⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
MyGO: Make your Goals Obvious, Avoiding Semantic Confusion in Prostate Cancer Lesion Region Segmentation
Authors:Zhengcheng Lin, Zuobin Ying, Zhenyu Li, Zhenyu Liu, Jian Lu, Weiping Ding
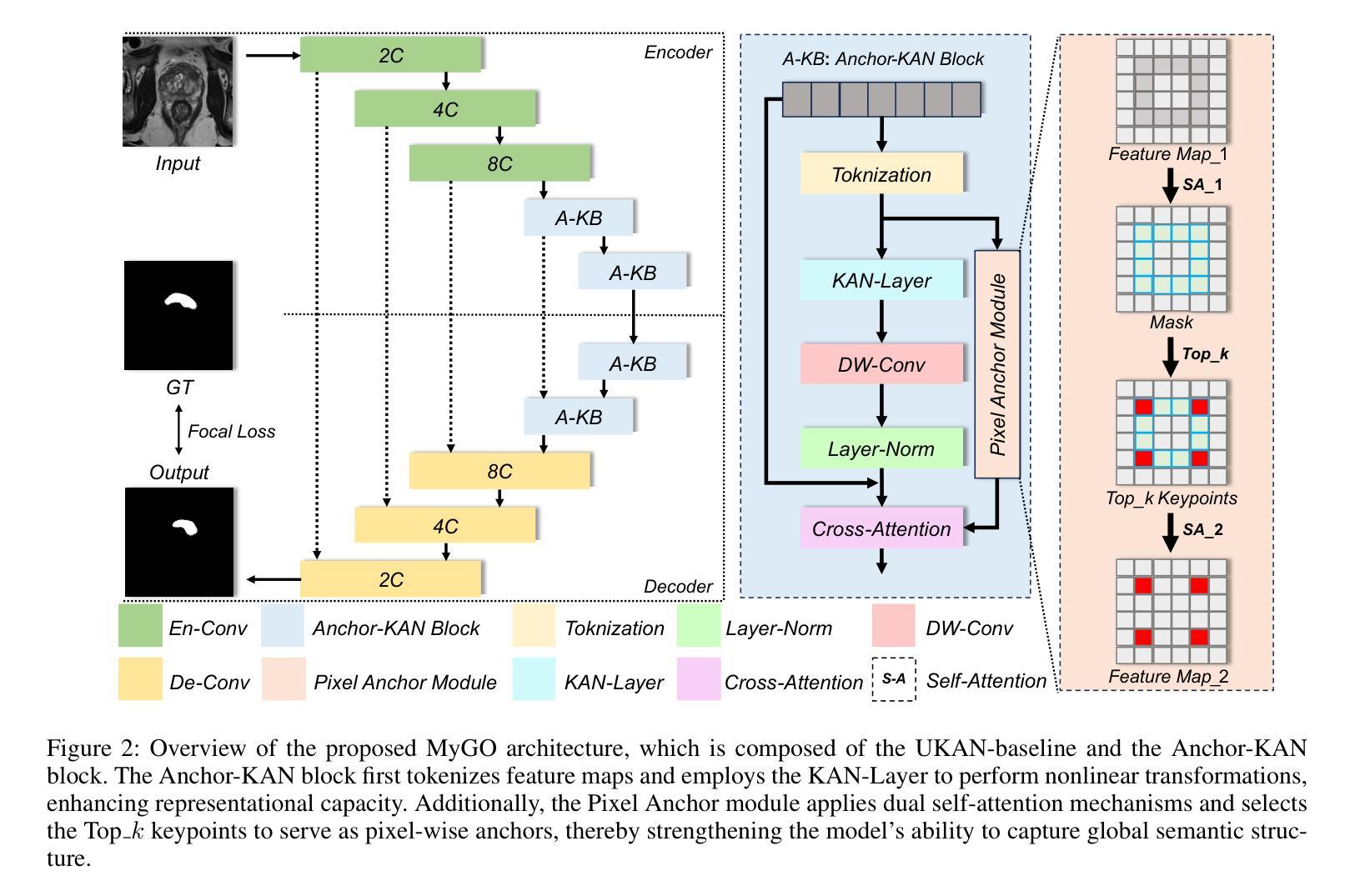
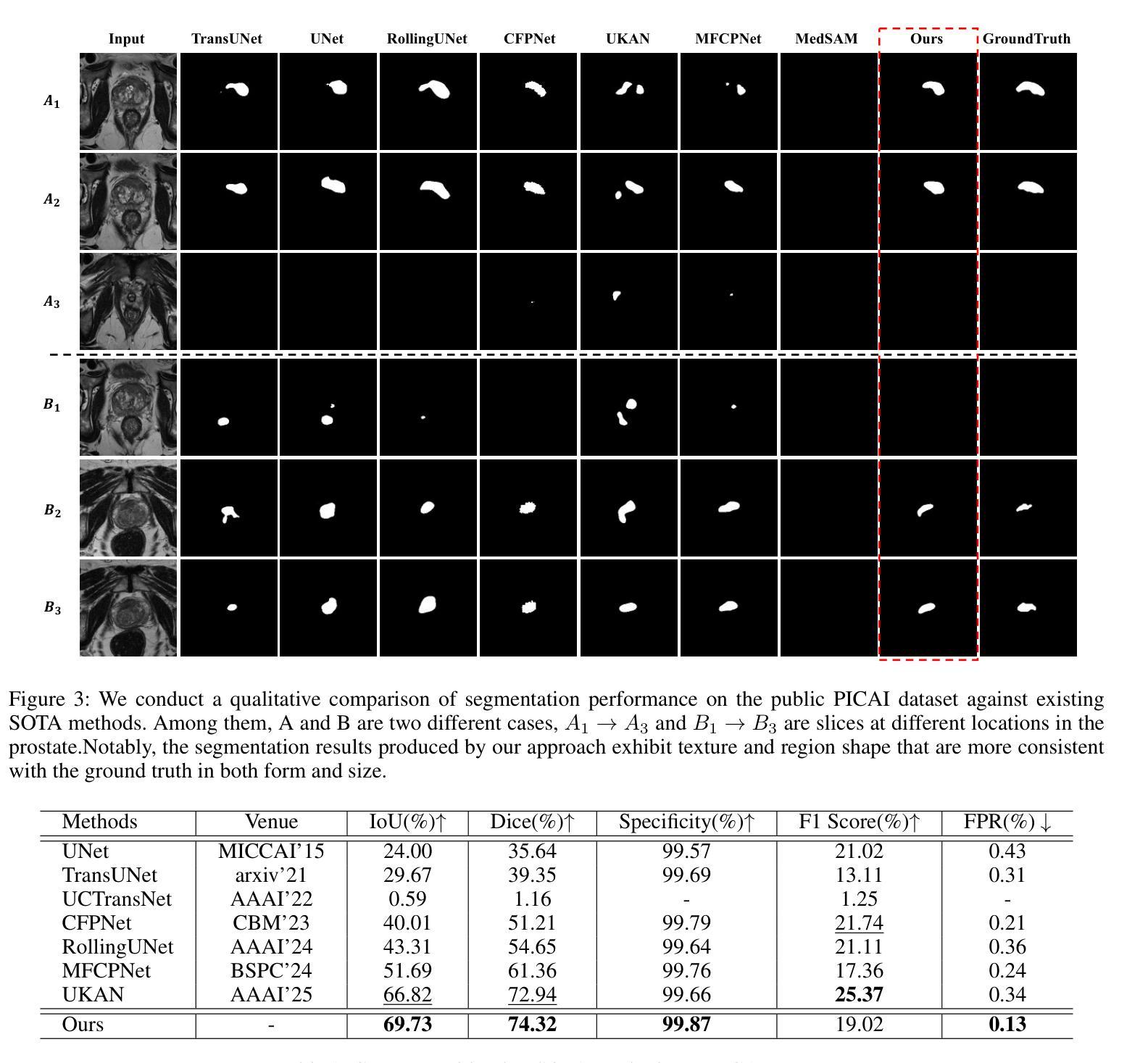
Early diagnosis and accurate identification of lesion location and progression in prostate cancer (PCa) are critical for assisting clinicians in formulating effective treatment strategies. However, due to the high semantic homogeneity between lesion and non-lesion areas, existing medical image segmentation methods often struggle to accurately comprehend lesion semantics, resulting in the problem of semantic confusion. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Pixel Anchor Module, which guides the model to discover a sparse set of feature anchors that serve to capture and interpret global contextual information. This mechanism enhances the model’s nonlinear representation capacity and improves segmentation accuracy within lesion regions. Moreover, we design a self-attention-based Top_k selection strategy to further refine the identification of these feature anchors, and incorporate a focal loss function to mitigate class imbalance, thereby facilitating more precise semantic interpretation across diverse regions. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PI-CAI dataset, demonstrating 69.73% IoU and 74.32% Dice scores, and significantly improving prostate cancer lesion detection.
早期诊断以及准确识别前列腺癌(PCa)的病变位置和进展对于帮助临床医生制定有效的治疗策略至关重要。然而,由于病变区域与非病变区域之间存在高度的语义同质性,现有的医学图像分割方法往往难以准确理解病变语义,从而导致语义混淆的问题。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的Pixel Anchor Module,该模块引导模型发现一组稀疏的特征锚点,用于捕获和解释全局上下文信息。这种机制增强了模型的非线性表示能力,提高了病变区域内的分割精度。此外,我们还设计了一种基于自注意力的Top_k选择策略,以进一步改进这些特征锚点的识别,并引入了一种焦点损失函数来缓解类别不平衡问题,从而在不同区域实现更精确的语义解释。我们的方法在PI-CAI数据集上实现了最佳性能,达到了69.73%的IoU和74.32%的Dice系数,显著提高了前列腺癌病变的检测效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Pixel Anchor Module的新方法,用于提高前列腺癌病变检测准确性。该方法通过发现稀疏的特征锚点来捕捉全局上下文信息,增强模型的非线性表示能力,从而提高病变区域的分割精度。此外,还设计了基于自注意力的Top_k选择策略来优化特征锚点的识别,并结合focal loss函数缓解类别不平衡问题,从而实现更精确的区域语义解释。该方法在PI-CAI数据集上取得了领先水平,达到69.73%的IoU和74.32%的Dice得分。
Key Takeaways
- Pixel Anchor Module被提出用于解决前列腺癌病变检测中的语义混淆问题。
- 通过发现稀疏的特征锚点来捕捉全局上下文信息,增强模型的表示能力。
- 设计的Top_k选择策略能优化特征锚点的识别。
- 结合focal loss函数来缓解类别不平衡问题。
- 方法在PI-CAI数据集上实现了先进的性能。
- 达到69.73%的IoU和74.32%的Dice得分。
点此查看论文截图


ScSAM: Debiasing Morphology and Distributional Variability in Subcellular Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Bo Fang, Jianan Fan, Dongnan Liu, Hang Chang, Gerald J. Shami, Filip Braet, Weidong Cai
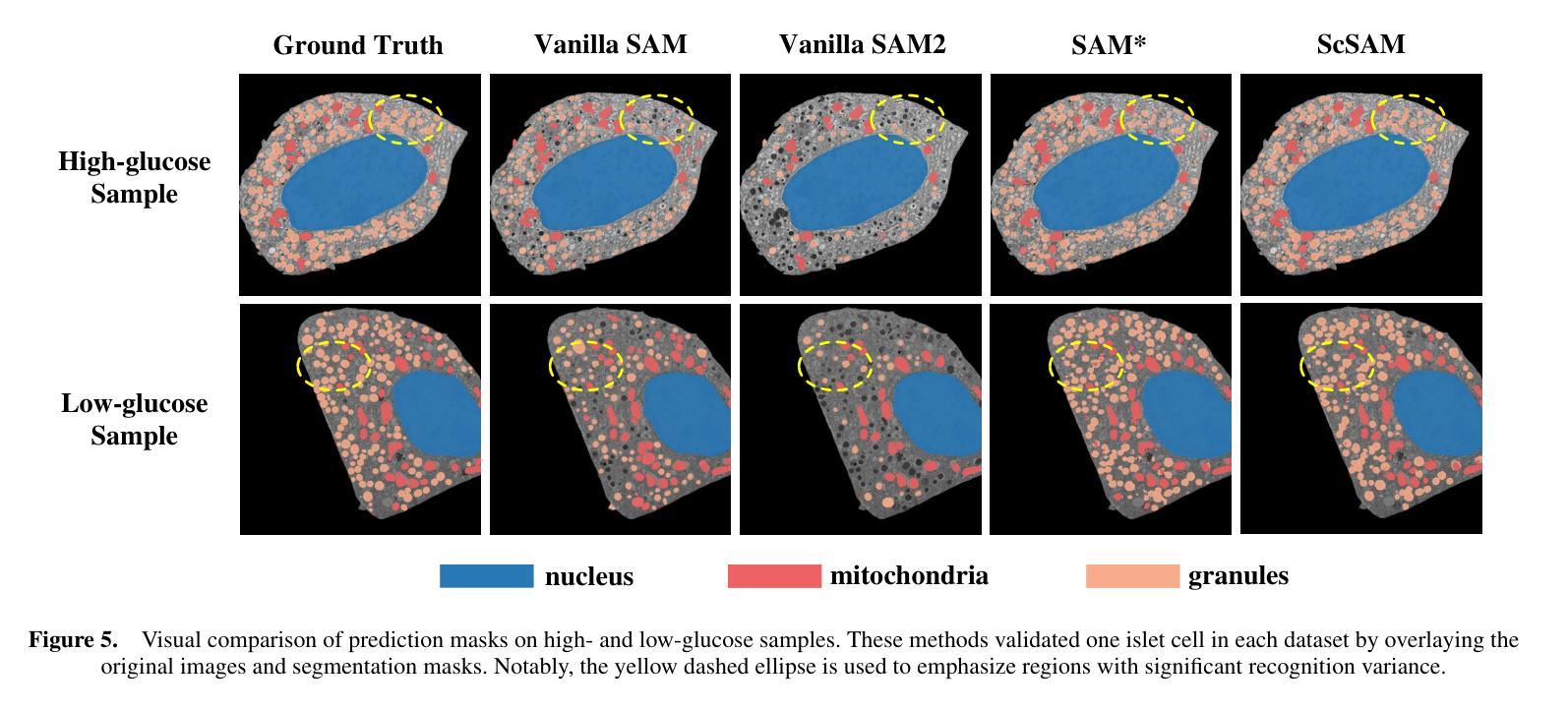
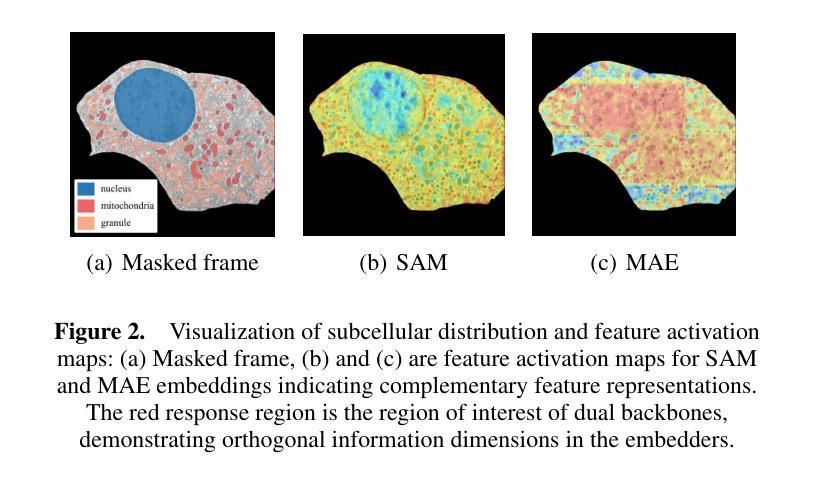
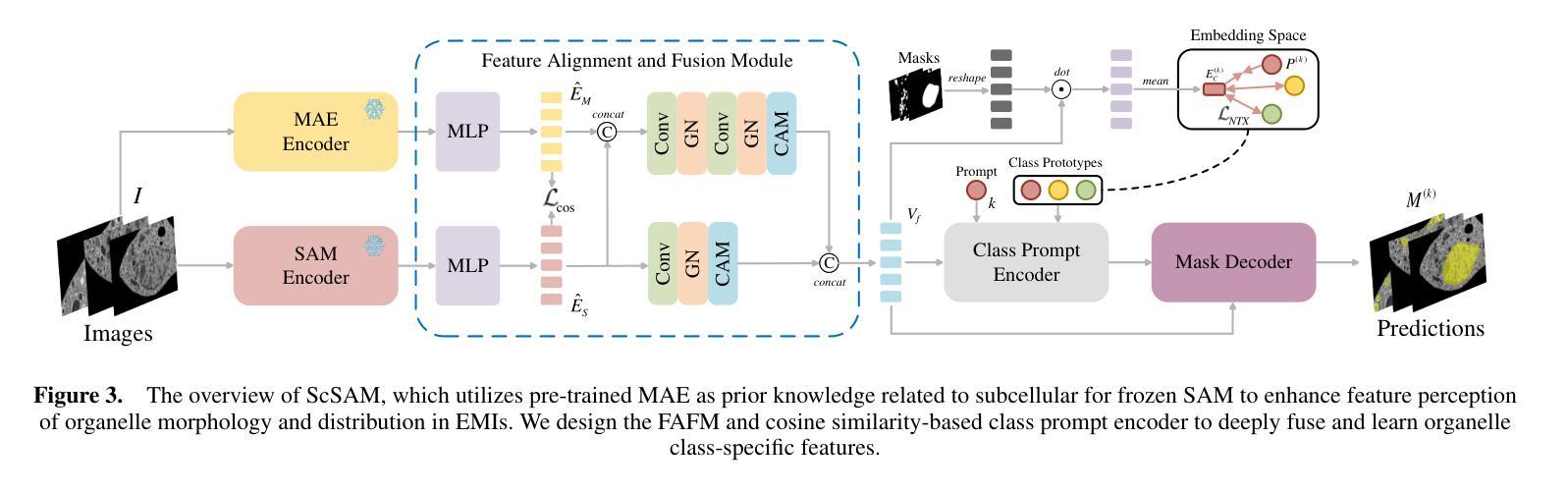
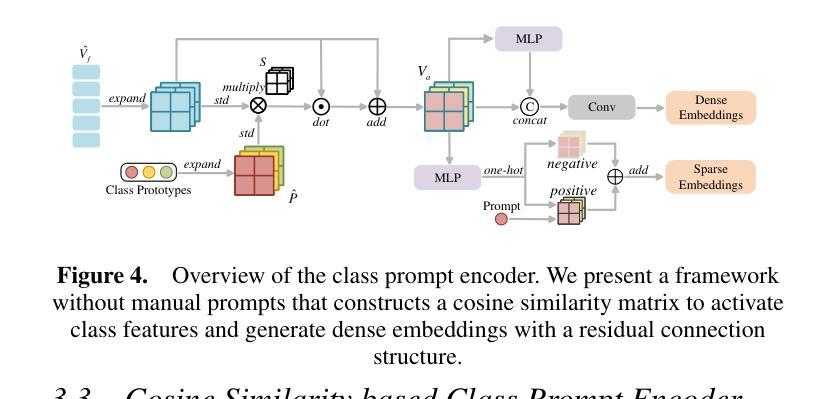
The significant morphological and distributional variability among subcellular components poses a long-standing challenge for learning-based organelle segmentation models, significantly increasing the risk of biased feature learning. Existing methods often rely on single mapping relationships, overlooking feature diversity and thereby inducing biased training. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) provides rich feature representations, its application to subcellular scenarios is hindered by two key challenges: (1) The variability in subcellular morphology and distribution creates gaps in the label space, leading the model to learn spurious or biased features. (2) SAM focuses on global contextual understanding and often ignores fine-grained spatial details, making it challenging to capture subtle structural alterations and cope with skewed data distributions. To address these challenges, we introduce ScSAM, a method that enhances feature robustness by fusing pre-trained SAM with Masked Autoencoder (MAE)-guided cellular prior knowledge to alleviate training bias from data imbalance. Specifically, we design a feature alignment and fusion module to align pre-trained embeddings to the same feature space and efficiently combine different representations. Moreover, we present a cosine similarity matrix-based class prompt encoder to activate class-specific features to recognize subcellular categories. Extensive experiments on diverse subcellular image datasets demonstrate that ScSAM outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
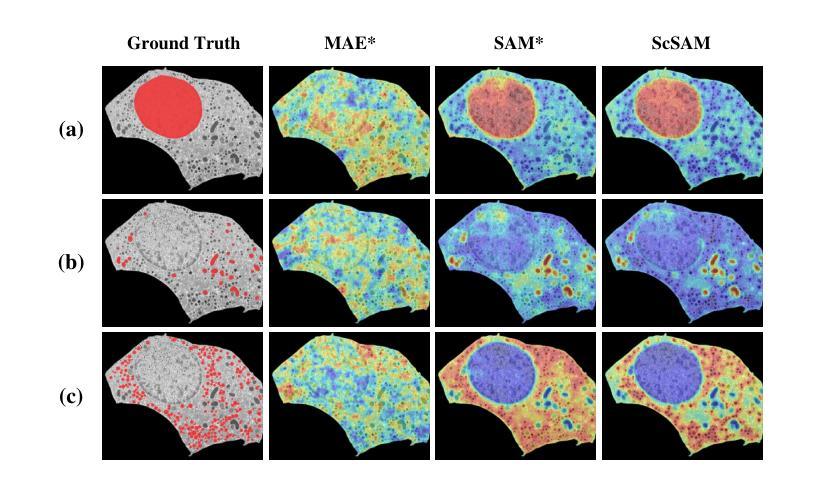
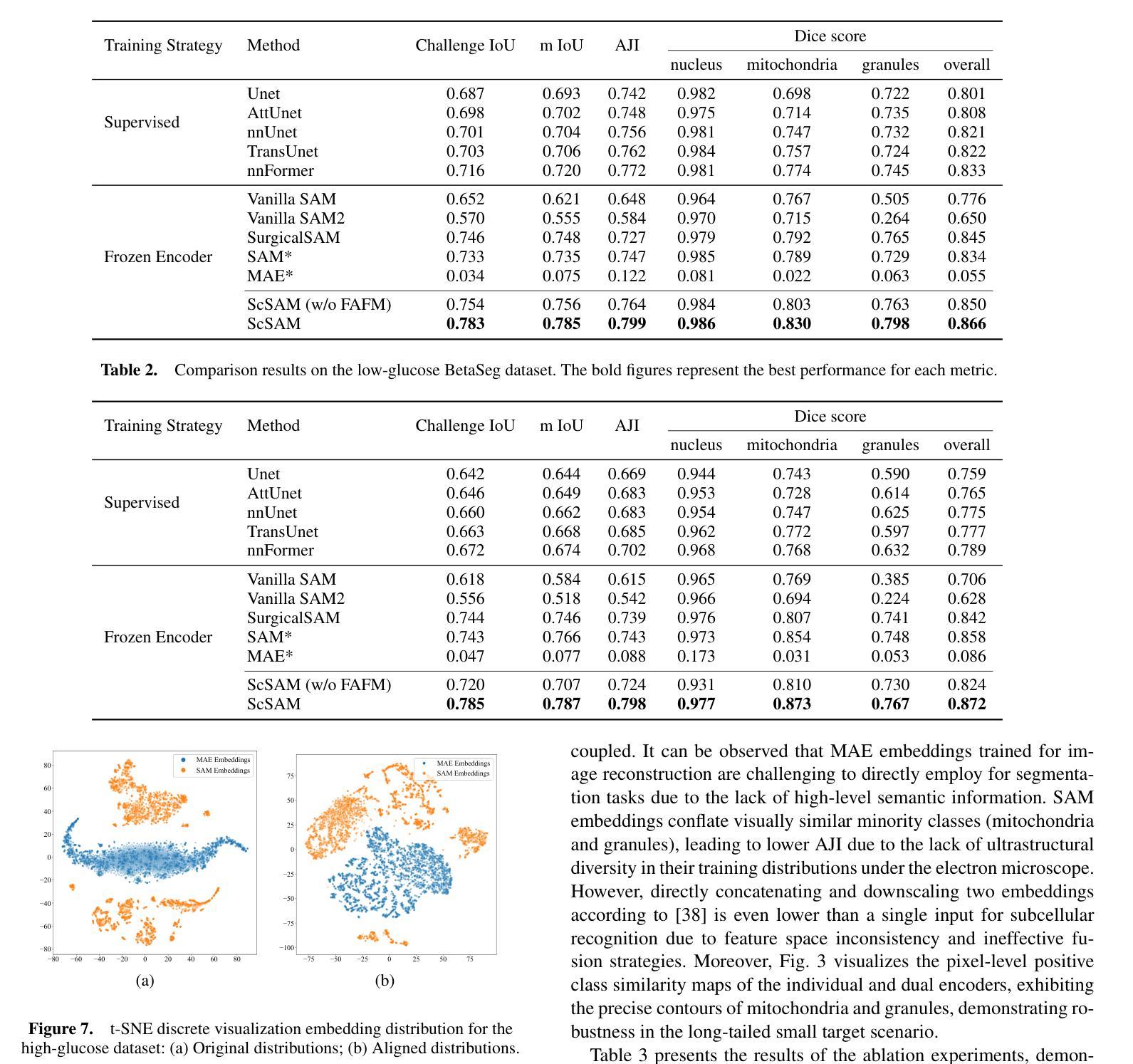
细胞亚组分之间显著的形态和分布变化给基于学习的细胞器分割模型带来了长期挑战,显著增加了特征学习偏向的风险。现有方法往往依赖于单一的映射关系,忽视了特征的多样性,从而导致训练偏向。尽管Segment Anything Model(SAM)提供了丰富的特征表示,但其在亚细胞场景中的应用受到两个关键挑战的制约:(1)亚细胞形态和分布的多样性导致标签空间中存在间隙,使模型学习特征时出现错误或偏向。(2)SAM侧重于全局上下文理解,往往忽视精细的空间细节,这使得捕捉微妙的结构变化和应对数据分布不均的情况具有挑战性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了ScSAM方法,它通过融合预训练的SAM和由Masked Autoencoder(MAE)引导的细胞先验知识,增强特征稳健性,以减轻因数据不平衡导致的训练偏差。具体来说,我们设计了一个特征对齐和融合模块,将预训练嵌入对齐到同一特征空间,并有效地结合不同的表示。此外,我们提出了一种基于余弦相似度矩阵的类提示编码器,以激活特定类别的特征来识别亚细胞类别。在多种亚细胞图像数据集上的广泛实验表明,ScSAM优于现有最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 28th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI)
Summary
本文指出了亚细胞结构形态和分布多样性的挑战,对基于学习的细胞器分割模型造成了影响。现有方法常常依赖单一映射关系,忽略了特征多样性,导致训练偏差。为解决这些问题,本文提出了ScSAM方法,通过融合预训练的Segment Anything Model(SAM)和Masked Autoencoder(MAE)引导的细胞先验知识,增强特征稳健性,以减轻因数据不平衡导致的训练偏差。实验证明,ScSAM在多种亚细胞图像数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 亚细胞结构的形态和分布多样性对基于学习的分割模型构成挑战。
- 现有方法因依赖单一映射关系而忽视特征多样性,易导致训练偏差。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)虽提供丰富的特征表示,但在亚细胞场景下应用受限。
- ScSAM方法通过融合预训练的SAM和MAE引导的细胞先验知识,增强特征稳健性。
- ScSAM设计特征对齐和融合模块,将预训练嵌入对齐到同一特征空间并有效结合不同表示。
- ScSAM采用余弦相似度矩阵的类提示编码器,激活类特定特征以识别亚细胞类别。
点此查看论文截图


Task-Specific Zero-shot Quantization-Aware Training for Object Detection
Authors:Changhao Li, Xinrui Chen, Ji Wang, Kang Zhao, Jianfei Chen
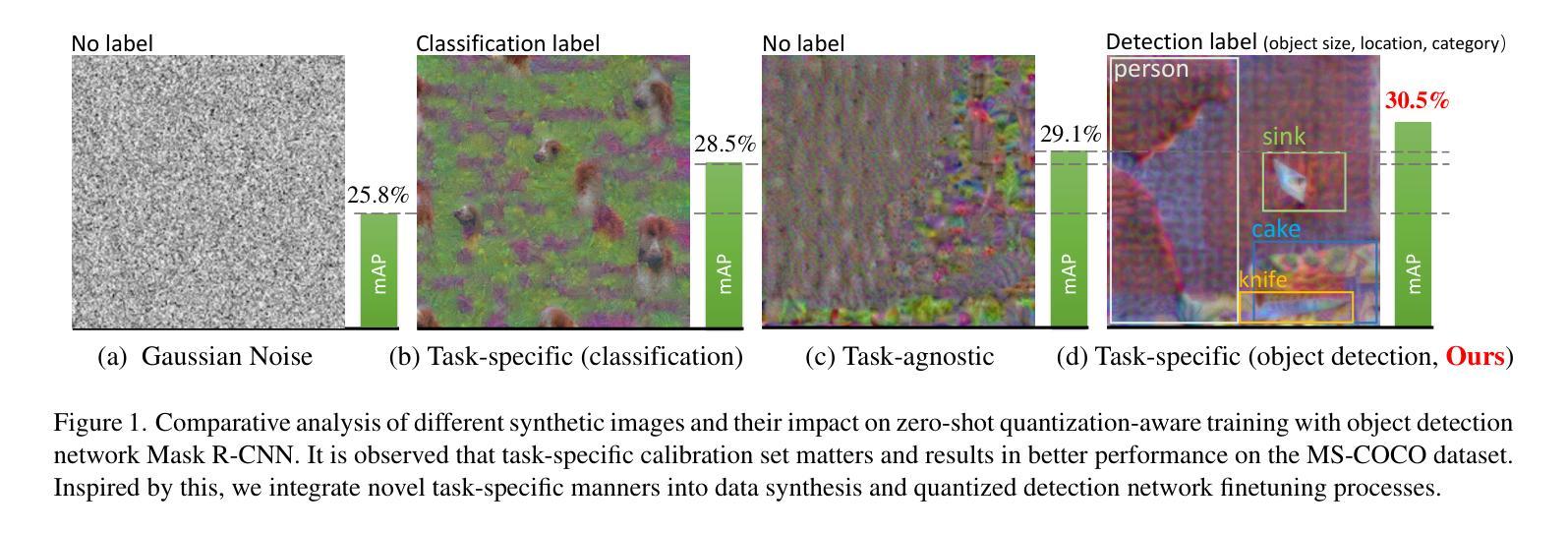
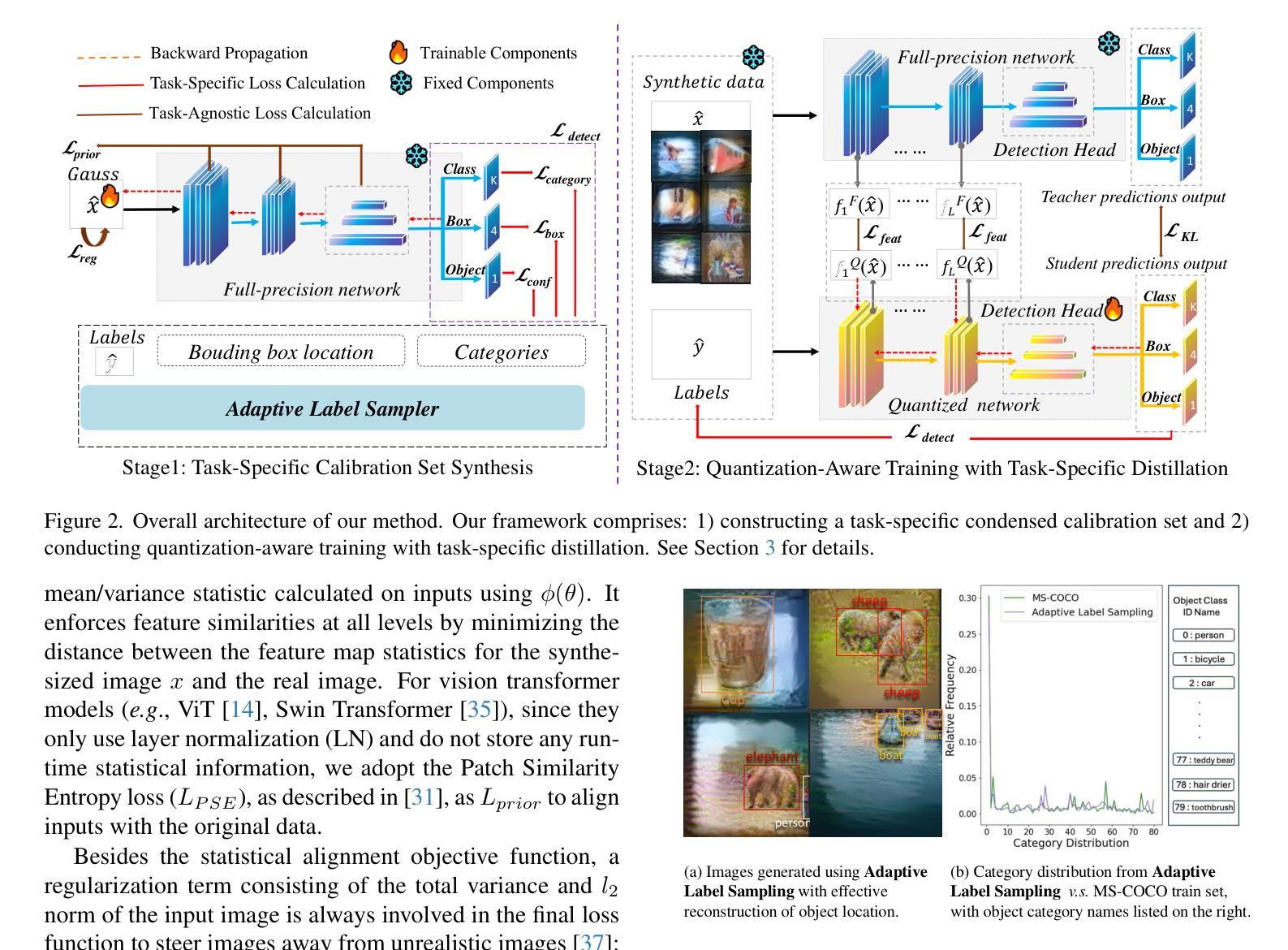
Quantization is a key technique to reduce network size and computational complexity by representing the network parameters with a lower precision. Traditional quantization methods rely on access to original training data, which is often restricted due to privacy concerns or security challenges. Zero-shot Quantization (ZSQ) addresses this by using synthetic data generated from pre-trained models, eliminating the need for real training data. Recently, ZSQ has been extended to object detection. However, existing methods use unlabeled task-agnostic synthetic images that lack the specific information required for object detection, leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose a novel task-specific ZSQ framework for object detection networks, which consists of two main stages. First, we introduce a bounding box and category sampling strategy to synthesize a task-specific calibration set from the pre-trained network, reconstructing object locations, sizes, and category distributions without any prior knowledge. Second, we integrate task-specific training into the knowledge distillation process to restore the performance of quantized detection networks. Extensive experiments conducted on the MS-COCO and Pascal VOC datasets demonstrate the efficiency and state-of-the-art performance of our method. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/DFQ-Dojo/dfq-toolkit .
量化是一种通过用较低的精度表示网络参数来减小网络规模和计算复杂性的关键技术。传统量化方法依赖于原始训练数据的访问,这通常由于隐私担忧或安全挑战而受到限制。零射量化(ZSQ)通过使用预先训练模型生成合成数据来解决这个问题,无需使用真实训练数据。最近,ZSQ已扩展到目标检测领域。然而,现有方法使用未标记的任务无关合成图像,缺乏目标检测所需的具体信息,导致性能不佳。本文提出了一种用于目标检测网络的新型任务特定ZSQ框架,该框架由两个阶段组成。首先,我们引入了一种边界框和类别采样策略,以从预训练网络合成任务特定校准集,重建对象位置、大小和类别分布,无需任何先验知识。其次,我们将任务特定训练集成到知识蒸馏过程中,以恢复量化检测网络的性能。在MS-COCO和Pascal VOC数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了我们的方法的效率和最先进的性能。我们的代码公开在:[https://github.com/DFQ-Dojo/dfq-toolkit。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
量化是网络缩减和降低计算复杂度的重要技术,它通过低精度表示网络参数来实现。传统量化方法依赖原始训练数据,但出于隐私或安全考虑,这些数据往往受到限制。零样本量化(ZSQ)通过使用预训练模型生成合成数据来解决这一问题,无需真实训练数据。最新研究将ZSQ扩展到目标检测领域,但现有方法使用无标签的任务无关合成图像,缺乏目标检测所需的具体信息,导致性能不佳。本文提出了一种用于目标检测网络的新型任务特定ZSQ框架,该框架分为两个阶段:首先,通过预训练网络合成任务特定校准集,重构目标位置、大小和类别分布,无需任何先验知识;其次,将任务特定训练集成到知识蒸馏过程中,以恢复量化检测网络的性能。在MS-COCO和Pascal VOC数据集上的大量实验证明了该方法的效率和最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 量化技术用于减少网络大小和计算复杂度,通过低精度表示网络参数实现。
- 传统量化方法依赖原始训练数据,但存在隐私或安全限制。
- 零样本量化(ZSQ)通过预训练模型生成的合成数据解决此问题,无需真实训练数据。
- 最新ZSQ研究已扩展到目标检测领域,但现有方法使用无标签的任务无关合成图像,性能不佳。
- 本文提出新型任务特定ZSQ框架,分为合成任务特定校准集和集成任务特定训练两个阶段。
- 框架能够重构目标位置、大小和类别分布,无需任何先验知识。
点此查看论文截图

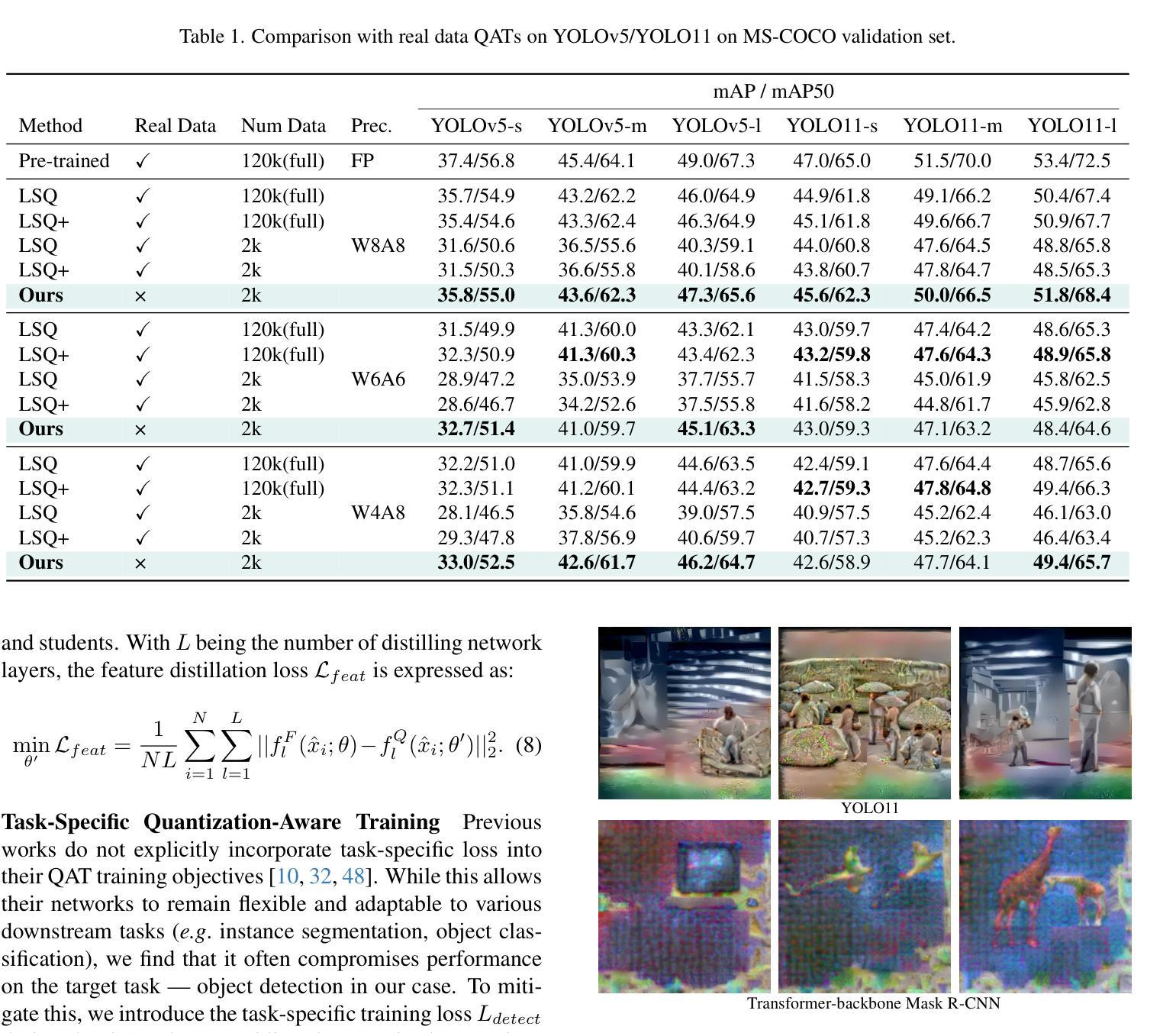
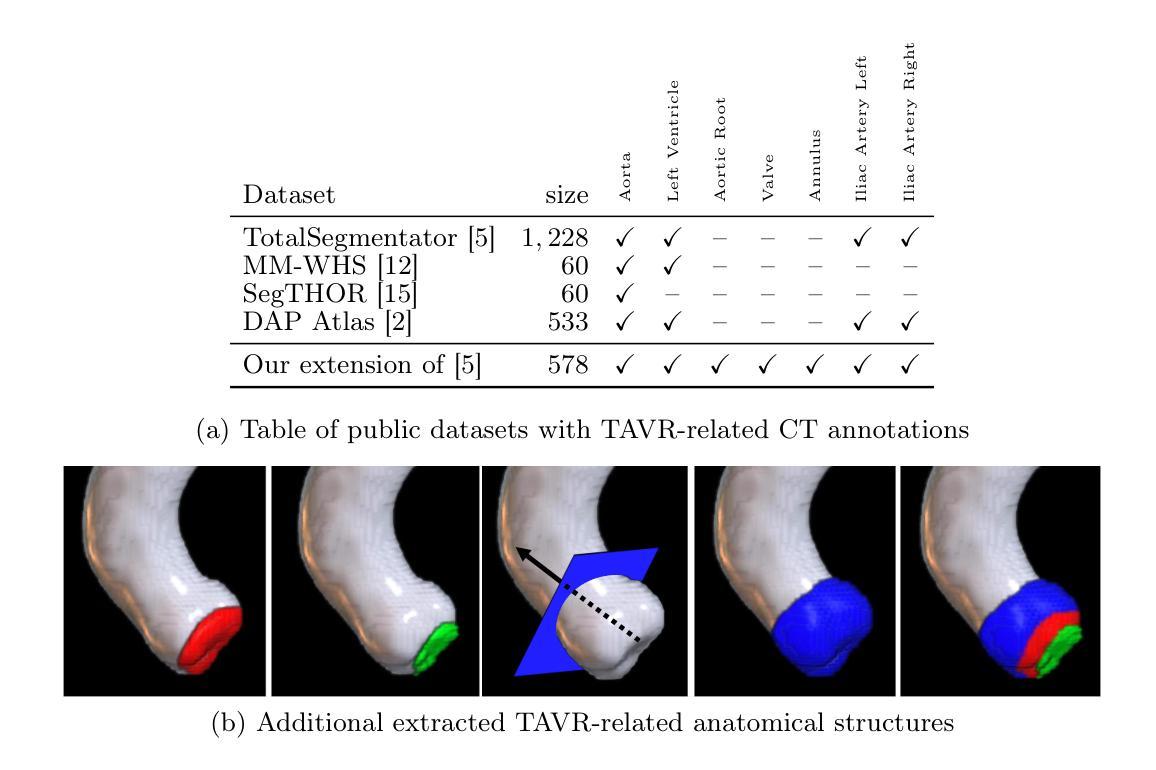
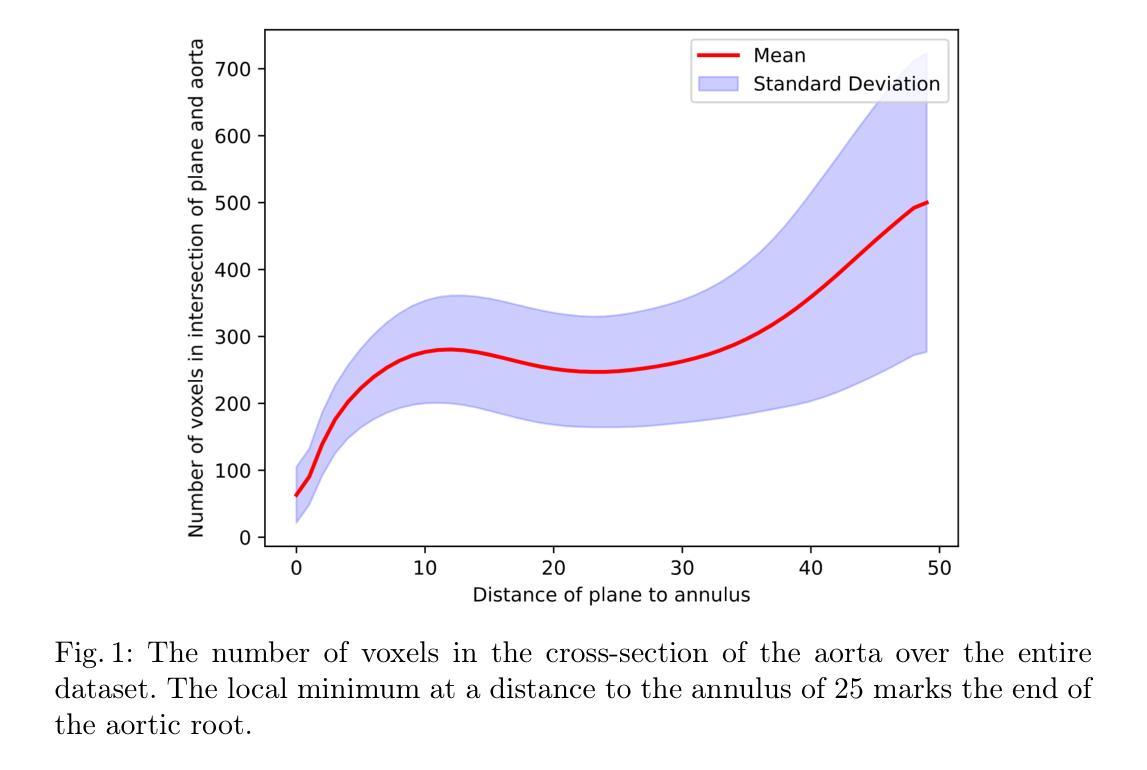
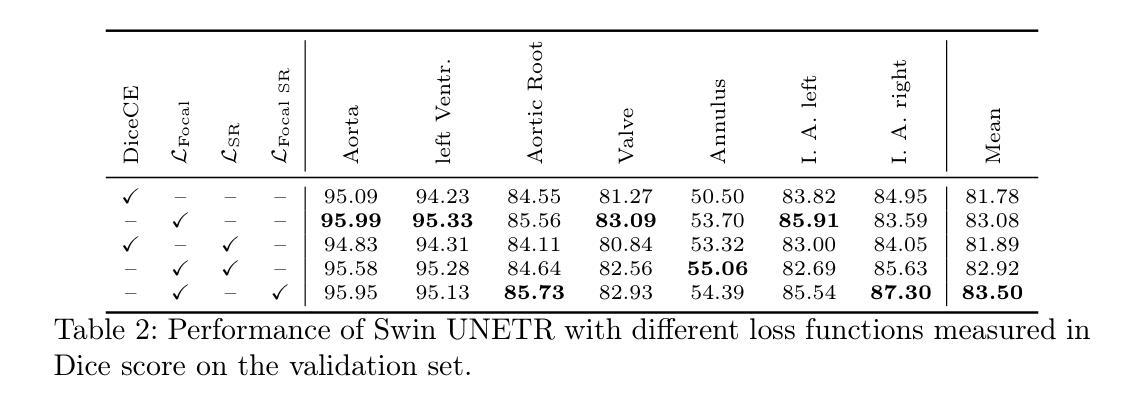
Semantic Segmentation for Preoperative Planning in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Authors:Cedric Zöllner, Simon Reiß, Alexander Jaus, Amroalalaa Sholi, Ralf Sodian, Rainer Stiefelhagen
When preoperative planning for surgeries is conducted on the basis of medical images, artificial intelligence methods can support medical doctors during assessment. In this work, we consider medical guidelines for preoperative planning of the transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and identify tasks, that may be supported via semantic segmentation models by making relevant anatomical structures measurable in computed tomography scans. We first derive fine-grained TAVR-relevant pseudo-labels from coarse-grained anatomical information, in order to train segmentation models and quantify how well they are able to find these structures in the scans. Furthermore, we propose an adaptation to the loss function in training these segmentation models and through this achieve a +1.27% Dice increase in performance. Our fine-grained TAVR-relevant pseudo-labels and the computed tomography scans we build upon are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16274176.
在基于医学图像进行手术术前规划时,人工智能方法可以在评估过程中为医生提供支持。在这项工作中,我们考虑了经导管主动脉瓣置换术(TAVR)的术前规划医学指南,并确定了可通过语义分割模型支持的任务,通过在计算机断层扫描中测量相关解剖结构来实现。我们首先从粗粒度的解剖信息中推导出精细粒度的TAVR相关伪标签,以训练分割模型并量化它们在扫描中发现这些结构的能力。此外,我们对训练这些分割模型的损失函数进行了调整,并因此实现了性能上1.27%的Dice增长。我们构建的精细粒度TAVR相关伪标签和计算机断层扫描数据可在https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16274176上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 16th MICCAI Workshop on Statistical Atlases and Computational Modeling of the Heart (STACOM)
Summary
本研究探讨在术前规划中运用人工智能辅助医学医生进行经导管主动脉瓣置换术(TAVR)的评估。通过从粗颗粒度的解剖信息中衍生出精细颗粒度的TAVR相关伪标签,训练分割模型以量化其在扫描中定位相关结构的能力。同时提出调整损失函数来训练这些分割模型,从而实现性能上的改进。数据集可在此处获取。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在术前规划中对医学图像的分析支持医生进行手术评估。
- 通过精细颗粒度的TAVR相关伪标签训练分割模型。
- 利用这些标签在计算机断层扫描中找到相关解剖结构。
- 调整损失函数以增强分割模型的性能,并实现更高的Dice系数得分。
- 该研究的数据集可供公开访问和使用。
- 此方法有助于提高术前规划的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

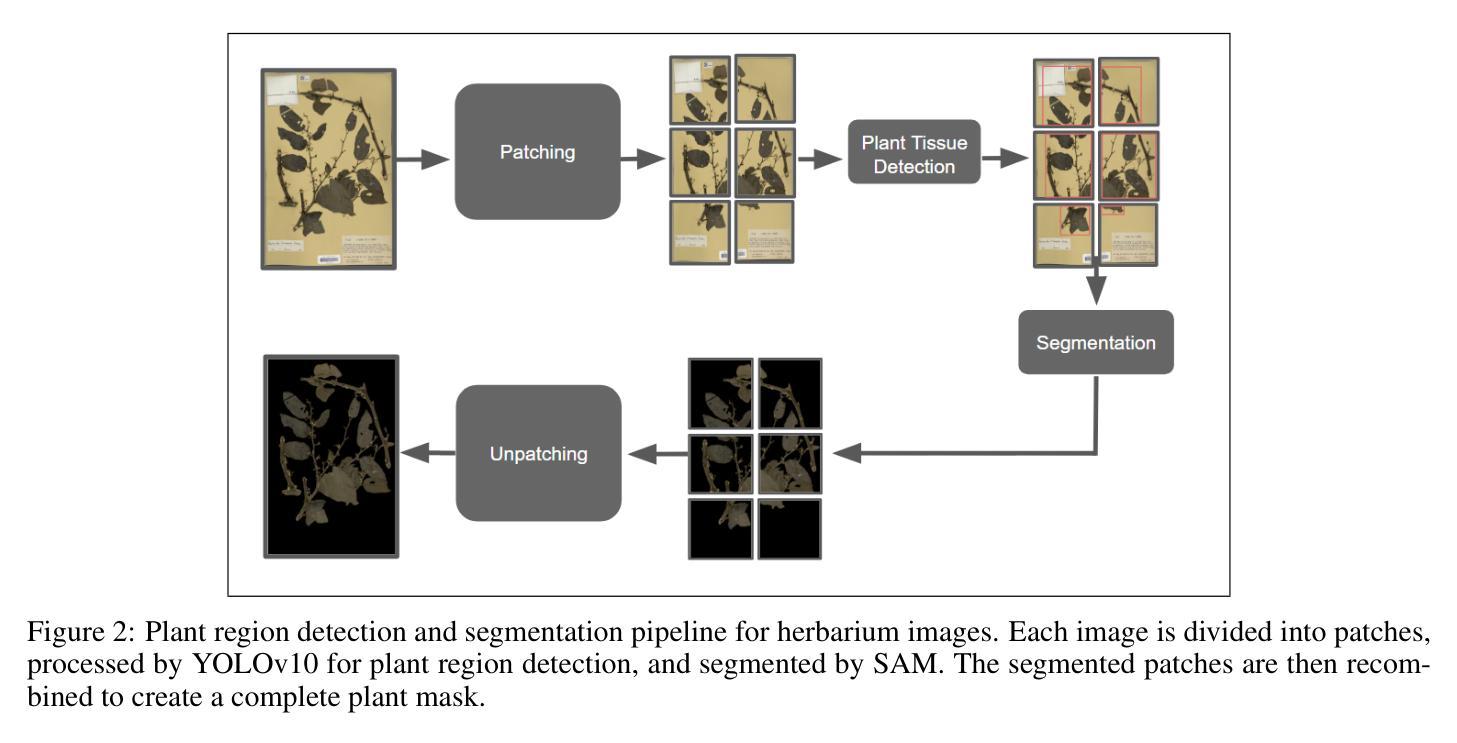
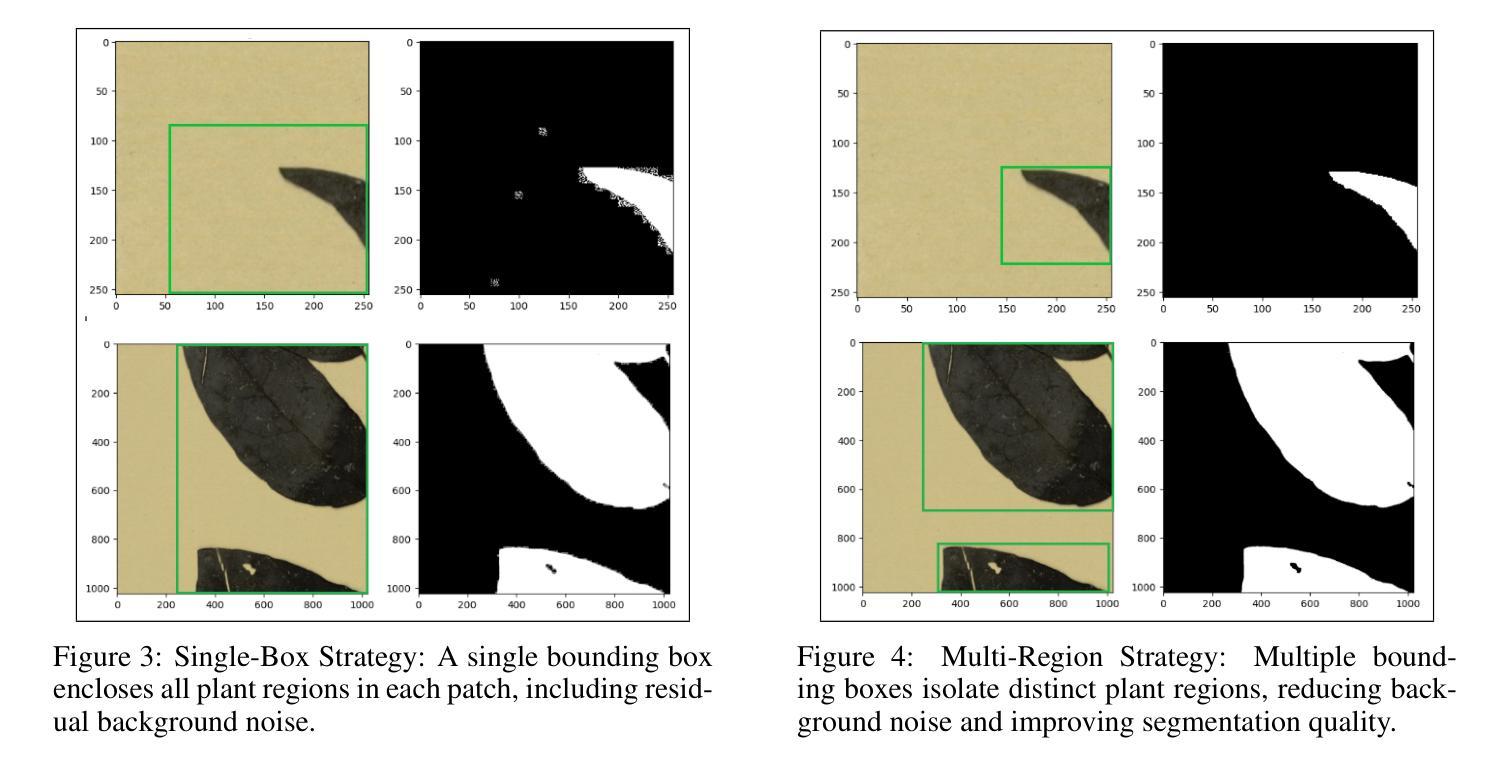
PlantSAM: An Object Detection-Driven Segmentation Pipeline for Herbarium Specimens
Authors:Youcef Sklab, Florian Castanet, Hanane Ariouat, Souhila Arib, Jean-Daniel Zucker, Eric Chenin, Edi Prifti
Deep learning-based classification of herbarium images is hampered by background heterogeneity, which introduces noise and artifacts that can potentially mislead models and reduce classification accuracy. Addressing these background-related challenges is critical to improving model performance. We introduce PlantSAM, an automated segmentation pipeline that integrates YOLOv10 for plant region detection and the Segment Anything Model (SAM2) for segmentation. YOLOv10 generates bounding box prompts to guide SAM2, enhancing segmentation accuracy. Both models were fine-tuned on herbarium images and evaluated using Intersection over Union (IoU) and Dice coefficient metrics. PlantSAM achieved state-of-the-art segmentation performance, with an IoU of 0.94 and a Dice coefficient of 0.97. Incorporating segmented images into classification models led to consistent performance improvements across five tested botanical traits, with accuracy gains of up to 4.36% and F1-score improvements of 4.15%. Our findings highlight the importance of background removal in herbarium image analysis, as it significantly enhances classification accuracy by allowing models to focus more effectively on the foreground plant structures.
基于深度学习的植物标本图像分类受到背景异质性的阻碍,背景异质性引入了噪声和伪影,这些可能会误导模型并降低分类准确性。解决这些与背景相关的挑战对于提高模型性能至关重要。我们引入了PlantSAM,这是一个集成了YOLOv10用于植物区域检测和Segment Anything Model(SAM2)用于分割的自动化分割管道。YOLOv10生成边界框提示来引导SAM2,提高分割精度。两个模型都在植物标本图像上进行了微调,并使用交集比(IoU)和Dice系数指标进行了评估。PlantSAM达到了最先进的分割性能,IoU为0.94,Dice系数为0.97。将分割图像纳入分类模型导致了五种测试的植物特征性能的一致性提高,准确率提高了高达4.36%,F1分数提高了4.15%。我们的研究结果表明,在植物标本图像分析中去除背景的重要性,因为它可以显著提高分类模型的准确性,使模型更有效地专注于前景植物结构。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 11 figures, 8 tables
Summary
基于深度学习的植物标本图像分类受到背景异质性的干扰,这引入了噪声和伪影,可能导致模型误导并降低分类准确性。为解决背景相关的挑战,我们推出了PlantSAM自动化分割管道,集成了YOLOv10用于植物区域检测和Segment Anything Model(SAM2)进行分割。YOLOv10生成边界框提示来引导SAM2,提高分割精度。这两个模型都在植物标本图像上进行微调,并使用交集比(IoU)和Dice系数指标进行评估。PlantSAM达到了先进的分割性能,IoU为0.94,Dice系数为0.97。将分割图像纳入分类模型导致在五个测试的植物学特征上性能一致提高,准确率提高高达4.36%,F1分数提高4.15%。我们的研究结果表明,背景去除在植物标本图像分析中非常重要,因为它可以显著提高分类准确性,使模型更有效地关注前景植物结构。
Key Takeaways
- 植物标本图像分类面临背景异质性的挑战。
- 背景异质性可能导致模型误导和降低分类准确性。
- PlantSAM是一个集成了YOLOv10和SAM2模型的自动化分割管道,用于解决背景干扰问题。
- PlantSAM在植物标本图像上实现了高分割性能,IoU达到0.94,Dice系数达到0.97。
- 将分割图像纳入分类模型可以提高分类准确性。
- 背景去除在植物标本图像分析中至关重要。
点此查看论文截图



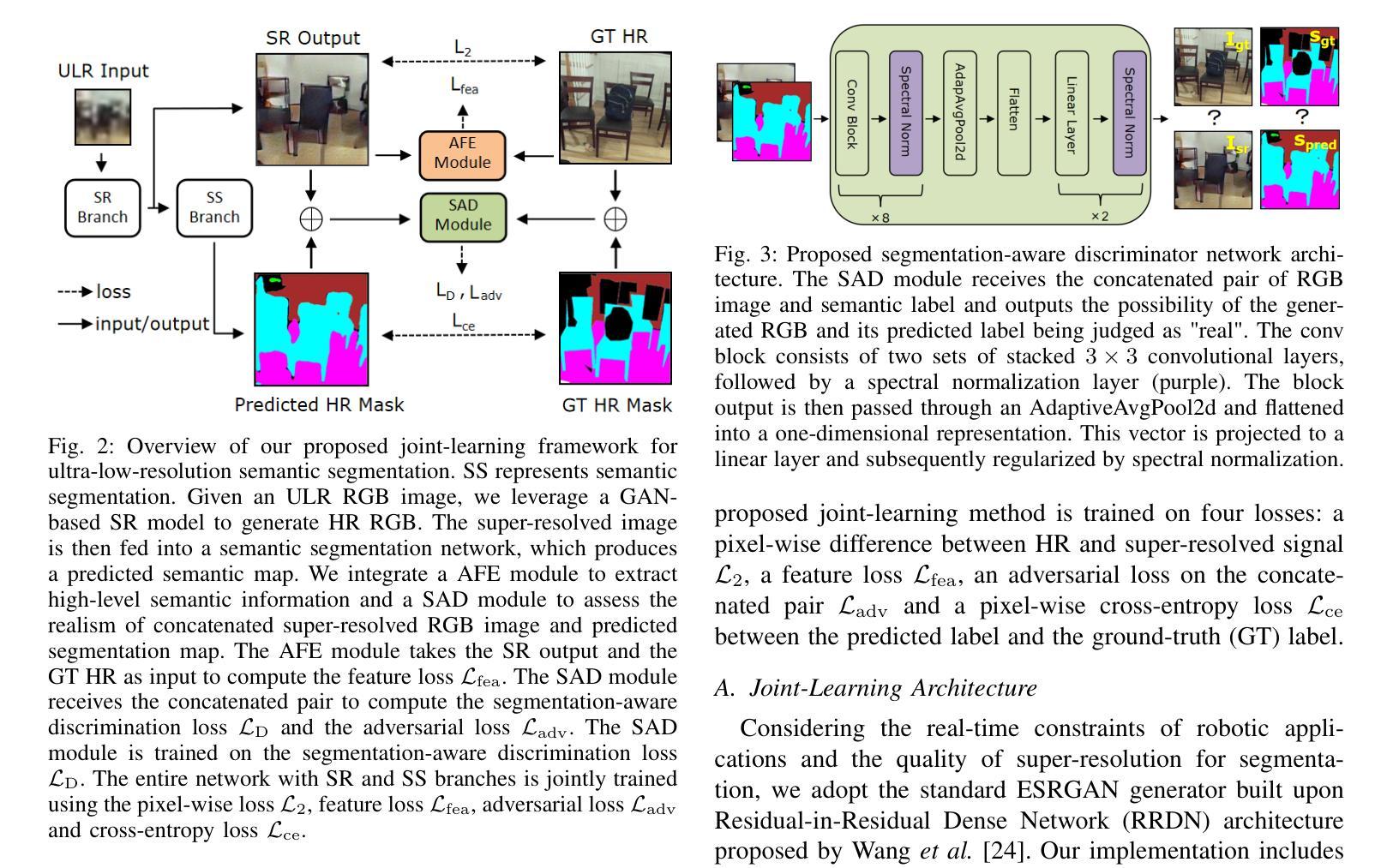
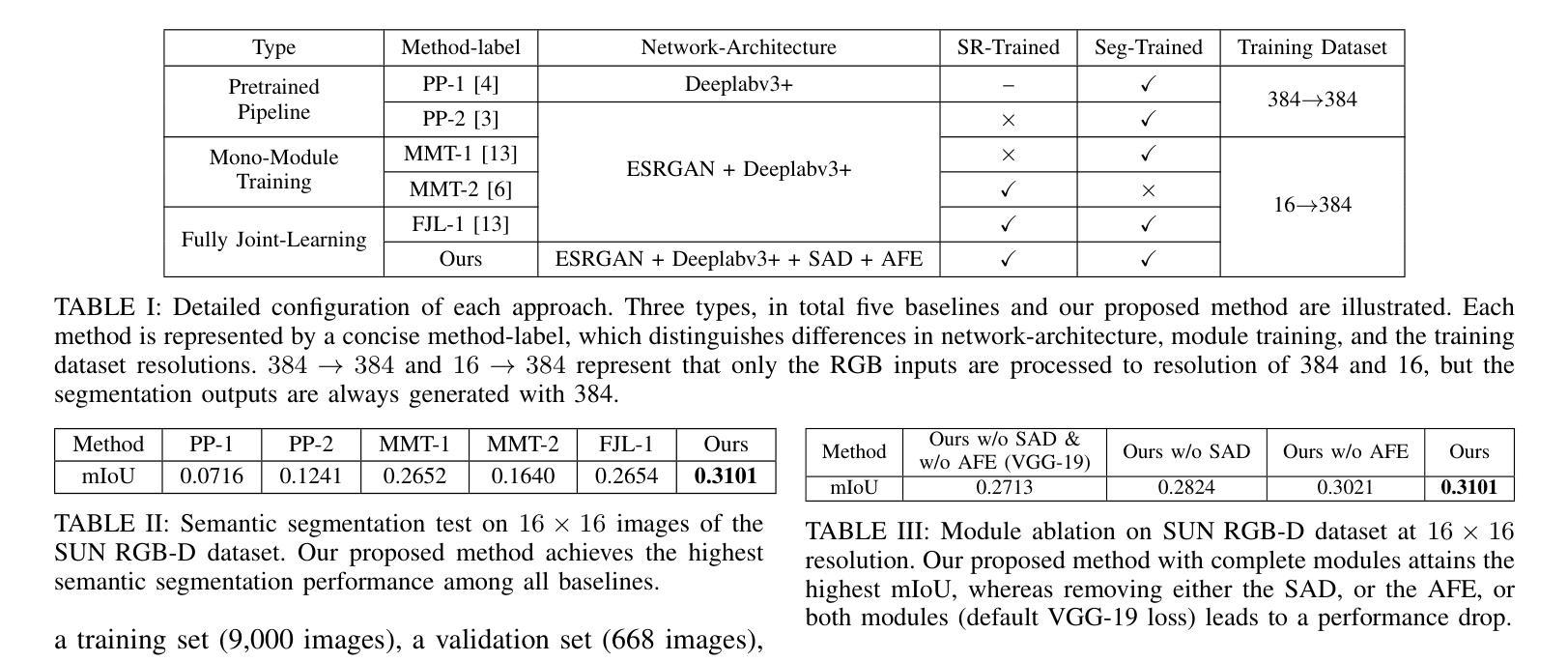
Improved Semantic Segmentation from Ultra-Low-Resolution RGB Images Applied to Privacy-Preserving Object-Goal Navigation
Authors:Xuying Huang, Sicong Pan, Olga Zatsarynna, Juergen Gall, Maren Bennewitz
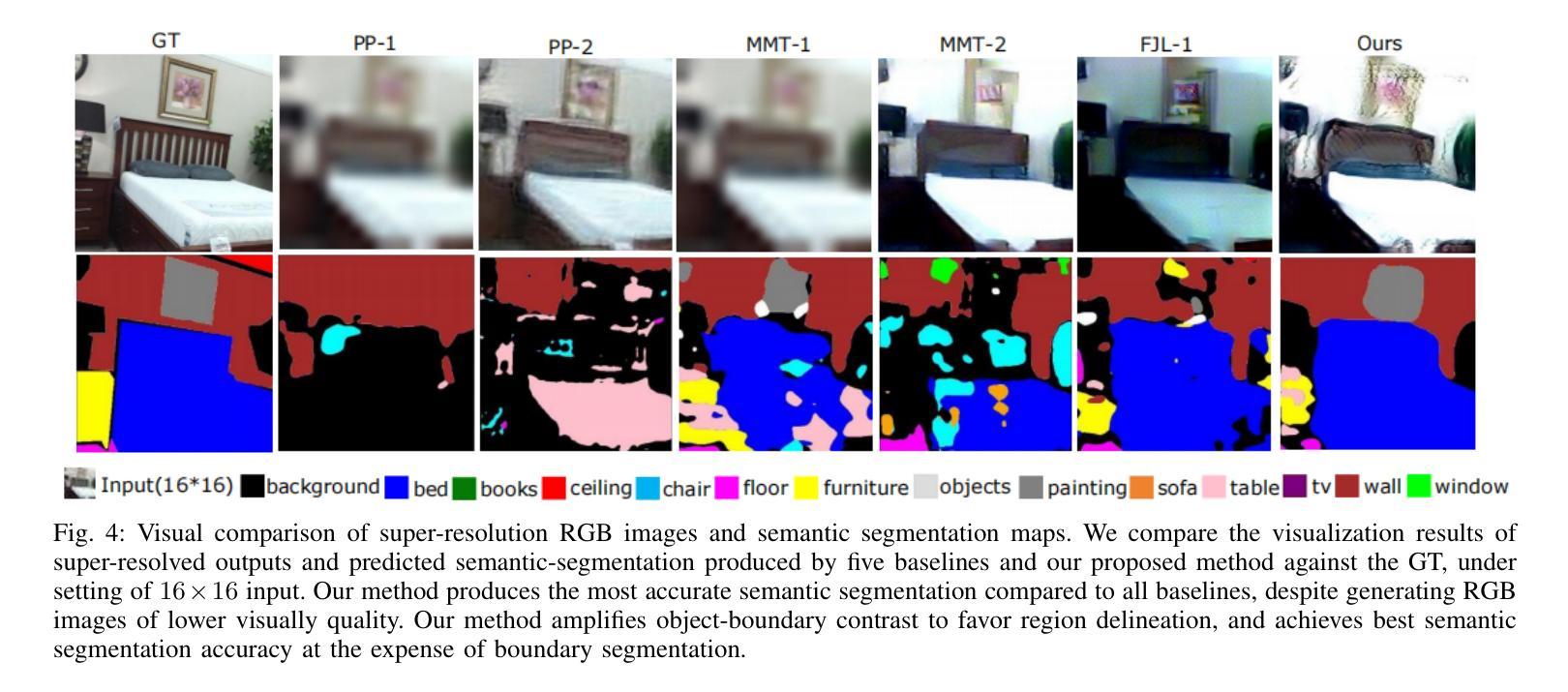
User privacy in mobile robotics has become a critical concern. Existing methods typically prioritize either the performance of downstream robotic tasks or privacy protection, with the latter often constraining the effectiveness of task execution. To jointly address both objectives, we study semantic-based robot navigation in an ultra-low-resolution setting to preserve visual privacy. A key challenge in such scenarios is recovering semantic segmentation from ultra-low-resolution RGB images. In this work, we introduce a novel fully joint-learning method that integrates an agglomerative feature extractor and a segmentation-aware discriminator to solve ultra-low-resolution semantic segmentation, thereby enabling privacy-preserving, semantic object-goal navigation. Our method outperforms different baselines on ultra-low-resolution semantic segmentation and our improved segmentation results increase the success rate of the semantic object-goal navigation in a real-world privacy-constrained scenario.
移动机器人的用户隐私已成为人们关注的重点。现有的方法通常侧重于下游机器人任务的性能或隐私保护,而后者往往会限制任务执行的有效性。为了同时解决这两个目标,我们研究在超低分辨率环境下基于语义的机器人导航以保护视觉隐私。此类场景中的一个关键挑战是从超低分辨率的RGB图像中恢复语义分割。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新颖的完全联合学习方法,该方法结合了聚合特征提取器和分割感知鉴别器来解决超低分辨率语义分割问题,从而实现可保护隐私的、语义目标导航。我们的方法在超低分辨率语义分割方面超越了不同的基线,并且我们改进的分割结果提高了在现实世界的隐私受限场景中语义目标导航的成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to RA-L
Summary
本摘要针对移动机器人用户隐私保护问题展开研究。针对现有方法侧重于机器人任务性能而忽视隐私保护的问题,提出在超低分辨率环境下进行语义基础机器人导航的方法,以保护视觉隐私。挑战在于从超低分辨率RGB图像中恢复语义分割。本研究引入了一种全新的联合学习方法,结合特征提取器和分割感知鉴别器,解决超低分辨率语义分割问题,实现隐私保护语义目标导航。该方法在超低分辨率语义分割方面优于不同基线,并且提高了隐私约束场景中语义目标导航的成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 移动机器人用户隐私保护成为重要关注点。
- 现有方法通常侧重机器人任务性能或隐私保护,二者兼顾存在挑战。
- 在超低分辨率环境下研究语义基础机器人导航以保护视觉隐私。
- 从超低分辨率RGB图像中恢复语义分割是此类场景的关键挑战。
- 引入全新的联合学习方法,结合特征提取器和分割感知鉴别器,解决超低分辨率语义分割问题。
- 所提方法优于其他基线方法,在超低分辨率语义分割方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图


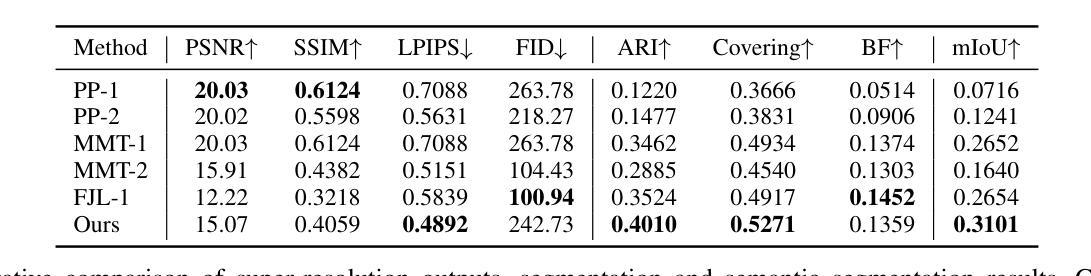
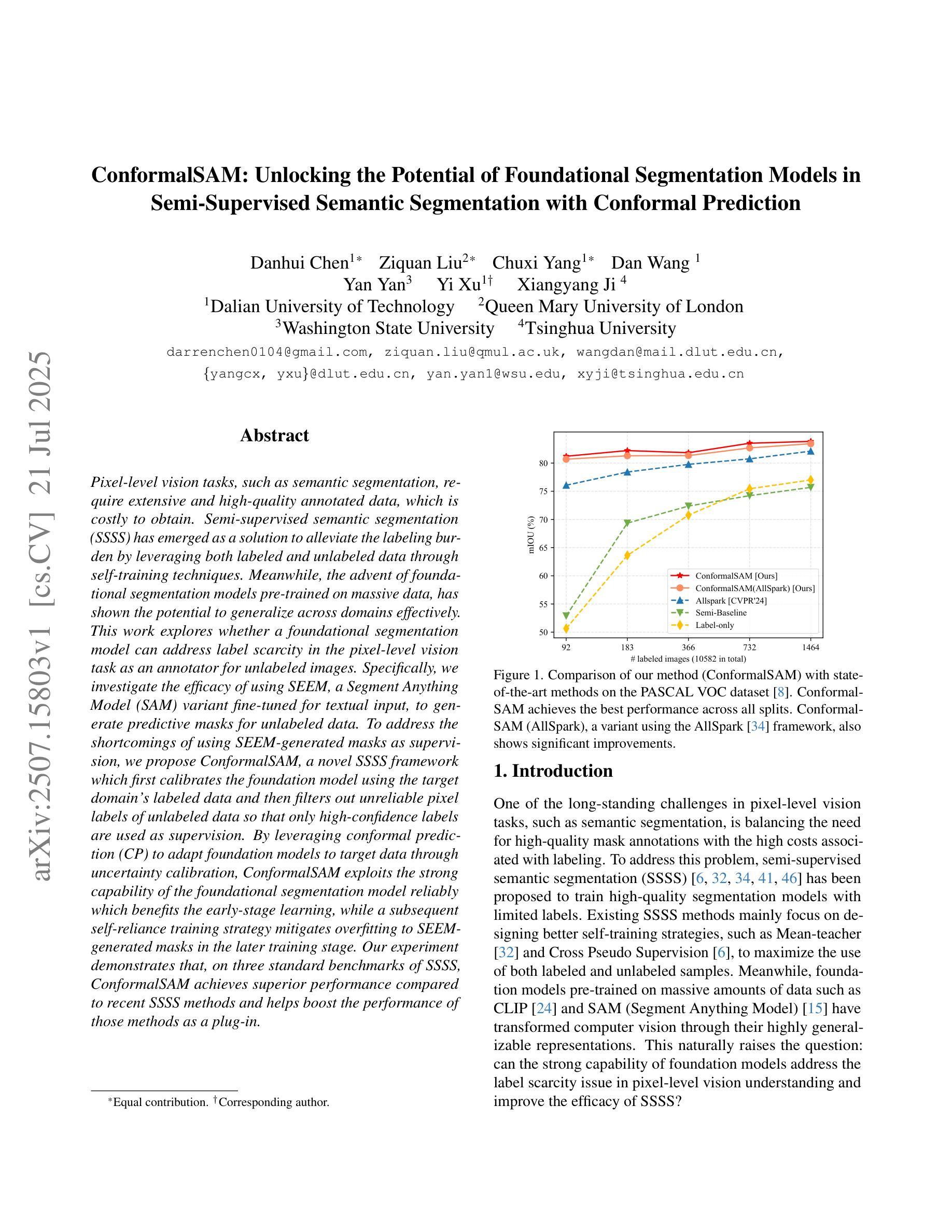
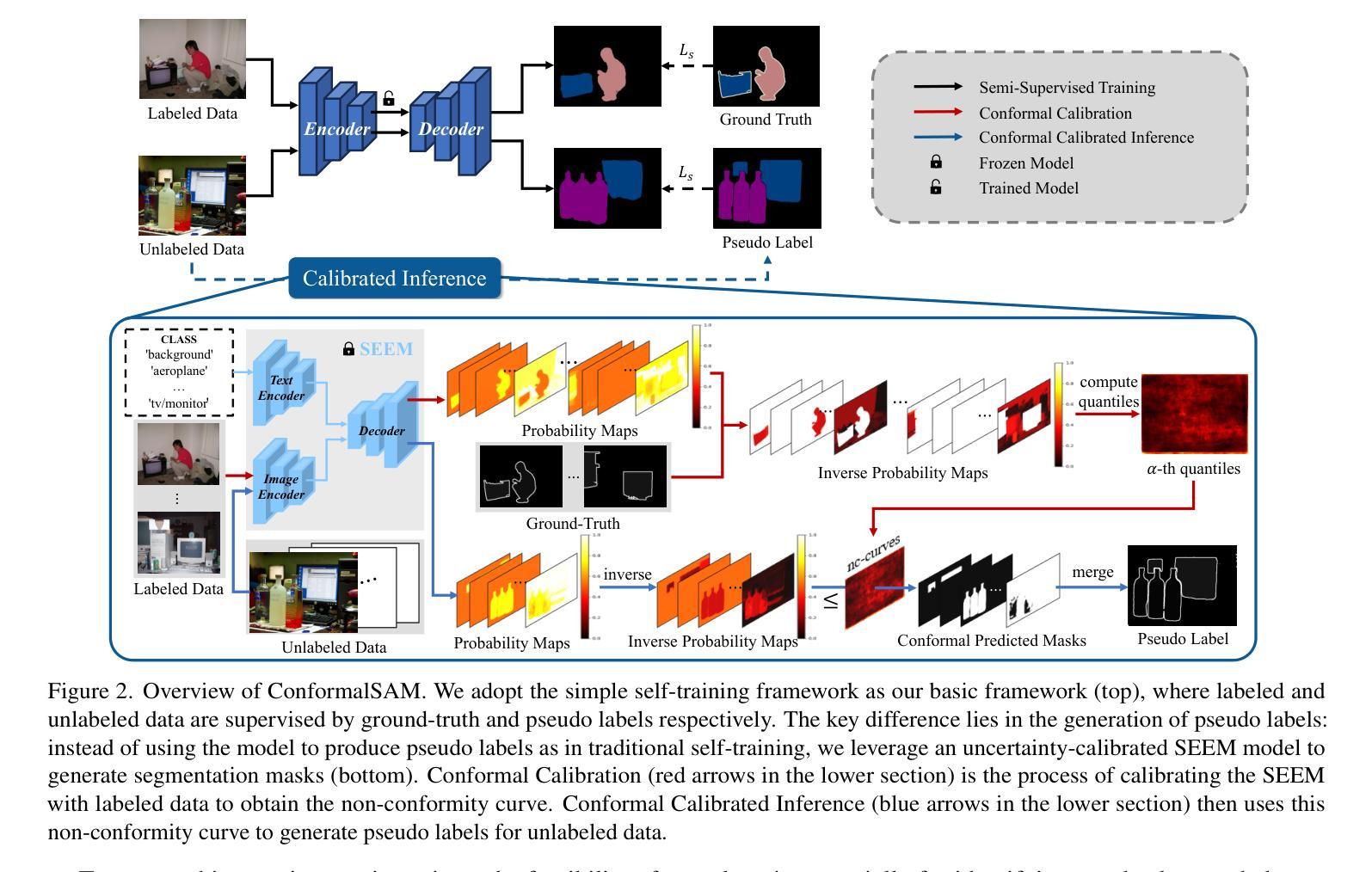
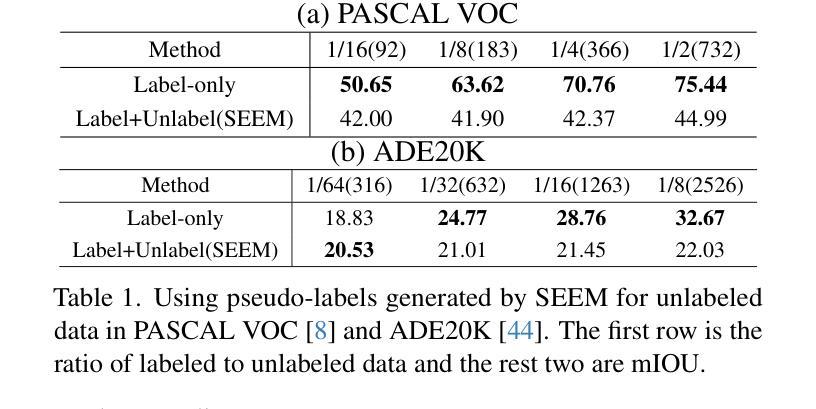
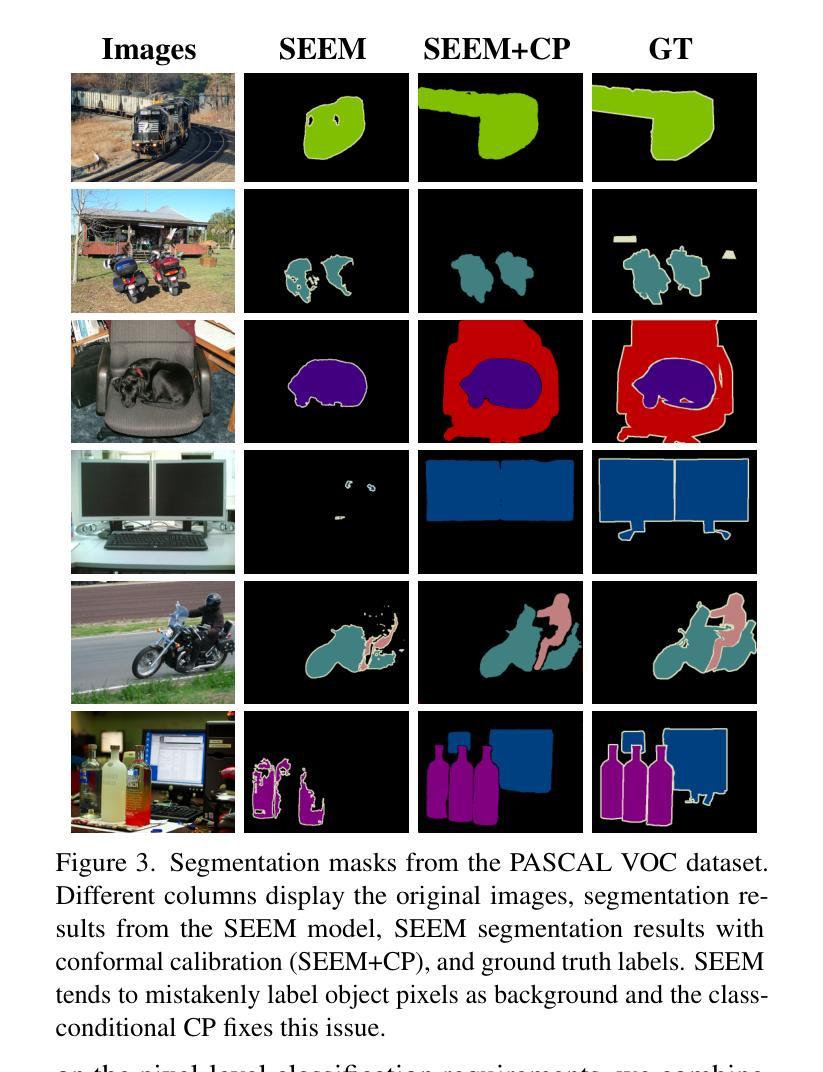
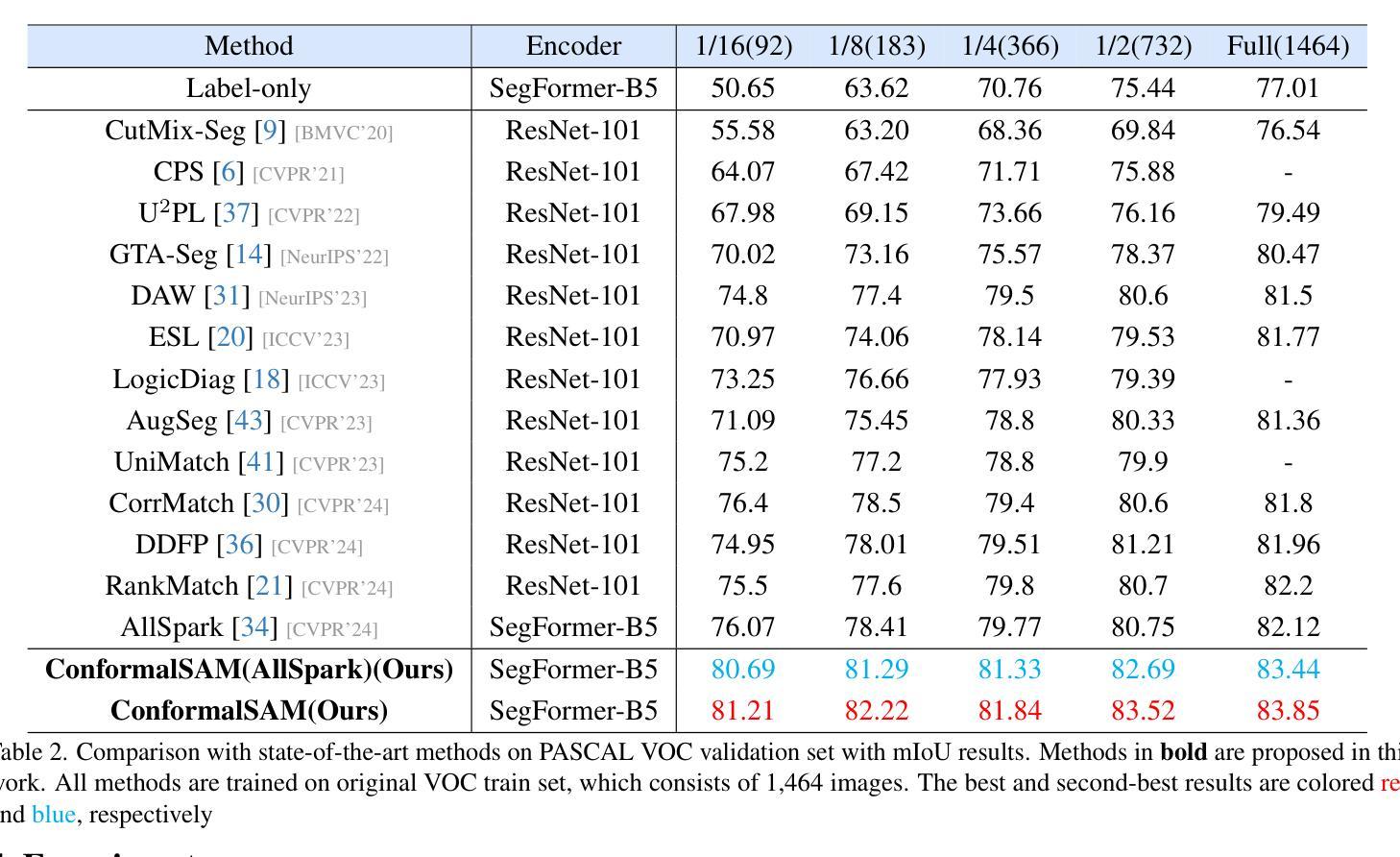
ConformalSAM: Unlocking the Potential of Foundational Segmentation Models in Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation with Conformal Prediction
Authors:Danhui Chen, Ziquan Liu, Chuxi Yang, Dan Wang, Yan Yan, Yi Xu, Xiangyang Ji
Pixel-level vision tasks, such as semantic segmentation, require extensive and high-quality annotated data, which is costly to obtain. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS) has emerged as a solution to alleviate the labeling burden by leveraging both labeled and unlabeled data through self-training techniques. Meanwhile, the advent of foundational segmentation models pre-trained on massive data, has shown the potential to generalize across domains effectively. This work explores whether a foundational segmentation model can address label scarcity in the pixel-level vision task as an annotator for unlabeled images. Specifically, we investigate the efficacy of using SEEM, a Segment Anything Model (SAM) variant fine-tuned for textual input, to generate predictive masks for unlabeled data. To address the shortcomings of using SEEM-generated masks as supervision, we propose ConformalSAM, a novel SSSS framework which first calibrates the foundation model using the target domain’s labeled data and then filters out unreliable pixel labels of unlabeled data so that only high-confidence labels are used as supervision. By leveraging conformal prediction (CP) to adapt foundation models to target data through uncertainty calibration, ConformalSAM exploits the strong capability of the foundational segmentation model reliably which benefits the early-stage learning, while a subsequent self-reliance training strategy mitigates overfitting to SEEM-generated masks in the later training stage. Our experiment demonstrates that, on three standard benchmarks of SSSS, ConformalSAM achieves superior performance compared to recent SSSS methods and helps boost the performance of those methods as a plug-in.
像素级视觉任务(如语义分割)需要大量的高质量标注数据,而这些数据的获取成本很高。半监督语义分割(SSSS)的出现作为一种解决方案,通过自训练技术利用有标签和无标签的数据来缓解标注负担。同时,在大量数据上预训练的基础分割模型的出现,显示出在不同领域进行有效推广的潜力。这项工作探讨了基础分割模型作为未标注图像的注释器,在像素级视觉任务中解决标签稀缺问题的能力。具体来说,我们研究了使用SEEM(一种为文本输入微调过的Segment Anything Model(SAM)变种)来为未标注数据生成预测掩膜的有效性。为了解决使用SEEM生成的掩膜作为监督的缺点,我们提出了ConformalSAM,这是一种新的SSSS框架。它首先使用目标领域的标注数据校准基础模型,然后过滤出未标注数据的不可靠像素标签,以便只有高置信度的标签被用作监督。通过利用合数预测(CP)来通过不确定性校准适应基础模型到目标数据,ConformalSAM可靠地利用基础分割模型的强大功能,这有利于早期学习,而随后的自我依赖训练策略则减轻了后期训练中过度依赖SEEM生成的掩膜的问题。我们的实验表明,在三个标准的SSSS基准测试中,ConformalSAM与最新的SSSS方法相比取得了优越的性能,并且作为插件有助于提高这些方法的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
基于像素级别的视觉任务,如语义分割,需要大量高质量标注数据,但获取这些数据成本高昂。为解决标注负担问题,半监督语义分割(SSSS)应运而生,它通过利用标注和无标签数据通过自训练技术来减轻负担。同时,预训练在大量数据上的基础分割模型显示出跨域有效泛化的潜力。本研究探讨基础分割模型作为未标注图像注释器来解决像素级视觉任务中的标签稀缺问题的可行性。特别是,我们研究了使用SEEM(一种针对文本输入的Segment Anything Model(SAM)变体)来为无标签数据生成预测掩膜的效果。为解决使用SEEM生成的掩膜作为监督的缺点,我们提出了ConformalSAM——一种新型SSSS框架。它首先使用目标域的标注数据校准基础模型,然后过滤出无标签数据中不可靠的像素标签,仅使用高置信度的标签作为监督。通过利用顺应性预测(CP)来适应目标数据的不确定性校准,ConformalSAM能够可靠地利用基础分割模型的强大能力,有益于早期学习阶段;随后采用自我依赖训练策略,缓解了对SEEM生成掩膜在后期训练阶段的过度拟合问题。实验表明,在三个标准的SSSS基准测试中,ConformalSAM相较于近期SSSS方法实现了优越的性能,并且作为插件有助于提升这些方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 像素级视觉任务如语义分割需要高质量的大量标注数据,但获取这些数据成本高昂。
- 半监督语义分割(SSSS)方法旨在通过利用标注和无标签数据来缓解标注负担。
- 基础分割模型具有跨域有效泛化的潜力。
- 使用SEEM模型为无标签数据生成预测掩膜是一种解决方案。
- ConformalSAM是一种新型SSSS框架,通过校准基础模型和过滤不可靠像素标签来提高性能。
- ConformalSAM利用顺应性预测(CP)以适应目标数据的不确定性校准,结合早期学习和自我依赖训练策略,提高模型的可靠性并缓解过度拟合问题。
点此查看论文截图
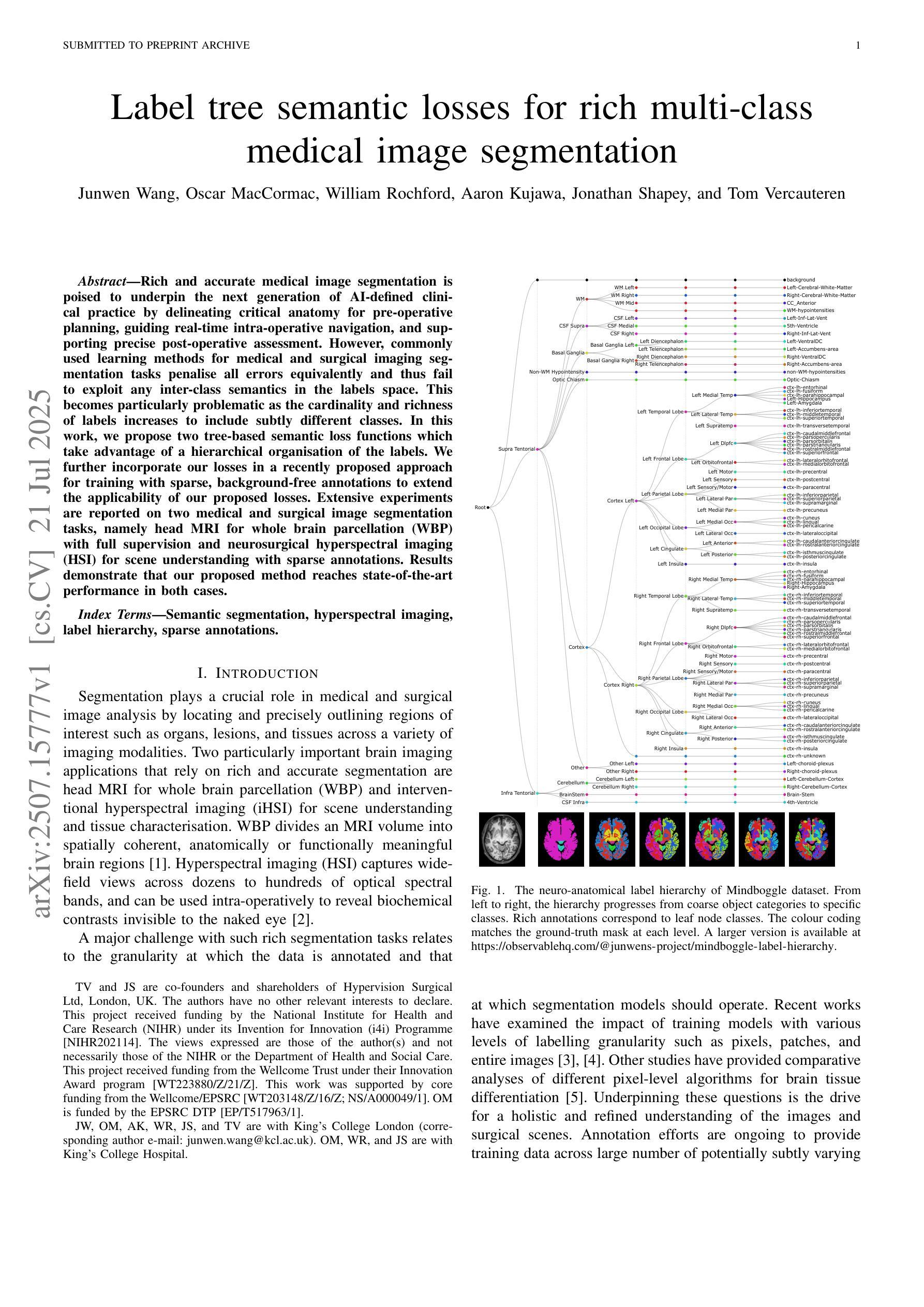
Label tree semantic losses for rich multi-class medical image segmentation
Authors:Junwen Wang, Oscar MacCormac, William Rochford, Aaron Kujawa, Jonathan Shapey, Tom Vercauteren
Rich and accurate medical image segmentation is poised to underpin the next generation of AI-defined clinical practice by delineating critical anatomy for pre-operative planning, guiding real-time intra-operative navigation, and supporting precise post-operative assessment. However, commonly used learning methods for medical and surgical imaging segmentation tasks penalise all errors equivalently and thus fail to exploit any inter-class semantics in the labels space. This becomes particularly problematic as the cardinality and richness of labels increases to include subtly different classes. In this work, we propose two tree-based semantic loss functions which take advantage of a hierarchical organisation of the labels. We further incorporate our losses in a recently proposed approach for training with sparse, background-free annotations to extend the applicability of our proposed losses. Extensive experiments are reported on two medical and surgical image segmentation tasks, namely head MRI for whole brain parcellation (WBP) with full supervision and neurosurgical hyperspectral imaging (HSI) for scene understanding with sparse annotations. Results demonstrate that our proposed method reaches state-of-the-art performance in both cases.
丰富而准确的医学图像分割技术将为下一代人工智能定义的临床实践提供支持,通过描绘关键解剖结构来进行术前规划,指导实时术中导航,并支持精确的术后评估。然而,医学和手术图像分割任务中常用的学习方法平等地惩罚所有错误,因此未能利用标签空间中的类间语义。当标签的基数和丰富性增加以包括细微不同的类别时,这变得特别成问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了两种基于树的语义损失函数,它们利用了标签的层次组织。我们进一步将我们的损失纳入最近提出的具有稀疏、无背景注释的训练方法中,以扩展我们提出的损失适用性。在两项医学和手术图像分割任务上报告了广泛实验的结果,分别是全监督的头MRI全脑分区(WBP)和具有稀疏注释的神经外科高光谱成像(HSI)的场景理解。结果表明,我们的方法在这两种情况下均达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2506.21150
Summary
本文强调医疗图像分割技术在新一代AI定义的临床实践中的重要性,包括在术前规划、术中实时导航和术后精确评估中的应用。然而,常用的学习方法和标签空间的语义之间缺乏关联,对于复杂的医疗和手术图像分割任务存在问题。本研究提出了两种基于树的语义损失函数,能够利用标签的层次结构。此外,将损失函数应用于稀疏、无背景注释的训练方法,扩大了其应用范围。在医疗和手术图像分割任务上的实验表明,该方法达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割技术在新一代AI临床实践中具有重要作用。
- 常用的医学和手术图像分割学习方法未充分利用标签空间中的语义关系。
- 提出两种基于树的语义损失函数,能够利用标签的层次结构提高分割性能。
- 损失函数应用于稀疏、无背景注释的训练方法,增强了其适用性。
- 实验结果表明该方法在医疗和手术图像分割任务上达到了最先进的性能。
- 在头部MRI全监督下进行全脑分块(WBP)和神经外科超光谱成像(HSI)场景理解的任务中验证了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
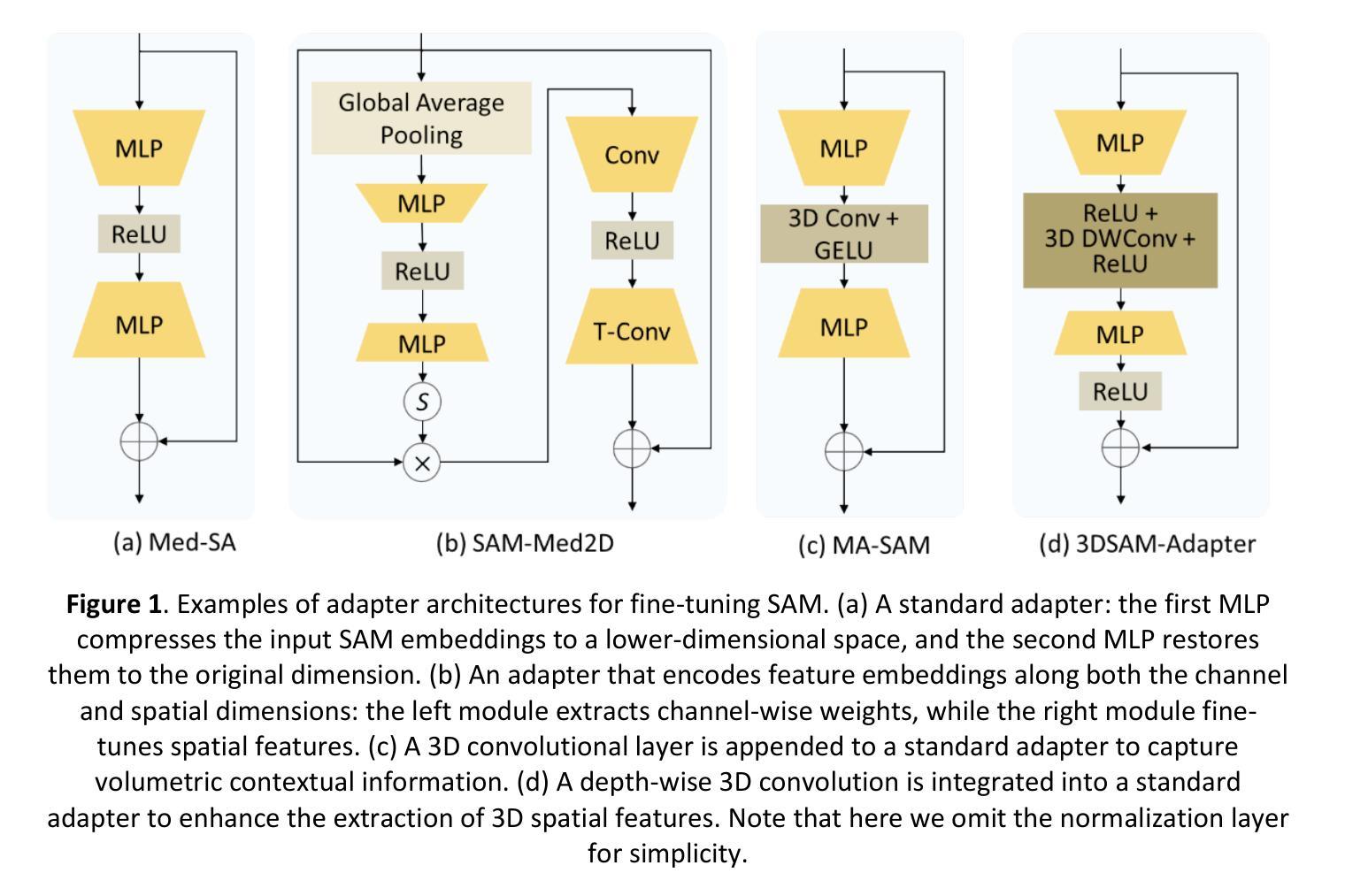
Depthwise-Dilated Convolutional Adapters for Medical Object Tracking and Segmentation Using the Segment Anything Model 2
Authors:Guoping Xu, Christopher Kabat, You Zhang
Recent advances in medical image segmentation have been driven by deep learning; however, most existing methods remain limited by modality-specific designs and exhibit poor adaptability to dynamic medical imaging scenarios. The Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) and its related variants, which introduce a streaming memory mechanism for real-time video segmentation, present new opportunities for prompt-based, generalizable solutions. Nevertheless, adapting these models to medical video scenarios typically requires large-scale datasets for retraining or transfer learning, leading to high computational costs and the risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose DD-SAM2, an efficient adaptation framework for SAM2 that incorporates a Depthwise-Dilated Adapter (DD-Adapter) to enhance multi-scale feature extraction with minimal parameter overhead. This design enables effective fine-tuning of SAM2 on medical videos with limited training data. Unlike existing adapter-based methods focused solely on static images, DD-SAM2 fully exploits SAM2’s streaming memory for medical video object tracking and segmentation. Comprehensive evaluations on TrackRad2025 (tumor segmentation) and EchoNet-Dynamic (left ventricle tracking) datasets demonstrate superior performance, achieving Dice scores of 0.93 and 0.97, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this work provides an initial attempt at systematically exploring adapter-based SAM2 fine-tuning for medical video segmentation and tracking. Code, datasets, and models will be publicly available at https://github.com/apple1986/DD-SAM2.
最近,医学图像分割领域的进展主要得益于深度学习。然而,大多数现有方法仍然受到特定模态设计的限制,在动态医学影像场景中适应性较差。Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)及其相关变体引入了实时视频分割的流式内存机制,为基于提示的通用解决方案提供了新的机会。然而,将这些模型适应到医学视频场景通常需要大规模数据集进行重新训练或迁移学习,这导致了较高的计算成本以及灾难性遗忘的风险。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DD-SAM2,这是一个SAM2的有效适配框架,它结合了Depthwise-Dilated Adapter(DD-Adapter)以增强多尺度特征提取能力,同时尽量减少参数开销。这种设计使得在有限的训练数据上对医学视频进行SAM2精细调整成为可能。与现有仅专注于静态图像的适配器方法不同,DD-SAM2充分利用SAM2的流式内存进行医学视频目标跟踪和分割。在TrackRad2025(肿瘤分割)和EchoNet-Dynamic(左心室跟踪)数据集上的综合评估表明,其性能卓越,分别实现了Dice得分0.93和0.97。据我们所知,这项工作初步尝试系统地探索基于适配器的SAM2精细调整在医学视频分割和跟踪中的应用。代码、数据集和模型将在https://github.com/apple1986/DD-SAM 公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于深度学习的医学图像分割技术取得新进展,但仍存在针对特定模态的设计限制以及适应动态医学影像场景的适应性差的问题。SAM2模型及其变体通过引入实时视频分割的流式内存机制,为基于提示的通用解决方案提供了新的机会。然而,将这些模型适应到医学视频场景通常需要大规模数据集进行重新训练或迁移学习,导致高计算成本和灾难性遗忘的风险。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了DD-SAM2,一个高效的SAM2适应框架,它采用Depthwise-Dilated Adapter(DD-Adapter)以增强多尺度特征提取,同时参数开销最小化。该设计可在有限的训练数据上实现对医学视频的SAM2精细调整。与现有仅专注于静态图像的适配器方法不同,DD-SAM2充分利用SAM2的流式内存进行医学视频目标跟踪和分割。在TrackRad2025(肿瘤分割)和EchoNet-Dynamic(左心室跟踪)数据集上的全面评估表明其卓越性能,分别实现了Dice得分0.93和0.97。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割领域取得进展,但仍存在模态特定设计和动态医学影像场景适应性问题。
- SAM2模型及其变体为基于提示的通用解决方案提供新机会,尤其适用于实时视频分割。
- 适应医学视频场景通常需要大规模数据集,导致高计算成本和灾难性遗忘风险。
- 提出DD-SAM2框架,通过Depthwise-Dilated Adapter增强多尺度特征提取,实现SAM2在医学视频上的精细调整。
- DD-SAM2不同于现有专注于静态图像的适配器方法,充分利用SAM2的流式内存进行医学视频目标跟踪和分割。
- 在TrackRad2025和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上评估,DD-SAM2表现出卓越性能。
- 研究者公开了代码、数据集和模型,便于他人访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

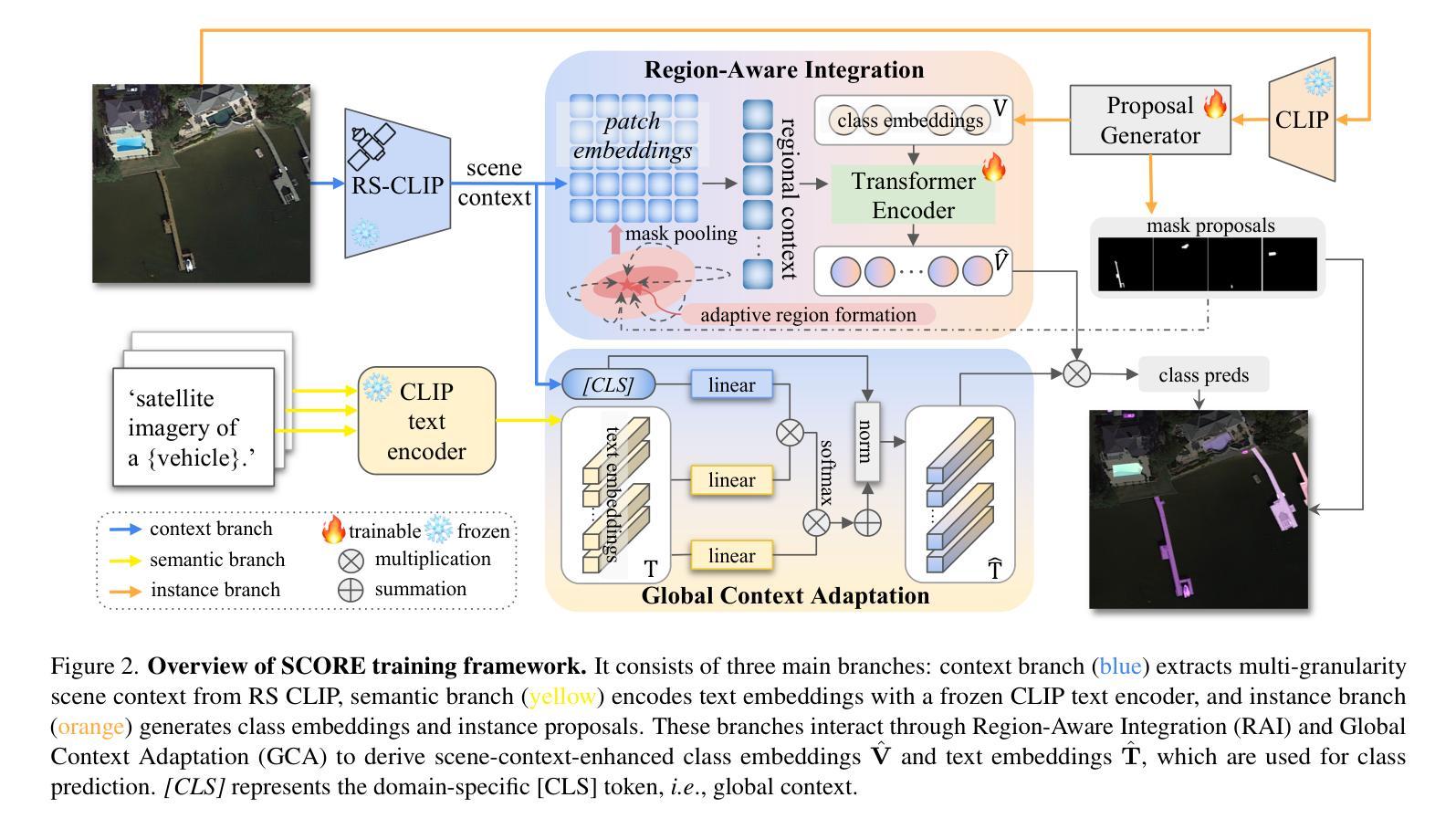
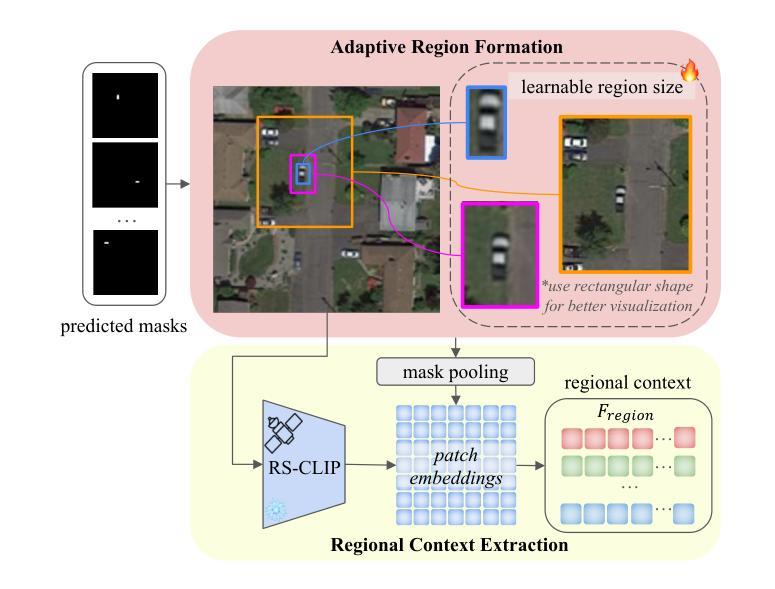
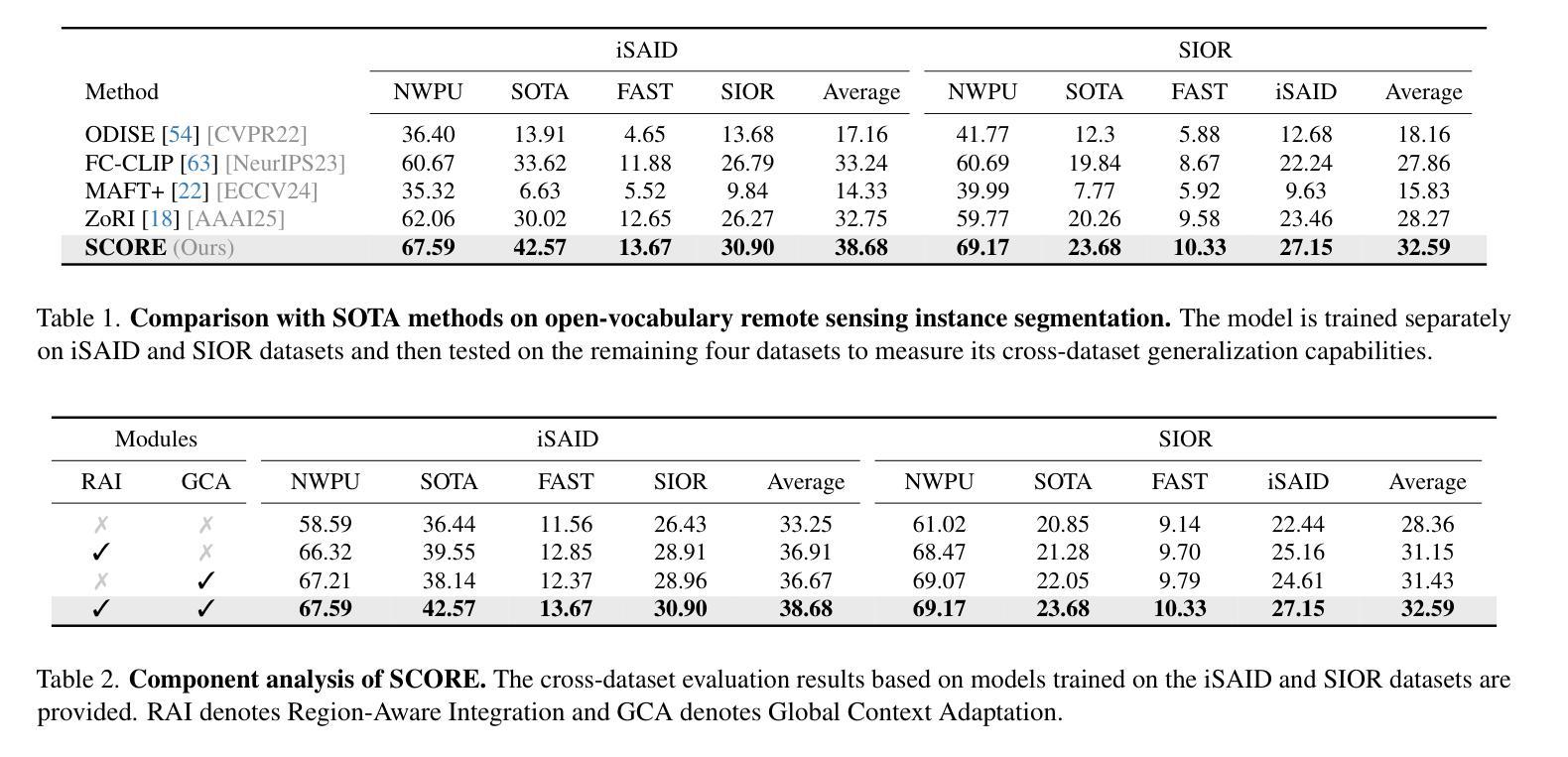
SCORE: Scene Context Matters in Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Instance Segmentation
Authors:Shiqi Huang, Shuting He, Huaiyuan Qin, Bihan Wen
Most existing remote sensing instance segmentation approaches are designed for close-vocabulary prediction, limiting their ability to recognize novel categories or generalize across datasets. This restricts their applicability in diverse Earth observation scenarios. To address this, we introduce open-vocabulary (OV) learning for remote sensing instance segmentation. While current OV segmentation models perform well on natural image datasets, their direct application to remote sensing faces challenges such as diverse landscapes, seasonal variations, and the presence of small or ambiguous objects in aerial imagery. To overcome these challenges, we propose $\textbf{SCORE}$ ($\textbf{S}$cene $\textbf{C}$ontext matters in $\textbf{O}$pen-vocabulary $\textbf{RE}$mote sensing instance segmentation), a framework that integrates multi-granularity scene context, i.e., regional context and global context, to enhance both visual and textual representations. Specifically, we introduce Region-Aware Integration, which refines class embeddings with regional context to improve object distinguishability. Additionally, we propose Global Context Adaptation, which enriches naive text embeddings with remote sensing global context, creating a more adaptable and expressive linguistic latent space for the classifier. We establish new benchmarks for OV remote sensing instance segmentation across diverse datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that, our proposed method achieves SOTA performance, which provides a robust solution for large-scale, real-world geospatial analysis. Our code is available at https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/SCORE.
当前大多数遥感实例分割方法都是针对封闭词汇预测设计的,这限制了它们对新型类别的识别能力,以及在数据集间的泛化能力。这限制了它们在多种地球观测场景中的应用。为了解决这个问题,我们为遥感实例分割引入了开放词汇(OV)学习。虽然当前的OV分割模型在自然图像数据集上表现良好,但它们直接应用于遥感却面临着挑战,例如景观多样性、季节变化和空中影像中小目标或模糊物体的存在。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了$\textbf{SCORE}$($\textbf{S}$cene $\textbf{C}$ontext matters in $\textbf{O}$pen-vocabulary $\textbf{RE}$mote sensing instance segmentation),一个整合多粒度场景上下文的框架,即区域上下文和全局上下文,以增强视觉和文本表示。具体来说,我们引入了区域感知集成,通过区域上下文细化类别嵌入,以提高目标可区分性。此外,我们提出了全局上下文适应,用遥感全局上下文丰富原始文本嵌入,为分类器创建一个更具适应性和表达能力的语言潜在空间。我们在多个数据集上建立了OV遥感实例分割的新基准。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法达到了最先进的性能,为大规模、真实世界的地理空间分析提供了稳健的解决方案。我们的代码可在https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/SCORE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 (Highlight), code see https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/SCORE
Summary
本文介绍了遥感实例分割领域中的开放词汇表学习方法。现有方法主要面向封闭词汇预测,难以识别新类别或跨数据集进行推广,限制了其在多样地球观测场景中的应用。为此,本文提出了一个名为SCORE的框架,该框架融合了多粒度场景上下文信息,包括区域上下文和全局上下文,以增强视觉和文本表示。实验结果表明,该方法实现了先进性能,为大规模地理空间分析提供了稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 当前遥感实例分割方法主要面向封闭词汇预测,限制了其在多样地球观测场景中的应用。
- 开放词汇(OV)学习是解决此问题的一种方法,但直接应用于遥感面临挑战。
- SCORE框架融合了多粒度场景上下文信息,包括区域上下文和全局上下文。
- Region-Aware Integration通过结合区域上下文信息优化类别嵌入,提高目标区分度。
- Global Context Adaptation丰富了文本嵌入的遥感全局上下文信息,使分类器更具适应性和表现力。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在开放词汇遥感实例分割方面达到了先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

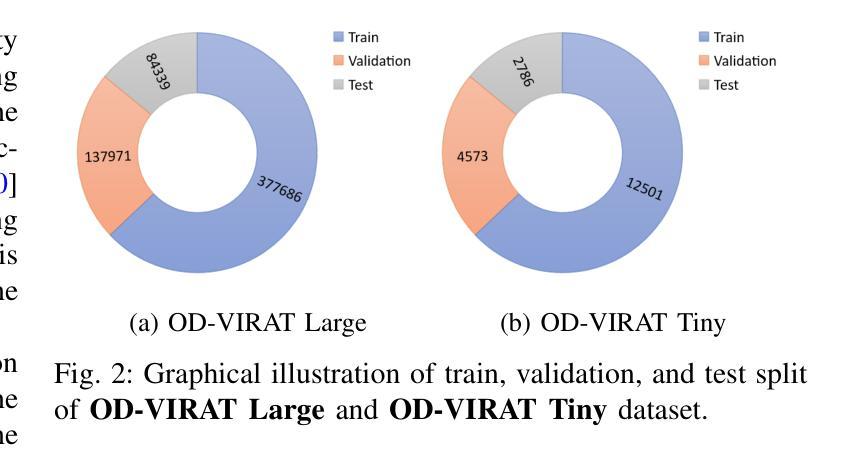
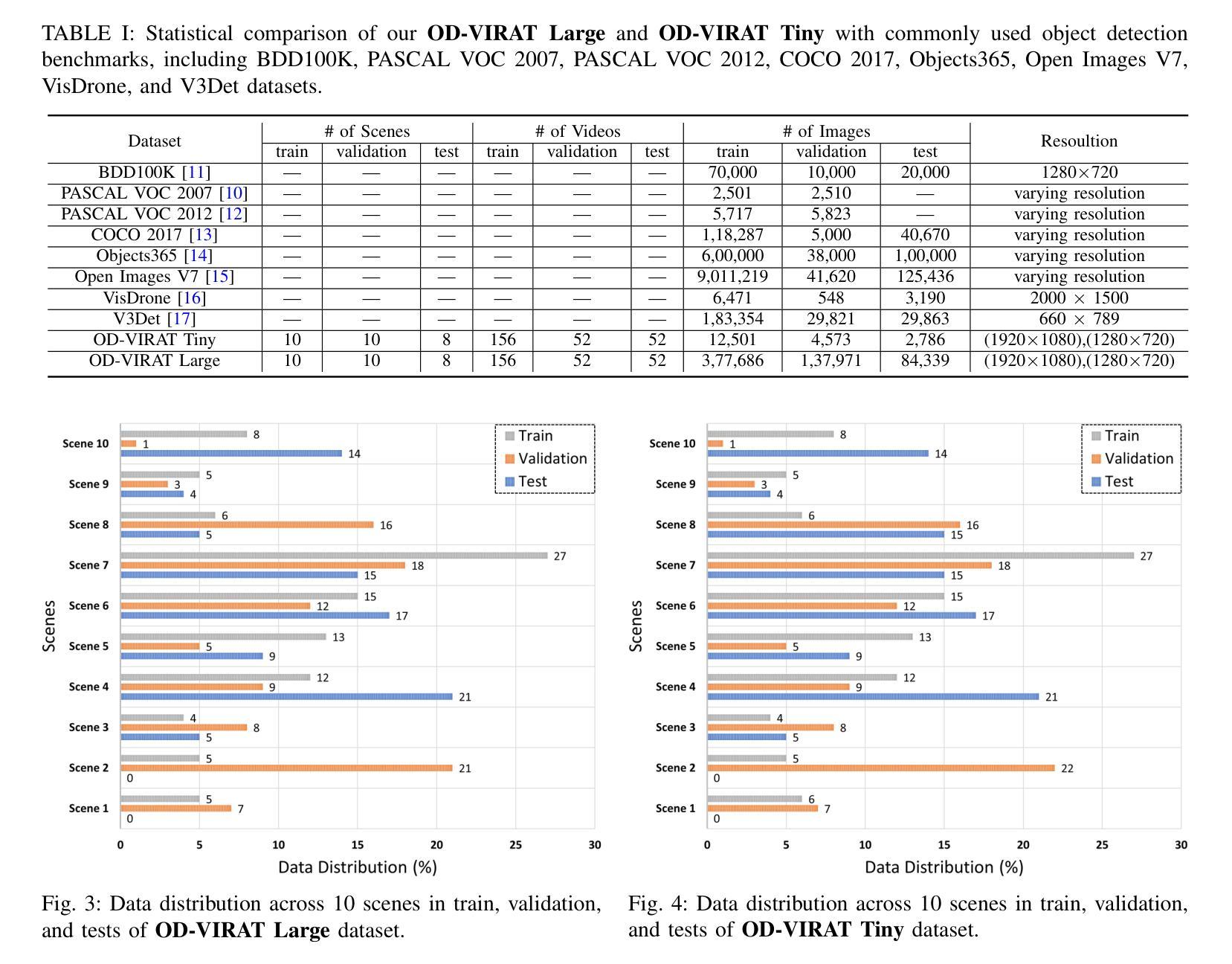
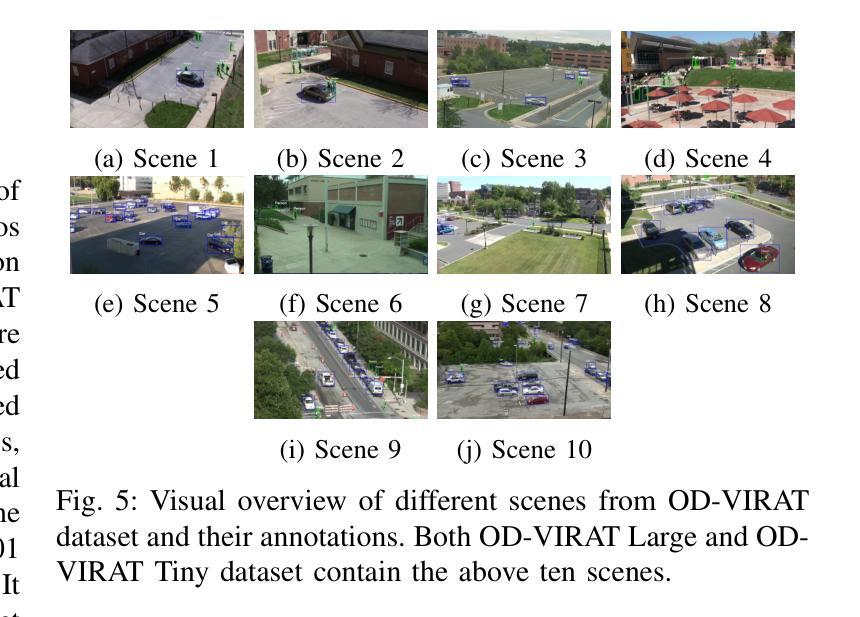
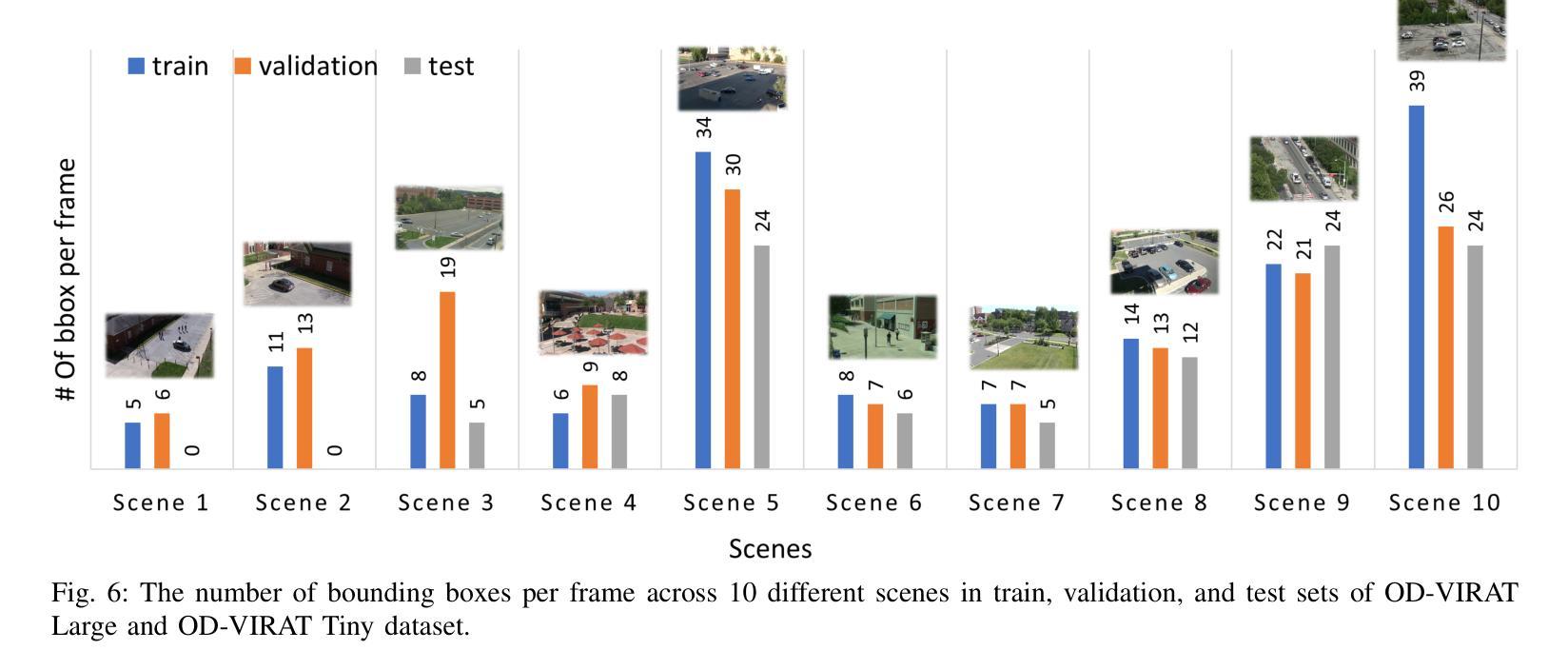
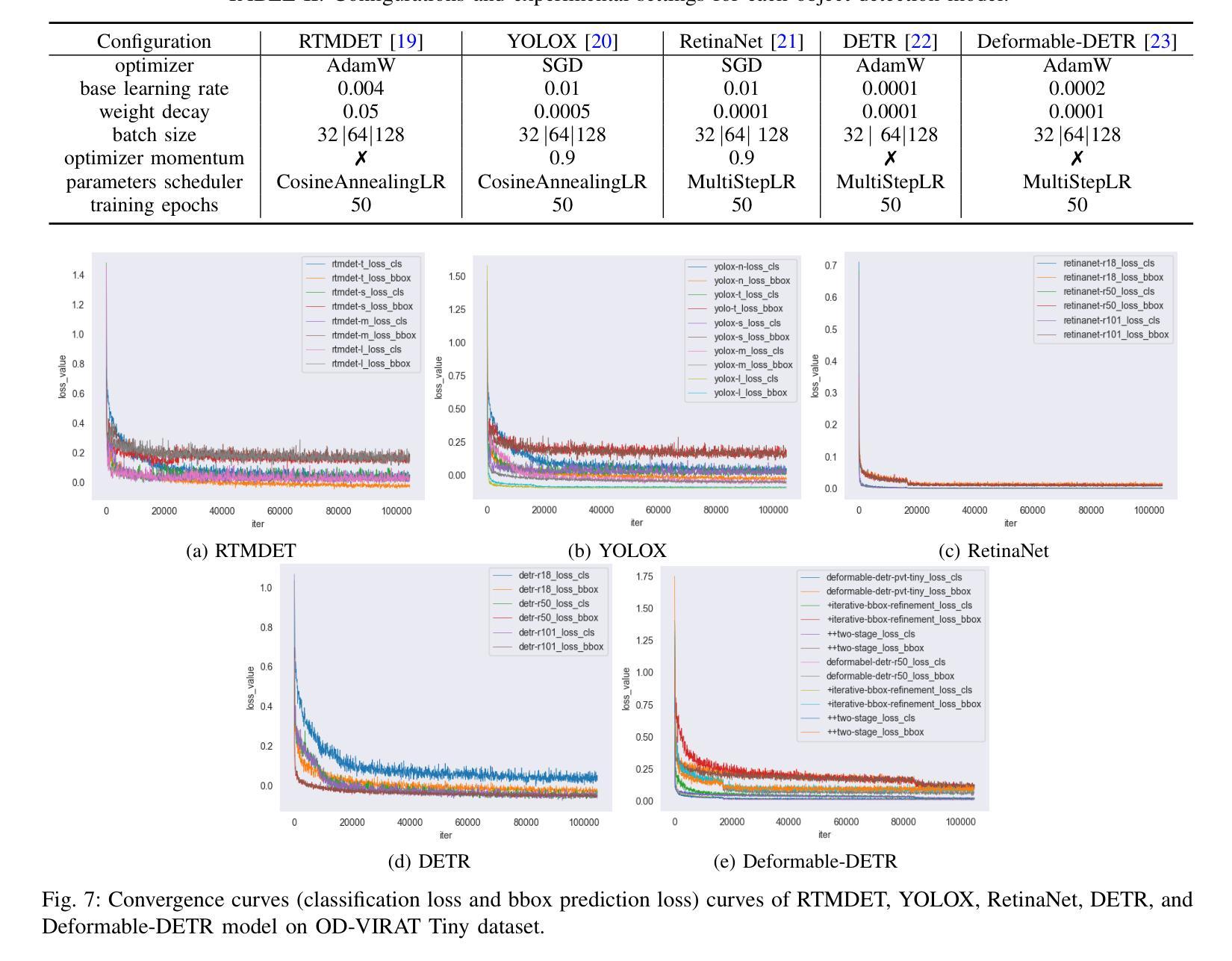
OD-VIRAT: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Object Detection in Realistic Surveillance Environments
Authors:Hayat Ullah, Abbas Khan, Arslan Munir, Hari Kalva
Realistic human surveillance datasets are crucial for training and evaluating computer vision models under real-world conditions, facilitating the development of robust algorithms for human and human-interacting object detection in complex environments. These datasets need to offer diverse and challenging data to enable a comprehensive assessment of model performance and the creation of more reliable surveillance systems for public safety. To this end, we present two visual object detection benchmarks named OD-VIRAT Large and OD-VIRAT Tiny, aiming at advancing visual understanding tasks in surveillance imagery. The video sequences in both benchmarks cover 10 different scenes of human surveillance recorded from significant height and distance. The proposed benchmarks offer rich annotations of bounding boxes and categories, where OD-VIRAT Large has 8.7 million annotated instances in 599,996 images and OD-VIRAT Tiny has 288,901 annotated instances in 19,860 images. This work also focuses on benchmarking state-of-the-art object detection architectures, including RETMDET, YOLOX, RetinaNet, DETR, and Deformable-DETR on this object detection-specific variant of VIRAT dataset. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first work to examine the performance of these recently published state-of-the-art object detection architectures on realistic surveillance imagery under challenging conditions such as complex backgrounds, occluded objects, and small-scale objects. The proposed benchmarking and experimental settings will help in providing insights concerning the performance of selected object detection models and set the base for developing more efficient and robust object detection architectures.
现实的人类监控数据集对于在现实条件下训练和评估计算机视觉模型至关重要,有助于在复杂环境中开发用于人类和人机交互对象检测的稳健算法。这些数据集需要提供多样化和具有挑战性的数据,以实现对模型性能的全面评估,并创建更可靠的公共安全监控系统。为此,我们提出了两个名为OD-VIRAT Large和OD-VIRAT Tiny的视觉目标检测基准测试,旨在推进监控图像中的视觉理解任务。这两个基准测试中的视频序列涵盖了从重大高度和距离记录的10个不同的人类监控场景。所提出基准测试提供了丰富的边界框和类别注释,其中OD-VIRAT Large有599,996张图像中的870万个注释实例,而OD-VIRAT Tiny有19,860张图像中的288,901个注释实例。这项工作还重点关注基于最新技术水平的对象检测架构的基准测试,包括在VIRAT数据集的这一特定对象检测变体上的RETMDET、YOLOX、RetinaNet、DETR和可变形DETR。据我们所知,这是第一项工作在复杂的现实监控图像上检验这些最近发布的最新目标检测架构的性能,如在复杂背景、遮挡物体和小规模物体等具有挑战性的条件下。所提出的基准测试和实验设置将有助于深入了解所选目标检测模型的性能,并为开发更高效和稳健的目标检测架构奠定基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
摘要
提出两个用于监控图像视觉理解任务的大型和微型视觉对象检测基准数据集OD-VIRAT Large和OD-VIRAT Tiny。这些数据集涵盖从不同高度和距离录制的真实人类监控视频序列,包含丰富的边界框和类别注释。该工作重点评估先进的对象检测架构在具有挑战性的现实监控图像上的性能,包括复杂背景、遮挡物体和小物体等条件。这些基准测试和实验设置有助于了解所选对象检测模型性能并为开发更高效和稳健的对象检测架构奠定基础。
关键见解
点此查看论文截图

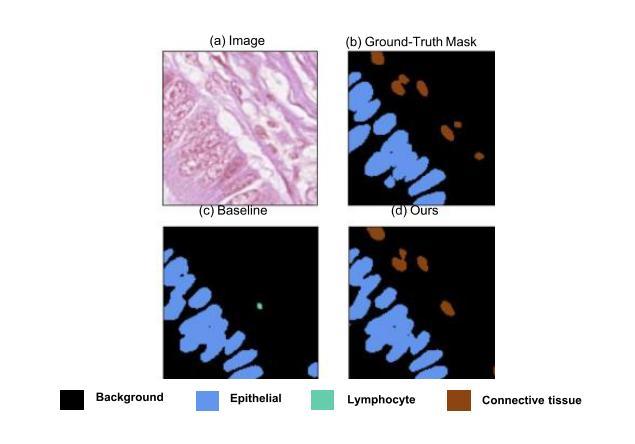
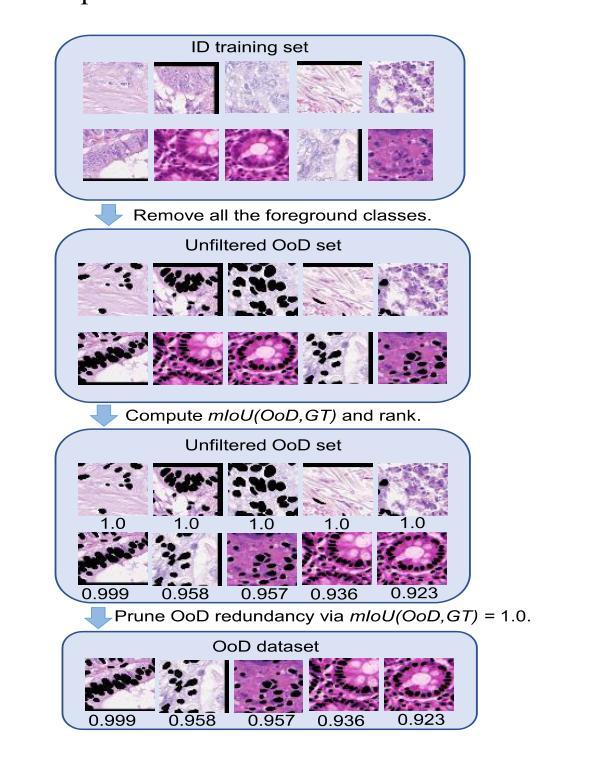
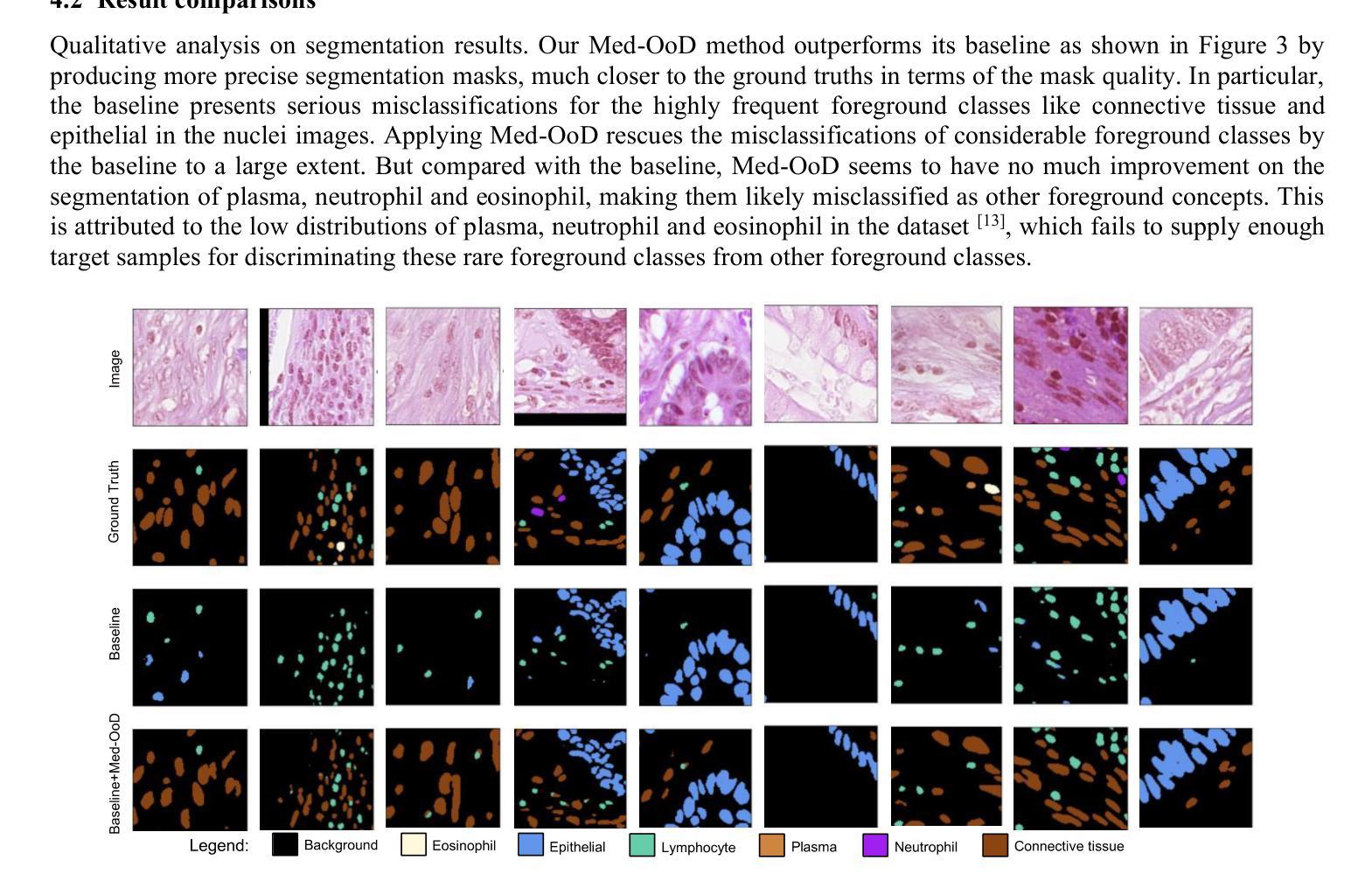
Out-of-distribution data supervision towards biomedical semantic segmentation
Authors:Yiquan Gao, Duohui Xu
Biomedical segmentation networks easily suffer from the unexpected misclassification between foreground and background objects when learning on limited and imperfect medical datasets. Inspired by the strong power of Out-of-Distribution (OoD) data on other visual tasks, we propose a data-centric framework, Med-OoD to address this issue by introducing OoD data supervision into fully-supervised biomedical segmentation with none of the following needs: (i) external data sources, (ii) feature regularization objectives, (iii) additional annotations. Our method can be seamlessly integrated into segmentation networks without any modification on the architectures. Extensive experiments show that Med-OoD largely prevents various segmentation networks from the pixel misclassification on medical images and achieves considerable performance improvements on Lizard dataset. We also present an emerging learning paradigm of training a medical segmentation network completely using OoD data devoid of foreground class labels, surprisingly turning out 76.1% mIoU as test result. We hope this learning paradigm will attract people to rethink the roles of OoD data. Code is made available at https://github.com/StudioYG/Med-OoD.
生物医学分割网络在有限且存在缺陷的医疗数据集上进行学习时,容易受到前景和背景对象之间意外误分类的影响。受其他视觉任务中异常数据(Out-of-Distribution,OoD)强大能力的启发,我们提出了一个以数据为中心的框架Med-OoD,通过引入OoD数据监督来解决这个问题,完全监督生物医学分割,无需以下需求:(i)外部数据源,(ii)特征正则化目标,(iii)额外的注释。我们的方法可以无缝集成到分割网络中,无需对架构进行任何修改。大量实验表明,Med-OoD在很大程度上防止了各种分割网络在医学图像上的像素误分类,并在蜥蜴数据集上实现了显著的性能改进。我们还提出了一种全新的学习范式,即完全使用不含前景类别标签的OoD数据来训练医学分割网络,令人惊讶的是,测试结果为mIoU达到76.1%。我们希望这种学习范式能吸引人们重新思考OoD数据的作用。代码已发布在https://github.com/StudioYG/Med-OoD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE Volume 13442 and is reprinted with permission. The official version is available at https://doi.org/10.1117/12.3052988. One personal copy is allowed. Reproduction, distribution, or commercial use is prohibited
Summary
生物医学分割网络在有限且非完美的医疗数据集上进行学习时,容易出现前景和背景对象之间的意外误分类。受其他视觉任务中异常分布(Out-of-Distribution,OoD)数据强大能力的启发,我们提出了一个以数据为中心的框架Med-OoD,通过引入OoD数据监督来解决这个问题,完全监督生物医学分割,无需以下需求:(i)外部数据源,(ii)特征正则化目标,(iii)额外注释。我们的方法可以无缝集成到分割网络中,无需对架构进行任何修改。大量实验表明,Med-OoD在很大程度上防止了各种分割网络在医学图像上的像素误分类,并在蜥蜴数据集上实现了显著的性能改进。我们还提出了一种全新的学习范式,即完全使用OoD数据训练医学分割网络,无需前景类别标签,令人惊讶的是,测试结果为mIoU 76.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 生物医学分割网络在有限且非完美的医疗数据集上易遭受前景和背景对象误分类的问题。
- 引入Out-of-Distribution (OoD) 数据监督能够提升生物医学分割网络的性能。
- 提出的Med-OoD框架无需外部数据源、特征正则化目标和额外注释。
- Med-OoD框架可无缝集成到分割网络中,无需对架构进行任何修改。
- Med-OoD在医学图像分割中显著减少了像素误分类。
- 在Lizard数据集上,Med-OoD实现了显著的性能改进。
点此查看论文截图

YOLOv8-SMOT: An Efficient and Robust Framework for Real-Time Small Object Tracking via Slice-Assisted Training and Adaptive Association
Authors:Xiang Yu, Xinyao Liu, Guang Liang
Tracking small, agile multi-objects (SMOT), such as birds, from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) perspective is a highly challenging computer vision task. The difficulty stems from three main sources: the extreme scarcity of target appearance features, the complex motion entanglement caused by the combined dynamics of the camera and the targets themselves, and the frequent occlusions and identity ambiguity arising from dense flocking behavior. This paper details our championship-winning solution in the MVA 2025 “Finding Birds” Small Multi-Object Tracking Challenge (SMOT4SB), which adopts the tracking-by-detection paradigm with targeted innovations at both the detection and association levels. On the detection side, we propose a systematic training enhancement framework named \textbf{SliceTrain}. This framework, through the synergy of ‘deterministic full-coverage slicing’ and ‘slice-level stochastic augmentation, effectively addresses the problem of insufficient learning for small objects in high-resolution image training. On the tracking side, we designed a robust tracker that is completely independent of appearance information. By integrating a \textbf{motion direction maintenance (EMA)} mechanism and an \textbf{adaptive similarity metric} combining \textbf{bounding box expansion and distance penalty} into the OC-SORT framework, our tracker can stably handle irregular motion and maintain target identities. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the SMOT4SB public test set, reaching an SO-HOTA score of \textbf{55.205}, which fully validates the effectiveness and advancement of our framework in solving complex real-world SMOT problems. The source code will be made available at https://github.com/Salvatore-Love/YOLOv8-SMOT.
从无人机(UAV)的角度跟踪小型敏捷多目标(SMOT),如鸟类,是一项极具挑战性的计算机视觉任务。难度主要来源于三个方面:目标外观特征的极度稀缺,由相机和目标本身动力学结合导致的复杂运动纠缠,以及由密集集群行为引起的频繁遮挡和身份模糊。本文详细介绍了我们在MVA 2025“寻找鸟类”小型多目标跟踪挑战赛(SMOT4SB)中夺冠的解决方案,该方案采用检测跟踪范式,在检测和关联层面都有针对性创新。在检测方面,我们提出了一个系统的训练增强框架,名为SliceTrain。该框架通过“确定性全覆盖切片”和“切片级随机增强”的协同作用,有效解决了高分辨率图像训练中目标过小导致的训练不足问题。在跟踪方面,我们设计了一个完全独立于外观信息的稳健跟踪器。通过将运动方向维护(EMA)机制和结合边界框扩展和距离惩罚的自适应相似度量融入OC-SORT框架,我们的跟踪器可以稳定处理不规则运动并保持目标身份。我们的方法在SMOT4SB公开测试集上达到了业界领先性能,SO-HOTA得分达到55.205,充分验证了我们的框架在解决复杂现实世界SMOT问题上的有效性和先进性。源代码将发布在https://github.com/Salvatore-Love/YOLOv8-SMOT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在无人飞行器视角中对小型敏捷多目标(如鸟类)进行跟踪的计算机视觉任务的高挑战性和其解决方案。文章详细描述了该团队在MVA 2025“寻找鸟类”小型多目标跟踪挑战赛(SMOT4SB)中的冠军解决方案,该方案采用检测跟踪范式,在检测和关联层面都有针对性创新。针对检测方面的问题,提出了名为SliceTrain的系统性训练增强框架,有效解决了高分辨率图像训练中目标学习不足的问题。在跟踪方面,设计了一个独立于外观信息的稳健跟踪器,通过融入运动方向维护机制和自适应相似性度量标准,实现了对不规则运动的稳定处理和目标身份的维持。该方法在SMOT4SB公开测试集上达到了业界领先水平,SO-HOTA得分为55.205,验证了该框架在解决复杂现实SMOT问题中的有效性和先进性。
Key Takeaways
- 无人飞行器视角对小型敏捷多目标进行跟踪是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战。
- 文章详述了在MVA 2025“寻找鸟类”小型多目标跟踪挑战赛中的冠军解决方案。
- 该方案采用检测跟踪范式,针对检测与关联层面进行创新。
- SliceTrain框架解决了高分辨率图像训练中目标学习不足的问题。
- 设计了一个独立于外观信息的稳健跟踪器,实现对不规则运动的稳定处理和目标身份的维持。
- 跟踪器融合了运动方向维护机制和自适应相似性度量标准。
点此查看论文截图

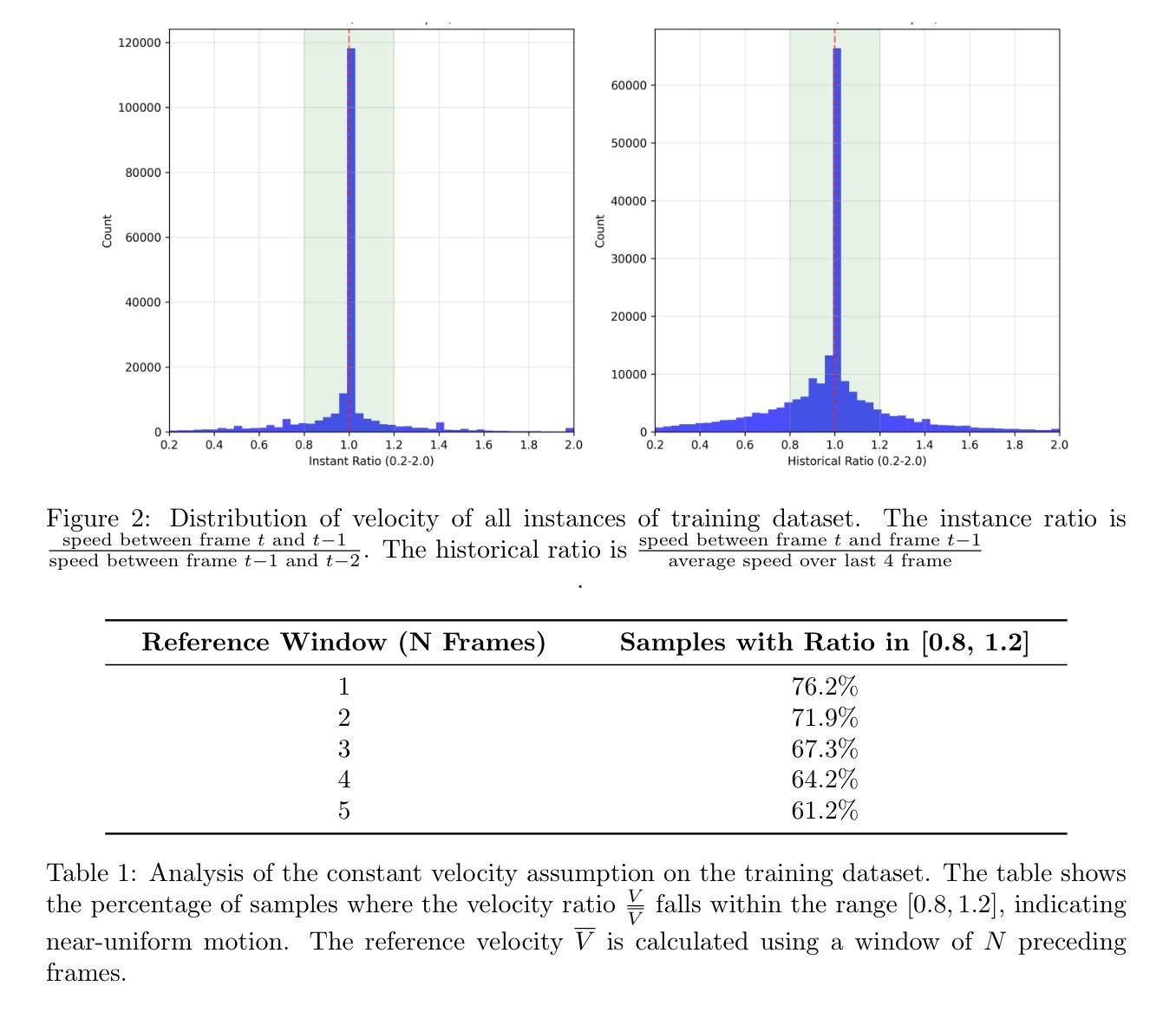
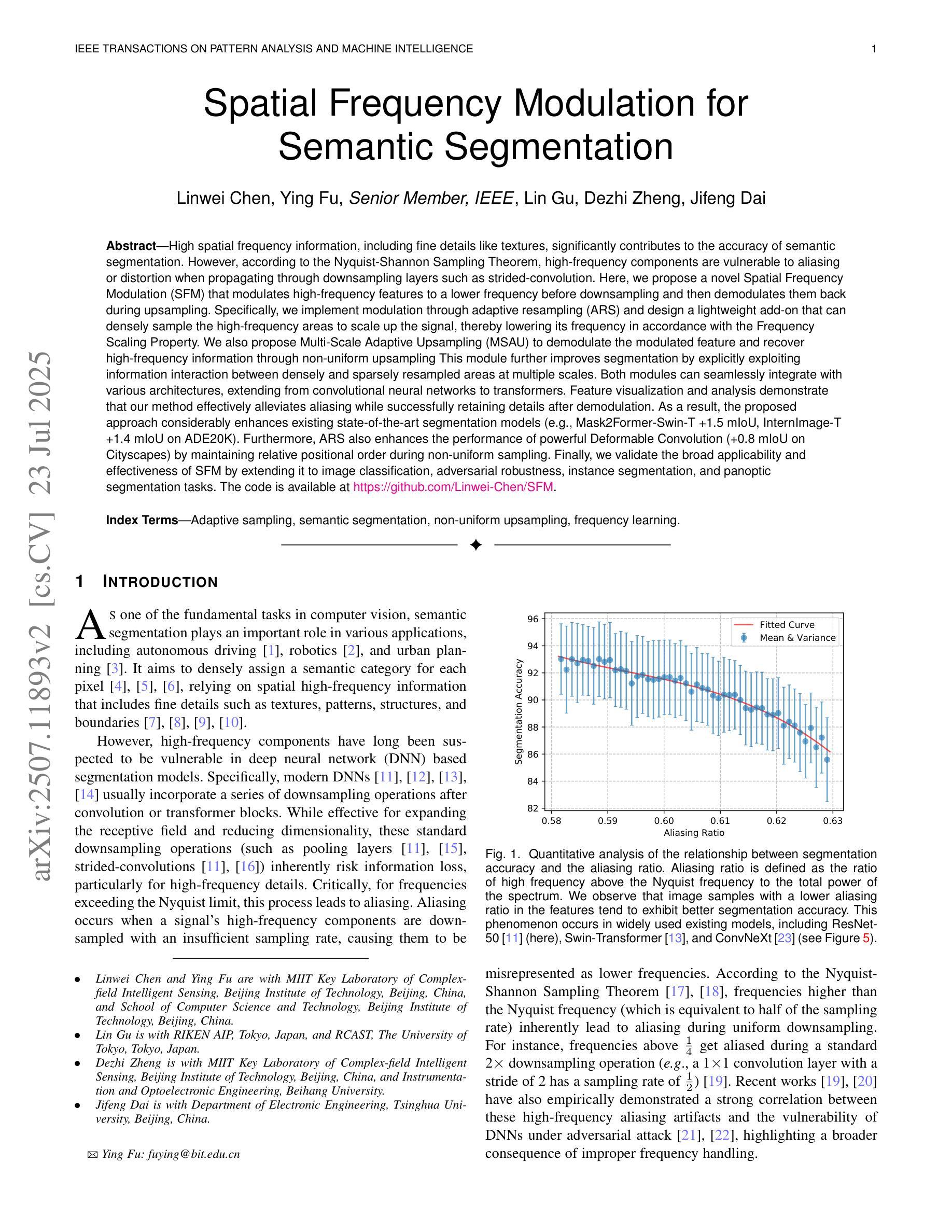
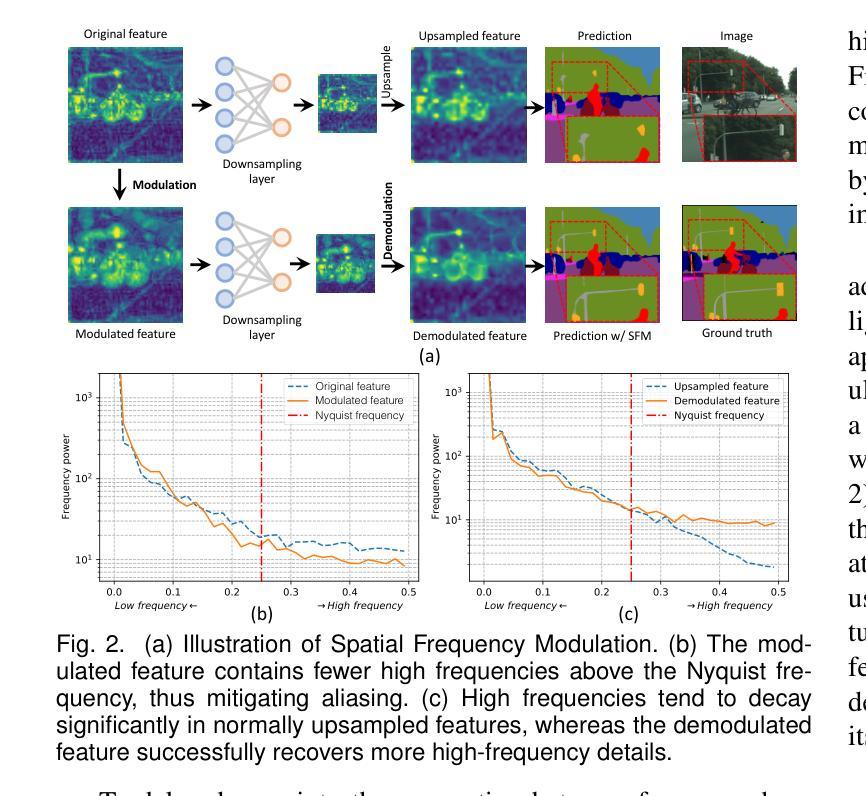
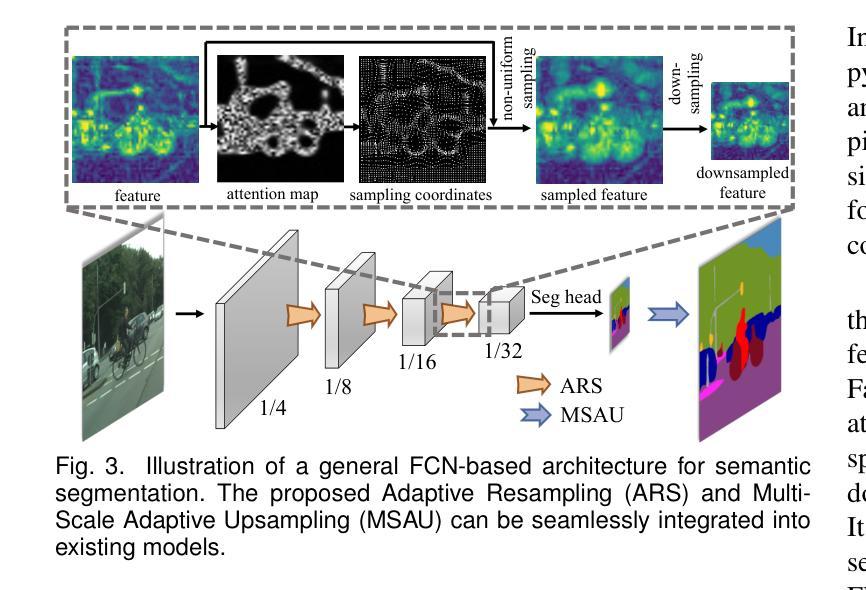
Spatial Frequency Modulation for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Linwei Chen, Ying Fu, Lin Gu, Dezhi Zheng, Jifeng Dai
High spatial frequency information, including fine details like textures, significantly contributes to the accuracy of semantic segmentation. However, according to the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, high-frequency components are vulnerable to aliasing or distortion when propagating through downsampling layers such as strided-convolution. Here, we propose a novel Spatial Frequency Modulation (SFM) that modulates high-frequency features to a lower frequency before downsampling and then demodulates them back during upsampling. Specifically, we implement modulation through adaptive resampling (ARS) and design a lightweight add-on that can densely sample the high-frequency areas to scale up the signal, thereby lowering its frequency in accordance with the Frequency Scaling Property. We also propose Multi-Scale Adaptive Upsampling (MSAU) to demodulate the modulated feature and recover high-frequency information through non-uniform upsampling This module further improves segmentation by explicitly exploiting information interaction between densely and sparsely resampled areas at multiple scales. Both modules can seamlessly integrate with various architectures, extending from convolutional neural networks to transformers. Feature visualization and analysis confirm that our method effectively alleviates aliasing while successfully retaining details after demodulation. Finally, we validate the broad applicability and effectiveness of SFM by extending it to image classification, adversarial robustness, instance segmentation, and panoptic segmentation tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/SFM.
高频空间信息,包括纹理等细节,对语义分割的准确性有很大贡献。然而,根据Nyquist-Shannon采样定理,高频分量在通过步幅卷积等降采样层传播时容易发生混叠或失真。在这里,我们提出了一种新的空间频率调制(SFM)方法,该方法在降采样之前将高频特征调制到较低频率,然后在上采样过程中进行解调。具体来说,我们通过自适应重采样(ARS)实现调制,并设计了一个轻量级的附加组件,可以密集地对高频区域进行采样以扩大信号,从而根据频率缩放属性降低其频率。我们还提出了多尺度自适应上采样(MSAU)来解调调制特征,并通过非均匀上采样恢复高频信息。该模块通过显式利用多个尺度上密集重采样和稀疏重采样区域之间的信息交互,进一步提高了分割效果。这两个模块可以无缝地集成到各种架构中,从卷积神经网络到转换器。特征可视化和分析证实,我们的方法有效地减轻了混叠现象,同时在解调后成功保留了细节。最后,我们通过将其扩展到图像分类、对抗稳健性、实例分割和全视分割任务来验证SFM的广泛适用性和有效性。代码可在https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/SFM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by TPAMI 2025
Summary
本文主要探讨了空间频率对语义分割准确度的影响,提出了空间频率调制(SFM)技术。该技术包括自适应重采样(ARS)和多尺度自适应上采样(MSAU),用于处理高频特征信息的失真问题,并通过实验验证了在多种任务中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 高频信息如纹理对语义分割的准确度有重要贡献。
- Nyquist-Shannon采样定理指出高频成分在传播过程中易受到混叠或失真影响。
- 提出空间频率调制(SFM)技术,通过自适应重采样(ARS)实现高频特征到低频的调制,再通过多尺度自适应上采样(MSAU)进行解调并恢复高频信息。
- 该方法能无缝集成到各种架构中,包括卷积神经网络和转换器。
- 特征可视化和分析证实该方法能有效减轻混叠现象,并在解调后成功保留细节。
- 实验验证了SFM在图像分类、对抗鲁棒性、实例分割和全景分割任务中的广泛应用和有效性。
点此查看论文截图
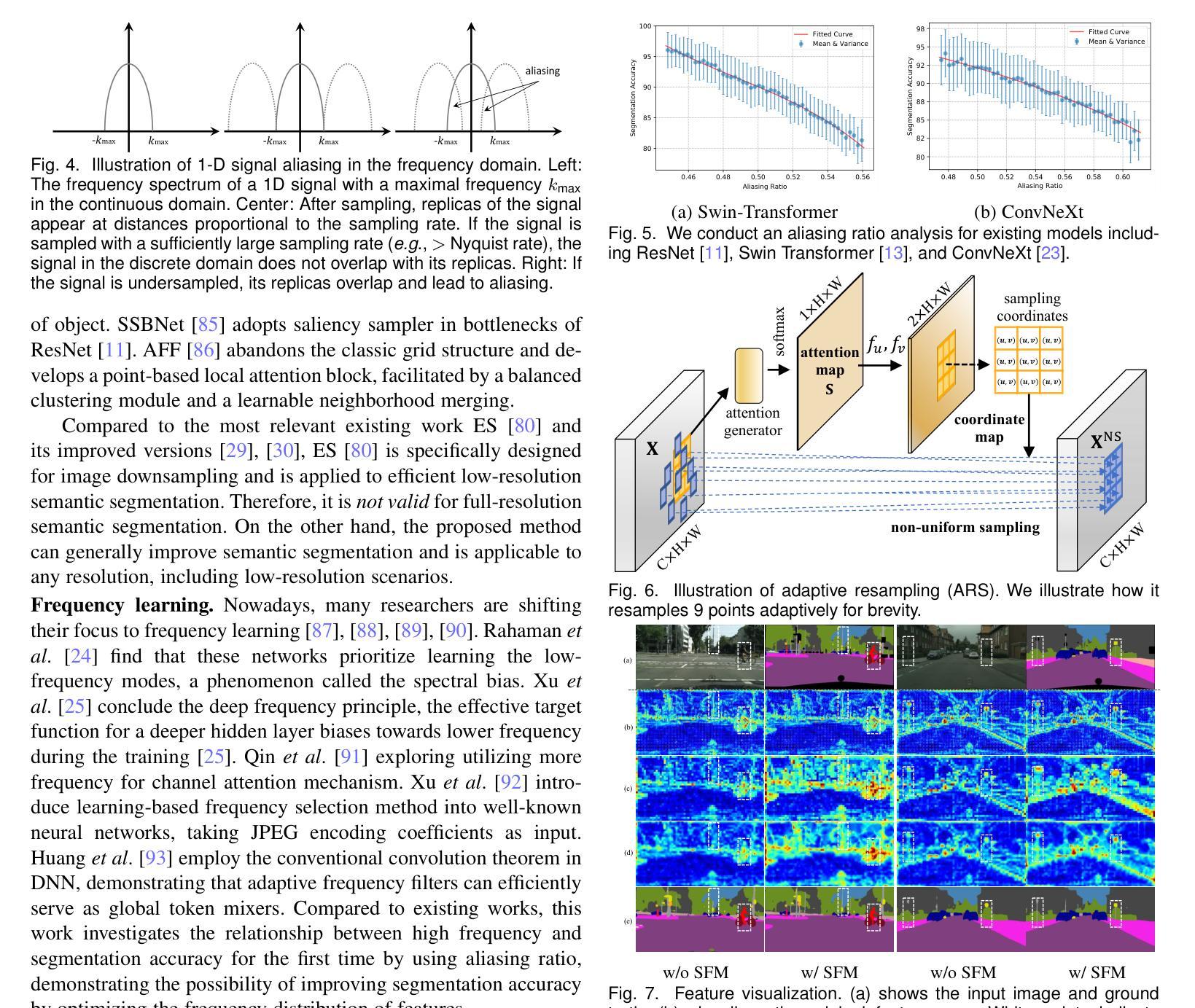
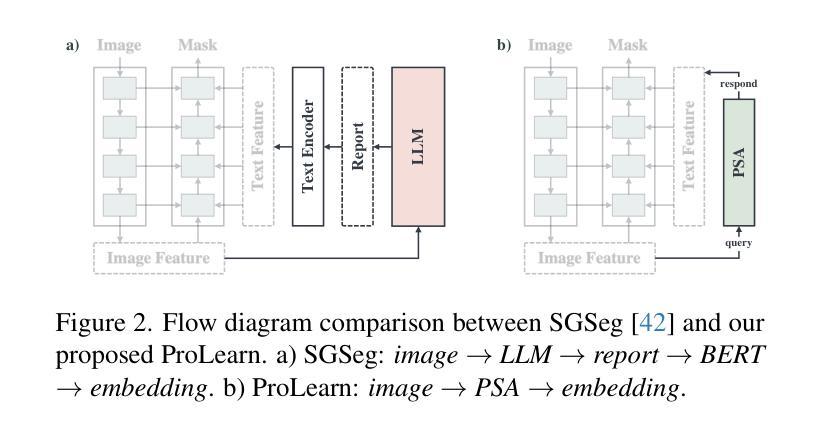
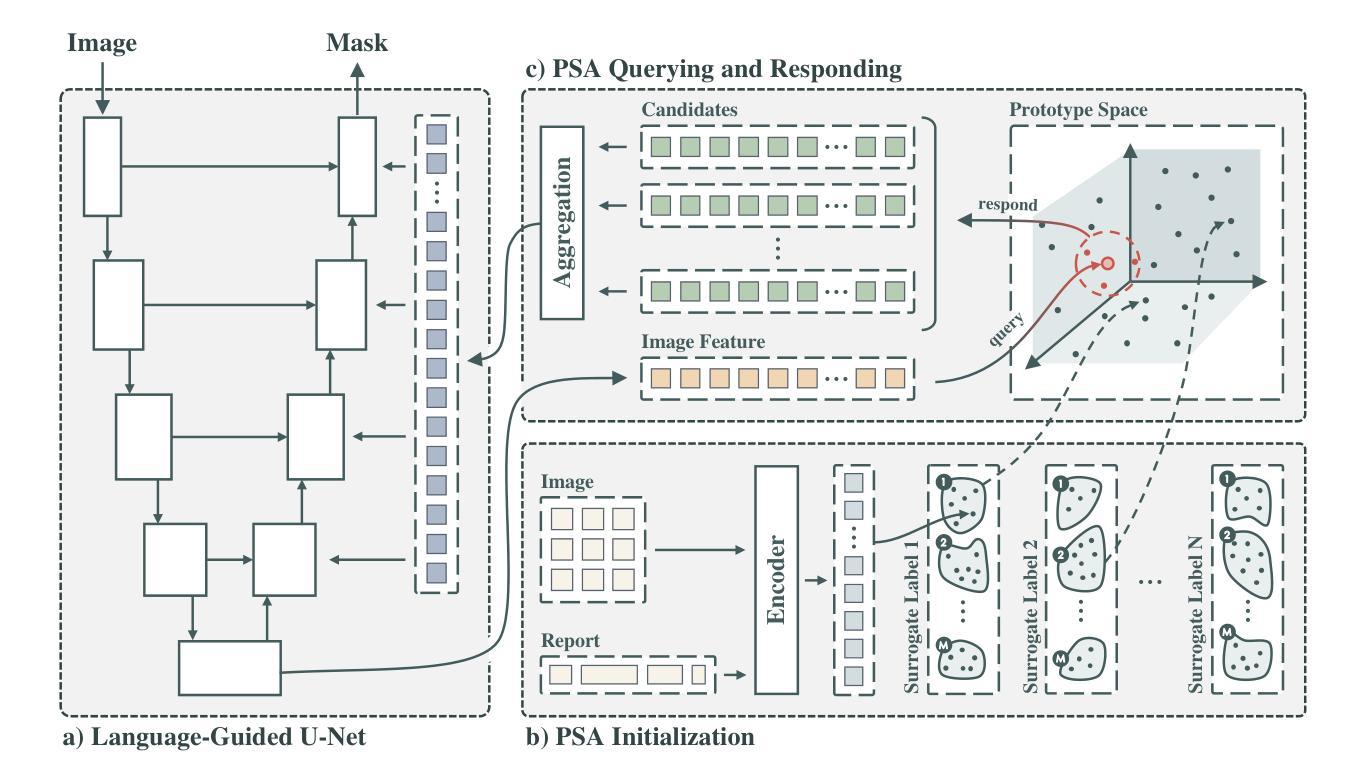
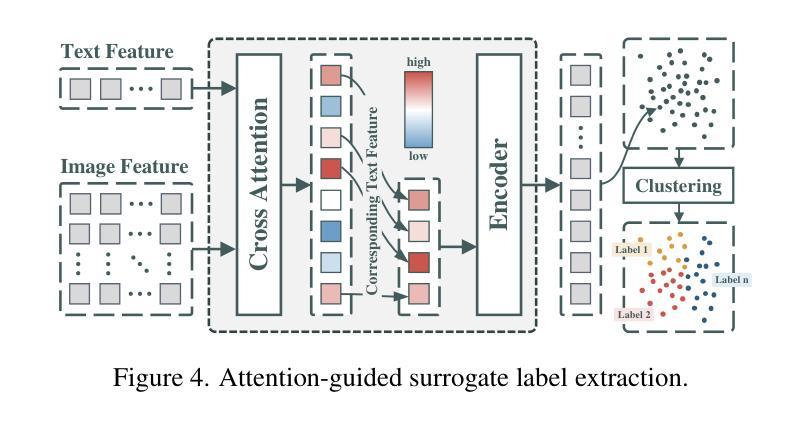
Alleviating Textual Reliance in Medical Language-guided Segmentation via Prototype-driven Semantic Approximation
Authors:Shuchang Ye, Usman Naseem, Mingyuan Meng, Jinman Kim
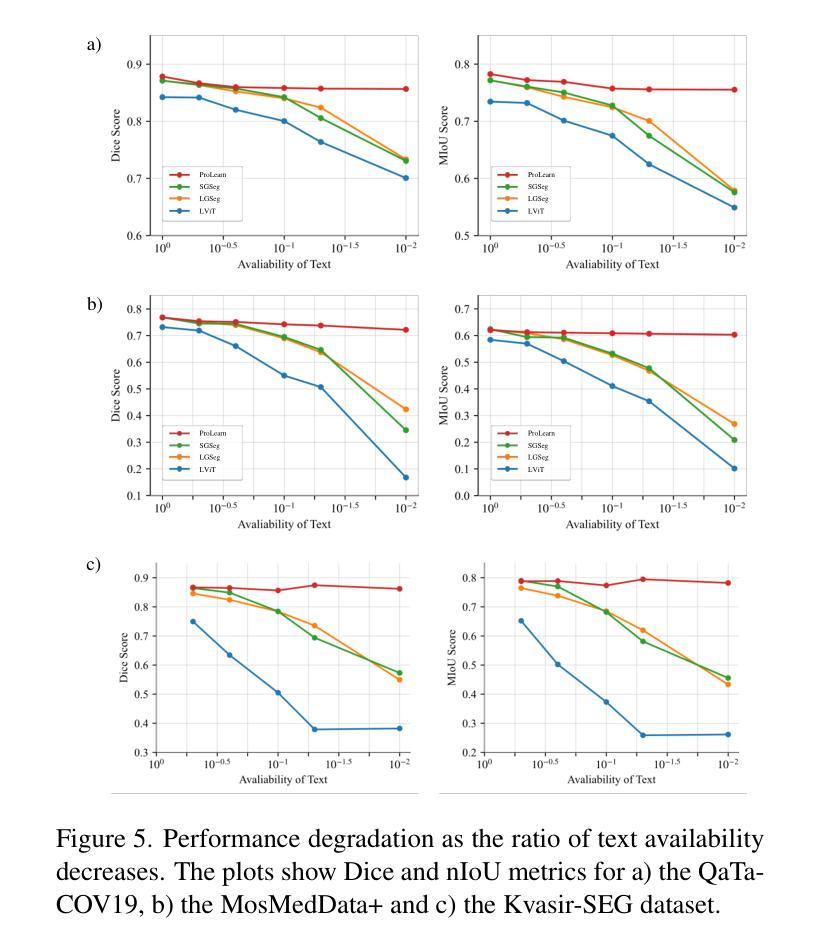
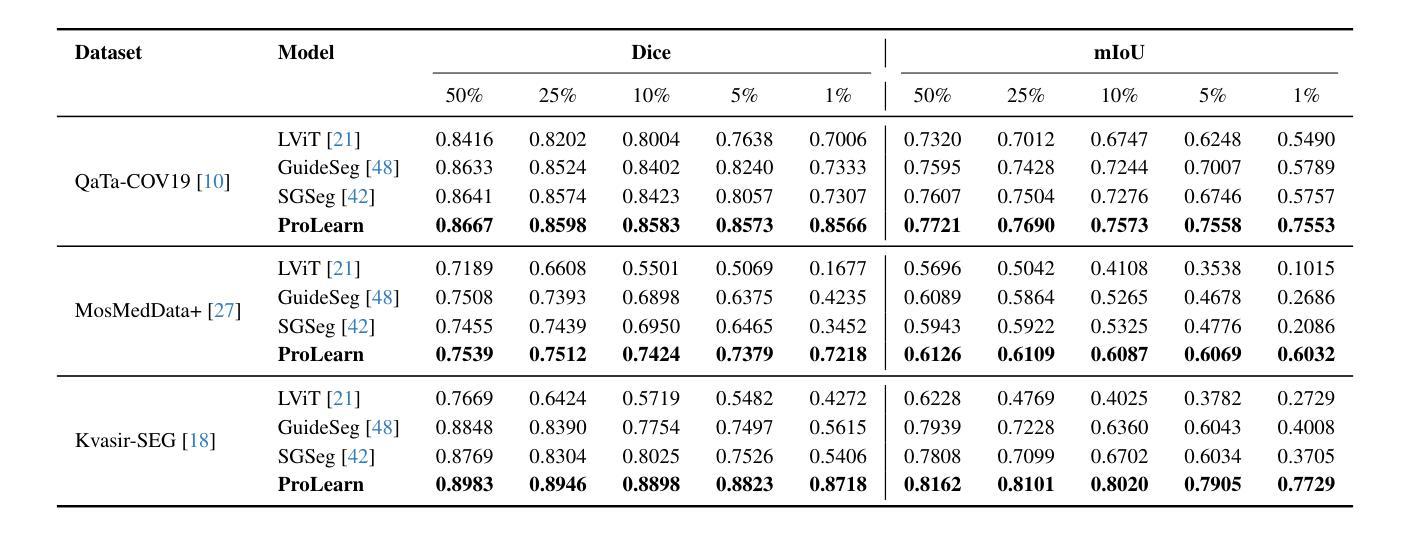
Medical language-guided segmentation, integrating textual clinical reports as auxiliary guidance to enhance image segmentation, has demonstrated significant improvements over unimodal approaches. However, its inherent reliance on paired image-text input, which we refer to as ``textual reliance”, presents two fundamental limitations: 1) many medical segmentation datasets lack paired reports, leaving a substantial portion of image-only data underutilized for training; and 2) inference is limited to retrospective analysis of cases with paired reports, limiting its applicability in most clinical scenarios where segmentation typically precedes reporting. To address these limitations, we propose ProLearn, the first Prototype-driven Learning framework for language-guided segmentation that fundamentally alleviates textual reliance. At its core, we introduce a novel Prototype-driven Semantic Approximation (PSA) module to enable approximation of semantic guidance from textual input. PSA initializes a discrete and compact prototype space by distilling segmentation-relevant semantics from textual reports. Once initialized, it supports a query-and-respond mechanism which approximates semantic guidance for images without textual input, thereby alleviating textual reliance. Extensive experiments on QaTa-COV19, MosMedData+ and Kvasir-SEG demonstrate that ProLearn outperforms state-of-the-art language-guided methods when limited text is available.
医疗语言引导分割技术通过将文本临床报告作为辅助指导来增强图像分割,已经证明其在单模态方法上取得了显著改进。然而,其对配对图像文本输入的固有依赖,我们称之为“文本依赖”,存在两个基本局限:1)许多医疗分割数据集缺乏配对报告,导致大量仅包含图像的数据未能得到充分利用;2)推理仅限于具有配对报告的病例的回顾性分析,限制了其在大多数临床场景中的应用,因为在大多数情况下,分割是在报告之前进行的。为了解决这些局限,我们提出了ProLearn,即首个用于语言引导分割的原型驱动学习框架,从根本上缓解了文本依赖问题。其核心在于,我们引入了一种新型原型驱动语义逼近(PSA)模块,以实现从文本输入中进行语义指导的逼近。PSA通过从文本报告中提炼出与分割相关的语义,初始化一个离散且紧凑的原型空间。初始化完成后,它支持查询和响应机制,能够在没有文本输入的情况下对图像进行语义指导逼近,从而缓解了对文本的依赖。在QaTa-COV19、MosMedData+和Kvasir-SEG上的大量实验表明,当文本有限时,ProLearn在现有语言引导方法中表现最佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
医学语言引导分割技术中,整合文本临床报告作为辅助指导来提升图像分割的效果已显现。然而,其固有依赖于配对图文输入(“文本依赖”)存在两大局限:一是许多医学分割数据集缺乏配对报告,导致大量仅图像数据未被充分利用于训练;二是推理仅限于有配对报告的回顾性案例分析,限制了其在大多数临床场景中的应用。为解决这个问题,我们提出ProLearn——首个原型驱动的学习框架用于语言引导分割,从根本上减轻文本依赖。其核心引入新颖的原型驱动语义近似模块,实现文本输入语义指导的近似。PSA通过蒸馏报告中的分割相关语义,初始化一个离散且紧凑的原型空间。初始化后,它支持查询和响应机制,为无文本输入的图像近似语义指导,从而减轻文本依赖。在QaTa-COV19、MosMedData+和Kvasir-SEG上的广泛实验证明,当文本有限时,ProLearn表现优于先进的语言引导方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学语言引导分割技术结合文本临床报告来提升图像分割效果。
- 该技术存在对配对图文输入的依赖,导致数据利用和实际应用场景受限。
- 提出ProLearn框架,通过原型驱动学习减轻对文本依赖。
- ProLearn引入原型驱动语义近似模块,实现文本语义指导的近似。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation for Weakly-Supervised Low-Light Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chunyan Wang, Dong Zhang, Jinhui Tang
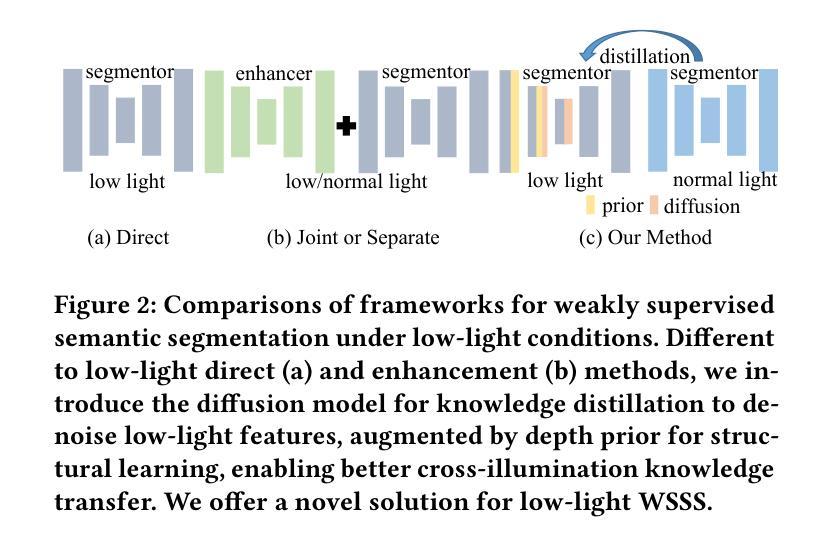
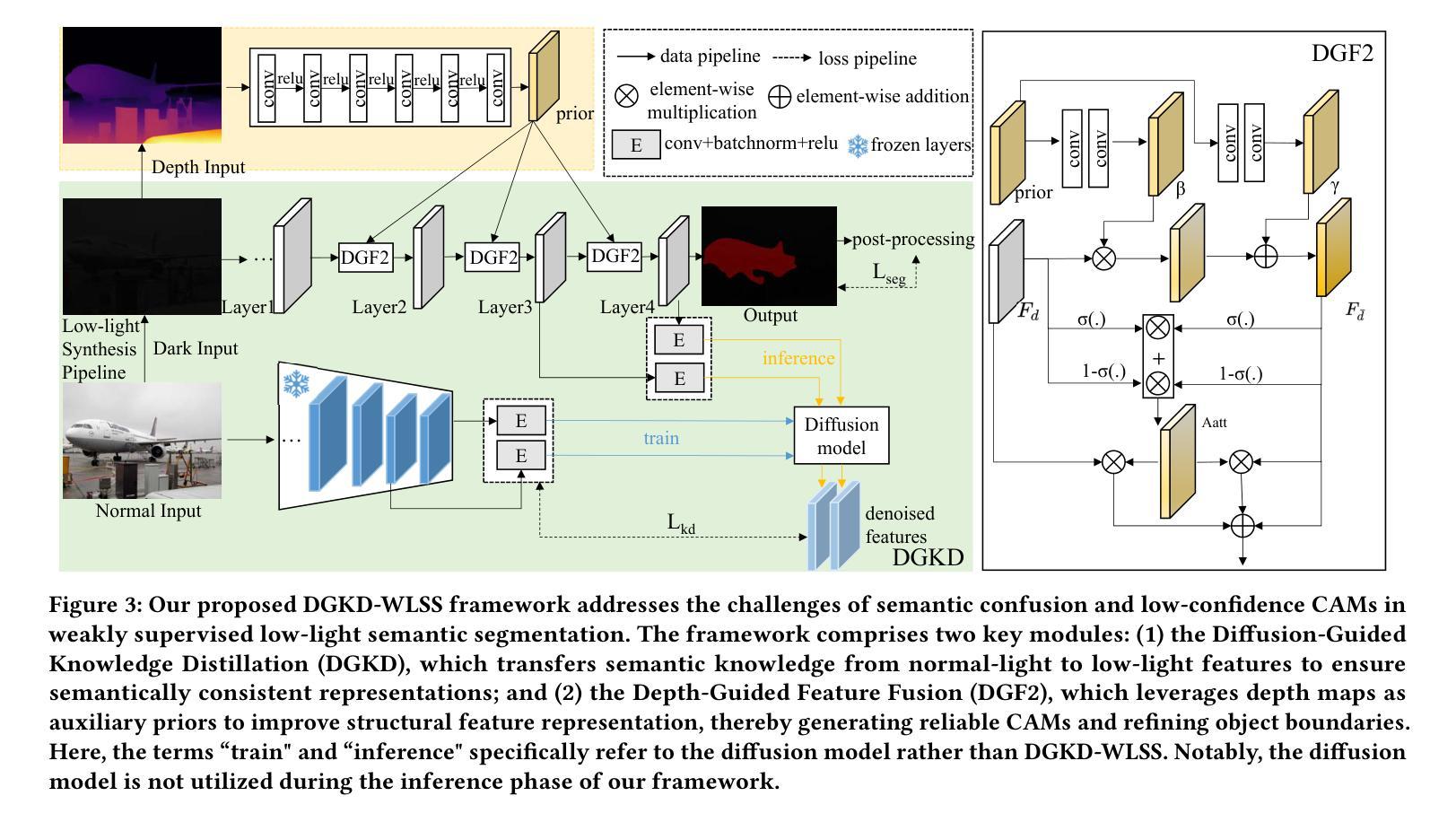
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation aims to assign category labels to each pixel using weak annotations, significantly reducing manual annotation costs. Although existing methods have achieved remarkable progress in well-lit scenarios, their performance significantly degrades in low-light environments due to two fundamental limitations: severe image quality degradation (e.g., low contrast, noise, and color distortion) and the inherent constraints of weak supervision. These factors collectively lead to unreliable class activation maps and semantically ambiguous pseudo-labels, ultimately compromising the model’s ability to learn discriminative feature representations. To address these problems, we propose Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation for Weakly-Supervised Low-light Semantic Segmentation (DGKD-WLSS), a novel framework that synergistically combines Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation (DGKD) with Depth-Guided Feature Fusion (DGF2). DGKD aligns normal-light and low-light features via diffusion-based denoising and knowledge distillation, while DGF2 integrates depth maps as illumination-invariant geometric priors to enhance structural feature learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DGKD-WLSS, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in weakly supervised semantic segmentation tasks under low-light conditions. The source codes have been released at:https://github.com/ChunyanWang1/DGKD-WLSS.
弱监督语义分割旨在利用弱标注为每个像素分配类别标签,从而显著降低手动标注成本。尽管现有方法在全光照场景下取得了显著的进步,但在低光环境中,由于两个基本局限性,它们的性能会显著下降:严重的图像质量下降(例如,低对比度、噪声和颜色失真)和弱监督的内在约束。这些因素共同作用,导致不可靠的类激活图和语义模糊的伪标签,最终损害模型学习判别特征表示的能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了用于弱监督低光语义分割的扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD-WLSS)这一新型框架,它协同结合了扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD)和深度引导特征融合(DGF2)。DGKD通过基于扩散的去噪和知识蒸馏对齐正常光和低光特征,而DGF2将深度图作为光照不变的几何先验进行集成,以增强结构特征学习。大量实验表明DGKD-WLSS的有效性,它在低光条件下的弱监督语义分割任务中实现了最佳性能。源代码已发布在:https://github.com/ChunyanWang1/DGKD-WLSS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM Multimedia
Summary
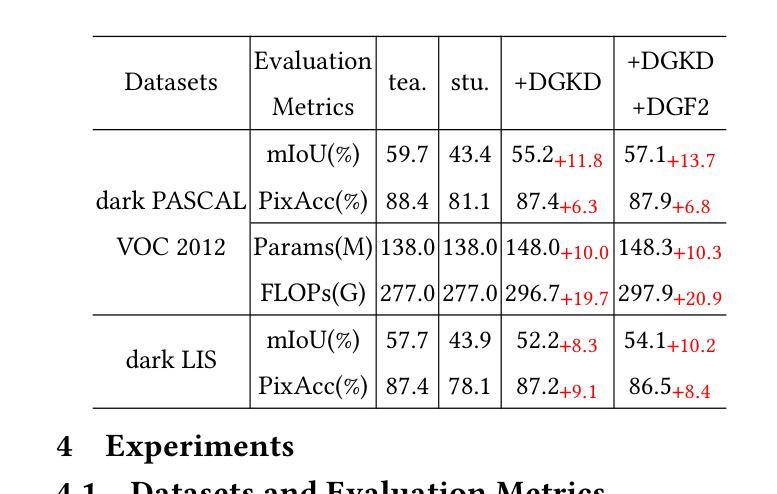
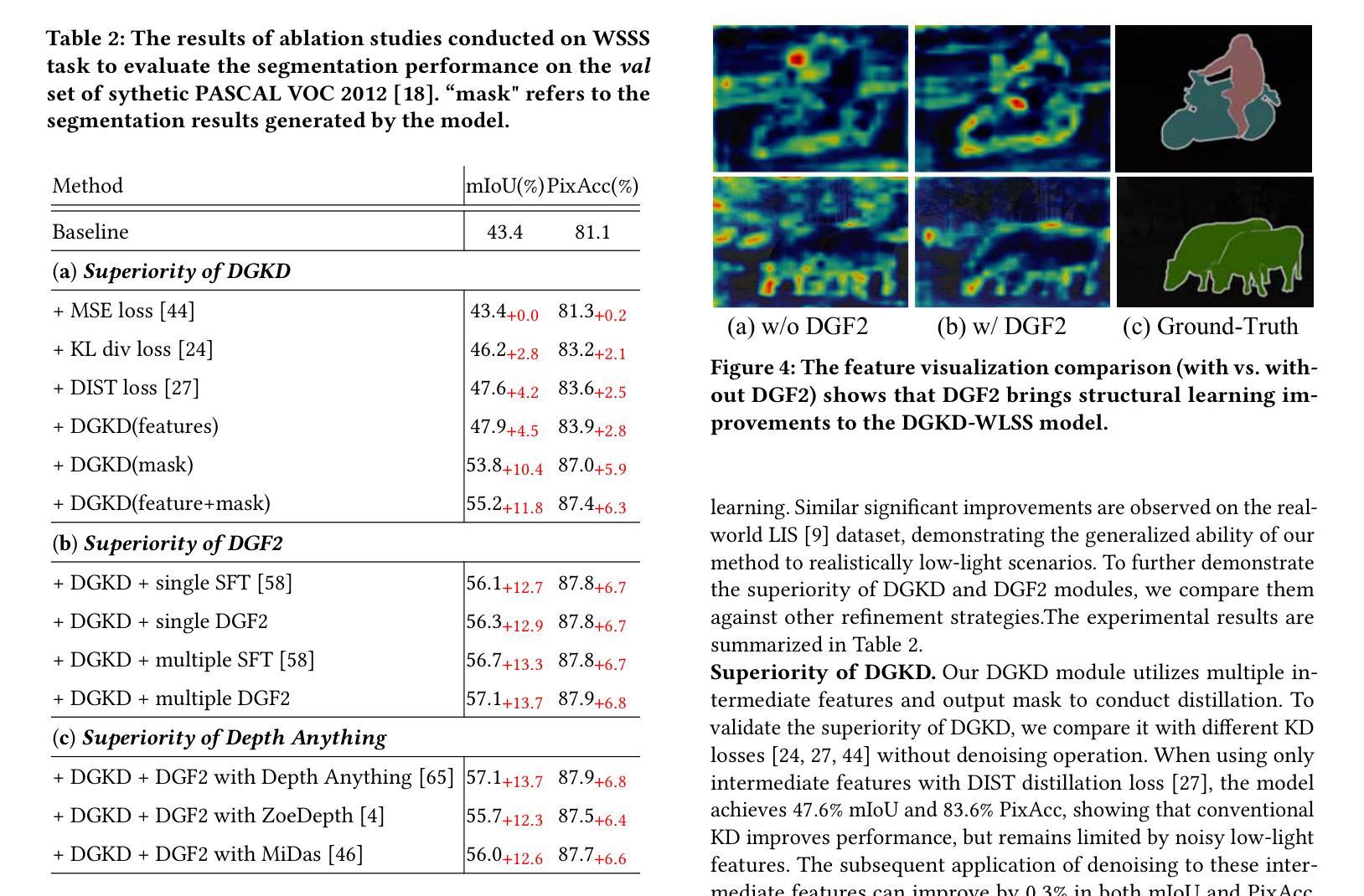
弱监督语义分割利用弱标注对每像素分配类别标签,显著降低手动标注成本。现有方法在光照充足场景中取得显著进展,但在低光环境下性能下降,主要由于图像质量严重退化和弱监督的内在约束。为解决这些问题,提出结合扩散引导知识蒸馏和深度引导特征融合的框架(DGKD-WLSS),通过扩散去噪和知识蒸馏对齐正常光和低光特征,同时利用深度图增强结构特征学习。DGKD-WLSS在弱监督语义分割任务中实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割旨在利用弱标注降低手动标注成本。
- 在低光环境下,现有方法性能下降,主要由于图像质量退化和弱监督约束。
- DGKD-WLSS框架结合扩散引导知识蒸馏和深度引导特征融合。
- 扩散去噪和知识蒸馏用于对齐正常光和低光特征。
- 深度图作为照明不变几何先验增强结构特征学习。
- DGKD-WLSS在弱监督语义分割任务中实现最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Accurate and Efficient 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving: A Mixture of Experts Computing System on Edge
Authors:Linshen Liu, Boyan Su, Junyue Jiang, Guanlin Wu, Cong Guo, Ceyu Xu, Hao Frank Yang
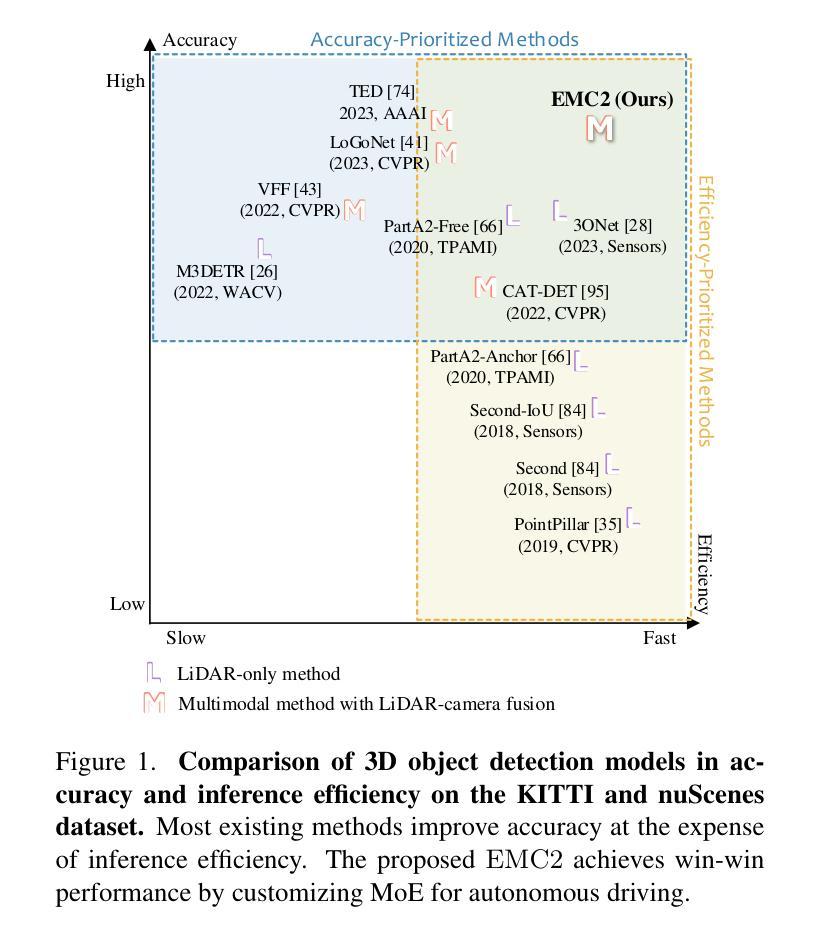
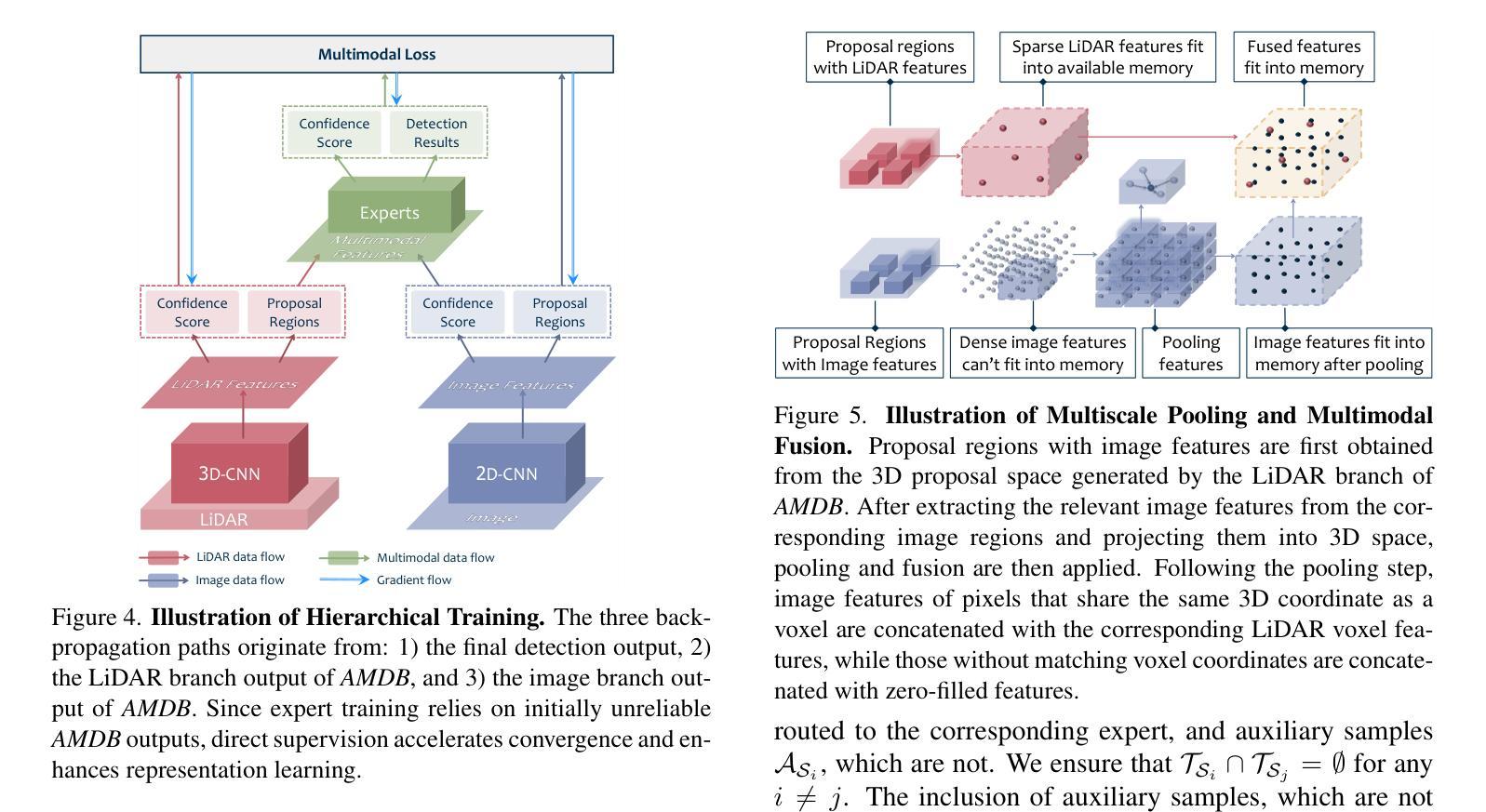
This paper presents Edge-based Mixture of Experts (MoE) Collaborative Computing (EMC2), an optimal computing system designed for autonomous vehicles (AVs) that simultaneously achieves low-latency and high-accuracy 3D object detection. Unlike conventional approaches, EMC2 incorporates a scenario-aware MoE architecture specifically optimized for edge platforms. By effectively fusing LiDAR and camera data, the system leverages the complementary strengths of sparse 3D point clouds and dense 2D images to generate robust multimodal representations. To enable this, EMC2 employs an adaptive multimodal data bridge that performs multi-scale preprocessing on sensor inputs, followed by a scenario-aware routing mechanism that dynamically dispatches features to dedicated expert models based on object visibility and distance. In addition, EMC2 integrates joint hardware-software optimizations, including hardware resource utilization optimization and computational graph simplification, to ensure efficient and real-time inference on resource-constrained edge devices. Experiments on open-source benchmarks clearly show the EMC2 advancements as an end-to-end system. On the KITTI dataset, it achieves an average accuracy improvement of 3.58% and a 159.06% inference speedup compared to 15 baseline methods on Jetson platforms, with similar performance gains on the nuScenes dataset, highlighting its capability to advance reliable, real-time 3D object detection tasks for AVs. The official implementation is available at https://github.com/LinshenLiu622/EMC2.
本文提出了基于边缘计算的混合专家(MoE)协同计算(EMC2)系统,这是一种专为自动驾驶车辆设计的优化计算系统,可同时进行低延迟和高精度的3D目标检测。与传统的不同,EMC2采用了针对边缘平台的场景感知MoE架构。通过有效地融合激光雷达和相机数据,系统利用稀疏的3D点云和密集的2D图像的优势,生成稳健的多模态表示。为此,EMC2采用自适应多模态数据桥进行多尺度预处理传感器输入,然后通过场景感知路由机制根据目标可见性和距离动态地将特征调度到专用的专家模型。此外,EMC2集成了联合硬件软件优化,包括硬件资源利用优化和计算图简化,以确保在资源受限的边缘设备上实现高效实时的推理。在开源基准测试上的实验清楚地表明了EMC2作为端到端系统的优势。在KITTI数据集上,与Jetson平台上的15种基线方法相比,其平均精度提高了3.58%,推理速度提高了159.06%,在nuscenes数据集上也取得了类似的性能提升,这突显了其在推动可靠、实时的自动驾驶车辆3D目标检测任务方面的能力。官方实现可在https://github.com/LinshenLiu622/EMC2获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary:
本文提出了基于边缘计算的混合专家协作计算系统(EMC2),专为自动驾驶车辆设计,可实现低延迟、高准确度的3D目标检测。EMC2采用情景感知的混合专家架构,优化边缘平台,结合激光雷达和相机数据,利用稀疏的3D点云和密集的2D图像生成稳健的多模式表示。通过自适应多模式数据桥和多尺度预处理,以及基于目标可见性和距离的情景感知路由机制,将特性动态分派给专用专家模型。此外,EMC2还集成了联合软硬件优化,包括硬件资源利用优化和计算图简化,以确保在资源受限的边缘设备上实现高效、实时的推理。在KITTI和nuscenes数据集上的实验表明,与基线方法相比,EMC2在准确性上有所提高,推理速度加快。
Key Takeaways:
- EMC2是一个为自动驾驶车辆设计的计算系统,实现低延迟、高准确度的3D目标检测。
- 采用情景感知的混合专家架构,优化边缘平台。
- 结合激光雷达和相机数据,生成稳健的多模式表示。
- 通过自适应多模式数据桥和多尺度预处理,以及情景感知路由机制,实现特性动态分配。
- EMC2集成了联合软硬件优化,包括硬件资源利用优化和计算图简化。
- 在KITTI和nuscenes数据集上,EMC2在准确性和推理速度上均有所改进。
点此查看论文截图


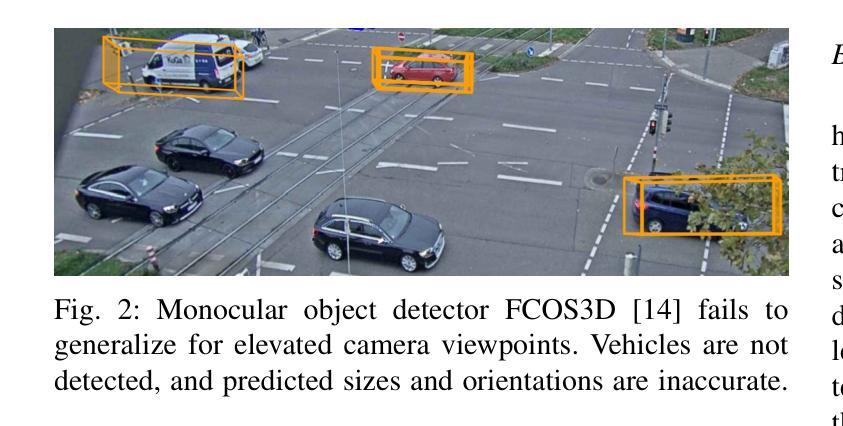
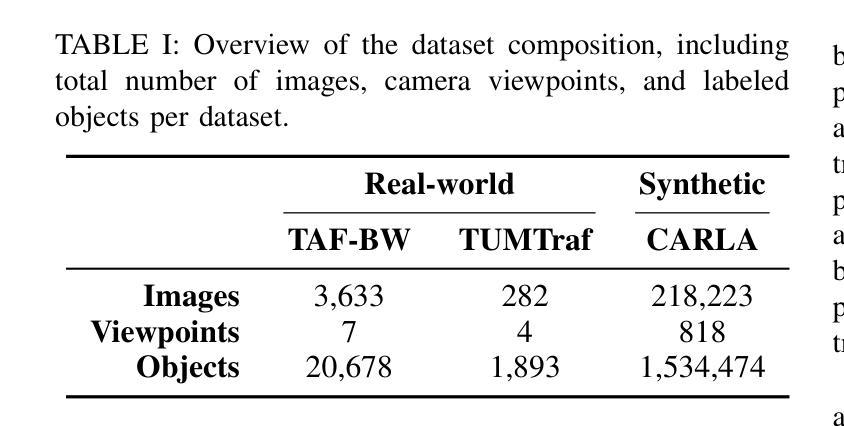
2.5D Object Detection for Intelligent Roadside Infrastructure
Authors:Nikolai Polley, Yacin Boualili, Ferdinand Mütsch, Maximilian Zipfl, Tobias Fleck, J. Marius Zöllner
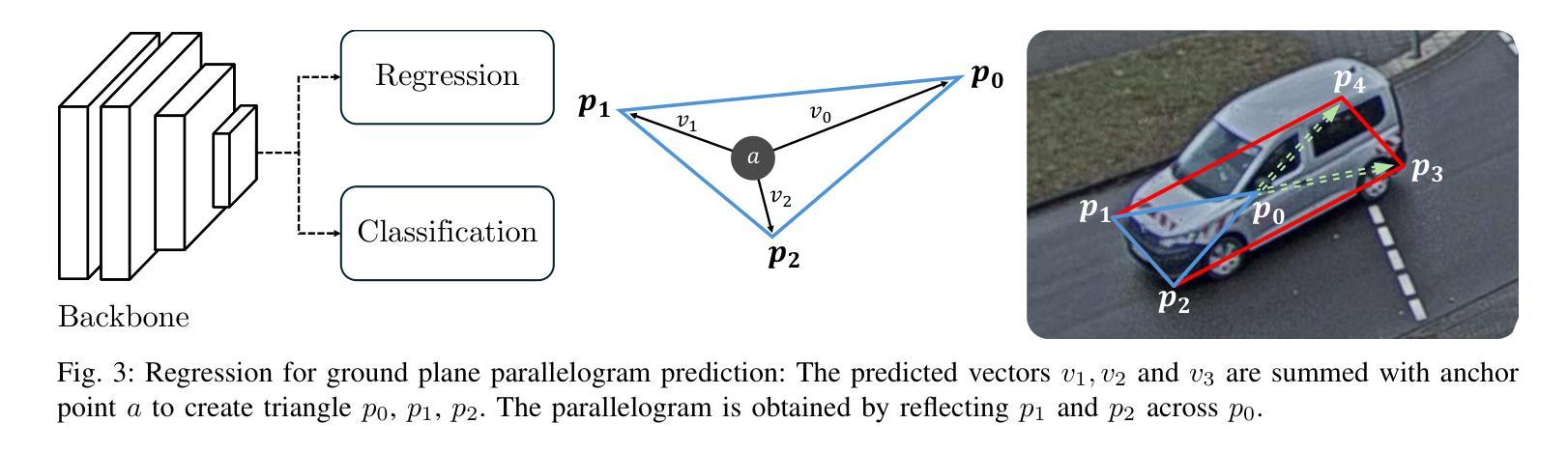
On-board sensors of autonomous vehicles can be obstructed, occluded, or limited by restricted fields of view, complicating downstream driving decisions. Intelligent roadside infrastructure perception systems, installed at elevated vantage points, can provide wide, unobstructed intersection coverage, supplying a complementary information stream to autonomous vehicles via vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. However, conventional 3D object-detection algorithms struggle to generalize under the domain shift introduced by top-down perspectives and steep camera angles. We introduce a 2.5D object detection framework, tailored specifically for infrastructure roadside-mounted cameras. Unlike conventional 2D or 3D object detection, we employ a prediction approach to detect ground planes of vehicles as parallelograms in the image frame. The parallelogram preserves the planar position, size, and orientation of objects while omitting their height, which is unnecessary for most downstream applications. For training, a mix of real-world and synthetically generated scenes is leveraged. We evaluate generalizability on a held-out camera viewpoint and in adverse-weather scenarios absent from the training set. Our results show high detection accuracy, strong cross-viewpoint generalization, and robustness to diverse lighting and weather conditions. Model weights and inference code are provided at: https://gitlab.kit.edu/kit/aifb/ATKS/public/digit4taf/2.5d-object-detection
自动驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能会受到遮挡、视线受限或其他障碍物的干扰,从而增加下游驾驶决策的难度。安装在有利位置的智能路边基础设施感知系统可以提供宽阔、无遮挡的交叉路口覆盖范围,并通过车对万物(V2X)通信为自动驾驶车辆提供补充信息流。然而,传统的三维物体检测算法在自上而下视角和陡峭相机角度引入的域偏移下难以进行泛化。我们引入了一个针对基础设施路边安装的相机专门设计的2.5D物体检测框架。与传统的二维或三维物体检测不同,我们采用预测方法来检测图像帧中的车辆地面平面作为平行四边形。平行四边形保留了物体的平面位置、大小和方位,同时省略了高度信息,这在大多数下游应用中是不必要的。我们利用现实场景和合成场景的结合进行训练。我们在不包括训练集的另一相机视角和恶劣天气场景下评估泛化能力。我们的结果展示了较高的检测精度、较强的跨视角泛化能力以及在不同光线和天气条件下的鲁棒性。模型权重和推理代码可以在以下网址找到:https://gitlab.kit.edu/kit/aifb/ATKS/public/digit4taf/2.5d-object-detection
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2025 IEEE 28th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC)
Summary:
自主驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能会受到遮挡、视野受限等影响,导致驾驶决策困难。智能路边感知系统可以安装在高位观察点,提供无遮挡的交叉口覆盖,并通过车对万物(V2X)通信为自主驾驶车辆提供补充信息。然而,传统的3D目标检测算法在应对由顶部向下视角和陡峭相机角度引起的领域变化时难以实现通用化。为此,我们提出了一种2.5D目标检测框架,专门用于路边基础设施安装的相机。我们采用预测方法检测车辆的地面平面,将其表示为图像帧中的平行四边形。平行四边形保留了物体的平面位置、大小和方向,同时省略了高度信息,这对于大多数下游应用来说是不必要的。我们使用真实场景和合成场景的组合数据进行训练,并在未参与训练的相机视角和恶劣天气场景下评估其通用性和鲁棒性。结果显示,该方法的检测精度高、跨视角通用性强,对不同的光照和天气条件具有稳健性。
Key Takeaways:
- 自主驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能受到遮挡或视野限制,导致驾驶决策复杂化。
- 智能路边基础设施感知系统可提供无遮挡的交叉口视图,通过V2X通信为自主驾驶车辆提供补充信息。
- 传统3D目标检测算法在应对领域变化时难以实现通用化,需要特定的2.5D目标检测框架。
- 提出的2.5D目标检测框架采用预测方法检测车辆的地面平面,表示为图像帧中的平行四边形。
- 该框架具有高度的检测精度和跨视角的通用性。
- 框架对不同的光照和天气条件具有稳健性,能够在恶劣天气场景下进行有效检测。
点此查看论文截图



UPRE: Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation for Object Detection via Unified Prompt and Representation Enhancement
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Fei Wei, Yong Wang, Wenda Zhao, Feiyi Li, Xiangxiang Chu
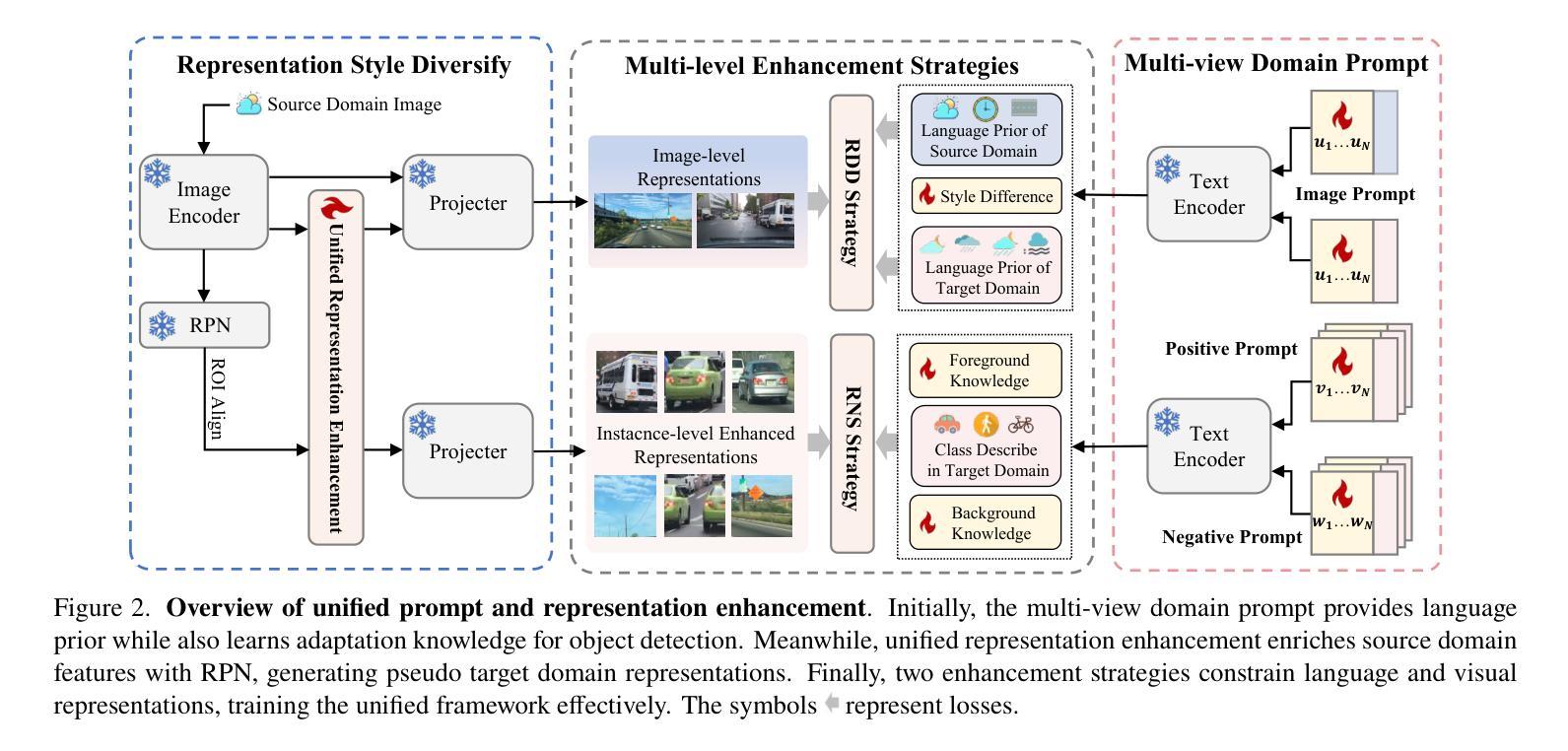
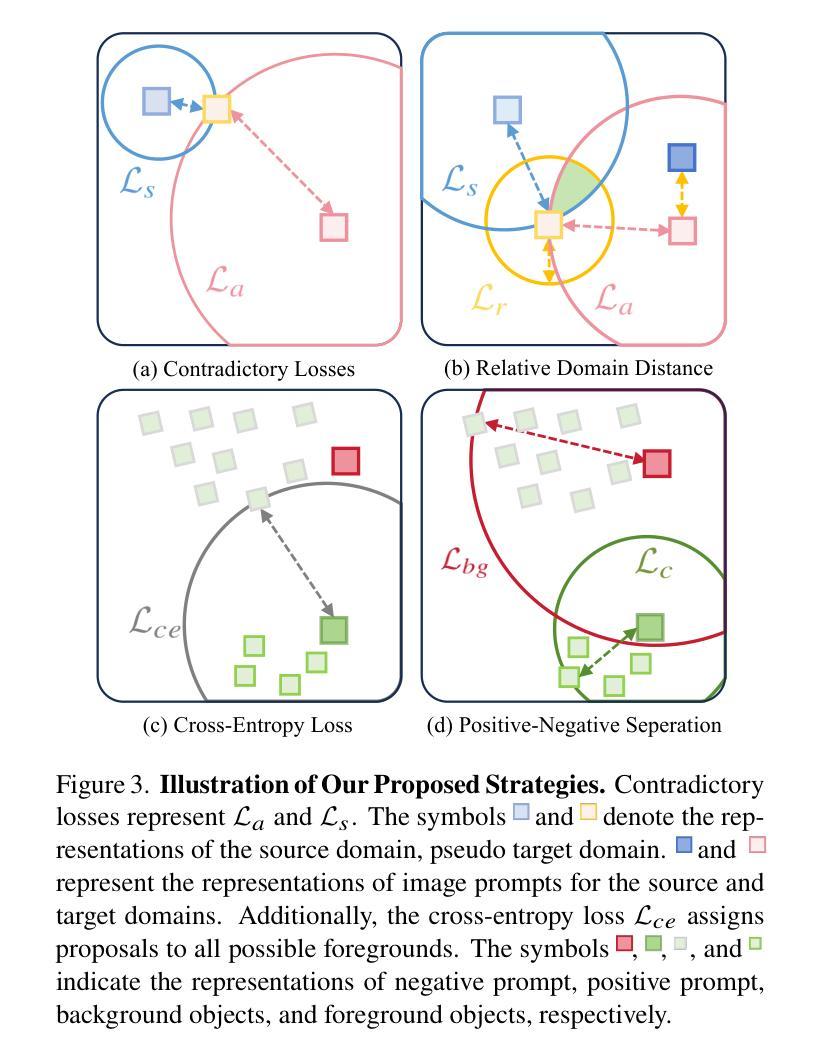
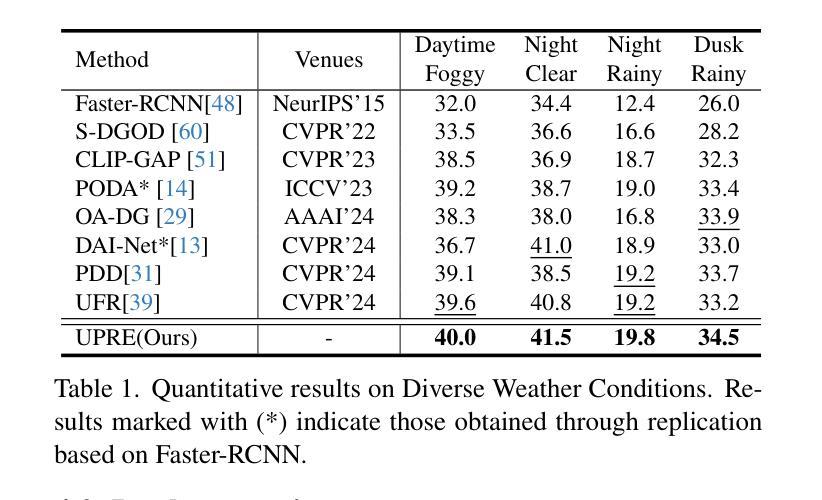
Zero-shot domain adaptation (ZSDA) presents substantial challenges due to the lack of images in the target domain. Previous approaches leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to tackle this challenge, exploiting their zero-shot learning capabilities. However, these methods primarily address domain distribution shifts and overlook the misalignment between the detection task and VLMs, which rely on manually crafted prompts. To overcome these limitations, we propose the unified prompt and representation enhancement (UPRE) framework, which jointly optimizes both textual prompts and visual representations. Specifically, our approach introduces a multi-view domain prompt that combines linguistic domain priors with detection-specific knowledge, and a visual representation enhancement module that produces domain style variations. Furthermore, we introduce multi-level enhancement strategies, including relative domain distance and positive-negative separation, which align multi-modal representations at the image level and capture diverse visual representations at the instance level, respectively. Extensive experiments conducted on nine benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our framework in ZSDA detection scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE.
零样本域自适应(ZSDA)由于缺乏目标域的图像而面临巨大挑战。之前的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)来解决这一挑战,利用其零样本学习能力。然而,这些方法主要解决域分布转移问题,而忽视了检测任务与VLMs之间的不匹配,后者依赖于手工制作的提示。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,该框架联合优化文本提示和视觉表示。具体来说,我们的方法引入了一种多视角域提示,它将语言域先验知识与检测特定知识相结合,以及一种视觉表示增强模块,用于生成域风格变化。此外,我们引入了多层次增强策略,包括相对域距离和正负分离,分别在图像级别对齐多模式表示,并在实例级别捕获多样化的视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在ZSDA检测场景中具有卓越的性能。代码可访问于 https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
文本介绍了零样本领域自适应(ZSDA)面临的挑战,尤其是目标领域缺乏图像的问题。为了解决这一问题,文章提出了一个统一的提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,该框架联合优化了文本提示和视觉表示。UPRE框架通过引入多视角领域提示和视觉表示增强模块来解决领域分布变化和检测任务与视觉语言模型之间的不匹配问题。此外,还引入了多层次增强策略,包括相对领域距离和正负分离,以在图像级别对齐多模式表示并在实例级别捕获多样化的视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上的实验表明,UPRE框架在ZSDA检测场景中表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ZSDA面临目标领域缺乏图像的挑战。
- UPRE框架通过联合优化文本提示和视觉表示来解决这个问题。
- UPRE引入多视角领域提示,结合语言领域先验知识和检测特定知识。
- UPRE框架包含视觉表示增强模块,用于生成领域风格变化。
- 多层次增强策略包括相对领域距离和正负分离,用于对齐多模式表示并捕获多样化的视觉表示。
- 在九个基准数据集上的实验表明UPRE框架在ZSDA检测场景中性能卓越。
点此查看论文截图

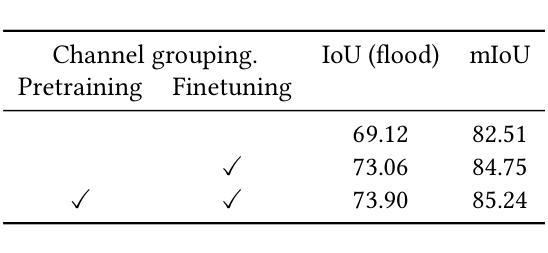
Position Prediction Self-Supervised Learning for Multimodal Satellite Imagery Semantic Segmentation
Authors:John Waithaka, Moise Busogi
Semantic segmentation of satellite imagery is crucial for Earth observation applications, but remains constrained by limited labelled training data. While self-supervised pretraining methods like Masked Autoencoders (MAE) have shown promise, they focus on reconstruction rather than localisation-a fundamental aspect of segmentation tasks. We propose adapting LOCA (Location-aware), a position prediction self-supervised learning method, for multimodal satellite imagery semantic segmentation. Our approach addresses the unique challenges of satellite data by extending SatMAE’s channel grouping from multispectral to multimodal data, enabling effective handling of multiple modalities, and introducing same-group attention masking to encourage cross-modal interaction during pretraining. The method uses relative patch position prediction, encouraging spatial reasoning for localisation rather than reconstruction. We evaluate our approach on the Sen1Floods11 flood mapping dataset, where it significantly outperforms existing reconstruction-based self-supervised learning methods for satellite imagery. Our results demonstrate that position prediction tasks, when properly adapted for multimodal satellite imagery, learn representations more effective for satellite image semantic segmentation than reconstruction-based approaches.
卫星图像的语义分割对于地球观测应用至关重要,但仍受限于标记训练数据的有限性。虽然像Masked Autoencoders(MAE)这样的自监督预训练方法在重建方面显示出潜力,但它们主要关注重建而非定位,这是分割任务的一个基本方面。我们提出适应LOCA(位置感知)方法,这是一种位置预测自监督学习方法,用于多模态卫星图像语义分割。我们的方法通过扩展SatMAE的渠道分组,从多光谱到多模态数据,解决了卫星数据的独特挑战,实现了多种模式的有效处理,并引入了同组注意力遮蔽,以鼓励在预训练期间进行跨模态交互。该方法使用相对斑块位置预测,鼓励定位的空间推理而非重建。我们在Sen1Floods11洪水测绘数据集上评估了我们的方法,在洪水测绘数据集上,我们的方法显著优于现有的基于重建的自监督学习方法。我们的结果表明,当适当适应多模态卫星图像时,位置预测任务对于卫星图像语义分割的代表性学习比基于重建的方法更有效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
卫星图像语义分割对地球观测应用至关重要,但受限于标记训练数据的不足。虽然自监督预训练方法(如Mask Autoencoders)已显示出潜力,但它们主要关注重建而非定位——分割任务的基本方面。本文提出将位置感知的自监督学习方法LOCA应用于多模态卫星图像语义分割。该方法通过扩展SatMAE的渠道组合能力以处理多模态数据,引入了同一群体注意力屏蔽机制来鼓励在预训练期间的跨模态交互。此方法使用相对补丁位置预测,鼓励定位的空间推理而非重建。在Sen1Floods11洪水测绘数据集上的评估显示,该方法显著优于基于重建的现有自监督学习方法。结果表明,适当适应多模态卫星图像的定位预测任务,对于卫星图像语义分割而言,比基于重建的方法更有效。
Key Takeaways
- 卫星图像语义分割是地球观测应用的关键挑战,主要受限于标记训练数据的缺乏。
- 自监督预训练方法如Mask Autoencoders虽然展现出潜力,但在解决定位问题上效果有限。
- 本文提出的LOCA方法是一种位置感知自监督学习方法,针对多模态卫星图像语义分割进行改进。
- 方法通过扩展SatMAE的渠道组合能力处理多模态数据,并引入跨模态交互机制。
- 采用相对补丁位置预测,强调空间推理和定位而非单纯的图像重建。
- 在Sen1Floods11数据集上的实验显示,LOCA方法显著优于传统的重建型自监督学习方法。
点此查看论文截图