⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
Efficient Masked Attention Transformer for Few-Shot Classification and Segmentation
Authors:Dustin Carrión-Ojeda, Stefan Roth, Simone Schaub-Meyer
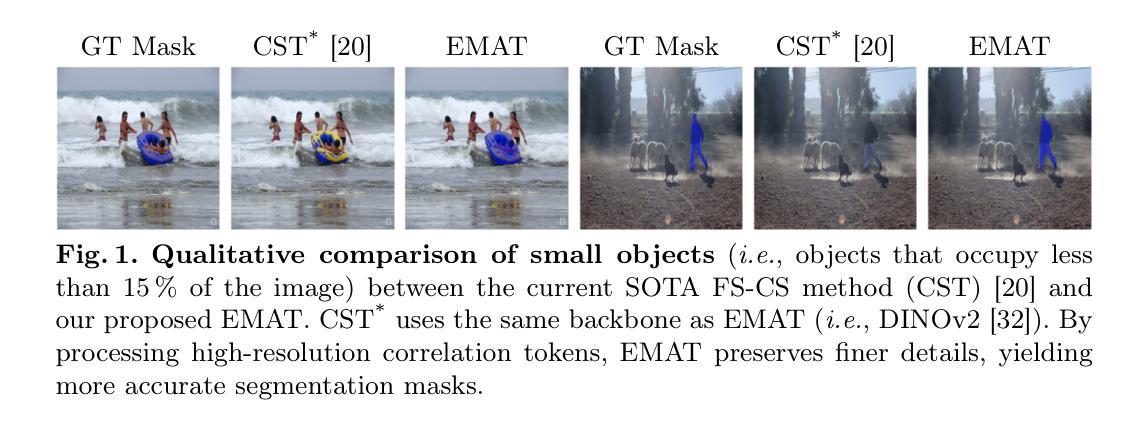
Few-shot classification and segmentation (FS-CS) focuses on jointly performing multi-label classification and multi-class segmentation using few annotated examples. Although the current state of the art (SOTA) achieves high accuracy in both tasks, it struggles with small objects. To overcome this, we propose the Efficient Masked Attention Transformer (EMAT), which improves classification and segmentation accuracy, especially for small objects. EMAT introduces three modifications: a novel memory-efficient masked attention mechanism, a learnable downscaling strategy, and parameter-efficiency enhancements. EMAT outperforms all FS-CS methods on the PASCAL-5$^i$ and COCO-20$^i$ datasets, using at least four times fewer trainable parameters. Moreover, as the current FS-CS evaluation setting discards available annotations, despite their costly collection, we introduce two novel evaluation settings that consider these annotations to better reflect practical scenarios.
少样本分类与分割(FS-CS)主要关注使用少量标注样本联合执行多标签分类和多类分割。尽管当前最先进的模型在这两项任务中都取得了较高的准确性,但在小目标上表现不佳。为了克服这一难题,我们提出了高效掩蔽注意力转换器(EMAT),它提高了分类和分割的准确性,尤其是对小目标。EMAT引入了三种改进:一种新型的内存高效掩蔽注意力机制、一种可学习的降尺度策略以及参数效率提升。EMAT在PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$数据集上的表现优于所有FS-CS方法,使用至少少四倍的可训练参数。此外,由于当前的FS-CS评估设置放弃了可用的注释,尽管这些注释的收集成本高昂,我们引入了两种考虑这些注释的新型评估设置,以更好地反映实际应用场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for GCPR 2025. Project page: https://visinf.github.io/emat
Summary
文本介绍了一种基于注意力的视觉转换模型Efficient Masked Attention Transformer(EMAT),旨在提高基于少数标注样本的图像分类和分割的准确性,特别关注对小物体的识别。相较于当前先进的模型,EMAT更为高效且具有优势,对PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$数据集上的少样本分类和分割方法表现优越。此外,鉴于现有评估设置忽略成本高昂的标注信息,本文还提出了两种新的评估设置以更接近实际应用场景。
Key Takeaways
- Efficient Masked Attention Transformer (EMAT)旨在改进基于少量标注样本的分类和分割效果。
- EMAT针对小物体识别进行了优化。
- EMAT通过引入三种改进——高效掩码注意力机制、可学习缩放策略和参数效率增强——提高了分类和分割的准确性。
- EMAT在PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$数据集上表现优于所有现有的少样本分类和分割方法。
- 当前FS-CS评估设置忽略了昂贵的标注信息,因此提出了两种新的评估设置以更接近实际应用场景。
点此查看论文截图


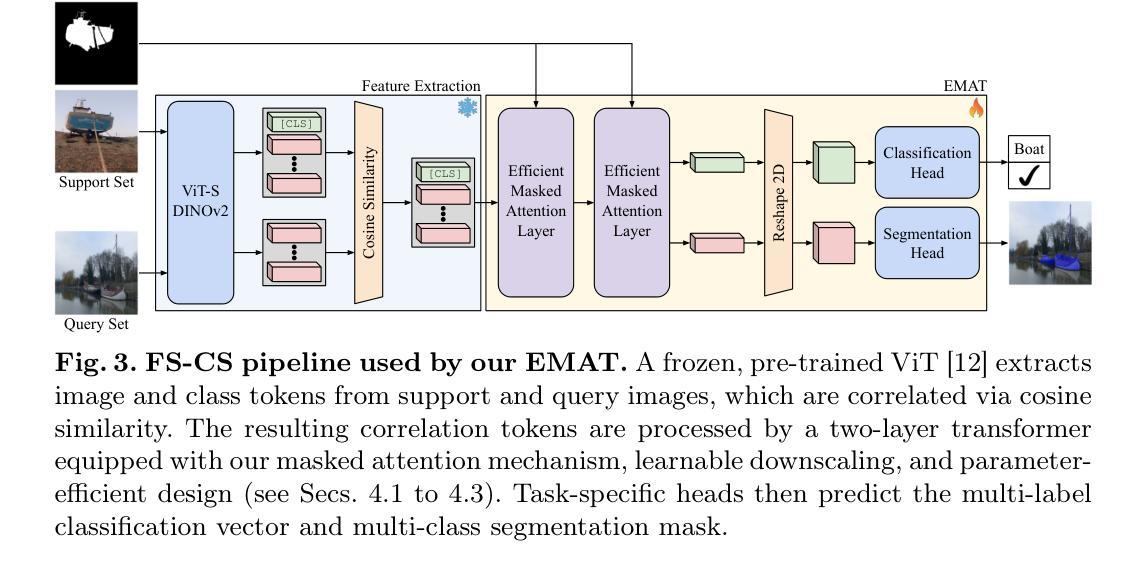
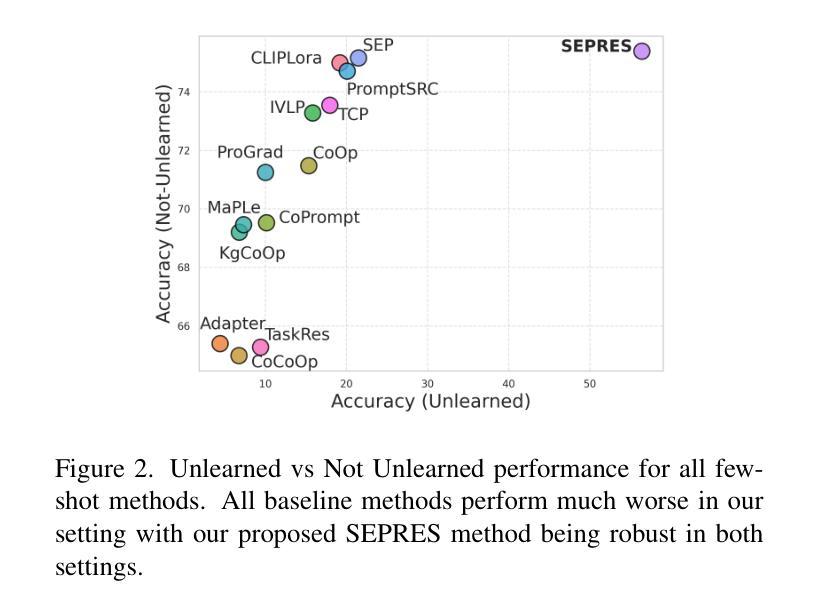
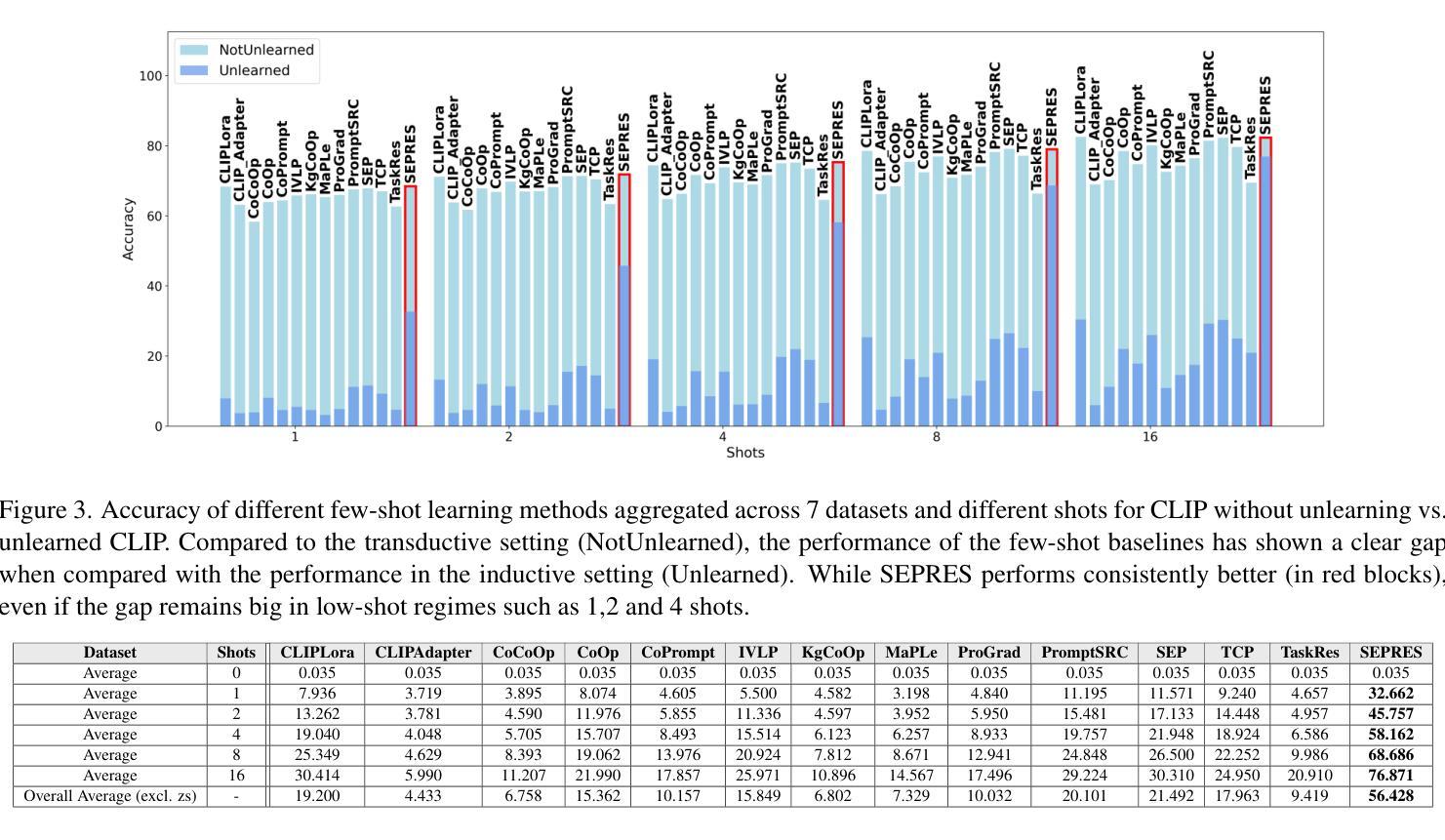
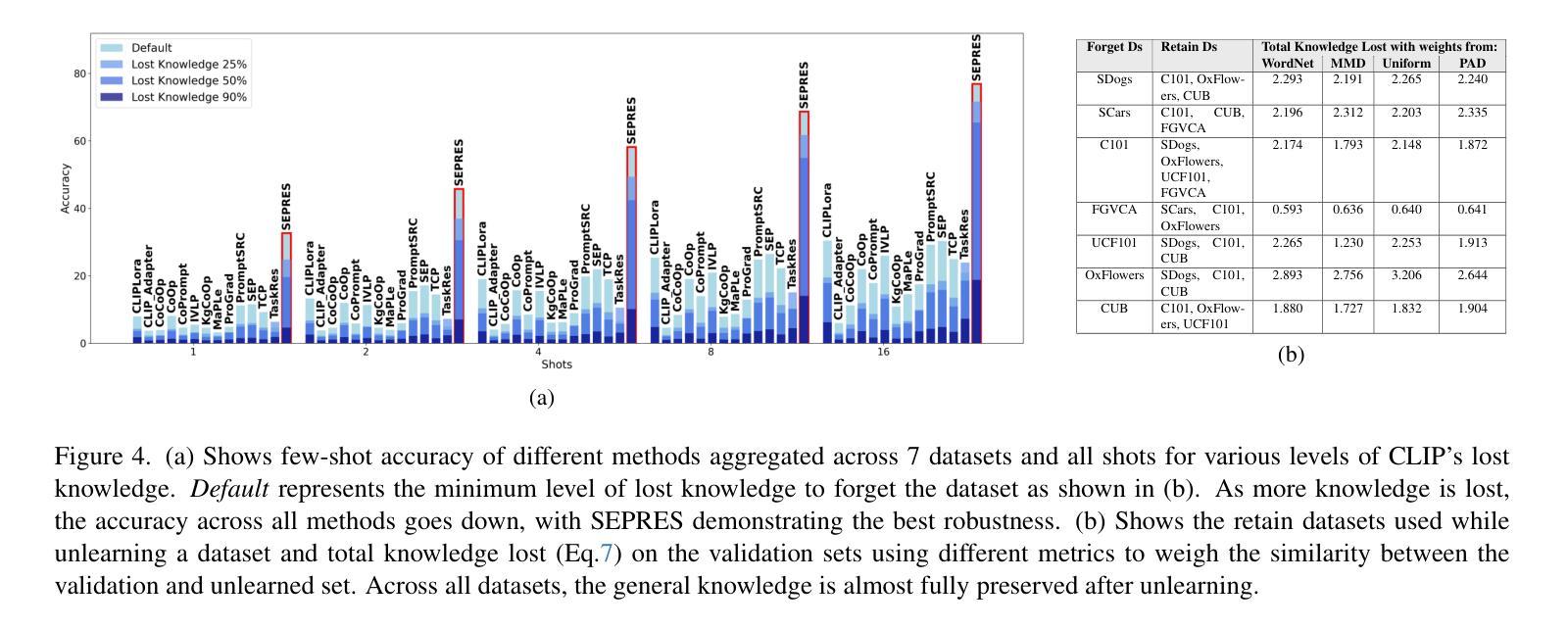
Rethinking Few Shot CLIP Benchmarks: A Critical Analysis in the Inductive Setting
Authors:Alexey Kravets, Da Chen, Vinay P. Namboodiri
CLIP is a foundational model with transferable classification performance in the few-shot setting. Several methods have shown improved performance of CLIP using few-shot examples. However, so far, all these techniques have been benchmarked using standard few-shot datasets. We argue that this mode of evaluation does not provide a true indication of the inductive generalization ability using few-shot examples. As most datasets have been seen by the CLIP model, the resultant setting can be termed as partially transductive. To solve this, we propose a pipeline that uses an unlearning technique to obtain true inductive baselines. In this new inductive setting, the methods show a significant drop in performance (-55% on average among 13 baselines with multiple datasets). We validate the unlearning technique using oracle baselines. An improved few-shot classification technique is proposed that consistently obtains state-of-the-art performance over 13 other recent baseline methods on a comprehensive analysis with 5880 experiments - varying the datasets, differing number of few-shot examples, unlearning setting, and with different seeds. Thus, we identify the issue with the evaluation of CLIP-based few-shot classification, provide a solution using unlearning, propose new benchmarks, and provide an improved method.
CLIP是一个适用于小样本设置的具有可迁移分类性能的基础模型。几种方法已经显示出使用小样本例子改进CLIP的性能。然而,到目前为止,所有这些技术都是用标准的小样本数据集进行基准测试的。我们认为,这种评估方式并不能真正反映出使用小样本例子进行归纳概括的能力。由于CLIP模型已经看到过大多数数据集,因此所得的设置可以被称为部分归纳性的。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种使用遗忘技术来获得真正的归纳基准的管道。在新的归纳设置中,这些方法表现出性能显著下降(在多个数据集的13个基准测试中平均下降55%)。我们使用Oracle基准验证了遗忘技术的有效性。提出了一种改进的小样本分类技术,在综合分析的13个其他最新基准测试中始终获得最先进的性能,共进行了5880次实验——改变了数据集、不同数量的小样本例子、遗忘设置和不同种子。因此,我们发现了基于CLIP的小样本分类评估的问题,提供了使用遗忘的解决方法,提出了新的基准测试,并提供了一种改进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP模型在少样本设置中具有可迁移的分类性能。虽然已有方法证明使用少量样本可以提高CLIP的性能,但目前的评估方式主要基于标准少样本数据集,并不能真正反映模型使用少量样本进行归纳泛化的能力。我们提出使用“遗忘技术”来解决这一问题,并在新的归纳设置下发现现有方法性能平均下降55%。我们验证了遗忘技术的有效性,并提出了一种改进的少样本分类技术,在多个数据集和大量实验分析中,相较于其他基线方法表现出最佳性能。因此,我们识别了CLIP少样本分类评估的问题,提供了基于遗忘技术的解决方案,并提供了新的基准方法和改进方法。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在少样本设置中具有分类性能。
- 当前评估方式不能真正反映模型使用少量样本进行归纳泛化的能力。
- 现有方法在真正的归纳设置下性能平均下降55%。
- 使用遗忘技术解决评估中的问题。
- 改进后的少样本分类技术在多个数据集和大量实验分析中表现最佳。
- 我们提供了基于遗忘技术的解决方案和新的基准方法。
点此查看论文截图

Improving Audio Classification by Transitioning from Zero- to Few-Shot
Authors:James Taylor, Wolfgang Mack
State-of-the-art audio classification often employs a zero-shot approach, which involves comparing audio embeddings with embeddings from text describing the respective audio class. These embeddings are usually generated by neural networks trained through contrastive learning to align audio and text representations. Identifying the optimal text description for an audio class is challenging, particularly when the class comprises a wide variety of sounds. This paper examines few-shot methods designed to improve classification accuracy beyond the zero-shot approach. Specifically, audio embeddings are grouped by class and processed to replace the inherently noisy text embeddings. Our results demonstrate that few-shot classification typically outperforms the zero-shot baseline.
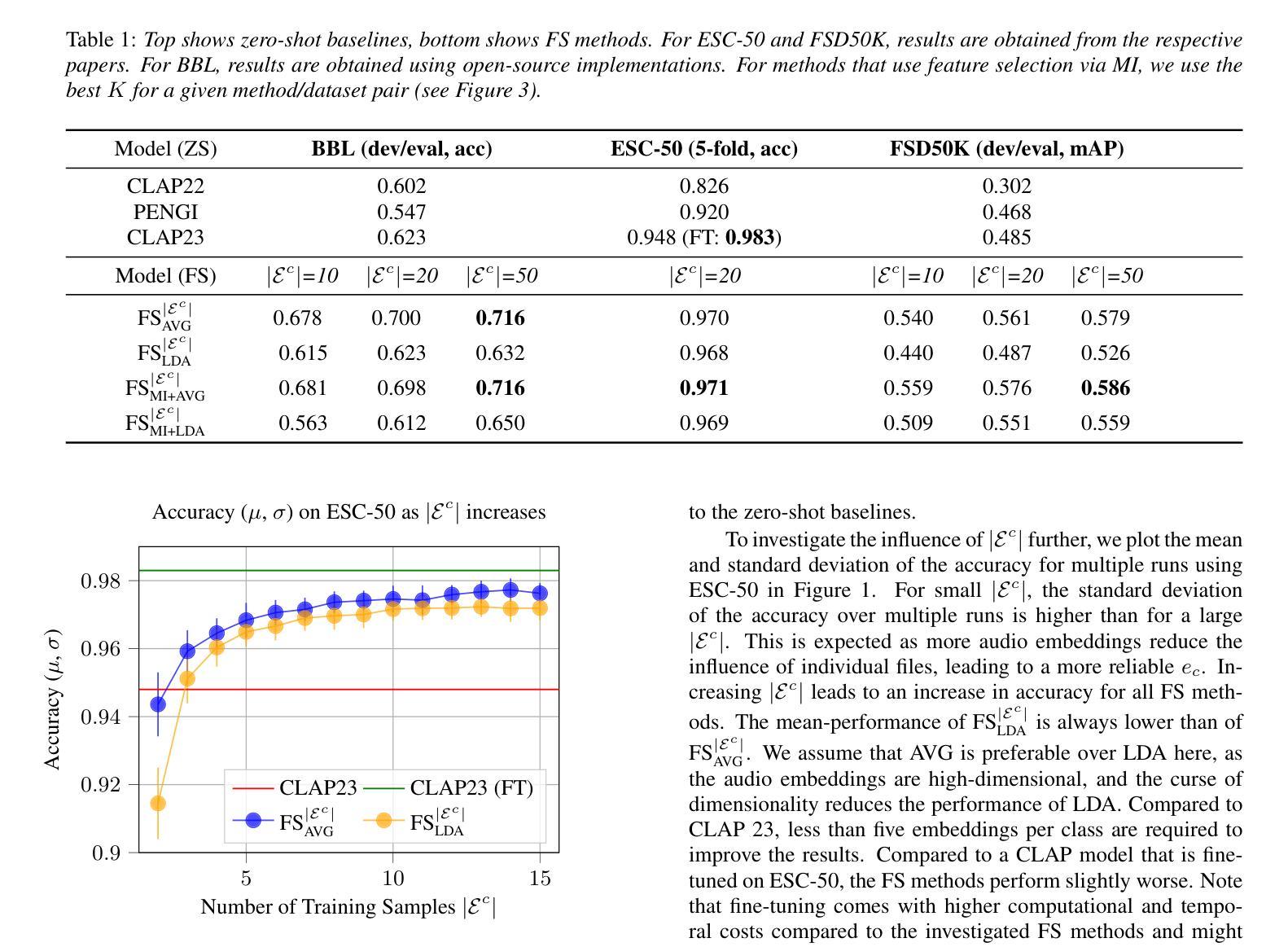
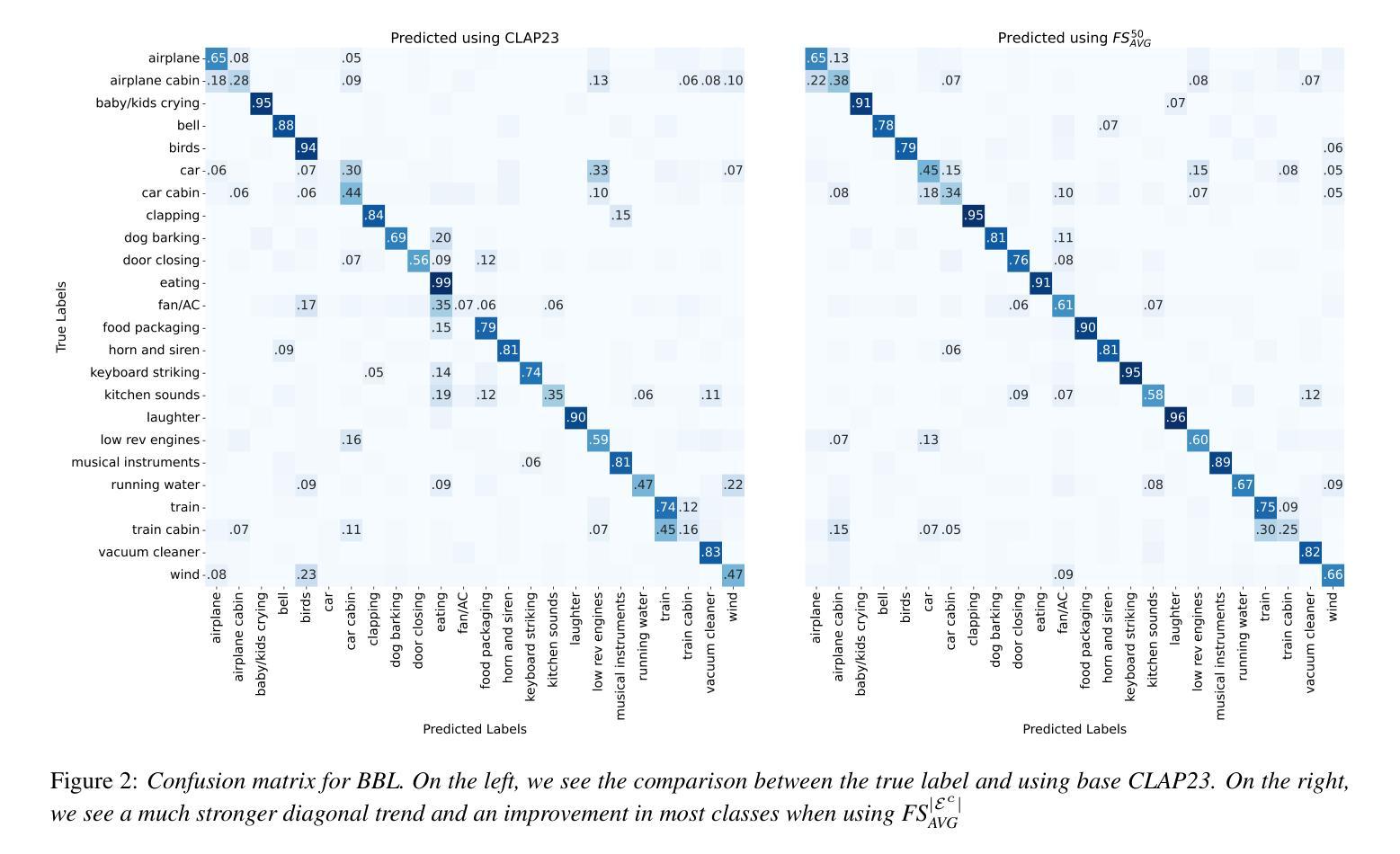
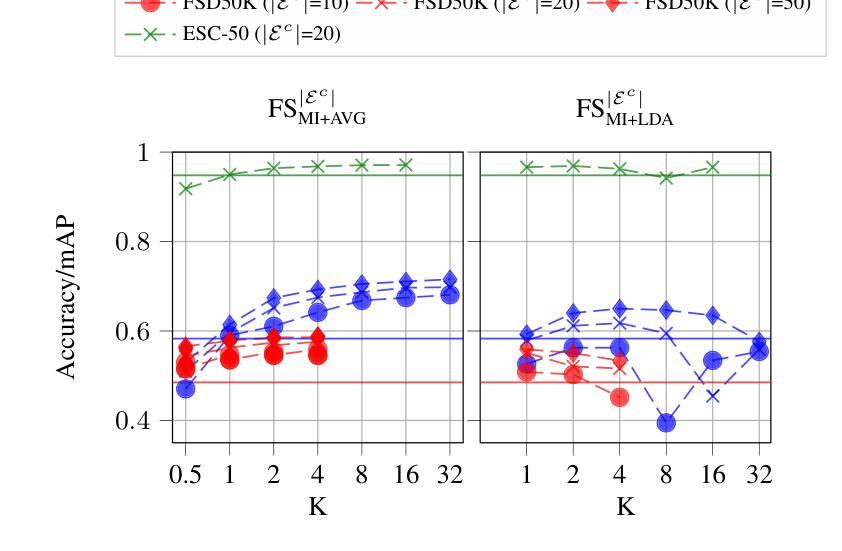
目前先进的音频分类通常采用零样本方法,该方法涉及将音频嵌入与描述相应音频类别的文本嵌入进行比较。这些嵌入通常由通过对比学习训练的神精网络生成,以对齐音频和文本表示。为音频类别确定最佳文本描述具有挑战性,特别是当类别包含多种声音时。本文研究了旨在提高零样本方法之外分类精度的少样本方法。具体来说,音频嵌入按类别分组并经过处理以替换固有的噪声文本嵌入。我们的结果表明,少样本分类通常优于零样本基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
这篇论文探讨了音频分类中的少样本方法,这些方法旨在改进零样本方法的分类准确性。论文采用对比学习训练的神经网络生成音频嵌入和文本嵌入,通过对音频嵌入进行分组处理以替代本质上存在噪声的文本嵌入,以实现更佳的分类效果。实验结果表明,少样本分类通常优于零样本基线。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文探讨了音频分类中的少样本方法,旨在改进零样本方法的分类准确性。
- 音频嵌入是通过神经网络生成的,这些网络通过对比学习进行训练,以对齐音频和文本表示。
- 在某些情况下,为音频类别找到最佳文本描述具有挑战性,特别是在类别包含多种声音时。
- 少样本分类通过利用有限的带标签数据来改善分类性能,这在现实世界的音频分类任务中尤其重要。
- 论文提出了一种方法,通过对音频嵌入进行分组处理来替代存在噪声的文本嵌入,从而提高分类准确性。
- 实验结果表明,少样本分类方法通常优于零样本基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

Anomaly Detection in Human Language via Meta-Learning: A Few-Shot Approach
Authors:Saurav Singla, Aarav Singla, Advik Gupta, Parnika Gupta
We propose a meta learning framework for detecting anomalies in human language across diverse domains with limited labeled data. Anomalies in language ranging from spam and fake news to hate speech pose a major challenge due to their sparsity and variability. We treat anomaly detection as a few shot binary classification problem and leverage meta-learning to train models that generalize across tasks. Using datasets from domains such as SMS spam, COVID-19 fake news, and hate speech, we evaluate model generalization on unseen tasks with minimal labeled anomalies. Our method combines episodic training with prototypical networks and domain resampling to adapt quickly to new anomaly detection tasks. Empirical results show that our method outperforms strong baselines in F1 and AUC scores. We also release the code and benchmarks to facilitate further research in few-shot text anomaly detection.
我们提出一个元学习框架,用于在多样领域和有限标注数据下检测人类语言的异常值。从垃圾邮件和假新闻到仇恨言论的异常语言表现出很大的挑战,因为其稀缺性和多样性。我们把异常检测视为小样本二分类问题,并利用元学习训练模型,使其能够在任务之间泛化。我们使用来自短信垃圾邮件、COVID-19假新闻和仇恨言论等领域的数据集,在未见过的任务上评估模型的泛化能力,其中标注的异常值很少。我们的方法结合了情境训练、原型网络和领域重采样,可以快速适应新的异常检测任务。经验结果表明,我们的方法在F1和AUC得分上优于强大的基线方法。我们还发布了代码和基准测试,以促进在少样本文本异常检测方面的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages. PyTorch code for few-shot anomaly detection using meta-learning is available upon request or can be shared via GitHub
Summary
本文提出了一种利用元学习框架进行跨领域人类语言异常检测的方法,尤其适用于有限标注数据下的场景。针对从垃圾邮件、假新闻到仇恨言论等多样化的语言异常问题,本文将异常检测视为小样本二分类问题,并借助元学习训练模型,实现跨任务泛化。通过来自短信垃圾邮件、COVID-19假新闻和仇恨言论等领域的数据集,对模型在新异常检测任务上的泛化能力进行评估。本文结合了情境训练、原型网络和领域重采样等方法,实现了快速适应新异常检测任务的能力。实验结果表明,该方法在F1和AUC分数上优于强大的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于元学习框架的跨领域人类语言异常检测方法。
- 将异常检测视为小样本二分类问题。
- 通过结合情境训练、原型网络和领域重采样,模型能迅速适应新异常检测任务。
- 使用来自多样化领域(如短信垃圾邮件、COVID-19假新闻和仇恨言论)的数据集进行评估。
- 实证结果表明,该方法在F1和AUC分数上超越了一些基线方法。
- 公开了代码和基准测试,便于进一步研究小样本文本异常检测。
- 对于有限标注数据的场景,该方法展现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

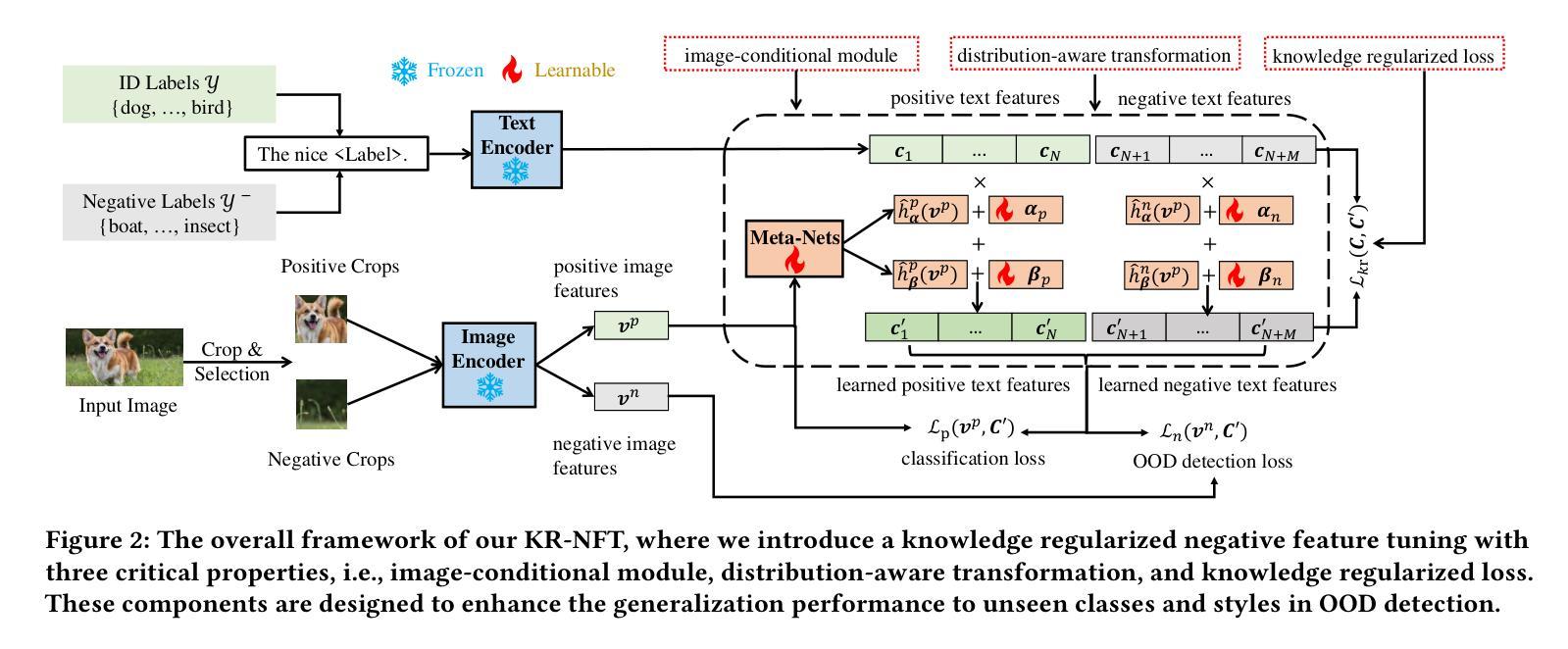
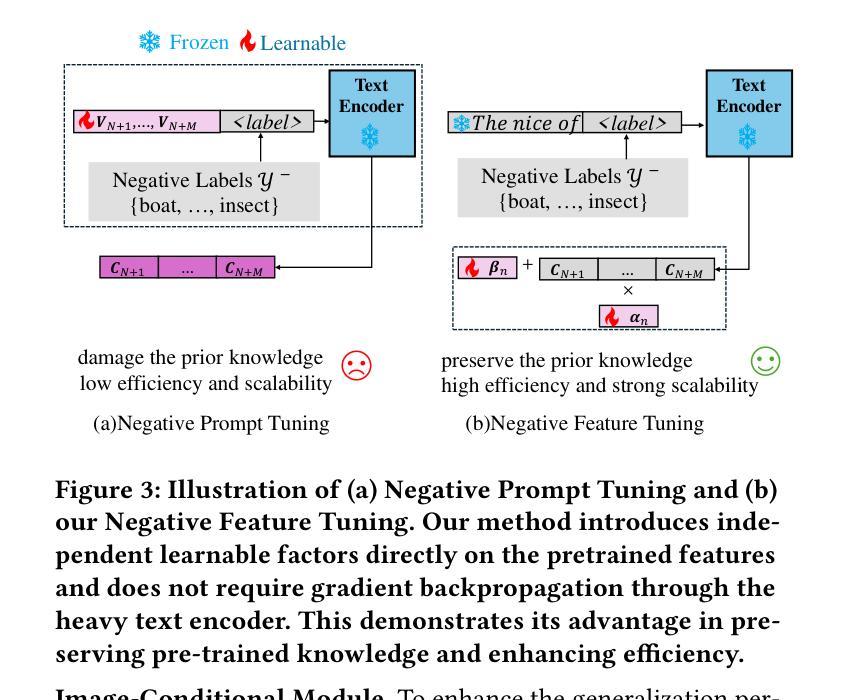
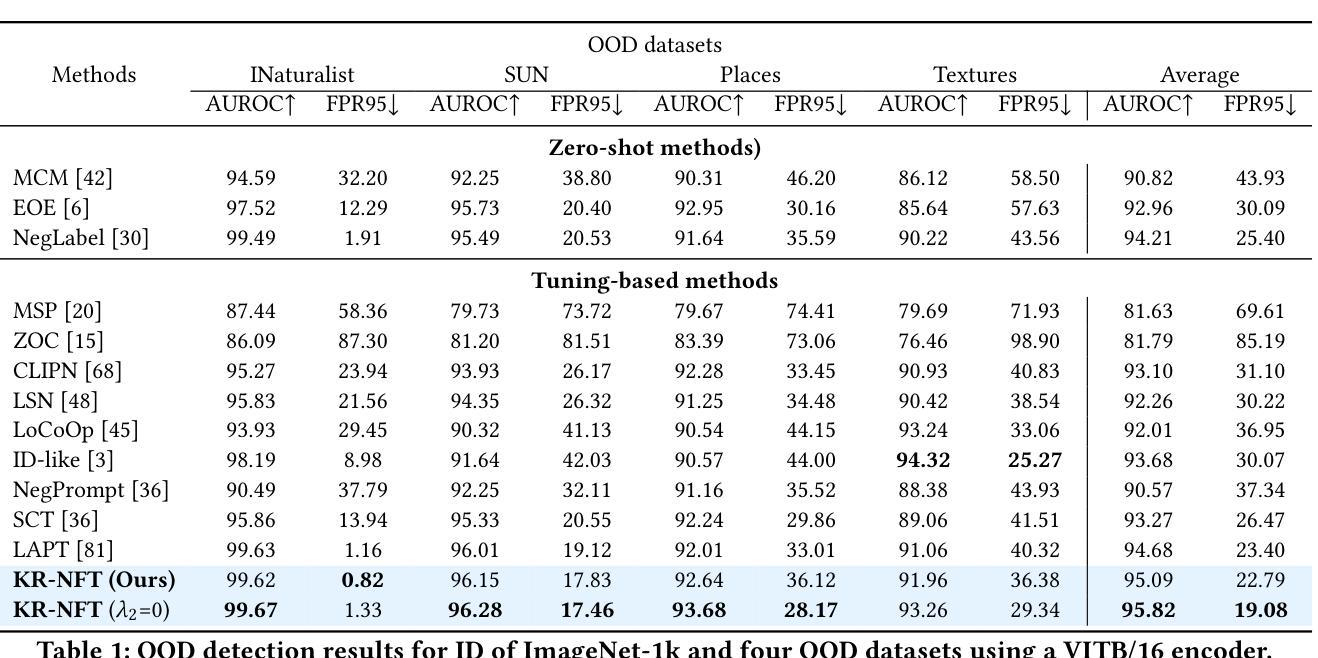
Knowledge Regularized Negative Feature Tuning of Vision-Language Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Wenjie Zhu, Yabin Zhang, Xin Jin, Wenjun Zeng, Lei Zhang
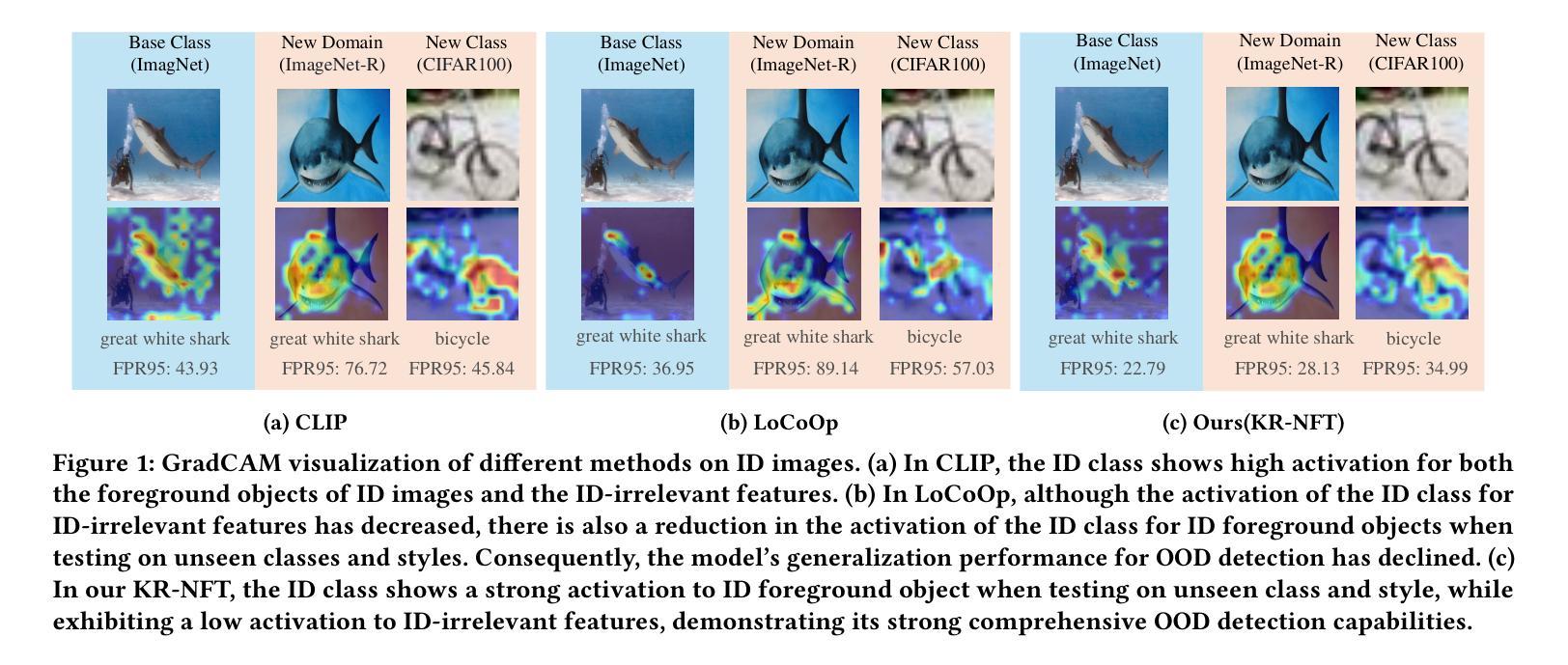
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for building reliable machine learning models. Although negative prompt tuning has enhanced the OOD detection capabilities of vision-language models, these tuned models often suffer from reduced generalization performance on unseen classes and styles. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method called Knowledge Regularized Negative Feature Tuning (KR-NFT), which integrates an innovative adaptation architecture termed Negative Feature Tuning (NFT) and a corresponding knowledge-regularization (KR) optimization strategy. Specifically, NFT applies distribution-aware transformations to pre-trained text features, effectively separating positive and negative features into distinct spaces. This separation maximizes the distinction between in-distribution (ID) and OOD images. Additionally, we introduce image-conditional learnable factors through a lightweight meta-network, enabling dynamic adaptation to individual images and mitigating sensitivity to class and style shifts. Compared to traditional negative prompt tuning, NFT demonstrates superior efficiency and scalability. To optimize this adaptation architecture, the KR optimization strategy is designed to enhance the discrimination between ID and OOD sets while mitigating pre-trained knowledge forgetting. This enhances OOD detection performance on trained ID classes while simultaneously improving OOD detection on unseen ID datasets. Notably, when trained with few-shot samples from ImageNet dataset, KR-NFT not only improves ID classification accuracy and OOD detection but also significantly reduces the FPR95 by 5.44% under an unexplored generalization setting with unseen ID categories. Codes can be found at \href{https://github.com/ZhuWenjie98/KRNFT}.
分布外(OOD)检测对于构建可靠的机器学习模型至关重要。尽管负提示调整提高了视觉语言模型的OOD检测能力,但这些调整后的模型往往在面对未见过的类别和风格时表现出降低的泛化性能。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新方法,称为知识正则化负特征调整(KR-NFT),它结合了名为负特征调整(NFT)的创新适应架构和相应的知识正则化(KR)优化策略。具体而言,NFT对预训练的文本特征进行分布感知转换,有效地将正负特征分离到不同的空间。这种分离最大限度地提高了内部分布(ID)和OOD图像之间的区别。此外,我们通过轻量级元网络引入图像条件可学习因子,实现动态适应个别图像并减轻对类别和风格变化的敏感性。与传统的负提示调整相比,NFT表现出更高的效率和可扩展性。为了优化此适应架构,KR优化策略旨在增强ID和OOD集之间的辨别力,同时减轻预训练知识的遗忘。这提高了在训练的ID类别上的OOD检测性能,同时改善了在未见过的ID数据集上的OOD检测。值得注意的是,当使用来自ImageNet数据集的少量样本进行训练时,KR-NFT不仅提高了ID分类精度和OOD检测,而且在未探索的具有未见过的ID类别的泛化设置下,将FPR95降低了5.44%。代码可在https://github.com/ZhuWenjie98/KRNFT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ACMMM 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为KR-NFT的新方法,用于增强机器学习任务中模型的分布外检测能力。该方法结合了负特征调优(NFT)和知识正则化(KR)策略,旨在解决传统负提示调优在应对未见类别和风格时的泛化性能下降问题。NFT通过分布感知转换来有效分离正负特征,提高模型对分布内(ID)和分布外(OOD)图像的识别能力。此外,引入的图像条件可学习因素通过轻量级元网络实现动态适应个体图像,减轻类别和风格变化的敏感性。与传统方法相比,KR-NFT具有更高的效率和可扩展性,能在保持对训练集的分类精度和提高未见数据集的OOD检测能力的同时,降低FPR95。此方法在ImageNet数据集少量样本训练下表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- KR-NFT方法结合了负特征调优(NFT)和知识正则化(KR)策略,旨在增强机器学习任务中模型的分布外检测能力。
- NFT通过分布感知转换有效分离正负特征,提高模型对分布内(ID)和分布外(OOD)图像的识别能力。
- 轻量级元网络引入图像条件可学习因素,实现模型对个体图像的动态适应,减少类别和风格变化的影响。
- KR优化策略旨在增强ID和OOD集之间的区分度,同时减少预训练知识的遗忘。
- KR-NFT方法能提高模型的分类精度和OOD检测能力,特别是在使用少量样本进行训练时表现优异。
- 在ImageNet数据集上进行的实验表明,KR-NFT能有效降低FPR95达5.44%。
点此查看论文截图

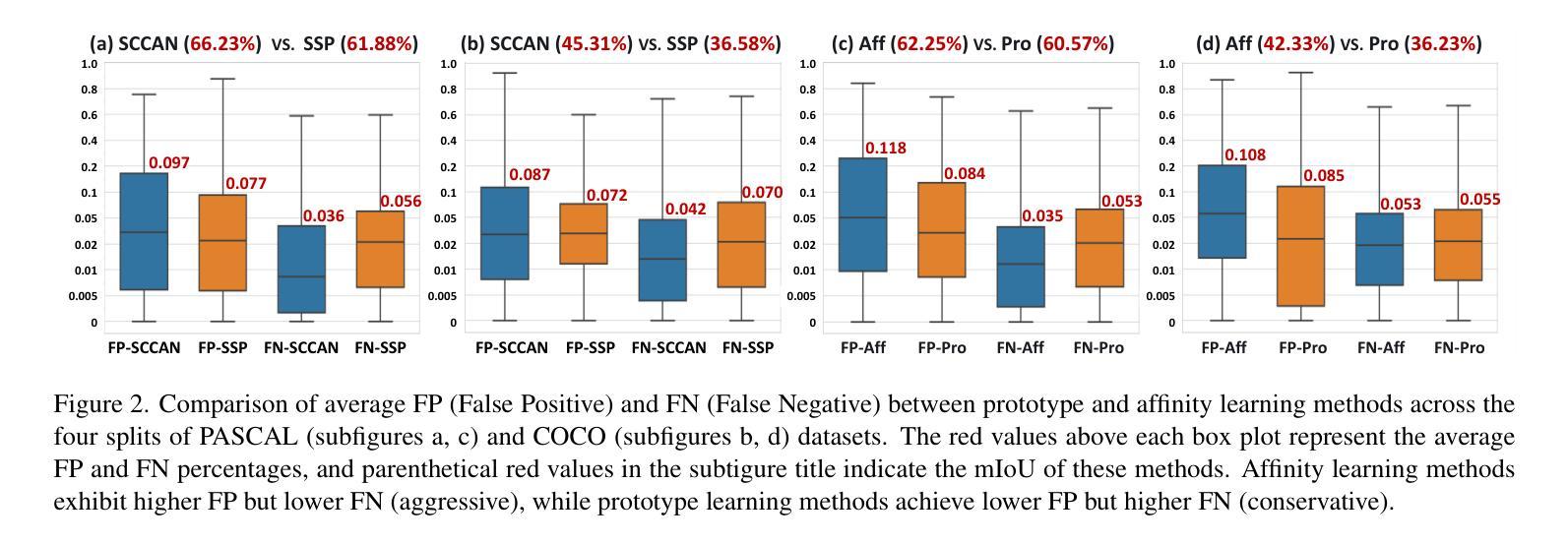
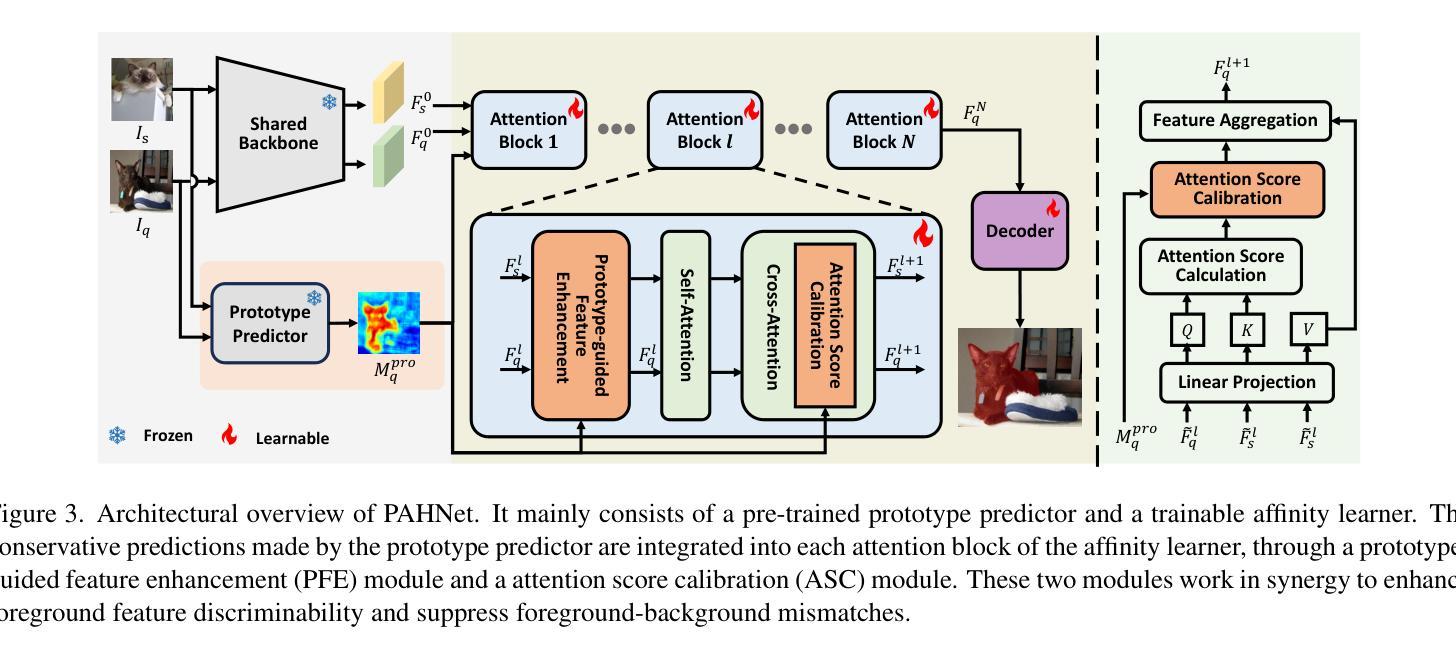
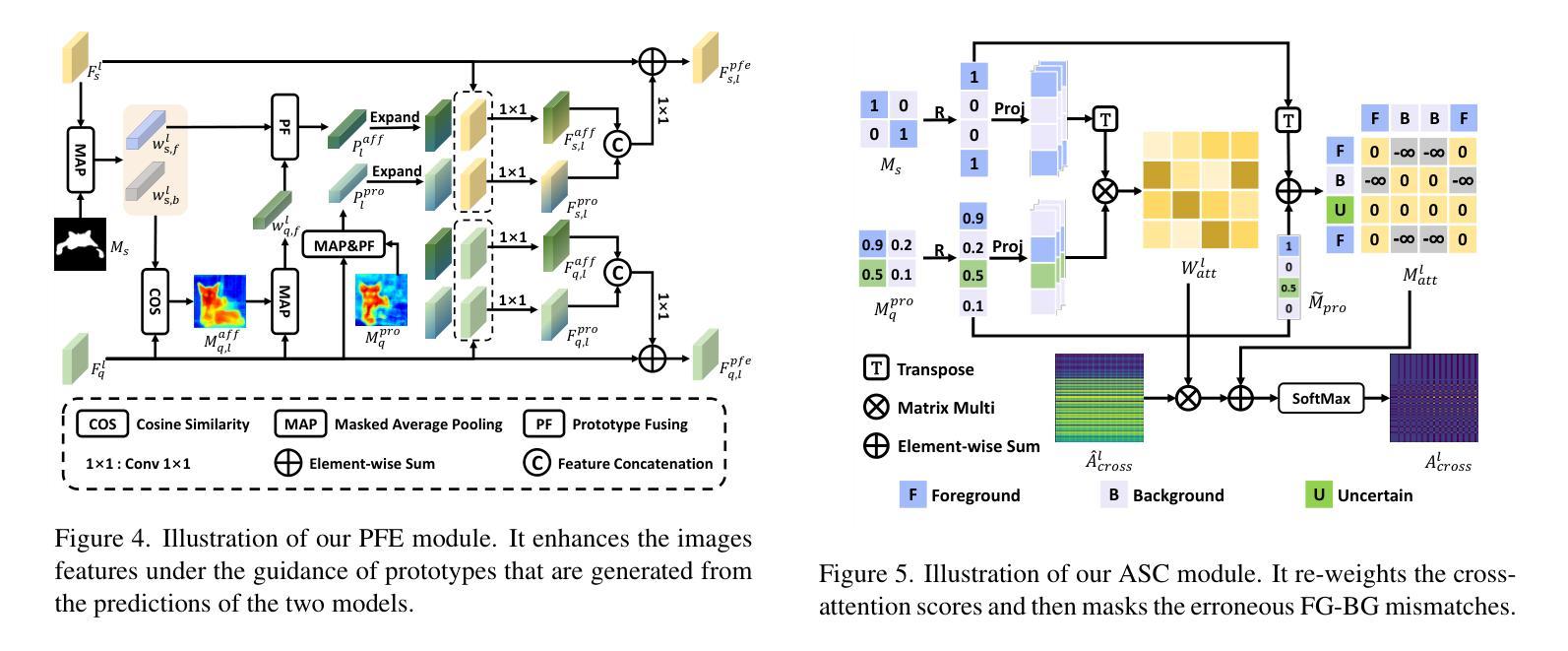
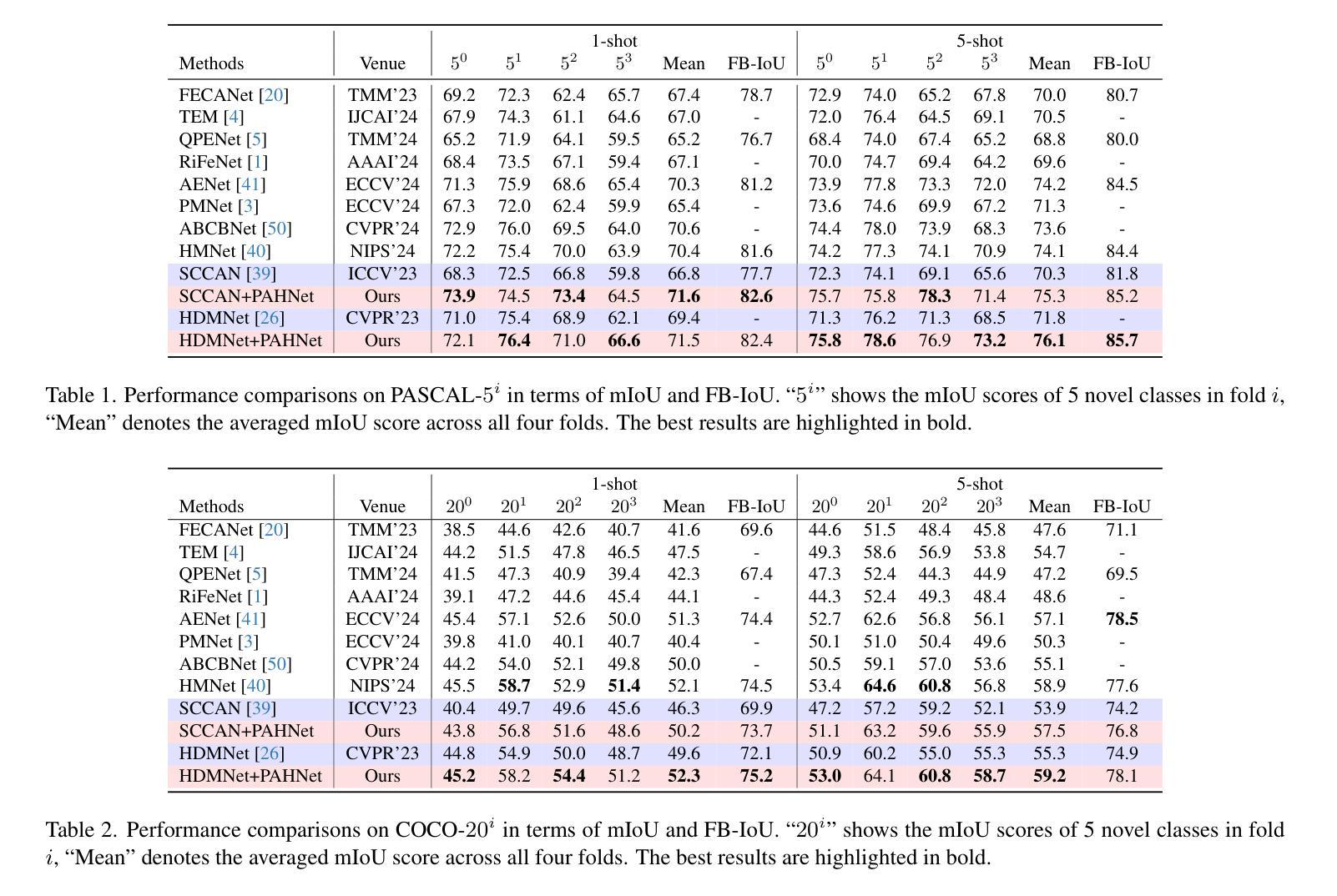
Balancing Conservatism and Aggressiveness: Prototype-Affinity Hybrid Network for Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Tianyu Zou, Shengwu Xiong, Ruilin Yao, Yi Rong
This paper studies the few-shot segmentation (FSS) task, which aims to segment objects belonging to unseen categories in a query image by learning a model on a small number of well-annotated support samples. Our analysis of two mainstream FSS paradigms reveals that the predictions made by prototype learning methods are usually conservative, while those of affinity learning methods tend to be more aggressive. This observation motivates us to balance the conservative and aggressive information captured by these two types of FSS frameworks so as to improve the segmentation performance. To achieve this, we propose a Prototype-Affinity Hybrid Network (PAHNet), which introduces a Prototype-guided Feature Enhancement (PFE) module and an Attention Score Calibration (ASC) module in each attention block of an affinity learning model (called affinity learner). These two modules utilize the predictions generated by a pre-trained prototype learning model (called prototype predictor) to enhance the foreground information in support and query image representations and suppress the mismatched foreground-background (FG-BG) relationships between them, respectively. In this way, the aggressiveness of the affinity learner can be effectively mitigated, thereby eventually increasing the segmentation accuracy of our PAHNet method. Experimental results show that PAHNet outperforms most recently proposed methods across 1-shot and 5-shot settings on both PASCAL-5$^i$ and COCO-20$^i$ datasets, suggesting its effectiveness. The code is available at: GitHub - tianyu-zou/PAHNet: Balancing Conservatism and Aggressiveness: Prototype-Affinity Hybrid Network for Few-Shot Segmentation (ICCV’25)
本文研究了小样本分割(FSS)任务,其目标是通过在少量标注良好的支撑样本上学习模型,对查询图像中属于未见类别的对象进行分割。我们对两种主流的FSS范式的分析表明,原型学习方法做出的预测通常较为保守,而亲和力学习方法做出的预测则更倾向于激进。这一观察结果促使我们平衡这两种FSS框架所捕获的保守和激进信息,以提高分割性能。为此,我们提出了一种Prototype-Affinity Hybrid Network(PAHNet),它在亲和力学习模型(称为亲和力学习者)的每个注意力块中引入了Prototype-guided Feature Enhancement(PFE)模块和Attention Score Calibration(ASC)模块。这两个模块利用由预训练的原型学习模型(称为原型预测器)生成的预测结果,增强支撑图像和查询图像表示中的前景信息,并分别抑制它们之间不匹配的前景-背景(FG-BG)关系。通过这种方式,可以有效地减轻亲和力学习者的激进性,从而最终提高我们的PAHNet方法的分割精度。实验结果表明,在PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$数据集上,PAHNet在1-shot和5-shot设置下均优于最近提出的大多数方法,这证明了其有效性。代码可在以下网址获取:GitHub - tianyu-zou/PAHNet: 平衡保守与激进:用于小样本分割的原型-亲和力混合网络(ICCV’25) 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures
Summary
该论文研究了小样本分割(FSS)任务,旨在通过少量标注良好的样本学习模型,对查询图像中未见类别进行对象分割。分析两种主流FSS范式后,发现原型学习方法预测通常保守,而亲和力学习方法预测更为激进。为此,论文提出了一个原型亲和力混合网络(PAHNet),通过引入原型引导特征增强(PFE)模块和注意力得分校准(ASC)模块,平衡两种方法的预测信息,提高分割性能。实验结果显示,PAHNet在PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$数据集上的1-shot和5-shot设置中表现出最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文研究了小样本分割(FSS)任务,旨在通过少量标注良好的样本对未见类别进行对象分割。
- 分析发现,原型学习方法预测通常保守,而亲和力学习方法预测较为激进。
- 为了平衡这两种方法的预测信息,论文提出了原型亲和力混合网络(PAHNet)。
- PAHNet通过引入PFE和ASC模块,提高了分割性能。
- 实验结果显示,PAHNet在多种数据集上实现了最佳性能。
- PAHNet方法能够有效缓解亲和力学习者的激进性。
- 代码已公开,可供进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图

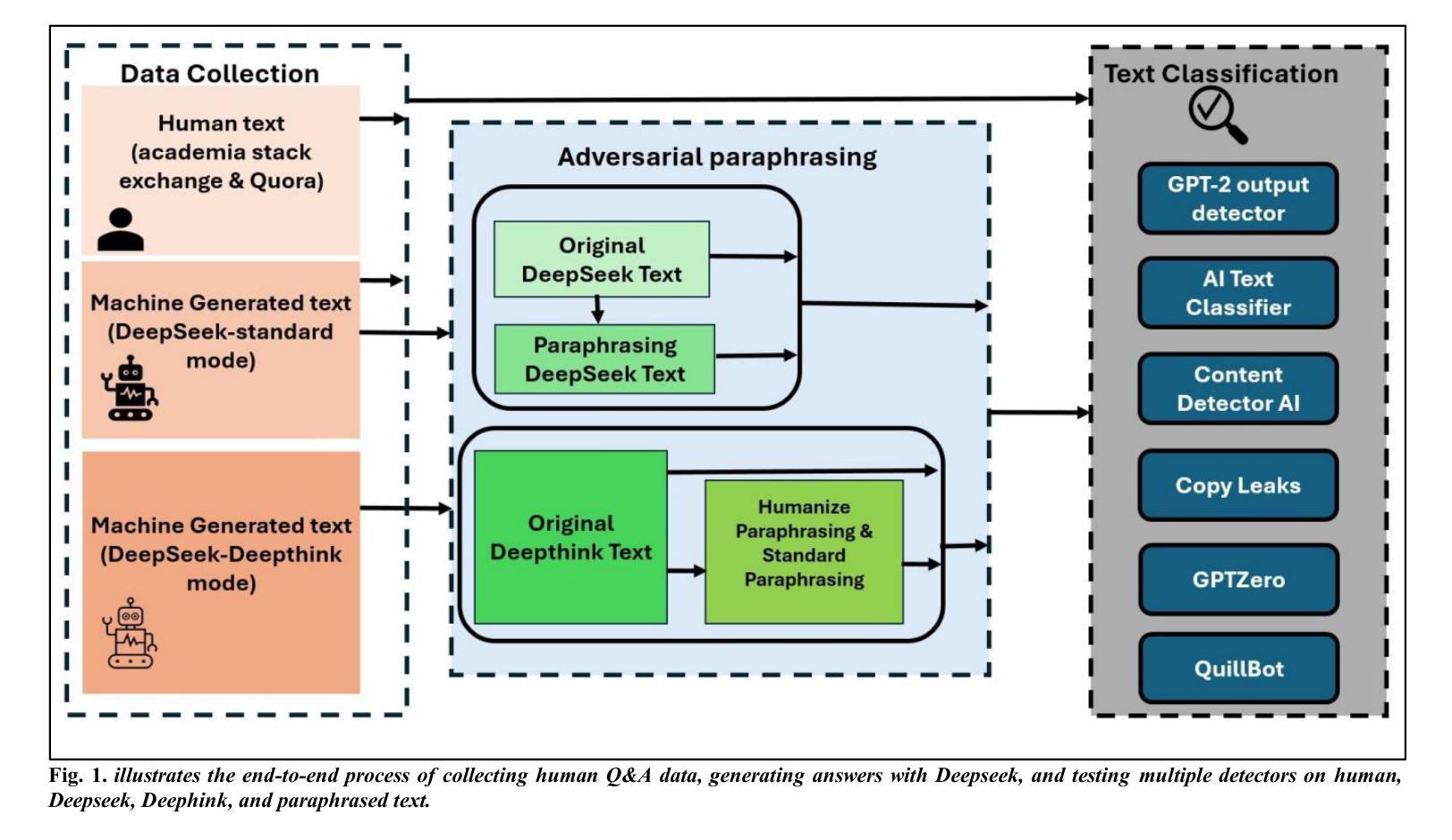
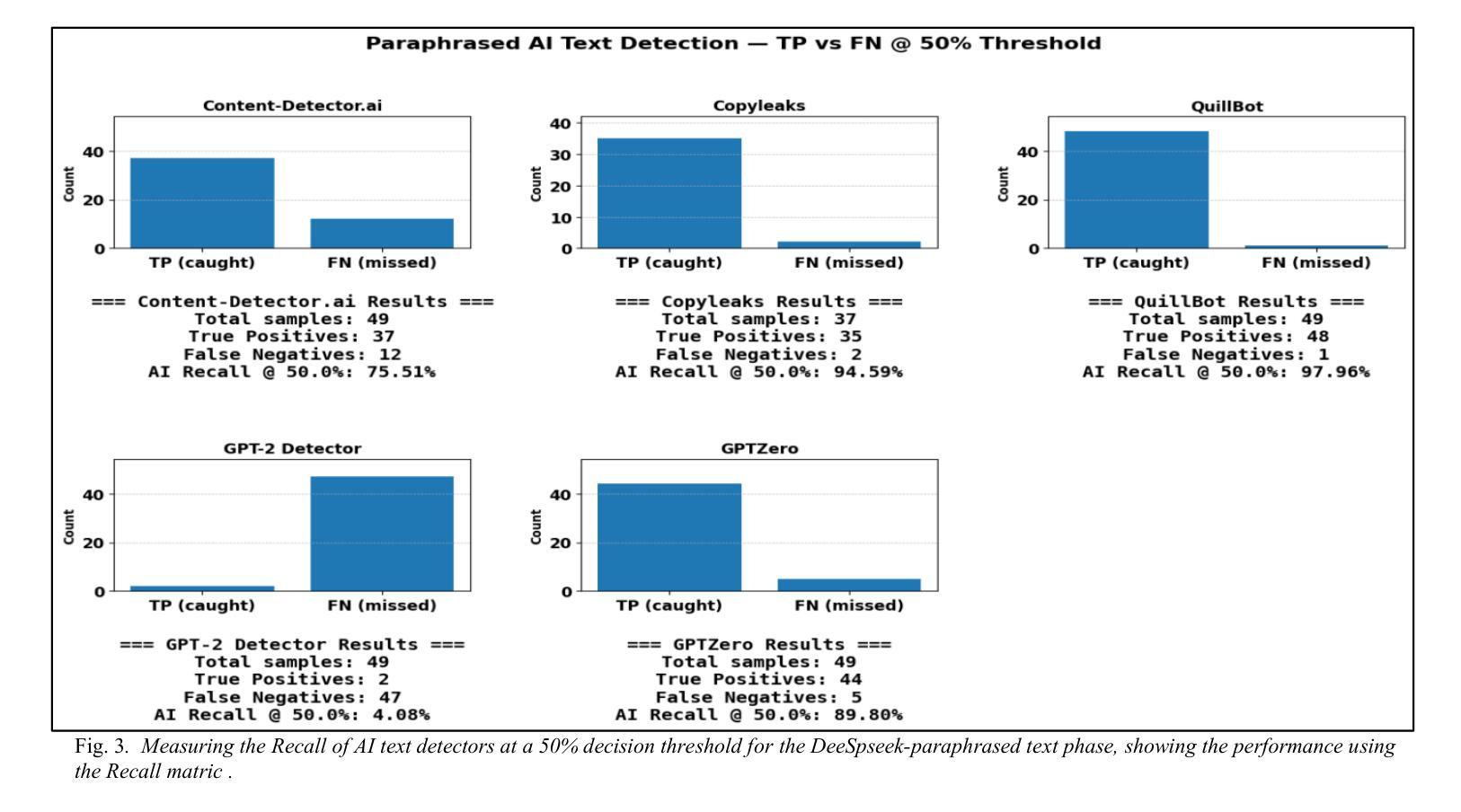
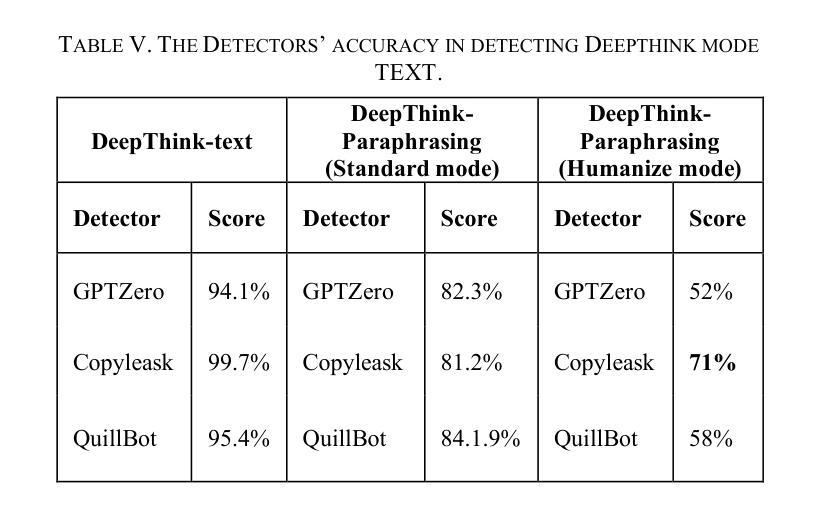
Evaluating the Performance of AI Text Detectors, Few-Shot and Chain-of-Thought Prompting Using DeepSeek Generated Text
Authors:Hulayyil Alshammari, Praveen Rao
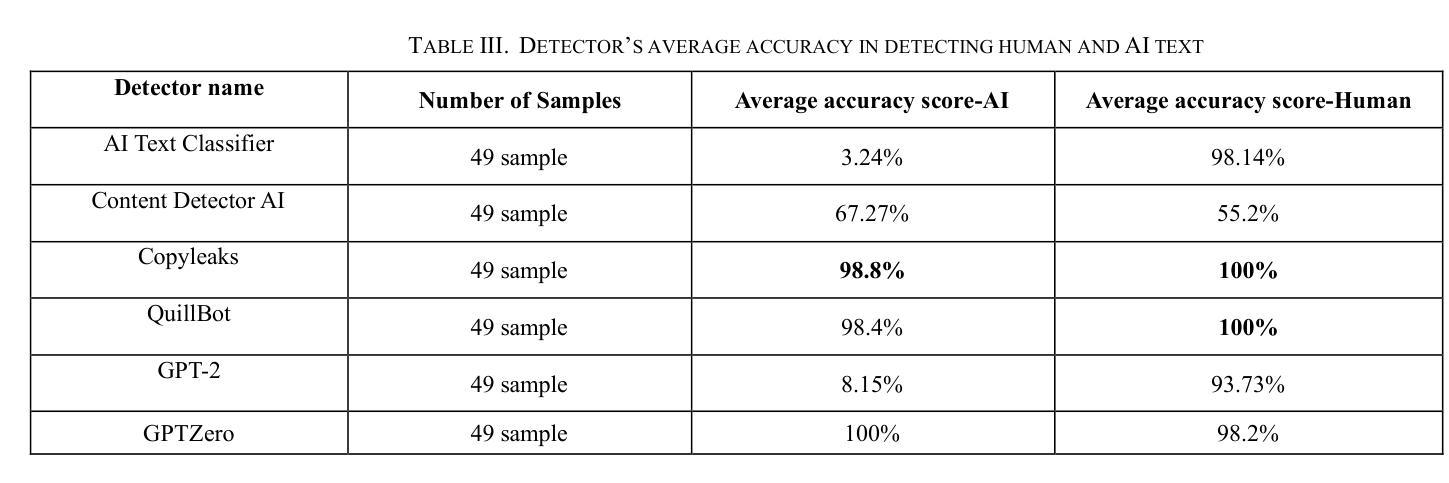
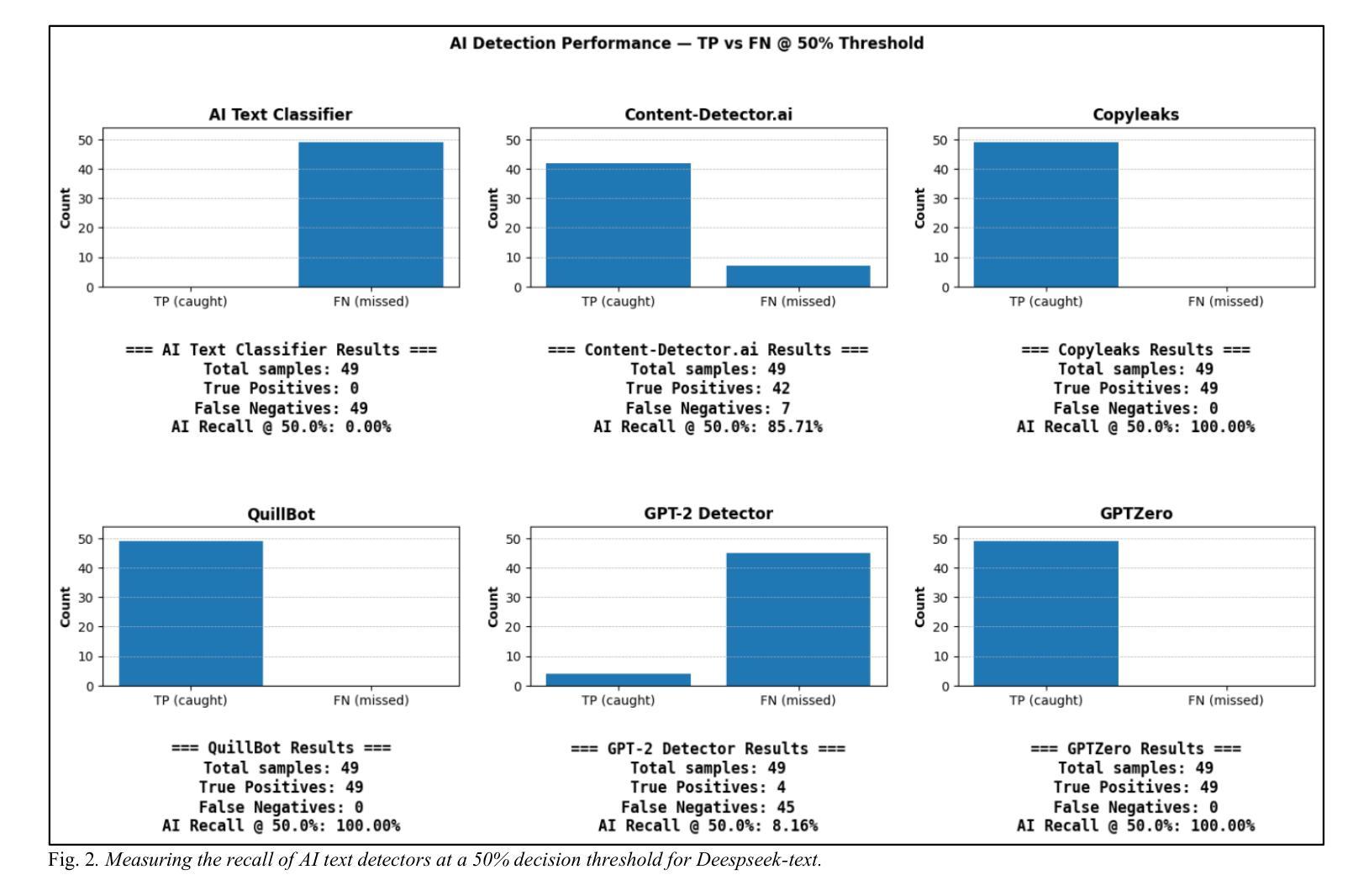
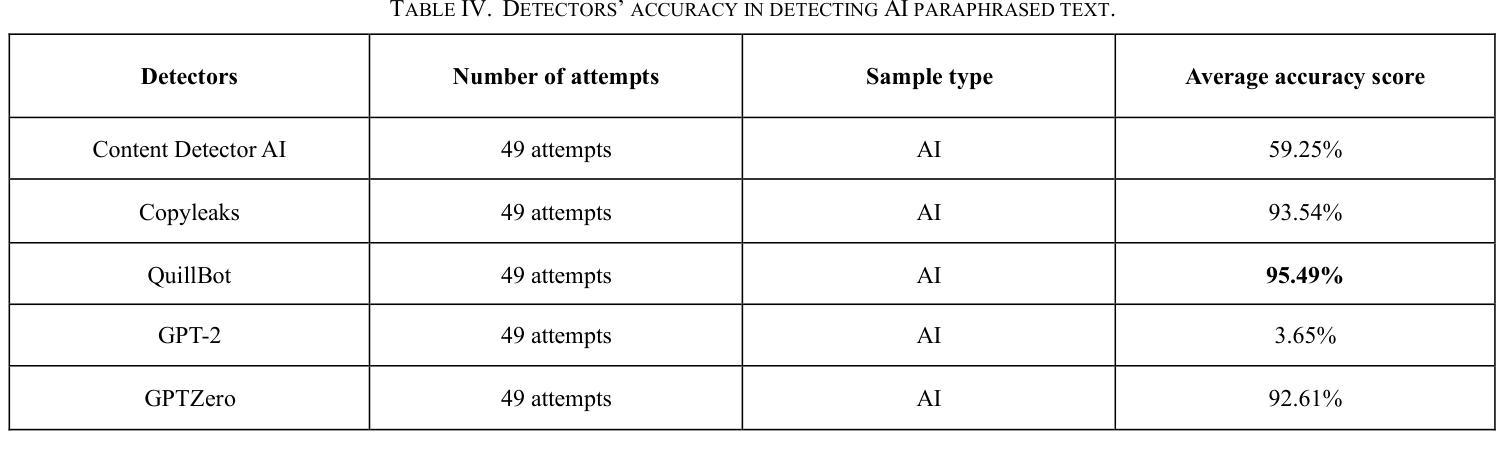
Large language models (LLMs) have rapidly transformed the creation of written materials. LLMs have led to questions about writing integrity, thereby driving the creation of artificial intelligence (AI) detection technologies. Adversarial attacks, such as standard and humanized paraphrasing, inhibit detectors’ ability to detect machine-generated text. Previous studies have mainly focused on ChatGPT and other well-known LLMs and have shown varying accuracy across detectors. However, there is a clear gap in the literature about DeepSeek, a recently published LLM. Therefore, in this work, we investigate whether six generally accessible AI detection tools – AI Text Classifier, Content Detector AI, Copyleaks, QuillBot, GPT-2, and GPTZero – can consistently recognize text generated by DeepSeek. The detectors were exposed to the aforementioned adversarial attacks. We also considered DeepSeek as a detector by performing few-shot prompting and chain-of-thought reasoning (CoT) for classifying AI and human-written text. We collected 49 human-authored question-answer pairs from before the LLM era and generated matching responses using DeepSeek-v3, producing 49 AI-generated samples. Then, we applied adversarial techniques such as paraphrasing and humanizing to add 196 more samples. These were used to challenge detector robustness and assess accuracy impact. While QuillBot and Copyleaks showed near-perfect performance on original and paraphrased DeepSeek text, others – particularly AI Text Classifier and GPT-2 – showed inconsistent results. The most effective attack was humanization, reducing accuracy to 71% for Copyleaks, 58% for QuillBot, and 52% for GPTZero. Few-shot and CoT prompting showed high accuracy, with the best five-shot result misclassifying only one of 49 samples (AI recall 96%, human recall 100%).
大型语言模型(LLM)迅速改变了书面材料的创作方式。它们引发了关于写作完整性的问题,从而推动了人工智能(AI)检测技术的发展。对抗性攻击,如标准复述和人性化复述,限制了检测器检测机器生成文本的能力。以往的研究主要集中在ChatGPT和其他知名的大型语言模型上,并且在检测器之间显示了不同的准确性。然而,关于最近发布的大型语言模型DeepSeek的文献中存在明显的空白。因此,在这项工作中,我们研究了六种普遍可用的AI检测工具——AI文本分类器、内容检测AI、Copyleaks、QuillBot、GPT-2和GPTZero,是否能一致地识别DeepSeek生成的文本。这些检测器受到了上述对抗性攻击的挑战。我们还通过进行少量提示和链式思维推理(CoT)将DeepSeek作为检测器来分类AI和人类撰写的文本。我们从大型语言模型时代之前收集了49个人类提问和回答的对,并使用DeepSeek-v3生成了匹配的回应,产生了49个AI生成的样本。然后,我们运用诸如复述和人性化等对抗技术,增加了196个样本。这些被用来挑战检测器的稳健性并评估准确性的影响。虽然QuillBot和Copyleaks在原始和复述的DeepSeek文本上表现出近乎完美的性能,但其他人——尤其是AI文本分类器和GPT-2——的结果却不尽一致。最有效的攻击是人性化攻击,将Copyleaks的准确率降低到71%,QuillBot的准确率降低到58%,GPTZero的准确率降低到52%。少量提示和链式思维推理表现出较高的准确性,其中最好的五镜头结果仅误判了49个样本中的一个(AI召回率为96%,人类召回率为100%)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展引发了关于写作完整性的问题,并推动了人工智能(AI)检测技术的进步。当前存在六种常用的AI检测工具,它们在对抗攻击下识别DeepSeek生成的文本的能力有所差异。通过采用少样本提示和链式思维推理(CoT)方法,研究评估了这些工具的准确性和鲁棒性。结果显示,DeepSeek在某些情况下表现出较高的生成文本能力,但对抗性技术如人性化处理仍能有效降低检测工具的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的普及引发对写作完整性和AI检测技术的关注。
- 目前常用的AI检测工具在面对DeepSeek生成的文本时,其检测能力存在差异。
- 对抗攻击,特别是人性化处理,能有效降低检测工具的准确性。
- AI检测工具在面对DeepSeek生成的文本时,QuillBot和Copyleaks表现较好。
- 少样本提示和链式思维推理(CoT)方法能显著提高DeepSeek的分类准确性。
- DeepSeek在某些情况下能够生成高质量的文本,但仍有改进空间,特别是在面对对抗性技术时。
点此查看论文截图

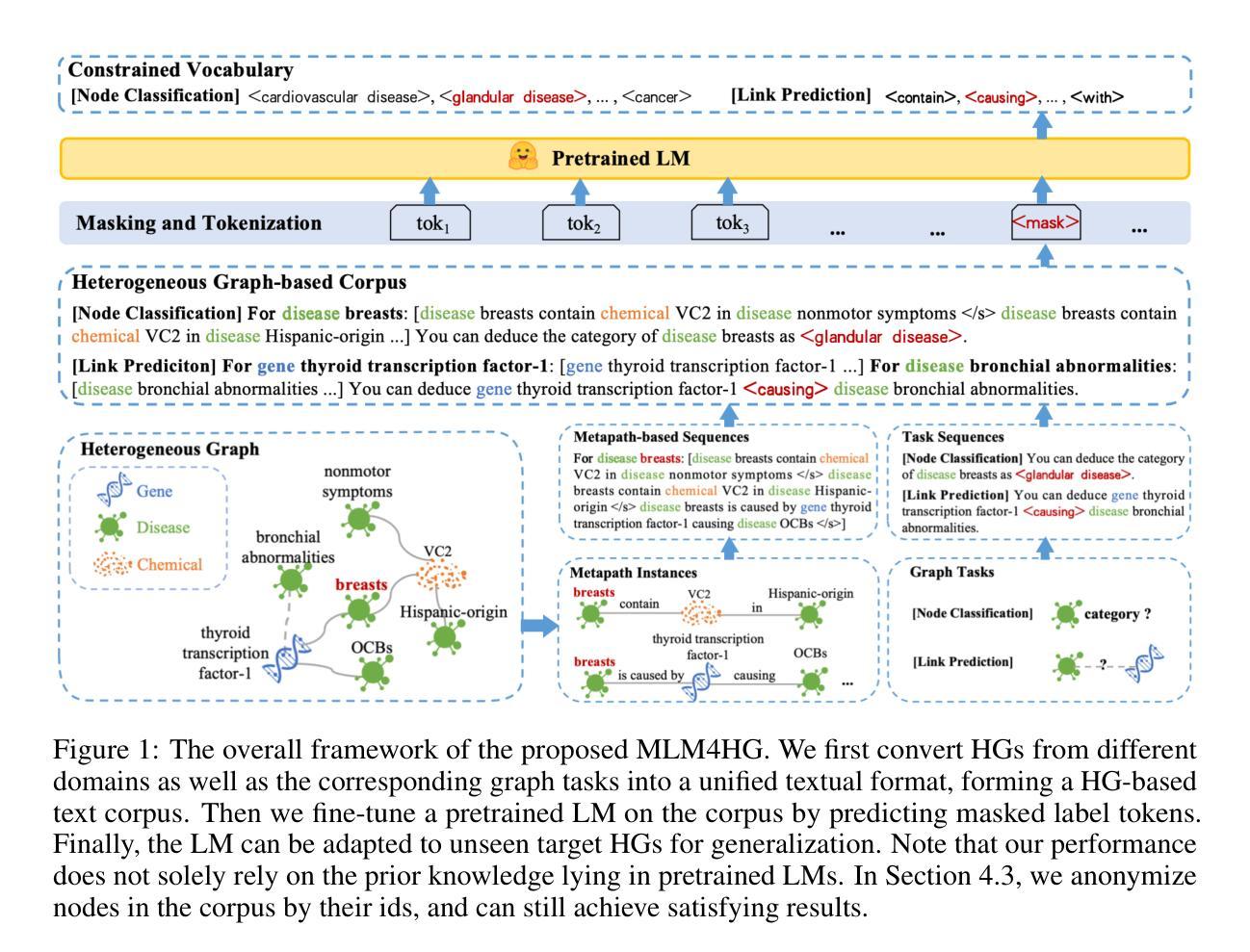
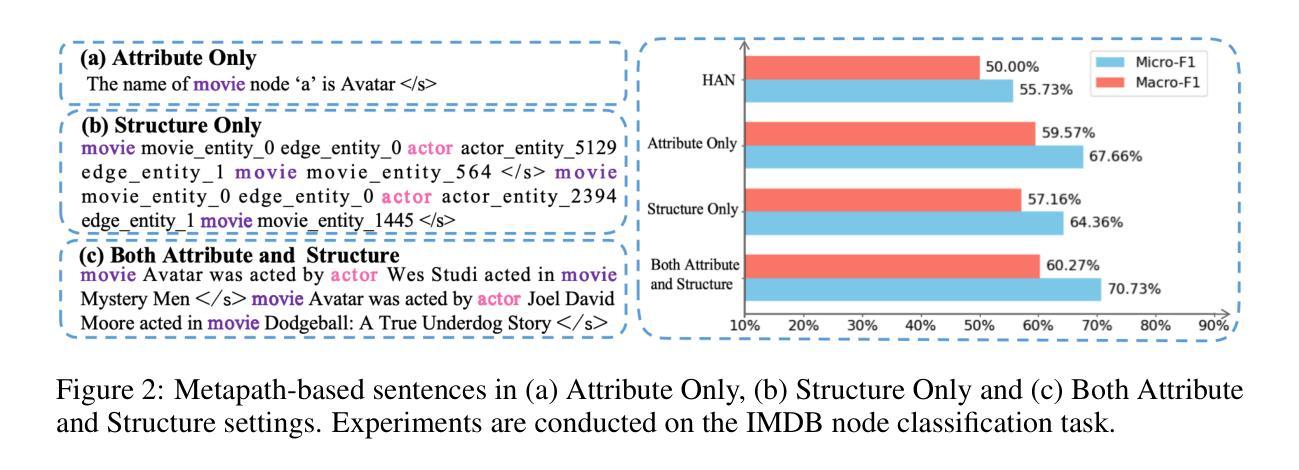
Masked Language Models are Good Heterogeneous Graph Generalizers
Authors:Jinyu Yang, Cheng Yang, Shanyuan Cui, Zeyuan Guo, Liangwei Yang, Muhan Zhang, Zhiqiang Zhang, Chuan Shi
Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) excel at capturing structural and semantic information in heterogeneous graphs (HGs), while struggling to generalize across domains and tasks. With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), a recent study explored the integration of HGNNs with LLMs for generalizable heterogeneous graph learning. However, this approach typically encodes structural information as HG tokens using HGNNs, and disparities in embedding spaces between HGNNs and LLMs have been shown to bias the LLM’s comprehension of HGs. Moreover, since these HG tokens are often derived from node-level tasks, the model’s ability to generalize across tasks remains limited. To this end, we propose a simple yet effective Masked Language Modeling-based method, called MLM4HG. MLM4HG introduces metapath-based textual sequences instead of HG tokens to extract structural and semantic information inherent in HGs, and designs customized textual templates to unify different graph tasks into a coherent cloze-style ‘mask’ token prediction paradigm. Specifically,MLM4HG first converts HGs from various domains to texts based on metapaths, and subsequently combines them with the unified task texts to form a HG-based corpus. Moreover, the corpus is fed into a pretrained LM for fine-tuning with a constrained target vocabulary, enabling the fine-tuned LM to generalize to unseen target HGs. Extensive cross-domain and multi-task experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate the superior generalization performance of MLM4HG over state-of-the-art methods in both few-shot and zero-shot scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/MLM4HG.
异质图神经网络(HGNNs)擅长捕获异质图(HG)中的结构和语义信息,但在跨域和任务之间的泛化方面遇到困难。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,最近的一项研究探索了将HGNNs与LLMs结合进行可泛化的异质图学习。然而,这种方法通常使用HGNNs将结构信息编码为HG令牌,HGNNs和LLMs之间的嵌入空间差异已证明会偏向LLM对HG的理解。此外,由于这些HG令牌通常来源于节点级任务,模型在跨任务泛化方面的能力仍然有限。为此,我们提出了一种简单有效的基于Masked Language Modeling的方法,称为MLM4HG。MLM4HG引入基于元路径的文本序列,而不是HG令牌,以提取HG固有的结构和语义信息,并设计定制的文本模板将不同的图任务统一为一个连贯的填充式“掩码”令牌预测范式。具体来说,MLM4HG首先根据元路径将来自不同领域的HG转换为文本,然后将其与统一的任务文本结合形成基于HG的语料库。此外,该语料库被输入到预训练的LM中进行微调,使用受限的目标词汇表,使微调后的LM能够泛化到未见过的目标HG。在四个真实世界数据集上的跨域和多任务实验广泛表明,MLM4HG在少样本和零样本场景中的泛化性能均优于最新方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/MLM4HG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
HGNN与LLM结合进行异质图学习的方法虽能捕捉结构语义信息,但在跨域跨任务泛化时存在挑战。为此,研究提出了MLM4HG方法,通过元路径文本序列替代HG令牌,设计统一任务文本,形成掩盖式“掩盖”令牌预测范式。MLM4HG能转化不同领域的异质图为文本,结合任务文本形成基于异质图的语料库,并微调预训练的语言模型以实现泛化。实验证明,MLM4HG在跨域多任务上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- HGNN在捕捉异质图的结构和语义信息方面表现出色,但在跨域和任务间的泛化能力上遇到困难。
- 结合LLMs的方法通常将结构信息编码为HG令牌,但存在嵌入空间差异问题,影响LLM对HG的理解。
- MLM4HG采用基于元路径的文本序列替代HG令牌,更有效地提取异质图中的结构语义信息。
- MLM4HG通过设计统一的任务文本,将不同的图任务整合到一致的掩盖式“掩盖”令牌预测范式中。
- MLM4HG能将异质图从各种领域转换为文本,与任务文本结合形成基于异质图的语料库。
- 通过使用预训练的语言模型进行微调,MLM4HG提高了对未见过的异质图的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

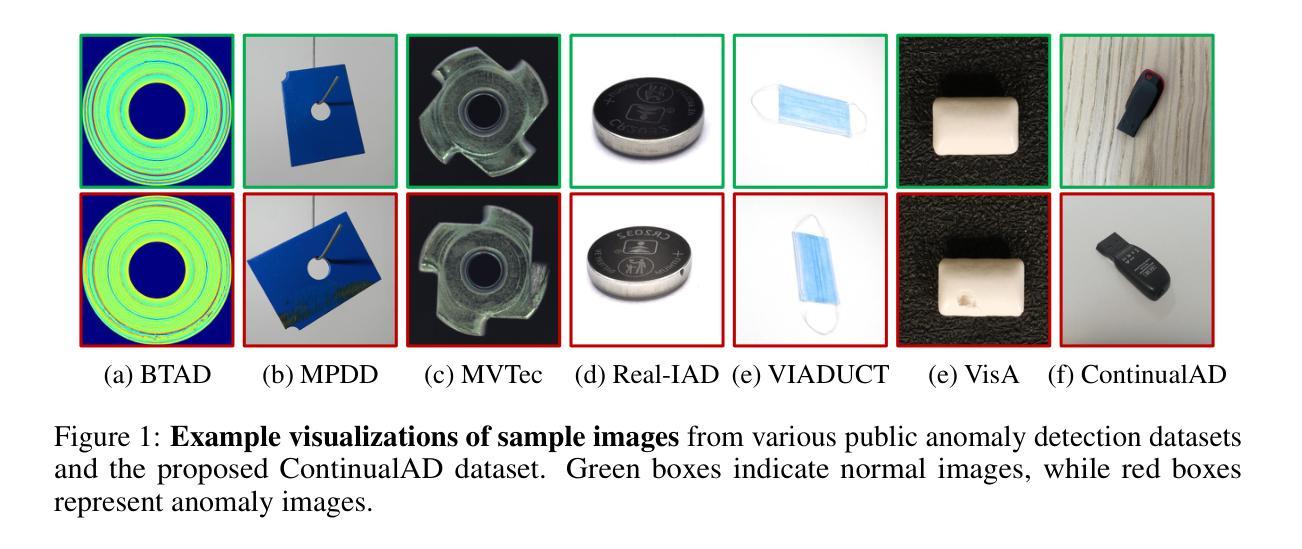
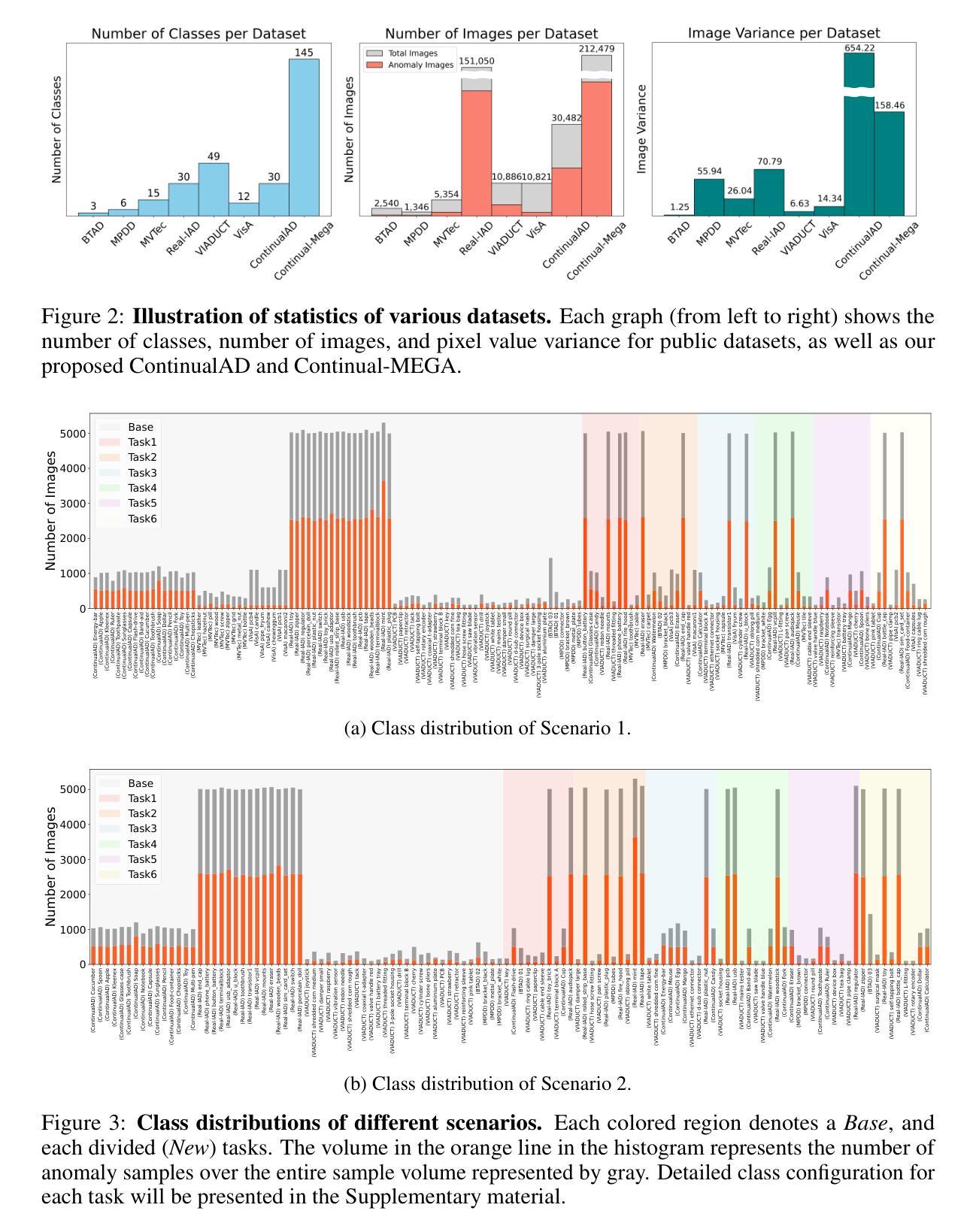
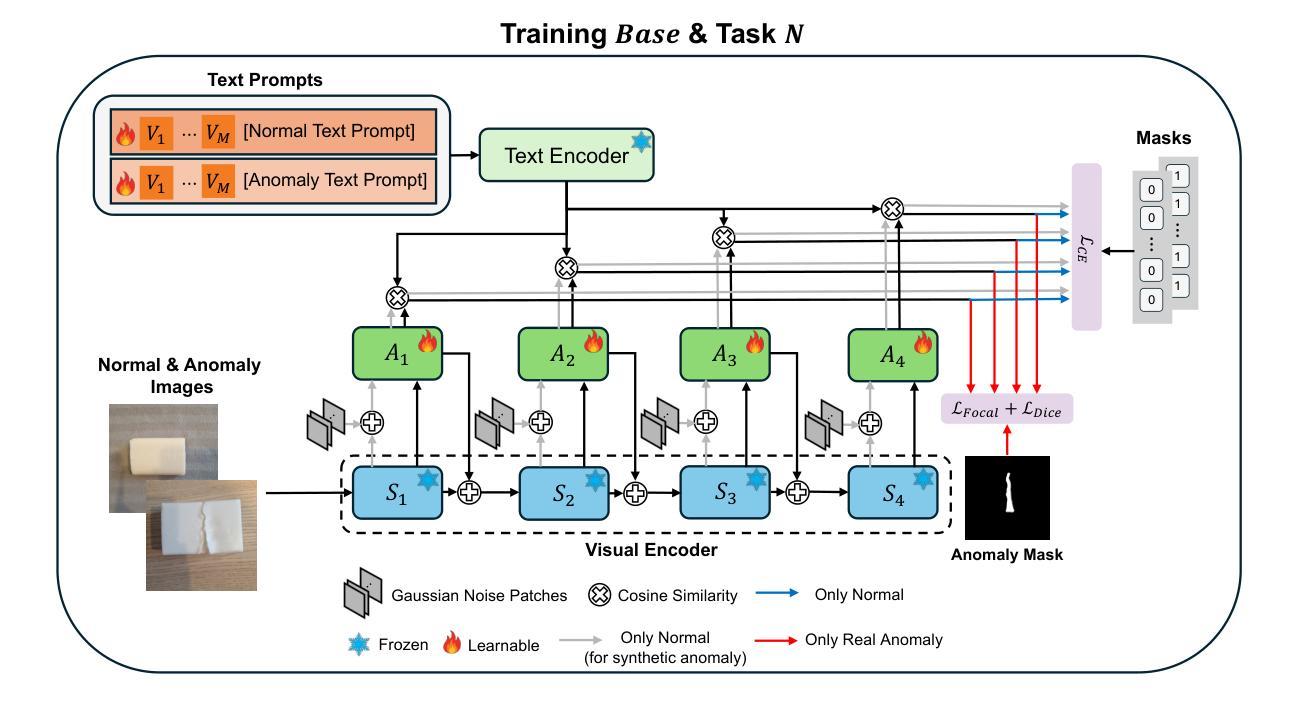
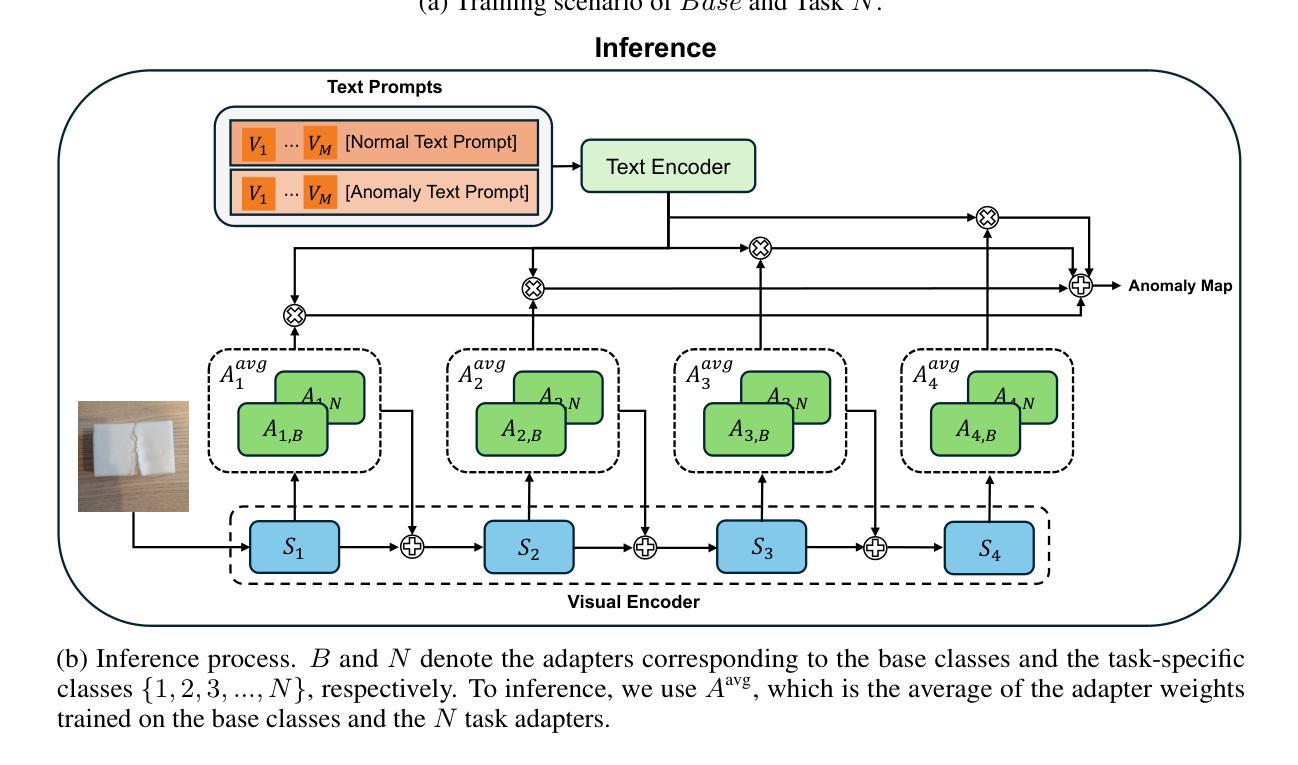
Continual-MEGA: A Large-scale Benchmark for Generalizable Continual Anomaly Detection
Authors:Geonu Lee, Yujeong Oh, Geonhui Jang, Soyoung Lee, Jeonghyo Song, Sungmin Cha, YoungJoon Yoo
In this paper, we introduce a new benchmark for continual learning in anomaly detection, aimed at better reflecting real-world deployment scenarios. Our benchmark, Continual-MEGA, includes a large and diverse dataset that significantly expands existing evaluation settings by combining carefully curated existing datasets with our newly proposed dataset, ContinualAD. In addition to standard continual learning with expanded quantity, we propose a novel scenario that measures zero-shot generalization to unseen classes, those not observed during continual adaptation. This setting poses a new problem setting that continual adaptation also enhances zero-shot performance. We also present a unified baseline algorithm that improves robustness in few-shot detection and maintains strong generalization. Through extensive evaluations, we report three key findings: (1) existing methods show substantial room for improvement, particularly in pixel-level defect localization; (2) our proposed method consistently outperforms prior approaches; and (3) the newly introduced ContinualAD dataset enhances the performance of strong anomaly detection models. We release the benchmark and code in https://github.com/Continual-Mega/Continual-Mega.
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了一个针对异常检测中的持续学习的新基准测试,旨在更好地反映真实世界的部署场景。我们的基准测试“Continual-MEGA”包括一个大规模和多样化的数据集,它通过结合精心策划的现有数据集和我们新提出的数据集ContinualAD,显著扩展了现有的评估设置。除了标准持续学习扩充数量之外,我们还提出了一种新的场景,即测量对未见类别的零样本泛化能力,这些类别在持续适应期间未被观察到。这一设置提出了一个新的难题,即持续适应也能提高零样本性能。我们还提出了一种统一的基线算法,该算法提高了少样本检测中的稳健性,并保持了强大的泛化能力。通过广泛的评估,我们报告了三个关键发现:(1)现有方法显示出有很大的改进空间,特别是在像素级缺陷定位方面;(2)我们提出的方法在持续适应期间始终优于以前的方法;(3)新推出的ContinualAD数据集增强了强大的异常检测模型的性能。我们在https://github.com/Continual-Mega/Continual-Mega上发布了基准测试和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对异常检测中的持续学习的新基准测试集,即Continual-MEGA。该基准测试集包括大规模多样化的数据集,通过结合现有精心挑选的数据集和新提出的ContinualAD数据集,扩展了现有的评估设置。除了标准持续学习的大规模扩展外,还提出了一种新的场景来衡量对未见类别的零样本泛化能力。此外,文章提出了一种统一的基线算法,提高了少样本检测的鲁棒性并保持了强大的泛化能力。通过广泛的评估,本文报告了三个关键发现:现有方法存在改进空间,特别是在像素级缺陷定位方面;所提方法始终优于先前的方法;新引入的ContinualAD数据集增强了强大的异常检测模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一个针对异常检测中的持续学习的新基准测试集——Continual-MEGA。
- 该基准测试集包括大规模多样化的数据集,扩展了现有评估设置。
- 除了标准持续学习外,还考虑了零样本泛化能力的衡量。
- 提出了一个统一的基线算法,用于提高少样本检测的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- 现有方法在像素级缺陷定位方面存在改进空间。
- 所提方法在某些关键方面始终优于先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Large Language Models for Bengali Math Word Problem Solving with Chain of Thought Reasoning
Authors:Bidyarthi Paul, Jalisha Jashim Era, Mirazur Rahman Zim, Tahmid Sattar Aothoi, Faisal Muhammad Shah
Solving Bengali Math Word Problems (MWPs) remains a major challenge in natural language processing (NLP) due to the language’s low-resource status and the multi-step reasoning required. Existing models struggle with complex Bengali MWPs, largely because no human-annotated Bengali dataset has previously addressed this task. This gap has limited progress in Bengali mathematical reasoning. To address this, we created SOMADHAN, a dataset of 8792 complex Bengali MWPs with manually written, step-by-step solutions. We designed this dataset to support reasoning-focused evaluation and model development in a linguistically underrepresented context. Using SOMADHAN, we evaluated a range of large language models (LLMs) - including GPT-4o, GPT-3.5 Turbo, LLaMA series models, Deepseek, and Qwen - through both zero-shot and few-shot prompting with and without Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning. CoT prompting consistently improved performance over standard prompting, especially in tasks requiring multi-step logic. LLaMA-3.3 70B achieved the highest accuracy of 88% with few-shot CoT prompting. We also applied Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune models efficiently, enabling them to adapt to Bengali MWPs with minimal computational cost. Our work fills a critical gap in Bengali NLP by providing a high-quality reasoning dataset and a scalable framework for solving complex MWPs. We aim to advance equitable research in low-resource languages and enhance reasoning capabilities in educational and language technologies.
解决孟加拉数学文字题(MWPs)仍然是自然语言处理(NLP)领域的一个重大挑战,这主要是由于孟加拉语的资源相对较少以及所需的多步骤推理造成的。现有模型在处理复杂的孟加拉数学问题时面临困难,很大程度上是因为之前没有人对孟加拉数据集进行人工标注来解决这一任务。这一差距限制了孟加拉数学推理的进展。为了解决这个问题,我们创建了SOMADHAN数据集,包含8792个复杂的孟加拉数学文字题和手动编写的分步解答。我们设计这个数据集是为了支持在缺乏代表性语境中的推理评估模型发展。使用SOMADHAN数据集,我们评估了一系列大型语言模型(LLM),包括GPT-4o、GPT-3.5 Turbo、LLaMA系列模型、Deepseek和Qwen等,通过零样本和少样本提示以及有无思维链(CoT)推理进行。思维链提示始终提高了性能,尤其是在需要多步骤逻辑的任务中。LLaMA-3.3 70B在少样本思维链提示下取得了88%的最高准确率。我们还应用了低秩适应(LoRA)来有效地微调模型,使其能够适应孟加拉数学文字题,并尽量减少计算成本。我们的工作通过提供高质量的推理数据集和解决复杂数学文字题的可扩展框架,填补了孟加拉NLP领域的一个关键空白。我们的目标是推动低资源语言的公平研究,并提升教育和语言技术中的推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
解决孟加拉数学文字题(MWPs)是自然语言处理(NLP)领域的主要挑战,因孟加拉语的低资源状态和多步骤推理的需求。先前模型难以处理复杂的孟加拉MWPs,因为没有针对此任务的孟加拉语人工标注数据集。为解决此问题,我们创建了SOMADHAN数据集,包含8792道复杂的孟加拉MWPs和手动编写的逐步解答。此数据集旨在支持语言上被忽视的情境中的推理评估模型发展。使用SOMADHAN数据集,我们评估了一系列大型语言模型(LLMs),包括GPT-4o、GPT-3.5 Turbo、LLaMA系列模型等,通过零镜头和少镜头提示,以及有无思维链(CoT)推理进行评价。思维链提示始终提高了性能,尤其是在需要多步骤逻辑的任务中。LLaMA-3.3 70B在少镜头CoT提示下达到88%的最高准确率。我们还应用了低秩适应(LoRA)来有效地微调模型,使其能够适应孟加拉MWPs,同时保持较低的计算成本。我们的工作通过提供高质量推理数据集和复杂MWPs的可扩展框架,填补了孟加拉NLP领域的一个关键空白。我们的目标是推动低资源语言的公平研究,提高教育和语言技术中的推理能力。
关键见解
- 孟加拉数学文字题(MWPs)解决是NLP领域的挑战,因语言的低资源状态和多步骤推理需求。
- 现有模型在处理复杂的孟加拉MWPs时遇到困难,因为没有专门的数据集。
- 引入了SOMADHAN数据集,包含8792道复杂的孟加拉MWPs及其逐步解答,以支持推理评估模型发展。
- 多种大型语言模型(LLMs)在SOMADHAN数据集上进行了评估,包括GPT系列和LLaMA系列模型。
- 思维链(CoT)提示在解决需要多步骤逻辑的问题时表现优异。
- LLaMA-3.3 70B在少镜头CoT提示下取得了最高准确率。
- 应用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法微调模型,以在保持较低计算成本的同时适应孟加拉MWPs。
点此查看论文截图

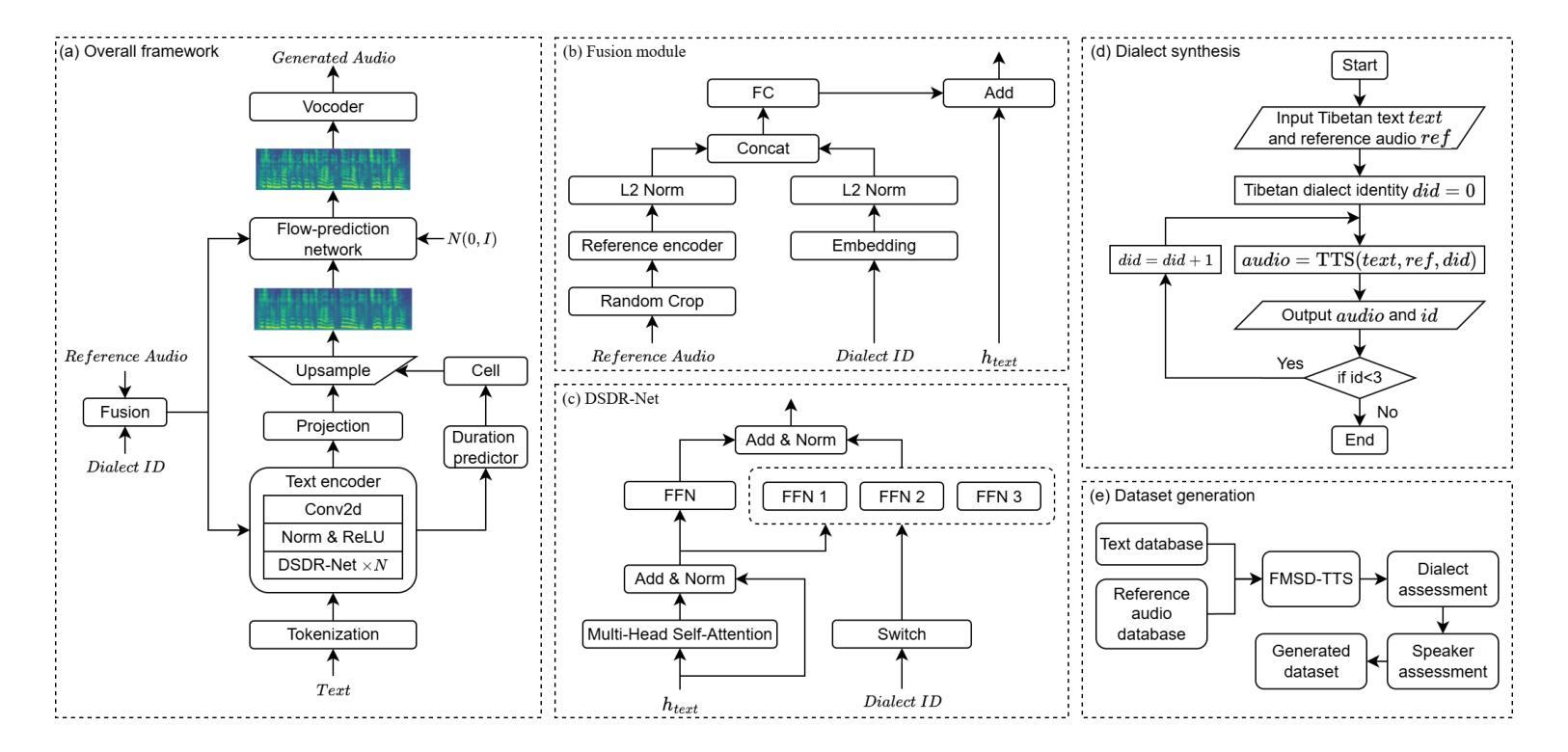
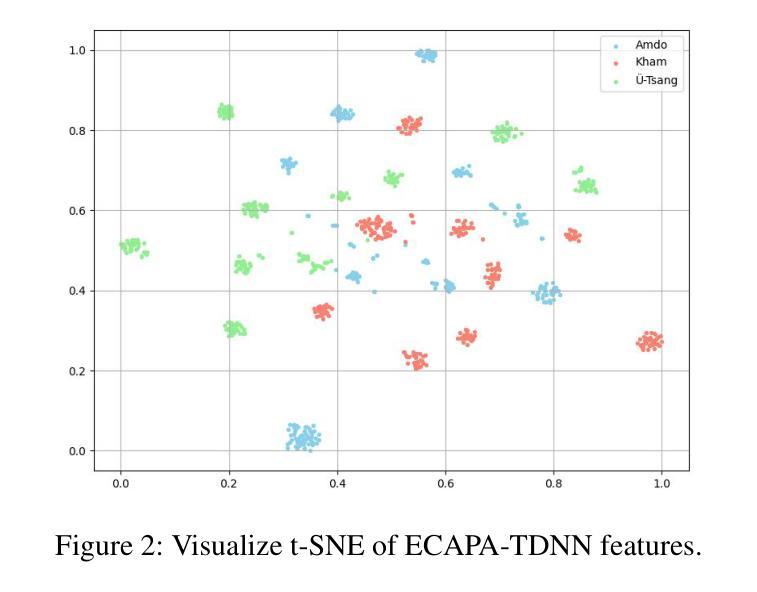
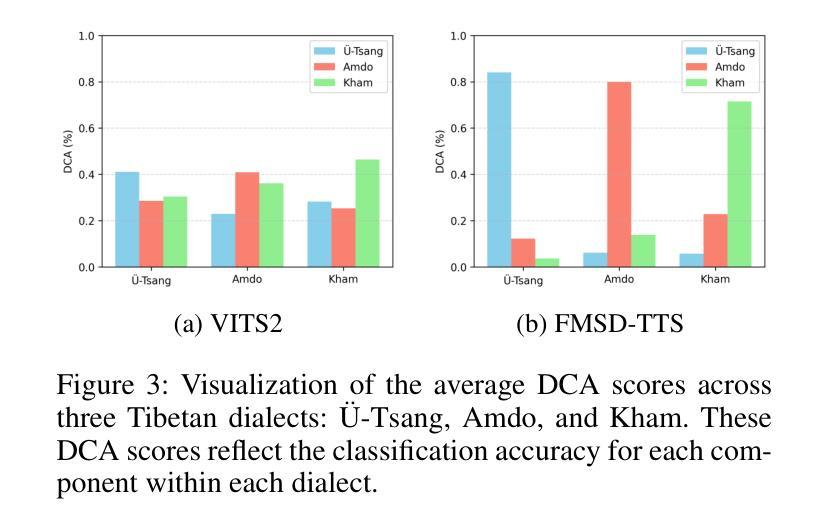
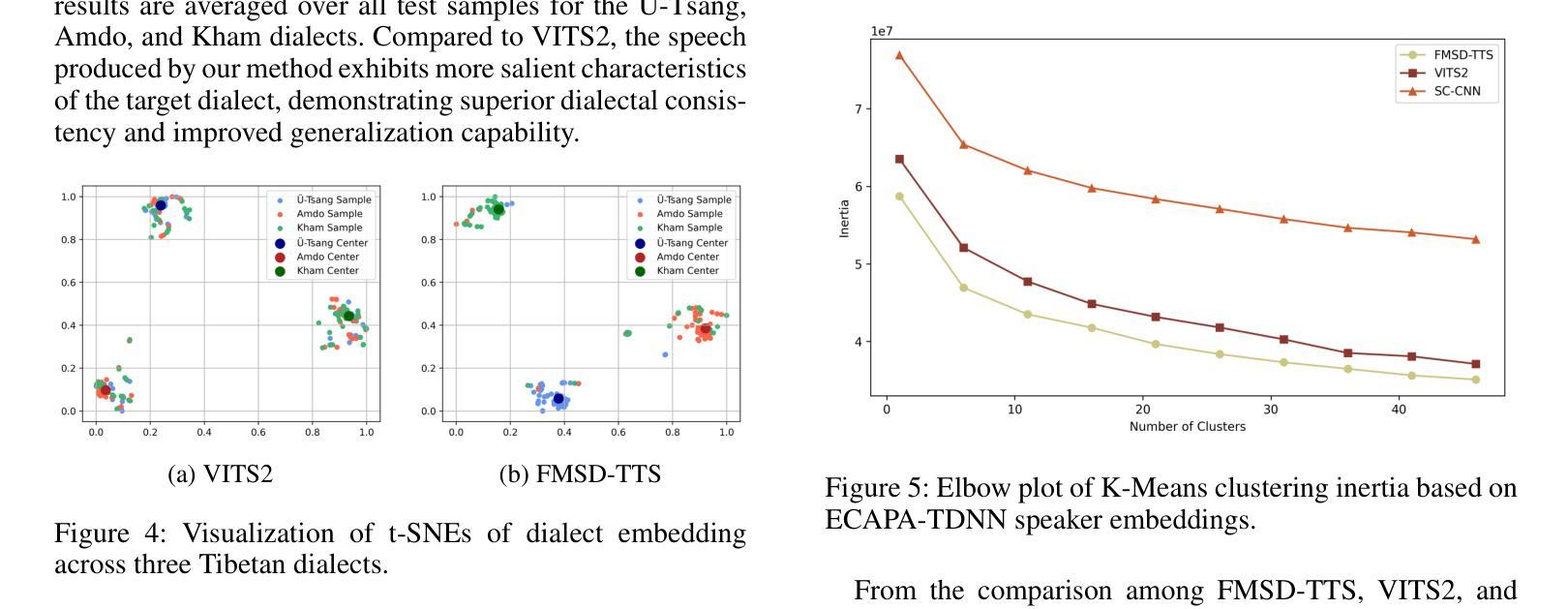
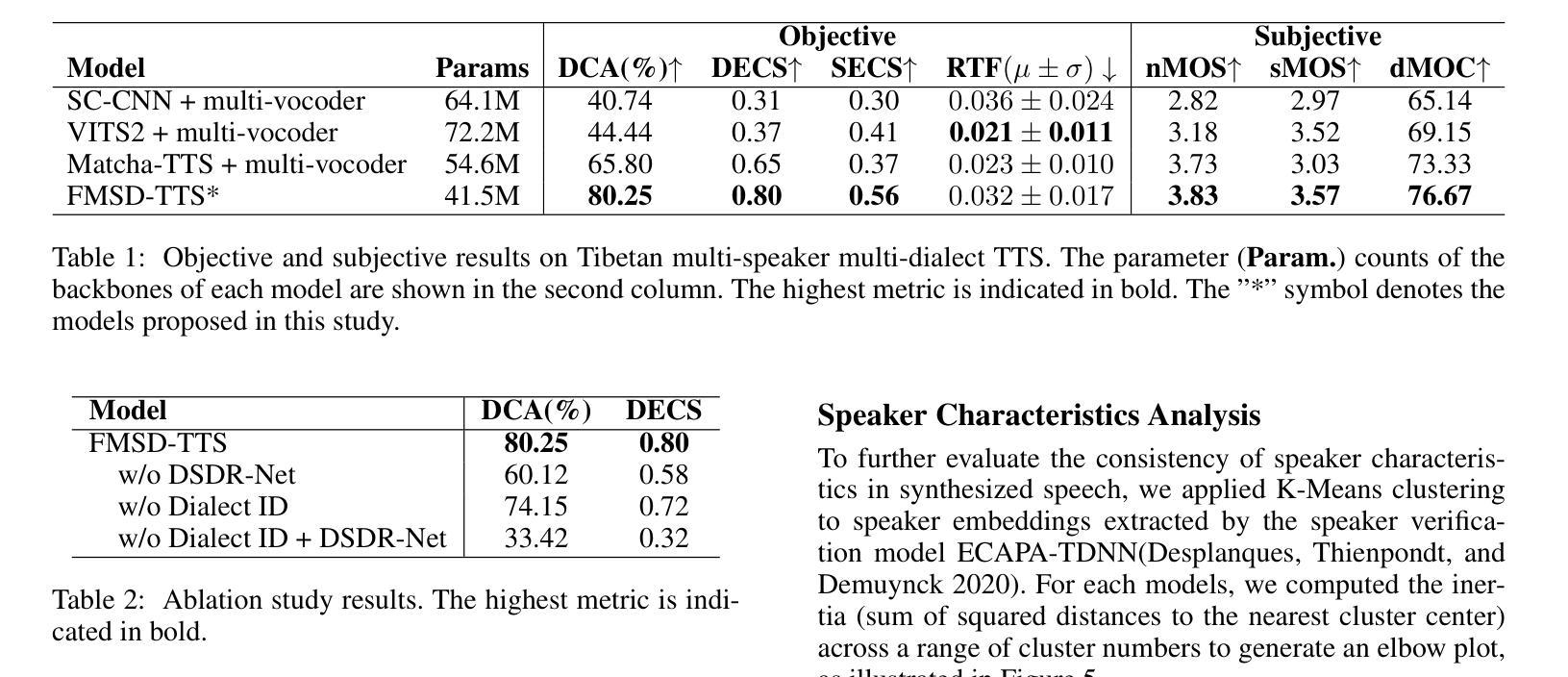
FMSD-TTS: Few-shot Multi-Speaker Multi-Dialect Text-to-Speech Synthesis for Ü-Tsang, Amdo and Kham Speech Dataset Generation
Authors:Yutong Liu, Ziyue Zhang, Ban Ma-bao, Yuqing Cai, Yongbin Yu, Renzeng Duojie, Xiangxiang Wang, Fan Gao, Cheng Huang, Nyima Tashi
Tibetan is a low-resource language with minimal parallel speech corpora spanning its three major dialects-"U-Tsang, Amdo, and Kham-limiting progress in speech modeling. To address this issue, we propose FMSD-TTS, a few-shot, multi-speaker, multi-dialect text-to-speech framework that synthesizes parallel dialectal speech from limited reference audio and explicit dialect labels. Our method features a novel speaker-dialect fusion module and a Dialect-Specialized Dynamic Routing Network (DSDR-Net) to capture fine-grained acoustic and linguistic variations across dialects while preserving speaker identity. Extensive objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that FMSD-TTS significantly outperforms baselines in both dialectal expressiveness and speaker similarity. We further validate the quality and utility of the synthesized speech through a challenging speech-to-speech dialect conversion task. Our contributions include: (1) a novel few-shot TTS system tailored for Tibetan multi-dialect speech synthesis, (2) the public release of a large-scale synthetic Tibetan speech corpus generated by FMSD-TTS, and (3) an open-source evaluation toolkit for standardized assessment of speaker similarity, dialect consistency, and audio quality.
藏语是一种资源匮乏的语言,其三大方言区——乌兹藏、安多和康区的平行语音语料库极为有限,限制了语音建模的进展。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FMSD-TTS,这是一个少样本、多发言人、多方言的文本-语音合成框架,它可以从有限的参考音频和明确的方言标签中合成平行的方言语音。我们的方法具有新颖的发声人-方言融合模块和方言专业化动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),能够捕捉不同方言之间精细的声学和语言变化,同时保留发声人的身份。大量的客观和主观评估表明,FMSD-TTS在方言表现力和发声人相似性方面都显著优于基准线。我们进一步通过具有挑战性的语音到语音的方言转换任务验证了合成语音的质量和实用性。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对藏语多方言语音合成的少样本TTS系统,(2)公开发布由FMSD-TTS生成的大规模藏语合成语音语料库,(3)开放源代码评估工具包,用于标准化评估发声人相似性、方言一致性和音频质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
该文本介绍了针对藏语这一低资源语言,如何利用有限参考音频和明确的方言标签,通过一种名为FMSD-TTS的少样本多说话者多方言文本转语音框架,合成并行方言语音。该框架具有说话者方言融合模块和方言特定动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),能够捕捉方言间的精细声学差异和语言学差异,同时保持说话者身份。经过客观和主观评估,FMSD-TTS在方言表达力和说话者相似性方面均显著优于基准模型。此外,该框架还通过具有挑战性的语音到语音方言转换任务验证了其合成语音的质量和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- FMSD-TTS是一种针对藏语多方言语音合成的少样本文本转语音系统。
- 系统通过融合说话者和方言模块,以及采用方言特定动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),能够捕捉方言间的声学差异和语言学差异。
- FMSD-TTS在客观和主观评估中表现出优异的性能,显著提高了方言表达力和说话者相似性。
- 通过挑战性的语音到语音方言转换任务验证了其合成语音的质量和实用性。
- FMSD-TTS公开发布了一个由该框架生成的大规模藏语合成语音语料库。
- 研究还贡献了一个开源评估工具包,用于标准化评估说话者相似性、方言一致性和音频质量。
- 此研究为藏语这一低资源语言的语音建模提供了新的解决方案和思路。
点此查看论文截图

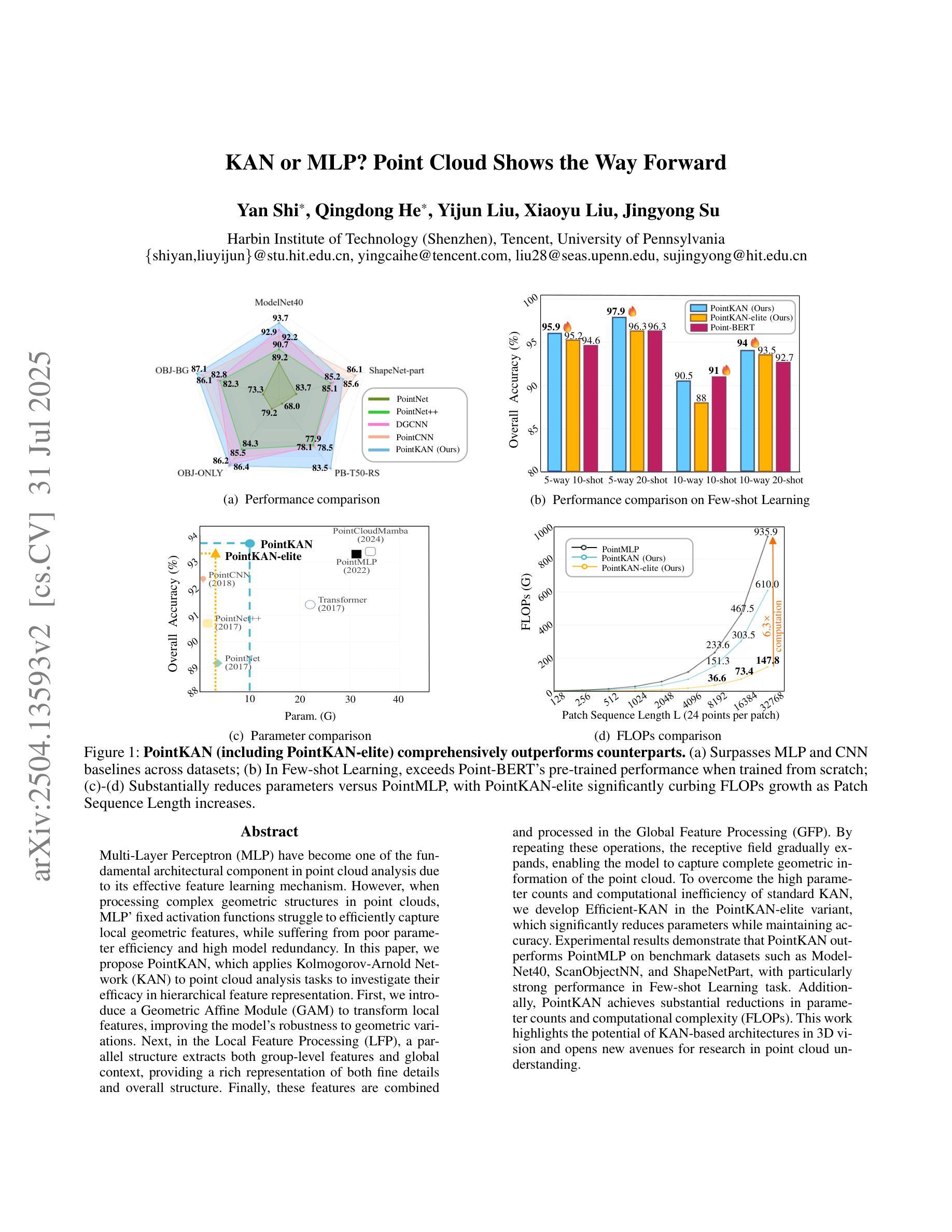
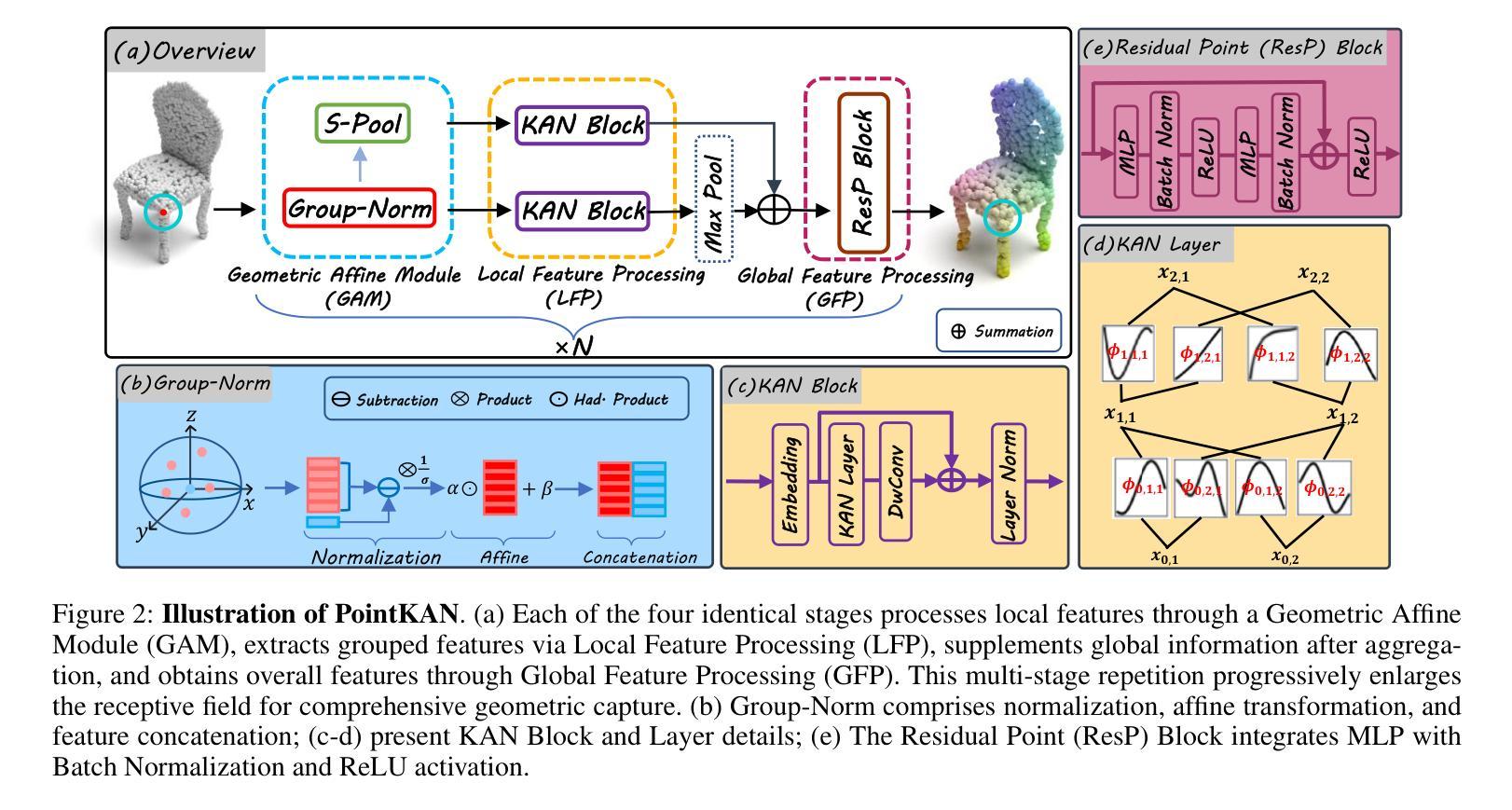
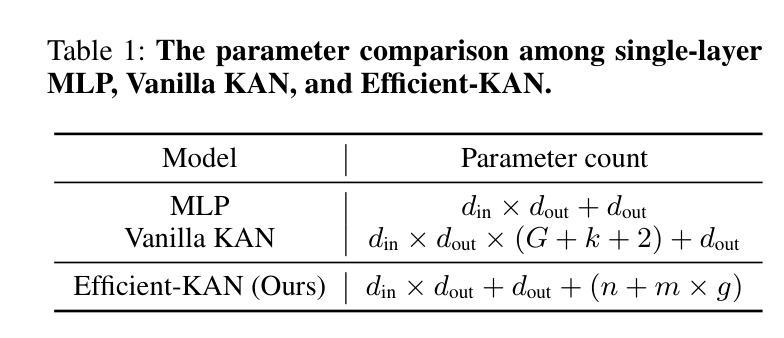
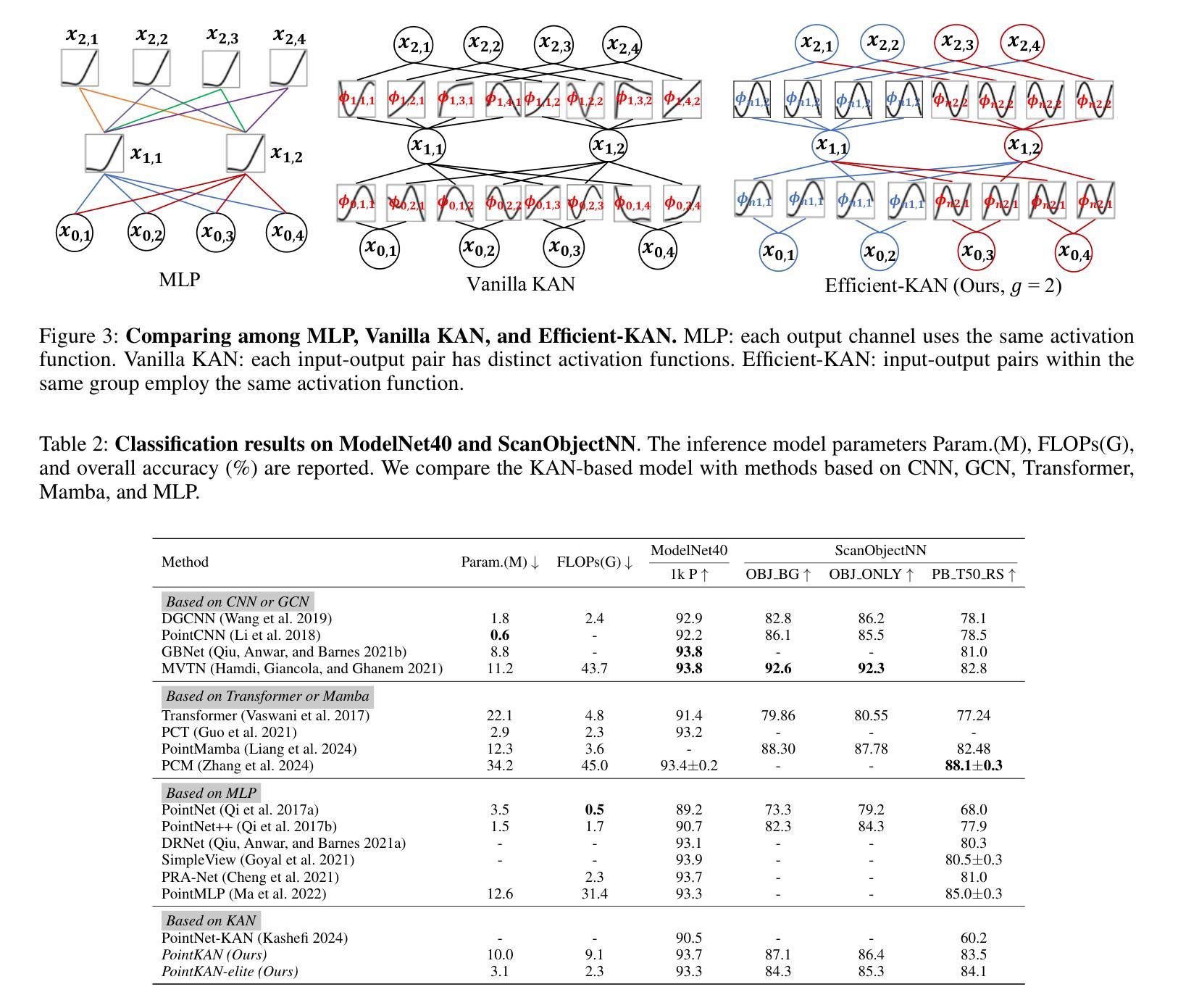
KAN or MLP? Point Cloud Shows the Way Forward
Authors:Yan Shi, Qingdong He, Yijun Liu, Xiaoyu Liu, Jingyong Su
Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) have become one of the fundamental architectural component in point cloud analysis due to its effective feature learning mechanism. However, when processing complex geometric structures in point clouds, MLPs’ fixed activation functions struggle to efficiently capture local geometric features, while suffering from poor parameter efficiency and high model redundancy. In this paper, we propose PointKAN, which applies Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) to point cloud analysis tasks to investigate their efficacy in hierarchical feature representation. First, we introduce a Geometric Affine Module (GAM) to transform local features, improving the model’s robustness to geometric variations. Next, in the Local Feature Processing (LFP), a parallel structure extracts both group-level features and global context, providing a rich representation of both fine details and overall structure. Finally, these features are combined and processed in the Global Feature Processing (GFP). By repeating these operations, the receptive field gradually expands, enabling the model to capture complete geometric information of the point cloud. To overcome the high parameter counts and computational inefficiency of standard KANs, we develop Efficient-KANs in the PointKAN-elite variant, which significantly reduces parameters while maintaining accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that PointKAN outperforms PointMLP on benchmark datasets such as ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN, and ShapeNetPart, with particularly strong performance in Few-shot Learning task. Additionally, PointKAN achieves substantial reductions in parameter counts and computational complexity (FLOPs). This work highlights the potential of KANs-based architectures in 3D vision and opens new avenues for research in point cloud understanding.
多层感知器(MLPs)由于其有效的特征学习机制,已成为点云分析中的基本架构组件之一。然而,在处理点云中的复杂几何结构时,MLPs的固定激活函数在有效地捕获局部几何特征方面遇到了困难,同时还存在参数效率低下和模型冗余的问题。在本文中,我们提出了PointKAN,它将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)应用于点云分析任务,以研究其在分层特征表示中的有效性。首先,我们引入了一个几何仿射模块(GAM)来变换局部特征,提高了模型对几何变化的鲁棒性。其次,在局部特征处理(LFP)中,并行结构提取了组级特征和全局上下文,提供了对精细细节和整体结构的丰富表示。最后,这些特征在全局特征处理(GFP)中进行组合和处理。通过重复这些操作,感受野逐渐扩大,使模型能够捕获点云的完整几何信息。为了克服标准KANs参数多、计算效率低的问题,我们在PointKAN-elite变种中开发了Efficient-KANs,它在保持准确性的同时显著减少了参数。实验结果表明,PointKAN在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart等基准数据集上的性能优于PointMLP,特别是在小样本学习任务中表现尤为出色。此外,PointKAN实现了参数数量和计算复杂度(FLOPs)的大幅减少。这项工作突出了基于KANs的架构在3D视觉中的潜力,为点云理解研究开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出PointKAN模型,将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)应用于点云分析任务,以研究其在分层特征表示中的有效性。通过引入几何仿射模块(GAM)和局部特征处理(LFP)来改进模型对几何变化的稳健性并丰富特征表示。此外,开发了点KAN精英版中的高效KANs,以在保持准确性的同时显著减少参数。PointKAN在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart等基准数据集上的表现优于PointMLP,特别是在小样本学习任务中表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- PointKAN模型结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)进行点云分析,旨在提高模型的效率和准确性。
- 引入几何仿射模块(GAM)以改善模型对几何变化的稳健性。
- 通过局部特征处理(LFP)结合并行结构提取组级特征和全局上下文,实现丰富的特征表示。
- 全球特征处理(GFP)结合并处理这些特征,通过重复操作逐渐扩大感受野,捕捉点云的完整几何信息。
- PointKAN-elite中的Efficient-KANs显著减少参数和计算复杂性,同时保持准确性。
- 在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart等基准数据集上,PointKAN模型表现优于PointMLP。
点此查看论文截图
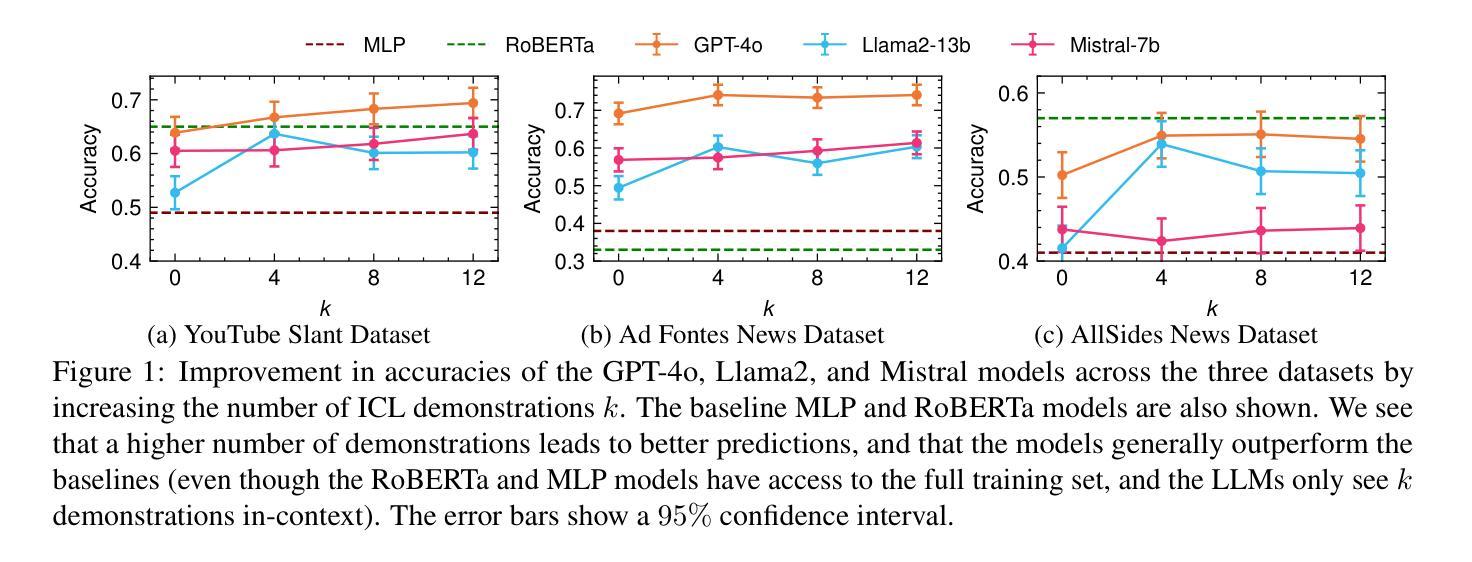
“Whose Side Are You On?” Estimating Ideology of Political and News Content Using Large Language Models and Few-shot Demonstration Selection
Authors:Muhammad Haroon, Magdalena Wojcieszak, Anshuman Chhabra
The rapid growth of social media platforms has led to concerns about radicalization, filter bubbles, and content bias. Existing approaches to classifying ideology are limited in that they require extensive human effort, the labeling of large datasets, and are not able to adapt to evolving ideological contexts. This paper explores the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) for classifying the political ideology of online content in the context of the two-party US political spectrum through in-context learning (ICL). Our extensive experiments involving demonstration selection in label-balanced fashion, conducted on three datasets comprising news articles and YouTube videos, reveal that our approach significantly outperforms zero-shot and traditional supervised methods. Additionally, we evaluate the influence of metadata (e.g., content source and descriptions) on ideological classification and discuss its implications. Finally, we show how providing the source for political and non-political content influences the LLM’s classification.
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了人们对极端化、信息茧房和内容偏见问题的担忧。现有的意识形态分类方法存在局限性,需要大量人工参与、标注大规模数据集,并且无法适应不断变化的意识形态环境。本文探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在基于美国两党政治谱系的在线内容政治意识形态分类中的潜力,通过上下文学习(ICL)进行意识形态分类。我们在三个包含新闻文章和YouTube视频的数据集上进行了广泛的实验,采用标签平衡的方式进行演示选择,结果表明我们的方法显著优于零样本和传统监督方法。此外,我们还评估了元数据(如内容来源和描述)对意识形态分类的影响,并讨论了其含义。最后,我们展示了政治和非政治内容来源对LLM分类的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了关于极端化、信息茧房和内容偏向的担忧。现有分类意识形态的方法需要大量人工操作、标注大量数据集,并且无法适应不断变化的意识形态环境。本文探索了大型语言模型(LLM)通过上下文学习(ICL)对美国两党政治光谱背景下在线内容的政治意识形态进行分类的潜力。我们在三个包含新闻文章和YouTube视频的数据集上进行了标签平衡方式下的演示选择实验,发现我们的方法显著优于零样本和传统监督方法。我们还评估了元数据(如内容来源和描述)对意识形态分类的影响,并讨论了其意义。最后,我们展示了提供政治和非政治内容的来源如何影响LLM的分类。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了关于极端化、信息茧房和内容偏向的担忧。
- 现有分类意识形态的方法需要大量资源和无法适应变化的环境。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过上下文学习(ICL)在分类政治意识形态方面具有潜力。
- 在三个数据集上的实验显示,相较于零样本和传统监督方法,LLM的表现更佳。
- 元数据对意识形态分类有影响。
- 内容来源对LLM分类结果有影响。
点此查看论文截图


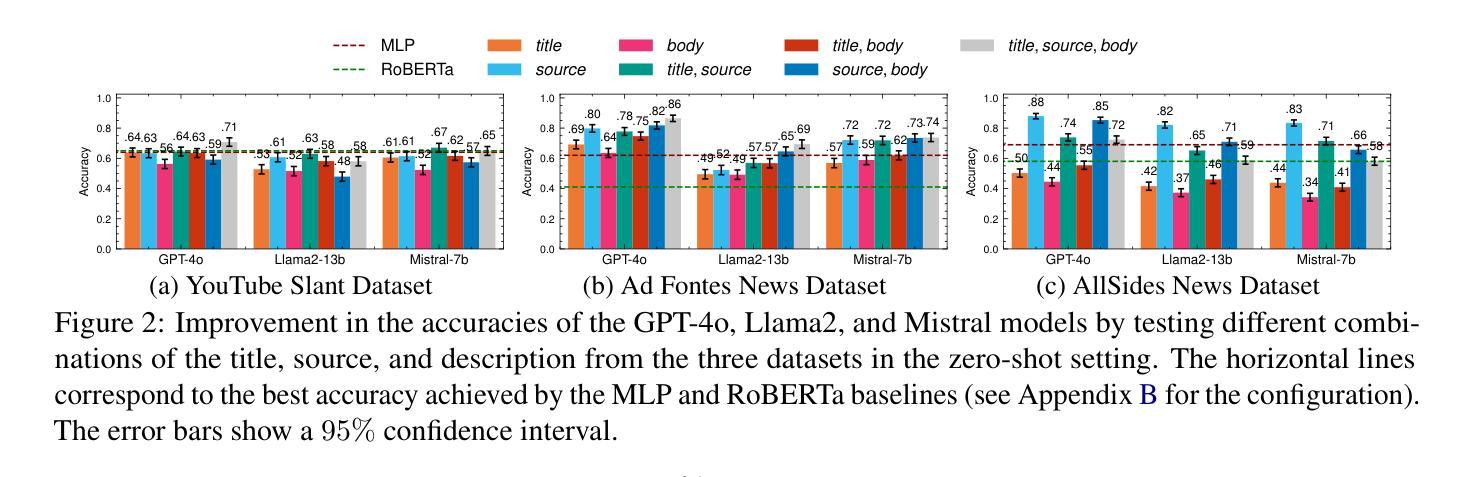
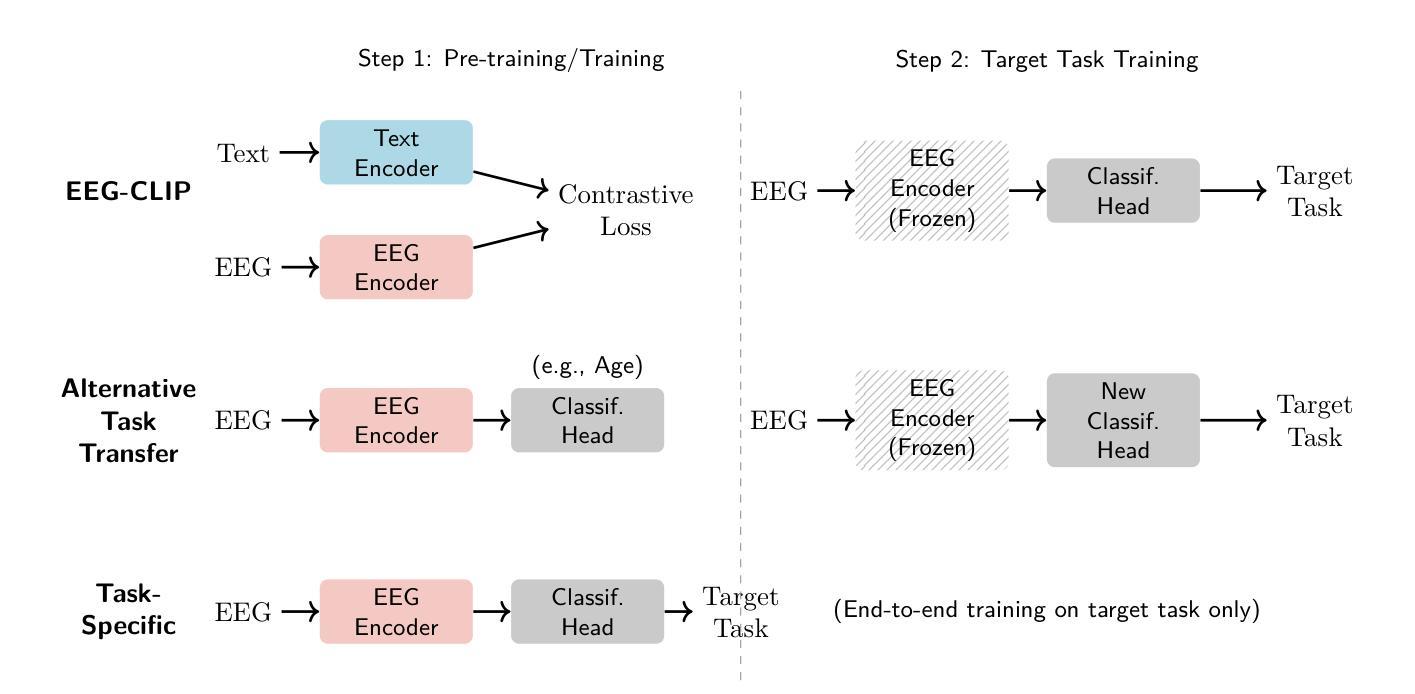
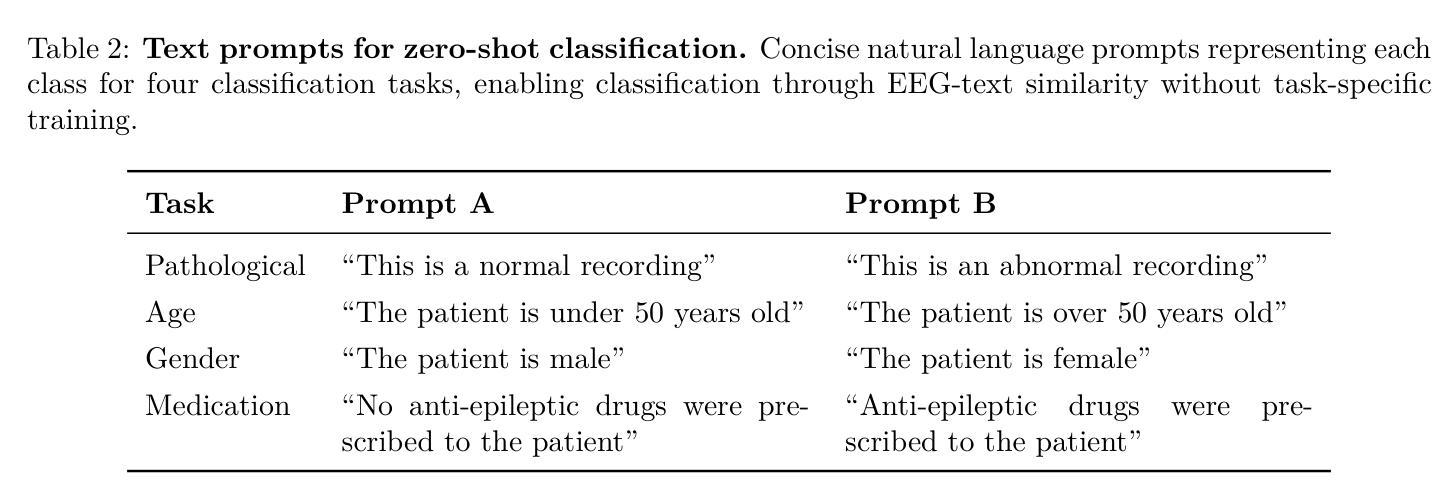
EEG-CLIP : Learning EEG representations from natural language descriptions
Authors:Tidiane Camaret Ndir, Robin Tibor Schirrmeister, Tonio Ball
Deep networks for electroencephalogram (EEG) decoding are often only trained to solve one specific task, such as pathology or age decoding. A more general task-agnostic approach is to train deep networks to match a (clinical) EEG recording to its corresponding textual medical report and vice versa. This approach was pioneered in the computer vision domain matching images and their text captions and subsequently allowed to do successful zero-shot decoding using textual class prompts. In this work, we follow this approach and develop a contrastive learning framework, EEG-CLIP, that aligns the EEG time series and the descriptions of the corresponding clinical text in a shared embedding space. We investigated its potential for versatile EEG decoding, evaluating performance in a range of few-shot and zero-shot settings. Overall, we show that EEG-CLIP manages to non-trivially align text and EEG representations. Our work presents a promising approach to learn general EEG representations, which could enable easier analyses of diverse decoding questions through zero-shot decoding or training task-specific models from fewer training examples. The code for reproducing our results is available at https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip
深度网络通常只用于解决脑电图(EEG)解码的单一特定任务,如病理学或年龄解码。一种更通用的任务无关方法是通过训练深度网络来匹配(临床)脑电图记录与其相应的文本医学报告,反之亦然。这种方法最初在计算机视觉领域用于匹配图像和文本标题,随后通过使用文本类别提示实现了零样本解码的成功。在这项工作中,我们遵循这种方法,开发了一个对比学习框架EEG-CLIP,它将脑电图时间序列与对应临床文本的说明对齐到一个共享嵌入空间中。我们对其在多种小样本次数和零样本设置下的通用脑电图解码潜力进行了调查。总体而言,我们证明了EEG-CLIP能够实现对文本和脑电图表示的非平凡对齐。我们的工作提出了一种学习通用脑电图表示的有前途的方法,这可能通过零样本解码或使用更少训练样本训练特定任务模型来更容易地分析各种解码问题。重现我们结果的代码可在 https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
EEG-CLIP是一种基于对比学习的框架,它将脑电图(EEG)记录和相应的医学报告文本匹配起来,并开发了一种通用的脑电图表示学习方法。该方法在多种小样本和零样本设置下表现出良好的性能,能够实现零样本解码或利用更少训练样本进行任务特定模型的训练。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究采用一种通用的任务无关方法,通过匹配脑电图(EEG)记录和相应的医学报告文本,训练深度网络。
- EEG-CLIP框架采用对比学习,将脑电图时间序列与相应的临床文本描述对齐在共享嵌入空间中。
- 该方法在多种小样本次数和零样本设置下进行了评估,证明了其有效性。
- EEG-CLIP成功实现了文本和脑电图表示的非平凡对齐。
- 该方法有望简化对多种解码问题的分析,通过零样本解码或使用更少训练样本进行任务特定模型的训练。
- 该研究的代码已公开发布,可供他人复现。
点此查看论文截图

GneissWeb: Preparing High Quality Data for LLMs at Scale
Authors:Hajar Emami Gohari, Swanand Ravindra Kadhe, Syed Yousaf Shah, Constantin Adam, Abdulhamid Adebayo, Praneet Adusumilli, Farhan Ahmed, Nathalie Baracaldo Angel, Santosh Subhashrao Borse, Yuan-Chi Chang, Xuan-Hong Dang, Nirmit Desai, Revital Eres, Ran Iwamoto, Alexei Karve, Yan Koyfman, Wei-Han Lee, Changchang Liu, Boris Lublinsky, Takuyo Ohko, Pablo Pesce, Maroun Touma, Shiqiang Wang, Shalisha Witherspoon, Herbert Woisetschläger, David Wood, Kun-Lung Wu, Issei Yoshida, Syed Zawad, Petros Zerfos, Yi Zhou, Bishwaranjan Bhattacharjee
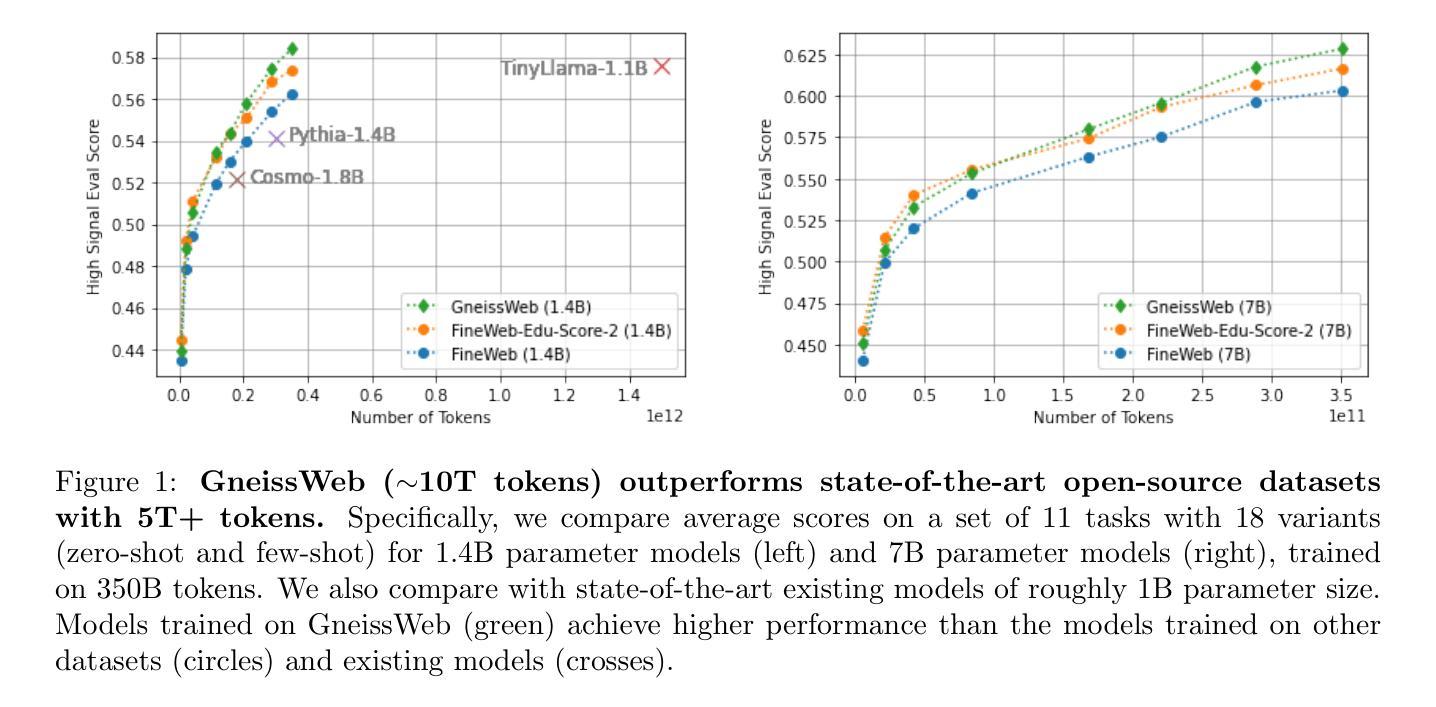
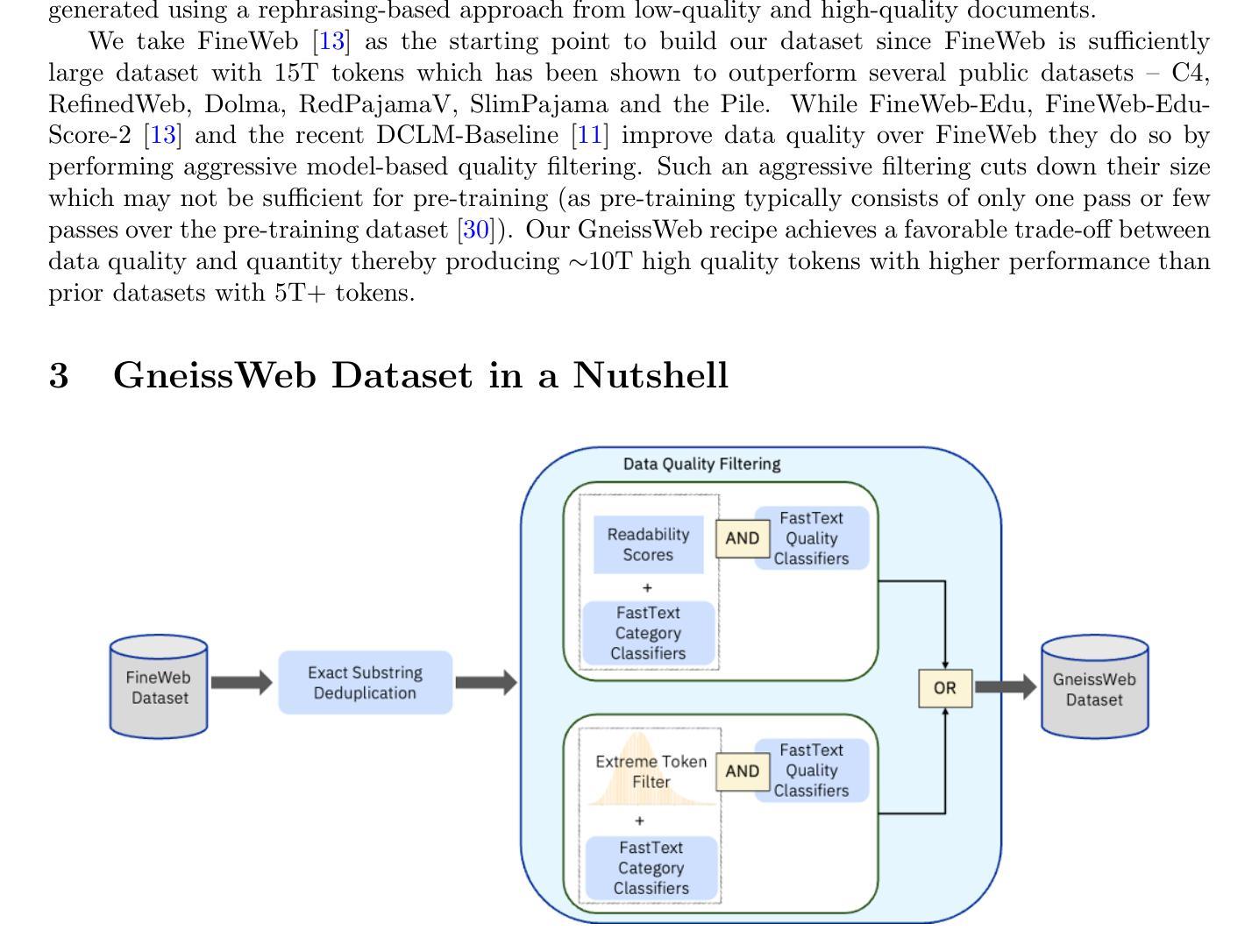
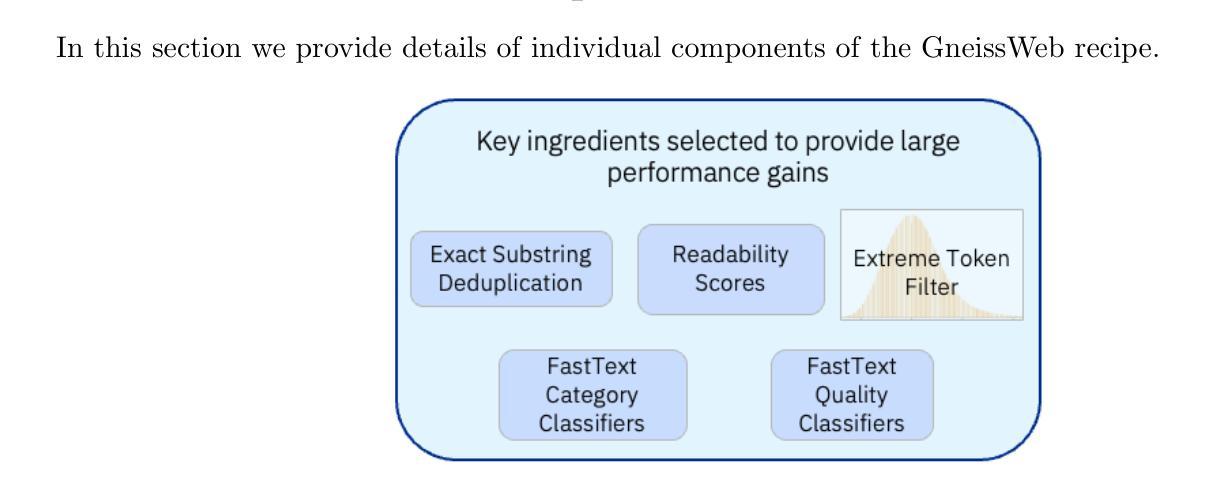
Data quantity and quality play a vital role in determining the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs). High-quality data, in particular, can significantly boost the LLM’s ability to generalize on a wide range of downstream tasks. Large pre-training datasets for leading LLMs remain inaccessible to the public, whereas many open datasets are small in size (less than 5 trillion tokens), limiting their suitability for training large models. In this paper, we introduce GneissWeb, a large dataset yielding around 10 trillion tokens that caters to the data quality and quantity requirements of training LLMs. Our GneissWeb recipe that produced the dataset consists of sharded exact sub-string deduplication and a judiciously constructed ensemble of quality filters. GneissWeb achieves a favorable trade-off between data quality and quantity, producing models that outperform models trained on state-of-the-art open large datasets (5+ trillion tokens). We show that models trained using GneissWeb dataset outperform those trained on FineWeb-V1.1.0 by 2.73 percentage points in terms of average score computed on a set of 11 commonly used benchmarks (both zero-shot and few-shot) for pre-training dataset evaluation. When the evaluation set is extended to 20 benchmarks (both zero-shot and few-shot), models trained using GneissWeb still achieve a 1.75 percentage points advantage over those trained on FineWeb-V1.1.0.
数据数量和品质在决定大型语言模型(LLM)性能上扮演着至关重要的角色。高品质的数据,尤其能显著提升LLM在广泛下游任务上的泛化能力。领先的大型语言模型所使用的大型预训练数据集仍然不对公众开放,而许多公开数据集规模较小(少于5万亿标记),限制了它们训练大型模型的适用性。在本文中,我们介绍了GneissWeb,这是一个产生大约10万亿标记的大型数据集,满足了训练LLM对数据质量和数量的要求。我们产生GneissWeb数据集的方案包括分片精确的子字符串去重和精心构建的质量过滤器组合。GneissWeb在数据质量和数量之间实现了有利的权衡,产生的模型在最新公开大型数据集(超过5万亿标记)训练的模型之上表现出优越性能。我们展示了使用GneissWeb数据集训练的模型在由常用的预训练数据集评估的基准测试中平均得分上比使用FineWeb-V1.1.0训练的模型高出2.73个百分点。当评估集扩展到包含20个基准测试(零样本和少量样本)时,使用GneissWeb训练的模型仍比使用FineWeb-V1.1.0训练的模型具有高达高达近 更大的优势(优势达高达近高出 超出标准以上提高将近百分之几点)。简而言之,通过我们创新的方法论创建的数据集实现了优秀的性能和前沿技术之间的平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了数据质量与数量在大型语言模型(LLM)性能上的重要作用。文章提出GneissWeb数据集,包含约10万亿个标记,解决了训练LLM所需的数据质量和数量要求问题。GneissWeb的配方包括分片精确的子字符串重复消除和精心构建的质量过滤器集合,可实现数据质量与数量之间的良好平衡。实验表明,使用GneissWeb数据集训练的模型在多个基准测试上的表现优于使用现有大型开放数据集训练的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 数据质量和数量在LLM性能中起关键作用。
- GneissWeb数据集含有约10万亿个标记,满足LLM训练的数据需求。
- GneissWeb采用分片精确的子字符串重复消除和精心构建的质量过滤器,确保数据质量。
- GneissWeb数据集训练的模型在多个基准测试上的表现优于使用其他大型数据集训练的模型。
- GneissWeb训练模型的优势在扩展至更多基准测试时依然显著。
- GneissWeb有助于提高LLM的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

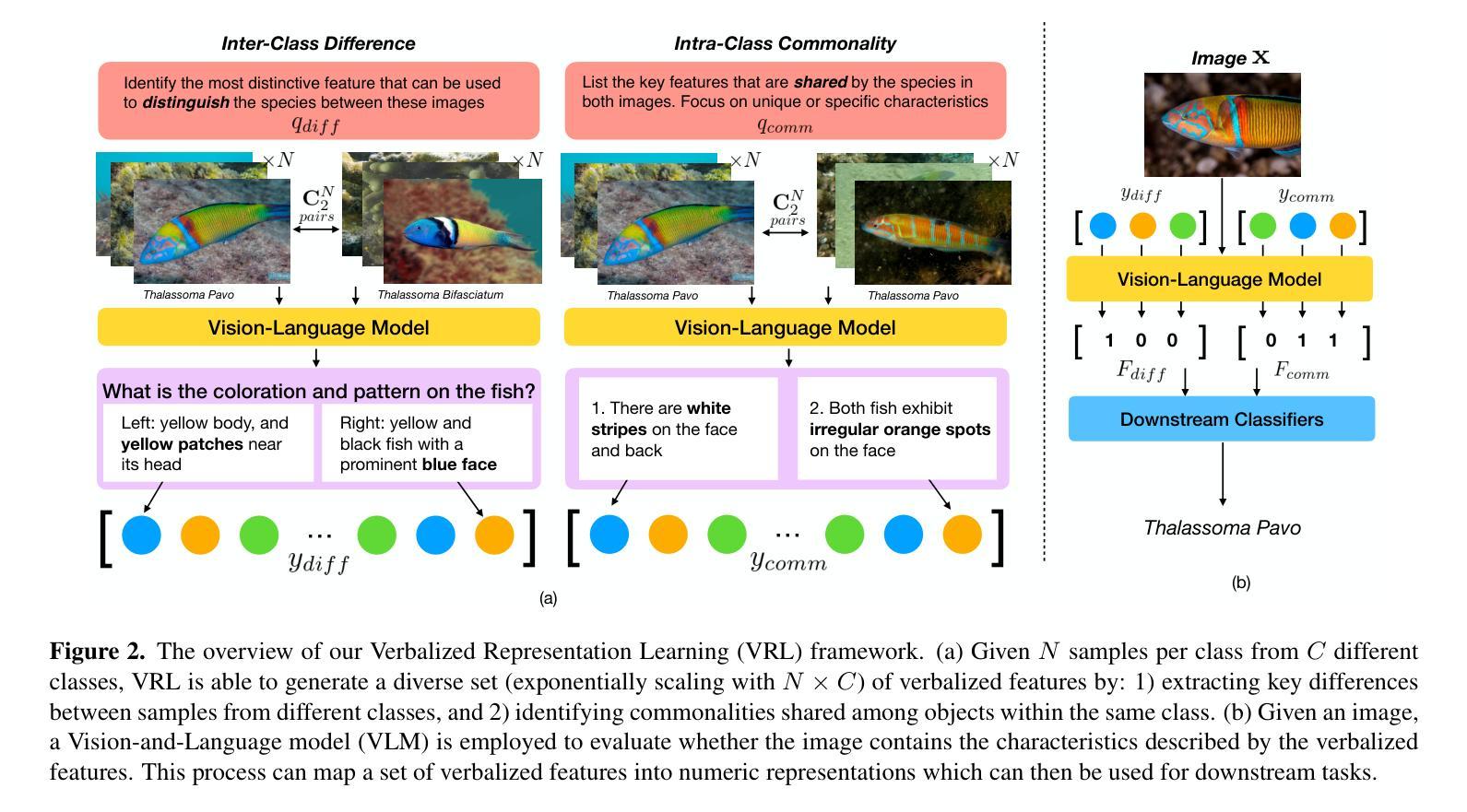
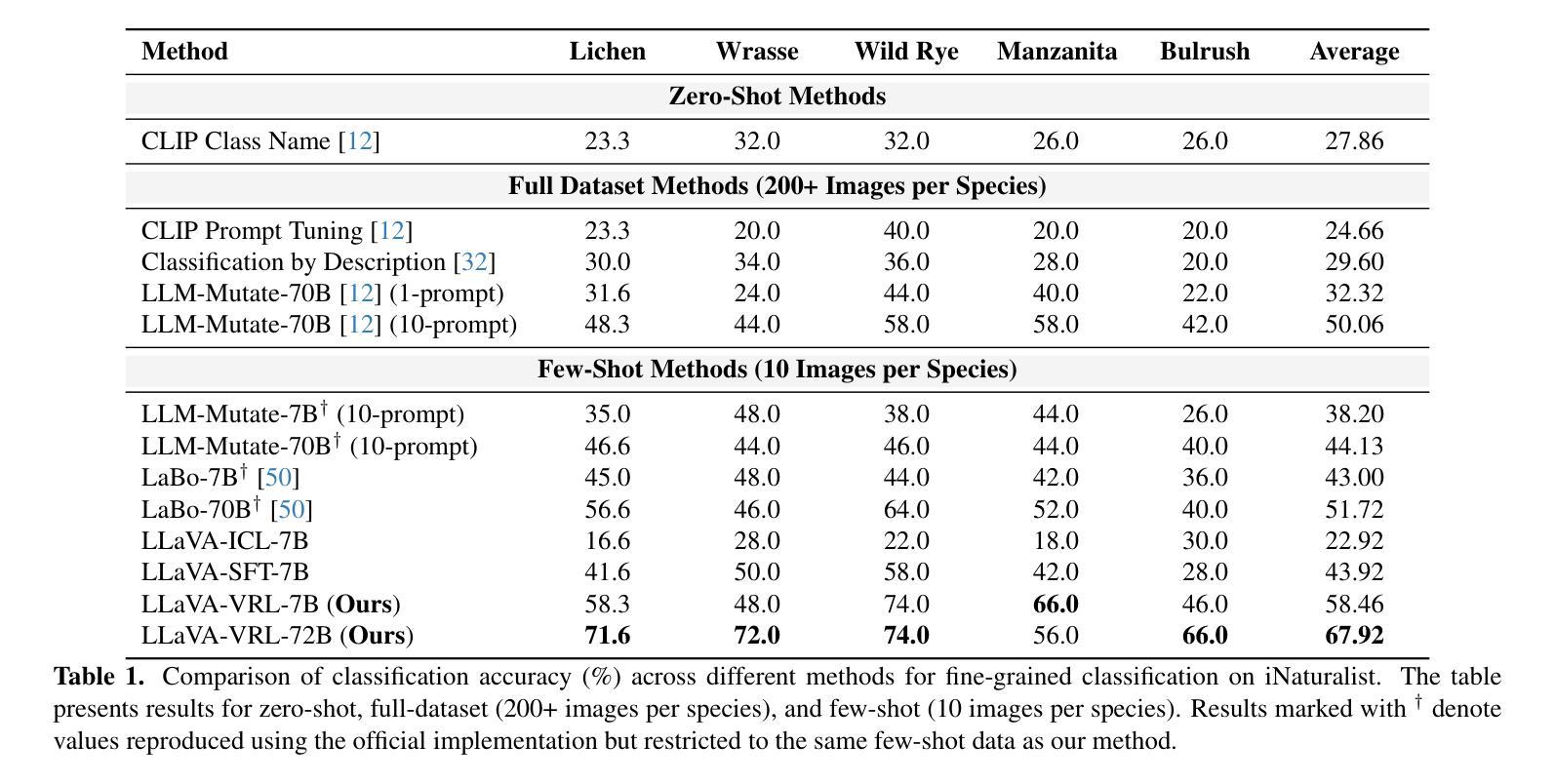
Verbalized Representation Learning for Interpretable Few-Shot Generalization
Authors:Cheng-Fu Yang, Da Yin, Wenbo Hu, Nanyun Peng, Bolei Zhou, Kai-Wei Chang
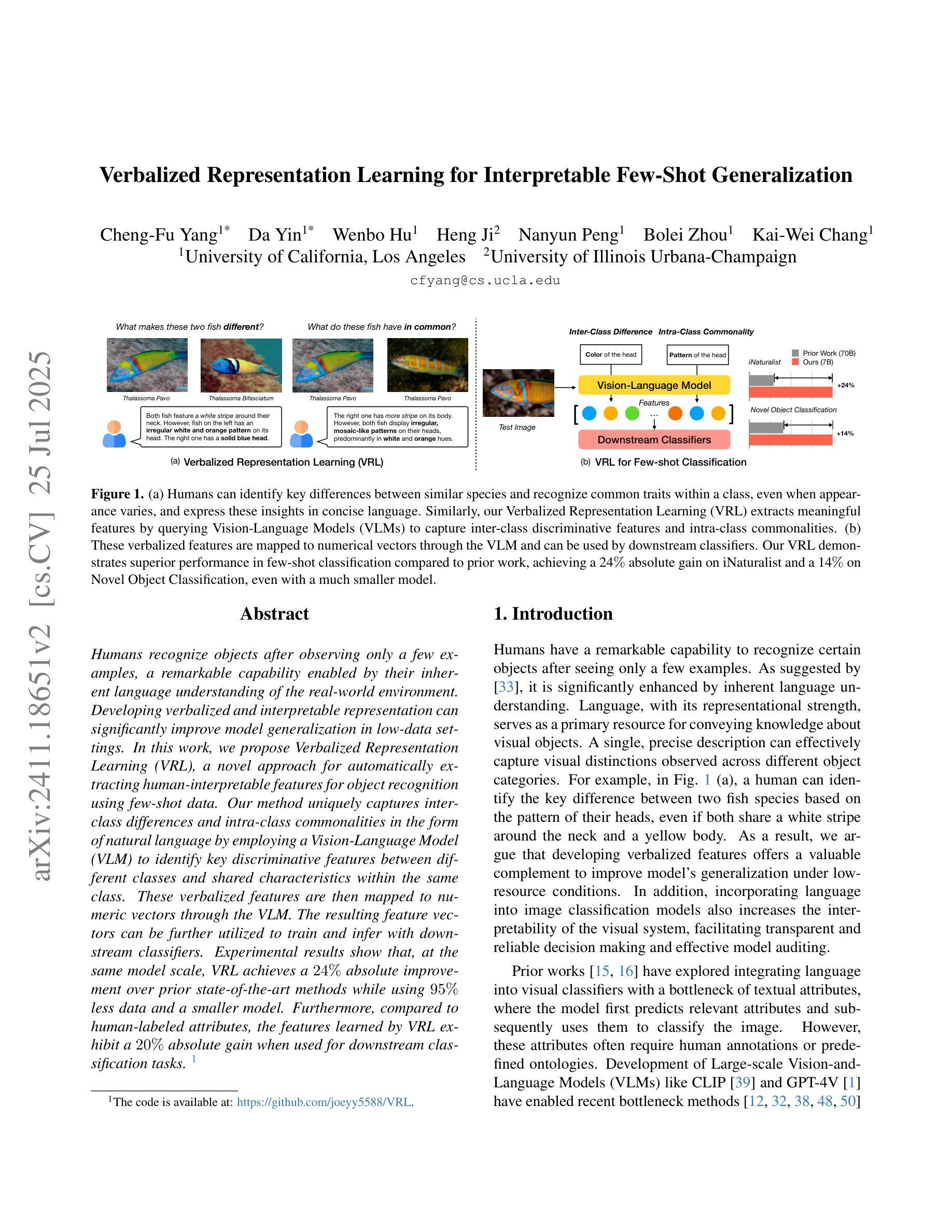
Humans recognize objects after observing only a few examples, a remarkable capability enabled by their inherent language understanding of the real-world environment. Developing verbalized and interpretable representation can significantly improve model generalization in low-data settings. In this work, we propose Verbalized Representation Learning (VRL), a novel approach for automatically extracting human-interpretable features for object recognition using few-shot data. Our method uniquely captures inter-class differences and intra-class commonalities in the form of natural language by employing a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to identify key discriminative features between different classes and shared characteristics within the same class. These verbalized features are then mapped to numeric vectors through the VLM. The resulting feature vectors can be further utilized to train and infer with downstream classifiers. Experimental results show that, at the same model scale, VRL achieves a 24% absolute improvement over prior state-of-the-art methods while using 95% less data and a smaller mode. Furthermore, compared to human-labeled attributes, the features learned by VRL exhibit a 20% absolute gain when used for downstream classification tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/joeyy5588/VRL/tree/main.
人类只需观察几个例子就能识别物体,这是由他们对现实环境固有理解所赋予的惊人能力。在数据稀缺的环境中,开发语言化的可解释表示可以极大地提高模型的泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了语言化表示学习(VRL)这一新方法,它可以通过少量数据自动提取人类可解释的特征来进行对象识别。我们的方法以自然语言的形式独特地捕捉了类间差异和类内共性,通过采用视觉语言模型(VLM)来识别不同类之间的关键判别特征以及同一类内的共享特征。这些语言化的特征然后通过VLM映射到数值向量上。所得的特征向量可进一步用于训练并用于下游分类器的推断。实验结果表明,在相同模型规模下,VRL在仅使用95%更少的数据和较小模型的情况下,较之前的最先进方法实现了24%的绝对改进。此外,与人工标注的属性相比,使用VRL学习的特征进行下游分类任务时表现出了20%的绝对优势。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/joeyy5588/VRL/tree/main。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Verbalized Representation Learning(VRL)的新方法,该方法能够利用少量数据自动提取人类可解释的特征进行对象识别。通过采用Vision-Language Model(VLM),VRL能够识别不同类别之间的关键判别特征以及同一类别内的共享特征,并将其转化为自然语言形式。这些语言化的特征进一步被映射为数值向量,可用于训练和推断下游分类器。实验结果表明,在相同模型规模下,VRL相较于现有先进技术实现了24%的绝对改进,并在使用95%更少数据和小型模型的情况下取得了显著成果。此外,与人工标注的属性相比,通过VRL学习的特征用于下游分类任务时表现出了20%的绝对优势。
Key Takeaways
- 人类仅需观察少量示例即可识别物体,这是由他们内在的对现实世界环境的理解所驱动的。
- 言语化表示学习(VRL)是一种新的方法,能够从少量数据中自动提取人类可解释的特征进行对象识别。
- VRL采用Vision-Language Model(VLM)识别不同类别间的关键判别特征和同一类别内的共享特征。
- VRL将语言化的特征映射为数值向量,这些向量可用于训练和推断下游分类器。
- 实验结果表明,在相同模型规模下,VRL相较于现有技术有显著改进。
- VRL在减少数据需求和使用小型模型方面表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图
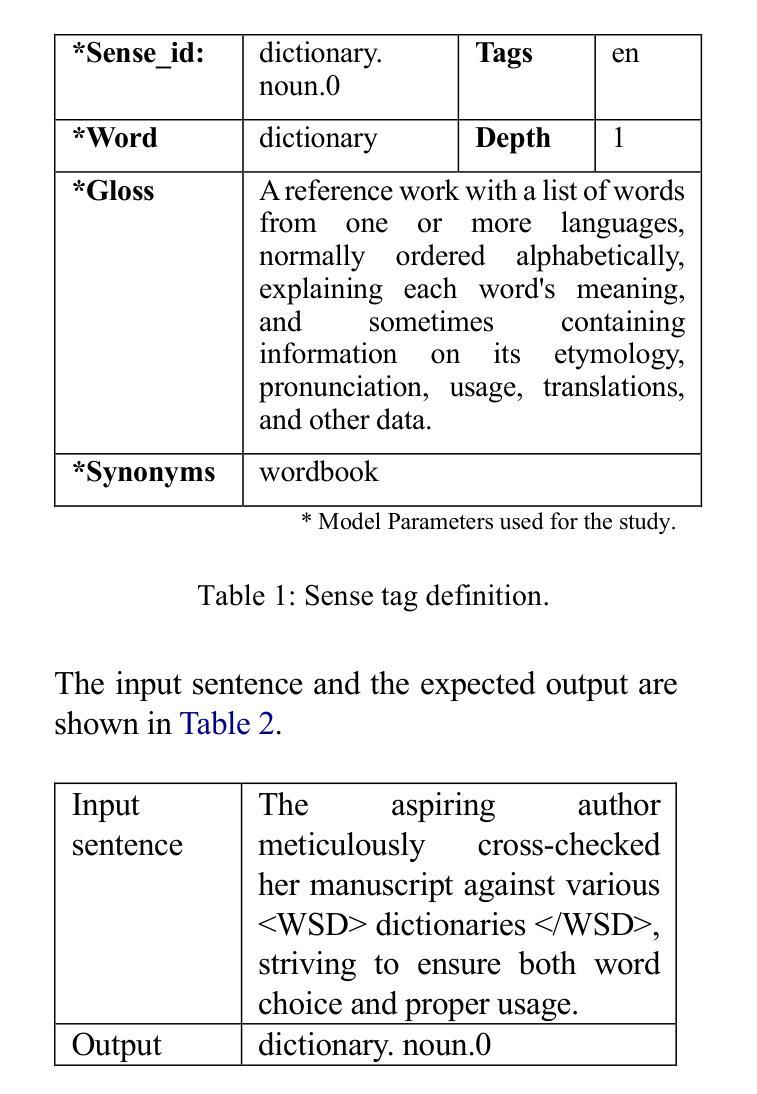
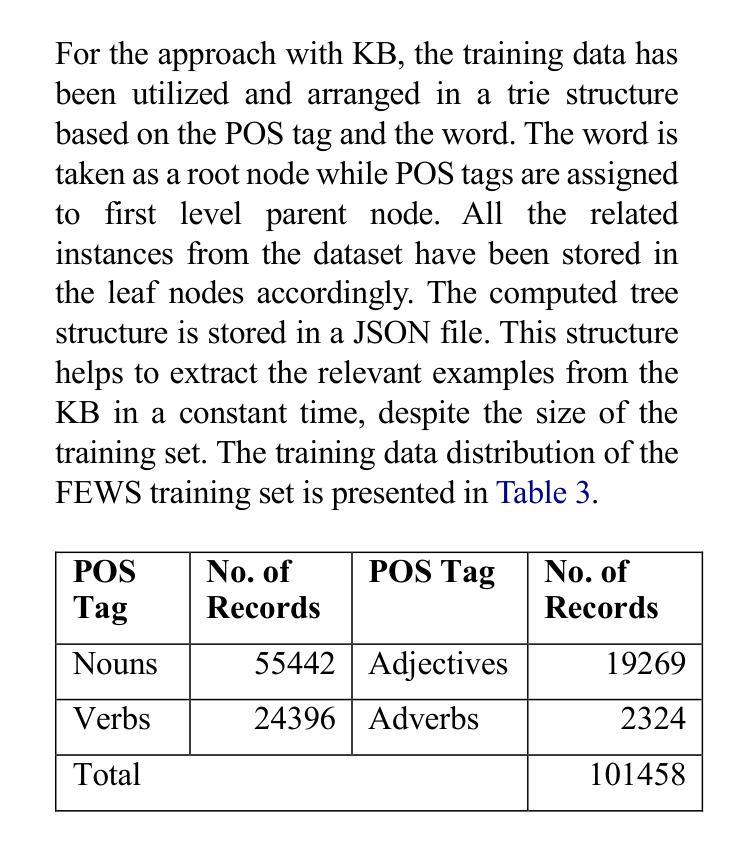
Can LLMs assist with Ambiguity? A Quantitative Evaluation of various Large Language Models on Word Sense Disambiguation
Authors:T. G. D. K. Sumanathilaka, Nicholas Micallef, Julian Hough
Ambiguous words are often found in modern digital communications. Lexical ambiguity challenges traditional Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) methods, due to limited data. Consequently, the efficiency of translation, information retrieval, and question-answering systems is hindered by these limitations. This study investigates the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve WSD using a novel approach combining a systematic prompt augmentation mechanism with a knowledge base (KB) consisting of different sense interpretations. The proposed method incorporates a human-in-loop approach for prompt augmentation where prompt is supported by Part-of-Speech (POS) tagging, synonyms of ambiguous words, aspect-based sense filtering and few-shot prompting to guide the LLM. By utilizing a few-shot Chain of Thought (COT) prompting-based approach, this work demonstrates a substantial improvement in performance. The evaluation was conducted using FEWS test data and sense tags. This research advances accurate word interpretation in social media and digital communication.
在现代数字通信中经常可以发现词义模糊的词语。由于数据有限,词汇的模糊性给传统的词义消歧(Word Sense Disambiguation, WSD)方法带来了挑战。因此,翻译、信息检索和问答系统的效率受到了这些限制的阻碍。本研究探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)结合一种系统的提示增强机制和包含不同词义解释的知识库(KB)来改善词义消歧的方法。所提出的方法采用了一种人类循环提示增强方法,该方法由词性标注、模糊词的同义词、基于方面的词义过滤和少量提示组成,以指导大型语言模型。通过采用基于少量提示链思维(COT)的提示方法,这项工作在性能上取得了显著的提升。评估工作是通过使用FEWS测试数据和词义标签进行的。该研究推动了社交媒体和数字通信中的准确词义解读。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages,6 tables, 1 figure, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on NLP & AI for Cyber Security
Summary
本文探讨了现代数字通信中常见的词汇歧义问题。针对传统词义消歧(WSD)方法因数据有限而面临的挑战,研究使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行改进。通过结合系统提示增强机制和包含不同词义解释的 knowledge base,提出了一种新的方法。该方法采用人工参与循环的提示增强方式,借助词性标注、模糊词同义词、基于方面的词义过滤和少量提示来引导LLM。通过基于少量提示的Chain of Thought(COT)方法,该研究展示了显著的性能提升。在FEWS测试数据和词义标签上进行了评估,为社交媒体和数字通信中的准确词汇解释提供了进展。
Key Takeaways
- 词汇歧义在现代数字通信中是常见问题。
- 传统词义消歧方法因数据有限而面临挑战。
- 大型语言模型被用于改进词义消歧。
- 结合系统提示增强机制和包含不同词义解释的 knowledge base 提出新方法。
- 采用人工参与循环的提示增强方式,包括词性标注、模糊词同义词等。
- 使用基于少量提示的Chain of Thought方法实现显著性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

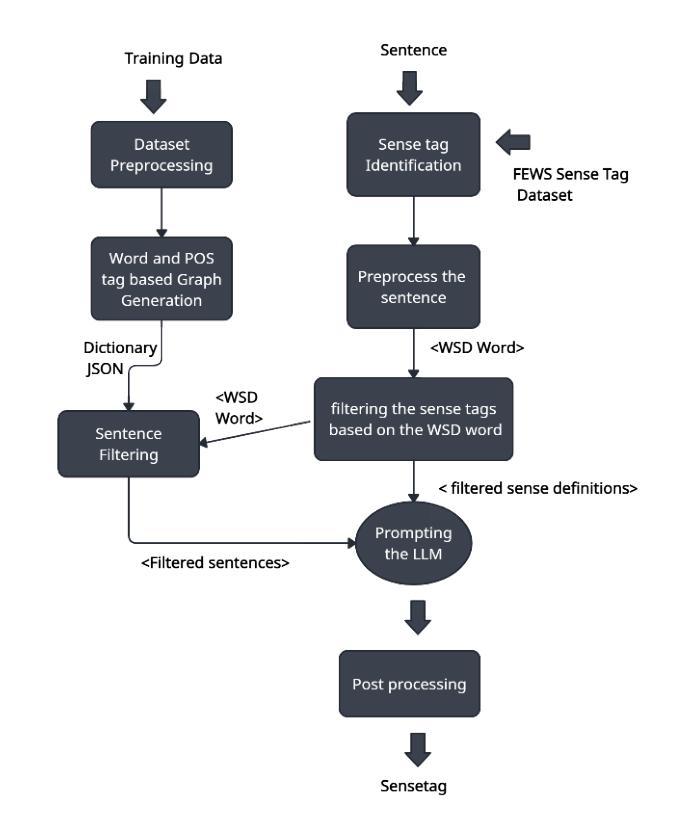
Label Anything: Multi-Class Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation with Visual Prompts
Authors:Pasquale De Marinis, Nicola Fanelli, Raffaele Scaringi, Emanuele Colonna, Giuseppe Fiameni, Gennaro Vessio, Giovanna Castellano
Few-shot semantic segmentation aims to segment objects from previously unseen classes using only a limited number of labeled examples. In this paper, we introduce Label Anything, a novel transformer-based architecture designed for multi-prompt, multi-way few-shot semantic segmentation. Our approach leverages diverse visual prompts – points, bounding boxes, and masks – to create a highly flexible and generalizable framework that significantly reduces annotation burden while maintaining high accuracy. Label Anything makes three key contributions: ($\textit{i}$) we introduce a new task formulation that relaxes conventional few-shot segmentation constraints by supporting various types of prompts, multi-class classification, and enabling multiple prompts within a single image; ($\textit{ii}$) we propose a novel architecture based on transformers and attention mechanisms; and ($\textit{iii}$) we design a versatile training procedure allowing our model to operate seamlessly across different $N$-way $K$-shot and prompt-type configurations with a single trained model. Our extensive experimental evaluation on the widely used COCO-$20^i$ benchmark demonstrates that Label Anything achieves state-of-the-art performance among existing multi-way few-shot segmentation methods, while significantly outperforming leading single-class models when evaluated in multi-class settings. Code and trained models are available at https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything.
少量样本语义分割旨在使用有限的标注样本对之前未见过的类别进行对象分割。在本文中,我们介绍了Label Anything,这是一种基于transformer的新型架构,专为多提示、多类别少量样本语义分割设计。我们的方法利用多样化的视觉提示——点、边界框和蒙版,创建一个高度灵活和可推广的框架,在保持高准确性的同时,显著减少标注工作量。Label Anything有三个主要贡献:(i)我们引入了一种新的任务形式化方法,通过支持各种提示类型、多类分类,并在单个图像内支持多个提示,放宽了传统的少量样本分割约束;(ii)我们提出了一种基于transformer和注意力机制的全新架构;(iii)我们设计了一种通用训练程序,使我们的模型能够在不同的N路K样本和提示类型配置中使用单个训练模型无缝运行。我们在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试上的大量实验评估表明,Label Anything在现有的多类别少量样本分割方法中实现了最先进的性能,同时在多类别设置中显著优于领先的单类别模型。相关代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECAI 2025 - 28th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文介绍了针对多提示、多类别少样本语义分割任务的新型转换器架构Label Anything。它利用多样化的视觉提示(点、边界框和掩膜),创建了一个灵活且通用的框架,在保持高准确性的同时,显著减少了标注的负担。Label Anything的贡献包括:引入支持多种提示、多类别分类和单图像内多个提示的新任务形式;提出基于转换器和注意力机制的全新架构;设计了一种通用训练程序,使模型能够在不同的N路K样本和提示类型配置中无缝运行。在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试中,Label Anything实现了现有多类别少样本分割方法中的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- Label Anything是一个为少样本语义分割任务设计的基于转换器的新型架构。
- 它支持多种类型的视觉提示,如点、边界框和掩膜。
- Label Anything显著减少了标注负担,同时保持了高准确性。
- 它引入了新的任务形式,支持多种提示、多类别分类和单图像内的多个提示。
- Label Anything通过基于转换器和注意力机制的架构实现。
- 它设计了一种通用训练程序,允许模型在不同配置中无缝运行。
点此查看论文截图

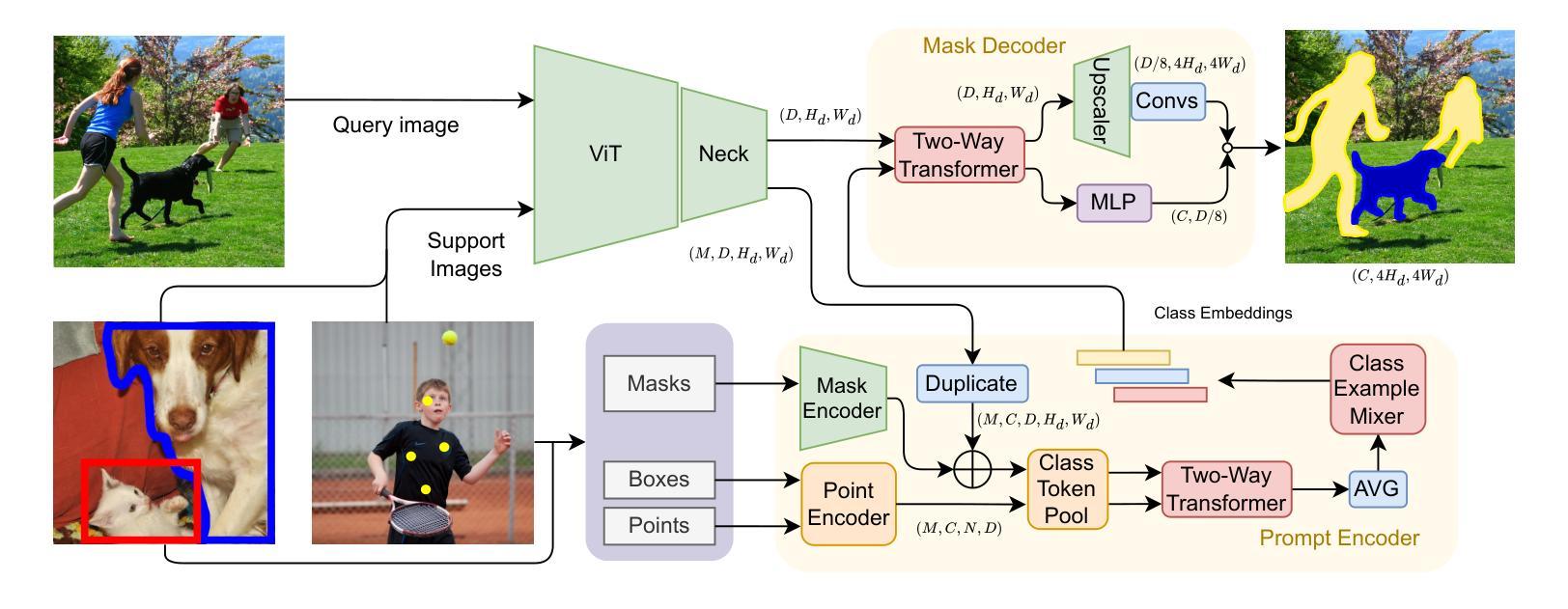
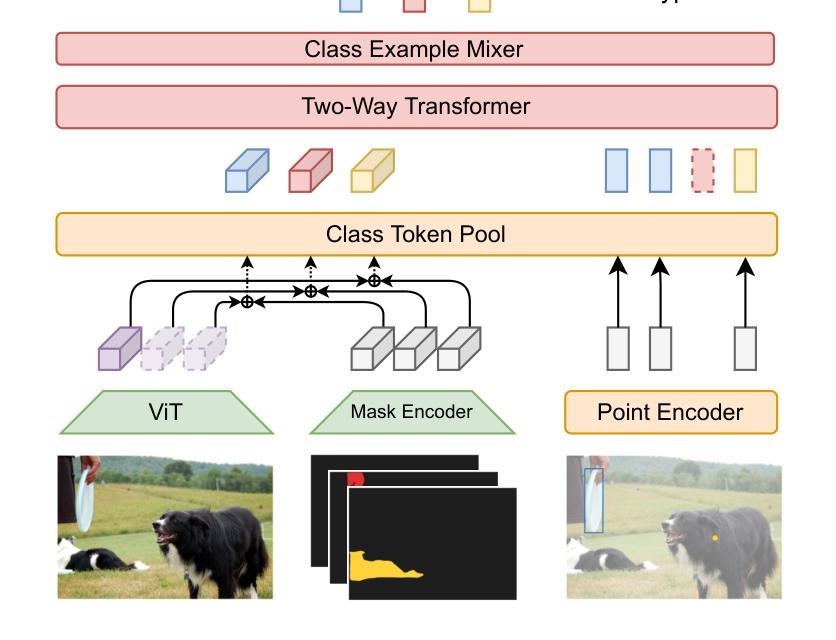
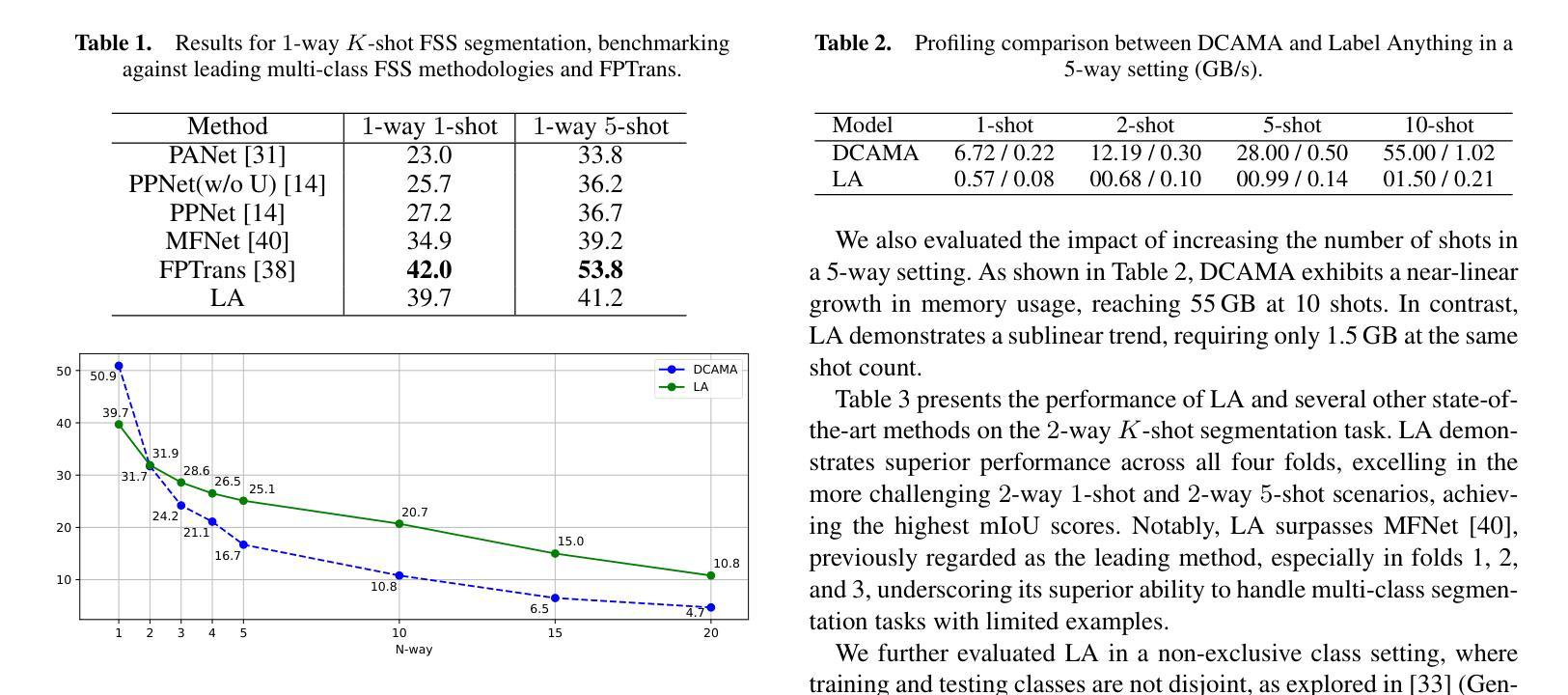
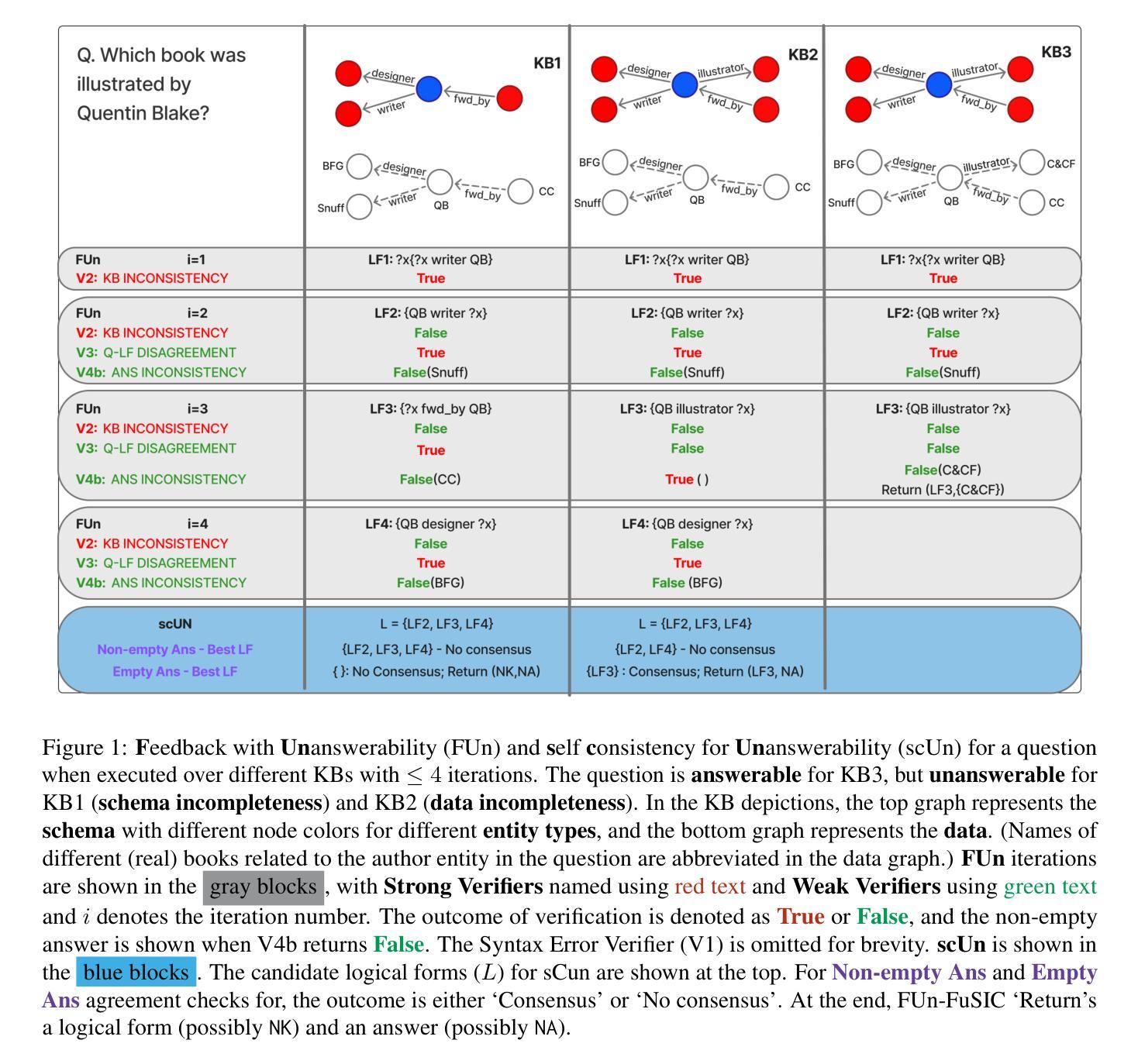
Iterative Repair with Weak Verifiers for Few-shot Transfer in KBQA with Unanswerability
Authors:Riya Sawhney, Samrat Yadav, Indrajit Bhattacharya, Mausam
Real-world applications of KBQA require models to handle unanswerable questions with a limited volume of in-domain labeled training data. We propose the novel task of few-shot transfer for KBQA with unanswerable questions and contribute two new datasets for performance evaluation. We present FUn-FuSIC - a novel solution for our task that extends FuSIC KBQA, the state-of-the-art few-shot transfer model for answerable-only KBQA. We first note that FuSIC-KBQA’s iterative repair makes a strong assumption that all questions are unanswerable. As a remedy, we propose Feedback for Unanswerability (FUn), which uses iterative repair using feedback from a suite of strong and weak verifiers, and an adaptation of self consistency for unanswerabilty to better assess the answerability of a question. Our experiments show that FUn-FuSIC significantly outperforms suitable adaptations of multiple LLM based and supervised SoTA models on our task, while establishing a new SoTA for answerable few-shot transfer as well.
现实世界中的KBQA应用要求模型能够处理无法回答的问题,并且在领域内部只有有限量的标记训练数据。我们针对带有无法回答问题的KBQA提出了新颖的少量转移任务,并为性能评估贡献了两个新数据集。我们展示了FUN-FuSIC是我们的解决方案的新颖之处,它扩展了FuSIC KBQA模型,即当前最先进的有答案KBQA的少量转移模型。我们首先注意到,FuSIC-KBQA的迭代修复假设所有问题都是无法回答的。为解决这一问题,我们提出了用于不可回答性的反馈(FUN),它通过一系列强验证器和弱验证器的反馈进行迭代修复,并适应自我一致性以更好地评估问题的可回答性。我们的实验表明,FUN-FuSIC在我们的任务上显著优于多个基于大型语言模型的适当适应模型和最新的监督模型,同时为我们可回答的答案型少量转移设定了新的最新标准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
KBQA在现实世界应用时面临处理不可回答问题的问题,特别是在有限领域内标签训练数据量较小的情况下。为此,我们提出了针对KBQA不可回答问题的新型few-shot迁移任务,并贡献了两个新的数据集用于性能评估。我们提出了FUn-FuSIC解决方案,它是FuSIC KBQA的扩展,用于处理可回答KBQA的few-shot迁移模型。我们注意到FuSIC-KBQA的迭代修复假设所有问题都是不可回答的,因此我们提出了Feedback for Unanswerability(FUn)方法,利用一系列强弱验证器的反馈和未回答问题自我一致性评估的适应性改进,来评估问题的可回答性。实验表明,FUn-FuSIC在我们的任务上显著优于多个大型语言模型(LLM)和现有监督模型的适应版本,同时为可回答问题的few-shot迁移任务建立了新的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- KBQA在现实世界应用中面临处理不可回答问题的问题,特别是在训练数据量有限的情况下。
- 提出了针对KBQA不可回答问题的新型few-shot迁移任务,并贡献了两个新的数据集用于评估。
- FUn-FuSIC是FuSIC KBQA的扩展,用于处理可回答KBQA的few-shot迁移。
- FuSIC-KBQA的迭代修复假设存在问题,所有问题都假设为不可回答的。
- 提出Feedback for Unanswerability(FUn)方法来解决这个问题,利用强弱验证器的反馈和未回答问题的自我一致性评估。
- 实验显示FUn-FuSIC在任务上表现优异,优于多个大型语言模型和现有监督模型的适应版本。
点此查看论文截图


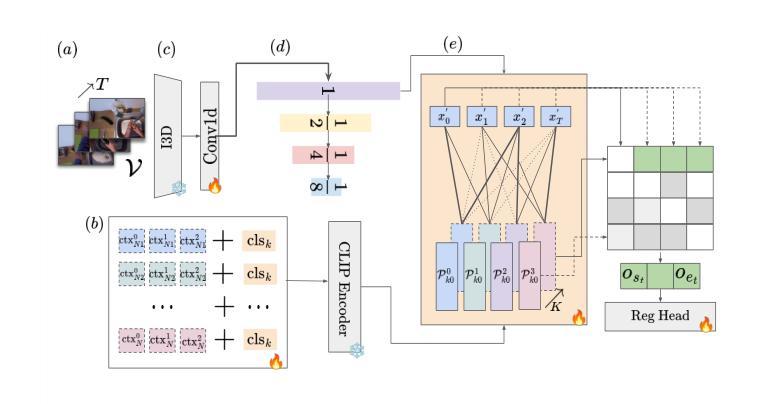
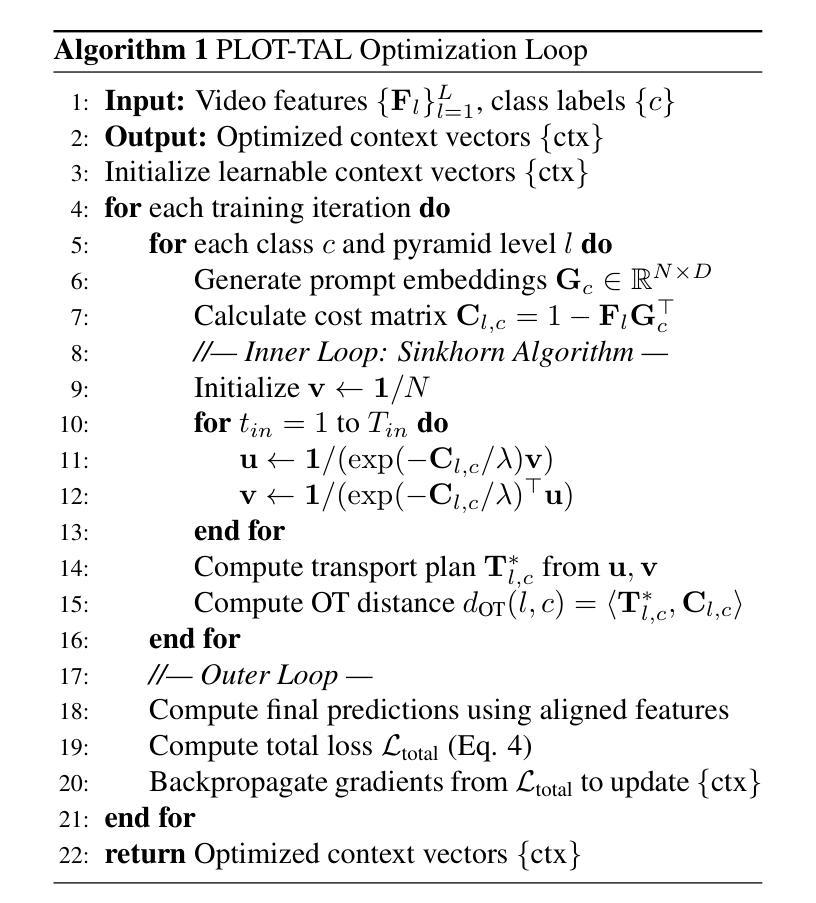
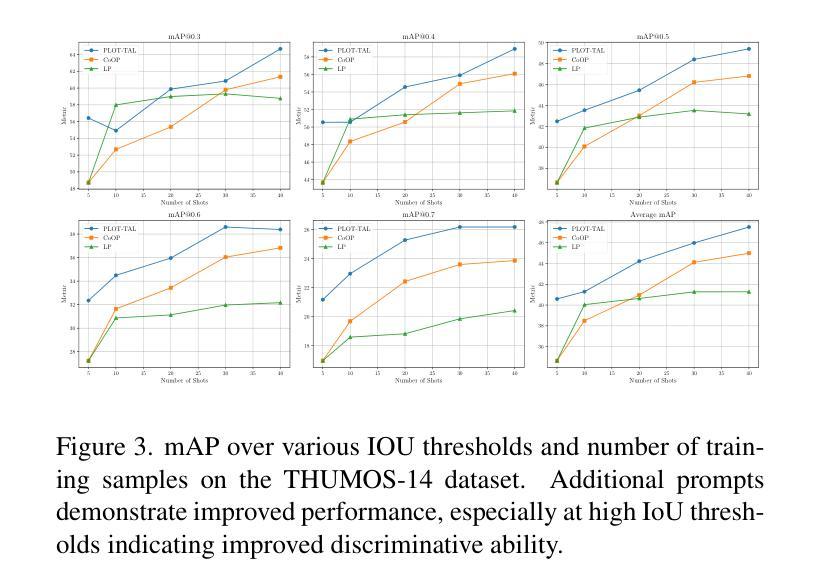
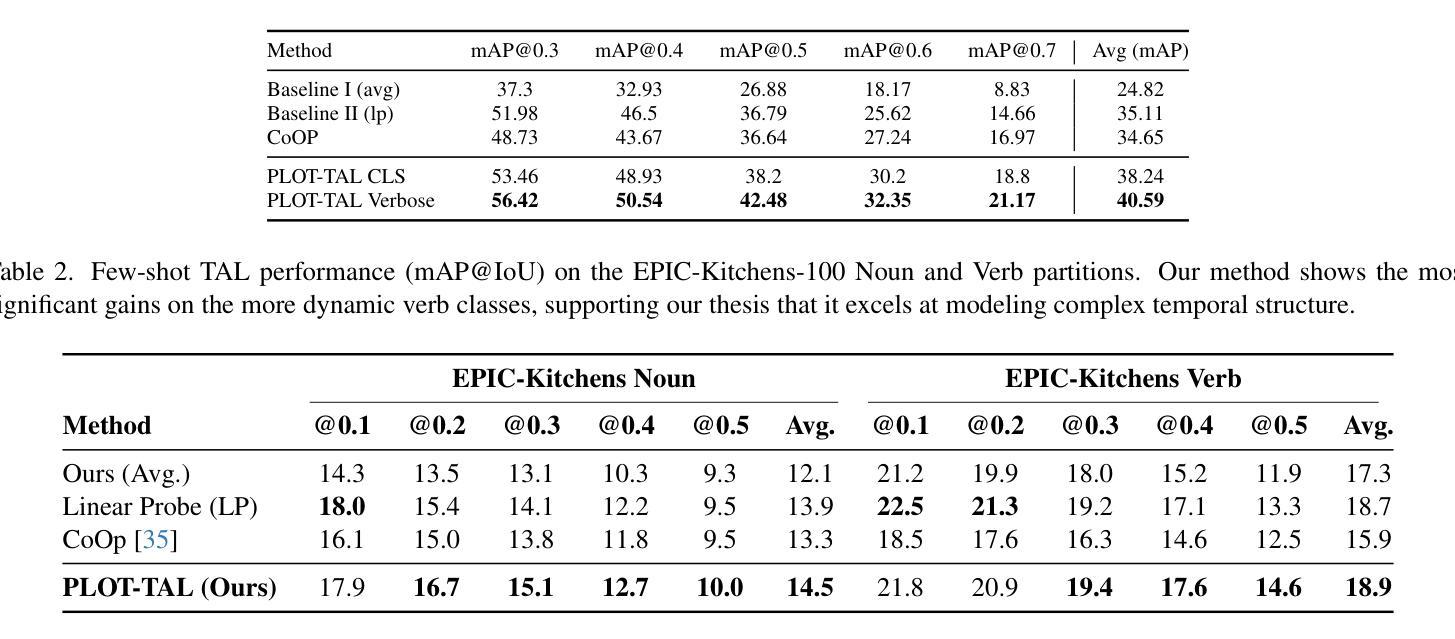
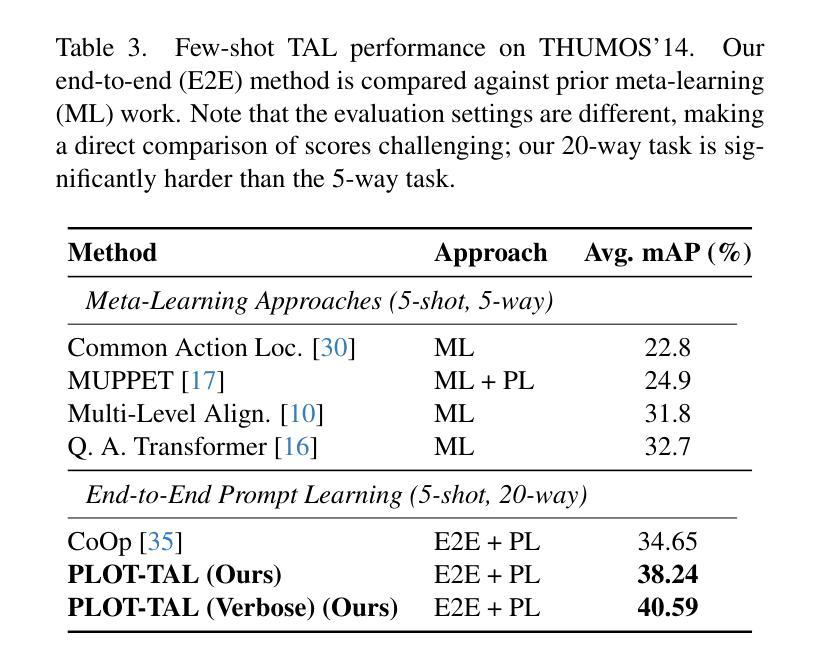
PLOT-TAL: Prompt Learning with Optimal Transport for Few-Shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Edward Fish, Andrew Gilbert
Few-shot temporal action localization (TAL) methods that adapt large models via single-prompt tuning often fail to produce precise temporal boundaries. This stems from the model learning a non-discriminative mean representation of an action from sparse data, which compromises generalization. We address this by proposing a new paradigm based on multi-prompt ensembles, where a set of diverse, learnable prompts for each action is encouraged to specialize on compositional sub-events. To enforce this specialization, we introduce PLOT-TAL, a framework that leverages Optimal Transport (OT) to find a globally optimal alignment between the prompt ensemble and the video’s temporal features. Our method establishes a new state-of-the-art on the challenging few-shot benchmarks of THUMOS’14 and EPIC-Kitchens, without requiring complex meta-learning. The significant performance gains, particularly at high IoU thresholds, validate our hypothesis and demonstrate the superiority of learning distributed, compositional representations for precise temporal localization.
少数样本时序动作定位(TAL)方法通过单次提示调整大型模型,但往往无法产生精确的时序边界。这源于模型从稀疏数据中学习动作的非判别性平均表示,从而损害了泛化能力。我们通过提出一种基于多提示集成的新范式来解决这个问题,该范式鼓励针对每个动作的一组多样、可学习的提示专注于组合子事件。为了实施专业化,我们引入了PLOT-TAL框架,该框架利用最优传输(OT)技术找到提示集成和视频时序特征之间的全局最优对齐。我们的方法在具有挑战性的THUMOS’14和EPIC-Kitchens少量样本基准测试上建立了新的最先进的性能,无需复杂的元学习。显著的性能提升,特别是在高IoU阈值上,验证了我们的假设,并证明了学习分布式组合表示进行精确时序定位的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCVWS
Summary
大型模型通过单提示调整进行小样本时序动作定位(TAL)时,往往难以产生精确的时序边界。本文提出一种基于多提示集成的新方法,通过鼓励每个动作的一组可学习、多样化的提示来专注于组合子事件,以解决这一问题。为了实施专业化,本文引入了PLOT-TAL框架,该框架利用最优传输(OT)来找到提示集合和视频时序特征之间的全局最优对齐。该方法在具有挑战性的THUMOS’14和EPIC-Kitchens少量样本基准测试中建立了新的标准,无需复杂的元学习。显著的性能提升,特别是在高IoU阈值上,验证了我们的假设并证明了学习分布式、组合表示进行精确时序定位的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于单提示调整的小样本TAL方法存在精确时序边界问题。
- 提出基于多提示集成的新方法来解决此问题,鼓励每个动作的提示专注于组合子事件。
- 引入PLOT-TAL框架,利用最优传输(OT)找到提示集合和视频时序特征之间的全局最优对齐。
- 在THUMOS’14和EPIC-Kitchens的少量样本基准测试中建立了新的标准。
- 方法无需复杂的元学习。
- 显著的性能提升,特别是在高IoU阈值上。
点此查看论文截图