⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-01 更新
IN45023 Neural Network Design Patterns in Computer Vision Seminar Report, Summer 2025
Authors:Radu-Andrei Bourceanu, Neil De La Fuente, Jan Grimm, Andrei Jardan, Andriy Manucharyan, Cornelius Weiss, Roman Pflugfelder
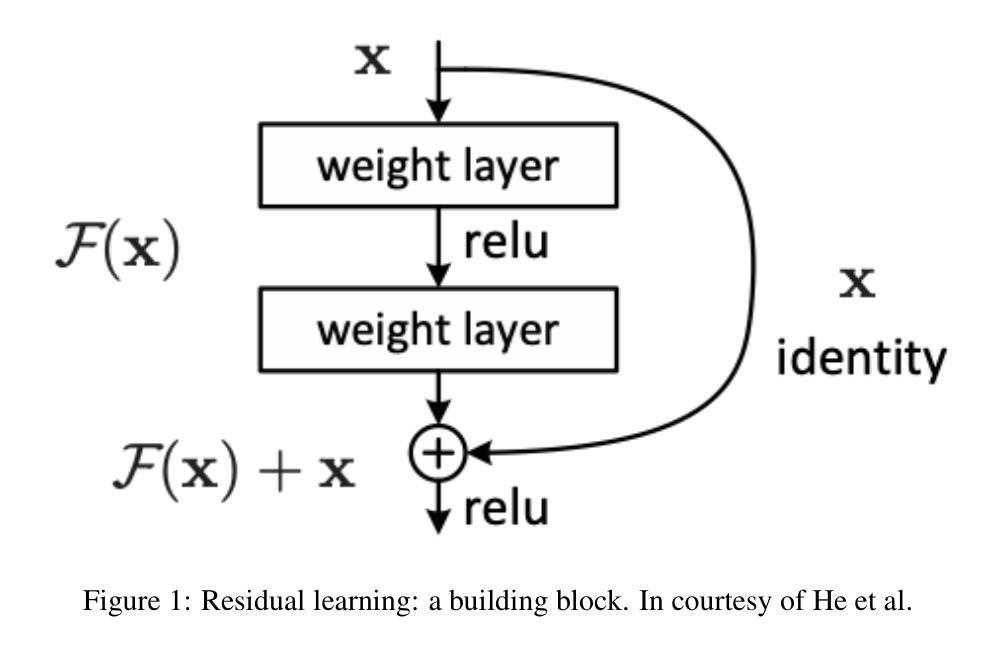
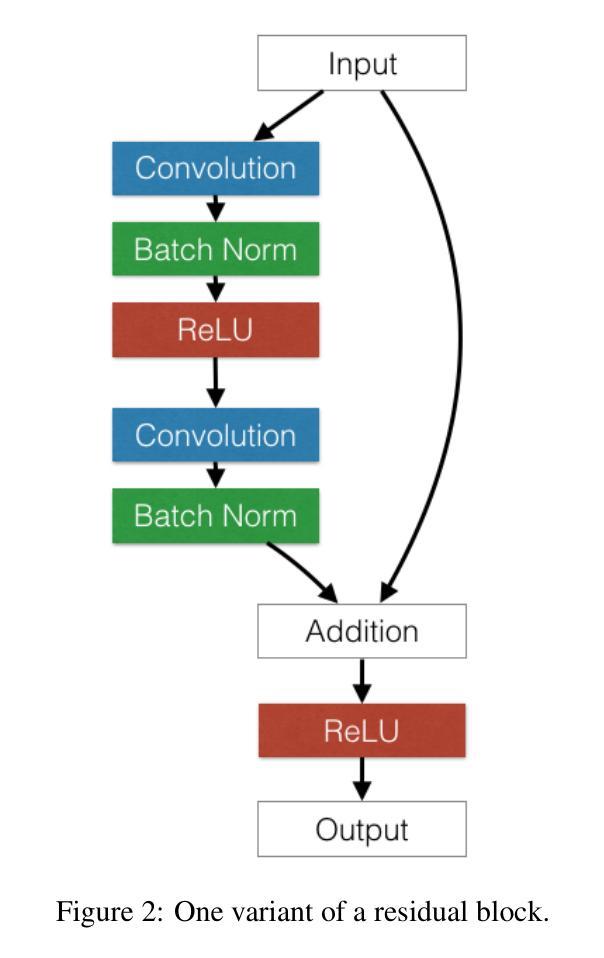
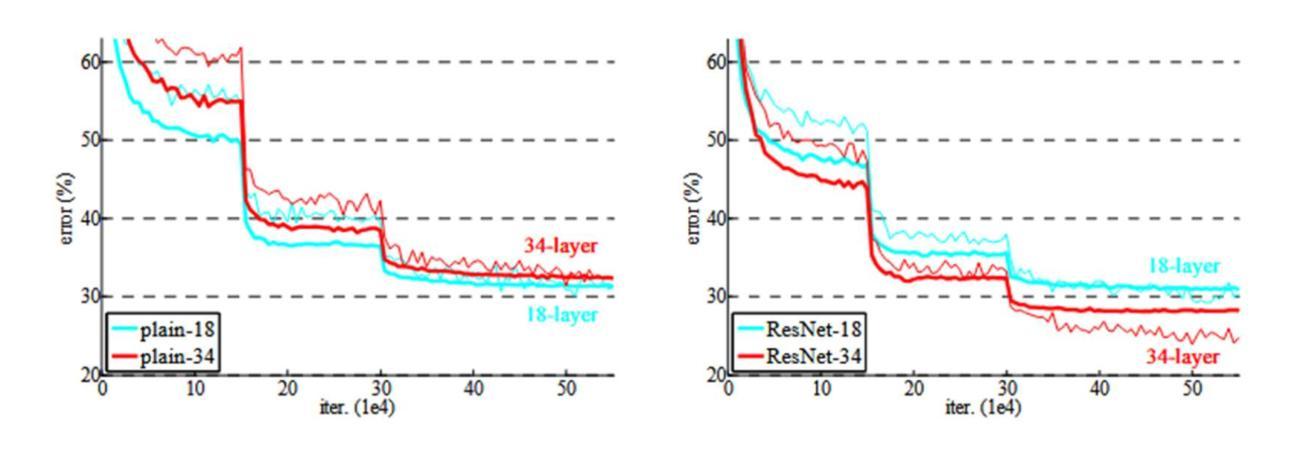
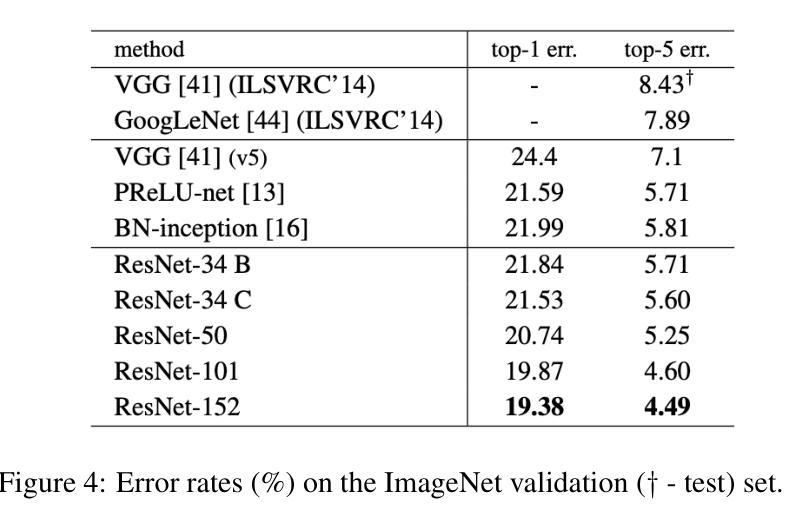
This report analyzes the evolution of key design patterns in computer vision by examining six influential papers. The analy- sis begins with foundational architectures for image recognition. We review ResNet, which introduced residual connections to overcome the vanishing gradient problem and enable effective training of significantly deeper convolutional networks. Subsequently, we examine the Vision Transformer (ViT), which established a new paradigm by applying the Transformer ar- chitecture to sequences of image patches, demonstrating the efficacy of attention-based models for large-scale image recogni- tion. Building on these visual representation backbones, we investigate generative models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are analyzed for their novel adversarial training process, which challenges a generator against a discriminator to learn complex data distributions. Then, Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) are covered, which improve upon prior generative methods by performing a sequential denoising process in a perceptually compressed latent space. LDMs achieve high-fidelity synthesis with greater computational efficiency, representing the current state-of-the-art for image generation. Finally, we explore self-supervised learning techniques that reduce dependency on labeled data. DINO is a self-distillation framework in which a student network learns to match the output of a momentum-updated teacher, yielding features with strong k-NN classification performance. We conclude with Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which utilize an asymmetric encoder-decoder design to reconstruct heavily masked inputs, providing a highly scalable and effective method for pre-training large-scale vision models.
本报告通过分析六篇有影响力的论文,分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变。分析从图像识别的基本架构开始。我们回顾了ResNet,它引入了残差连接,克服了梯度消失问题,实现了对更深卷积网络的有效训练。之后,我们研究了视觉转换器(ViT),它将转换器架构应用于图像补丁序列,建立了新的范式,证明了注意力模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。在这些视觉表示骨干的基础上,我们研究了生成模型。分析了生成对抗网络(GANs)的新型对抗训练过程,该过程使生成器与鉴别器相互学习复杂的数据分布。然后介绍了潜在扩散模型(LDMs),通过感知压缩的潜在空间中的连续去噪过程改进了先前的生成方法。LDMs实现了高保真合成,具有更高的计算效率,代表了当前图像生成的最新技术。最后,我们探索了减少对比标签数据依赖性的自监督学习技术。DINO是一种自蒸馏框架,学生网络学习匹配动量更新的教师输出,产生具有强大k-NN分类性能的特征。最终,我们得出结论,Masked Autoencoders(MAE)利用对称的编码器-解码器设计来重建高度遮罩的输入,提供了一种高度可扩展和有效的预训练大规模视觉模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变,通过考察六篇有影响力的论文,从图像识别的基本架构开始,介绍了ResNet、Vision Transformer(ViT)、生成对抗网络(GANs)、潜在扩散模型(LDMs)、自监督学习技术和MAE等关键技术和方法的发展和应用。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机视觉中的设计模式不断演变,从图像识别的基本架构发展到更复杂的模型和技术。
- ResNet通过引入残差连接克服了梯度消失问题,有效地训练了更深的卷积神经网络。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列,证明了注意力模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)通过对抗性训练过程学习复杂的数据分布,挑战生成器与鉴别器的对抗。
- 潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在感知压缩的潜在空间中进行序贯去噪过程,实现了高保真合成和更高的计算效率。
- 自监督学习技术减少了对比学习的依赖性,采用自蒸馏等框架降低对标注数据的依赖。
点此查看论文截图

The Cow of Rembrandt - Analyzing Artistic Prompt Interpretation in Text-to-Image Models
Authors:Alfio Ferrara, Sergio Picascia, Elisabetta Rocchetti
Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating artistic content by learning from billions of images, including popular artworks. However, the fundamental question of how these models internally represent concepts, such as content and style in paintings, remains unexplored. Traditional computer vision assumes content and style are orthogonal, but diffusion models receive no explicit guidance about this distinction during training. In this work, we investigate how transformer-based text-to-image diffusion models encode content and style concepts when generating artworks. We leverage cross-attention heatmaps to attribute pixels in generated images to specific prompt tokens, enabling us to isolate image regions influenced by content-describing versus style-describing tokens. Our findings reveal that diffusion models demonstrate varying degrees of content-style separation depending on the specific artistic prompt and style requested. In many cases, content tokens primarily influence object-related regions while style tokens affect background and texture areas, suggesting an emergent understanding of the content-style distinction. These insights contribute to our understanding of how large-scale generative models internally represent complex artistic concepts without explicit supervision. We share the code and dataset, together with an exploratory tool for visualizing attention maps at https://github.com/umilISLab/artistic-prompt-interpretation.
文本到图像的扩散模型已经显示出从数十亿张图像(包括流行艺术作品)中学习并生成艺术内容的显著能力。然而,这些模型如何在内部代表绘画中的内容和风格等概念的基本问题仍未被探索。传统计算机视觉假设内容和风格是正交的,但扩散模型在训练过程中没有关于这种区别的明确指导。在这项工作中,我们调查了基于变压器的文本到图像扩散模型如何在生成艺术作品时编码内容和风格概念。我们利用交叉注意力热图将生成图像的像素归因于特定的提示标记,这使我们能够隔离受内容描述标记与风格描述标记影响的图像区域。我们的研究结果表明,扩散模型的内容和风格分离程度因特定的艺术提示和所请求的风格而异。在许多情况下,内容标记主要影响对象相关区域,而风格标记影响背景和纹理区域,这表明对内容和风格区别的理解正在显现。这些见解有助于我们了解大规模生成模型如何在没有显式监督的情况下内部表示复杂艺术概念。我们在https://github.com/umilISLab/artistic-prompt-interpretation上分享了代码、数据集以及用于可视化注意力图的探索工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to be published in: Applications of AI in the Analysis of Cultural and Artistic Heritage, organized within the 35th IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP) 2025
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型能从不计其数的图像中学习生成艺术内容,展现出显著的能力,尤其是在模仿流行艺术作品方面。然而,这些模型在内部如何区分画作中的内容和风格等概念尚未可知。本研究探讨了基于转换器的文本到图像扩散模型在生成艺术作品时如何编码内容和风格概念。通过利用交叉注意力热图,将生成图像中的像素归于特定提示令牌,我们能够区分受内容描述和风格描述令牌影响的图像区域。研究发现,扩散模型的的内容与风格分离程度因特定的艺术提示和要求的风格而不同。在许多情况下,内容令牌主要影响对象相关区域,而风格令牌影响背景和纹理区域,这表明对内容和风格区分的潜在理解。这些见解有助于我们了解大规模生成模型如何在没有显式监督的情况下内部表示复杂艺术概念。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型能生成高质量的艺术内容,其能力令人瞩目。
- 这些模型在内部如何区分画作中的内容和风格尚未被研究。
- 通过交叉注意力热图,可以区分受内容描述令牌和风格描述令牌影响的图像区域。
- 扩散模型展示出的内容和风格的分离程度是灵活的,取决于特定的艺术提示和所需风格。
- 在许多情况下,内容令牌主要影响对象区域,而风格令牌影响背景和纹理。
- 这表明扩散模型对内容和风格的区别有一定的理解,尽管这种理解是隐性的。
点此查看论文截图
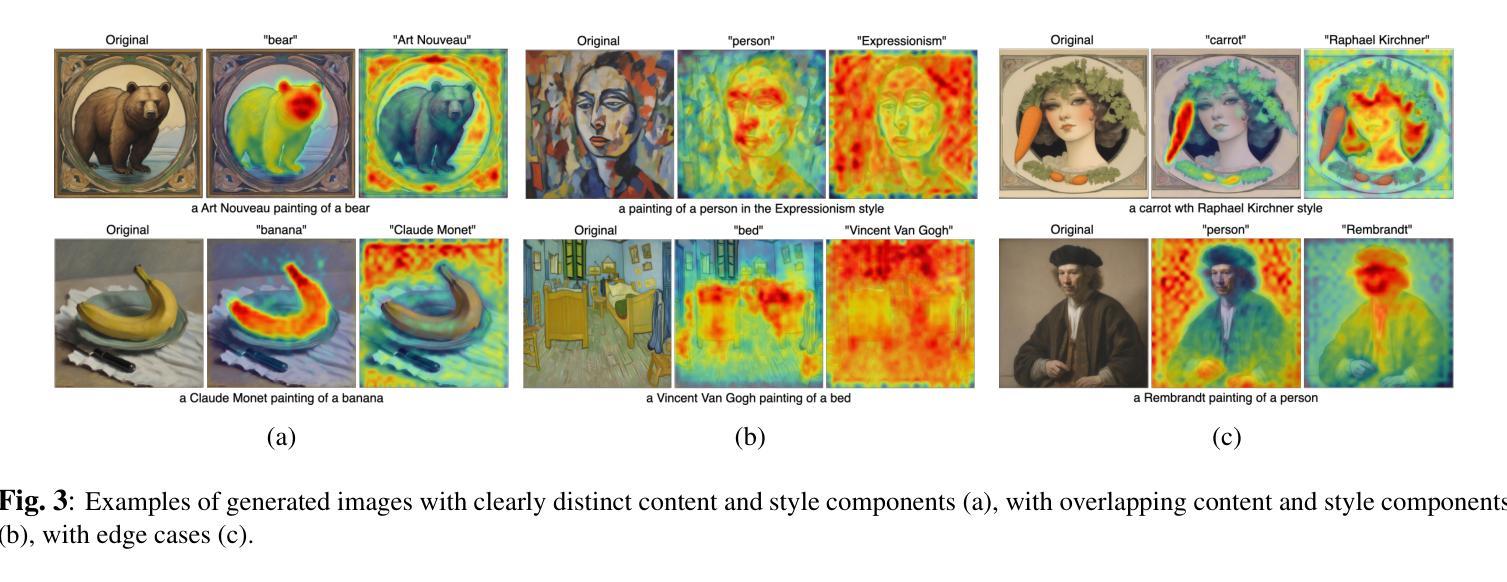


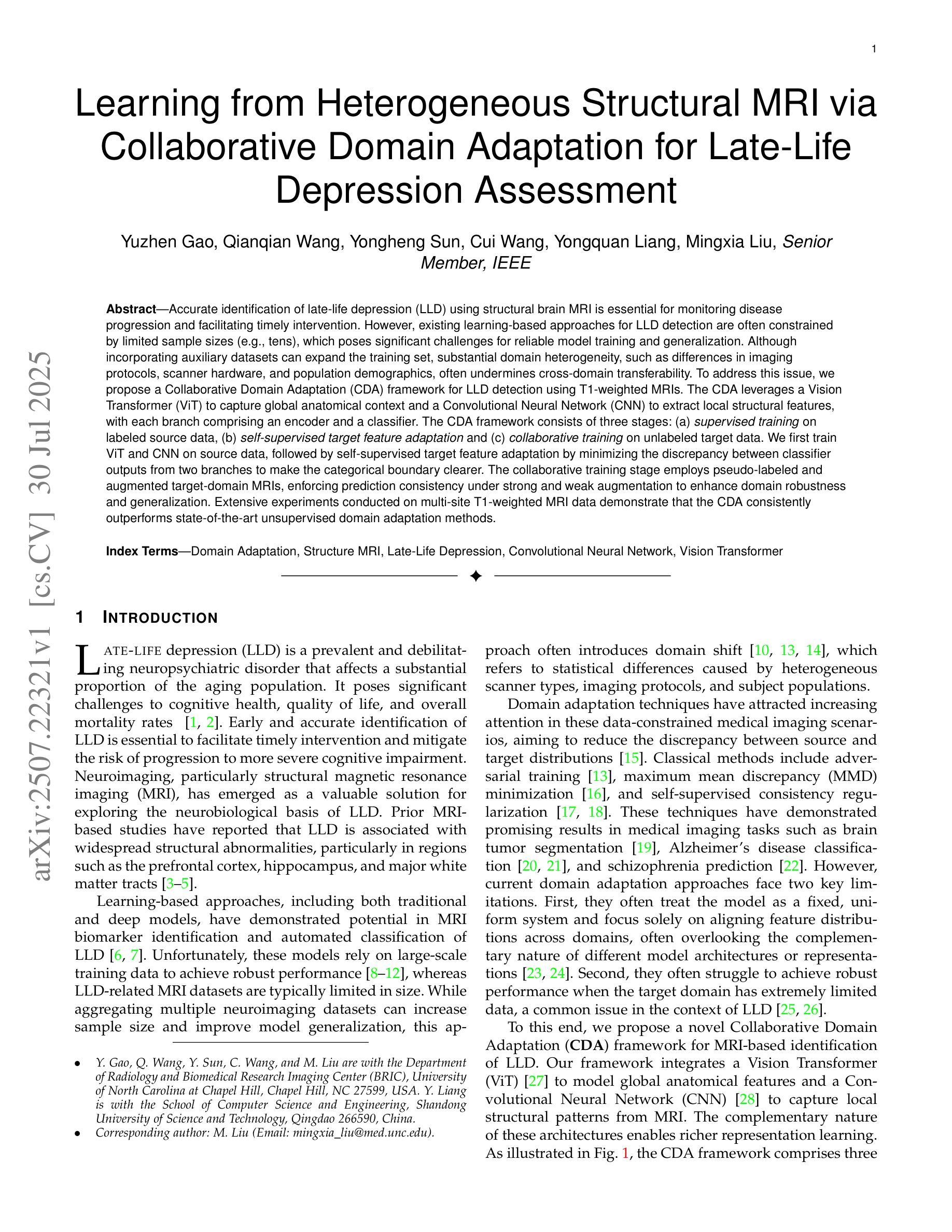
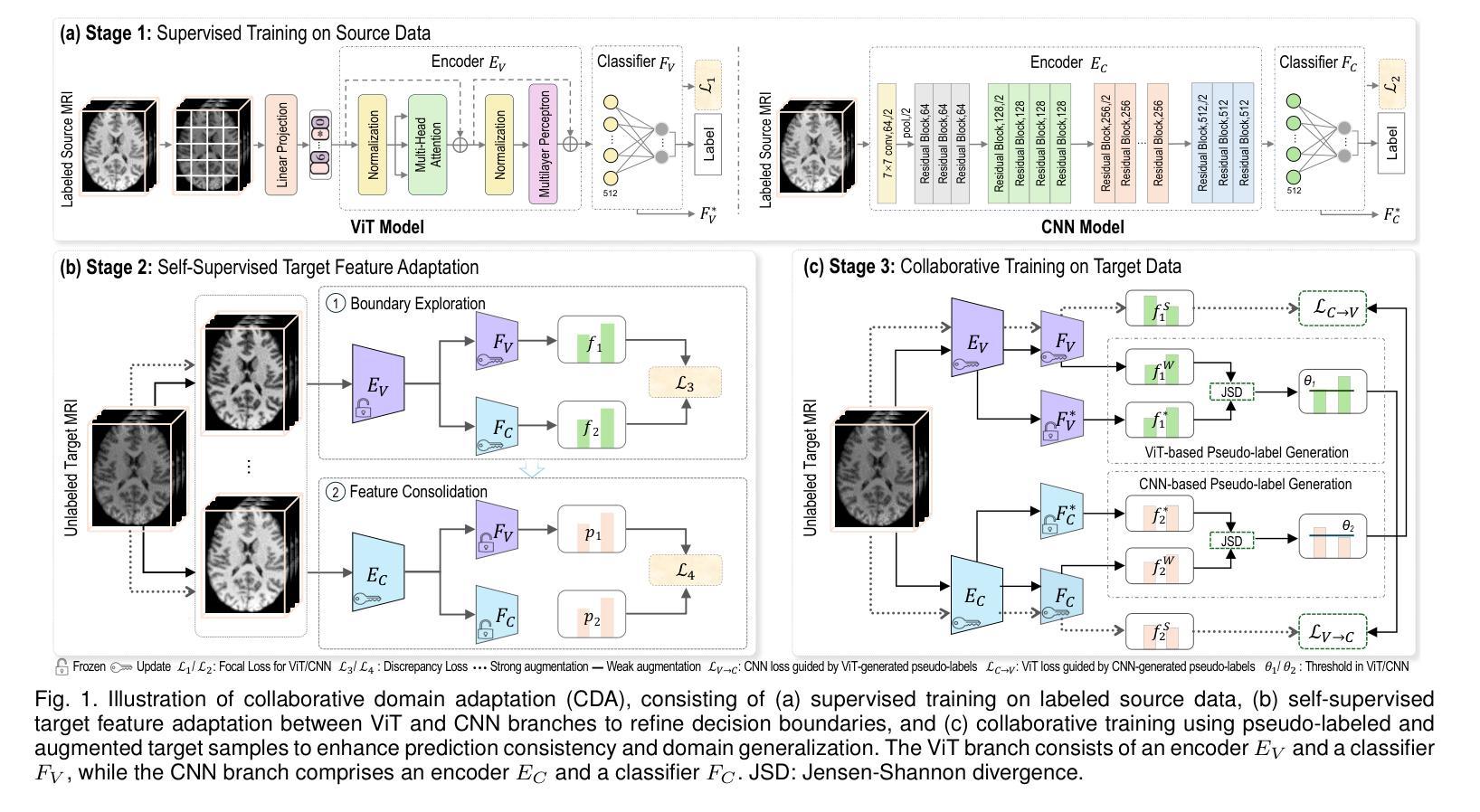
Learning from Heterogeneous Structural MRI via Collaborative Domain Adaptation for Late-Life Depression Assessment
Authors:Yuzhen Gao, Qianqian Wang, Yongheng Sun, Cui Wang, Yongquan Liang, Mingxia Liu
Accurate identification of late-life depression (LLD) using structural brain MRI is essential for monitoring disease progression and facilitating timely intervention. However, existing learning-based approaches for LLD detection are often constrained by limited sample sizes (e.g., tens), which poses significant challenges for reliable model training and generalization. Although incorporating auxiliary datasets can expand the training set, substantial domain heterogeneity, such as differences in imaging protocols, scanner hardware, and population demographics, often undermines cross-domain transferability. To address this issue, we propose a Collaborative Domain Adaptation (CDA) framework for LLD detection using T1-weighted MRIs. The CDA leverages a Vision Transformer (ViT) to capture global anatomical context and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to extract local structural features, with each branch comprising an encoder and a classifier. The CDA framework consists of three stages: (a) supervised training on labeled source data, (b) self-supervised target feature adaptation and (c) collaborative training on unlabeled target data. We first train ViT and CNN on source data, followed by self-supervised target feature adaptation by minimizing the discrepancy between classifier outputs from two branches to make the categorical boundary clearer. The collaborative training stage employs pseudo-labeled and augmented target-domain MRIs, enforcing prediction consistency under strong and weak augmentation to enhance domain robustness and generalization. Extensive experiments conducted on multi-site T1-weighted MRI data demonstrate that the CDA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised domain adaptation methods.
利用结构性脑MRI准确识别晚期抑郁症(LLD)对于监测疾病进展和促进及时干预至关重要。然而,现有的基于学习的LLD检测方法往往受限于有限的样本规模(例如,仅几十个样本),这给可靠的模型训练和普及带来了重大挑战。虽然加入辅助数据集可以扩大训练集,但诸如成像协议、扫描仪硬件和人口统计学等方面的巨大领域差异通常会破坏跨领域的可迁移性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对LLD检测的协作领域适应(CDA)框架,该框架使用T1加权MRI数据。CDA利用视觉变压器(ViT)捕捉全局解剖上下文信息,并利用卷积神经网络(CNN)提取局部结构特征,每个分支都包含编码器和分类器。CDA框架包括三个阶段:(a)在标记源数据上进行监督训练;(b)自我监督的目标特征适应;(c)在标记目标数据上进行协作训练。我们首先在源数据上训练ViT和CNN,然后通过最小化两个分支分类器输出之间的差异进行自监督目标特征适应,以使类别边界更加清晰。协作训练阶段采用伪标记和增强的目标域MRI数据,通过强增强和弱增强下预测的一致性,提高领域稳健性和普及性。在多站点T1加权MRI数据上进行的广泛实验表明,CDA持续优于最新的无监督领域适应方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对晚年抑郁症(LLD)的准确识别,利用结构性脑MRI至关重要。现有学习类方法受限于样本量,面临模型训练和泛化挑战。为解决跨域传输问题,我们提出一种基于T1加权MRI的协同域适应(CDA)框架,利用视觉转换器(ViT)捕捉全局解剖背景和卷积神经网络(CNN)提取局部结构特征,进行LLD检测。CDA框架包括三个阶段:标记源数据的监督训练、自我监督的目标特征适应和协作训练。实验证明,CDA在跨站点的T1加权MRI数据上表现优于其他最新无监督域适应方法。
Key Takeaways
- 晚年抑郁症(LLD)的准确识别对监测疾病进展和及时干预至关重要。
- 现有学习类方法因样本量限制面临模型训练和泛化的挑战。
- 协同域适应(CDA)框架结合了视觉转换器(ViT)和卷积神经网络(CNN),用于LLD检测。
- CDA框架包括监督训练、自我监督的目标特征适应和协作训练三个阶段。
- CDA利用伪标记和增强的目标域MRI图像,提高域稳健性和泛化能力。
- 实验证明,CDA在跨站点的T1加权MRI数据上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
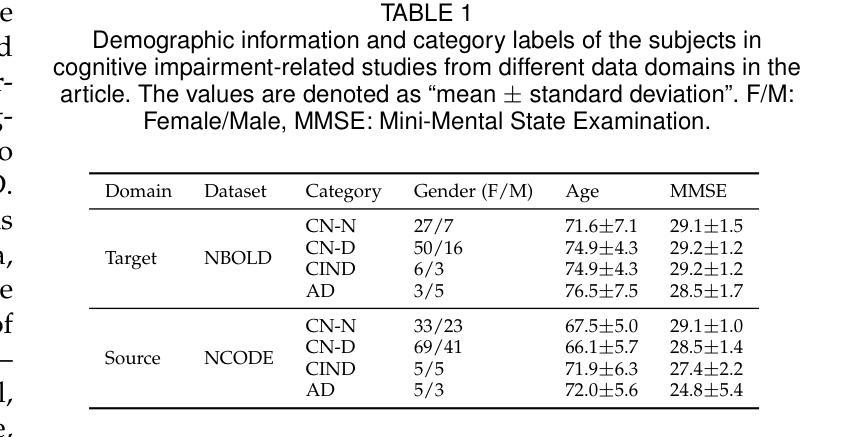
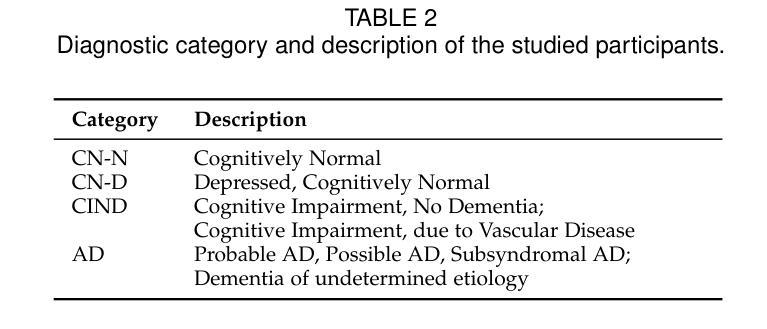
SmartCLIP: Modular Vision-language Alignment with Identification Guarantees
Authors:Shaoan Xie, Lingjing Kong, Yujia Zheng, Yu Yao, Zeyu Tang, Eric P. Xing, Guangyi Chen, Kun Zhang
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP)~\citep{radford2021learning} has emerged as a pivotal model in computer vision and multimodal learning, achieving state-of-the-art performance at aligning visual and textual representations through contrastive learning. However, CLIP struggles with potential information misalignment in many image-text datasets and suffers from entangled representation. On the one hand, short captions for a single image in datasets like MSCOCO may describe disjoint regions in the image, leaving the model uncertain about which visual features to retain or disregard. On the other hand, directly aligning long captions with images can lead to the retention of entangled details, preventing the model from learning disentangled, atomic concepts – ultimately limiting its generalization on certain downstream tasks involving short prompts. In this paper, we establish theoretical conditions that enable flexible alignment between textual and visual representations across varying levels of granularity. Specifically, our framework ensures that a model can not only \emph{preserve} cross-modal semantic information in its entirety but also \emph{disentangle} visual representations to capture fine-grained textual concepts. Building on this foundation, we introduce \ours, a novel approach that identifies and aligns the most relevant visual and textual representations in a modular manner. Superior performance across various tasks demonstrates its capability to handle information misalignment and supports our identification theory. The code is available at https://github.com/Mid-Push/SmartCLIP.
对比语言图像预训练模型(CLIP)在计算机视觉和多模态学习中起到了关键作用,通过对比学习实现了视觉和文本表示的对齐,并达到了最先进的性能。然而,CLIP在多个图像文本数据集中存在潜在的信息对齐问题,并受到纠缠表示的影响。一方面,在MSCOCO等数据集的单张图片的简短字幕可能描述图像中的不同区域,使模型不确定应保留或忽略哪些视觉特征。另一方面,直接将长字幕与图像对齐可能导致保留纠缠的细节,阻碍模型学习解耦的基本概念,最终限制其在涉及简短提示的某些下游任务上的泛化能力。在本文中,我们建立了理论条件,使文本和视觉表示在不同粒度级别上实现灵活对齐。具体来说,我们的框架不仅保证模型能够完整保留跨模态语义信息,而且能够解耦视觉表示以捕获精细的文本概念。在此基础上,我们引入了我们的方法(\ours),以一种模块化的方式识别和对齐最相关的视觉和文本表示。在各种任务上的出色表现证明了其处理信息不对齐的能力,并验证了我们的识别理论。代码可在https://github.com/Mid-Push/SmartCLIP中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
基于CLIP模型的文本图像预训练在计算机视觉和多模态学习中扮演重要角色,但存在信息错位问题。本文提出一种新方法,能够在不同粒度上实现文本和视觉表示之间的灵活对齐,同时保留跨模态语义信息并解耦视觉表示以捕捉精细的文本概念。引入的方法以模块化的方式识别和对齐最相关的视觉和文本表示,并在各种任务中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在多模态学习和计算机视觉中表现卓越,但在图像文本数据集上存在潜在的信息错位问题。
- 信息错位问题源于图像和文本描述的不一致性,导致模型在处理不同图像区域描述时面临不确定性。
- 直接对齐长描述和图像可能导致纠缠的细节被保留,影响模型学习原子概念的解耦能力。
- 本文建立的理论条件允许文本和视觉表示在不同粒度上的灵活对齐。
- 介绍了一种新方法,可以在保留跨模态语义信息的同时解耦视觉表示,以捕捉精细的文本概念。
- 模块化的方式有助于识别和对齐最相关的视觉和文本表示。
点此查看论文截图

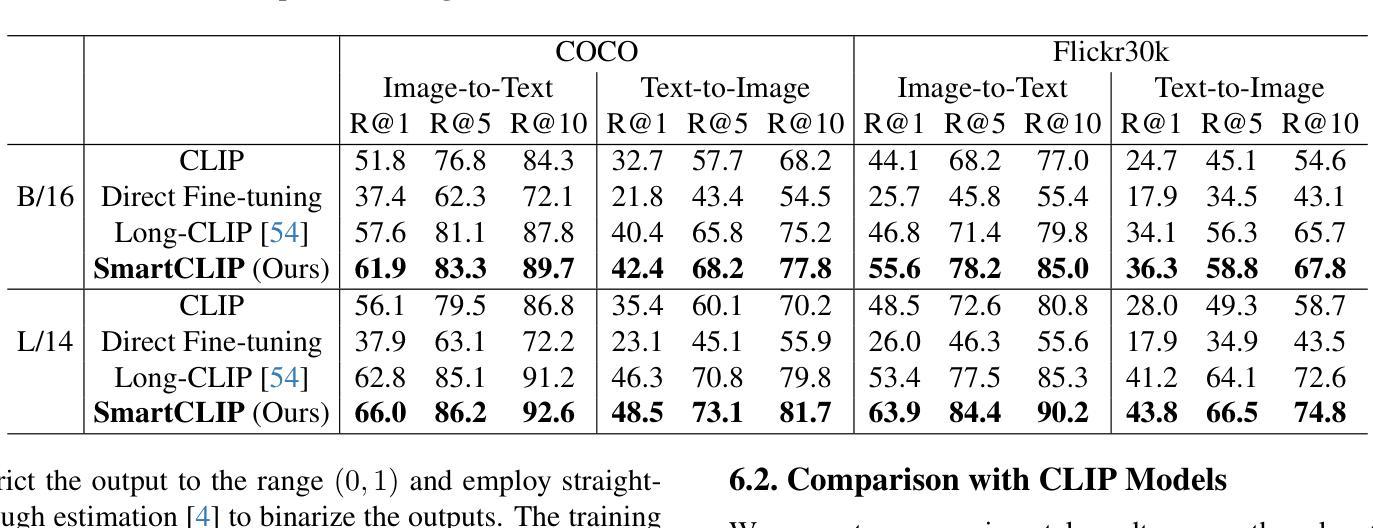
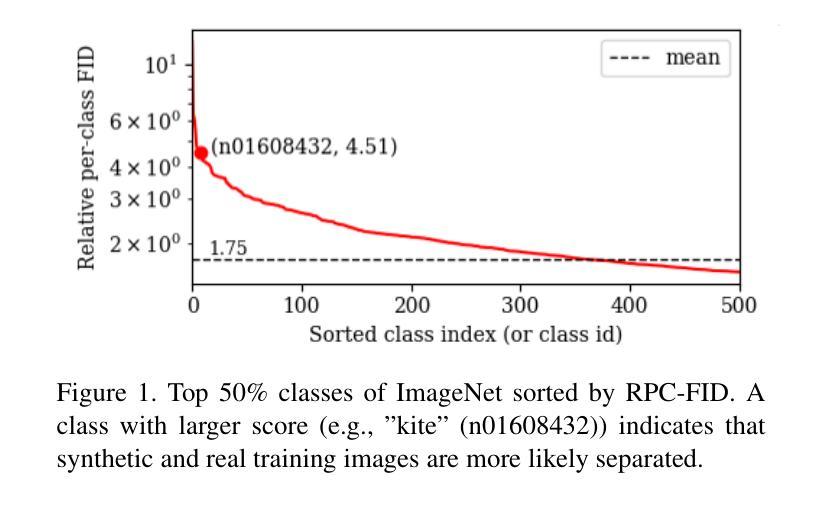
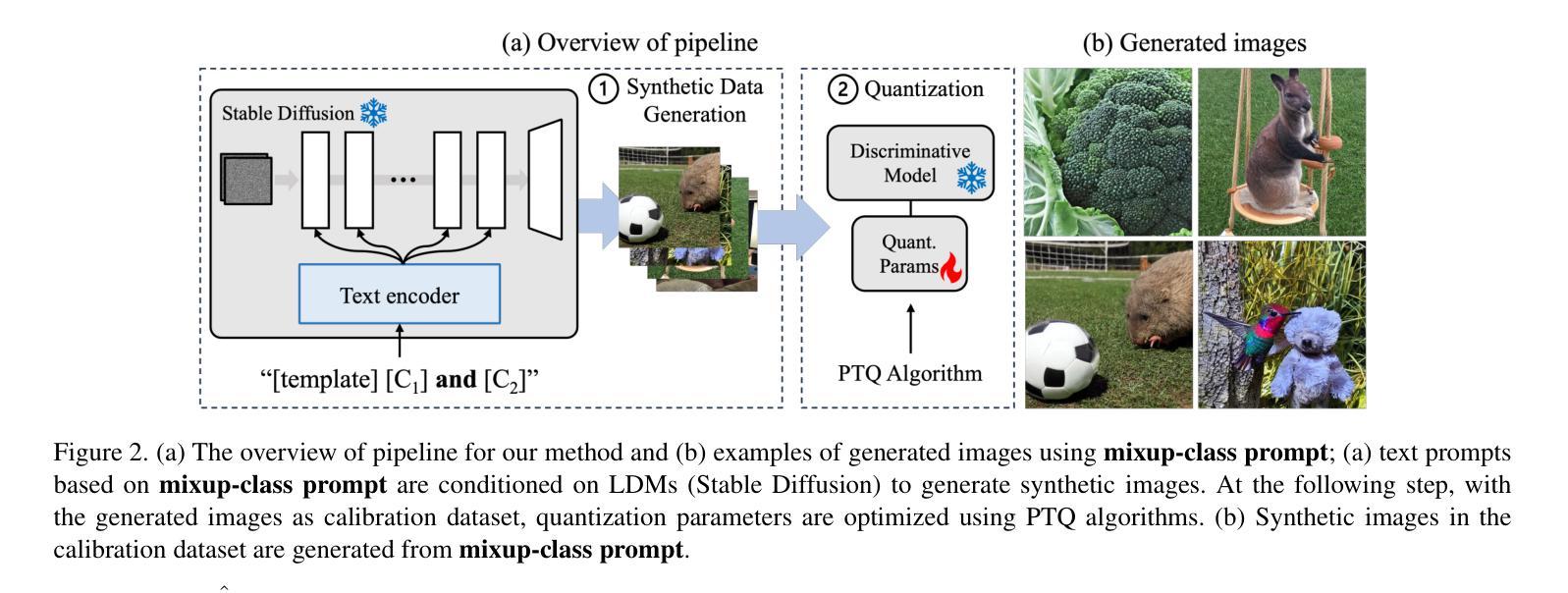
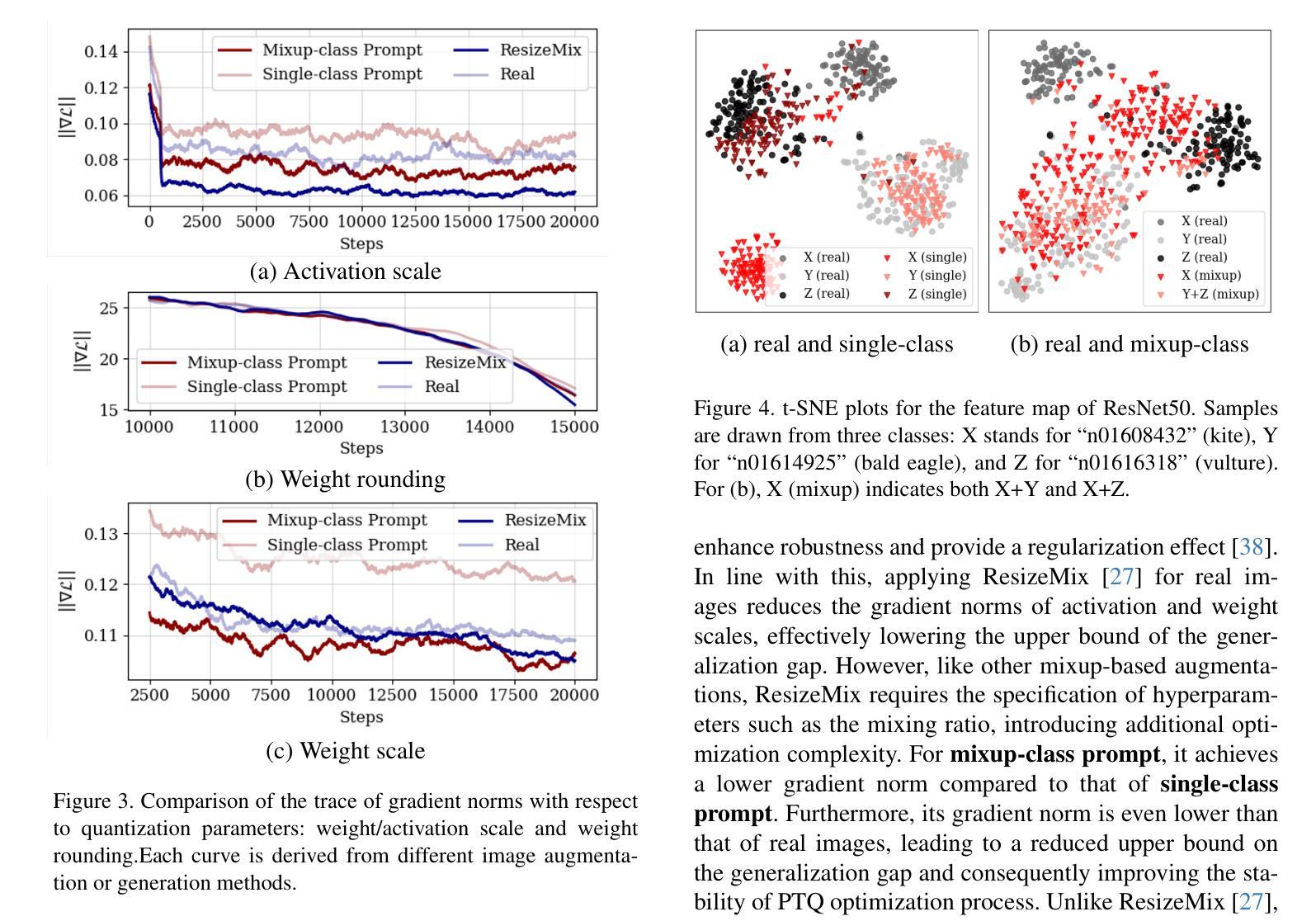
Enhancing Generalization in Data-free Quantization via Mixup-class Prompting
Authors:Jiwoong Park, Chaeun Lee, Yongseok Choi, Sein Park, Deokki Hong, Jungwook Choi
Post-training quantization (PTQ) improves efficiency but struggles with limited calibration data, especially under privacy constraints. Data-free quantization (DFQ) mitigates this by generating synthetic images using generative models such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and text-conditioned latent diffusion models (LDMs), while applying existing PTQ algorithms. However, the relationship between generated synthetic images and the generalizability of the quantized model during PTQ remains underexplored. Without investigating this relationship, synthetic images generated by previous prompt engineering methods based on single-class prompts suffer from issues such as polysemy, leading to performance degradation. We propose \textbf{mixup-class prompt}, a mixup-based text prompting strategy that fuses multiple class labels at the text prompt level to generate diverse, robust synthetic data. This approach enhances generalization, and improves optimization stability in PTQ. We provide quantitative insights through gradient norm and generalization error analysis. Experiments on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art DFQ methods like GenQ. Furthermore, it pushes the performance boundary in extremely low-bit scenarios, achieving new state-of-the-art accuracy in challenging 2-bit weight, 4-bit activation (W2A4) quantization.
后训练量化(PTQ)提高了效率,但在有限的校准数据方面遇到了困难,特别是在隐私约束下。无数据量化(DFQ)通过利用生成模型(如生成对抗网络(GANs)和文本条件潜在扩散模型(LDMs))生成合成图像,并应用现有的PTQ算法来缓解这个问题。然而,在PTQ期间,生成的合成图像与量化模型通用性之间的关系尚未得到足够的研究。由于没有研究这种关系,以前基于单类提示的提示工程方法生成的合成图像存在多义性问题,导致性能下降。我们提出混合类提示,这是一种基于混合的文本提示策略,它在文本提示层面融合多个类标签,以生成多样、稳健的合成数据。此方法提高了通用性,并增强了PTQ中的优化稳定性。我们通过梯度范数和泛化误差分析提供了定量见解。在卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最新的DFQ方法,如GenQ。此外,它在极低位的场景中推动了性能边界,在具有挑战性的2位权重、4位激活(W2A4)量化中达到了新的最高精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无训练量化(PTQ)在有限的校准数据下性能受限,特别是在隐私约束条件下。数据免费量化(DFQ)通过生成对抗性网络(GANs)和文本条件潜在扩散模型(LDMs)等生成合成图像,并应用现有PTQ算法进行改进。然而,生成的合成图像与PTQ期间量化模型的一般化之间的关系尚未得到充分探索。为解决此问题,我们提出基于混合文本提示策略的“mixup-class prompt”,该策略在文本提示层面融合多个类别标签,生成多样且稳健的合成数据,增强模型泛化能力,提高PTQ的优化稳定性。实验表明,我们的方法在CNN和Vision Transformer上均优于最新的DFQ方法,且在极低比特场景下表现突出,达到W2A4量化新境界。
Key Takeaways
- PTQ在有限的校准数据下性能受限,特别是在隐私约束条件下。
- DFQ通过生成合成图像改进了PTQ,但合成图像与量化模型泛化能力之间的关系尚未明确。
- 提出基于混合文本提示策略的“mixup-class prompt”,生成多样且稳健的合成数据。
- 该策略增强了模型的泛化能力,并提高了PTQ的优化稳定性。
- 与最新的DFQ方法相比,该方法在CNN和Vision Transformer上都有优越表现。
- 该方法在极低比特场景下表现突出,达到了新的量化境界。
点此查看论文截图

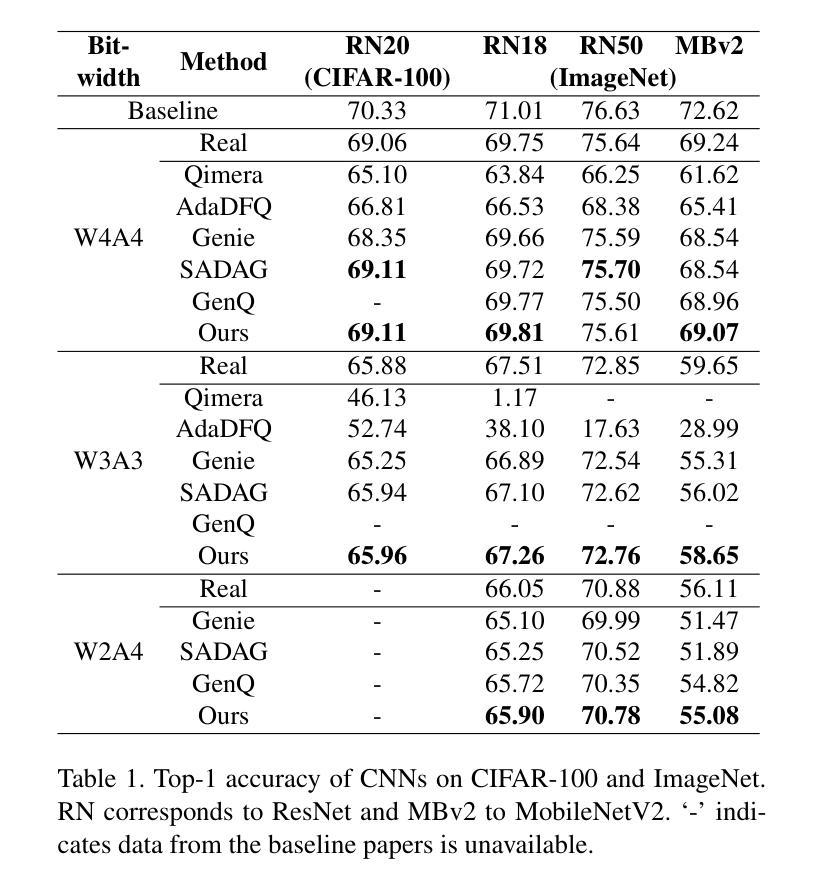
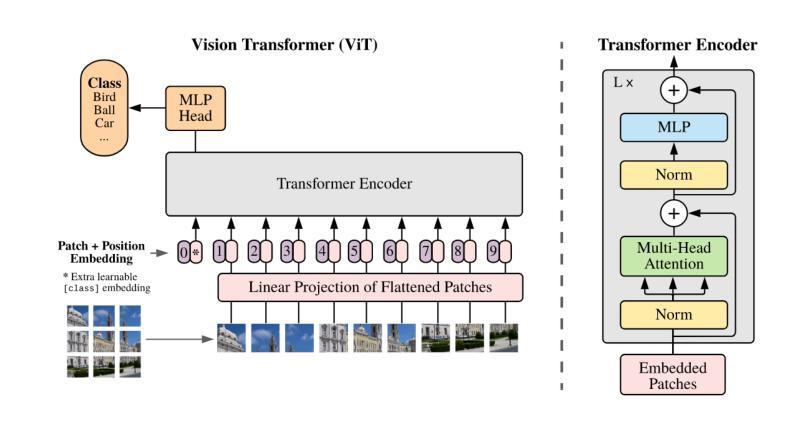
MOR-VIT: Efficient Vision Transformer with Mixture-of-Recursions
Authors:YiZhou Li
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved remarkable success in image recognition, yet standard ViT architectures are hampered by substantial parameter redundancy and high computational cost, limiting their practical deployment. While recent efforts on efficient ViTs primarily focus on static model compression or token-level sparsification, they remain constrained by fixed computational depth for all tokens. In this work, we present MoR-ViT, a novel vision transformer framework that, for the first time, incorporates a token-level dynamic recursion mechanism inspired by the Mixture-of-Recursions (MoR) paradigm. This approach enables each token to adaptively determine its processing depth, yielding a flexible and input-dependent allocation of computational resources. Extensive experiments on ImageNet-1K and transfer benchmarks demonstrate that MoR-ViT not only achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with up to 70% parameter reduction and 2.5x inference acceleration, but also outperforms leading efficient ViT baselines such as DynamicViT and TinyViT under comparable conditions. These results establish dynamic recursion as an effective strategy for efficient vision transformers and open new avenues for scalable and deployable deep learning models in real-world scenarios.
视觉转换器(ViTs)在图像识别方面取得了显著的成功,然而,标准的ViT架构存在大量的参数冗余和较高的计算成本,限制了其实际部署。尽管最近的关于高效ViT的研究主要集中在静态模型压缩或令牌级稀疏化上,但它们仍然受到所有令牌的固定计算深度的限制。在这项工作中,我们提出了MoR-ViT,这是一种新的视觉转换器框架,它首次采用了受递归混合(MoR)范式启发的令牌级动态递归机制。这种方法允许每个令牌自适应地确定其处理深度,从而实现计算资源的灵活和输入依赖分配。在ImageNet-1K和迁移基准测试的大量实验表明,MoR-ViT不仅实现了最先进的准确性,同时减少了高达70%的参数和2.5倍的推理加速,而且在同等条件下优于领先的高效ViT基准测试,如DynamicViT和TinyViT。这些结果证明了动态递归是高效视觉转换器的有效策略,并为现实世界中可扩展和可部署的深度学习模型打开了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages,9 figuers
Summary
本文提出了MoR-ViT,一种新型视觉转换器框架,首次采用基于混合递归(MoR)范式的令牌级动态递归机制。该方法使每个令牌能够自适应地确定其处理深度,实现计算资源的灵活和输入依赖分配。在ImageNet-1K和传输基准测试上,MoR-ViT不仅实现了高达70%的参数减少和2.5倍的推理加速,而且还在可比条件下优于领先的效率ViT基线,如DynamicViT和TinyViT。
Key Takeaways
- MoR-ViT是一种新型的视觉转换器框架,引入了基于混合递归范式的令牌级动态递归机制。
- 该方法允许每个令牌自适应地确定其处理深度,实现计算资源的灵活分配。
- MoR-ViT实现了高达70%的参数减少和2.5倍的推理加速。
- MoR-ViT在ImageNet-1K和传输基准测试上达到了先进的准确性。
- MoR-ViT优于其他领先的效率ViT基线,如DynamicViT和TinyViT。
- 动态递归被证明是一种有效的策略,用于提高视觉转换器的效率。
点此查看论文截图

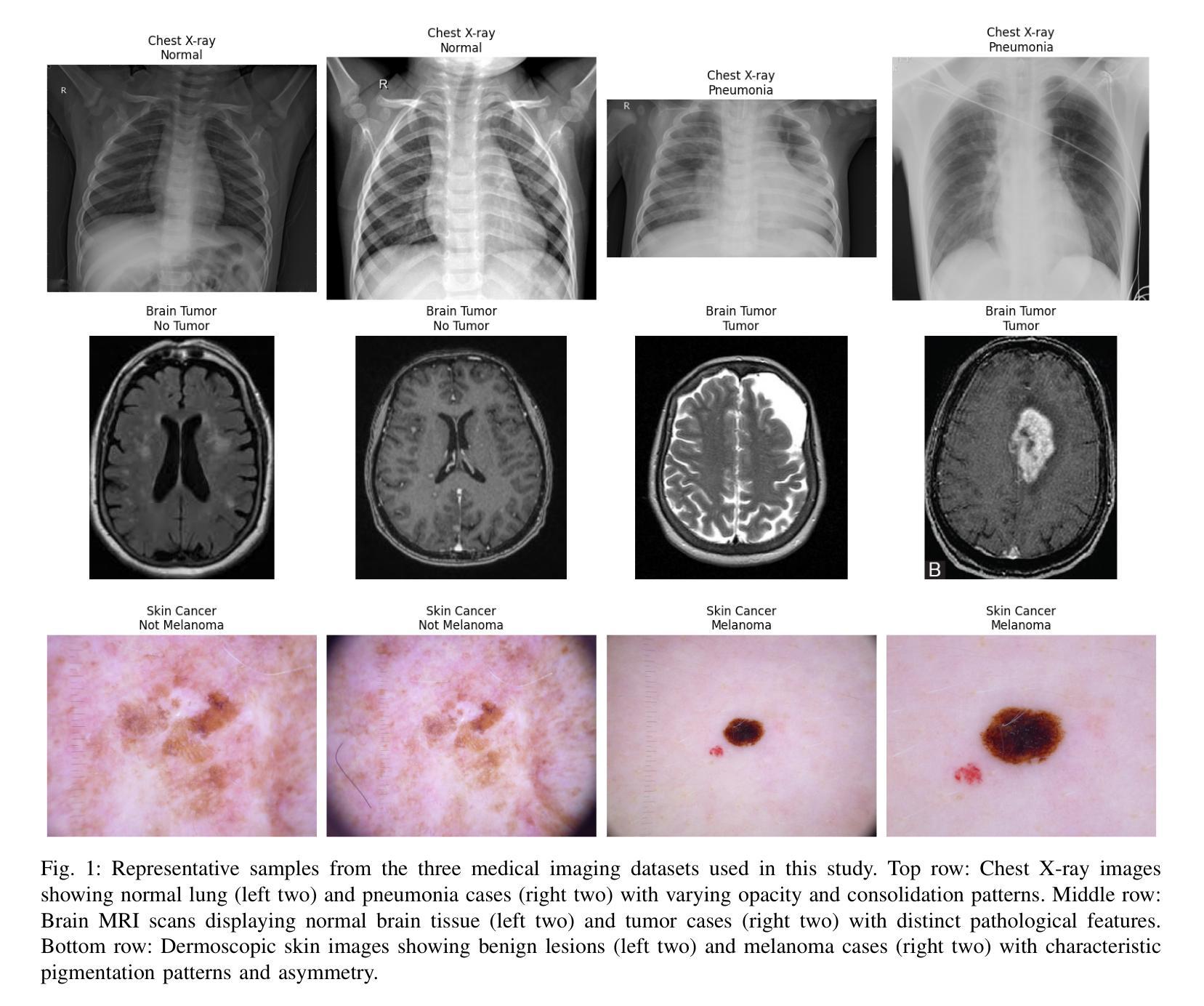
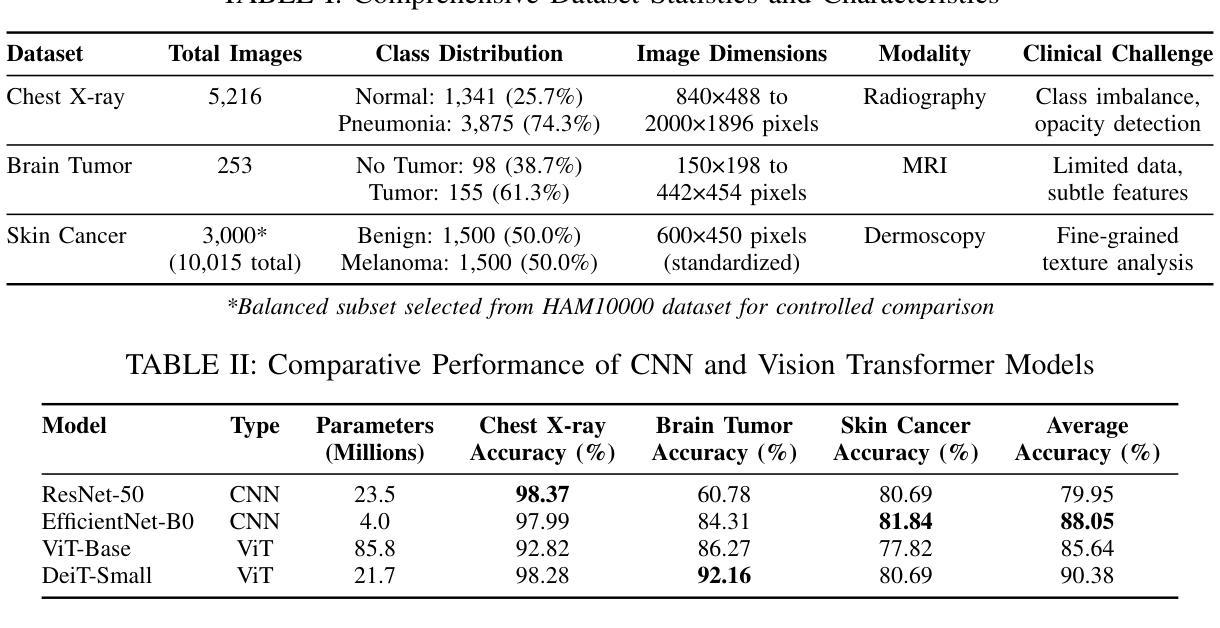
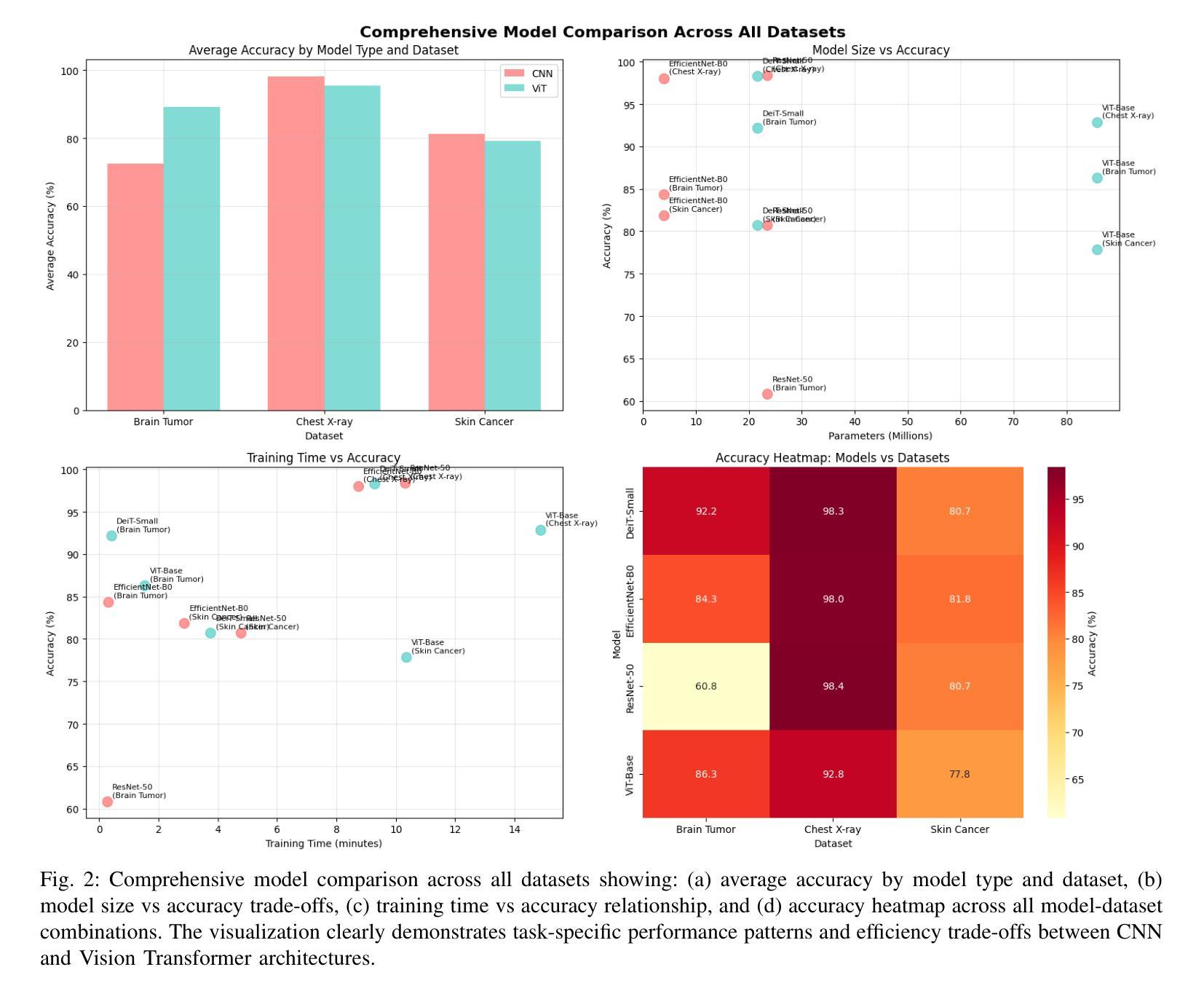
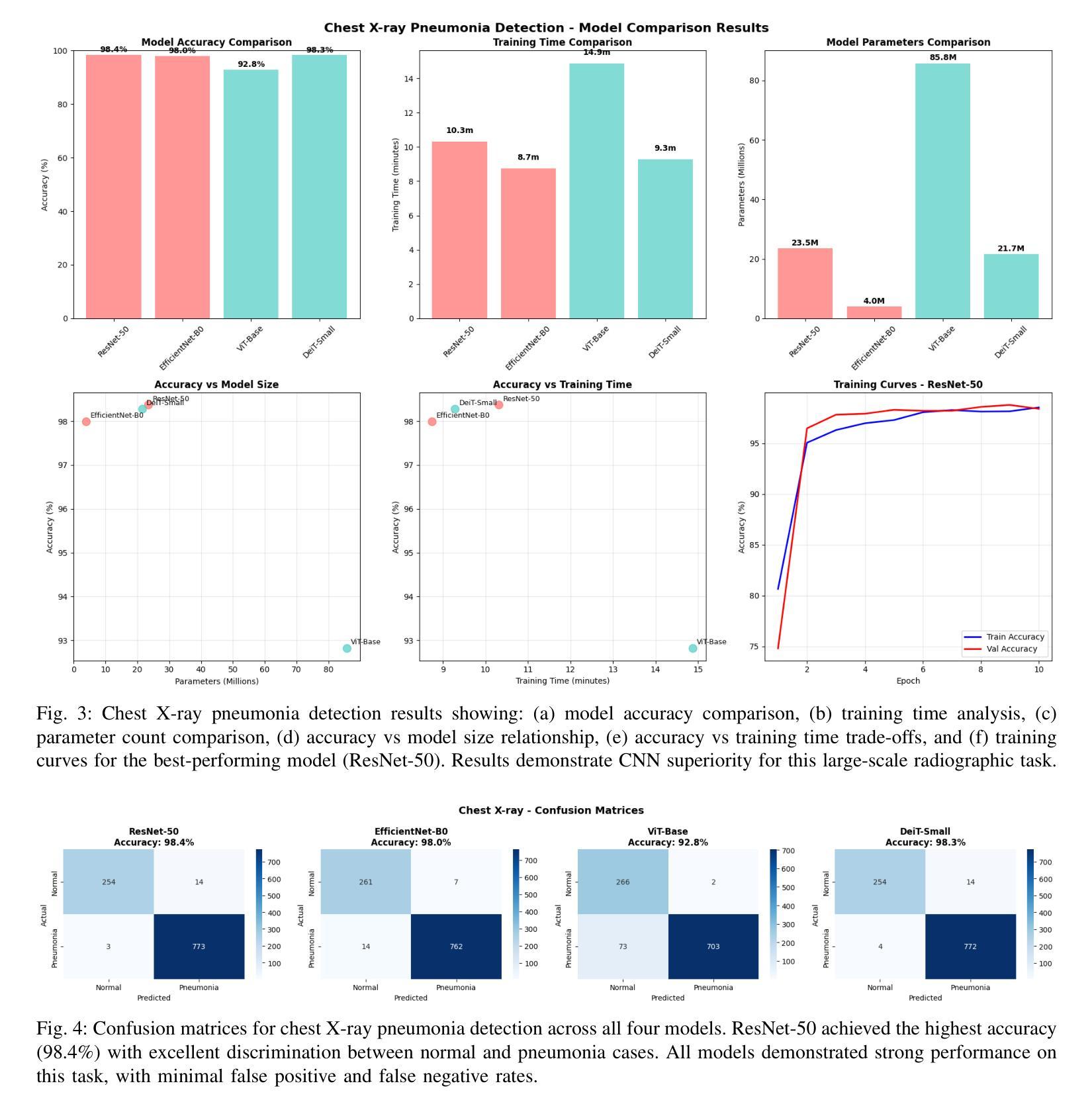
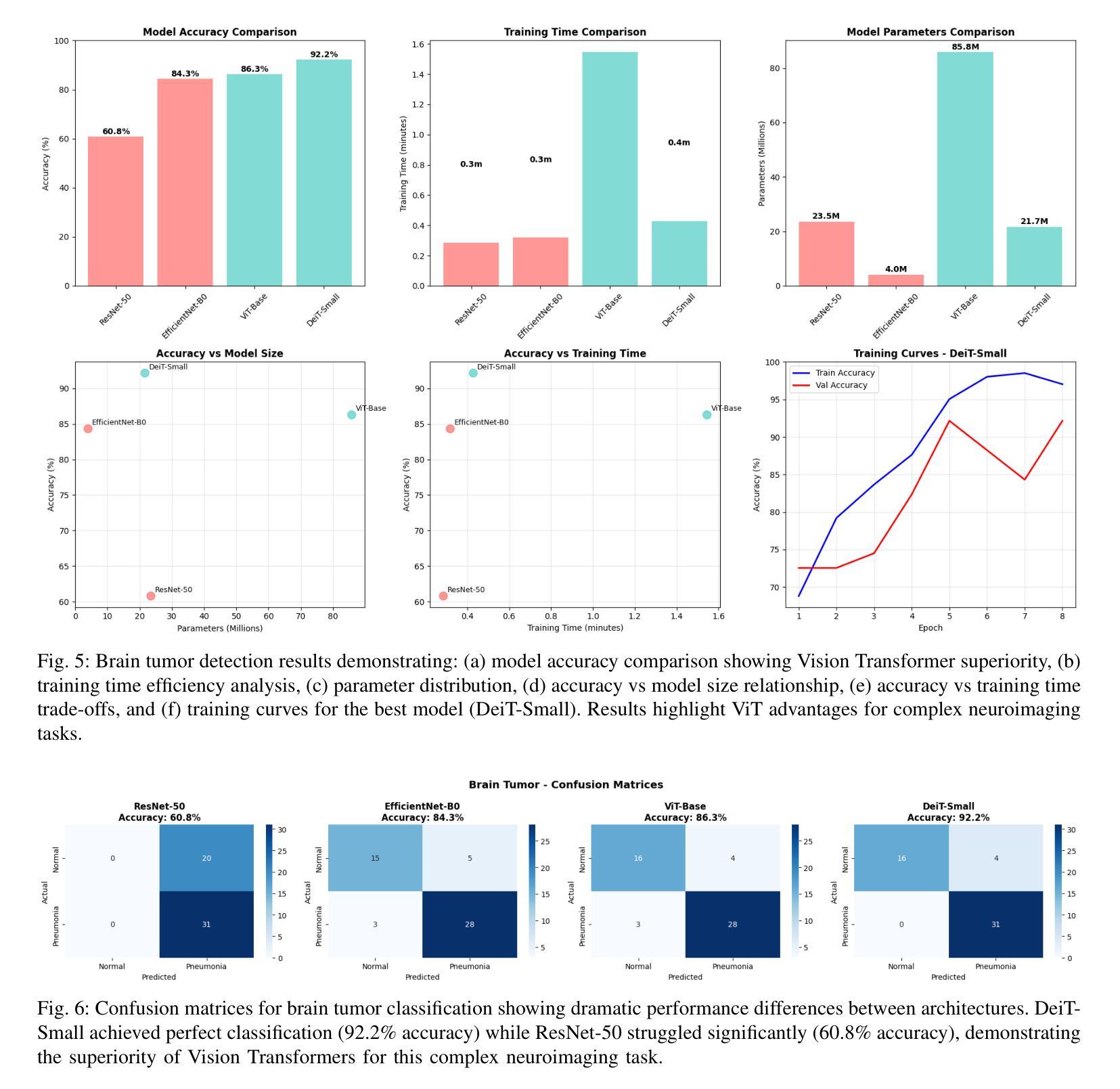
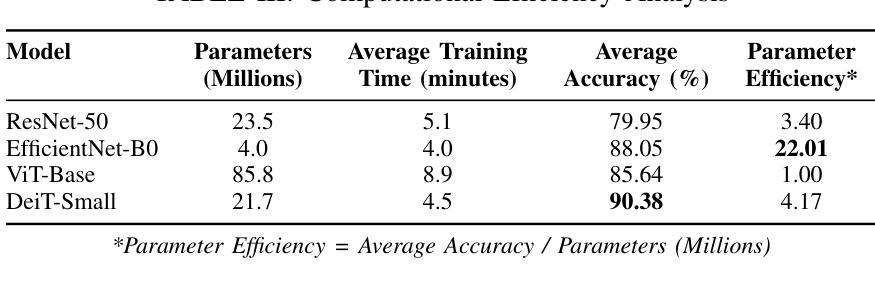
Comparative Analysis of Vision Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Kunal Kawadkar
The emergence of Vision Transformers (ViTs) has revolutionized computer vision, yet their effectiveness compared to traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in medical imaging remains under-explored. This study presents a comprehensive comparative analysis of CNN and ViT architectures across three critical medical imaging tasks: chest X-ray pneumonia detection, brain tumor classification, and skin cancer melanoma detection. We evaluated four state-of-the-art models - ResNet-50, EfficientNet-B0, ViT-Base, and DeiT-Small - across datasets totaling 8,469 medical images. Our results demonstrate task-specific model advantages: ResNet-50 achieved 98.37% accuracy on chest X-ray classification, DeiT-Small excelled at brain tumor detection with 92.16% accuracy, and EfficientNet-B0 led skin cancer classification at 81.84% accuracy. These findings provide crucial insights for practitioners selecting architectures for medical AI applications, highlighting the importance of task-specific architecture selection in clinical decision support systems.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)的出现已经彻底改变了计算机视觉领域,然而,其在医学影像方面与传统卷积神经网络(CNNs)的有效性对比仍然有待探索。本研究针对三种重要的医学影像任务:胸部X射线肺炎检测、脑肿瘤分类和皮肤癌黑色素瘤检测,对CNN和ViT架构进行了全面的对比分析。我们在包含总计8469张医学影像的数据集上评估了四种最新模型——ResNet-50、EfficientNet-B0、ViT-Base和DeiT-Small。我们的结果显示出针对特定任务的模型优势:在胸部X射线分类中,ResNet-50取得了98.37%的准确率;在脑肿瘤检测方面,DeiT-Small以92.16%的准确率表现出卓越性能;而在皮肤癌分类中,EfficientNet-B0以81.84%的准确率领先。这些发现对于从业者选择医学人工智能应用的架构至关重要,并强调在临床决策支持系统任务中特定架构选择的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables. Submitted to IEEE Access
Summary
本文研究了Vision Transformers(ViTs)相较于传统卷积神经网络(CNNs)在医疗影像领域的应用效果。通过对ResNet-50、EfficientNet-B0、ViT-Base和DeiT-Small四种前沿模型在三项重要医疗影像任务上的比较分析,发现不同模型在不同任务上的优势。这些结果对医疗人工智能应用的架构选择提供了重要参考,强调任务特定架构选择在临床决策支持系统中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)在计算机视觉领域已引起革命性变革,但在医疗影像领域的研究仍然有限。
- 对比研究了四种顶尖模型在三项医疗影像任务上的表现。
- ResNet-50在胸部X光肺炎检测方面表现最佳,达到98.37%准确率。
- DeiT-Small在脑肿瘤分类任务上表现优异,准确率为92.16%。
- EfficientNet-B0在皮肤癌黑色素瘤检测方面领先,准确率为81.84%。
- 不同模型在不同任务上的表现存在差异,选择适合的模型架构对医疗AI应用至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

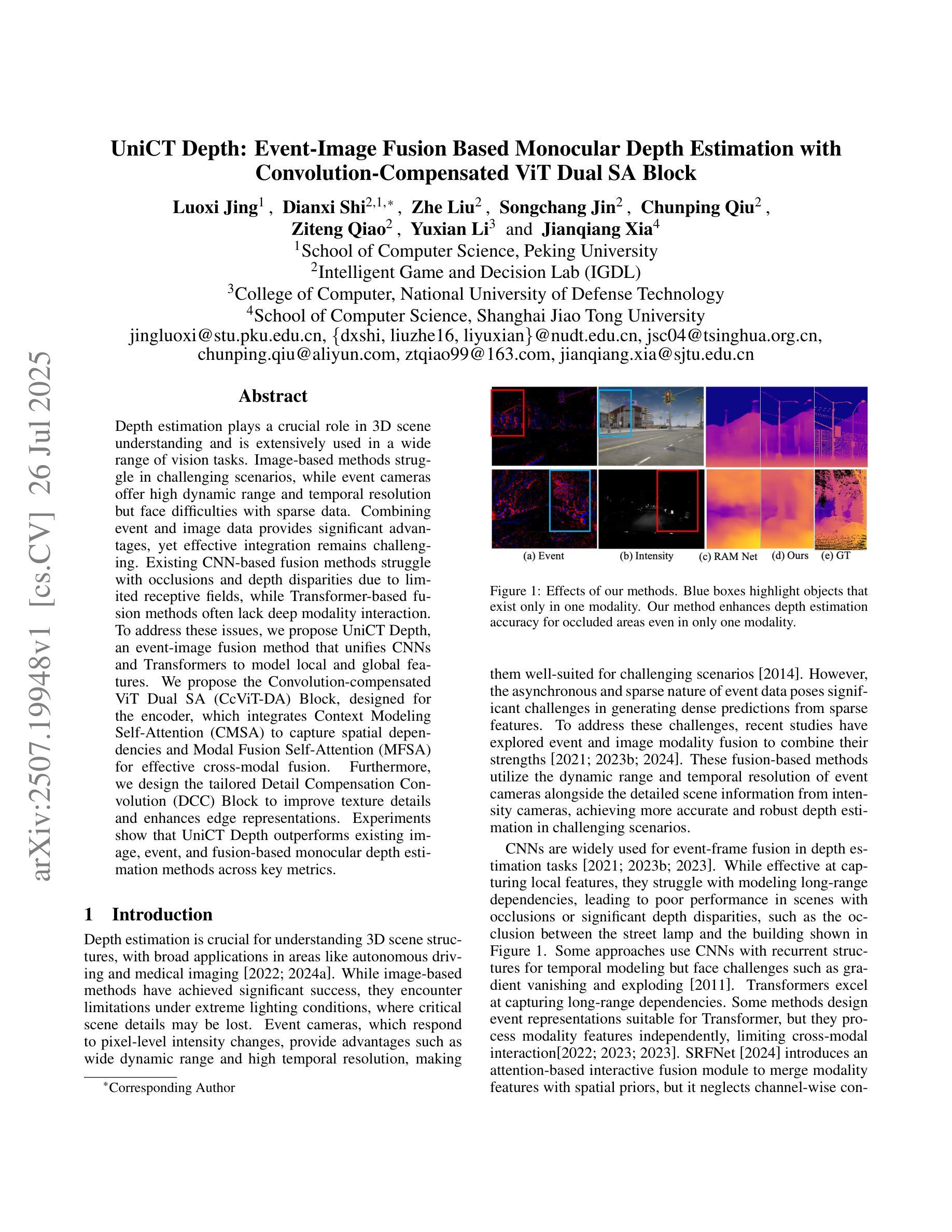
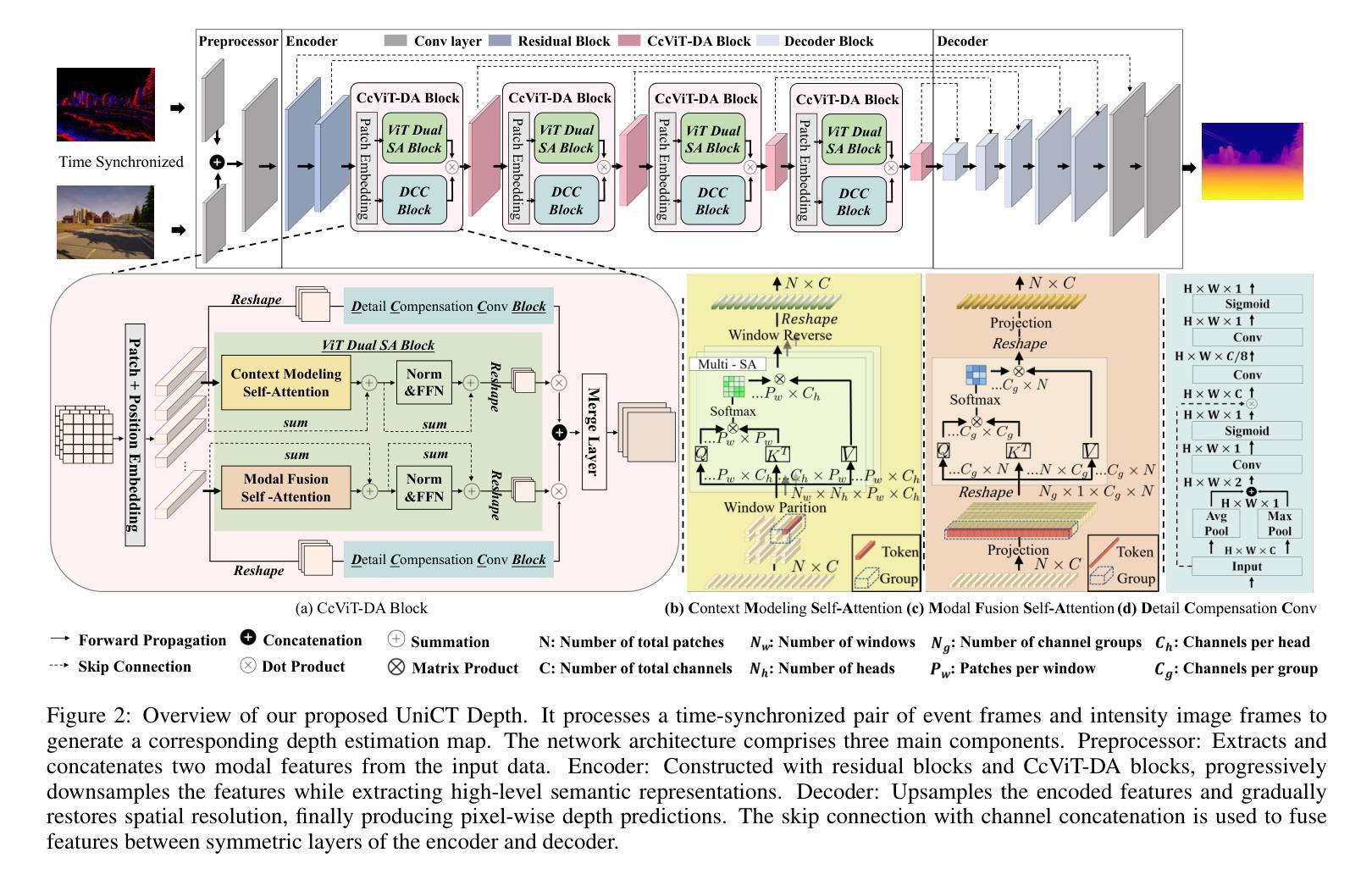
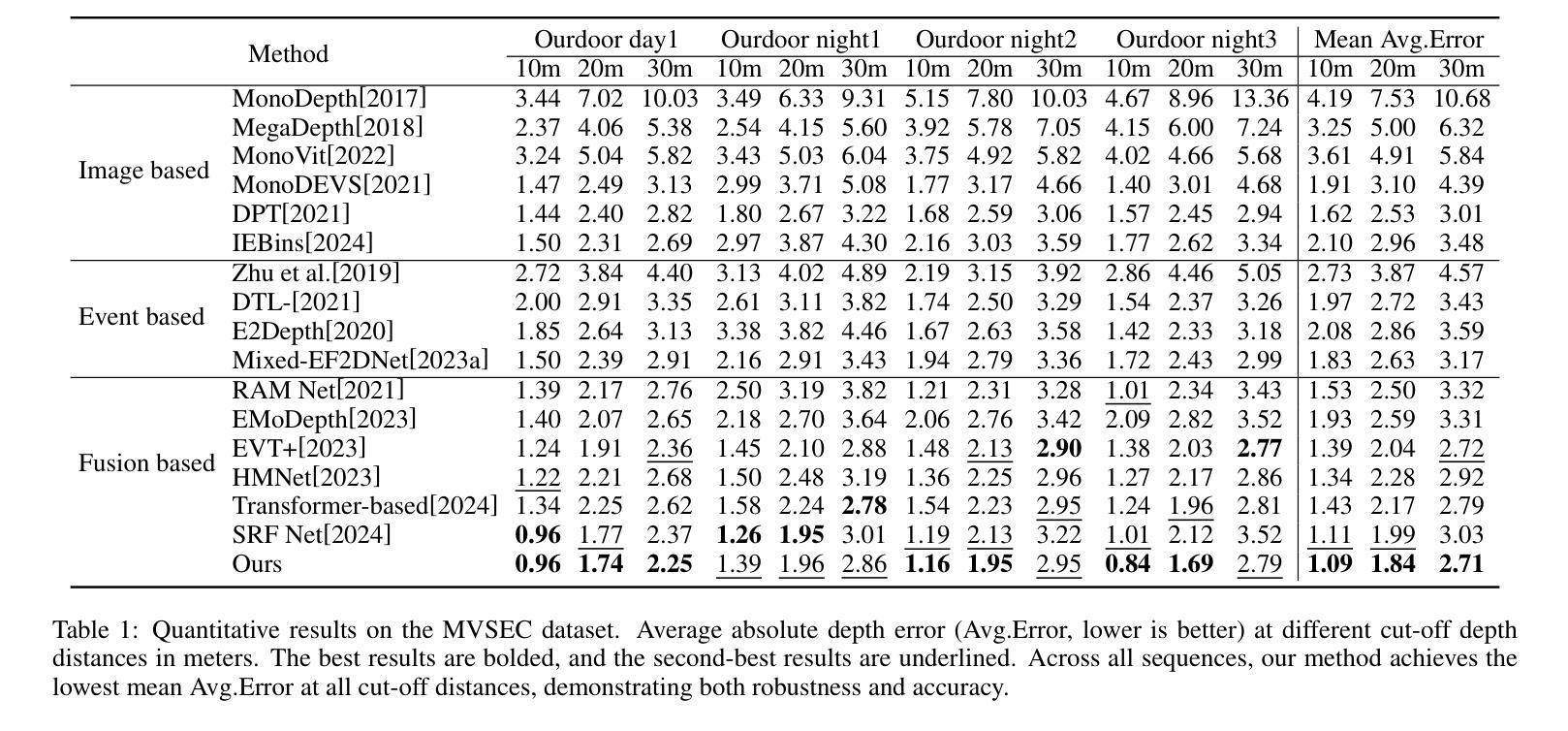
UniCT Depth: Event-Image Fusion Based Monocular Depth Estimation with Convolution-Compensated ViT Dual SA Block
Authors:Luoxi Jing, Dianxi Shi, Zhe Liu, Songchang Jin, Chunping Qiu, Ziteng Qiao, Yuxian Li, Jianqiang Xia
Depth estimation plays a crucial role in 3D scene understanding and is extensively used in a wide range of vision tasks. Image-based methods struggle in challenging scenarios, while event cameras offer high dynamic range and temporal resolution but face difficulties with sparse data. Combining event and image data provides significant advantages, yet effective integration remains challenging. Existing CNN-based fusion methods struggle with occlusions and depth disparities due to limited receptive fields, while Transformer-based fusion methods often lack deep modality interaction. To address these issues, we propose UniCT Depth, an event-image fusion method that unifies CNNs and Transformers to model local and global features. We propose the Convolution-compensated ViT Dual SA (CcViT-DA) Block, designed for the encoder, which integrates Context Modeling Self-Attention (CMSA) to capture spatial dependencies and Modal Fusion Self-Attention (MFSA) for effective cross-modal fusion. Furthermore, we design the tailored Detail Compensation Convolution (DCC) Block to improve texture details and enhances edge representations. Experiments show that UniCT Depth outperforms existing image, event, and fusion-based monocular depth estimation methods across key metrics.
深度估计在3D场景理解中起着至关重要的作用,并广泛应用于各种视觉任务。基于图像的方法在具有挑战性的场景中表现挣扎,而事件相机虽然提供了高动态范围和时序分辨率,但在处理稀疏数据时面临困难。结合事件和图像数据具有显著优势,但有效集成仍然是一个挑战。现有的基于CNN的融合方法由于有限的感受野而难以处理遮挡和深度差异问题,而基于Transformer的融合方法通常缺乏深度模态交互。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了UniCT Depth,这是一种结合CNN和Transformer的事件图像融合方法,用于建模局部和全局特征。我们为编码器设计了卷积补偿ViT双SA(CcViT-DA)块,该块集成了上下文建模自注意力(CMSA)以捕获空间依赖关系,并集成了模态融合自注意力(MFSA)以实现有效的跨模态融合。此外,我们还设计了专门的细节补偿卷积(DCC)块,以提高纹理细节并增强边缘表示。实验表明,UniCT Depth在关键指标上优于现有的图像、事件和基于融合的单目深度估计方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025 (International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence)
Summary
事件相机与图像数据的结合在深度估计中具有显著优势,但有效集成仍具挑战性。现有方法面临有限感受野和模态交互不足的问题。为此,UniCT Depth方法融合CNN和Transformer,建立局部与全局特征模型。提出CcViT-DA块与CMSA和MFSA,用于捕获空间依赖性和有效跨模态融合。设计DCC块改善纹理细节和边缘表示。实验表明,UniCT Depth在关键指标上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机与图像数据结合对于深度估计至关重要。
- 现有方法面临有效集成挑战,如CNN的有限感受野和Transformer的模态交互不足。
- UniCT Depth方法融合CNN和Transformer,建立局部与全局特征模型。
- CcViT-DA块结合了CMSA和MFSA,分别用于捕获空间依赖性和实现跨模态融合。
- DCC块设计用于改善纹理细节和边缘表示。
- UniCT Depth在深度估计方面表现优异,优于现有图像、事件和融合方法。
点此查看论文截图
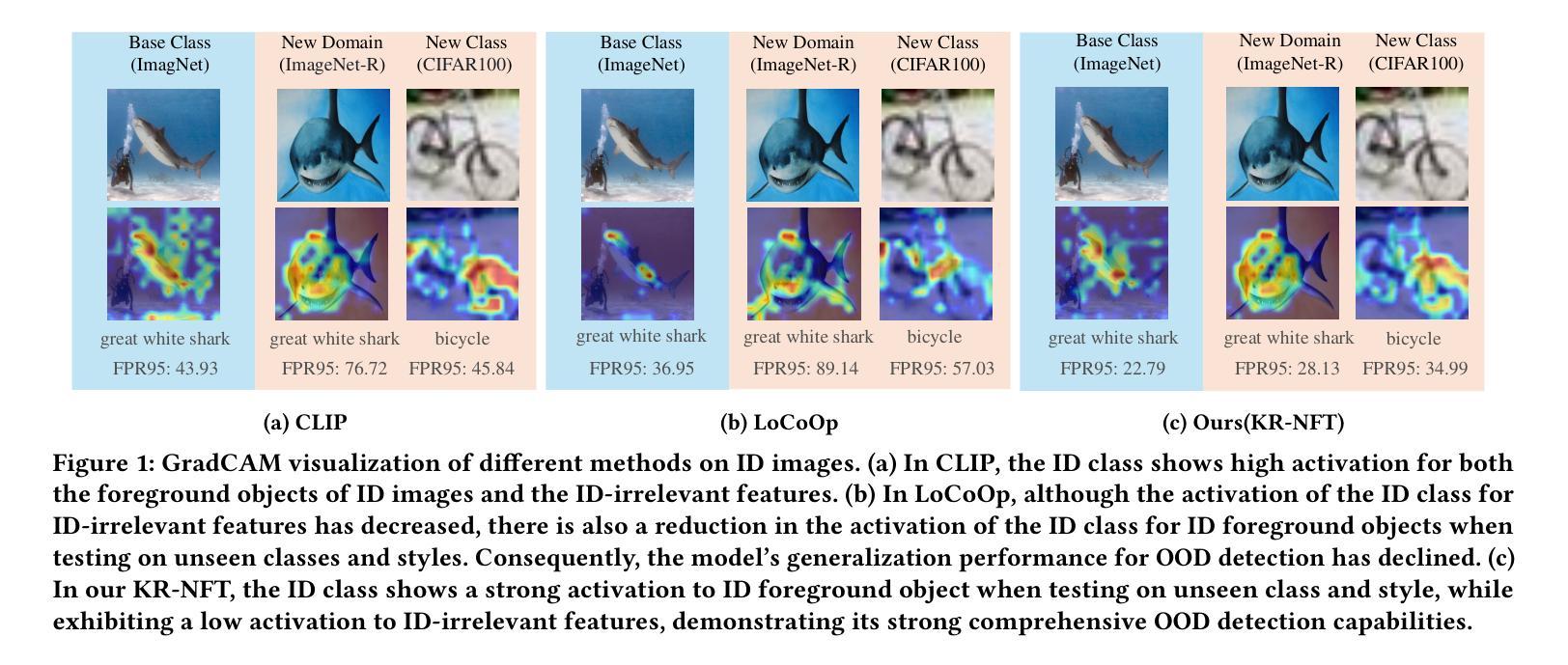
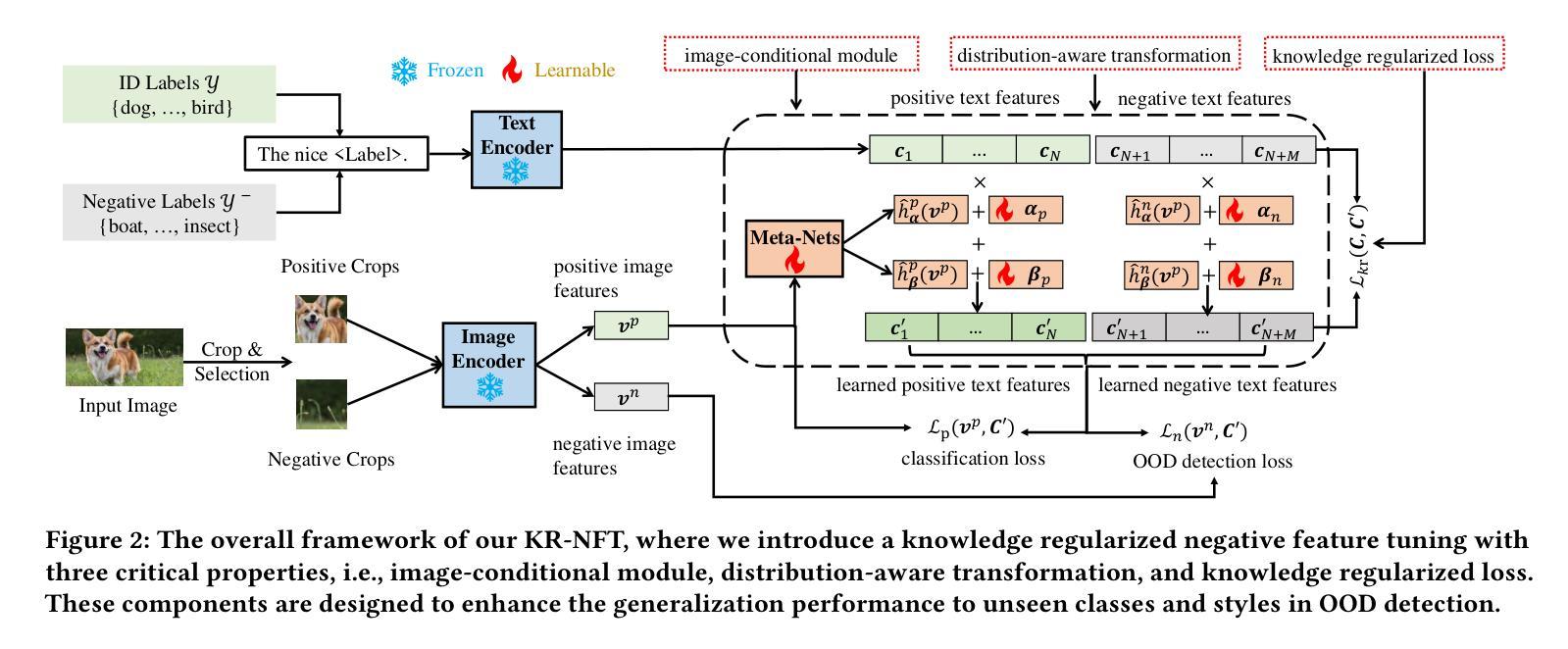
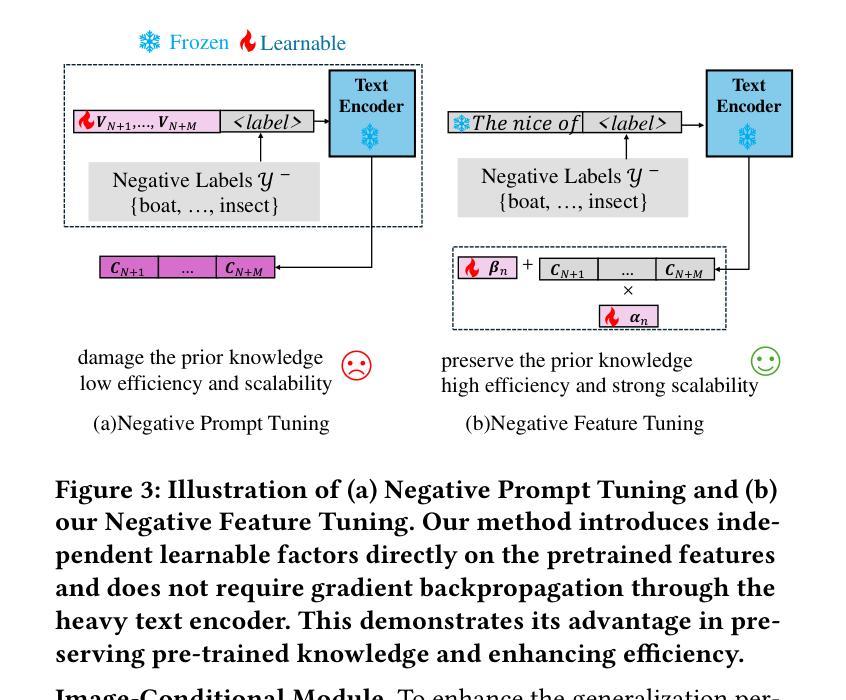
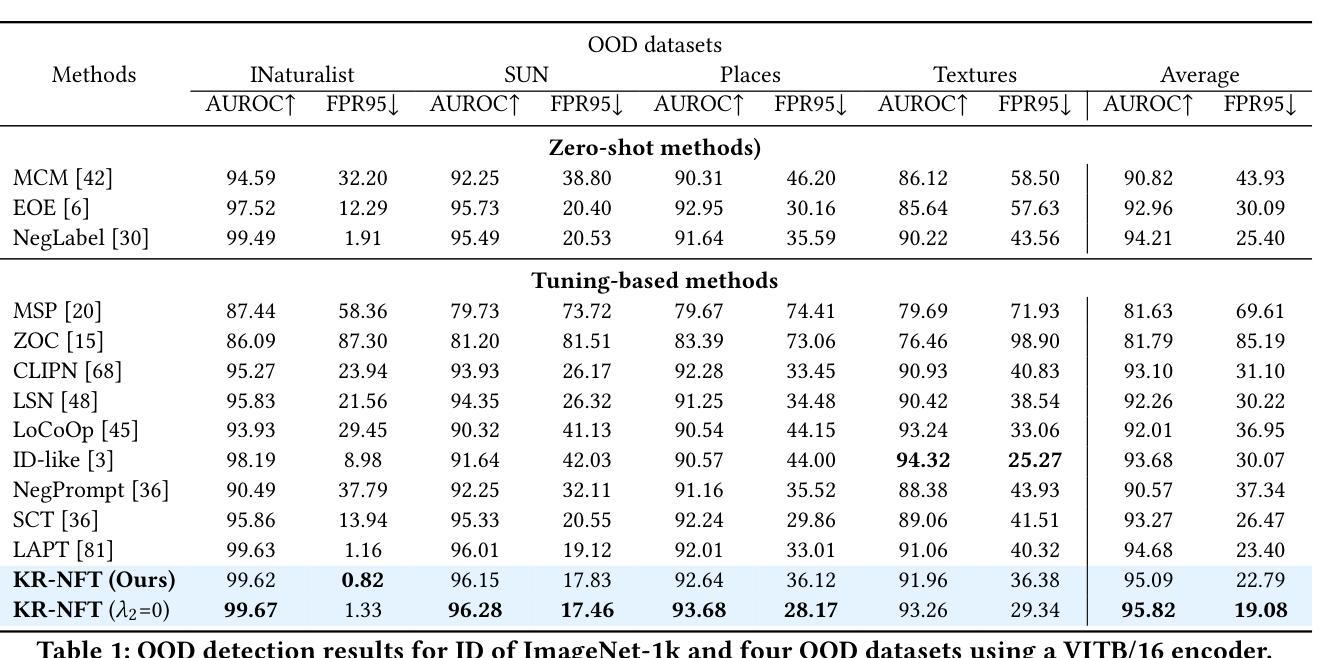
Knowledge Regularized Negative Feature Tuning of Vision-Language Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Wenjie Zhu, Yabin Zhang, Xin Jin, Wenjun Zeng, Lei Zhang
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for building reliable machine learning models. Although negative prompt tuning has enhanced the OOD detection capabilities of vision-language models, these tuned models often suffer from reduced generalization performance on unseen classes and styles. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method called Knowledge Regularized Negative Feature Tuning (KR-NFT), which integrates an innovative adaptation architecture termed Negative Feature Tuning (NFT) and a corresponding knowledge-regularization (KR) optimization strategy. Specifically, NFT applies distribution-aware transformations to pre-trained text features, effectively separating positive and negative features into distinct spaces. This separation maximizes the distinction between in-distribution (ID) and OOD images. Additionally, we introduce image-conditional learnable factors through a lightweight meta-network, enabling dynamic adaptation to individual images and mitigating sensitivity to class and style shifts. Compared to traditional negative prompt tuning, NFT demonstrates superior efficiency and scalability. To optimize this adaptation architecture, the KR optimization strategy is designed to enhance the discrimination between ID and OOD sets while mitigating pre-trained knowledge forgetting. This enhances OOD detection performance on trained ID classes while simultaneously improving OOD detection on unseen ID datasets. Notably, when trained with few-shot samples from ImageNet dataset, KR-NFT not only improves ID classification accuracy and OOD detection but also significantly reduces the FPR95 by 5.44% under an unexplored generalization setting with unseen ID categories. Codes can be found at \href{https://github.com/ZhuWenjie98/KRNFT}.
在构建可靠的机器学习模型时,离群分布(OOD)检测至关重要。尽管负提示调整增强了视觉语言模型的OOD检测能力,但这些调整后的模型往往在未见类别和风格上的泛化性能降低。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种名为知识正则负特征调整(KR-NFT)的新方法,它结合了名为负特征调整(NFT)的创新适应架构和相应的知识正则(KR)优化策略。具体而言,NFT对预训练的文本特征进行分布感知转换,有效地将正负特征分离到不同的空间。这种分离最大限度地提高了内分布(ID)和OOD图像之间的区别。此外,我们通过轻量级元网络引入图像条件可学习因子,实现动态适应个别图像并减轻对类别和风格变化的敏感性。与传统的负提示调整相比,NFT显示出更高的效率和可扩展性。为了优化此适应架构,KR优化策略旨在增强ID和OOD集之间的辨别力,同时减轻预训练知识的遗忘。这提高了训练ID类别上的OOD检测性能,同时改进了未见ID数据集上的OOD检测。值得注意的是,当使用来自ImageNet数据集的少量样本进行训练时,KR-NFT不仅提高了ID分类精度和OOD检测能力,而且在未见ID类别的未探索泛化设置下将FPR95降低了5.44%。代码可在https://github.com/ZhuWenjie98/KRNFT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ACMMM 2025
摘要
本文提出了针对机器学习模型中的OOD检测难题的解决方案,引入了知识正则化负特征调优(KR-NFT)这一新方法。它通过创新地引入负特征调优(NFT)架构和相应的知识正则化(KR)优化策略,解决了传统负提示调优在未见类别和风格上的泛化性能下降的问题。NFT通过对预训练文本特征进行分布感知转换,有效地将正负特征分离到不同的空间,最大化ID和OOD图像之间的区分。同时,通过轻量级元网络引入图像条件学习因子,实现动态适应个体图像并缓解类别和风格变化的影响。与传统的负提示调优相比,NFT表现出更高的效率和可扩展性。KR优化策略旨在优化这一适应架构,增强ID和OOD集之间的鉴别力,同时减少预训练知识的遗忘,从而在不损失ID分类准确性的前提下提高OOD检测性能。特别是在对ImageNet数据集进行少量样本训练的情况下,KR-NFT不仅提高了ID分类精度和OOD检测能力,而且在未见ID类别的情况下将FPR95降低了5.44%。代码可在相关链接中找到。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的方法KR-NFT,用于解决机器学习模型中的OOD检测问题。
- 通过负特征调优(NFT)架构将正负特征分离到不同的空间,增强了ID和OOD图像之间的区分。
- 引入图像条件学习因子,通过轻量级元网络实现动态适应个体图像。
- NFT相较于传统负提示调优展现出更高的效率和可扩展性。
- KR优化策略增强了ID和OOD集之间的鉴别力,并减少了预训练知识的遗忘。
- 在少量样本训练的情况下,KR-NFT显著提高OOD检测性能并降低FPR95。
点此查看论文截图

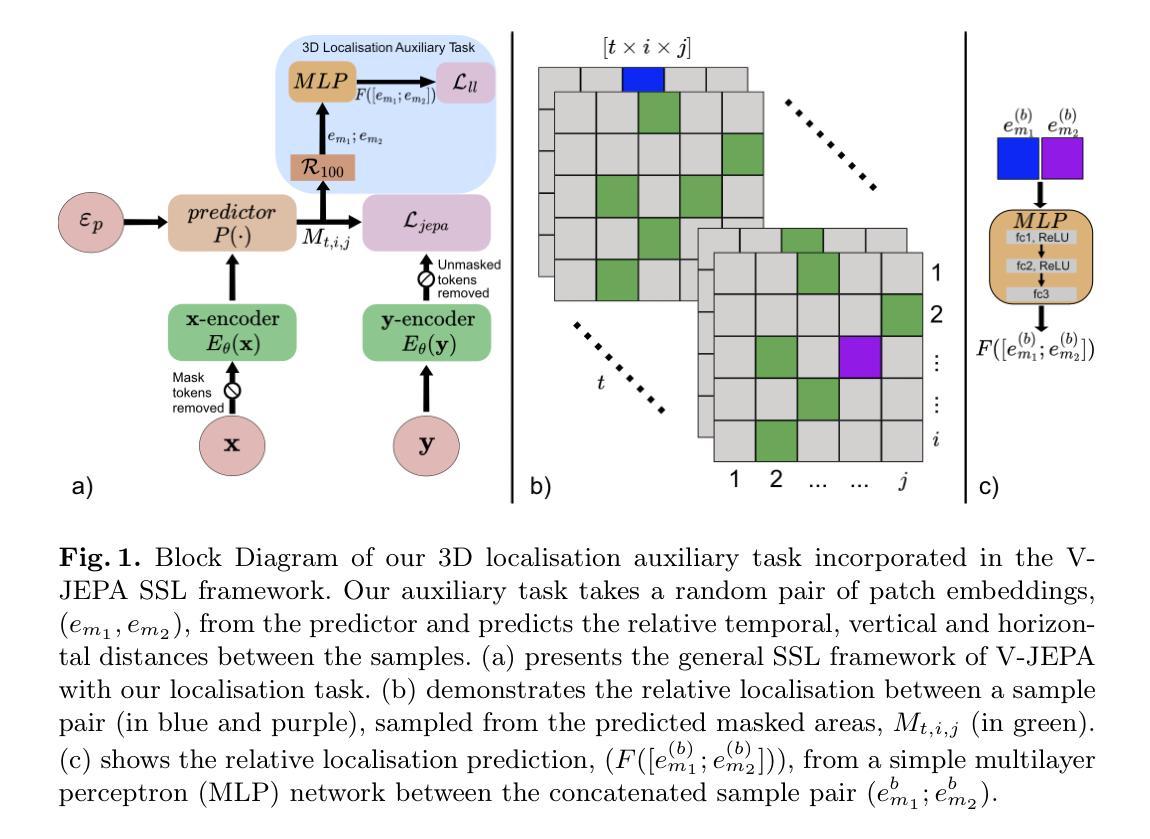
Self-Supervised Ultrasound-Video Segmentation with Feature Prediction and 3D Localised Loss
Authors:Edward Ellis, Robert Mendel, Andrew Bulpitt, Nasim Parsa, Michael F Byrne, Sharib Ali
Acquiring and annotating large datasets in ultrasound imaging is challenging due to low contrast, high noise, and susceptibility to artefacts. This process requires significant time and clinical expertise. Self-supervised learning (SSL) offers a promising solution by leveraging unlabelled data to learn useful representations, enabling improved segmentation performance when annotated data is limited. Recent state-of-the-art developments in SSL for video data include V-JEPA, a framework solely based on feature prediction, avoiding pixel level reconstruction or negative samples. We hypothesise that V-JEPA is well-suited to ultrasound imaging, as it is less sensitive to noisy pixel-level detail while effectively leveraging temporal information. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to adopt V-JEPA for ultrasound video data. Similar to other patch-based masking SSL techniques such as VideoMAE, V-JEPA is well-suited to ViT-based models. However, ViTs can underperform on small medical datasets due to lack of inductive biases, limited spatial locality and absence of hierarchical feature learning. To improve locality understanding, we propose a novel 3D localisation auxiliary task to improve locality in ViT representations during V-JEPA pre-training. Our results show V-JEPA with our auxiliary task improves segmentation performance significantly across various frozen encoder configurations, with gains up to 3.4% using 100% and up to 8.35% using only 10% of the training data.
在超声成像中,获取和标注大型数据集是一项挑战,因为存在对比度低、噪声高以及容易受伪影影响等问题。这个过程需要大量的时间和临床专业知识。自监督学习(SSL)利用无标签数据学习有用的表示,提供了一种有前景的解决方案,在标注数据有限的情况下,能够提高分割性能。最近视频数据自监督学习的最新发展包括V-JEPA,这是一个仅基于特征预测的框架,避免了像素级重建或负样本。我们假设V-JEPA非常适合超声成像,因为它对嘈杂的像素级细节不太敏感,同时能有效地利用时间信息。据我们所知,这是首次将V-JEPA用于超声视频数据的研究。与其他基于补丁的掩码SSL技术(如VideoMAE)类似,V-JEPA非常适合ViT模型。然而,由于缺乏归纳偏见、空间局部性有限以及缺乏层次特征学习,ViT在小医疗数据集上可能会表现不佳。为了提高对局部性的理解,我们提出了一种新型的3D定位辅助任务,以在V-JEPA预训练期间改善ViT表示的局部性。我们的结果表明,使用我们的辅助任务的V-JEPA在各种固定的编码器配置中显著提高了分割性能,使用100%的数据增益高达3.4%,而只使用10%的训练数据则高达8.35%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超声成像中采集和标注大规模数据集具有挑战性,因为存在低对比度、高噪声和易受到干扰的问题。这一过程需要耗费大量时间和临床专业知识。自监督学习(SSL)通过利用未标注数据学习有用的表示形式,为解决标注数据有限时的分割性能提升问题提供了有前景的解决方案。本研究首次将V-JEPA应用于超声视频数据,通过提出一个新型的三维定位辅助任务,改善了ViT模型在预训练过程中的局部理解问题。结果显示,结合辅助任务的V-JEPA在不同冻结编码器配置下均显著提高分割性能,使用全部训练数据时增益达3.4%,仅使用10%训练数据时增益达8.35%。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像数据集中获取和标注存在挑战,包括低对比度、高噪声和易受到干扰。
- 自监督学习(SSL)能利用未标注数据提升模型性能。
- V-JEPA适用于超声视频数据,对噪声像素级的细节不太敏感,同时能有效利用时间信息。
- V-JEPA结合ViT模型在超声视频数据处理上具有优势。
- ViT模型在小规模医疗数据集上可能会因缺乏归纳偏置、空间局限性和缺乏层次特征学习而表现不佳。
- 为改善ViT模型的局部理解,提出了一种新型的三维定位辅助任务。
点此查看论文截图

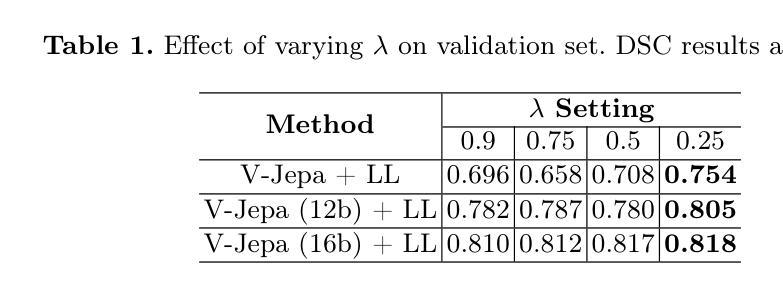
GRR-CoCa: Leveraging LLM Mechanisms in Multimodal Model Architectures
Authors:Jake R. Patock, Nicole Catherine Lewis, Kevin McCoy, Christina Gomez, Canling Chen, Lorenzo Luzi
State-of-the-art (SOTA) image and text generation models are multimodal models that have many similarities to large language models (LLMs). Despite achieving strong performances, leading foundational multimodal model architectures frequently lag behind the architectural sophistication of contemporary LLMs. We propose GRR-CoCa, an improved SOTA Contrastive Captioner (CoCa) model that incorporates Gaussian error gated linear units, root mean squared normalization, and rotary positional embedding into the textual decoders and the vision transformer (ViT) encoder. Each architectural modification has been shown to improve model performance in LLMs, but has yet to be adopted in CoCa. We benchmarked GRR-CoCa against Baseline CoCa, a model with the same modified textual decoders but with CoCa’s original ViT encoder. We used standard pretraining and fine-tuning workflows to benchmark the models on contrastive and generative tasks. Our GRR-CoCa significantly outperformed Baseline CoCa on the pretraining dataset and three diverse fine-tuning datasets. Pretraining improvements were 27.25% in contrastive loss, 3.71% in perplexity, and 7.15% in CoCa loss. The average fine-tuning improvements were 13.66% in contrastive loss, 5.18% in perplexity, and 5.55% in CoCa loss. We show that GRR-CoCa’s modified architecture improves performance and generalization across vision-language domains.
最先进的图像和文本生成模型是多模态模型,它们与大型语言模型(LLM)有许多相似之处。尽管性能强劲,但领先的基础多模态模型架构通常落后于当代LLM的架构复杂性。我们提出了GRR-CoCa,这是一个改进的最先进对比字幕模型(CoCa),它结合了高斯误差门控线性单元、均方根归一化和旋转位置嵌入到文本解码器和视觉变压器(ViT)编码器。在LLM中,每项架构修改都被证明可以提高模型性能,但尚未在CoCa中使用。我们将GRR-CoCa与带有相同修改文本解码器但使用CoCa原始ViT编码器的基线CoCa进行了比较。我们使用标准的预训练和微调工作流程,在对比和生成任务上对模型进行基准测试。我们的GRR-CoCa在预训练数据集和三组不同的微调数据集上显著优于基线CoCa。预训练改进包括对比损失降低27.25%,困惑度降低3.71%,CoCa损失降低7.15%。平均微调改进包括对比损失降低13.66%,困惑度降低5.18%,CoCa损失降低5.55%。我们证明GRR-CoCa的改进架构提高了性能和跨视觉语言领域的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 figures
摘要
GRR-CoCa模型在SOTA图像和文本生成模型中引入了多项技术改进,如高斯误差门控线性单元、均方根归一化和旋转位置嵌入等,这些技术改进提高了模型的性能。实验结果表明,GRR-CoCa在预训练数据集和三个不同的微调数据集上的表现均优于基线CoCa模型。这些改进在对比损失、困惑度和CoCa损失等方面都有显著的提升。本研究表明GRR-CoCa的改进架构提高了性能和跨视觉语言领域的泛化能力。
关键见解
- GRR-CoCa模型是对现有SOTA图像和文本生成模型的改进,它结合了多项技术提升,如高斯误差门控线性单元等。
- 与基线CoCa模型相比,GRR-CoCa模型在预训练数据集上的表现有显著提升,对比损失降低了27.25%,困惑度降低了3.71%,CoCa损失降低了7.15%。
- 在微调数据集上,GRR-CoCa的平均表现优于基线模型,对比损失平均提高了13.66%,困惑度平均降低了5.18%,CoCa损失平均降低了5.55%。
- GRR-CoCa模型在视觉和语言领域的性能提升和泛化能力得到了验证。这表明改进后的架构能够有效地提高模型的效率和准确性。
- 此研究展示了如何将一些在大型语言模型中表现良好的技术改进应用到图像和文本生成模型中,这为进一步改进相关研究提供了新思路。
- GRR-CoCa模型的引入有助于缩小当前最先进的多媒体模型与当代大型语言模型之间的架构差距。这对于创建更复杂的多媒体应用至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

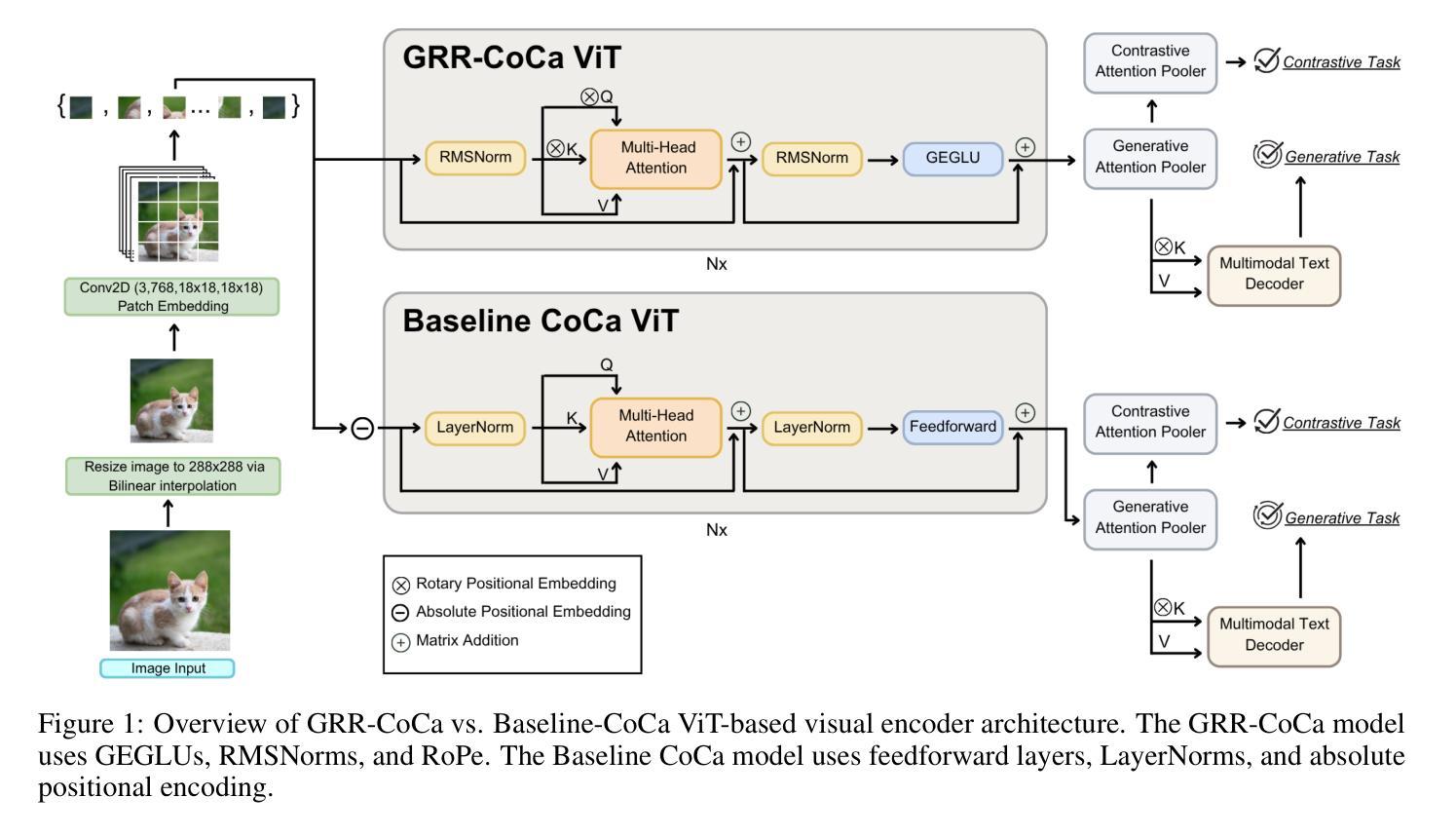
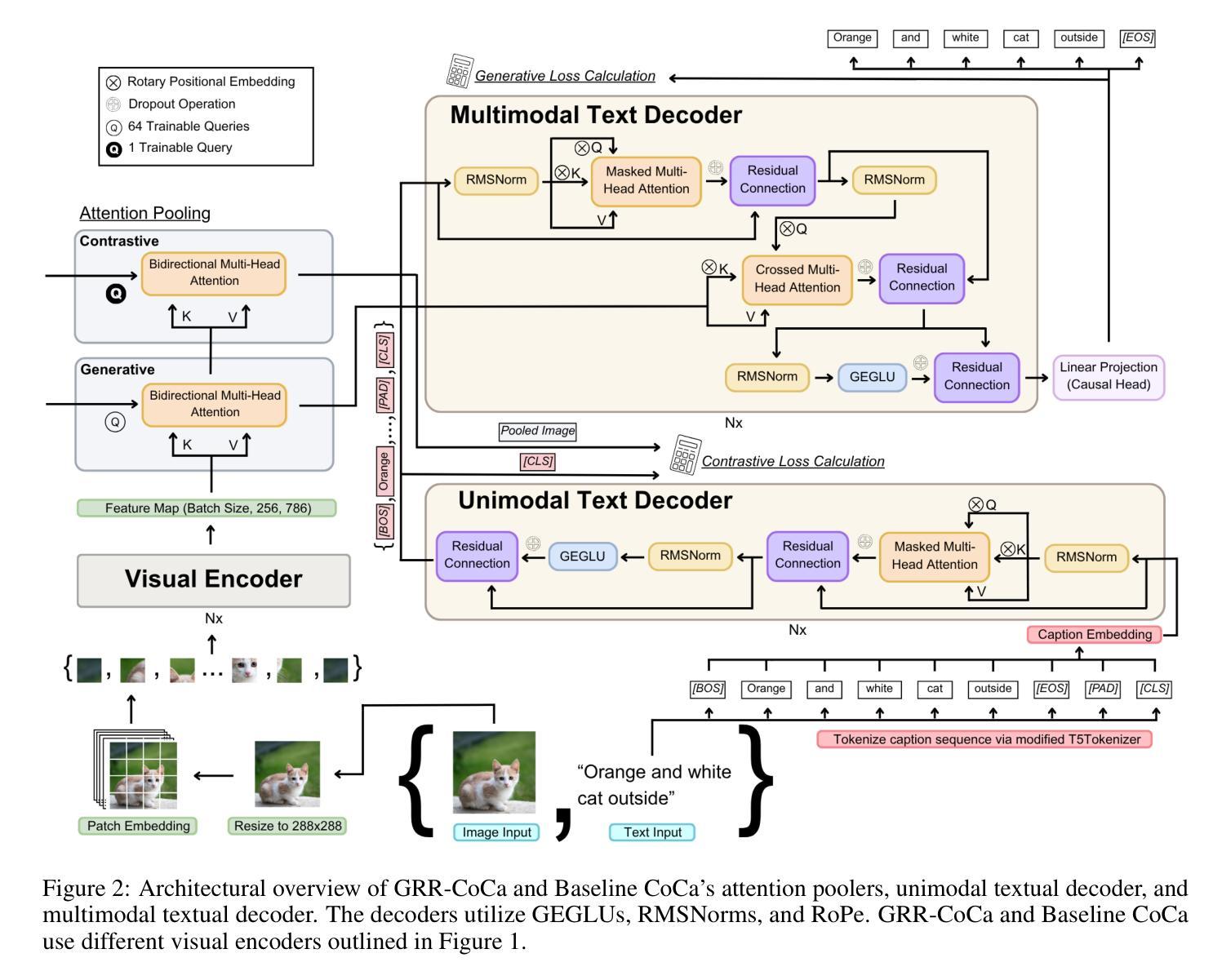
Dual-branch Prompting for Multimodal Machine Translation
Authors:Jie Wang, Zhendong Yang, Liansong Zong, Xiaobo Zhang, Dexian Wang, Ji Zhang
Multimodal Machine Translation (MMT) typically enhances text-only translation by incorporating aligned visual features. Despite the remarkable progress, state-of-the-art MMT approaches often rely on paired image-text inputs at inference and are sensitive to irrelevant visual noise, which limits their robustness and practical applicability. To address these issues, we propose D2P-MMT, a diffusion-based dual-branch prompting framework for robust vision-guided translation. Specifically, D2P-MMT requires only the source text and a reconstructed image generated by a pre-trained diffusion model, which naturally filters out distracting visual details while preserving semantic cues. During training, the model jointly learns from both authentic and reconstructed images using a dual-branch prompting strategy, encouraging rich cross-modal interactions. To bridge the modality gap and mitigate training-inference discrepancies, we introduce a distributional alignment loss that enforces consistency between the output distributions of the two branches. Extensive experiments on the Multi30K dataset demonstrate that D2P-MMT achieves superior translation performance compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
多模态机器翻译(MMT)通常通过融入对齐的视觉特征来增强纯文本翻译。尽管取得了显著的进步,但最先进的MMT方法通常在推理阶段依赖于配对的图像文本输入,并对不相关的视觉噪声敏感,这限制了它们的稳健性和实际应用能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了D2P-MMT,这是一种基于扩散的双分支提示框架,用于实现稳健的视觉引导翻译。具体来说,D2P-MMT仅需要源文本和由预训练扩散模型生成的重建图像,这可以自然地过滤掉令人分心的视觉细节,同时保留语义线索。在训练过程中,模型使用双分支提示策略从真实和重建的图像中学习,鼓励丰富的跨模态交互。为了缩小模态差距并减轻训练与推理之间的差异,我们引入了一种分布对齐损失,以强制两个分支的输出分布保持一致。在Multi30K数据集上的大量实验表明,与现有最先进的方法相比,D2P-MMT实现了卓越的翻译性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态机器翻译(MMT)通过引入对齐的视觉特征来增强纯文本翻译。然而,最先进的MMT方法通常依赖于推理阶段的配对图像文本输入,并对不相关的视觉噪声敏感,这限制了其稳健性和实际应用。为解决这些问题,我们提出了基于扩散的双分支提示框架D2P-MMT,用于稳健的视觉指导翻译。具体而言,D2P-MMT仅需要源文本和由预训练扩散模型生成的重构图像,该图像可自然过滤掉令人分心的视觉细节,同时保留语义线索。在训练过程中,模型采用双分支提示策略,从真实和重构的图像中学习,促进丰富的跨模态交互。为了缩小模态差距并减轻训练与推理之间的差异,我们引入了一种分布对齐损失,以强制两个分支的输出分布保持一致。在Multi30K数据集上的广泛实验表明,D2P-MMT相较于现有最先进的方法实现了更优越的翻译性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态机器翻译(MMT)结合了文本和视觉特征以增强翻译性能。
- 当前MMT方法对图像文本输入的配对依赖性强,且对视觉噪声敏感。
- D2P-MMT框架通过扩散模型生成的重构图像进行翻译,以提高稳健性。
- D2P-MMT利用双分支提示策略训练模型,促进跨模态交互。
- 引入分布对齐损失以缩小模态差距和训练与推理差异。
- D2P-MMT在Multi30K数据集上实现了优越的翻译性能。
- D2P-MMT方法有助于推动机器翻译领域的发展,特别是在处理含噪声或复杂视觉信息的场景。
点此查看论文截图

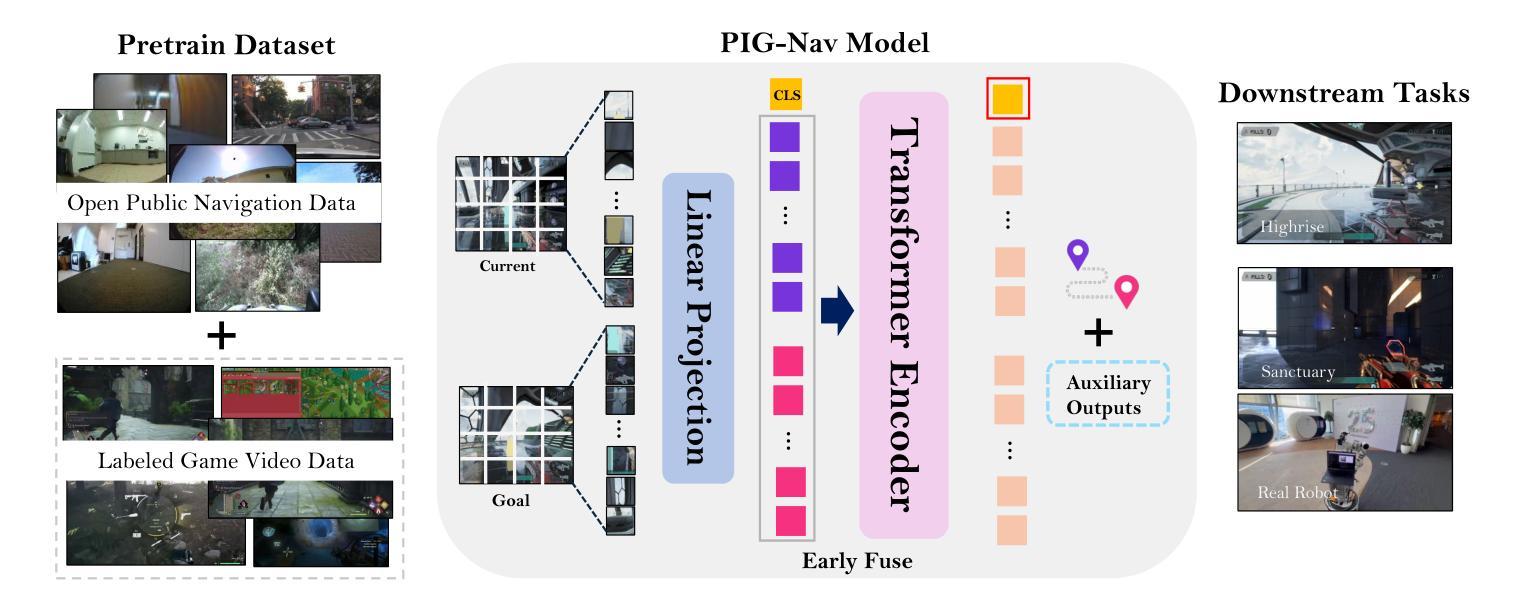
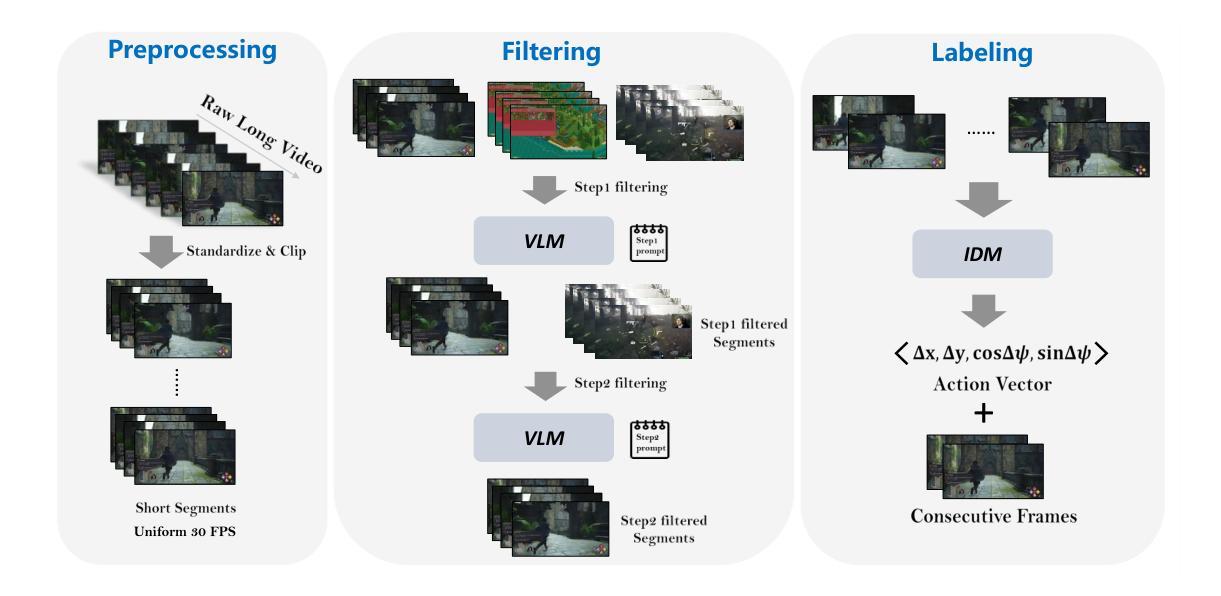
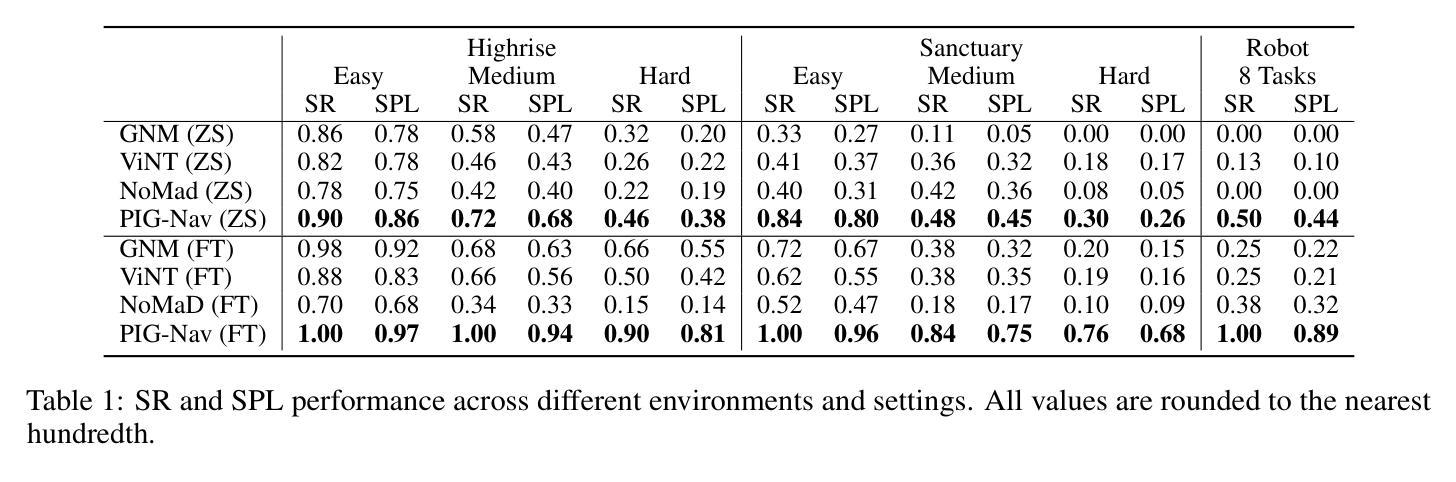
PIG-Nav: Key Insights for Pretrained Image Goal Navigation Models
Authors:Jiansong Wan, Chengming Zhou, Jinkua Liu, Xiangge Huang, Xiaoyu Chen, Xiaohan Yi, Qisen Yang, Baiting Zhu, Xin-Qiang Cai, Lixing Liu, Rushuai Yang, Chuheng Zhang, Sherif Abdelfattah, Hayong Shin, Pushi Zhang, Li Zhao, Jiang Bian
Recent studies have explored pretrained (foundation) models for vision-based robotic navigation, aiming to achieve generalizable navigation and positive transfer across diverse environments while enhancing zero-shot performance in unseen settings. In this work, we introduce PIG-Nav (Pretrained Image-Goal Navigation), a new approach that further investigates pretraining strategies for vision-based navigation models and contributes in two key areas. Model-wise, we identify two critical design choices that consistently improve the performance of pretrained navigation models: (1) integrating an early-fusion network structure to combine visual observations and goal images via appropriately pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT) image encoder, and (2) introducing suitable auxiliary tasks to enhance global navigation representation learning, thus further improving navigation performance. Dataset-wise, we propose a novel data preprocessing pipeline for efficiently labeling large-scale game video datasets for navigation model training. We demonstrate that augmenting existing open navigation datasets with diverse gameplay videos improves model performance. Our model achieves an average improvement of 22.6% in zero-shot settings and a 37.5% improvement in fine-tuning settings over existing visual navigation foundation models in two complex simulated environments and one real-world environment. These results advance the state-of-the-art in pretrained image-goal navigation models. Notably, our model maintains competitive performance while requiring significantly less fine-tuning data, highlighting its potential for real-world deployment with minimal labeled supervision.
最近的研究探讨了基于视觉的机器人导航的预训练(基础)模型,旨在实现在不同环境下的可推广导航和正向迁移,同时提高在未见场景中的零样本性能。在这项工作中,我们介绍了PIG-Nav(预训练图像目标导航),这是一种进一步探索基于视觉的导航模型的预训练策略的新方法,并在两个关键领域有所贡献。在模型方面,我们确定了两种关键的设计选择,这些选择一致地提高了预训练导航模型的性能:(1)采用早期融合网络结构,通过适当预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)图像编码器将视觉观察和目标图像相结合;(2)引入合适的辅助任务以增强全局导航表示学习,从而进一步提高导航性能。在数据集方面,我们提出了一种用于高效标注大规模游戏视频数据集的新数据预处理管道,用于训练导航模型。我们证明,通过增强现有开放导航数据集与多种游戏视频的融合,可以提高模型性能。我们的模型在两个复杂的模拟环境和一个真实世界环境中,在零样本设置上平均提高了22.6%,在微调设置上提高了37.5%,超越了现有视觉导航基础模型的性能。这些结果代表了预训练图像目标导航模型的最先进技术。值得注意的是,我们的模型在需要更少的微调数据的同时保持了竞争力,这凸显了其在最小标注监督下在现实世界部署的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PIG-Nav(预训练图像目标导航)新方法,该方法进一步研究基于视觉的导航模型的预训练策略,并在两个关键领域做出贡献。模型方面,通过整合早期融合网络结构和引入合适的辅助任务来提高预训练导航模型的性能。数据集方面,提出了用于导航模型训练的大型游戏视频数据集的新型数据预处理管道,并证明其对模型性能的改进。相较于现有的视觉导航预训练模型,该模型在模拟环境和真实世界环境中均有显著提升,特别是在零样本和微调场景下。这表明PIG-Nav有望在实际应用中实现更高效和精确的导航。
Key Takeaways
- PIG-Nav是一个针对图像目标导航的预训练模型,它通过探索新的预训练策略来提升模型的性能。
- 在模型方面,引入早期融合网络结构以及合适的辅助任务能够提升预训练导航模型的性能。
- 在数据集方面,通过提出新的数据预处理管道来高效标注大型游戏视频数据集用于训练导航模型。
- 实验结果表明,与其他视觉导航预训练模型相比,PIG-Nav在复杂模拟环境和真实世界环境中均有显著提高的导航性能。特别是在零样本和微调场景下,平均提升了22.6%和37.5%。
点此查看论文截图

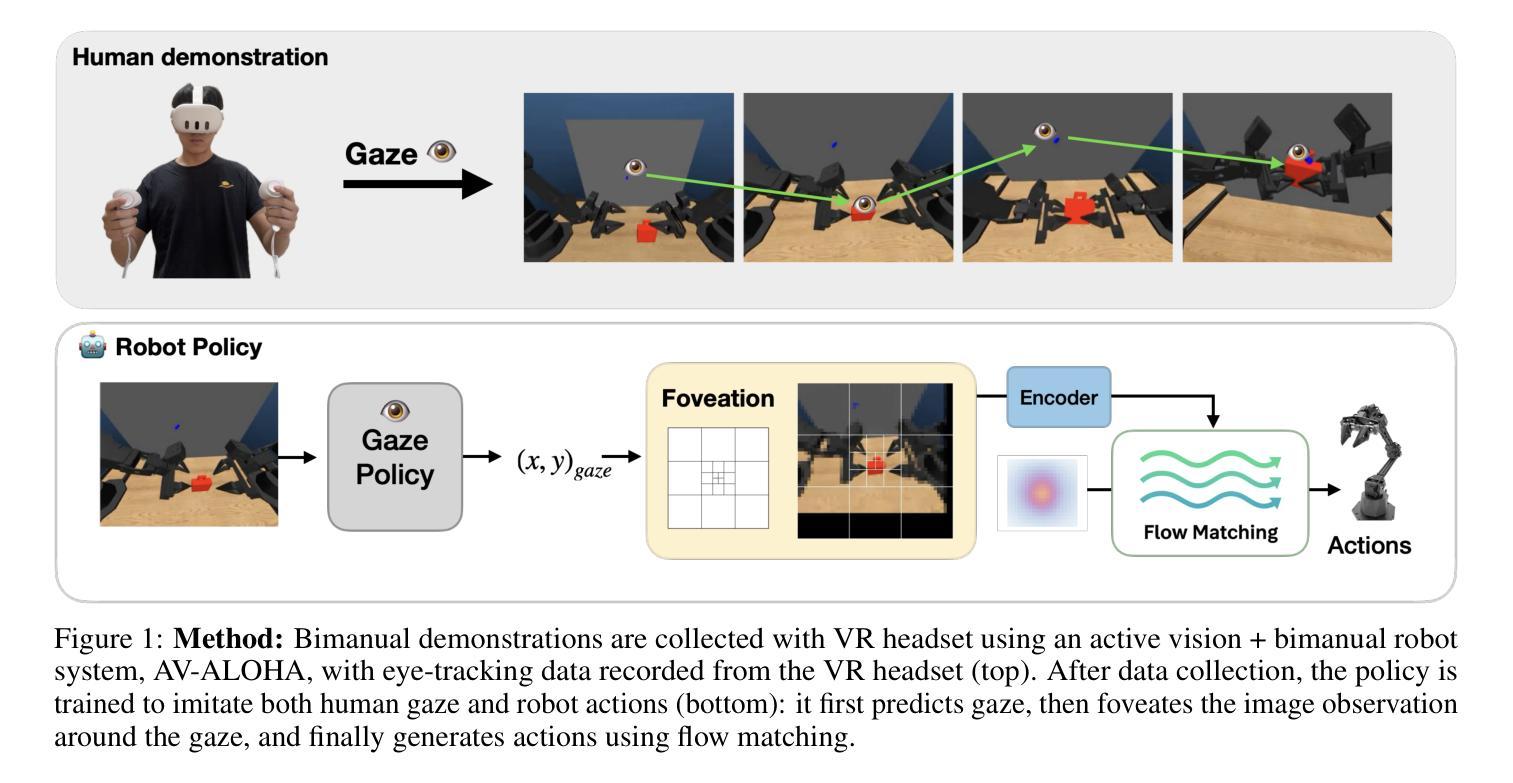
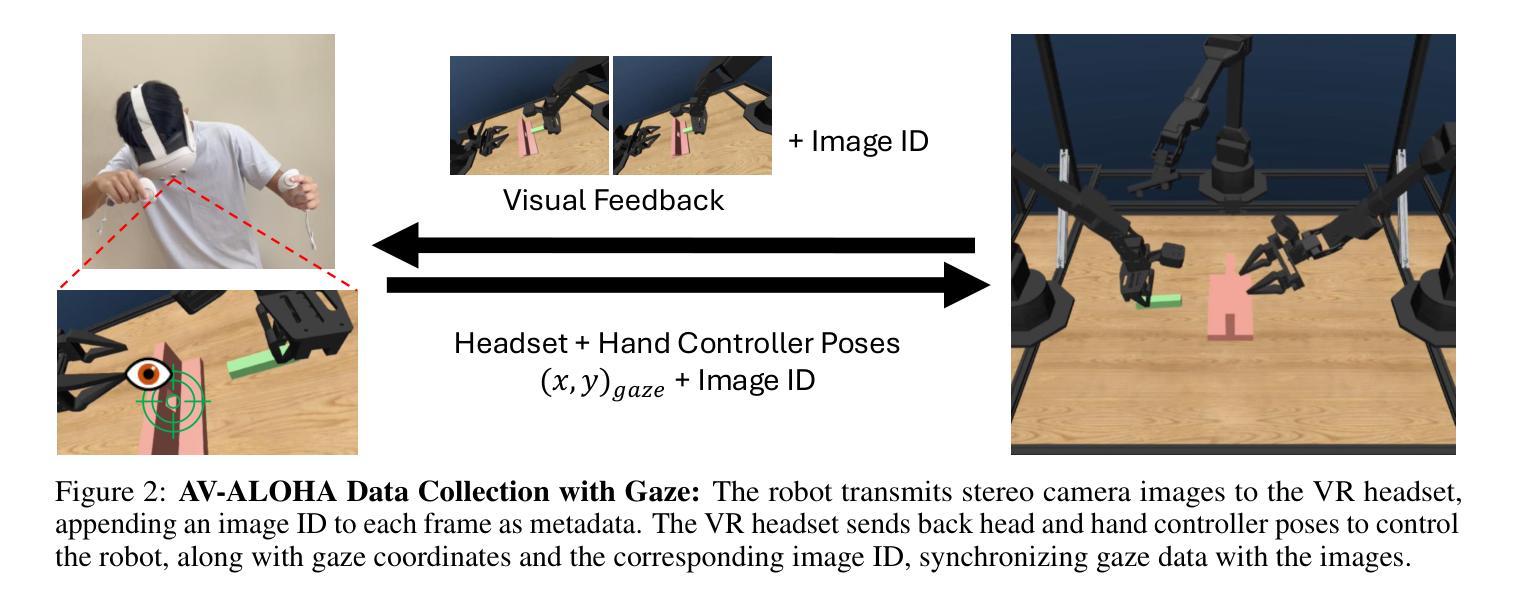
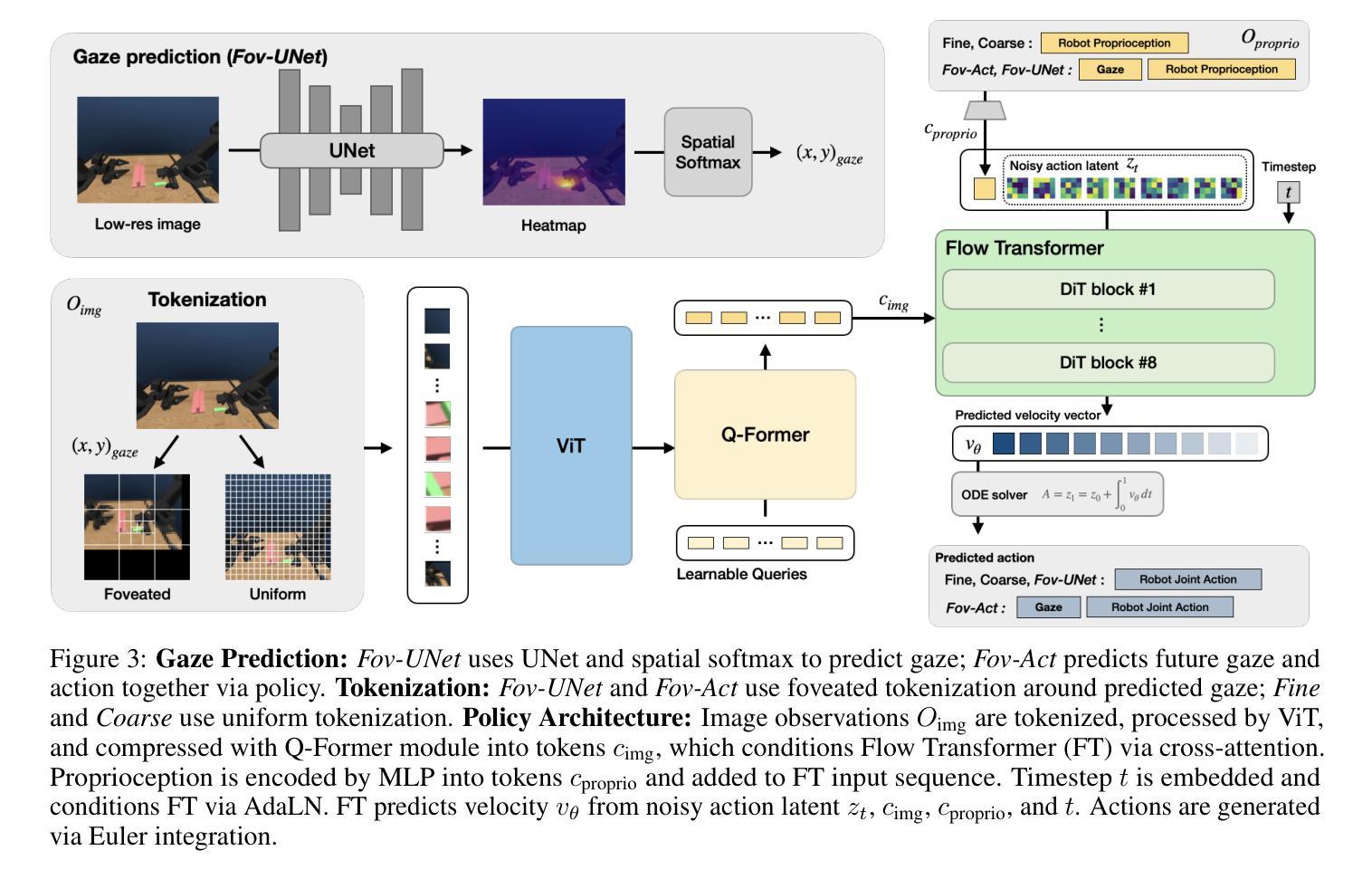
Look, Focus, Act: Efficient and Robust Robot Learning via Human Gaze and Foveated Vision Transformers
Authors:Ian Chuang, Andrew Lee, Dechen Gao, Jinyu Zou, Iman Soltani
Human vision is a highly active process driven by gaze, which directs attention and fixation to task-relevant regions and dramatically reduces visual processing. In contrast, robot learning systems typically rely on passive, uniform processing of raw camera images. In this work, we explore how incorporating human-like active gaze into robotic policies can enhance both efficiency and performance. We build on recent advances in foveated image processing and apply them to an Active Vision robot system that emulates both human head movement and eye tracking. Extending prior work on the AV-ALOHA robot simulation platform, we introduce a framework for simultaneously collecting eye-tracking data and robot demonstrations from a human operator as well as a simulation benchmark and dataset for training robot policies that incorporate human gaze. Given the widespread use of Vision Transformers (ViTs) in robot learning, we integrate gaze information into ViTs using a foveated patch tokenization scheme inspired by recent work in image segmentation. Compared to uniform patch tokenization, this significantly reduces the number of tokens-and thus computation-without sacrificing visual fidelity near regions of interest. We also explore two approaches to gaze imitation and prediction from human data. The first is a two-stage model that predicts gaze to guide foveation and action; the second integrates gaze into the action space, allowing the policy to jointly predict gaze and actions end-to-end. Our results show that our method for foveated robot vision not only drastically reduces computational overhead, but also improves performance for high precision tasks and robustness to unseen distractors. Together, these findings suggest that human-inspired visual processing offers a useful inductive bias for robotic vision systems. https://ian-chuang.github.io/gaze-av-aloha/
人类视觉是一个由目光驱动的积极过程,它能够将注意力集中在与任务相关的区域,并极大地减少视觉处理。相比之下,机器人的学习系统通常依赖于对原始相机图像的被动均匀处理。在这项工作中,我们探讨了将人类式的主动目光融入机器人策略如何增强效率和性能。我们基于最新的焦点图像处理技术的进展,将其应用于模拟人类头部运动和眼球追踪的主动视觉机器人系统。在AV-ALOHA机器人仿真平台的前期工作基础上,我们引入了一个框架,可以同时从人类操作者那里收集眼动数据和机器人演示数据,以及一个模拟基准和用于训练融入人类目光的机器人策略的数据集。考虑到Vision Transformers(ViTs)在机器人学习中的广泛应用,我们将目光信息融入ViTs,采用一种受最新图像分割工作启发的焦点补丁标记方案。与均匀的补丁标记相比,这显著减少了标记的数量(因此也减少了计算),同时不会牺牲感兴趣区域的视觉保真度。我们还探索了两种从人类数据中模仿和预测目光的方法。第一种是预测目光以指导焦点和行动的两阶段模型;第二种是将目光整合到动作空间,使策略能够端到端地预测目光和动作。我们的结果表明,我们的机器人视觉方法不仅极大地减少了计算开销,而且提高了高精度任务的性能和未见干扰项的稳健性。总的来说,这些发现表明,人类启发的视觉处理为机器人视觉系统提供了有用的先验知识。详情访问:https://ian-chuang.github.io/gaze-av-aloha/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures
Summary
机器人视觉系统通常依赖于被动、均匀处理原始相机图像,与人类活跃、选择性关注的视觉处理方式形成对比。本研究探索了将人类式的主动注视融入机器人策略,以提高效率和性能。研究基于最近关于凝视图像处理的进展,将其应用于模拟人类头部运动和眼球追踪的主动视觉机器人系统。研究扩展了AV-ALOHA机器人仿真平台,引入了一个框架,可以同时收集来自人类操作员的眼动数据和机器人演示数据,以及用于训练融入人类注视的机器人策略仿真基准和数据集。结合机器人学习中广泛使用的Vision Transformers(ViTs),研究通过一种受图像分割最新工作启发的凝视斑块标记方案,将注视信息融入ViTs。与均匀斑块标记相比,这显著减少了令牌数量,从而减少了计算量,同时在不牺牲感兴趣区域附近视觉保真度的情况下实现了这一点。此外,该研究还探索了两种从人类数据中模仿和预测注视的方法。第一种是预测注视以指导观察和行动的两阶段模型;第二种是将注视整合到动作空间,使策略能够端到端地联合预测注视和动作。结果不仅大大降低了计算开销,而且在执行高精密任务和应对未见干扰物时提高了性能。这表明人类启发式的视觉处理为机器人视觉系统提供了有用的先验知识。
Key Takeaways
- 人类视觉是一个活跃的过程,通过注视来指导注意力和固定任务相关区域,这显著减少了视觉处理。
- 现有机器人系统大多依赖于被动、均匀的图像处理方式,本研究探索了融入人类主动注视的方式来提高机器人的效率和性能。
- 通过结合最新的凝视图像处理技术和AV-ALOHA机器人仿真平台,研究展示了如何同时收集眼动数据和机器人演示数据。
- 引入了基于凝视的斑块标记方案,将其融入Vision Transformers(ViTs),以减少计算量并维持感兴趣区域的视觉保真度。
- 通过实验验证了融入人类注视信息的机器人视觉系统对于高精密任务和应对未见干扰物时的性能提升。
- 研究提出了两种从人类数据中模仿和预测注视的方法:一种是两阶段模型,另一种是整合注视到动作空间的端到端联合预测模型。
点此查看论文截图

Smart Eyes for Silent Threats: VLMs and In-Context Learning for THz Imaging
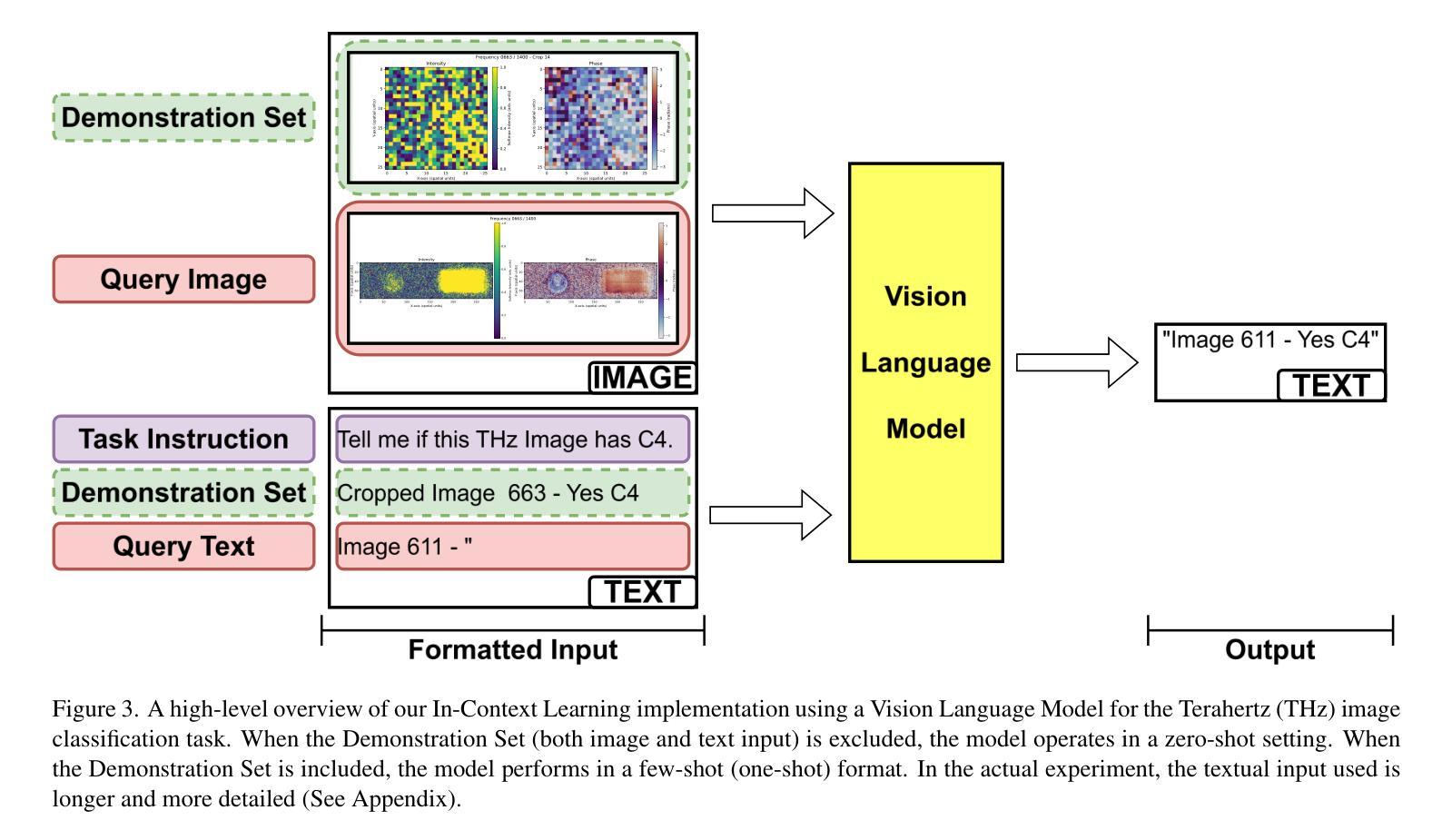
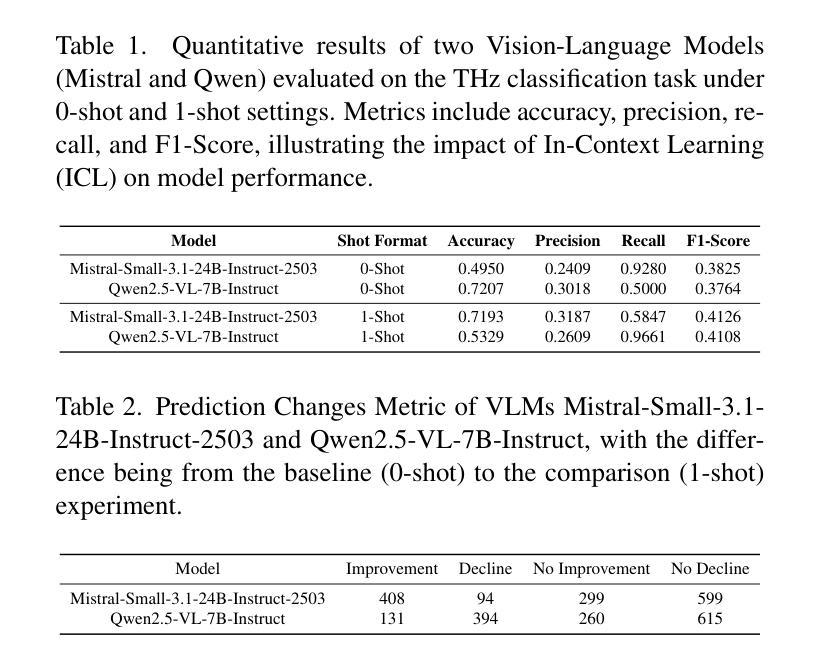
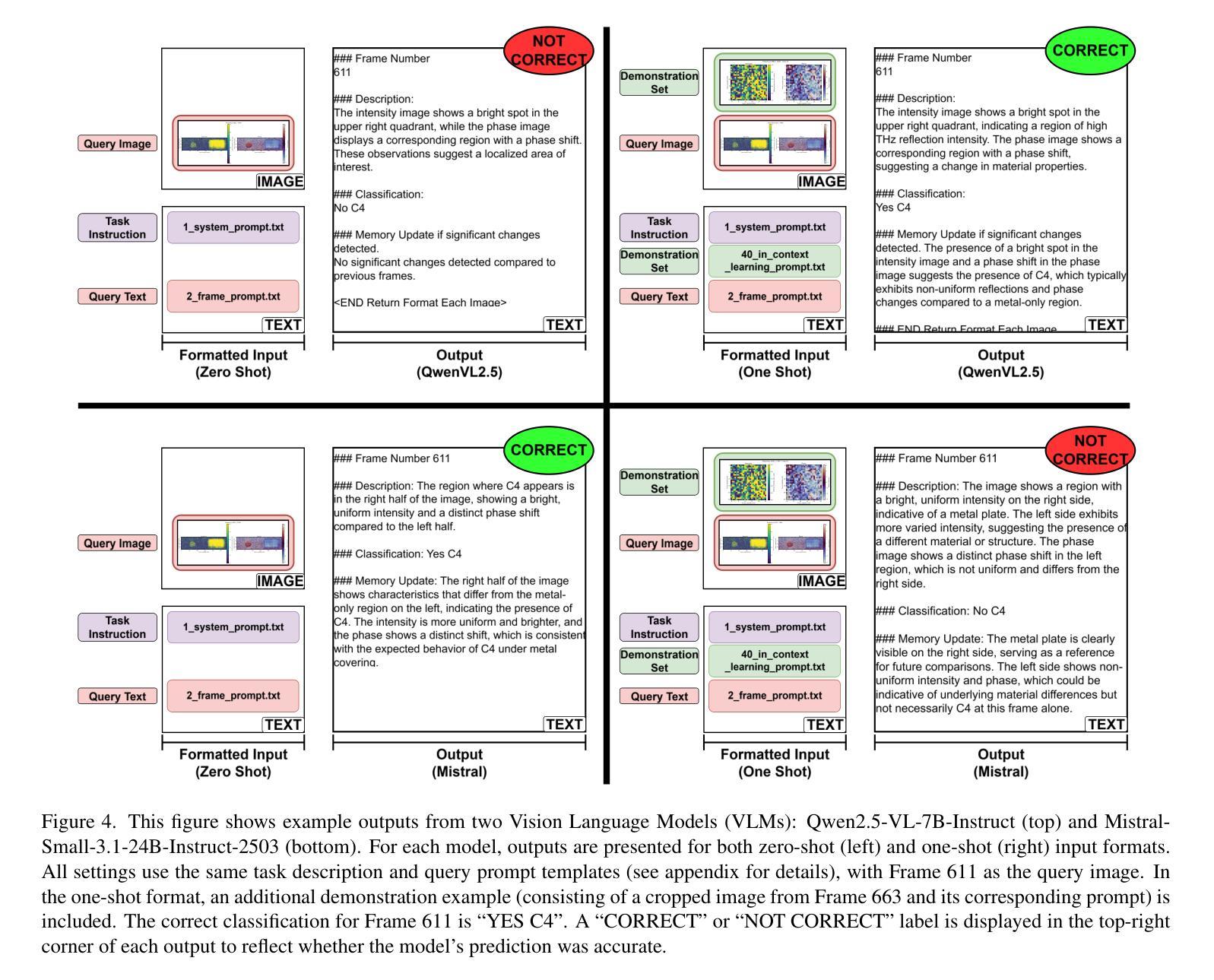
Authors:Nicolas Poggi, Shashank Agnihotri, Margret Keuper
Terahertz (THz) imaging enables non-invasive analysis for applications such as security screening and material classification, but effective image classification remains challenging due to limited annotations, low resolution, and visual ambiguity. We introduce In-Context Learning (ICL) with Vision-Language Models (VLMs) as a flexible, interpretable alternative that requires no fine-tuning. Using a modality-aligned prompting framework, we adapt two open-weight VLMs to the THz domain and evaluate them under zero-shot and one-shot settings. Our results show that ICL improves classification and interpretability in low-data regimes. This is the first application of ICL-enhanced VLMs to THz imaging, offering a promising direction for resource-constrained scientific domains. Code: \href{https://github.com/Nicolas-Poggi/Project_THz_Classification/tree/main}{GitHub repository}.
太赫兹(THz)成像能够实现安全检查和材料分类等应用中的无创分析,但由于标注有限、分辨率低和视觉模糊,有效的图像分类仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了基于视觉语言模型的上下文学习(ICL),作为一种无需精细调整的灵活、可解释的替代方案。通过使用模态对齐提示框架,我们适应了两个开源的VLM到太赫兹领域,并在零样本和单样本设置下进行了评估。结果表明,ICL在低数据情况下提高了分类和可解释性。这是首次将增强型ICL应用于太赫兹成像的VLM应用,为资源受限的科学领域提供了有前景的研究方向。代码:\href{https://github.com/Nicolas-Poggi/Project_THz_Classification/tree/main}{GitHub仓库}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了太赫兹(THz)成像在非侵入性分析中的应用,如安检和物料分类。针对THz成像中由于标注有限、分辨率低和视觉模糊导致的图像分类挑战,本文引入了基于语境学习(ICL)的跨视觉语言模型(VLMs)作为无需精细调整的灵活、可解释的替代方案。通过使用模态对齐提示框架,本文适应了两个开放权重的VLMs到太赫兹领域,并在零样本和少样本场景下进行了评估。结果显示,ICL在数据稀缺的情况下提高了分类和解释性。这是首次将ICL增强的VLMs应用于太赫兹成像,为资源受限的科学领域提供了有前景的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 太赫兹(THz)成像在安检和物料分类等非侵入性分析中具有广泛应用。
- 由于标注有限、分辨率低和视觉模糊等问题,THz图像分类面临挑战。
- 引入基于语境学习(ICL)的跨视觉语言模型(VLMs)作为解决方案。
- 模态对齐提示框架用于适应VLMs到太赫兹领域。
- 在零样本和少样本场景下评估了VLMs的表现。
- ICL提高了在数据稀缺情况下的分类和解释性能。
点此查看论文截图

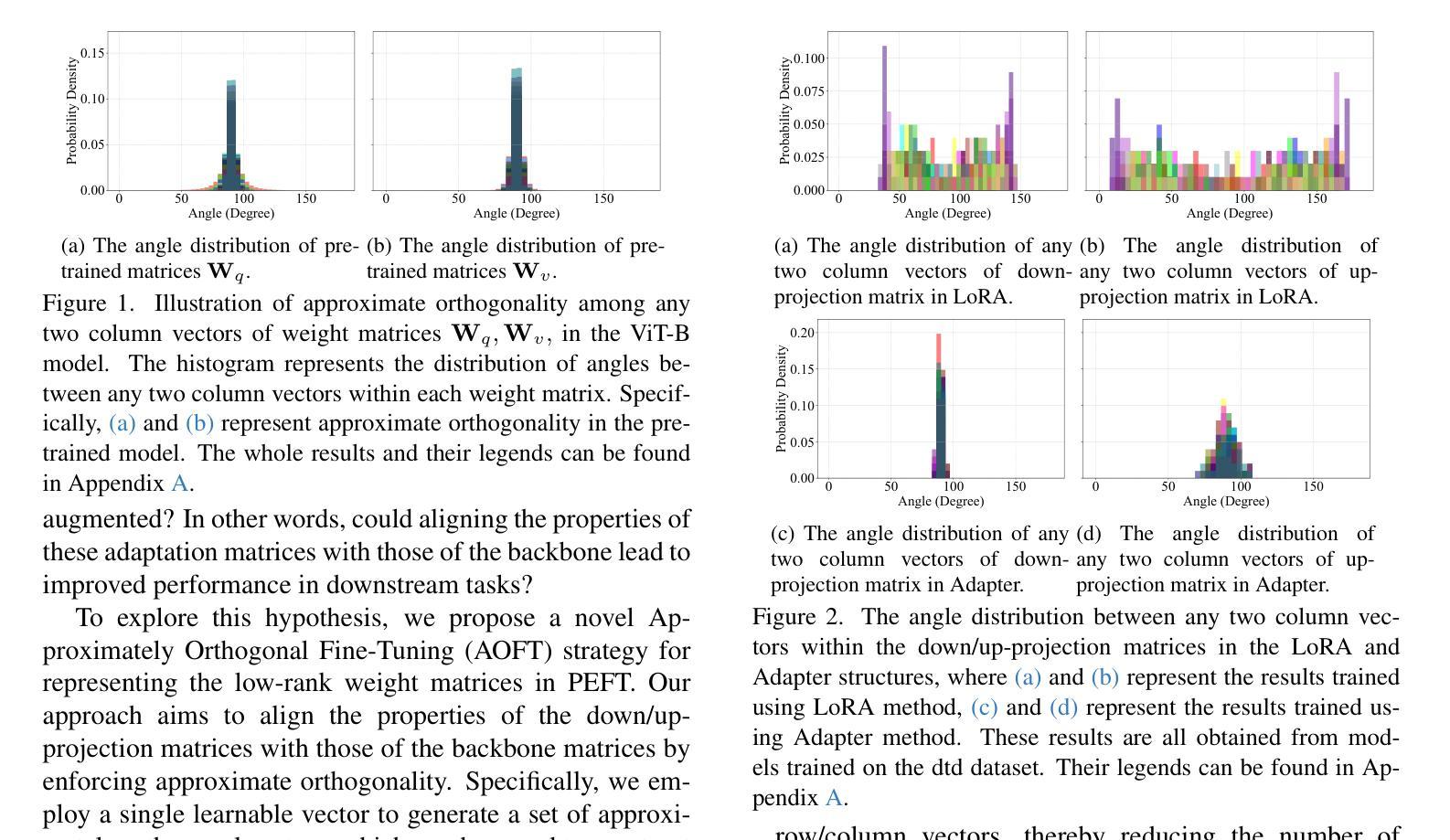
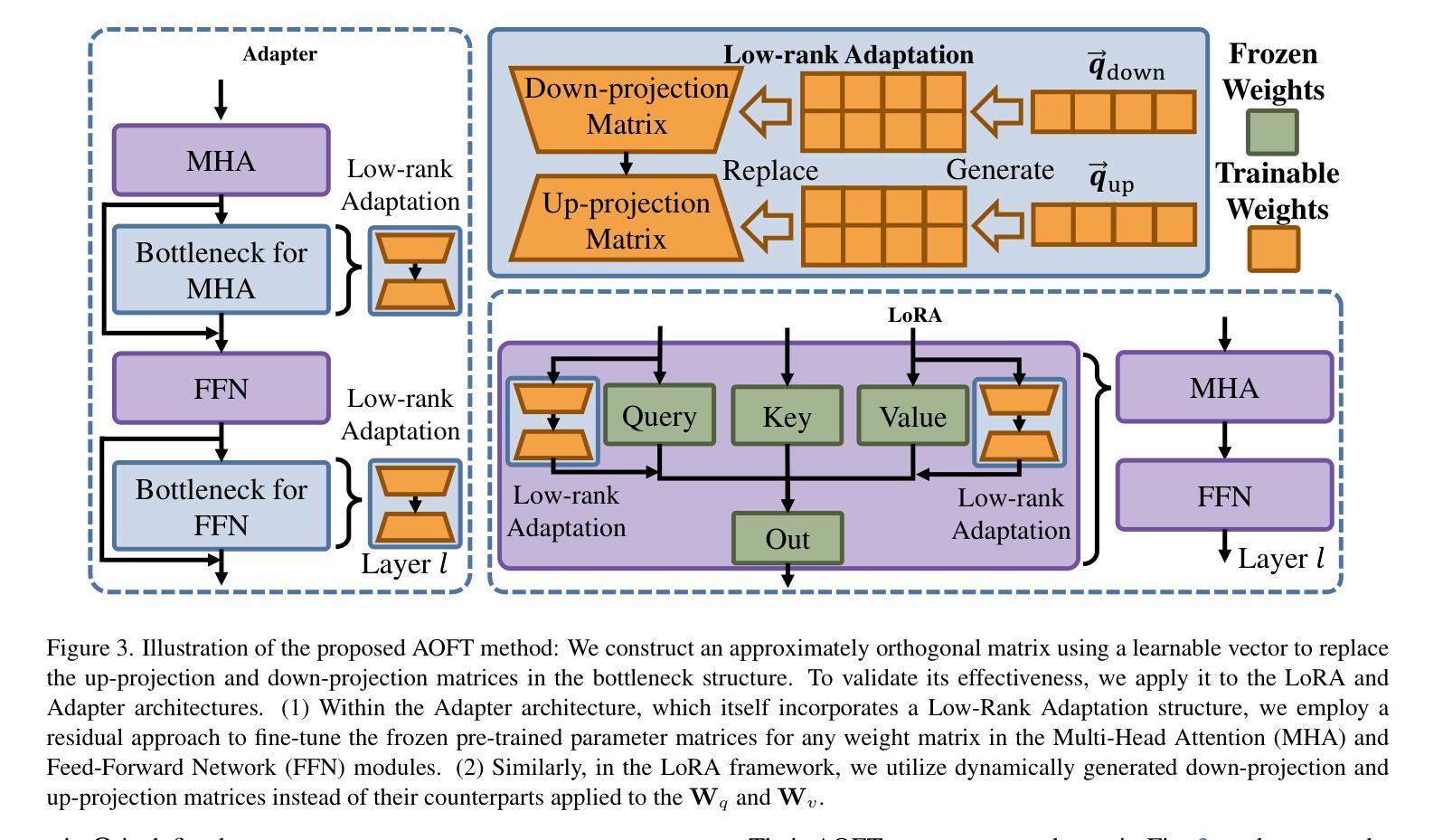
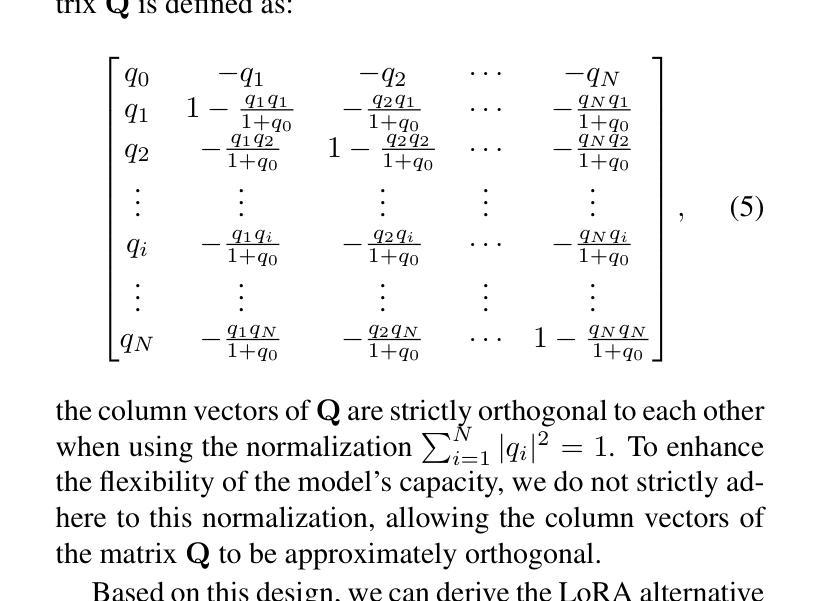
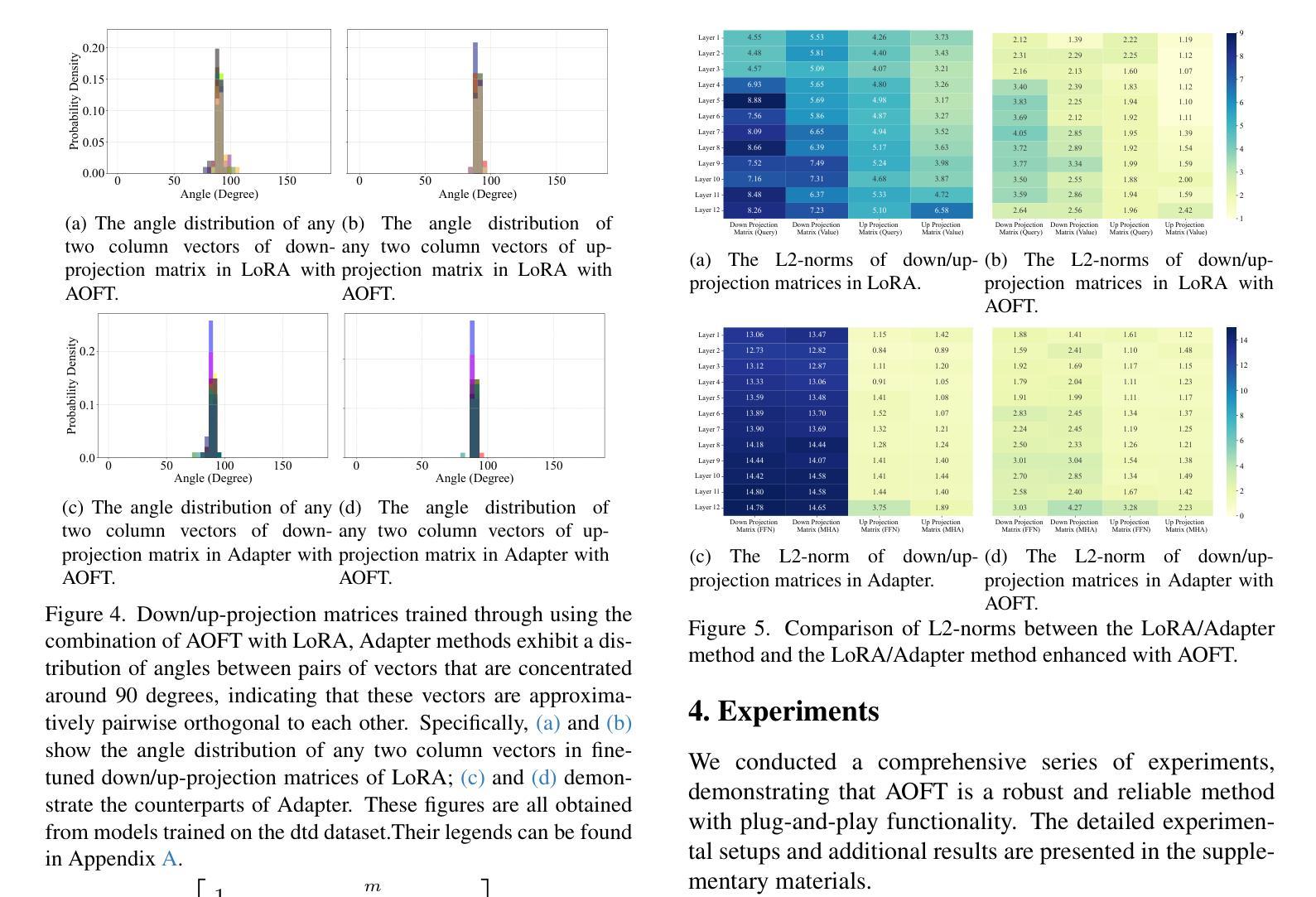
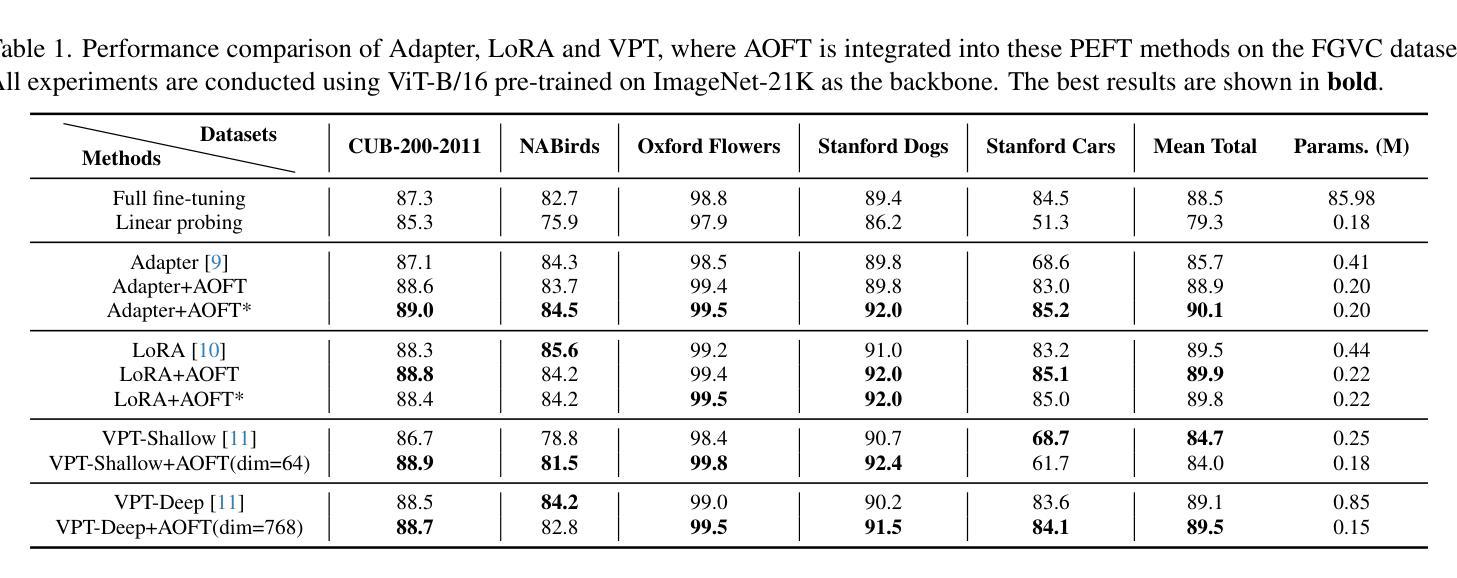
Efficient Adaptation of Pre-trained Vision Transformer underpinned by Approximately Orthogonal Fine-Tuning Strategy
Authors:Yiting Yang, Hao Luo, Yuan Sun, Qingsen Yan, Haokui Zhang, Wei Dong, Guoqing Wang, Peng Wang, Yang Yang, Hengtao Shen
A prevalent approach in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) of pre-trained Vision Transformers (ViT) involves freezing the majority of the backbone parameters and solely learning low-rank adaptation weight matrices to accommodate downstream tasks. These low-rank matrices are commonly derived through the multiplication structure of down-projection and up-projection matrices, exemplified by methods such as LoRA and Adapter. In this work, we observe an approximate orthogonality among any two row or column vectors within any weight matrix of the backbone parameters; however, this property is absent in the vectors of the down/up-projection matrices. Approximate orthogonality implies a reduction in the upper bound of the model’s generalization error, signifying that the model possesses enhanced generalization capability. If the fine-tuned down/up-projection matrices were to exhibit this same property as the pre-trained backbone matrices, could the generalization capability of fine-tuned ViTs be further augmented? To address this question, we propose an Approximately Orthogonal Fine-Tuning (AOFT) strategy for representing the low-rank weight matrices. This strategy employs a single learnable vector to generate a set of approximately orthogonal vectors, which form the down/up-projection matrices, thereby aligning the properties of these matrices with those of the backbone. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance across a range of downstream image classification tasks, confirming the efficacy of the enhanced generalization capability embedded in the down/up-projection matrices.
在预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)的参数高效微调(PEFT)中,一种普遍的方法是冻结大部分主干参数,只学习低秩适应权重矩阵,以适应下游任务。这些低秩矩阵通常通过下投影和上投影矩阵的乘法结构得到,例如LoRA和Adapter等方法。在这项工作中,我们观察到预训练主干参数的任何权重矩阵中的任何两个行或列向量之间的大致正交性,然而这一特性在下/上投影矩阵的向量中并不存在。近似正交性意味着模型泛化误差的上界降低,表明模型的泛化能力增强。如果微调的下/上投影矩阵能够展现出与预训练主干矩阵相同的特性,那么微调后的ViT的泛化能力能否进一步增强?为了回答这个问题,我们提出了一种近似正交微调(AOFT)策略来表示低秩权重矩阵。该策略使用单个可学习的向量生成一组近似正交的向量,这些向量形成下/上投影矩阵,从而使这些矩阵的属性与主干对齐。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在多个下游图像分类任务上取得了具有竞争力的性能,证实了嵌入在下/上投影矩阵中的增强泛化能力的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了预训练Vision Transformer(ViT)的参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,主要冻结大部分主干参数,仅学习低秩适应权重矩阵以适应下游任务。研究中观察到主干参数权重矩阵中的任意两个行或列向量之间存在近似正交性,而这种现象在低秩矩阵中缺失。近似正交性有助于降低模型泛化误差的上界,提高模型的泛化能力。为此,研究提出了一种名为AOFT(近似正交微调)的策略,利用单个可学习向量生成一组近似正交的向量,形成低秩权重矩阵,使这些矩阵的特性与主干相匹配。实验结果表明,该方法在多个下游图像分类任务中表现优异,验证了增强泛化能力在低秩矩阵中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer在参数高效微调(PEFT)中主要冻结主干参数,仅通过低秩适应权重矩阵适应下游任务。
- 主干参数权重矩阵中的向量存在近似正交性。
- 低秩适应权重矩阵(如LoRA和Adapter方法)中的向量缺乏近似正交性。
- 近似正交性有助于降低模型泛化误差的上界,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 提出了一种名为AOFT的策略,利用单个可学习向量生成近似正交的向量,形成低秩权重矩阵。
- AOFT策略使低秩权重矩阵的特性与主干参数相匹配。
点此查看论文截图

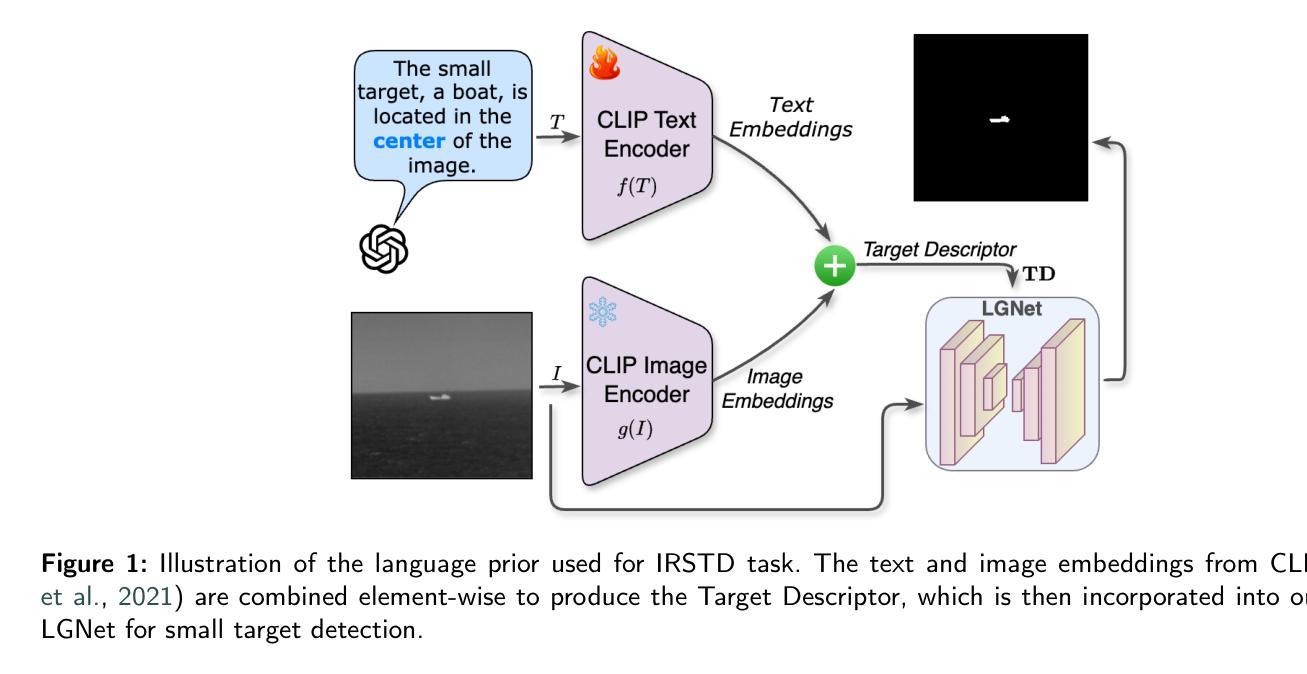
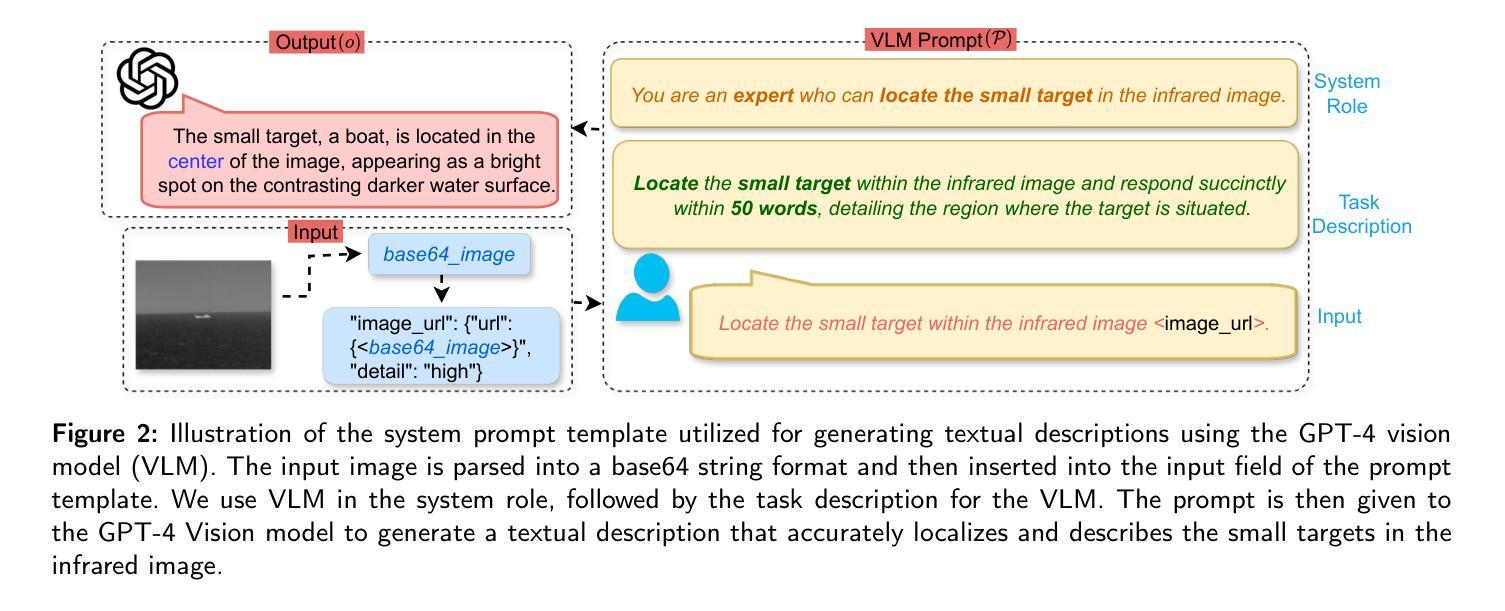
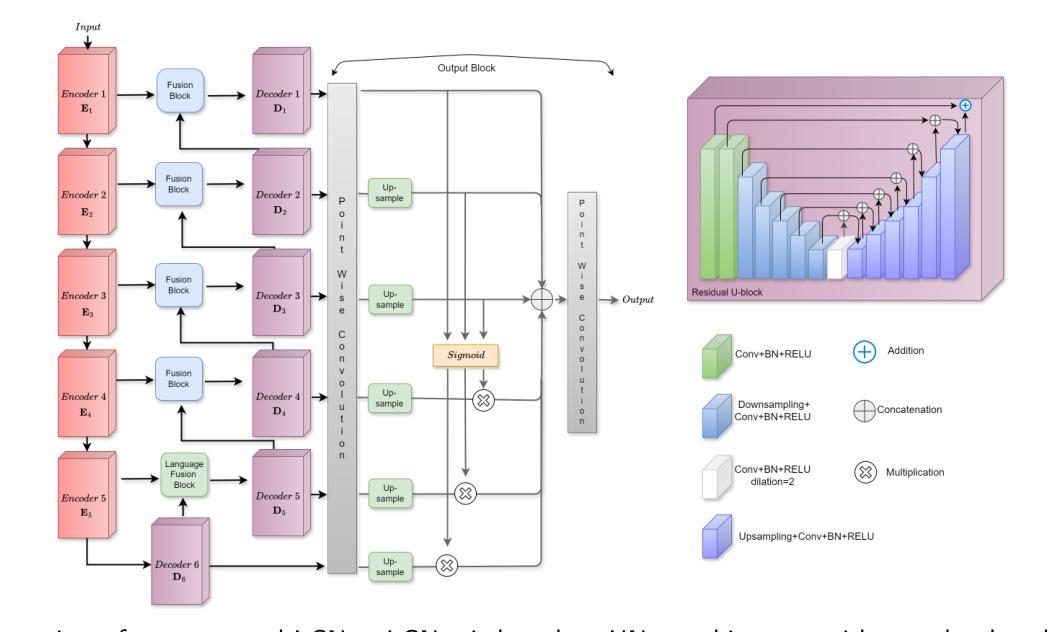
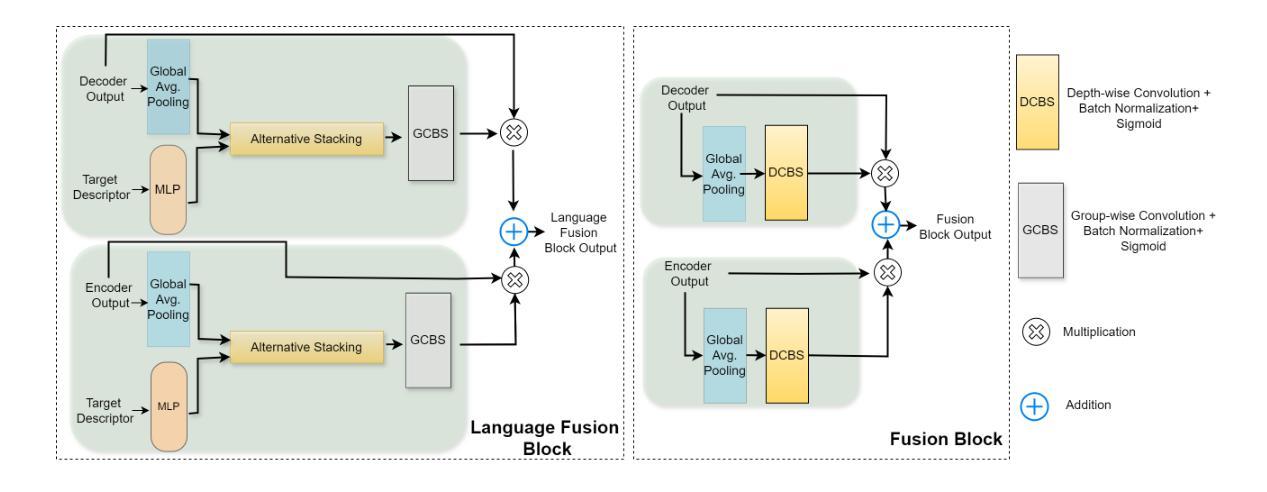
Leveraging Language Prior for Infrared Small Target Detection
Authors:Pranav Singh, Pravendra Singh
IRSTD (InfraRed Small Target Detection) detects small targets in infrared blurry backgrounds and is essential for various applications. The detection task is challenging due to the small size of the targets and their sparse distribution in infrared small target datasets. Although existing IRSTD methods and datasets have led to significant advancements, they are limited by their reliance solely on the image modality. Recent advances in deep learning and large vision-language models have shown remarkable performance in various visual recognition tasks. In this work, we propose a novel multimodal IRSTD framework that incorporates language priors to guide small target detection. We leverage language-guided attention weights derived from the language prior to enhance the model’s ability for IRSTD, presenting a novel approach that combines textual information with image data to improve IRSTD capabilities. Utilizing the state-of-the-art GPT-4 vision model, we generate text descriptions that provide the locations of small targets in infrared images, employing careful prompt engineering to ensure improved accuracy. Due to the absence of multimodal IR datasets, existing IRSTD methods rely solely on image data. To address this shortcoming, we have curated a multimodal infrared dataset that includes both image and text modalities for small target detection, expanding upon the popular IRSTD-1k and NUDT-SIRST datasets. We validate the effectiveness of our approach through extensive experiments and comprehensive ablation studies. The results demonstrate significant improvements over the state-of-the-art method, with relative percentage differences of 9.74%, 13.02%, 1.25%, and 67.87% in IoU, nIoU, Pd, and Fa on the NUAA-SIRST subset, and 4.41%, 2.04%, 2.01%, and 113.43% on the IRSTD-1k subset of the LangIR dataset, respectively.
红外小目标检测(IRSTD)能够在红外模糊背景中检测到小目标,对于各种应用至关重要。由于目标尺寸小以及红外小目标数据集中分布稀疏,检测任务具有挑战性。尽管现有的IRSTD方法和数据集已经带来了显著的进步,但它们仅依赖于图像模态,存在一定的局限性。最近,深度学习和大规模视觉语言模型的进步在各种视觉识别任务中表现出了卓越的性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种结合语言先验知识引导小目标检测的新型多模态IRSTD框架。我们利用语言先验知识衍生的语言引导注意力权重来提升模型进行IRSTD的能力,提出了一种结合文本信息和图像数据的新型方法来提高IRSTD能力。我们利用最先进的GPT-4视觉模型生成文本描述,提供红外图像中小目标的位置,并通过精心设计的提示来确保提高准确性。由于缺少多模态IR数据集,现有的IRSTD方法仅依赖于图像数据。为了弥补这一不足,我们整理了一个多模态红外数据集,该数据集包含用于小目标检测的图象和文本模态,在流行的IRSTD-1k和NUDT-SIRST数据集基础上进行了扩展。我们通过广泛的实验和全面的消融研究验证了我们的方法的有效性。结果表明,与最新方法相比,我们的方法在NUAA-SIRST子集上的IoU、nIoU、Pd和Fa分别有9.74%、13.02%、1.25%和67.87%的相对百分比差异,在LangIR数据集的IRSTD-1k子集上分别有4.41%、2.04%、2.01%和113.43%的相对百分比差异。这些改进是显著的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了红外小目标检测(IRSTD)的挑战性,并提出了一种新的多模态IRSTD框架。该框架结合了语言先验来指导小目标检测,通过使用语言引导的注意力权重增强模型能力。利用先进的GPT-4视觉模型生成文本描述,提供红外图像中小目标的位置。为解决缺乏多模态IR数据集的问题,作者还整理了一个包含图像和文本模态的多模态红外数据集。实验结果显示,该方法在NUAA-SIRST和IRSTD-1k子集上相较于现有方法有明显提升。
Key Takeaways
- 红外小目标检测(IRSTD)面临挑战,因目标小且在红外背景中分布稀疏。
- 现有IRSTD方法和数据集受限于仅使用图像模态。
- 提出了新的多模态IRSTD框架,结合语言先验指导小目标检测。
- 利用GPT-4视觉模型生成文本描述,提供红外图像小目标位置。
- 整理了一个包含图像和文本模态的多模态红外数据集,以扩展IRSTD数据集。
- 通过广泛实验和综合分析验证了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

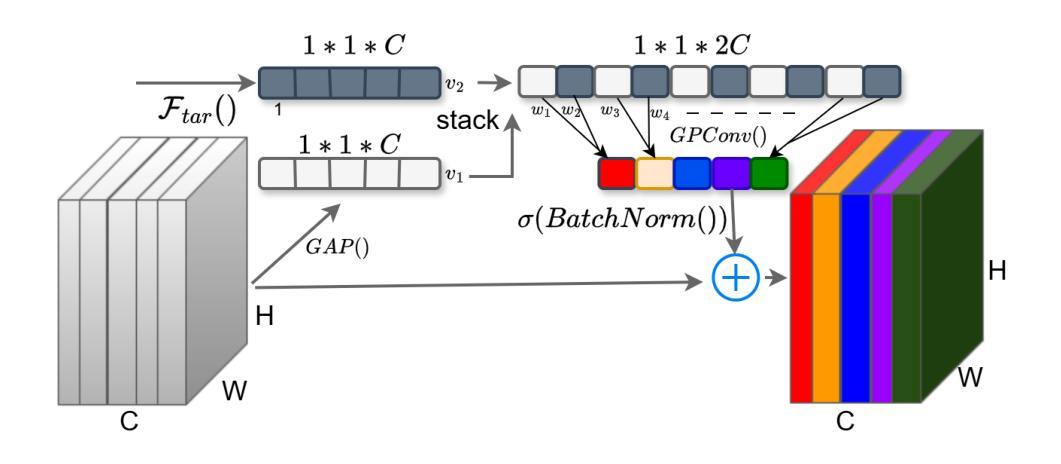
GLAD: Generalizable Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yuqi Peng, Pengfei Wang, Jianzhuang Liu, Shifeng Chen
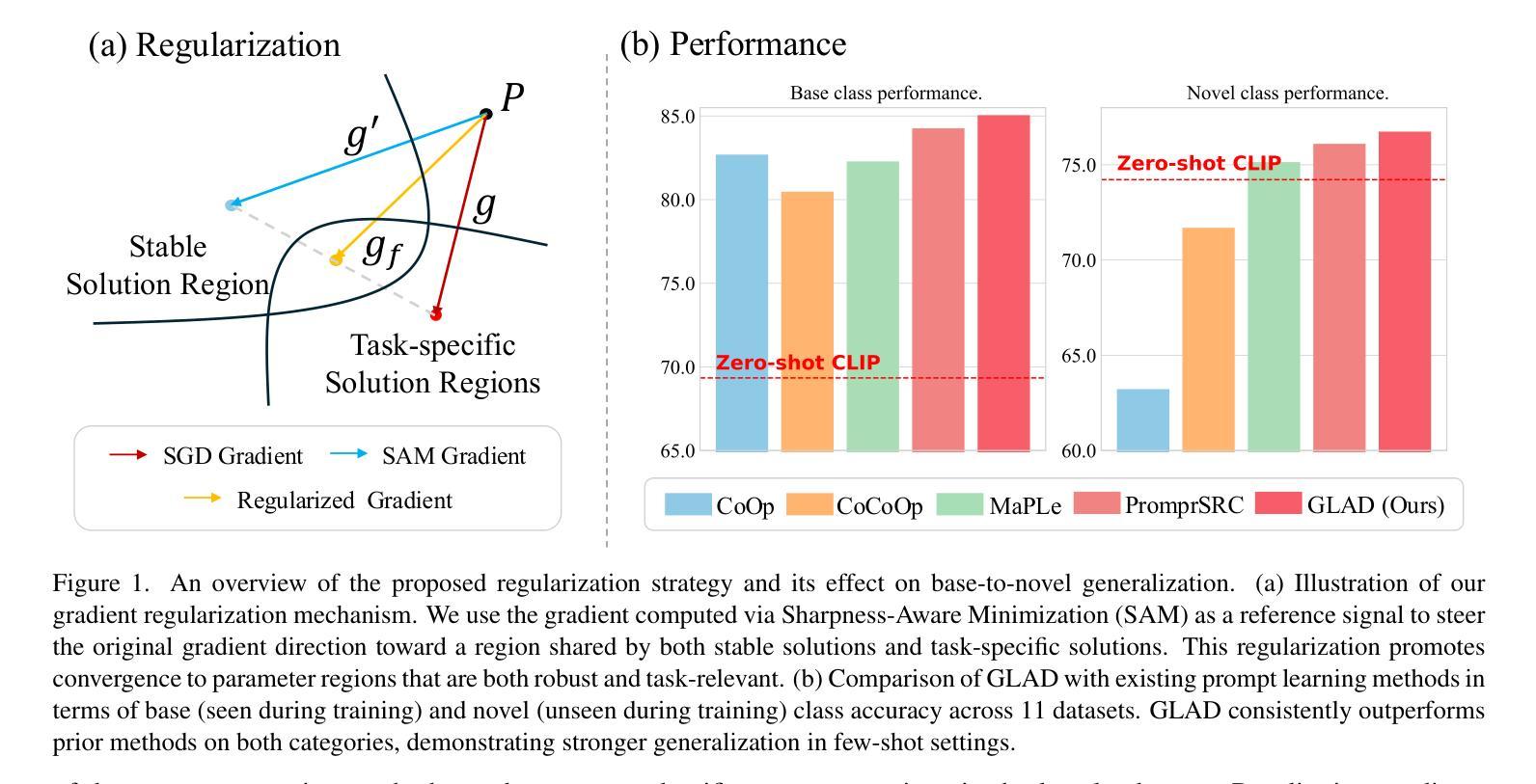
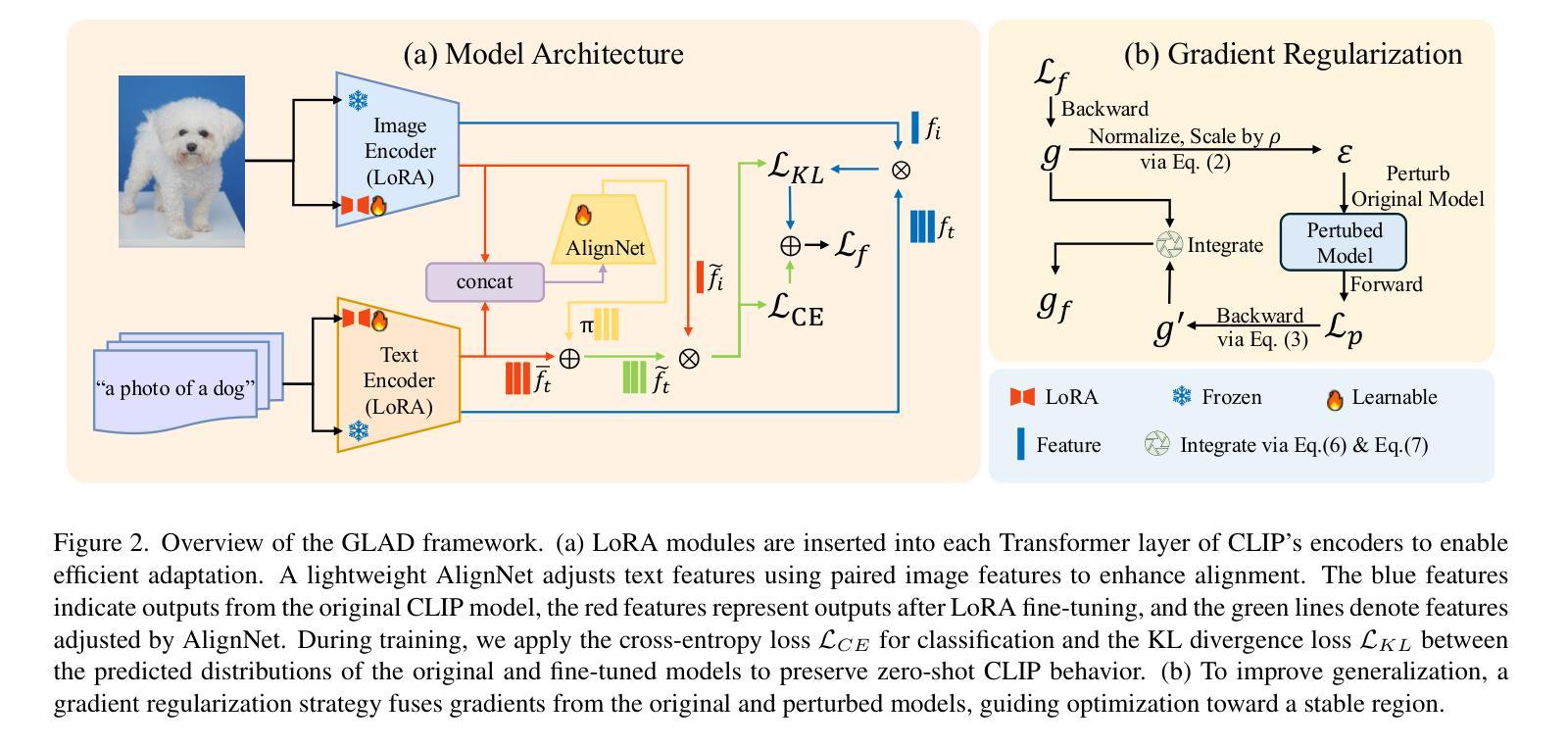
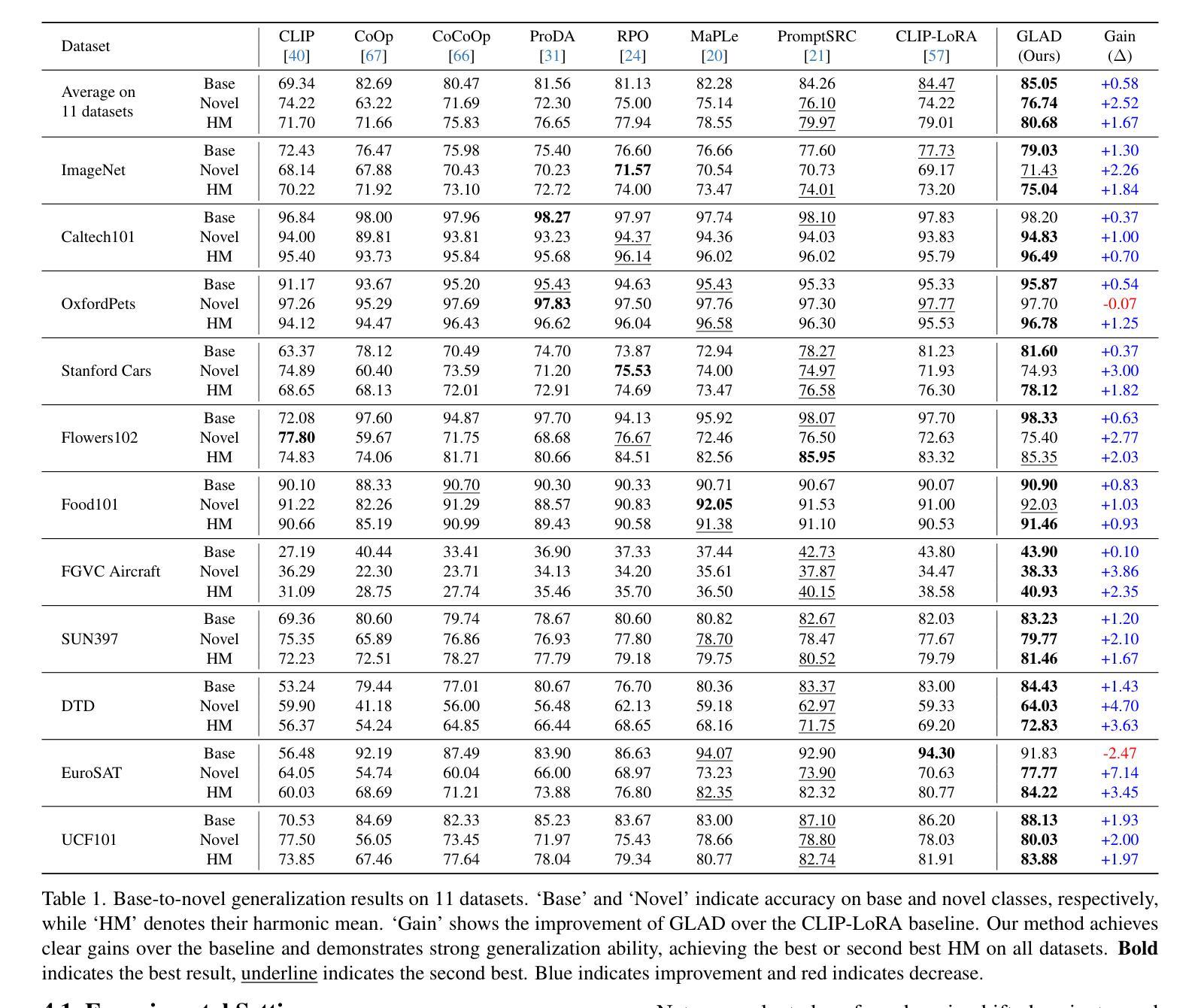
Pre-trained vision-language models, such as CLIP, show impressive zero-shot recognition ability and can be easily transferred to specific downstream tasks via prompt tuning, even with limited training data. However, existing prompt tuning methods face two main challenges: (1) In few-shot scenarios, data scarcity often leads to overfitting, making the model sensitive to changes in the input domain. (2) To mitigate overfitting, these methods typically rely on complex task-specific model architectures and sensitive hyperparameter tuning, severely restricting their general applicability. To address these issues, we propose a simpler and more general framework called GLAD (Generalizable LoRA tuning with RegulArized GraDient). We show that merely applying LoRA achieves performance in downstream tasks comparable to current state-of-the-art prompt-based methods. While LoRA is effective and easy to use, it remains susceptible to overfitting in few-shot learning scenarios. To mitigate this risk, we introduce a gradient-based regularization technique. This technique effectively steers the optimization trajectory, encouraging the model to find a more stable parameter region that is robust to variations in data distribution. Through extensive experiments conducted on 15 benchmark datasets, we demonstrate that GLAD outperforms previous tuning approaches in terms of base-to-novel class generalization, image domain generalization, and cross-dataset generalization. The code will be publicly available.
预训练视觉语言模型,如CLIP,展现出令人印象深刻的零样本识别能力,并且可以通过提示微调轻松转移到特定的下游任务,即使训练数据有限也是如此。然而,现有的提示微调方法面临两个主要挑战:(1)在少量样本情况下,数据稀缺往往导致过拟合,使模型对输入域的变化敏感。(2)为了缓解过拟合,这些方法通常依赖于复杂的特定任务模型架构和敏感的超参数调整,严重限制了它们的通用适用性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一个更简单、更通用的框架,称为GLAD(通过正则化梯度实现的可泛化的LoRA调整)。我们表明,仅仅应用LoRA就能在实现下游任务性能的同时,与当前最先进的基于提示的方法相媲美。虽然LoRA有效且易于使用,但在少量样本学习场景中仍然容易过拟合。为了缓解这一风险,我们引入了一种基于梯度的正则化技术。该技术有效地引导了优化轨迹,鼓励模型找到一个更稳定的参数区域,该区域对数据分布的变化具有鲁棒性。通过对15个基准数据集进行的广泛实验,我们证明了GLAD在基础到新颖类的泛化、图像域泛化和跨数据集泛化方面优于以前的调整方法。代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 workshop
Summary
本文提出一种名为GLAD的通用框架,用于解决预训练视觉语言模型在特定下游任务中的局限性问题。通过应用LoRA技术,该框架在下游任务中表现出与当前先进的提示方法相当的性能。为了缓解在少量样本学习场景中的过拟合风险,引入了基于梯度的正则化技术,鼓励模型找到更稳定的参数区域,从而提高对不同数据分布的鲁棒性。经过在15个基准数据集上的实验验证,GLAD在基础到新颖类别的泛化、图像域泛化和跨数据集泛化方面均优于之前的微调方法。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型如CLIP具有强大的零样本识别能力,可通过提示微调轻松应用于特定下游任务,即使训练数据有限。
- 现有提示微调方法面临两大挑战:少量样本场景中的数据稀缺导致过拟合,以及需要复杂任务特定的模型架构和敏感的超参数调整,限制了其通用性。
- GLAD框架通过应用LoRA技术,表现出强大的性能,与当前先进的提示方法相当。
- LoRA技术简单易用,但在少量样本学习场景中仍易过拟合。
- GLAD引入基于梯度的正则化技术,以缓解过拟合风险,鼓励模型找到更稳定的参数区域,提高对不同数据分布的鲁棒性。
- 在15个基准数据集上的实验验证显示,GLAD在多个方面的泛化性能优于先前的微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

Fine-Grained Image Recognition from Scratch with Teacher-Guided Data Augmentation
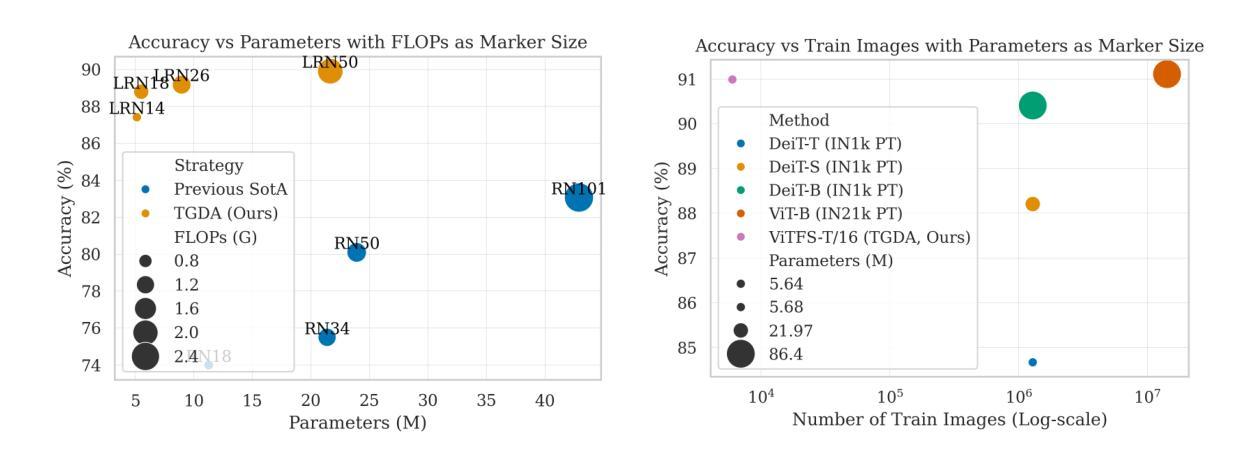
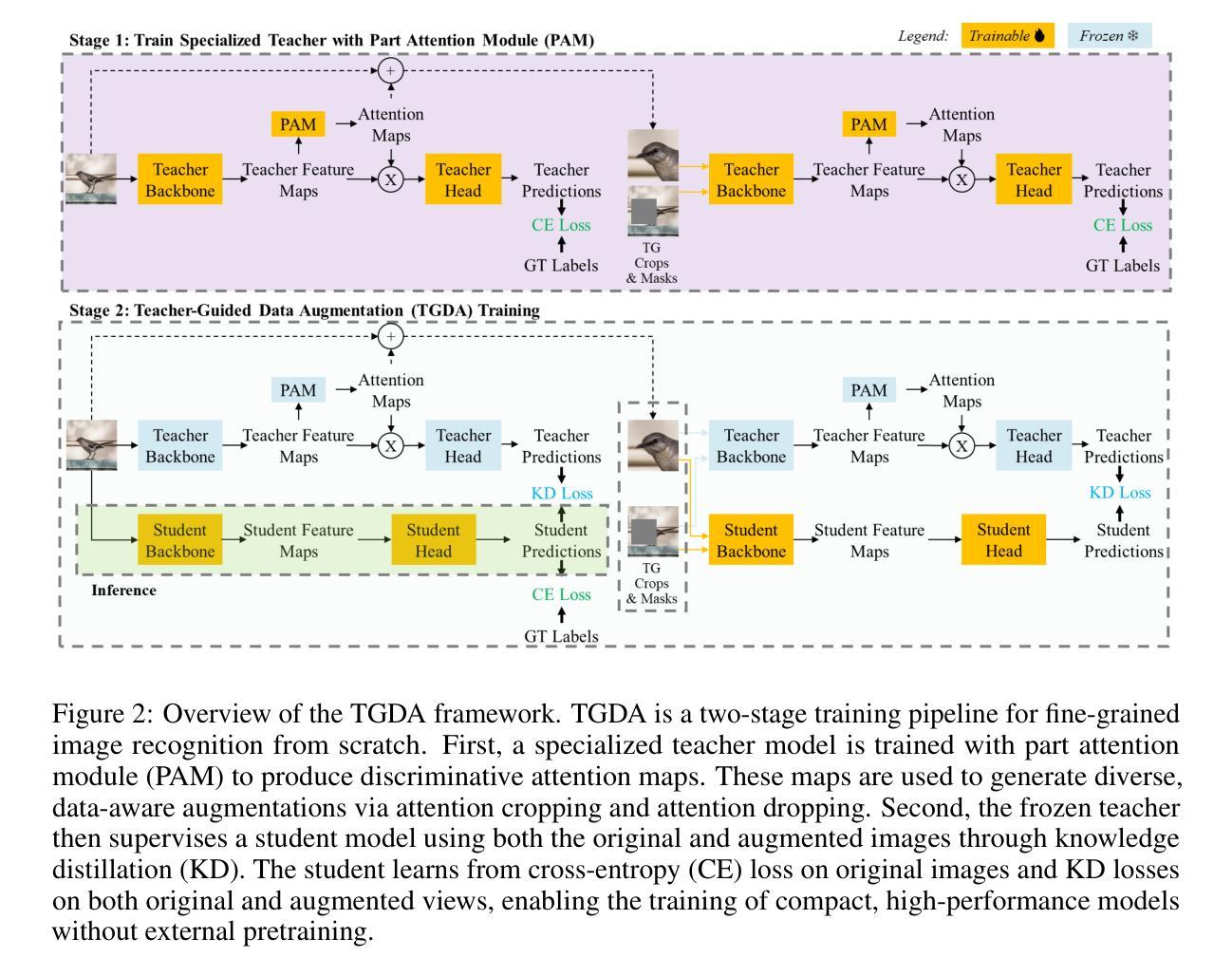
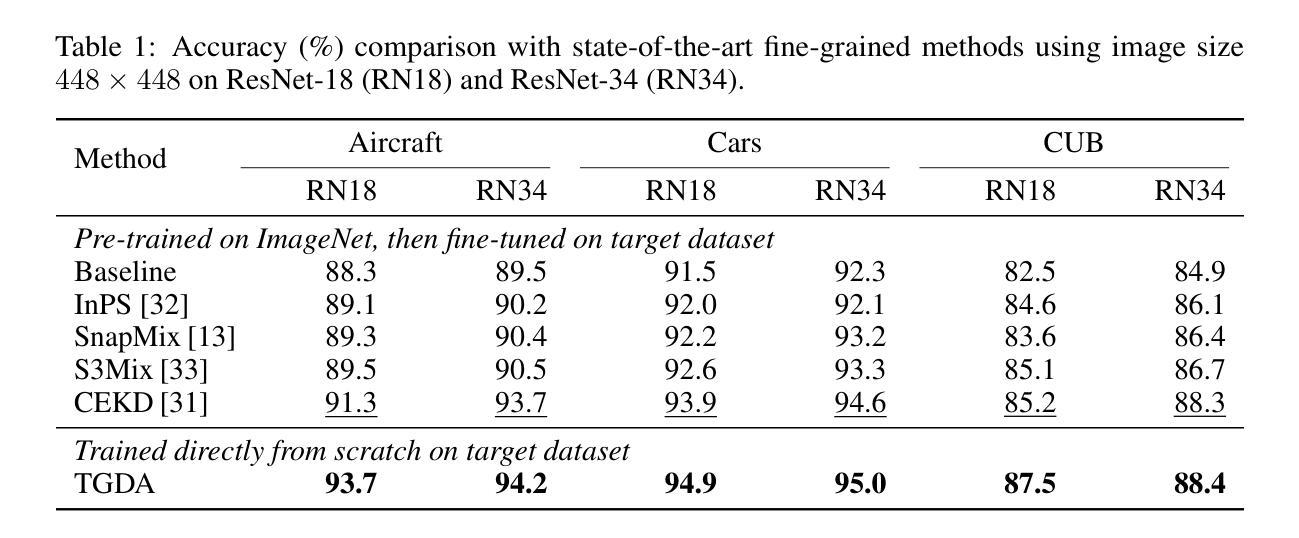
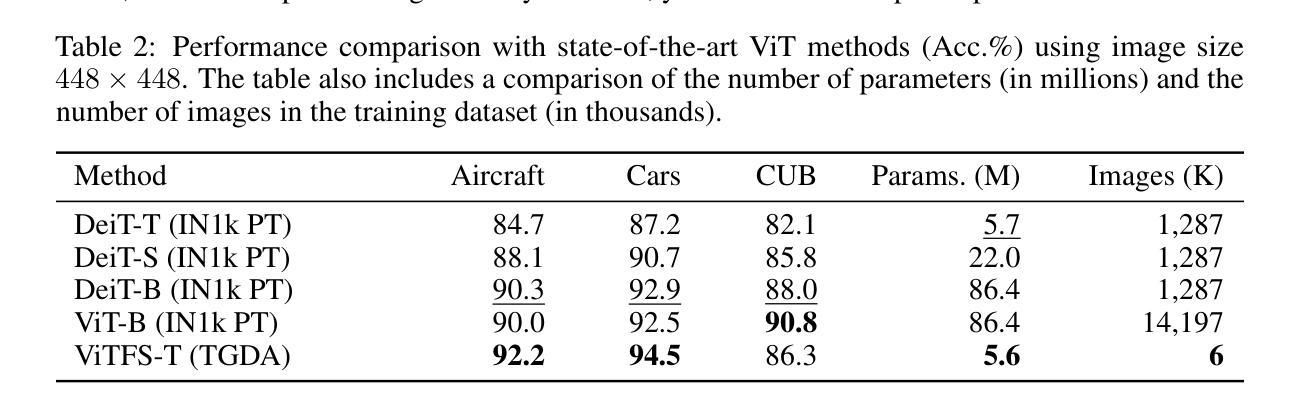
Authors:Edwin Arkel Rios, Fernando Mikael, Oswin Gosal, Femiloye Oyerinde, Hao-Chun Liang, Bo-Cheng Lai, Min-Chun Hu
Fine-grained image recognition (FGIR) aims to distinguish visually similar sub-categories within a broader class, such as identifying bird species. While most existing FGIR methods rely on backbones pretrained on large-scale datasets like ImageNet, this dependence limits adaptability to resource-constrained environments and hinders the development of task-specific architectures tailored to the unique challenges of FGIR. In this work, we challenge the conventional reliance on pretrained models by demonstrating that high-performance FGIR systems can be trained entirely from scratch. We introduce a novel training framework, TGDA, that integrates data-aware augmentation with weak supervision via a fine-grained-aware teacher model, implemented through knowledge distillation. This framework unlocks the design of task-specific and hardware-aware architectures, including LRNets for low-resolution FGIR and ViTFS, a family of Vision Transformers optimized for efficient inference. Extensive experiments across three FGIR benchmarks over diverse settings involving low-resolution and high-resolution inputs show that our method consistently matches or surpasses state-of-the-art pretrained counterparts. In particular, in the low-resolution setting, LRNets trained with TGDA improve accuracy by up to 23% over prior methods while requiring up to 20.6x less parameters, lower FLOPs, and significantly less training data. Similarly, ViTFS-T can match the performance of a ViT B-16 pretrained on ImageNet-21k while using 15.3x fewer trainable parameters and requiring orders of magnitudes less data. These results highlight TGDA’s potential as an adaptable alternative to pretraining, paving the way for more efficient fine-grained vision systems.
细粒度图像识别(FGIR)旨在区分广泛类别中视觉上相似的子类别,例如识别鸟类物种。虽然大多数现有的FGIR方法依赖于在大型数据集(如ImageNet)上预训练的backbone,但这种依赖限制了其在资源受限环境中的适应性,并阻碍了针对FGIR的独特挑战而设计的任务特定架构的发展。在这项工作中,我们通过证明可以完全不依赖预训练模型来训练高性能的FGIR系统,从而质疑了传统的依赖预训练模型的做法。我们引入了一种新型训练框架TGDA,它将数据感知增强与弱监督相结合,通过细粒度感知教师模型实现知识蒸馏。该框架可以解锁任务特定和硬件感知架构的设计,包括用于低分辨率FGIR的LRNets以及针对高效推理优化的Vision Transformer家族ViTFS。在涉及低分辨率和高分辨率输入的三个FGIR基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终能与最先进的预训练模型相匹配或超越。特别是在低分辨率环境下,使用TGDA训练的LRNets在精度上较先前方法提高了高达23%,同时减少了高达20.6倍的参数、FLOPs和大量的训练数据需求。同样,ViTFS-T可以在使用比ImageNet-21k上预训练的ViT B-16少15.3倍的可训练参数和需要更少数据量的情况下达到相同的性能。这些结果突显了TGDA作为可适应的预训练替代方案的潜力,为更有效的细粒度视觉系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main: 10 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的训练框架TGDA,用于解决细粒度图像识别(FGIR)问题。该框架无需依赖预训练模型,通过数据感知增强技术与弱监督方式,结合精细粒度感知教师模型实现知识蒸馏,实现从头开始训练高性能FGIR系统。引入的任务特定和硬件感知架构,如用于低分辨率FGIR的LRNets和针对高效推理优化的Vision Transformer家族ViTFS,在三个FGIR基准测试中的低分辨率和高分辨率输入环境下,表现均达到或超越了预训练模型。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种全新的训练框架TGDA,用于解决细粒度图像识别问题,不依赖预训练模型。
- 通过数据感知增强技术和弱监督方式实现知识蒸馏。
- 引入了任务特定和硬件感知架构,如LRNets和ViTFS。
- 在三个FGIR基准测试中表现优异,低分辨率环境下LRNets准确率提升高达23%。
- ViTFS-T在匹配预训练模型性能的同时,使用参数减少15.3倍,所需数据量大幅降低。
- TGDA作为一种适应性的替代方案具有潜力,为实现更高效的细粒度视觉系统铺平了道路。
点此查看论文截图

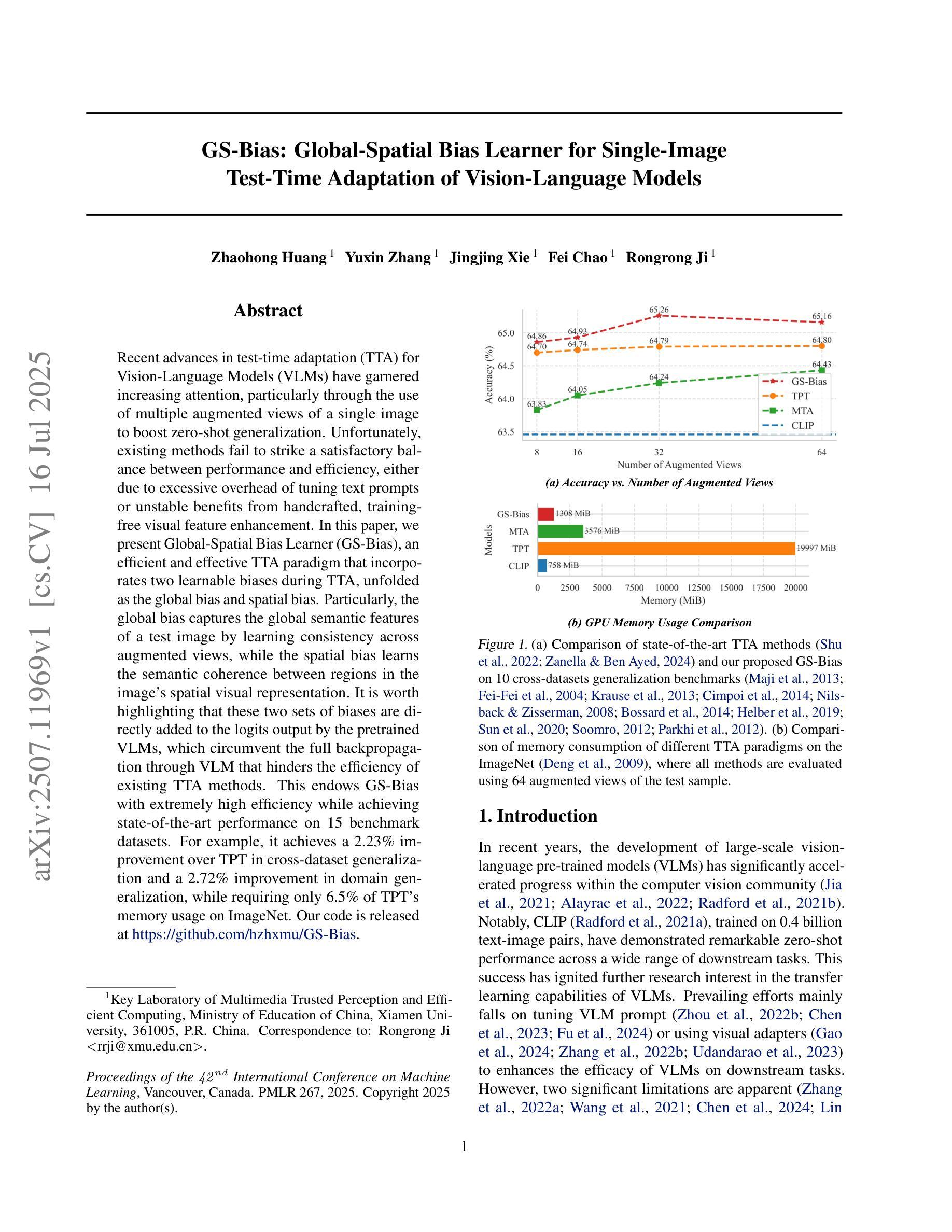
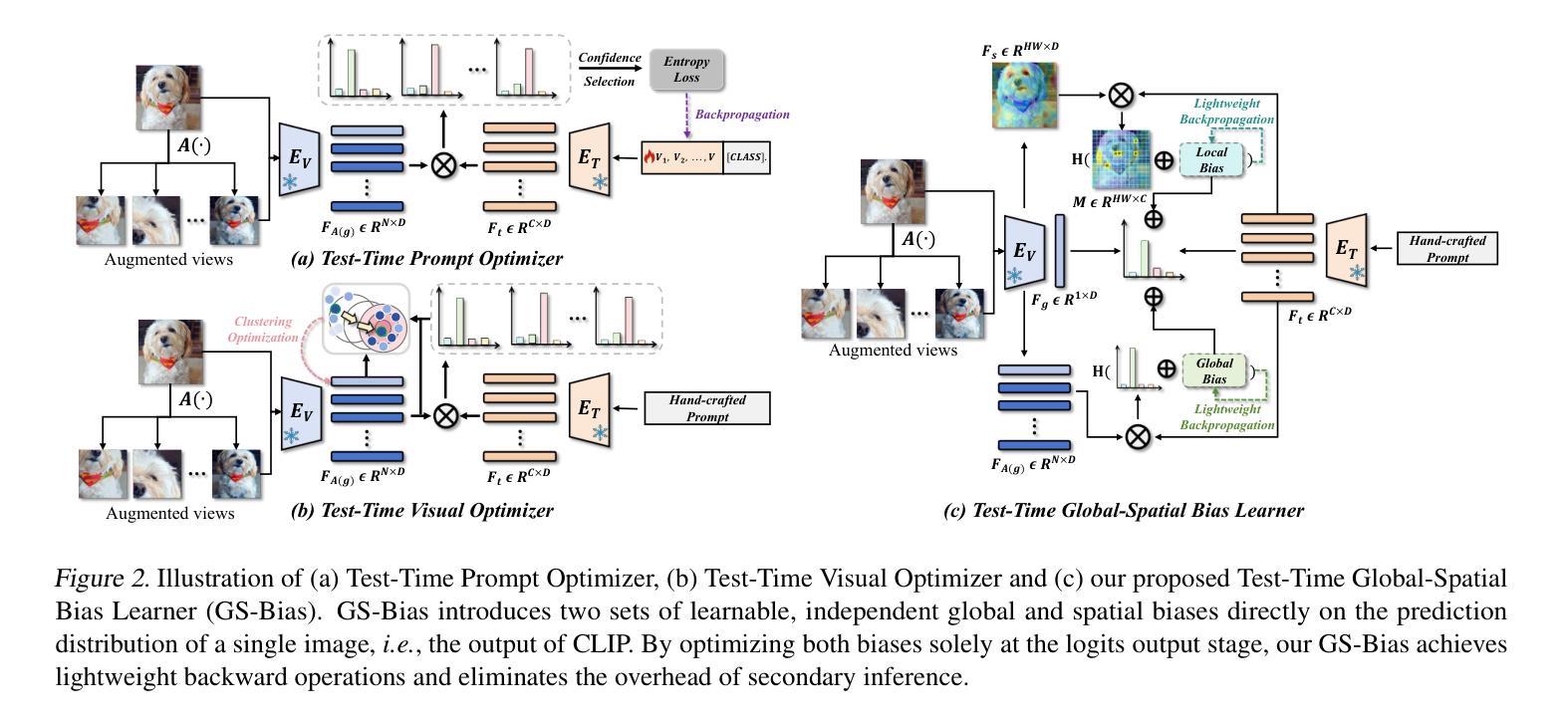
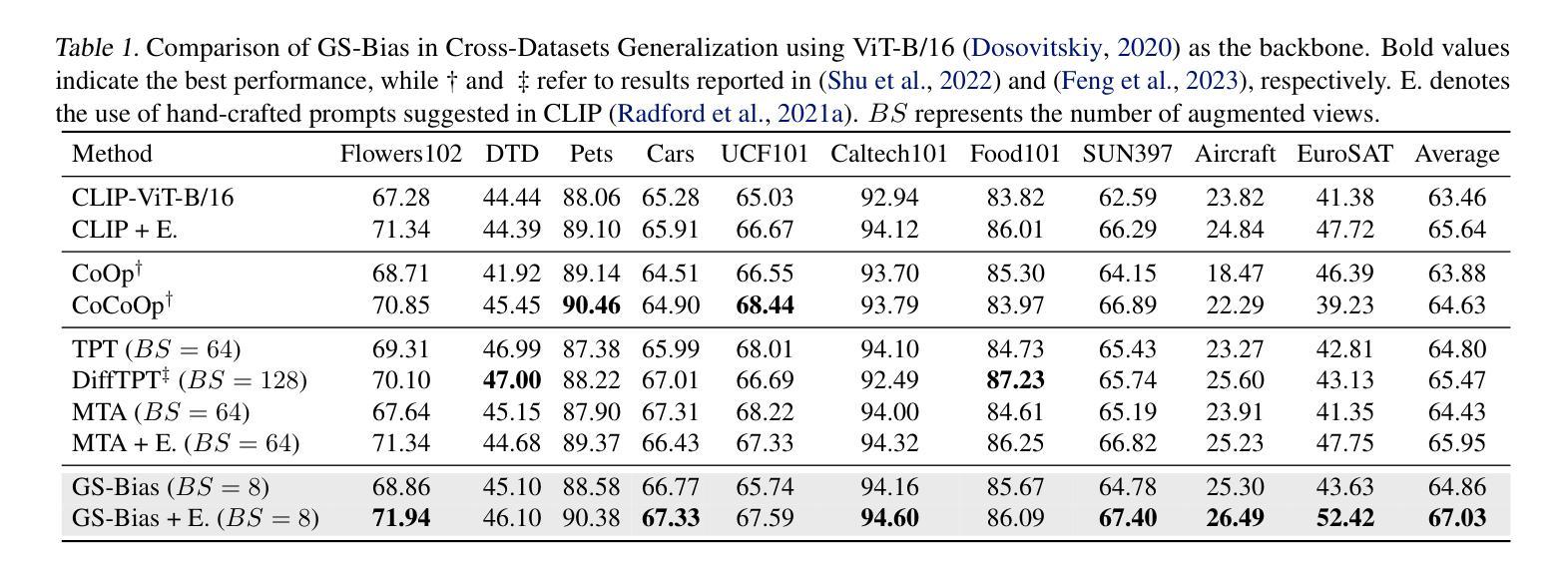
GS-Bias: Global-Spatial Bias Learner for Single-Image Test-Time Adaptation of Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zhaohong Huang, Yuxin Zhang, Jingjing Xie, Fei Chao, Rongrong Ji
Recent advances in test-time adaptation (TTA) for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have garnered increasing attention, particularly through the use of multiple augmented views of a single image to boost zero-shot generalization. Unfortunately, existing methods fail to strike a satisfactory balance between performance and efficiency, either due to excessive overhead of tuning text prompts or unstable benefits from handcrafted, training-free visual feature enhancement. In this paper, we present Global-Spatial Bias Learner (GS-Bias), an efficient and effective TTA paradigm that incorporates two learnable biases during TTA, unfolded as the global bias and spatial bias. Particularly, the global bias captures the global semantic features of a test image by learning consistency across augmented views, while spatial bias learns the semantic coherence between regions in the image’s spatial visual representation. It is worth highlighting that these two sets of biases are directly added to the logits outputed by the pretrained VLMs, which circumvent the full backpropagation through VLM that hinders the efficiency of existing TTA methods. This endows GS-Bias with extremely high efficiency while achieving state-of-the-art performance on 15 benchmark datasets. For example, it achieves a 2.23% improvement over TPT in cross-dataset generalization and a 2.72% improvement in domain generalization, while requiring only 6.5% of TPT’s memory usage on ImageNet.
测试时自适应(TTA)在视觉语言模型(VLM)方面的最新进展已经引起了越来越多的关注,特别是通过使用单一图像的多重增强视图来提升零样本泛化能力。然而,现有方法未能在性能和效率之间取得令人满意的平衡,这可能是由于文本提示调整过度或手工制作的、无需训练即可提升视觉特征的收益不稳定所致。在本文中,我们提出了Global-Spatial Bias Learner(GS-Bias),这是一种高效且有效的TTA方法,它在测试时引入了两种可学习的偏差,分别为全局偏差和空间偏差。具体来说,全局偏差通过捕捉增强视图之间的共识来习得测试图像的全局语义特征,而空间偏差则学习图像空间视觉表示中区域之间的语义一致性。值得一提的是,这两组偏差直接添加到预训练VLM输出的logits上,避免了通过VLM进行全反向传播,从而提高现有TTA方法的效率。这为GS-Bias带来了极高的效率,同时在15个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。例如,它在跨数据集泛化方面比TPT提高了2.23%,在域泛化方面提高了2.72%,而在ImageNet上的内存使用率仅为TPT的6.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出一种称为Global-Spatial Bias Learner(GS-Bias)的测试时自适应(TTA)方法,通过引入全局偏差和空间偏差两个可学习的偏差,在TTA过程中提高视觉语言模型(VLMs)的零样本泛化能力。GS-Bias能够高效地在多个增强视图上捕获测试图像的全局语义特征,并学习图像空间视觉表示中区域间的语义一致性。该方法直接在预训练的VLMs输出的logits上添加偏差,避免了现有TTA方法效率低下的问题,实现了极高的效率和出色的性能,在多个基准数据集上达到最先进的性能水平。例如,相较于TPT方法,GS-Bias在跨数据集泛化和域泛化上分别提升了2.23%和2.72%,同时只需要TPT的6.5%内存。
Key Takeaways
- Global-Spatial Bias Learner (GS-Bias)是一种新的测试时自适应(TTA)方法,用于提高视觉语言模型(VLMs)的零样本泛化能力。
- GS-Bias通过引入全局偏差和空间偏差两个可学习偏差来增强模型性能。全局偏差用于捕获测试图像的全局语义特征,空间偏差则学习图像空间视觉表示中区域间的语义一致性。
- GS-Bias通过在预训练的VLMs输出的logits上直接添加偏差,提高了效率并避免了现有TTA方法的不足。
- GS-Bias在多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能水平,相较于其他方法具有显著优势。
- GS-Bias在跨数据集泛化和域泛化方面表现出色,相较于TPT方法分别提升了2.23%和2.72%。
- GS-Bias具有极高的内存效率,只需要TPT的6.5%内存即可实现优越性能。
点此查看论文截图