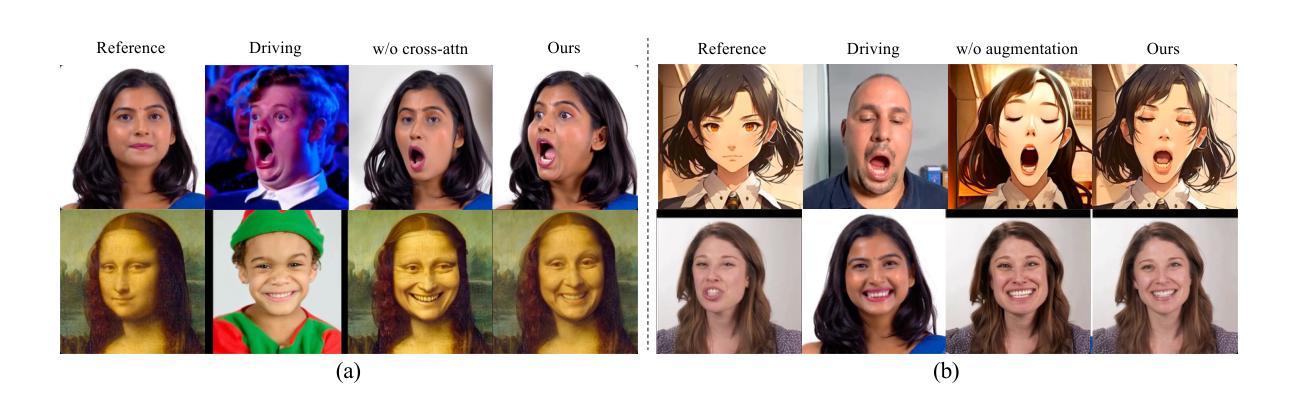
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
X-NeMo: Expressive Neural Motion Reenactment via Disentangled Latent Attention
Authors:Xiaochen Zhao, Hongyi Xu, Guoxian Song, You Xie, Chenxu Zhang, Xiu Li, Linjie Luo, Jinli Suo, Yebin Liu
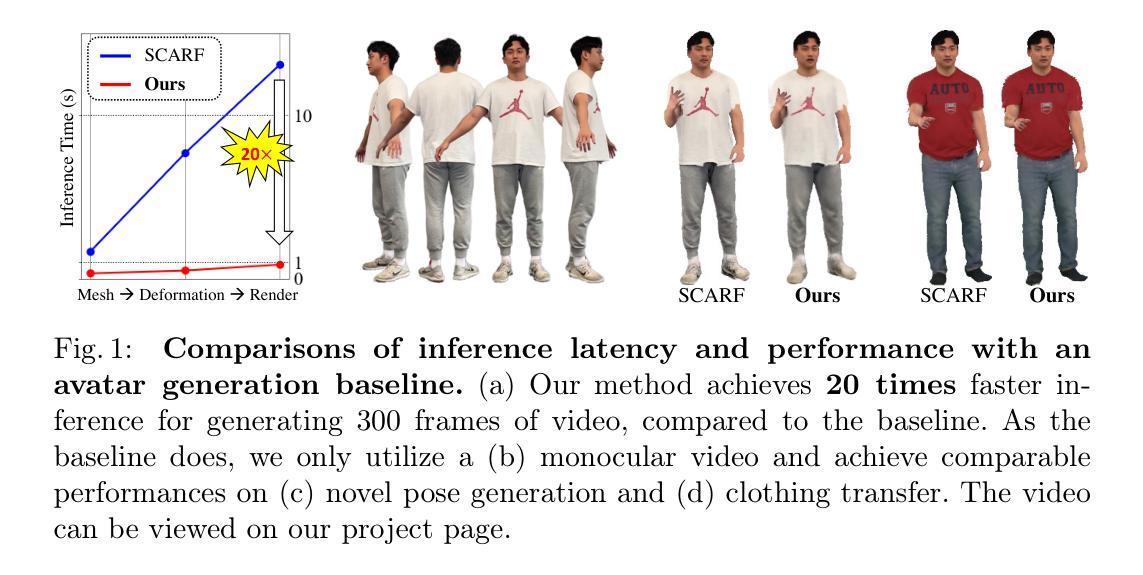
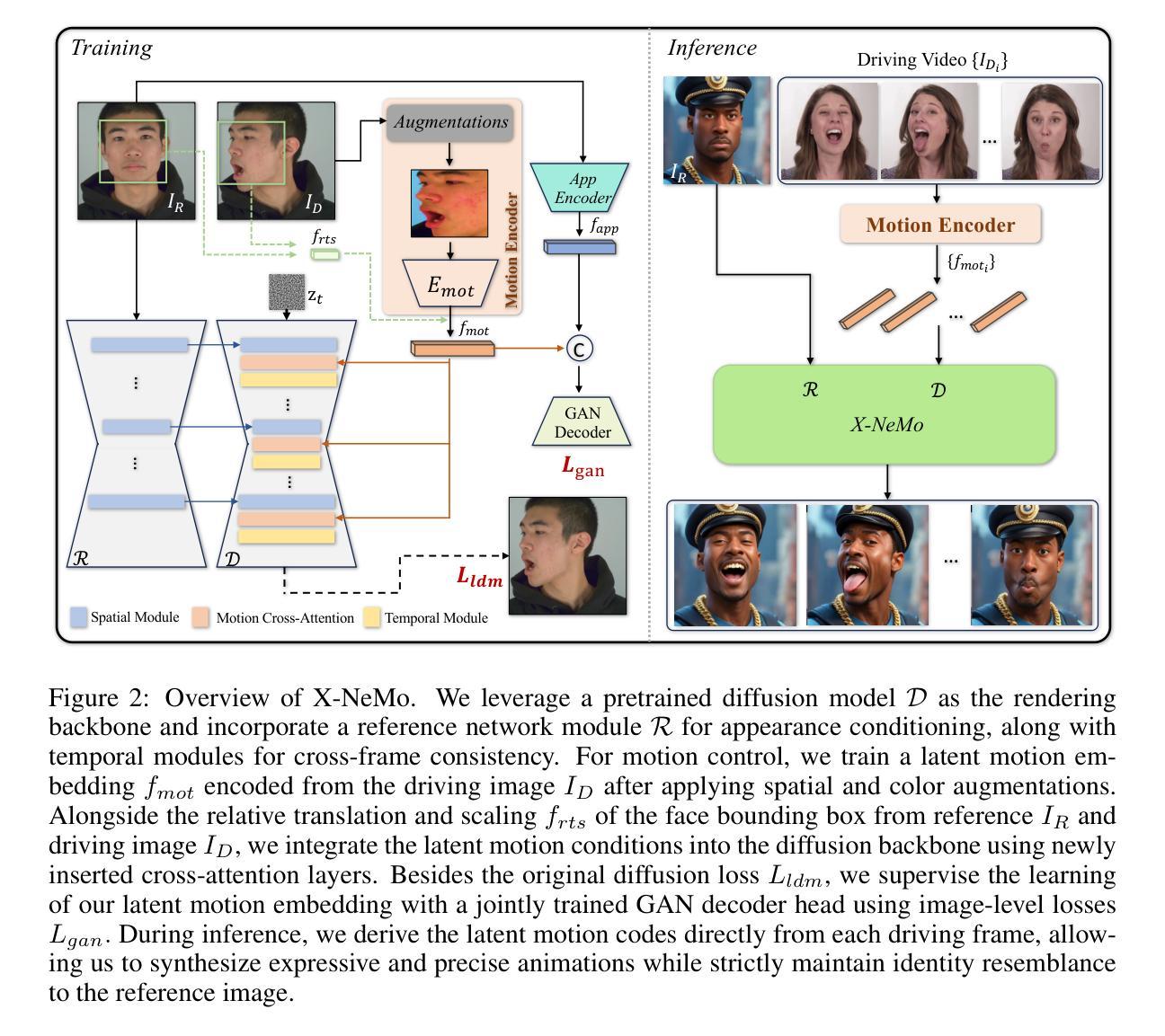
We propose X-NeMo, a novel zero-shot diffusion-based portrait animation pipeline that animates a static portrait using facial movements from a driving video of a different individual. Our work first identifies the root causes of the key issues in prior approaches, such as identity leakage and difficulty in capturing subtle and extreme expressions. To address these challenges, we introduce a fully end-to-end training framework that distills a 1D identity-agnostic latent motion descriptor from driving image, effectively controlling motion through cross-attention during image generation. Our implicit motion descriptor captures expressive facial motion in fine detail, learned end-to-end from a diverse video dataset without reliance on pretrained motion detectors. We further enhance expressiveness and disentangle motion latents from identity cues by supervising their learning with a dual GAN decoder, alongside spatial and color augmentations. By embedding the driving motion into a 1D latent vector and controlling motion via cross-attention rather than additive spatial guidance, our design eliminates the transmission of spatial-aligned structural clues from the driving condition to the diffusion backbone, substantially mitigating identity leakage. Extensive experiments demonstrate that X-NeMo surpasses state-of-the-art baselines, producing highly expressive animations with superior identity resemblance. Our code and models are available for research.
我们提出了X-NeMo,这是一种新型零样本扩散式肖像动画流水线,它使用来自不同个体驱动视频的面部动作来动画静态肖像。我们的工作首先确定了先前方法中的主要问题的根本原因,例如身份泄露和捕捉微妙及极端表情的困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一个全新的端到端训练框架,从驱动图像中提炼出1D身份无关潜在运动描述符,通过交叉注意有效控制在图像生成过程中的运动。我们的隐性运动描述符以精细的方式捕捉表情丰富的面部运动,从多样化的视频数据集中进行端到端学习,无需依赖预训练的运动检测器。我们进一步通过双GAN解码器进行空间和时间增强来增强表现能力,并将运动潜在性与身份线索分开。通过将驱动运动嵌入到1D潜在向量中,并通过交叉注意而不是附加的空间指导来控制运动,我们的设计消除了从驱动条件到扩散主干的空间对齐结构线索的传输,极大地减轻了身份泄露问题。大量实验表明,X-NeMo超越了最先进的基线,产生了具有高度表现力且与身份高度相似的动画。我们的代码和模型可供研究使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025, code is available at https://github.com/bytedance/x-nemo-inference
Summary
基于上述技术文本的描述,该研究提出了一种新型零样本扩散式肖像动画管道X-NeMo,该管道能够以另一人的面部动作驱动静态肖像动画。该研究解决了先前方法中的身份泄露和捕捉微妙及极端表情困难等核心问题。通过引入端到端的训练框架和双重GAN解码器等技术手段,该研究实现了精细的面部表情捕捉和身份信息的解耦,有效提升了动画的表达力和质量。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型的零样本扩散式肖像动画方法X-NeMo,能够使用不同个体的面部动作驱动静态肖像动画。
- 解决了身份泄露和捕捉微妙及极端表情困难等核心问题。
- 通过端到端的训练框架,从驱动图像中提炼出身份无关的一维潜在运动描述符,有效控制动画过程中的运动。
- 引入了一种隐式运动描述符,能够精细捕捉面部表情。
- 通过双重GAN解码器、空间和时间增强技术,提高了动画的表达力和质量,实现了运动潜力和身份线索的解耦。
- 通过将驱动动作嵌入到一维潜在向量中,并通过交叉注意力控制运动,避免了空间对齐的结构线索从驱动条件传递到扩散主干,有效减轻了身份泄露问题。
点此查看论文截图


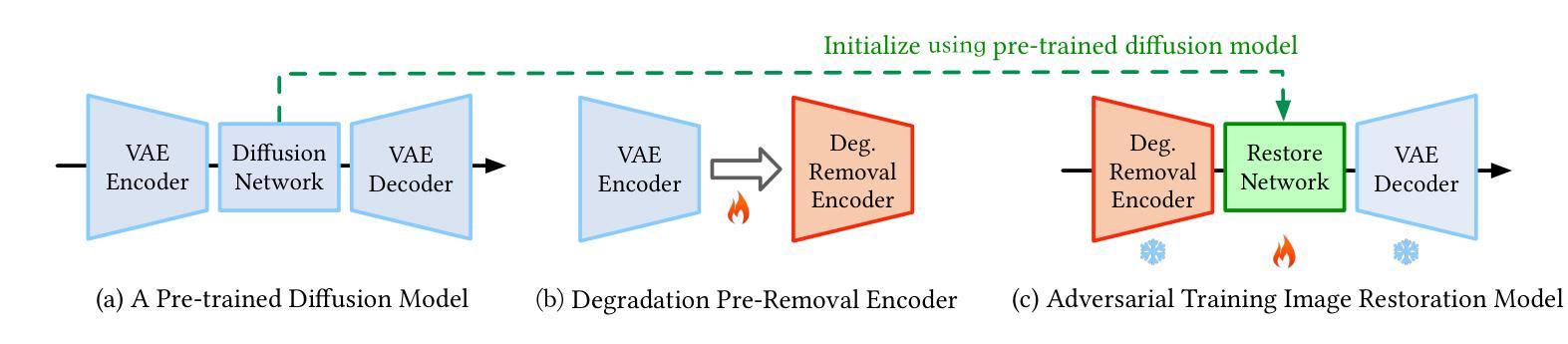
Harnessing Diffusion-Yielded Score Priors for Image Restoration
Authors:Xinqi Lin, Fanghua Yu, Jinfan Hu, Zhiyuan You, Wu Shi, Jimmy S. Ren, Jinjin Gu, Chao Dong
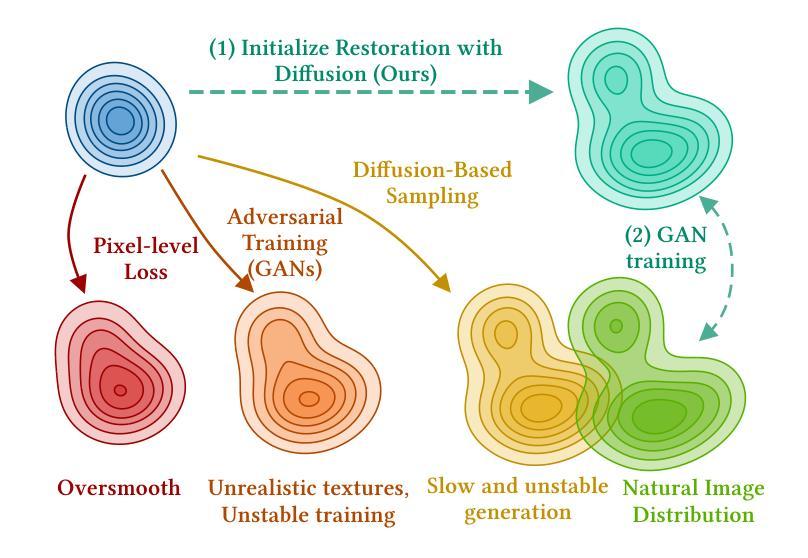
Deep image restoration models aim to learn a mapping from degraded image space to natural image space. However, they face several critical challenges: removing degradation, generating realistic details, and ensuring pixel-level consistency. Over time, three major classes of methods have emerged, including MSE-based, GAN-based, and diffusion-based methods. However, they fail to achieve a good balance between restoration quality, fidelity, and speed. We propose a novel method, HYPIR, to address these challenges. Our solution pipeline is straightforward: it involves initializing the image restoration model with a pre-trained diffusion model and then fine-tuning it with adversarial training. This approach does not rely on diffusion loss, iterative sampling, or additional adapters. We theoretically demonstrate that initializing adversarial training from a pre-trained diffusion model positions the initial restoration model very close to the natural image distribution. Consequently, this initialization improves numerical stability, avoids mode collapse, and substantially accelerates the convergence of adversarial training. Moreover, HYPIR inherits the capabilities of diffusion models with rich user control, enabling text-guided restoration and adjustable texture richness. Requiring only a single forward pass, it achieves faster convergence and inference speed than diffusion-based methods. Extensive experiments show that HYPIR outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods, achieving efficient and high-quality image restoration.
深度图像恢复模型旨在从退化图像空间学习映射到自然图像空间。然而,它们面临几个关键挑战:去除退化因素、生成逼真的细节,以及确保像素级别的一致性。随着时间的推移,出现了三大类方法,包括基于MSE的方法、基于GAN的方法和基于扩散的方法。然而,它们在恢复质量、保真度和速度之间并未取得良好的平衡。我们提出了一种新方法HYPIR来解决这些挑战。我们的解决方案流程很简单:它涉及使用预训练的扩散模型初始化图像恢复模型,然后使用对抗性训练进行微调。这种方法不需要依赖扩散损失、迭代采样或额外的适配器。从理论上讲,我们从预训练的扩散模型开始对抗性训练,使初始恢复模型非常接近自然图像分布。因此,这种初始化提高了数值稳定性,避免了模式崩溃,并大大加速了对抗性训练的收敛。此外,HYPIR继承了扩散模型的丰富用户控制功能,可实现文本引导的恢复和可调整纹理丰富度。仅需一次前向传递,它的收敛和推理速度就超过了基于扩散的方法。大量实验表明,HYPIR优于以前的最先进方法,实现了高效和高质量的图像恢复。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种新型的图像修复方法HYPIR,旨在解决现有方法面临的关键挑战,包括去除退化、生成逼真的细节以及确保像素级别的连贯性。通过初始化图像修复模型并使用预训练的扩散模型进行对抗训练,该方法无需依赖扩散损失、迭代采样或额外的适配器。初始化对抗训练的策略将修复模型更接近自然图像分布,从而提高了数值稳定性,避免了模式崩溃,并大大加快了对抗训练的收敛速度。同时,HYPIR继承了扩散模型的丰富用户控制功能,支持文本引导修复和调整纹理丰富度。只需单次前向传递,它的收敛速度和推理速度都比基于扩散的方法更快,且实验表明HYPIR的性能优于现有最佳方法,可实现高效且高质量的图像修复。
Key Takeaways
- HYPIR是一种新型的图像修复方法,旨在解决现有方法面临的挑战,包括去除图像退化、生成逼真细节和确保像素级一致性。
- HYPIR通过初始化图像修复模型并使用预训练的扩散模型进行对抗训练,简化了解决方案流程。
- 初始化对抗训练使修复模型更接近自然图像分布,提高了数值稳定性和收敛速度。
- HYPIR无需依赖扩散损失、迭代采样或额外的适配器,实现了快速收敛和推理速度。
- HYPIR继承了扩散模型的丰富用户控制功能,支持文本引导修复和调整纹理丰富度。
- HYPIR的性能优于现有最佳方法,可实现高效且高质量的图像修复。
点此查看论文截图

Unsupervised anomaly detection using Bayesian flow networks: application to brain FDG PET in the context of Alzheimer’s disease
Authors:Hugues Roy, Reuben Dorent, Ninon Burgos
Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) plays a crucial role in neuroimaging for identifying deviations from healthy subject data and thus facilitating the diagnosis of neurological disorders. In this work, we focus on Bayesian flow networks (BFNs), a novel class of generative models, which have not yet been applied to medical imaging or anomaly detection. BFNs combine the strength of diffusion frameworks and Bayesian inference. We introduce AnoBFN, an extension of BFNs for UAD, designed to: i) perform conditional image generation under high levels of spatially correlated noise, and ii) preserve subject specificity by incorporating a recursive feedback from the input image throughout the generative process. We evaluate AnoBFN on the challenging task of Alzheimer’s disease-related anomaly detection in FDG PET images. Our approach outperforms other state-of-the-art methods based on VAEs (beta-VAE), GANs (f-AnoGAN), and diffusion models (AnoDDPM), demonstrating its effectiveness at detecting anomalies while reducing false positive rates.
无监督异常检测(UAD)在神经成像中发挥着关键作用,能够识别健康受试者数据的偏差,从而有助于神经紊乱疾病的诊断。在这项工作中,我们专注于贝叶斯流网络(BFNs)这一新型生成模型,尚未应用于医学成像或异常检测。BFNs结合了扩散框架和贝叶斯推断的优势。我们介绍了AnoBFN,这是BFNs在UAD方面的扩展,旨在:i)在高水平空间相关噪声下进行条件图像生成,以及ii)通过在整个生成过程中融入来自输入图像的递归反馈来保持受试者特异性。我们在阿尔茨海默病相关的异常检测这一具有挑战性的任务上评估了AnoBFN在FDG PET图像中的应用。我们的方法优于其他基于VAEs(beta-VAE)、GANs(f-AnoGAN)和扩散模型(AnoDDPM)的最先进方法,证明其在检测异常时降低误报率的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于贝叶斯流网络(BFNs)的UAD技术在医学影像中扮演重要角色,用于识别偏离健康主体的数据偏差,进而辅助诊断神经性疾病。本研究推出了一种针对医学影像的无监督异常检测新方法——AnoBFN,它结合了扩散框架和贝叶斯推断的优势,能在高空间相关噪声下进行条件图像生成,并能在生成过程中通过递归反馈保留主题特异性。在阿尔茨海默病相关的异常检测任务中,与beta-VAEs、f-AnoGAN和扩散模型等先进方法相比,其表现更为出色。
Key Takeaways
- UAD在医学影像中扮演重要角色,用于识别偏离健康主体的数据偏差。
- 本研究引入了一种针对医学影像的无监督异常检测新方法——AnoBFN。
- AnoBFN结合了扩散框架和贝叶斯推断的优势。
- AnoBFN能在高空间相关噪声下进行条件图像生成。
- AnoBFN通过递归反馈保留主题特异性。
- 在阿尔茨海默病相关的异常检测任务中,AnoBFN表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

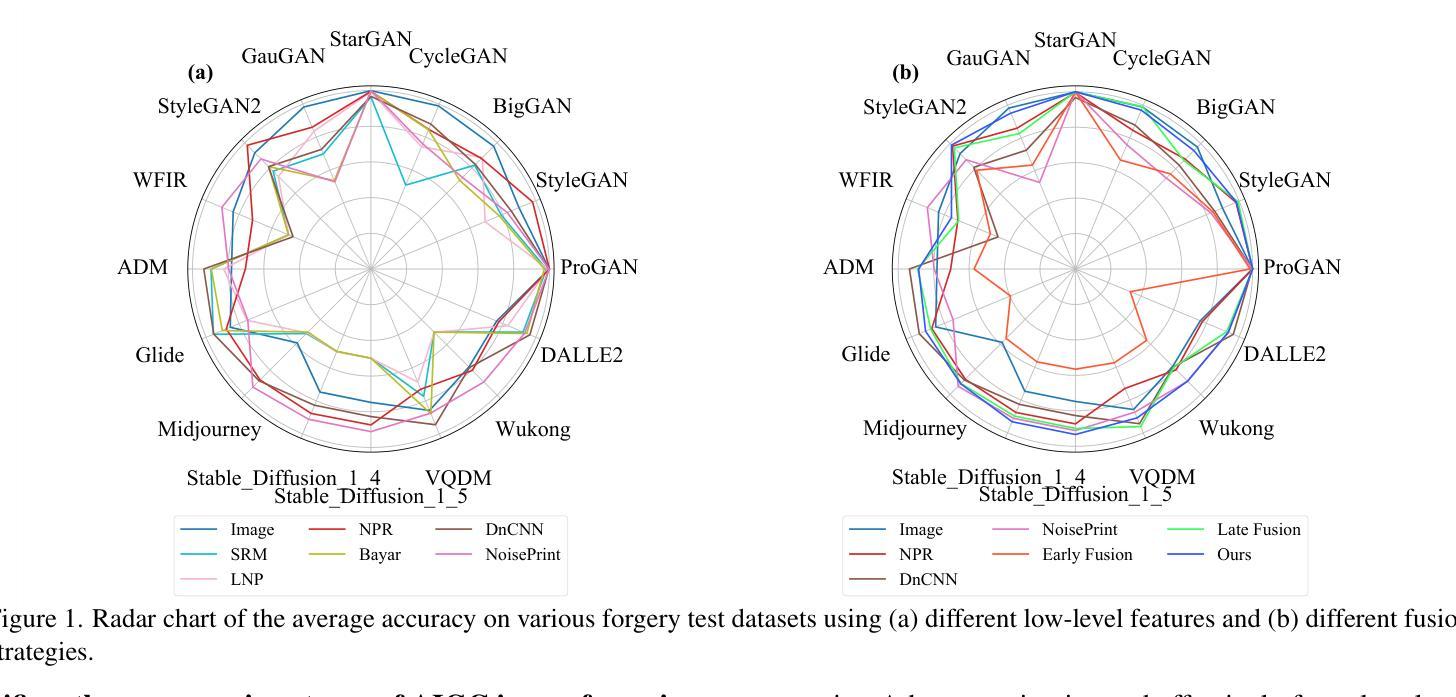
Exploring the Collaborative Advantage of Low-level Information on Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Ziyin Zhou, Ke Sun, Zhongxi Chen, Xianming Lin, Yunpeng Luo, Ke Yan, Shouhong Ding, Xiaoshuai Sun
Existing state-of-the-art AI-Generated image detection methods mostly consider extracting low-level information from RGB images to help improve the generalization of AI-Generated image detection, such as noise patterns. However, these methods often consider only a single type of low-level information, which may lead to suboptimal generalization. Through empirical analysis, we have discovered a key insight: different low-level information often exhibits generalization capabilities for different types of forgeries. Furthermore, we found that simple fusion strategies are insufficient to leverage the detection advantages of each low-level and high-level information for various forgery types. Therefore, we propose the Adaptive Low-level Experts Injection (ALEI) framework. Our approach introduces Lora Experts, enabling the backbone network, which is trained with high-level semantic RGB images, to accept and learn knowledge from different low-level information. We utilize a cross-attention method to adaptively fuse these features at intermediate layers. To prevent the backbone network from losing the modeling capabilities of different low-level features during the later stages of modeling, we developed a Low-level Information Adapter that interacts with the features extracted by the backbone network. Finally, we propose Dynamic Feature Selection, which dynamically selects the most suitable features for detecting the current image to maximize generalization detection capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method, finetuned on only four categories of mainstream ProGAN data, performs excellently and achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple datasets containing unseen GAN and Diffusion methods.
现有最先进的AI生成图像检测方法大多考虑从RGB图像中提取低级信息,以帮助提高AI生成图像检测的泛化能力,例如噪声模式。然而,这些方法通常只考虑一种低级信息,可能导致泛化效果不佳。通过实证分析,我们发现了关键见解:不同的低级信息通常对不同类型的伪造表现出不同的泛化能力。此外,我们发现简单的融合策略不足以利用每种低级和高级信息在不同类型伪造检测中的优势。因此,我们提出了自适应低级专家注入(ALEI)框架。我们的方法引入了Lora专家,使主干网络(用高级语义RGB图像进行训练)能够接受和学习来自不同低级信息的知识。我们使用交叉注意力方法来自适应地融合中间层中的这些特征。为了防止主干网络在建模后期失去对不同低级特征的建模能力,我们开发了一个低级信息适配器,与主干网络提取的特征进行交互。最后,我们提出了动态特征选择,它动态选择最适合检测当前图像的特征,以最大限度地提高泛化检测能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法仅在四个主流ProGAN数据类别上进行微调,就表现出卓越性能,并在包含未见过的GAN和Diffusion方法的多个数据集上实现了最新技术成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现有主流AI图像检测方法多依赖从RGB图像中提取低层次信息来提高图像检测的泛化能力,但存在信息单一和融合策略简单的问题。本研究发现不同低层次信息对不同类型伪造图像的泛化能力不同,因此提出自适应低层次专家注入(ALEI)框架。该框架引入Lora专家,使训练有高级语义RGB图像的主干网络能够接受和学习不同低层次信息的知识。通过跨注意力方法自适应融合这些特征,并开发了低层次信息适配器来与主干网络提取的特征进行交互。同时提出动态特征选择,可动态选择最适于当前图像检测的特征以实现最佳的泛化检测能力。本研究通过实验验证了该方法的优秀性能和前沿成果。
Key Takeaways
- AI图像检测方法多依赖低层次信息提高泛化能力。
- 现有方法存在信息单一和融合策略不足的问题。
- 不同低层次信息对不同类型伪造图像的泛化能力不同。
- 提出自适应低层次专家注入(ALEI)框架来解决上述问题。
- ALEI框架引入Lora专家,结合跨注意力方法自适应融合特征。
- 开发低层次信息适配器来增强主干网络的特征交互能力。
点此查看论文截图

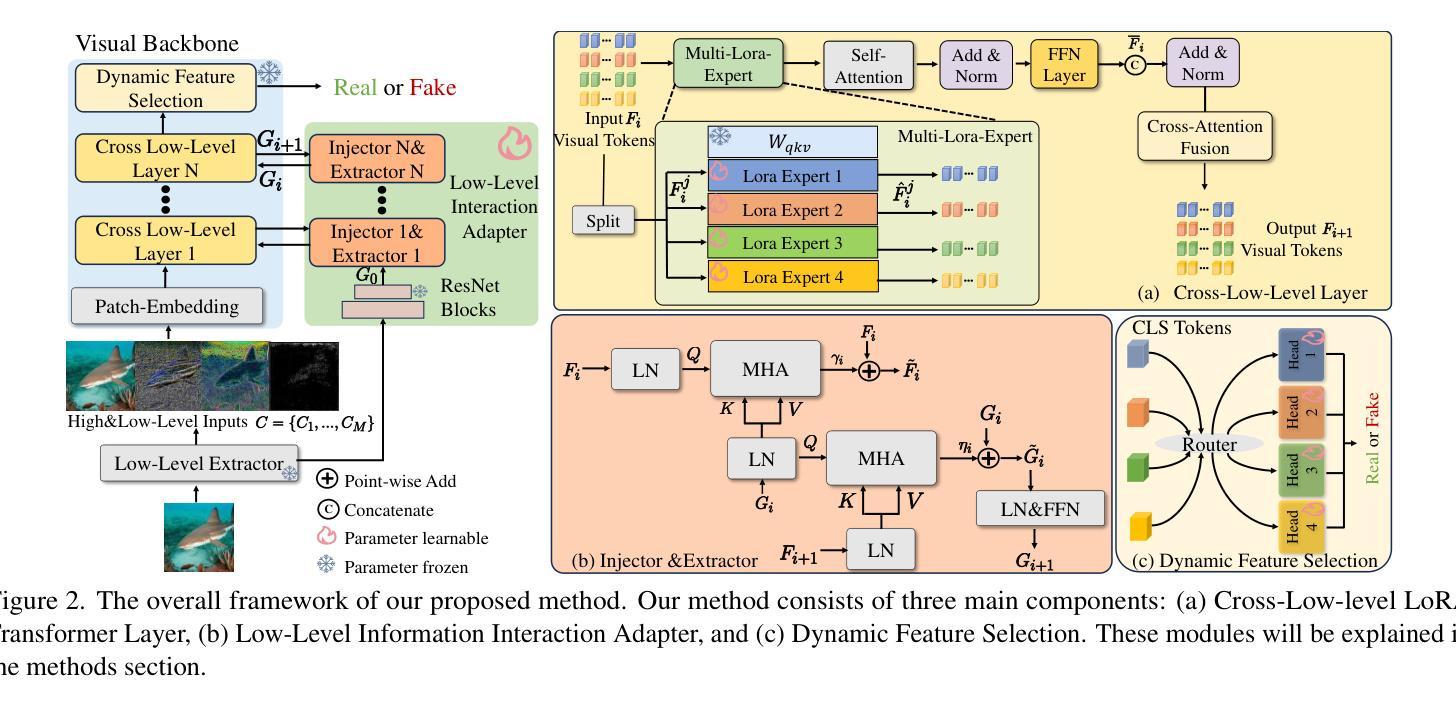
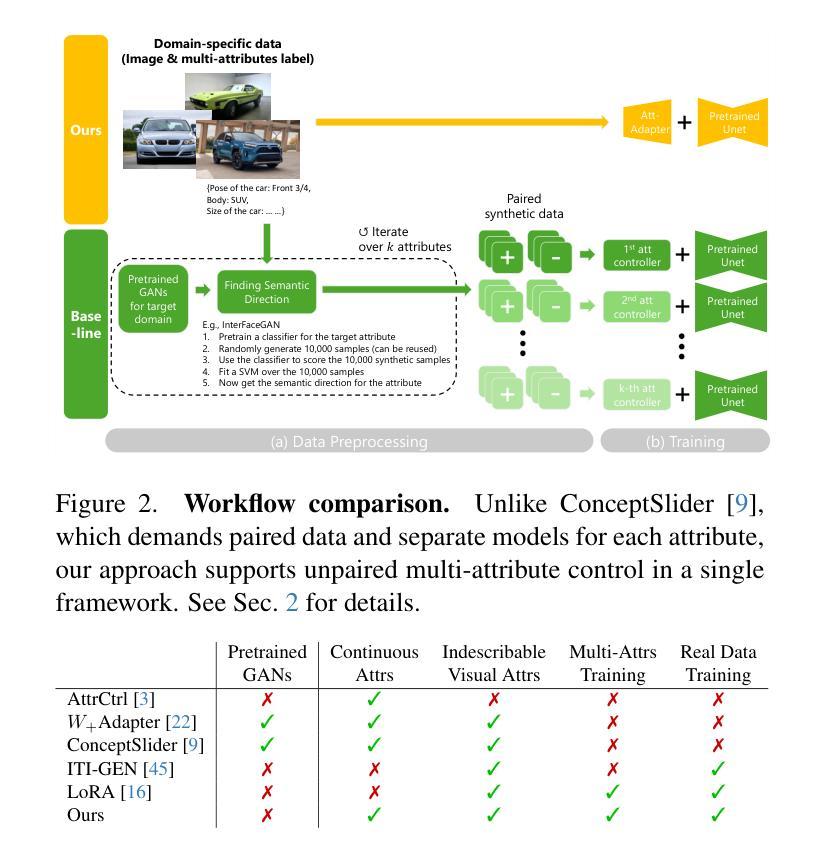
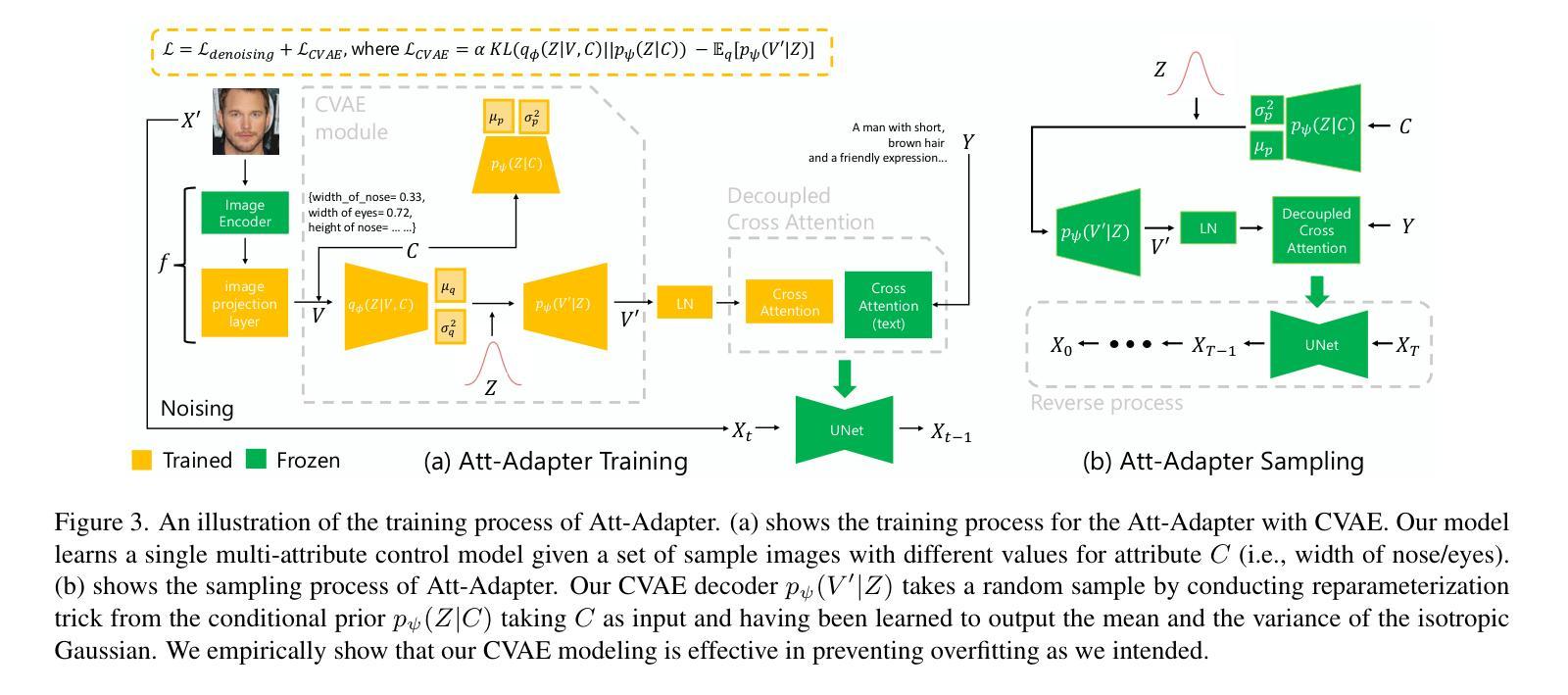
Att-Adapter: A Robust and Precise Domain-Specific Multi-Attributes T2I Diffusion Adapter via Conditional Variational Autoencoder
Authors:Wonwoong Cho, Yan-Ying Chen, Matthew Klenk, David I. Inouye, Yanxia Zhang
Text-to-Image (T2I) Diffusion Models have achieved remarkable performance in generating high quality images. However, enabling precise control of continuous attributes, especially multiple attributes simultaneously, in a new domain (e.g., numeric values like eye openness or car width) with text-only guidance remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce the Attribute (Att) Adapter, a novel plug-and-play module designed to enable fine-grained, multi-attributes control in pretrained diffusion models. Our approach learns a single control adapter from a set of sample images that can be unpaired and contain multiple visual attributes. The Att-Adapter leverages the decoupled cross attention module to naturally harmonize the multiple domain attributes with text conditioning. We further introduce Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to the Att-Adapter to mitigate overfitting, matching the diverse nature of the visual world. Evaluations on two public datasets show that Att-Adapter outperforms all LoRA-based baselines in controlling continuous attributes. Additionally, our method enables a broader control range and also improves disentanglement across multiple attributes, surpassing StyleGAN-based techniques. Notably, Att-Adapter is flexible, requiring no paired synthetic data for training, and is easily scalable to multiple attributes within a single model.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的成绩。然而,在新的领域(如眼睛睁开程度或汽车宽度等数值)实现连续属性的精确控制,尤其是同时控制多个属性,仅凭文本指导仍是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了属性(Att)适配器,这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在在预训练的扩散模型中实现精细的多属性控制。我们的方法从一组样本图像中学习单个控制适配器,这些图像可以是未配对的,并包含多个视觉属性。Att-Adapter利用解耦交叉注意模块,自然地协调多个域属性与文本条件。为了进一步缓解过拟合问题,并匹配视觉世界的多样性,我们在Att-Adapter中引入了条件变分自编码器(CVAE)。在两个公共数据集上的评估表明,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的方法。此外,我们的方法扩大了控制范围,并改善了多个属性之间的解纠缠,超越了基于StyleGAN的技术。值得注意的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,并且很容易在单个模型中扩展到多个属性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV’25 (Highlight), The project page is available at https://tri-mac.github.io/att-adapter/
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型已生成高质量图像方面取得了显著成效。然而,使用纯文本指导在新领域(如眼睛睁开程度或汽车宽度等数值)实现连续属性的精确控制,尤其是同时控制多个属性,仍然是一个重大挑战。为解决此问题,我们引入了属性适配器(Att-Adapter),这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在实现在预训练扩散模型中的精细粒度多属性控制。我们的方法从一组非配对包含多个视觉属性的样本图像中学习单个控制适配器。Att-Adapter利用解耦交叉注意力模块,自然地协调多个域属性与文本条件。为进一步缓解过拟合问题并匹配视觉世界的多样性,我们还在Att-Adapter中引入了条件变分自编码器(CVAE)。在两个公共数据集上的评估显示,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的基线。此外,我们的方法具有更广泛的控制范围,并在多个属性之间改善了分离性,超越了StyleGAN技术。值得一提的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,并且很容易在单个模型中扩展到多个属性。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在新领域实现多属性连续控制仍存在挑战。
- 引入属性适配器(Att-Adapter)模块,旨在解决预训练扩散模型中的精细粒度多属性控制问题。
- Att-Adapter通过利用解耦交叉注意力模块和条件变分自编码器(CVAE)实现多域属性与文本条件的自然协调。
- Att-Adapter的优势在于其灵活性,无需配对合成数据即可训练,并且容易扩展到单个模型中的多个属性。
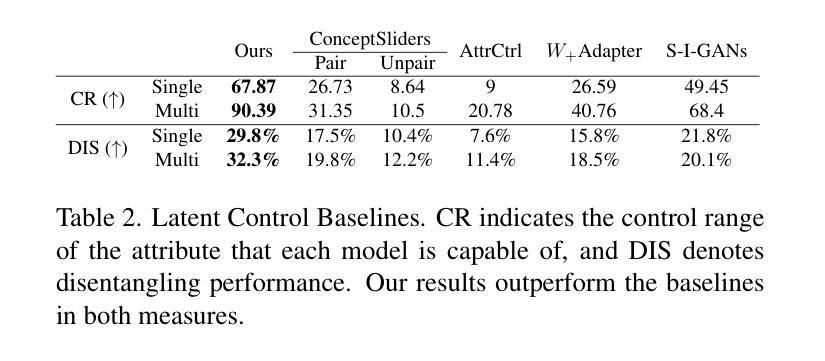
- 在两个公共数据集上的评估显示,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性和提高多个属性的分离性方面优于其他技术。
- Att-Adapter具有更广泛的控制范围,并且可以缓解过拟合问题。
点此查看论文截图


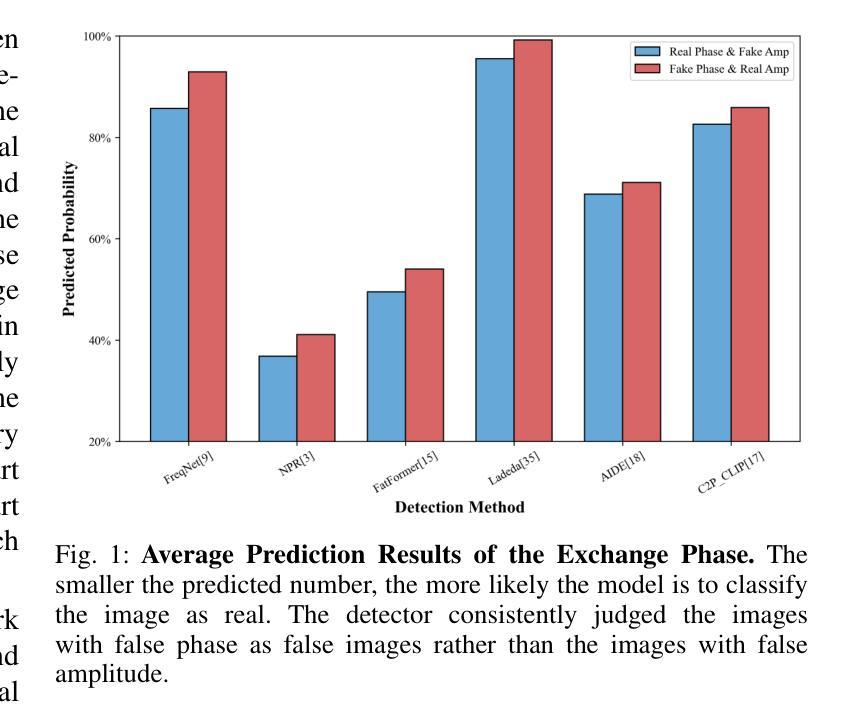
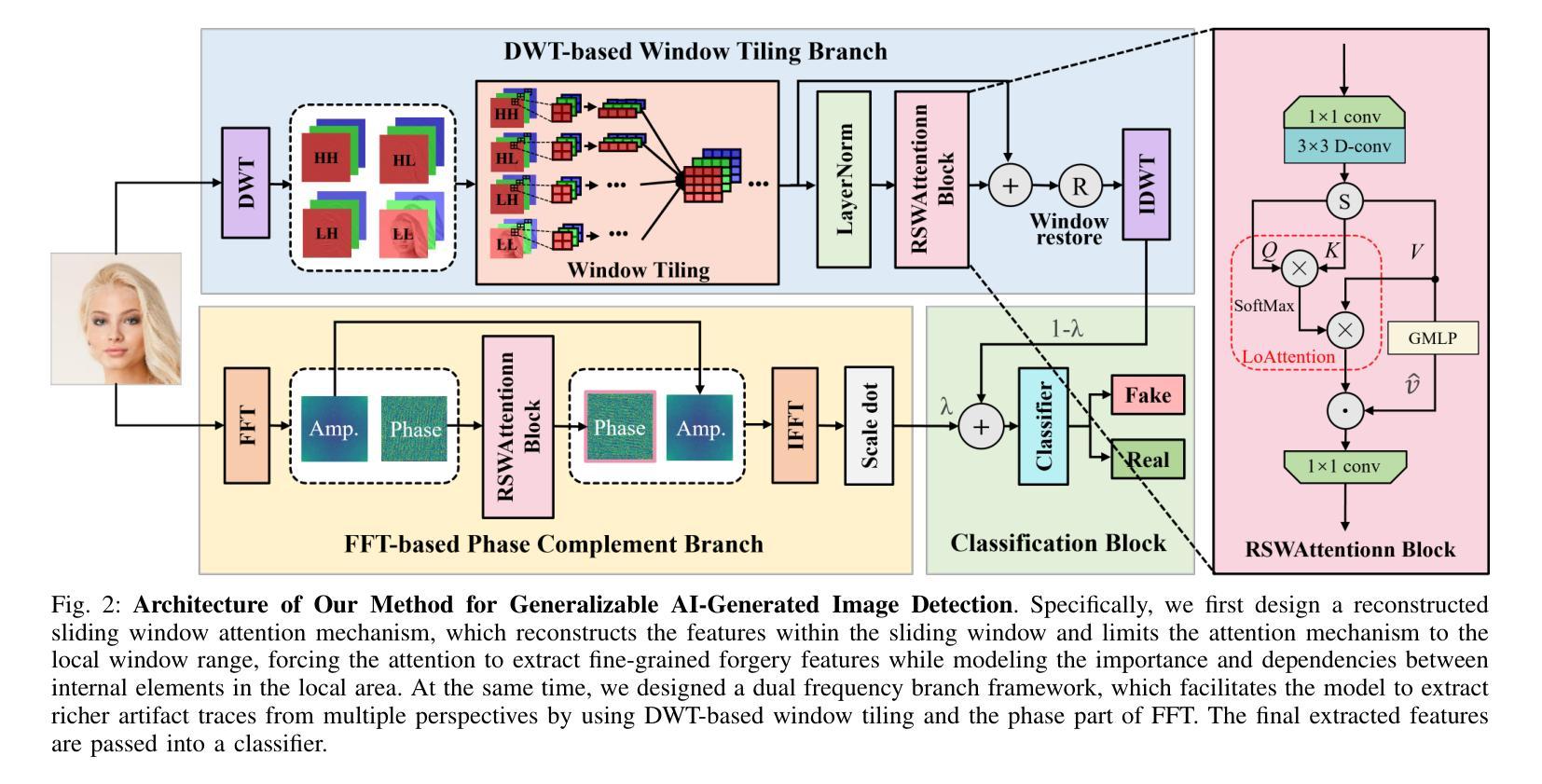
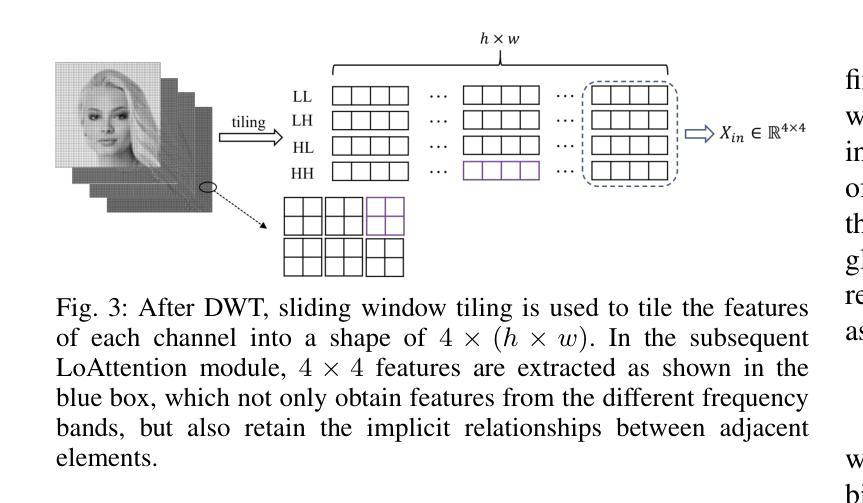
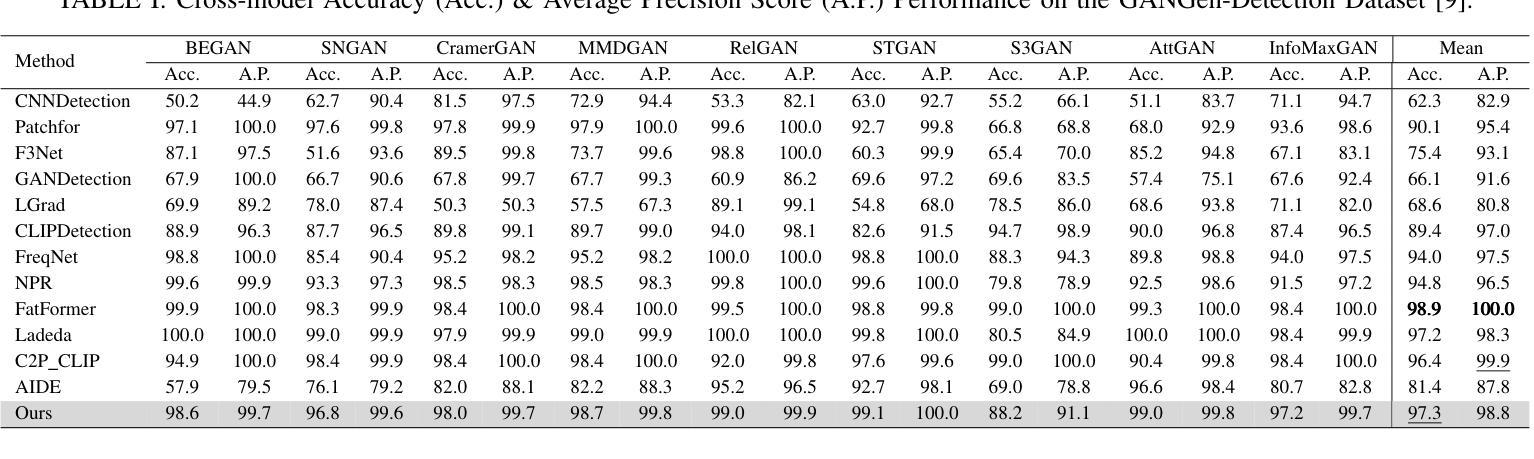
Dual Frequency Branch Framework with Reconstructed Sliding Windows Attention for AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Jiazhen Yan, Ziqiang Li, Fan Wang, Ziwen He, Zhangjie Fu
The rapid advancement of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models has enabled the creation of highly realistic synthetic images, presenting significant societal risks, such as misinformation and deception. As a result, detecting AI-generated images has emerged as a critical challenge. Existing researches emphasize extracting fine-grained features to enhance detector generalization, yet they often lack consideration for the importance and interdependencies of internal elements within local regions and are limited to a single frequency domain, hindering the capture of general forgery traces. To overcome the aforementioned limitations, we first utilize a sliding window to restrict the attention mechanism to a local window, and reconstruct the features within the window to model the relationships between neighboring internal elements within the local region. Then, we design a dual frequency domain branch framework consisting of four frequency domain subbands of DWT and the phase part of FFT to enrich the extraction of local forgery features from different perspectives. Through feature enrichment of dual frequency domain branches and fine-grained feature extraction of reconstruction sliding window attention, our method achieves superior generalization detection capabilities on both GAN and diffusion model-based generative images. Evaluated on diverse datasets comprising images from 65 distinct generative models, our approach achieves a 2.13% improvement in detection accuracy over state-of-the-art methods.
生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的快速发展使得能够创建高度逼真的合成图像,这带来了诸如虚假信息和欺骗等重大社会风险。因此,检测AI生成的图像已成为一项重大挑战。现有研究强调提取精细特征以增强检测器的泛化能力,但它们往往忽略了局部内部元素的重要性和相互依赖性,并且仅限于单一频率域,这阻碍了通用伪造痕迹的捕获。为了克服上述局限性,我们首先使用滑动窗口将注意力机制限制在局部窗口内,并重建窗口内的特征以建模局部区域内相邻内部元素之间的关系。然后,我们设计了一个由四个DWT频率域子带和FFT相位部分组成的双频域分支框架,以丰富从不同角度提取的局部伪造特征。通过双频域分支的特征丰富和重建滑动窗口注意力的精细特征提取,我们的方法在基于GAN和扩散模型的生成图像上实现了卓越的检测泛化能力。在包含来自65个不同生成模型的图像的多样化数据集上评估,我们的方法在检测精度上比现有最新方法提高了2.13%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的快速发展能够生成高度逼真的合成图像,带来了诸如虚假信息和欺骗等重大社会风险。因此,检测AI生成的图像成为了一项关键挑战。为了克服现有研究的局限性,本文采用局部窗口注意力机制重构局部区域内的特征关系,并设计包含小波变换四个频率子带和快速傅里叶变换相位部分的双频域分支框架,从不同角度丰富局部伪造特征的提取。此方法在GAN和扩散模型生成的图像上实现了出色的检测能力,并在包含来自65种不同生成模型的图像的数据集上实现了相较于现有方法2.13%的检测准确性提升。
Key Takeaways
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型能快速生成逼真合成图像,引发社会风险。
- 检测AI生成图像成为重要挑战,现有研究侧重于提取精细特征以增强检测器的泛化能力。
- 现有研究忽略了局部内部元素的重要性和互依赖性,且仅限于单一频域。
- 本文采用局部窗口注意力机制重构局部区域特征关系,并设计双频域分支框架丰富局部伪造特征的提取。
- 方法实现了在GAN和扩散模型生成的图像上的出色检测能力。
- 在包含多种生成模型的图像数据集上实现了较高的检测准确性。
点此查看论文截图

On the Statistical Properties of Generative Adversarial Models for Low Intrinsic Data Dimension
Authors:Saptarshi Chakraborty, Peter L. Bartlett
Despite the remarkable empirical successes of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), the theoretical guarantees for their statistical accuracy remain rather pessimistic. In particular, the data distributions on which GANs are applied, such as natural images, are often hypothesized to have an intrinsic low-dimensional structure in a typically high-dimensional feature space, but this is often not reflected in the derived rates in the state-of-the-art analyses. In this paper, we attempt to bridge the gap between the theory and practice of GANs and their bidirectional variant, Bi-directional GANs (BiGANs), by deriving statistical guarantees on the estimated densities in terms of the intrinsic dimension of the data and the latent space. We analytically show that if one has access to $n$ samples from the unknown target distribution and the network architectures are properly chosen, the expected Wasserstein-1 distance of the estimates from the target scales as $O\left( n^{-1/d_\mu } \right)$ for GANs and $\tilde{O}\left( n^{-1/(d_\mu+\ell)} \right)$ for BiGANs, where $d_\mu$ and $\ell$ are the upper Wasserstein-1 dimension of the data-distribution and latent-space dimension, respectively. The theoretical analyses not only suggest that these methods successfully avoid the curse of dimensionality, in the sense that the exponent of $n$ in the error rates does not depend on the data dimension but also serve to bridge the gap between the theoretical analyses of GANs and the known sharp rates from optimal transport literature. Additionally, we demonstrate that GANs can effectively achieve the minimax optimal rate even for non-smooth underlying distributions, with the use of interpolating generator networks.
尽管生成对抗网络(GANs)在经验上取得了显著的成果,但其统计精度的理论保证仍然相当悲观。特别是,GANs所应用的数据分布,如自然图像,通常假设在通常的高维特征空间中具有内在的低维结构,但这在最新分析中并未得到反映。在本文中,我们试图通过推导关于数据固有维度和潜在空间的估计密度的统计保证,来填补GANs及其双向变体Bi-directional GANs(BiGANs)理论与实践之间的鸿沟。我们分析表明,如果我们有来自未知目标分布的n个样本,并且网络架构选择得当,那么估计值与目标的Wasserstein-1距离期望值对于GANs来说会按照O(n^-1/d_μ)的比例进行缩放,而对于BiGANs来说则按照O~(n^-1/(d_μ+\ell))的比例进行缩放,其中d_μ和l分别是数据分布和潜在空间维度的Wasserstein-1维数的上限。理论分析不仅表明这些方法成功地避免了维数诅咒,即误差率中的n的指数不依赖于数据维度,而且弥合了GANs的理论分析与最优传输文献中已知尖锐速率之间的鸿沟。此外,我们还证明了即使对于非平滑的基础分布,通过使用插值生成网络,GANs也可以有效地实现最小最大最优率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal of Machine Learning Research (2025), volume 26
Summary
本文探讨了生成对抗网络(GANs)的理论与实践之间的鸿沟,特别是在统计数据分布方面的理论保证。文章通过推导统计数据保证,尝试弥合了GANs及其双向变体BiGANs之间的这一差距。研究表明,在合理选择网络架构的情况下,GANs和BiGANs能够从目标分布中获得有效的密度估计,并且在特定的维度条件下实现了优化。理论分析显示,这些方法成功避免了维度诅咒,并且与最优传输文献中的已知尖锐率建立了联系。此外,使用插值生成器网络,GANs可以有效实现最小最大最优率,即使对于非平滑的基础分布也是如此。
Key Takeaways
- GANs的理论保证对其统计准确性相对悲观,特别是在实际应用中的数据分布上。
- GANs和BiGANs的理论与实践之间存在差距,本文尝试通过推导统计数据保证来弥合这一差距。
- 在合理选择网络架构的情况下,GANs和BiGANs能够从目标分布中获得有效的密度估计。
- 理论分析显示,这些方法成功避免了维度诅咒,即误差率中的指数不依赖于数据维度。
- GANs的理论分析与最优传输文献中的已知尖锐率建立了联系。
- 使用插值生成器网络,GANs可以有效处理非平滑的基础分布,并实现最小最大最优率。
点此查看论文截图