⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
TaoAvatar: Real-Time Lifelike Full-Body Talking Avatars for Augmented Reality via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jianchuan Chen, Jingchuan Hu, Gaige Wang, Zhonghua Jiang, Tiansong Zhou, Zhiwen Chen, Chengfei Lv
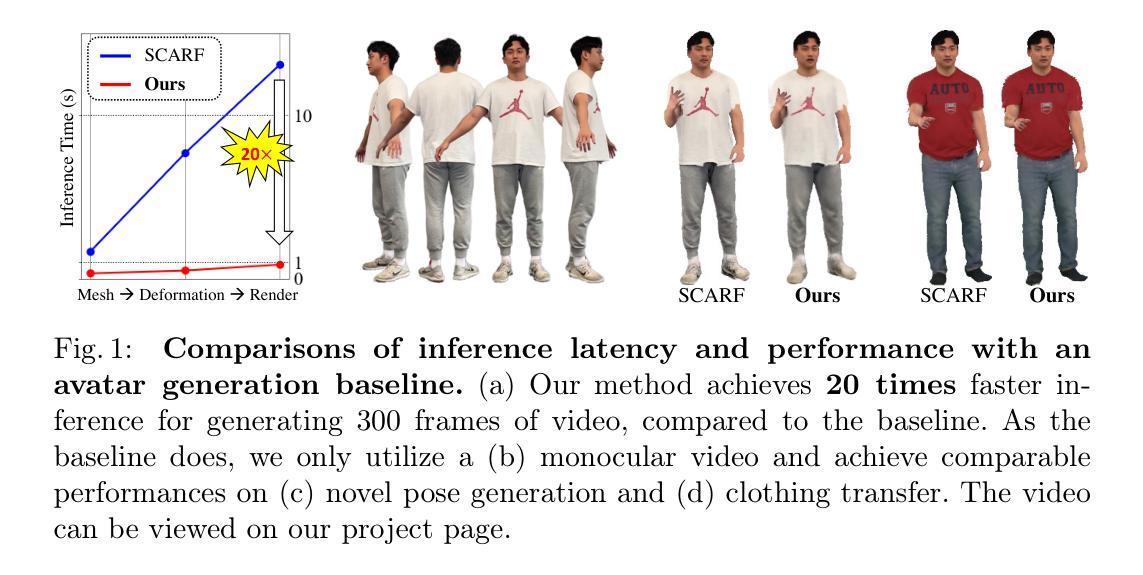
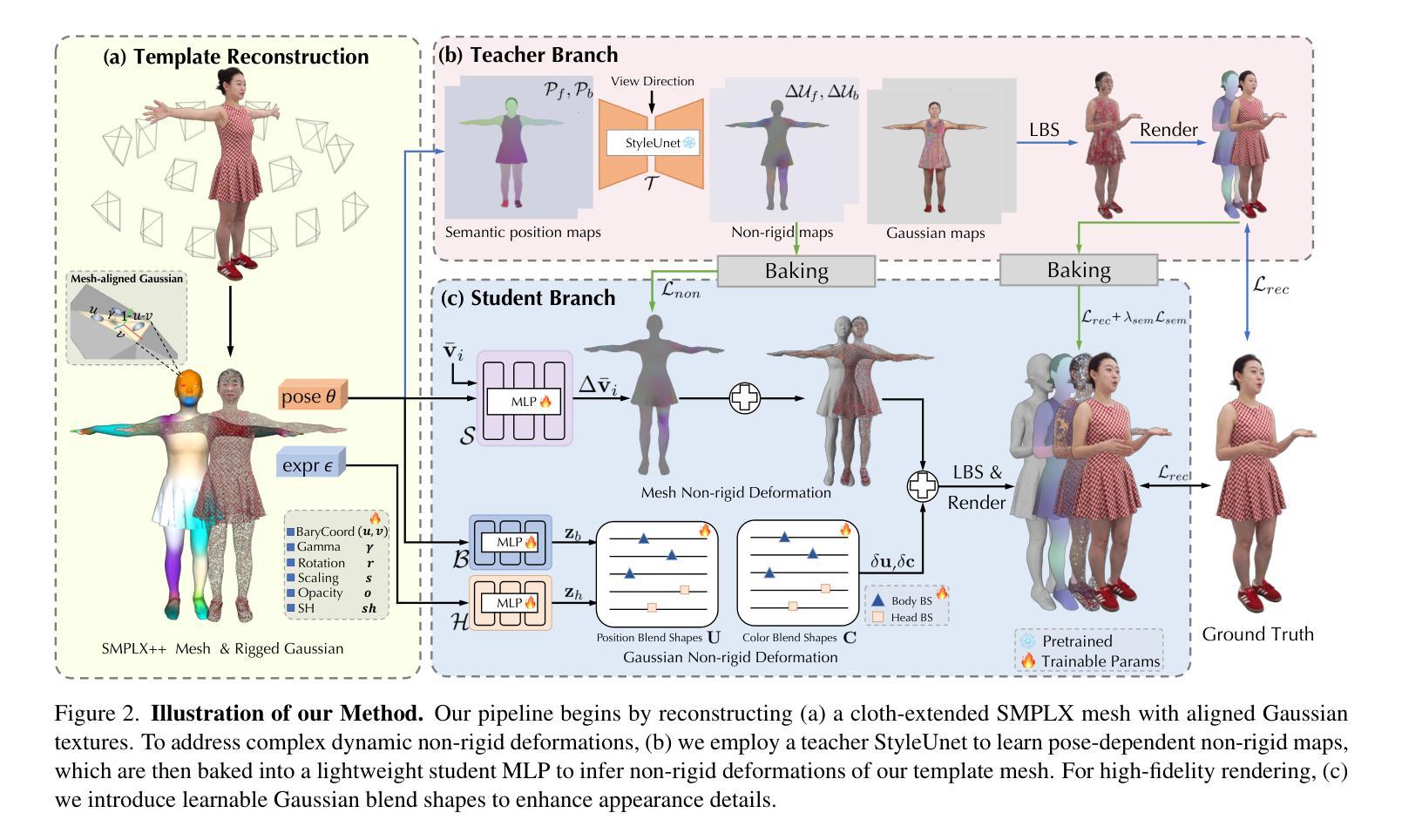
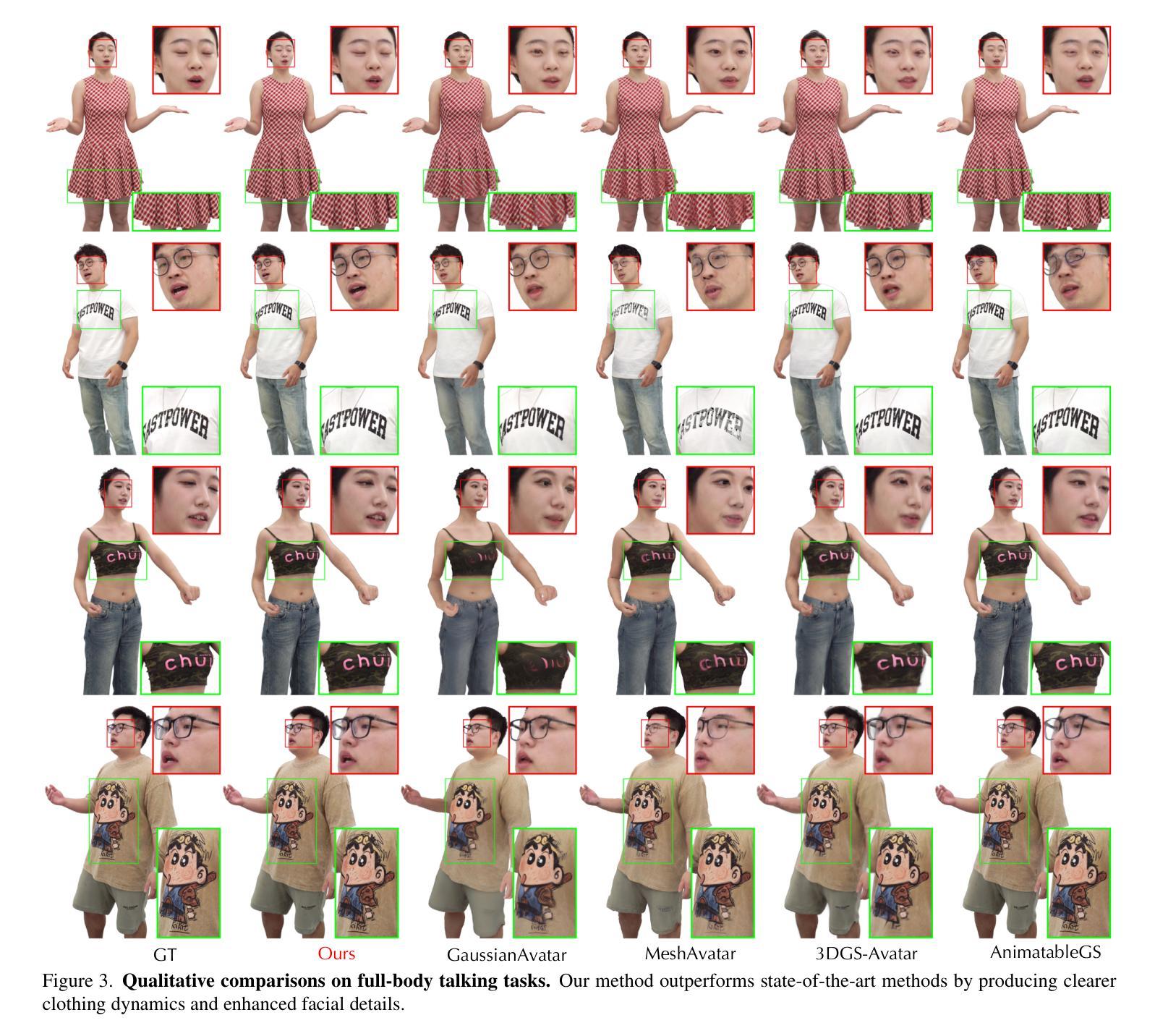
Realistic 3D full-body talking avatars hold great potential in AR, with applications ranging from e-commerce live streaming to holographic communication. Despite advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for lifelike avatar creation, existing methods struggle with fine-grained control of facial expressions and body movements in full-body talking tasks. Additionally, they often lack sufficient details and cannot run in real-time on mobile devices. We present TaoAvatar, a high-fidelity, lightweight, 3DGS-based full-body talking avatar driven by various signals. Our approach starts by creating a personalized clothed human parametric template that binds Gaussians to represent appearances. We then pre-train a StyleUnet-based network to handle complex pose-dependent non-rigid deformation, which can capture high-frequency appearance details but is too resource-intensive for mobile devices. To overcome this, we “bake” the non-rigid deformations into a lightweight MLP-based network using a distillation technique and develop blend shapes to compensate for details. Extensive experiments show that TaoAvatar achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality while running in real-time across various devices, maintaining 90 FPS on high-definition stereo devices such as the Apple Vision Pro.
现实主义的3D全身谈话角色在增强现实(AR)中具有巨大的潜力,应用范围从电子商务直播到全息通信。尽管在用于创建逼真角色的三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)方面取得了进展,但现有方法在全身谈话任务的面部表情和动作精细控制方面仍然面临挑战。此外,它们通常缺乏足够的细节,无法在移动设备上实时运行。我们推出了TaoAvatar,一个基于高保真、轻量级的3DGS全身谈话角色,由各种信号驱动。我们的方法首先创建一个个性化的穿衣人参数模板,将高斯绑定以表示外观。然后,我们基于StyleUnet网络进行预训练,以处理复杂的姿态相关非刚性变形,该网络可以捕获高频外观细节,但对于移动设备而言资源消耗过大。为了克服这一问题,我们使用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到基于MLP的轻量级网络中,并开发混合形状以补偿细节。大量实验表明,TaoAvatar在实时运行的情况下达到了最先进的渲染质量,可在各种设备上实现实时运行,在高分辨率立体声设备上(如Apple Vision Pro)保持90帧/秒的帧率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 (Highlight), project page: https://PixelAI-Team.github.io/TaoAvatar
Summary
基于现实的三维全身对话虚拟人具有广泛的应用前景,包括电子商务直播和全息通信等领域。本文提出了TaoAvatar,一种基于三维高斯喷射技术的高精度轻量级全身对话虚拟人系统。通过创建个性化的衣物人类参数模板和使用预训练的StyleUnet网络处理复杂的姿态相关非刚性变形,系统可以精细控制面部表情和身体动作。为了解决资源密集型的计算问题,系统采用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到基于MLP的轻量级网络中,并开发补偿细节的细节形状。实验表明,TaoAvatar实现了出色的渲染质量,同时可在各种设备上实时运行,在高清立体声设备上保持90帧/秒的帧率。
Key Takeaways
- TaoAvatar是一种全新的三维全身对话虚拟人技术。它可以用于广泛的应用领域,包括电子商务直播和全息通信等。这项技术依赖于高斯喷射模型实现高精度的动态场景创建和人体参数模板。此技术为用户带来更为逼真、交互式的体验。更重要的是这项技术克服了现有的面部动作和复杂动态渲染问题,推动了现实场景中互动社交方式的技术创新和发展。为电子商务等虚拟场景提供了全新的交互体验方式。
点此查看论文截图

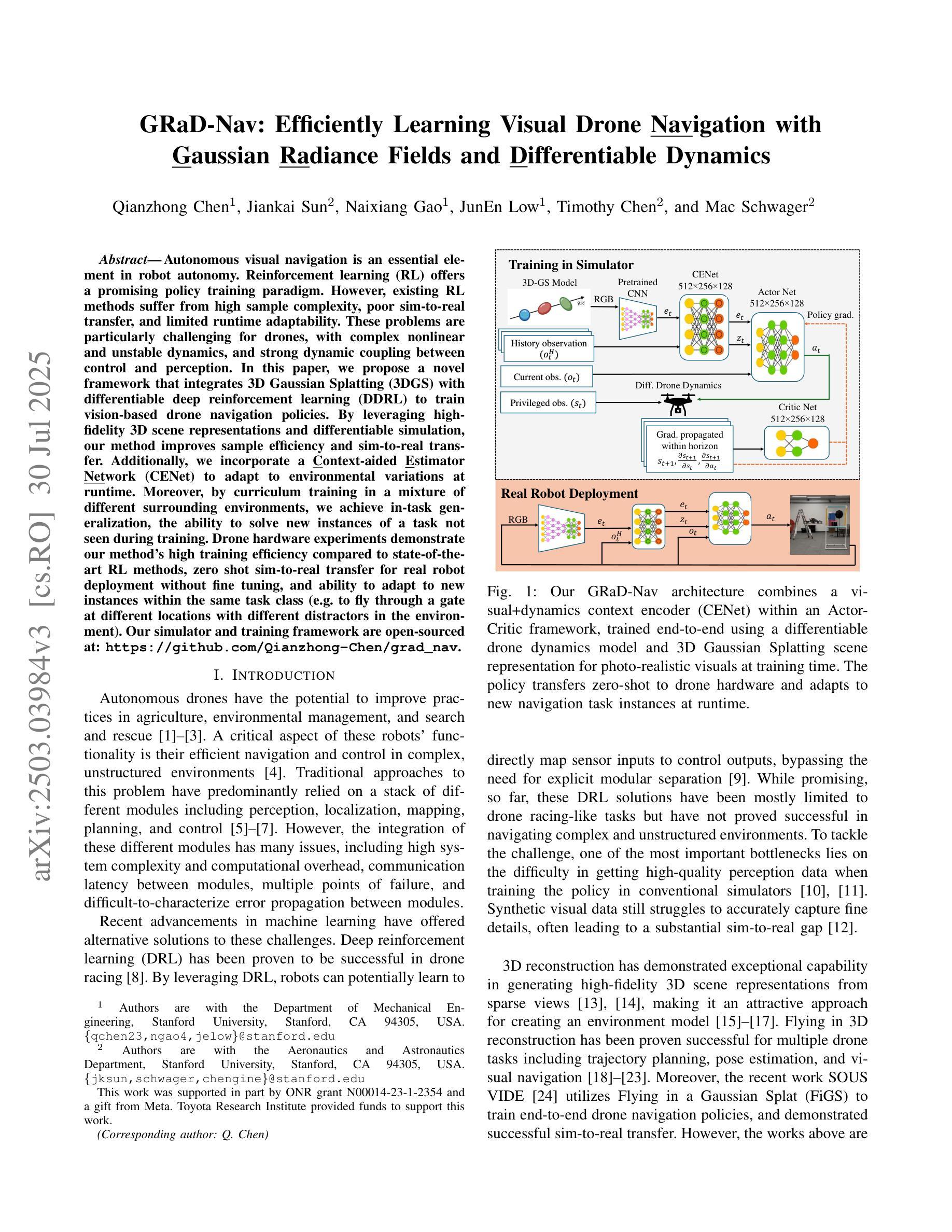
GRaD-Nav: Efficiently Learning Visual Drone Navigation with Gaussian Radiance Fields and Differentiable Dynamics
Authors:Qianzhong Chen, Jiankai Sun, Naixiang Gao, JunEn Low, Timothy Chen, Mac Schwager
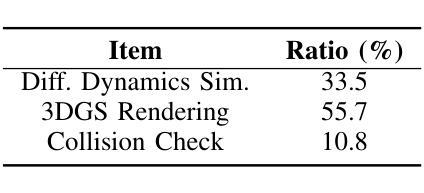
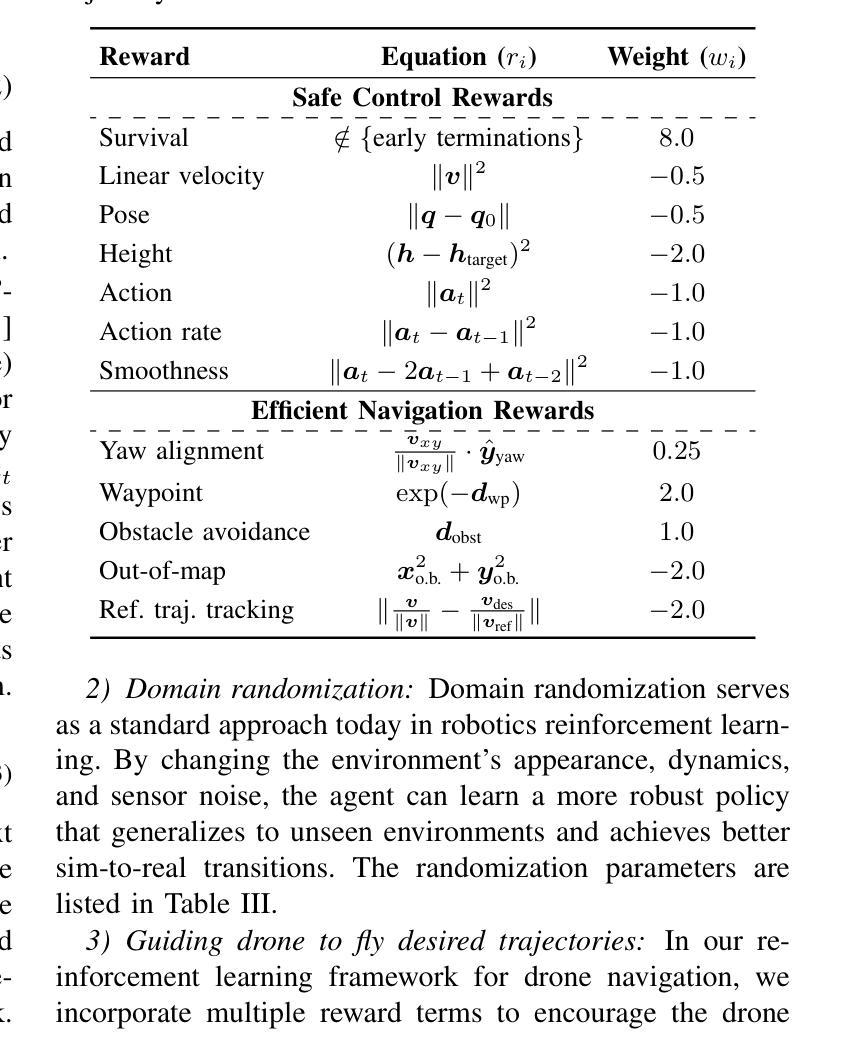
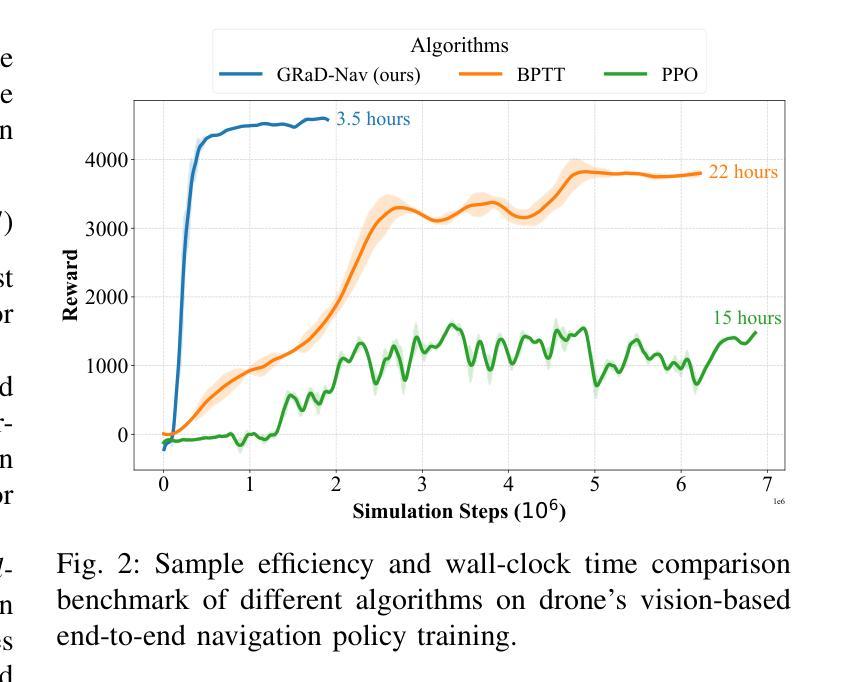
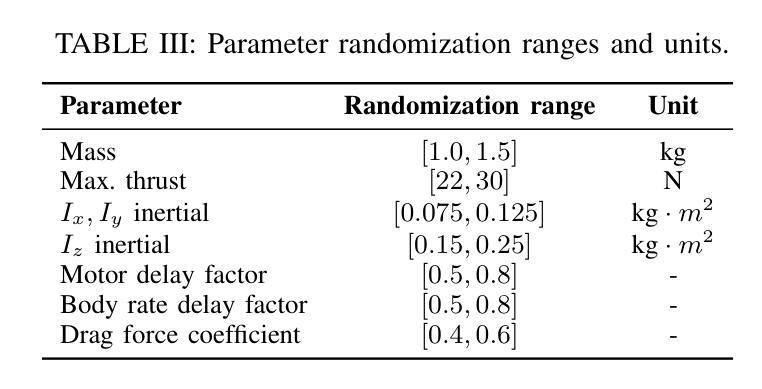
Autonomous visual navigation is an essential element in robot autonomy. Reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising policy training paradigm. However existing RL methods suffer from high sample complexity, poor sim-to-real transfer, and limited runtime adaptability to navigation scenarios not seen during training. These problems are particularly challenging for drones, with complex nonlinear and unstable dynamics, and strong dynamic coupling between control and perception. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with differentiable deep reinforcement learning (DDRL) to train vision-based drone navigation policies. By leveraging high-fidelity 3D scene representations and differentiable simulation, our method improves sample efficiency and sim-to-real transfer. Additionally, we incorporate a Context-aided Estimator Network (CENet) to adapt to environmental variations at runtime. Moreover, by curriculum training in a mixture of different surrounding environments, we achieve in-task generalization, the ability to solve new instances of a task not seen during training. Drone hardware experiments demonstrate our method’s high training efficiency compared to state-of-the-art RL methods, zero shot sim-to-real transfer for real robot deployment without fine tuning, and ability to adapt to new instances within the same task class (e.g. to fly through a gate at different locations with different distractors in the environment). Our simulator and training framework are open-sourced at: https://github.com/Qianzhong-Chen/grad_nav.
自主视觉导航是机器人自主性的一个重要组成部分。强化学习(RL)提供了一个有前景的策略训练范式。然而,现有的强化学习方法存在样本复杂性高、仿真到现实的转移性差以及在训练过程中对新导航场景的实时适应性有限等问题。对于具有复杂非线性、不稳定动力学以及控制和感知之间强烈动态耦合的无人机来说,这些问题更具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖框架,它将3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)与可微分深度强化学习(DDRL)相结合,以训练基于视觉的无人机导航策略。通过利用高保真3D场景表示和可微分仿真,我们的方法提高了样本效率和仿真到现实的转移能力。此外,我们引入了上下文辅助估计网络(CENet)以在运行时适应环境变化。而且,通过在不同周围环境混合中的课程训练,我们实现了任务内泛化,即解决训练期间未见的新任务实例的能力。无人机硬件实验证明,与最新强化学习方法相比,我们的方法具有高效的训练效率、零射击仿真到真实机器人的转移能力,以及适应同一任务类中新实例的能力(例如,在不同位置飞过闸门,环境中存在不同的干扰物)。我们的模拟器和训练框架已公开源代码:https://github.com/Qianzhong-Chen/grad_nav。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合3D高斯融合(3DGS)与可微深度学习强化学习(DDRL)框架训练无人机导航策略的新方法。利用高精度三维场景表征和可微仿真提高样本效率和仿真到现实的转移能力。此外,通过结合环境辅助估计网络(CENet)以适应环境变化,并在混合不同环境中进行课程训练实现任务内泛化。实验证明,该方法提高了训练效率,实现了零射击仿真到现实转移,并能适应新任务实例。
Key Takeaways
- 自主视觉导航是机器人自主性的重要组成部分,强化学习为该领域提供了政策培训范例。
- 当前强化学习方法存在样本复杂性高、仿真到现实转移能力差以及面对训练时未见场景的适应性问题。
- 针对无人机(具有复杂非线性、不稳定动力学以及控制和感知之间的强烈动态耦合)的特定挑战,本文提出了一种结合3DGS和DDRL的新框架。
- 利用高精度三维场景表征和可微仿真,提高了样本效率和仿真到现实的转移能力。
- 引入环境辅助估计网络(CENet)以适应环境变化的运行时调整。
- 通过在不同环境中进行课程训练,实现了任务内的泛化能力,即解决在训练期间未见的新实例任务。
点此查看论文截图
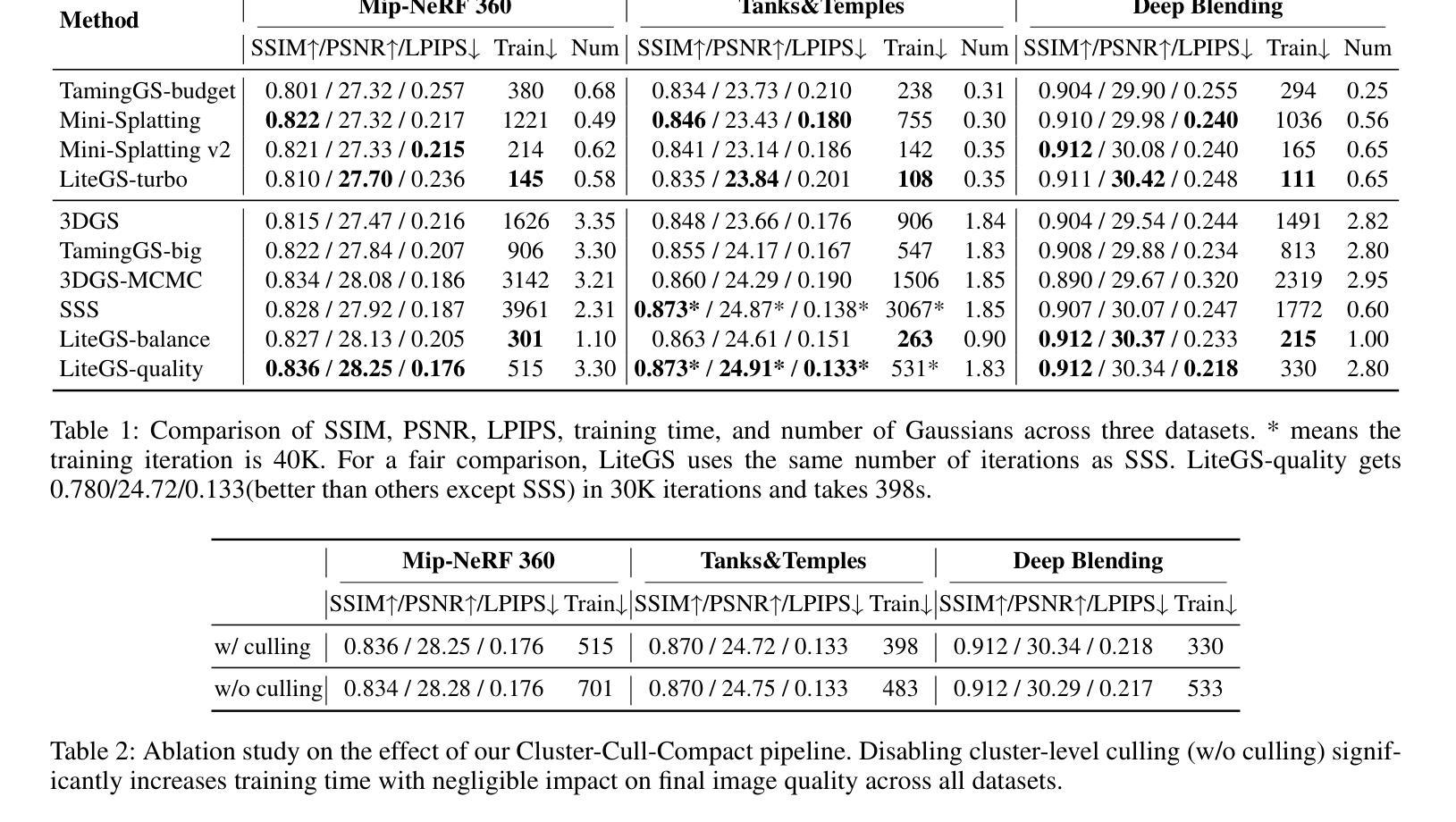
LiteGS: A High-performance Framework to Train 3DGS in Subminutes via System and Algorithm Codesign
Authors:Kaimin Liao, Hua Wang, Zhi Chen, Luchao Wang, Yaohua Tang
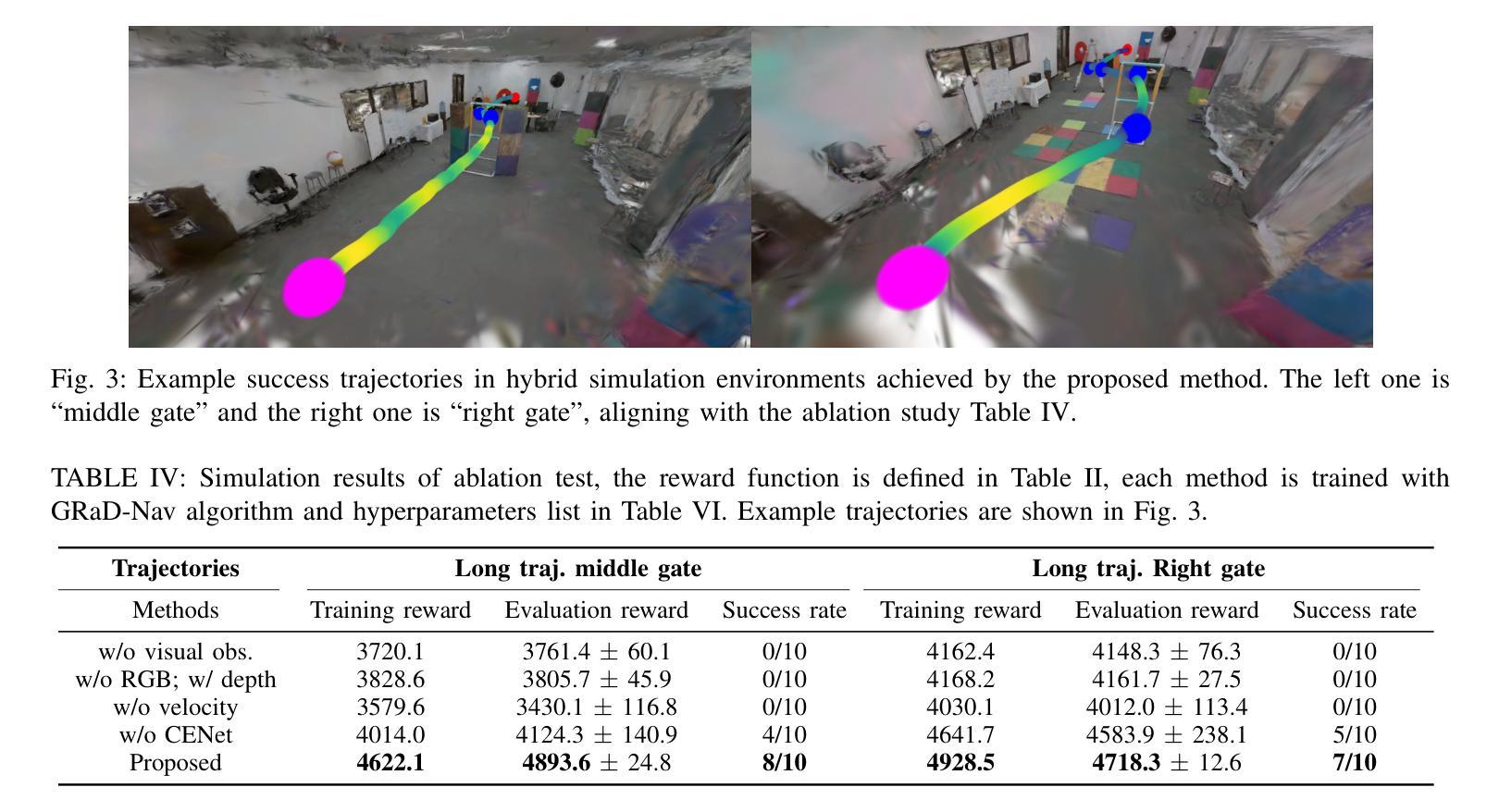
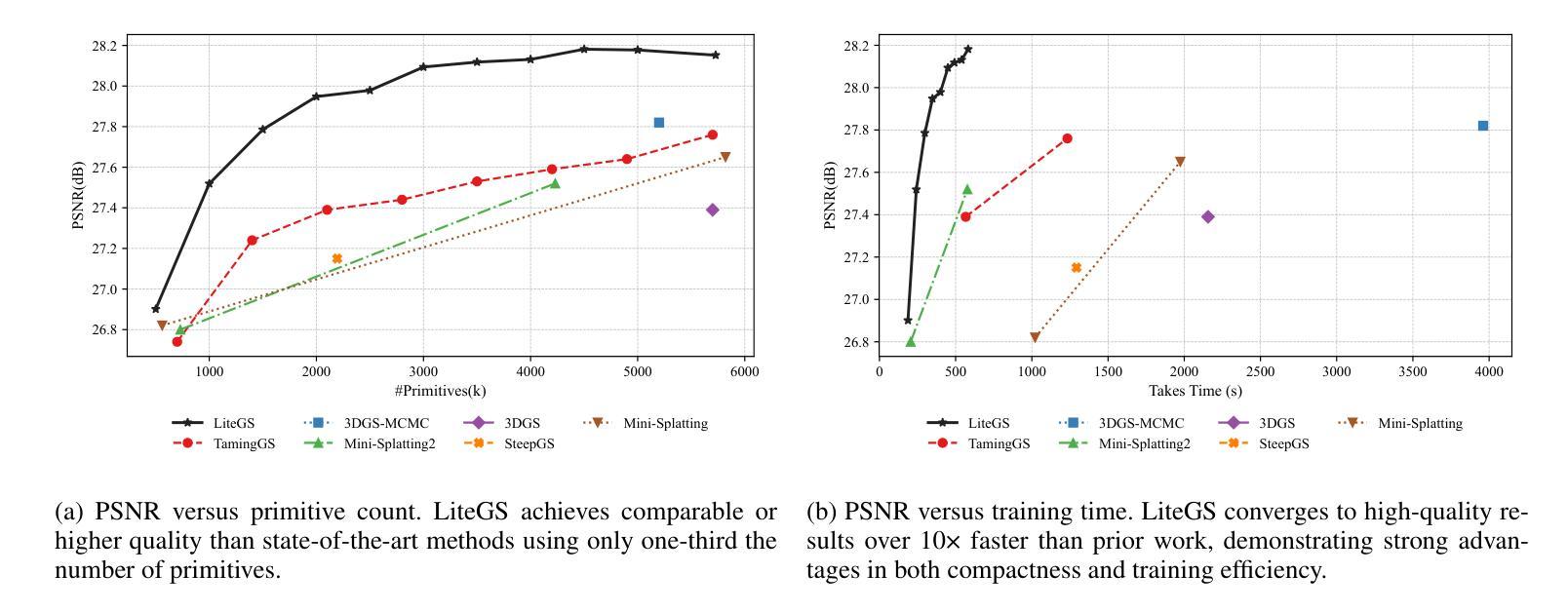
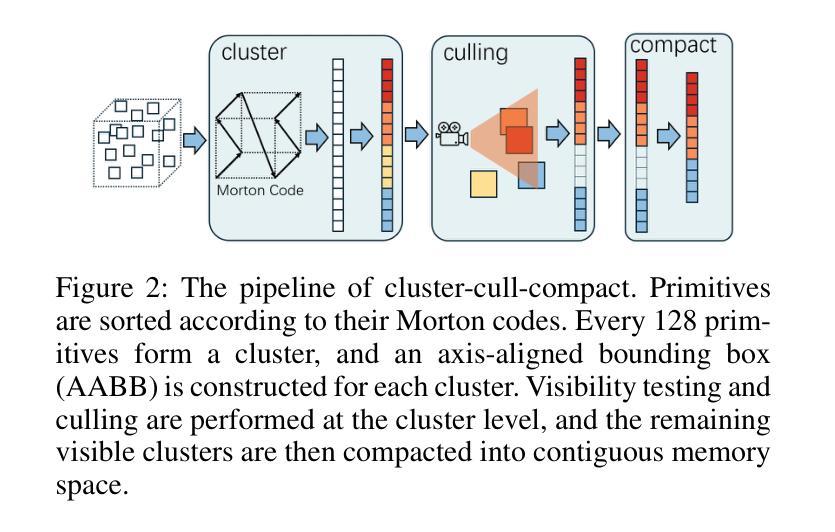
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as promising alternative in 3D representation. However, it still suffers from high training cost. This paper introduces LiteGS, a high performance framework that systematically optimizes the 3DGS training pipeline from multiple aspects. At the low-level computation layer, we design a warp-based raster'' associated with two hardware-aware optimizations to significantly reduce gradient reduction overhead. At the mid-level data management layer, we introduce dynamic spatial sorting based on Morton coding to enable a performant Cluster-Cull-Compact’’ pipeline and improve data locality, therefore reducing cache misses. At the top-level algorithm layer, we establish a new robust densification criterion based on the variance of the opacity gradient, paired with a more stable opacity control mechanism, to achieve more precise parameter growth. Experimental results demonstrate that LiteGS accelerates the original 3DGS training by up to 13.4x with comparable or superior quality and surpasses the current SOTA in lightweight models by up to 1.4x speedup. For high-quality reconstruction tasks, LiteGS sets a new accuracy record and decreases the training time by an order of magnitude.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)作为3D表示的一种有前途的替代方案已经出现。然而,它仍然存在着训练成本高的问题。本文介绍了LiteGS,一个高性能框架,从多个方面系统地优化了3DGS训练管道。在底层计算层,我们设计了一种基于warping的raster,并辅以两种硬件感知优化,显著减少了梯度降低的开销。在中层数据管理层,我们引入了基于Morton编码的动态空间排序,以实现高效的“Cluster-Cull-Compact”管道,提高数据局部性,从而减少缓存未命中。在高级算法层,我们建立了一个新的基于不透明度梯度方差稳健密实化标准,并配有一种更稳定的不透明度控制机制,以实现更精确的参数增长。实验结果表明,LiteGS加速原始3DGS训练高达13.4倍,质量相当或更好,并且在轻量级模型上最多达到1.4倍的速度提升。对于高质量重建任务,LiteGS创造了新的精度记录,并将训练时间减少了十倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于本文介绍的LiteGS框架优化技术,其对3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 训练流程进行了全面优化。通过设计基于warp的raster算法并引入硬件感知优化技术,大幅降低了梯度计算开销;利用动态空间排序与Morton编码结合,提高了数据访问性能并降低了缓存错误。同时提出了新颖的致密化标准及稳定性良好的透光控制机制。实验结果证实,LiteGS不仅将原有训练速度提升了最高达13.4倍且质量不减甚至更佳,而且在轻量级模型上优于当前最佳解的速度提升了高达1.4倍。对于高质量重建任务,LiteGS开创了新的精度记录并将训练时间缩短了十倍。
关键见解
- LiteGS框架对3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 训练流程进行了系统性优化,提高了性能。
- LiteGS设计了基于warp的raster算法并引入硬件感知优化技术,减少了梯度计算开销。
- 动态空间排序与Morton编码结合使用,优化了数据访问性能并降低了缓存错误率。
- 提出了新的致密化标准和稳定的透光控制机制,提高了参数增长的精确度。
- LiteGS加速了原始3DGS训练高达13.4倍,同时保持或提高了质量。
- LiteGS在轻量级模型上超越了当前最佳解的速度,提升了高达1.4倍。
点此查看论文截图


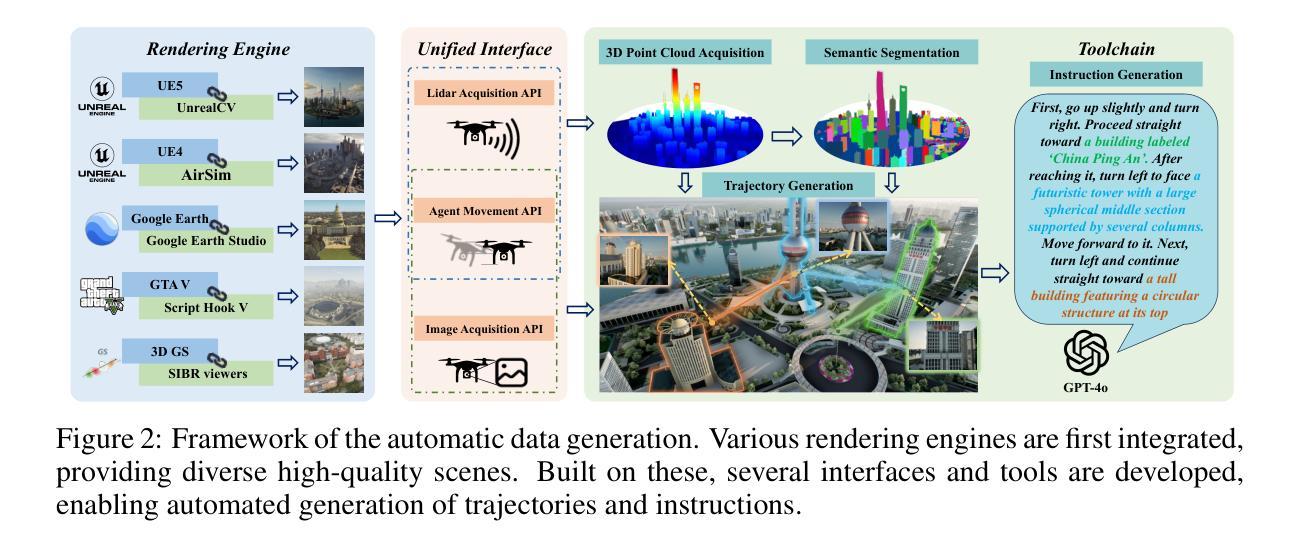
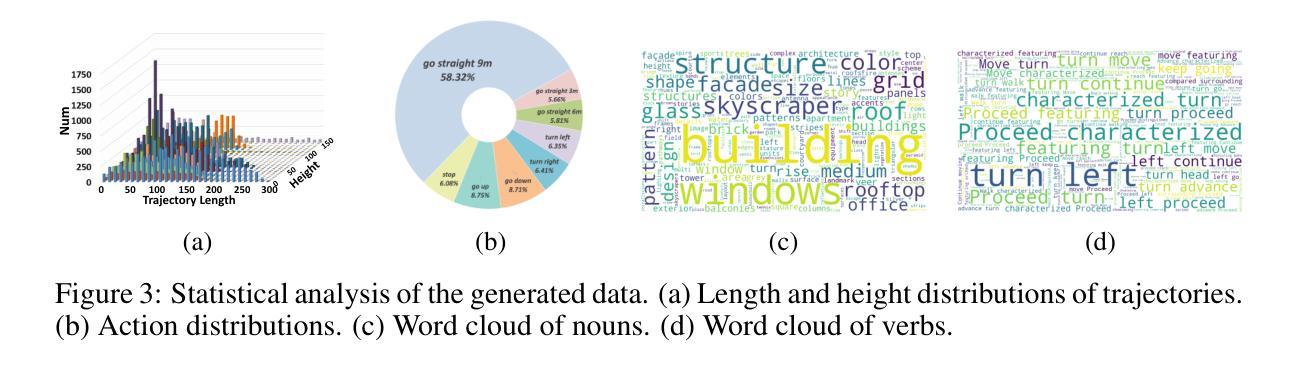
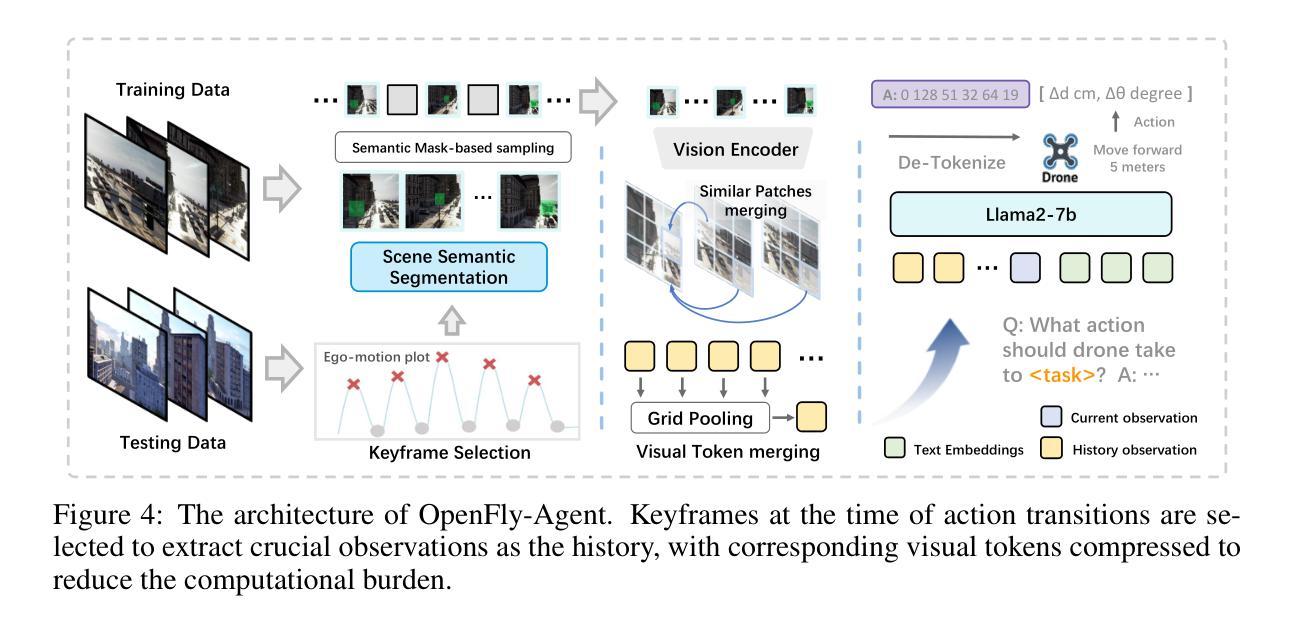
OpenFly: A Comprehensive Platform for Aerial Vision-Language Navigation
Authors:Yunpeng Gao, Chenhui Li, Zhongrui You, Junli Liu, Zhen Li, Pengan Chen, Qizhi Chen, Zhonghan Tang, Liansheng Wang, Penghui Yang, Yiwen Tang, Yuhang Tang, Shuai Liang, Songyi Zhu, Ziqin Xiong, Yifei Su, Xinyi Ye, Jianan Li, Yan Ding, Dong Wang, Zhigang Wang, Bin Zhao, Xuelong Li
Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) aims to guide agents by leveraging language instructions and visual cues, playing a pivotal role in embodied AI. Indoor VLN has been extensively studied, whereas outdoor aerial VLN remains underexplored. The potential reason is that outdoor aerial view encompasses vast areas, making data collection more challenging, which results in a lack of benchmarks. To address this problem, we propose OpenFly, a platform comprising various rendering engines, a versatile toolchain, and a large-scale benchmark for aerial VLN. Firstly, we integrate diverse rendering engines and advanced techniques for environment simulation, including Unreal Engine, GTA V, Google Earth, and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D GS). Particularly, 3D GS supports real-to-sim rendering, further enhancing the realism of our environments. Secondly, we develop a highly automated toolchain for aerial VLN data collection, streamlining point cloud acquisition, scene semantic segmentation, flight trajectory creation, and instruction generation. Thirdly, based on the toolchain, we construct a large-scale aerial VLN dataset with 100k trajectories, covering diverse heights and lengths across 18 scenes. Moreover, we propose OpenFly-Agent, a keyframe-aware VLN model emphasizing key observations during flight. For benchmarking, extensive experiments and analyses are conducted, evaluating several recent VLN methods and showcasing the superiority of our OpenFly platform and agent. The toolchain, dataset, and codes will be open-sourced.
视觉语言导航(VLN)旨在利用语言指令和视觉线索来引导智能体,在嵌入式人工智能中发挥着至关重要的作用。室内VLN已经得到了广泛的研究,而户外空中VLN仍然被较少探索。可能的原因是户外空中视角涉及大片区域,使得数据收集更具挑战性,从而导致缺乏基准测试。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了OpenFly平台,该平台包括各种渲染引擎、通用工具链和用于空中VLN的大规模基准测试。首先,我们集成了多种渲染引擎和先进的环境模拟技术,包括Unreal Engine、GTA V、Google Earth和3D高斯泼溅技术(3D GS)。特别是,3D GS支持真实到模拟渲染,进一步增强了我们的环境真实性。其次,我们开发了一个高度自动化的空中VLN数据收集工具链,用于点云采集、场景语义分割、飞行轨迹创建和指令生成。第三,基于该工具链,我们构建了一个大规模的空中VLN数据集,包含10万条轨迹,覆盖18个场景的多种高度和长度。此外,我们提出了OpenFly-Agent,这是一种关键帧感知的VLN模型,强调飞行过程中的关键观察。为了进行基准测试,我们进行了广泛的实验和分析,评估了几种最新的VLN方法,并展示了我们的OpenFly平台和代理的优越性。工具链、数据集和代码将开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对户外高空视觉语言导航(VLN)的挑战,提出了一种名为OpenFly的平台。该平台集成了多种渲染引擎和先进技术进行环境模拟,并开发了一个高度自动化的工具链,用于收集高空VLN数据。基于该工具链,构建了一个大规模的高空VLN数据集,并提出了一种关键帧感知的VLN模型OpenFly-Agent。此平台及模型的优势通过广泛的实验和分析得以验证。
Key Takeaways
- VLN旨在利用语言指令和视觉线索引导代理,在室内有广泛研究,但户外高空VLN仍处于探索阶段。
- 户外高空视角涵盖大范围区域,使数据收集更具挑战性,导致缺乏基准测试数据。
- OpenFly平台解决了这一问题,集成了多种渲染引擎和先进技术进行环境模拟。
- 开发了一个高度自动化的工具链,用于收集高空VLN数据,包括点云获取、场景语义分割、飞行轨迹创建和指令生成。
- 基于工具链,构建了一个大规模的高空VLN数据集,包含10万条轨迹,覆盖18个场景的多种高度和长度。
- 提出了关键帧感知的VLN模型OpenFly-Agent,强调飞行过程中的关键观察。
点此查看论文截图

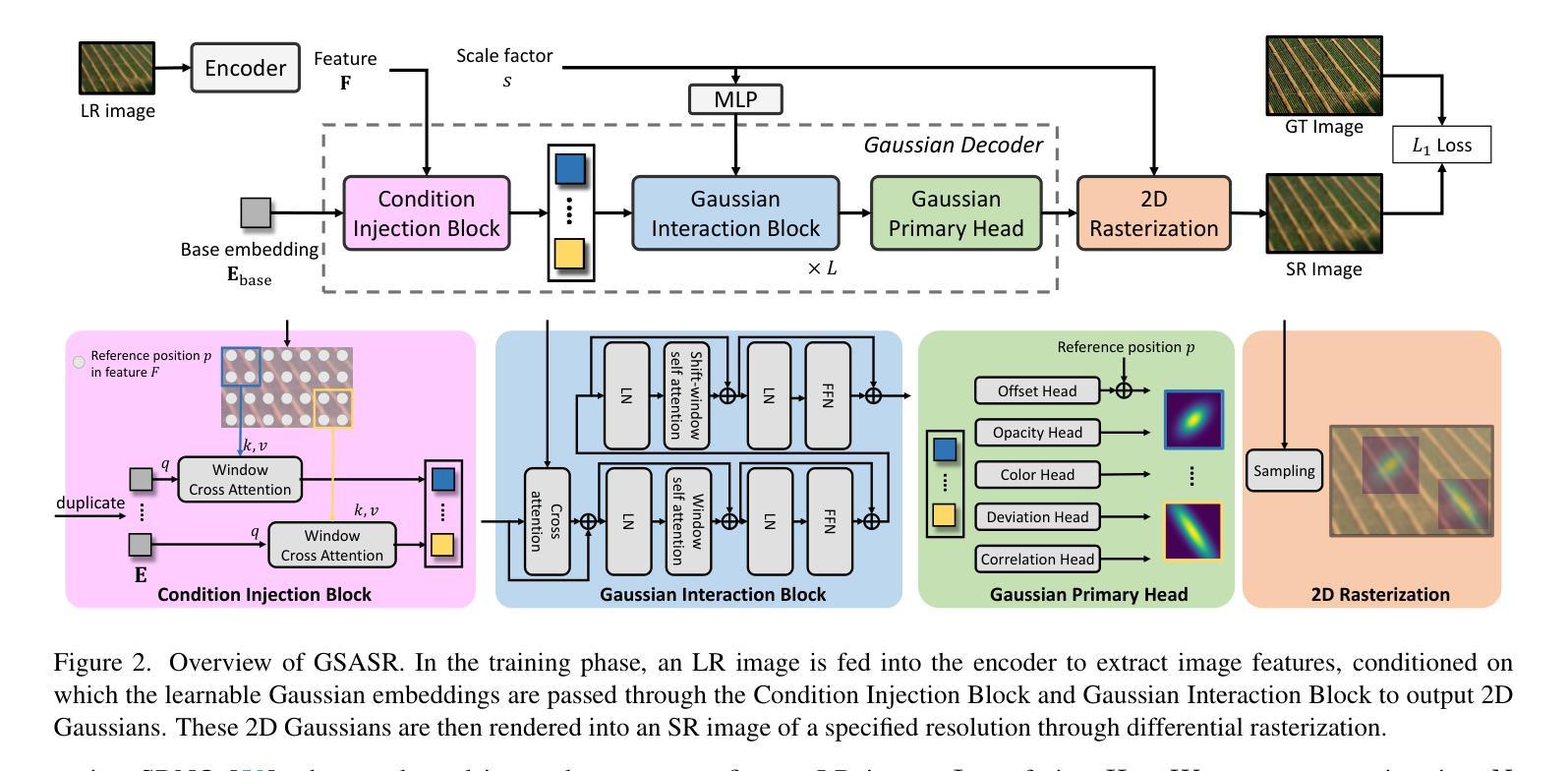
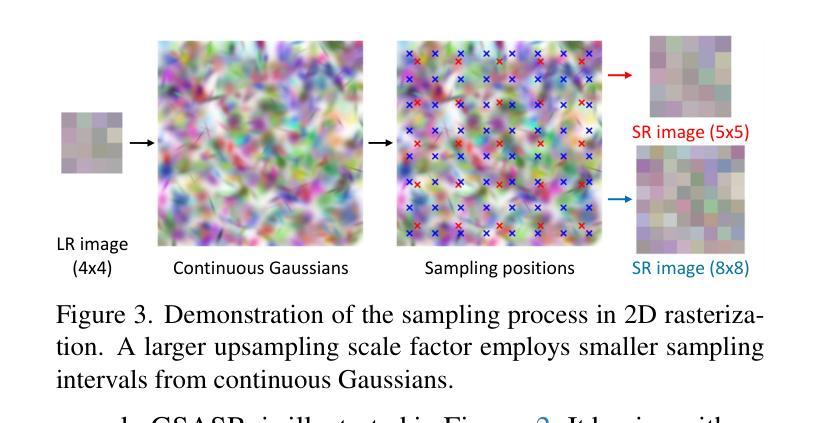
Generalized and Efficient 2D Gaussian Splatting for Arbitrary-scale Super-Resolution
Authors:Du Chen, Liyi Chen, Zhengqiang Zhang, Lei Zhang
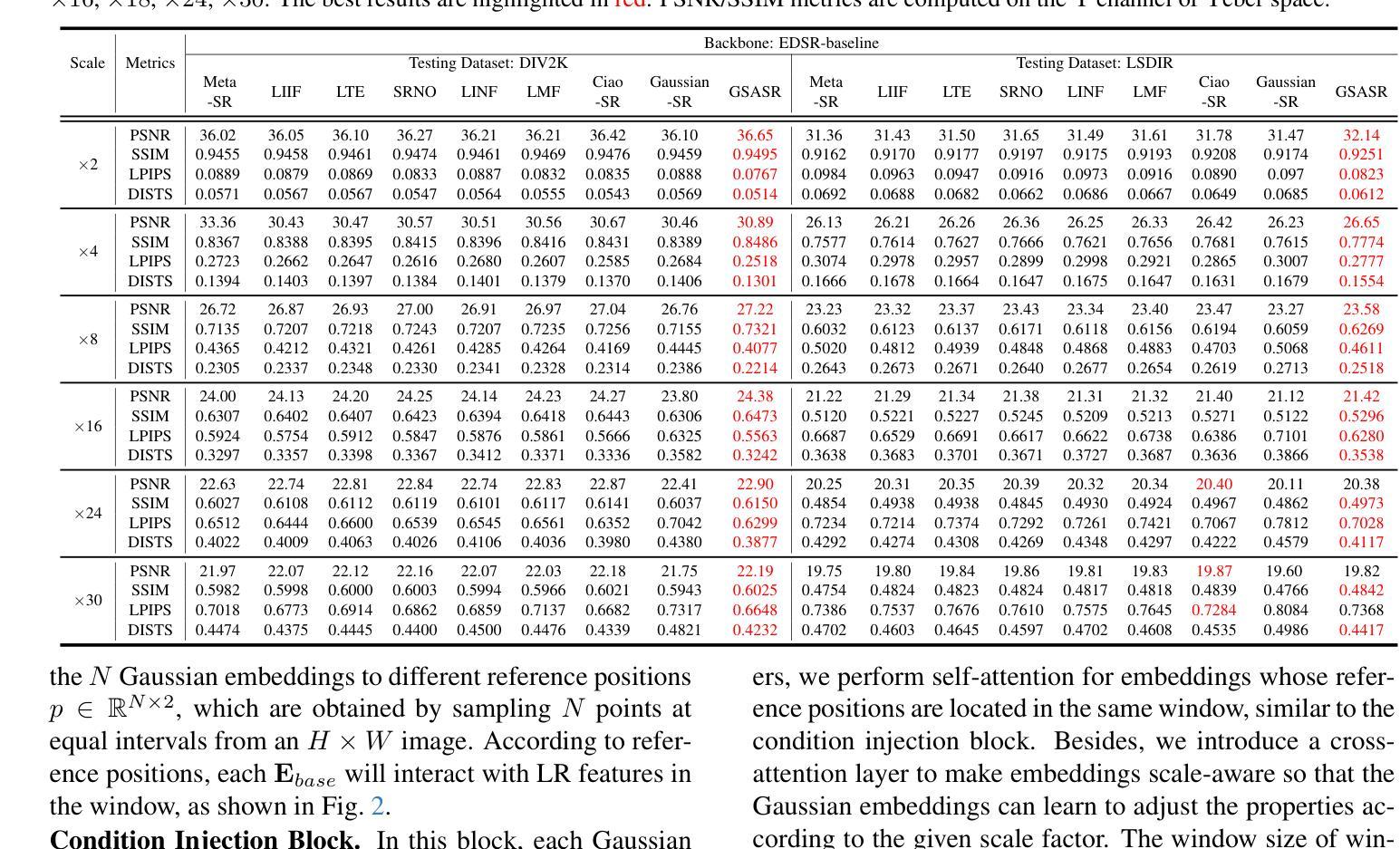
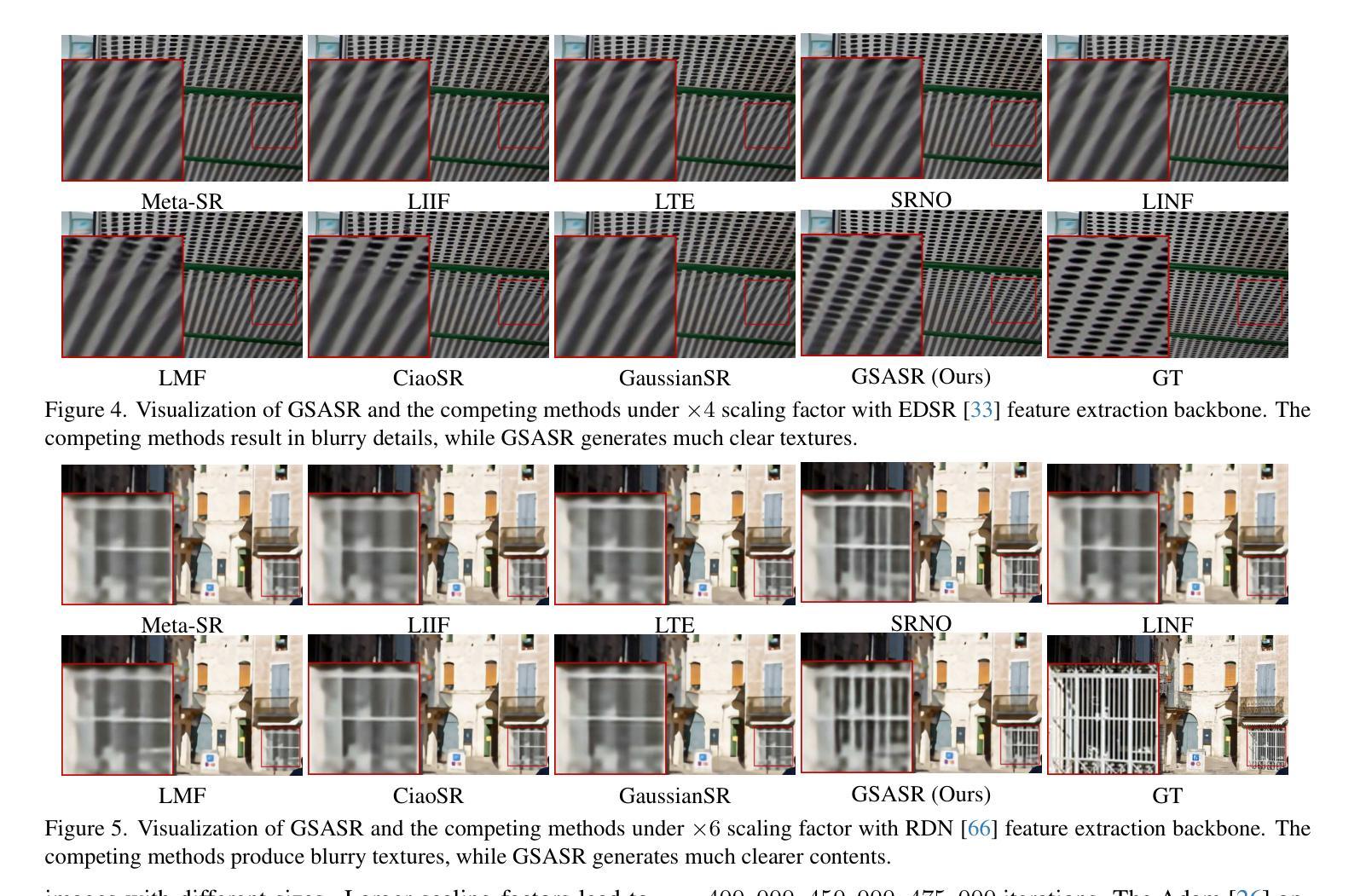
Implicit Neural Representations (INR) have been successfully employed for Arbitrary-scale Super-Resolution (ASR). However, INR-based models need to query the multi-layer perceptron module numerous times and render a pixel in each query, resulting in insufficient representation capability and low computational efficiency. Recently, Gaussian Splatting (GS) has shown its advantages over INR in both visual quality and rendering speed in 3D tasks, which motivates us to explore whether GS can be employed for the ASR task. However, directly applying GS to ASR is exceptionally challenging because the original GS is an optimization-based method through overfitting each single scene, while in ASR we aim to learn a single model that can generalize to different images and scaling factors. We overcome these challenges by developing two novel techniques. Firstly, to generalize GS for ASR, we elaborately design an architecture to predict the corresponding image-conditioned Gaussians of the input low-resolution image in a feed-forward manner. Each Gaussian can fit the shape and direction of an area of complex textures, showing powerful representation capability. Secondly, we implement an efficient differentiable 2D GPU/CUDA-based scale-aware rasterization to render super-resolved images by sampling discrete RGB values from the predicted continuous Gaussians. Via end-to-end training, our optimized network, namely GSASR, can perform ASR for any image and unseen scaling factors. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The code and models are available at https://github.com/ChrisDud0257/GSASR.
隐式神经表示(INR)已成功应用于任意尺度超分辨率(ASR)。然而,基于INR的模型需要多次查询多层感知器模块,并在每次查询中呈现一个像素,导致表示能力不足和计算效率低下。最近,高斯涂抹(GS)在3D任务的视觉质量和渲染速度方面显示出其相对于INR的优势,这激励我们探索是否可以将GS应用于ASR任务。然而,直接将GS应用于ASR具有极大的挑战性,因为原始的GS是一种通过过度拟合每个单一场景的优化方法,而在ASR中,我们的目标是学习一个可以推广到不同图像和缩放因子的单一模型。我们通过开发两种新技术来克服这些挑战。首先,为了将GS推广到ASR,我们精心设计了一种架构,以前馈方式预测输入低分辨率图像对应的图像条件高斯分布。每个高斯分布都能适应复杂纹理区域的形状和方向,显示出强大的表示能力。其次,我们实现了一种高效的可区分2D GPU/CUDA基尺度感知光栅化,通过从预测的持续高斯分布中采样离散RGB值来呈现超分辨率图像。通过端到端的训练,我们优化的网络,即GSASR,可以对任何图像和未见过的缩放因子执行ASR。大量的实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码和模型可在https://github.com/ChrisDud0257/GSASR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
该研究将高斯涂抹技术应用于任意尺度超分辨率任务,解决了隐神经表示在计算效率和表现力上的不足。通过设计新型架构和使用高效的可微分渲染技术,实现了图像的任意尺度超分辨率。GSASR网络具有强大的泛化能力,能够处理不同图像和缩放因子。实验验证该方法的有效性,代码和模型已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 研究将高斯涂抹技术(GS)应用于任意尺度超分辨率(ASR)任务。
- GS在视觉质量和渲染速度上优于隐神经表示(INR)。
- 直接将GS应用于ASR面临挑战,需要设计新型架构和技术来适应。
- 提出一种新型架构,以图像条件高斯分布预测输入低分辨率图像的高斯分布,每个高斯能适配复杂纹理区域的形状和方向。
- 实现高效的可微分渲染技术,通过采样预测连续高斯分布中的离散RGB值来渲染超分辨率图像。
点此查看论文截图