⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
The Impact of Image Resolution on Face Detection: A Comparative Analysis of MTCNN, YOLOv XI and YOLOv XII models
Authors:Ahmet Can Ömercikoğlu, Mustafa Mansur Yönügül, Pakize Erdoğmuş
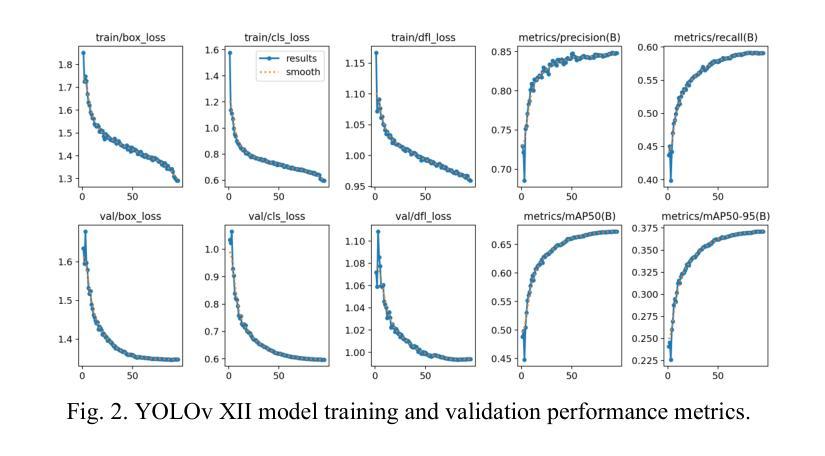
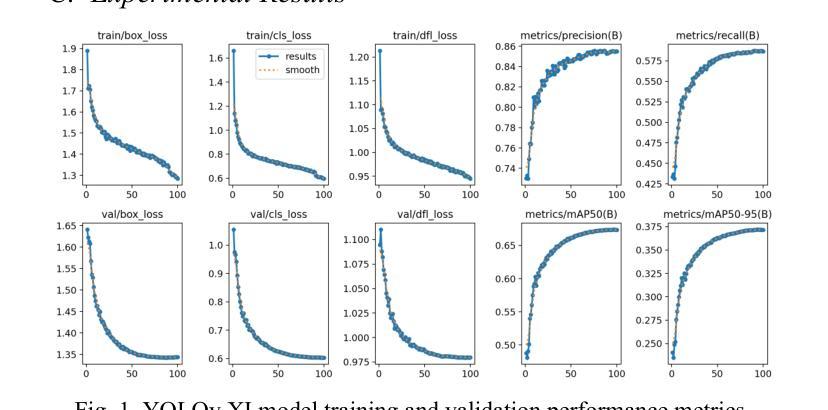
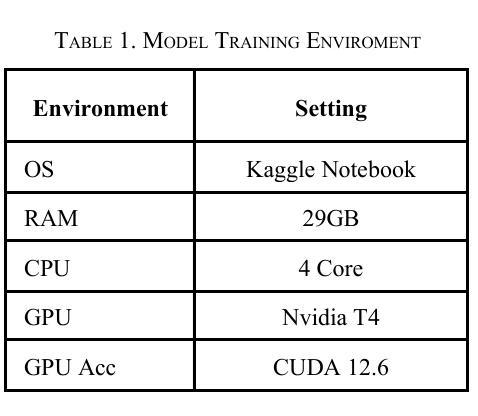
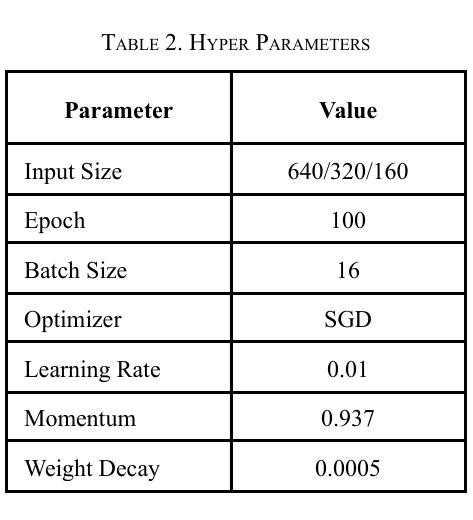
Face detection is a crucial component in many AI-driven applications such as surveillance, biometric authentication, and human-computer interaction. However, real-world conditions like low-resolution imagery present significant challenges that degrade detection performance. In this study, we systematically investigate the impact of input resolution on the accuracy and robustness of three prominent deep learning-based face detectors: YOLOv11, YOLOv12, and MTCNN. Using the WIDER FACE dataset, we conduct extensive evaluations across multiple image resolutions (160x160, 320x320, and 640x640) and assess each model’s performance using metrics such as precision, recall, mAP50, mAP50-95, and inference time. Results indicate that YOLOv11 outperforms YOLOv12 and MTCNN in terms of detection accuracy, especially at higher resolutions, while YOLOv12 exhibits slightly better recall. MTCNN, although competitive in landmark localization, lags in real-time inference speed. Our findings provide actionable insights for selecting resolution-aware face detection models suitable for varying operational constraints.
人脸识别在许多人工智能驱动的应用(如监控、生物识别认证和人机交互)中都是至关重要的组成部分。然而,现实世界中的条件,如低分辨率图像,给检测性能带来了重大挑战。在这项研究中,我们系统地研究了输入分辨率对三种流行的基于深度学习的人脸检测器(YOLOv11、YOLOv12和MTCNN)的准确性和稳健性的影响。我们使用WIDERFACE数据集,在多种图像分辨率(160x160、320x320和640x640)下进行了广泛评估,并使用精度、召回率、mAP50、mAP50-95和推理时间等指标评估了每个模型的性能。结果表明,YOLOv11在检测精度方面优于YOLOv12和MTCNN,尤其是在高分辨率下;而YOLOv12的召回率略高。虽然MTCNN在标志性地点定位方面颇具竞争力,但在实时推理速度上有所滞后。我们的研究结果为选择适合不同操作约束的具有分辨率感知能力的人脸检测模型提供了实用见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Summary
人脸识别技术在AI驱动应用中扮演着重要角色,如监控、生物识别认证和人机交互等。面对真实世界的低分辨率图像等挑战,本文系统地研究了输入分辨率对三大深度学习人脸识别器(YOLOv11、YOLOv12和MTCNN)准确性和鲁棒性的影响。在WIDERFACE数据集上进行的评估表明,YOLOv11在检测准确性方面优于YOLOv12和MTCNN,尤其是在高分辨率下;而YOLOv12的召回率略高。MTCNN在面部特征定位方面颇具竞争力,但在实时推理速度上稍显不足。本研究为不同操作环境下选择具有分辨率感知功能的人脸识别模型提供了有益参考。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别技术在多种AI应用中占据重要地位,如监控和生物识别认证。
- 输入分辨率对深度学习人脸识别模型的性能有显著影响。
- YOLOv11在较高分辨率下表现出较高的检测准确性。
- YOLOv12在召回率方面略胜一筹。
- MTCNN在面部特征定位方面表现出竞争力,但实时推理速度较慢。
点此查看论文截图

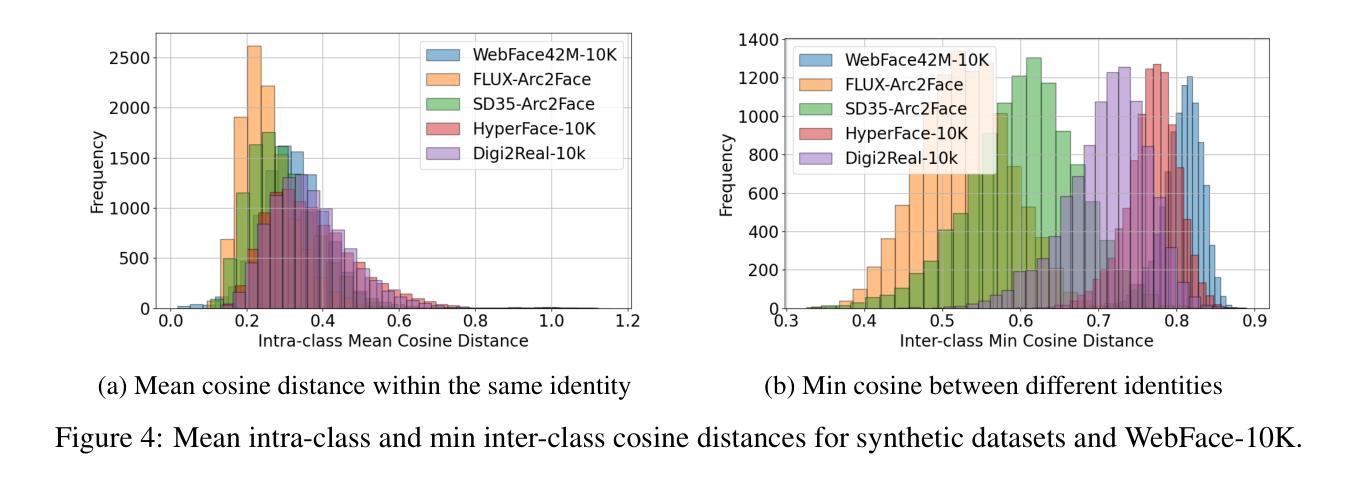
Investigation of Accuracy and Bias in Face Recognition Trained with Synthetic Data
Authors:Pavel Korshunov, Ketan Kotwal, Christophe Ecabert, Vidit Vidit, Amir Mohammadi, Sebastien Marcel
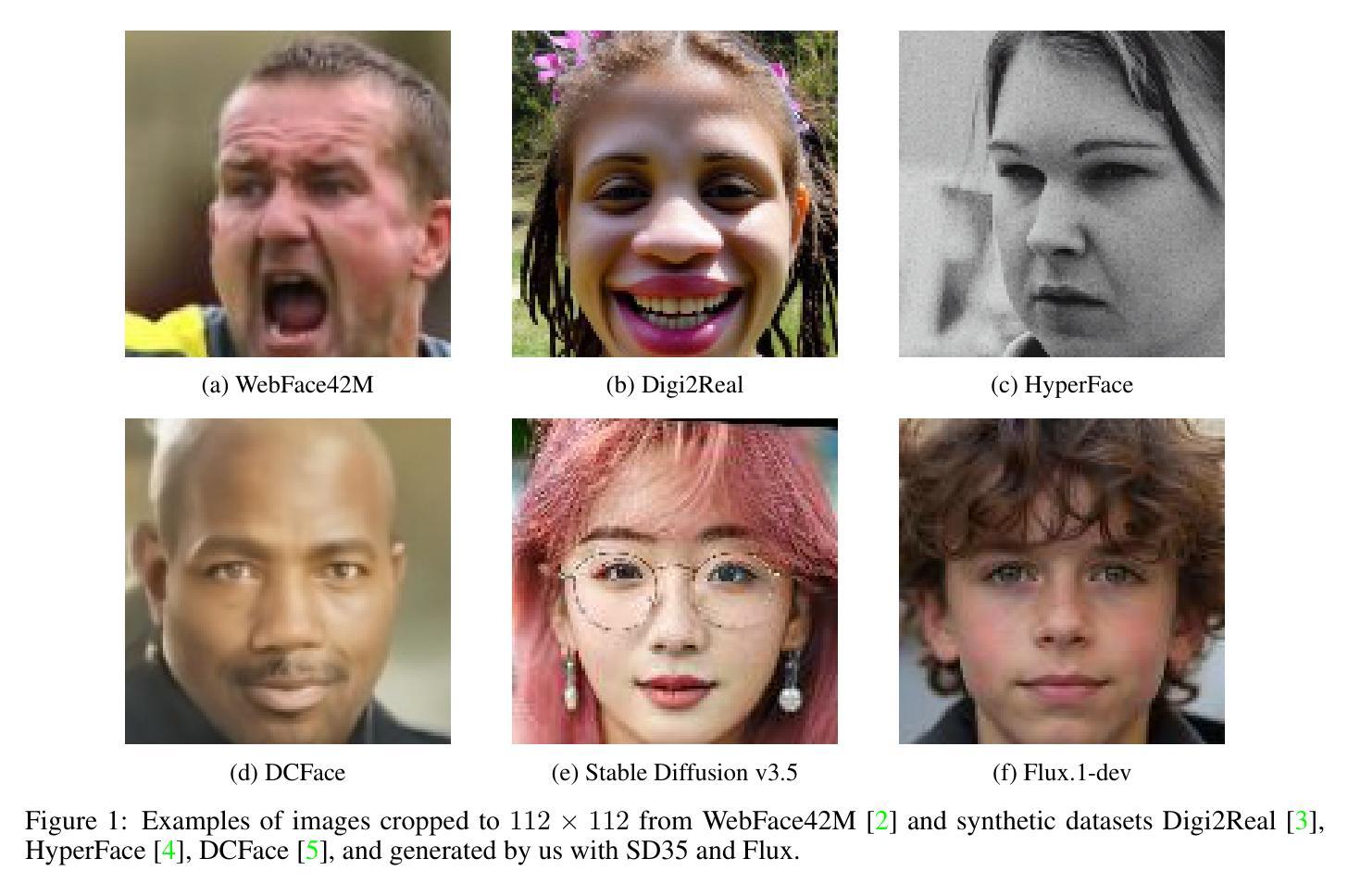
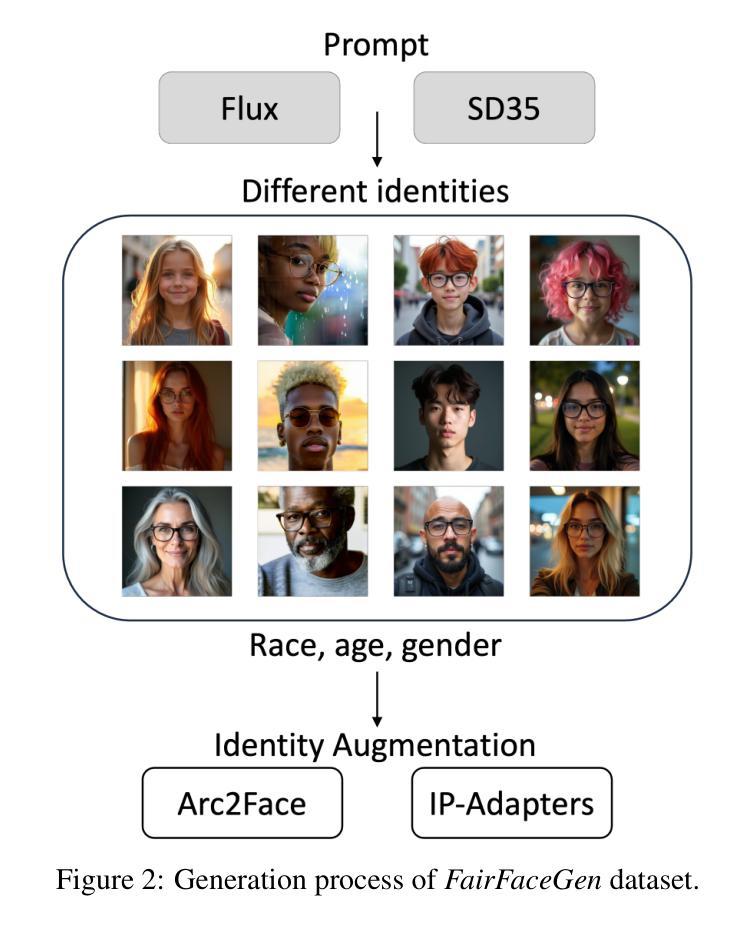
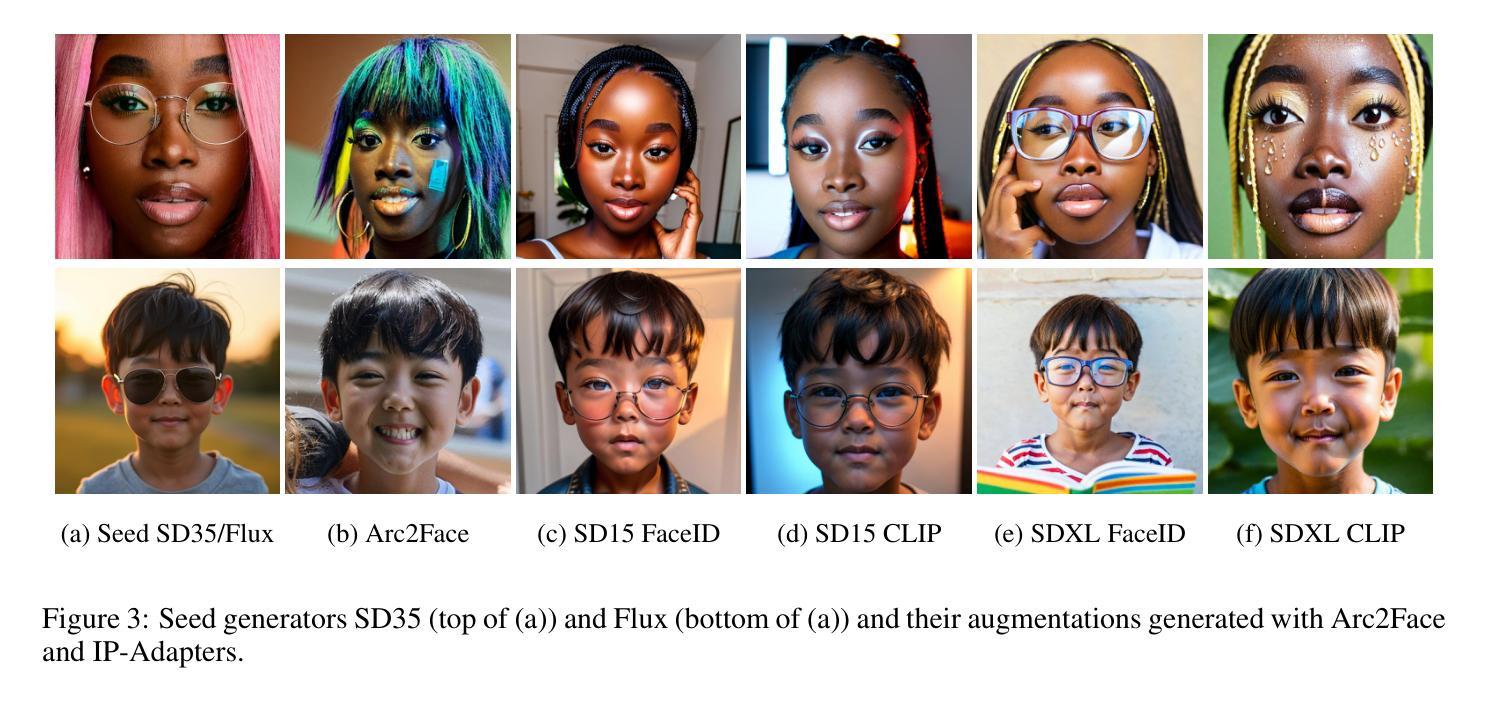
Synthetic data has emerged as a promising alternative for training face recognition (FR) models, offering advantages in scalability, privacy compliance, and potential for bias mitigation. However, critical questions remain on whether both high accuracy and fairness can be achieved with synthetic data. In this work, we evaluate the impact of synthetic data on bias and performance of FR systems. We generate balanced face dataset, FairFaceGen, using two state of the art text-to-image generators, Flux.1-dev and Stable Diffusion v3.5 (SD35), and combine them with several identity augmentation methods, including Arc2Face and four IP-Adapters. By maintaining equal identity count across synthetic and real datasets, we ensure fair comparisons when evaluating FR performance on standard (LFW, AgeDB-30, etc.) and challenging IJB-B/C benchmarks and FR bias on Racial Faces in-the-Wild (RFW) dataset. Our results demonstrate that although synthetic data still lags behind the real datasets in the generalization on IJB-B/C, demographically balanced synthetic datasets, especially those generated with SD35, show potential for bias mitigation. We also observe that the number and quality of intra-class augmentations significantly affect FR accuracy and fairness. These findings provide practical guidelines for constructing fairer FR systems using synthetic data.
合成数据作为人脸识别(FR)模型训练的有前途的替代方案已经出现,其在可扩展性、隐私合规性和减轻偏见潜力方面具有优势。然而,关于是否可以使用合成数据实现高准确性和公平性的问题仍然悬而未决。在这项工作中,我们评估了合成数据对人脸识别系统偏见和性能的影响。我们使用两种最先进的文本到图像生成器Flux.1-dev和Stable Diffusion v3.5(SD35),并结合几种身份增强方法(包括Arc2Face和四种IP-Adapters),生成了平衡的人脸数据集FairFaceGen。通过保持合成数据集和真实数据集的身份计数相等,我们在标准(LFW、AgeDB-30等)和挑战性IJB-B/C基准测试集上评估人脸识别性能时,确保了公平的比较。我们的结果表明,虽然在IJB-B/C上的泛化能力上,合成数据仍然落后于真实数据,但人口统计学上平衡的合成数据,尤其是使用SD35生成的合成数据,显示出减轻偏见的潜力。我们还观察到,同类内的增广数量和质最显著地影响人脸识别准确性和公平性。这些发现提供了使用合成数据构建更公平的人脸识别系统的实用指南。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), 2025
Summary
本文探讨了合成数据在人脸识别(FR)模型训练中的应用,分析了合成数据对FR系统偏见和性能的影响。研究团队通过生成平衡的面部数据集FairFaceGen,结合多种身份增强方法,评估了合成数据在人脸识别方面的潜力。研究发现,尽管合成数据在某些方面仍落后于真实数据集,但其在偏见缓解方面显示出潜力,同时指出增强数量和质量对FR准确性和公平性的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 合成数据已成为人脸识别模型训练的有前途的替代方案,具有可扩展性、隐私合规性和减少偏见等优势。
- 通过生成平衡的面部数据集FairFaceGen和多种身份增强方法,研究了合成数据对人脸识别性能的影响。
- 合成数据在某些人脸识别标准测试集上的性能仍然低于真实数据,但在具有人口统计学特征的面部图像上显示出减少偏见的潜力。
- 使用不同文本到图像生成器生成的合成数据集在人脸识别方面的性能存在差异。
- 增强的人脸图像的数量和质量对人脸识别系统的准确性和公平性有重要影响。
- 使用合成数据构建更公平的人脸识别系统具有实际指导意义。
点此查看论文截图




Bias Analysis for Synthetic Face Detection: A Case Study of the Impact of Facial Attributes
Authors:Asmae Lamsaf, Lucia Cascone, Hugo Proença, João Neves
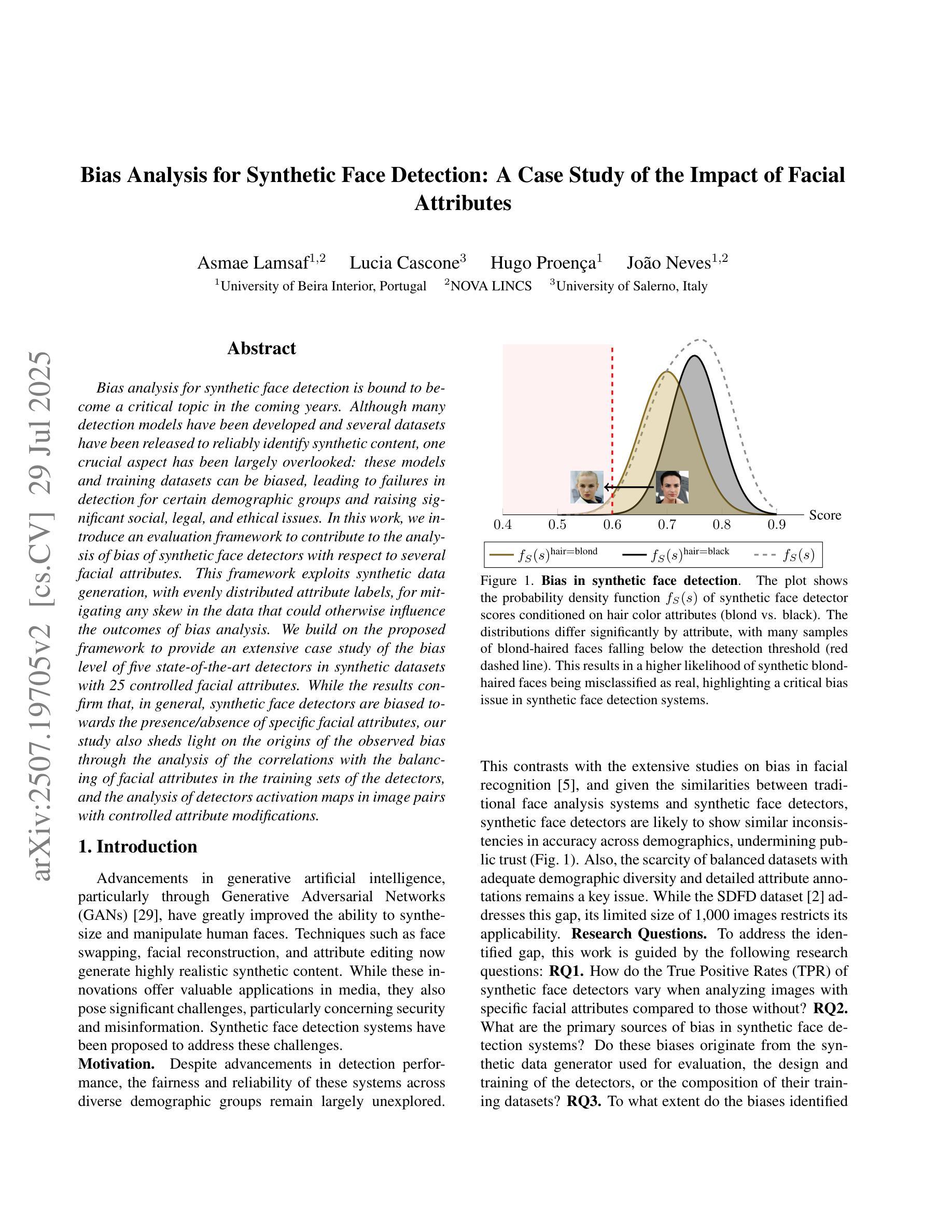
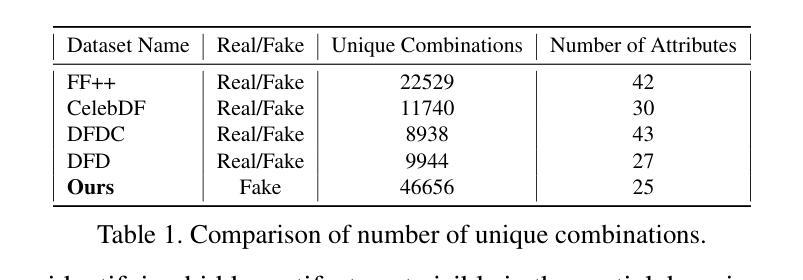
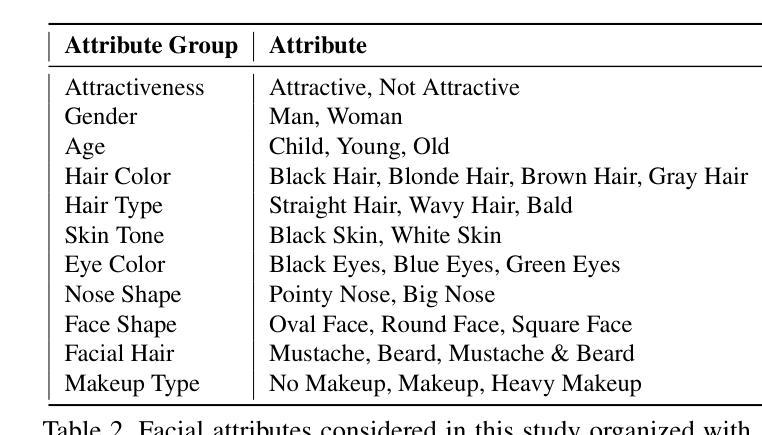
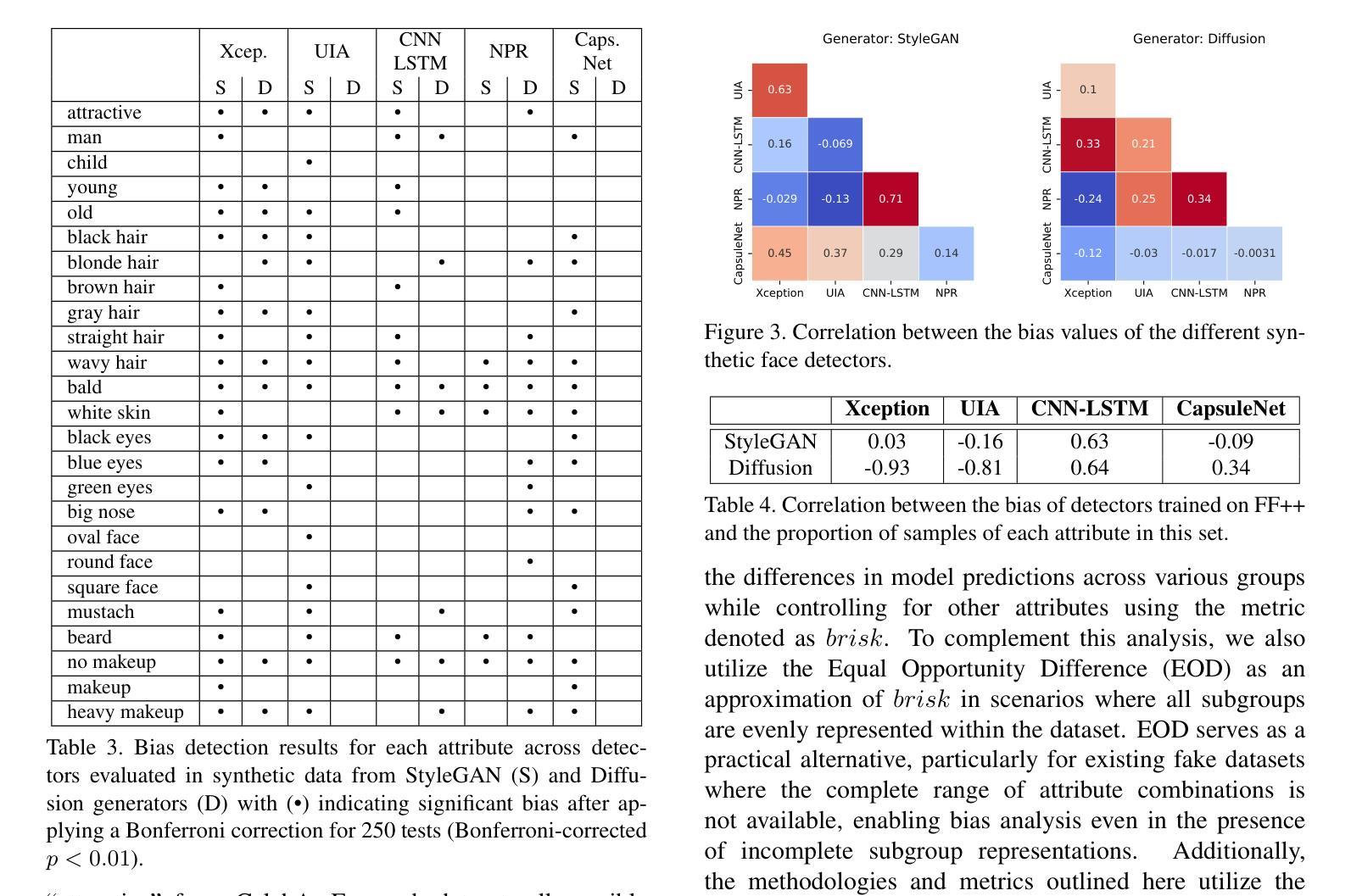
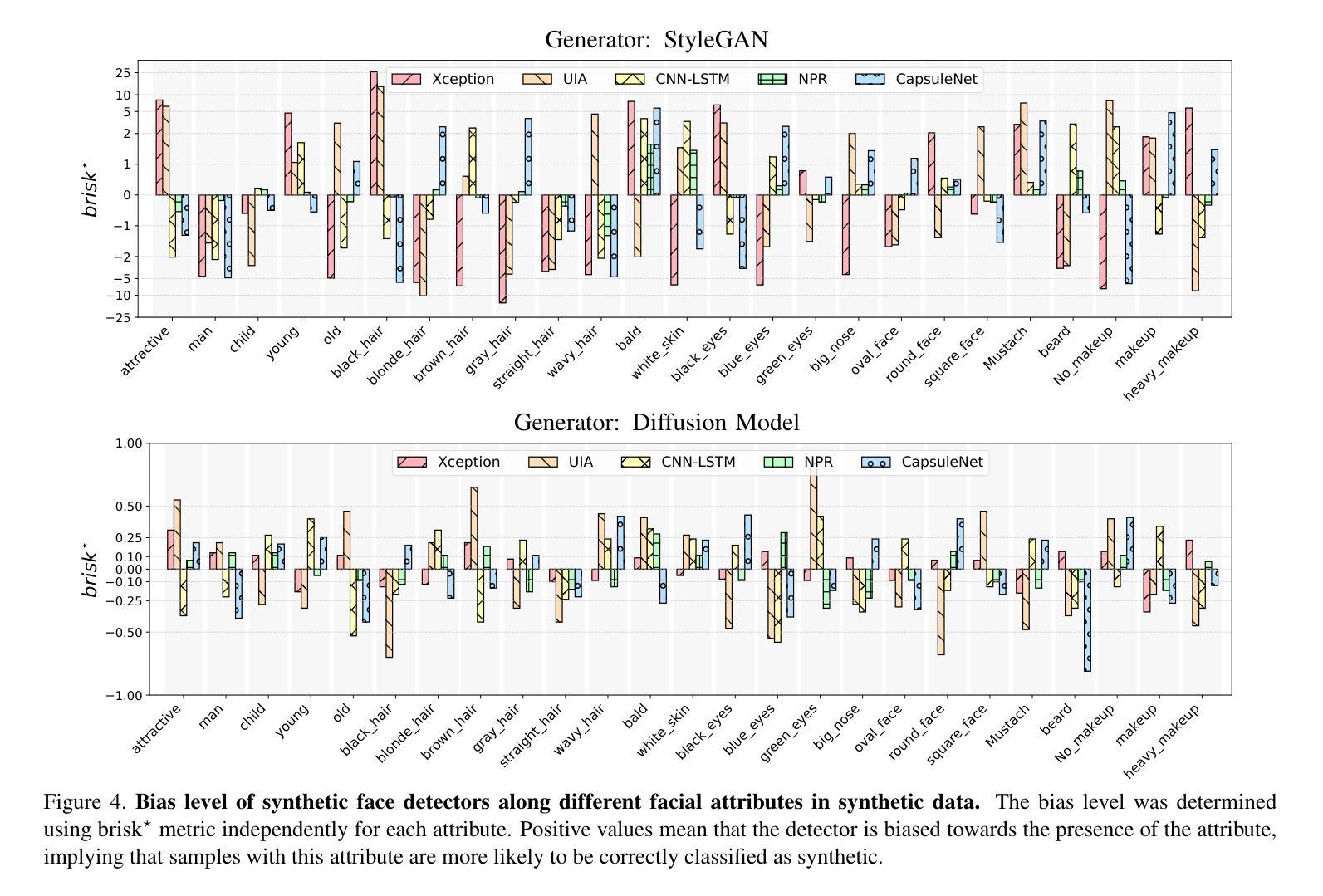
Bias analysis for synthetic face detection is bound to become a critical topic in the coming years. Although many detection models have been developed and several datasets have been released to reliably identify synthetic content, one crucial aspect has been largely overlooked: these models and training datasets can be biased, leading to failures in detection for certain demographic groups and raising significant social, legal, and ethical issues. In this work, we introduce an evaluation framework to contribute to the analysis of bias of synthetic face detectors with respect to several facial attributes. This framework exploits synthetic data generation, with evenly distributed attribute labels, for mitigating any skew in the data that could otherwise influence the outcomes of bias analysis. We build on the proposed framework to provide an extensive case study of the bias level of five state-of-the-art detectors in synthetic datasets with 25 controlled facial attributes. While the results confirm that, in general, synthetic face detectors are biased towards the presence/absence of specific facial attributes, our study also sheds light on the origins of the observed bias through the analysis of the correlations with the balancing of facial attributes in the training sets of the detectors, and the analysis of detectors activation maps in image pairs with controlled attribute modifications.
人脸识别检测中的偏见分析在未来几年必将成为一个重要话题。虽然已开发了许多检测模型,并且已发布了一些数据集,可以可靠地识别合成内容,但一个至关重要的方面却被忽视了:这些模型和训练数据集可能存在偏见,导致对某些人群的检测失败,并引发重大的社会、法律和伦理问题。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个评估框架,以分析合成面部检测器相对于多个面部属性的偏见问题。该框架利用合成数据生成,通过均匀分布的属性标签,减轻数据中的任何偏差,否则可能会影响偏见分析的结果。我们在提出的框架基础上,对五个最新检测器在合成数据集上的偏见程度进行了深入研究,涉及25个受控面部属性。虽然结果表明,总体上合成面部检测器倾向于面部属性的存在/缺失方面存在偏见,但我们的研究还通过分析和训练检测器数据集中的面部属性平衡与具有受控属性修改的图像对之间的相关性揭示了观察到的偏见的来源,以及分析了检测器的激活映射。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCB2025
Summary
人脸识别合成检测中的偏见分析将在未来几年成为关键话题。尽管已经开发了许多检测模型并发布了数据集来可靠地识别合成内容,但一个重要方面却被忽视了:这些模型和训练数据集可能存在偏见,导致对某些人群的检测失败,并引发重大的社会、法律和道德问题。本研究引入了一个评估框架,以分析合成面部检测器与多种面部属性相关的偏见。该框架利用合成数据生成,具有均匀分布的标签属性,以减轻数据中可能导致偏见分析结果的任何偏差。基于对提出的框架的构建,我们对五个最新检测器在具有25个受控面部属性的合成数据集中的偏见程度进行了深入研究。虽然结果表明,合成面部检测器通常偏向于特定面部属性的存在与否,但我们的研究还通过分析与训练集中面部属性的平衡以及分析图像对中具有受控属性修改的检测器激活图来揭示观察到的偏见的根源。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别合成检测中的偏见分析在未来几年将变得重要。
- 当前检测模型和训练数据集存在偏见问题,可能导致某些人群的检测失败。
- 提出的评估框架旨在分析合成面部检测器与多种面部属性相关的偏见。
- 利用合成数据生成具有均匀分布的标签属性,以减轻数据偏差对偏见分析的影响。
- 研究表明合成面部检测器通常偏向于特定面部属性的存在与否。
- 偏见的来源与训练集中面部属性的平衡有关。
点此查看论文截图

TruthLens: Explainable DeepFake Detection for Face Manipulated and Fully Synthetic Data
Authors:Rohit Kundu, Shan Jia, Vishal Mohanty, Athula Balachandran, Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury
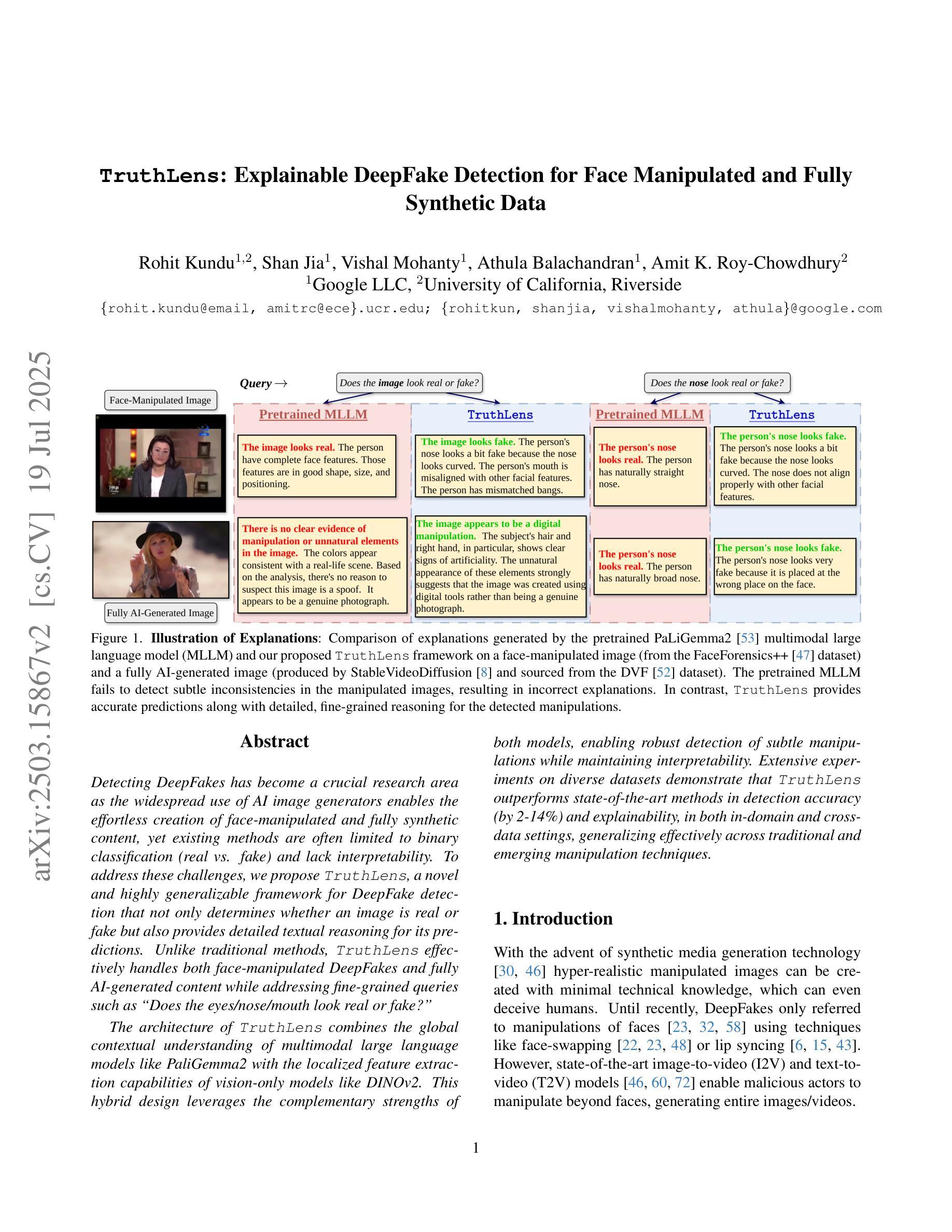
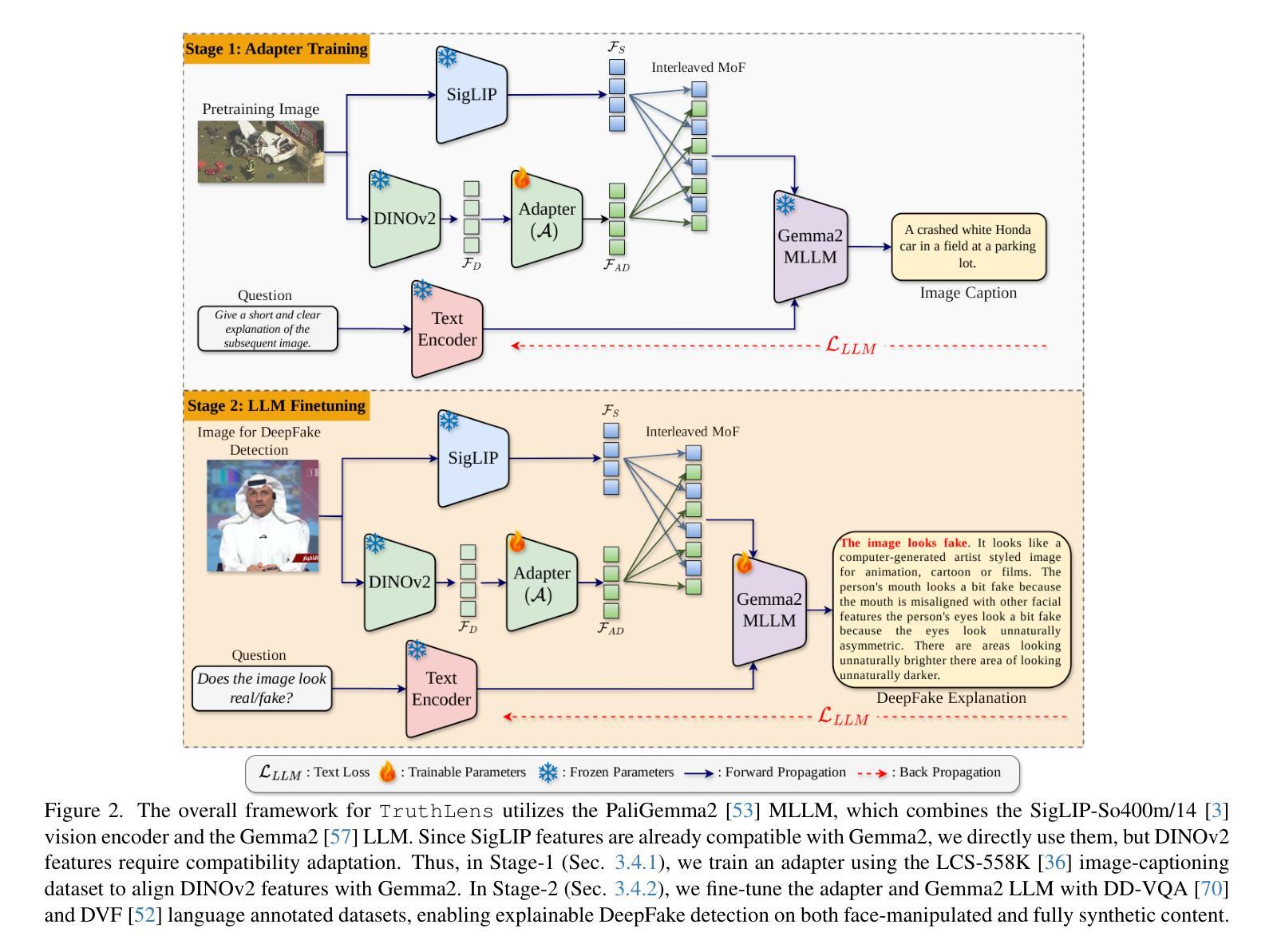
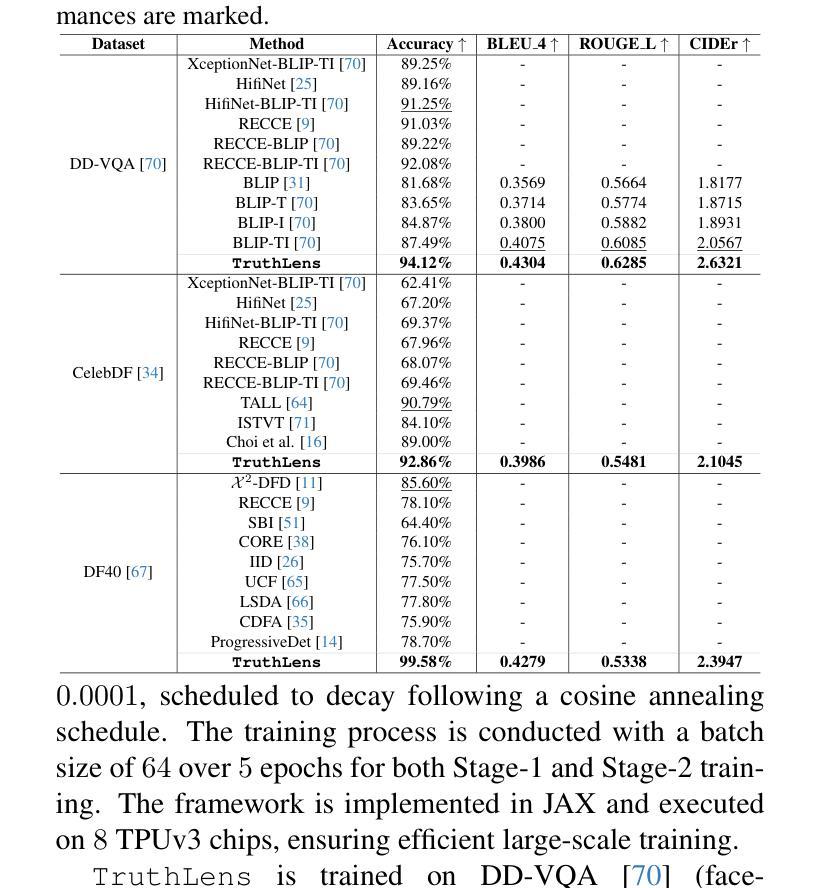
Detecting DeepFakes has become a crucial research area as the widespread use of AI image generators enables the effortless creation of face-manipulated and fully synthetic content, yet existing methods are often limited to binary classification (real vs. fake) and lack interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose TruthLens, a novel and highly generalizable framework for DeepFake detection that not only determines whether an image is real or fake but also provides detailed textual reasoning for its predictions. Unlike traditional methods, TruthLens effectively handles both face-manipulated DeepFakes and fully AI-generated content while addressing fine-grained queries such as “Does the eyes/nose/mouth look real or fake?” The architecture of TruthLens combines the global contextual understanding of multimodal large language models like PaliGemma2 with the localized feature extraction capabilities of vision-only models like DINOv2. This hybrid design leverages the complementary strengths of both models, enabling robust detection of subtle manipulations while maintaining interpretability. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets demonstrate that TruthLens outperforms state-of-the-art methods in detection accuracy (by 2-14%) and explainability, in both in-domain and cross-data settings, generalizing effectively across traditional and emerging manipulation techniques.
检测DeepFakes已经成为一个关键的研究领域,随着人工智能图像生成器的广泛应用,可以轻松创建面部操作和完全合成的内容。然而,现有的方法通常仅限于二元分类(真实与虚假),并且缺乏可解释性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了TruthLens,这是一个用于DeepFake检测的新型且高度通用的框架。它不仅确定图像是真实的还是假的,而且还为其预测提供了详细的文本理由。与传统的检测方法不同,TruthLens能够有效地处理面部操作的DeepFakes和完全AI生成的内容,并解决了细微的查询,例如“眼睛/鼻子/嘴巴看起来是真实还是假的?” TruthLens的架构结合了多模态大型语言模型(如PaliGemma2)的全局上下文理解与仅视觉模型(如DINOv2)的局部特征提取能力。这种混合设计利用了两者的互补优势,能够在保持可解释性的同时,实现微妙的操作的稳健检测。在多种数据集上的广泛实验表明,TruthLens在检测准确率(提高2-14%)和可解释性方面均优于现有技术,并且在跨领域和数据交叉设置中表现有效,能够很好地适应传统和新兴的操作技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
真理透镜(TruthLens)框架是一种用于检测DeepFakes的新型通用化框架,不仅能够确定图像是否真实,还能为预测提供详细的文本解释。它结合了多模态大型语言模型(如PaliGemma2)的全局上下文理解和仅视觉模型(如DINOv2)的局部特征提取能力,在多种数据集上的实验表明,TruthLens在检测准确性和解释性方面都优于最新技术方法,并且在跨数据设置中对传统和新兴操作技术都具有有效泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- TruthLens是一种用于检测DeepFakes的新型框架,能够判断图像真伪并提供预测依据的详细文本解释。
- TruthLens结合了多模态大型语言模型和视觉模型的优点,具备全局上下文理解和局部特征提取能力。
- TruthLens不仅能处理面部操作的DeepFakes,还能处理完全AI生成的内容。
- TruthLens可以处理精细粒度查询,如眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴的真实性或虚假性。
- TruthLens在检测准确性和解释性方面优于现有方法。
- TruthLens在跨数据设置中对传统和新兴操作技术具有有效泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
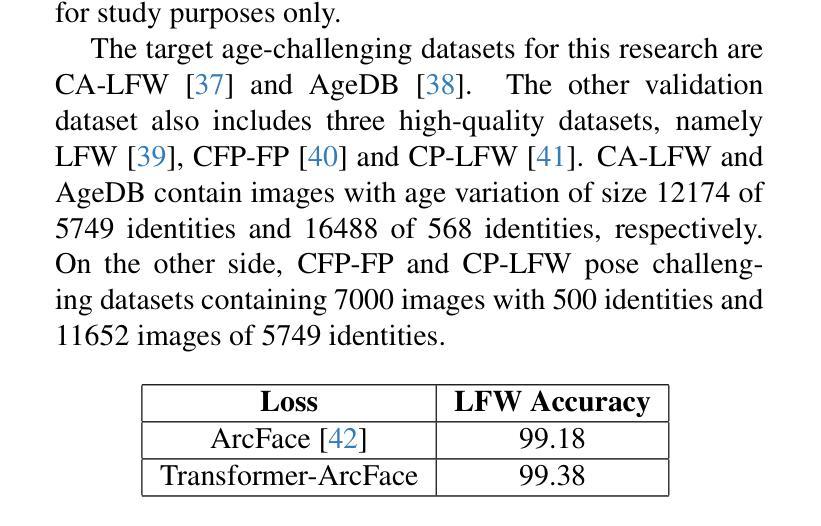
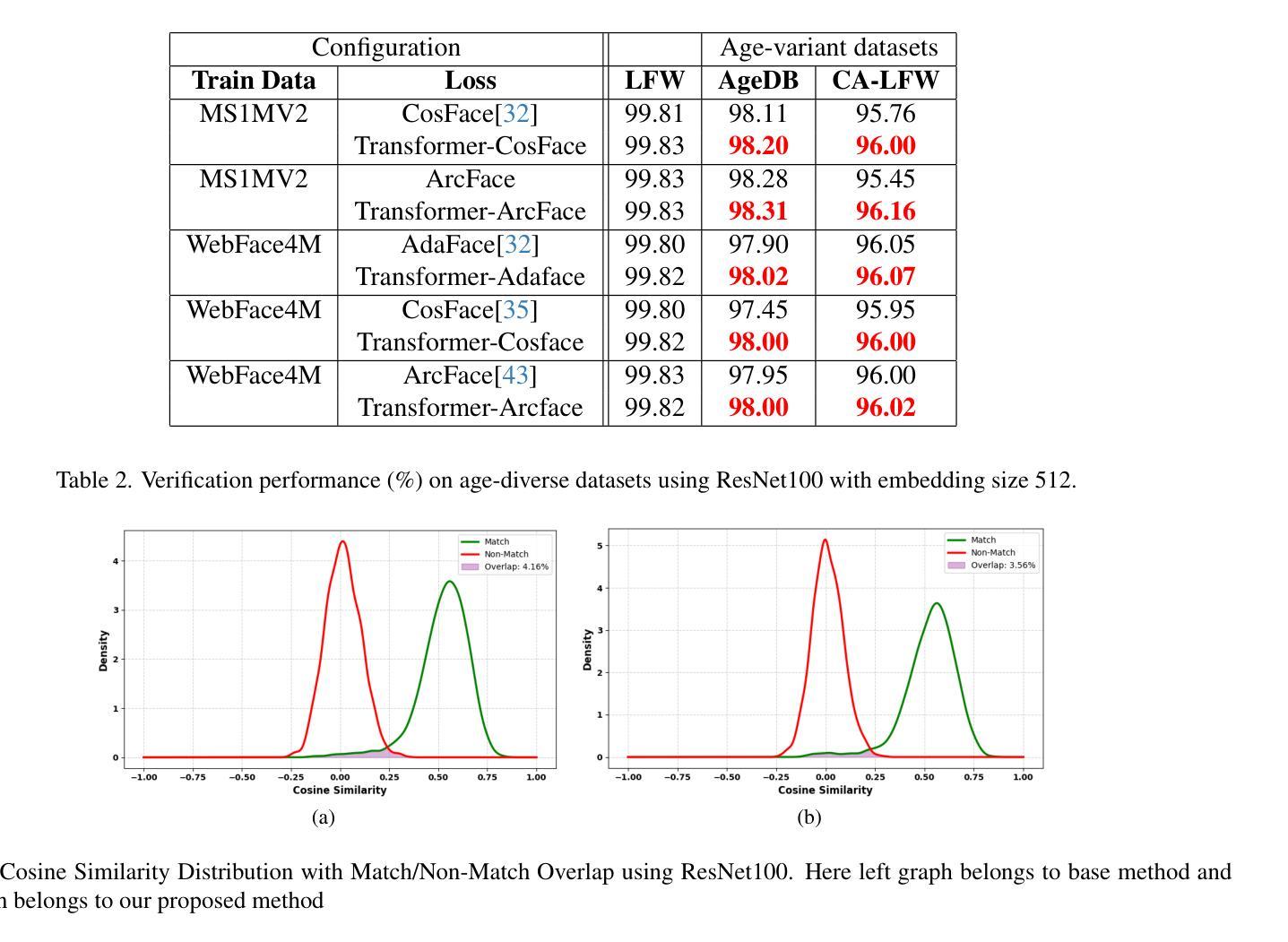
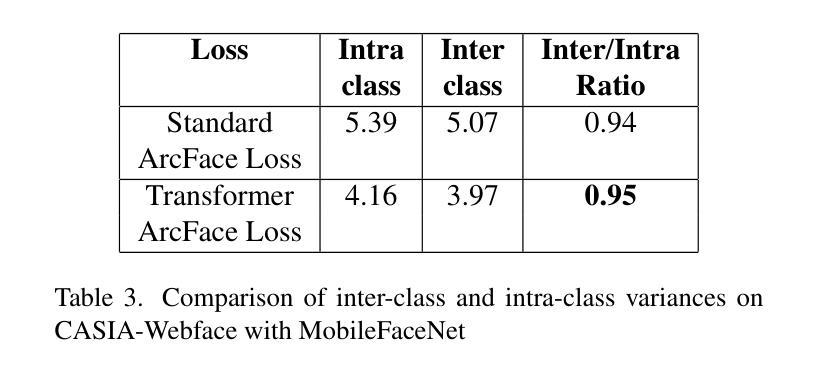
Transformer-Based Auxiliary Loss for Face Recognition Across Age Variations
Authors:Pritesh Prakash, S Umamaheswaran
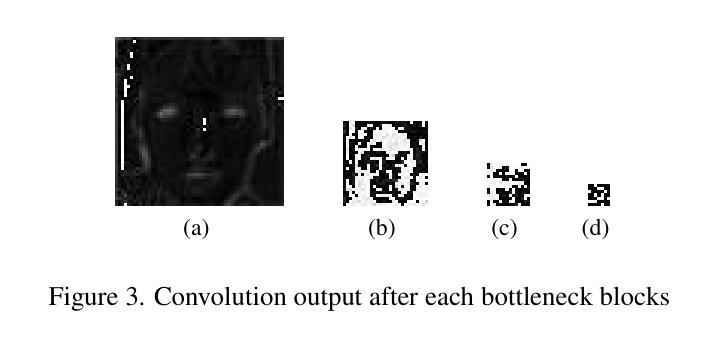
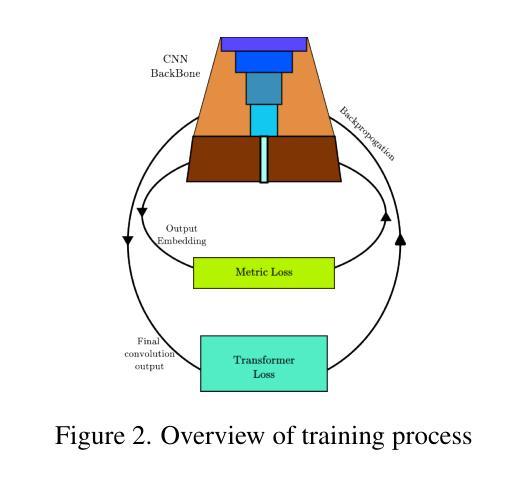
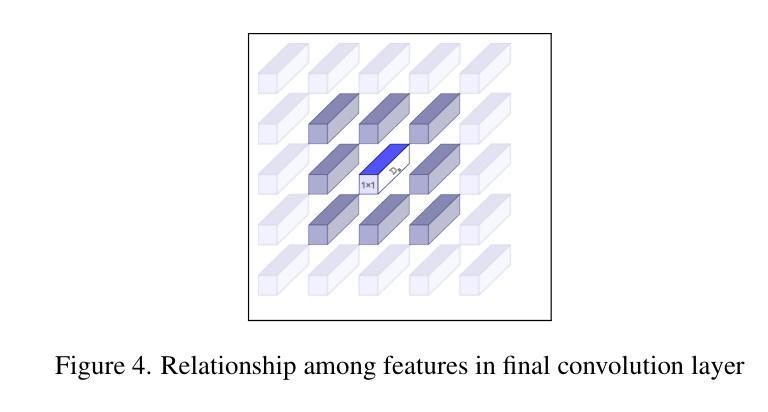
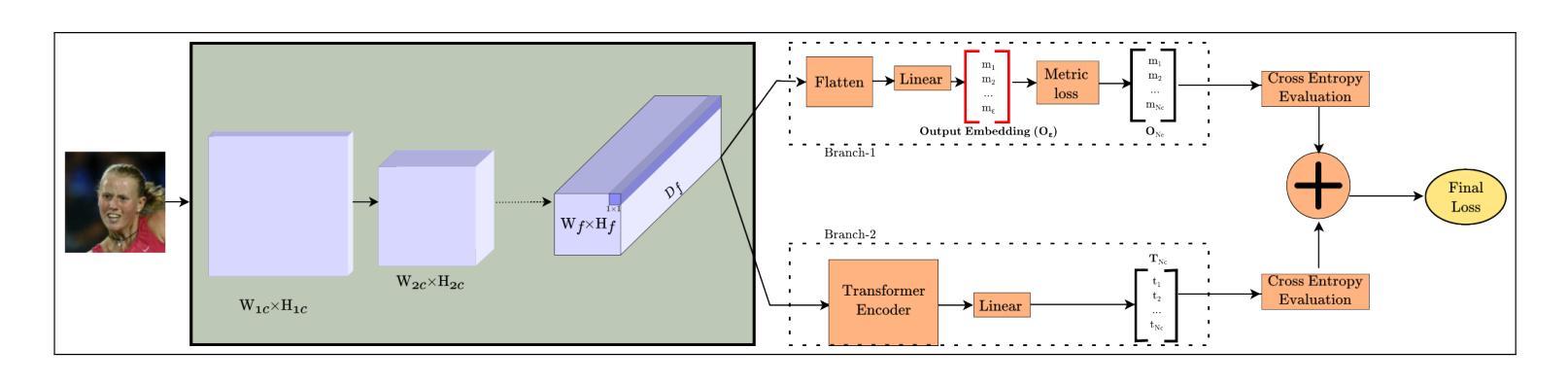
Aging presents a significant challenge in face recognition, as changes in skin texture and tone can alter facial features over time, making it particularly difficult to compare images of the same individual taken years apart, such as in long-term identification scenarios. Transformer networks have the strength to preserve sequential spatial relationships caused by aging effect. This paper presents a technique for loss evaluation that uses a transformer network as an additive loss in the face recognition domain. The standard metric loss function typically takes the final embedding of the main CNN backbone as its input. Here, we employ a transformer-metric loss, a combined approach that integrates both transformer-loss and metric-loss. This research intends to analyze the transformer behavior on the convolution output when the CNN outcome is arranged in a sequential vector. These sequential vectors have the potential to overcome the texture or regional structure referred to as wrinkles or sagging skin affected by aging. The transformer encoder takes input from the contextual vectors obtained from the final convolution layer of the network. The learned features can be more age-invariant, complementing the discriminative power of the standard metric loss embedding. With this technique, we use transformer loss with various base metric-loss functions to evaluate the effect of the combined loss functions. We observe that such a configuration allows the network to achieve SoTA results in LFW and age-variant datasets (CA-LFW and AgeDB). This research expands the role of transformers in the machine vision domain and opens new possibilities for exploring transformers as a loss function.
人脸识别中,老化构成了一大挑战。随着时间的推移,皮肤纹理和颜色的变化可能会改变面部特征,导致多年前的同一个人照片对比变得特别困难,如在长期识别场景中。Transformer网络擅长保留由老化效应引起的连续空间关系。本文介绍了一种用于损失评估的技术,该技术使用transformer网络作为人脸识别领域的附加损失。标准的度量损失函数通常将主CNN骨干的最终嵌入作为其输入。在这里,我们采用了transformer-metric损失这一综合方法,结合了transformer损失和度量损失。本研究旨在分析CNN输出以序列向量形式排列时transformer在卷积输出上的行为。这些序列向量具有克服由老化引起的纹理或称为皱纹或皮肤松弛的区域结构的潜力。Transformer编码器以从网络最终卷积层获得的上下文向量为输入。学习的特征可以更不受年龄影响,补充标准度量损失嵌入的辨别力。使用此技术,我们将transformer损失与各种基本度量损失函数结合,以评估组合损失函数的效果。我们发现这种配置允许网络在LFW和年龄变化数据集(CA-LFW和AgeDB)上达到最新结果。该研究扩大了transformer在机器视觉领域的作用,为探索将transformer作为损失函数开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Face Recognition for Age-variant Datasets
Summary
该论文探讨了使用Transformer网络在人脸识别领域中的损失评估技术。针对因年龄增长导致的面部特征变化,该研究提出了一种结合Transformer损失和度量损失的混合方法。通过利用Transformer网络处理CNN输出的卷积序列向量,该方法能够克服因老化引起的皮肤纹理或区域结构变化,从而提高人脸识别的准确性。该配置在LFW、CA-LFW和AgeDB等数据集上取得了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 年龄增长对人脸识别构成了挑战,导致面部特征和皮肤纹理的变化。
- Transformer网络有能力处理由老化引起的序列空间关系的变化。
- 该论文提出了结合Transformer损失和度量损失的混合方法,用于人脸识别领域的损失评估。
- Transformer网络处理CNN输出的卷积序列向量,有助于克服老化引起的皮肤纹理或区域结构变化。
- 该方法在多个数据集上取得了先进的人脸识别成果。
- 此研究扩展了Transformer在机器视觉领域的应用,并为未来探索提供了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图