⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
Who is a Better Talker: Subjective and Objective Quality Assessment for AI-Generated Talking Heads
Authors:Yingjie Zhou, Jiezhang Cao, Zicheng Zhang, Farong Wen, Yanwei Jiang, Jun Jia, Xiaohong Liu, Xiongkuo Min, Guangtao Zhai
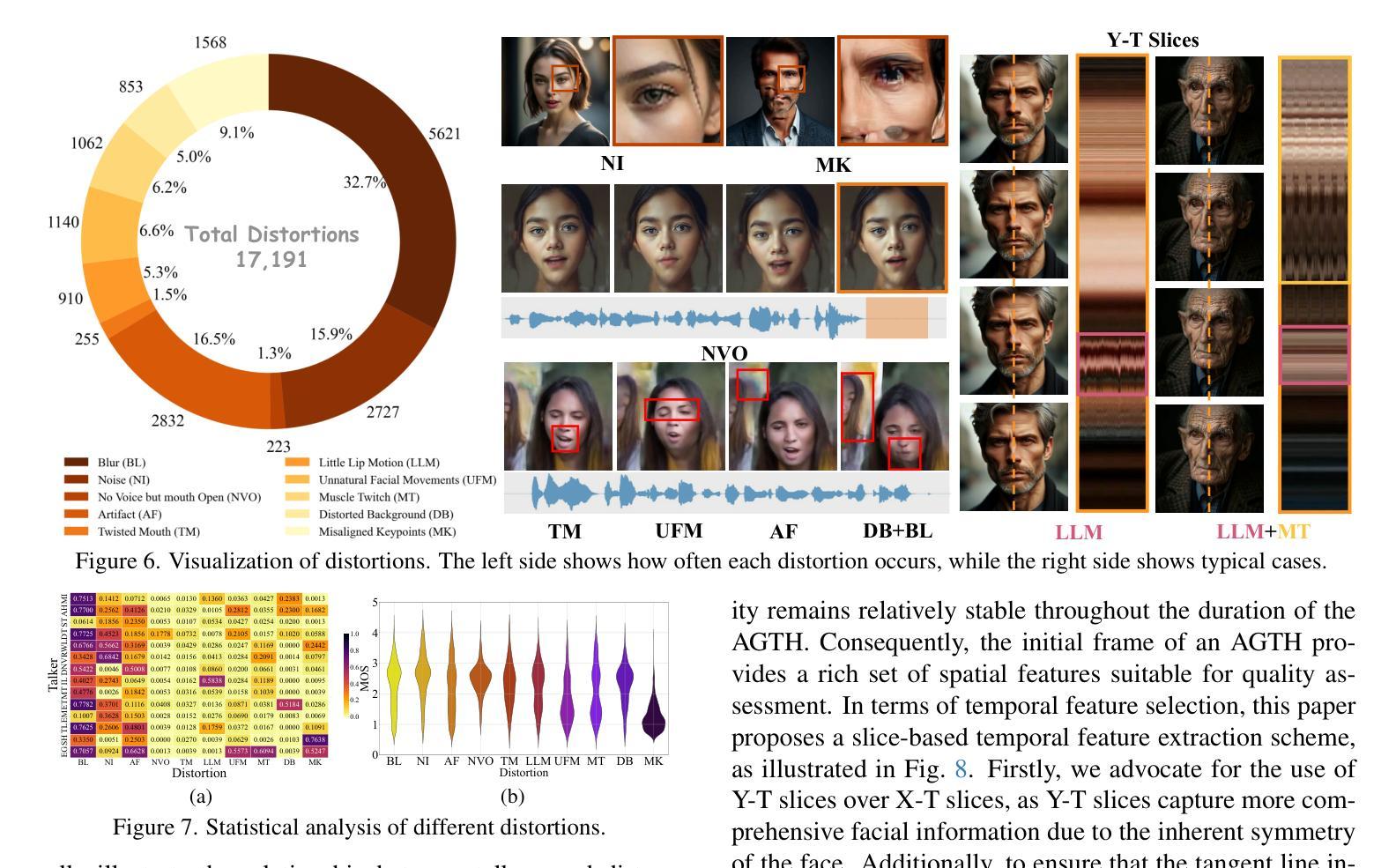
Speech-driven methods for portraits are figuratively known as “Talkers” because of their capability to synthesize speaking mouth shapes and facial movements. Especially with the rapid development of the Text-to-Image (T2I) models, AI-Generated Talking Heads (AGTHs) have gradually become an emerging digital human media. However, challenges persist regarding the quality of these talkers and AGTHs they generate, and comprehensive studies addressing these issues remain limited. To address this gap, this paper presents the largest AGTH quality assessment dataset THQA-10K to date, which selects 12 prominent T2I models and 14 advanced talkers to generate AGTHs for 14 prompts. After excluding instances where AGTH generation is unsuccessful, the THQA-10K dataset contains 10,457 AGTHs. Then, volunteers are recruited to subjectively rate the AGTHs and give the corresponding distortion categories. In our analysis for subjective experimental results, we evaluate the performance of talkers in terms of generalizability and quality, and also expose the distortions of existing AGTHs. Finally, an objective quality assessment method based on the first frame, Y-T slice and tone-lip consistency is proposed. Experimental results show that this method can achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in AGTH quality assessment. The work is released at https://github.com/zyj-2000/Talker.
语音驱动的肖像生成方法被称为“说话者”,因为它们能够合成说话的嘴巴形状和面部动作。尤其是随着文本到图像(T2I)模型的快速发展,AI生成的说话头像(AGTH)已逐渐成为新兴的数字人类媒体。然而,关于这些说话者和他们生成的AGTH的质量挑战仍然存在,针对这些问题的综合研究仍然有限。为了弥补这一空白,本文提出了迄今为止最大的AGTH质量评估数据集THQA-10K。该数据集选择了12个突出的T2I模型和14个先进的说话者,为14个提示生成AGTH。在排除AGTH生成不成功的情况后,THQA-10K数据集包含10,457个AGTH。然后,招募志愿者对AGTH进行主观评分并给出相应的失真类别。在我们的主观实验分析结果中,我们评估了说话者的通用性和质量方面的性能,并暴露了现有AGTH的失真情况。最后,提出了一种基于第一帧、Y-T切片和音色唇同步的客观质量评估方法。实验结果表明,该方法在AGTH质量评估中达到了最新技术水平。该工作发布在https://github.com/zyj-2000/Talker。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了AI生成说话头部(AGTH)的挑战和现状。为解决当前研究空白,本文构建了迄今为止最大的AGTH质量评估数据集THQA-10K。数据集涵盖了不同模型与算法的头部合成样本,并由志愿者主观评估其质量并进行分类。通过对数据的分析,研究提出了一种基于主观评价的新型客观质量评估方法,并取得行业领先性能。项目详情可访问GitHub项目网站了解。
Key Takeaways
- AGTH已成为新兴的数字媒体形式,但存在质量挑战。
- 构建了一个大型AGTH质量评估数据集THQA-10K。
- 对志愿者进行了头部合成样本的主观评价并进行分类分析。
- 分析了当前头部生成技术在普遍性和质量上的表现以及存在的失真问题。
- 提出了一种基于第一帧、Y-T切片和音调唇同步的新型客观质量评估方法。
- 此方法实现了业界领先的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图


JWB-DH-V1: Benchmark for Joint Whole-Body Talking Avatar and Speech Generation Version 1
Authors:Xinhan Di, Kristin Qi, Pengqian Yu
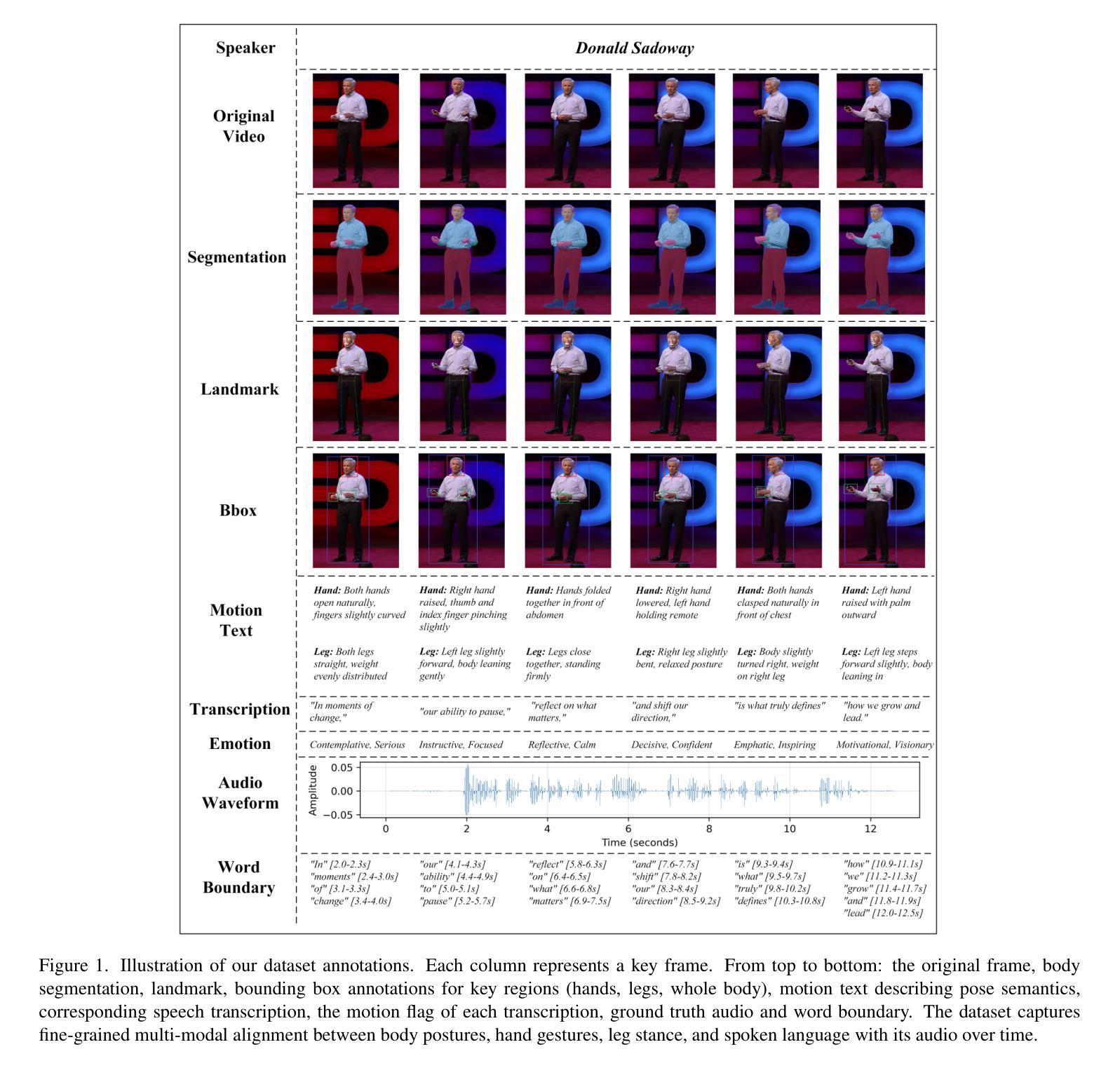
Recent advances in diffusion-based video generation have enabled photo-realistic short clips, but current methods still struggle to achieve multi-modal consistency when jointly generating whole-body motion and natural speech. Current approaches lack comprehensive evaluation frameworks that assess both visual and audio quality, and there are insufficient benchmarks for region-specific performance analysis. To address these gaps, we introduce the Joint Whole-Body Talking Avatar and Speech Generation Version I(JWB-DH-V1), comprising a large-scale multi-modal dataset with 10,000 unique identities across 2 million video samples, and an evaluation protocol for assessing joint audio-video generation of whole-body animatable avatars. Our evaluation of SOTA models reveals consistent performance disparities between face/hand-centric and whole-body performance, which incidates essential areas for future research. The dataset and evaluation tools are publicly available at https://github.com/deepreasonings/WholeBodyBenchmark.
基于扩散的视频生成技术最新进展已能够实现照片般逼真的短片,但当前的方法在联合生成全身运动和自然语音时,仍难以达到多模式一致性。当前的方法缺乏同时评估视觉和音频质量的综合评估框架,以及针对特定区域的性能分析的基准测试。为了弥补这些空白,我们推出了联合全身谈话Avatar和语音生成版本I(JWB-DH-V1),其中包括一个大规模多模式数据集,涵盖10,000个唯一身份和200万个视频样本,以及一个用于评估全身可动画Avatars联合音视频生成的评估协议。我们对最新模型的评估表明,面部/手部为中心和全身性能之间存在持续的性能差异,这暗示了未来研究的关键领域。数据集和评估工具可在https://github.com/deepreasonings/WholeBodyBenchmark公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WiCV @ ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对扩散视频生成技术的最新进展及其在多模态一致性方面的挑战。为了解决当前方法在全身运动与自然语音联合生成方面的不足,提出了Joint Whole-Body Talking Avatar and Speech Generation Version I(JWB-DH-V1)。该模型包含大规模多模态数据集,涵盖10,000个独特身份、2百万视频样本,并提供了评估全身可动画虚拟人联合音视频生成的评估协议。对现有模型的评估显示,面部/手部中心与全身性能之间存在性能差异,这为未来研究指明了方向。数据集和评估工具已在https://github.com/deepreasonings/WholeBodyBenchmark公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散视频生成技术虽能生成逼真的短片,但在全身运动与自然语音的联合生成上仍面临多模态一致性挑战。
- 现有方法缺乏同时评估视觉和音频质量的综合评估框架以及区域特定性能分析的基准。
- 引入的JWB-DH-V1模型包含大规模多模态数据集,涵盖多种身份和视频样本,为解决上述问题提供资源。
- 评估显示,现有模型在面部/手部与全身性能上存在差距,指示未来研究方向。
- JWB-DH-V1提供了评估协议,用于评估全身可动画虚拟人的联合音视频生成。
- 数据集和评估工具已公开可用,便于研究人员进行相关研究和开发。
- 该工作填补了现有技术在实际应用中的一项空白,为未来全身动态虚拟角色的生成和发展打下基础。
点此查看论文截图

Mask-Free Audio-driven Talking Face Generation for Enhanced Visual Quality and Identity Preservation
Authors:Dogucan Yaman, Fevziye Irem Eyiokur, Leonard Bärmann, Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Alexander Waibel
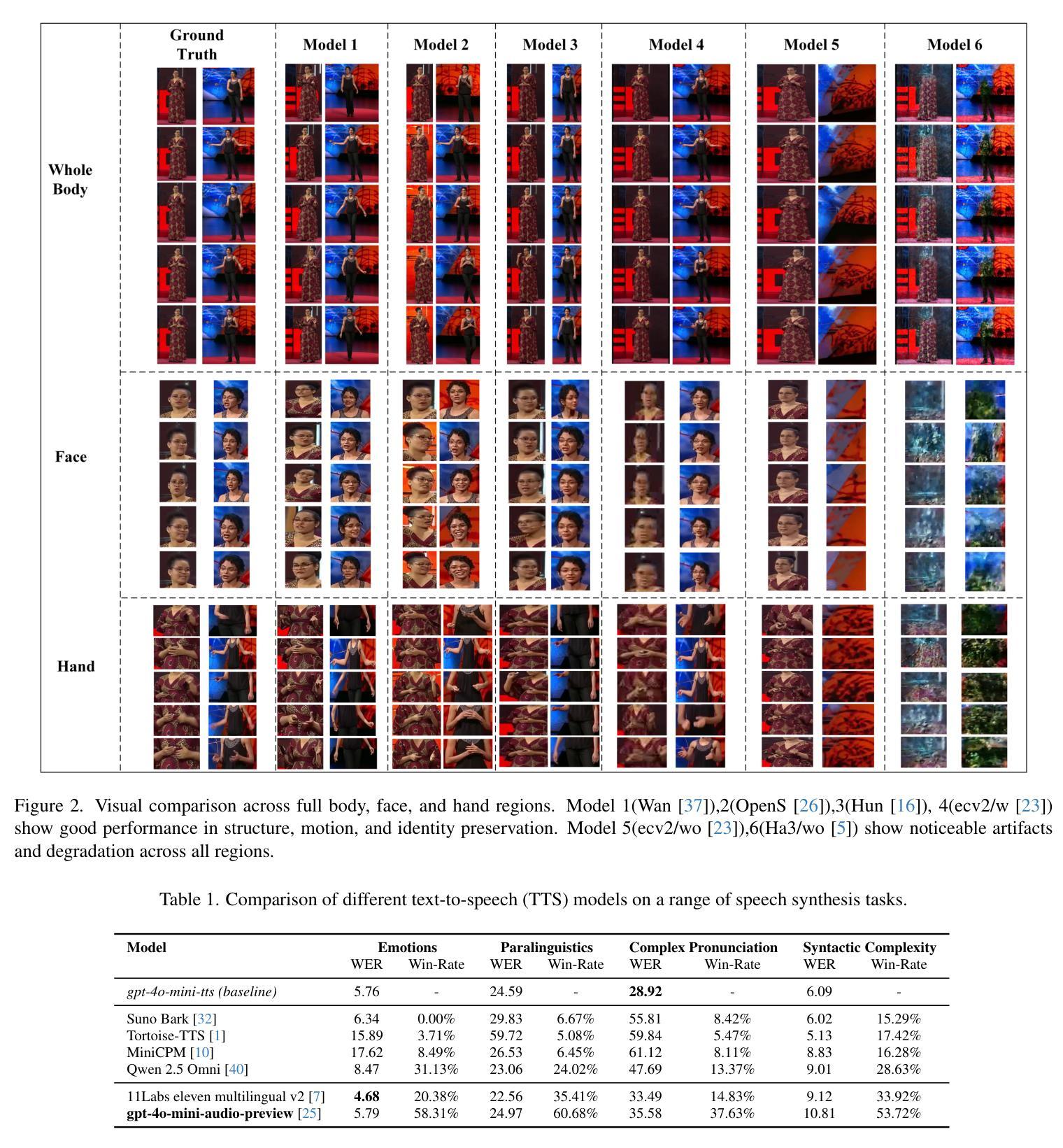
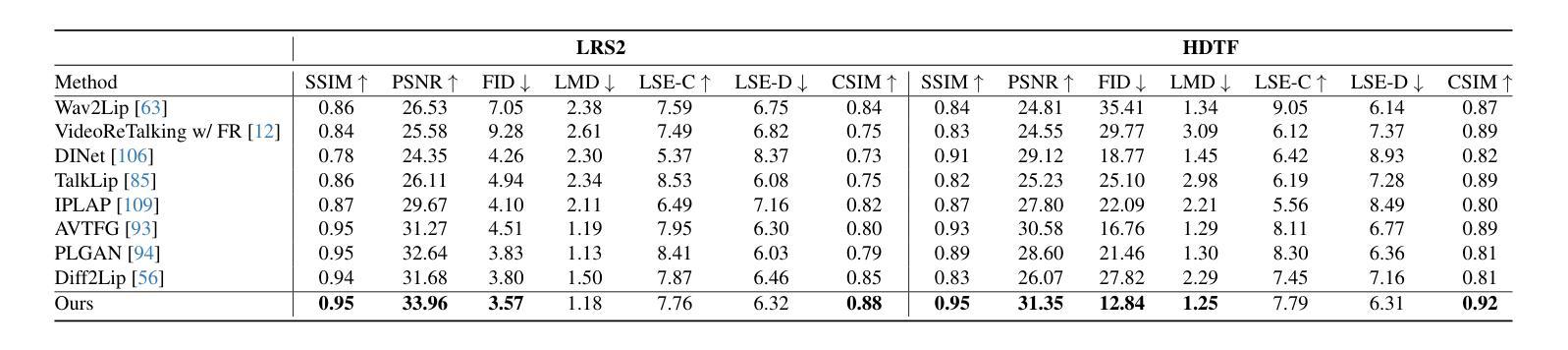
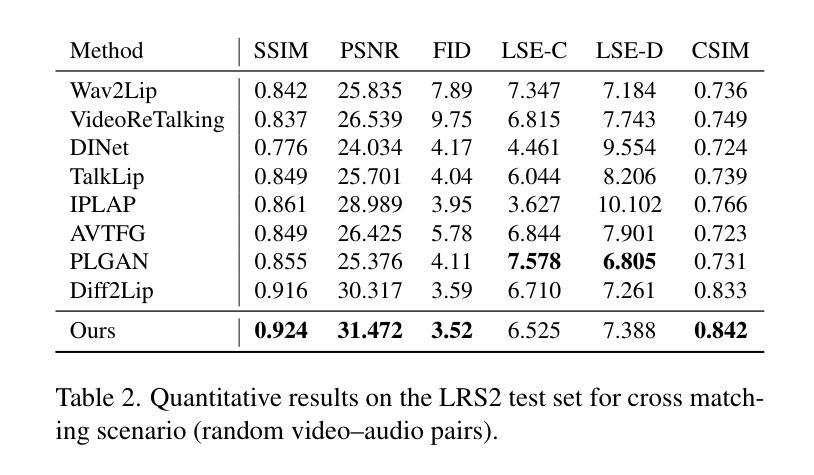
Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation aims at generating realistic videos of talking faces, focusing on accurate audio-lip synchronization without deteriorating any identity-related visual details. Recent state-of-the-art methods are based on inpainting, meaning that the lower half of the input face is masked, and the model fills the masked region by generating lips aligned with the given audio. Hence, to preserve identity-related visual details from the lower half, these approaches additionally require an unmasked identity reference image randomly selected from the same video. However, this common masking strategy suffers from (1) information loss in the input faces, significantly affecting the networks’ ability to preserve visual quality and identity details, (2) variation between identity reference and input image degrading reconstruction performance, and (3) the identity reference negatively impacting the model, causing unintended copying of elements unaligned with the audio. To address these issues, we propose a mask-free talking face generation approach while maintaining the 2D-based face editing task. Instead of masking the lower half, we transform the input images to have closed mouths, using a two-step landmark-based approach trained in an unpaired manner. Subsequently, we provide these edited but unmasked faces to a lip adaptation model alongside the audio to generate appropriate lip movements. Thus, our approach needs neither masked input images nor identity reference images. We conduct experiments on the benchmark LRS2 and HDTF datasets and perform various ablation studies to validate our contributions.
音频驱动说话人脸生成的目标是为了生成逼真的说话人脸视频,重点在于实现准确的音频与嘴唇同步,而不损害任何与身份相关的视觉细节。最近的最先进的方法基于插值技术,意味着输入脸的下半部分会被掩盖,模型通过在给定的音频下填充掩盖区域来生成相应的嘴唇。因此,为了保留下半部与身份相关的视觉细节,这些方法还需要从同一视频中随机选择一个未遮蔽的身份参考图像。然而,这种常见的遮蔽策略存在以下缺点:(1)输入人脸信息丢失,严重影响网络保留视觉质量和身份细节的能力;(2)身份参考与输入图像之间的差异导致重建性能下降;(3)身份参考对模型产生负面影响,导致出现与音频未对齐元素的意外复制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种无遮蔽的说话人脸生成方法,同时保持基于2D的面部编辑任务。我们不在下半部分进行遮蔽,而是使用基于标记的两步方法将输入图像转换为闭嘴状态,该方法以不成对的方式进行训练。随后,我们将这些经过编辑但未遮蔽的面孔与音频一起提供给唇部适应模型,以生成适当的唇部运动。因此,我们的方法既不需要遮蔽的输入图像,也不需要身份参考图像。我们在基准LRS2和HDTF数据集上进行实验,并通过各种消融研究验证我们的贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频驱动的说话人脸生成技术的新进展,提出了一种无需遮罩和身份参考图像的新的面部生成方法。该技术采用无遮罩输入图像的方法,通过变换输入图像使嘴巴闭合,再配合音频进行唇动作生成,从而实现了音频与唇部的同步。该方法避免了传统遮罩策略带来的信息丢失和身份参考图像带来的性能下降问题。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的说话人脸生成技术旨在生成与现实相似的视频,准确同步音频与唇部动作,同时保留身份相关的视觉细节。
- 现有方法基于遮罩策略,存在信息丢失、身份参考图像与输入图像之间的差异以及身份参考对模型产生的负面影响等问题。
- 新方法采用无遮罩策略,通过变换输入图像使嘴巴闭合,并使用唇适应模型配合音频进行面部生成。
- 该方法既不需要遮罩输入图像,也不需要身份参考图像。
- 实验在LRS2和HDTF数据集上进行,验证了新方法的有效性。
- 新方法避免了传统遮罩策略带来的问题,提高了面部生成的准确性和质量。
点此查看论文截图


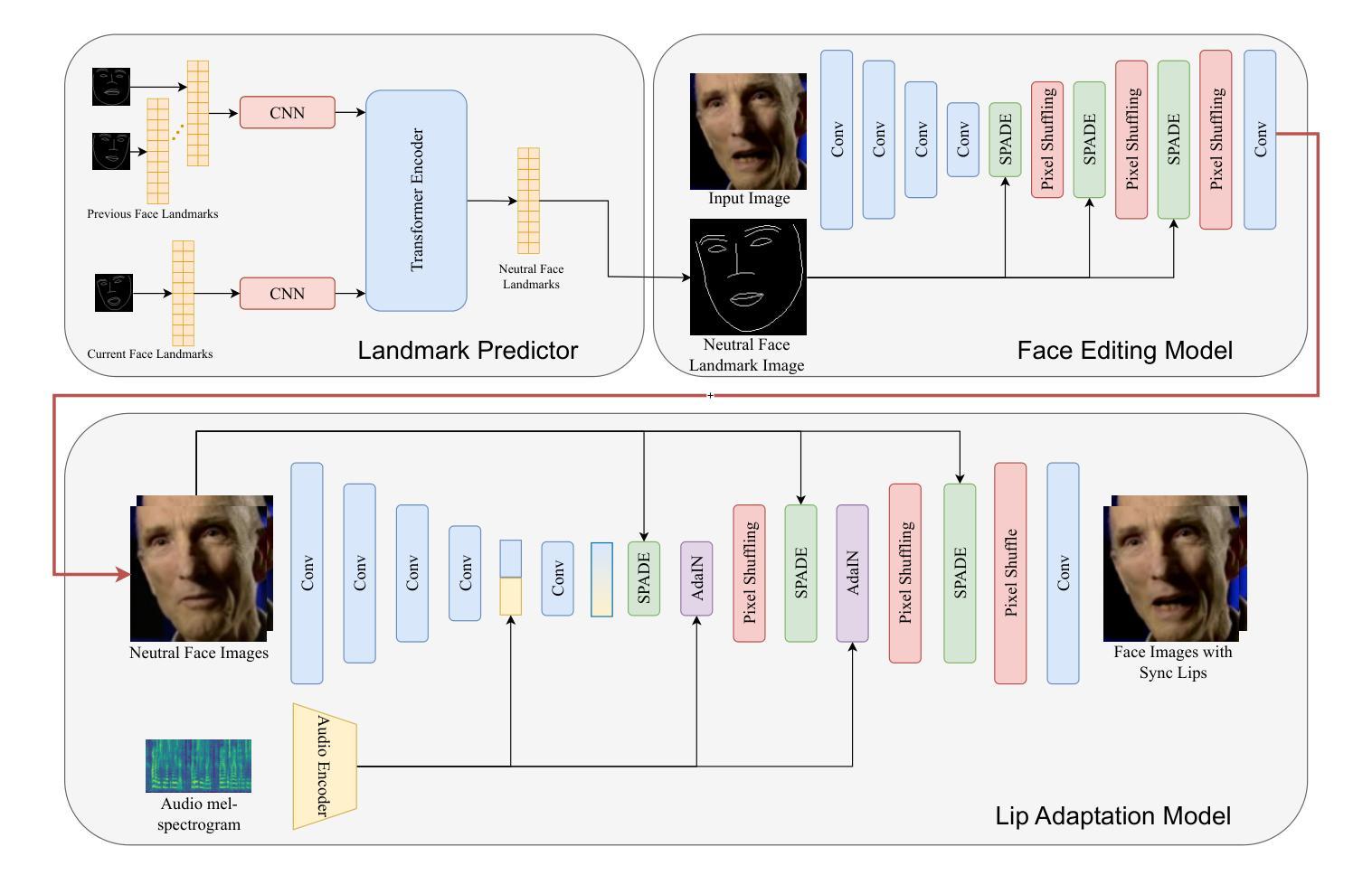
Learning Phonetic Context-Dependent Viseme for Enhancing Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation
Authors:Hyung Kyu Kim, Hak Gu Kim
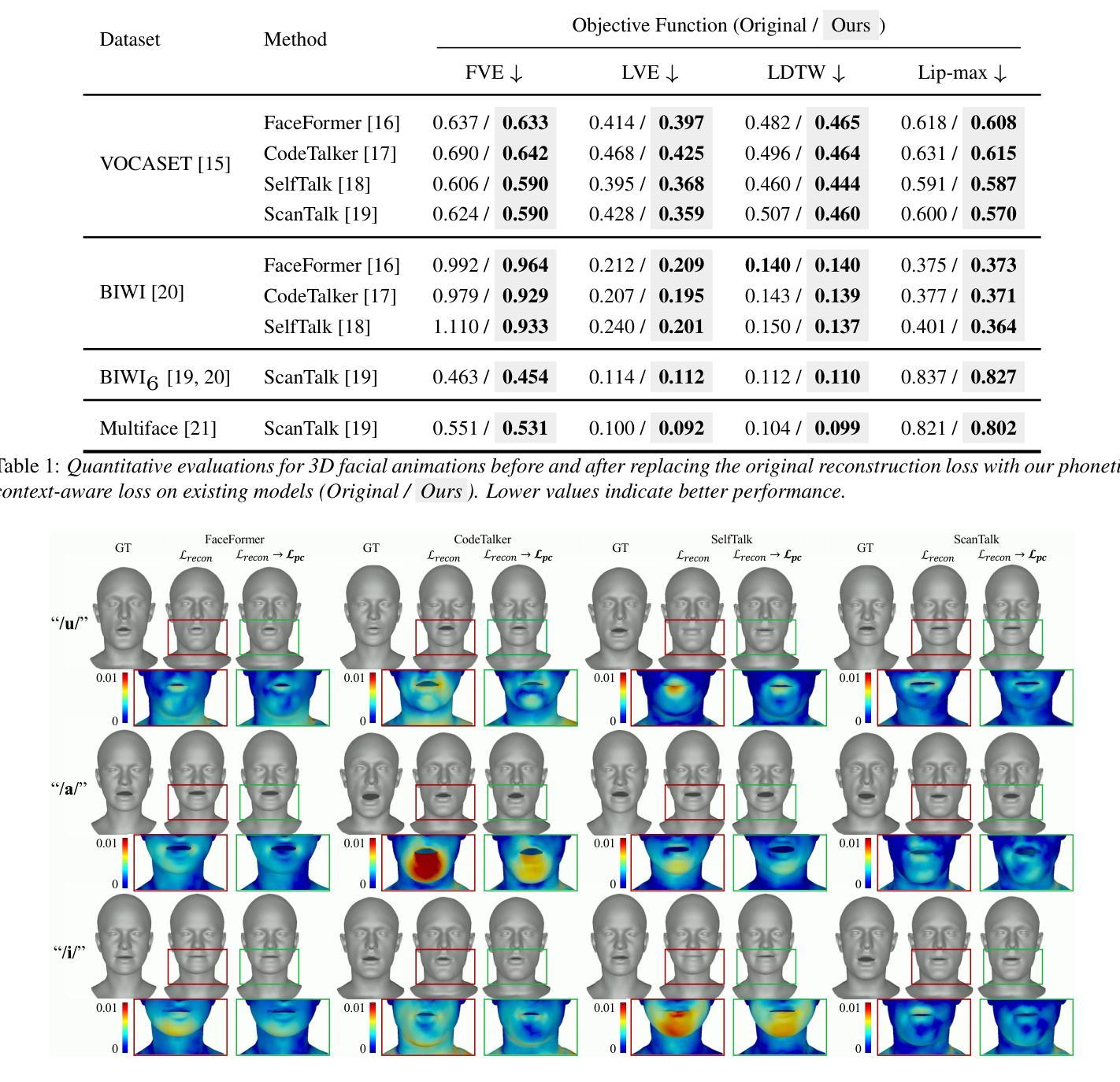
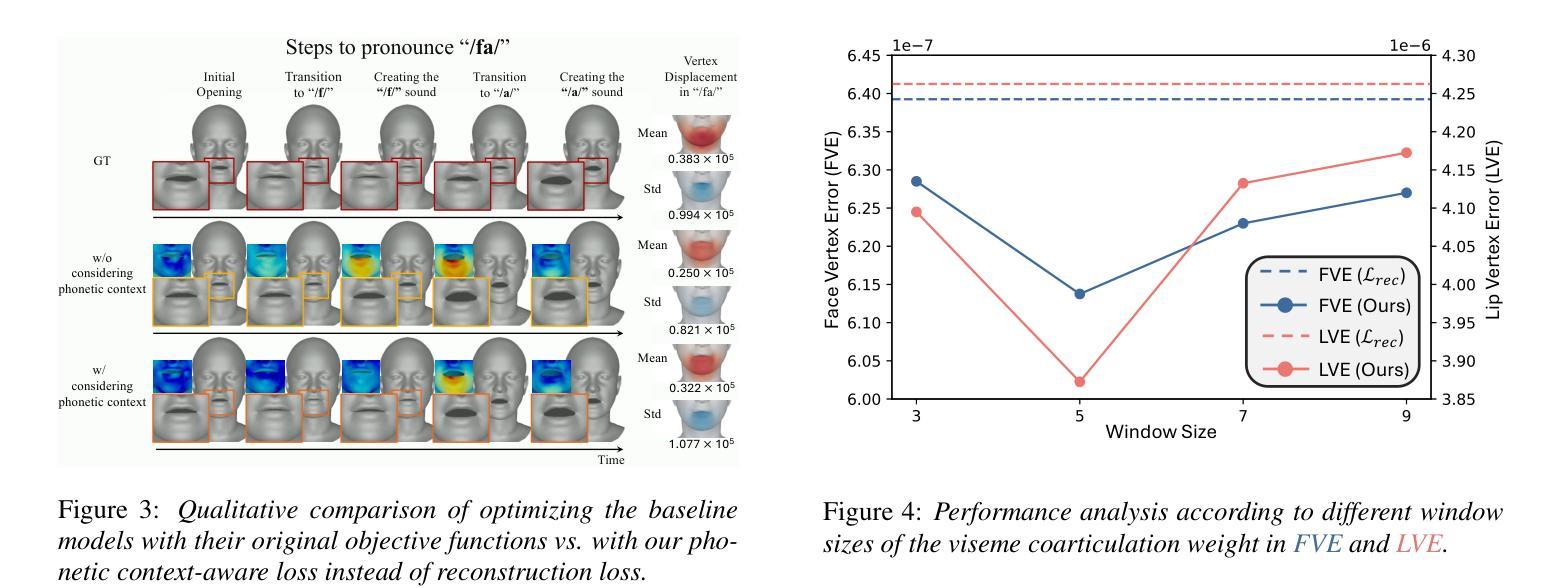
Speech-driven 3D facial animation aims to generate realistic facial movements synchronized with audio. Traditional methods primarily minimize reconstruction loss by aligning each frame with ground-truth. However, this frame-wise approach often fails to capture the continuity of facial motion, leading to jittery and unnatural outputs due to coarticulation. To address this, we propose a novel phonetic context-aware loss, which explicitly models the influence of phonetic context on viseme transitions. By incorporating a viseme coarticulation weight, we assign adaptive importance to facial movements based on their dynamic changes over time, ensuring smoother and perceptually consistent animations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that replacing the conventional reconstruction loss with ours improves both quantitative metrics and visual quality. It highlights the importance of explicitly modeling phonetic context-dependent visemes in synthesizing natural speech-driven 3D facial animation. Project page: https://cau-irislab.github.io/interspeech25/
语音驱动的3D面部动画旨在生成与音频同步的真实面部运动。传统方法主要通过将每一帧与地面真实数据进行比对来最小化重建损失。然而,这种逐帧的方法往往无法捕捉面部运动的连续性,由于协同发音导致输出产生抖动和不自然。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型语音上下文感知损失,该损失能明确建模语音上下文对面部运动的影响。通过引入面部协同发音权重,我们根据面部运动随时间变化的动态变化为其分配自适应重要性,确保更平滑、感知一致的动画。大量实验表明,用我们的方法替换传统的重建损失可以提高定量指标和视觉质量。它强调了明确建模语音上下文相关的面部运动在合成自然语音驱动的3D面部动画中的重要性。项目页面:https://cau-irislab.github.io/interspeech25/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for Interspeech 2025 Project Page: https://cau-irislab.github.io/interspeech25/
Summary
面部动画技术旨在生成与音频同步的真实面部运动。传统方法主要通过与地面真实数据帧对齐来最小化重建损失,但这种方法忽略了面部运动的连续性,导致输出效果不自然。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的语音语境感知损失函数,该函数显式地模拟语音语境对语音表情过渡的影响。通过引入语音表情协同发音权重,我们根据面部运动随时间的变化动态变化来调整其重要性,从而确保动画更为流畅和感知一致。实验证明,与传统的重建损失函数相比,该新函数可以提高量化指标和视觉效果,突出了明确模拟语音语境依赖的语音表情在合成自然面部动画中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音驱动的三维面部动画旨在生成与音频同步的真实面部运动。
- 传统方法主要通过最小化重建损失来创建面部动画,但这种方法可能导致输出效果不自然,因为忽略了面部运动的连续性。
- 提出了一种新的语音语境感知损失函数来解决这个问题,该函数可以显式地模拟语音语境对语音表情过渡的影响。
- 通过引入语音表情协同发音权重,新函数确保了更流畅和感知一致的动画。
- 实验表明,新的语音语境感知损失函数可以提高量化指标和视觉效果。
- 新的损失函数提高了重建面部动画的自然性和连续性。
点此查看论文截图

MemoryTalker: Personalized Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation via Audio-Guided Stylization
Authors:Hyung Kyu Kim, Sangmin Lee, Hak Gu Kim
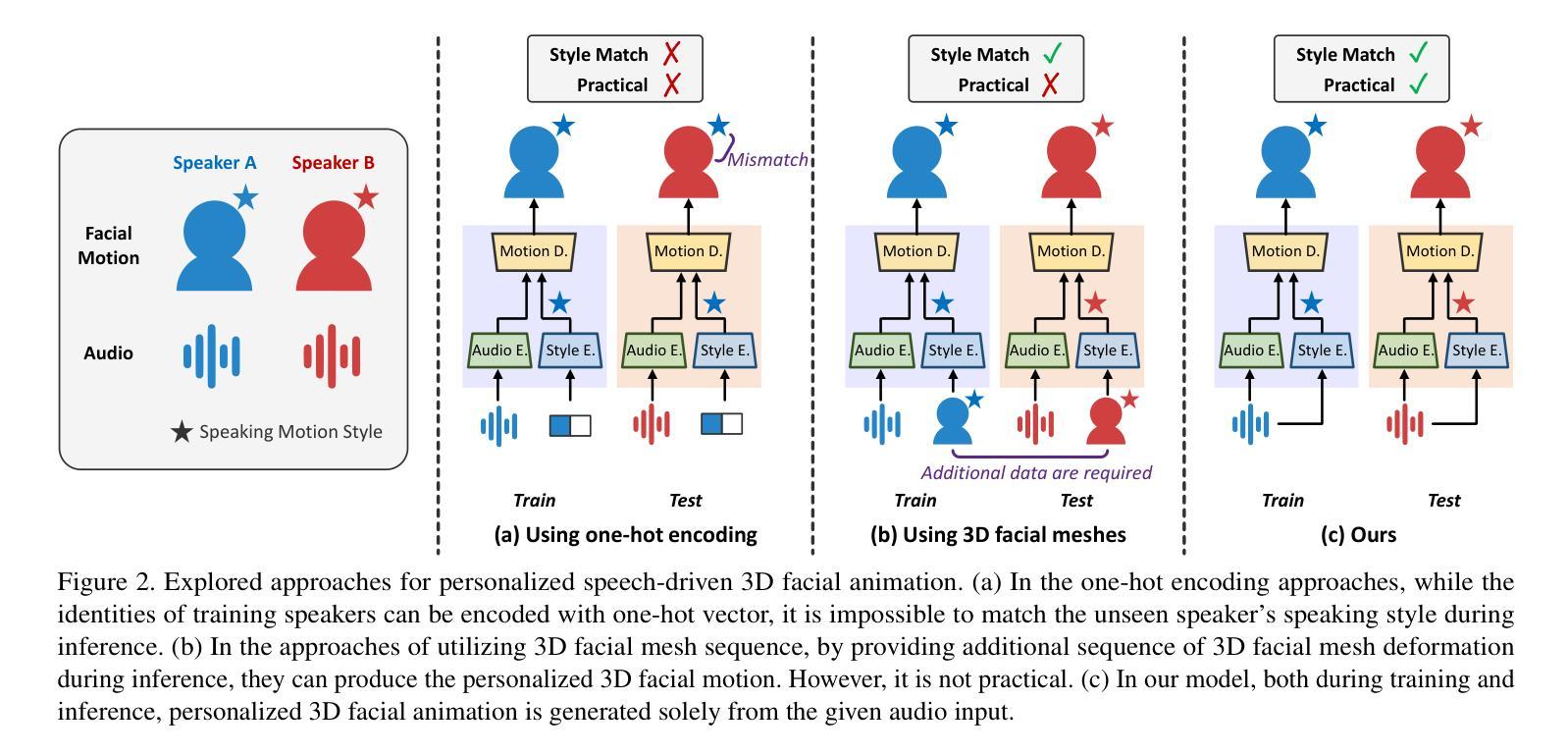
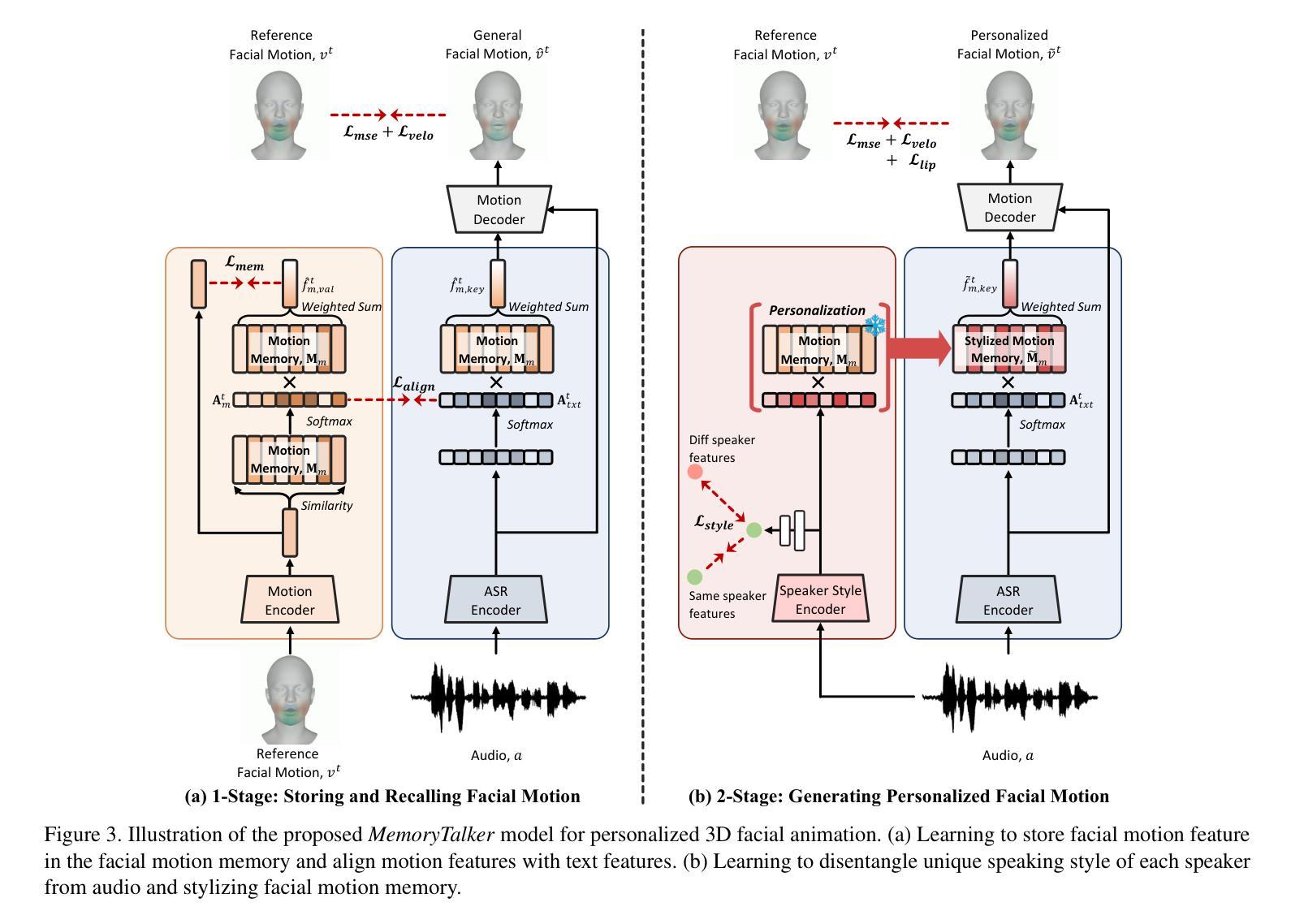
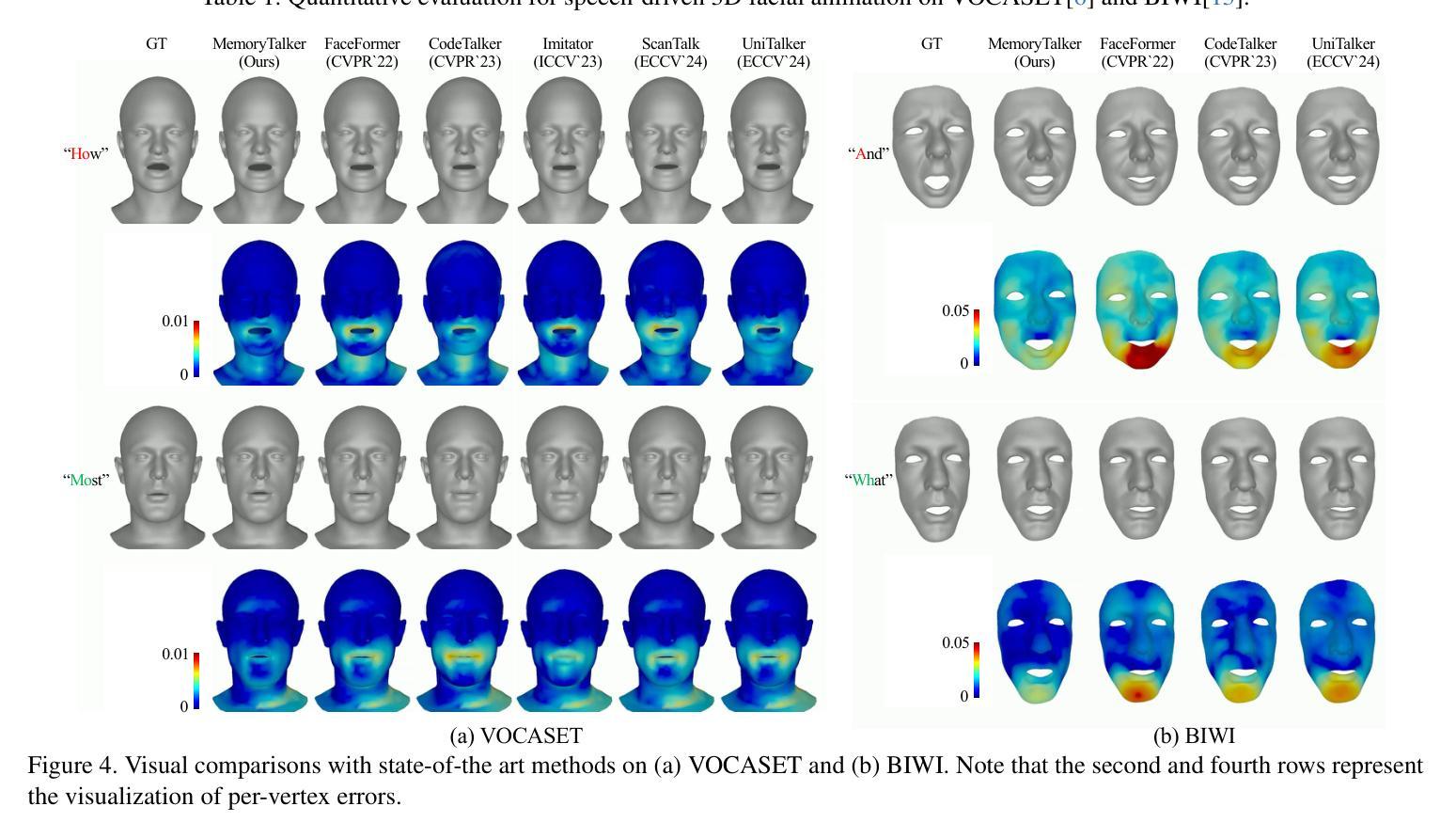
Speech-driven 3D facial animation aims to synthesize realistic facial motion sequences from given audio, matching the speaker’s speaking style. However, previous works often require priors such as class labels of a speaker or additional 3D facial meshes at inference, which makes them fail to reflect the speaking style and limits their practical use. To address these issues, we propose MemoryTalker which enables realistic and accurate 3D facial motion synthesis by reflecting speaking style only with audio input to maximize usability in applications. Our framework consists of two training stages: 1-stage is storing and retrieving general motion (i.e., Memorizing), and 2-stage is to perform the personalized facial motion synthesis (i.e., Animating) with the motion memory stylized by the audio-driven speaking style feature. In this second stage, our model learns about which facial motion types should be emphasized for a particular piece of audio. As a result, our MemoryTalker can generate a reliable personalized facial animation without additional prior information. With quantitative and qualitative evaluations, as well as user study, we show the effectiveness of our model and its performance enhancement for personalized facial animation over state-of-the-art methods.
语音驱动的3D面部动画旨在根据给定的音频合成逼真的面部运动序列,以匹配说话者的说话风格。然而,之前的工作通常需要先验信息,如说话者的类别标签或推理时的额外3D面部网格,这使得它们无法反映说话风格,并限制了其实际应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MemoryTalker,它能够通过仅使用音频输入反映说话风格,实现逼真且准确的3D面部运动合成,以最大化在应用程序中的实用性。我们的框架由两个训练阶段组成:第一阶段是存储和检索一般运动(即记忆),第二阶段是借助由音频驱动的说话风格特征进行个性化面部运动合成(即动画)。在第二阶段,我们的模型学习对于特定音频应该强调哪种面部运动类型。因此,我们的MemoryTalker可以在没有额外先验信息的情况下生成可靠的个性化面部动画。通过定量和定性评估以及用户研究,我们展示了我们的模型的有效性及其在个性化面部动画方面的性能提升,超过了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for ICCV 2025 Project Page: https://cau-irislab.github.io/ICCV25-MemoryTalker/
Summary
本文介绍了Speech-driven 3D面部动画技术的新进展。针对现有技术存在的问题,如需要额外的先验信息(如说话人的类别标签或额外的3D面部网格),提出了一种新的方法MemoryTalker。该方法仅通过音频输入就能反映说话风格,使3D面部动画的合成更加真实、准确,并可在各种应用场合中最大化实用性。新方法包括两个训练阶段:一是存储和检索通用动作(即记忆阶段),二是利用音频驱动的说话风格特征进行个性化面部动画合成(即动画阶段)。该方法能学习针对特定音频应强调哪些面部动作类型,从而实现可靠且个性化的面部动画生成,无需额外的先验信息。
Key Takeaways
- Speech-driven 3D面部动画技术旨在从给定的音频中合成逼真的面部动作序列,匹配说话人的说话风格。
- 现有方法通常需要额外的先验信息,如说话人的类别标签或3D面部网格,这限制了其实际应用。
- MemoryTalker方法通过仅使用音频输入来反映说话风格,使3D面部动画的合成更加真实和准确。
- MemoryTalker包括两个训练阶段:存储和检索通用动作(记忆阶段)以及利用音频驱动的说话风格特征进行个性化面部动画合成(动画阶段)。
- 模型能学习针对特定音频应强调哪些面部动作类型,以实现个性化的面部动画生成。
- MemoryTalker方法无需额外的先验信息,即可生成可靠的个性化面部动画。
点此查看论文截图

Face2VoiceSync: Lightweight Face-Voice Consistency for Text-Driven Talking Face Generation
Authors:Fang Kang, Yin Cao, Haoyu Chen
Recent studies in speech-driven talking face generation achieve promising results, but their reliance on fixed-driven speech limits further applications (e.g., face-voice mismatch). Thus, we extend the task to a more challenging setting: given a face image and text to speak, generating both talking face animation and its corresponding speeches. Accordingly, we propose a novel framework, Face2VoiceSync, with several novel contributions: 1) Voice-Face Alignment, ensuring generated voices match facial appearance; 2) Diversity & Manipulation, enabling generated voice control over paralinguistic features space; 3) Efficient Training, using a lightweight VAE to bridge visual and audio large-pretrained models, with significantly fewer trainable parameters than existing methods; 4) New Evaluation Metric, fairly assessing the diversity and identity consistency. Experiments show Face2VoiceSync achieves both visual and audio state-of-the-art performances on a single 40GB GPU.
近期关于语音驱动说话人脸生成的研究取得了有前景的结果,但它们对固定驱动语音的依赖限制了进一步应用(例如,人脸与语音不匹配)。因此,我们将任务扩展到一个更具挑战性的场景:给定一张人脸图像和要说的文本,生成说话的人脸动画及其对应的语音。据此,我们提出了一种新型框架Face2VoiceSync,包含几个新颖的贡献:1)语音-人脸对齐,确保生成的语音与面部外观相匹配;2)多样性和操控性,能够对语言特征空间中的生成语音进行控制;3)高效训练,使用轻量级的VAE来连接视觉和音频大型预训练模型,与现有方法相比,可训练参数大大减少;4)新的评价指标,公正地评估多样性和身份一致性。实验表明,Face2VoiceSync在单个40GB GPU上实现了视觉和音频的业界最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本摘要:近期语音驱动说话人脸生成研究取得显著成果,但受限于固定驱动语音,应用场景受限(如人脸与语音不匹配)。为此,我们扩展任务至更具挑战性的场景:给定人脸图像和文本内容,生成对应的说话人脸动画和语音。我们提出一种新型框架Face2VoiceSync,包含多项创新贡献:1)语音人脸对齐,确保生成语音与面部外观匹配;2)多样性和操控性,能够控制生成语音的副语言特征空间;3)高效训练,使用轻量级VAE来连接视觉和音频大型预训练模型,相比现有方法大大减少可训练参数;4)新的评价指标,公平评估多样性和身份一致性。实验表明Face2VoiceSync在视觉和音频方面都达到了单张40GB GPU上的最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- 近期语音驱动说话人脸生成研究虽取得进展,但仍存在固定驱动语音带来的应用场景限制问题。
- 扩展任务至更挑战的场景:根据人脸图像和文本内容生成对应的说话人脸动画和语音。
- 提出新型框架Face2VoiceSync,包含多项创新贡献,如语音人脸对齐、多样性和操控性、高效训练、新的评价指标等。
- Face2VoiceSync能够实现生成语音与面部外观的匹配。
- 相比现有方法,Face2VoiceSync在训练参数上大大减少。
- 实验表明Face2VoiceSync在视觉和音频方面都达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

Livatar-1: Real-Time Talking Heads Generation with Tailored Flow Matching
Authors:Haiyang Liu, Xiaolin Hong, Xuancheng Yang, Yudi Ruan, Xiang Lian, Michael Lingelbach, Hongwei Yi, Wei Li
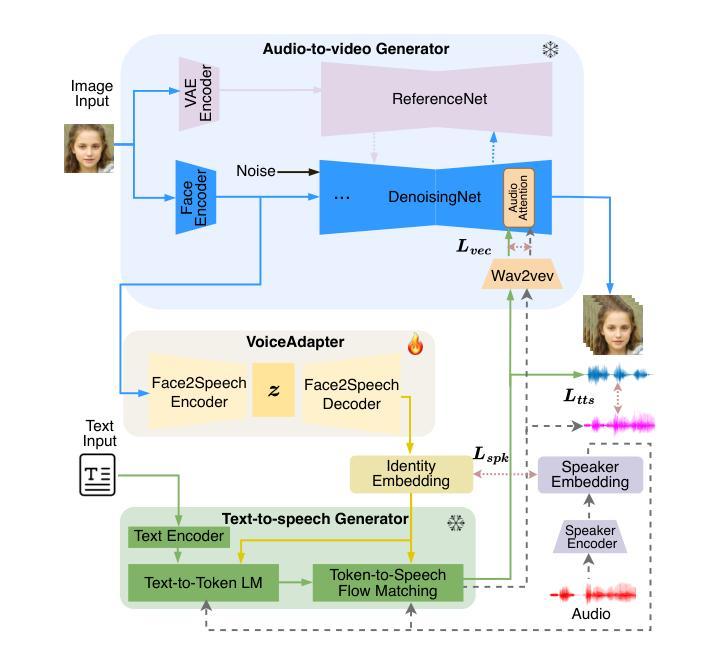
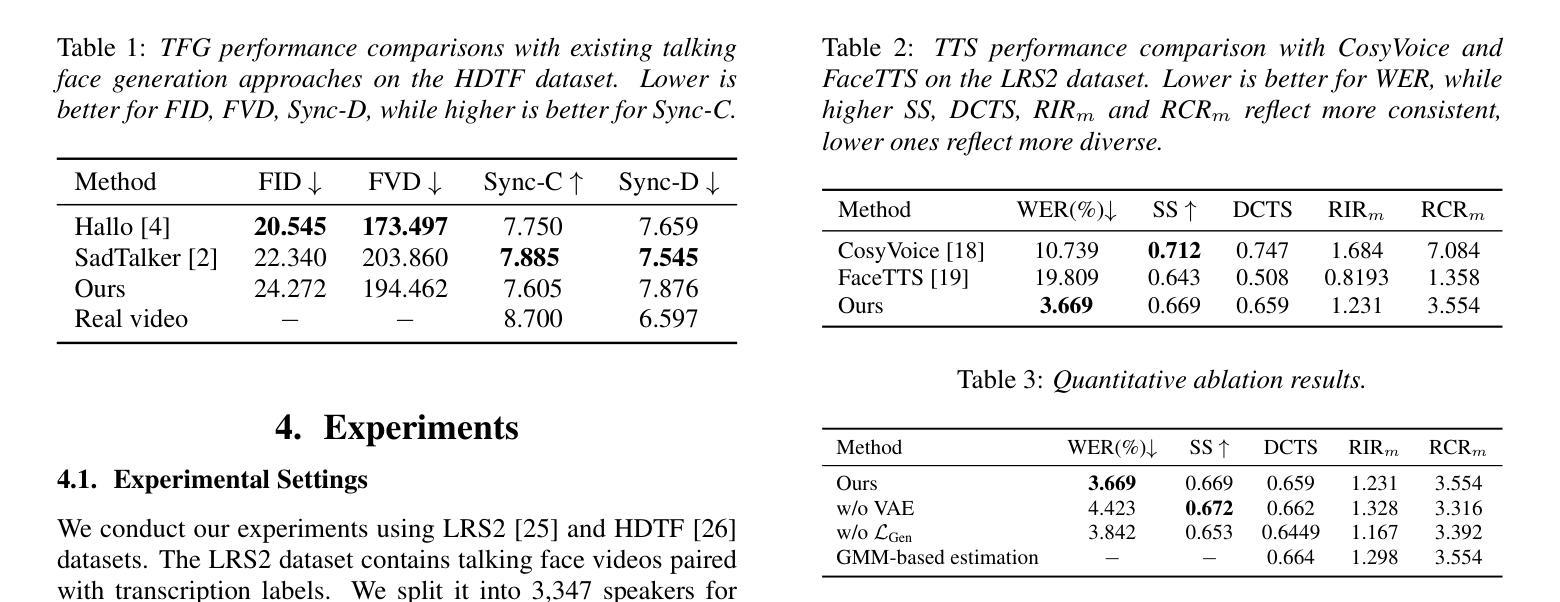
We present Livatar, a real-time audio-driven talking heads videos generation framework. Existing baselines suffer from limited lip-sync accuracy and long-term pose drift. We address these limitations with a flow matching based framework. Coupled with system optimizations, Livatar achieves competitive lip-sync quality with a 8.50 LipSync Confidence on the HDTF dataset, and reaches a throughput of 141 FPS with an end-to-end latency of 0.17s on a single A10 GPU. This makes high-fidelity avatars accessible to broader applications. Our project is available at https://www.hedra.com/ with with examples at https://h-liu1997.github.io/Livatar-1/
我们推出了Livatar,这是一个实时音频驱动谈话视频生成框架。现有基准测试在唇同步准确性和长期姿势漂移方面存在局限性。我们通过基于流匹配的框架来解决这些问题。结合系统优化,Livatar在HDTF数据集上实现了具有竞争力的唇同步质量,置信度为8.5分;并在单个A10 GPU上以每秒141帧的吞吐量达到了端到端的低延迟仅为0.17秒。这使得高保真头像能更广泛地应用于各个领域。我们的项目可通过链接 https://www.hedra.com/ 了解详情,具体案例展示链接为 https://h-liu1997.github.io/Livatar-1/ 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary:我们推出了Livatar,一个实时音频驱动的说唱人头视频生成框架。现有基准测试存在唇同步精度有限和长期姿态漂移的问题。我们通过基于流匹配的框架解决了这些局限性。结合系统优化,Livatar在HDTF数据集上实现了具有竞争力的唇同步质量,达到了8.50的LipSync置信度,并在单个A10 GPU上实现了每秒141帧的吞吐量和仅0.17秒的端到端延迟。这使得高保真化身更适用于广泛的应用。我们的项目可在https://www.hedra.com/找到,示例可在https://h-liu1997.github.io/Livatar-1/查看。
Key Takeaways:
- Livatar是一个实时音频驱动的说唱人头视频生成框架,旨在解决现有技术的局限性。
- 现有技术存在唇同步精度有限和长期姿态漂移的问题,而Livatar通过基于流匹配的框架解决了这些问题。
- Livatar在HDTF数据集上实现了8.50的LipSync置信度,显示出其出色的唇同步质量。
- 该系统具有高效的性能,能够在单个A10 GPU上实现每秒141帧的吞吐量和仅0.17秒的端到端延迟。
- 高保真化身更适用于广泛的应用,包括娱乐、教育、培训等领域。
- 项目可以在https://www.hedra.com/找到,并且提供了示例链接https://h-liu1997.github.io/Livatar-1/以供查看和学习。
- 该技术可能会推动虚拟形象生成的发展,并为用户提供更加逼真的互动体验。
点此查看论文截图

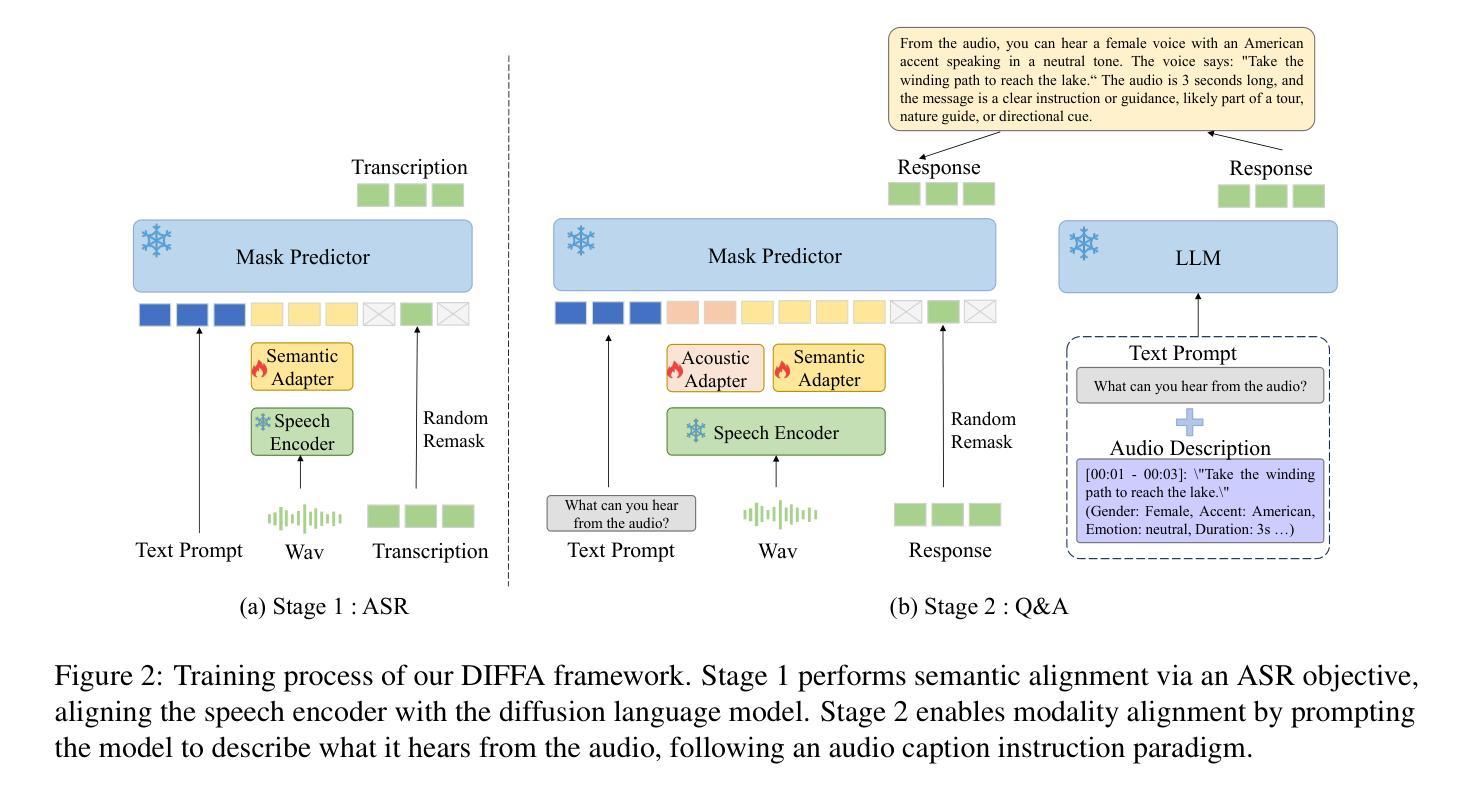
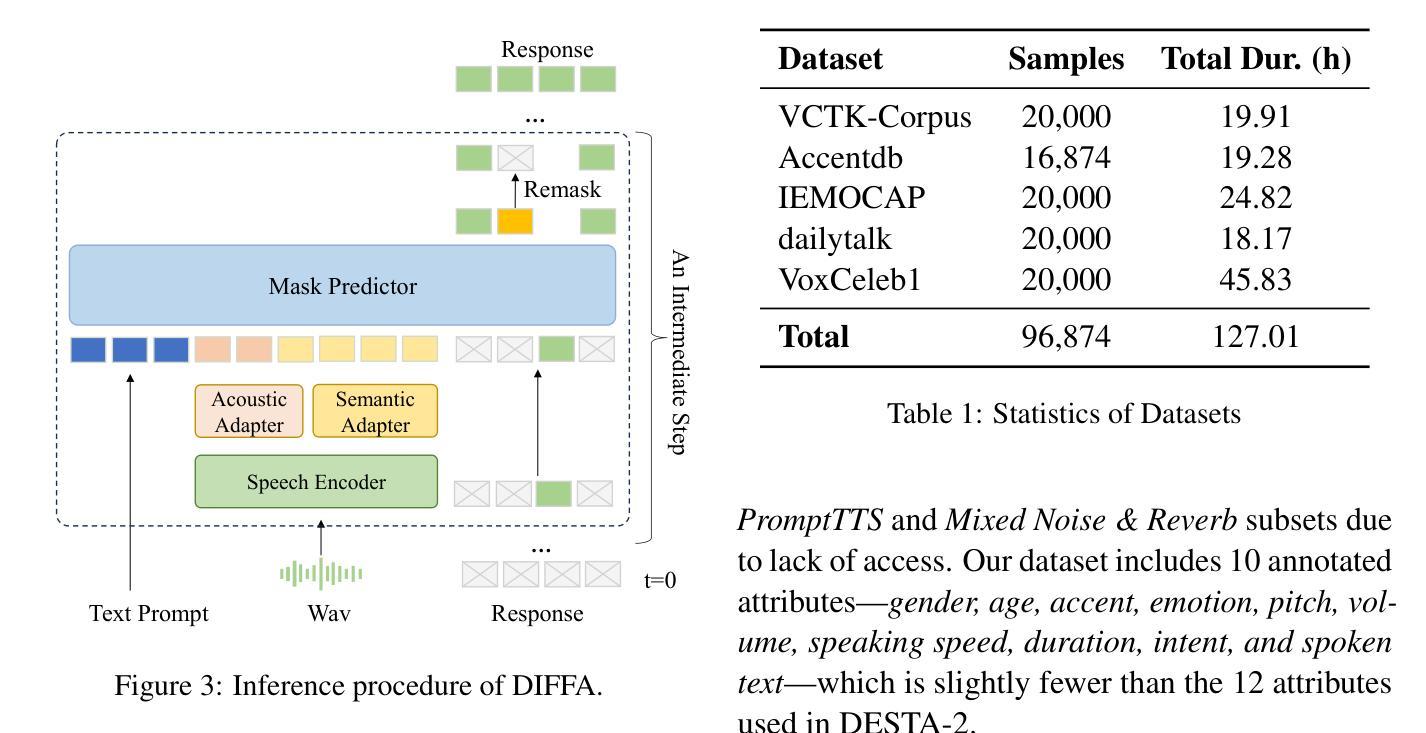
DIFFA: Large Language Diffusion Models Can Listen and Understand
Authors:Jiaming Zhou, Hongjie Chen, Shiwan Zhao, Jian Kang, Jie Li, Enzhi Wang, Yujie Guo, Haoqin Sun, Hui Wang, Aobo Kong, Yong Qin, Xuelong Li
Recent advances in Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across textual and multimodal domains. In parallel, diffusion-based language models have emerged as a promising alternative to the autoregressive paradigm, offering improved controllability, bidirectional context modeling, and robust generation. However, their application to the audio modality remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce \textbf{DIFFA}, the first diffusion-based Large Audio-Language Model designed to perform spoken language understanding. DIFFA integrates a frozen diffusion language model with a lightweight dual-adapter architecture that bridges speech understanding and natural language reasoning. We employ a two-stage training pipeline: first, aligning semantic representations via an ASR objective; then, learning instruction-following abilities through synthetic audio-caption pairs automatically generated by prompting LLMs. Despite being trained on only 960 hours of ASR and 127 hours of synthetic instruction data, DIFFA demonstrates competitive performance on major benchmarks, including MMSU, MMAU, and VoiceBench, outperforming several autoregressive open-source baselines. Our results reveal the potential of diffusion-based language models for efficient and scalable audio understanding, opening a new direction for speech-driven AI. Our code will be available at https://github.com/NKU-HLT/DIFFA.git.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进展在文本和多模态领域展现出了显著的能力。同时,基于扩散的语言模型作为一种有前景的自回归范式替代方案而出现,提供了更好的可控性、双向上下文建模和稳健的生成能力。然而,它们在音频模态的应用仍然被较少探索。在这项工作中,我们介绍了\textbf{DIFFA},这是第一个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型,旨在进行口语理解。DIFFA将冻结的扩散语言模型与轻量级的双适配器架构相结合,这座桥梁连接了语音理解和自然语言推理。我们采用了两阶段训练管道:首先,通过ASR目标对齐语义表示;然后,通过LLMs自动生成的合成音频字幕对来学习指令执行能力。尽管只在960小时的ASR和127小时的合成指令数据上进行训练,DIFFA在主要基准测试上表现出竞争力,包括MMSU、MMAU和VoiceBench,超越了多个自回归开源基准。我们的结果揭示了基于扩散的语言模型在高效和可扩展音频理解方面的潜力,为语音驱动的人工智能开启了新的方向。我们的代码将在https://github.com/NKU-HLT/DIFFA.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在文本和多模态领域展现出卓越的能力。本研究引入首个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型DIFFA,旨在实现语音理解。DIFFA结合了冻结的扩散语言模型和轻量级双适配器架构,实现语音理解和自然语言推理之间的桥梁。通过两阶段训练流程:首先通过对齐语义表示进行ASR目标;然后通过学习合成音频字幕对来跟随指令,这些合成音频字幕对是通过提示LLM自动生成的。尽管只在960小时的ASR和127小时的合成指令数据上进行训练,DIFFA在主要基准测试中表现出竞争力,包括MMSU、MMAU和VoiceBench,优于多个自动回归开源基准。这表明扩散模型在音频理解方面具有高效性和可扩展性潜力,为语音驱动的AI开启了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- DIFFA是首个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型,旨在实现语音理解。
- DIFFA结合了冻结的扩散语言模型和轻量级双适配器架构。
- DIFFA采用两阶段训练流程,首先进行ASR目标对齐语义表示,然后学习跟随指令的能力。
- DIFFA通过LLM生成的合成音频字幕对进行训练。
- 在主要基准测试中,DIFFA表现出竞争力,优于多个自动回归开源基准。
- DIFFA的潜在应用表明扩散模型在音频理解方面具有高效性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

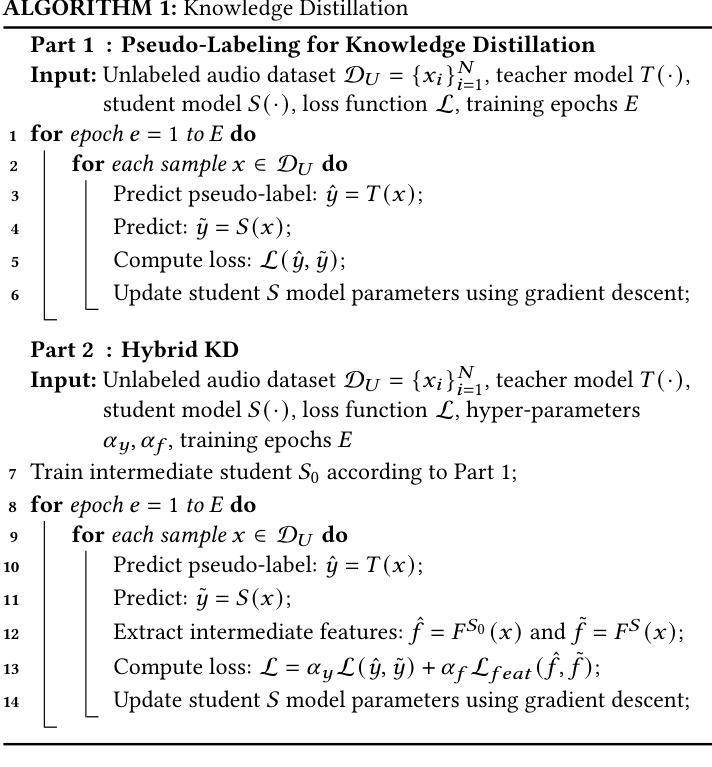
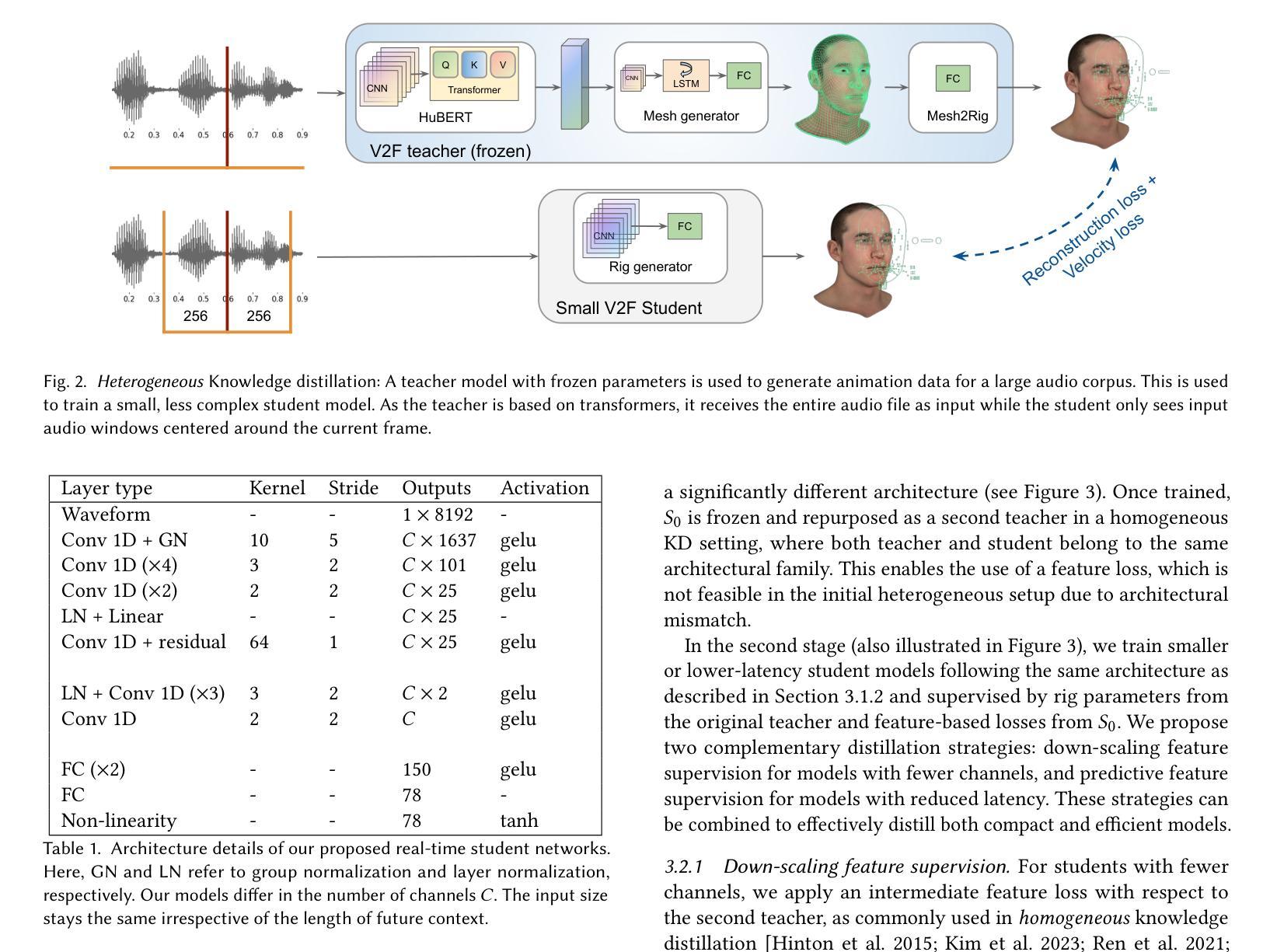
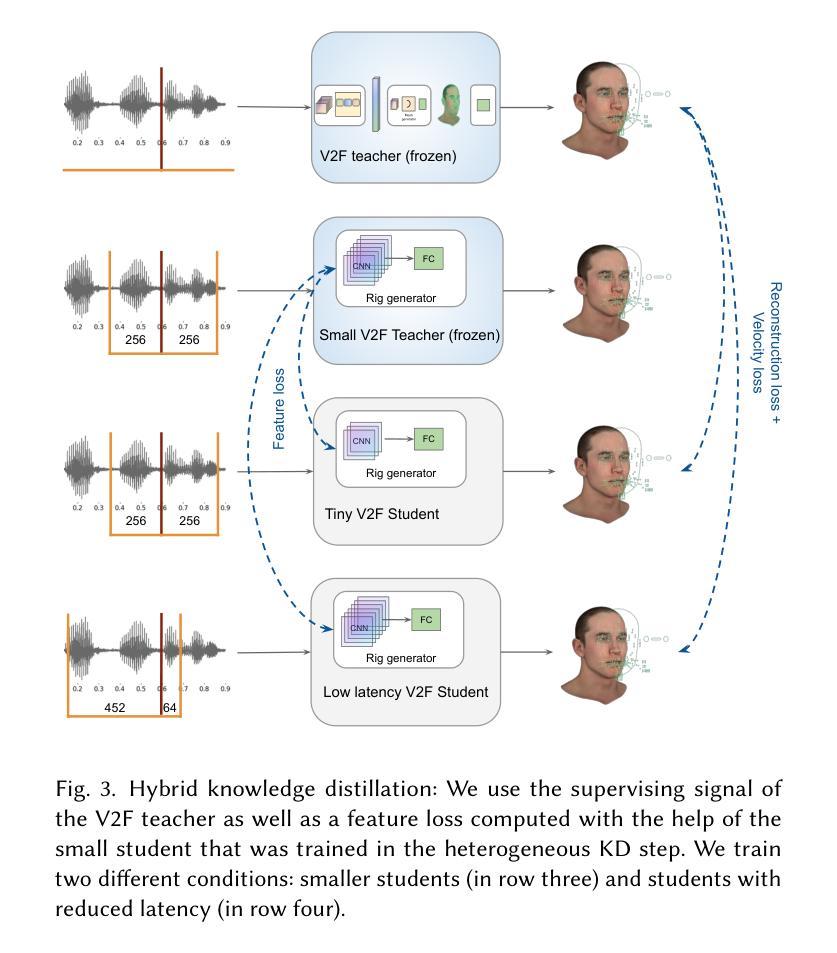
Tiny is not small enough: High-quality, low-resource facial animation models through hybrid knowledge distillation
Authors:Zhen Han, Mattias Teye, Derek Yadgaroff, Judith Bütepage
The training of high-quality, robust machine learning models for speech-driven 3D facial animation requires a large, diverse dataset of high-quality audio-animation pairs. To overcome the lack of such a dataset, recent work has introduced large pre-trained speech encoders that are robust to variations in the input audio and, therefore, enable the facial animation model to generalize across speakers, audio quality, and languages. However, the resulting facial animation models are prohibitively large and lend themselves only to offline inference on a dedicated machine. In this work, we explore on-device, real-time facial animation models in the context of game development. We overcome the lack of large datasets by using hybrid knowledge distillation with pseudo-labeling. Given a large audio dataset, we employ a high-performing teacher model to train very small student models. In contrast to the pre-trained speech encoders, our student models only consist of convolutional and fully-connected layers, removing the need for attention context or recurrent updates. In our experiments, we demonstrate that we can reduce the memory footprint to up to 3.4 MB and required future audio context to up to 81 ms while maintaining high-quality animations. This paves the way for on-device inference, an important step towards realistic, model-driven digital characters.
对于高质量、稳健的机器学习模型进行语音驱动的3D面部动画训练,需要大量的高质量音频动画对构成的多样化数据集。为了克服缺乏这样的数据集,近期的工作引入了大型预训练语音编码器,该编码器对输入音频的变化具有鲁棒性,因此能够使面部动画模型在发言人、音频质量和语言方面实现泛化。然而,由此产生的面部动画模型过于庞大,只适用于专用机器上的离线推理。在这项工作中,我们在游戏开发的背景下探索了设备端的实时面部动画模型。我们通过混合知识蒸馏和伪标签技术来克服缺乏大型数据集的问题。给定一个大型音频数据集,我们使用高性能的教师模型来训练非常小的学生模型。与预训练的语音编码器不同,我们的学生模型只包含卷积层和全连接层,无需注意上下文或循环更新。在我们的实验中,我们证明可以将内存占用减少到最多3.4MB,并将未来所需的音频上下文时间减少到最多81毫秒,同时保持高质量的动画。这为设备端推理铺平了道路,是朝着现实、模型驱动的数字角色迈进的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Transactions on Graphics 2025 (SIGGRAPH journal track)
Summary
本文介绍了针对语音驱动的3D面部动画的高质量机器学习模型训练需求,指出需要大规模、多样化的高质量音频动画对数据集。为克服缺乏此类数据集的问题,本研究采用大型预训练语音编码器,该编码器对输入音频的变异具有鲁棒性,使面部动画模型能够在不同说话者、音频质量和语言上进行泛化。然而,这些模型体积庞大,仅适用于专用机器上的离线推理。本研究在游戏开发背景下探索了实时面部动画模型,通过使用混合知识蒸馏与伪标签技术来克服缺乏大型数据集的问题。利用大型音频数据集和高效教师模型训练小型学生模型,无需注意力上下文或循环更新。实验表明,在保持高质量动画的同时,可减小内存占用至3.4MB,并将未来音频上下文需求减少至81ms,这为设备端推理铺平了道路,是朝着逼真模型驱动的数字角色发展的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量语音驱动的3D面部动画需要大规模、多样化的高质量音频动画对数据集。
- 缺乏此类数据集是面部动画模型发展的主要挑战之一。
- 预训练语音编码器对输入音频变异具有鲁棒性,使模型能够泛化。
- 现有模型体积庞大,仅适用于离线推理。
- 本研究通过混合知识蒸馏与伪标签技术克服缺乏大型数据集的问题。
- 利用高效教师模型训练小型学生模型,降低模型复杂度。
点此查看论文截图

Talking Like a Phisher: LLM-Based Attacks on Voice Phishing Classifiers
Authors:Wenhao Li, Selvakumar Manickam, Yung-wey Chong, Shankar Karuppayah
Voice phishing (vishing) remains a persistent threat in cybersecurity, exploiting human trust through persuasive speech. While machine learning (ML)-based classifiers have shown promise in detecting malicious call transcripts, they remain vulnerable to adversarial manipulations that preserve semantic content. In this study, we explore a novel attack vector where large language models (LLMs) are leveraged to generate adversarial vishing transcripts that evade detection while maintaining deceptive intent. We construct a systematic attack pipeline that employs prompt engineering and semantic obfuscation to transform real-world vishing scripts using four commercial LLMs. The generated transcripts are evaluated against multiple ML classifiers trained on a real-world Korean vishing dataset (KorCCViD) with statistical testing. Our experiments reveal that LLM-generated transcripts are both practically and statistically effective against ML-based classifiers. In particular, transcripts crafted by GPT-4o significantly reduce classifier accuracy (by up to 30.96%) while maintaining high semantic similarity, as measured by BERTScore. Moreover, these attacks are both time-efficient and cost-effective, with average generation times under 9 seconds and negligible financial cost per query. The results underscore the pressing need for more resilient vishing detection frameworks and highlight the imperative for LLM providers to enforce stronger safeguards against prompt misuse in adversarial social engineering contexts.
语音钓鱼(vishish)仍然是网络安全中的持续威胁,它通过说服性话语来利用人类的信任。虽然基于机器学习的分类器在检测恶意通话记录方面显示出潜力,但它们仍然容易受到保留语义内容的对抗性操纵的影响。在这项研究中,我们探索了一种新的攻击向量,利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成对抗性的钓鱼记录,以躲避检测同时保持欺骗意图。我们构建了一个系统的攻击管道,采用提示工程和语义模糊化来转换现实世界中的钓鱼脚本,使用四种商业LLM。生成的记录针对在现实世界中的韩国钓鱼数据集(KorCCViD)上训练的多个机器学习分类器进行评估,并进行统计测试。我们的实验表明,LLM生成的记录在针对基于机器学习的分类器时,具有实际和统计上的有效性。特别是通过GPT-4o制作的记录显著降低了分类器的准确性(最高达30.96%),同时保持了较高的语义相似性,通过BERTScore衡量。此外,这些攻击既高效又经济,平均生成时间不到9秒,每次查询的财务成本微乎其微。结果突显了对更具弹性的钓鱼检测框架的迫切需求,并强调大型语言模型提供商需要在对抗性社会工程环境中加强防止提示误用的保障措施。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by EAI ICDF2C 2025
Summary:本研究探讨了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成对抗性语音钓鱼(vishing)脚本的新型攻击向量,以躲避检测并保持欺骗意图。研究通过提示工程和语义模糊化等技术手段,使用四种商用LLMs对真实世界的vishing脚本进行转换。实验证明,LLM生成的脚本在实际和统计上都能有效地对抗基于机器学习的分类器。特别是GPT-4o生成的脚本在保持高语义相似性的同时,能显著降低分类器的准确率(最高达30.96%)。这些攻击既高效又经济,平均生成时间不到9秒,每次查询的财务成本几乎为零。这突显了对更具弹性的vishing检测框架的迫切需求,并强调LLM提供商需要在对抗性社会工程环境中加强对提示误用的保护。
Key Takeaways:
- 语音钓鱼(vishing)仍是网络安全中的持久威胁,利用人类信任通过说服性话语进行攻击。
- 机器学习的分类器在检测恶意语音钓鱼转录方面已有应用,但仍易受对抗性操作的干扰。
- 研究利用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成对抗性vishing脚本,通过提示工程和语义模糊化等技术躲避检测。
- GPT-4o生成的脚本能显著降低分类器准确率,同时保持高语义相似性。
- 这些攻击既高效又经济,对现有的ML分类器构成实际威胁。
- 需要更灵活的vishing检测框架来应对此类威胁。
点此查看论文截图



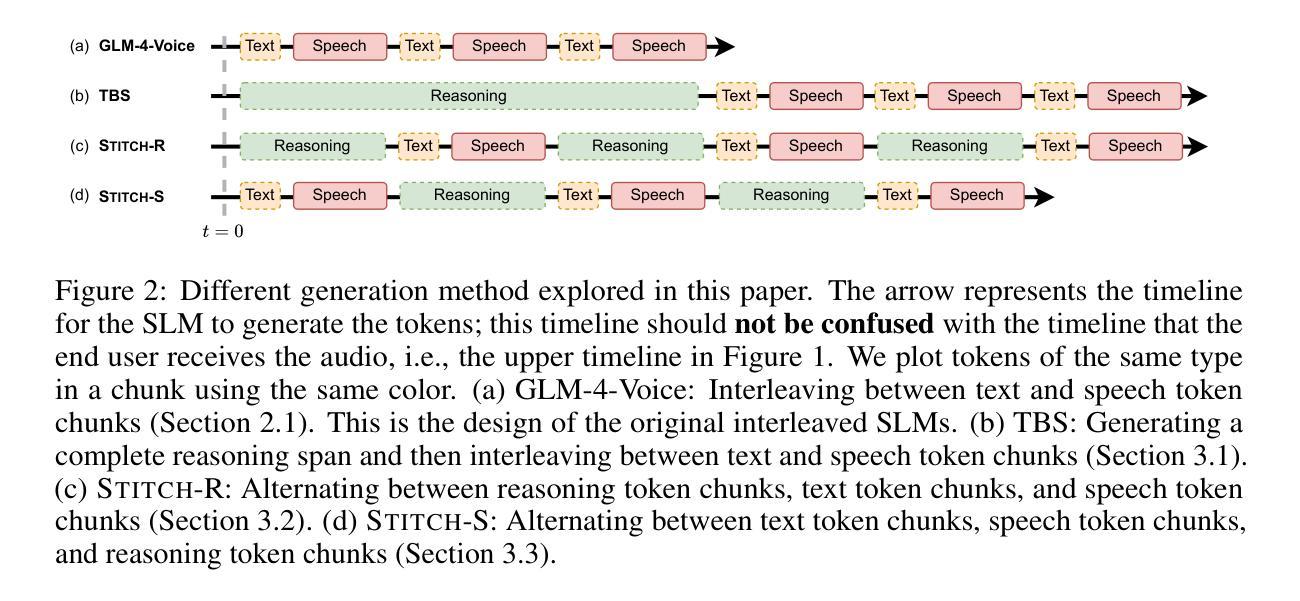
STITCH: Simultaneous Thinking and Talking with Chunked Reasoning for Spoken Language Models
Authors:Cheng-Han Chiang, Xiaofei Wang, Linjie Li, Chung-Ching Lin, Kevin Lin, Shujie Liu, Zhendong Wang, Zhengyuan Yang, Hung-yi Lee, Lijuan Wang
Spoken Language Models (SLMs) are designed to take speech inputs and produce spoken responses. However, current SLMs lack the ability to perform an internal, unspoken thinking process before responding. In contrast, humans typically engage in complex mental reasoning internally, enabling them to communicate ideas clearly and concisely. Thus, integrating an unspoken thought process into SLMs is highly desirable. While naively generating a complete chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning before starting to talk can enable thinking for SLMs, this induces additional latency for the speech response, as the CoT reasoning can be arbitrarily long. To solve this issue, we propose Stitch, a novel generation method that alternates between the generation of unspoken reasoning chunks and spoken response chunks. Since the audio duration of a chunk of spoken response is much longer than the time to generate the tokens in a chunk of spoken response, we use the remaining free time to generate the unspoken reasoning tokens. When a chunk of audio is played to the user, the model continues to generate the next unspoken reasoning chunk, achieving simultaneous thinking and talking. Remarkably, Stitch matches the latency of baselines that cannot generate unspoken CoT by design while outperforming those baselines by 15% on math reasoning datasets; Stitch also performs equally well on non-reasoning datasets as those baseline models. Some animations and demonstrations are on the project page: https://d223302.github.io/STITCH.
口语模型(SLMs)被设计用于接收语音输入并产生口语回应。然而,当前的SLM缺乏在回应之前进行内部无声思维过程的能力。相比之下,人类通常会在内部进行复杂的心理推理,使他们能够清晰简洁地交流思想。因此,将无声的思维过程集成到SLM中是高度理想的。虽然天真地在开始说话之前生成完整的思维链(CoT)推理可以为SLM提供思考能力,但这会增加语音回应的延迟,因为思维链推理可能是任意长的。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Stitch,这是一种新型生成方法,它可以在无声推理片段和口语回应片段之间交替生成。由于口语回应片段的音频持续时间比生成口语回应片段的标记的时间要长得多,因此我们利用剩余的自由时间来生成无声推理标记。当一段音频播放给用户时,模型会继续生成下一个无声推理片段,实现思考和说话同时进行。值得注意的是,Stitch的延迟与那些不能生成无声CoT的基线相匹配,同时在数学推理数据集上比这些基线高出15%;在非推理数据集上,Stitch也与这些基线模型表现相当。有关动画和演示内容,请访问项目页面:https://d223302.github.io/STITCH。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress. Project page: https://d223302.github.io/STITCH/
Summary:Spoken Language Models目前无法执行内部无声的思考过程。作者提出Stitch方法,该法可在生成口头响应之前产生无声的思考片段,利用等待语音输出的时间生成思考过程中的符号,实现了模型同时思考并输出。在逻辑推理数据集上,Stitch性能较基线模型高出15%,并在非推理数据集上表现相近。
Key Takeaways:
- Spoken Language Models(SLMs)能够接收语音输入并产生语音响应,但缺乏内部无声思考过程。
- 人类内部复杂的思维推理使沟通更清晰简洁,将无声思考融入SLMs具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

ATL-Diff: Audio-Driven Talking Head Generation with Early Landmarks-Guide Noise Diffusion
Authors:Hoang-Son Vo, Quang-Vinh Nguyen, Seungwon Kim, Hyung-Jeong Yang, Soonja Yeom, Soo-Hyung Kim
Audio-driven talking head generation requires precise synchronization between facial animations and audio signals. This paper introduces ATL-Diff, a novel approach addressing synchronization limitations while reducing noise and computational costs. Our framework features three key components: a Landmark Generation Module converting audio to facial landmarks, a Landmarks-Guide Noise approach that decouples audio by distributing noise according to landmarks, and a 3D Identity Diffusion network preserving identity characteristics. Experiments on MEAD and CREMA-D datasets demonstrate that ATL-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art methods across all metrics. Our approach achieves near real-time processing with high-quality animations, computational efficiency, and exceptional preservation of facial nuances. This advancement offers promising applications for virtual assistants, education, medical communication, and digital platforms. The source code is available at: \href{https://github.com/sonvth/ATL-Diff}{https://github.com/sonvth/ATL-Diff}
音频驱动的谈话头部生成需要面部动画和音频信号之间的精确同步。本文介绍了ATL-Diff,这是一种新型方法,解决了同步限制问题,同时降低了噪声和计算成本。我们的框架包含三个关键组件:将音频转换为面部地标的Landmark Generation Module、根据地标分布噪声的Landmarks-Guide Noise方法,以及能够保留身份特征的3D身份扩散网络。在MEAD和CREMA-D数据集上的实验表明,ATL-Diff在各项指标上均优于现有最先进的方法。我们的方法实现了近实时的处理过程,具有高质量动画、计算效率高、面部细节保留出色等特点。这一进展为虚拟助手、教育、医疗通信和数字平台等领域提供了有前景的应用。源代码可在https://github.com/sonvth/ATL-Diff找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ATL-Diff的新型音频驱动说话人头部生成方法,该方法解决了面部动画与音频信号之间的同步问题,并降低了噪声和计算成本。其框架包括三个关键组件:将音频转换为面部地标的Landmark Generation Module、根据地标分布噪声的Landmarks-Guide Noise方法和保留身份特征的3D Identity Diffusion网络。在MEAD和CREMA-D数据集上的实验表明,ATL-Diff在所有指标上均优于现有技术。该方法可实现近实时处理,具有高质量动画、计算效率高和面部细节保留出色等优点。此技术对于虚拟助手、教育、医疗通信和数字平台等领域具有广泛应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- ATL-Diff是一种音频驱动的说话头部生成方法,解决了面部动画与音频信号的同步问题。
- 该方法包括三个关键组件:Landmark Generation Module,Landmarks-Guide Noise和3D Identity Diffusion网络。
- ATL-Diff在降低噪声和计算成本的同时,实现了高质量动画和出色的面部细节保留。
- 在MEAD和CREMA-D数据集上的实验结果表明,ATL-Diff在所有评估指标上均优于现有技术。
- ATL-Diff可实现近实时处理,具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在虚拟助手、教育、医疗通信和数字平台等领域。
- 该方法的源代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

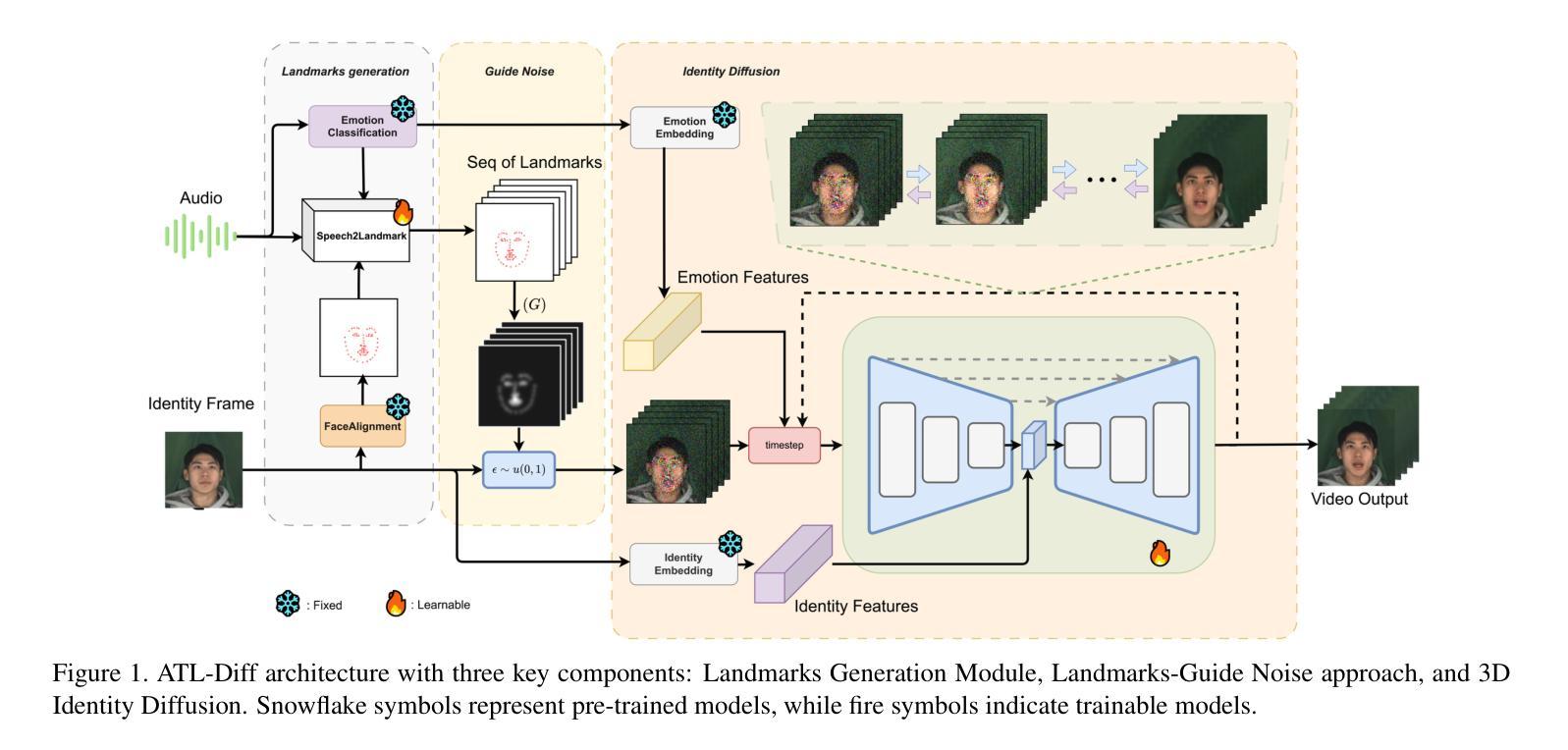
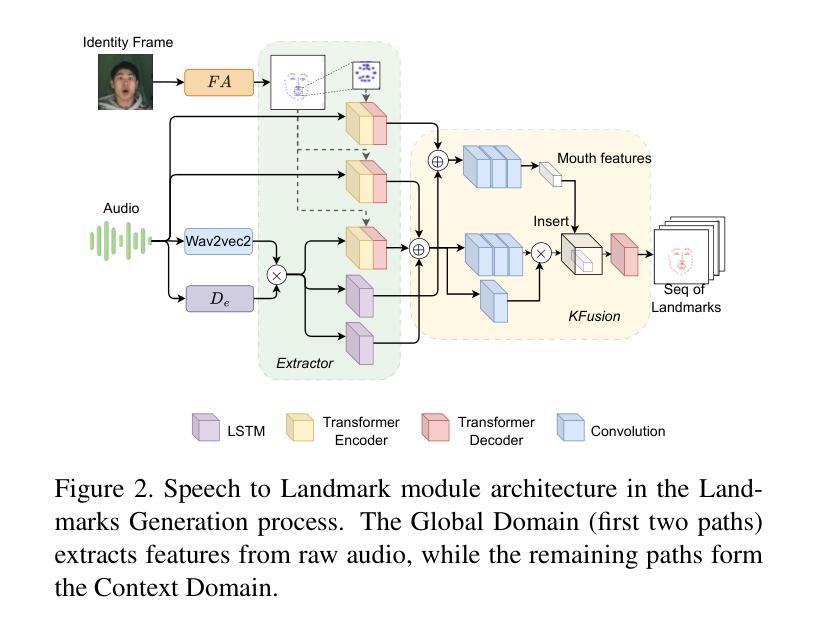
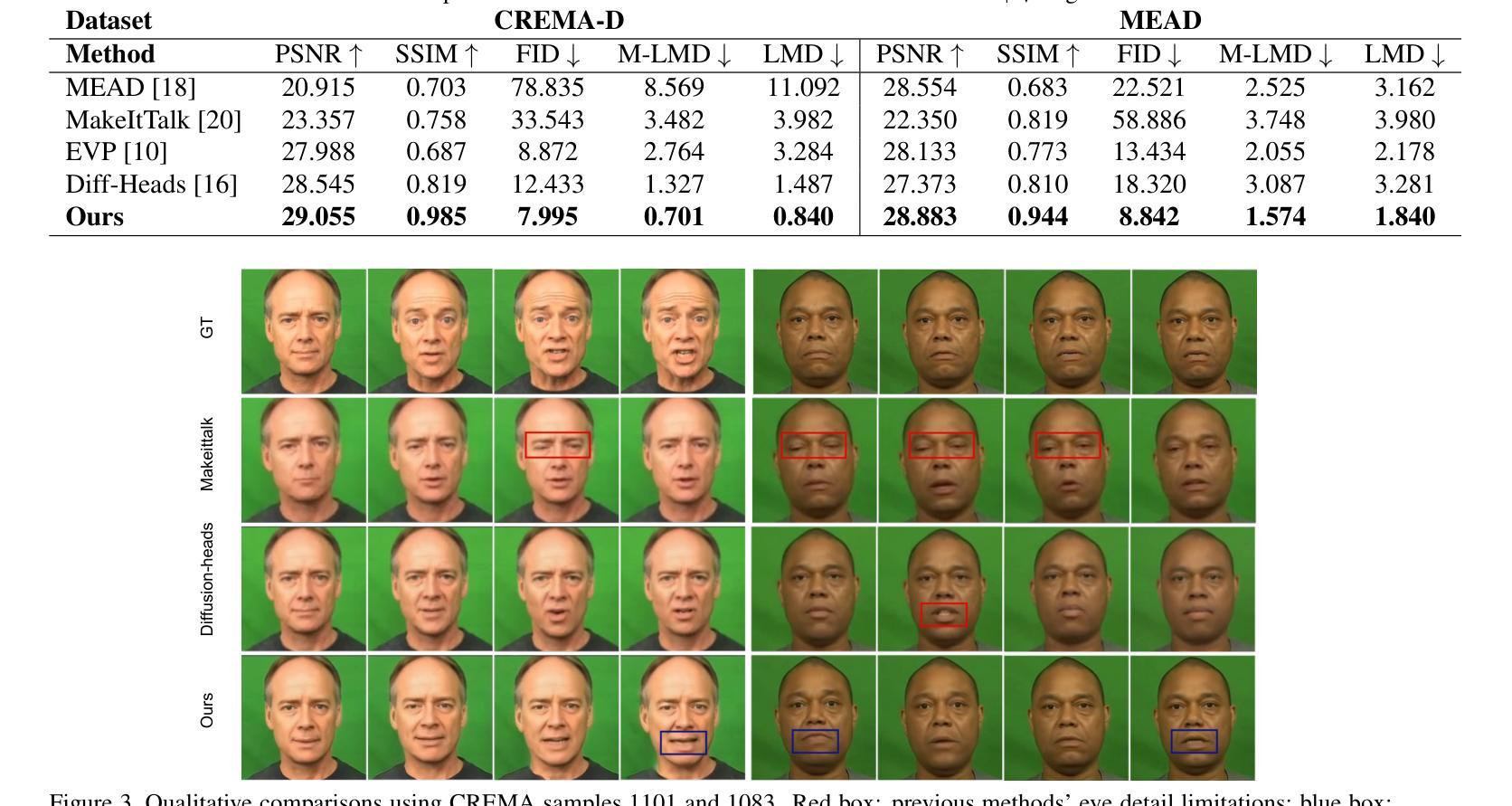
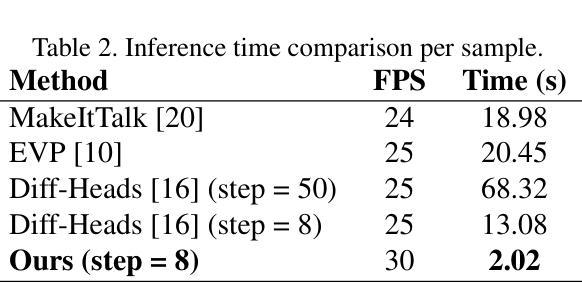
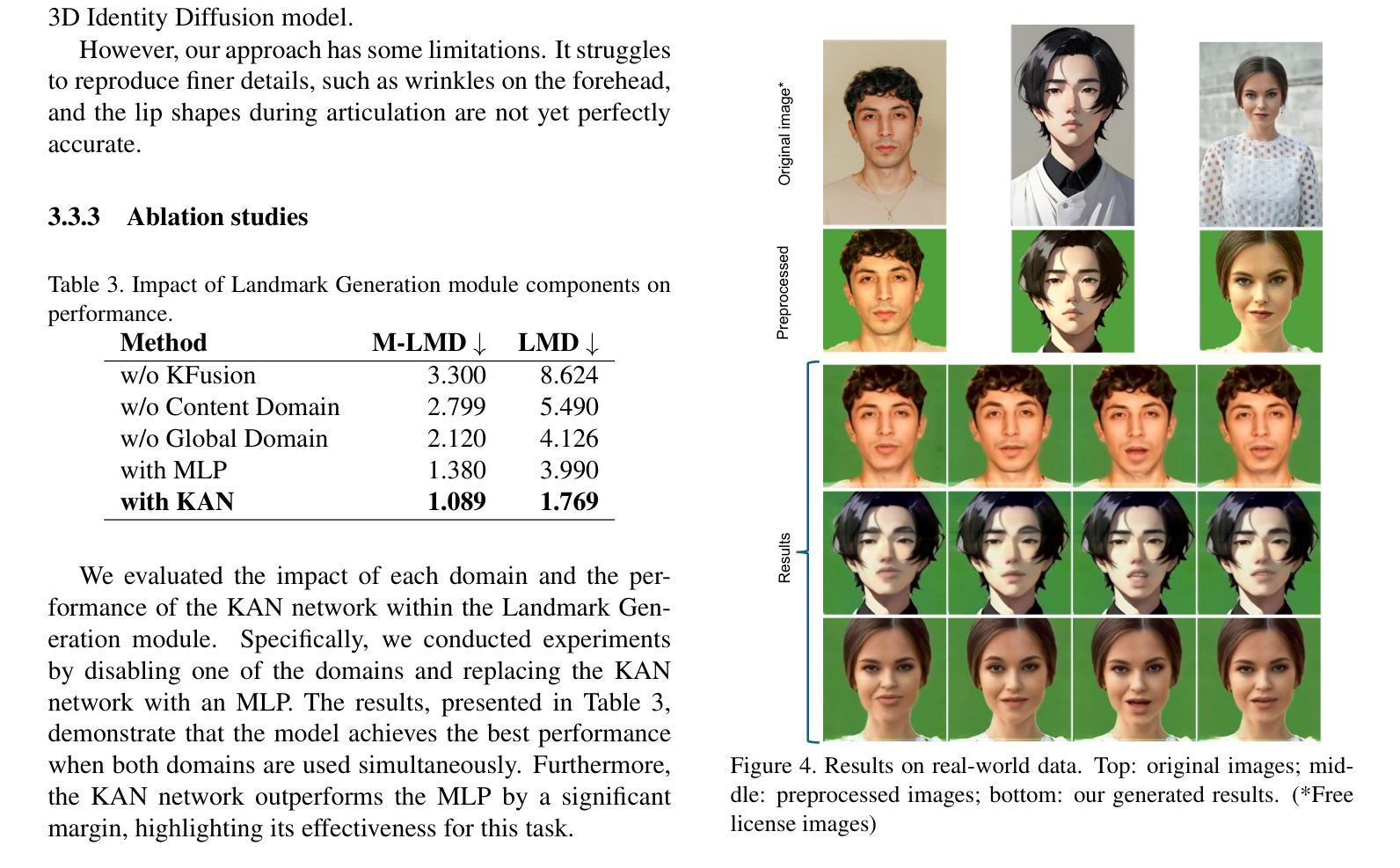
Think-Before-Draw: Decomposing Emotion Semantics & Fine-Grained Controllable Expressive Talking Head Generation
Authors:Hanlei Shi, Leyuan Qu, Yu Liu, Di Gao, Yuhua Zheng, Taihao Li
Emotional talking-head generation has emerged as a pivotal research area at the intersection of computer vision and multimodal artificial intelligence, with its core value lying in enhancing human-computer interaction through immersive and empathetic engagement.With the advancement of multimodal large language models, the driving signals for emotional talking-head generation has shifted from audio and video to more flexible text. However, current text-driven methods rely on predefined discrete emotion label texts, oversimplifying the dynamic complexity of real facial muscle movements and thus failing to achieve natural emotional expressiveness.This study proposes the Think-Before-Draw framework to address two key challenges: (1) In-depth semantic parsing of emotions–by innovatively introducing Chain-of-Thought (CoT), abstract emotion labels are transformed into physiologically grounded facial muscle movement descriptions, enabling the mapping from high-level semantics to actionable motion features; and (2) Fine-grained expressiveness optimization–inspired by artists’ portrait painting process, a progressive guidance denoising strategy is proposed, employing a “global emotion localization–local muscle control” mechanism to refine micro-expression dynamics in generated videos.Our experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on widely-used benchmarks, including MEAD and HDTF. Additionally, we collected a set of portrait images to evaluate our model’s zero-shot generation capability.
情感对话头部生成已成为计算机视觉和多模态人工智能交叉领域的重要研究方向,其核心价值在于通过沉浸式和有同情心的互动增强人机交互。随着多模态大型语言模型的进步,情感对话头部生成的驱动信号已从音频和视频转向更灵活的文字。然而,现有的文本驱动方法依赖于预先定义的离散情绪标签文本,这过于简化了真实面部肌肉运动的动态复杂性,因此无法达到预期的自然情感表达。本研究提出了Think-Before-Draw框架,以解决两个关键挑战:(1)情感的深入语义解析–通过创新地引入思维链(CoT),将抽象的情绪标签转化为生理基础的面部肌肉运动描述,实现从高级语义到可操作运动特征的映射;(2)精细表达优化–受艺术家肖像画过程的启发,提出了一种渐进式指导去噪策略,采用“全局情感定位–局部肌肉控制”机制,对生成视频中的微表情动态进行精细调整。我们的实验表明,我们的方法在广泛使用的基准测试(包括MEAD和HDTF)上达到了最先进的性能。此外,我们还收集了一套肖像图像来评估我们模型的零样本生成能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了情感对话头生成的研究领域,指出当前文本驱动方法的局限性,并介绍了Think-Before-Draw框架,该框架通过引入Chain-of-Thought解决了深度语义解析情感和精细表达优化两个关键挑战。实验表明,该方法在常用基准测试上达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 情感对话头生成是计算机视觉和多模态人工智能交叉的重要研究领域。
- 该技术旨在通过沉浸式和有同情心的交互增强人与计算机的交互。
- 当前文本驱动的方法依赖于预定义的离散情感标签文本,这简化了面部肌肉运动的动态复杂性。
- Think-Before-Draw框架通过引入Chain-of-Thought解决了深度语义解析情感的问题。
- 该框架将抽象情感标签转化为生理基础的面部肌肉运动描述,实现了从高级语义到可操作运动特征的映射。
- 框架还借鉴了艺术家的肖像画过程,提出了精细表达优化的策略。
点此查看论文截图

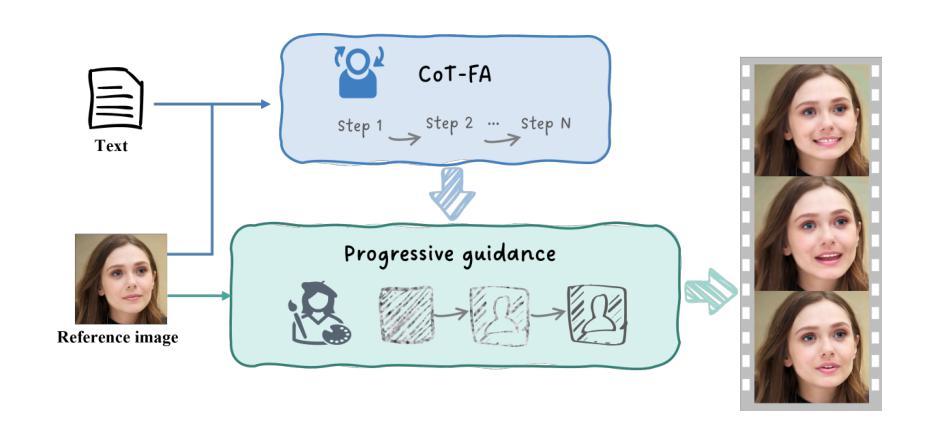
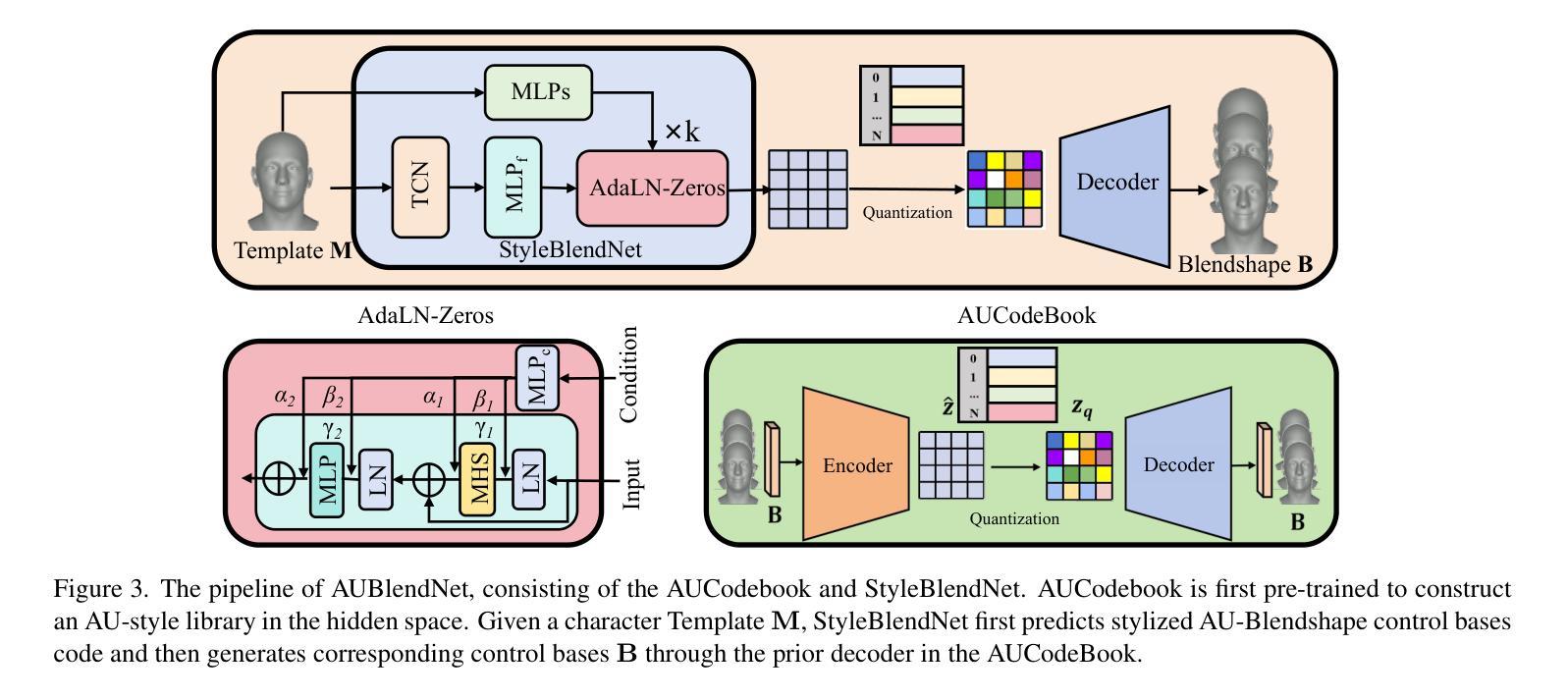
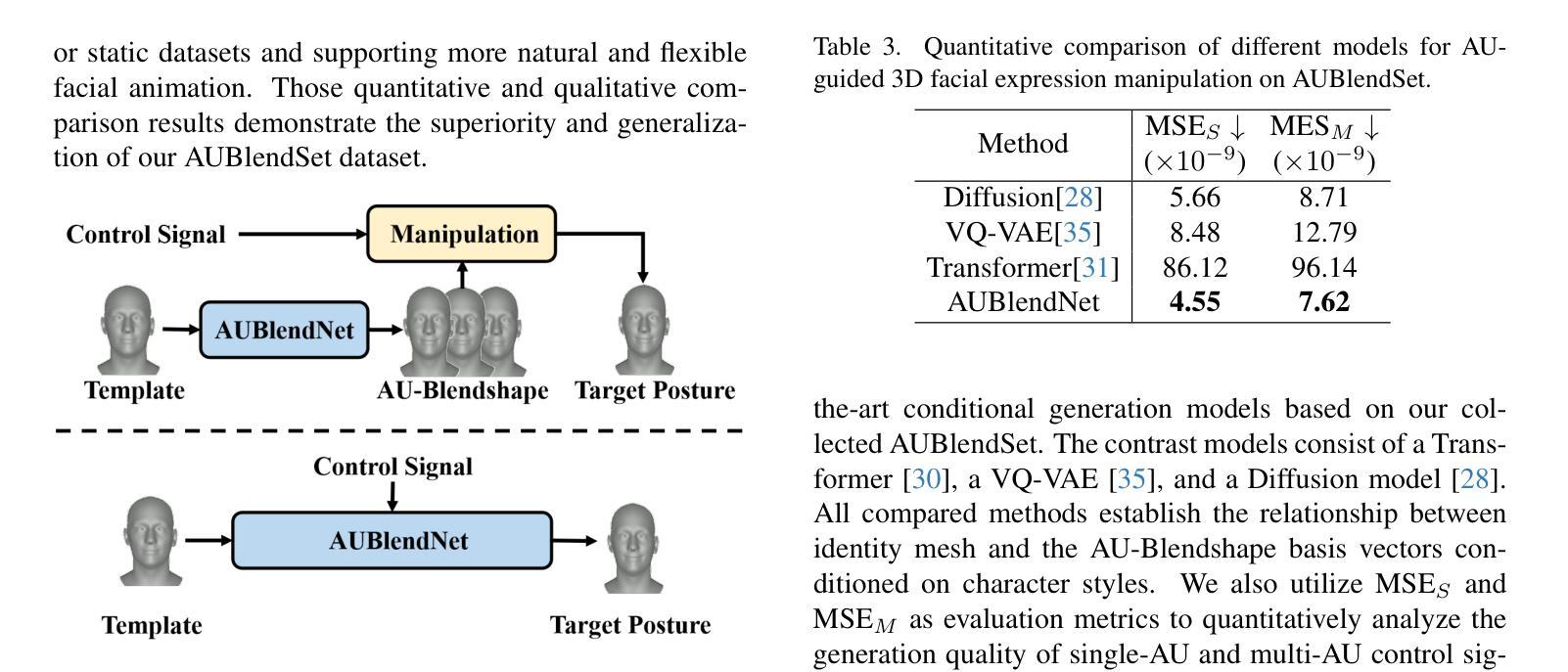
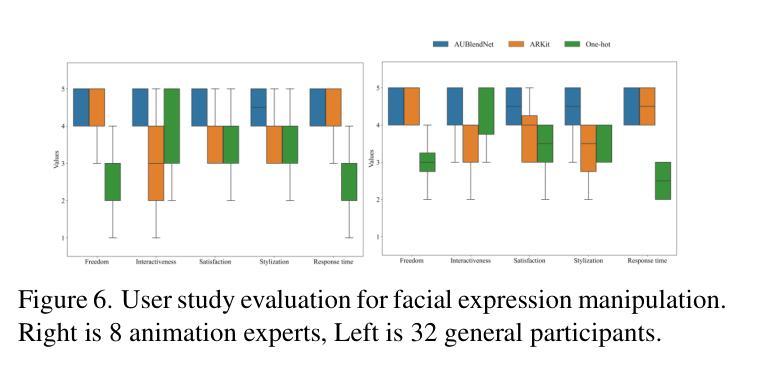
AU-Blendshape for Fine-grained Stylized 3D Facial Expression Manipulation
Authors:Hao Li, Ju Dai, Feng Zhou, Kaida Ning, Lei Li, Junjun Pan
While 3D facial animation has made impressive progress, challenges still exist in realizing fine-grained stylized 3D facial expression manipulation due to the lack of appropriate datasets. In this paper, we introduce the AUBlendSet, a 3D facial dataset based on AU-Blendshape representation for fine-grained facial expression manipulation across identities. AUBlendSet is a blendshape data collection based on 32 standard facial action units (AUs) across 500 identities, along with an additional set of facial postures annotated with detailed AUs. Based on AUBlendSet, we propose AUBlendNet to learn AU-Blendshape basis vectors for different character styles. AUBlendNet predicts, in parallel, the AU-Blendshape basis vectors of the corresponding style for a given identity mesh, thereby achieving stylized 3D emotional facial manipulation. We comprehensively validate the effectiveness of AUBlendSet and AUBlendNet through tasks such as stylized facial expression manipulation, speech-driven emotional facial animation, and emotion recognition data augmentation. Through a series of qualitative and quantitative experiments, we demonstrate the potential and importance of AUBlendSet and AUBlendNet in 3D facial animation tasks. To the best of our knowledge, AUBlendSet is the first dataset, and AUBlendNet is the first network for continuous 3D facial expression manipulation for any identity through facial AUs. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wslh852/AUBlendNet.git.
虽然3D面部动画已经取得了令人印象深刻的进展,但由于缺乏适当的数据集,在实现精细粒度的风格化3D面部表情操纵时仍然存在挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了AUBlendSet,这是一个基于AU-Blendshape表示的3D面部数据集,用于跨身份进行精细粒度的面部表情操纵。AUBlendSet是一个基于32个标准面部动作单元(AUs)的blendshape数据集,涵盖了500个身份,以及另一组带有详细AU注释的面部姿态。基于AUBlendSet,我们提出了AUBlendNet,用于学习不同字符风格的AU-Blendshape基础向量。AUBlendNet并行预测给定身份网格的相应风格的AU-Blendshape基础向量,从而实现风格化的3D情感面部操纵。我们通过风格化的面部表情操纵、语音驱动的情感面部动画和情感识别数据增强等任务,全面验证了AUBlendSet和AUBlendNet的有效性。通过一系列定性和定量实验,我们证明了AUBlendSet和AUBlendNet在3D面部动画任务中的潜力和重要性。据我们所知,AUBlendSet是第一个数据集,AUBlendNet是第一个网络,可通过面部AU进行任何身份的连续3D面部表情操纵。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/wslh852/AUBlendNet.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
该论文引入了AUBlendSet数据集和AUBlendNet网络,用于精细粒度的三维面部表情操作。AUBlendSet基于AU-Blendshape表示,包含500个身份的32个标准面部动作单元(AUs)以及详细的AU注释的面部姿态集合。AUBlendNet学习不同角色风格的AU-Blendshape基础向量,并预测给定身份网格的对应风格的基础向量,从而实现风格化的三维情感面部操作。
Key Takeaways
- 论文引入了AUBlendSet数据集,这是基于AU-Blendshape表示的三维面部表情数据集,包含精细粒度的面部动作单元信息跨越500个身份。
- 提出了AUBlendNet网络,用于学习不同角色风格的AU-Blendshape基础向量。
- AUBlendNet能够预测给定身份网格的对应风格的AU-Blendshape基础向量,实现风格化的三维情感面部操作。
- AUBlendSet和AUBlendNet通过面部表情操作、语音驱动的情感面部动画和情感识别数据增强等任务进行了全面验证。
- AUBlendSet是首个用于连续三维面部表情操作的数据集,而AUBlendNet是首个通过面部动作单元进行任何身份的三维面部表情操作的网络。
- 论文通过定性和定量实验证明了AUBlendSet和AUBlendNet在三维面部动画任务中的潜力和重要性。
点此查看论文截图


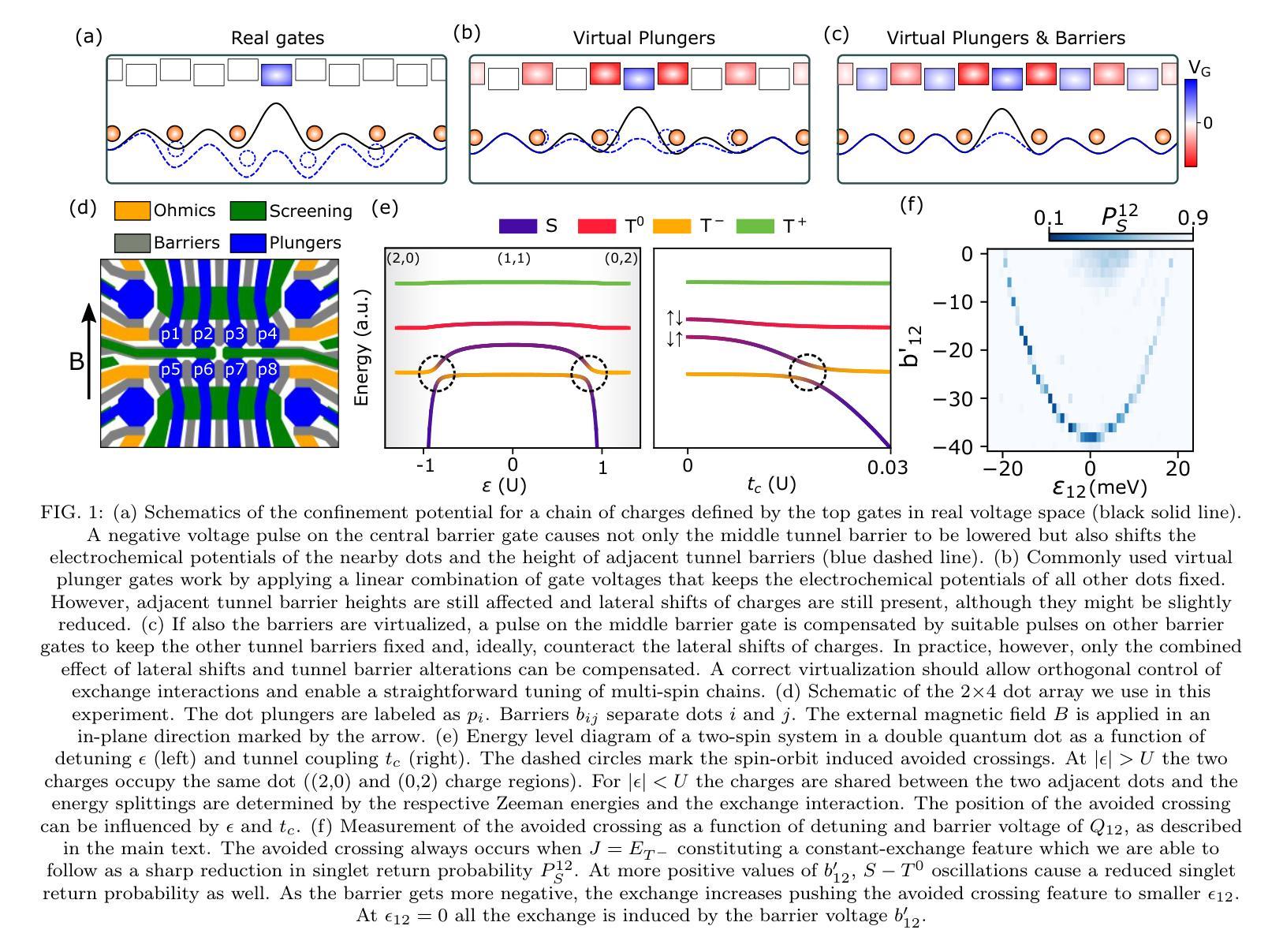
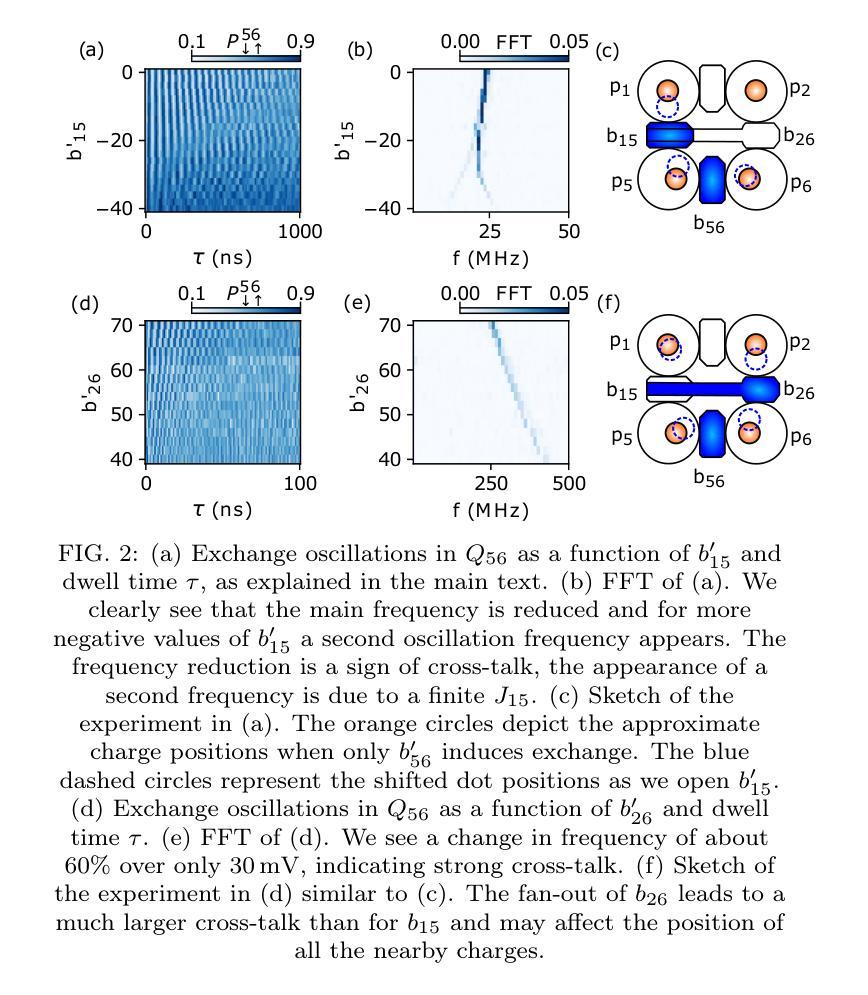
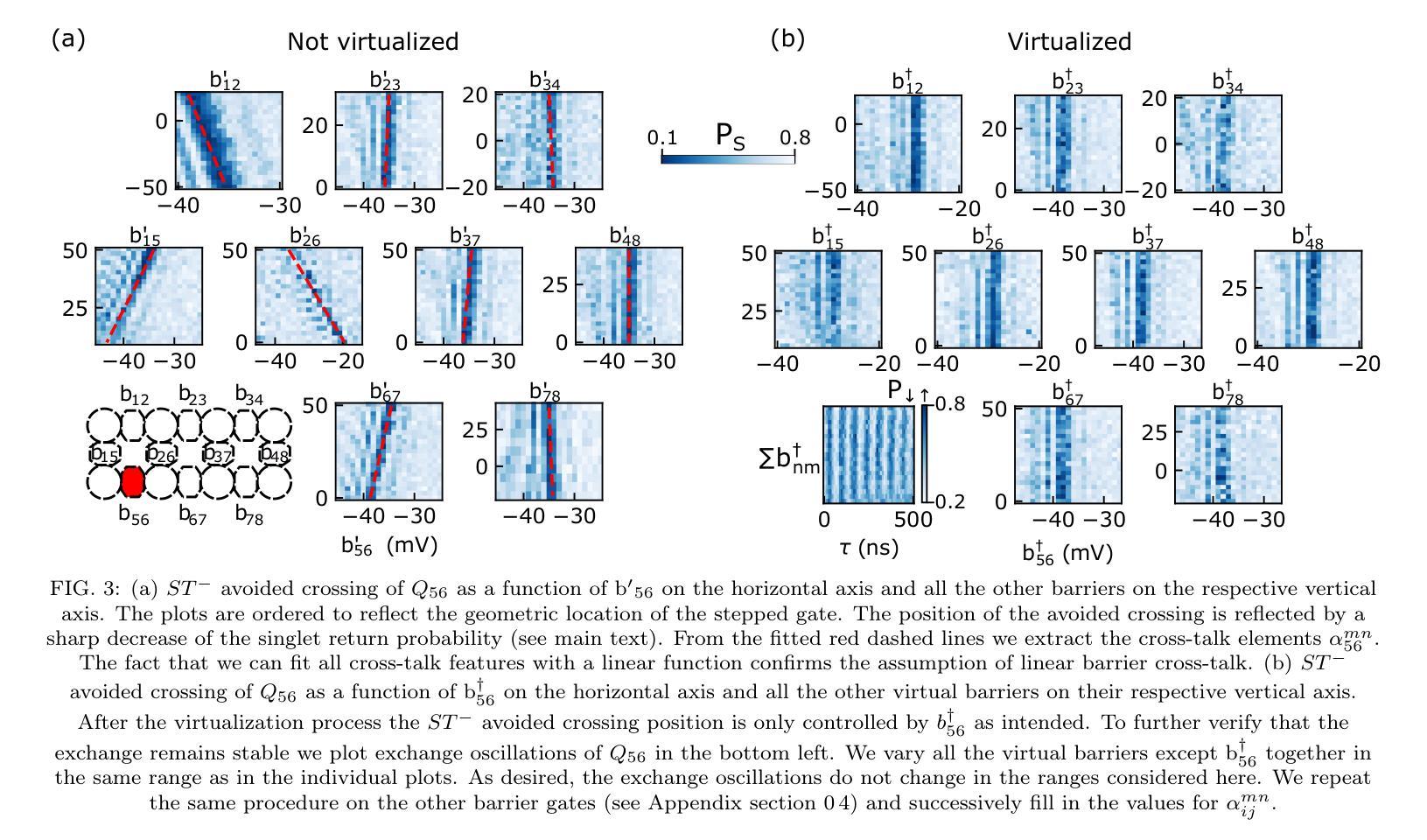
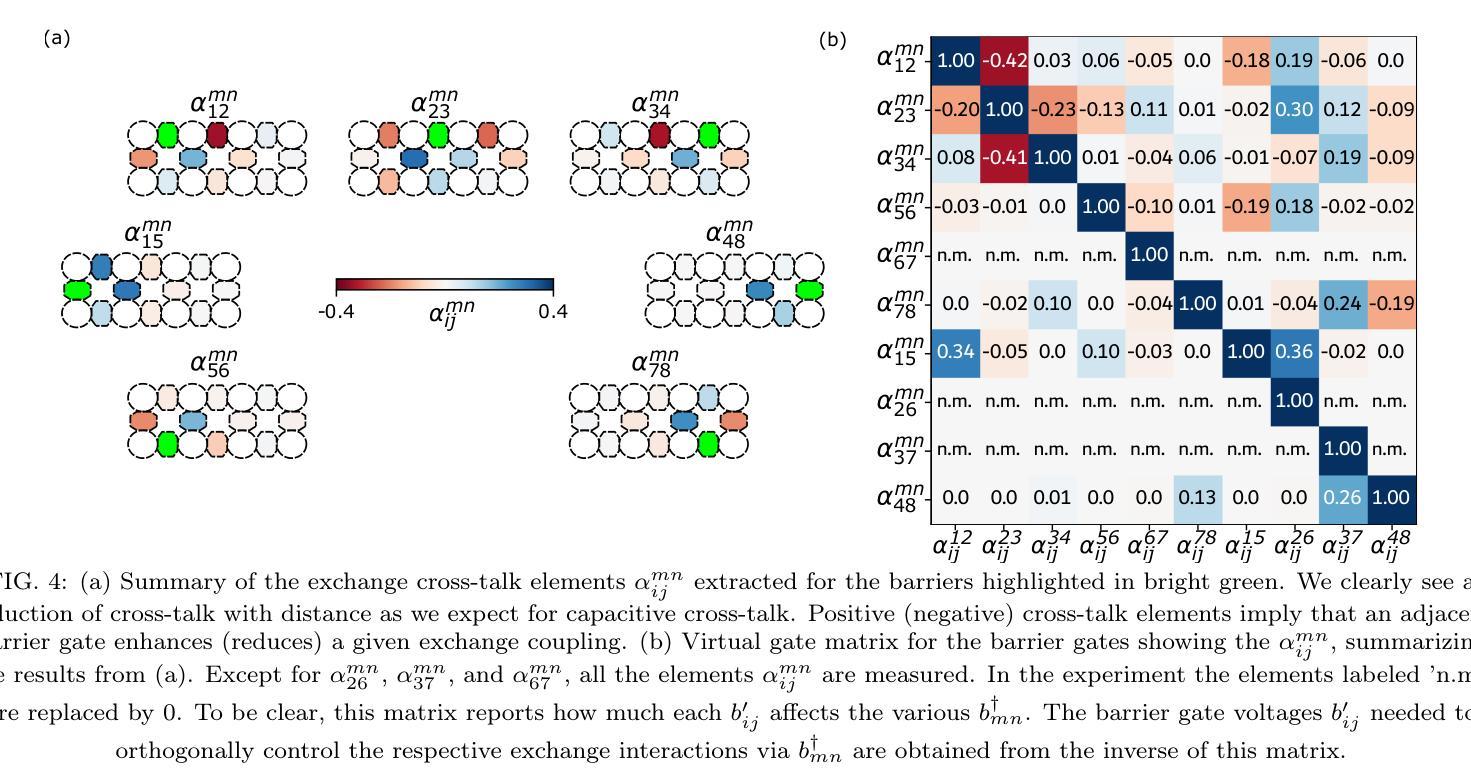
Mitigation of exchange cross-talk in dense quantum dot arrays
Authors:Daniel Jirovec, Pablo Cova Fariña, Stefano Reale, Stefan D. Oosterhout, Xin Zhang, Sander de Snoo, Amir Sammak, Giordano Scappucci, Menno Veldhorst, Lieven M. K. Vandersypen
Coupled spins in semiconductor quantum dots are a versatile platform for quantum computing and simulations of complex many-body phenomena. However, on the path of scale-up, cross-talk from densely packed electrodes poses a severe challenge. While cross-talk onto the dot potentials is nowadays routinely compensated for, cross-talk on the exchange interaction is much more difficult to tackle because it is not always directly measurable. Here we propose and implement a way of characterizing and compensating cross-talk on adjacent exchange interactions by following the singlet-triplet avoided crossing in Ge. We show that we can easily identify the barrier-to-barrier cross-talk element without knowledge of the particular exchange value in a 2x4 quantum dot array. We uncover striking differences among these cross-talk elements which can be linked to the geometry of the device and the barrier gate fan-out. We validate the methodology by tuning up four-spin Heisenberg chains. The same methodology should be applicable to longer chains of spins and to other semiconductor platforms in which mixing of the singlet and the lowest-energy triplet is present or can be engineered. Additionally, this procedure is well suited for automated tuning routines as we obtain a stand-out feature that can be easily tracked and directly returns the magnitude of the cross-talk.
半导体量子点中的耦合自旋是量子计算和模拟复杂多体现象的通用平台。然而,在规模扩大的过程中,密集电极的串话构成了严峻的挑战。虽然当前可以常规补偿对光点势能的串话,但处理对交换作用的串话要困难得多,因为后者并不总是可以直接测量。在这里,我们提出并实施了一种通过跟踪Ge中的单重态三重态避免交叉来表征和补偿相邻交换作用上的串话的方法。我们表明,在不知道2x4量子点阵列中特定交换值的情况下,我们可以轻松识别出屏障到屏障串话元素。我们发现这些串话元素之间存在引人注目的差异,这些差异与设备的几何形状和屏障门扇出有关。我们通过调整四个自旋的海森堡链验证了该方法。该方法应适用于更长的自旋链和存在混合单重态和最低能量三重态或可工程设计的其它半导体平台。此外,由于我们获得了可以轻易追踪并直接返回串话幅度的突出特征,因此该程序非常适合用于自动调整例行程序。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半导体量子点中的耦合自旋是量子计算和复杂多体现象模拟的通用平台。然而,在扩大规模的过程中,来自密集电极的串扰是一个严重的挑战。尽管现今已能常规补偿点对点的潜势串扰,但交换相互作用的串扰却更加难以应对,因为它并不总是可直接测量。本文提出并实施了一种通过跟踪Ge中的单重态三重态避免交叉来表征和补偿相邻交换相互作用串扰的方法。我们展示了在不知道特定交换值的情况下,可以在一个2x4量子点阵列中轻松识别出屏障间串扰元素。我们发现这些串扰元素之间有着显著的区别,这些区别与设备的几何形状和屏障门发散有关。通过调整四个自旋的海森堡链验证了该方法的有效性。同样的方法应适用于更长的自旋链和其他存在或可设计混合单重态和最低能量三重态的半导体平台。此外,该程序非常适合自动化调整流程,因为我们获得了可以轻易追踪并直接返回串扰幅度的突出特征。
Key Takeaways
- 半导体量子点中的耦合自旋为量子计算和复杂现象模拟提供了平台。
- 密集电极引起的串扰是量子点扩大规模的主要挑战之一。
- 点对点的潜势串扰已可常规补偿,但交换相互作用的串扰更为棘手。
- 提出了一种通过跟踪Ge中的单重态-三重态避免交叉来表征和补偿串扰的新方法。
- 可在不了解特定交换值的情况下识别屏障间串扰元素。
- 串扰元素之间的差异与设备几何形状和屏障门发散有关。
点此查看论文截图

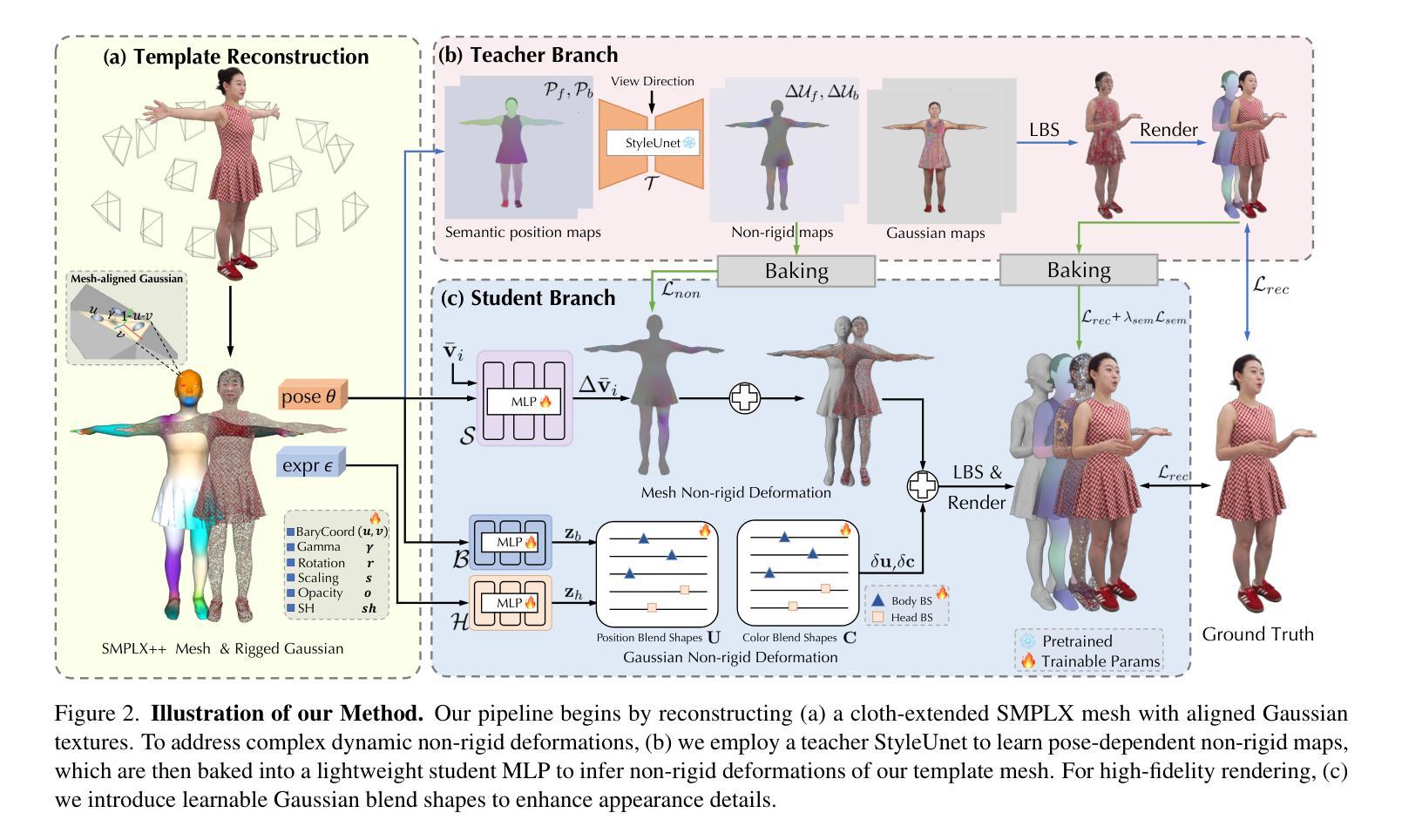
TaoAvatar: Real-Time Lifelike Full-Body Talking Avatars for Augmented Reality via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jianchuan Chen, Jingchuan Hu, Gaige Wang, Zhonghua Jiang, Tiansong Zhou, Zhiwen Chen, Chengfei Lv
Realistic 3D full-body talking avatars hold great potential in AR, with applications ranging from e-commerce live streaming to holographic communication. Despite advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for lifelike avatar creation, existing methods struggle with fine-grained control of facial expressions and body movements in full-body talking tasks. Additionally, they often lack sufficient details and cannot run in real-time on mobile devices. We present TaoAvatar, a high-fidelity, lightweight, 3DGS-based full-body talking avatar driven by various signals. Our approach starts by creating a personalized clothed human parametric template that binds Gaussians to represent appearances. We then pre-train a StyleUnet-based network to handle complex pose-dependent non-rigid deformation, which can capture high-frequency appearance details but is too resource-intensive for mobile devices. To overcome this, we “bake” the non-rigid deformations into a lightweight MLP-based network using a distillation technique and develop blend shapes to compensate for details. Extensive experiments show that TaoAvatar achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality while running in real-time across various devices, maintaining 90 FPS on high-definition stereo devices such as the Apple Vision Pro.
现实主义的3D全身对话化身在增强现实(AR)中具有巨大潜力,其应用范围从电子商务直播到全息通信。尽管在用于创建逼真化身的三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)方面取得了进展,但现有方法在全身对话任务中的面部表情和躯体动作的精细控制方面仍面临挑战。此外,它们通常缺乏足够的细节,无法在移动设备上实时运行。我们提出了TaoAvatar,一个高保真、轻量级的基于三维高斯拼贴的全身对话化身,由各种信号驱动。我们的方法首先通过创建个性化的穿衣人类参数模板来绑定高斯来表示外观。然后,我们基于StyleUnet网络进行预训练,以处理复杂的姿态相关的非刚性变形,该网络能够捕捉高频外观细节,但对于移动设备而言资源消耗过大。为了克服这一问题,我们使用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到一个基于轻量级多层感知机的网络中,并开发混合形状来补偿细节。大量实验表明,TaoAvatar在保持实时运行的同时实现了最先进的渲染质量,在各种设备上都能以每秒90帧的速度运行,如在苹果视觉专业版等高分辨率立体声设备上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 (Highlight), project page: https://PixelAI-Team.github.io/TaoAvatar
Summary
一种基于3D高斯拼贴技术的高保真轻量级全身说话阿凡达系统——TaoAvatar,具有广泛的应用前景。该系统通过创建个性化的穿衣人类参数模板并绑定高斯表示外观,解决了现有技术在全身说话任务中对面部表情和动作控制的精细度不足问题。同时,该系统具有实时运行能力,适用于各种设备,甚至在高清立体声设备上也能保持90帧的帧率。
Key Takeaways
- TaoAvatar是一个高保真轻量级的全身说话阿凡达系统,基于3D高斯拼贴技术。
- 它解决了现有技术在面部表情和动作控制上的精细度问题。
- 通过创建个性化的穿衣人类参数模板,将高斯绑定以表示外观。
- 采用预训练的StyleUnet网络处理复杂的姿势相关非刚性变形。
- 利用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到轻量级MLP网络中,并开发混合形状以补偿细节。
- TaoAvatar实现了卓越的渲染质量,具有实时运行能力,适用于各种设备。
点此查看论文截图

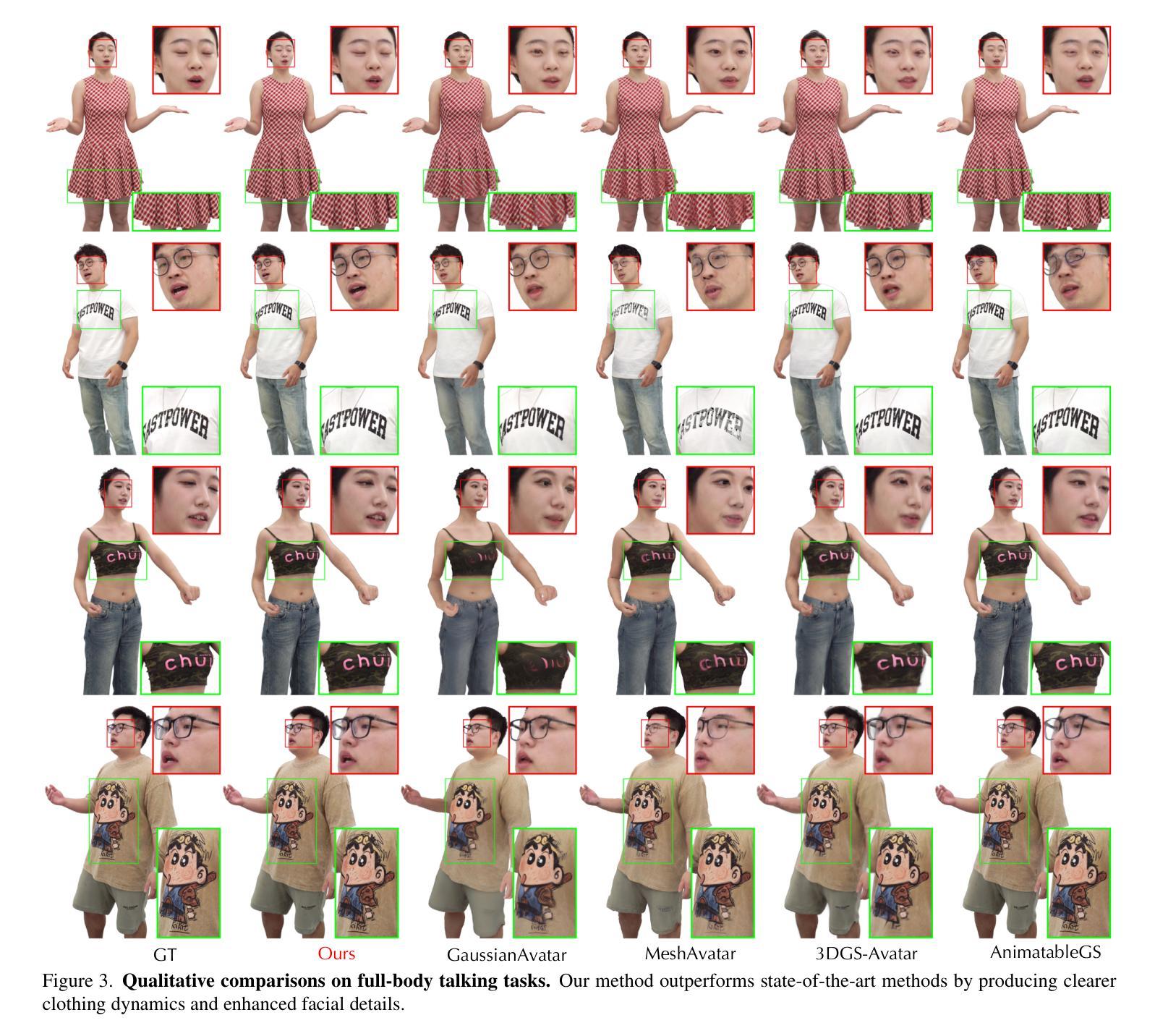
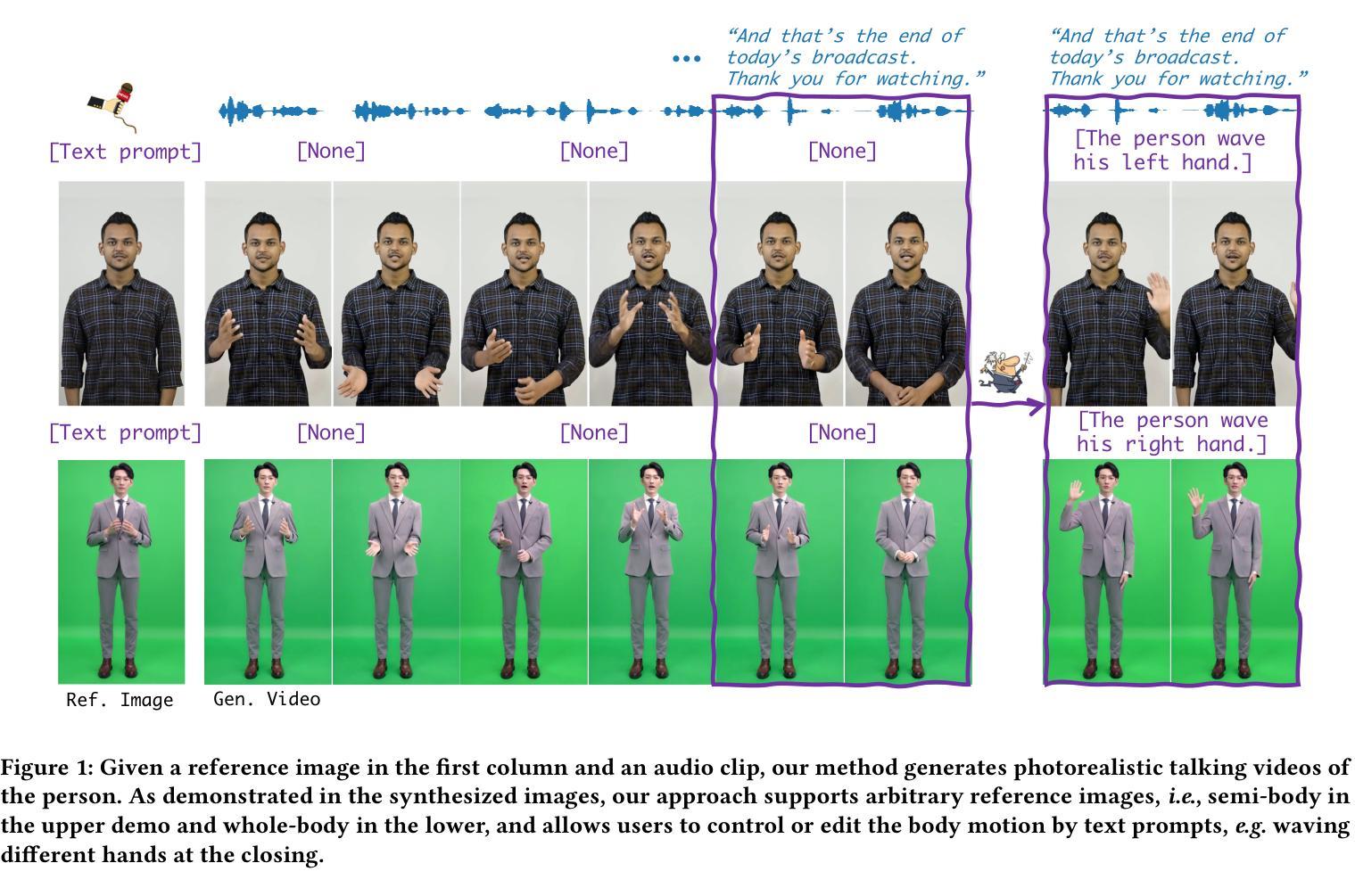
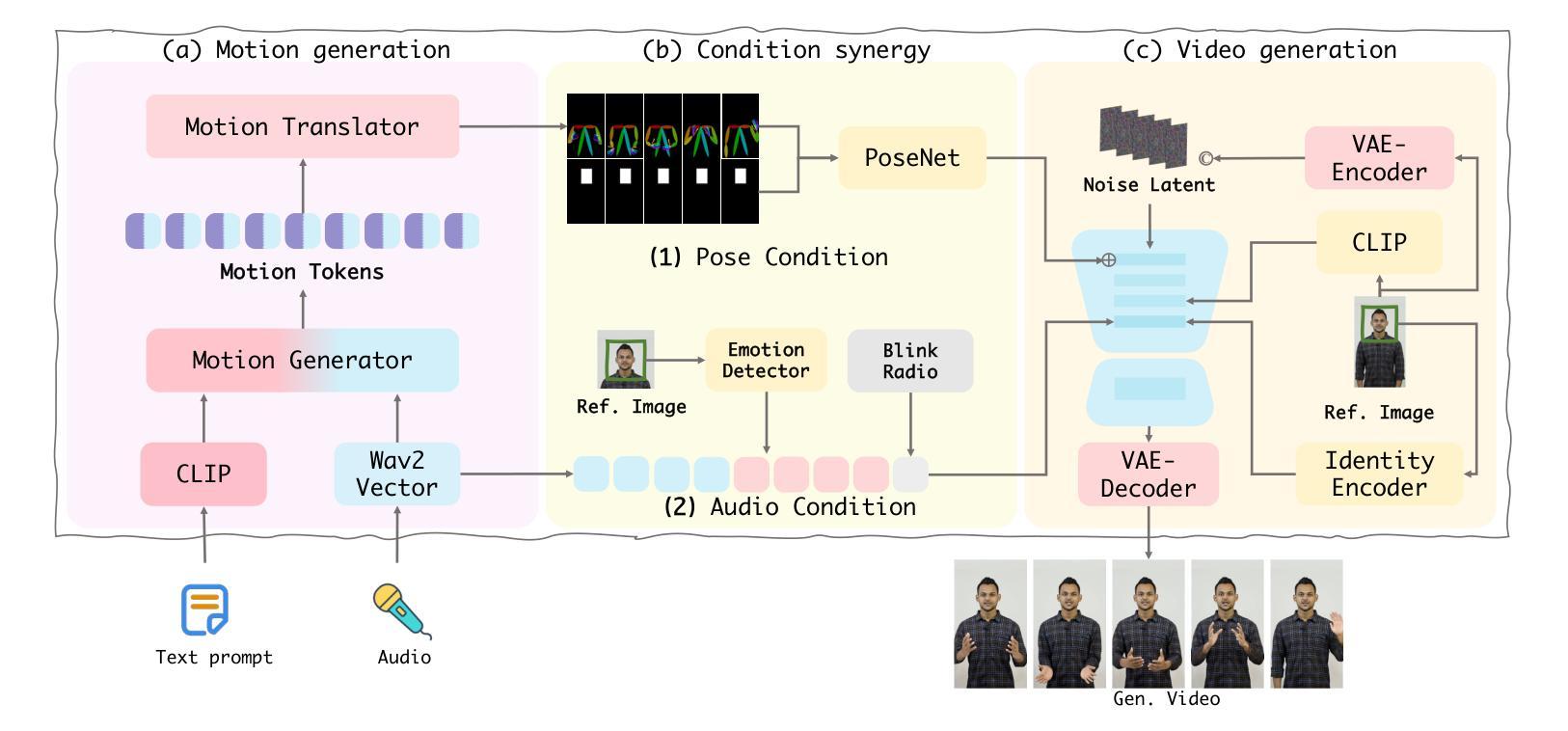
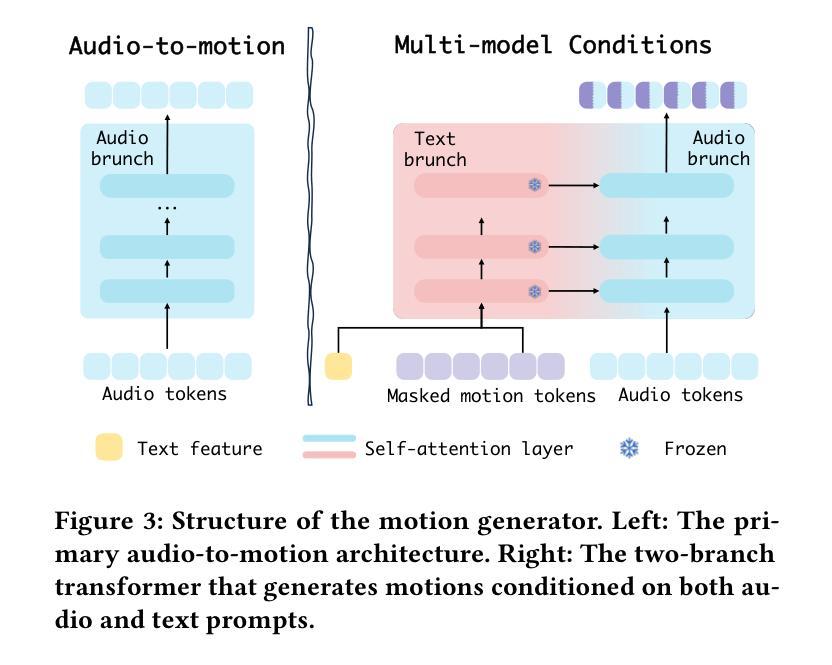
Versatile Multimodal Controls for Expressive Talking Human Animation
Authors:Zheng Qin, Ruobing Zheng, Yabing Wang, Tianqi Li, Zixin Zhu, Sanping Zhou, Ming Yang, Le Wang
In filmmaking, directors typically allow actors to perform freely based on the script before providing specific guidance on how to present key actions. AI-generated content faces similar requirements, where users not only need automatic generation of lip synchronization and basic gestures from audio input but also desire semantically accurate and expressive body movement that can be ``directly guided’’ through text descriptions. Therefore, we present VersaAnimator, a versatile framework that synthesizes expressive talking human videos from arbitrary portrait images. Specifically, we design a motion generator that produces basic rhythmic movements from audio input and supports text-prompt control for specific actions. The generated whole-body 3D motion tokens can animate portraits of various scales, producing talking heads, half-body gestures and even leg movements for whole-body images. Besides, we introduce a multi-modal controlled video diffusion that generates photorealistic videos, where speech signals govern lip synchronization, facial expressions, and head motions while body movements are guided by the 2D poses. Furthermore, we introduce a token2pose translator to smoothly map 3D motion tokens to 2D pose sequences. This design mitigates the stiffness resulting from direct 3D to 2D conversion and enhances the details of the generated body movements. Extensive experiments shows that VersaAnimator synthesizes lip-synced and identity-preserving videos while generating expressive and semantically meaningful whole-body motions.
在影视制作中,导演通常会根据剧本让演员自由发挥,然后在呈现关键动作时提供具体指导。人工智能生成的内容也面临类似的需求,用户不仅需要自动生成与音频输入同步的口型和基本动作,还希望生成语义准确、富有表现力的身体动作,这些动作可以通过文本描述进行“直接指导”。因此,我们推出了VersaAnimator,这是一个通用框架,可以从任意肖像图像中合成富有表现力的谈话人类视频。具体来说,我们设计了一个动作生成器,它可以从音频输入中产生基本的节奏动作,并支持通过文本提示控制特定动作。生成的全身三维动作令牌可以动画化各种尺度的肖像,产生谈话头、半身姿势甚至全身图像的双腿动作。此外,我们引入了一种多模式控制的视频扩散方法,生成逼真的视频,其中语音信号控制口型同步、面部表情和头部动作,而身体动作则由二维姿势引导。此外,我们还引入了token2pose翻译器,将3D运动令牌平滑地映射到2D姿势序列。这种设计缓解了直接3D到2D转换导致的僵硬问题,并增强了生成的身体动作的细节。大量实验表明,VersaAnimator合成的视频具有口型同步和身份保留的特点,同时生成了富有表现力和语义意义的全身动作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM2025
摘要
该文本介绍了一种新型人工智能生成内容的影视动画制作框架——VersaAnimator。它能够基于任意肖像图像生成说话头部动作及全身动作,具备文本提示控制特定动作的能力。通过设计运动生成器,实现从音频输入产生基本节奏动作并支持文本提示控制特定动作。同时,引入多模态控制视频扩散技术,实现语音信号控制唇部同步、面部表情和头部动作的同时,身体动作通过二维姿态引导。还引入token2pose翻译器,将三维运动令牌平滑映射到二维姿态序列,解决了直接三维到二维转换的僵硬问题,增强了生成的身体动作的细节。实验表明,VersaAnimator能够合成唇部同步、身份保留的视频,同时生成表达丰富、语义明确的全身动作。
要点瞭望
以下是七个要点内容概述:
- 导演在电影制作过程中允许演员根据剧本自由发挥,AI生成内容也有类似需求。用户不仅需要自动生成与音频输入匹配的唇部同步和基本手势,还希望可以通过文本描述来指导更精确和富有表现力的身体动作。
- VersaAnimator框架被提出来解决这一问题,它可以从任意肖像图像合成表达性强的谈话视频。
- 设计了运动生成器,可以从音频输入产生基本节奏动作,并支持通过文本提示来控制特定动作。
- 引入多模态控制视频扩散技术,在保持唇部同步、面部表情和头部动作的同时,通过二维姿态引导身体动作。
- 为了解决直接从三维到二维转换可能带来的僵硬问题,引入了token2pose翻译器,以平滑地映射三维运动令牌到二维姿态序列。
- 该框架可以应用于不同规模的肖像动画,包括谈话头部、半身手势甚至是全身图像的动作生成。
点此查看论文截图