⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
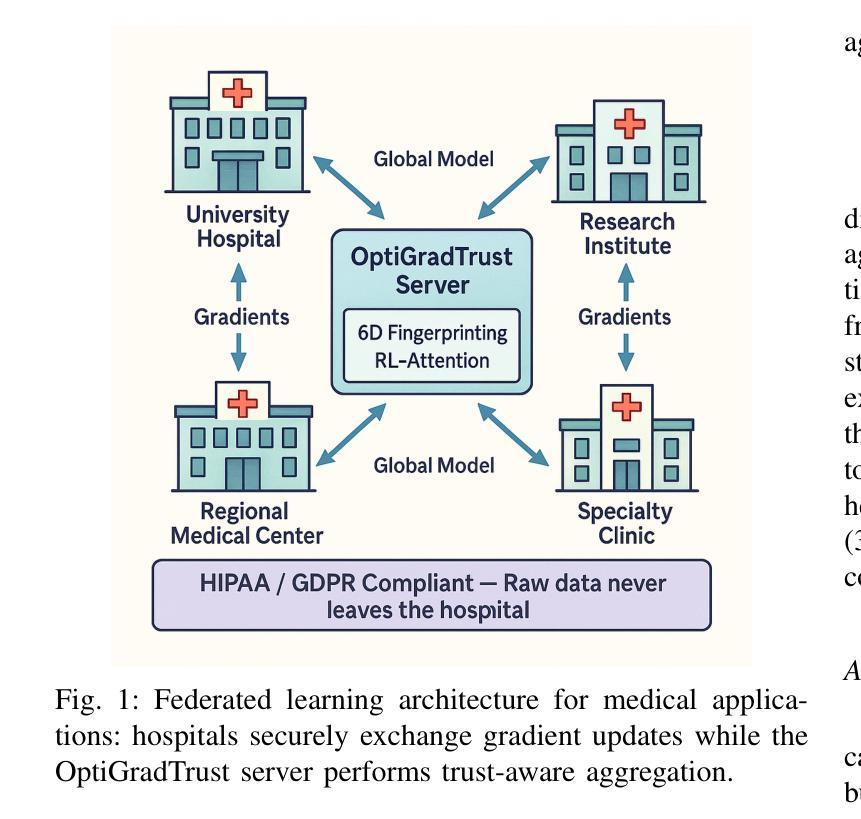
OptiGradTrust: Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning with Multi-Feature Gradient Analysis and Reinforcement Learning-Based Trust Weighting
Authors:Mohammad Karami, Fatemeh Ghassemi, Hamed Kebriaei, Hamid Azadegan
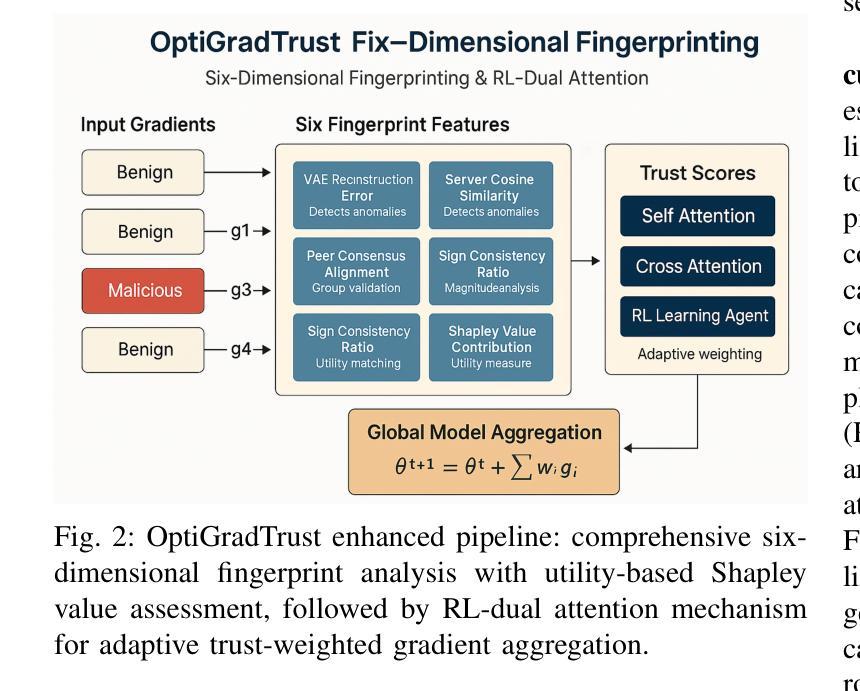
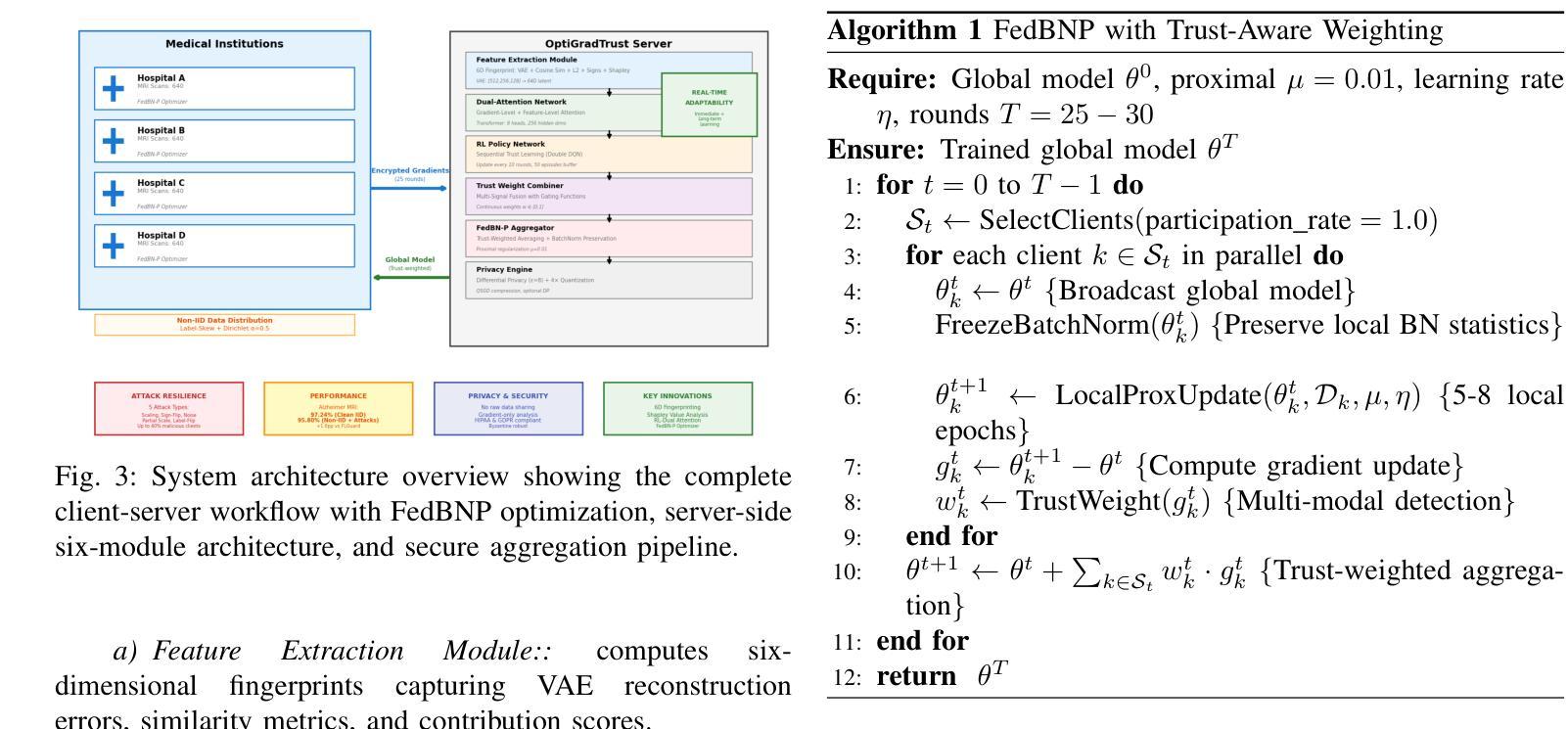
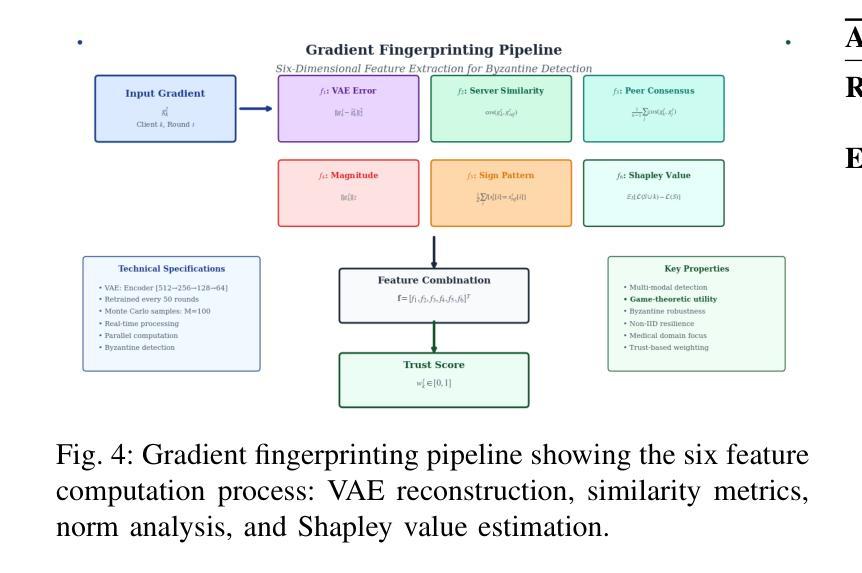
Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across distributed medical institutions while preserving patient privacy, but remains vulnerable to Byzantine attacks and statistical heterogeneity. We present OptiGradTrust, a comprehensive defense framework that evaluates gradient updates through a novel six-dimensional fingerprint including VAE reconstruction error, cosine similarity metrics, $L_2$ norm, sign-consistency ratio, and Monte Carlo Shapley value, which drive a hybrid RL-attention module for adaptive trust scoring. To address convergence challenges under data heterogeneity, we develop FedBN-Prox (FedBN-P), combining Federated Batch Normalization with proximal regularization for optimal accuracy-convergence trade-offs. Extensive evaluation across MNIST, CIFAR-10, and Alzheimer’s MRI datasets under various Byzantine attack scenarios demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art defenses, achieving up to +1.6 percentage points over FLGuard under non-IID conditions while maintaining robust performance against diverse attack patterns through our adaptive learning approach.
联邦学习(FL)能够在分布式医疗机构之间进行协作模型训练,同时保护患者隐私,但仍易受到拜占庭攻击和统计异质性的威胁。我们提出了OptiGradTrust,这是一个全面的防御框架,它通过一种新型六维指纹来评估梯度更新,包括VAE重建误差、余弦相似度指标、L2范数、符号一致性比率以及蒙特卡洛沙普利值,这些指标驱动混合RL-注意力模块进行自适应信任评分。为了解决数据异质性下的收敛挑战,我们开发了FedBN-Prox(FedBN-P),它将联邦批标准化与近端正则化相结合,以实现最优的精度-收敛权衡。在MNIST、CIFAR-10和阿尔茨海默症MRI数据集上的各种拜占庭攻击场景下的广泛评估表明,与最先进的防御手段相比,我们的防御策略有着显著的提升。在非IID条件下,与FLGuard相比,我们的方法提高了高达1.6个百分点;通过我们的自适应学习方法,对多种攻击模式保持了稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像领域中的联邦学习(FL)面临拜占庭攻击和统计异质性的挑战。提出OptiGradTrust框架,通过六维指纹评估梯度更新,包括VAE重建误差、余弦相似度度量、L2范数等,驱动混合RL-注意力模块进行自适应信任评分。为解决数据异质性下的收敛挑战,开发FedBN-Prox结合联邦批归一化与近端正则化,实现精度与收敛的平衡。在MNIST、CIFAR-10和阿尔茨海默症MRI数据集下的拜占庭攻击场景中评估表现卓越,相较于现有防御手段有显著改进,在非IID条件下较FLGuard提升最多达+1.6个百分点,并能在各种攻击模式下保持稳健性能。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习在医学图像领域面临拜占庭攻击和统计异质性的挑战。
- OptiGradTrust框架通过六维指纹评估梯度更新,包括多种指标如VAE重建误差等。
- 该框架采用混合RL-注意力模块进行自适应信任评分。
- FedBN-Prox结合联邦批归一化与近端正则化以解决数据异质性下的收敛挑战。
- 在多个数据集和攻击场景下的评估显示OptiGradTrust较现有防御手段有显著改进。
- 在非IID条件下较FLGuard提升最多达+1.6个百分点。
点此查看论文截图

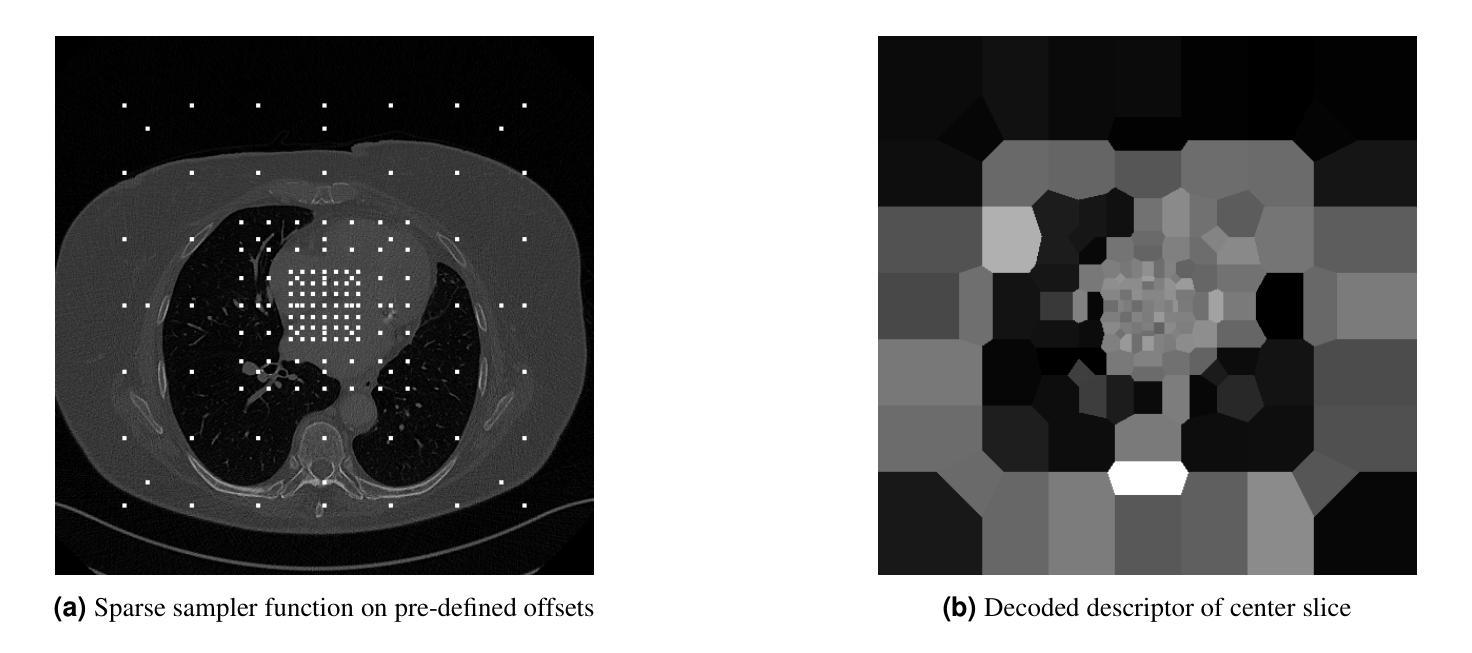
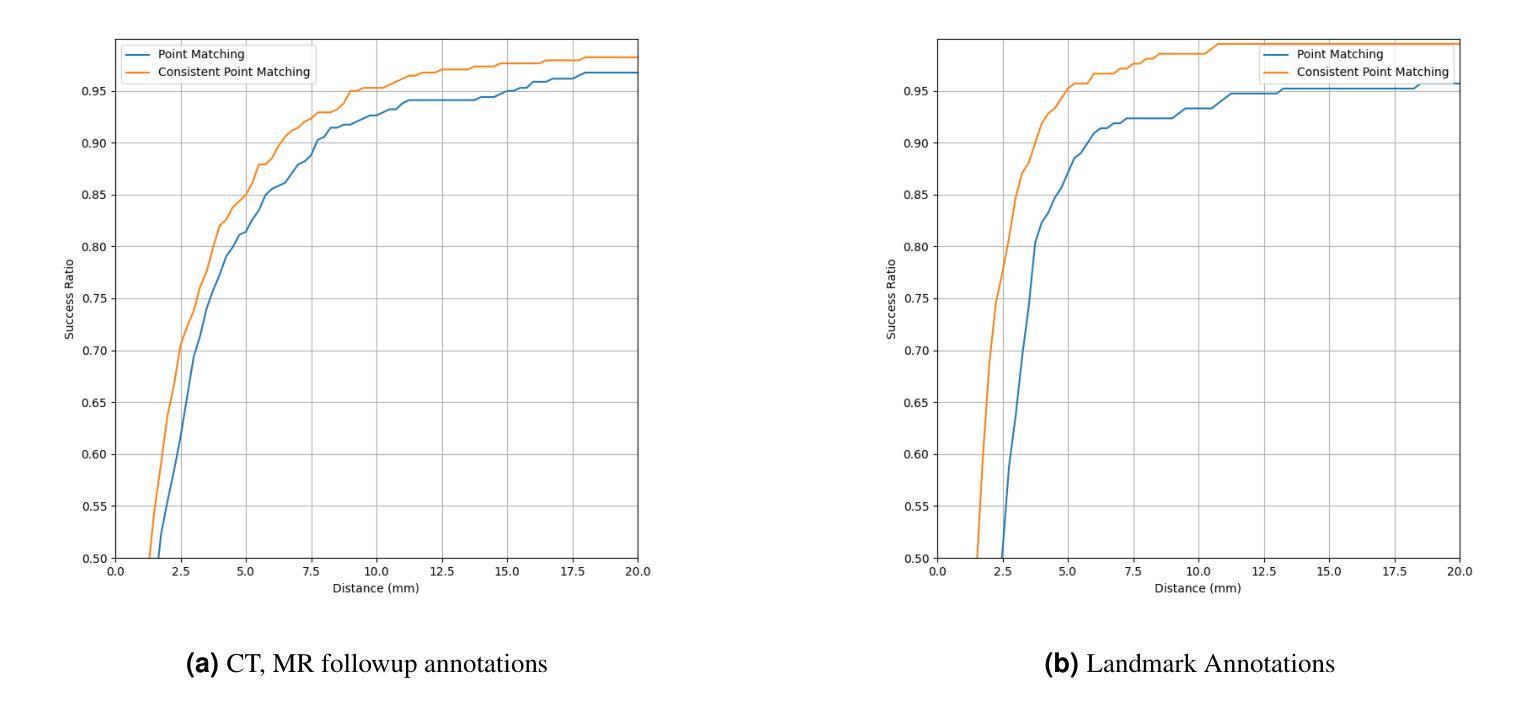
Consistent Point Matching
Authors:Halid Ziya Yerebakan, Gerardo Hermosillo Valadez
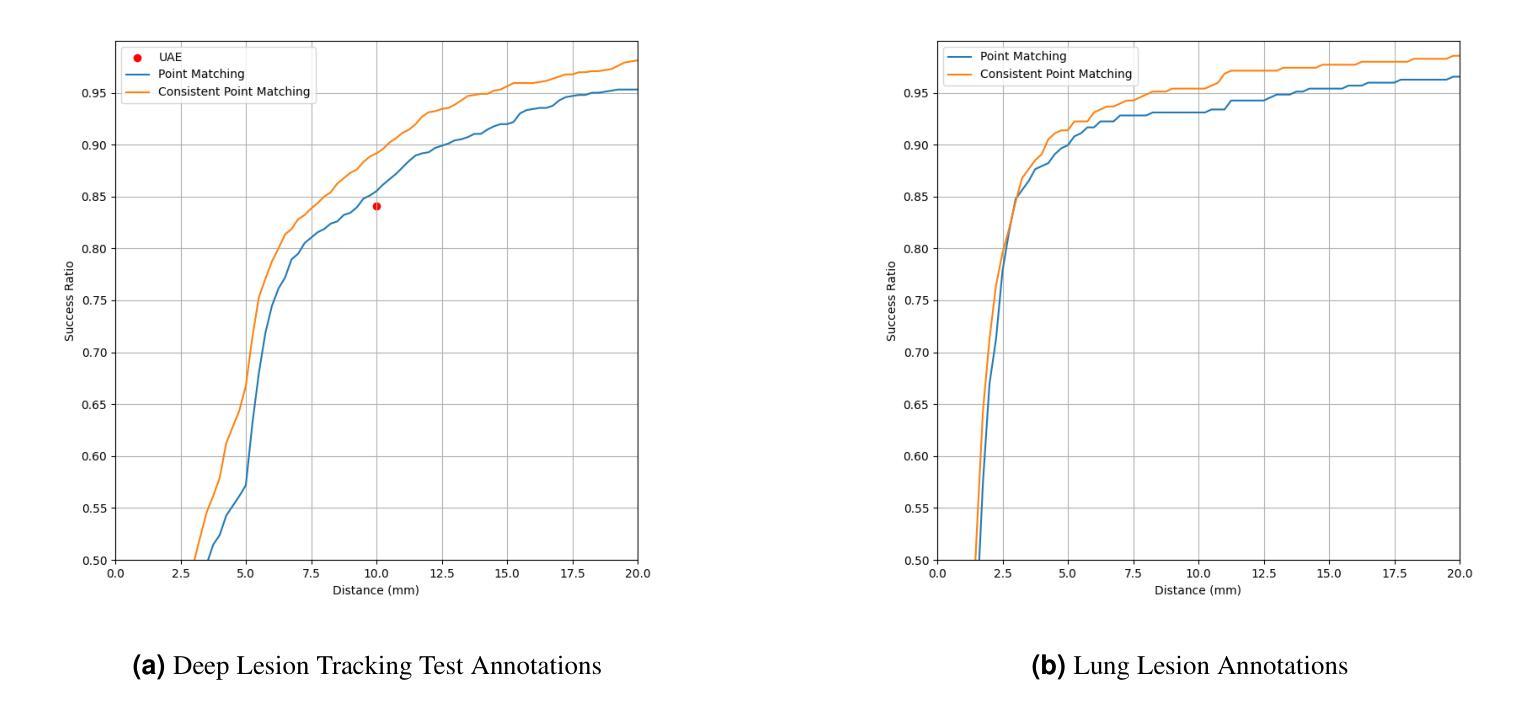
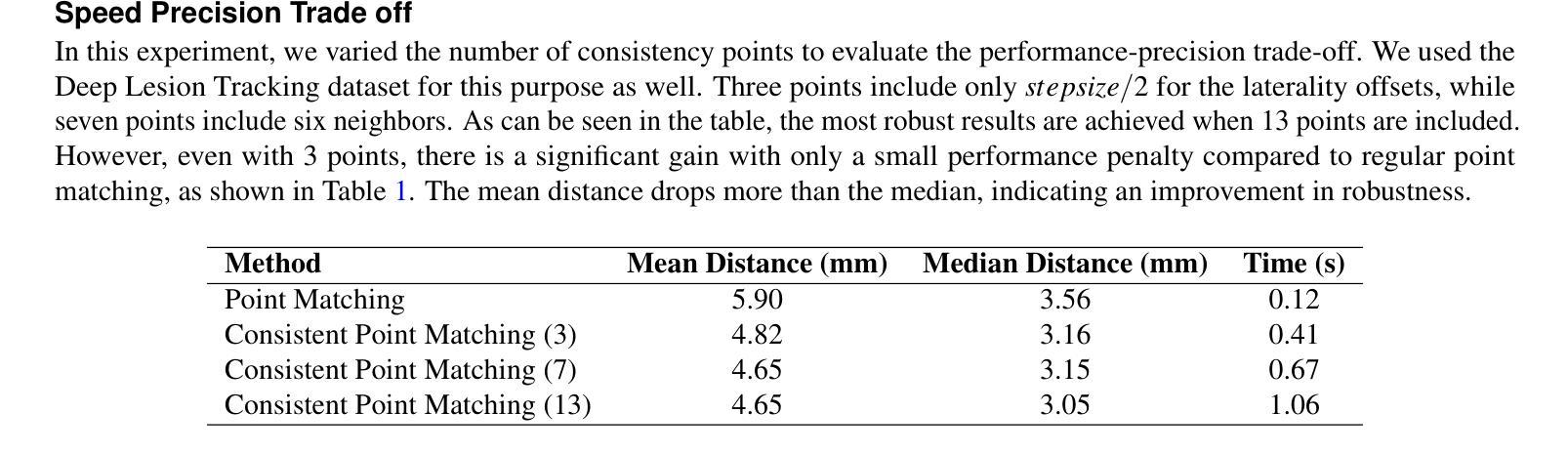
This study demonstrates that incorporating a consistency heuristic into the point-matching algorithm \cite{yerebakan2023hierarchical} improves robustness in matching anatomical locations across pairs of medical images. We validated our approach on diverse longitudinal internal and public datasets spanning CT and MRI modalities. Notably, it surpasses state-of-the-art results on the Deep Lesion Tracking dataset. Additionally, we show that the method effectively addresses landmark localization. The algorithm operates efficiently on standard CPU hardware and allows configurable trade-offs between speed and robustness. The method enables high-precision navigation between medical images without requiring a machine learning model or training data.
本研究展示了将一致性启发式策略融入点匹配算法(引用自yerebakan2023hierarchical)中,可以提高跨对医学图像匹配解剖位置的稳健性。我们在涵盖CT和MRI模态的多样纵向内部和公开数据集上验证了我们的方法。值得注意的是,它在Deep Lesion Tracking数据集上的表现超过了最新技术。此外,我们还证明了该方法可以有效地解决地标定位问题。该算法在标准CPU硬件上运行高效,允许在速度和稳健性之间进行可配置的权衡。该方法无需机器学习模型或训练数据,即可实现医学图像之间的高精度导航。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文展示了在点匹配算法中引入一致性启发式方法,提高了在不同医学图像对之间匹配解剖位置的稳健性。该算法在多种纵向内部和公共数据集上进行了验证,包括CT和MRI模态。该方法在Deep Lesion Tracking数据集上的表现超过了现有技术,并有效地解决了地标定位问题。算法在标准CPU硬件上运行高效,可实现速度和稳健性之间的可配置权衡。该方法无需机器学习模型或训练数据即可实现医学图像之间的高精度导航。
Key Takeaways
- 引入一致性启发式方法改进了点匹配算法的稳健性。
- 在多种纵向内部和公共数据集(包括CT和MRI模态)上验证了该算法的有效性。
- 该方法在Deep Lesion Tracking数据集上的表现超越了现有技术。
- 算法解决了地标定位问题。
- 算法在标准CPU硬件上运行高效。
- 算法可实现速度和稳健性之间的可配置权衡。
点此查看论文截图




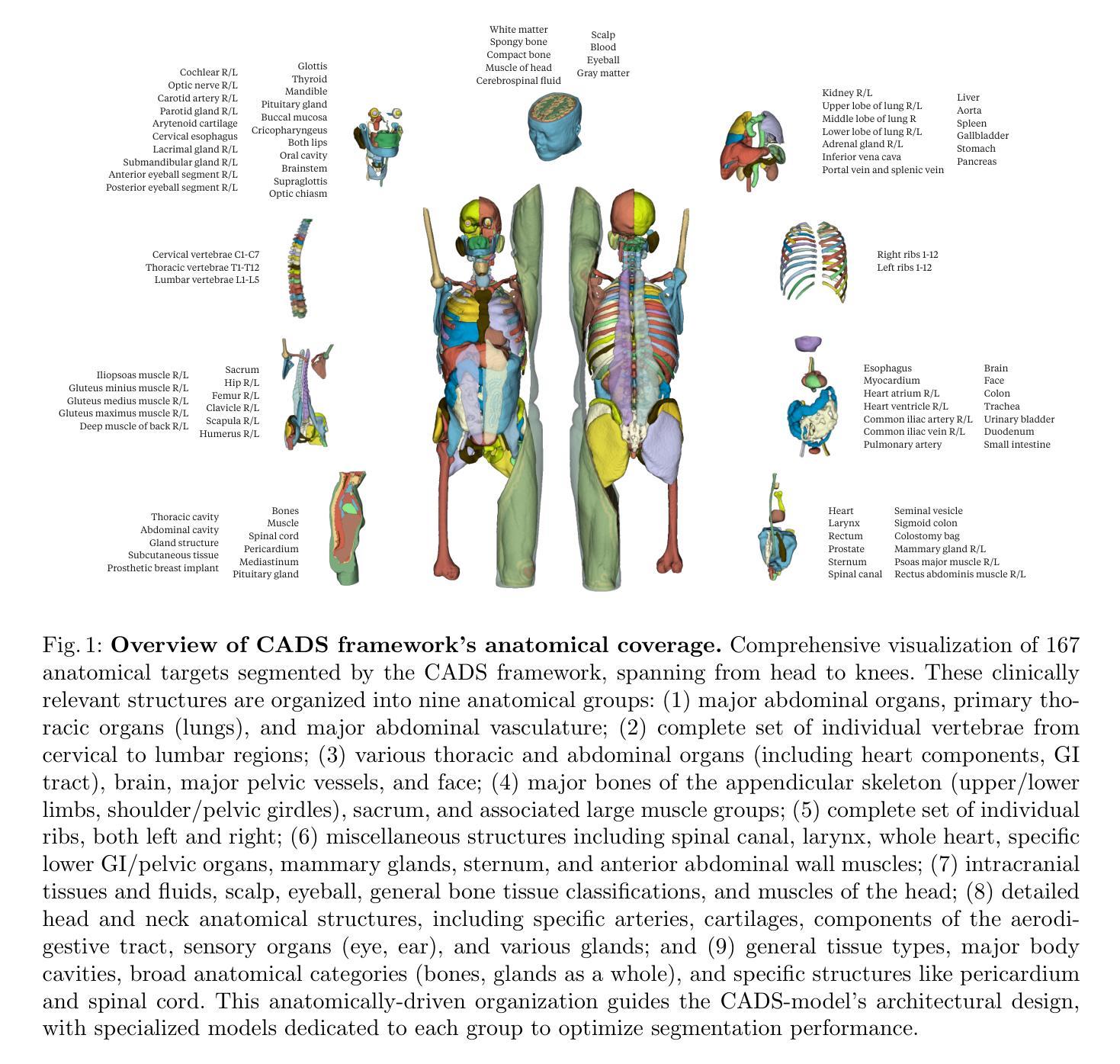
CADS: A Comprehensive Anatomical Dataset and Segmentation for Whole-Body Anatomy in Computed Tomography
Authors:Murong Xu, Tamaz Amiranashvili, Fernando Navarro, Maksym Fritsak, Ibrahim Ethem Hamamci, Suprosanna Shit, Bastian Wittmann, Sezgin Er, Sebastian M. Christ, Ezequiel de la Rosa, Julian Deseoe, Robert Graf, Hendrik Möller, Anjany Sekuboyina, Jan C. Peeken, Sven Becker, Giulia Baldini, Johannes Haubold, Felix Nensa, René Hosch, Nikhil Mirajkar, Saad Khalid, Stefan Zachow, Marc-André Weber, Georg Langs, Jakob Wasserthal, Mehmet Kemal Ozdemir, Andrey Fedorov, Ron Kikinis, Stephanie Tanadini-Lang, Jan S. Kirschke, Stephanie E. Combs, Bjoern Menze
Accurate delineation of anatomical structures in volumetric CT scans is crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning. While AI has advanced automated segmentation, current approaches typically target individual structures, creating a fragmented landscape of incompatible models with varying performance and disparate evaluation protocols. Foundational segmentation models address these limitations by providing a holistic anatomical view through a single model. Yet, robust clinical deployment demands comprehensive training data, which is lacking in existing whole-body approaches, both in terms of data heterogeneity and, more importantly, anatomical coverage. In this work, rather than pursuing incremental optimizations in model architecture, we present CADS, an open-source framework that prioritizes the systematic integration, standardization, and labeling of heterogeneous data sources for whole-body CT segmentation. At its core is a large-scale dataset of 22,022 CT volumes with complete annotations for 167 anatomical structures, representing a significant advancement in both scale and coverage, with 18 times more scans than existing collections and 60% more distinct anatomical targets. Building on this diverse dataset, we develop the CADS-model using established architectures for accessible and automated full-body CT segmentation. Through comprehensive evaluation across 18 public datasets and an independent real-world hospital cohort, we demonstrate advantages over SoTA approaches. Notably, thorough testing of the model’s performance in segmentation tasks from radiation oncology validates its direct utility for clinical interventions. By making our large-scale dataset, our segmentation models, and our clinical software tool publicly available, we aim to advance robust AI solutions in radiology and make comprehensive anatomical analysis accessible to clinicians and researchers alike.
在三维CT扫描中对解剖结构的精确描绘对诊断和治疗计划的制定至关重要。虽然人工智能已经推动了自动化分割的发展,但当前的方法通常针对单个结构,导致出现了分割模型表现不一、评价协议各异的不统一局面。基础分割模型通过单一模型提供整体解剖视图来解决这些局限性。然而,在临床上的稳健部署需要全面的训练数据,而现有的全身方法在这方面缺乏数据,既体现在数据异质性上,更重要的是体现在解剖结构覆盖方面。在这项工作中,我们并没有追求模型架构的增量优化,而是推出了CADS,这是一个优先整合、标准化和标注异质数据源的全身CT分割开源框架。其核心是一个包含22,022个CT体积的大规模数据集,对167个解剖结构进行了完整标注,无论是在规模还是覆盖面上,这代表了一次重大进步,其包含的扫描次数是现有集合的18倍,独特的解剖目标增加了60%。基于这个多样化的数据集,我们建立了CADS模型,采用已建立的架构进行可访问和自动化的全身CT分割。通过对18个公共数据集和一个独立的真实世界医院队列的全面评估,我们展示了相较于最新方法的好处。值得注意的是,该模型在放射肿瘤学中的分割任务方面的出色表现验证了其在临床干预中的直接效用。我们致力于将大规模数据集、我们的分割模型和临床软件工具公开提供,以推动放射学的稳健人工智能解决方案的发展,使临床医生和研究人员都能获得全面的解剖分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在容积CT扫描中对解剖结构进行精确描绘的重要性,对于诊断和治疗计划至关重要。虽然人工智能已经推动了自动化分割的进展,但当前的方法通常针对单个结构,存在模型不兼容、性能差异大以及评估协议不统一等问题。基础分割模型通过单一模型提供整体解剖视图来解决这些限制。然而,要在临床实践中稳健应用仍需要全面的训练数据,而现有的全身方法缺乏数据异质性和更重要的解剖覆盖。因此,本文提出了一种名为CADS的开源框架,它优先整合、标准化和标记异质数据源,用于全身CT分割。该框架的核心是一个大规模数据集,包含22,022个CT体积和167个解剖结构的完整注释,无论在规模还是覆盖范围上都代表了重大进展。在此基础上,本文建立了CADS模型,采用现有架构实现可访问和自动化的全身CT分割。通过跨18个公共数据集和独立医院队列的全面评估,证明了与最新技术相比的优势。特别是在辐射肿瘤学中的分割任务中验证了其临床干预的直接效用。本文公开提供了大规模数据集、分割模型和临床软件工具,旨在推动放射学中稳健的人工智能解决方案,使临床医生和研究人员都能进行综合分析。
Key Takeaways
- AI在医学图像分割中的应用对于诊断与治疗计划至关重要。
- 当前AI模型在医学图像分割上多针对单一结构,存在模型不兼容、性能差异大等问题。
- 基础分割模型提供整体解剖视图来解决上述问题。
- 临床实践中的稳健应用需要全面的训练数据。
- CADS框架整合、标准化和标记异质数据源用于全身CT分割。
- CADS框架包含大规模数据集,覆盖更多解剖结构和更多扫描次数。
点此查看论文截图

LAMA-Net: A Convergent Network Architecture for Dual-Domain Reconstruction
Authors:Chi Ding, Qingchao Zhang, Ge Wang, Xiaojing Ye, Yunmei Chen
We propose a learnable variational model that learns the features and leverages complementary information from both image and measurement domains for image reconstruction. In particular, we introduce a learned alternating minimization algorithm (LAMA) from our prior work, which tackles two-block nonconvex and nonsmooth optimization problems by incorporating a residual learning architecture in a proximal alternating framework. In this work, our goal is to provide a complete and rigorous convergence proof of LAMA and show that all accumulation points of a specified subsequence of LAMA must be Clarke stationary points of the problem. LAMA directly yields a highly interpretable neural network architecture called LAMA-Net. Notably, in addition to the results shown in our prior work, we demonstrate that the convergence property of LAMA yields outstanding stability and robustness of LAMA-Net in this work. We also show that the performance of LAMA-Net can be further improved by integrating a properly designed network that generates suitable initials, which we call iLAMA-Net. To evaluate LAMA-Net/iLAMA-Net, we conduct several experiments and compare them with several state-of-the-art methods on popular benchmark datasets for Sparse-View Computed Tomography.
我们提出了一种可学习的变分模型,该模型学习图像和测量域的特征并利用两者之间的互补信息进行图像重建。特别是,我们引入了先前工作中提出的可学习交替最小化算法(LAMA),该算法通过在有近端交替框架中融入残差学习架构,解决了两块非凸和非平滑优化问题。在这项工作中,我们的目标是提供LAMA的完整且严格的收敛性证明,并表明LAMA指定子序列的所有累积点都必须是该问题的Clarke稳定点。LAMA直接产生了一种高度可解释的神经网络架构,称为LAMA-Net。值得注意的是,除了先前工作中的结果之外,我们还证明LAMA的收敛性在本研究中为LAMA-Net带来了出色的稳定性和鲁棒性。我们还表明,通过整合适当设计的网络来生成合适的初始值,可以进一步提高LAMA-Net的性能,我们称之为iLAMA-Net。为了评估LAMA-Net/iLAMA-Net,我们进行了几项实验,并将它们与稀疏视图计算机断层扫描流行基准数据集上的几种最新方法进行了比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2410.21111
Summary
提出一种可学习的变分模型,结合图像和测量领域的特征,并借助互补信息进行图像重建。引入先前工作中的可学习交替最小化算法(LAMA),解决两块非凸和非平滑优化问题,并在近端交替框架中融入残差学习架构。本工作的目标是提供LAMA的完整收敛性证明,并展示LAMA所有累积点都是问题的Clarke稳定点。LAMA直接产生高度可解释的神经网络架构——LAMA-Net。除先前的工作成果外,本工作还展示了LAMA的收敛性为LAMA-Net的稳定性和稳健性提供了有力保障。通过整合适当设计的网络来生成初始值,进一步提高LAMA-Net的性能,称之为iLAMA-Net。通过在流行的稀疏视图计算机断层扫描基准数据集上进行实验,评估LAMA-Net/iLAMA-Net与最新技术方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入可学习的变分模型,结合图像和测量领域的特征进行图像重建。
- 采用先前工作中的可学习交替最小化算法(LAMA)解决非凸和非平滑优化问题。
- LAMA算法提供完整收敛性证明,累积点是Clarke稳定点。
- LAMA产生高度可解释的神经网络架构——LAMA-Net。
- 除先前工作外,展示了LAMA的收敛性增强了LAMA-Net的稳定性和稳健性。
- 通过整合适当设计的网络生成初始值,进一步提高性能,形成iLAMA-Net。
点此查看论文截图

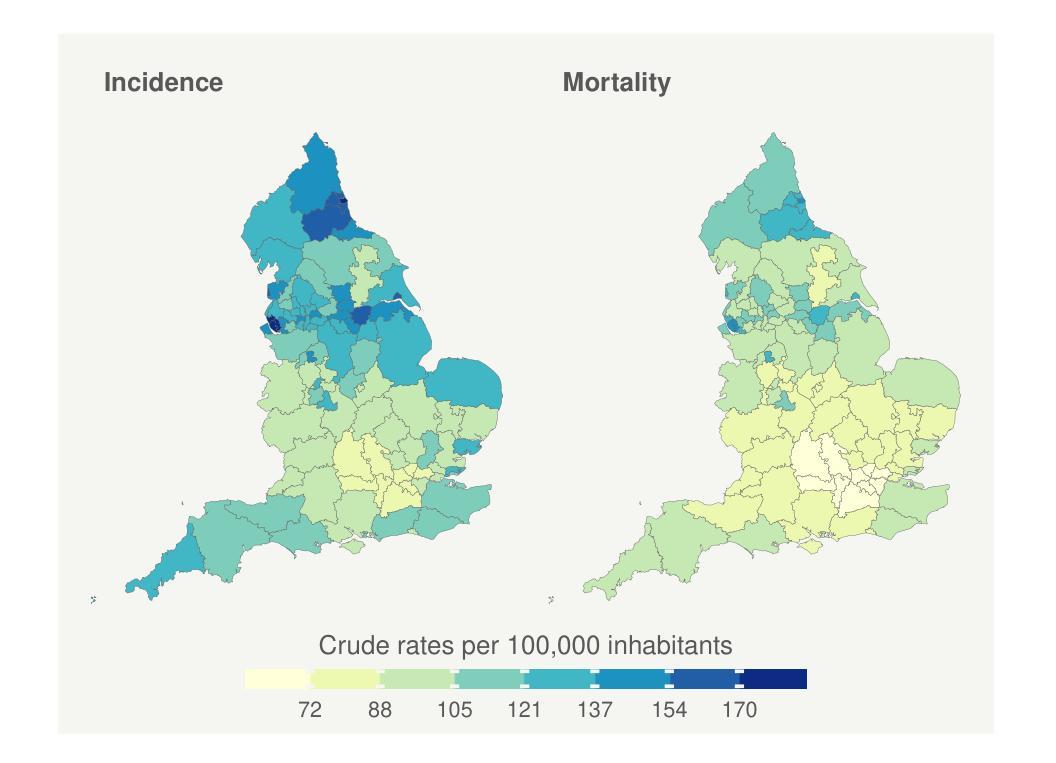
Multivariate Spatio-temporal Modelling for Completing Cancer Registries and Forecasting Incidence
Authors:Garazi Retegui, Jaione Etxeberria, María Dolores Ugarte
Cancer data, particularly cancer incidence and mortality, are fundamental to understand the cancer burden, to set targets for cancer control and to evaluate the evolution of the implementation of a cancer control policy. However, the complexity of data collection, classification, validation and processing result in cancer incidence figures often lagging two to three years behind the calendar year. In response, national or regional population-based cancer registries (PBCRs) are increasingly interested in methods for forecasting cancer incidence. However, in many countries there is an additional difficulty in projecting cancer incidence as regional registries are usually not established in the same year and therefore cancer incidence data series between different regions of a country are not harmonised over time. This study addresses the challenge of forecasting cancer incidence with incomplete data at both regional and national levels. To achieve our objective, we propose the use of multivariate spatio-temporal shared component models that jointly model mortality data and available cancer incidence data. The performance of these multivariate models are analyzed using lung cancer incidence data, together with the number of deaths reported in England in the period 2001-2019. Different model predictive measures have been calculated to select the best model.
癌症数据,特别是癌症发病率和死亡率数据,对于了解癌症负担、设定癌症控制目标以及评估癌症控制政策的实施进展至关重要。然而,数据收集、分类、验证和处理的复杂性导致癌症发病率数据通常滞后于日历年份两到三年。因此,国家或区域性人口为基础的癌症登记处(PBCRs)越来越关注癌症发病率的预测方法。然而,在许多国家,预测癌症发病率还存在额外困难,因为区域性登记通常不是在同一年份建立的,因此,一个国家不同区域之间的癌症发病率数据系列在时间上并没有统一。本研究解决了在区域和国家层面数据不完整的情况下预测癌症发病率的挑战。为了实现我们的目标,我们提出了使用多元时空共享成分模型,该模型同时对死亡数据和可用的癌症发病率数据进行建模。这些多元模型的表现通过分析肺癌发病率数据和2001-2019年英格兰的死亡报告数据来评估。已经计算了不同的模型预测指标来选择最佳模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages
Summary
该文本介绍了癌症数据的重要性,包括癌症发病率和死亡率数据对于了解癌症负担、设定癌症控制目标以及评估癌症控制政策实施情况的作用。由于数据收集、分类、验证和处理的复杂性,癌症发病率数据往往滞后于日历年份两到三年。因此,国家或区域性的人口基础癌症登记处(PBCRs)越来越关注预测癌症发病率的方法。本研究旨在解决区域和国家层面数据不完整情况下预测癌症发病率的挑战,提出了多元时空共享成分模型,该模型联合建模死亡数据和可用的癌症发病率数据。利用英格兰2001-2019年的肺癌发病率数据和死亡人数数据,对多元模型的性能进行了分析,通过计算不同的模型预测指标来选择最佳模型。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症数据,特别是发病率和死亡率数据,对于了解癌症负担、设定控制目标和评估政策实施至关重要。
- 癌症数据存在收集、分类、验证和处理的复杂性,导致癌症发病率数据经常滞后。
- 人口基础癌症登记处(PBCRs)正越来越多地关注预测癌症发病率的方法。
- 本研究提出了多元时空共享成分模型以预测癌症发病率,该模型可联合建模死亡数据和癌症发病率数据。
- 研究使用的数据集为英格兰的肺癌发病率数据和2001-2019年的死亡人数数据。
- 通过分析不同模型预测指标来评估模型性能并选择最佳模型。
点此查看论文截图

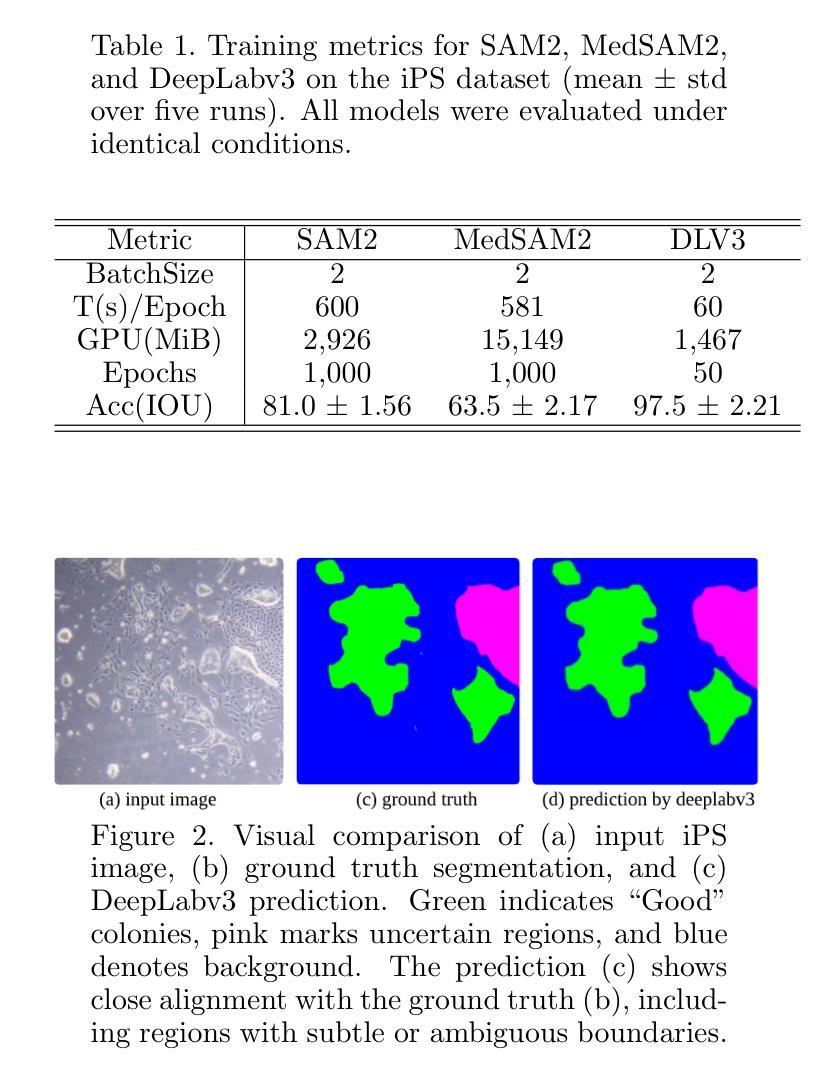
Semantic Segmentation of iPS Cells: Case Study on Model Complexity in Biomedical Imaging
Authors:Maoquan Zhang, Bisser Raytchev, Xiujuan Sun
Medical image segmentation requires not only accuracy but also robustness under challenging imaging conditions. In this study, we show that a carefully configured DeepLabv3 model can achieve high performance in segmenting induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell colonies, and, under our experimental conditions, outperforms large-scale foundation models such as SAM2 and its medical variant MedSAM2 without structural modifications. These results suggest that, for specialized tasks characterized by subtle, low-contrast boundaries, increased model complexity does not necessarily translate to better performance. Our work revisits the assumption that ever-larger and more generalized architectures are always preferable, and provides evidence that appropriately adapted, simpler models may offer strong accuracy and practical reliability in domain-specific biomedical applications. We also offer an open-source implementation that includes strategies for small datasets and domain-specific encoding, with the aim of supporting further advances in semantic segmentation for regenerative medicine and related fields.
医学图像分割不仅需要准确性,还需要在具有挑战性的成像条件下保持稳健性。本研究表明,经过精心配置的DeepLabv3模型在分割诱导多能干细胞(iPS)菌落方面表现出高性能,并且在我们的实验条件下,无需结构修改即可超越大规模基础模型,如SAM2及其医学变体MedSAM2。这些结果表明,对于特征为细微、低对比度边界的专项任务,增加模型复杂性并不一定转化为更好的性能。我们的工作重新考虑了假设更大、更通用的架构始终是可取的,并提供了证据支持,适当简化并适应的模型可能在特定领域的生物医学应用中提供强大的准确性和实际可靠性。我们还提供了一个开源实现,包括针对小数据集和特定领域的编码策略,旨在支持再生医学和相关领域的语义分割的进一步进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications MVA2025
Summary
医学图像分割不仅需要准确性,还需在复杂的成像条件下保持稳健性。本研究表明,经过精心配置的DeepLabv3模型在分割诱导多能干细胞(iPS)菌落方面表现出高性能,并在实验条件下,未经结构修改即超越了大规模基础模型,如SAM2及其医学变体MedSAM2。对于具有细微、低对比度边界特征的专业任务,增加模型复杂性并不一定能提高性能。研究重新审视了更大的、更通用的架构总是更可取这一假设,并提供证据表明适当简化模型可能在特定领域的生物医学应用中提供强大的准确性和实际可靠性。我们还提供了开源实现,包括针对小数据集和特定领域编码的策略,旨在支持再生医学和相关领域的语义分割的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割需要兼顾准确性和稳健性,特别是在复杂成像条件下。
- 精心配置的DeepLabv3模型在分割iPS细胞菌落方面表现出高性能。
- 在实验条件下,DeepLabv3模型性能超越了大规模的基础模型,如SAM2和MedSAM2。
- 对于具有细微、低对比度边界特征的专业任务,模型复杂性并非性能提升的关键。
- 研究重新评估了大规模、通用架构模型是否总是更优的问题,提出适当简化的模型可能在特定生物医学应用中表现出强大的性能和可靠性。
- 研究提供了开源实现,包含针对小数据集和特定领域编码的策略。
点此查看论文截图

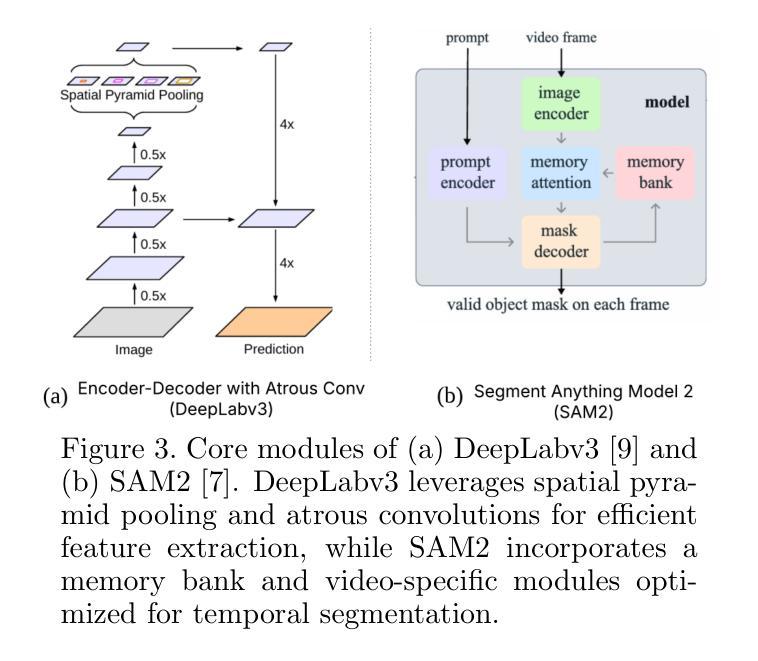
Dual Cross-image Semantic Consistency with Self-aware Pseudo Labeling for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Han Wu, Chong Wang, Zhiming Cui
Semi-supervised learning has proven highly effective in tackling the challenge of limited labeled training data in medical image segmentation. In general, current approaches, which rely on intra-image pixel-wise consistency training via pseudo-labeling, overlook the consistency at more comprehensive semantic levels (e.g., object region) and suffer from severe discrepancy of extracted features resulting from an imbalanced number of labeled and unlabeled data. To overcome these limitations, we present a new \underline{Du}al \underline{C}ross-\underline{i}mage \underline{S}emantic \underline{C}onsistency (DuCiSC) learning framework, for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Concretely, beyond enforcing pixel-wise semantic consistency, DuCiSC proposes dual paradigms to encourage region-level semantic consistency across: 1) labeled and unlabeled images; and 2) labeled and fused images, by explicitly aligning their prototypes. Relying on the dual paradigms, DuCiSC can effectively establish consistent cross-image semantics via prototype representations, thereby addressing the feature discrepancy issue. Moreover, we devise a novel self-aware confidence estimation strategy to accurately select reliable pseudo labels, allowing for exploiting the training dynamics of unlabeled data. Our DuCiSC method is extensively validated on four datasets, including two popular binary benchmarks in segmenting the left atrium and pancreas, a multi-class Automatic Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge dataset, and a challenging scenario of segmenting the inferior alveolar nerve that features complicated anatomical structures, showing superior segmentation results over previous state-of-the-art approaches. Our code is publicly available at \href{https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC}{https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC}.
半监督学习已经证明在解决医学图像分割中标签训练数据有限的问题时非常有效。一般来说,当前的方法依赖于通过伪标签进行图像内像素级的一致性训练,而忽略了更全面的语义级别的一致性(例如,对象区域),并因标签和无标签数据数量不平衡而遭受所提取特征的严重差异影响。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的Dual Cross-Image Semantic Consistency(DuCiSC)半监督医学图像分割学习框架。具体来说,除了强制像素级语义一致性外,DuCiSC还提出了两种范式来鼓励区域级语义一致性:(1)跨标签和无标签图像;(2)跨标签和融合图像,通过明确地对其原型进行对齐。依赖于双重范式,DuCiSC可以通过原型表示有效地建立一致的跨图像语义,从而解决特征差异问题。此外,我们设计了一种新型的自感知置信度估计策略,以准确选择可靠的伪标签,从而利用未标记数据的训练动态。我们的DuCiSC方法在四个数据集上进行了广泛验证,包括两个流行的左心房和胰腺分割二元基准测试、一个用于自动心脏诊断的多类挑战数据集,以及一个具有复杂解剖结构的下牙槽神经分割挑战场景。它表现出优于以前的最先进方法。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DuCiSC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE TMI
Summary
半监督学习在处理医学图像分割中有限的标记训练数据问题时表现高效。现有方法多依赖于伪标签技术的像素级一致性训练,但忽视了更全面的语义级别一致性,且在处理标记与未标记数据特征不平衡时会出现严重偏差。本研究提出了新型的DuCiSC(双跨图像语义一致性)半监督医学图像分割学习框架。除了像素级语义一致性外,DuCiSC还通过原型对齐提出了跨图像的区域级语义一致性,解决了特征不一致问题。此外,DuCiSC还设计了一种新的自我感知置信度估计策略,以准确选择可靠的伪标签来利用未标记数据的训练动态。在四个数据集上的实验表明,DuCiSC的分割结果优于先前最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在处理医学图像分割中的有限标记数据挑战时效果显著。
- 当前方法依赖伪标签技术的像素级一致性训练,但忽视了更全面的语义级别一致性。
- DuCiSC框架通过原型对齐提出跨图像的区域级语义一致性,以解决特征不一致问题。
- DuCiSC设计了一种自我感知置信度估计策略,准确选择可靠的伪标签。
- DuCiSC在四个数据集上的表现优于先前最先进的方法。
- DuCiSC框架具有广泛的应用潜力,适用于不同类型的医学图像分割任务。
点此查看论文截图

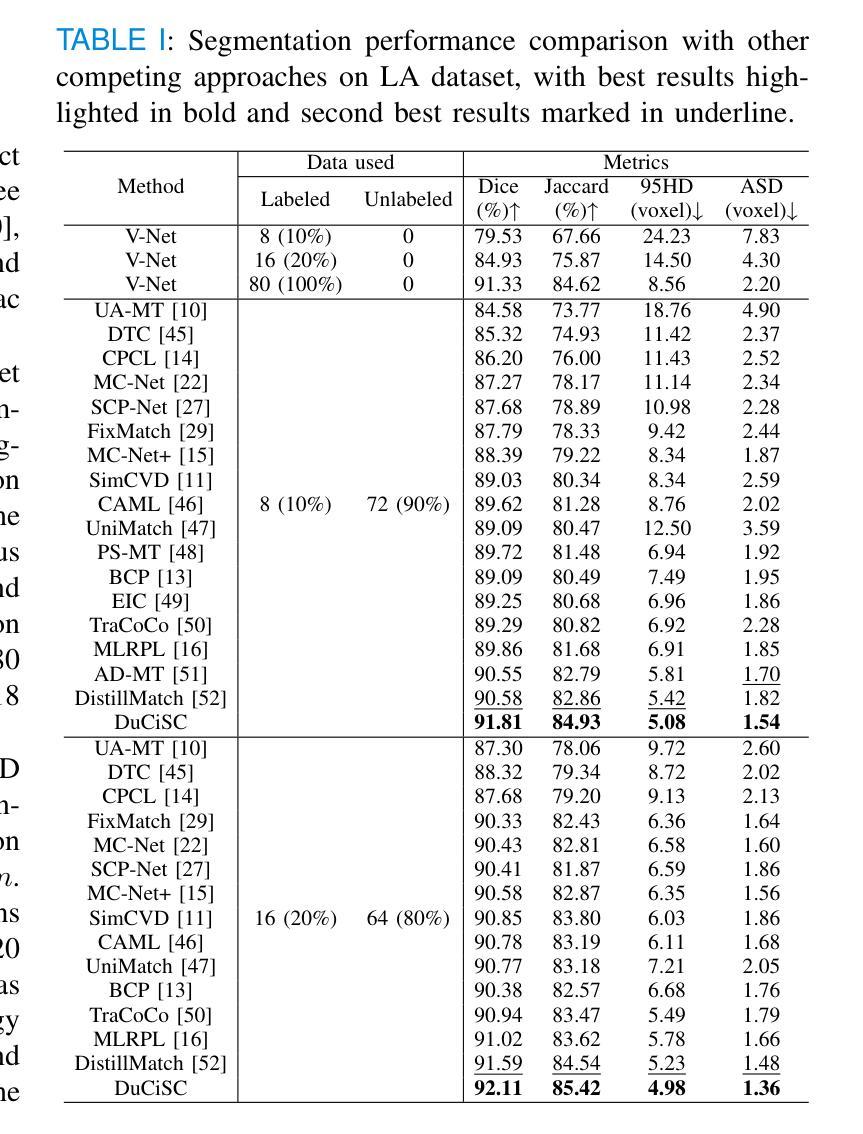
Enhancing and Accelerating Brain MRI through Deep Learning Reconstruction Using Prior Subject-Specific Imaging
Authors:Amirmohammad Shamaei, Alexander Stebner, Salome, Bosshart, Johanna Ospel, Gouri Ginde, Mariana Bento, Roberto Souza
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a crucial medical imaging modality. However, long acquisition times remain a significant challenge, leading to increased costs, and reduced patient comfort. Recent studies have shown the potential of using deep learning models that incorporate information from prior subject-specific MRI scans to improve reconstruction quality of present scans. Integrating this prior information requires registration of the previous scan to the current image reconstruction, which can be time-consuming. We propose a novel deep-learning-based MRI reconstruction framework which consists of an initial reconstruction network, a deep registration model, and a transformer-based enhancement network. We validated our method on a longitudinal dataset of T1-weighted MRI scans with 2,808 images from 18 subjects at four acceleration factors (R5, R10, R15, R20). Quantitative metrics confirmed our approach’s superiority over existing methods (p < 0.05, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Furthermore, we analyzed the impact of our MRI reconstruction method on the downstream task of brain segmentation and observed improved accuracy and volumetric agreement with reference segmentations. Our approach also achieved a substantial reduction in total reconstruction time compared to methods that use traditional registration algorithms, making it more suitable for real-time clinical applications. The code associated with this work is publicly available at https://github.com/amirshamaei/longitudinal-mri-deep-recon.
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种关键的医学成像方式。然而,长时间的采集仍然是一个巨大的挑战,导致了成本的增加和患者舒适度的降低。最近的研究表明,使用深度学习模型结合来自先前特定主题的MRI扫描信息,可以提高当前扫描的重建质量。集成此先前信息需要进行先前扫描与当前图像重建之间的配准,这可能会很耗时。我们提出了一种基于深度学习的MRI重建新框架,该框架包括初始重建网络、深度配准模型和基于变压器的增强网络。我们在纵向数据集上对T1加权MRI扫描的2808张图像进行了验证,这些图像来自四个加速因子(R5、R10、R15、R20)的18个受试者。定量指标证实了我们的方法优于现有方法(p < 0.05,Wilcoxon符号秩检验)。此外,我们分析了我们的MRI重建方法对下游脑分割任务的影响,并观察到与参考分割相比,准确性和体积一致性都有所提高。与采用传统配准算法的方法相比,我们的方法在总重建时间上实现了显著减少,使其更适合实时临床应用。与此工作相关的代码可在公开网站https://github.com/amirshamaei/longitudinal-mri-deep-recon上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种基于深度学习的MRI重建框架,包含初始重建网络、深度注册模型及基于转换器的增强网络。在纵向数据集上验证了该方法,相较于现有方法表现更优,并显著提高重建速度,适用于实时临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究解决了MRI成像中采集时间长的问题,提高了成像效率,降低了成本,并提升了患者舒适度。
- 研究采用深度学习模型,利用先前特定对象的MRI扫描信息改善当前扫描的重建质量。
- 框架包括初始重建网络、深度注册模型和基于转换器的增强网络,能有效提高MRI图像的质量。
- 在包含18个主体、共2808张图像的纵向数据集上进行了验证,加速因子达到R5至R20。
- 对比定量指标显示,新方法优于现有方法(p < 0.05,Wilcoxon符号秩检验)。
- 分析表明,新MRI重建方法对下游的大脑分割任务有更高的准确性和体积一致性。
点此查看论文截图

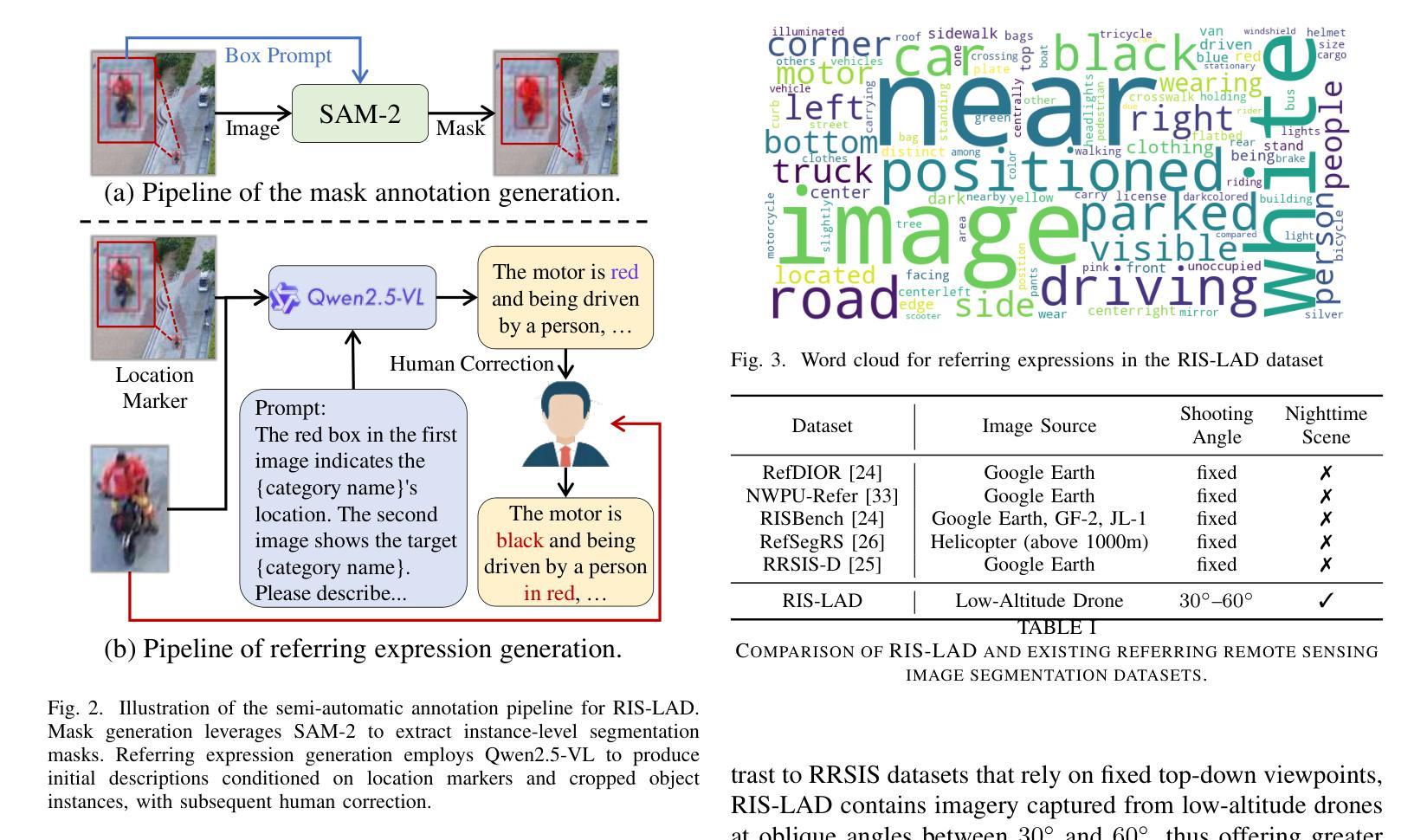
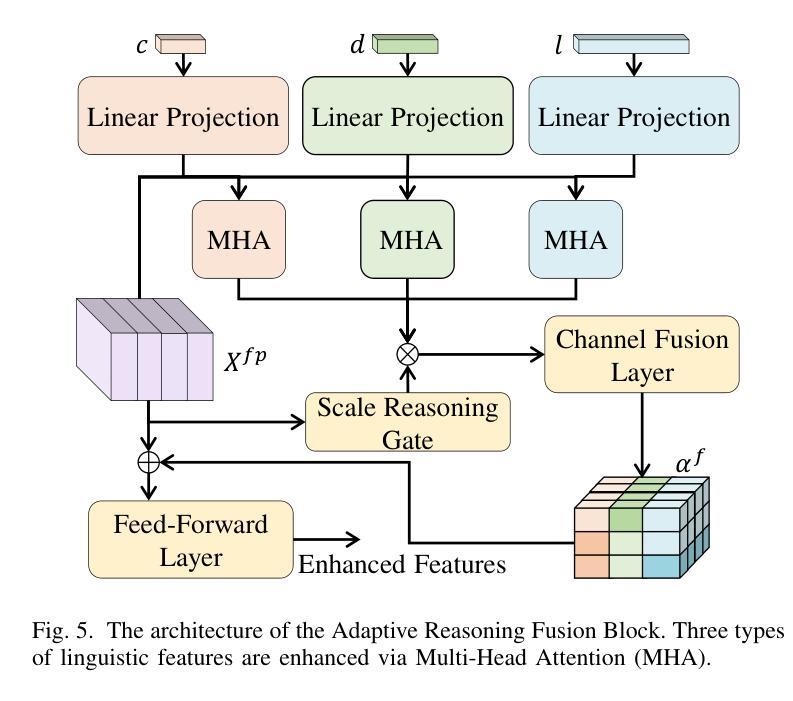
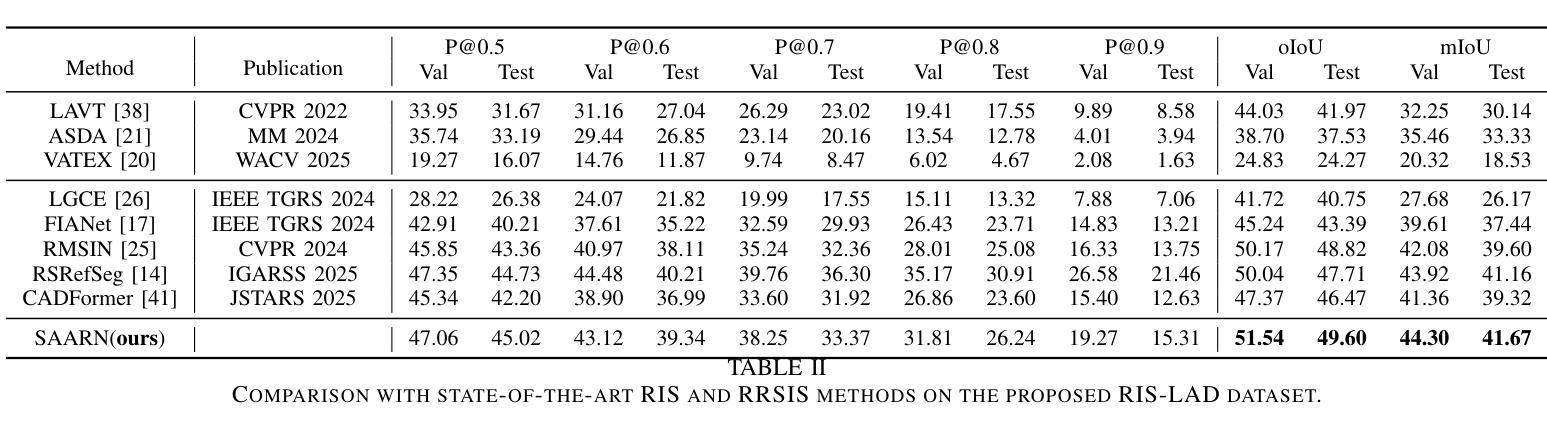
RIS-LAD: A Benchmark and Model for Referring Low-Altitude Drone Image Segmentation
Authors:Kai Ye, YingShi Luan, Zhudi Chen, Guangyue Meng, Pingyang Dai, Liujuan Cao
Referring Image Segmentation (RIS), which aims to segment specific objects based on natural language descriptions, plays an essential role in vision-language understanding. Despite its progress in remote sensing applications, RIS in Low-Altitude Drone (LAD) scenarios remains underexplored. Existing datasets and methods are typically designed for high-altitude and static-view imagery. They struggle to handle the unique characteristics of LAD views, such as diverse viewpoints and high object density. To fill this gap, we present RIS-LAD, the first fine-grained RIS benchmark tailored for LAD scenarios. This dataset comprises 13,871 carefully annotated image-text-mask triplets collected from realistic drone footage, with a focus on small, cluttered, and multi-viewpoint scenes. It highlights new challenges absent in previous benchmarks, such as category drift caused by tiny objects and object drift under crowded same-class objects. To tackle these issues, we propose the Semantic-Aware Adaptive Reasoning Network (SAARN). Rather than uniformly injecting all linguistic features, SAARN decomposes and routes semantic information to different stages of the network. Specifically, the Category-Dominated Linguistic Enhancement (CDLE) aligns visual features with object categories during early encoding, while the Adaptive Reasoning Fusion Module (ARFM) dynamically selects semantic cues across scales to improve reasoning in complex scenes. The experimental evaluation reveals that RIS-LAD presents substantial challenges to state-of-the-art RIS algorithms, and also demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed model in addressing these challenges. The dataset and code will be publicly released soon at: https://github.com/AHideoKuzeA/RIS-LAD/.
参照图像分割(RIS)旨在根据自然语言描述对特定对象进行分割,在视觉语言理解中起着至关重要的作用。尽管其在遥感应用方面取得了进展,但低空无人机(LAD)场景中的RIS仍然未被充分探索。现有的数据集和方法通常针对高空和静态视图图像设计,它们难以处理LAD视图的独特特征,例如多样化的视角和高对象密度。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了RIS-LAD,这是专门为LAD场景定制的首个精细粒度RIS基准数据集。该数据集包含从现实无人机影像中收集的13871个经过仔细注释的图像-文本-遮罩三元组,重点是小规模、杂乱和多点视图场景。它突出了以前基准测试中不存在的新的挑战,例如由于微小物体和拥挤的同类物体引起的类别漂移和物体漂移。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了语义感知自适应推理网络(SAARN)。SAARN不是统一注入所有语言特征,而是分解和将语义信息路由到网络的不同阶段。具体来说,类别主导的语言增强(CDLE)在早期编码时将视觉特征与对象类别对齐,而自适应推理融合模块(ARFM)则动态选择跨尺度的语义线索,以改进复杂场景中的推理。实验评估表明,RIS-LAD给最先进的RIS算法带来了巨大的挑战,同时也证明了我们提出的模型在解决这些挑战方面的有效性。数据集和代码将很快在以下网址公开发布:https://github.com/AHideoKuzeA/RIS-LAD/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对低空无人机(LAD)场景的参照图像分割(RIS)研究存在空白。现有数据集和方法主要面向高空和静态图像,难以处理LAD视角的独特特点。为此,提出了RIS-LAD,首个针对LAD场景的精细RIS基准数据集。它包含从真实无人机影像中收集的13,871个精心标注的图像-文本-遮罩三元组,重点关注小、杂乱和多视角场景。为解决新出现的挑战,如类别漂移和对象漂移,提出了语义感知自适应推理网络(SAARN)。该网络分解并路由语义信息,通过类别主导的语言增强(CDLE)和自适应推理融合模块(ARFM)改善复杂场景的推理。
Key Takeaways
- 低空无人机(LAD)场景的参照图像分割(RIS)研究尚未得到充分探索。
- 现有数据集和方法主要面向高空和静态图像,难以满足LAD视角的独特需求。
- 提出了首个针对LAD场景的精细RIS基准数据集——RIS-LAD。
- RIS-LAD包含从现实无人机影像中收集的13,871个精心标注的图像-文本-遮罩三元组。
- RIS-LAD重点关注小、杂乱和多视角场景,这些场景带来了新的挑战,如类别漂移和对象漂移。
- 为了解决这些挑战,提出了语义感知自适应推理网络(SAARN)。
点此查看论文截图

ATR-UMMIM: A Benchmark Dataset for UAV-Based Multimodal Image Registration under Complex Imaging Conditions
Authors:Kangcheng Bin, Chen Chen, Ting Hu, Jiahao Qi, Ping Zhong
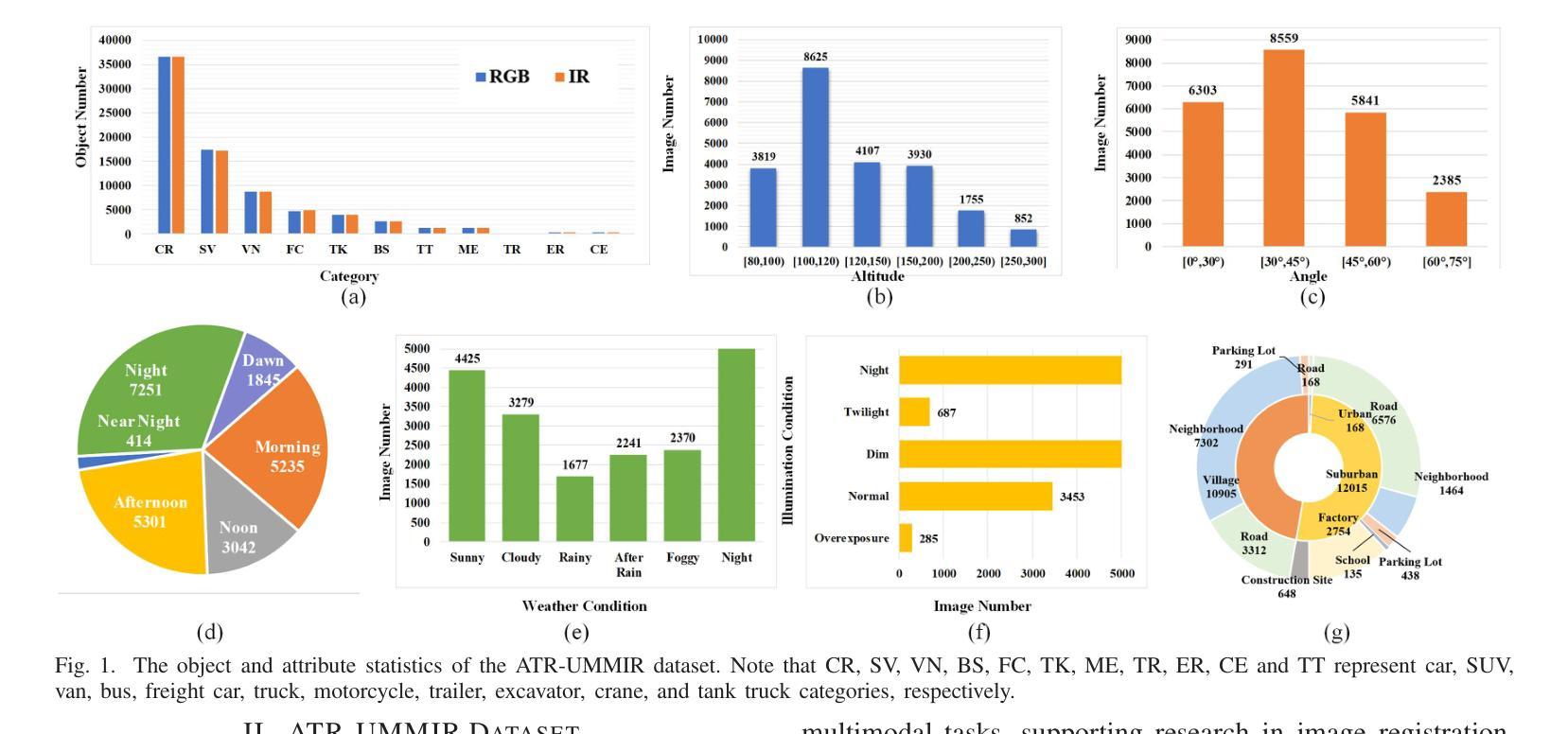
Multimodal fusion has become a key enabler for UAV-based object detection, as each modality provides complementary cues for robust feature extraction. However, due to significant differences in resolution, field of view, and sensing characteristics across modalities, accurate registration is a prerequisite before fusion. Despite its importance, there is currently no publicly available benchmark specifically designed for multimodal registration in UAV-based aerial scenarios, which severely limits the development and evaluation of advanced registration methods under real-world conditions. To bridge this gap, we present ATR-UMMIM, the first benchmark dataset specifically tailored for multimodal image registration in UAV-based applications. This dataset includes 7,969 triplets of raw visible, infrared, and precisely registered visible images captured covers diverse scenarios including flight altitudes from 80m to 300m, camera angles from 0{\deg} to 75{\deg}, and all-day, all-year temporal variations under rich weather and illumination conditions. To ensure high registration quality, we design a semi-automated annotation pipeline to introduce reliable pixel-level ground truth to each triplet. In addition, each triplet is annotated with six imaging condition attributes, enabling benchmarking of registration robustness under real-world deployment settings. To further support downstream tasks, we provide object-level annotations on all registered images, covering 11 object categories with 77,753 visible and 78,409 infrared bounding boxes. We believe ATR-UMMIM will serve as a foundational benchmark for advancing multimodal registration, fusion, and perception in real-world UAV scenarios. The datatset can be download from https://github.com/supercpy/ATR-UMMIM
多模态融合已成为无人机目标检测的关键技术,因为每个模态都能为稳健的特征提取提供互补线索。然而,由于不同模态的分辨率、视野和感知特性存在显著差异,因此在融合之前,准确的配准是必备条件。尽管其重要性,但目前还没有针对无人机空中场景的多模态配准的公开基准测试,这严重限制了先进配准方法在真实条件下的开发和评估。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了ATR-UMMIM,这是专门为无人机应用中的多模态图像配准设计的首个基准数据集。该数据集包含7969张原始可见光、红外和精确配准的可见图像三元组,覆盖了多种场景,包括飞行高度从80米至300米、相机角度从0°至75°,以及全年全天候的丰富天气和照明条件下的时间变化。为了确保高注册质量,我们设计了一个半自动注释管道,为每个三元组引入可靠的像素级真实标签。此外,每个三元组都标注了六个成像条件属性,能够在真实部署环境中对配准的稳健性进行基准测试。为了进一步支持下游任务,我们在所有已注册的图像上提供了对象级别的注释,覆盖11个对象类别,包含77753张可见光和78409张红外边界框。我们相信ATR-UMMIM将为推进多模态配准、融合和真实世界无人机场景中的感知奠定基石。数据集可以从https://github.com/supercpy/ATR-UMMIM下载。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一个名为ATR-UMMIM的基准数据集,该数据集专门为无人机应用中多模态图像注册而设计。数据集包含多种场景的图像,如飞行高度、相机角度、时间变化等,具有可靠的像素级地面真实性和成像条件属性标注。数据集支持下游任务,包括注册、融合和感知等。
Key Takeaways
- ATR-UMMIM是首个为无人机应用中多模态图像注册而设计的基准数据集。
- 数据集包含7,969张图像,包括可见光、红外和精确注册的可见光图像。
- 数据集涵盖多种场景,如不同的飞行高度、相机角度、时间和天气条件。
- 数据集采用半自动标注管道,确保高质量的注册和可靠的像素级地面真实性。
- 每个图像三元组都标注了六个成像条件属性,可在实际部署环境中评估注册的稳健性。
- 数据集还提供对象级别的注释和11个对象类别的边界框。
点此查看论文截图

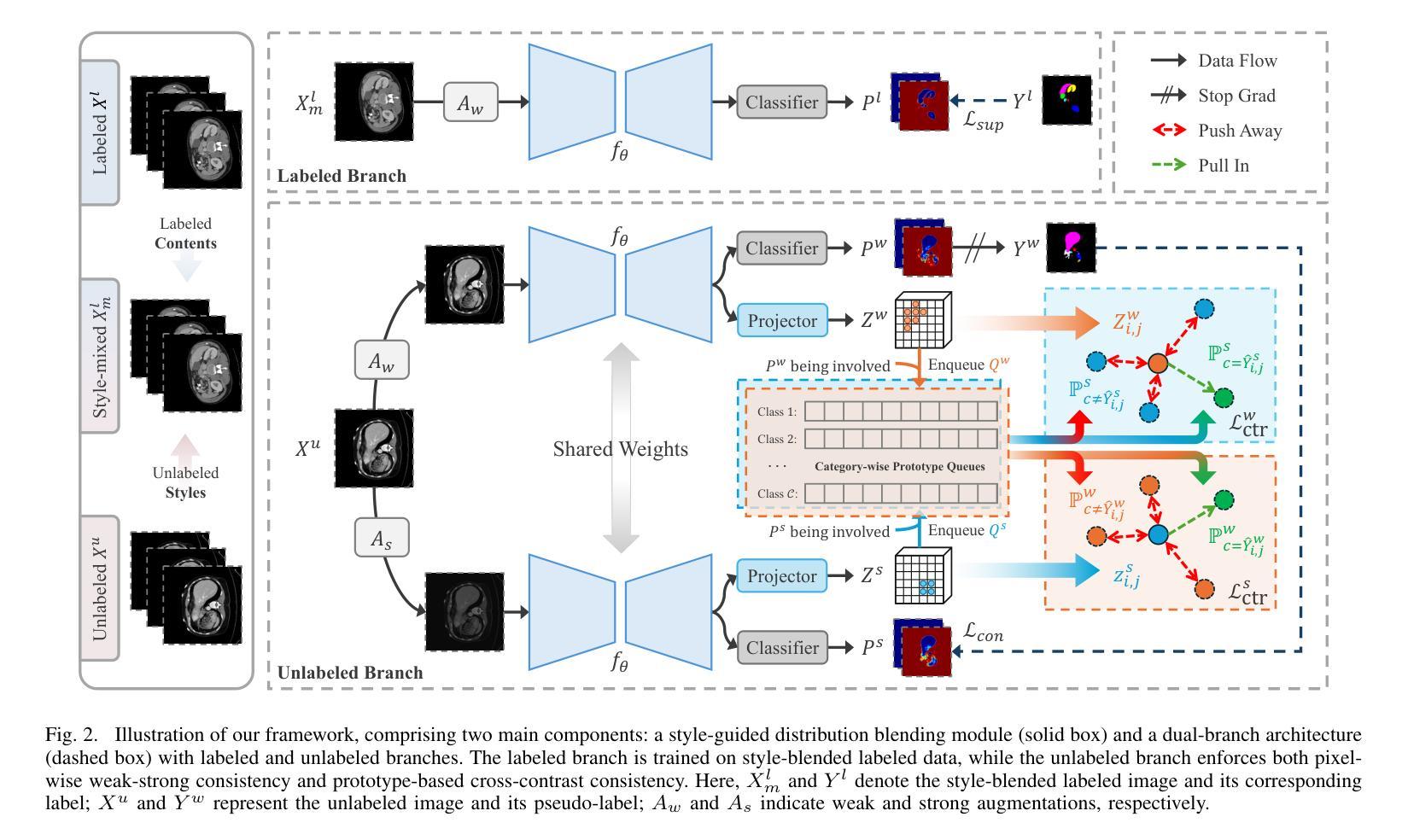
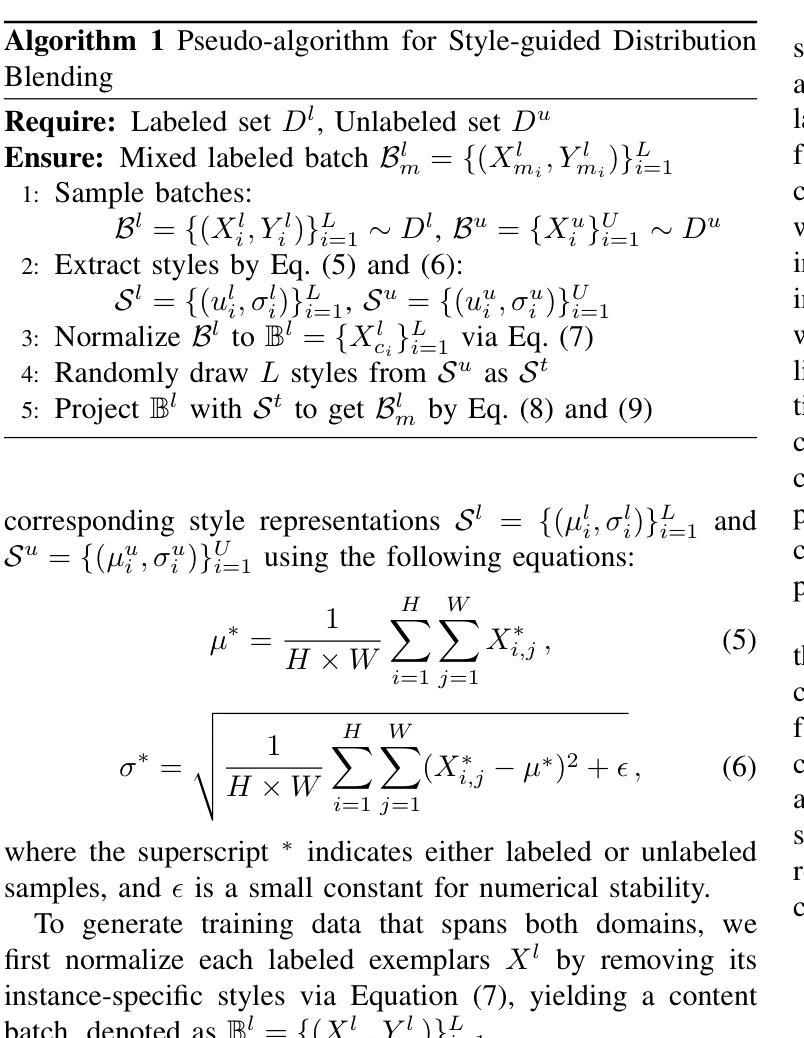
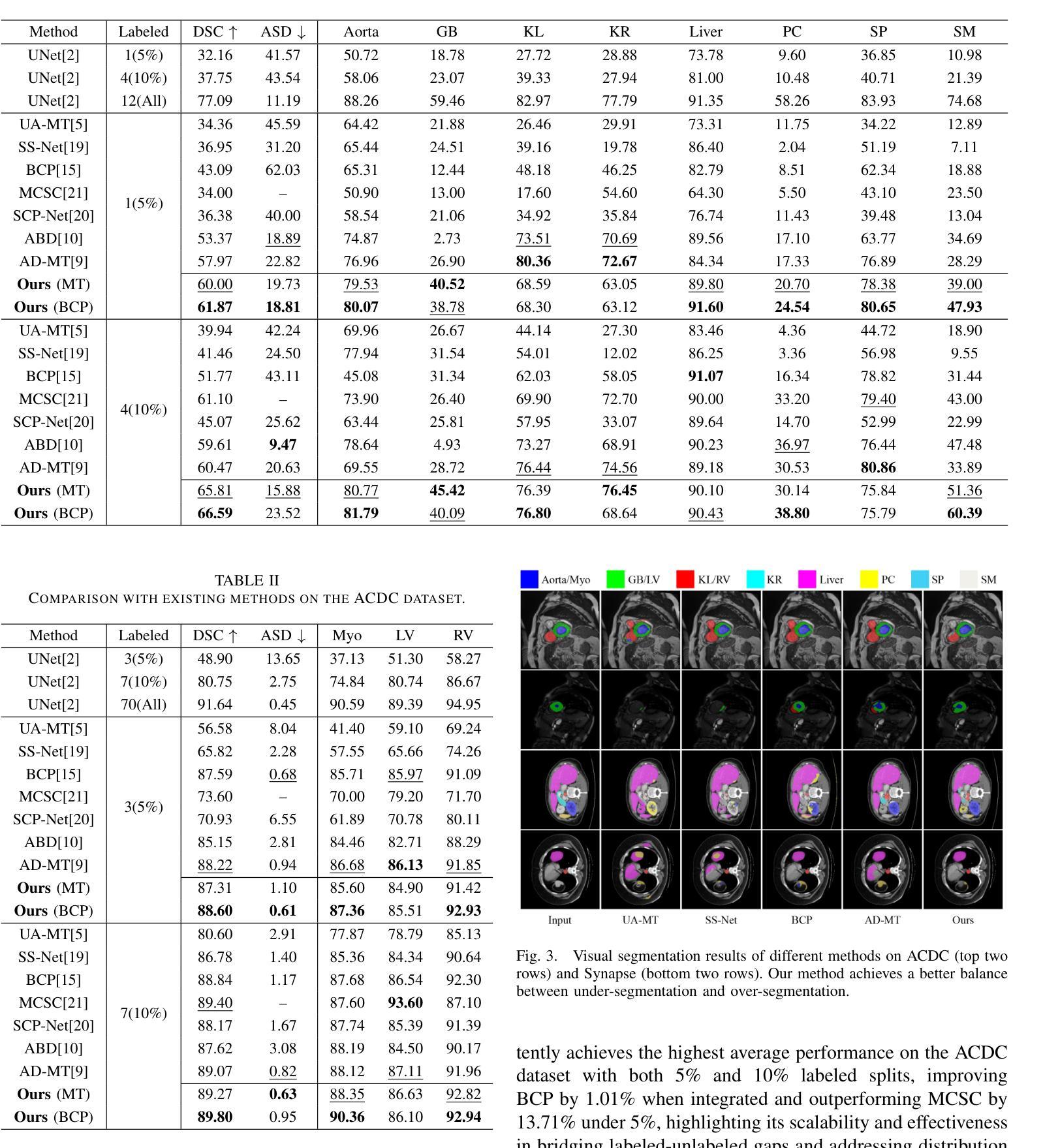
Style-Aware Blending and Prototype-Based Cross-Contrast Consistency for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chaowei Chen, Xiang Zhang, Honglie Guo, Shunfang Wang
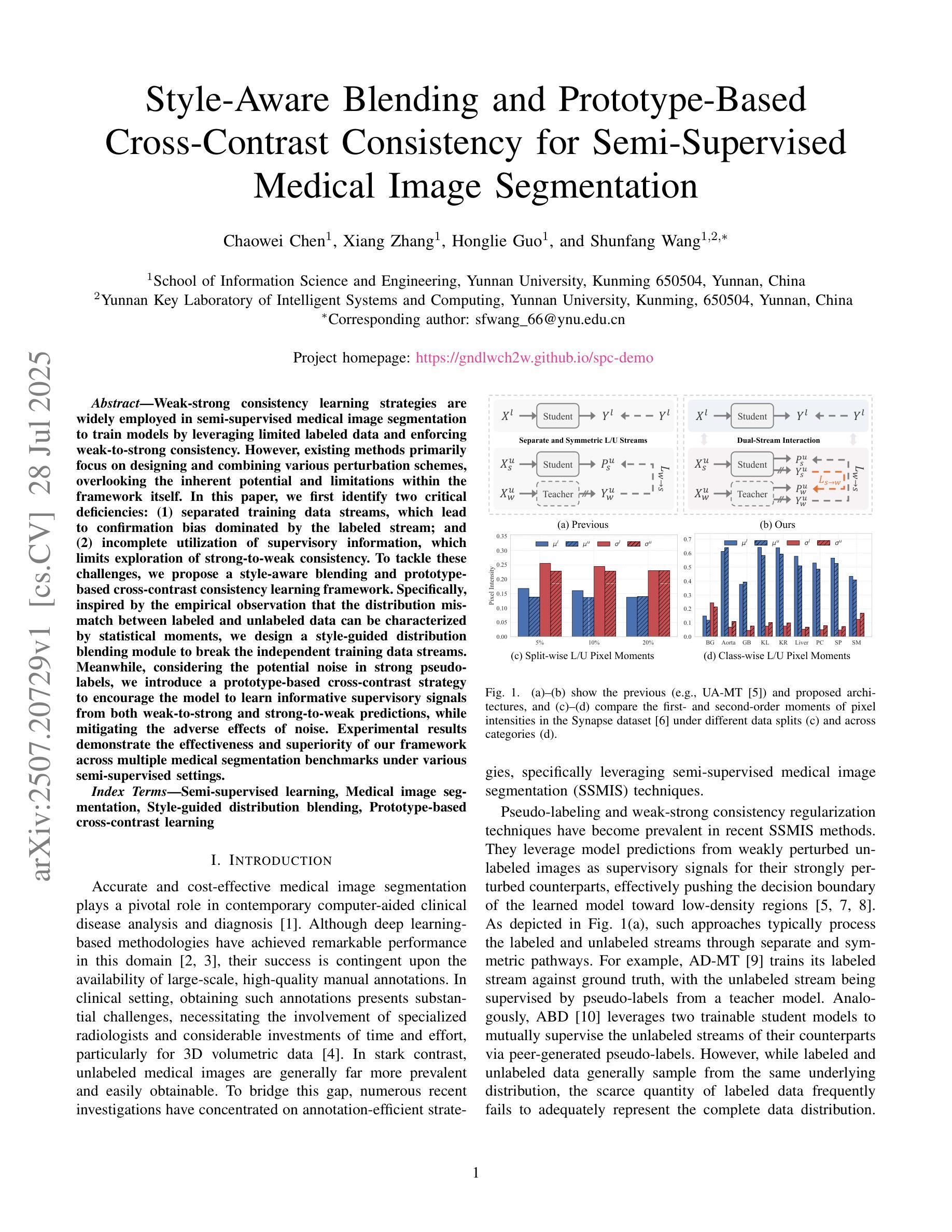
Weak-strong consistency learning strategies are widely employed in semi-supervised medical image segmentation to train models by leveraging limited labeled data and enforcing weak-to-strong consistency. However, existing methods primarily focus on designing and combining various perturbation schemes, overlooking the inherent potential and limitations within the framework itself. In this paper, we first identify two critical deficiencies: (1) separated training data streams, which lead to confirmation bias dominated by the labeled stream; and (2) incomplete utilization of supervisory information, which limits exploration of strong-to-weak consistency. To tackle these challenges, we propose a style-aware blending and prototype-based cross-contrast consistency learning framework. Specifically, inspired by the empirical observation that the distribution mismatch between labeled and unlabeled data can be characterized by statistical moments, we design a style-guided distribution blending module to break the independent training data streams. Meanwhile, considering the potential noise in strong pseudo-labels, we introduce a prototype-based cross-contrast strategy to encourage the model to learn informative supervisory signals from both weak-to-strong and strong-to-weak predictions, while mitigating the adverse effects of noise. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our framework across multiple medical segmentation benchmarks under various semi-supervised settings.
弱强一致性学习策略在半监督医学图像分割中得到了广泛应用,通过利用有限的标记数据并强制执行弱到强的一致性来训练模型。然而,现有方法主要集中在设计和组合各种扰动方案上,忽视了框架本身的内在潜力和局限性。在本文中,我们首先识别出两个关键缺陷:一是训练数据流分离,这导致以标记流为主的确认偏见;二是监督信息利用不完全,这限制了从强到弱的一致性的探索。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个风格感知的混合和基于原型的交叉对比一致性学习框架。具体而言,受实证观察启发,即标记和无标记数据之间的分布不匹配可以通过统计矩来表征,我们设计了一个风格引导的分布混合模块来打破独立的训练数据流。同时,考虑到强伪标签中的潜在噪声,我们引入了一种基于原型的交叉对比策略,以鼓励模型从弱到强和强到弱的预测中学习有用的监督信号,同时减轻噪声的不利影响。实验结果表明,我们的框架在多个医学分割基准测试下具有优越性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像半监督分割中常采用弱强一致性学习策略,利用有限标注数据进行训练并强制实施弱到强的一致性。但现有方法主要关注设计各种扰动方案并进行组合,忽略了框架本身的潜在优势和局限性。本文首先指出两大缺陷:一是独立训练数据流导致的确认偏见;二是监督信息利用不足,限制了强到弱一致性的探索。为解决这些问题,本文提出了风格感知混合与基于原型的交叉对比一致性学习框架。通过设计风格引导的分布混合模块打破独立训练数据流,同时考虑强伪标签中的潜在噪声,引入基于原型的交叉对比策略,鼓励模型从弱到强和强到弱的预测中学习有用的监督信号,同时减少噪声的不利影响。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像半监督分割中弱强一致性学习策略的应用广泛。
- 现有方法主要关注扰动方案的设计,忽视了框架的潜在优势和局限性。
- 指出独立训练数据流导致的确认偏见和监督信息利用不足的问题。
- 提出风格感知混合与基于原型的交叉对比一致性学习框架。
- 通过设计风格引导的分布混合模块来解决独立训练数据流问题。
- 引入基于原型的交叉对比策略,以减轻强伪标签中的潜在噪声影响。
点此查看论文截图
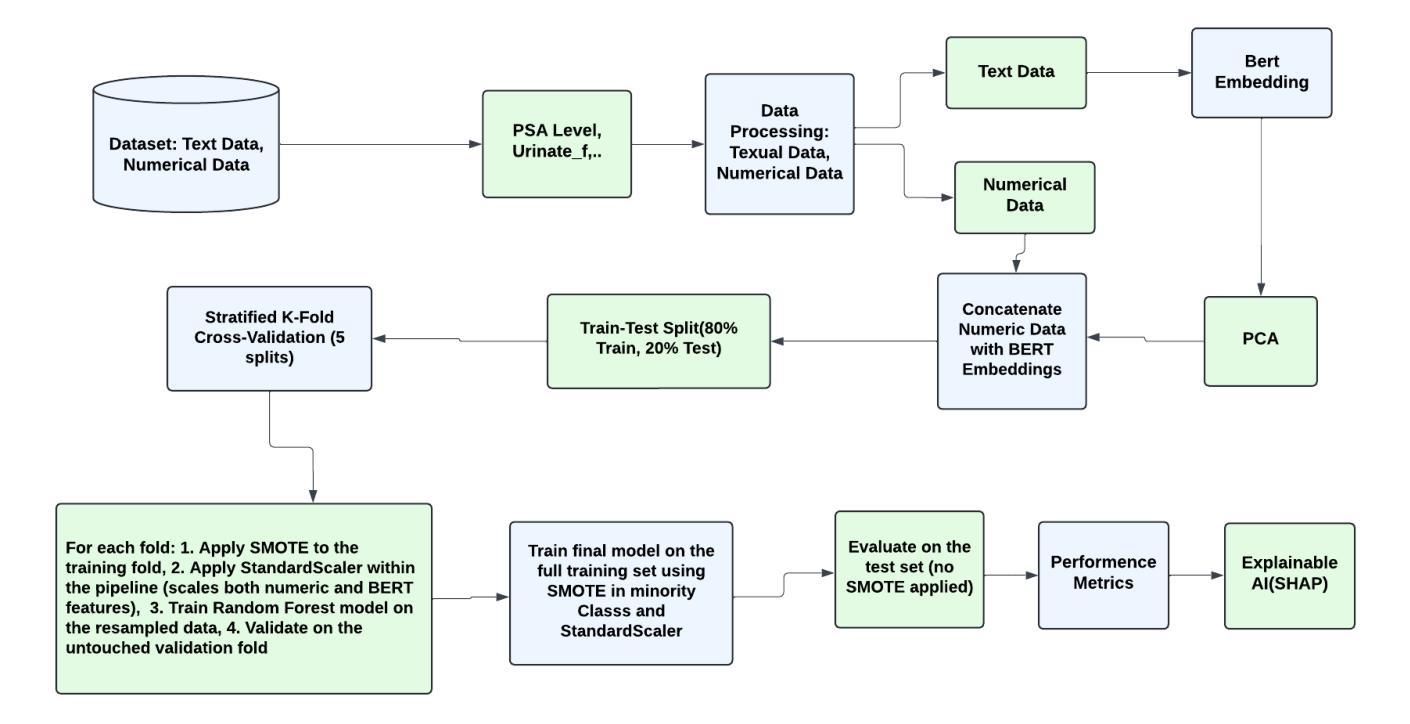
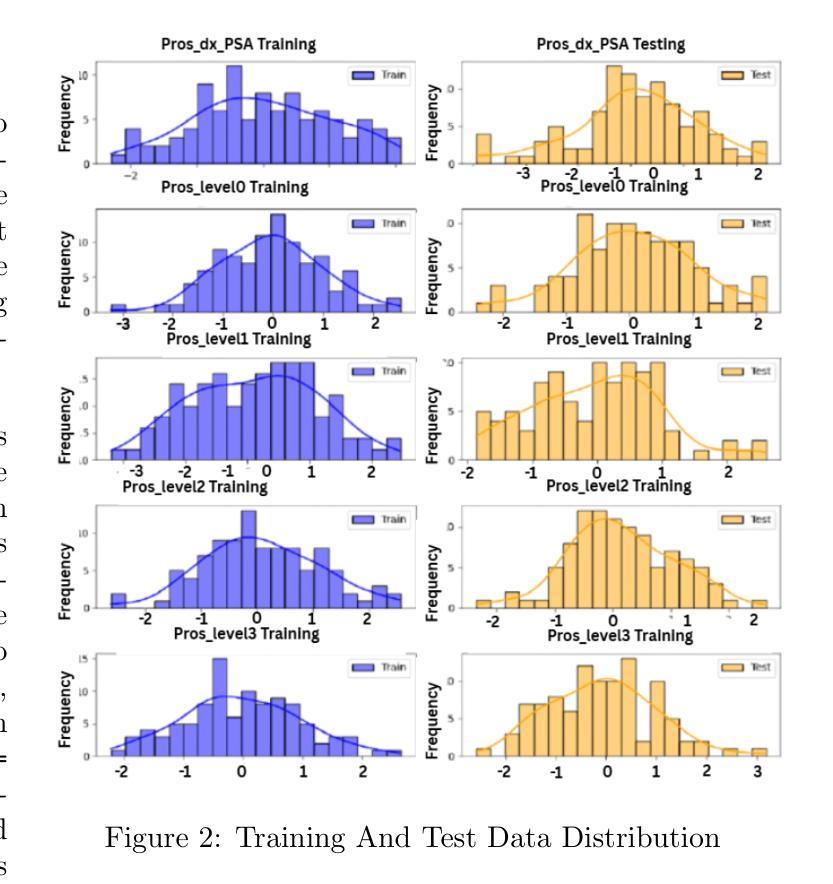
Prostate Cancer Classification Using Multimodal Feature Fusion and Explainable AI
Authors:Asma Sadia Khan, Fariba Tasnia Khan, Tanjim Mahmud, Salman Karim Khan, Rishita Chakma, Nahed Sharmen, Mohammad Shahadat Hossain, Karl Andersson
Prostate cancer, the second most prevalent male malignancy, requires advanced diagnostic tools. We propose an explainable AI system combining BERT (for textual clinical notes) and Random Forest (for numerical lab data) through a novel multimodal fusion strategy, achieving superior classification performance on PLCO-NIH dataset (98% accuracy, 99% AUC). While multimodal fusion is established, our work demonstrates that a simple yet interpretable BERT+RF pipeline delivers clinically significant improvements - particularly for intermediate cancer stages (Class 2/3 recall: 0.900 combined vs 0.824 numerical/0.725 textual). SHAP analysis provides transparent feature importance rankings, while ablation studies prove textual features’ complementary value. This accessible approach offers hospitals a balance of high performance (F1=89%), computational efficiency, and clinical interpretability - addressing critical needs in prostate cancer diagnostics.
前列腺癌是男性第二常见的恶性肿瘤,需要先进的诊断工具。我们提出了一种可解释的人工智能系统,通过新型的多模式融合策略结合了BERT(用于文本临床笔记)和随机森林(用于数值实验室数据),在PLCO-NIH数据集上实现了卓越的分类性能(准确度98%,AUC 99%)。虽然多模式融合已经建立,但我们的工作证明,简单但可解释的BERT+RF管道带来了临床上显著的改进——特别是对中间阶段的癌症(第2/3类召回率:结合为0.900 vs数值为0.824/文本为0.725)。SHAP分析提供了透明的特征重要性排名,而消融研究证明了文本特征的补充价值。这种可行的方法为医院提供了高性能(F1=89%)、计算效率和临床可解释性的平衡,满足了前列腺癌诊断中的关键需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种结合BERT(用于文本临床笔记)和随机森林(用于数值实验室数据)的可解释人工智能系统,通过新型多模式融合策略,在PLCO-NIH数据集上实现优异的分类性能(准确度98%,AUC 99%)。研究证明,该简单但可解释的BERT+RF流程,特别是针对中间癌症阶段(第二类和第三类召回率:结合为0.900,数值/文本分别为0.824和0.725),可实现临床上的显著改善。SHAP分析提供了透明的特征重要性排名,而消融研究证明了文本特征的补充价值。这种易于实施的方法实现了高性能(F1=89%)、计算效率和临床可解释性的平衡,满足了前列腺癌诊断的关键需求。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种结合BERT和随机森林的新型前列腺癌诊断方法。
- 该方法结合了文本临床笔记和数值实验室数据,实现多模式融合策略。
- 在PLCO-NIH数据集上取得较高分类性能(准确度98%,AUC 99%)。
- 研究针对中间癌症阶段表现优异,特别是第二类和第三类召回率的提升显著。
- SHAP分析提供了特征重要性的透明排名。
- 消融研究证明了文本特征在诊断中的补充价值。
点此查看论文截图

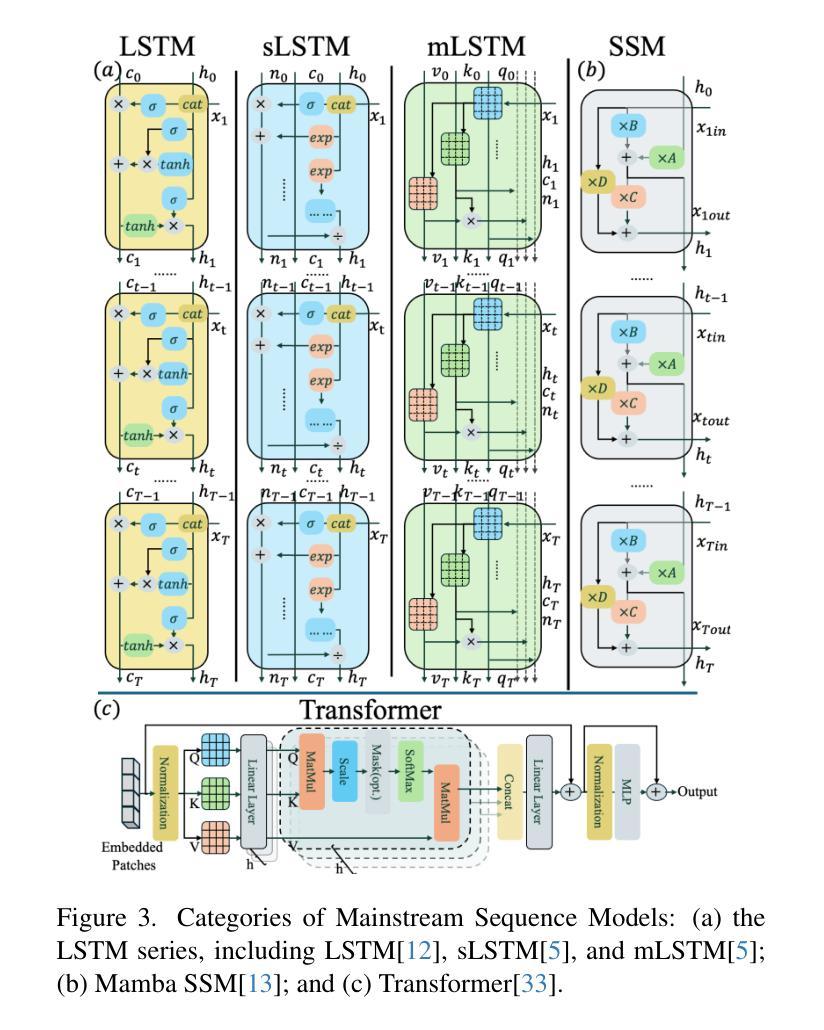
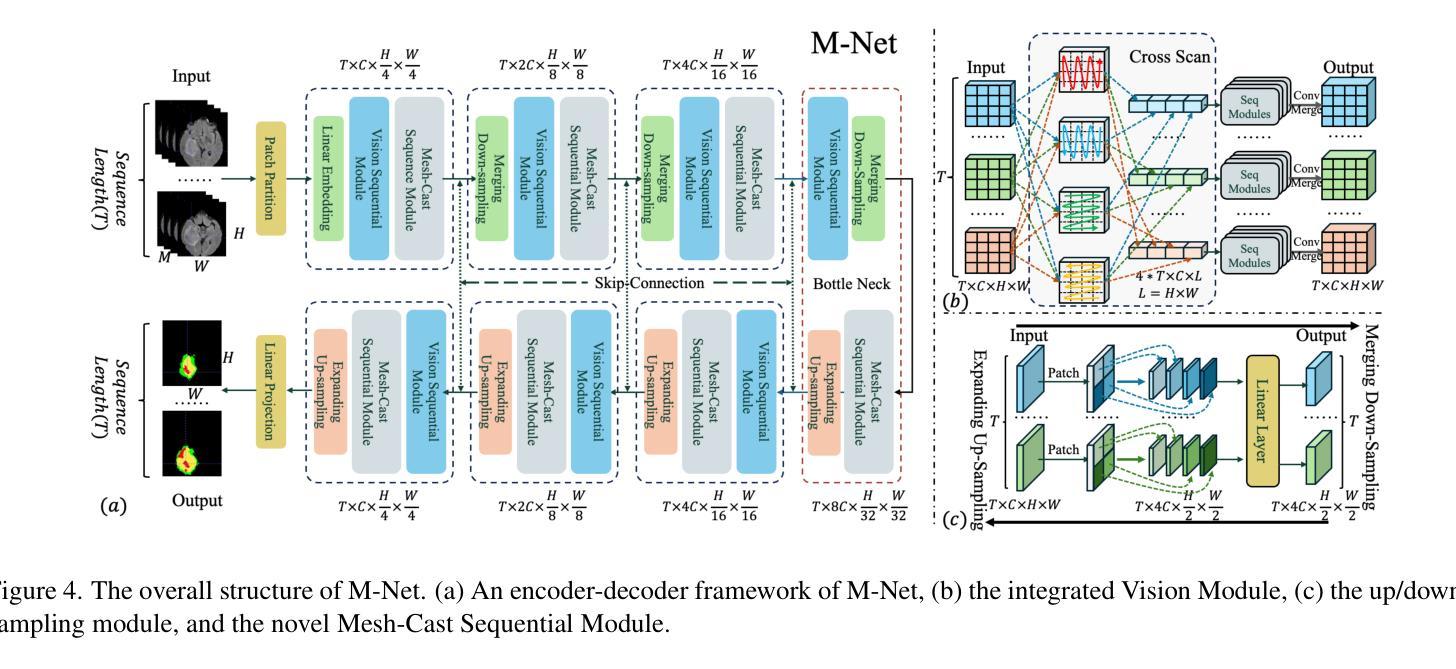
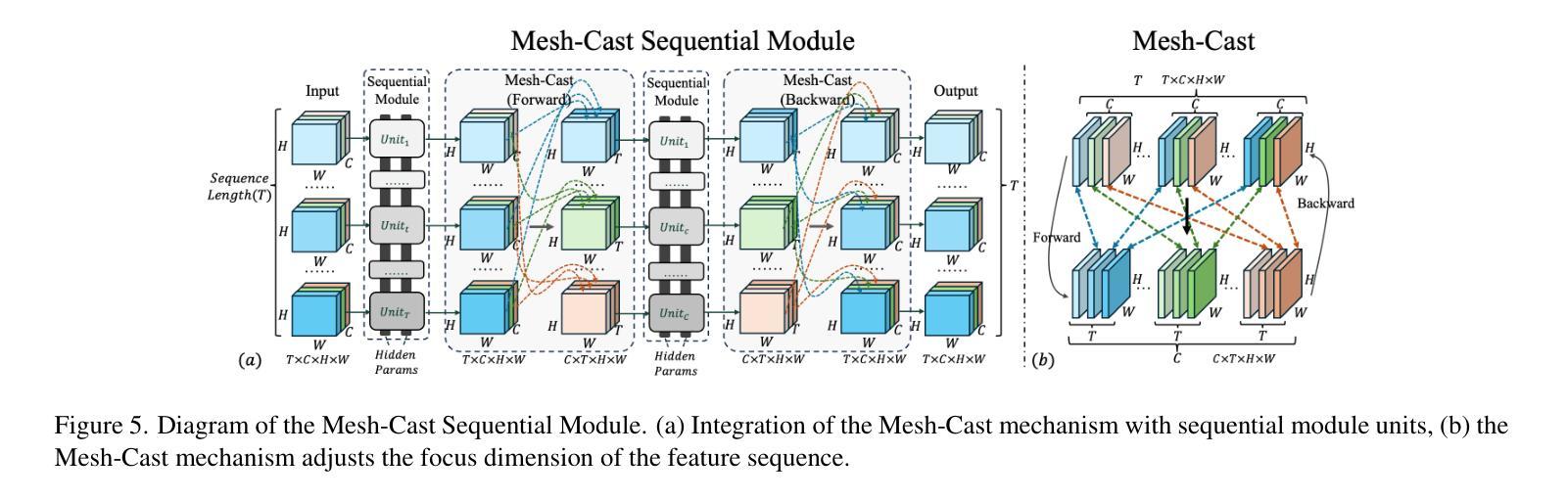
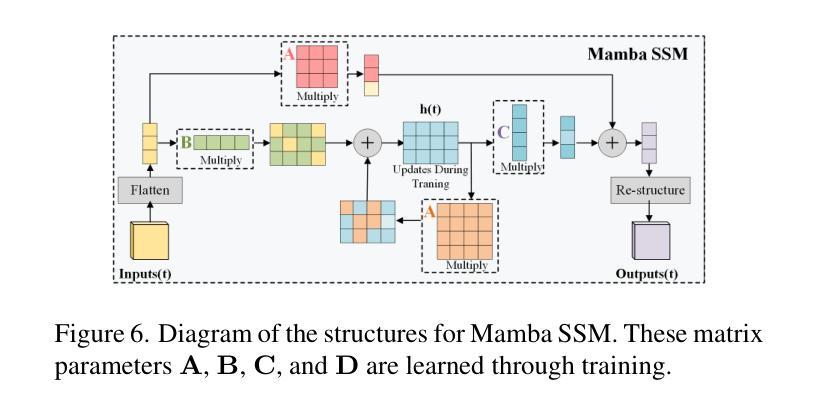
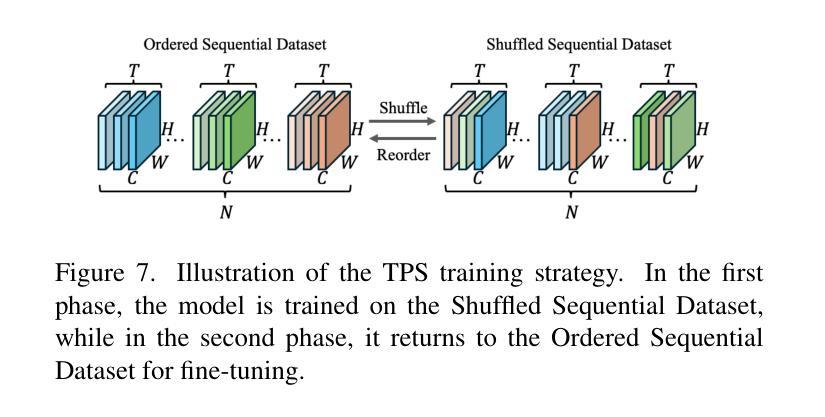
M-Net: MRI Brain Tumor Sequential Segmentation Network via Mesh-Cast
Authors:Jiacheng Lu, Hui Ding, Shiyu Zhang, Guoping Huo
MRI tumor segmentation remains a critical challenge in medical imaging, where volumetric analysis faces unique computational demands due to the complexity of 3D data. The spatially sequential arrangement of adjacent MRI slices provides valuable information that enhances segmentation continuity and accuracy, yet this characteristic remains underutilized in many existing models. The spatial correlations between adjacent MRI slices can be regarded as “temporal-like” data, similar to frame sequences in video segmentation tasks. To bridge this gap, we propose M-Net, a flexible framework specifically designed for sequential image segmentation. M-Net introduces the novel Mesh-Cast mechanism, which seamlessly integrates arbitrary sequential models into the processing of both channel and temporal information, thereby systematically capturing the inherent “temporal-like” spatial correlations between MRI slices. Additionally, we define an MRI sequential input pattern and design a Two-Phase Sequential (TPS) training strategy, which first focuses on learning common patterns across sequences before refining slice-specific feature extraction. This approach leverages temporal modeling techniques to preserve volumetric contextual information while avoiding the high computational cost of full 3D convolutions, thereby enhancing the generalizability and robustness of M-Net in sequential segmentation tasks. Experiments on the BraTS2019 and BraTS2023 datasets demonstrate that M-Net outperforms existing methods across all key metrics, establishing itself as a robust solution for temporally-aware MRI tumor segmentation.
MRI肿瘤分割在医学成像中仍然是一个关键的挑战。由于3D数据的复杂性,体积分析面临着独特的计算需求。相邻MRI切片的空间序列排列提供了有价值的信息,可以提高分割的连续性和准确性,但在许多现有模型中,这一特征的使用并不充分。相邻MRI切片之间的空间相关性可以被视为类似于视频分割任务中的帧序列的“时间性”数据。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了M-Net,这是一个专为顺序图像分割设计的灵活框架。M-Net引入了新颖的Mesh-Cast机制,该机制无缝集成了任意顺序模型,以处理通道和时间信息,从而系统地捕获MRI切片之间固有的“时间性”空间相关性。此外,我们定义了MRI序列输入模式,并设计了两阶段顺序(TPS)训练策略,该策略首先专注于学习序列中的通用模式,然后再细化切片特定的特征提取。这种方法利用时间序列建模技术来保留体积上下文信息,同时避免了全3D卷积的高计算成本,从而提高了M-Net在顺序分割任务中的通用性和稳健性。在BraTS2019和BraTS2023数据集上的实验表明,M-Net在所有关键指标上均优于现有方法,成为了一种用于时间感知MRI肿瘤分割的稳健解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Accepted
Summary
本文提出MRI肿瘤分割是医学成像中的一项重要挑战,因三维数据的复杂性而面临独特的计算需求。文章利用MRI切片的空间序列排列信息,增强分割的连续性和准确性,但这一特性在许多现有模型中未被充分利用。为此,提出M-Net框架,通过Mesh-Cast机制和两阶段序贯训练策略,有效捕捉MRI切片间的“时间性”空间关联,实现序列图像分割。实验证明,M-Net在BraTS2019和BraTS2023数据集上的表现优于现有方法,成为了一种在时序感知MRI肿瘤分割中的稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- MRI肿瘤分割是医学成像中的关键挑战,涉及复杂的三维数据处理和独特的计算需求。
- MRI切片的空间序列排列信息对于提高分割的连续性和准确性具有重要价值,但在许多模型中未得到充分利用。
- M-Net框架通过Mesh-Cast机制整合任意序列模型,处理通道和时序信息,捕捉MRI切片间的“时间性”空间关联。
- 定义了MRI序列输入模式,并采用两阶段序贯训练策略,先学习序列间的通用模式,再细化切片特征提取。
- M-Net通过时序建模技术保留体积上下文信息,避免全3D卷积的高计算成本。
- M-Net在BraTS2019和BraTS2023数据集上的表现优于现有方法,展现出其稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

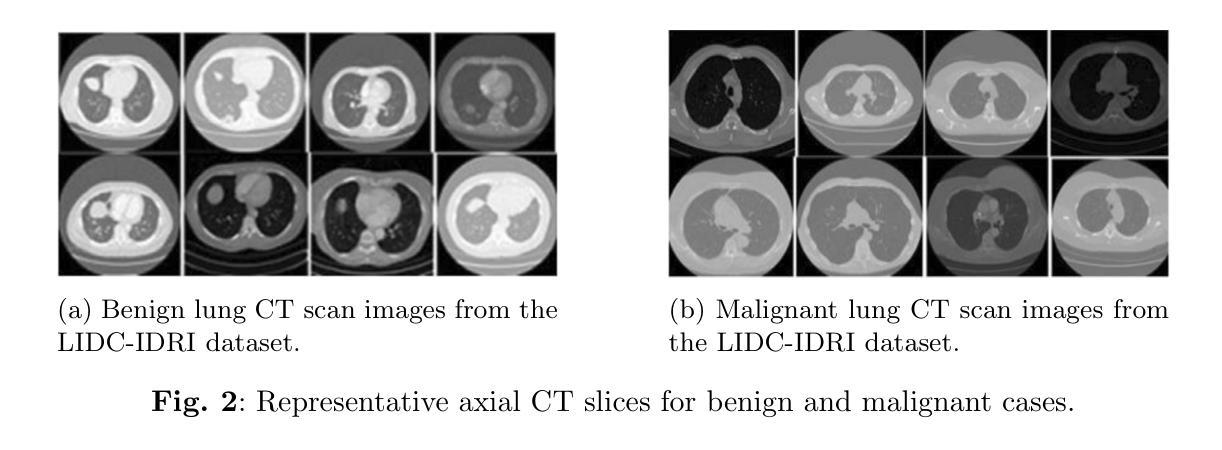
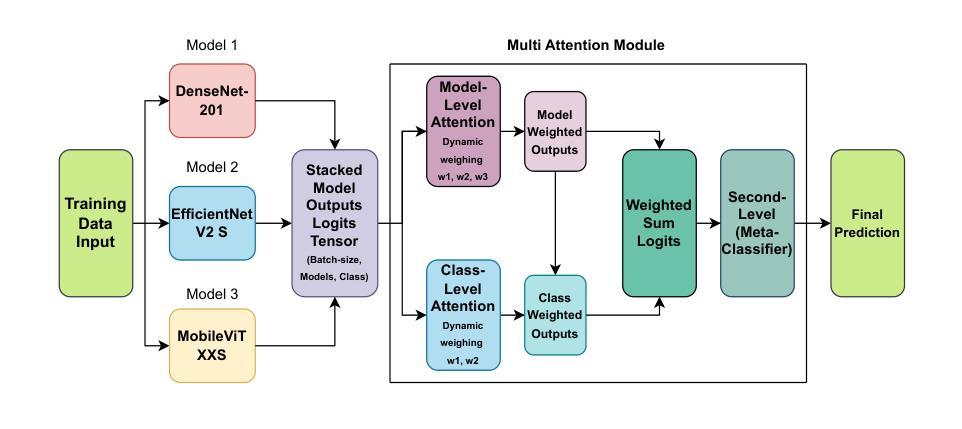
Multi-Attention Stacked Ensemble for Lung Cancer Detection in CT Scans
Authors:Uzzal Saha, Surya Prakash
In this work, we address the challenge of binary lung nodule classification (benign vs malignant) using CT images by proposing a multi-level attention stacked ensemble of deep neural networks. Three pretrained backbones – EfficientNet V2 S, MobileViT XXS, and DenseNet201 – are each adapted with a custom classification head tailored to 96 x 96 pixel inputs. A two-stage attention mechanism learns both model-wise and class-wise importance scores from concatenated logits, and a lightweight meta-learner refines the final prediction. To mitigate class imbalance and improve generalization, we employ dynamic focal loss with empirically calculated class weights, MixUp augmentation during training, and test-time augmentation at inference. Experiments on the LIDC-IDRI dataset demonstrate exceptional performance, achieving 98.09 accuracy and 0.9961 AUC, representing a 35 percent reduction in error rate compared to state-of-the-art methods. The model exhibits balanced performance across sensitivity (98.73) and specificity (98.96), with particularly strong results on challenging cases where radiologist disagreement was high. Statistical significance testing confirms the robustness of these improvements across multiple experimental runs. Our approach can serve as a robust, automated aid for radiologists in lung cancer screening.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一个基于多层注意力堆叠深度神经网络集合来解决使用CT图像进行二分类肺结节(良性与恶性)的挑战。我们采用了三种预训练模型——EfficientNet V2 S、MobileViT XXS和DenseNet201,并为每个模型适配了一个针对96x96像素输入的定制分类头。两阶段注意力机制学习模型间和类别间的重要性得分,并通过对数几率进行组合,同时一个轻量级元学习者对最终预测进行微调。为了缓解类别不平衡和提高泛化能力,我们采用动态焦点损失与经验计算得到的类别权重、训练过程中的MixUp数据增强以及在推理时的测试时间数据增强。在LIDC-IDRI数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法表现出卓越的性能,达到了98.09%的准确率和0.9961的AUC值,与最新方法相比,误差率降低了35%。该模型在灵敏度和特异度方面表现出平衡的性能(分别为98.73和98.96),特别是在放射科医生意见分歧较大的挑战性病例中表现尤为出色。统计显著性测试证实了这些改进在多次实验中的稳健性。我们的方法可以作为放射科医生在肺癌筛查中的稳健自动化辅助工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 14 figures
Summary
本研究通过提出多层次的注意力深度神经网络集成方法,解决基于CT图像的肺部结节良恶性分类挑战。通过采用三种预训练模型(EfficientNet V2 S、MobileViT XXS和DenseNet201),结合定制的96x96像素输入分类头,并采用两阶段注意力机制,学习模型间和类别间的权重。为缓解类别不平衡和提高泛化能力,研究采用动态焦点损失与经验计算类别权重、训练期间的MixUp增强和推理时的测试增强。在LIDC-IDRI数据集上的实验表明,该方法取得了卓越的性能,准确率为98.09%,AUC为0.9961,相比最新方法误差率降低了35%。该模型在灵敏度和特异度方面表现均衡,特别是在放射科医生意见不一致的病例中表现出色。统计测试证明这些改进在多次实验中均稳健。本研究可为放射科医生肺癌筛查提供稳健的自动化辅助。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出一种多层次的注意力深度神经网络集成方法用于解决基于CT图像的肺部结节良恶性分类问题。
- 采用三种预训练模型,并结合定制的输入分类头处理图像数据。
- 使用两阶段注意力机制以学习模型间和类别间的权重分配。
- 通过动态焦点损失、经验计算类别权重、训练时的数据增强等方法改善类别不平衡和提高模型泛化能力。
- 在LIDC-IDRI数据集上的实验结果显示出卓越的性能,准确率和AUC均超过现有方法。
- 模型在灵敏度和特异度方面表现均衡,尤其适用于放射科医生诊断意见不一致的病例。
- 统计测试证明了模型改进的稳定性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

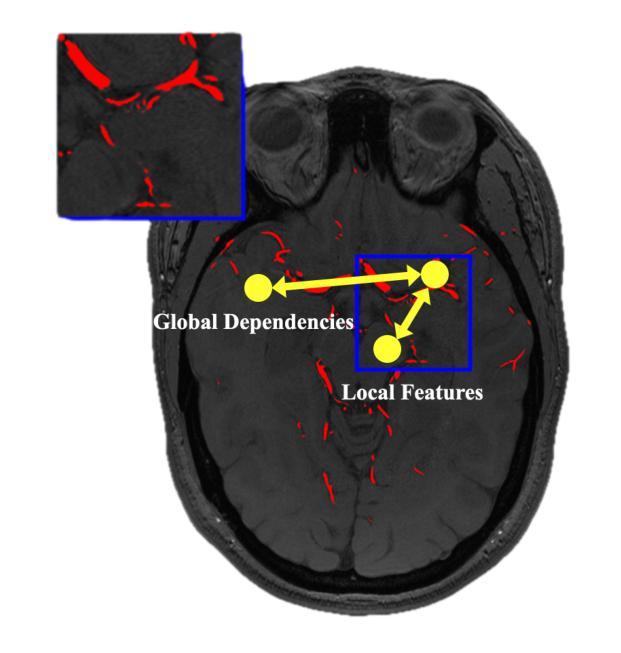
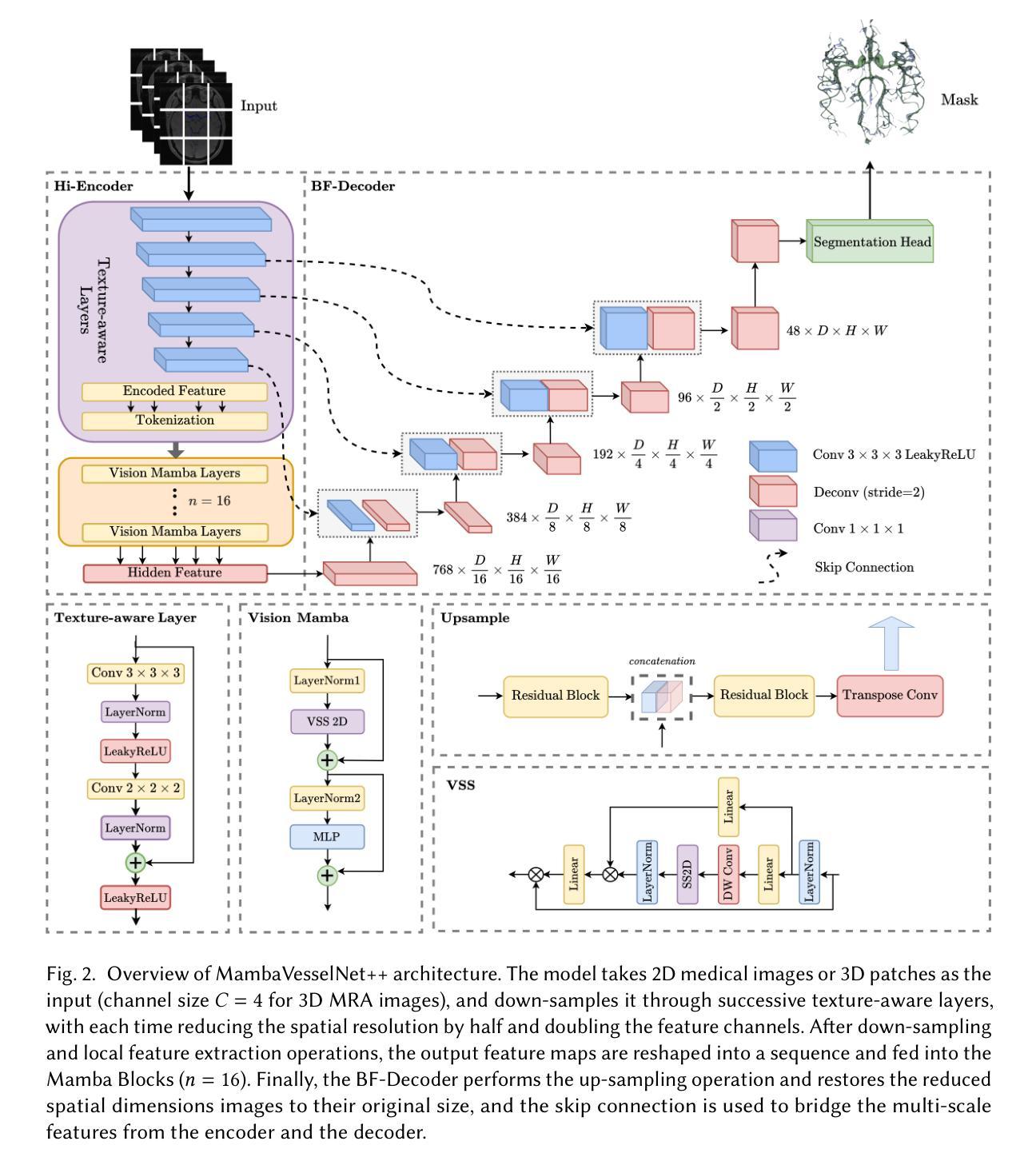
MambaVesselNet++: A Hybrid CNN-Mamba Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Qing Xu, Yanming Chen, Yue Li, Ziyu Liu, Zhenye Lou, Yixuan Zhang, Xiangjian He
Medical image segmentation plays an important role in computer-aided diagnosis. Traditional convolution-based U-shape segmentation architectures are usually limited by the local receptive field. Existing vision transformers have been widely applied to diverse medical segmentation frameworks due to their superior capabilities of capturing global contexts. Despite the advantage, the real-world application of vision transformers is challenged by their non-linear self-attention mechanism, requiring huge computational costs. To address this issue, the selective state space model (SSM) Mamba has gained recognition for its adeptness in modeling long-range dependencies in sequential data, particularly noted for its efficient memory costs. In this paper, we propose MambaVesselNet++, a Hybrid CNN-Mamba framework for medical image segmentation. Our MambaVesselNet++ is comprised of a hybrid image encoder (Hi-Encoder) and a bifocal fusion decoder (BF-Decoder). In Hi-Encoder, we first devise the texture-aware layer to capture low-level semantic features by leveraging convolutions. Then, we utilize Mamba to effectively model long-range dependencies with linear complexity. The Bi-Decoder adopts skip connections to combine local and global information of the Hi-Encoder for the accurate generation of segmentation masks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MambaVesselNet++ outperforms current convolution-based, transformer-based, and Mamba-based state-of-the-arts across diverse medical 2D, 3D, and instance segmentation tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/CC0117/MambaVesselNet.
医学图像分割在计算机辅助诊断中扮演着重要角色。传统的基于卷积的U型分割架构通常受到局部感受野的限制。由于捕捉全局上下文的优势,现有的视觉转换器已被广泛应用于各种医学分割框架。尽管如此,视觉转换器在现实世界的应用中面临着其非线性自注意力机制的挑战,需要巨大的计算成本。为了解决这一问题,选择性状态空间模型(SSM)Mamba因其对序列数据中长距离依赖关系的建模能力而受到认可,尤其值得一提的是其高效的内存成本。在本文中,我们提出了MambaVesselNet++,这是一个用于医学图像分割的混合CNN-Mamba框架。我们的MambaVesselNet++由混合图像编码器(Hi-Encoder)和双焦点融合解码器(BF-Decoder)组成。在Hi-Encoder中,我们首先设计了一个纹理感知层,利用卷积来捕捉低级别语义特征。然后,我们使用Mamba有效地对长距离依赖关系进行建模,具有线性复杂性。Bi-Decoder采用跳跃连接,结合Hi-Encoder的局部和全局信息,以准确生成分割掩膜。大量实验表明,MambaVesselNet++在多种医学二维、三维和实例分割任务上的性能优于当前的基于卷积、基于转换器和基于Mamba的最先进方法。代码可在[https://github.com/CC0117/MambaVesselNet找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TOMM
摘要
医学图像分割在计算机辅助诊断中扮演重要角色。本文提出MambaVesselNet++,一个混合CNN-Mamba框架,用于医学图像分割。该框架包含混合图像编码器(Hi-Encoder)和双焦点融合解码器(BF-Decoder)。Hi-Encoder利用纹理感知层捕捉低级别语义特征,并利用Mamba有效建模长距离依赖关系。BF-Decoder通过跳过连接结合Hi-Encoder的局部和全局信息,以生成精确的分割掩膜。实验表明,MambaVesselNet++在多种医学二维、三维和实例分割任务上超越了当前的卷积基、转换器基和Mamba基先进技术。
要点
- 医学图像分割在计算机辅助诊断中的重要性。
- 传统基于卷积的U型分割架构受限于局部感受野。
- 视觉转换器因捕捉全局上下文的能力而广泛应用于医学分割框架。
- 视觉转换器在现实世界应用中的挑战是其非线性自注意力机制,需要巨大的计算成本。
- 选择性状态空间模型(SSM)Mamba擅长对序列数据的长距离依赖进行建模,具有高效的内存成本。
- 提出的MambaVesselNet++是一个混合CNN-Mamba框架,包含Hi-Encoder和BF-Decoder。
- MambaVesselNet++在多种医学分割任务上表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

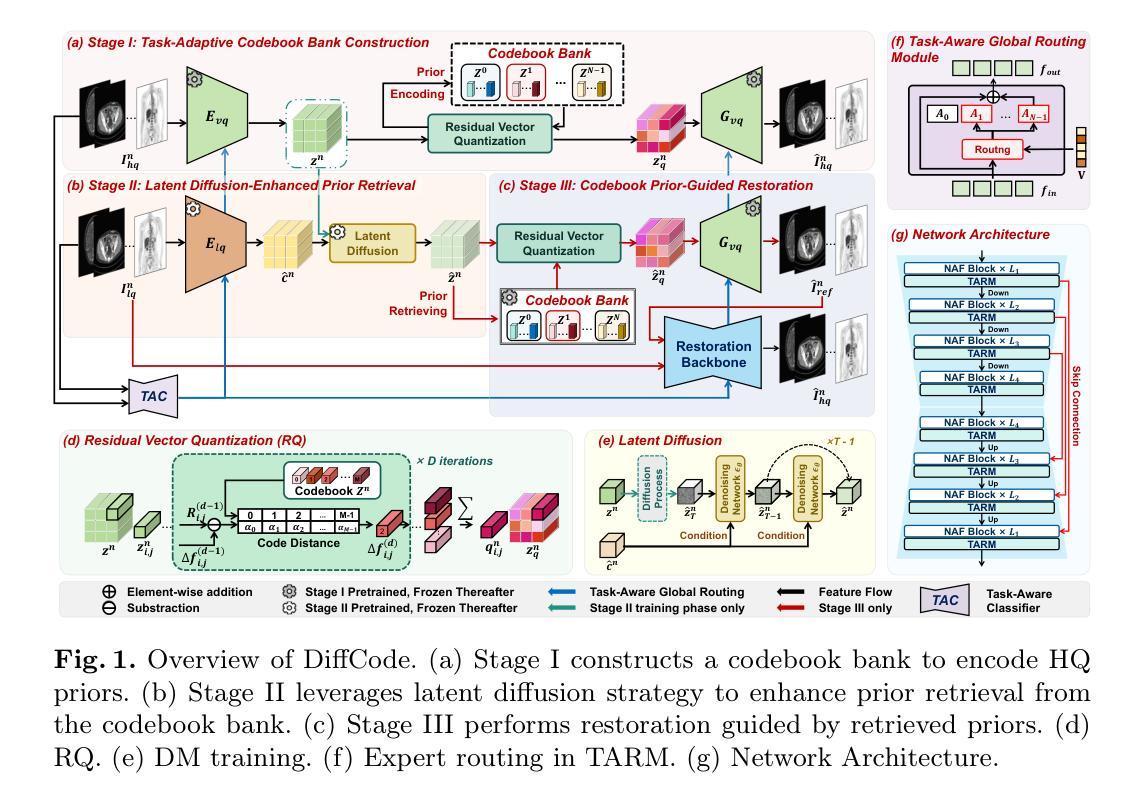
All-in-One Medical Image Restoration with Latent Diffusion-Enhanced Vector-Quantized Codebook Prior
Authors:Haowei Chen, Zhiwen Yang, Haotian Hou, Hui Zhang, Bingzheng Wei, Gang Zhou, Yan Xu
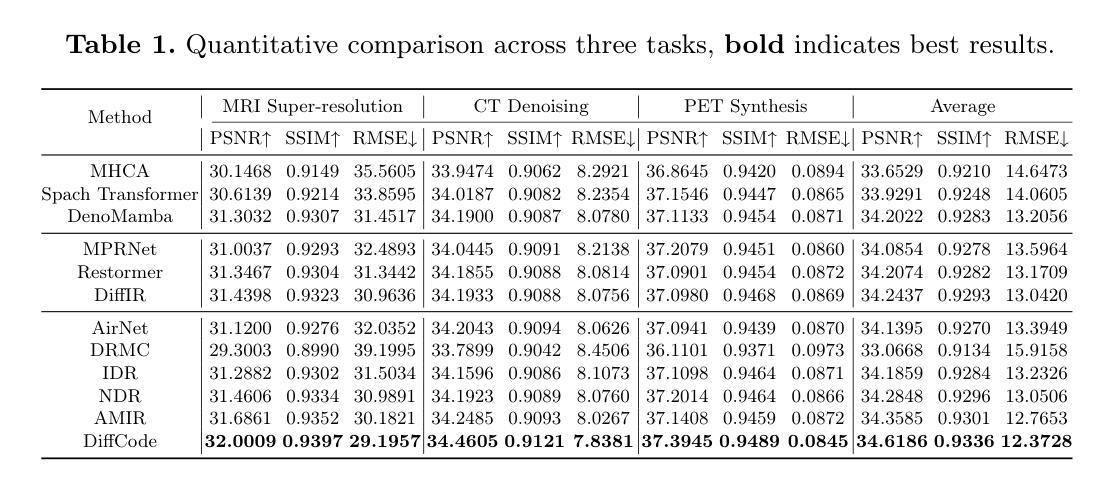
All-in-one medical image restoration (MedIR) aims to address multiple MedIR tasks using a unified model, concurrently recovering various high-quality (HQ) medical images (e.g., MRI, CT, and PET) from low-quality (LQ) counterparts. However, all-in-one MedIR presents significant challenges due to the heterogeneity across different tasks. Each task involves distinct degradations, leading to diverse information losses in LQ images. Existing methods struggle to handle these diverse information losses associated with different tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a latent diffusion-enhanced vector-quantized codebook prior and develop \textbf{DiffCode}, a novel framework leveraging this prior for all-in-one MedIR. Specifically, to compensate for diverse information losses associated with different tasks, DiffCode constructs a task-adaptive codebook bank to integrate task-specific HQ prior features across tasks, capturing a comprehensive prior. Furthermore, to enhance prior retrieval from the codebook bank, DiffCode introduces a latent diffusion strategy that utilizes the diffusion model’s powerful mapping capabilities to iteratively refine the latent feature distribution, estimating more accurate HQ prior features during restoration. With the help of the task-adaptive codebook bank and latent diffusion strategy, DiffCode achieves superior performance in both quantitative metrics and visual quality across three MedIR tasks: MRI super-resolution, CT denoising, and PET synthesis.
全功能医学影像修复(MedIR)旨在使用统一模型解决多个MedIR任务,同时从低质量(LQ)医学影像中恢复多种高质量(HQ)医学影像(例如MRI、CT和PET)。然而,全功能MedIR由于不同任务之间的异质性而面临重大挑战。每个任务涉及不同的退化,导致低质量图像中信息损失多样。现有方法难以处理与不同任务相关的多样信息损失。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种潜在扩散增强向量量化码本先验,并开发了新型框架DiffCode,该框架利用此先验进行全功能MedIR。具体来说,为了补偿与不同任务相关的信息损失多样性,DiffCode构建了一个任务自适应码本银行,以整合任务特定的高质量先验特征,从而捕捉全面的先验知识。此外,为了从码本银行中增强先验检索,DiffCode引入了一种潜在扩散策略,该策略利用扩散模型的强大映射能力来迭代优化潜在特征分布,在修复过程中估计更准确的高质量先验特征。借助任务自适应码本银行和潜在扩散策略,DiffCode在三个MedIR任务:MRI超分辨率、CT去噪和PET合成中,无论是在定量指标还是视觉质量方面都实现了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11pages, 3figures, MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了全功能医疗图像修复(MedIR)面临的挑战,并提出了DiffCode框架来解决这些问题。该框架采用潜在扩散增强向量量化码本先验,通过构建任务适应性码本银行和引入潜在扩散策略,提高了对不同任务的适应性,从而在不同医疗图像修复任务中取得了优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- MedIR的目标是使用统一模型解决多个任务,从低质量图像中恢复高质量医疗图像。
- 全功能MedIR面临的任务间异质性是其主要挑战。
- 每个任务涉及不同的降解,导致低质量图像中的信息损失多样化。
- 现有方法难以处理与不同任务相关的多样化信息损失。
- DiffCode框架通过采用潜在扩散增强向量量化码本先验来解决这些挑战。
- DiffCode构建了任务适应性码本银行来集成跨任务的特定高质量先验特征,并引入了潜在扩散策略来增强码本银行中的先验检索。
点此查看论文截图

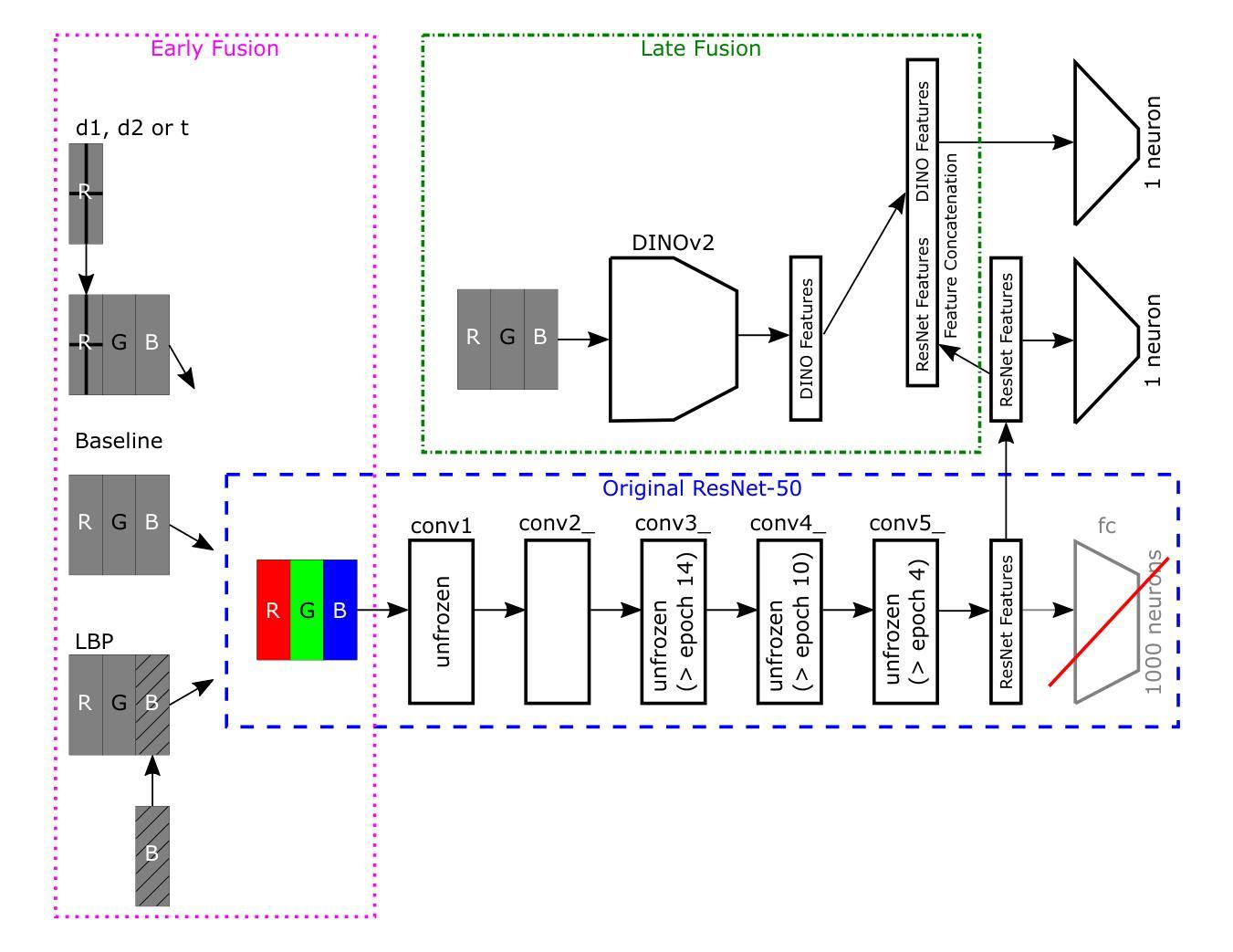
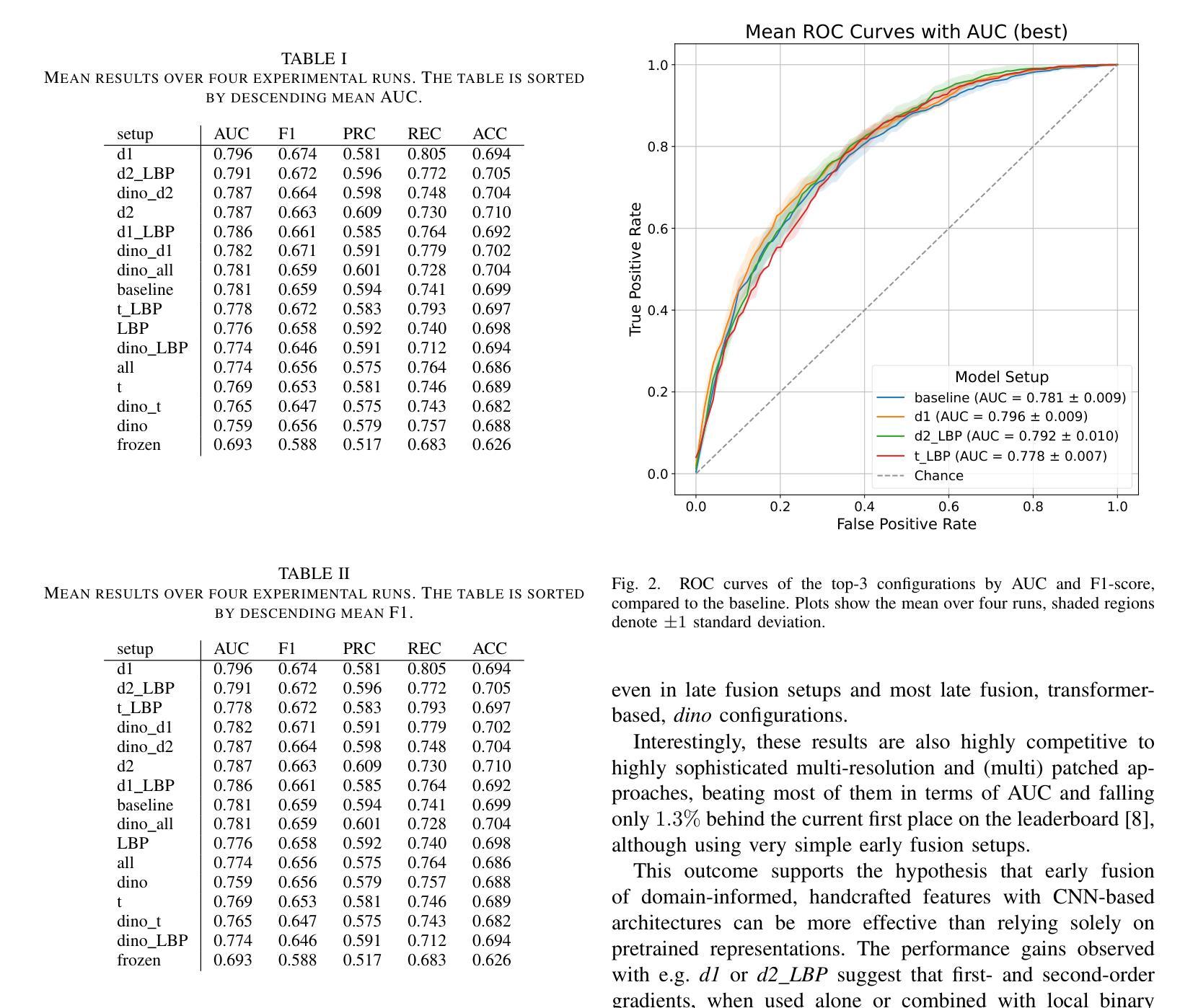
Hybrid Deep Learning and Handcrafted Feature Fusion for Mammographic Breast Cancer Classification
Authors:Maximilian Tschuchnig, Michael Gadermayr, Khalifa Djemal
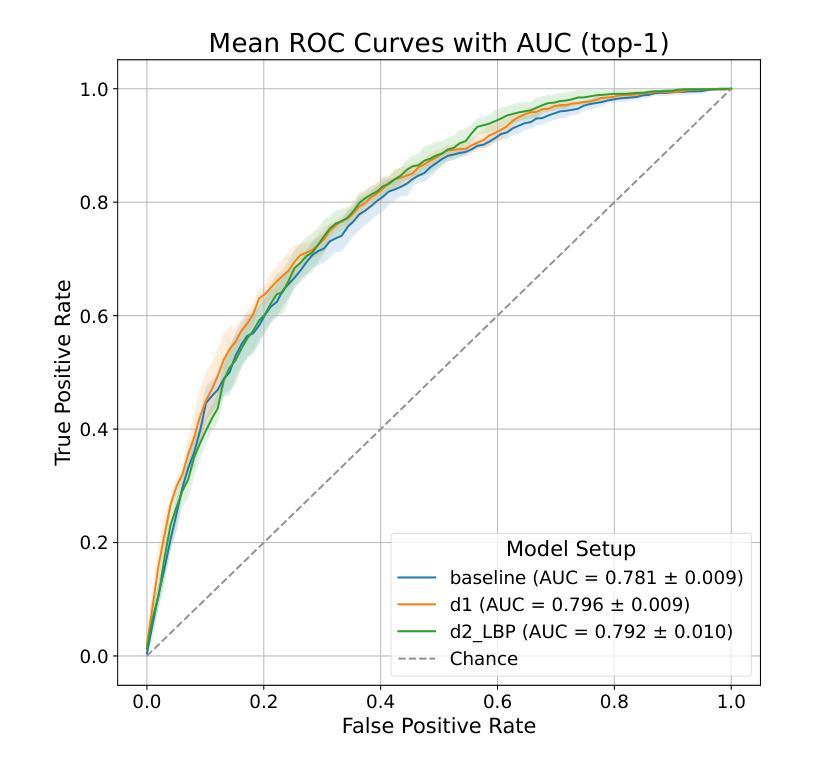
Automated breast cancer classification from mammography remains a significant challenge due to subtle distinctions between benign and malignant tissue. In this work, we present a hybrid framework combining deep convolutional features from a ResNet-50 backbone with handcrafted descriptors and transformer-based embeddings. Using the CBIS-DDSM dataset, we benchmark our ResNet-50 baseline (AUC: 78.1%) and demonstrate that fusing handcrafted features with deep ResNet-50 and DINOv2 features improves AUC to 79.6% (setup d1), with a peak recall of 80.5% (setup d1) and highest F1 score of 67.4% (setup d1). Our experiments show that handcrafted features not only complement deep representations but also enhance performance beyond transformer-based embeddings. This hybrid fusion approach achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art methods while maintaining architectural simplicity and computational efficiency, making it a practical and effective solution for clinical decision support.
自动化乳腺癌分类从乳腺钼靶图像仍然是一个重大挑战,因为良性和恶性组织之间的区别很微妙。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个混合框架,结合了ResNet-50主干的深度卷积特征、手工描述符和基于变压器的嵌入。我们使用CBIS-DDSM数据集对ResNet-50基线进行了评估(AUC:78.1%),并证明将手工特征与深度ResNet-50和DINOv2特征融合,可以将AUC提高到79.6%(设置d1),最高召回率为80.5%(设置d1),最高F1分数为67.4%(设置d1)。我们的实验表明,手工特征不仅补充了深度表示,还提高了基于变压器的嵌入的性能。这种混合融合方法的结果与最先进的方法相当,同时保持了架构的简洁性和计算效率,使其成为临床决策支持的一种实用有效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IPTA2025
Summary
乳腺癌自动分类仍然是医学影像学中的一大挑战,因良恶性组织间的差异细微。本研究结合ResNet-50骨干网络的深度卷积特征、手工特征以及基于转换器的嵌入,提出了一种混合框架。利用CBIS-DDSM数据集,基准ResNet-50模型的AUC为78.1%,融合手工特征与深度ResNet-50和DINOv2特征后,AUC提高到79.6%(设置d1),最高召回率为80.5%(设置d1),最高F1分数为67.4%(设置d1)。实验表明,手工特征不仅补充了深度表示,还提高了基于转换器的嵌入的性能。这种混合融合方法的结果与最先进的方法相当,同时保持了架构的简洁性和计算效率,使其成为临床决策支持的实际有效解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌自动分类面临挑战,因为良恶性组织之间的差异很细微。
- 研究提出了一种混合框架,结合了深度卷积特征、手工特征以及基于转换器的嵌入。
- 使用CBIS-DDSM数据集进行基准测试,ResNet-50模型的AUC为78.1%。
- 融合手工特征与深度ResNet-50和DINOv2特征后,AUC有所提升。
- 该方法在提高召回率和F1分数方面也表现出良好的效果。
- 手工特征不仅补充了深度表示,也增强了基于转换器的嵌入的性能。
点此查看论文截图

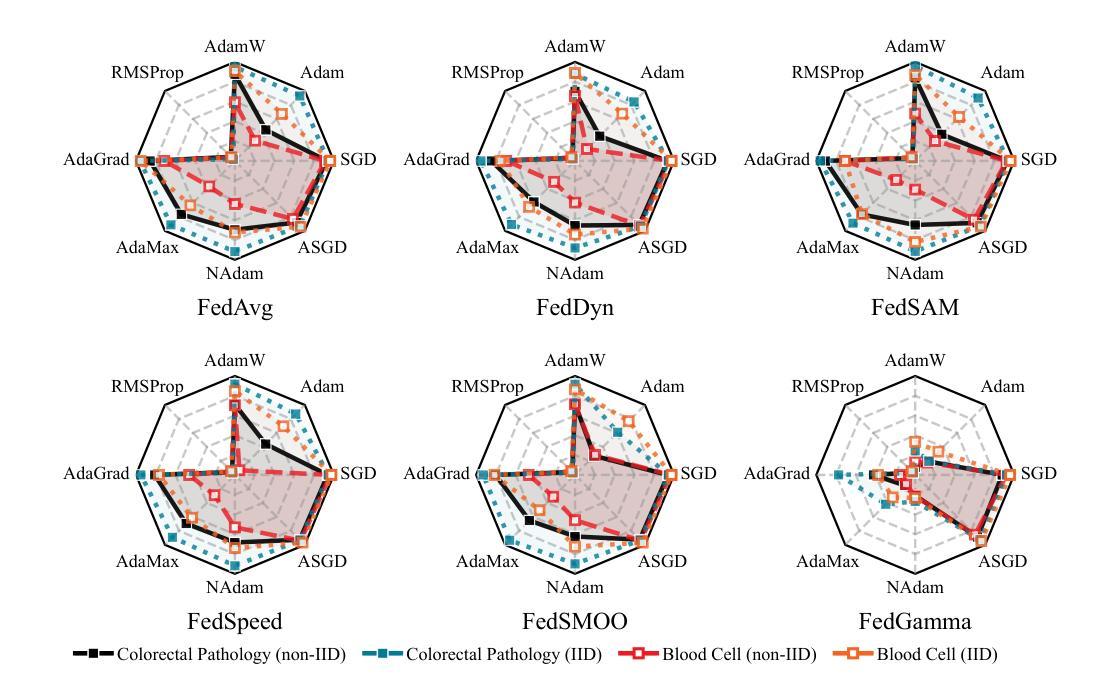
Debunking Optimization Myths in Federated Learning for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Youngjoon Lee, Hyukjoon Lee, Jinu Gong, Yang Cao, Joonhyuk Kang
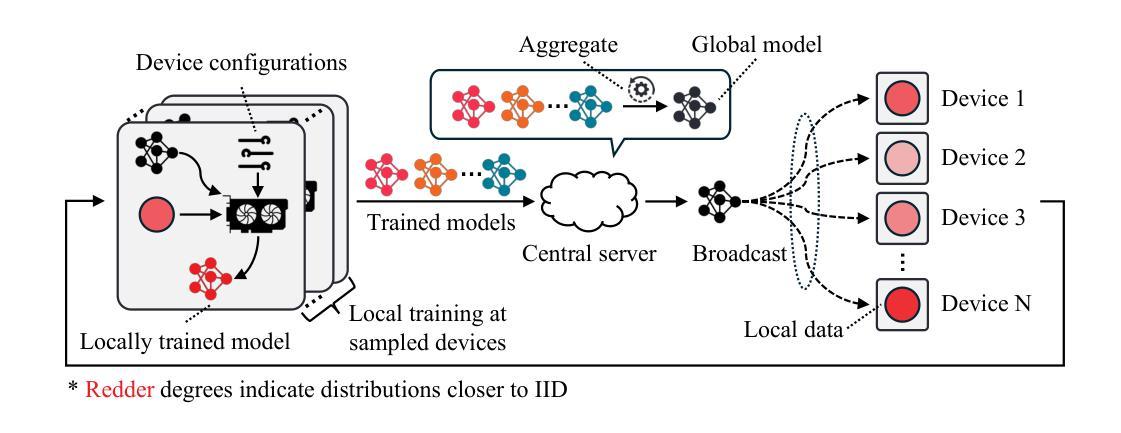
Federated Learning (FL) is a collaborative learning method that enables decentralized model training while preserving data privacy. Despite its promise in medical imaging, recent FL methods are often sensitive to local factors such as optimizers and learning rates, limiting their robustness in practical deployments. In this work, we revisit vanilla FL to clarify the impact of edge device configurations, benchmarking recent FL methods on colorectal pathology and blood cell classification task. We numerically show that the choice of local optimizer and learning rate has a greater effect on performance than the specific FL method. Moreover, we find that increasing local training epochs can either enhance or impair convergence, depending on the FL method. These findings indicate that appropriate edge-specific configuration is more crucial than algorithmic complexity for achieving effective FL.
联合学习(FL)是一种协作学习方法,能够在保持数据隐私的同时实现分散式模型训练。尽管其在医学成像方面有很大潜力,但最近的联合学习方法通常对本地因素(如优化器和学习率)很敏感,这限制了它们在实际应用中的稳健性。在这项工作中,我们重新审视了基本的联合学习方法,以阐明边缘设备配置的影响,并在结直肠癌病理和血液细胞分类任务上评估了最近的联合学习方法。我们通过数值分析表明,本地优化器和学习率的选择对性能的影响大于特定的联合学习方法。此外,我们发现增加本地训练周期可能会增强或损害收敛性,这取决于联合学习方法。这些结果表明,对于实现有效的联合学习而言,适当的边缘特定配置比算法复杂性更重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Efficient Medical AI Workshop - MICCAI 2025
Summary
联邦学习(FL)是一种协作学习方法,可实现分散式模型训练,同时保护数据隐私。尽管其在医学成像领域具有潜力,但现有的联邦学习方法对本地因素(如优化器和学习率)很敏感,这限制了其在实际应用中的稳健性。本文重新审视了普通联邦学习,以明确边缘设备配置的影响,并在结肠病理和血液细胞分类任务上评估了最近的联邦学习方法。数值结果表明,本地优化器和学习率的选择对性能的影响大于特定的联邦学习方法。此外,我们发现增加本地训练周期可能会增强或损害收敛性,这取决于联邦学习方法。这些发现表明,对于实现有效的联邦学习而言,适当的边缘特定配置比算法复杂性更重要。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)是一种能在保护数据隐私的同时实现模型分散训练的方法。
- 在医学成像领域,联邦学习具有潜力但实际应用中存在稳健性问题。
- 本地因素(如优化器和学习率)对联邦学习性能影响较大。
- 不同联邦学习方法对于增加本地训练周期的反应不同,可能增强或损害收敛性。
- 选择适当的边缘设备配置对于实现有效的联邦学习至关重要。
- 相较于算法复杂性,边缘特定配置对联邦学习效果影响更大。
点此查看论文截图

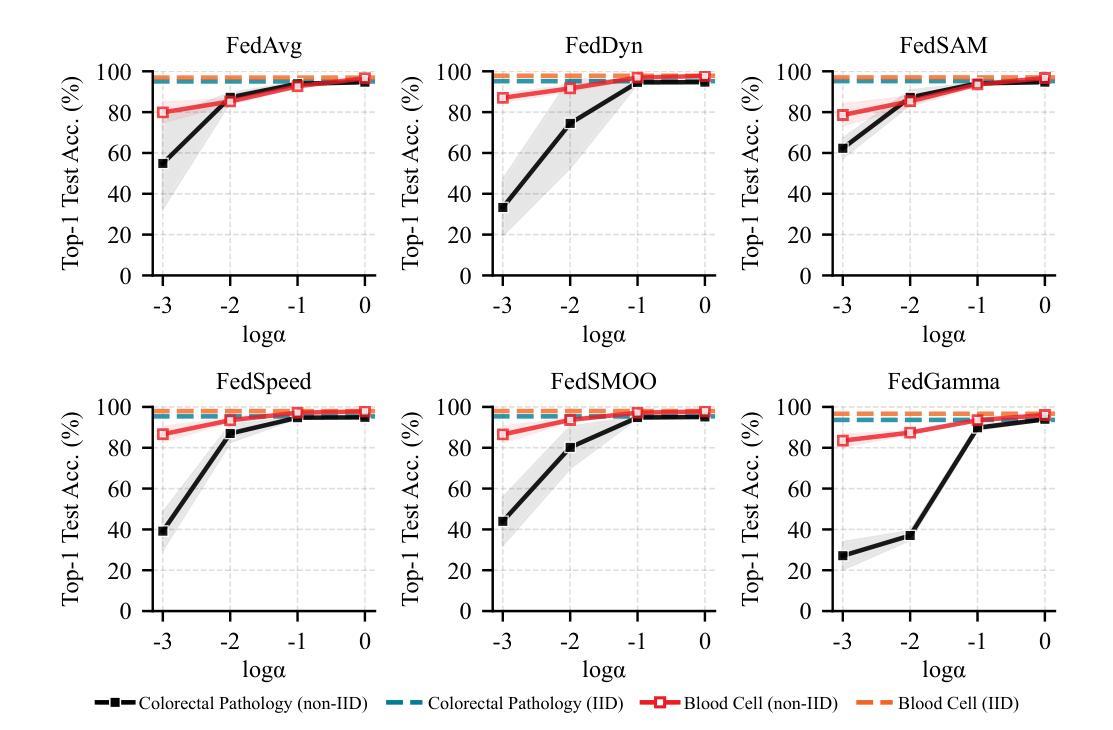
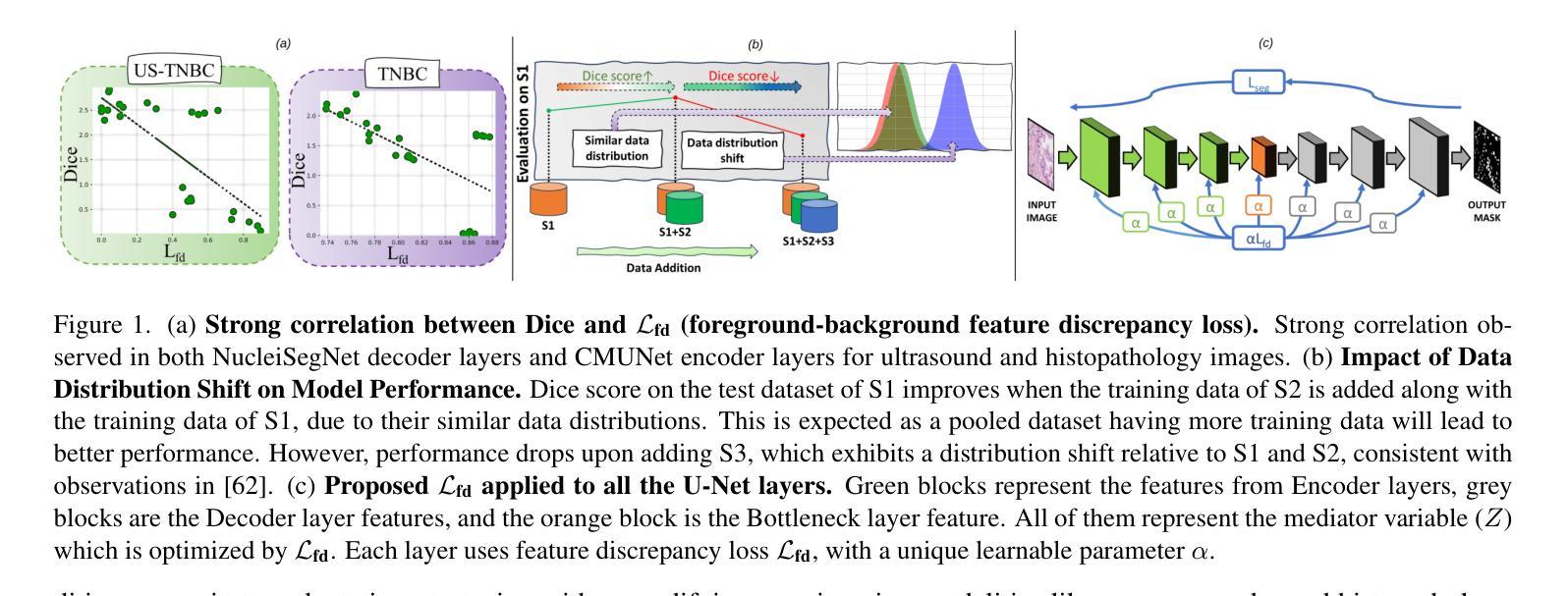
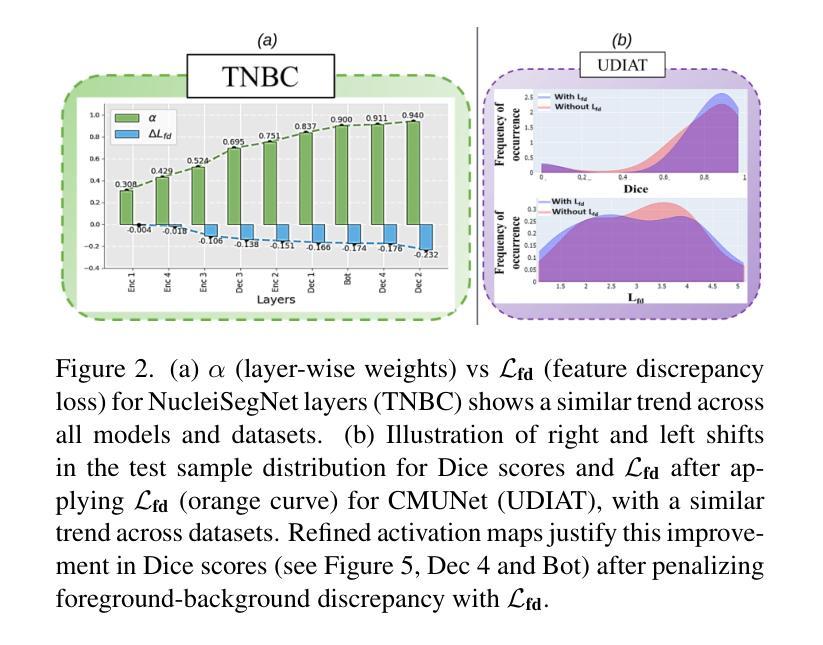
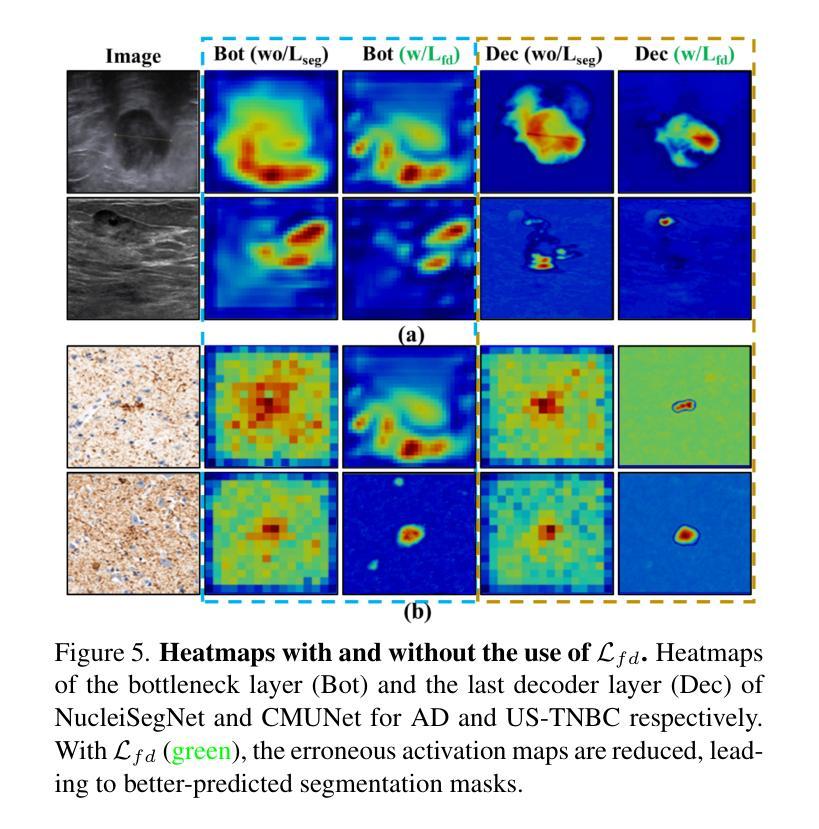
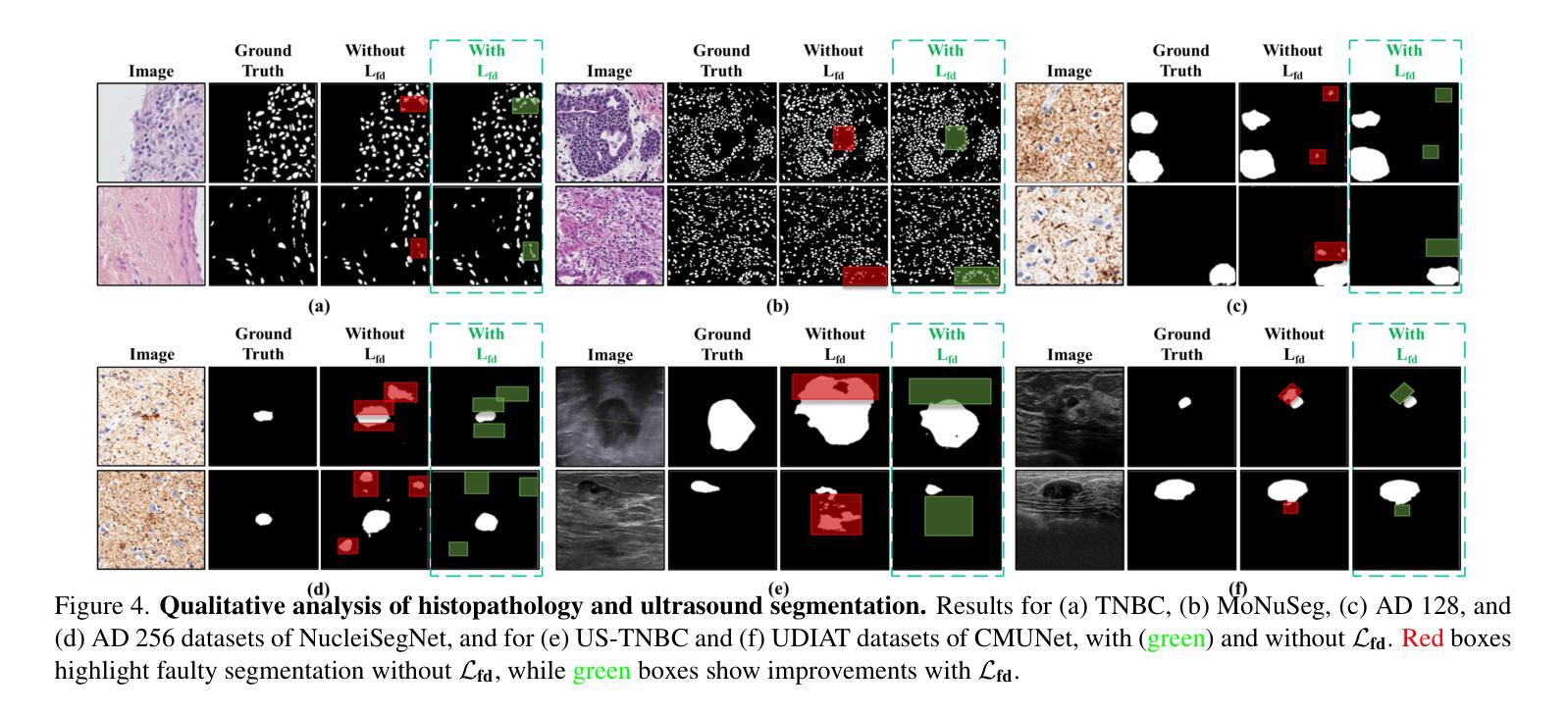
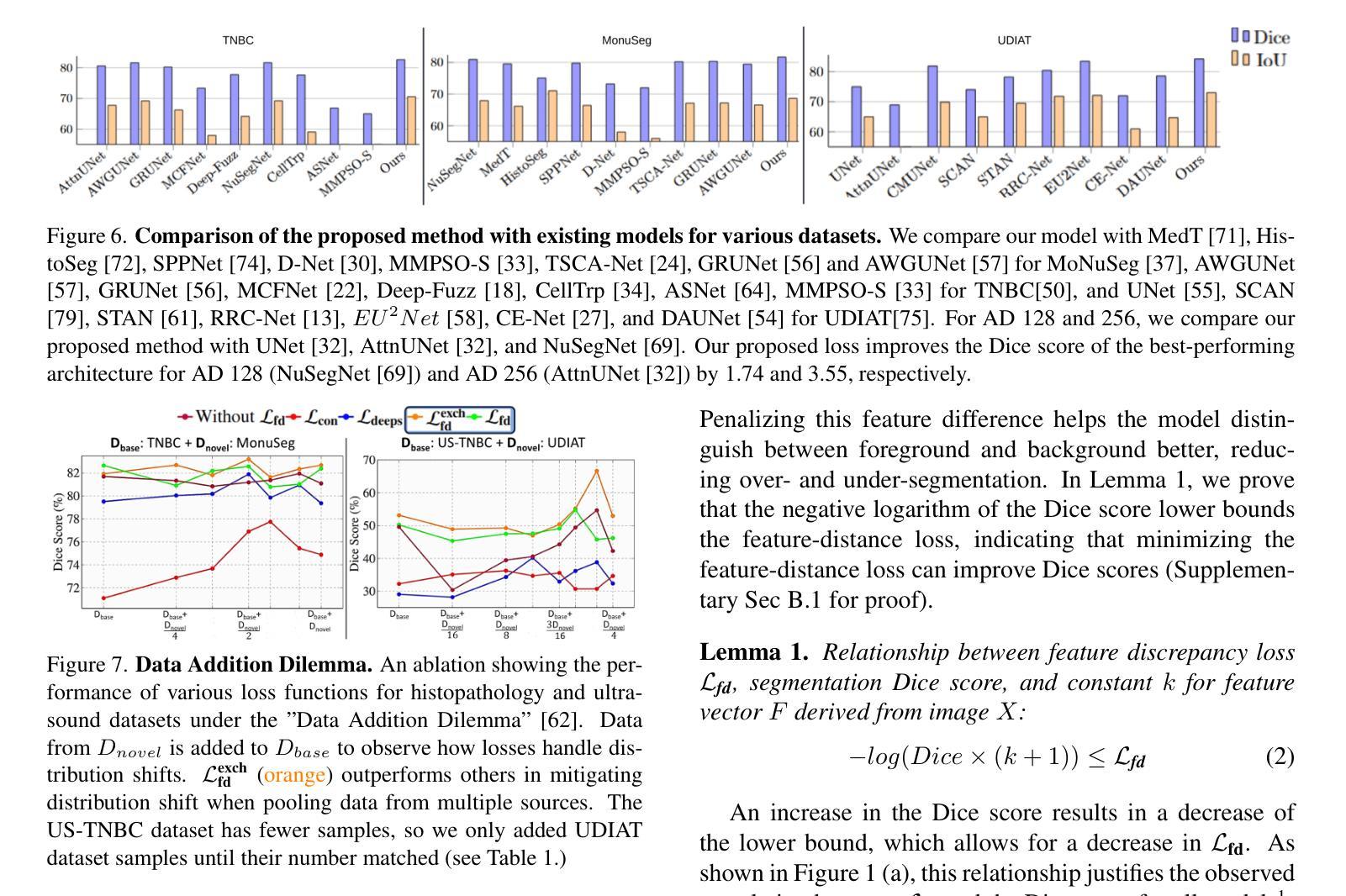
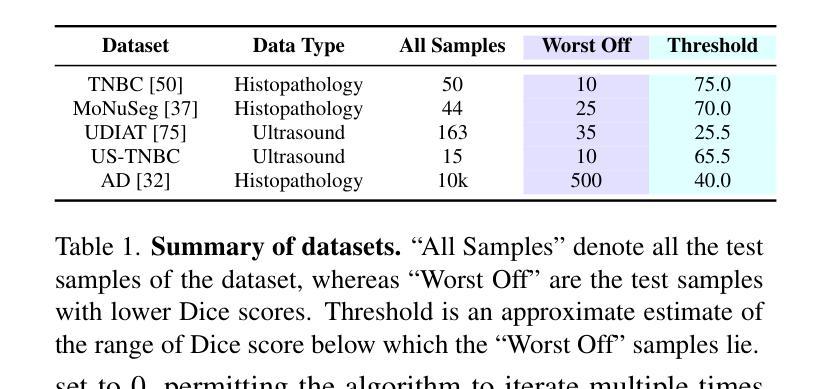
Is Exchangeability better than I.I.D to handle Data Distribution Shifts while Pooling Data for Data-scarce Medical image segmentation?
Authors:Ayush Roy, Samin Enam, Jun Xia, Vishnu Suresh Lokhande, Won Hwa Kim
Data scarcity is a major challenge in medical imaging, particularly for deep learning models. While data pooling (combining datasets from multiple sources) and data addition (adding more data from a new dataset) have been shown to enhance model performance, they are not without complications. Specifically, increasing the size of the training dataset through pooling or addition can induce distributional shifts, negatively affecting downstream model performance, a phenomenon known as the “Data Addition Dilemma”. While the traditional i.i.d. assumption may not hold in multi-source contexts, assuming exchangeability across datasets provides a more practical framework for data pooling. In this work, we investigate medical image segmentation under these conditions, drawing insights from causal frameworks to propose a method for controlling foreground-background feature discrepancies across all layers of deep networks. This approach improves feature representations, which are crucial in data-addition scenarios. Our method achieves state-of-the-art segmentation performance on histopathology and ultrasound images across five datasets, including a novel ultrasound dataset that we have curated and contributed. Qualitative results demonstrate more refined and accurate segmentation maps compared to prominent baselines across three model architectures. The code will be available on Github.
数据稀缺是医学影像领域的一个重大挑战,尤其是对于深度学习模型而言。虽然数据整合(将多个来源的数据集合并)和数据增加(添加新的数据集中的数据)已被证明可以提高模型性能,但它们并非没有复杂性。具体来说,通过整合或增加数据来增加训练数据集的大小可能会导致分布偏移,从而负面影响下游模型性能,这种现象被称为“数据增加困境”。虽然在多源环境中传统的独立同分布假设可能不成立,但假设不同数据集之间的可交换性为数据整合提供了一个更实用的框架。在这项工作中,我们在这些条件下研究医学图像分割,从因果框架中汲取灵感,提出了一种控制深层网络中所有层的前景背景特征差异的方法。这种方法改进了特征表示,在数据增加场景中至关重要。我们的方法在五个数据集上的病理学和超声图像分割性能上达到了最新水平,包括我们整理并贡献的一个新型超声数据集。定性结果表明,与三种模型架构的主要基线相比,我们的方法产生了更精细和准确的分割图。代码将在Github上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据稀缺是医学影像领域深度学习模型面临的主要挑战之一。数据池化(整合多源数据集)和数据增加(添加新数据集)虽能提高模型性能,但也会引发分布偏移问题,影响模型的后续表现,这种现象被称为“数据增加困境”。本文研究多源数据环境下的医学图像分割问题,利用因果框架提出一种控制深层网络中前景背景特征差异的方法。该方法提高了特征表示能力,在数据增加场景中表现优异。实验结果显示,该方法在五个数据集上的病理学和超声图像分割性能达到领先水平,包括我们整理并贡献的一个新型超声数据集。定性结果展示了三种模型架构的精细和准确的分割图。
Key Takeaways
- 数据稀缺是医学影像深度学习模型的主要挑战之一。
- 数据池化和数据增加能提高模型性能,但可能引发分布偏移问题。
- 分布偏移问题被称为“数据增加困境”,会影响模型的后续表现。
- 研究提出一种在多源数据环境下控制医学图像分割中前景背景特征差异的方法。
- 该方法利用因果框架,提高了特征表示能力,尤其在数据增加场景中表现优异。
- 实验结果显示该方法在五个数据集上的病理学和超声图像分割性能达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

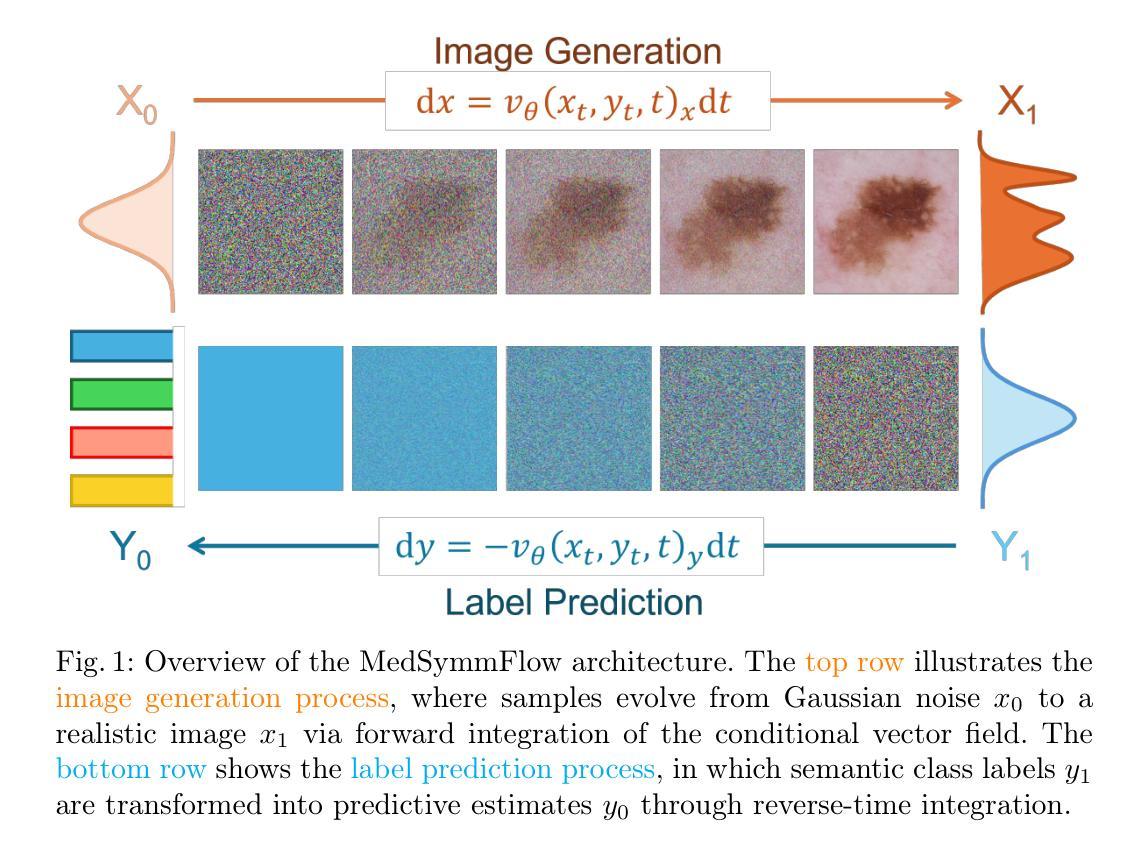
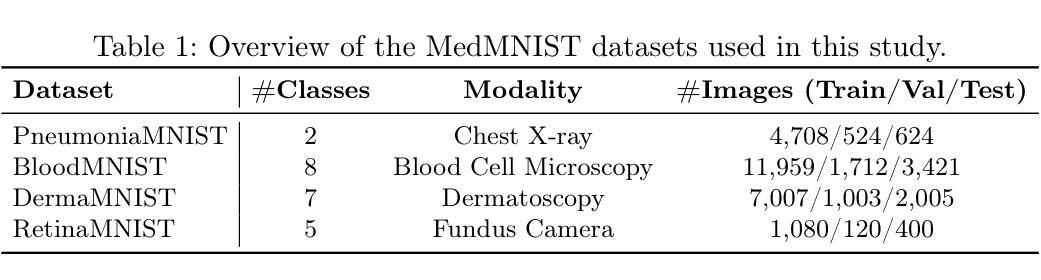
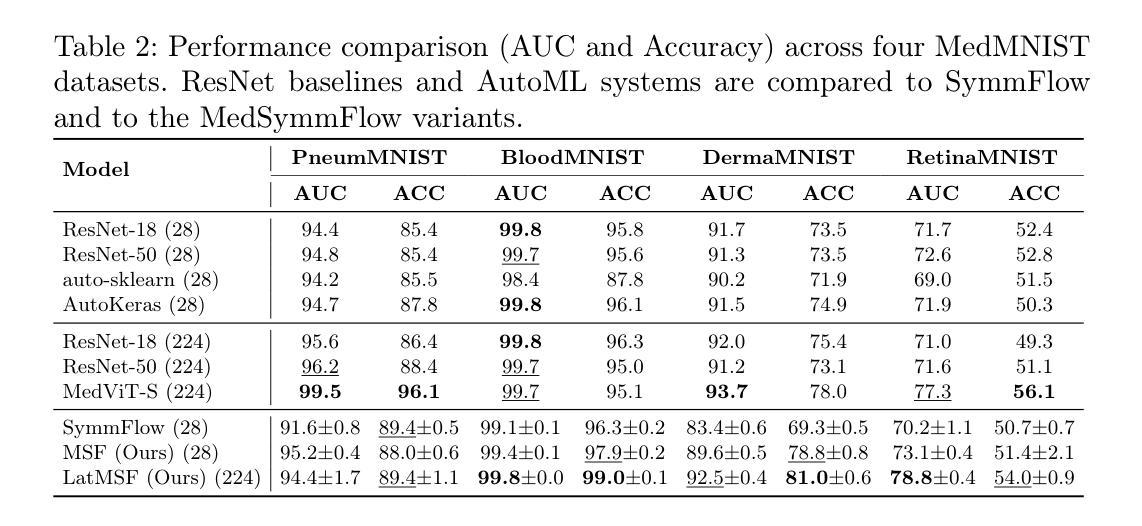
MedSymmFlow: Bridging Generative Modeling and Classification in Medical Imaging through Symmetrical Flow Matching
Authors:Francisco Caetano, Lemar Abdi, Christiaan Viviers, Amaan Valiuddin, Fons van der Sommen
Reliable medical image classification requires accurate predictions and well-calibrated uncertainty estimates, especially in high-stakes clinical settings. This work presents MedSymmFlow, a generative-discriminative hybrid model built on Symmetrical Flow Matching, designed to unify classification, generation, and uncertainty quantification in medical imaging. MedSymmFlow leverages a latent-space formulation that scales to high-resolution inputs and introduces a semantic mask conditioning mechanism to enhance diagnostic relevance. Unlike standard discriminative models, it naturally estimates uncertainty through its generative sampling process. The model is evaluated on four MedMNIST datasets, covering a range of modalities and pathologies. The results show that MedSymmFlow matches or exceeds the performance of established baselines in classification accuracy and AUC, while also delivering reliable uncertainty estimates validated by performance improvements under selective prediction.
可靠的医学图像分类需要准确的预测和校准良好的不确定性估计,特别是在高风险的临床环境中。本研究提出了MedSymmFlow,这是一种基于对称流匹配的生成-判别混合模型,旨在统一医学成像中的分类、生成和不确定性量化。MedSymmFlow利用潜在空间公式,可扩展到高分辨率输入,并引入语义掩模调节机制以提高诊断相关性。与标准判别模型不同,它可以通过生成采样过程自然地估计不确定性。该模型在四个MedMNIST数据集上进行了评估,涵盖了多种模态和病理。结果表明,MedSymmFlow在分类精度和AUC方面的性能与既定基线相匹配或超过,同时提供了可靠的不确定性估计,并通过选择性预测下的性能改进得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF DGM4MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了MedSymmFlow模型,这是一种基于对称流匹配的生成-判别混合模型,旨在统一医学成像中的分类、生成和不确定性量化。该模型利用潜在空间公式,可扩展到高分辨率输入,并引入语义掩模条件机制以提高诊断相关性。与传统的判别模型不同,它可以通过生成采样过程自然地估计不确定性。在四个MedMNIST数据集上的评估结果表明,MedSymmFlow在分类准确性和AUC方面与现有基线相当或表现更好,同时提供可靠的不确定性估计,并通过选择性预测的性能改进得到验证。
Key Takeaways
- MedSymmFlow是一个生成-判别混合模型,用于医学图像分类、生成和不确定性量化。
- 该模型利用潜在空间公式,可处理高分辨率输入,并通过语义掩模条件机制提高诊断相关性。
- MedSymmFlow能够自然地估计不确定性,这是传统判别模型所缺乏的。
- MedSymmFlow在分类性能和AUC方面表现出色,与现有基线相当或更好。
- 该模型在四个不同的MedMNIST数据集上进行了评估,涵盖了多种模态和病理。
- MedSymmFlow提供可靠的不确定性估计,这有助于在高风险的临床环境中做出更准确的预测。
点此查看论文截图