared between nodes. Experimental results shows that our approach demonstrates consistent and significant improvements across key performance metrics, where it achieves 1.1x – 2.2x higher image generation scores, an average 10% boost in classification metrics (up to 50% in multi-domain non-IID settings), in much lower latency compared to several benchmarks. Find our code at https://github.com/youssefga28/HuSCF-GAN.
联邦学习因其能够使多个节点在不共享原始数据的情况下协同训练机器学习模型的能力而受到越来越多的关注。与此同时,生成式人工智能——特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)在医疗保健、安全、图像生成等多个领域取得了显著的成就。然而,训练生成模型通常需要大量的数据集和计算资源,这在现实世界中往往无法获得。获取此类资源可能成本高昂且效率低下,尤其是当许多使用不足的设备(如物联网设备和边缘设备)具有不同的能力并保持闲置状态时。此外,由于隐私担忧和版权限制,获得大量数据集具有挑战性,因为大多数设备不愿意共享其数据。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的分布式GAN训练方法,该方法能够在不共享数据原始形式的情况下利用分布式数据和利用不足的低端设备。我们的方法旨在解决分布式环境中的关键挑战,结合KLD加权聚类联邦学习来解决数据异质性和多域数据集的问题,以及异质U形分割学习来解决严格数据共享约束下的设备异质性的挑战——确保节点之间不共享任何真实或合成的标签或原始数据。实验结果表明,我们的方法在关键性能指标上表现出持续而显著的改进,其中图像生成得分提高了1.1倍至2.2倍,分类指标平均提高了10%(在多域非独立同分布设置中最高可达50%),并且延迟时间更低,超过了多个基准测试。您可以在https://github.com/youssefga28/HuSCF-GAN找到我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于联邦学习的方法实现了无需分享原始数据的多个节点协同训练机器学习模型的能力。针对生成式人工智能(特别是生成对抗网络GANs)训练需要大量数据和计算资源的问题,提出了一种新型的去中心化GAN训练方法。该方法能够在不分享原始数据的前提下,利用分散的数据和闲置的低性能设备。该方法通过KLD加权聚类联邦学习解决数据多样性和多域数据集问题,通过异质U型分割学习解决设备差异性的严格数据共享约束问题。实验结果显示,该方法在关键性能指标上持续且显著提高,图像生成分数提高1.1倍至2.2倍,分类指标平均提升10%(在多域非独立同分布环境中最高提升50%),且延迟更低。相关代码可通过https://github.com/youssefga28/HuSCF-GAN 获取。
关键收获点
- 联邦学习可以允许多个节点协同训练机器学习模型而不直接分享原始数据。
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)在各个领域(如医疗、安全、图像生成等)取得了显著的成功。
- GAN训练需要大量的数据集和计算资源,这在现实世界中是一大挑战。
- 利用闲置的低性能设备(如物联网设备和边缘设备)可以有助于解决资源不足的问题。
- 提出了一种新型的去中心化GAN训练方法,可以在不分享原始数据的情况下利用分散的数据和这些设备。
- 该方法结合了KLD加权聚类联邦学习和异质U型分割学习,以处理数据多样性和设备差异问题。
点此查看论文截图

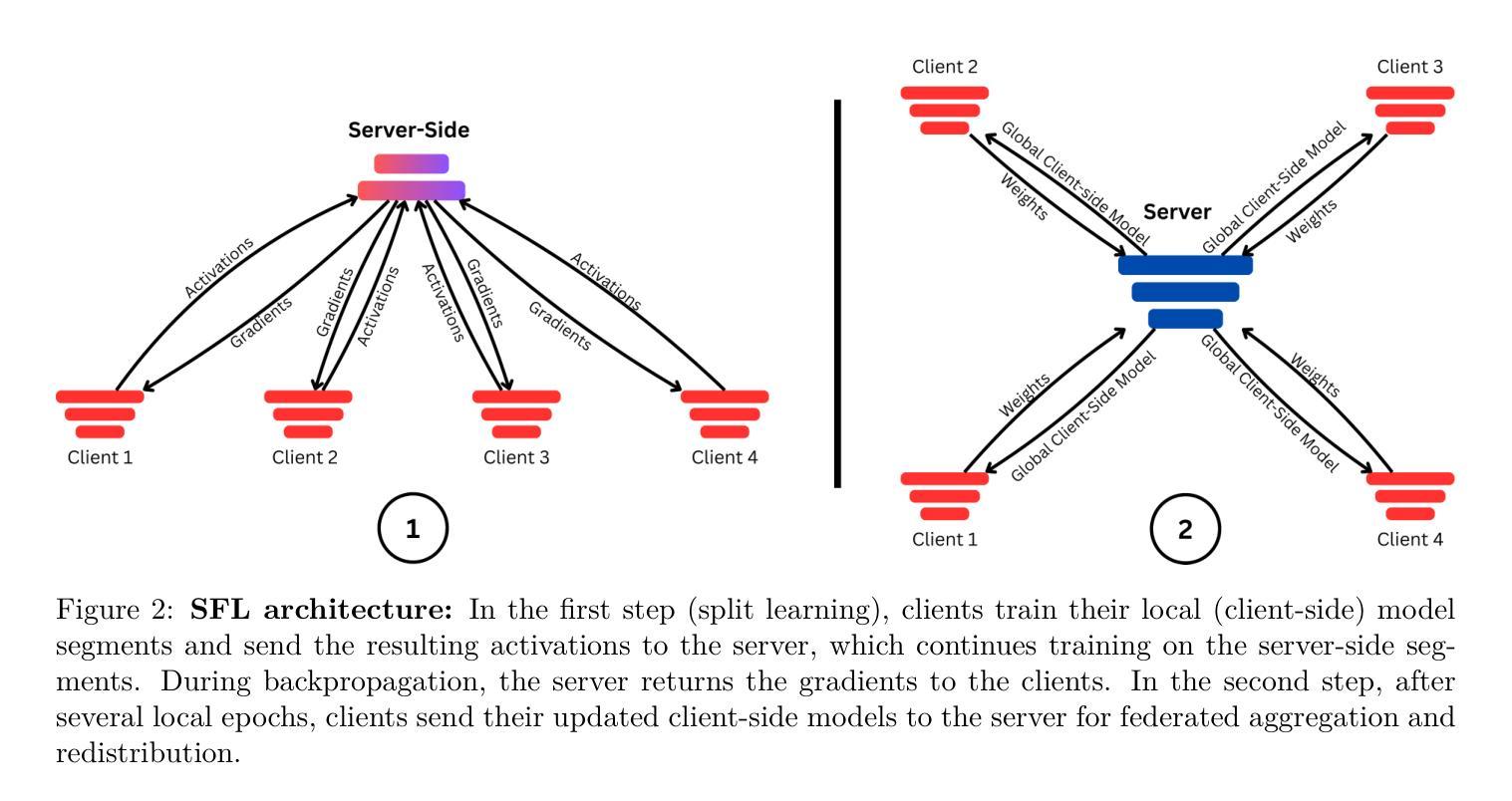
Pixel Perfect MegaMed: A Megapixel-Scale Vision-Language Foundation Model for Generating High Resolution Medical Images
Authors:Zahra TehraniNasab, Amar Kumar, Tal Arbel
Medical image synthesis presents unique challenges due to the inherent complexity and high-resolution details required in clinical contexts. Traditional generative architectures such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Auto Encoder (VAEs) have shown great promise for high-resolution image generation but struggle with preserving fine-grained details that are key for accurate diagnosis. To address this issue, we introduce Pixel Perfect MegaMed, the first vision-language foundation model to synthesize images at resolutions of 1024x1024. Our method deploys a multi-scale transformer architecture designed specifically for ultra-high resolution medical image generation, enabling the preservation of both global anatomical context and local image-level details. By leveraging vision-language alignment techniques tailored to medical terminology and imaging modalities, Pixel Perfect MegaMed bridges the gap between textual descriptions and visual representations at unprecedented resolution levels. We apply our model to the CheXpert dataset and demonstrate its ability to generate clinically faithful chest X-rays from text prompts. Beyond visual quality, these high-resolution synthetic images prove valuable for downstream tasks such as classification, showing measurable performance gains when used for data augmentation, particularly in low-data regimes. Our code is accessible through the project website - https://tehraninasab.github.io/pixelperfect-megamed.
医学影像合成因其固有的复杂性和临床环境中所需的高分辨率细节而面临独特的挑战。传统的生成架构,如生成对抗网络(GANs)或变分自动编码器(VAEs),在高分辨率图像生成方面展现出巨大潜力,但在保留对于准确诊断至关重要的细微细节方面存在困难。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了Pixel Perfect MegaMed,它是第一个能够在1024x1024分辨率下合成图像的视觉语言基础模型。我们的方法采用专门用于超高分辨率医学影像生成的多尺度变压器架构,能够同时保留全局解剖上下文和局部图像级细节。通过利用针对医学术语和成像模式定制的视觉语言对齐技术,Pixel Perfect MegaMed在前所未有的高分辨率水平上搭建了文本描述和视觉表示之间的桥梁。我们将其模型应用于CheXpert数据集,并展示了其根据文本提示生成临床真实感胸部X射线的能力。除了视觉质量外,这些高分辨率合成图像对于下游任务(如分类)也证明是有价值的,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下,用于数据增强时显示出可衡量的性能提升。我们的代码可通过项目网站访问:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代Pixel Perfect MegaMed模型通过结合多尺度transformer架构和医学术语的视力语言对齐技术,实现了超分辨率的医学图像合成。该模型在CheXpert数据集上生成逼真的胸部X光片,并证明其在数据增强方面的价值,特别是在低数据场景下。
Key Takeaways
- Pixel Perfect MegaMed是首个用于合成超分辨率医学图像的视觉语言基础模型。
- 该模型采用多尺度transformer架构,旨在生成超高分辨率医学图像。
- 模型能够保留全局解剖结构和局部图像级别的细节信息。
- 通过针对医学术语和成像模式的视力语言对齐技术,Pixel Perfect MegaMed实现了文本描述和视觉表示之间的无缝连接。
- 在CheXpert数据集上应用模型,成功生成基于文本提示的临床真实胸部X光片。
- 高分辨率合成图像不仅具有视觉质量,而且对于下游任务(如分类)也证明其价值。
点此查看论文截图

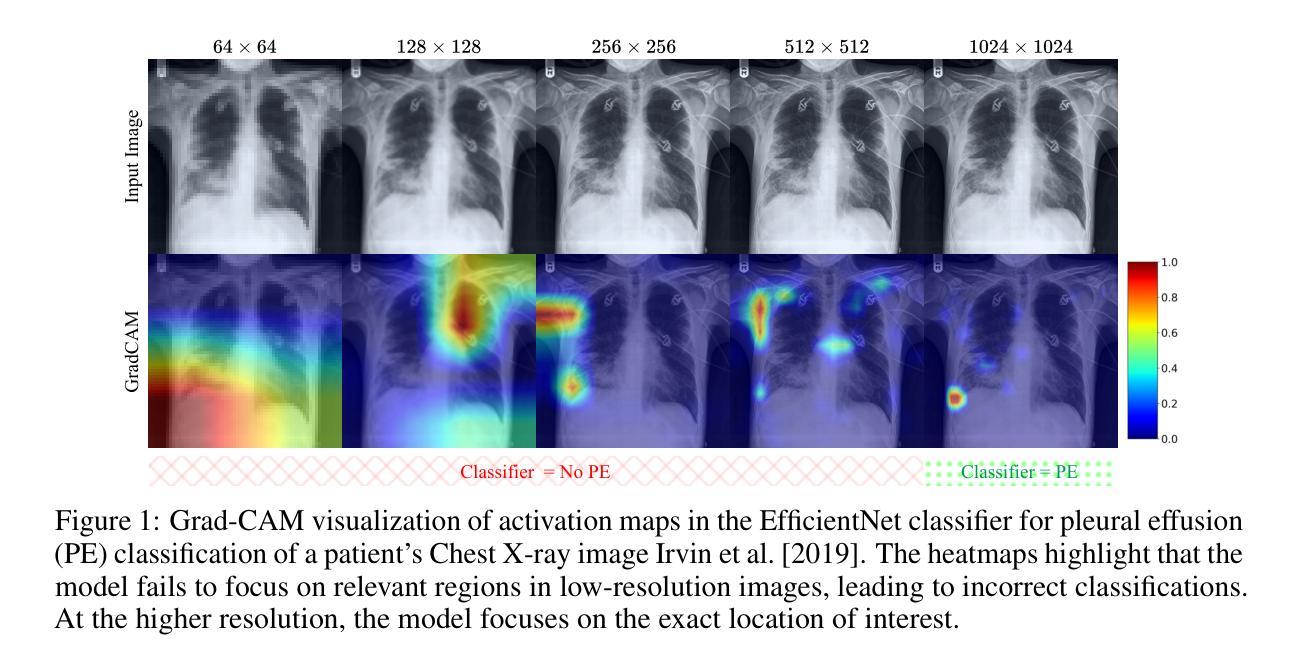
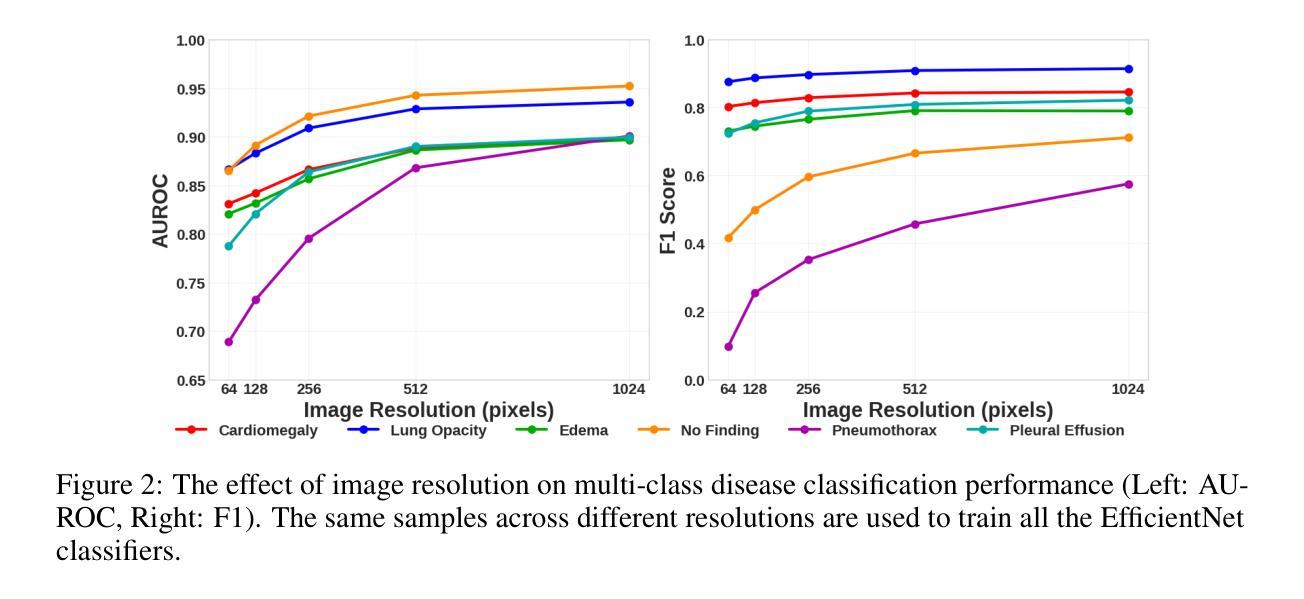
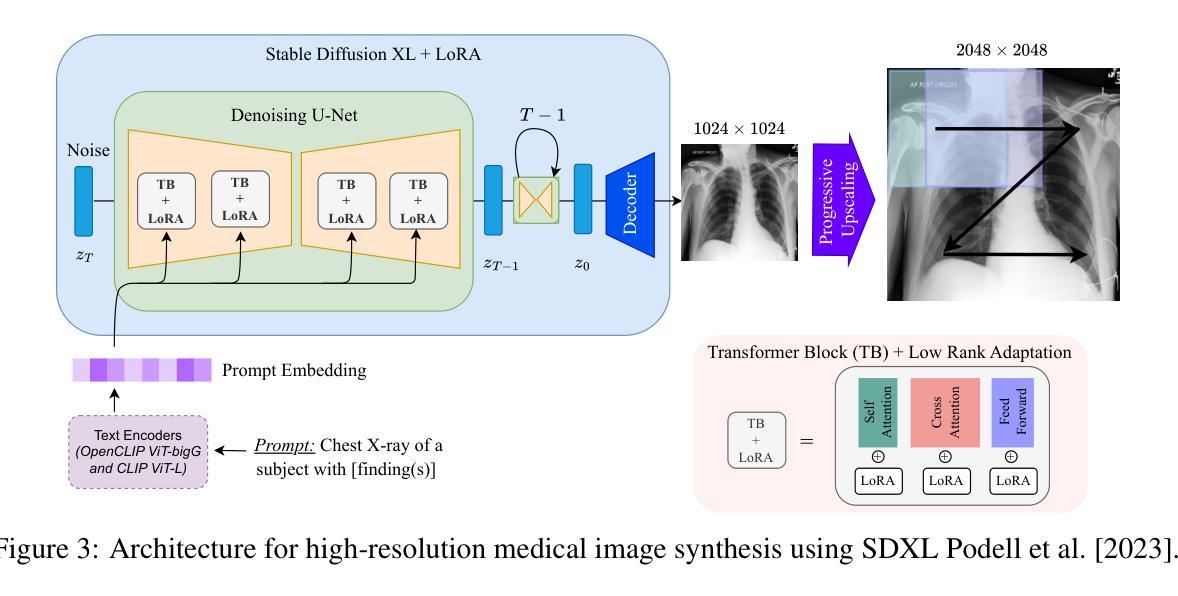
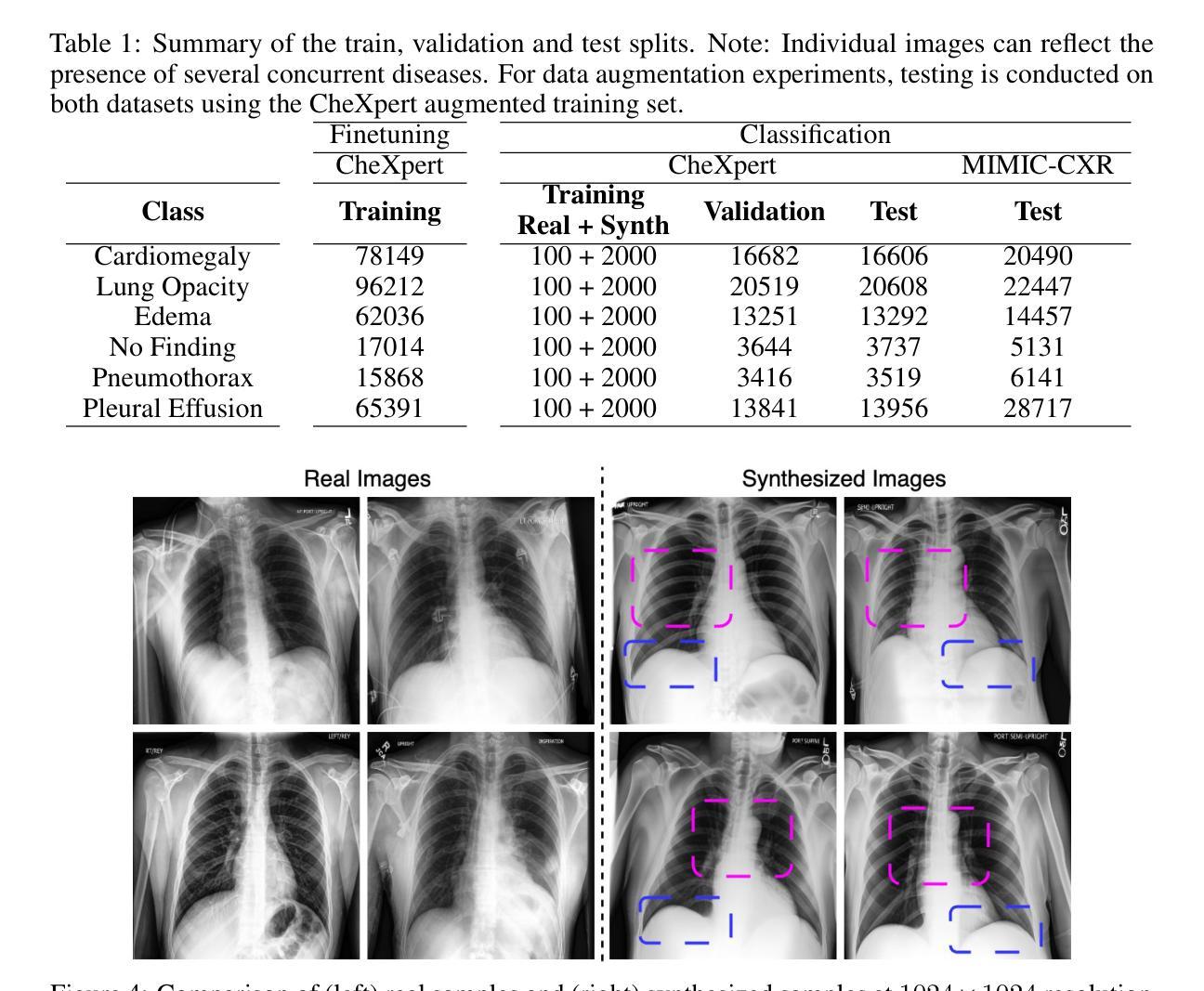
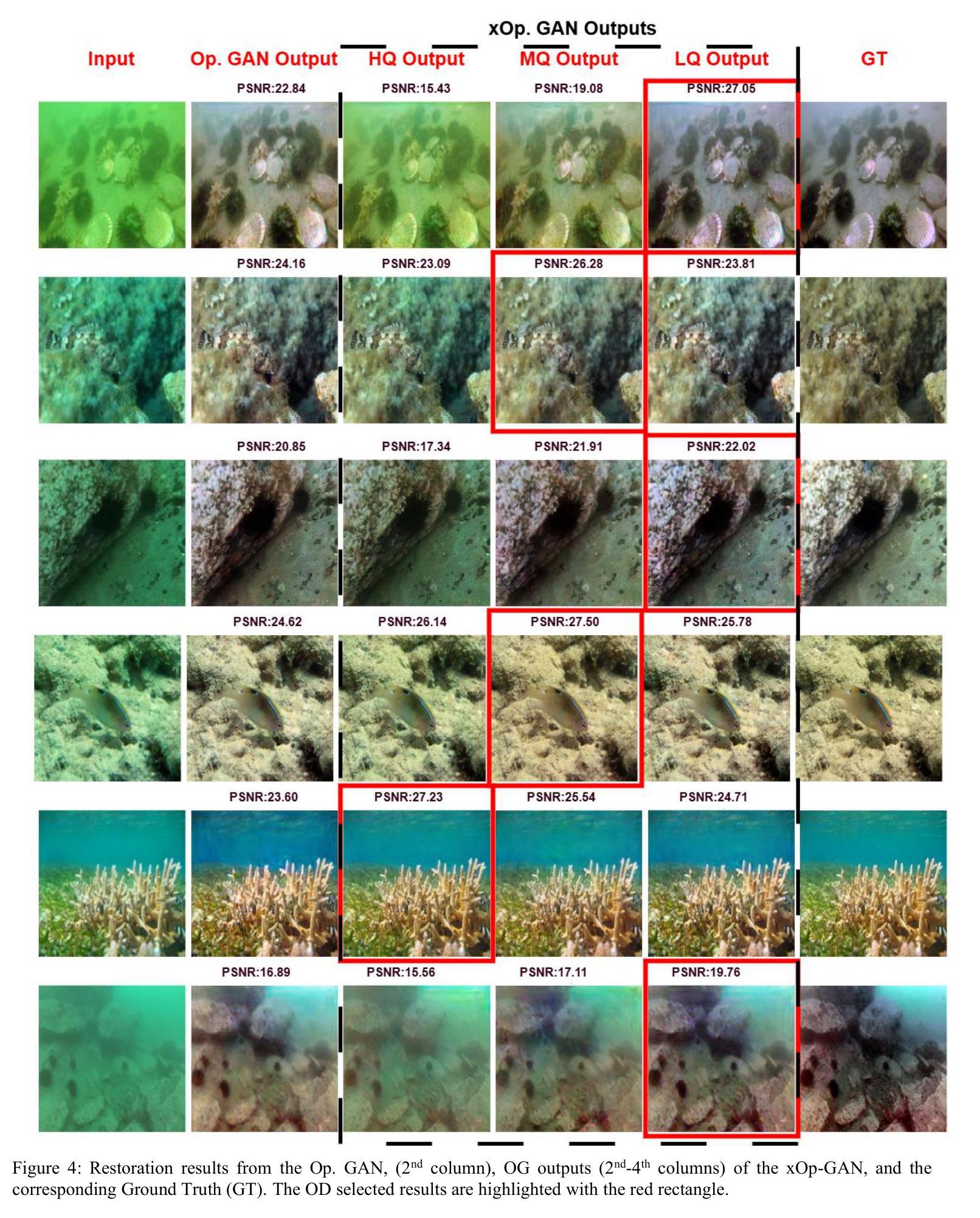
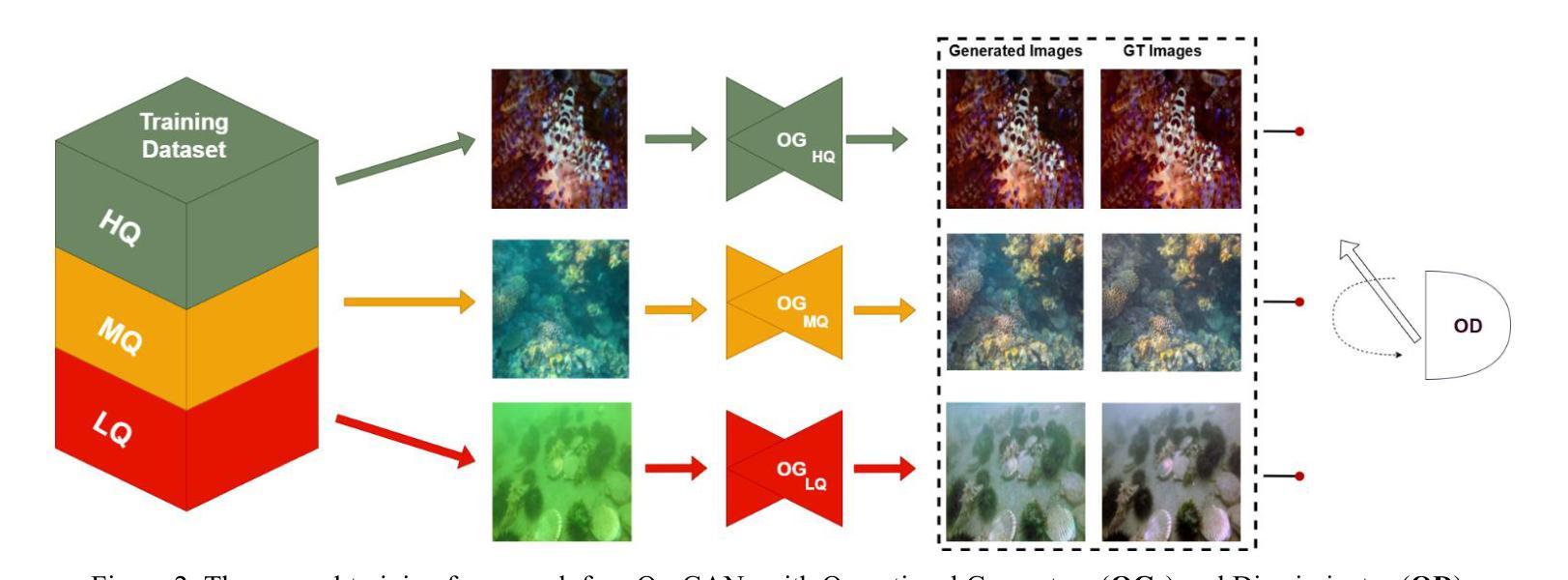
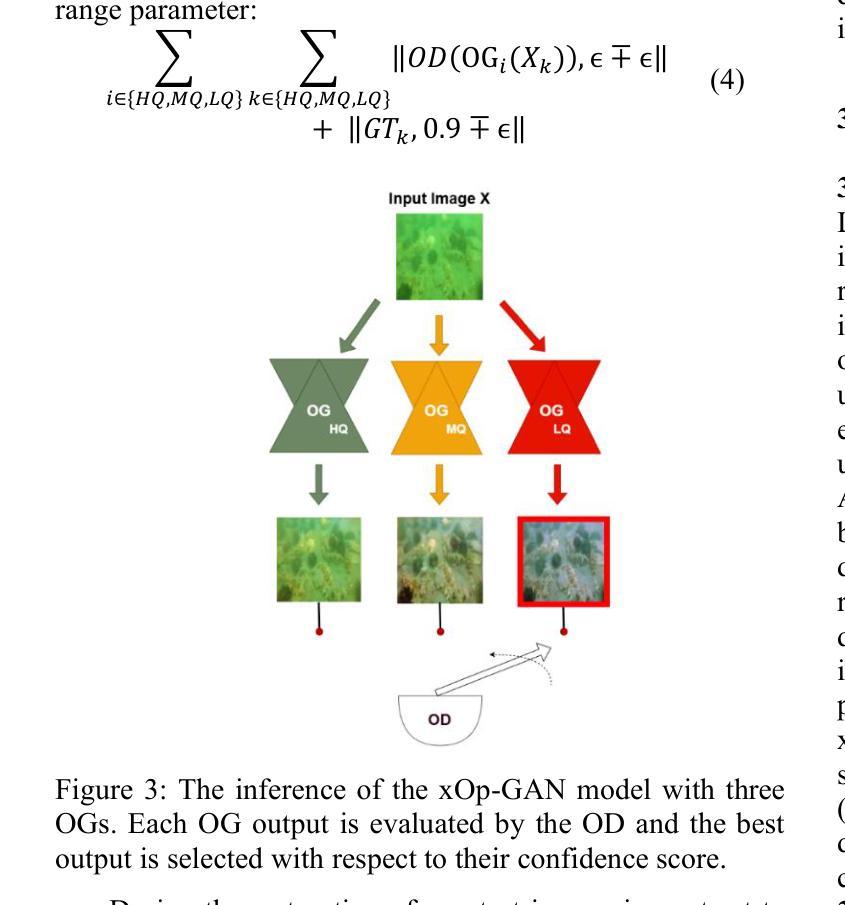
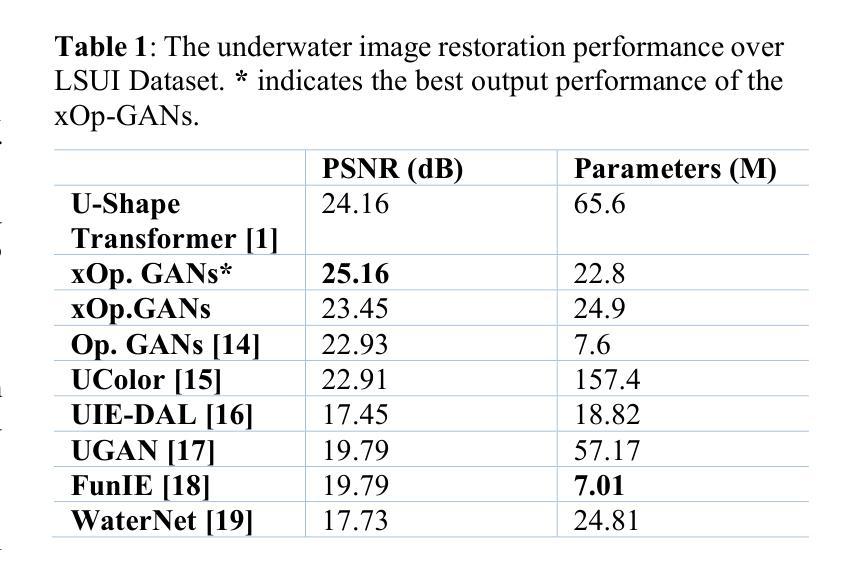
Expert Operational GANS: Towards Real-Color Underwater Image Restoration
Authors:Ozer Can Devecioglu, Serkan Kiranyaz, Mehmet Yamac, Moncef Gabbouj
The wide range of deformation artifacts that arise from complex light propagation, scattering, and depth-dependent attenuation makes the underwater image restoration to remain a challenging problem. Like other single deep regressor networks, conventional GAN-based restoration methods struggle to perform well across this heterogeneous domain, since a single generator network is typically insufficient to capture the full range of visual degradations. In order to overcome this limitation, we propose xOp-GAN, a novel GAN model with several expert generator networks, each trained solely on a particular subset with a certain image quality. Thus, each generator can learn to maximize its restoration performance for a particular quality range. Once a xOp-GAN is trained, each generator can restore the input image and the best restored image can then be selected by the discriminator based on its perceptual confidence score. As a result, xOP-GAN is the first GAN model with multiple generators where the discriminator is being used during the inference of the regression task. Experimental results on benchmark Large Scale Underwater Image (LSUI) dataset demonstrates that xOp-GAN achieves PSNR levels up to 25.16 dB, surpassing all single-regressor models by a large margin even, with reduced complexity.
由于复杂的光传播、散射和深度相关的衰减所产生的各种变形伪影,水下图像恢复仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。与其他单一深度回归网络一样,传统的基于GAN的修复方法在这个异构领域表现不佳,因为单个生成器网络通常不足以捕获全范围的视觉退化。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了xOp-GAN,这是一种新型GAN模型,包含多个专家生成器网络,每个网络仅针对特定子集和特定图像质量进行训练。因此,每个生成器都可以学习在特定质量范围内最大化其修复性能。一旦训练好xOp-GAN模型,每个生成器都可以恢复输入图像,然后由鉴别器根据感知置信度分数选择最佳恢复图像。因此,xOp-GAN是第一个采用多个生成器的GAN模型,在回归任务的推断过程中会使用鉴别器。在大规模水下图像基准数据集上的实验结果表明,xOp-GAN的峰值信噪比可达25.16分贝,在降低复杂度的同时大幅超越了所有单一回归模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
针对水下图像恢复的问题,xOp-GAN作为一种新型的多生成器GAN模型,旨在解决由复杂的光传播、散射和深度依赖衰减导致的变形问题。它包含多个专业生成器网络,每个网络针对特定图像质量进行训练,可最大化其恢复性能。在LSUI数据集上的实验结果表明,xOp-GAN实现了高达25.16 dB的PSNR水平,大幅超越了所有单一回归模型,同时降低了复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像恢复是一个具有挑战性的难题,涉及到复杂的光传播、散射和深度依赖衰减等多种因素。
- 传统GAN恢复方法在面对多种视觉失真时表现有限,单个生成器网络难以覆盖全部退化范围。
- xOp-GAN提出了一种包含多个专业生成器网络的模型架构,每个生成器针对特定图像质量进行训练。
- 每个生成器网络能最大化特定质量范围内的恢复性能。
- 在xOp-GAN中,鉴别器在回归任务的推断过程中发挥选择最佳恢复图像的作用,基于感知置信度评分进行判定。
- 在LSUI数据集上的实验显示,xOp-GAN达到了高PSNR水平(25.16 dB),显著优于单一回归模型。
点此查看论文截图

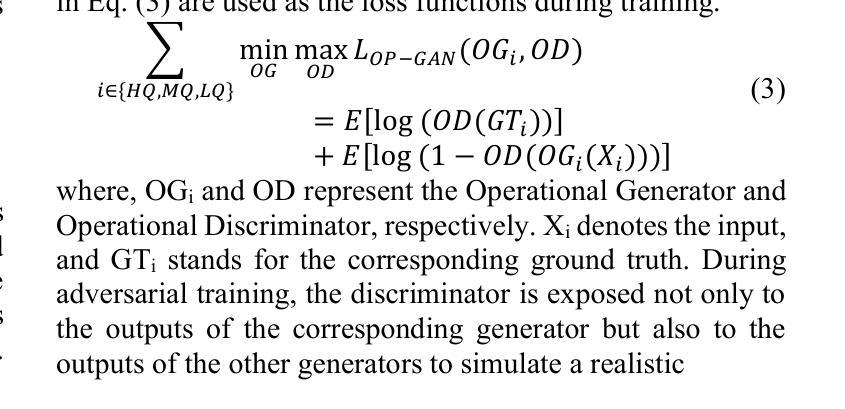

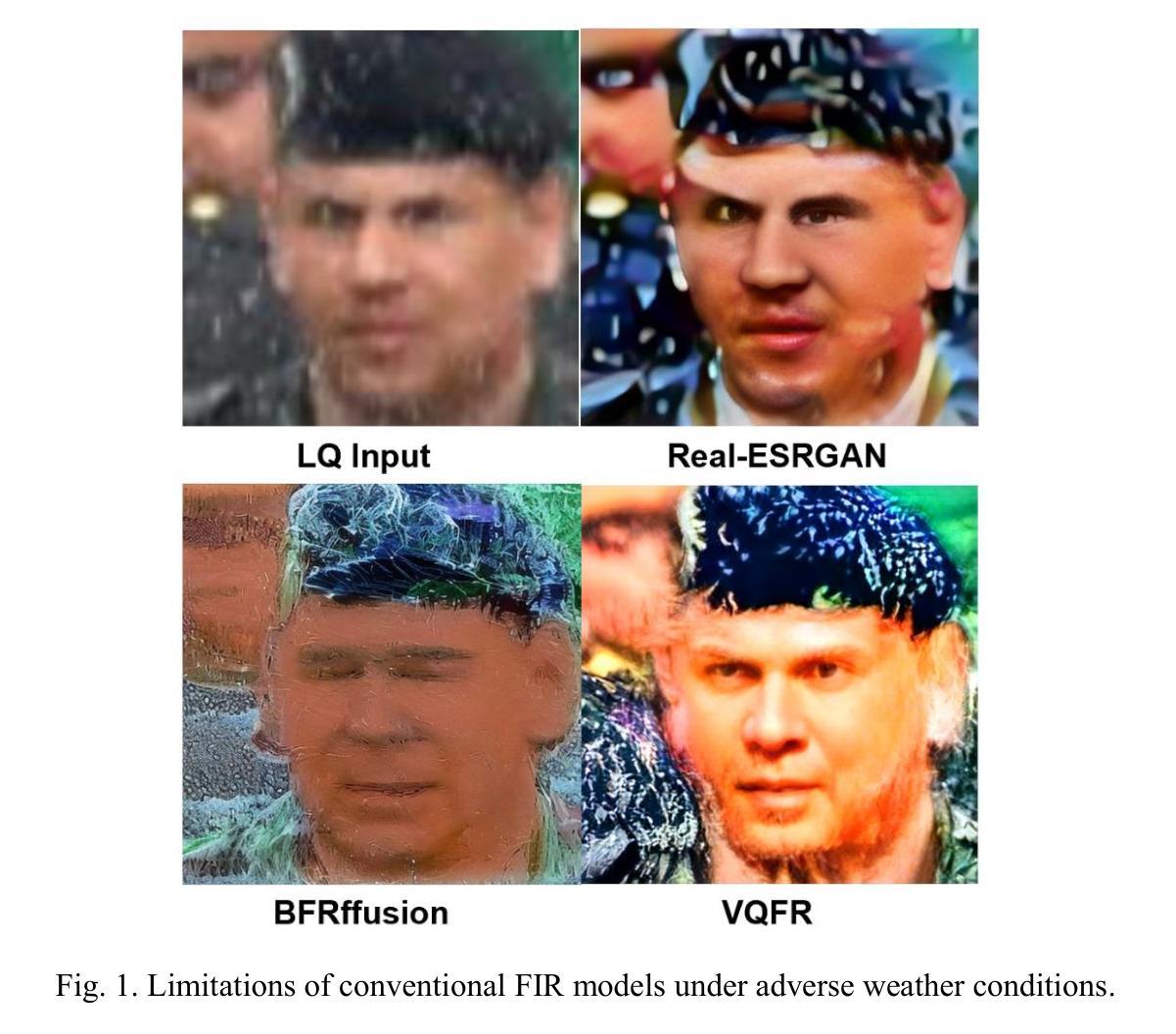
Degradation-Agnostic Statistical Facial Feature Transformation for Blind Face Restoration in Adverse Weather Conditions
Authors:Chang-Hwan Son
With the increasing deployment of intelligent CCTV systems in outdoor environments, there is a growing demand for face recognition systems optimized for challenging weather conditions. Adverse weather significantly degrades image quality, which in turn reduces recognition accuracy. Although recent face image restoration (FIR) models based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models have shown progress, their performance remains limited due to the lack of dedicated modules that explicitly address weather-induced degradations. This leads to distorted facial textures and structures. To address these limitations, we propose a novel GAN-based blind FIR framework that integrates two key components: local Statistical Facial Feature Transformation (SFFT) and Degradation-Agnostic Feature Embedding (DAFE). The local SFFT module enhances facial structure and color fidelity by aligning the local statistical distributions of low-quality (LQ) facial regions with those of high-quality (HQ) counterparts. Complementarily, the DAFE module enables robust statistical facial feature extraction under adverse weather conditions by aligning LQ and HQ encoder representations, thereby making the restoration process adaptive to severe weather-induced degradations. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed degradation-agnostic SFFT model outperforms existing state-of-the-art FIR methods based on GAN and diffusion models, particularly in suppressing texture distortions and accurately reconstructing facial structures. Furthermore, both the SFFT and DAFE modules are empirically validated in enhancing structural fidelity and perceptual quality in face restoration under challenging weather scenarios.
随着智能CCTV系统在户外环境中的部署越来越多,对于适应恶劣天气条件的面部识别系统的需求也在日益增长。恶劣天气会严重降低图像质量,进而导致识别准确度下降。尽管基于生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的面部图像恢复(FIR)模型已经取得了进展,但由于缺乏专门解决天气引起的退化的模块,其性能仍然受到限制。这会导致面部纹理和结构失真。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种基于GAN的盲FIR框架,该框架包含两个关键组件:局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和退化无关特征嵌入(DAFE)。局部SFFT模块通过对齐低质量(LQ)面部区域的局部统计分布与高质量(HQ)对应区域的统计分布,增强面部结构和颜色保真度。作为补充,DAFE模块通过对齐LQ和HQ编码器表示,实现在恶劣天气条件下的稳健统计面部特征提取,从而使恢复过程适应严重的天气引起的退化。实验结果表明,所提出的退化无关SFFT模型优于基于GAN和扩散模型的现有先进FIR方法,特别是在抑制纹理失真和准确重建面部结构方面。此外,SFFT和DAFE模块在具有挑战性的天气场景下提高面部恢复的结构保真度和感知质量方面也得到了实证验证。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对室外环境中智能监控系统的广泛应用,对面部识别系统提出了在恶劣天气条件下的优化需求。虽然基于生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型的面部图像恢复(FIR)模型已有所进展,但由于缺乏专门应对天气引起的降质的模块,其性能仍有局限。为此,提出了一种新的基于GAN的盲FIR框架,包含两个关键组件:局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和降质无关特征嵌入(DAFE)。SFFT模块通过对齐低质量(LQ)面部区域与高质量(HQ)区域的局部统计分布,增强面部结构和色彩保真度。DAFE模块则通过对齐LQ和HQ编码器表示,使面部恢复过程适应恶劣天气引起的降质,实现在各种天气条件下的稳健面部特征提取。实验结果表明,所提出的降质无关SFFT模型在面部恢复方面优于现有基于GAN和扩散模型的先进FIR方法,特别是在抑制纹理失真和准确重建面部结构方面。
Key Takeaways
- 智能监控系统在室外环境中的广泛应用推动了面部识别系统在恶劣天气条件下的优化需求。
- 现有基于GAN和扩散模型的面部图像恢复(FIR)模型虽有所进展,但性能受限于缺乏应对天气引起的降质的专门模块。
- 提出的盲FIR框架包含两个关键组件:局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和降质无关特征嵌入(DAFE)。
- SFFT模块通过对齐LQ和HQ面部区域的统计分布,增强面部结构和色彩保真度。
- DAFE模块实现了在各种天气条件下的稳健面部特征提取,通过对齐LQ和HQ编码器表示,使恢复过程适应恶劣天气引起的降质。
- 提出的降质无关SFFT模型在面部恢复方面优于现有先进FIR方法。
点此查看论文截图


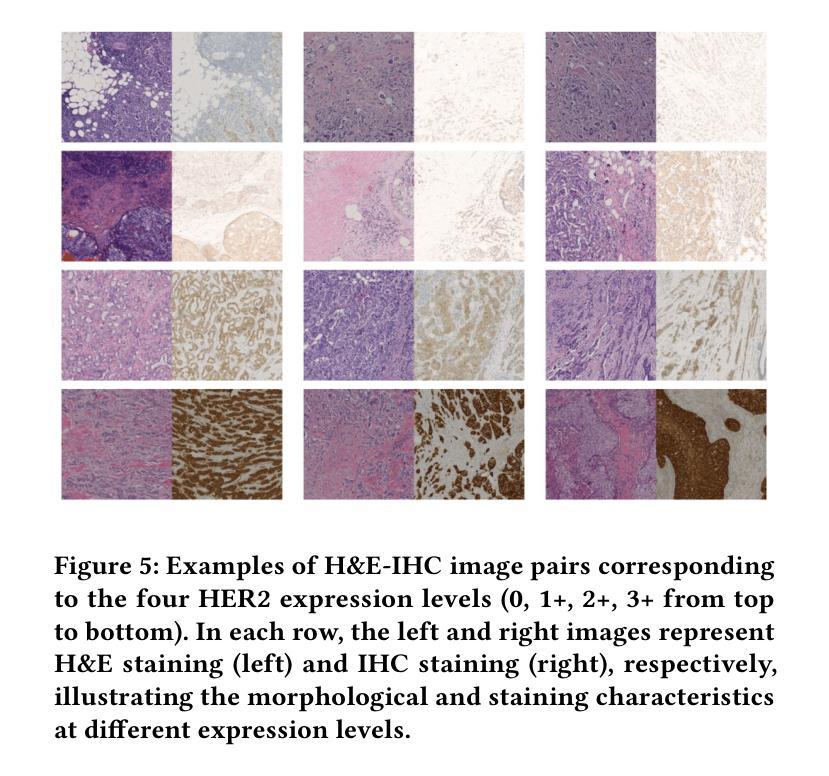
HER2 Expression Prediction with Flexible Multi-Modal Inputs via Dynamic Bidirectional Reconstruction
Authors:Jie Qin, Wei Yang, Yan Su, Yiran Zhu, Weizhen Li, Yunyue Pan, Chengchang Pan, Honggang Qi
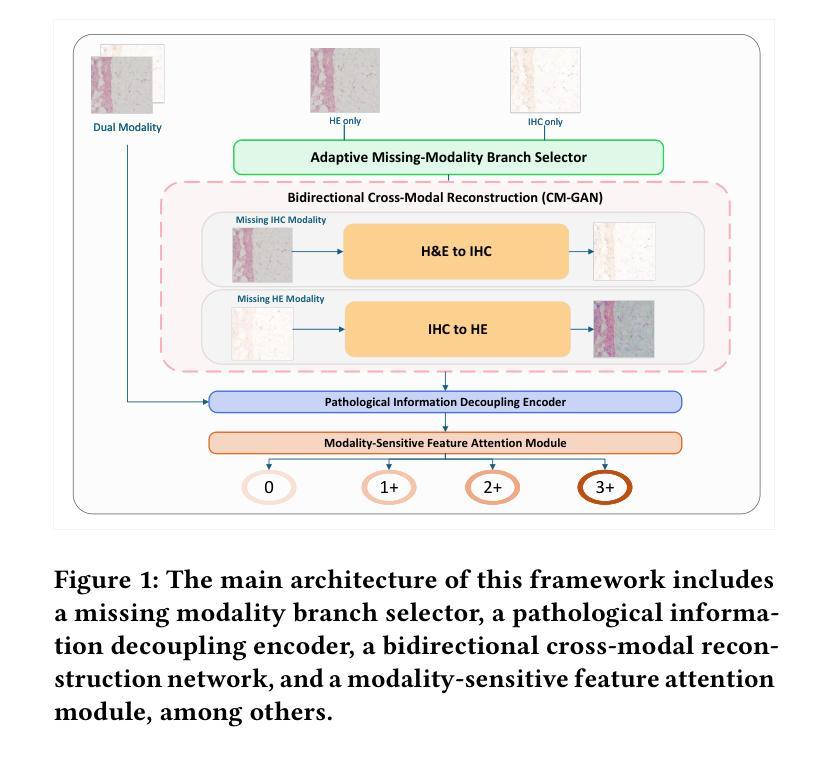
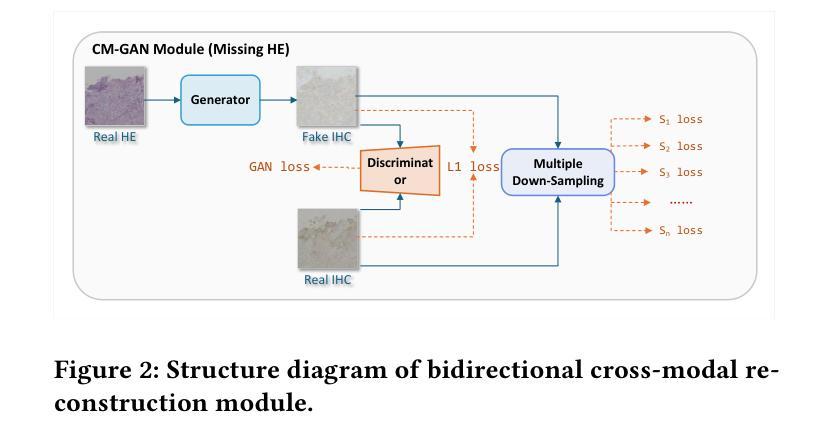
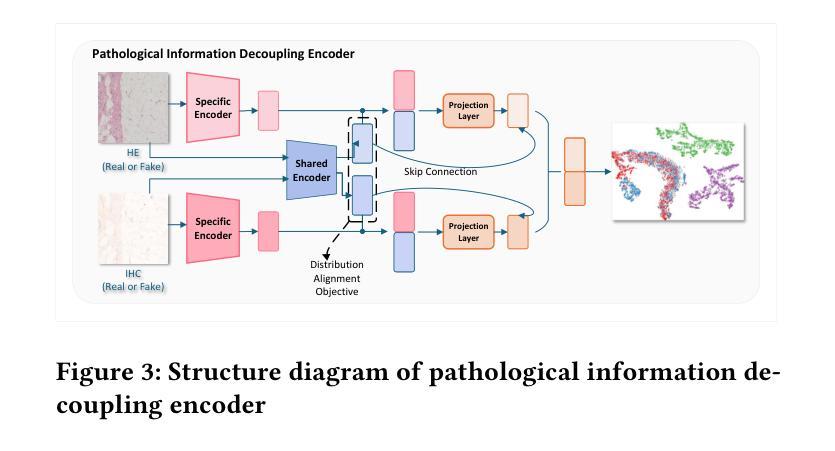
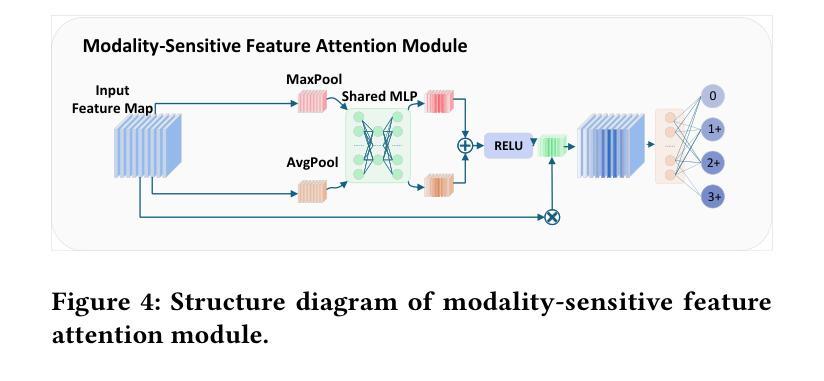
In breast cancer HER2 assessment, clinical evaluation relies on combined H&E and IHC images, yet acquiring both modalities is often hindered by clinical constraints and cost. We propose an adaptive bimodal prediction framework that flexibly supports single- or dual-modality inputs through two core innovations: a dynamic branch selector activating modality completion or joint inference based on input availability, and a cross-modal GAN (CM-GAN) enabling feature-space reconstruction of missing modalities. This design dramatically improves H&E-only accuracy from 71.44% to 94.25%, achieves 95.09% with full dual-modality inputs, and maintains 90.28% reliability under single-modality conditions. The “dual-modality preferred, single-modality compatible” architecture delivers near-dual-modality accuracy without mandatory synchronized acquisition, offering a cost-effective solution for resource-limited regions and significantly improving HER2 assessment accessibility.
在乳腺癌HER2评估中,临床评估依赖于H&E和IHC图像的联合分析,然而,由于临床限制和成本问题,经常难以获得这两种模式。我们提出了一种自适应双模态预测框架,通过两个核心创新点灵活地支持单模态或双模态输入:一个动态分支选择器,根据输入可用性激活模态完成或联合推断;一个跨模态生成对抗网络(CM-GAN),能够实现缺失模态的特征空间重建。这一设计大大提高了仅使用H&E的准确性,从71.44%提高到94.25%,在全双模态输入的情况下达到95.09%,在单模态条件下保持90.28%的可靠性。这种“以双模态为主,单模态兼容”的架构,在不强制同步采集的情况下实现了接近双模态的准确性,为资源有限的地区提供了经济高效的解决方案,并大大提高了HER2评估的可达性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages,6 figures,3 tables,accepted by the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia(ACM MM 2025)
Summary
在乳腺癌HER2评估中,临床评估依赖于H&E和IHC图像的联合使用,但获取这两种模式常常受到临床限制和成本的影响。本研究提出了一种自适应双模态预测框架,通过两个核心创新点灵活支持单模态或双模态输入:动态分支选择器根据输入可用性激活模态完成或联合推理,以及跨模态GAN(CM-GAN)实现缺失模态的特征空间重建。该设计显著提高了仅使用H&E的准确性,从71.44%提高到94.25%,在完整的双模态输入下达到95.09%,在单模态条件下保持90.28%的可靠性。这种“以双模态为主,单模态兼容”的架构在不强制同步采集的情况下实现了接近双模态的准确性,为资源有限的地区提供了经济高效的解决方案,并显着提高了HER2评估的可达性。
Key Takeaways
- 临床评估乳腺癌HER2时,常依赖H&E和IHC两种图像的联合使用。
- 获取H&E和IHC图像有时受临床限制和成本影响。
- 提出了自适应双模态预测框架,该框架能灵活处理单模态或双模态输入。
- 框架包括动态分支选择器和跨模态GAN(CM-GAN)两大核心创新。
- 该设计显著提高了仅使用H&E的准确性,并且能在双模态输入下达到高准确性。
- 框架能在单模态条件下保持高可靠性,实现了接近双模态的准确性。
点此查看论文截图