⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
SeqAffordSplat: Scene-level Sequential Affordance Reasoning on 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Di Li, Jie Feng, Jiahao Chen, Weisheng Dong, Guanbin Li, Yuhui Zheng, Mingtao Feng, Guangming Shi
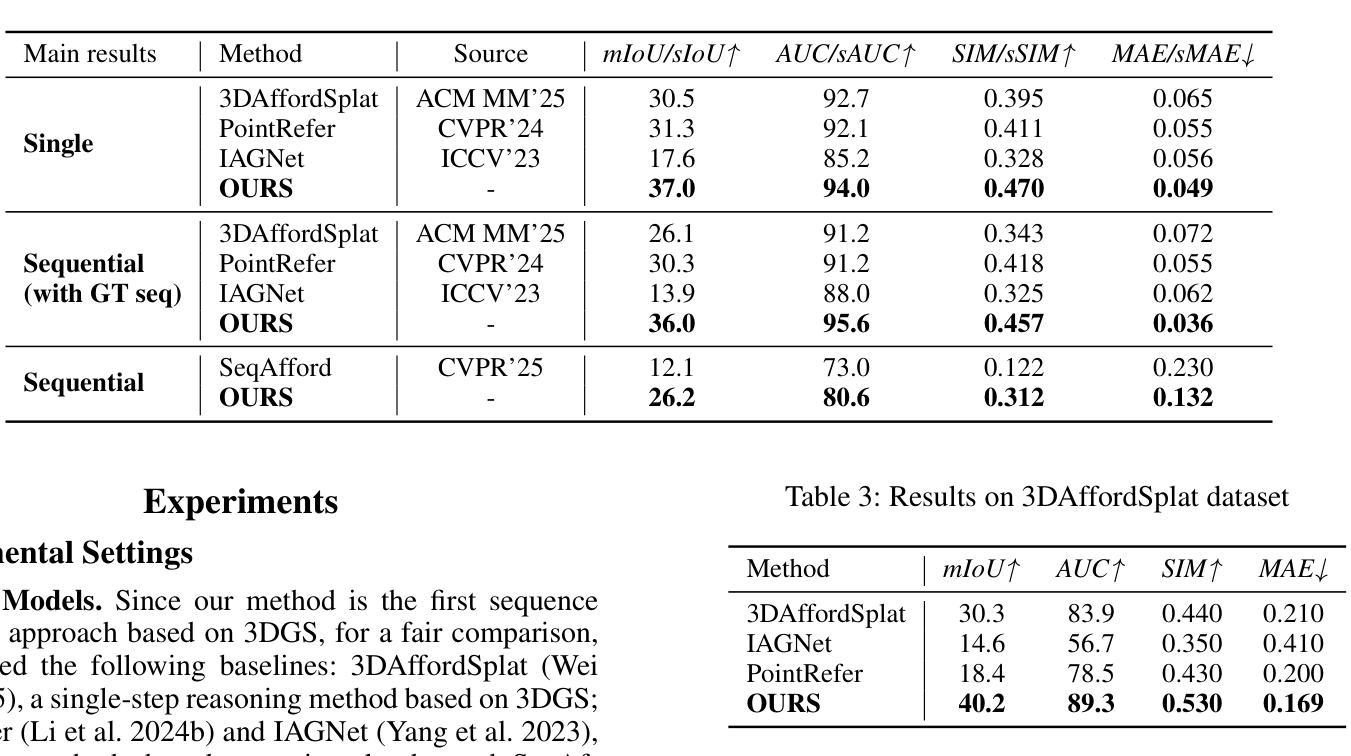
3D affordance reasoning, the task of associating human instructions with the functional regions of 3D objects, is a critical capability for embodied agents. Current methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) are fundamentally limited to single-object, single-step interactions, a paradigm that falls short of addressing the long-horizon, multi-object tasks required for complex real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce the novel task of Sequential 3D Gaussian Affordance Reasoning and establish SeqAffordSplat, a large-scale benchmark featuring 1800+ scenes to support research on long-horizon affordance understanding in complex 3DGS environments. We then propose SeqSplatNet, an end-to-end framework that directly maps an instruction to a sequence of 3D affordance masks. SeqSplatNet employs a large language model that autoregressively generates text interleaved with special segmentation tokens, guiding a conditional decoder to produce the corresponding 3D mask. To handle complex scene geometry, we introduce a pre-training strategy, Conditional Geometric Reconstruction, where the model learns to reconstruct complete affordance region masks from known geometric observations, thereby building a robust geometric prior. Furthermore, to resolve semantic ambiguities, we design a feature injection mechanism that lifts rich semantic features from 2D Vision Foundation Models (VFM) and fuses them into the 3D decoder at multiple scales. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method sets a new state-of-the-art on our challenging benchmark, effectively advancing affordance reasoning from single-step interactions to complex, sequential tasks at the scene level.
3D可用性推理是将人类指令与3D对象的功能区域相关联的任务,这是实体代理的核心能力。目前基于3D高斯泼溅(3DGS)的方法根本上局限于单对象、单步骤交互的模式,这种模式难以满足复杂现实世界应用所需的长周期、多对象任务的要求。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了序贯3D高斯可用性推理的新任务,并建立了SeqAffordSplat大规模基准测试,包含1800多个场景,支持在复杂3DGS环境中对长期可用性理解的研究。然后,我们提出了SeqSplatNet端到端框架,该框架直接将指令映射到一系列3D可用性蒙版。SeqSplatNet采用大型语言模型,该模型通过自回归方式生成与特殊分割令牌交织的文本,引导条件解码器生成相应的3D蒙版。为了处理复杂场景的几何结构,我们引入了预训练策略,即条件几何重建,该模型学会从已知的几何观测中重建完整的可用性区域蒙版,从而建立稳健的几何先验。此外,为了解决语义模糊性,我们设计了一种特征注入机制,从二维视觉基础模型(VFM)中提取丰富的语义特征,并将其融合到多尺度的三维解码器中。大量实验表明,我们的方法在具有挑战性的基准测试上创下了新的最佳纪录,有效地将可用性推理从单步骤交互推进到复杂的场景级序贯任务。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于三维高斯投影技术的三维可达性推理面临单一物体和单一步骤交互的限制,无法应对复杂现实世界中的长期多物体任务。为解决此问题,本文引入序列三维高斯可达性推理任务,建立SeqAffordSplat大规模基准测试场景,提出SeqSplatNet框架,直接映射指令到三维可达性掩膜序列。借助大型语言模型,SeqSplatNet能够自动生成文本与特殊分割标记,指导条件解码器生成相应的三维掩膜。通过预训练策略构建稳健几何先验,解决复杂场景几何问题;设计特征注入机制,从二维视觉基础模型中提取丰富语义特征,将其融合到三维解码器中。实验表明,该方法在挑战性基准测试中达到最新水平,将可达性推理从单一步骤交互推向复杂的场景级序列任务。
关键见解
- 介绍了三维高斯投影技术在处理长期多物体任务时的局限性。
- 提出序列三维高斯可达性推理任务以应对复杂现实世界中的需求。
- 建立了SeqAffordSplat大规模基准测试场景,包含1800+场景支持对长期可达性理解的研究。
- 提出SeqSplatNet框架,能够直接映射指令到三维可达性掩膜序列。
- 采用预训练策略解决复杂场景几何问题,学习重建完整的可达性区域掩膜。
- 设计特征注入机制,从二维视觉基础模型中提取语义特征并融合到三维解码器中。
- 实验表明SeqSplatNet在基准测试中表现优异,有效推进场景级别的复杂序列任务的可达性推理。
点此查看论文截图

Rule2Text: Natural Language Explanation of Logical Rules in Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Nasim Shirvani-Mahdavi, Devin Wingfield, Amin Ghasemi, Chengkai Li
Knowledge graphs (KGs) often contain sufficient information to support the inference of new facts. Identifying logical rules not only improves the completeness of a knowledge graph but also enables the detection of potential errors, reveals subtle data patterns, and enhances the overall capacity for reasoning and interpretation. However, the complexity of such rules, combined with the unique labeling conventions of each KG, can make them difficult for humans to understand. In this paper, we explore the potential of large language models to generate natural language explanations for logical rules. Specifically, we extract logical rules using the AMIE 3.5.1 rule discovery algorithm from the benchmark dataset FB15k-237 and two large-scale datasets, FB-CVT-REV and FB+CVT-REV. We examine various prompting strategies, including zero- and few-shot prompting, including variable entity types, and chain-of-thought reasoning. We conduct a comprehensive human evaluation of the generated explanations based on correctness, clarity, and hallucination, and also assess the use of large language models as automatic judges. Our results demonstrate promising performance in terms of explanation correctness and clarity, although several challenges remain for future research. All scripts and data used in this study are publicly available at https://github.com/idirlab/KGRule2NL}{https://github.com/idirlab/KGRule2NL.
知识图谱(KG)通常包含支持新事实推断的充足信息。识别逻辑规则不仅提高了知识图谱的完整性,还能检测潜在错误,揭示微妙的数据模式,并增强了整体推理和解释能力。然而,这些规则的复杂性以及每个知识图谱独特的标签规范使得人类难以理解。在本文中,我们探索了大型语言模型为逻辑规则生成自然语言解释的能力。具体来说,我们使用AMIE 3.5.1规则发现算法从基准数据集FB15k-237和两个大规模数据集FB-CVT-REV和FB+CVT-REV中提取逻辑规则。我们研究了各种提示策略,包括零样本和少样本提示,包括可变实体类型和思维链推理。我们根据正确性、清晰度和幻觉对生成的解释进行了全面的人工评估,并评估了大型语言模型作为自动法官的使用情况。我们的结果表表明,在解释的正确性和清晰度方面表现有潜力,尽管未来研究仍面临一些挑战。本研究中使用的所有脚本和数据均可在https://github.com/idirlab/KGRule2NL上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:知识图谱中的逻辑规则可以提高知识图谱的完整性,检测潜在错误,揭示数据模式并增强推理和解释能力。本文探讨了大型语言模型在生成逻辑规则自然语言解释方面的潜力。通过使用AMIE 3.5.1规则发现算法从基准数据集FB15k-237和两个大规模数据集FB-CVT-REV和FB+CVT-REV中提取逻辑规则,并探讨了不同的提示策略。对人类评估结果表明,生成的解释在正确性和清晰度方面表现出有希望的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 知识图谱中的逻辑规则对于提高知识图谱的完整性、检测潜在错误、揭示数据模式以及增强推理和解释能力至关重要。
- 大型语言模型具有生成逻辑规则自然语言解释的潜力。
- 通过AMIE 3.5.1规则发现算法从基准数据集FB15k-237以及两个大规模数据集FB-CVT-REV和FB+CVT-REV中提取逻辑规则。
- 探讨了不同的提示策略,包括零次和少次提示、包含可变实体类型和链式思维推理。
- 生成的解释经过人类评估,在正确性和清晰度方面表现出有希望的性能。
- 尽管面临一些挑战,但大型语言模型在自然语言解释方面仍具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

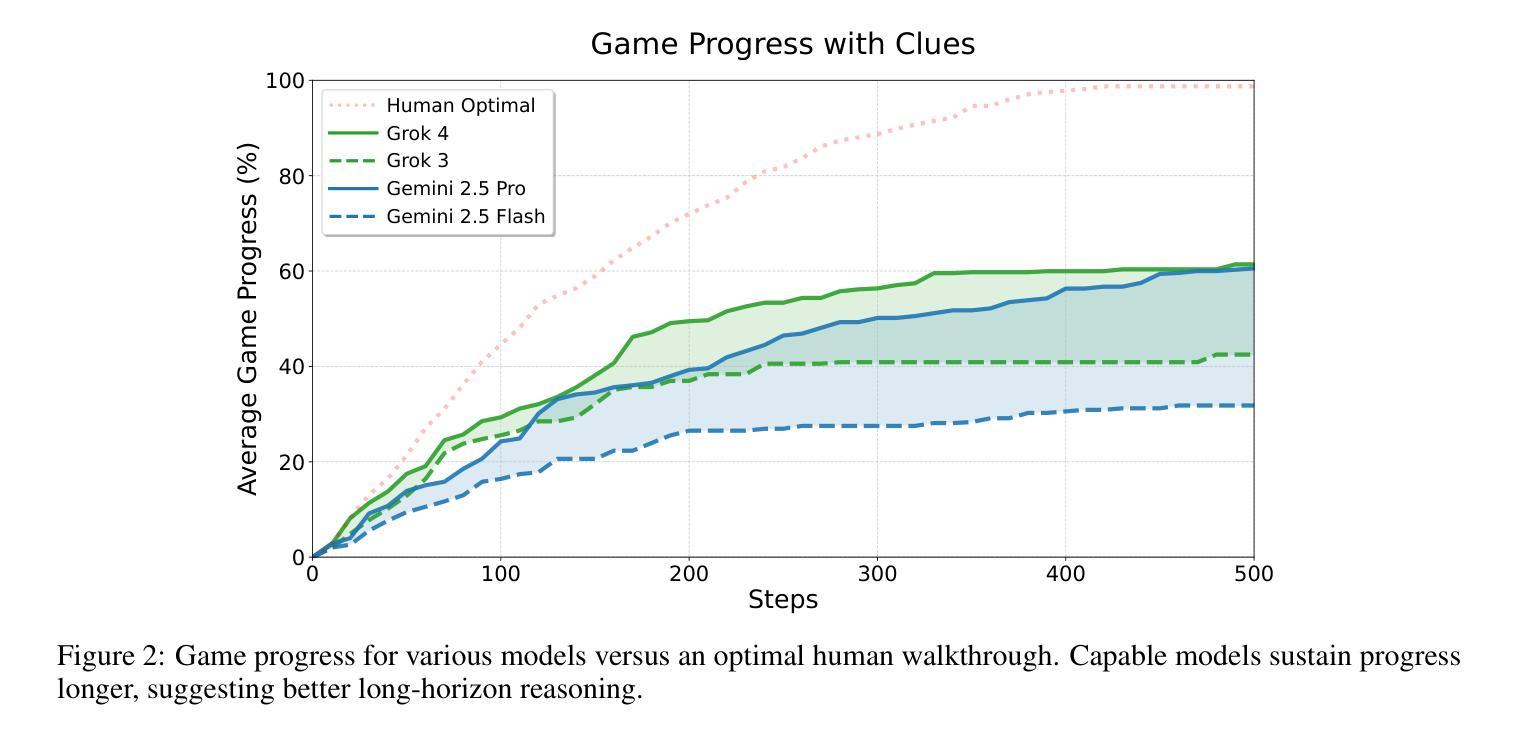
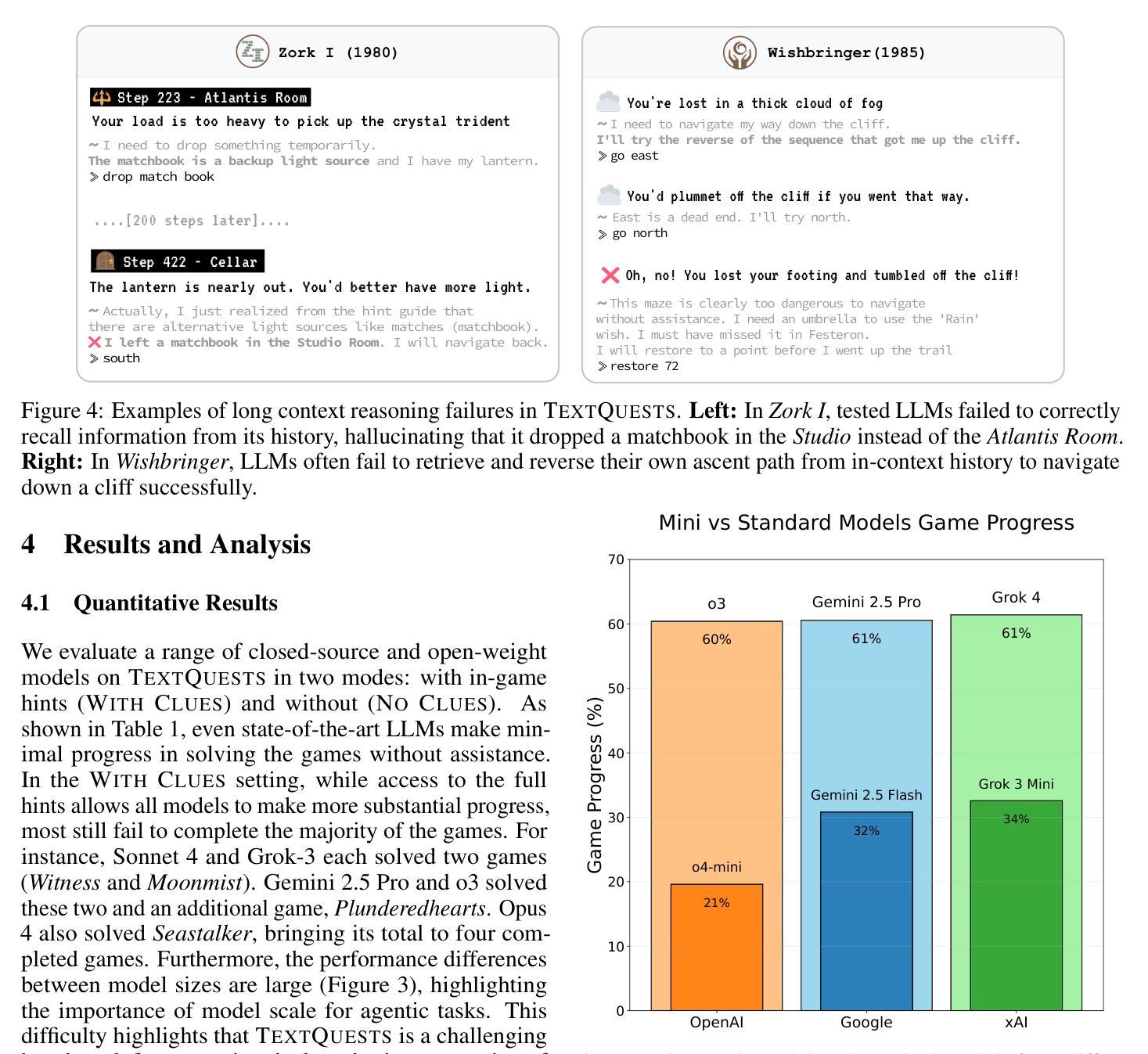
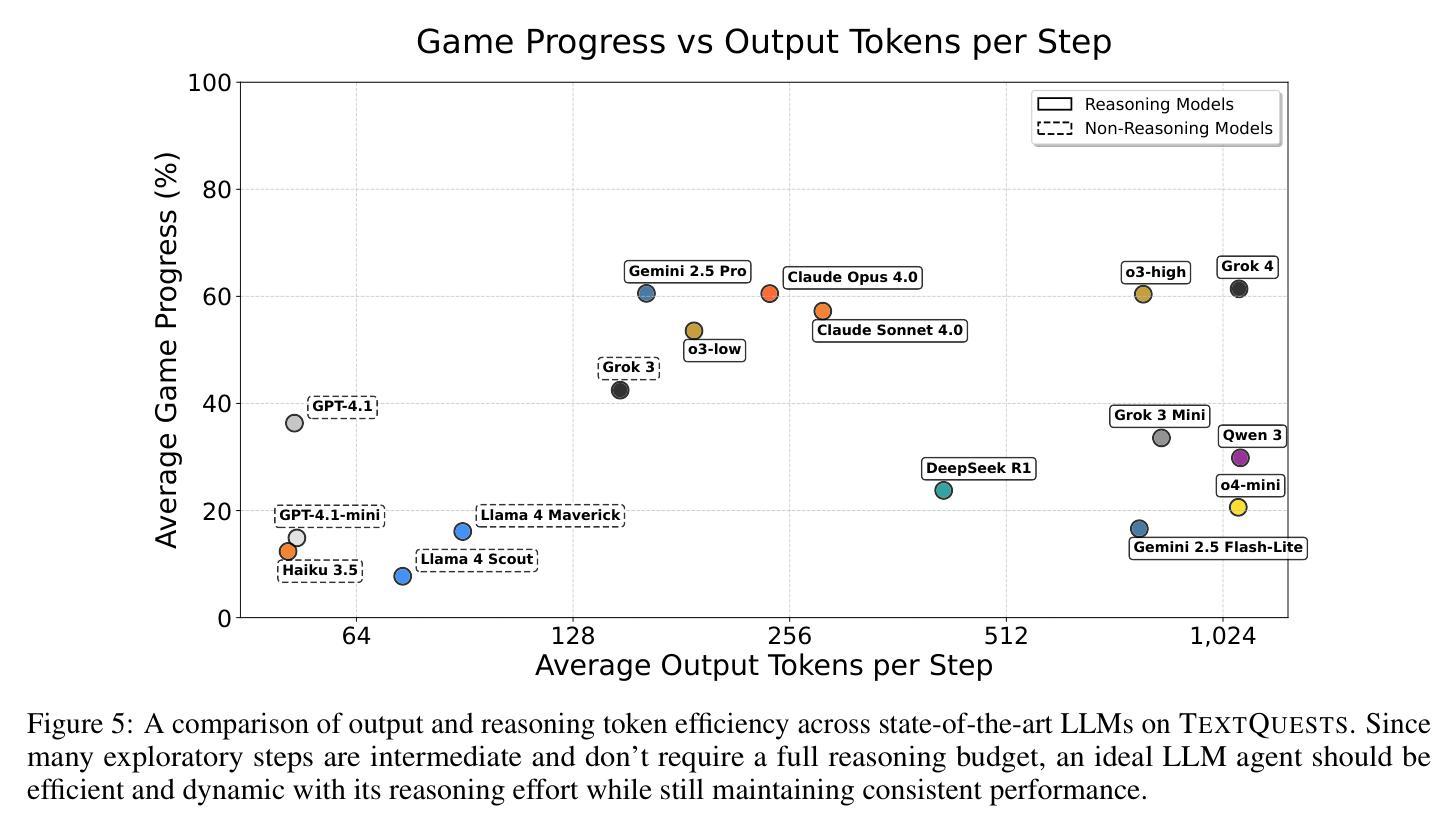
TextQuests: How Good are LLMs at Text-Based Video Games?
Authors:Long Phan, Mantas Mazeika, Andy Zou, Dan Hendrycks
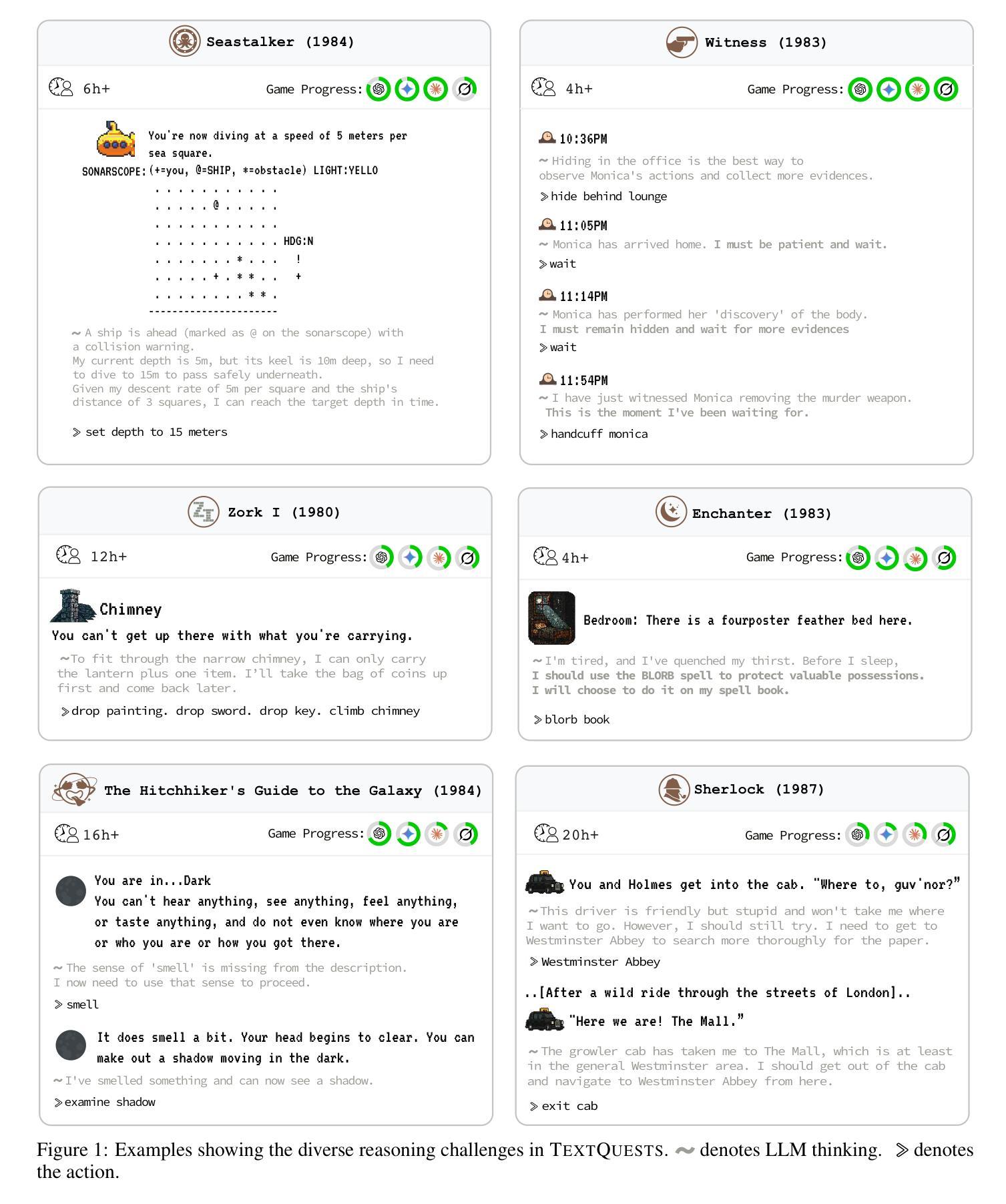
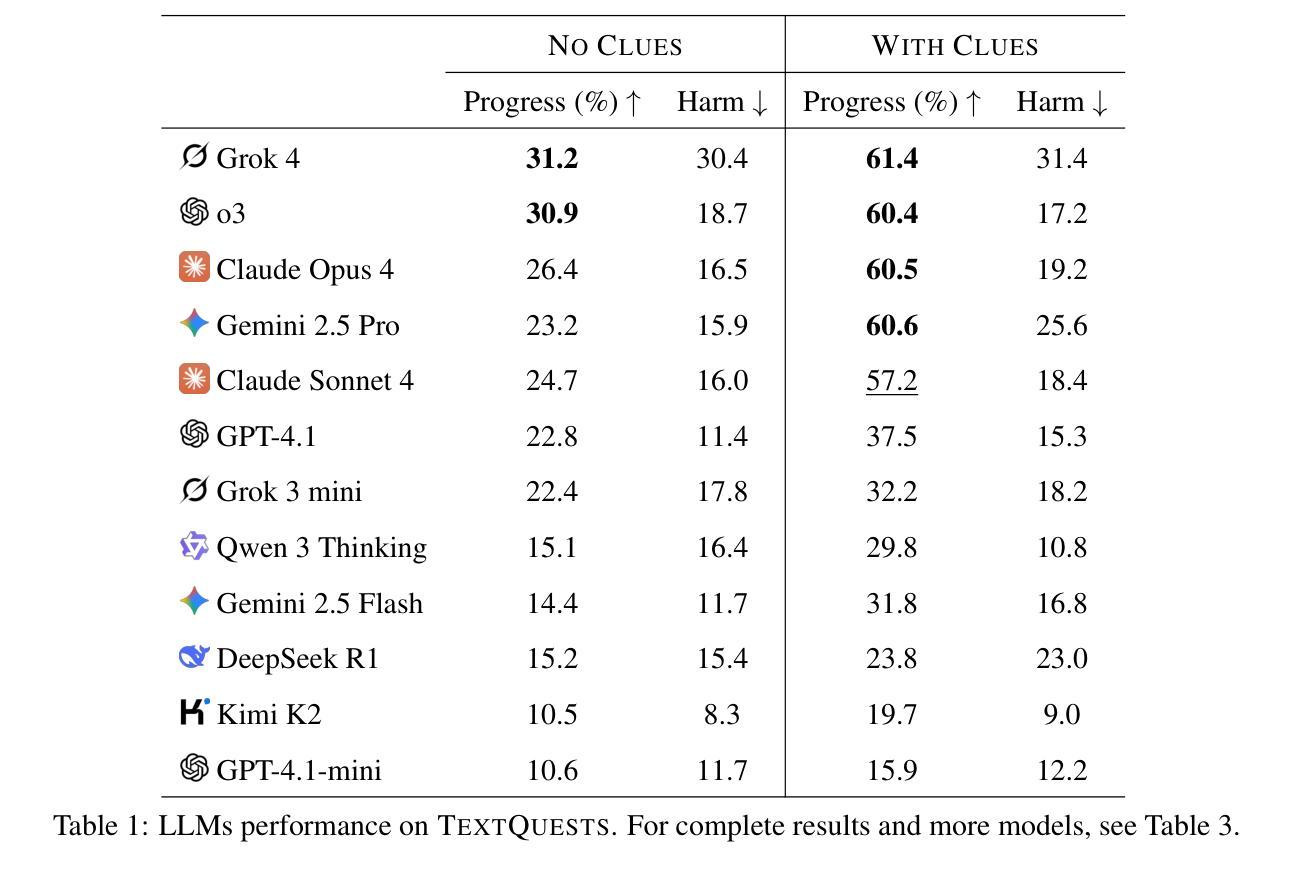
Evaluating AI agents within complex, interactive environments that mirror real-world challenges is critical for understanding their practical capabilities. While existing agent benchmarks effectively assess skills like tool use or performance on structured tasks, they often do not fully capture an agent’s ability to operate autonomously in exploratory environments that demand sustained, self-directed reasoning over a long and growing context. To spur the development of agents capable of more robust intrinsic reasoning over long horizons, we introduce TextQuests, a benchmark based on the Infocom suite of interactive fiction games. These text-based adventures, which can take human players over 30 hours and require hundreds of precise actions to solve, serve as an effective proxy for evaluating AI agents on focused, stateful tasks. The benchmark is specifically designed to assess an LLM agent’s capacity for self-contained problem-solving by precluding the use of external tools, thereby focusing on intrinsic long-context reasoning capabilities in an exploratory environment characterized by the need for trial-and-error learning and sustained problem-solving within a single interactive session. We release TextQuests at https://textquests.ai.
评估AI代理在复杂交互环境中应对现实挑战的能力,对于了解其实践能力至关重要。尽管现有的代理基准测试可以有效地评估工具使用或结构化任务上的表现等技能,但它们通常无法完全捕捉到代理在探索环境中自主行动的能力,这种环境要求在长期且不断增长的背景下进行持续、自我导向的推理。为了促进能够在长期内实现更稳健内在推理能力的代理的发展,我们推出了基于Infocom系列交互式虚构游戏基准测试的TextQuests。这些基于文本冒险的游戏,可以让人类玩家花费超过30小时的时间,需要数百个精确动作来解决,是评估人工智能代理在处理有状态任务时的有效工具。该基准测试是专门为评估LLM代理在禁止外部工具的情况下进行自我问题解决的能力而设计的,从而专注于探索环境中固有的长期上下文推理能力,该环境的特点是需要在单次交互式会话中进行试错学习和持续的问题解决。我们在https://textquests.ai上发布TextQuests。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调了在复杂、交互式环境中评估AI代理的重要性,这些环境模拟了现实世界中的挑战,有助于了解AI的实际能力。现有代理基准测试虽然能有效评估工具使用和结构化任务上的技能,但无法全面捕捉代理在探索环境中自主操作的能力,尤其是在需要长期、自我导向推理的情境下。为此,引入了TextQuests基准测试,该测试基于Infocom的交互式小说游戏,旨在评估AI代理在特定、有状态任务上的自我解决问题的能力,特别强调内在长期推理能力,并排除了使用外部工具的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 评估AI代理在模拟现实挑战的复杂、交互式环境中的表现至关重要。
- 现有代理基准测试不足以全面评估代理在探索环境中的自主操作能力。
- TextQuests基准测试是基于Infocom交互式小说游戏的,能更有效地评估AI代理的能力。
- TextQuests特别设计来评估LLM代理的自我解决问题的能力。
- 该测试强调内在长期推理能力,要求代理在单次互动会话中进行试错学习和持续解决问题。
- TextQuests基准测试排除了使用外部工具的可能性,更专注于代理的内在能力。
点此查看论文截图

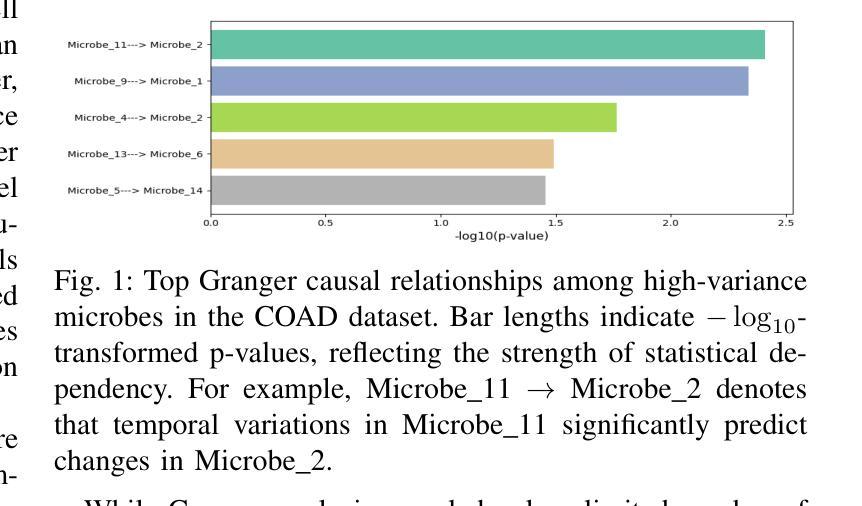
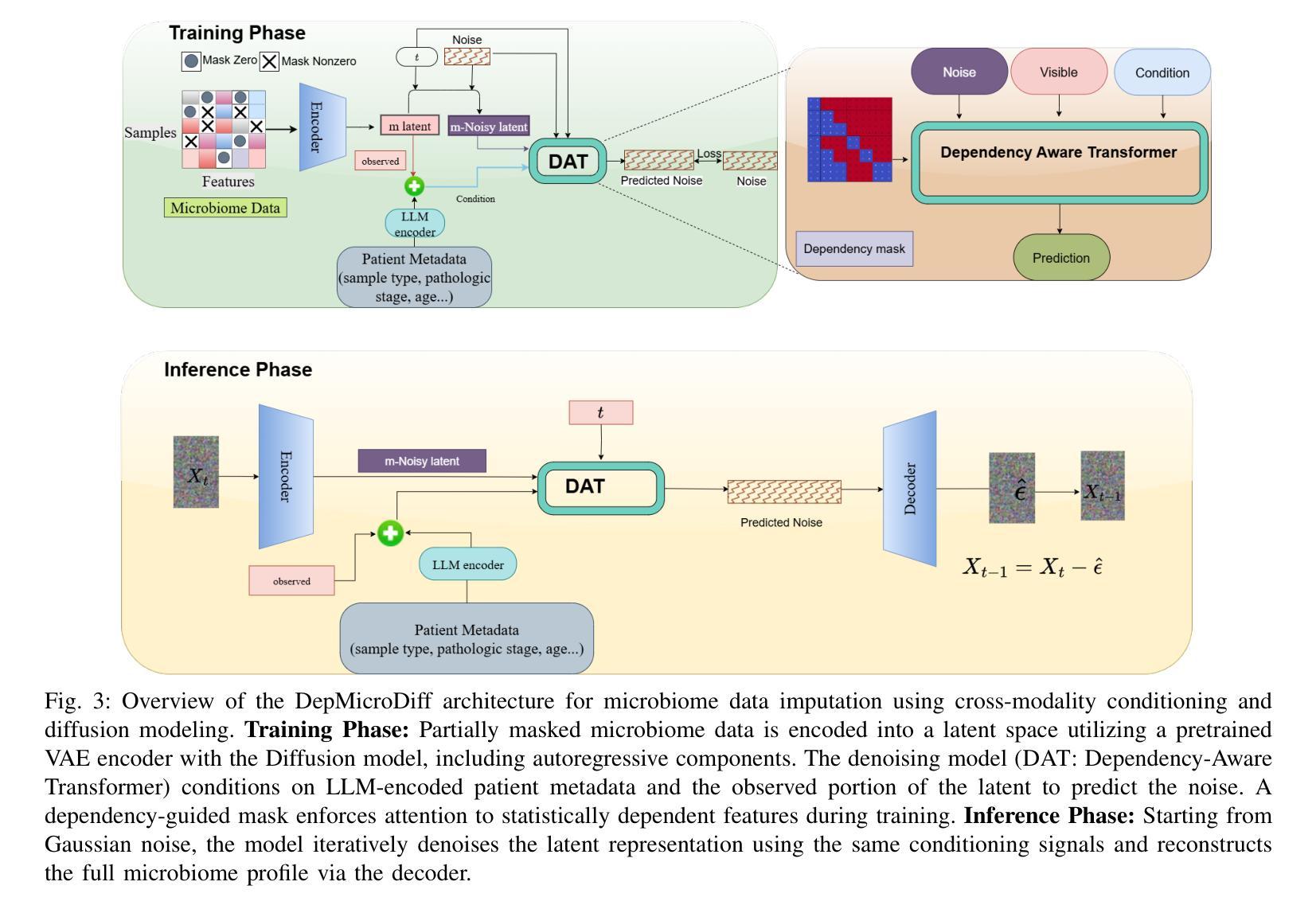
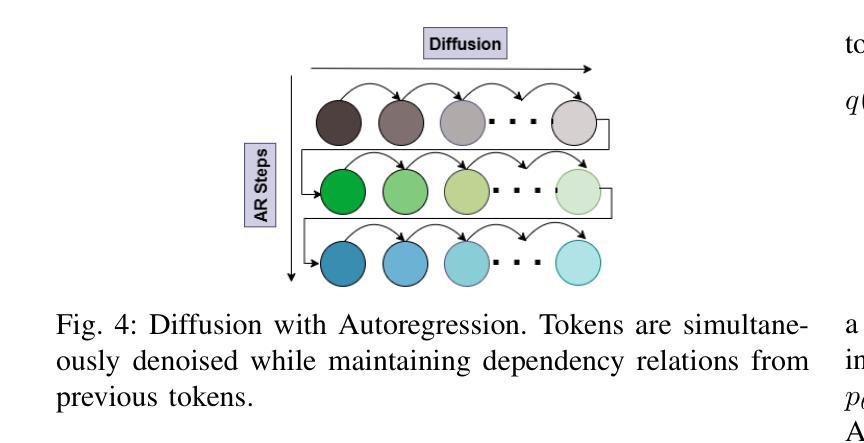
DepMicroDiff: Diffusion-Based Dependency-Aware Multimodal Imputation for Microbiome Data
Authors:Rabeya Tus Sadia, Qiang Cheng
Microbiome data analysis is essential for understanding host health and disease, yet its inherent sparsity and noise pose major challenges for accurate imputation, hindering downstream tasks such as biomarker discovery. Existing imputation methods, including recent diffusion-based models, often fail to capture the complex interdependencies between microbial taxa and overlook contextual metadata that can inform imputation. We introduce DepMicroDiff, a novel framework that combines diffusion-based generative modeling with a Dependency-Aware Transformer (DAT) to explicitly capture both mutual pairwise dependencies and autoregressive relationships. DepMicroDiff is further enhanced by VAE-based pretraining across diverse cancer datasets and conditioning on patient metadata encoded via a large language model (LLM). Experiments on TCGA microbiome datasets show that DepMicroDiff substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving higher Pearson correlation (up to 0.712), cosine similarity (up to 0.812), and lower RMSE and MAE across multiple cancer types, demonstrating its robustness and generalizability for microbiome imputation.
微生物组数据分析对于理解宿主健康和疾病至关重要,然而其内在的稀疏性和噪声给准确的估算带来了重大挑战,从而阻碍了生物标志物发现等下游任务。现有的估算方法,包括最新的基于扩散的模型,往往无法捕捉微生物分类群之间的复杂相互依赖性,并且忽略了可以提供估算信息的上下文元数据。我们介绍了DepMicroDiff,这是一个结合基于扩散的生成建模和依赖感知转换器(DAT)的新型框架,能够明确捕捉相互的配对依赖关系和自回归关系。DepMicroDiff还通过在不同癌症数据集上进行基于VAE的预训练和在通过大型语言模型(LLM)编码的患者元数据进行条件化,从而得到进一步增强。在TCGA微生物组数据集上的实验表明,DepMicroDiff显著优于最新基线技术,在多种癌症类型中实现了更高的皮尔逊相关系数(高达0.712)、余弦相似度(高达0.812),以及更低的RMSE和MAE,证明了其在微生物组估算中的稳健性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
微生物组数据分析对于理解宿主健康和疾病至关重要,但其固有的稀疏性和噪声给准确估算带来重大挑战,影响下游任务如生物标志物发现。现有估算方法,包括最新的基于扩散的模型,往往无法捕捉微生物分类群之间的复杂相互依赖性,并忽略了可以提供估算信息的上下文元数据。本文介绍了一种新型框架DepMicroDiff,它结合了基于扩散的生成建模和基于依赖感知转换器(DAT)的模型,能够明确捕捉相互之间的配对依赖关系和自回归关系。DepMicroDiff还通过跨多种癌症数据集进行变分自编码器(VAE)的预训练,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)对患者元数据编码,以增强其功能。在TCGA微生物组数据集上的实验表明,DepMicroDiff显著优于最新基线方法,实现了更高的皮尔逊相关系数(高达0.712)、余弦相似度(高达0.812),以及更低的RMSE和MAE值,证明其在微生物估算中的稳健性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 微生物组数据分析对理解宿主健康和疾病至关重要,但数据稀疏性和噪声影响了准确估算。
- 现有估算方法难以捕捉微生物分类群间的复杂相互依赖性。
- DepMicroDiff是一种新型框架,结合了扩散生成建模和依赖感知转换器(DAT)。
- DepMicroDiff能够捕捉微生物间的配对依赖关系和自回归关系。
- DepMicroDiff通过VAE预训练和大型语言模型(LLM)增强功能。
- 实验证明DepMicroDiff在微生物估算上显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


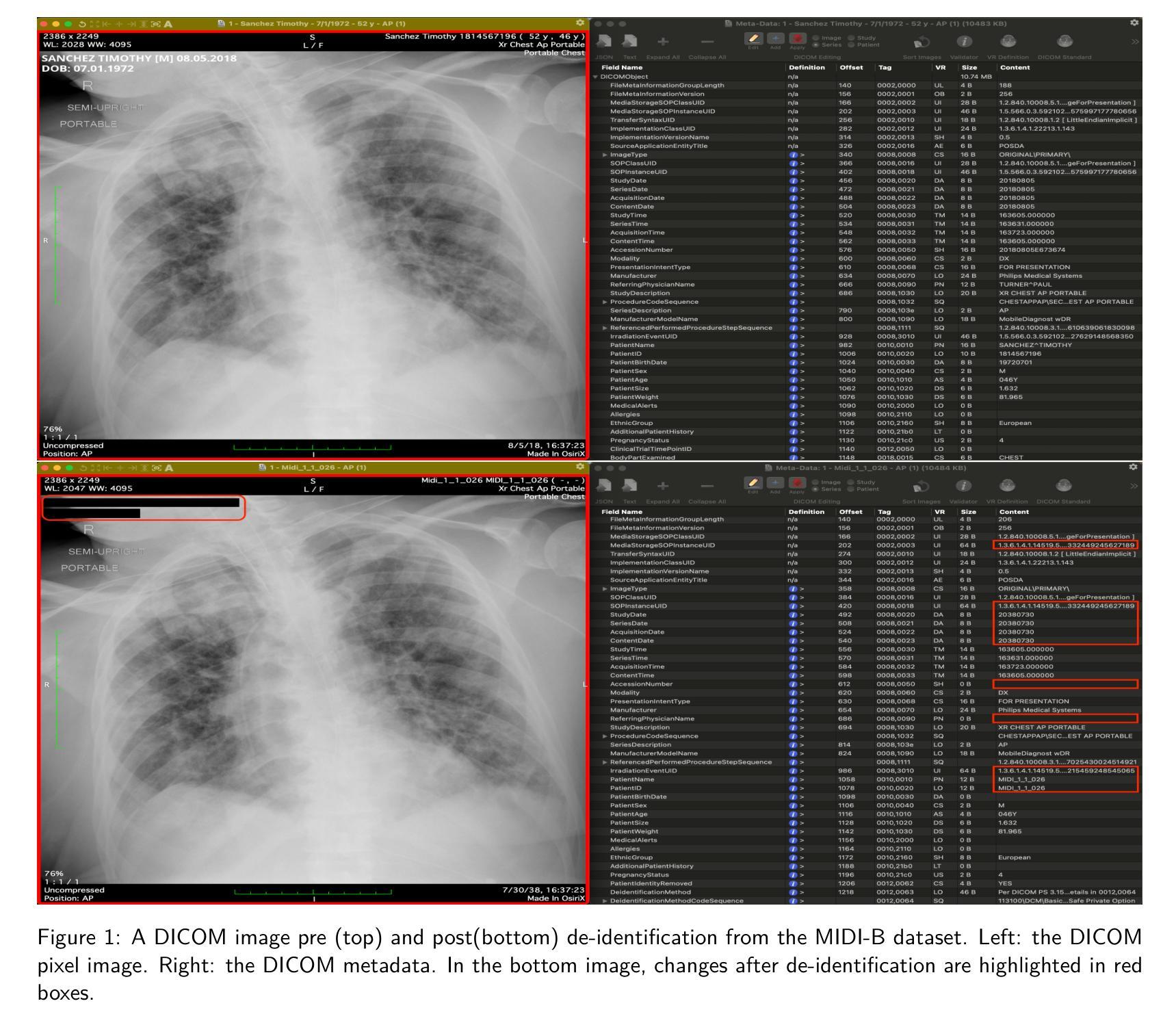
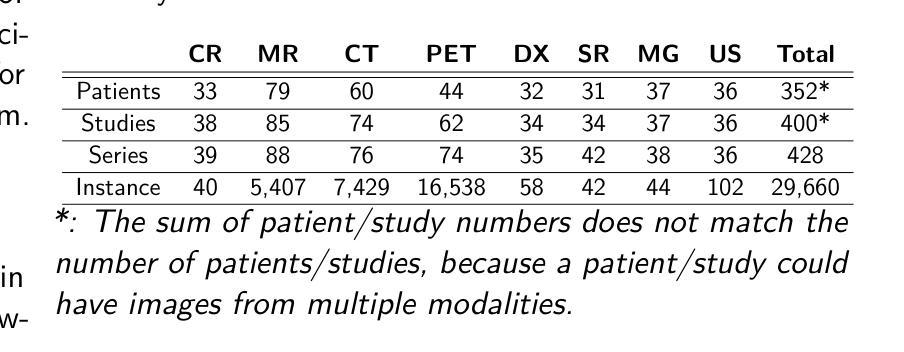
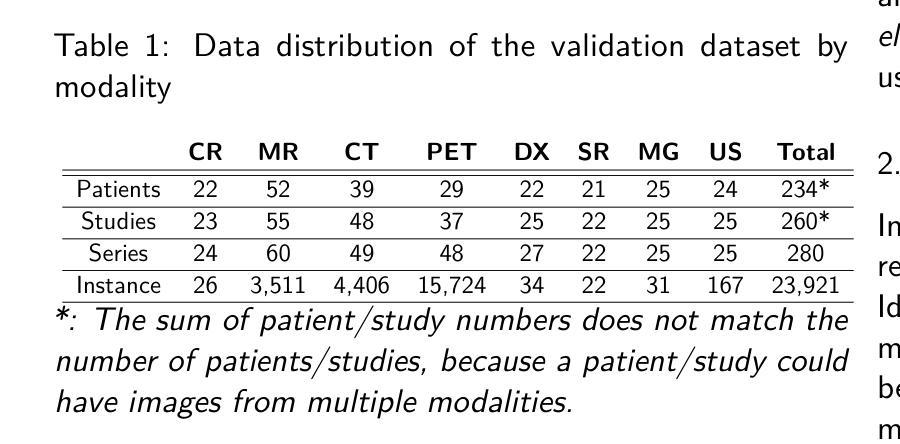
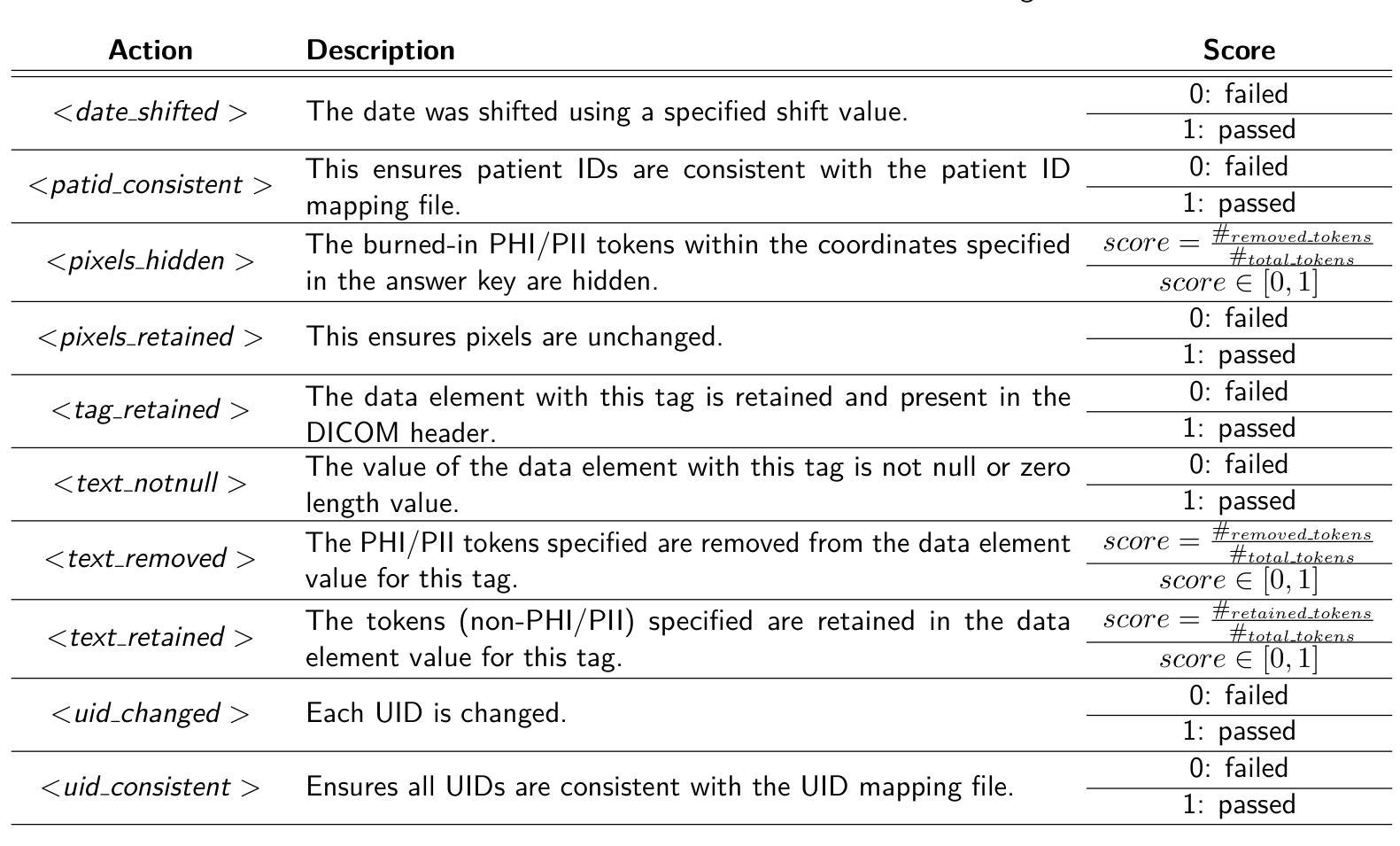
Medical Image De-Identification Benchmark Challenge
Authors:Linmin Pei, Granger Sutton, Michael Rutherford, Ulrike Wagner, Tracy Nolan, Kirk Smith, Phillip Farmer, Peter Gu, Ambar Rana, Kailing Chen, Thomas Ferleman, Brian Park, Ye Wu, Jordan Kojouharov, Gargi Singh, Jon Lemon, Tyler Willis, Milos Vukadinovic, Grant Duffy, Bryan He, David Ouyang, Marco Pereanez, Daniel Samber, Derek A. Smith, Christopher Cannistraci, Zahi Fayad, David S. Mendelson, Michele Bufano, Elmar Kotter, Hamideh Haghiri, Rajesh Baidya, Stefan Dvoretskii, Klaus H. Maier-Hein, Marco Nolden, Christopher Ablett, Silvia Siggillino, Sandeep Kaushik, Hongzhu Jiang, Sihan Xie, Zhiyu Wan, Alex Michie, Simon J Doran, Angeline Aurelia Waly, Felix A. Nathaniel Liang, Humam Arshad Mustagfirin, Michelle Grace Felicia, Kuo Po Chih, Rahul Krish, Ghulam Rasool, Nidhal Bouaynaya, Nikolas Koutsoubis, Kyle Naddeo, Kartik Pandit, Tony O’Sullivan, Raj Krish, Qinyan Pan, Scott Gustafson, Benjamin Kopchick, Laura Opsahl-Ong, Andrea Olvera-Morales, Jonathan Pinney, Kathryn Johnson, Theresa Do, Juergen Klenk, Maria Diaz, Arti Singh, Rong Chai, David A. Clunie, Fred Prior, Keyvan Farahani
The de-identification (deID) of protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII) is a fundamental requirement for sharing medical images, particularly through public repositories, to ensure compliance with patient privacy laws. In addition, preservation of non-PHI metadata to inform and enable downstream development of imaging artificial intelligence (AI) is an important consideration in biomedical research. The goal of MIDI-B was to provide a standardized platform for benchmarking of DICOM image deID tools based on a set of rules conformant to the HIPAA Safe Harbor regulation, the DICOM Attribute Confidentiality Profiles, and best practices in preservation of research-critical metadata, as defined by The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). The challenge employed a large, diverse, multi-center, and multi-modality set of real de-identified radiology images with synthetic PHI/PII inserted. The MIDI-B Challenge consisted of three phases: training, validation, and test. Eighty individuals registered for the challenge. In the training phase, we encouraged participants to tune their algorithms using their in-house or public data. The validation and test phases utilized the DICOM images containing synthetic identifiers (of 216 and 322 subjects, respectively). Ten teams successfully completed the test phase of the challenge. To measure success of a rule-based approach to image deID, scores were computed as the percentage of correct actions from the total number of required actions. The scores ranged from 97.91% to 99.93%. Participants employed a variety of open-source and proprietary tools with customized configurations, large language models, and optical character recognition (OCR). In this paper we provide a comprehensive report on the MIDI-B Challenge’s design, implementation, results, and lessons learned.
受保护的健康信息(PHI)和个人可识别信息(PII)的去标识化是共享医疗图像的基本要求,特别是通过公共存储库共享时,以确保符合患者隐私法规。此外,保留非PHI元数据以告知并促进成像人工智能(AI)的下游发展是生物医学研究中的重要考虑因素。MIDI-B的目标是提供一个标准化的平台,以基于一组符合HIPAA安全港法规、DICOM属性保密配置文件以及癌症成像存档(TCIA)定义的保留研究关键元数据的最佳实践来评估DICOM图像去标识化工具。该挑战采用了大量多样化、多中心、多模式的真实去标识化放射学图像,并插入了合成PHI/PII。MIDI-B挑战分为三个阶段:培训、验证和测试。有80人报名参加挑战。在培训阶段,我们鼓励参与者使用内部或公开数据调整其算法。验证和测试阶段使用了包含合成标识符的DICOM图像(分别为216名和322名受试者)。有十支队伍成功完成了测试阶段的挑战。为了衡量基于规则的去图像标识方法成功与否,分数是根据完成所有必需动作的正确行动百分比来计算的。分数范围从97.91%到99.93%。参与者使用了各种开源和专有工具,具有自定义配置、大型语言模型和光学字符识别(OCR)。在本文中,我们提供了关于MIDI-B挑战的设计、实施、结果和经验教训的全面报告。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages
Summary
MIDI-B挑战旨在提供一个标准化平台,用于基于DICOM图像去标识(deID)工具的性能基准测试。挑战的目的是确保医学图像共享时遵守患者隐私法规,同时保留非PHI元数据以支持下游的成像人工智能(AI)发展。该挑战包括培训、验证和测试三个阶段,涉及大量真实去标识的放射图像,并成功完成测试的团队有十支。规则方法的成功度量是基于正确行动占总行动百分比的评分,评分范围在97.91%至99.93%之间。该论文详细报告了MIDI-B挑战的设计、实施、结果和经验教训。
Key Takeaways
- MIDI-B挑战提供了一个标准化平台,用于评估DICOM图像去标识(deID)工具的性能。
- 挑战的目的是确保医学图像共享时遵守患者隐私法规,同时保留非PHI元数据支持AI研究。
- 挑战涉及大量多中心、多模态的真实去标识放射图像和插入的合成PHI/PII。
- 挑战包括培训、验证和测试三个阶段,共有80人注册参与。
- 有十支团队成功完成了测试阶段的挑战。
- 成功度量是基于正确行动占总行动百分比的评分,显示规则方法的高度准确性。
点此查看论文截图

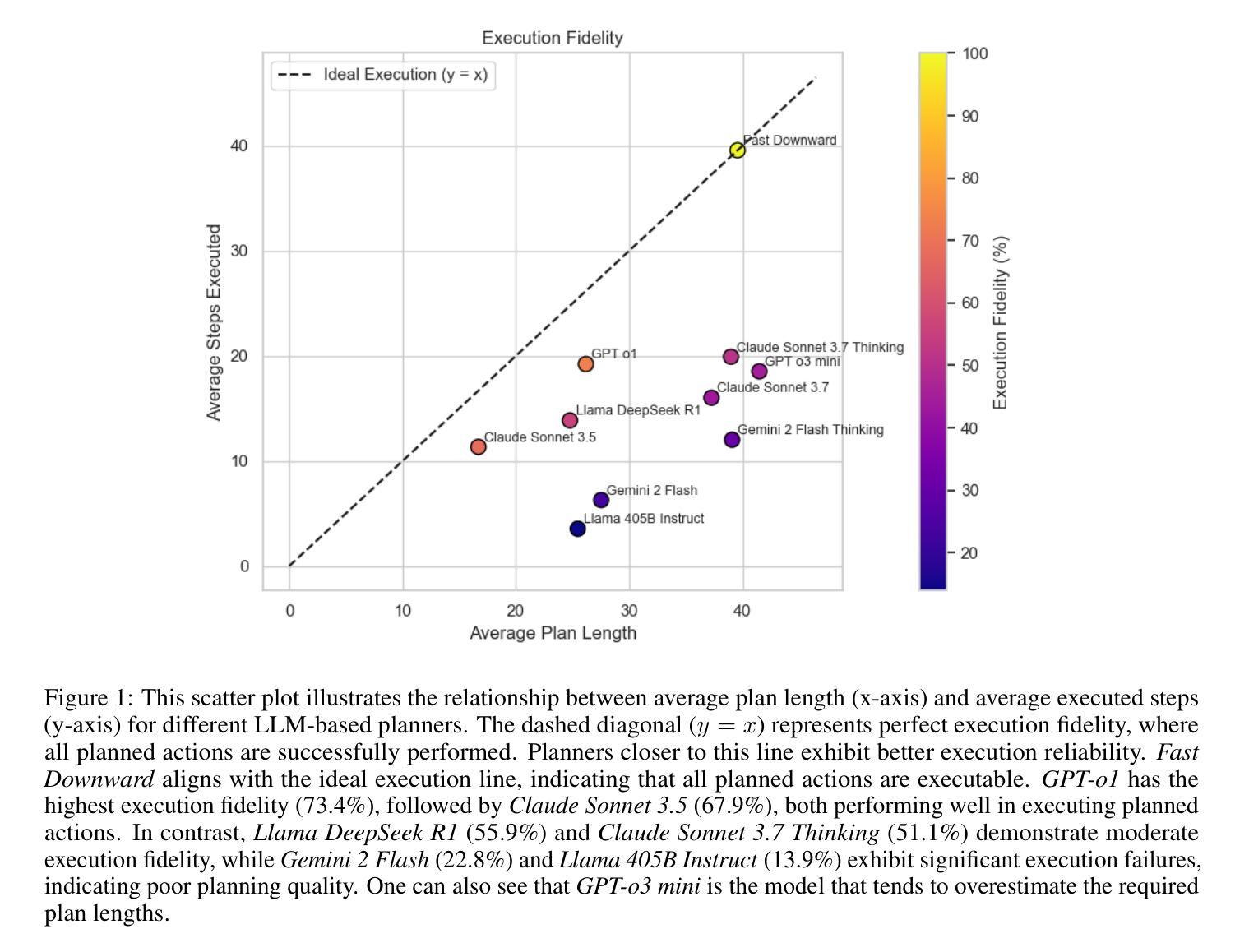
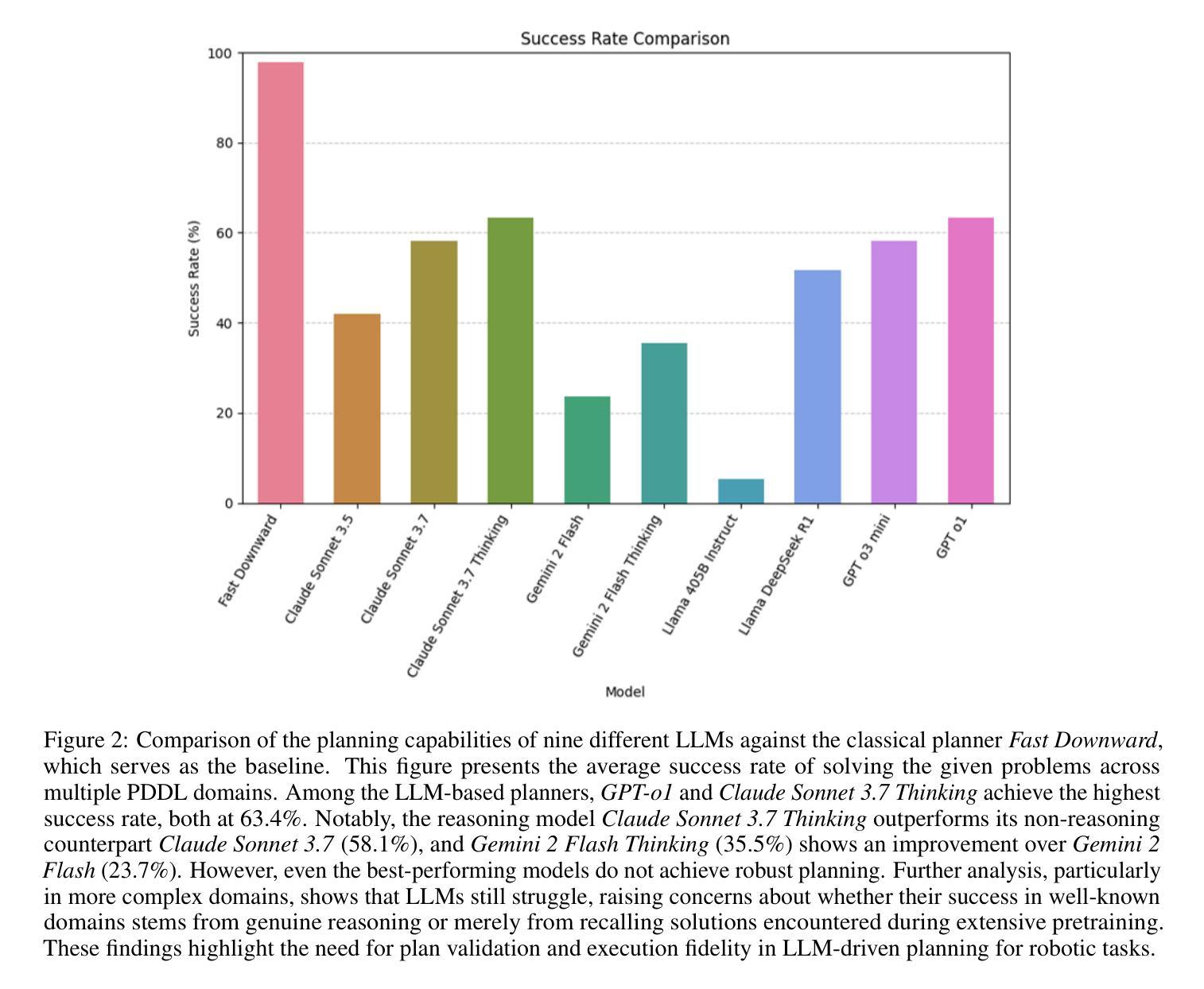
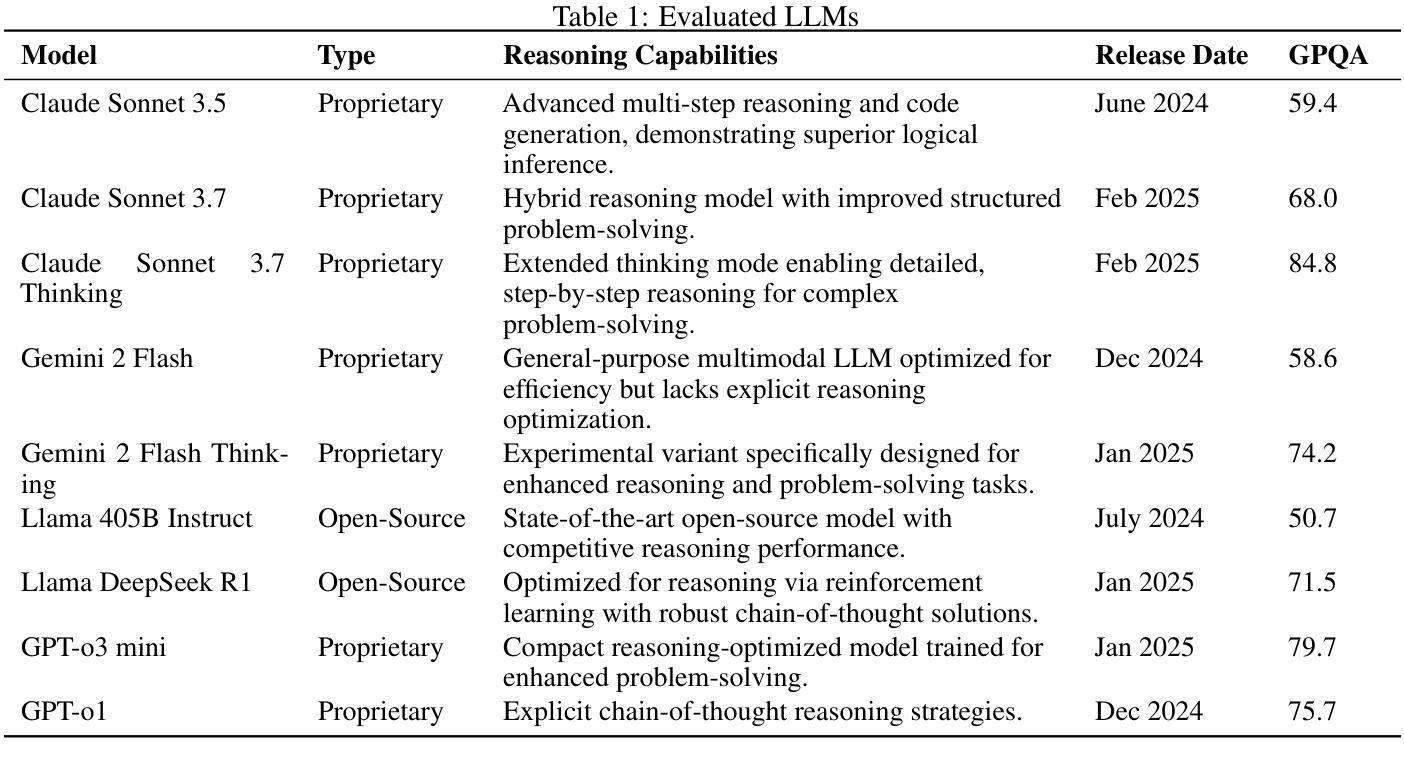
Can LLM-Reasoning Models Replace Classical Planning? A Benchmark Study
Authors:Kai Goebel, Patrik Zips
Recent advancements in Large Language Models have sparked interest in their potential for robotic task planning. While these models demonstrate strong generative capabilities, their effectiveness in producing structured and executable plans remains uncertain. This paper presents a systematic evaluation of a broad spectrum of current state of the art language models, each directly prompted using Planning Domain Definition Language domain and problem files, and compares their planning performance with the Fast Downward planner across a variety of benchmarks. In addition to measuring success rates, we assess how faithfully the generated plans translate into sequences of actions that can actually be executed, identifying both strengths and limitations of using these models in this setting. Our findings show that while the models perform well on simpler planning tasks, they continue to struggle with more complex scenarios that require precise resource management, consistent state tracking, and strict constraint compliance. These results underscore fundamental challenges in applying language models to robotic planning in real world environments. By outlining the gaps that emerge during execution, we aim to guide future research toward combined approaches that integrate language models with classical planners in order to enhance the reliability and scalability of planning in autonomous robotics.
最近大型语言模型的进步激发了人们对机器任务规划潜在可能性的兴趣。虽然这些模型表现出了强大的生成能力,但它们对于结构化执行规划的效用仍然存在不确定性。本文系统地评估了一系列当前先进的语言模型,使用规划领域定义语言和问题文件直接提示每个模型,并在各种基准测试中将它们的规划性能与快速向下规划器进行比较。除了衡量成功率之外,我们还评估了生成的计划转化为可实际执行的行动序列的程度,以识别在这种环境中使用这些模型的优缺点。我们的研究结果表明,虽然这些模型在简单的规划任务上表现良好,但在需要精确资源管理、持续状态跟踪和严格约束遵守的复杂场景中仍面临挑战。这些结果突显了在现实环境将语言模型应用于机器人规划时所面临的基本挑战。通过阐述执行过程中出现的差距,我们的目标是为未来研究指明方向,采用将语言模型与经典规划器相结合的方法,以提高自主机器人规划的可靠性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期大型语言模型在机器人任务规划方面的潜力引发了广泛关注。本文对一系列先进语言模型进行了系统评估,使用规划领域定义语言域和问题文件直接提示,与快速向下规划器在各种基准测试上进行规划性能比较。除了成功率外,还评估了生成计划转化为可执行动作序列的忠实度,探讨了在这些场景下使用这些模型的优缺点。研究发现在简单规划任务上表现良好,但在需要精确资源管理、持续状态跟踪和严格约束遵守的复杂场景中仍面临挑战。本研究旨在指导未来研究结合语言模型和经典规划器,以提高自主机器人规划的可靠性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在机器人任务规划方面的潜力引发关注。
- 系统评估了一系列先进语言模型在规划性能方面的表现。
- 使用规划领域定义语言进行直接提示,并与快速向下规划器进行比较。
- 在简单规划任务上表现良好,但在复杂场景中仍面临挑战。
- 生成计划的忠实度转化为可执行动作序列是评估重点。
- 研究指出了在机器人任务规划中语言模型的优缺点。
点此查看论文截图


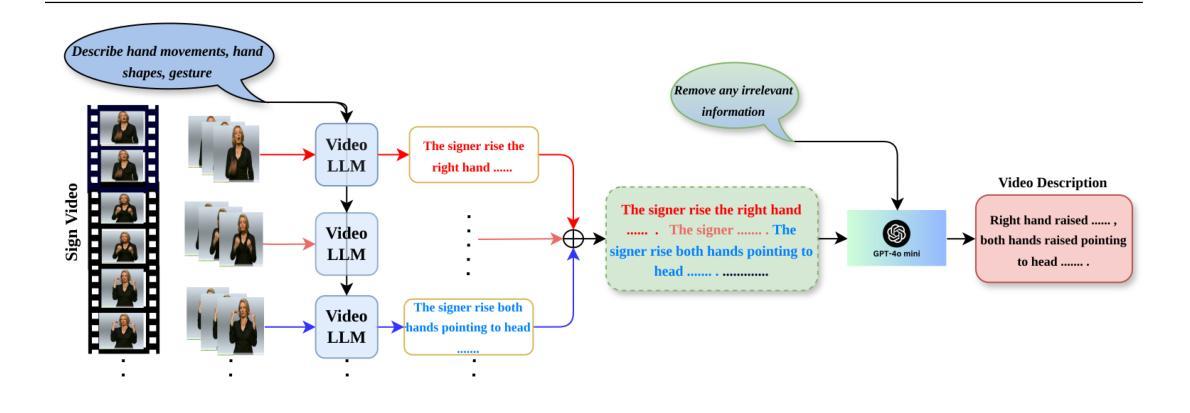
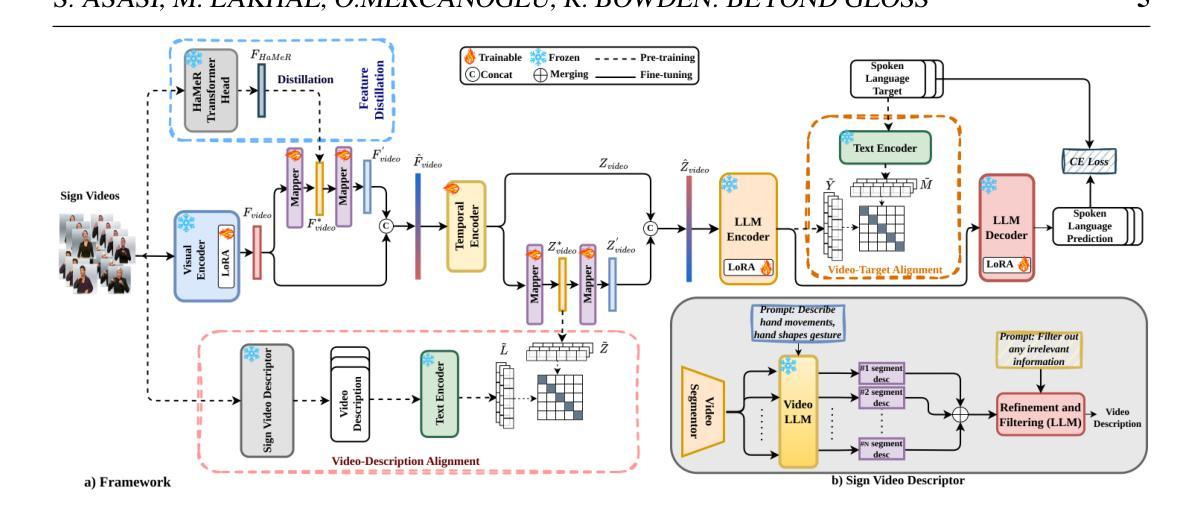
Beyond Gloss: A Hand-Centric Framework for Gloss-Free Sign Language Translation
Authors:Sobhan Asasi, Mohamed Ilyas Lakhal, Ozge Mercanoglu Sincan, Richard Bowden
Sign Language Translation (SLT) is a challenging task that requires bridging the modality gap between visual and linguistic information while capturing subtle variations in hand shapes and movements. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{BeyondGloss}, a novel gloss-free SLT framework that leverages the spatio-temporal reasoning capabilities of Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs). Since existing VideoLLMs struggle to model long videos in detail, we propose a novel approach to generate fine-grained, temporally-aware textual descriptions of hand motion. A contrastive alignment module aligns these descriptions with video features during pre-training, encouraging the model to focus on hand-centric temporal dynamics and distinguish signs more effectively. To further enrich hand-specific representations, we distill fine-grained features from HaMeR. Additionally, we apply a contrastive loss between sign video representations and target language embeddings to reduce the modality gap in pre-training. \textbf{BeyondGloss} achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Phoenix14T and CSL-Daily benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed framework. We will release the code upon acceptance of the paper.
手势语言翻译(SLT)是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要弥合视觉和语言信息之间的模式差距,同时捕捉手部形状和动作的细微变化。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了BeyondGloss,这是一种全新的无字幕SLT框架,它利用视频大语言模型(VideoLLM)的时空推理能力。由于现有的VideoLLM在详细建模长视频方面存在困难,我们提出了一种新方法,生成手部运动的精细时间感知文本描述。对比对齐模块在预训练过程中将这些描述与视频特征对齐,鼓励模型关注以手为中心的临时动态,更有效地区分手势。为了丰富手部特定表示,我们从HaMeR中提炼出精细特征。此外,我们在预训练过程中,在手势视频表示和目标语言嵌入之间应用对比损失,以减少模式差距。BeyondGloss在Phoenix14T和CSL-Daily基准测试中达到了最先进的性能表现,证明了该框架的有效性。论文被接受后,我们将公开代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at BMVC 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一项新的研究,针对手语翻译中的视觉与语言信息交互难题,提出了BeyondGloss这一全新无词注手语翻译框架。它通过视频大语言模型的空间时间推理能力,解决现有模型对长视频细节建模能力不足的问题,生成精细的时间感知手部运动文本描述。采用对比对齐模块在预训练过程中将这些描述与视频特征对齐,以提高模型对手部为中心的时间动态的关注度和辨识效果。此外,还引入了HamRe精细特征蒸馏技术,并应用对比损失来缩小预训练中的模态差距。BeyondGloss在Phoenix14T和CSL-Daily基准测试中实现了业界领先的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- BeyondGloss是一个全新的无词注手语翻译框架,用于解决手语翻译中的视觉与语言信息交互难题。
- 利用视频大语言模型的空间时间推理能力处理手语翻译任务。
- 提出了生成精细时间感知手部运动文本描述的方法,以解决现有模型对长视频细节建模能力不足的问题。
- 采用对比对齐模块在预训练过程中对齐文本描述与视频特征,提高模型对手部为中心的时间动态的关注度。
- 引入HamRe精细特征蒸馏技术来丰富手部特定的表现。
- 应用对比损失来缩小手语视频的表示与目标语言嵌入之间的模态差距。
- BeyondGloss在Phoenix14T和CSL-Daily基准测试中取得了业界领先的性能。
点此查看论文截图

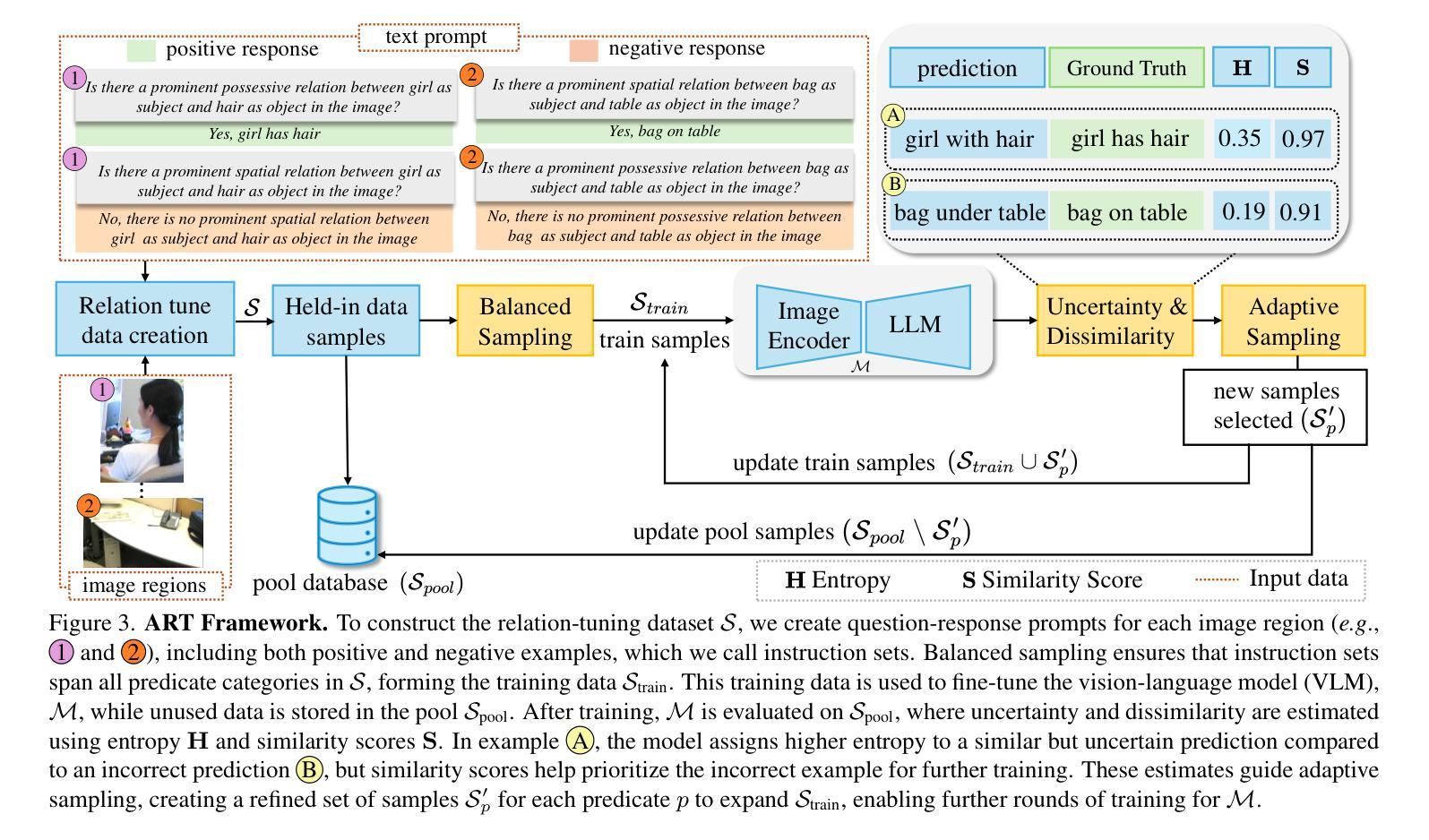
ART: Adaptive Relation Tuning for Generalized Relation Prediction
Authors:Gopika Sudhakaran, Hikaru Shindo, Patrick Schramowski, Simone Schaub-Meyer, Kristian Kersting, Stefan Roth
Visual relation detection (VRD) is the task of identifying the relationships between objects in a scene. VRD models trained solely on relation detection data struggle to generalize beyond the relations on which they are trained. While prompt tuning has been used to adapt vision-language models (VLMs) for VRD, it uses handcrafted prompts and struggles with novel or complex relations. We argue that instruction tuning offers a more effective solution by fine-tuning VLMs on diverse instructional data. We thus introduce ART, an Adaptive Relation Tuning framework that adapts VLMs for VRD through instruction tuning and strategic instance selection. By converting VRD datasets into an instruction tuning format and employing an adaptive sampling algorithm, ART directs the VLM to focus on informative relations while maintaining generalizability. Specifically, we focus on the relation classification, where subject-object boxes are given and the model predicts the predicate between them. We tune on a held-in set and evaluate across multiple held-out datasets of varying complexity. Our approach strongly improves over its baselines and can infer unseen relation concepts, a capability absent in mainstream VRD methods. We demonstrate ART’s practical value by using the predicted relations for segmenting complex scenes.
视觉关系检测(VRD)是识别场景中物体之间关系的任务。仅通过关系检测数据进行训练的VRD模型很难推广到其未训练过的关系之外。虽然提示调整已被用于适应视觉语言模型(VLM)进行VRD,但它使用手工制作的提示,并在面对新颖或复杂关系时面临困难。我们认为,指令调整通过在对多样化的指令数据进行微调时,为VLM提供更有效的解决方案。因此,我们引入了ART,这是一种自适应关系调整框架,它通过指令调整和策略性实例选择来适应VLM进行VRD。通过将VRD数据集转换为指令调整格式并采用自适应采样算法,ART指导VLM专注于信息丰富的关系,同时保持其泛化能力。具体来说,我们关注关系分类,其中给定主体-对象框,模型会预测它们之间的谓语。我们在保留集上进行调整,并在多个复杂的保留数据集上进行评估。我们的方法比其基线方法有显著改善,并且可以推断出未见的关系概念,这是主流VRD方法所不具备的能力。我们通过使用预测的关系来分割复杂场景,展示了ART的实际价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in ICCV 2025
Summary
视觉关系检测(VRD)的任务是识别场景中物体之间的关系。仅通过关系检测数据训练的VRD模型难以泛化到未经过训练的关系上。虽然提示调整已被用于适应视觉语言模型(VLM)进行VRD,但它依赖于手工制作的提示,对于新颖或复杂的关系处理起来较为困难。本文提出通过指令调整来更有效地解决这一问题,即通过多样化指令数据对VLM进行微调。因此,我们引入了ART(自适应关系调整框架),它通过指令调整和策略性实例选择来适应VLM进行VRD。通过将VRD数据集转换为指令调整格式并采用自适应采样算法,ART指导VLM关注有信息量的关系,同时保持泛化能力。我们专注于关系分类任务,其中给定主体-对象框,模型预测它们之间的谓语。我们在保留集上进行调整,并在多个复杂的保留外数据集上进行评估。我们的方法相较于基线方法有明显的改进,并能够推断未见过的关系概念,这是主流VRD方法所不具备的能力。我们通过使用预测的关分割复杂场景来展示ART的实际价值。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉关系检测(VRD)是识别场景中物体间关系的任务。
- 单纯依赖关系检测数据训练的VRD模型泛化能力有限。
- 指令调整相比手工提示更能有效适应视觉语言模型(VLM)进行VRD。
- 引入ART框架,通过指令调整和策略性实例选择来优化VLM的VRD性能。
- ART能将VRD数据集转换为指令调整格式,并通过自适应采样算法指导模型关注有信息量的关系。
- ART在关系分类任务上表现优异,特别是在预测主体与对象间谓语的任务上。
点此查看论文截图



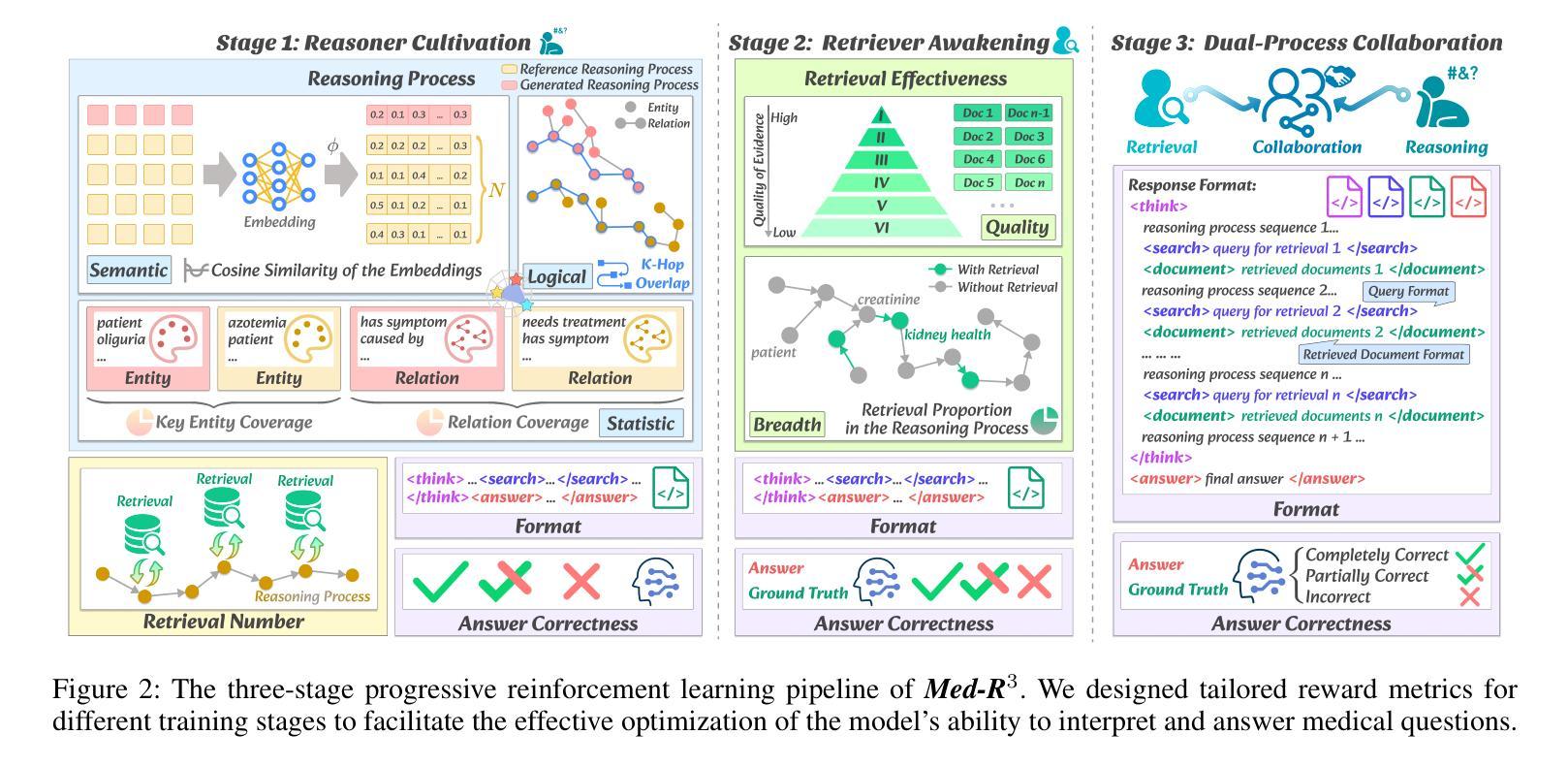
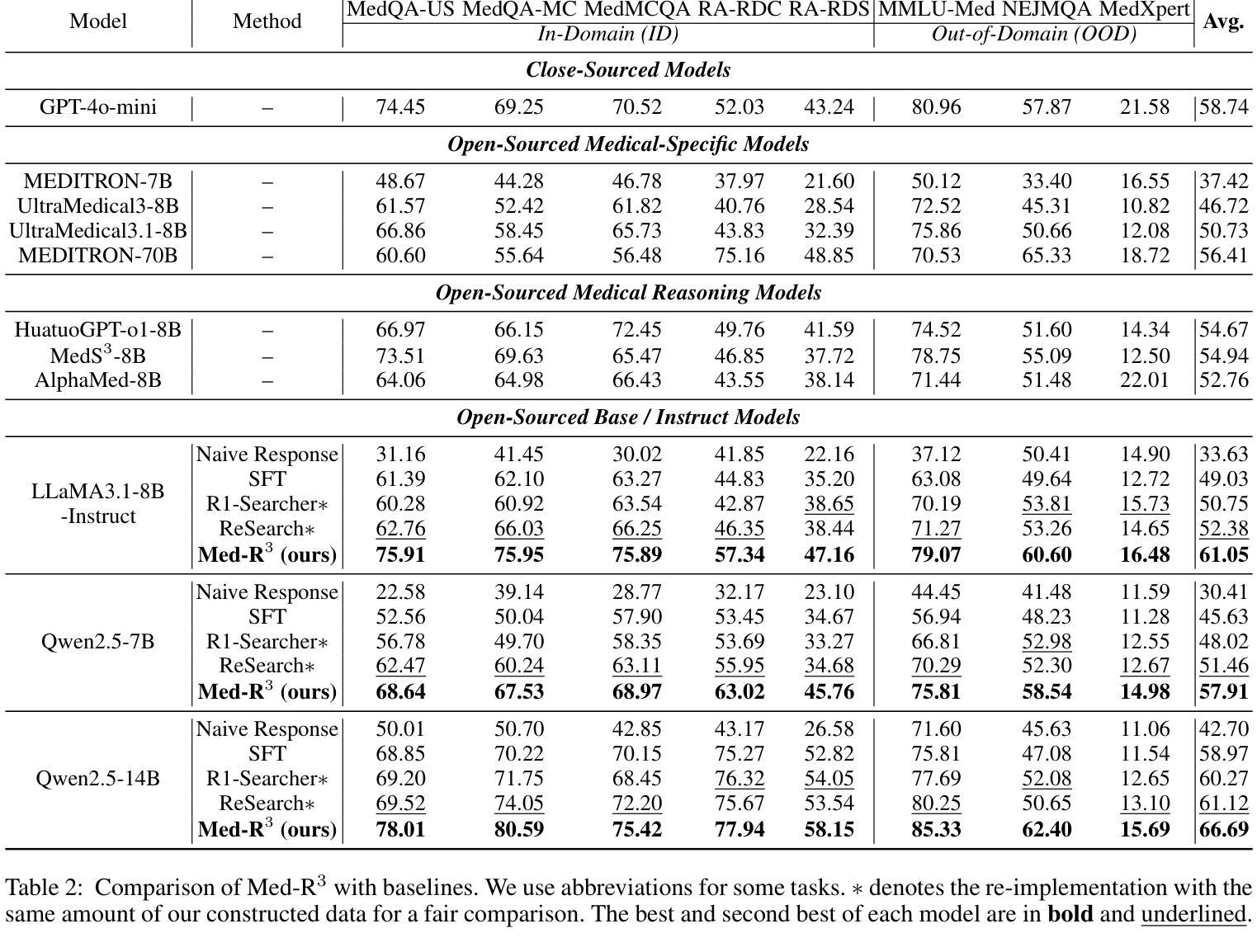
Med-R$^3$: Enhancing Medical Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning of LLMs via Progressive Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Keer Lu, Zheng Liang, Youquan Li, Jiejun Tan, Da Pan, Shusen Zhang, Guosheng Dong, Huang Leng
In medical scenarios, effectively retrieving external knowledge and leveraging it for rigorous logical reasoning is of significant importance. Despite their potential, existing work has predominantly focused on enhancing either retrieval or reasoning capabilities of the models in isolation, with little attention given to their joint optimization, which leads to limited coordination between the two processes. Additionally, current methods rely heavily on supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which can cause models to memorize existing problem-solving pathways, thereby restricting their generalization ability when confronted with novel problem contexts. Furthermore, while some studies have explored to improve retrieval-augmented reasoning in general domains via reinforcement learning, their reward function designs do not adequately capture the specific demands of the medical domain. To address these challenges, we introduce Med-R$^3$, a Medical Retrieval-augmented Reasoning framework driven by progressive Reinforcement learning. In this framework, we first develop the model’s ability to perform logical reasoning over medical problems. Subsequently, on the basis of this foundation, we adaptively optimize the retrieval capability to better align with the characteristics of knowledge corpus and external information utilization throughout the reasoning process. Finally, we conduct joint optimization of the model’s retrieval and reasoning coordination. Extensive experiments indicate that Med-R$^3$ could achieve state-of-the-art performances, with LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + Med-R$^3$ surpassing closed-sourced GPT-4o-mini by 3.93% at a comparable parameter scale, while Qwen2.5-14B augmented with Med-R$^3$ shows a more substantial gain of 13.53%.
在医疗场景中,有效地检索外部知识并充分利用其进行严格的逻辑推理具有非常重要的意义。尽管存在潜在的改进空间,但现有的工作主要集中在增强模型的检索或推理能力方面,而对两者的联合优化关注较少,导致这两个过程之间的协调有限。此外,当前的方法严重依赖于有监督的微调(SFT),这可能导致模型记忆现有的问题解决路径,从而在面对新的问题情境时限制其泛化能力。虽然一些研究已经探索了通过强化学习改进一般领域的检索增强推理,但其奖励函数设计并没有充分捕捉到医疗领域的特定需求。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Med-R$^3$,这是一个由渐进强化学习驱动的Medical Retrieval-augmented Reasoning框架。在这个框架中,我们首先开发模型解决医疗问题的逻辑推理能力。随后,在此基础上,我们自适应地优化检索能力,以更好地适应知识语料库和外部信息在推理过程中的利用特点。最后,我们对模型的检索和推理协调进行联合优化。大量实验表明,Med-R$^3$**能够达到最先进的性能,在参数规模相当的情况下,LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + Med-R$^3$超越了闭源的GPT-4o-mini,性能提升了3.93%,而Qwen2.5-14B与Med-R$^3$相结合则显示出更大的性能提升,达到了13.53%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在医疗场景中,外部知识的检索和逻辑推理的有效结合至关重要。现有研究主要关注模型的检索或推理能力的单一提升,而忽视了二者的联合优化,导致两者之间的协调受限。此外,现有方法过于依赖监督微调(SFT),限制了模型的泛化能力。针对这些挑战,我们提出了由渐进式强化学习驱动的Med-R$^3$医疗检索增强推理框架。该框架首先培养模型解决医疗问题的能力,并在此基础上自适应优化检索能力,使其与知识库和外部信息利用的特性相匹配。联合优化模型的检索和推理协调。实验表明,Med-R$^3$达到了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗场景中外部知识的检索和逻辑推理结合至关重要。
- 现有研究主要关注单一能力的提升,缺乏联合优化,导致协调受限。
- 现有方法过于依赖监督微调(SFT),限制了模型的泛化能力。
- Med-R$^3$框架旨在解决以上挑战,通过渐进式强化学习驱动医疗检索增强推理。
- Med-R$^3$首先培养模型解决医疗问题的能力,再优化检索能力。
- Med-R$^3$实现了模型的检索和推理的联合优化。
点此查看论文截图

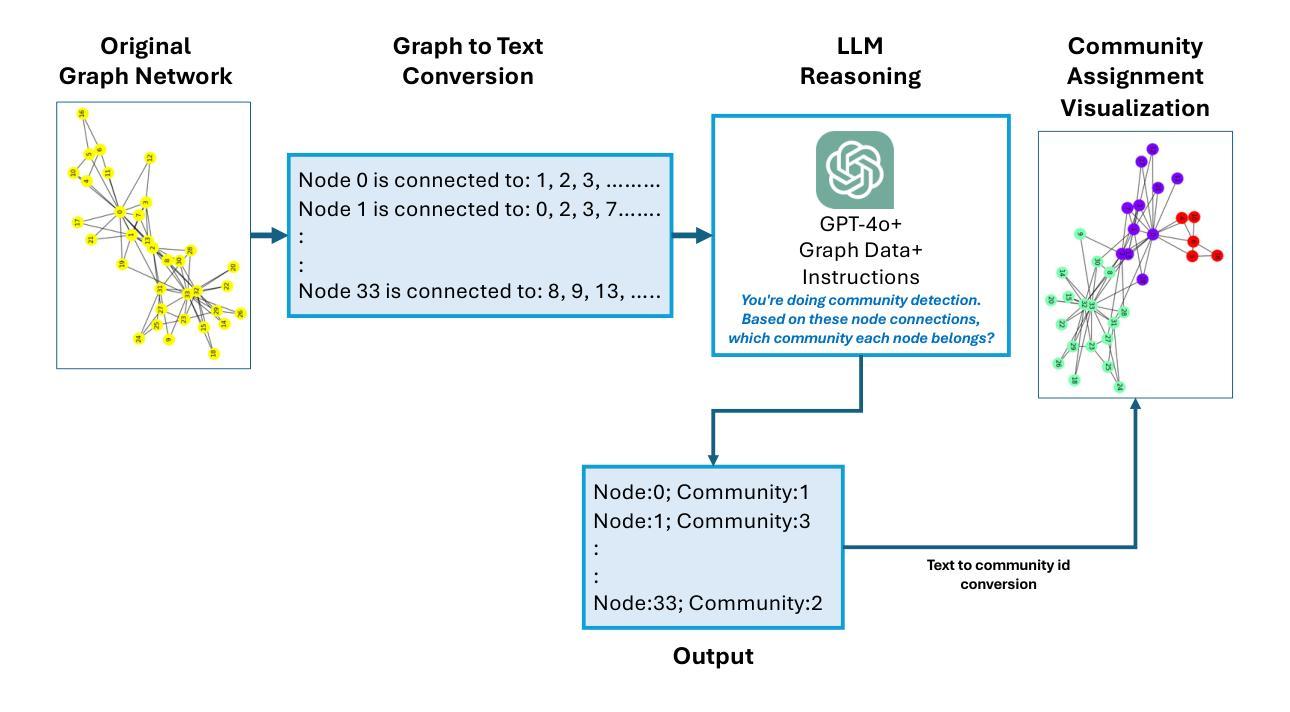
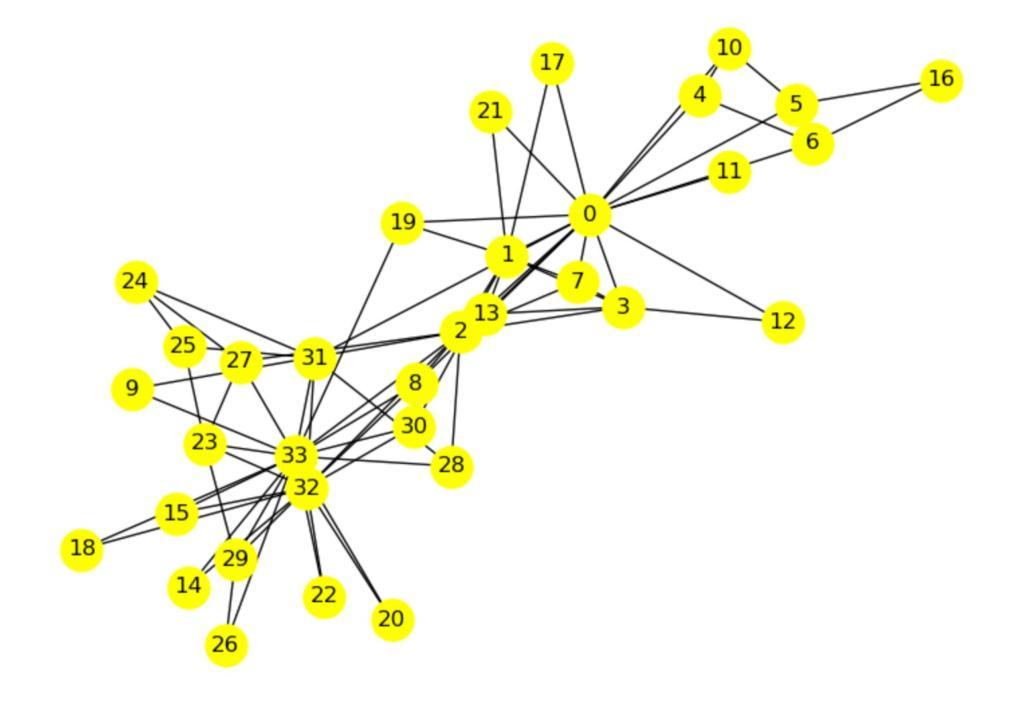
LLMs Between the Nodes: Community Discovery Beyond Vectors
Authors:Ekta Gujral, Apurva Sinha
Community detection in social network graphs plays a vital role in uncovering group dynamics, influence pathways, and the spread of information. Traditional methods focus primarily on graph structural properties, but recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) open up new avenues for integrating semantic and contextual information into this task. In this paper, we present a detailed investigation into how various LLM-based approaches perform in identifying communities within social graphs. We introduce a two-step framework called CommLLM, which leverages the GPT-4o model along with prompt-based reasoning to fuse language model outputs with graph structure. Evaluations are conducted on six real-world social network datasets, measuring performance using key metrics such as Normalized Mutual Information (NMI), Adjusted Rand Index (ARI), Variation of Information (VOI), and cluster purity. Our findings reveal that LLMs, particularly when guided by graph-aware strategies, can be successfully applied to community detection tasks in small to medium-sized graphs. We observe that the integration of instruction-tuned models and carefully engineered prompts significantly improves the accuracy and coherence of detected communities. These insights not only highlight the potential of LLMs in graph-based research but also underscore the importance of tailoring model interactions to the specific structure of graph data.
社交网络图中的社区检测在揭示群体动态、影响路径和信息传播方面起着至关重要的作用。传统方法主要关注图的结构属性,但大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为将此任务与语义和上下文信息集成开辟了新途径。在本文中,我们对基于LLM的不同方法在识别社交网络图内社区时的表现进行了详细调查。我们介绍了一个分两步进行的框架,称为CommLLM,它利用GPT-4o模型和基于提示的推理来融合语言模型输出和图结构。我们在六个真实世界的社交网络数据集上进行了评估,使用归一化互信息(NMI)、调整兰德指数(ARI)、信息变异(VOI)和集群纯度等关键指标来衡量性能。我们的研究发现,LLM,尤其是当采用图感知策略进行引导时,可以成功应用于中小型图的社区检测任务。我们发现指令微调模型的集成和精心设计的提示可以显著提高检测到的社区的准确性和连贯性。这些见解不仅突出了LLM在图基研究中的潜力,也强调了针对图形数据的特定结构定制模型交互的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社区检测在社会网络图中发挥着重要作用,揭示群体动态、影响路径和信息传播。传统方法主要关注图的结构属性,但大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为集成语义和上下文信息提供了新的途径。本文详细调查了LLM在各种方法中的表现,并介绍了一个名为CommLLM的两步框架,它利用GPT-4o模型和基于提示的推理将语言模型输出与图形结构相融合。在六个真实世界的社会网络数据集上进行了评估,使用归一化互信息(NMI)、调整兰德指数(ARI)、变异信息(VOI)和聚类纯度等关键指标衡量性能。研究发现,LLM在小型至中型图中的社区检测任务中表现良好,特别是采用图感知策略指导时。集成指令微调模型和精心设计提示显著提高了检测到的社区的准确性和连贯性。这些见解不仅突显了LLM在图基研究中的潜力,也强调了针对图形数据特定结构定制模型交互的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 社区检测在社会网络图中具有重要作用,能揭示群体动态、影响路径和信息传播。
- 传统社区检测方法主要关注图的结构属性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进展为社区检测任务提供了新的途径,能集成语义和上下文信息。
- 论文介绍了一个名为CommLLM的两步框架,利用GPT-4o模型和基于提示的推理来融合语言模型输出和图形结构。
- 在多个真实世界的社会网络数据集上的评估表明LLM在小型至中型图的社区检测任务中表现良好。
- 采用图感知策略指导的LLM集成方法能提高社区检测的准确性和连贯性。
点此查看论文截图

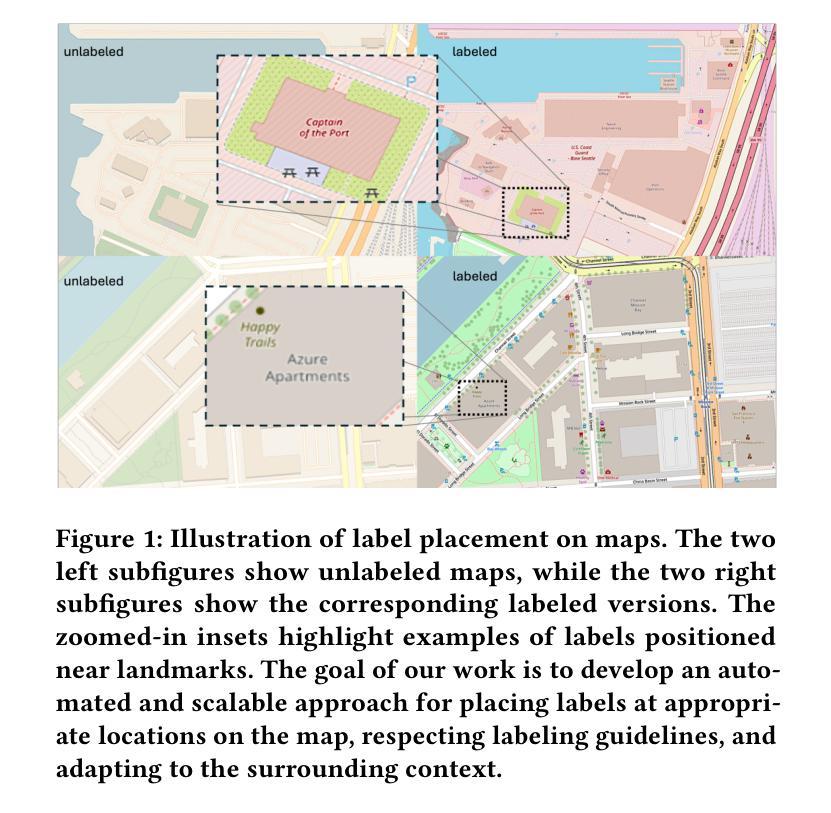
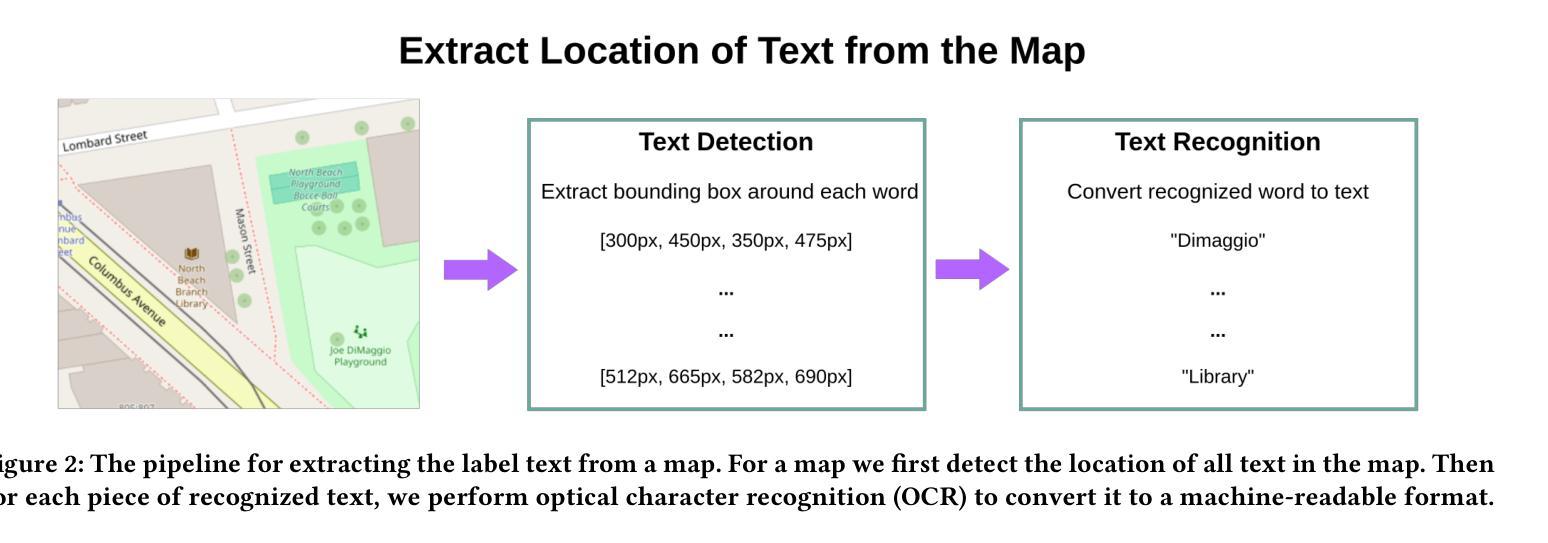
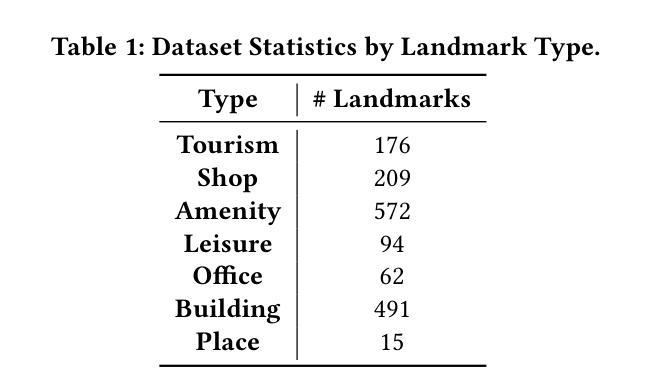
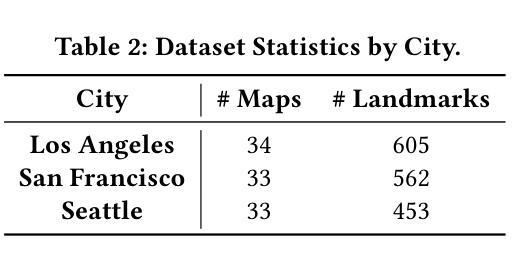
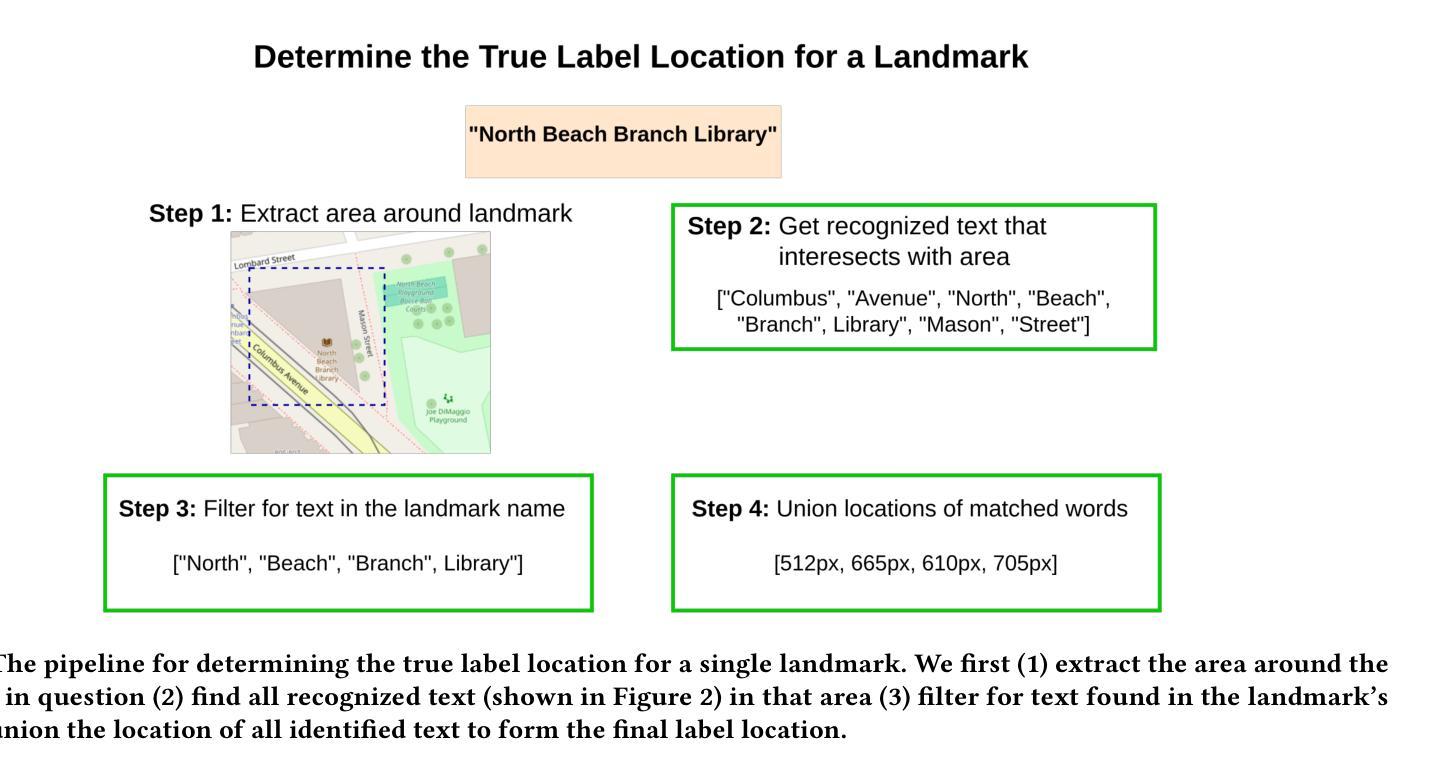
Automated Label Placement on Maps via Large Language Models
Authors:Harry Shomer, Jiejun Xu
Label placement is a critical aspect of map design, serving as a form of spatial annotation that directly impacts clarity and interpretability. Despite its importance, label placement remains largely manual and difficult to scale, as existing automated systems struggle to integrate cartographic conventions, adapt to context, or interpret labeling instructions. In this work, we introduce a new paradigm for automatic label placement (ALP) that formulates the task as a data editing problem and leverages large language models (LLMs) for context-aware spatial annotation. To support this direction, we curate MAPLE, the first known benchmarking dataset for evaluating ALP on real-world maps, encompassing diverse landmark types and label placement annotations from open-source data. Our method retrieves labeling guidelines relevant to each landmark type leveraging retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), integrates them into prompts, and employs instruction-tuned LLMs to generate ideal label coordinates. We evaluate four open-source LLMs on MAPLE, analyzing both overall performance and generalization across different types of landmarks. This includes both zero-shot and instruction-tuned performance. Our results demonstrate that LLMs, when guided by structured prompts and domain-specific retrieval, can learn to perform accurate spatial edits, aligning the generated outputs with expert cartographic standards. Overall, our work presents a scalable framework for AI-assisted map finishing and demonstrates the potential of foundation models in structured data editing tasks. The code and data can be found at https://github.com/HarryShomer/MAPLE.
标签放置是地图设计中的一个关键方面,作为一种空间注释,它直接影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。尽管其重要性很高,但标签放置仍然主要是手动操作,难以扩展,因为现有的自动化系统很难融入地图制作规范、适应上下文或解释标签指令。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新的自动标签放置(ALP)范式,将任务制定为数据编辑问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知空间注释。为了支持这一方向,我们整理了MAPLE数据集,这是首个已知用于评估真实世界地图上ALP性能的基准数据集,涵盖了多种地标类型和标签放置注释,这些数据均来自开源数据。我们的方法通过利用检索增强生成(RAG)检索与每种地标类型相关的标签指南,将其集成到提示中,并使用指令微调LLM生成理想的标签坐标。我们在MAPLE上评估了四个开源LLM,分析了整体性能以及在不同类型地标之间的泛化能力。这包括零样本和指令微调性能。结果表明,当受到结构化提示和领域特定检索的指导时,LLM可以学习执行精确的空间编辑,使生成输出与专家地图制作标准相符。总的来说,我们的工作为AI辅助地图制作提供了一个可扩展的框架,并展示了基础模型在结构化数据编辑任务中的潜力。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/HarryShomer/MAPLE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Workshop on AI for Data Editing (AI4DE) at KDD 2025
Summary
标签放置在地图设计中至关重要,直接影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。尽管其重要性显著,但标签放置仍主要依赖手动操作,难以实现规模化。现有自动系统难以融入地图制作规范、适应上下文或解释标签指示。本研究引入了一种新的自动标签放置(ALP)范式,将任务形式化为数据编辑问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知的空间注释。为此,我们整理了MAPLE数据集,这是首个已知的在现实地图中评估ALP的基准数据集,涵盖了多种地标类型和标签放置注释的开源数据。我们的方法通过检索增强生成(RAG)利用与每种地标类型相关的标注指南,将其整合到提示中,并采用指令优化LLM生成理想标签坐标。我们在MAPLE数据集上评估了四个开源LLM的整体性能和在不同类型地标上的泛化能力,包括零样本和指令优化性能。结果表明,在结构化提示和领域特定检索的指导下,LLM可以学习执行精确的空间编辑,使生成输出与专家地图制作标准相符。总体而言,我们的工作为AI辅助地图完成提供了一个可扩展的框架,并展示了基础模型在结构化数据编辑任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 标签放置在地图设计中具有重要影响,直接影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。
- 现有自动标签放置系统存在困难,难以融入地图制作规范、适应上下文或解释标签指示。
- 引入了一种新的自动标签放置(ALP)范式,将任务形式化为数据编辑问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知的空间注释。
- 整理了MAPLE数据集,用于评估在现实地图中的ALP性能。
- 通过检索增强生成(RAG)利用与地标类型相关的标注指南,并采用指令优化LLM生成理想标签坐标。
- LLM在结构化提示和领域特定检索的指导下,可以学习执行精确的空间编辑。
点此查看论文截图

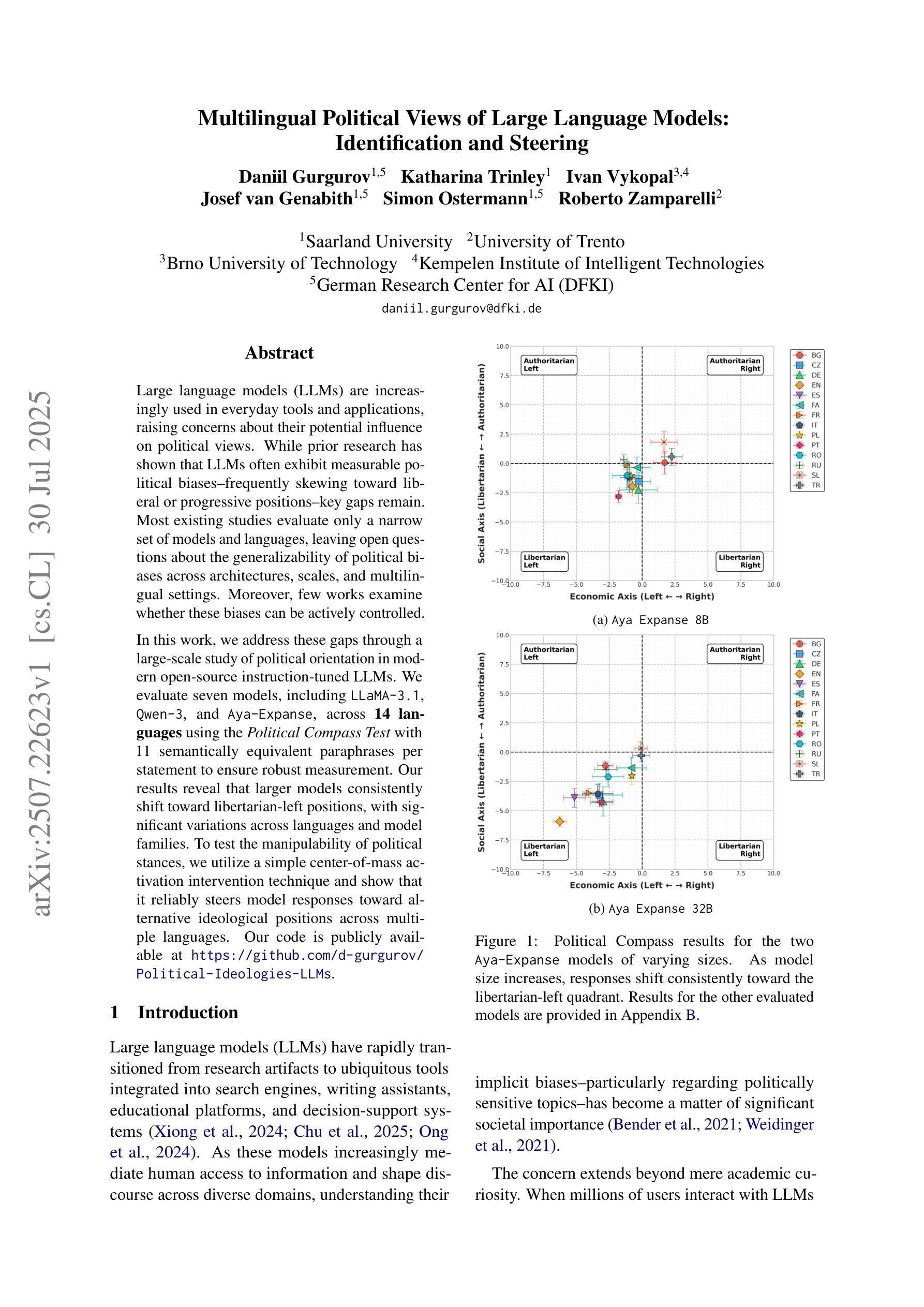
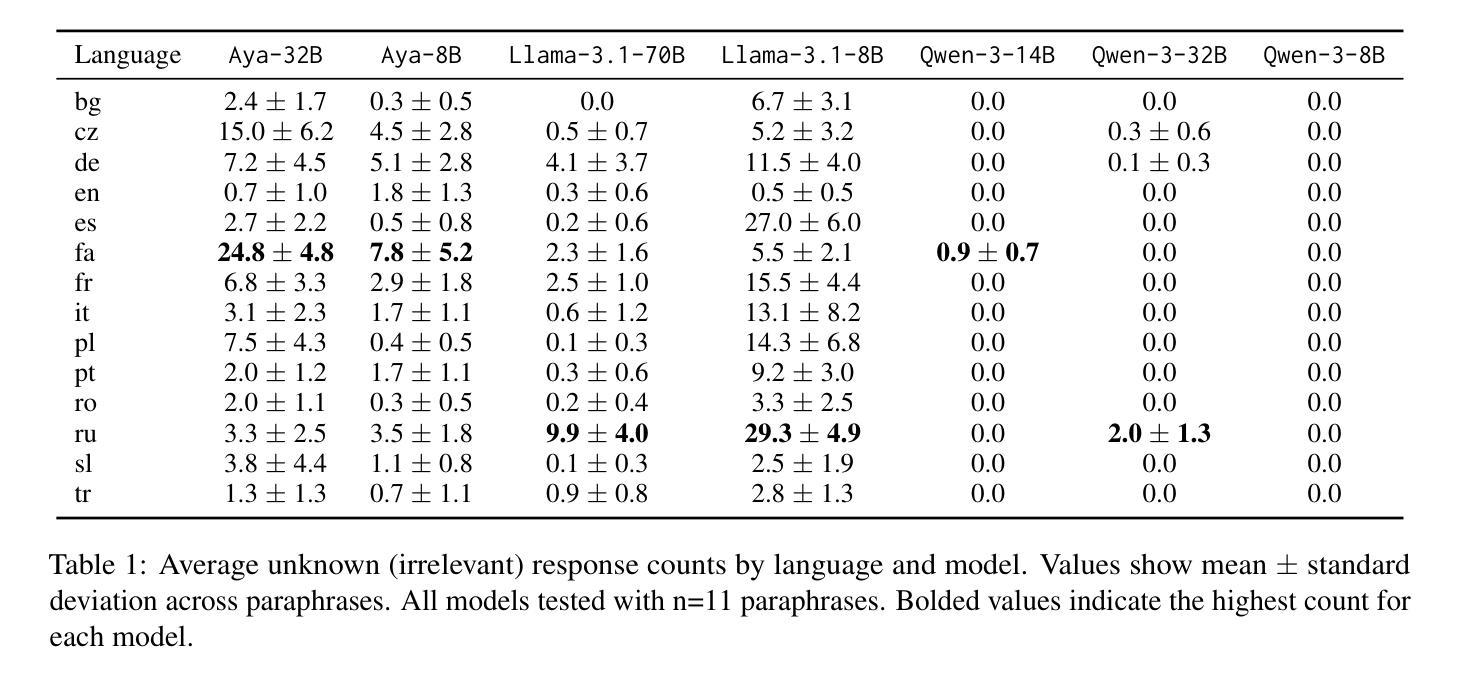
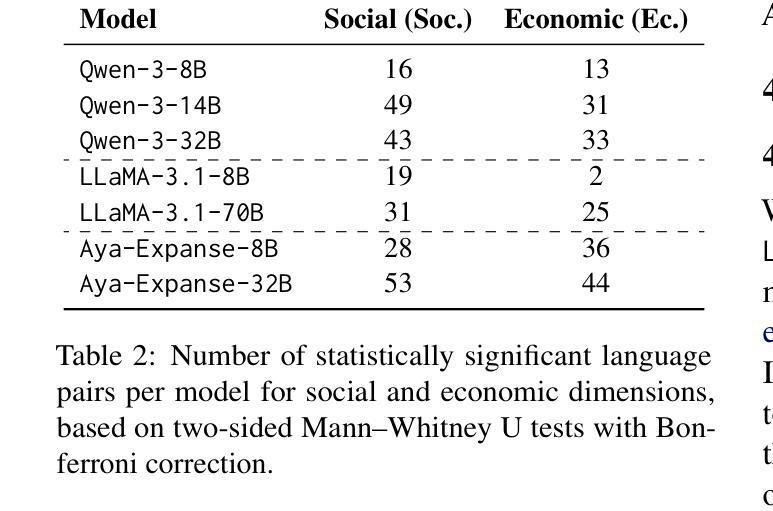
Multilingual Political Views of Large Language Models: Identification and Steering
Authors:Daniil Gurgurov, Katharina Trinley, Ivan Vykopal, Josef van Genabith, Simon Ostermann, Roberto Zamparelli
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in everyday tools and applications, raising concerns about their potential influence on political views. While prior research has shown that LLMs often exhibit measurable political biases–frequently skewing toward liberal or progressive positions–key gaps remain. Most existing studies evaluate only a narrow set of models and languages, leaving open questions about the generalizability of political biases across architectures, scales, and multilingual settings. Moreover, few works examine whether these biases can be actively controlled. In this work, we address these gaps through a large-scale study of political orientation in modern open-source instruction-tuned LLMs. We evaluate seven models, including LLaMA-3.1, Qwen-3, and Aya-Expanse, across 14 languages using the Political Compass Test with 11 semantically equivalent paraphrases per statement to ensure robust measurement. Our results reveal that larger models consistently shift toward libertarian-left positions, with significant variations across languages and model families. To test the manipulability of political stances, we utilize a simple center-of-mass activation intervention technique and show that it reliably steers model responses toward alternative ideological positions across multiple languages. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/d-gurgurov/Political-Ideologies-LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)在日常工具和应用程序中的使用越来越广泛,引发了人们对它们对政治观点潜在影响的担忧。虽然先前的研究表明,LLM通常表现出可衡量的政治偏见,常常倾向于自由或进步立场,但仍存在关键差距。大多数现有研究只评估了有限的模型和语言,对于跨架构、规模和跨语言环境中政治偏见的普遍性仍存在开放问题。此外,很少有研究探讨是否可以主动控制这些偏见。在这项工作中,我们通过一项针对现代开源指令调整的大型语言模型中政治倾向的大规模研究来填补这些空白。我们评估了七个模型,包括LLaMA-3.1、Qwen-3和Aya-Expanse等,跨越14种语言使用政治指南针测试,每个陈述都有11个语义等价的同义替换以确保稳健测量。我们的结果表明,更大的模型往往倾向于自由主义左翼立场,不同语言和模型家族之间存在显著变化。为了测试政治立场的可操控性,我们采用了一种简单的重心激活干预技术,并证明该技术可以可靠地引导模型响应向多种语言的替代意识形态立场靠拢。我们的代码可在https://github.com/d-gurgurov/Political-Ideologies-LLMs公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF pre-print
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)在日常工具和应用中的使用日益普及,引发人们对其可能对政治观点产生影响的担忧。现有研究表明,LLM常表现出可衡量的政治偏见,通常偏向自由或进步立场,但仍存在关键差距。多数现有研究仅评估了有限的模型和语言,关于政治偏见在架构、规模和跨语言环境中的普遍性问题尚存疑问。此外,很少有研究探讨这些偏见是否可以得到主动控制。本研究通过在现代开源指令训练LLM中进行大规模政治倾向研究,填补这些空白。我们评估了七个模型,包括LLaMA-3.1、Qwen-3和Aya-Expanse等,使用政治量表测试在14种语言中的政治倾向,同时采用11个语义等效的同义替换句以确保稳健测量。结果显示,大型模型持续向自由左倾立场转变,不同语言和模型家族间存在显著差异。为测试政治立场的可操控性,我们采用简单的重心激活干预技术,并证明其在多种语言中可靠地引导模型响应走向替代意识形态立场。我们的代码可在https://github.com/d-gurgurov/Political-Ideologies-LLMs 中获取。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在日常应用中的普及引发对政治观点潜在影响的担忧。
- 现有研究仅对有限的模型和语言进行了评估,存在关于政治偏见普遍性的重要问题。
- 研究发现大型模型倾向于自由左倾立场,不同语言和模型间存在显著差异。
- 采用重心激活干预技术可有效操控模型的政治立场响应。
- 研究涵盖了多种语言和模型,为全面理解LLM中的政治偏见提供了重要见解。
- 公共可用代码为未来的研究和开发提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图
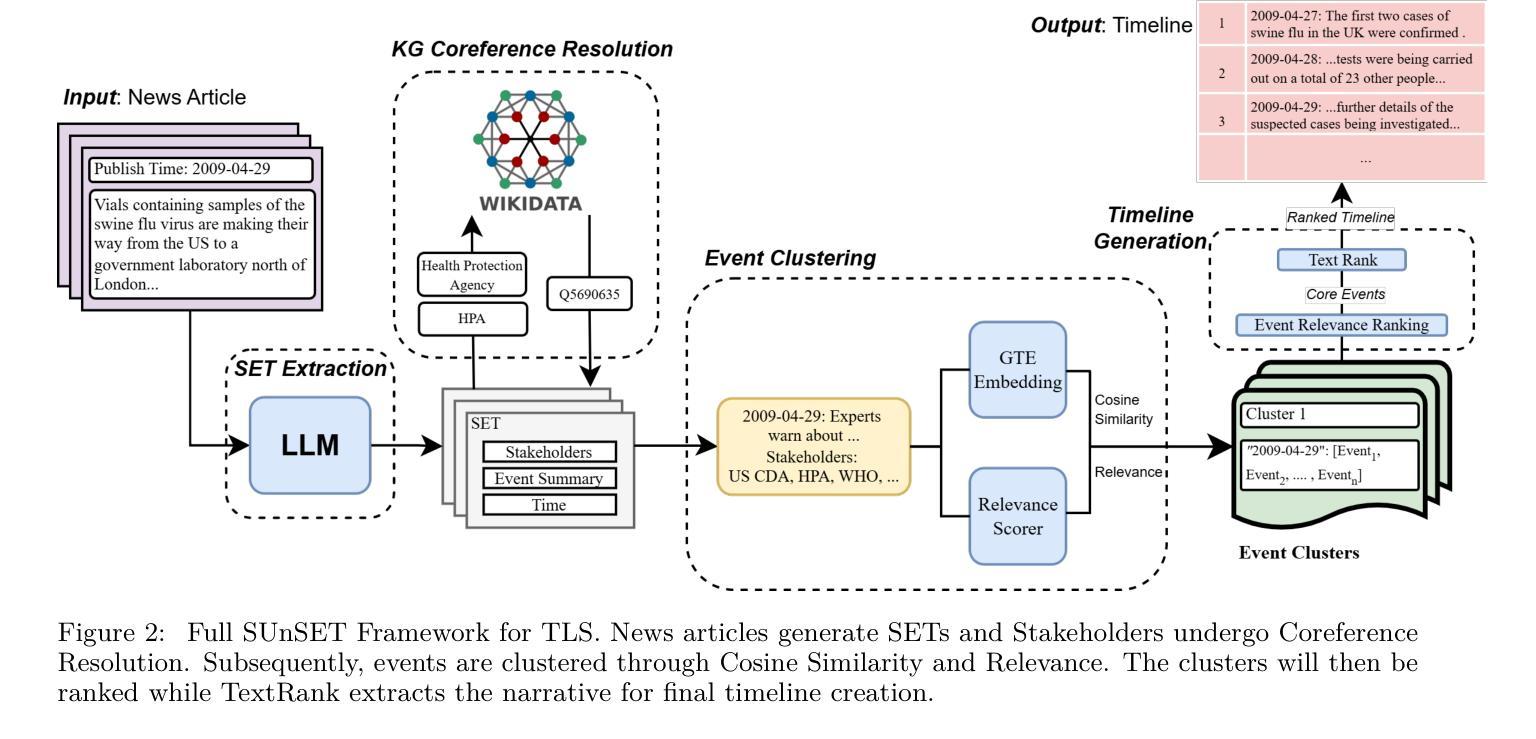
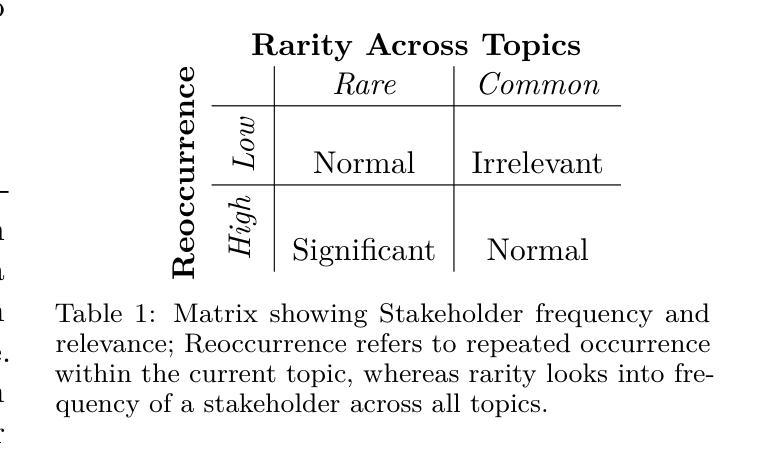
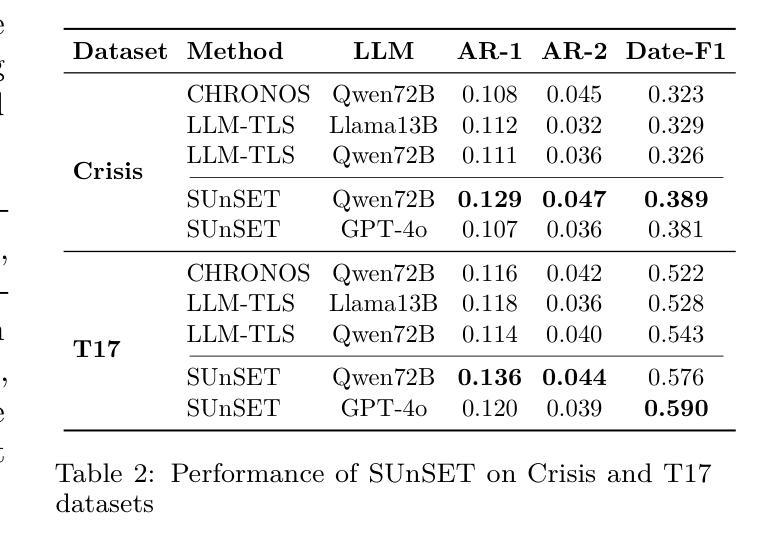
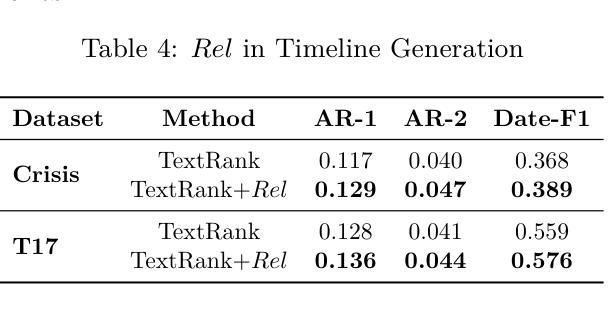
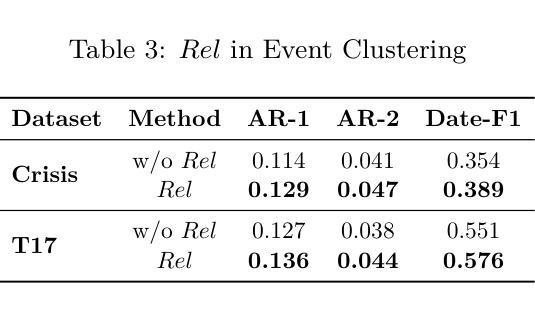
Who’s important? – SUnSET: Synergistic Understanding of Stakeholder, Events and Time for Timeline Generation
Authors:Tiviatis Sim, Kaiwen Yang, Shen Xin, Kenji Kawaguchi
As news reporting becomes increasingly global and decentralized online, tracking related events across multiple sources presents significant challenges. Existing news summarization methods typically utilizes Large Language Models and Graphical methods on article-based summaries. However, this is not effective since it only considers the textual content of similarly dated articles to understand the gist of the event. To counteract the lack of analysis on the parties involved, it is essential to come up with a novel framework to gauge the importance of stakeholders and the connection of related events through the relevant entities involved. Therefore, we present SUnSET: Synergistic Understanding of Stakeholder, Events and Time for the task of Timeline Summarization (TLS). We leverage powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) to build SET triplets and introduced the use of stakeholder-based ranking to construct a $Relevancy$ metric, which can be extended into general situations. Our experimental results outperform all prior baselines and emerged as the new State-of-the-Art, highlighting the impact of stakeholder information within news article.
随着新闻报道越来越全球化和在线分散化,从多个来源追踪相关事件带来了巨大的挑战。现有的新闻摘要方法通常基于文章使用大型语言模型和图形方法。然而,这并不有效,因为它只考虑具有相同日期的文章的文本内容来了解事件的大意。为了弥补对参与方的分析不足,提出一个新颖框架来衡量利益相关方的重要性以及相关实体所涉及相关事件之间的联系至关重要。因此,我们提出SUnSET:协同理解利益相关方、事件和时间,用于时间线摘要(TLS)任务。我们利用强大的大型语言模型(LLM)构建SET三元组,并引入基于利益相关方的排名来构建$Relevancy$指标,该指标可扩展到一般情况。我们的实验结果优于所有先前基线,成为新的最先进的成果,突显新闻文章中利益相关方信息的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新闻报道日益全球化和在线分散化,追踪跨多个来源的相关事件带来重大挑战。现有新闻摘要方法主要利用大型语言模型和图形方法基于文章的摘要,但仅考虑文本内容无法全面理解事件。为应对对参与方分析不足的难题,提出SUnSET框架,通过相关实体评估参与方重要性及事件关联。利用强大的大型语言模型构建SET三元组,并引入基于参与方的排名构建相关性指标,可扩展到一般情况。实验结果优于所有先前基线,成为新的技术前沿,突显参与方信息在新闻报道中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 新闻报道的全球性化和在线分散化使得追踪跨多个来源的相关事件具有挑战。
- 现有新闻摘要方法主要关注文本内容,但无法全面理解事件。
- 提出SUnSET框架,旨在通过评估参与方的重要性及相关实体的连接来解决这个问题。
- 利用大型语言模型构建SET三元组以增强理解。
- 引入基于参与方的排名来构建相关性指标,适用于各种情境。
- 实验结果显示该框架优于先前技术,成为新的技术前沿。
点此查看论文截图

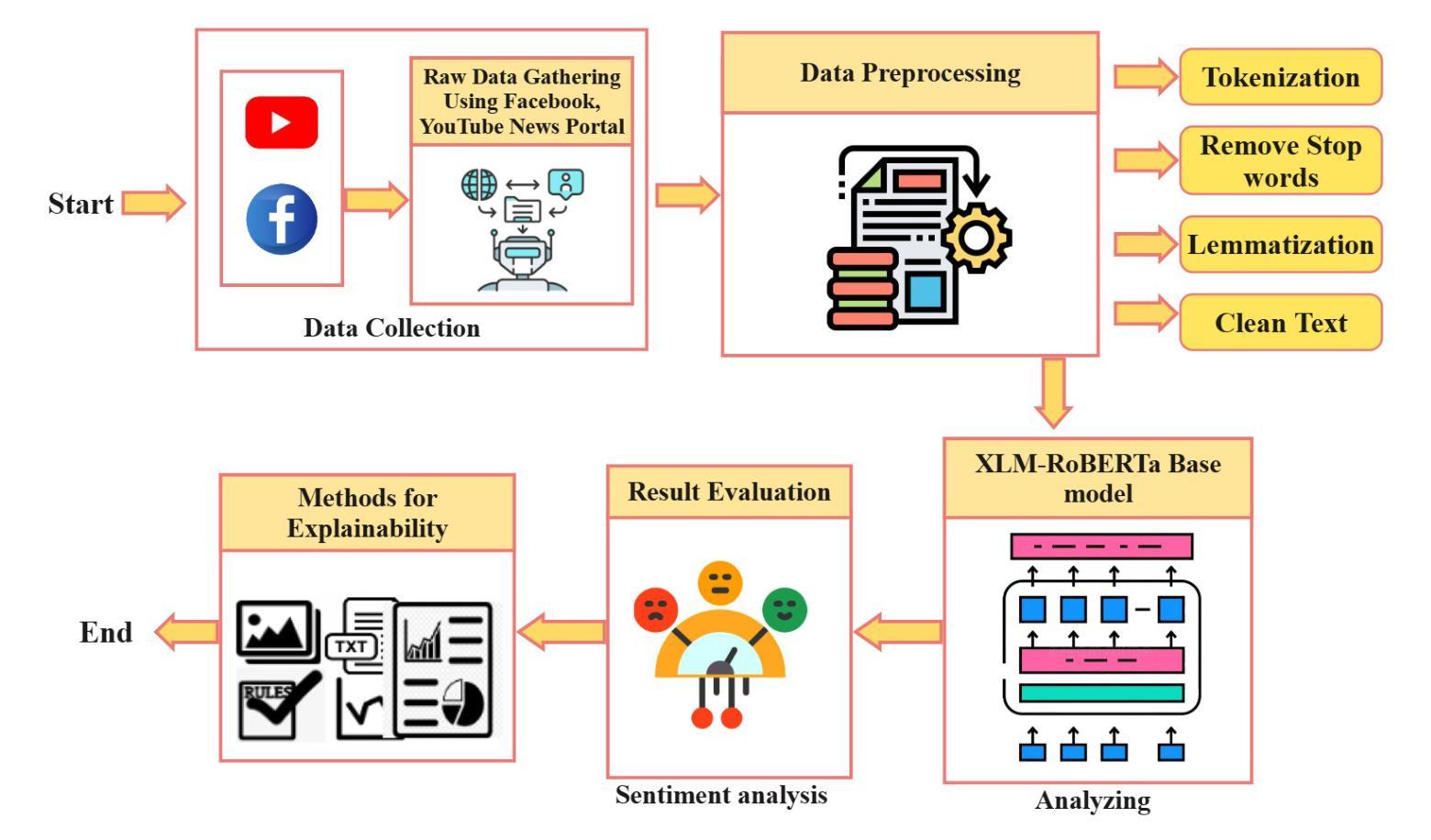
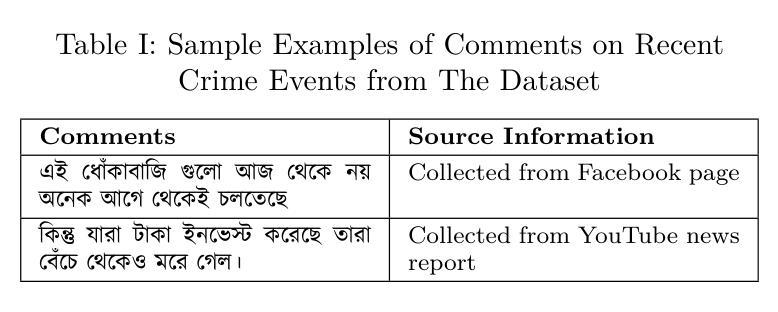
Understanding Public Perception of Crime in Bangladesh: A Transformer-Based Approach with Explainability
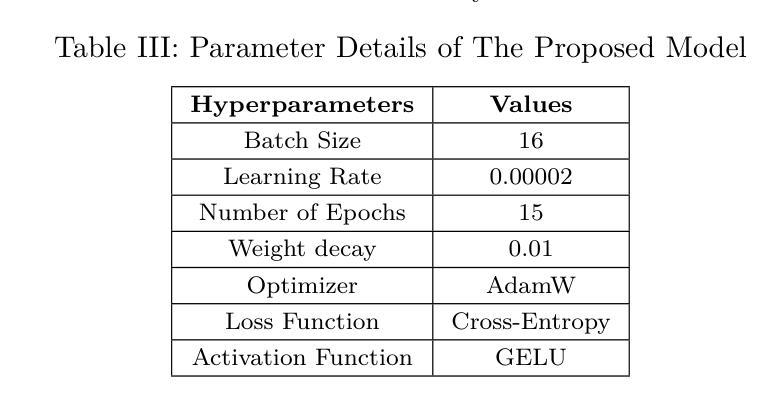
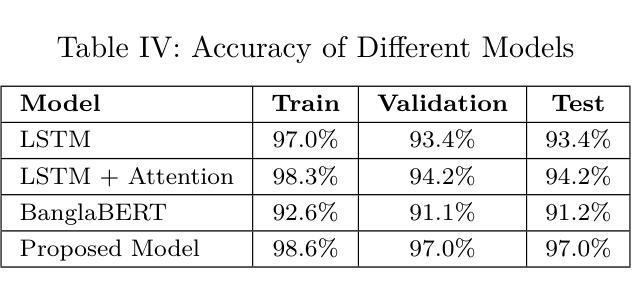
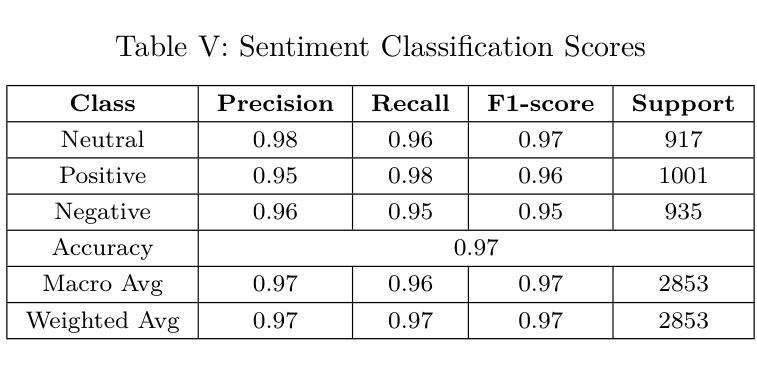
Authors:Fatema Binte Hassan, Md Al Jubair, Mohammad Mehadi Hasan, Tahmid Hossain, S M Mehebubur Rahman Khan Shuvo, Mohammad Shamsul Arefin
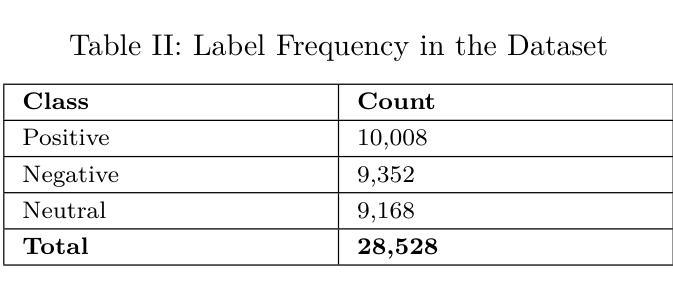
In recent years, social media platforms have become prominent spaces for individuals to express their opinions on ongoing events, including criminal incidents. As a result, public sentiment can shift dynamically over time. This study investigates the evolving public perception of crime-related news by classifying user-generated comments into three categories: positive, negative, and neutral. A newly curated dataset comprising 28,528 Bangla-language social media comments was developed for this purpose. We propose a transformer-based model utilizing the XLM-RoBERTa Base architecture, which achieves a classification accuracy of 97%, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods in Bangla sentiment analysis. To enhance model interpretability, explainable AI technique is employed to identify the most influential features driving sentiment classification. The results underscore the effectiveness of transformer-based models in processing low-resource languages such as Bengali and demonstrate their potential to extract actionable insights that can support public policy formulation and crime prevention strategies.
近年来,社交媒体平台已成为个人表达对正在发生的事件,包括刑事事件看法的重要空间。因此,公众情绪会随时间动态变化。本研究通过将用户生成的评论分为积极、消极和中性三个类别,调查了与犯罪相关的新闻的公众认知的演变。为此,我们开发了一个新整理的数据集,包含28528条孟加拉语社交媒体评论。我们提出了一种基于transformer的模型,该模型利用XLM-RoBERTa Base架构,实现了97%的分类准确率,优于孟加拉情感分析中现有的最先进方法。为了提高模型的可解释性,我们采用了可解释的AI技术来识别驱动情感分类的最具影响力的特征。结果强调了基于transformer的模型在处理低资源语言(如孟加拉语)方面的有效性,并展示了其提取可操作见解的潜力,这些见解可以支持公共政策制定和犯罪预防策略。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
社交媒体平台成为公众表达犯罪事件相关意见的重要场所,公众情绪随时间动态变化。本研究旨在探究犯罪相关新闻的公众感知变化,将用户生成的评论分为积极、消极和中性三类。为此开发了一个包含28,528条孟加拉语社交媒体评论的新数据集,提出了一个基于XLM-RoBERTa基础的架构的转换模型,其分类准确度达到了97%,在孟加拉情感分析中优于现有先进技术方法。为提高模型的可解释性,采用了可解释的AI技术来确定影响情感分类的最具影响力的特征。结果强调了基于转换器的模型在处理低资源语言如孟加拉语方面的有效性,并展示了它们提取支持公共政策制定和犯罪预防策略的行动性见解的潜力。
要点分析
- 社交媒体平台成为公众表达对犯罪事件意见的重要场所,公众情绪会随时间动态变化。
- 研究通过分类用户生成的评论来探究公众对犯罪相关新闻的看法。
- 为此研究目的开发了一个包含大量孟加拉语社交媒体评论的新数据集。
- 采用基于XLM-RoBERTa基础的架构的转换模型,实现了高达97%的分类准确度。
- 该模型在孟加拉情感分析中表现优于现有技术。
- 采用可解释的AI技术确定影响情感分类的最关键特征,以提高模型的可解释性。
- 结果强调了基于转换器的模型在处理低资源语言的有效性,并展示了其在公共政策制定和犯罪预防策略方面的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

A ChatGPT-based approach for questions generation in higher education
Authors:Sinh Trong Vu, Huong Thu Truong, Oanh Tien Do, Tu Anh Le, Tai Tan Mai
Large language models have been widely applied in many aspects of real life, bringing significant efficiency to businesses and offering distinctive user experiences. In this paper, we focus on exploring the application of ChatGPT, a chatbot based on a large language model, to support higher educator in generating quiz questions and assessing learners. Specifically, we explore interactive prompting patterns to design an optimal AI-powered question bank creation process. The generated questions are evaluated through a “Blind test” survey sent to various stakeholders including lecturers and learners. Initial results at the Banking Academy of Vietnam are relatively promising, suggesting a potential direction to streamline the time and effort involved in assessing learners at higher education institutes.
大型语言模型已广泛应用于现实生活的各个方面,为企业带来了显著效率,并为用户提供了独特体验。本文重点探索基于大型语言模型的聊天机器人ChatGPT在支持高等教育生成题和评估学习者方面的应用。具体来说,我们探索交互式提示模式,以设计最佳的AI支持的题库创建过程。通过向包括讲师和学习者在内的各种利益相关者发送“盲测试卷”来评估生成的问题。在越南银行学院的初步结果相当令人鼓舞,为高等教育机构在评估学习者方面节省时间和努力提供了潜在方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on AI-Powered Q&A Systems for Multimedia. 2024
Summary
大型语言模型在现实生活多个领域广泛应用,为提升业务效率和提供独特用户体验起到了重要作用。本文关注基于大型语言模型的聊天机器人ChatGPT在高等教育中的应用,支持教师生成测验问题并评估学习者。通过探索交互式提示模式,设计最优的AI助力问题库创建流程。生成的测验问题通过发送给讲师和学习者的“盲测”调查进行评估。越南银行学院的初步结果令人鼓舞,显示了一个潜在的、帮助高校简化评估学习者耗费的时间和精力的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在现实生活中的应用广泛,为业务效率和用户体验带来积极影响。
- ChatGPT作为一种基于大型语言模型的聊天机器人,被应用于支持高等教育中的测验问题生成和评估。
- 通过交互式提示模式探索,设计了一个最优的AI助力问题库创建流程。
- 生成的测验问题通过“盲测”调查进行评估。
- 初步在越南银行学院的应用结果具有鼓舞性。
- ChatGPT有潜力帮助高校简化评估学习者的过程,减少时间和精力的消耗。
点此查看论文截图



Predicting Cognition from fMRI:A Comparative Study of Graph, Transformer, and Kernel Models Across Task and Rest Conditions
Authors:Jagruti Patel, Mikkel Schöttner, Thomas A. W. Bolton, Patric Hagmann
Predicting cognition from neuroimaging data in healthy individuals offers insights into the neural mechanisms underlying cognitive abilities, with potential applications in precision medicine and early detection of neurological and psychiatric conditions. This study systematically benchmarked classical machine learning (Kernel Ridge Regression (KRR)) and advanced deep learning (DL) models (Graph Neural Networks (GNN) and Transformer-GNN (TGNN)) for cognitive prediction using Resting-state (RS), Working Memory, and Language task fMRI data from the Human Connectome Project Young Adult dataset. Our results, based on R2 scores, Pearson correlation coefficient, and mean absolute error, revealed that task-based fMRI, eliciting neural responses directly tied to cognition, outperformed RS fMRI in predicting cognitive behavior. Among the methods compared, a GNN combining structural connectivity (SC) and functional connectivity (FC) consistently achieved the highest performance across all fMRI modalities; however, its advantage over KRR using FC alone was not statistically significant. The TGNN, designed to model temporal dynamics with SC as a prior, performed competitively with FC-based approaches for task-fMRI but struggled with RS data, where its performance aligned with the lower-performing GNN that directly used fMRI time-series data as node features. These findings emphasize the importance of selecting appropriate model architectures and feature representations to fully leverage the spatial and temporal richness of neuroimaging data. This study highlights the potential of multimodal graph-aware DL models to combine SC and FC for cognitive prediction, as well as the promise of Transformer-based approaches for capturing temporal dynamics. By providing a comprehensive comparison of models, this work serves as a guide for advancing brain-behavior modeling using fMRI, SC and DL.
预测健康人群中的神经影像数据认知能为认知能力的神经机制提供见解,在精准医疗和神经精神疾病的早期检测中具有潜在应用。本研究系统地基准测试了经典机器学习(核岭回归(KRR))和先进的深度学习(DL)模型(图神经网络(GNN)和Transformer-GNN(TGNN))进行认知预测,使用了人类连接组项目青年数据集中的静息态(RS)、工作记忆和语言任务fMRI数据。我们的结果基于R2分数、皮尔逊相关系数和平均绝对误差,显示基于任务的fMRI,激发与认知直接相关的神经反应,在预测认知行为方面优于静息态fMRI。在比较的方法中,结合结构连通性(SC)和功能连通性(FC)的GNN在所有fMRI模式中都实现了最佳性能;然而,其与仅使用FC的KRR相比的优势并未达到统计显著水平。TGNN旨在用SC作为先验来建模时间动态,对于任务fMRI来说,其表现与基于FC的方法相当,但在处理RS数据时遇到困难,其性能与直接使用fMRI时间序列数据作为节点特征的较低性能GNN相符。这些发现强调选择适当的模型架构和特征表示的重要性,以充分利用神经成像数据的空间和时间丰富性。本研究突出了多模态图感知深度学习模型在结合SC和FC进行认知预测方面的潜力,以及基于Transformer的方法在捕捉时间动态方面的前景。通过全面比较各种模型,这项工作为利用fMRI、SC和DL推进脑行为建模提供了指南。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preliminary version; a revised version will be uploaded later
Summary
基于机器学习和深度学习模型对健康个体的神经成像数据进行认知预测的研究,揭示了神经机制与认知能力之间的关系,并有望应用于精准医疗及神经和精神疾病的早期检测。本研究对比了经典机器学习(如核岭回归)和先进的深度学习模型(如图神经网络和Transformer-GNN)在基于静息态、工作记忆和语言任务的fMRI数据上的认知预测性能。结果表明任务态fMRI在预测认知行为方面优于静息态fMRI。此外,结合结构连接(SC)和功能连接(FC)的图神经网络(GNN)在所有fMRI模态上的表现最佳,但其相对于仅使用功能连接的KRR方法的优势并未达到统计显著水平。研究强调了选择适当模型架构和特征表示的重要性,以便充分利用神经成像数据的空间和时间丰富性。这项研究突出了多模态图感知深度学习模型在结合结构连接和功能连接进行认知预测方面的潜力,以及基于Transformer的方法在捕捉时间动态方面的前景。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用机器学习和深度学习模型从神经成像数据中预测认知,为精准医疗和神经精神疾病早期检测提供线索。
- 任务态fMRI在预测认知行为方面优于静息态fMRI。
- 图神经网络(GNN)结合结构连接(SC)和功能连接(FC)在所有fMRI模态上的表现最佳。
- Transformer-GNN在处理包含时间动态信息的数据时表现良好。
- 选择适当的模型架构和特征表示对有效利用神经成像数据至关重要。
- 研究表明深度学习模型在认知预测方面展现出潜力,特别是在结合结构连接和功能连接方面。
点此查看论文截图

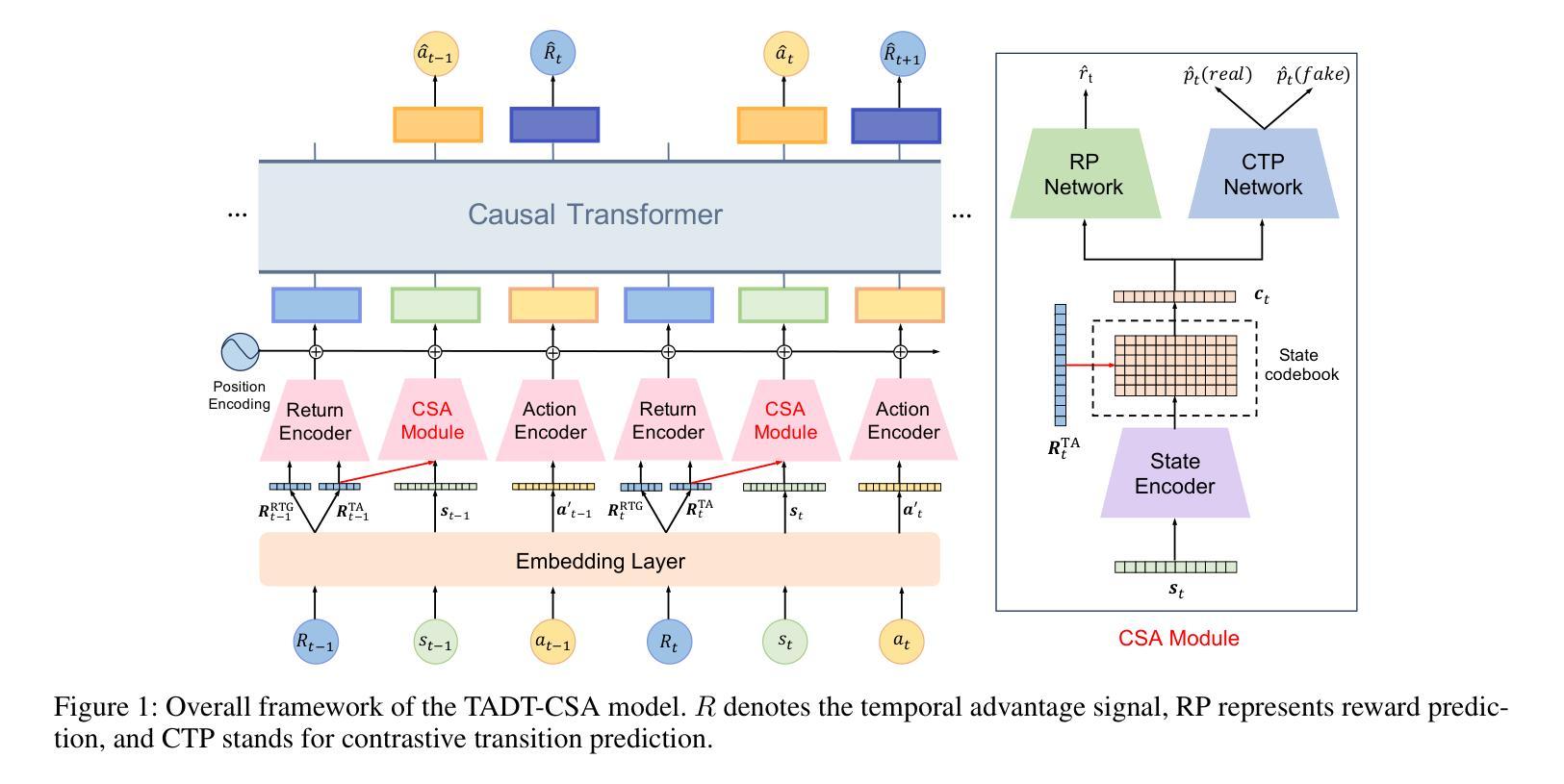
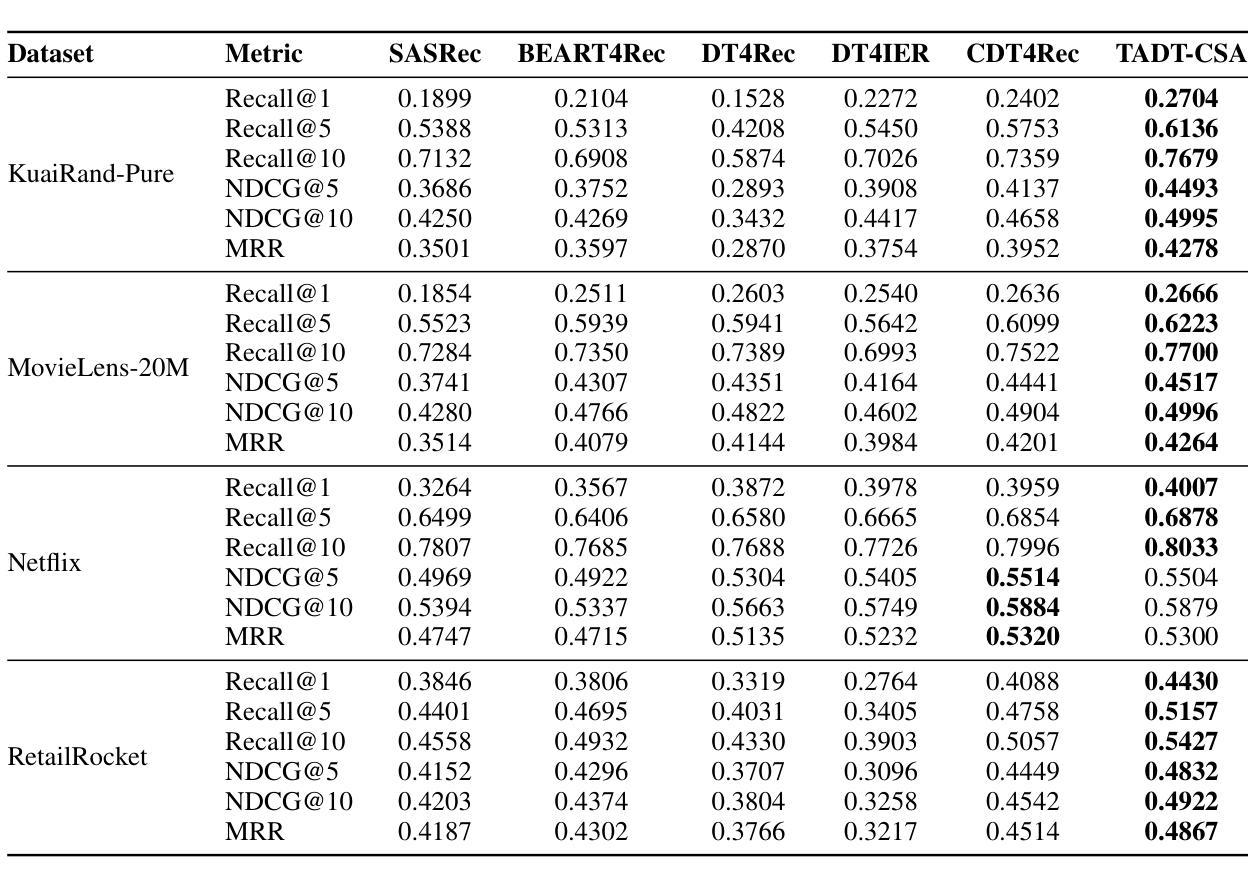
TADT-CSA: Temporal Advantage Decision Transformer with Contrastive State Abstraction for Generative Recommendation
Authors:Xiang Gao, Tianyuan Liu, Yisha Li, Jingxin Liu, Lexi Gao, Xin Li, Haiyang Lu, Liyin Hong
With the rapid advancement of Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), generative recommendation has shown great potential in enhancing both the accuracy and semantic understanding of modern recommender systems. Compared to LLMs, the Decision Transformer (DT) is a lightweight generative model applied to sequential recommendation tasks. However, DT faces challenges in trajectory stitching, often producing suboptimal trajectories. Moreover, due to the high dimensionality of user states and the vast state space inherent in recommendation scenarios, DT can incur significant computational costs and struggle to learn effective state representations. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel Temporal Advantage Decision Transformer with Contrastive State Abstraction (TADT-CSA) model. Specifically, we combine the conventional Return-To-Go (RTG) signal with a novel temporal advantage (TA) signal that encourages the model to capture both long-term returns and their sequential trend. Furthermore, we integrate a contrastive state abstraction module into the DT framework to learn more effective and expressive state representations. Within this module, we introduce a TA-conditioned State Vector Quantization (TAC-SVQ) strategy, where the TA score guides the state codebooks to incorporate contextual token information. Additionally, a reward prediction network and a contrastive transition prediction (CTP) network are employed to ensure the state codebook preserves both the reward information of the current state and the transition information between adjacent states. Empirical results on both public datasets and an online recommendation system demonstrate the effectiveness of the TADT-CSA model and its superiority over baseline methods.
随着基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,生成式推荐在提高现代推荐系统的准确性和语义理解方面显示出巨大潜力。与LLM相比,决策变压器(DT)是一个用于序列推荐任务的轻量级生成模型。然而,DT在轨迹拼接方面面临挑战,经常产生次优轨迹。此外,由于用户状态的高维性和推荐场景中的固有大规模状态空间,DT可能会产生显著的计算成本,并且难以学习有效的状态表示。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了新型的时间优势决策变压器与对比状态抽象(TADT-CSA)模型。具体来说,我们将传统的返回目标(RTG)信号与新型的时间优势(TA)信号相结合,鼓励模型捕捉长期回报及其序列趋势。此外,我们将对比状态抽象模块集成到DT框架中,学习更有效、更具表现力的状态表示。在此模块中,我们引入了一种时间优势条件状态向量量化(TAC-SVQ)策略,其中时间优势评分指导状态码本融入上下文标记信息。此外,还采用了奖励预测网络和对比过渡预测(CTP)网络,以确保状态码本保留当前状态的奖励信息和相邻状态之间的过渡信息。在公共数据集和在线推荐系统上的经验结果证明了TADT-CSA模型的有效性,以及其优于基准方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着Transformer基大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,生成式推荐在提高现代推荐系统的准确性和语义理解方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,与LLM相比,用于序列推荐任务的决策变压器(DT)是一个轻量级的生成模型,面临轨迹拼接的挑战,常产生次优轨迹。针对这些问题,我们提出了结合传统Return-To-Go信号与新型时序优势信号的新模型TADT-CSA。此外,我们还将对比状态抽象模块集成到DT框架中,以学习更有效的状态表示。TAC-SVQ策略等策略的引入确保状态编码簿融入上下文标记信息。在公共数据集和在线推荐系统上的实证结果表明,TADT-CSA模型的有效性及其对基准方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer基大语言模型(LLM)在生成式推荐中展现出巨大潜力。
- 决策变压器(DT)是应用于序列推荐任务的轻量级生成模型。
- DT面临轨迹拼接的挑战,常产生次优轨迹。
- TADT-CSA模型结合了传统Return-To-Go信号与新型时序优势信号。
- 对比状态抽象模块被集成到DT框架中以提高状态表示的有效性。
- TAC-SVQ策略等策略确保状态编码簿融入上下文信息。
点此查看论文截图

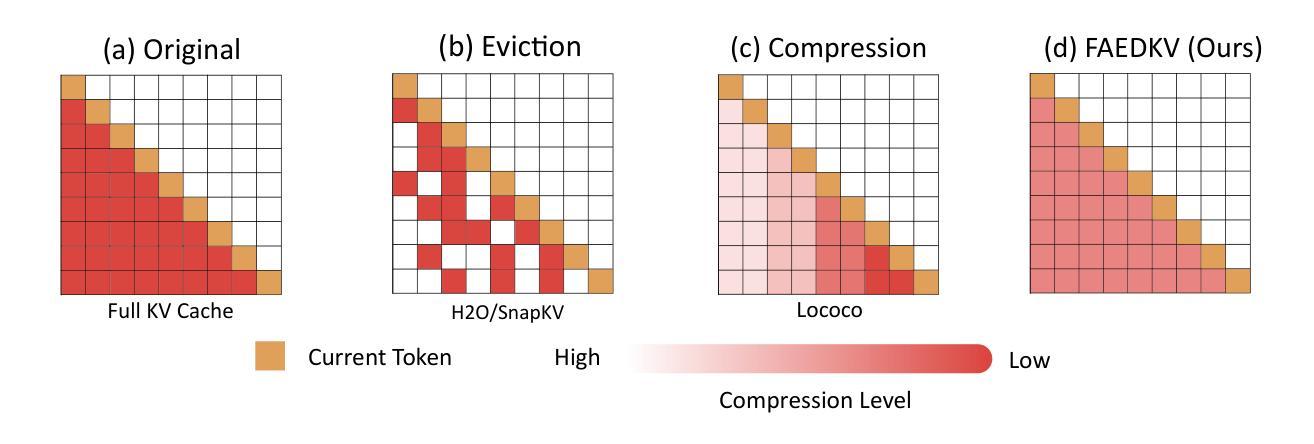
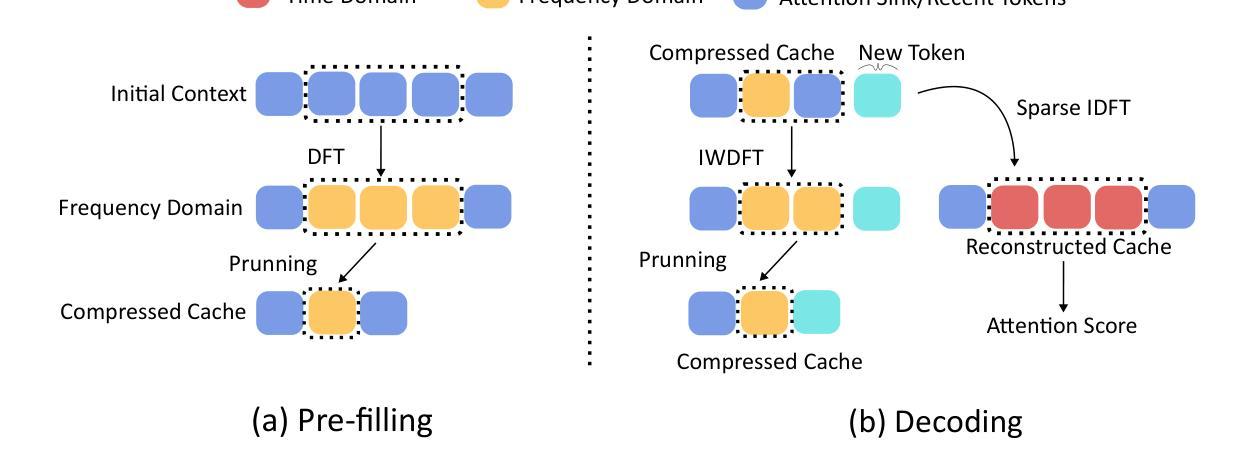
FAEDKV: Infinite-Window Fourier Transform for Unbiased KV Cache Compression
Authors:Runchao Li, Yao Fu, Mu Sheng, Xianxuan Long, Haotian Yu, Pan Li
The efficacy of Large Language Models (LLMs) in long-context tasks is often hampered by the substantial memory footprint and computational demands of the Key-Value (KV) cache. Current compression strategies, including token eviction and learned projections, frequently lead to biased representations – either by overemphasizing recent/high-attention tokens or by repeatedly degrading information from earlier context – and may require costly model retraining. We present FAEDKV (Frequency-Adaptive Infinite-Window for KV cache), a novel, training-free KV cache compression framework that ensures unbiased information retention. FAEDKV operates by transforming the KV cache into the frequency domain using a proposed Infinite-Window Fourier Transform (IWDFT). This approach allows for the equalized contribution of all tokens to the compressed representation, effectively preserving both early and recent contextual information. A preliminary frequency ablation study identifies critical spectral components for layer-wise, targeted compression. Experiments on LongBench benchmark demonstrate FAEDKV’s superiority over existing methods by up to 22%. In addition, our method shows superior, position-agnostic retrieval accuracy on the Needle-In-A-Haystack task compared to compression based approaches.
大型语言模型(LLM)在长上下文任务中的效能常常受到键值(KV)缓存的巨大内存占用和计算需求的限制。当前的压缩策略,包括令牌驱逐和学得投影,常常会导致表示偏见——要么过分强调近期/高注意力令牌,要么反复降低早期上下文的信息——并且可能需要昂贵的模型重新训练。我们提出了FAEDKV(键值缓存的频率自适应无限窗口),这是一种新型、无需训练的键值缓存压缩框架,可确保保留无偏见的信息。FAEDKV通过将键值缓存转换为频率域来运行,使用所提出的无限窗口傅里叶变换(IWDFT)。这种方法允许所有令牌对压缩表示做出均等贡献,有效地保留早期和近期的上下文信息。初步的频谱消融研究确定了针对分层压缩的关键频谱分量。在LongBench基准测试上的实验表明,FAEDKV相较于现有方法最多高出22%。此外,我们的方法在Haystack任务中的needle-in-haystack测试上显示出优于基于压缩的方法的位置无关检索精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在长文本任务中的效率因键值(KV)缓存的巨大内存占用和计算需求而受到限制。当前压缩策略,如令牌驱逐和学得投影,经常导致表征偏差,可能需耗费成本重新训练模型。我们提出FAEDKV(用于KV缓存的频率自适应无限窗口),这是一种新型、无需训练、确保信息无偏保留的KV缓存压缩框架。FAEDKV通过将KV缓存转换为频率域来操作,利用提出的无限窗口傅里叶变换(IWDFT)。这种方法使得所有令牌对压缩表示的贡献均等,有效保留早期和近期的上下文信息。初步频率消融研究表明了针对层内目标压缩的关键频谱成分。在长椅基准测试上的实验表明,FAEDKV相较于现有方法的优越性高达22%。此外,我们的方法在“针尖在稻草堆中”任务上的位置无关检索准确率优于基于压缩的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在长文本任务中面临KV缓存的内存和计算效率问题。
- 当前压缩策略可能导致表征偏差,需重新训练模型。
- 提出的FAEDKV框架是一种无需训练的KV缓存压缩方法,确保信息无偏保留。
- FAEDKV利用无限窗口傅里叶变换(IWDFT)将KV缓存转换为频率域。
- 该方法使得所有令牌对压缩表示的贡献均等,保留早期和近期的上下文信息。
- 初步频率消融研究确定了针对层内目标压缩的关键频谱成分。
点此查看论文截图

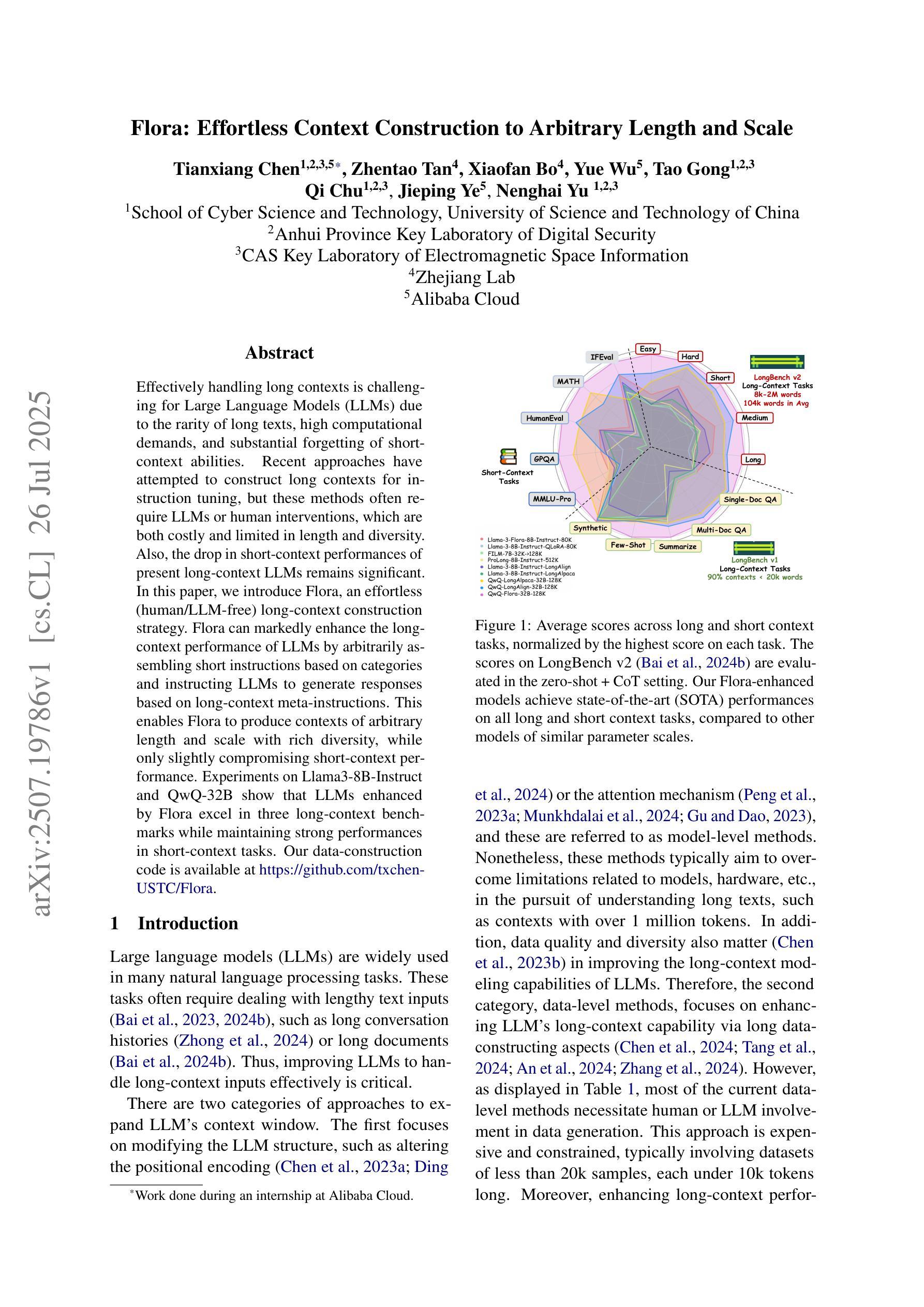
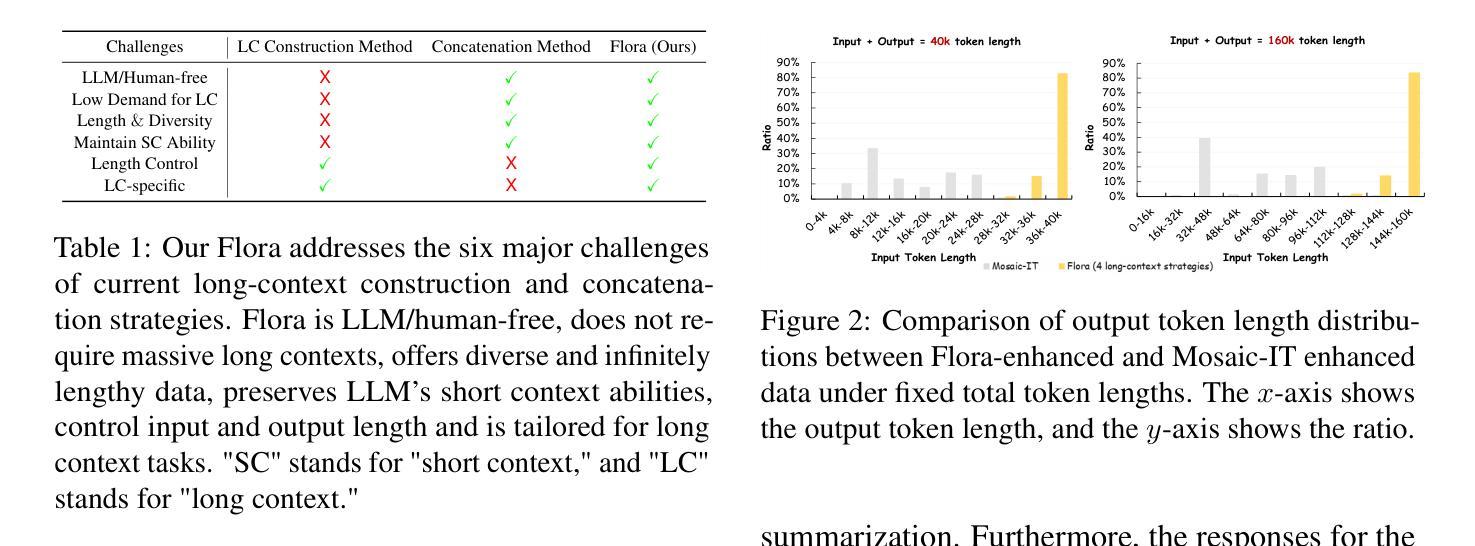
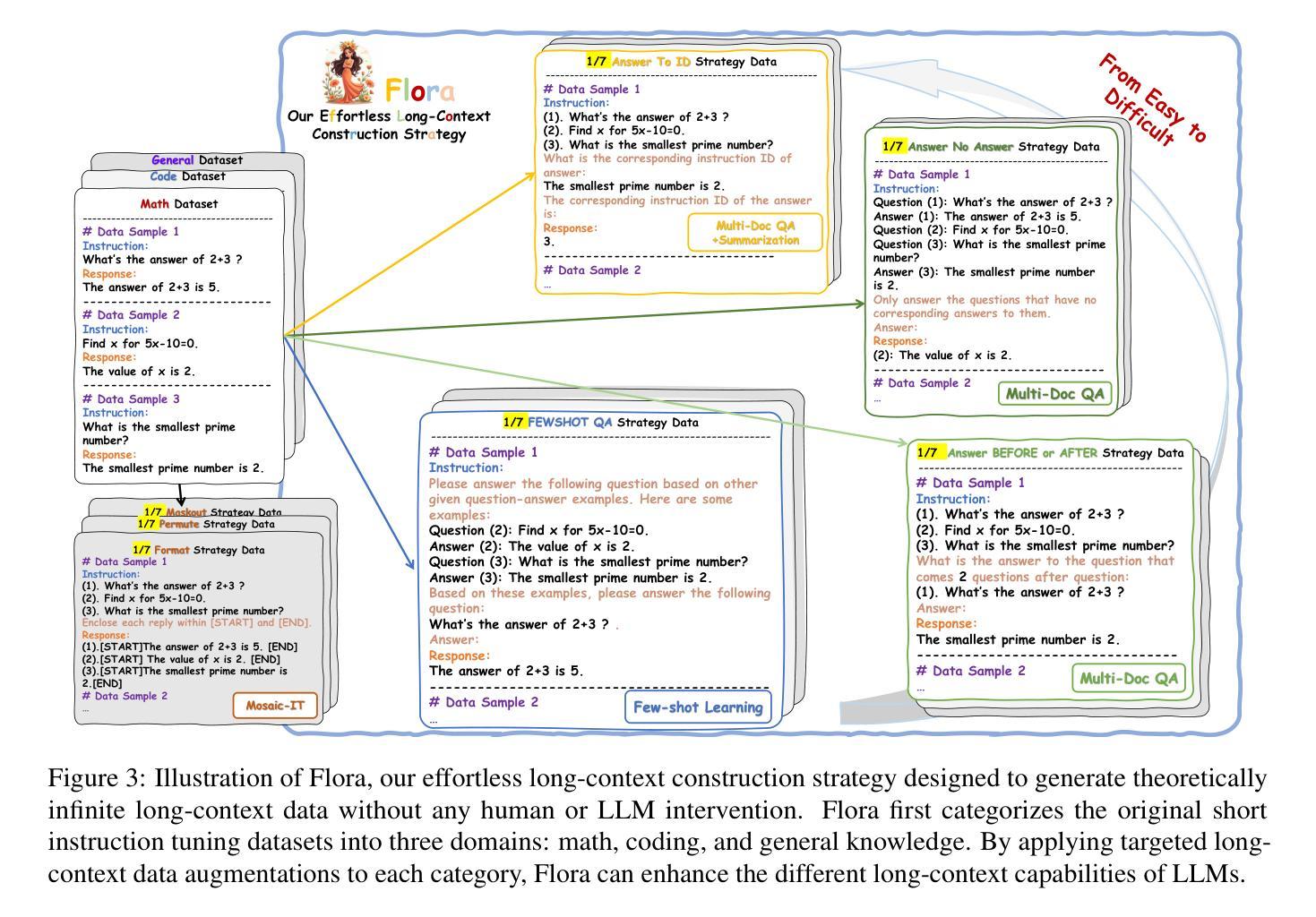
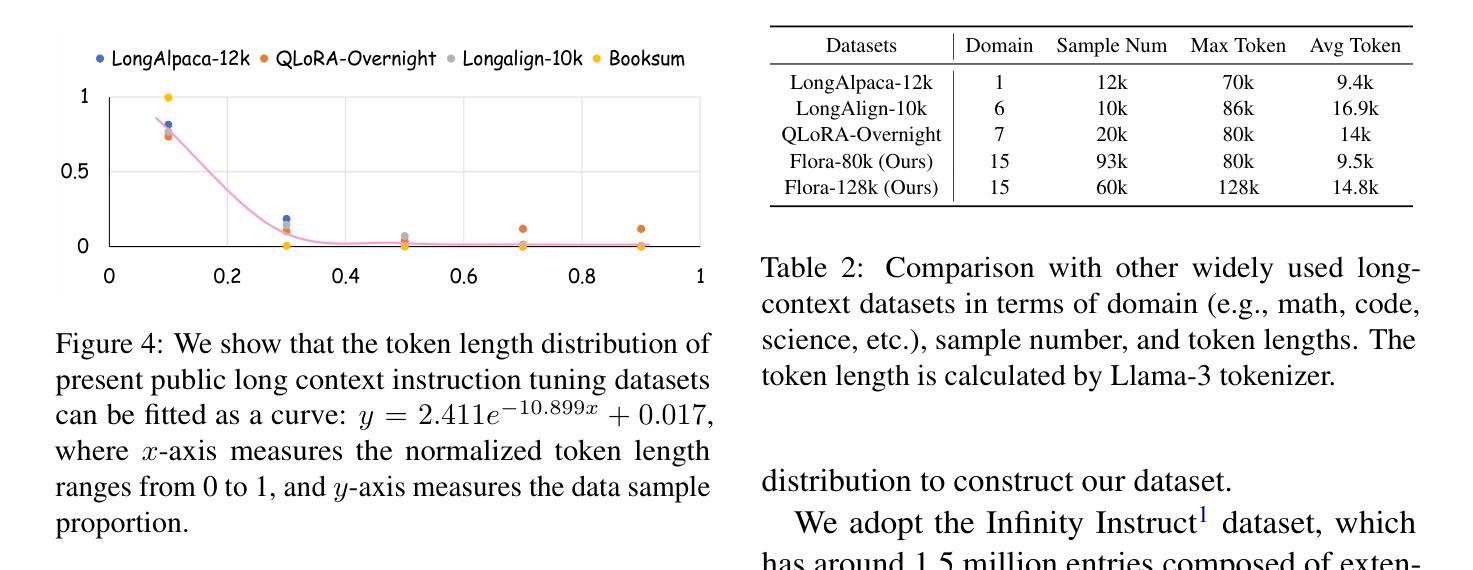
Flora: Effortless Context Construction to Arbitrary Length and Scale
Authors:Tianxiang Chen, Zhentao Tan, Xiaofan Bo, Yue Wu, Tao Gong, Qi Chu, Jieping Ye, Nenghai Yu
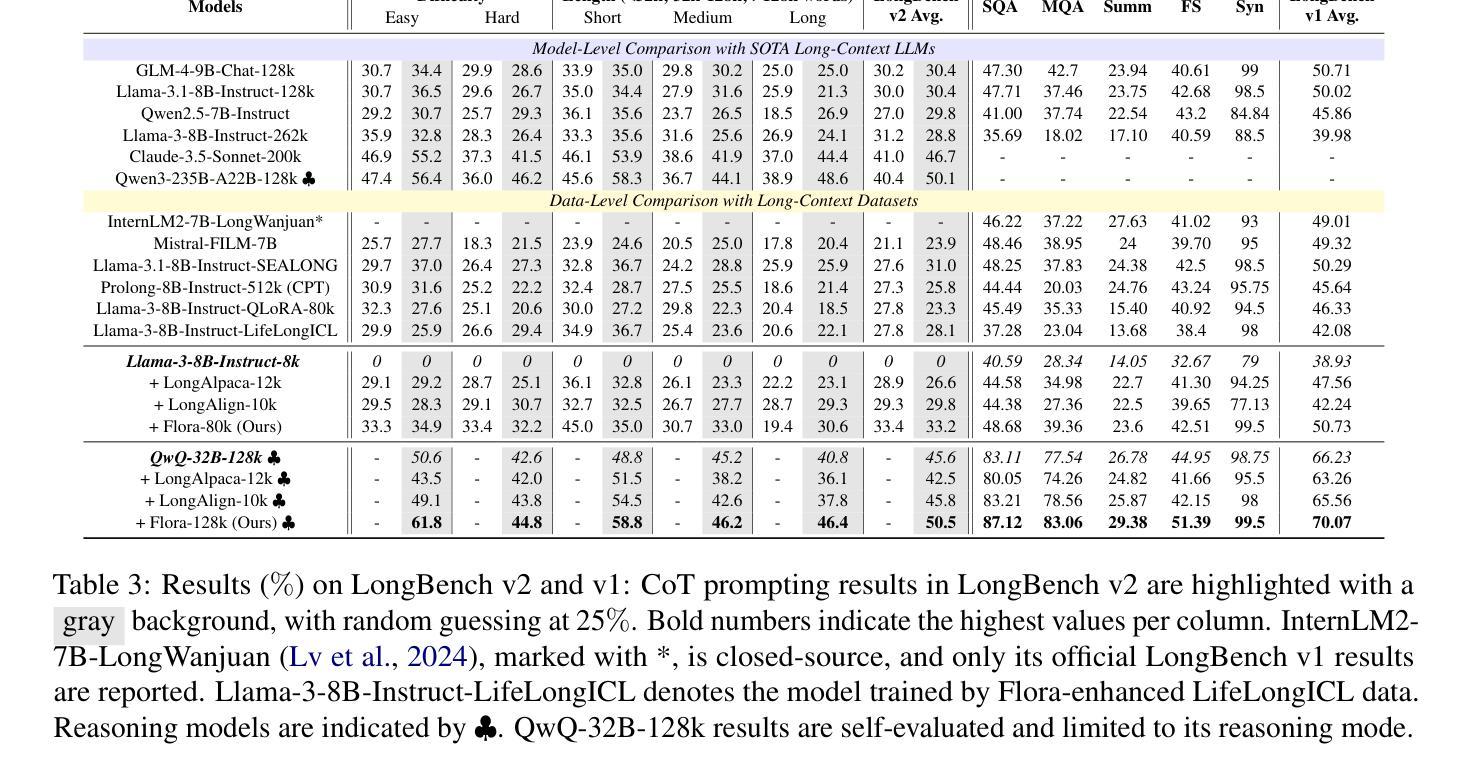
Effectively handling long contexts is challenging for Large Language Models (LLMs) due to the rarity of long texts, high computational demands, and substantial forgetting of short-context abilities. Recent approaches have attempted to construct long contexts for instruction tuning, but these methods often require LLMs or human interventions, which are both costly and limited in length and diversity. Also, the drop in short-context performances of present long-context LLMs remains significant. In this paper, we introduce Flora, an effortless (human/LLM-free) long-context construction strategy. Flora can markedly enhance the long-context performance of LLMs by arbitrarily assembling short instructions based on categories and instructing LLMs to generate responses based on long-context meta-instructions. This enables Flora to produce contexts of arbitrary length and scale with rich diversity, while only slightly compromising short-context performance. Experiments on Llama3-8B-Instruct and QwQ-32B show that LLMs enhanced by Flora excel in three long-context benchmarks while maintaining strong performances in short-context tasks. Our data-construction code is available at \href{https://github.com/txchen-USTC/Flora}{https://github.com/txchen-USTC/Flora}.
有效地处理长语境对大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一项挑战,这是由于长文本稀少、计算需求高以及短语境能力的显著遗忘。近期的方法试图构建长语境进行指令调整,但这些方法通常需要大型语言模型或人工干预,二者成本高昂,且在长度和多样性方面存在局限。此外,当前长语境大型语言模型的短语境性能下降仍然显著。在本文中,我们介绍了Flora,这是一种轻松(无需人工/大型语言模型参与)的长语境构建策略。Flora可以通过基于类别任意组合短指令,并指令大型语言模型基于长语境元指令生成响应,从而显著增强大型语言模型的长语境性能。这使得Flora能够产生任意长度和规模、丰富多样的语境,同时仅略微影响短语境性能。在Llama3-8B-Instruct和QwQ-32B上的实验表明,通过Flora增强的大型语言模型在三个长语境基准测试中表现出色,同时在短语境任务中保持强劲表现。我们的数据构建代码可在https://github.com/txchen-USTC/Flora处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM在处理长文本时面临挑战,包括长文本稀缺、计算需求高以及短文本能力的显著遗忘。现有构建长文本的方法常需依赖LLM或人工干预,成本高昂且长度和多样性受限。为此,本文提出了Flora策略,无需人工或LLM介入即可轻松构建长文本。Flora能通过分类任意组合短指令,并基于长文本元指令指导LLM生成响应,从而显著增强LLM的长文本处理能力,同时保证短文本性能不受太大影响。实验表明,使用Flora增强的LLM在长文本任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在处理长文本时面临挑战,主要由于长文本稀缺、计算需求高和短文本能力遗忘。
- 现有构建长文本的方法成本高昂且受限。
- Flora策略无需人工或LLM介入即可轻松构建长文本。
- Flora通过组合短指令和基于长文本元指令指导LLM生成响应,增强LLM的长文本处理能力。
- 使用Flora增强的LLM在长文本任务上表现优异。
- Flora在保证长文本性能的同时,保证了短文本的性能力。
点此查看论文截图