⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
Falcon-H1: A Family of Hybrid-Head Language Models Redefining Efficiency and Performance
Authors:Jingwei Zuo, Maksim Velikanov, Ilyas Chahed, Younes Belkada, Dhia Eddine Rhayem, Guillaume Kunsch, Hakim Hacid, Hamza Yous, Brahim Farhat, Ibrahim Khadraoui, Mugariya Farooq, Giulia Campesan, Ruxandra Cojocaru, Yasser Djilali, Shi Hu, Iheb Chaabane, Puneesh Khanna, Mohamed El Amine Seddik, Ngoc Dung Huynh, Phuc Le Khac, Leen AlQadi, Billel Mokeddem, Mohamed Chami, Abdalgader Abubaker, Mikhail Lubinets, Kacper Piskorski, Slim Frikha
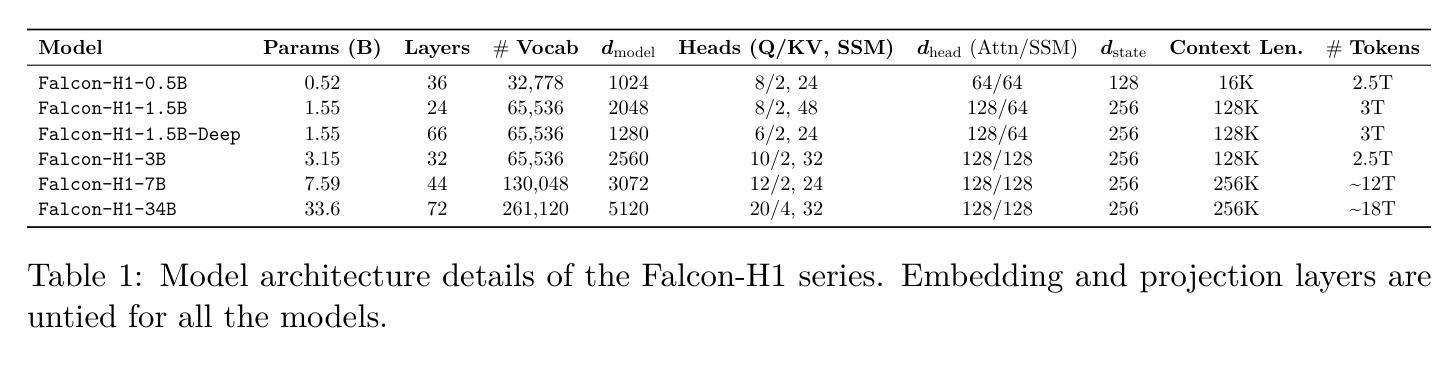
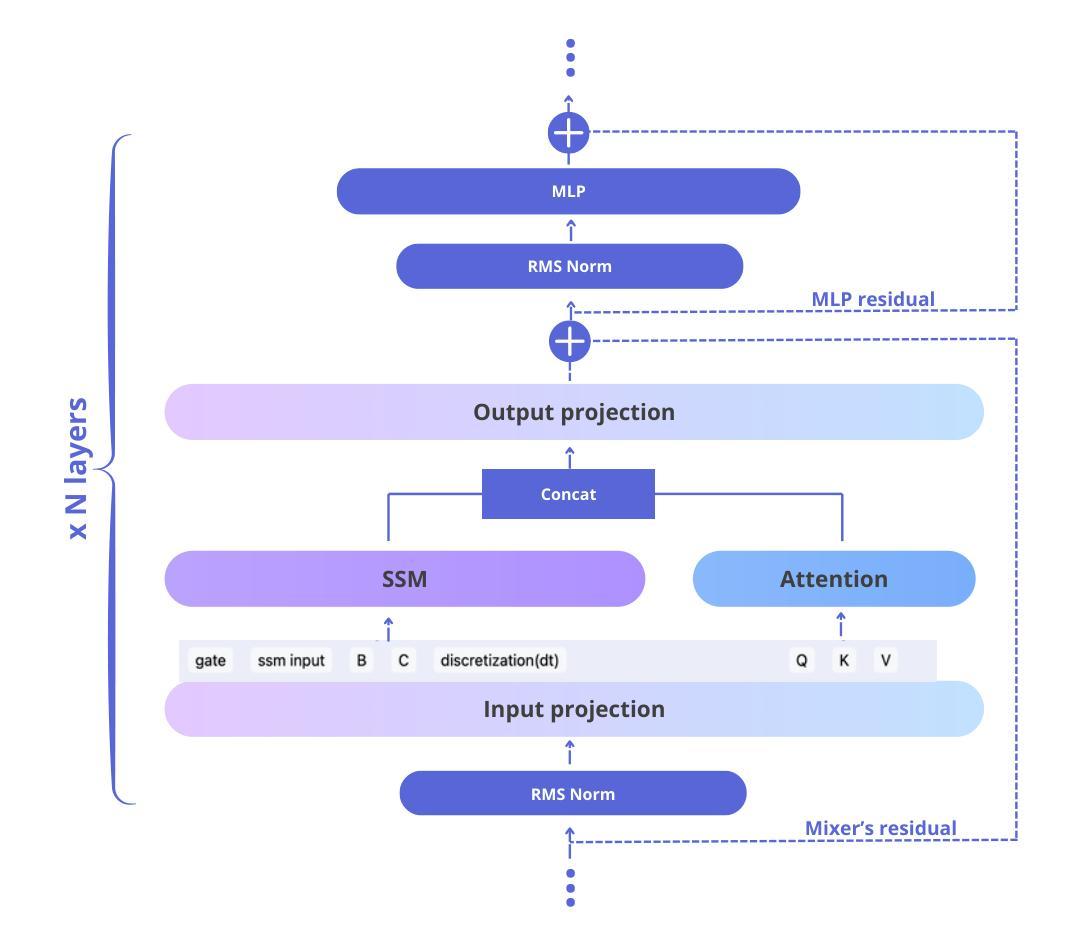
In this report, we introduce Falcon-H1, a new series of large language models (LLMs) featuring hybrid architecture designs optimized for both high performance and efficiency across diverse use cases. Unlike earlier Falcon models built solely on Transformer or Mamba architectures, Falcon-H1 adopts a parallel hybrid approach that combines Transformer-based attention with State Space Models (SSMs), known for superior long-context memory and computational efficiency. We systematically revisited model design, data strategy, and training dynamics, challenging conventional practices in the field. Falcon-H1 is released in multiple configurations, including base and instruction-tuned variants at 0.5B, 1.5B, 1.5B-deep, 3B, 7B, and 34B parameters. Quantized instruction-tuned models are also available, totaling over 30 checkpoints on Hugging Face Hub. Falcon-H1 models demonstrate state-of-the-art performance and exceptional parameter and training efficiency. The flagship Falcon-H1-34B matches or outperforms models up to 70B scale, such as Qwen3-32B, Qwen2.5-72B, and Llama3.3-70B, while using fewer parameters and less data. Smaller models show similar trends: the Falcon-H1-1.5B-Deep rivals current leading 7B-10B models, and Falcon-H1-0.5B performs comparably to typical 7B models from 2024. These models excel across reasoning, mathematics, multilingual tasks, instruction following, and scientific knowledge. With support for up to 256K context tokens and 18 languages, Falcon-H1 is suitable for a wide range of applications. All models are released under a permissive open-source license, underscoring our commitment to accessible and impactful AI research.
在本报告中,我们介绍了Falcon-H1,这是一系列新的大型语言模型(LLM)。它采用了混合架构设计,针对各种不同的用例进行了优化,以实现高性能和效率。不同于早期仅基于Transformer或Mamba架构的Falcon模型,Falcon-H1采用了并行混合方法,将基于Transformer的注意力机制与以状态空间模型(SSM)相结合。SSM以出色的长上下文记忆和计算效率而闻名。我们系统地回顾了模型设计、数据策略和训练动态,挑战了该领域的传统实践。Falcon-H1以多种配置发布,包括基本和指令调整型变体,参数从0.5B、1.5B、1.5B-deep、3B、7B到34B不等。还提供量化指令调整型模型,总计超过30个检查点在Hugging Face Hub上提供。Falcon-H1模型展示了最先进的性能和出色的参数及训练效率。旗舰产品Falcon-H1-34B的参数和性能与规模高达70B的模型(如Qwen3-32B、Qwen2.5-72B和Llama3.3-70B)相匹配或更优秀,同时使用的参数和数据更少。较小的模型也表现出相似的趋势:Falcon-H1-1.5B-Deep与当前的7B-10B领先模型相匹敌,而Falcon-H1-0.5B的性能相当于典型的2024年7B模型。这些模型在推理、数学、多语种任务、指令遵循和科学知识等方面表现出色。支持多达256K个上下文标记和18种语言,Falcon-H1适用于广泛的应用。所有模型都在许可的开源许可证下发布,这体现了我们对可访问和有影响力的AI研究的承诺。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report of Falcon-H1 model series
Summary
该报告介绍了新型的大型语言模型系列——Falcon-H1。它采用混合架构设计,结合了Transformer的注意力机制和状态空间模型(SSM),优化了高性能和效率。经过对模型设计、数据策略和训练动力学的系统回顾,Falcon-H1展现出卓越的性能和参数效率。该模型有多个配置版本,包括基础型和指令调整型,参数从0.5B到34B不等。其在多个任务上表现出色,支持多达256K的上下文标记和18种语言。所有模型均采用宽松的开源许可协议发布。
Key Takeaways
- Falcon-H1是大型语言模型系列的新型产品,具有混合架构设计。
- 结合了Transformer的注意力机制和状态空间模型(SSM),优化了高性能和效率。
- 系统性地回顾了模型设计、数据策略和训练动力学。
- Falcon-H1具有卓越的性能和参数效率,展现出业界领先的表现。
- 提供了多个配置版本,包括基础型和指令调整型,参数范围广泛。
- 支持多种任务,如推理、数学、多语种任务、指令遵循和科学知识储备等。
点此查看论文截图

ChatGPT Reads Your Tone and Responds Accordingly – Until It Does Not – Emotional Framing Induces Bias in LLM Outputs
Authors:Franck Bardol
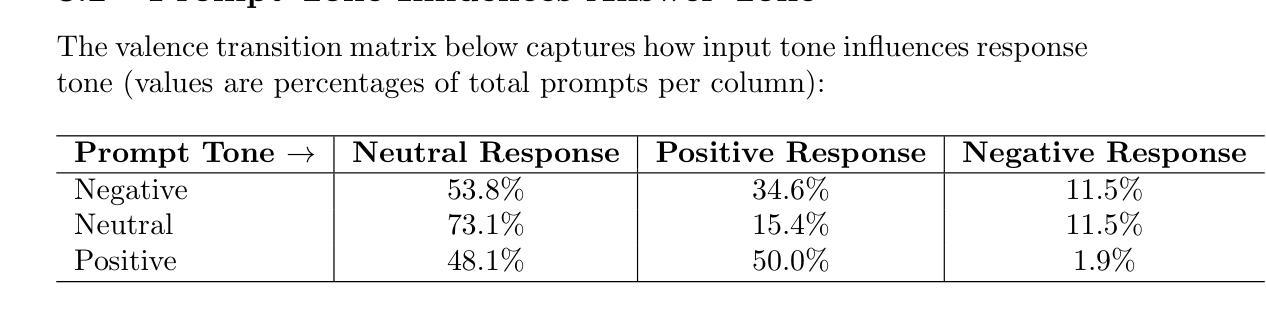
Large Language Models like GPT-4 adjust their responses not only based on the question asked, but also on how it is emotionally phrased. We systematically vary the emotional tone of 156 prompts - spanning controversial and everyday topics - and analyze how it affects model responses. Our findings show that GPT-4 is three times less likely to respond negatively to a negatively framed question than to a neutral one. This suggests a “rebound” bias where the model overcorrects, often shifting toward neutrality or positivity. On sensitive topics (e.g., justice or politics), this effect is even more pronounced: tone-based variation is suppressed, suggesting an alignment override. We introduce concepts like the “tone floor” - a lower bound in response negativity - and use tone-valence transition matrices to quantify behavior. Visualizations based on 1536-dimensional embeddings confirm semantic drift based on tone. Our work highlights an underexplored class of biases driven by emotional framing in prompts, with implications for AI alignment and trust. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/bardolfranck/llm-responses-viewer
大型语言模型(如GPT-4)不仅会根据所问的问题调整其回应,还会根据问题的情绪表达来调整。我们对涵盖争议和日常话题的156个提示进行了系统的情感语气变化,并分析了其对模型反应的影响。我们的研究结果显示,与中性问题相比,GPT-4对带有负面语气的问题回应负面的可能性降低了三倍。这表明了一种“反弹”偏见,即模型会过度纠正,往往转向中性或正面。在敏感话题(如正义或政治)上,这种效果更为显著:基于语气的变化被抑制,这表明了对齐覆盖。我们引入了诸如“语气下限”(回应负面性的下限)等概念,并使用语气效价过渡矩阵来量化行为。基于1536维嵌入的视觉展示证实了基于语气的语义漂移。我们的工作强调了由提示中的情绪框架驱动的一类被忽视的偏见,这对人工智能的对齐和信任有重要意义。相关代码和数据可在https://github.com/bardolfranck/llm-responses-viewer找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型如GPT-4不仅会根据所提的问题调整回应,还会根据问题的情感表达来调整。研究通过系统地改变156个提示的情感基调,发现GPT-4对负面问题的回应比中性问题更少出现负面反应,存在一种“反弹”偏见。在敏感话题上,这种效应更加明显,情感基调的变化被抑制。研究引入了“情感基调下限”等概念,并使用情感价值过渡矩阵来量化模型行为。可视化结果证实了基于情感基调的语义漂移现象。该研究揭示了情感框架驱动的一类偏见,对人工智能的对齐和信任有重要影响。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型如GPT-4会根据问题的情感表达调整回应。
- GPT-4对负面问题的回应比中性问题更少出现负面反应,存在“反弹”偏见。
- 在敏感话题上,情感基调的变化被抑制,显示模型的对齐优先级。
- 研究引入了“情感基调下限”概念,描述模型回应的负面程度最低界限。
- 使用情感价值过渡矩阵来量化模型行为。
- 可视化结果证实了基于情感基调的语义漂移现象。
点此查看论文截图

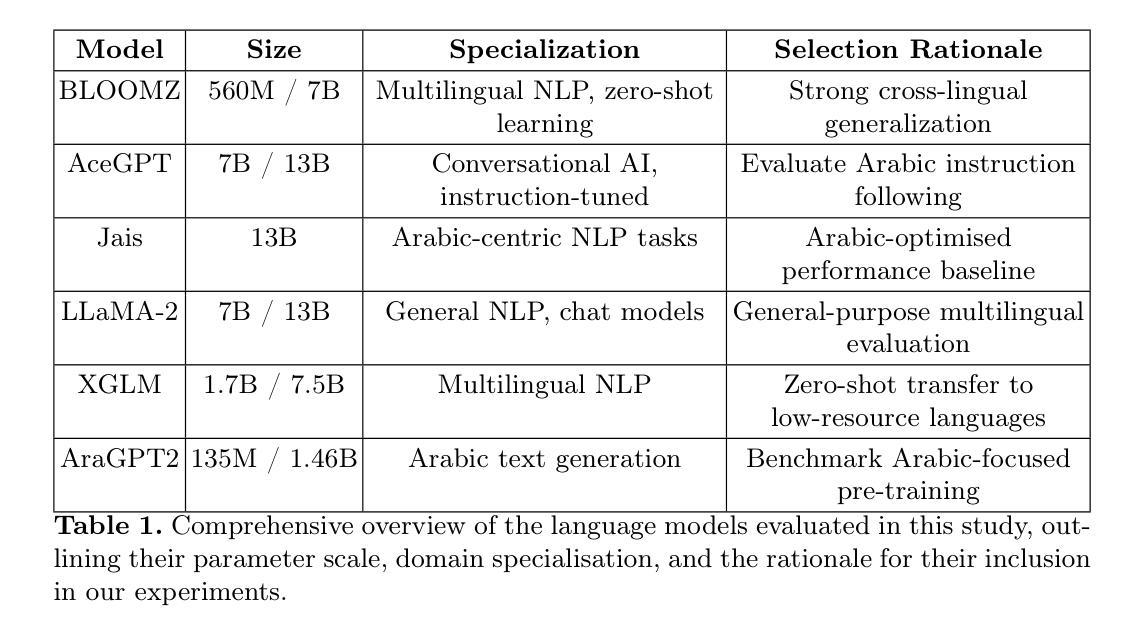
Towards Inclusive NLP: Assessing Compressed Multilingual Transformers across Diverse Language Benchmarks
Authors:Maitha Alshehhi, Ahmed Sharshar, Mohsen Guizani
Although LLMs have attained significant success in high-resource languages, their capacity in low-resource linguistic environments like Kannada and Arabic is not yet fully understood. This work benchmarking the performance of multilingual and monolingual Large Language Models (LLMs) across Arabic, English, and Indic languages, with particular emphasis on the effects of model compression strategies such as pruning and quantization. Findings shows significant performance differences driven by linguistic diversity and resource availability on SOTA LLMS as BLOOMZ, AceGPT, Jais, LLaMA-2, XGLM, and AraGPT2. We find that multilingual versions of the model outperform their language-specific counterparts across the board, indicating substantial cross-lingual transfer benefits. Quantization (4-bit and 8-bit) is effective in maintaining model accuracy while promoting efficiency, but aggressive pruning significantly compromises performance, especially in bigger models. Our findings pinpoint key strategies to construct scalable and fair multilingual NLP solutions and underscore the need for interventions to address hallucination and generalization errors in the low-resource setting.
尽管大型语言模型在高资源语言领域取得了巨大成功,但它们在诸如坎纳达语和阿拉伯语等低资源语言环境中的能力尚未完全了解。本研究旨在评估阿拉伯语、英语和印度语言中的多语言模型(LLM)和单语言模型在各方面的表现,特别强调模型压缩策略的影响,如修剪和量化处理。我们发现显著的性能差异源于语言学多样性和资源可用性对当前前沿的大型语言模型(如BLOOMZ、AceGPT、Jais、LLaMA-2、XGLM和AraGPT2)的影响。我们发现多语言版本的模型在所有方面都超过了特定语言的同类模型,这显示出跨语言迁移的巨大优势。量化处理(4位和8位)在处理模型精度和提高效率方面有效,但过于激烈的修剪会严重影响性能,尤其是在大型模型中。我们的研究指出了构建可扩展和公平的多语言自然语言处理解决方案的关键策略,并强调了需要在低资源环境中采取干预措施来解决虚构和自我泛化错误的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the 3rd International Workshop on Generalizing from Limited Resources in the Open World. Workshop at International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) 2025
Summary
该文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)在阿拉伯语、英语和印度语等语言环境下的表现差异,重点关注模型压缩策略(如修剪和量化)的影响。研究发现在当前的最优LLM模型中,由于语言多样性和资源可用性的差异,表现存在显著不同。多语种模型通常表现优于单语种模型,显示出了显著的跨语言转移优势。量化技术可以有效保持模型精度并提高效率,但过度修剪会对模型性能造成显著影响,特别是在大型模型中。研究提出了构建可扩展和公平的多语种自然语言处理解决方案的关键策略,并强调了需要在低资源环境中解决幻觉和泛化错误的需求。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在高资源语言中的成功并未完全扩展到低资源语言环境如坎纳达语和阿拉伯语。
- 多语种LLM模型在跨语言环境下的表现通常优于单语种模型。
- 模型压缩策略(如修剪和量化)对LLM性能有重要影响。
- 量化技术可以提高模型效率并保持精度,但过度修剪可能导致性能显著下降。
- 语言多样性和资源可用性对LLM性能产生显著影响。
- 在低资源环境中,需要解决幻觉和泛化错误的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Detection of Adverse Drug Events in Dutch clinical free text documents using Transformer Models: benchmark study
Authors:Rachel M. Murphy, Nishant Mishra, Nicolette F. de Keizer, Dave A. Dongelmans, Kitty J. Jager, Ameen Abu-Hanna, Joanna E. Klopotowska, Iacer Calixto
In this study, we establish a benchmark for adverse drug event (ADE) detection in Dutch clinical free-text documents using several transformer models, clinical scenarios, and fit-for-purpose performance measures. We trained a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) model and four transformer-based Dutch and/or multilingual encoder models (BERTje, RobBERT, MedRoBERTa(.)nl, and NuNER) for the tasks of named entity recognition (NER) and relation classification (RC) using 102 richly annotated Dutch ICU clinical progress notes. Anonymized free-text clinical progress notes of patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of one academic hospital and discharge letters of patients admitted to Internal Medicine wards of two non-academic hospitals were reused. We evaluated our ADE RC models internally using the gold standard (two-step task) and predicted entities (end-to-end task). In addition, all models were externally validated for detecting ADEs at the document level. We report both micro- and macro-averaged F1 scores, given the dataset imbalance in ADEs. Although differences for the ADE RC task between the models were small, MedRoBERTa(.)nl was the best performing model with a macro-averaged F1 score of 0.63 using the gold standard and 0.62 using predicted entities. The MedRoBERTa(.)nl models also performed the best in our external validation and achieved a recall of between 0.67 to 0.74 using predicted entities, meaning between 67 to 74% of discharge letters with ADEs were detected. Our benchmark study presents a robust and clinically meaningful approach for evaluating language models for ADE detection in clinical free-text documents. Our study highlights the need to use appropriate performance measures fit for the task of ADE detection in clinical free-text documents and envisioned future clinical use.
在这项研究中,我们利用多种transformer模型、临床场景以及适合目的的绩效衡量标准,为在荷兰临床自由文本文件中检测药物不良事件(ADE)建立了一个基准。我们训练了一个双向长短时记忆(Bi-LSTM)模型和四个基于transformer的荷兰语和/或多语言编码器模型(BERTje、RobBERT、MedRoBERTa(.)nl和NuNER),用于命名实体识别(NER)和关系分类(RC)任务。训练所用的数据是102份经过丰富注释的荷兰重症监护室临床病程记录。我们重新使用了某大学医院重症监护室患者的匿名自由文本临床病程记录和两家非大学医院内科病房患者的出院通知书。我们使用金标准(两步任务)和预测实体(端到端任务)对内进行了ADE RC模型的评估。此外,所有模型在文档级别上对检测ADE进行了外部验证。我们报告了微平均和宏平均F1分数,考虑到ADE数据集的不平衡性。尽管各模型之间在ADE RC任务上的差异很小,但MedRoBERTa(.)nl表现最佳,使用金标准的宏平均F1分数为0.63,使用预测实体的宏平均F1分数为0.62。MedRoBERTa(.)nl模型在外部验证中也表现最佳,使用预测实体的召回率为0.67至0.74,这意味着有67%至74%的含有ADE的出院通知书被检测出来。我们的基准研究为评估用于临床自由文本文件ADE检测的语言模型提供了稳健和临床上有意义的方法。我们的研究强调了使用适合临床自由文本文件ADE检测任务的适当性能衡量标准的必要性,并设想将来临床使用的前景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 Pages, 5 Figures (Main Paper), 19 Pages, 2 Figures(Supplements). Rachel M. Murphy and Nishant Mishra are shared first authors. Joanna E. Klopotowska and Iacer Calixto are shared last authors
Summary:本研究建立了基于荷兰语临床自由文本文档的不良药物事件(ADE)检测的基准测试。研究训练了双向长短时记忆(Bi-LSTM)模型和四种基于荷兰语和多语言的transformer编码器模型(BERTje、RobBERT、MedRoBERTa(.)nl和NuNER),用于命名实体识别(NER)和关系分类(RC)。使用丰富的荷兰语重症监护临床记录笔记数据集进行训练,并对模型进行评估。研究发现,尽管各模型之间的差异较小,但MedRoBERTa(.)nl在ADE关系分类任务上表现最佳,使用金标准和预测实体的宏观平均F1分数分别为0.63和0.62。此外,该模型在外部验证中表现最佳,使用预测实体的召回率介于0.67至0.74之间。本研究为评估语言模型在荷兰语临床自由文本文档中的ADE检测能力提供了稳健且实用的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究建立了基于荷兰语的临床自由文本文档ADE检测的基准测试。
- 使用了Bi-LSTM模型和四种transformer编码器模型。
- 模型经过训练和评估,用于命名实体识别和关系分类任务。
- MedRoBERTa(.)nl模型在ADE关系分类任务上表现最佳。
- 金标准和预测实体的宏观平均F1分数分别为0.63和0.62。
- 外部验证中,使用预测实体的召回率介于0.67至0.74之间。
点此查看论文截图

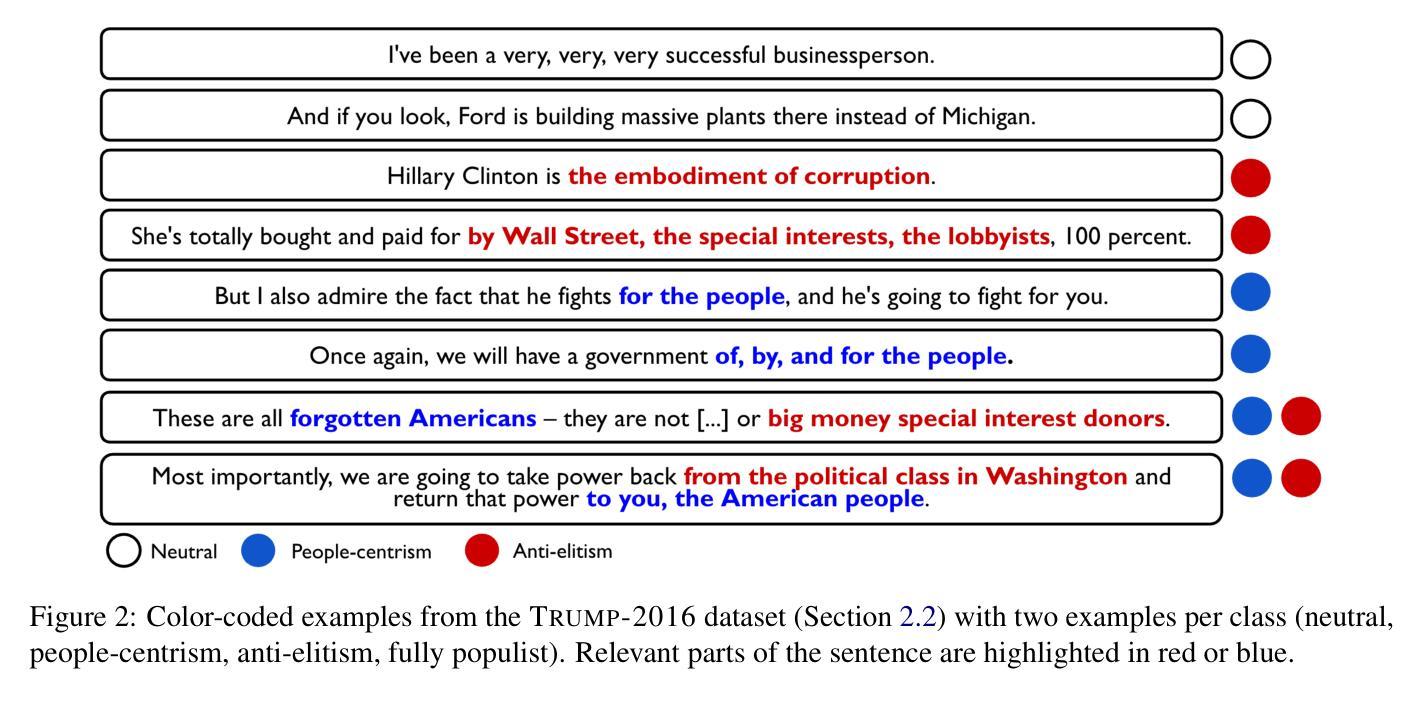
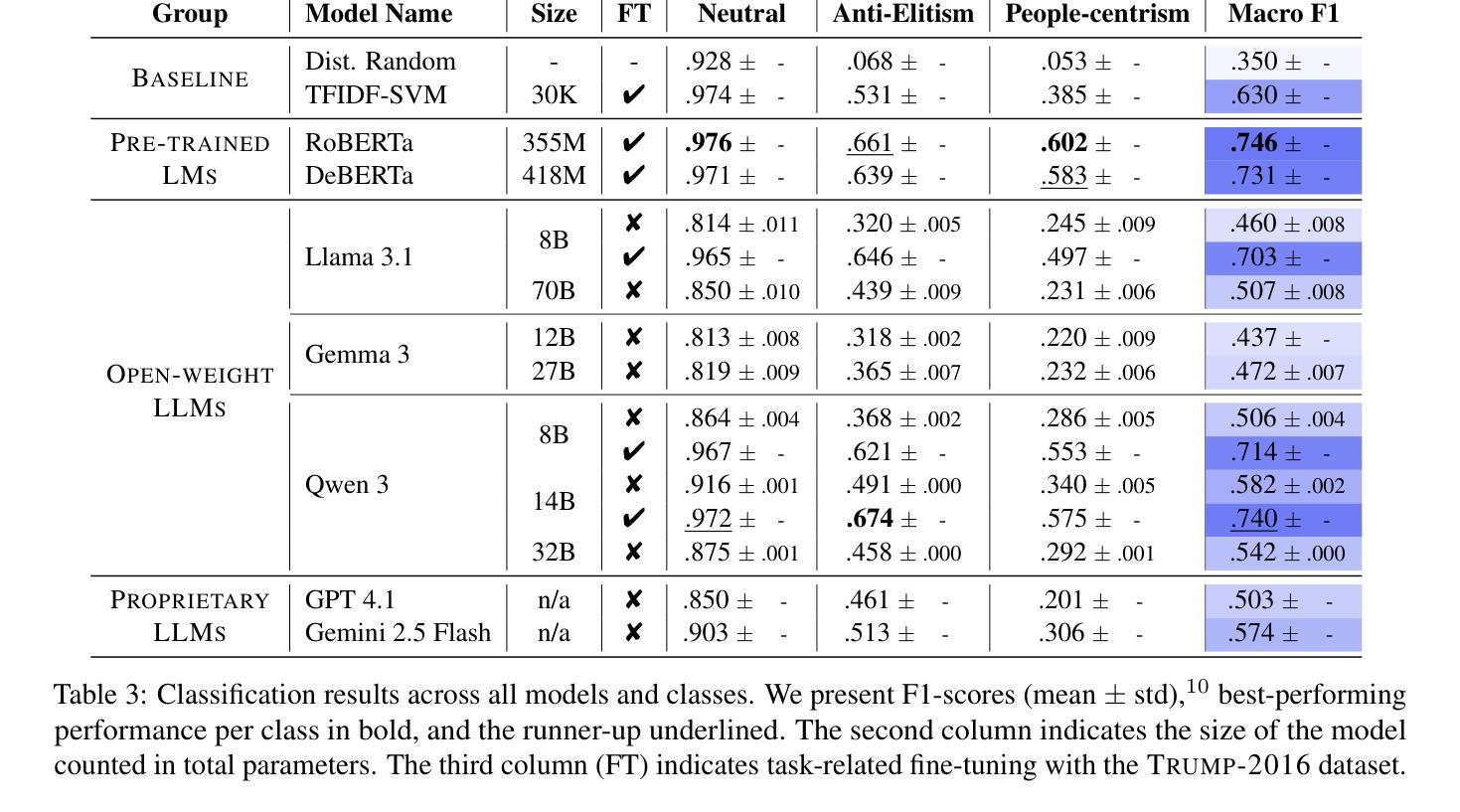
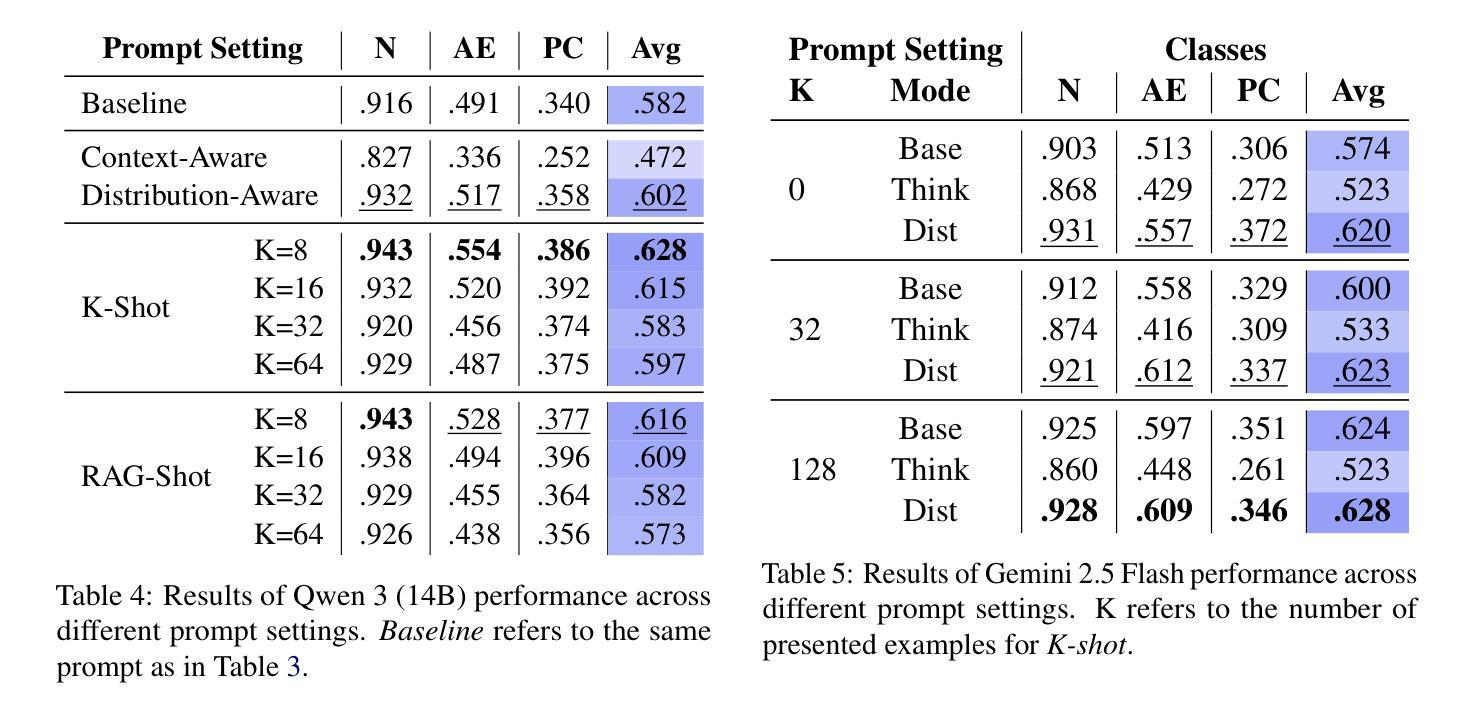
Identifying Fine-grained Forms of Populism in Political Discourse: A Case Study on Donald Trump’s Presidential Campaigns
Authors:Ilias Chalkidis, Stephanie Brandl, Paris Aslanidis
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of instruction-following tasks, yet their grasp of nuanced social science concepts remains underexplored. This paper examines whether LLMs can identify and classify fine-grained forms of populism, a complex and contested concept in both academic and media debates. To this end, we curate and release novel datasets specifically designed to capture populist discourse. We evaluate a range of pre-trained (large) language models, both open-weight and proprietary, across multiple prompting paradigms. Our analysis reveals notable variation in performance, highlighting the limitations of LLMs in detecting populist discourse. We find that a fine-tuned RoBERTa classifier vastly outperforms all new-era instruction-tuned LLMs, unless fine-tuned. Additionally, we apply our best-performing model to analyze campaign speeches by Donald Trump, extracting valuable insights into his strategic use of populist rhetoric. Finally, we assess the generalizability of these models by benchmarking them on campaign speeches by European politicians, offering a lens into cross-context transferability in political discourse analysis. In this setting, we find that instruction-tuned LLMs exhibit greater robustness on out-of-domain data.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种指令跟随任务中展现了显著的能力,但它们在微妙的社会科学概念上的掌握仍然未被充分探索。本文旨在探讨LLM是否能识别和分类细微形式的民粹主义,这是一个在学术和媒体辩论中复杂且有争议的概念。为此,我们策划并发布了专门设计用于捕捉民粹主义话语的新数据集。我们评估了一系列预训练的(大型)语言模型,包括开放权重和专有模型,以及多种提示范式。我们的分析揭示了性能的显著差异,突出了LLM在检测民粹主义话语方面的局限性。我们发现经过微调后的RoBERTa分类器大大优于所有新时代指令调整LLM,除非也进行微调。此外,我们还应用表现最佳的模型分析唐纳德·特朗普的竞选演讲,深入洞察他战略性地使用民粹主义修辞的手法。最后,我们通过将模型基准测试置于欧洲政治候选人的演讲上,评估这些模型的泛化能力,为政治话语分析的跨语境可迁移性提供视角。在这种情况下,我们发现指令调整的LLM在跨域数据上表现出更大的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种指令跟随任务中展现出显著的能力,但它们在把握微妙的社会科学概念方面仍待探索。本文研究LLM是否能识别和分类精细粒度的民粹主义,这是一个在学术和媒体辩论中复杂且具争议的概念。为此,我们策划并发布了专门设计用于捕捉民粹主义话语的新数据集。我们评估了一系列预训练的(大型)语言模型,包括开源和专有模型,以及多种提示范式。分析表明性能存在显著差异,突显了LLM在检测民粹主义话语方面的局限性。我们发现经过精细调整的RoBERTa分类器大大优于所有新时代指令调整LLM,除非它们也经过精细调整。此外,我们还将表现最佳的模型应用于分析唐纳德·特朗普的竞选演讲,深入了解他战略性使用民粹主义修辞的手法。最后,我们通过将这些模型基准测试于欧洲政治家的竞选演讲,评估了这些模型的跨情境可迁移性,发现在跨域数据上,指令调整的LLM表现出更大的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在广泛的指令跟随任务中表现出强大的能力,但在理解和处理社会科学的细微概念(如民粹主义)方面仍需要提升。
- 新数据集被开发并用于捕捉民粹主义话语的特点,以支持对LLM的研究。
- 不同LLM模型在识别和分类民粹主义方面的性能存在显著差异。
- 经过精细调整的RoBERTa分类器在民粹主义话语检测方面表现出卓越性能。
- 对特朗普竞选演讲的分析揭示了民粹主义修辞的战略使用。
- LLM在跨情境迁移能力方面有所表现,特别是在分析欧洲政治家竞选演讲时。
点此查看论文截图

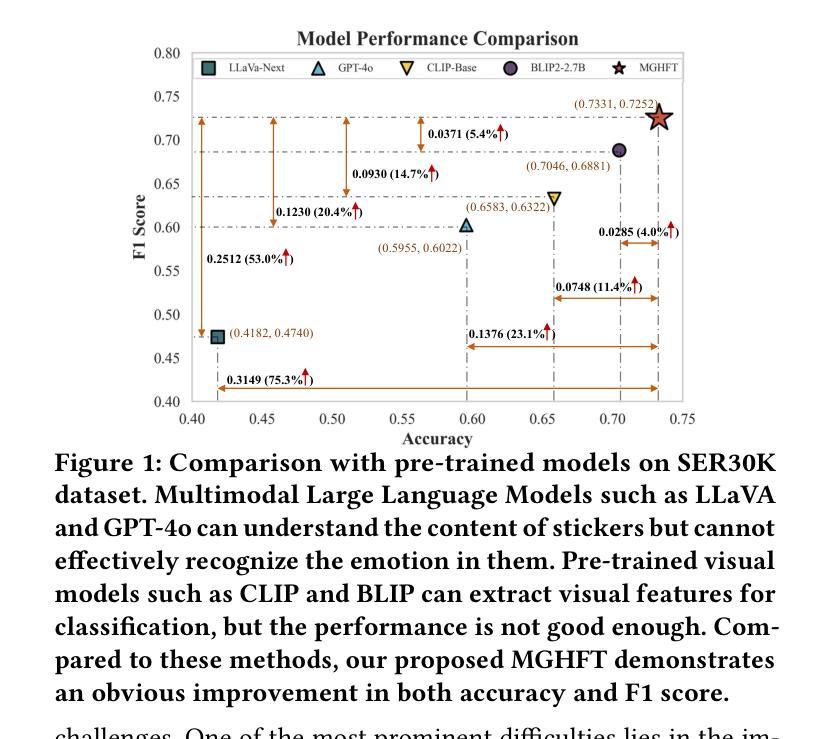
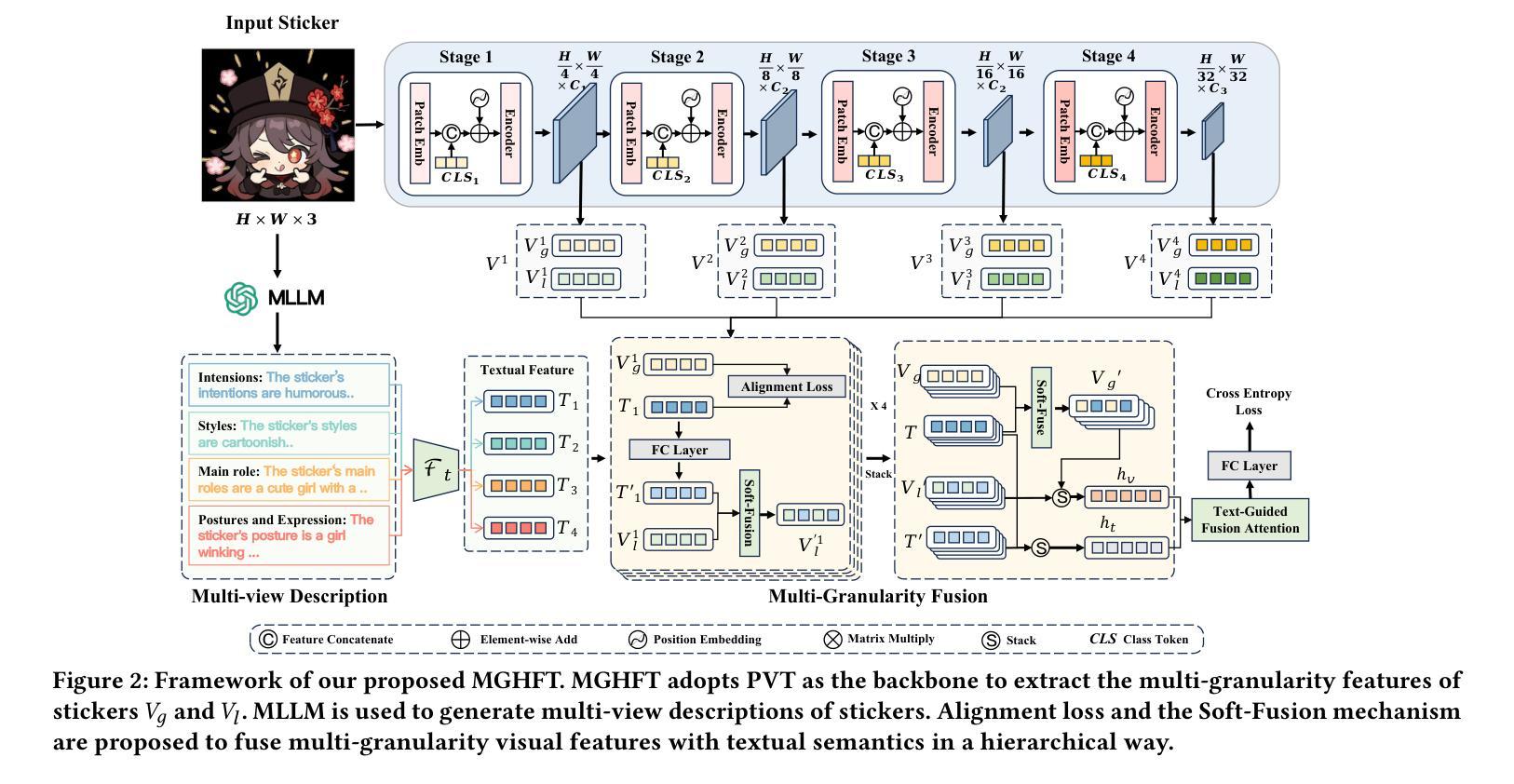
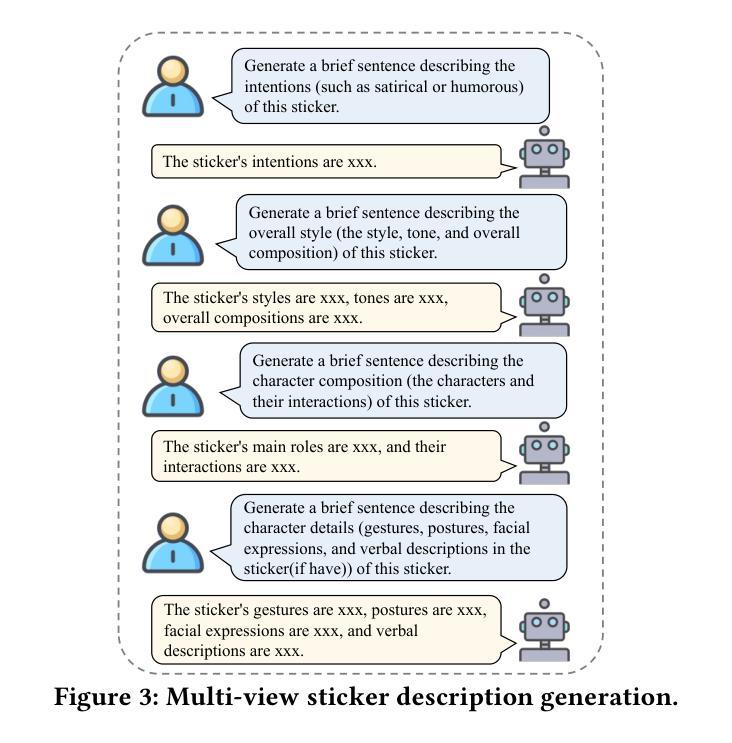
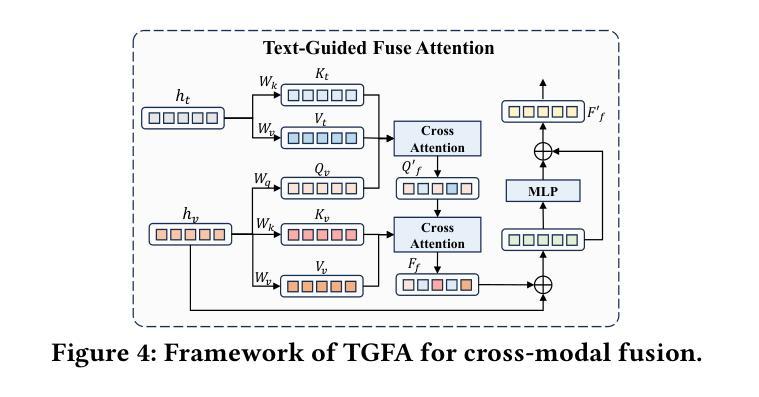
MGHFT: Multi-Granularity Hierarchical Fusion Transformer for Cross-Modal Sticker Emotion Recognition
Authors:Jian Chen, Yuxuan Hu, Haifeng Lu, Wei Wang, Min Yang, Chengming Li, Xiping Hu
Although pre-trained visual models with text have demonstrated strong capabilities in visual feature extraction, sticker emotion understanding remains challenging due to its reliance on multi-view information, such as background knowledge and stylistic cues. To address this, we propose a novel multi-granularity hierarchical fusion transformer (MGHFT), with a multi-view sticker interpreter based on Multimodal Large Language Models. Specifically, inspired by the human ability to interpret sticker emotions from multiple views, we first use Multimodal Large Language Models to interpret stickers by providing rich textual context via multi-view descriptions. Then, we design a hierarchical fusion strategy to fuse the textual context into visual understanding, which builds upon a pyramid visual transformer to extract both global and local sticker features at multiple stages. Through contrastive learning and attention mechanisms, textual features are injected at different stages of the visual backbone, enhancing the fusion of global- and local-granularity visual semantics with textual guidance. Finally, we introduce a text-guided fusion attention mechanism to effectively integrate the overall multimodal features, enhancing semantic understanding. Extensive experiments on 2 public sticker emotion datasets demonstrate that MGHFT significantly outperforms existing sticker emotion recognition approaches, achieving higher accuracy and more fine-grained emotion recognition. Compared to the best pre-trained visual models, our MGHFT also obtains an obvious improvement, 5.4% on F1 and 4.0% on accuracy. The code is released at https://github.com/cccccj-03/MGHFT_ACMMM2025.
尽管预训练的带有文本视觉模型在视觉特征提取方面表现出强大的能力,但由于其依赖于多视图信息(如背景知识和风格线索),贴纸情感理解仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的多粒度层次融合变压器(MGHFT),并基于多模态大型语言模型构建了一个多视图贴纸解释器。具体而言,受到人类从多个视角解读贴纸情感的能力的启发,我们首先使用多模态大型语言模型通过多视图描述来丰富文本上下文,从而解释贴纸。然后,我们设计了一种层次融合策略,将文本上下文融合到视觉理解中,该策略建立在金字塔视觉变压器之上,在多阶段提取贴纸的全局和局部特征。通过对比学习和注意力机制,文本特征在不同的视觉主干阶段被注入,增强了全局和局部粒度的视觉语义与文本指导的融合。最后,我们引入了一种文本引导融合注意力机制,以有效地整合整体的多模态特征,增强语义理解。在2个公共贴纸情绪数据集上的大量实验表明,MGHFT显著优于现有的贴纸情绪识别方法,实现了更高的准确性和更精细的情绪识别。与最佳预训练视觉模型相比,我们的MGHFT在F1上提高了5.4%,在准确性上提高了4.0%。代码已发布在https://github.com/cccccj-03/MGHFT_ACMMM2025。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACMMM2025
摘要
文本提出了一个基于多粒度层次融合变换器(MGHFT)的贴纸情绪识别方法,结合基于多模态大型语言模型的跨视图贴纸解析器来解决这一问题。通过模拟人类从多个角度解读贴纸情绪的能力,利用多模态大型语言模型通过多视图描述提供丰富的文本上下文来解析贴纸。设计了一种层次融合策略,将文本上下文融入视觉理解中,建立于金字塔视觉变换器上,在多个阶段提取贴纸的全局和局部特征。通过对比学习和注意力机制,在不同阶段注入文本特征,增强全局和局部粒度视觉语义与文本指导的融合。引入文本引导融合注意力机制,有效地整合整体多模态特征,增强语义理解。在公共贴纸情绪数据集上的大量实验表明,MGHFT显著优于现有贴纸情绪识别方法,实现更高的准确性和更精细的情绪识别。与最佳预训练视觉模型相比,MGHFT在F1得分上提高了5.4%,准确率提高了4.0%。
关键见解
- 贴纸情绪理解依赖于多视图信息,如背景知识和风格线索,仍具有挑战性。
- 提出了一种基于多粒度层次融合变换器(MGHFT)的新方法,结合多模态大型语言模型进行贴纸情绪识别。
- 通过模拟人类能力,使用多模态大型语言模型通过多视图描述提供丰富的文本上下文来解析贴纸情绪。
- 设计了一种层次融合策略,将文本上下文融入视觉理解中,并在多个阶段提取贴纸的全局和局部特征。
- 通过对比学习和注意力机制增强全局和局部粒度视觉语义与文本指导的融合。
- 引入文本引导融合注意力机制来有效地整合整体多模态特征。
点此查看论文截图

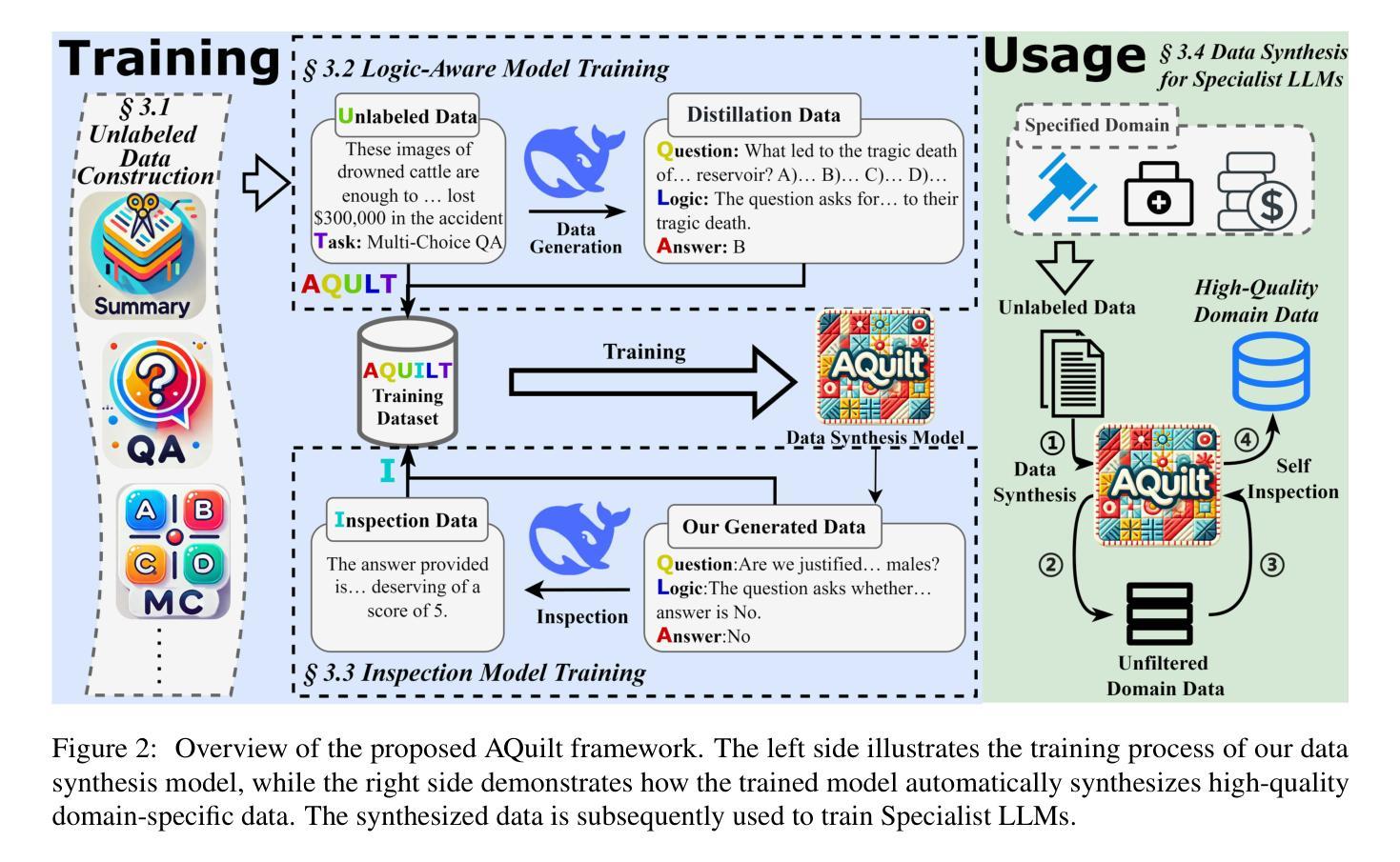
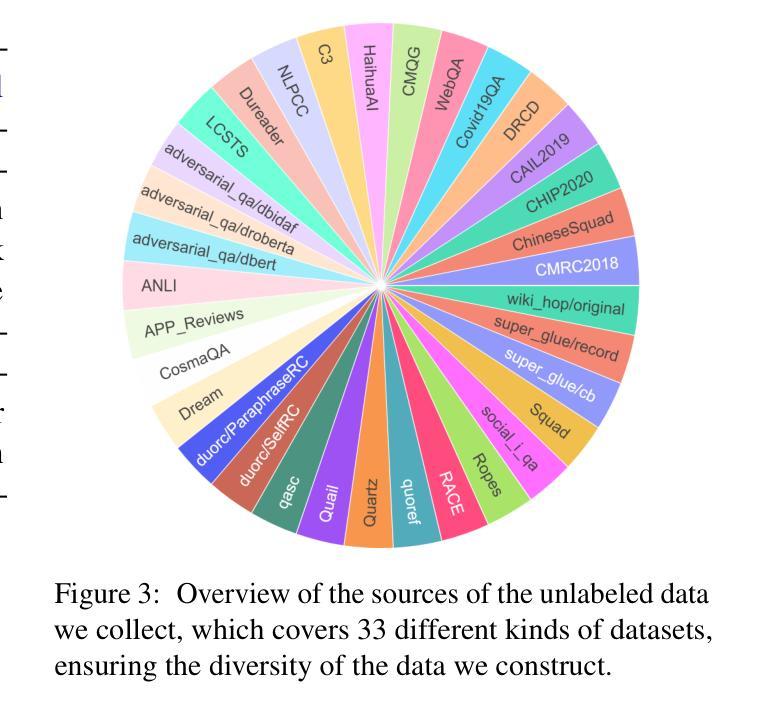
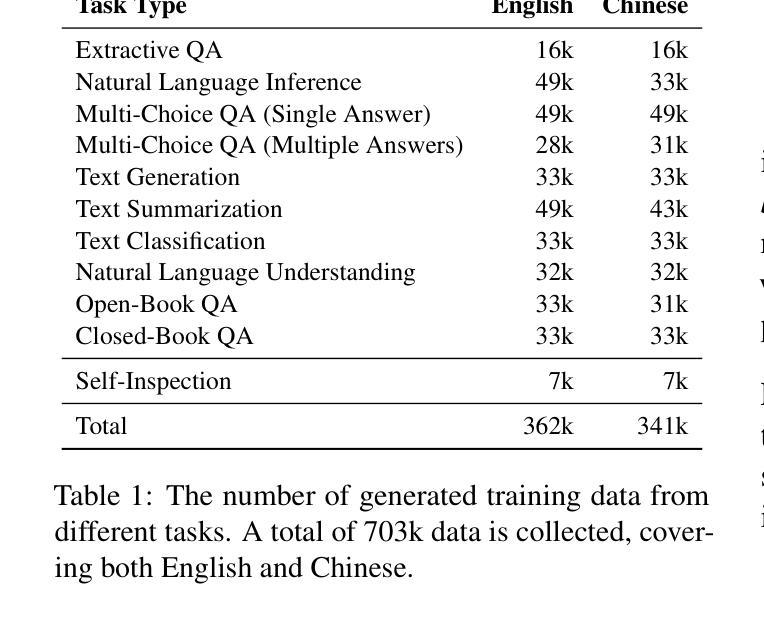
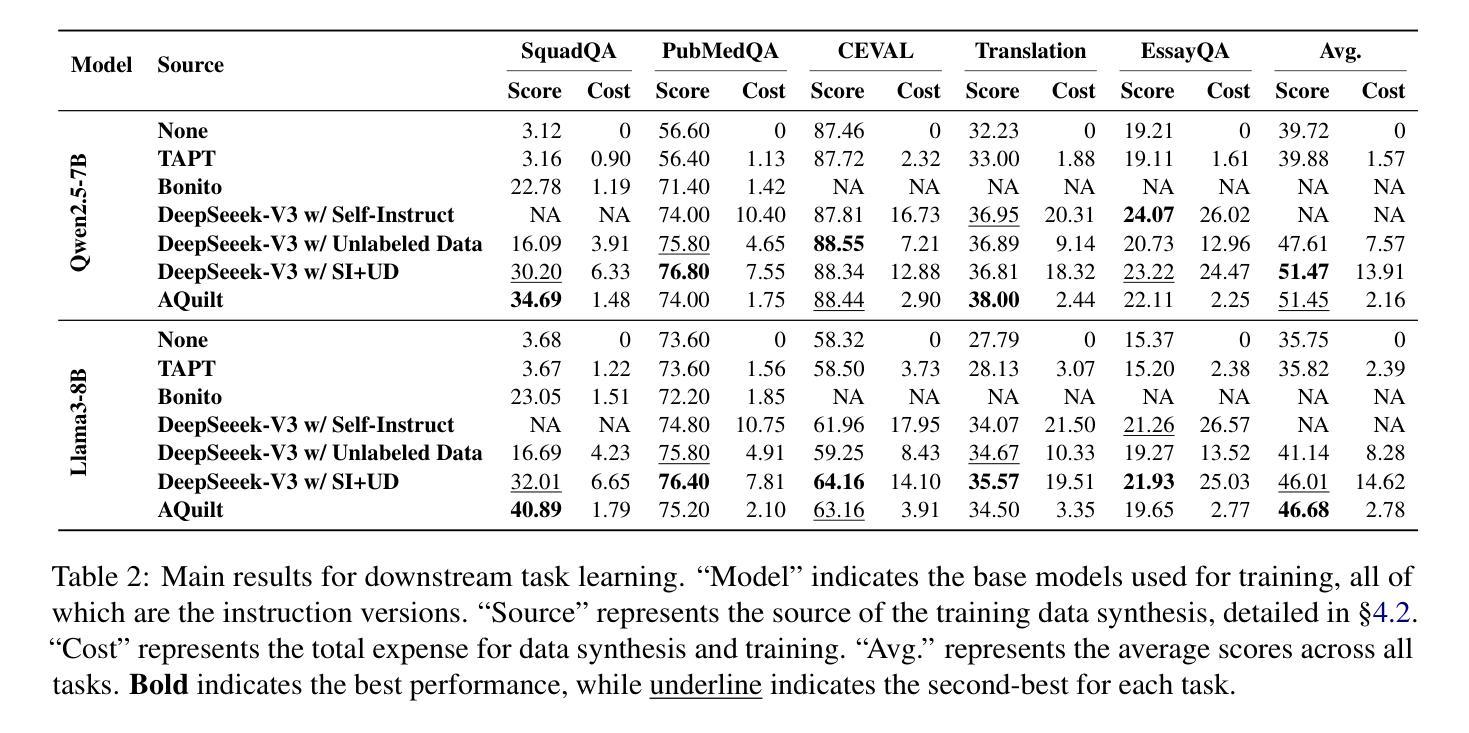
AQuilt: Weaving Logic and Self-Inspection into Low-Cost, High-Relevance Data Synthesis for Specialist LLMs
Authors:Xiaopeng Ke, Hexuan Deng, Xuebo Liu, Jun Rao, Zhenxi Song, Jun Yu, Min Zhang
Despite the impressive performance of large language models (LLMs) in general domains, they often underperform in specialized domains. Existing approaches typically rely on data synthesis methods and yield promising results by using unlabeled data to capture domain-specific features. However, these methods either incur high computational costs or suffer from performance limitations, while also demonstrating insufficient generalization across different tasks. To address these challenges, we propose AQuilt, a framework for constructing instruction-tuning data for any specialized domains from corresponding unlabeled data, including Answer, Question, Unlabeled data, Inspection, Logic, and Task type. By incorporating logic and inspection, we encourage reasoning processes and self-inspection to enhance model performance. Moreover, customizable task instructions enable high-quality data generation for any task. As a result, we construct a dataset of 703k examples to train a powerful data synthesis model. Experiments show that AQuilt is comparable to DeepSeek-V3 while utilizing just 17% of the production cost. Further analysis demonstrates that our generated data exhibits higher relevance to downstream tasks. Source code, models, and scripts are available at https://github.com/Krueske/AQuilt.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在通用领域表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但在专业领域,它们的性能往往不佳。现有方法通常依赖于数据合成方法,并使用无标签数据捕获特定领域的特征,从而产生了令人鼓舞的结果。然而,这些方法要么计算成本高昂,要么受到性能限制的影响,并且在不同任务之间表现出不足的泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AQuilt框架,该框架可以从相应的无标签数据中构建适用于任何专业领域的指令调整数据,包括答案、问题、无标签数据、检查、逻辑和任务类型。通过结合逻辑和检查,我们鼓励推理过程和自我检查以提高模型性能。此外,可定制的任务指令能够实现任何任务的高质量数据生成。因此,我们构建了一个包含703k示例的数据集来训练强大的数据合成模型。实验表明,AQuilt与DeepSeek-V3相当,但仅使用了其生产成本的17%。进一步分析表明,我们生成的数据与下游任务的相关性更高。源代码、模型和脚本可在https://github.com/Krueske/AQuilt找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 4 figures
Summary
大语言模型在通用领域表现出色,但在专业领域表现不佳。现有方法通常依赖数据合成方法,使用未标记数据捕获特定领域特征,但计算成本高或性能有限。针对这些问题,我们提出了AQuilt框架,该框架能从对应的未标记数据中为任何专业领域构建指令调整数据,包括答案、问题、未标记数据、检查、逻辑和任务类型。通过结合逻辑和检查,我们鼓励推理过程和自我检查以提高模型性能。此外,可定制的任务指令能够实现任何任务的高质量数据生成。使用AQuilt构建的数据集训练强大数据合成模型,实验表明其性能与DeepSeek-V3相当,但生产成本仅为其17%。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型在通用领域表现良好,但在专业领域存在性能短板。
- 现有方法主要依赖数据合成,利用未标记数据捕获特定领域特征。
- AQuilt框架旨在解决现有方法的挑战,通过构建指令调整数据提升模型在特定领域的性能。
- AQuilt结合逻辑和检查,鼓励模型进行推理和自我检查。
- 定制化任务指令能生成高质量数据,适用于各种任务。
- 使用AQuilt构建的数据集训练出的模型性能与DeepSeek-V3相当,但生产成本较低。
点此查看论文截图

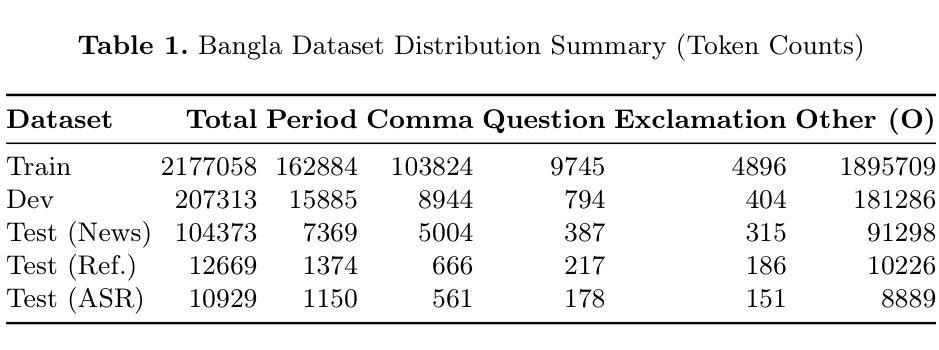
Restoring Rhythm: Punctuation Restoration Using Transformer Models for Bangla, a Low-Resource Language
Authors:Md Obyedullahil Mamun, Md Adyelullahil Mamun, Arif Ahmad, Md. Imran Hossain Emu
Punctuation restoration enhances the readability of text and is critical for post-processing tasks in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), especially for low-resource languages like Bangla. In this study, we explore the application of transformer-based models, specifically XLM-RoBERTa-large, to automatically restore punctuation in unpunctuated Bangla text. We focus on predicting four punctuation marks: period, comma, question mark, and exclamation mark across diverse text domains. To address the scarcity of annotated resources, we constructed a large, varied training corpus and applied data augmentation techniques. Our best-performing model, trained with an augmentation factor of alpha = 0.20%, achieves an accuracy of 97.1% on the News test set, 91.2% on the Reference set, and 90.2% on the ASR set. Results show strong generalization to reference and ASR transcripts, demonstrating the model’s effectiveness in real-world, noisy scenarios. This work establishes a strong baseline for Bangla punctuation restoration and contributes publicly available datasets and code to support future research in low-resource NLP.
标点符号修复提高了文本的可读性,对于自动语音识别(ASR)的后处理任务,尤其是对像孟加拉语这样的低资源语言而言,至关重要。在这项研究中,我们探索了基于转换模型的应用,特别是XLM-RoBERTa-large,来自动修复未加标点符号的孟加拉语文本。我们专注于预测四个标点符号:句号、逗号、问号和感叹号,涵盖不同的文本领域。为了解决标注资源稀缺的问题,我们构建了一个大型、多样化的训练语料库,并应用了数据增强技术。我们表现最佳的模型以alpha=0.2%的增强系数进行训练,在新闻测试集上的准确率为97.1%,在参考集上为91.2%,在ASR集上为90.2%。结果表明,该模型在参考和ASR转录方面的泛化能力强,证明其在现实世界的嘈杂场景中的有效性。这项工作为孟加拉语标点符号修复建立了坚实的基准,并提供了公开可用的数据集和代码,以支持未来低资源NLP的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究应用基于变压器的模型XLM-RoBERTa-large对未加标点的孟加拉语文本进行自动标点恢复,以提高文本的可读性,并改善自动语音识别(ASR)的后处理任务。研究构建了大型多元训练语料库,并应用数据增强技术解决标注资源稀缺的问题。最佳模型在新闻测试集上的准确度达到97.1%,参考集上为91.2%,语音识别集上为90.2%。结果证明该模型在真实世界的嘈杂场景中具有良好的泛化能力,为孟加拉语标点恢复建立了强大的基线,并为低资源自然语言处理的研究提供了公开可用的数据集和代码支持。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注于标点恢复在自动语音识别中的重要性,特别是在低资源语言如孟加拉语中。
- 采用基于XLM-RoBERTa-large模型的深度学习技术进行标点恢复。
- 研究构建了大型多元训练语料库以解决标注资源稀缺的问题。
- 通过数据增强技术提高模型的性能。
- 最佳模型在新闻、参考和语音识别等不同测试集上表现出高准确性。
- 模型在真实世界的嘈杂场景中具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

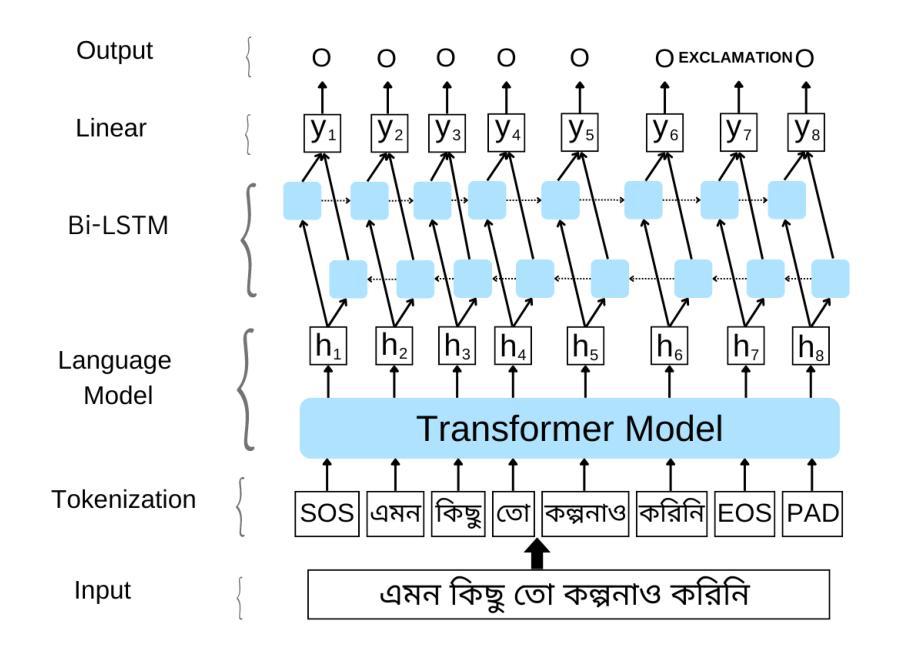
A Multimodal Seq2Seq Transformer for Predicting Brain Responses to Naturalistic Stimuli
Authors:Qianyi He, Yuan Chang Leong
The Algonauts 2025 Challenge called on the community to develop encoding models that predict whole-brain fMRI responses to naturalistic multimodal movies. In this submission, we propose a sequence-to-sequence Transformer that autoregressively predicts fMRI activity from visual, auditory, and language inputs. Stimulus features were extracted using pretrained models including VideoMAE, HuBERT, Qwen, and BridgeTower. The decoder integrates information from prior brain states and current stimuli via dual cross-attention mechanisms that attend to both perceptual information extracted from the stimulus as well as narrative information provided by high-level summaries of the content. One core innovation of our approach is the use of sequences of multimodal context to predict sequences of brain activity, enabling the model to capture long-range temporal structure in both stimuli and neural responses. Another is the combination of a shared encoder with partial subject-specific decoder, which leverages common representational structure across subjects while accounting for individual variability. Our model achieves strong performance on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution data, demonstrating the effectiveness of temporally-aware, multimodal sequence modeling for brain activity prediction. The code is available at https://github.com/Angelneer926/Algonauts_challenge.
阿尔贡纳茨2025挑战赛号召社区开发编码模型,预测大脑对自然主义多媒体电影的fMRI响应。在本次提交中,我们提出了一种序列到序列的转换器,该转换器能够根据视觉、听觉和语言输入进行自动回归预测fMRI活动。刺激特征是使用预训练模型提取的,包括VideoMAE、HuBERT、Qwen和BridgeTower。解码器通过双重交叉注意机制整合来自先前大脑状态和当前刺激的信息,这些机制既关注从刺激中提取的感知信息,也关注由内容高级摘要提供的叙事信息。我们方法的核心创新之一是使用多模式上下文序列来预测大脑活动序列,使模型能够捕捉刺激和神经反应中的长期时间结构。另一项创新是结合使用共享编码器和部分特定主题的解码器,这既可以利用跨主题的常见代表性结构,又可以考虑个体差异。我们的模型在内部和外部数据上都表现出强大的性能,证明了时间感知、多模式序列建模在预测大脑活动方面的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/Angelneer926/Algonauts_challenge找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Algonauts 2025挑战赛社区开发编码模型的情况。该研究团队提出了一种序列到序列的Transformer模型,可以自动预测自然主义多模态电影引发的全脑fMRI响应。该研究通过预训练模型提取刺激特征,并使用解码器整合先前脑状态和当前刺激的信息。该模型的核心创新之处在于使用多模态上下文序列预测脑活动序列,能够捕捉刺激和神经反应的长期时间结构。该模型在内部数据和外部数据上都表现出强劲性能,证明了时序感知、多模态序列建模在预测脑活动方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Algonauts 2025挑战赛旨在开发能够预测自然主义多模态电影引发的全脑fMRI响应的编码模型。
- 研究团队提出了一种序列到序列的Transformer模型进行预测。
- 该模型通过预训练模型提取刺激特征,包括视频、音频和语言输入。
- 解码器整合了先前脑状态和当前刺激的信息,通过双重交叉注意机制关注刺激中的感知信息以及内容的高级摘要中的叙事信息。
- 模型核心创新之一是使用多模态上下文序列预测脑活动序列,能够捕捉刺激和神经反应的长期时间结构。
- 模型结合了共享编码器与部分特定主题的解码器,利用跨主题的代表性结构,同时考虑个体差异。
点此查看论文截图

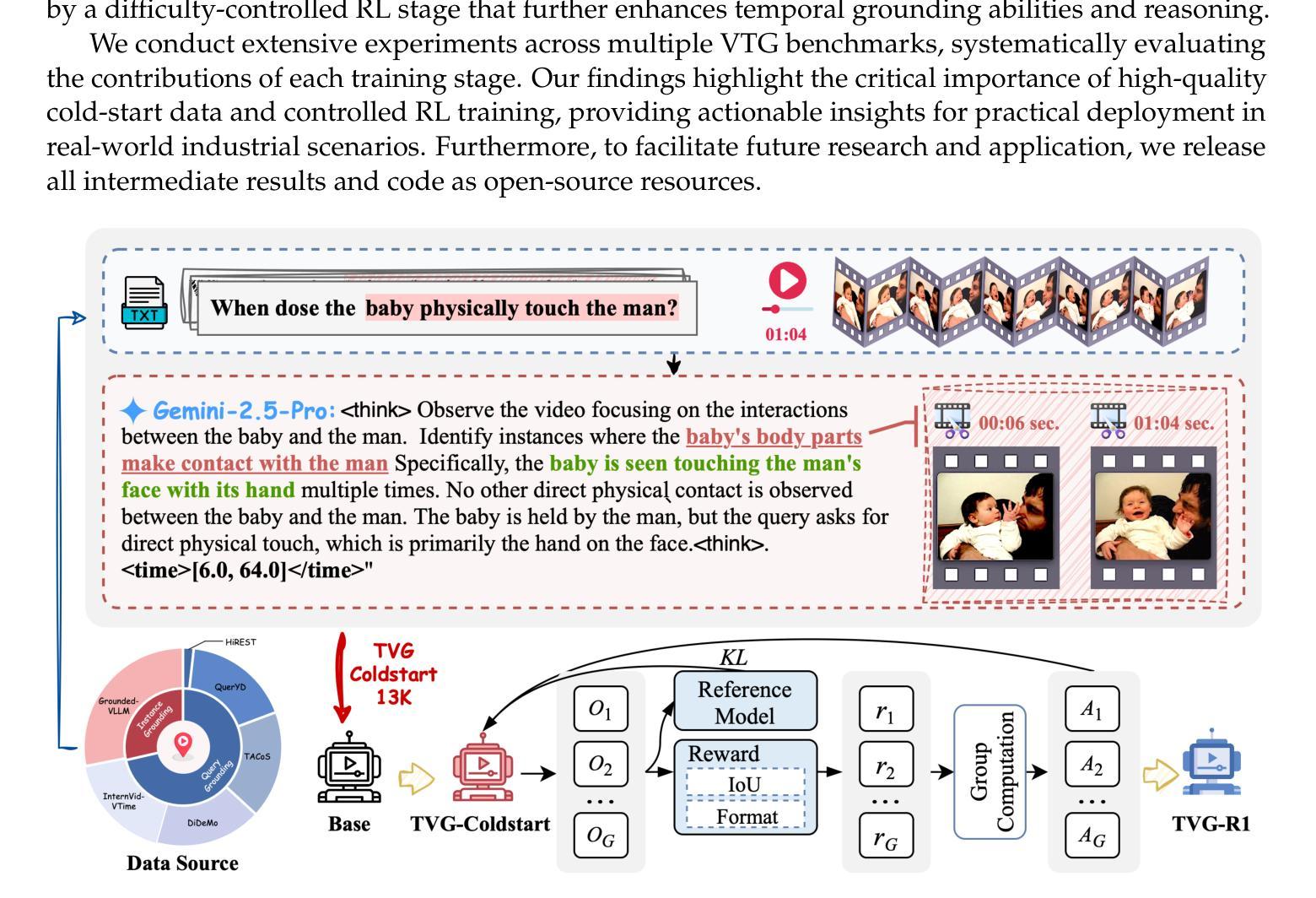
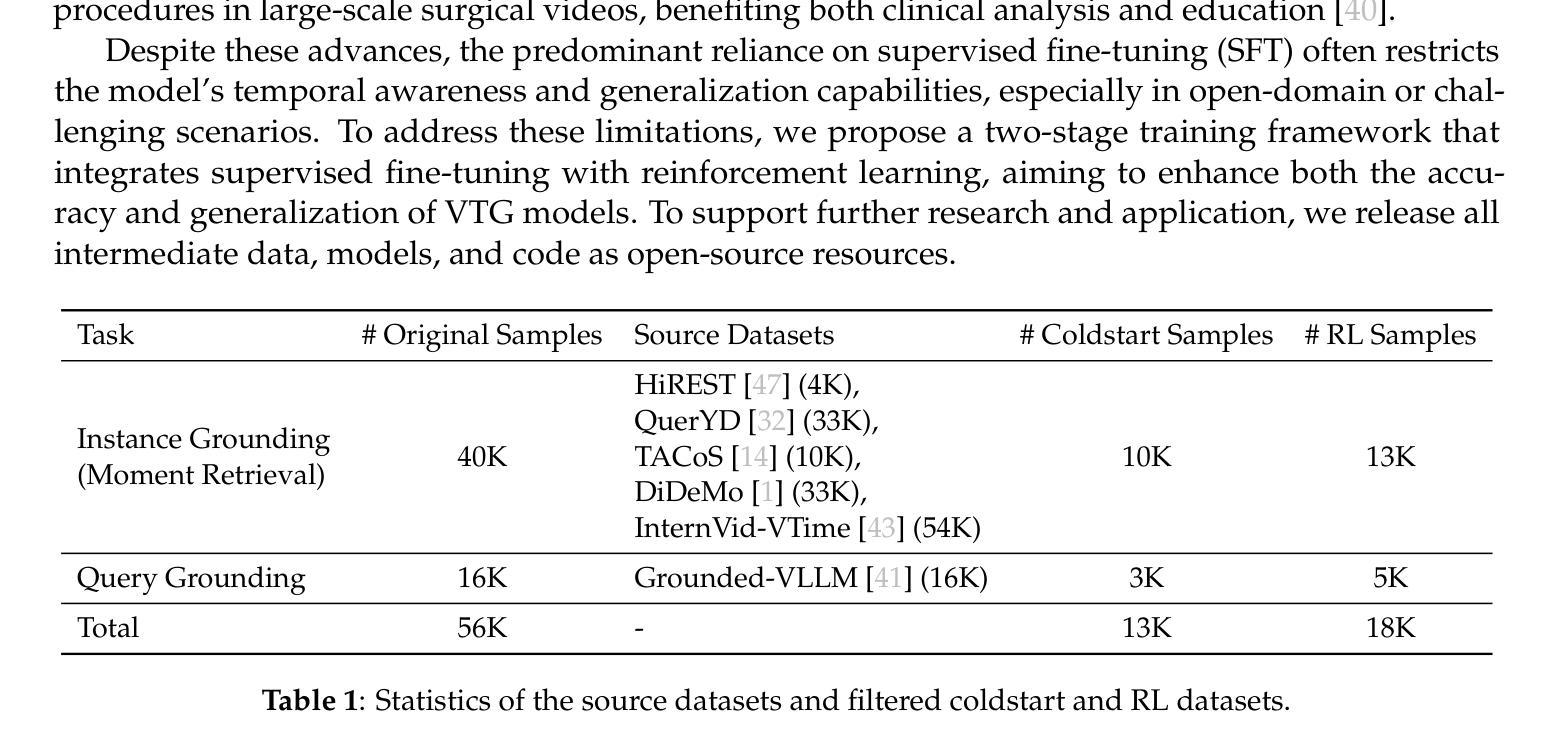
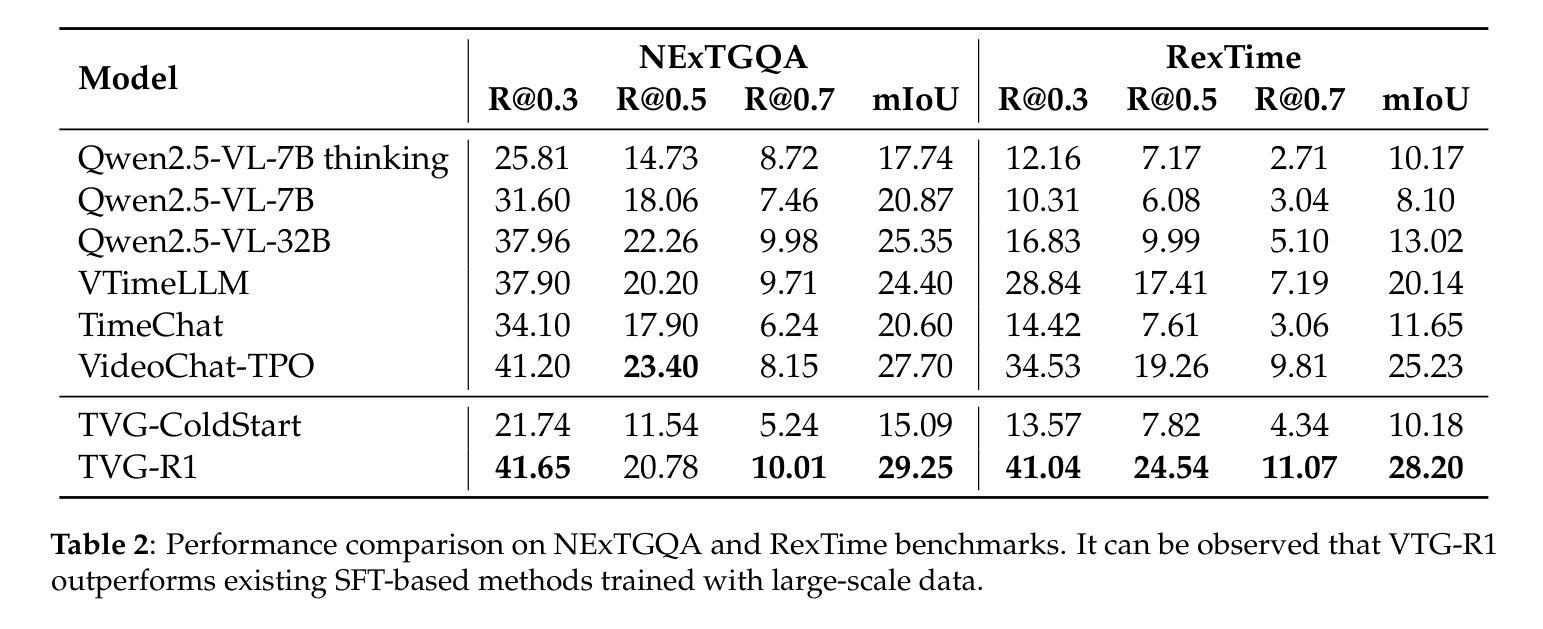
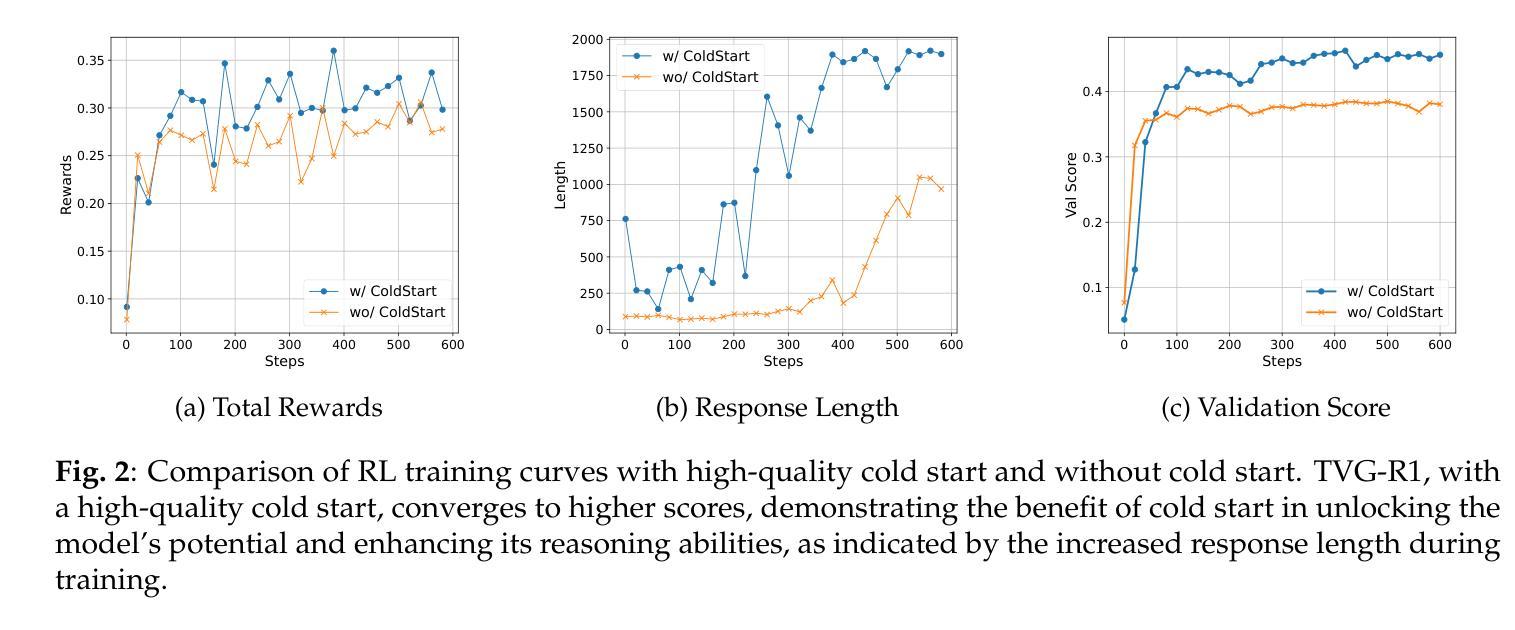
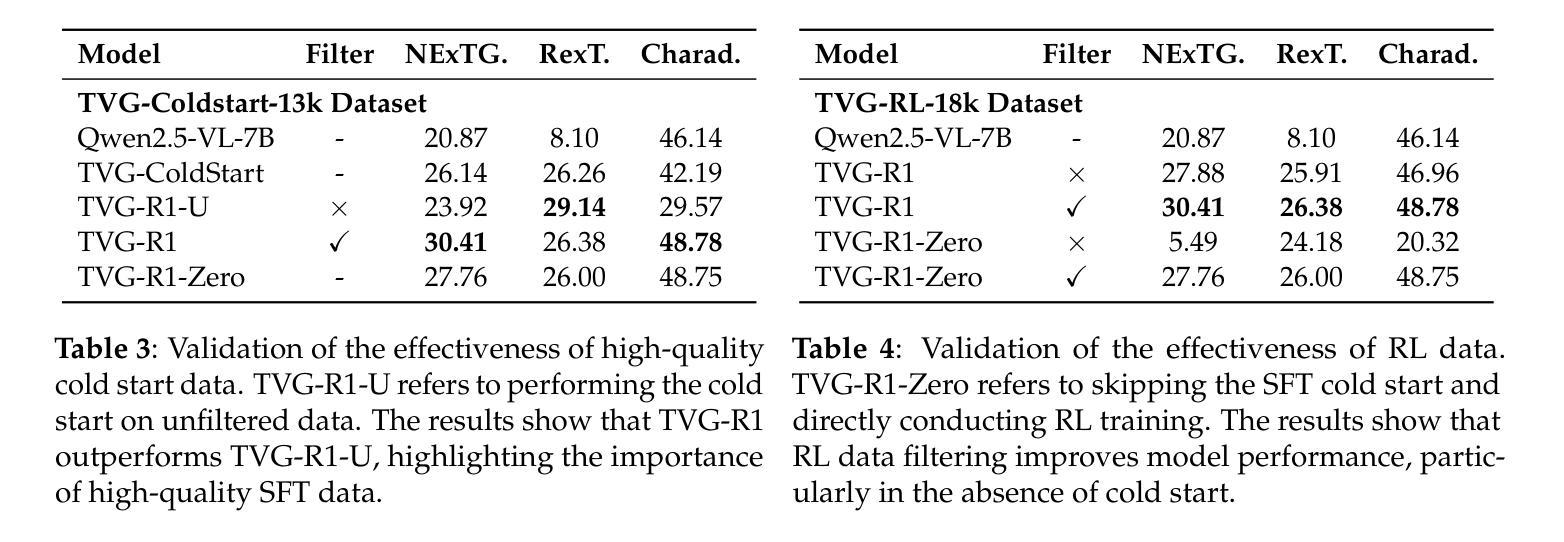
Datasets and Recipes for Video Temporal Grounding via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Ruizhe Chen, Zhiting Fan, Tianze Luo, Heqing Zou, Zhaopeng Feng, Guiyang Xie, Hansheng Zhang, Zhuochen Wang, Zuozhu Liu, Huaijian Zhang
Video Temporal Grounding (VTG) aims to localize relevant temporal segments in videos given natural language queries. Despite recent progress with large vision-language models (LVLMs) and instruction-tuning, existing approaches often suffer from limited temporal awareness and poor generalization. In this work, we introduce a two-stage training framework that integrates supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning (RL) to improve both the accuracy and robustness of VTG models. Our approach first leverages high-quality curated cold start data for SFT initialization, followed by difficulty-controlled RL to further enhance temporal localization and reasoning abilities. Comprehensive experiments on multiple VTG benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing models, particularly in challenging and open-domain scenarios. We conduct an in-depth analysis of training strategies and dataset curation, highlighting the importance of both high-quality cold start data and difficulty-controlled RL. To facilitate further research and industrial adoption, we release all intermediate datasets, models, and code to the community.
视频时序定位(VTG)旨在根据自然语言查询定位视频中的相关时序片段。尽管最近使用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)和指令微调取得了进展,但现有方法往往存在时序感知能力有限和泛化能力较差的问题。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个两阶段训练框架,该框架将监督微调与强化学习(RL)相结合,以提高VTG模型的准确性和鲁棒性。我们的方法首先利用高质量的精选冷启动数据进行SFT初始化,然后通过难度控制的RL来进一步增强时序定位和推理能力。在多个VTG基准测试上的综合实验表明,我们的方法一直优于现有模型,特别是在具有挑战性和开放领域的场景中。我们对训练策略和数据集编制进行了深入分析,强调了高质量冷启动数据和难度控制RL的重要性。为了促进进一步的研究和工业应用,我们向社区发布所有中间数据集、模型和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频时序定位(VTG)旨在根据自然语言查询定位视频中的相关时序片段。尽管近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)和指令微调取得了一定进展,但现有方法往往存在时序感知能力有限和泛化能力较差的问题。本研究引入了一个两阶段训练框架,将监督微调与强化学习(RL)相结合,旨在提高VTG模型的准确性和稳健性。该方法首先利用高质量预设冷启动数据进行SFT初始化,然后通过难度控制的RL进一步改善时序定位和推理能力。在多个VTG基准测试上的综合实验表明,该方法持续优于现有模型,尤其在具有挑战性和开放领域的场景中表现突出。我们对训练策略和数据集构建进行了深入分析,强调了高质量冷启动数据和难度控制RL的重要性。为促进进一步研究和工业应用,我们向社区发布了所有中间数据集、模型和代码。
Key Takeaways
- VTG旨在根据自然语言查询定位视频中的相关时序片段。
- 现有方法存在时序感知能力有限和泛化能力较差的问题。
- 研究引入了一个两阶段训练框架,结合了监督微调与强化学习。
- 该方法利用高质量预设冷启动数据进行SFT初始化。
- 通过难度控制的RL进一步改善时序定位和推理能力。
- 在多个基准测试上表现出优于现有模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

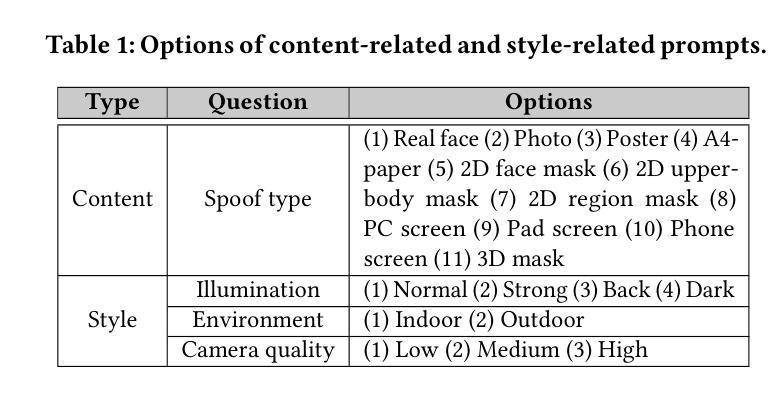
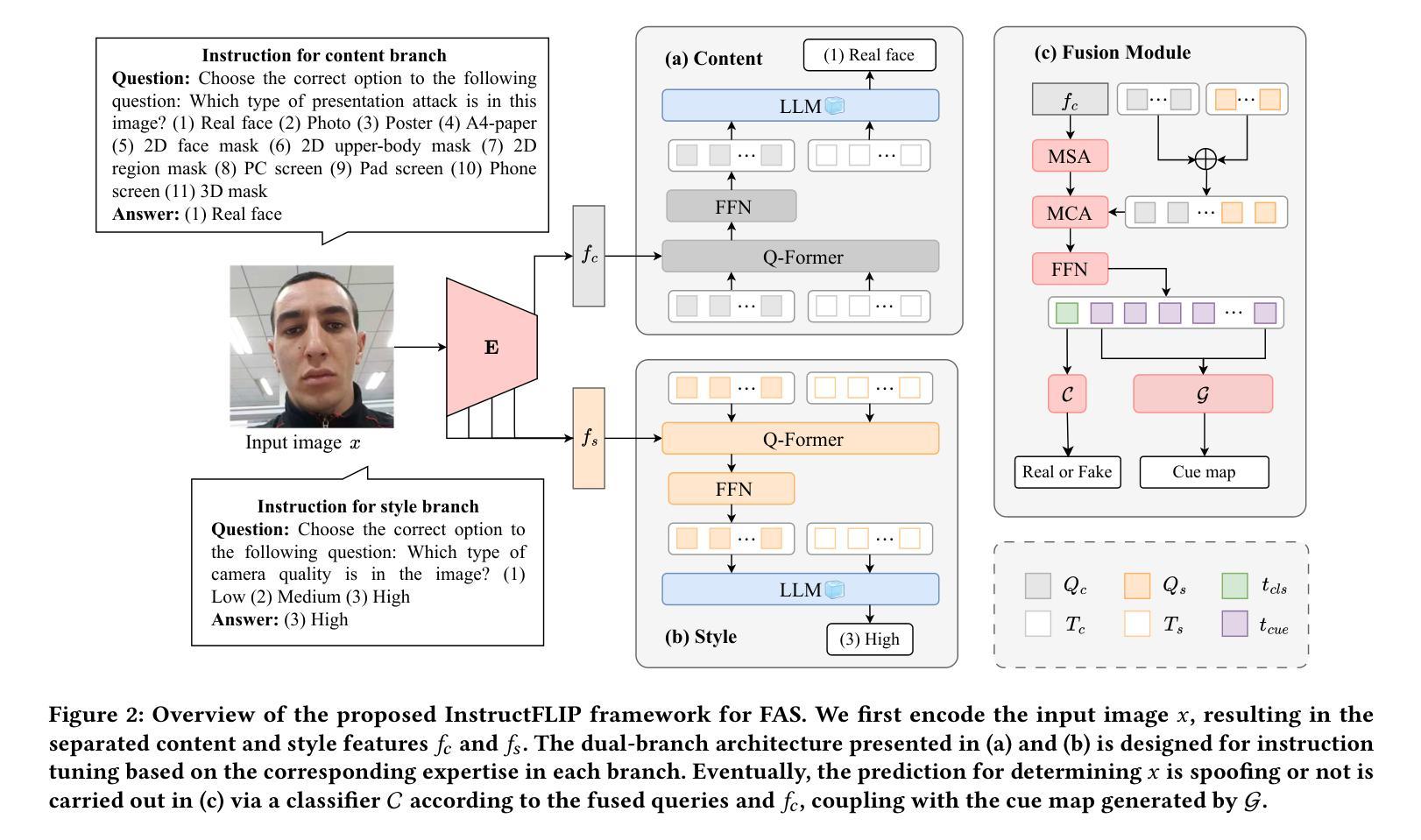
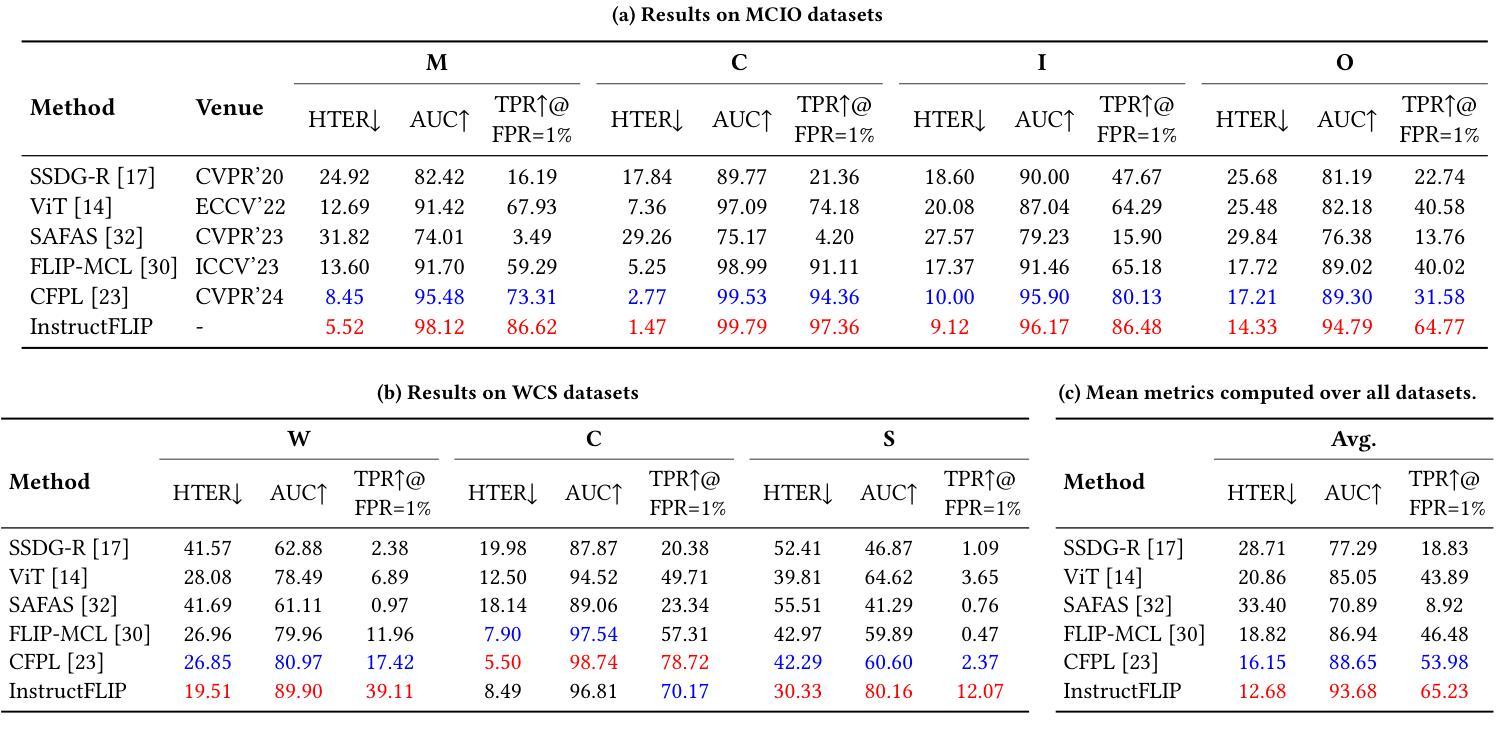
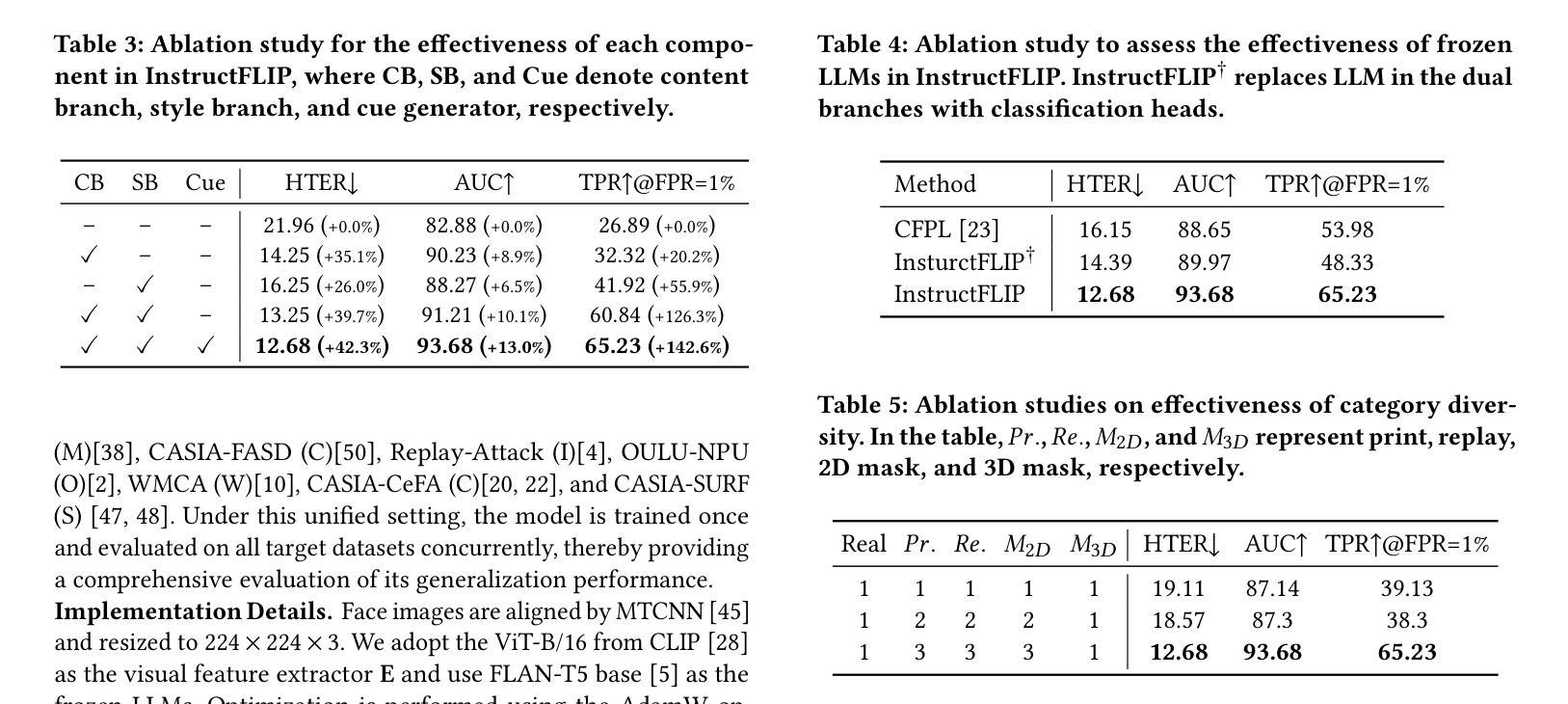
InstructFLIP: Exploring Unified Vision-Language Model for Face Anti-spoofing
Authors:Kun-Hsiang Lin, Yu-Wen Tseng, Kang-Yang Huang, Jhih-Ciang Wu, Wen-Huang Cheng
Face anti-spoofing (FAS) aims to construct a robust system that can withstand diverse attacks. While recent efforts have concentrated mainly on cross-domain generalization, two significant challenges persist: limited semantic understanding of attack types and training redundancy across domains. We address the first by integrating vision-language models (VLMs) to enhance the perception of visual input. For the second challenge, we employ a meta-domain strategy to learn a unified model that generalizes well across multiple domains. Our proposed InstructFLIP is a novel instruction-tuned framework that leverages VLMs to enhance generalization via textual guidance trained solely on a single domain. At its core, InstructFLIP explicitly decouples instructions into content and style components, where content-based instructions focus on the essential semantics of spoofing, and style-based instructions consider variations related to the environment and camera characteristics. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of InstructFLIP by outperforming SOTA models in accuracy and substantially reducing training redundancy across diverse domains in FAS. Project website is available at https://kunkunlin1221.github.io/InstructFLIP.
人脸识别防伪(FAS)旨在构建一个稳健的系统,能够抵御各种攻击。虽然最近的努力主要集中在跨域泛化上,但仍然存在两个重大挑战:对攻击类型的语义理解有限以及跨域的训练冗余。我们通过整合视觉语言模型(VLMs)来解决第一个挑战,以增强对视觉输入的感知。对于第二个挑战,我们采用元域策略来学习一个能在多个领域间良好泛化的统一模型。我们提出的InstructFLIP是一个新型指令调优框架,它利用VLMs通过文本指导增强泛化能力,仅在单个领域进行训练。InstructFLIP的核心显式地将指令解耦为内容和风格组件,其中基于内容的指令侧重于欺骗的本质语义,而基于风格的指令则考虑与环境特性和相机特性相关的变化。大量实验表明,InstructFLIP在准确性方面优于SOTA模型,并且在人脸识别防伪的多个领域中显著减少了跨域训练冗余。项目网站位于https://kunkunlin1221.github.io/InstructFLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MM’25
Summary
人工智能人脸识别防伪系统在视觉和语言的结合下实现了更强的攻击类型语义理解,并解决了跨域训练冗余的问题。InstructFLIP框架通过利用视觉语言模型增强感知能力,并通过统一模型实现跨多个领域的良好泛化能力。该框架通过明确区分指令的内容和风格,实现基于内容的指令专注于防伪的本质语义,而基于风格的指令则考虑与环境、相机特性相关的变化。实验结果证明,InstructFLIP在准确性上优于其他先进模型,并在人脸识别防伪系统的不同领域有效降低了训练冗余。详细信息请参考相关网站 https://kunkunlin1221.github.io/InstructFLIP。
Key Takeaways
- 利用视觉语言模型增强感知能力以解决语义理解有限的挑战。
- 提出一种基于指令调谐的方法来处理跨领域冗余训练问题。
- 通过内容风格和指令的明确区分提高模型泛化能力。
- InstructFLIP框架实现攻击类型语义的核心理解并增强防伪系统的泛化能力。
- 实验结果显示InstructFLIP在准确性上优于其他模型。
- 该框架有效降低了人脸识别防伪系统在不同领域的训练冗余。
点此查看论文截图

Can GPT-4o mini and Gemini 2.0 Flash Predict Fine-Grained Fashion Product Attributes? A Zero-Shot Analysis
Authors:Shubham Shukla, Kunal Sonalkar
The fashion retail business is centered around the capacity to comprehend products. Product attribution helps in comprehending products depending on the business process. Quality attribution improves the customer experience as they navigate through millions of products offered by a retail website. It leads to well-organized product catalogs. In the end, product attribution directly impacts the ‘discovery experience’ of the customer. Although large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in understanding multimodal data, their performance on fine-grained fashion attribute recognition remains under-explored. This paper presents a zero-shot evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs that balance performance with speed and cost efficiency, mainly GPT-4o-mini and Gemini 2.0 Flash. We have used the dataset DeepFashion-MultiModal (https://github.com/yumingj/DeepFashion-MultiModal) to evaluate these models in the attribution tasks of fashion products. Our study evaluates these models across 18 categories of fashion attributes, offering insight into where these models excel. We only use images as the sole input for product information to create a constrained environment. Our analysis shows that Gemini 2.0 Flash demonstrates the strongest overall performance with a macro F1 score of 56.79% across all attributes, while GPT-4o-mini scored a macro F1 score of 43.28%. Through detailed error analysis, our findings provide practical insights for deploying these LLMs in production e-commerce product attribution-related tasks and highlight the need for domain-specific fine-tuning approaches. This work also lays the groundwork for future research in fashion AI and multimodal attribute extraction.
时尚零售行业的核心在于理解产品的能力。产品属性有助于根据业务流程理解产品。质量属性提高了客户在浏览零售网站提供的数百万产品时的体验,这导致了组织良好的产品目录。最终,产品属性直接影响客户的“发现体验”。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在理解多模式数据方面表现出显著的能力,但在精细的时尚属性识别方面,它们的性能仍然未被充分探索。本文对所采用的大型语言模型进行了零样本评估,这些模型在性能和速度以及成本效益之间取得了平衡,主要包括GPT-4o-mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash。我们使用DeepFashion-MultiModal数据集(https://github.com/yumingj/DeepFashion-MultiModal)来评估这些模型在时尚产品属性任务中的表现。我们的研究在时尚属性的18个类别中评估了这些模型,洞察了这些模型的优势所在。我们只使用图像作为产品信息的唯一输入,以创建一个受限制的环境。我们的分析表明,Gemini 2.0 Flash在所有属性上的宏观F1分数表现最佳,达到56.79%,而GPT-4o-mini的宏观F1分数为43.28%。通过详细的误差分析,我们的发现提供了将这些大型语言模型部署在生产环境中的电子商务产品属性相关任务的实用见解,并强调了需要进行特定领域的微调方法。这项工作也为未来的时尚人工智能和多模式属性提取研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Version 2: Added a missing citation
Summary
本论文主要探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在时尚产品属性识别方面的应用。研究采用了DeepFashion-MultiModal数据集,对GPT-4o-mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash模型进行了评估,涉及18类时尚属性。实验结果表明,Gemini 2.0 Flash在整体性能上表现最佳,而GPT-4o-mini则相对较弱。研究还通过错误分析提供了实际见解,为这些LLMs在生产环境中的电子商务产品属性识别任务的应用提供了指导,并强调了领域特定微调方法的需求。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在时尚产品属性识别方面存在应用潜力。
- 研究采用了DeepFashion-MultiModal数据集进行模型评估。
- GPT-4o-mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash模型参与了评估,涉及18类时尚属性。
- Gemini 2.0 Flash在整体性能上表现最佳。
- 通过错误分析,研究提供了实际见解,指导了这些LLMs在生产环境中的电子商务产品属性识别任务的应用。
- 领域特定的微调方法对于提高LLMs在时尚产品属性识别方面的性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


A comprehensive study of LLM-based argument classification: from LLAMA through GPT-4o to Deepseek-R1
Authors:Marcin Pietroń, Rafał Olszowski, Jakub Gomułka, Filip Gampel, Andrzej Tomski
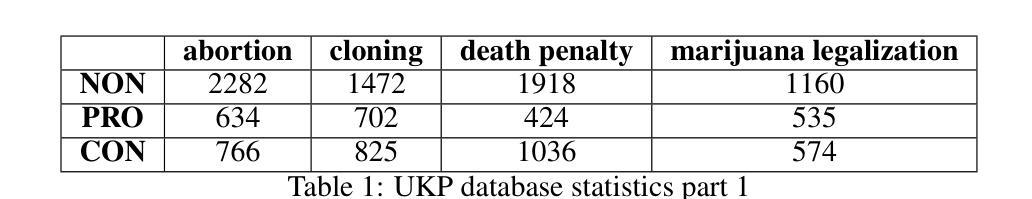
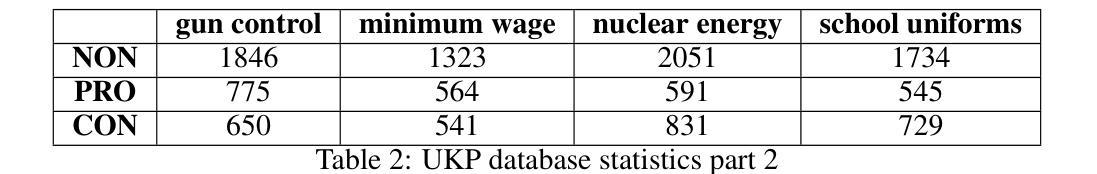
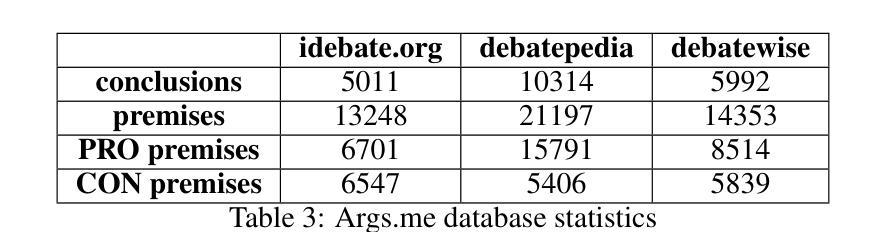
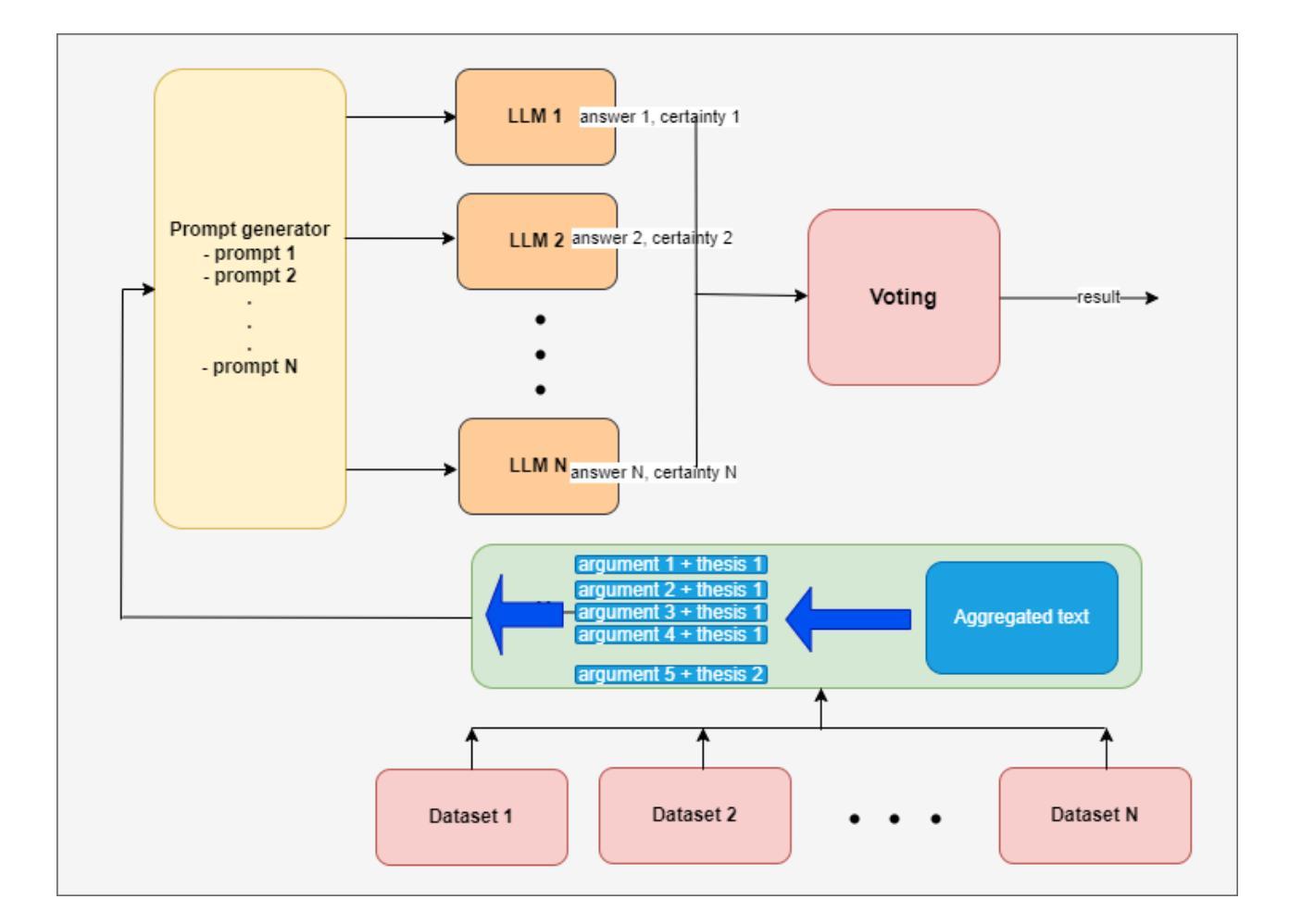
Argument mining (AM) is an interdisciplinary research field that integrates insights from logic, philosophy, linguistics, rhetoric, law, psychology, and computer science. It involves the automatic identification and extraction of argumentative components, such as premises and claims, and the detection of relationships between them, such as support, attack, or neutrality. Recently, the field has advanced significantly, especially with the advent of large language models (LLMs), which have enhanced the efficiency of analyzing and extracting argument semantics compared to traditional methods and other deep learning models. There are many benchmarks for testing and verifying the quality of LLM, but there is still a lack of research and results on the operation of these models in publicly available argument classification databases. This paper presents a study of a selection of LLM’s, using diverse datasets such as Args.me and UKP. The models tested include versions of GPT, Llama, and DeepSeek, along with reasoning-enhanced variants incorporating the Chain-of-Thoughts algorithm. The results indicate that ChatGPT-4o outperforms the others in the argument classification benchmarks. In case of models incorporated with reasoning capabilities, the Deepseek-R1 shows its superiority. However, despite their superiority, GPT-4o and Deepseek-R1 still make errors. The most common errors are discussed for all models. To our knowledge, the presented work is the first broader analysis of the mentioned datasets using LLM and prompt algorithms. The work also shows some weaknesses of known prompt algorithms in argument analysis, while indicating directions for their improvement. The added value of the work is the in-depth analysis of the available argument datasets and the demonstration of their shortcomings.
论证挖掘(AM)是一个跨学科的研究领域,它融合了逻辑、哲学、语言学、修辞学、法律、心理学和计算机科学等领域的见解。它涉及自动识别和提取论证性成分,如前提和论断,以及检测它们之间的关系,如支持、攻击或中立。最近,随着大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,该领域取得了显著进展,与传统的方法和其他深度学习模型相比,LLM提高了分析提取论证语义的效率。虽然有很多基准测试用于测试和验证LLM的质量,但在公开可用的论证分类数据库中关于这些模型操作的研究和结果仍然缺乏。本文使用Args.me和UKP等多样化数据集对部分LLM进行了研究。测试的模型包括GPT、Llama和DeepSeek的版本,以及采用Chain-of-Thoughts算法的推理增强变体。结果表明,在论证分类基准测试中,ChatGPT-4o的表现优于其他模型。在融入推理能力的模型中,Deepseek-R1表现出其优越性。然而,尽管GPT-4o和Deepseek-R1具有优势,但它们仍然会出错。本文讨论了所有模型最常见的错误。据我们所知,所呈现的工作是使用LLM和提示算法对所述数据集进行的首次更广泛的分析。该工作还展示了已知提示算法在论证分析中的一些弱点,并指出了改进方向。该工作的附加值是对可用论证数据集进行深入分析和展示其不足。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了论证挖掘(AM)这一跨学科研究领域,特别关注了大型语言模型(LLM)在论证语义分析提取中的应用。文章对多个LLM进行了测试与比较,包括GPT、Llama和DeepSeek等模型及其结合思维链算法的变体。结果显示,ChatGPT-4o在论证分类基准测试中表现最佳,而结合推理能力的Deepseek-R1也表现出其优越性。但即便是这些优秀模型也存在错误,文章对最常见的错误进行了讨论。此项研究是首次使用LLM和提示算法对提到的数据集进行广泛分析,展示了现有提示算法在论证分析中的弱点,并为改进指明了方向。
Key Takeaways
- 论证挖掘是一个涉及多个学科的研究领域,包括逻辑、哲学、语言学、修辞学、法律、心理学和计算机科学。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已用于增强论证语义分析和提取的效率。
- 在使用的模型测试中,ChatGPT-4o在论证分类基准测试中表现最佳。
- 结合推理能力的Deepseek-R1模型也显示出其优越性。
- 尽管存在优越性,但GPT-4o和Deepseek-R1等模型仍然会犯错误,文章指出了这些错误中最常见的问题。
- 该研究首次使用大型语言模型(LLM)和提示算法对特定数据集进行了深入分析。
点此查看论文截图

White-Basilisk: A Hybrid Model for Code Vulnerability Detection
Authors:Ioannis Lamprou, Alexander Shevtsov, Ioannis Arapakis, Sotiris Ioannidis
The proliferation of software vulnerabilities presents a significant challenge to cybersecurity, necessitating more effective detection methodologies. We introduce White-Basilisk, a novel approach to vulnerability detection that demonstrates superior performance while challenging prevailing assumptions in AI model scaling. Utilizing an innovative architecture that integrates Mamba layers, linear self-attention, and a Mixture of Experts framework, White-Basilisk achieves state-of-the-art results in vulnerability detection tasks with a parameter count of only 200M. The model’s capacity to process sequences of unprecedented length enables comprehensive analysis of extensive codebases in a single pass, surpassing the context limitations of current Large Language Models (LLMs). White-Basilisk exhibits robust performance on imbalanced, real-world datasets, while maintaining computational efficiency that facilitates deployment across diverse organizational scales. This research not only establishes new benchmarks in code security but also provides empirical evidence that compact, efficiently designed models can outperform larger counterparts in specialized tasks, potentially redefining optimization strategies in AI development for domain-specific applications.
软件漏洞的激增对网络安全构成了重大挑战,需要更有效的检测方法。我们引入了White-Basilisk,这是一种新型的漏洞检测方法,它在挑战人工智能模型扩展的普遍假设的同时,表现出了卓越的性能。White-Basilisk利用了一种创新架构,该架构结合了Mamba层、线性自注意力机制和专家混合框架,仅在参数计数为200M的情况下,就在漏洞检测任务中实现了最新结果。该模型处理前所未有的序列长度的能力,能够在单次传递中对广泛的代码库进行全面分析,超越了当前大型语言模型(LLM)的上下文限制。White-Basilisk在不平衡、现实世界的数据集上表现出稳健的性能,同时保持计算效率,便于在各类组织规模上部署。这项研究不仅为代码安全建立了新的基准线,而且还提供了实证证据,证明在特定任务中,设计紧凑、高效的模型可以超越较大的模型,这有可能重新定义人工智能开发中的优化策略,为领域特定应用提供支持。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
白巴西尔是全球首次采用融合独特技术打造的尖端软件漏洞检测模型,结合技术精湛的多项成果推出革命性表现。使用涵盖融合骊狼层级(Mamba layers)、线性自注意(linear self-attention)及专业顾问组融合(Mixture of Experts framework)的综合技术体系,“白巴西尔”成功实现漏洞检测领域的顶尖成果,仅通过2亿参数即达到卓越性能。其强大的序列处理能力可一次性全面分析大型代码库,突破当前大型语言模型对语境的限制。“白巴西尔”面对现实世界数据集也表现稳健,尤其展现出其在不平衡数据处理能力上的高超表现,并通过高度精确计算进一步推动了各种组织的广泛使用部署。本研究不仅树立了代码安全的新标杆,而且实证表明紧凑、高效设计的模型在特定任务上可超越大型模型,为领域特定应用的AI开发优化策略提供了全新视角。
关键见解
一、白巴西尔模型通过融合多种技术实现高效漏洞检测,包括创新的模型架构以及特殊的线性自注意机制和专家系统。模型参数量仅需较少的数值便具有优秀表现,这种卓越的性能提供了机会窗口进行更广泛的部署和应用。
二、白巴西尔模型具有处理超长序列的能力,能够全面分析大型代码库,突破了现有大型语言模型的语境限制。这种突破对于应对复杂的软件代码安全挑战至关重要。
三、白巴西尔模型在真实世界的不平衡数据集上表现出强大的稳健性。这意味着该模型能够应对各种实际场景下的数据挑战,具有极高的实用价值。
四、白巴西尔的计算效率极高,能够在各种组织规模上实现快速部署和应用。这种高效的计算性能对于大规模的软件安全检测任务至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

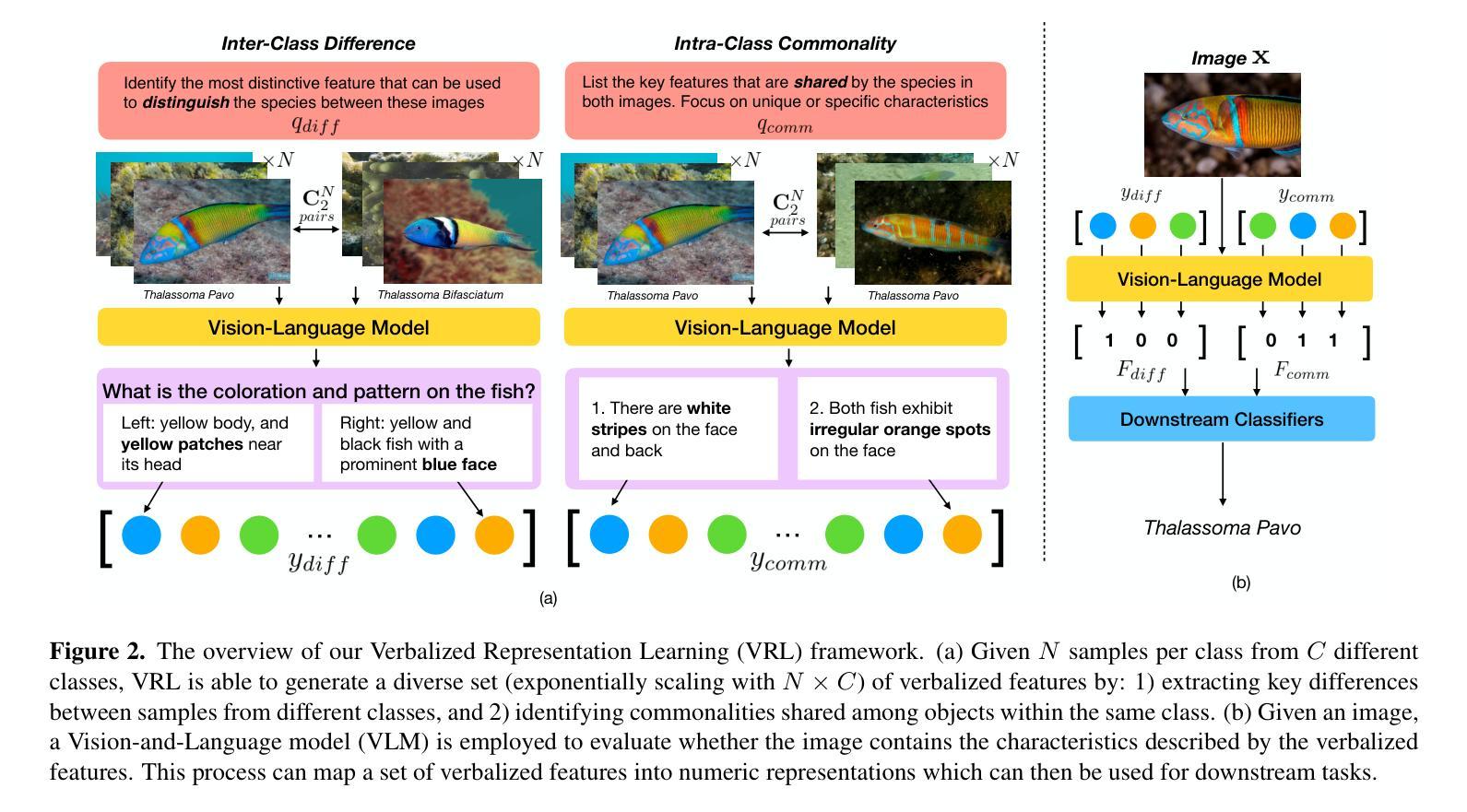
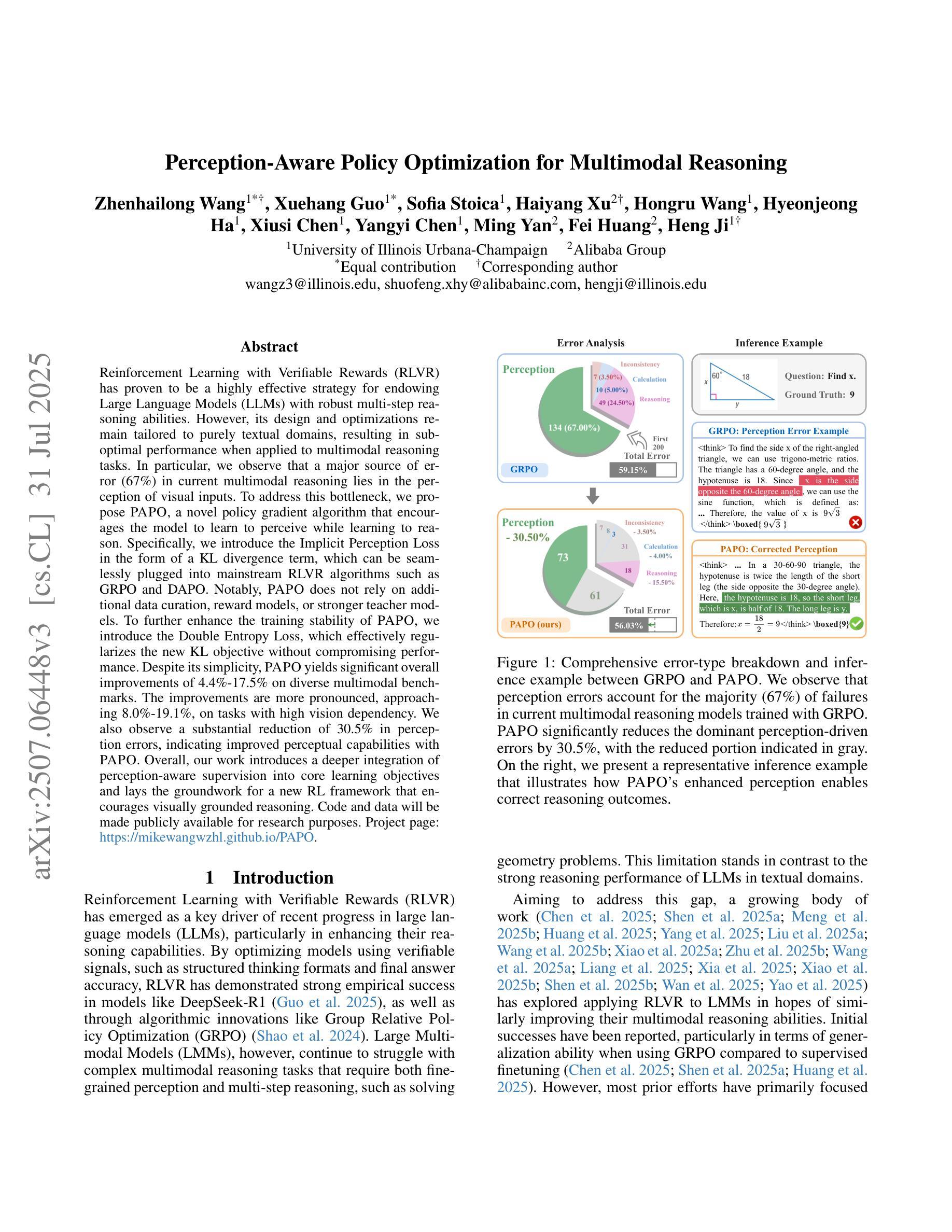
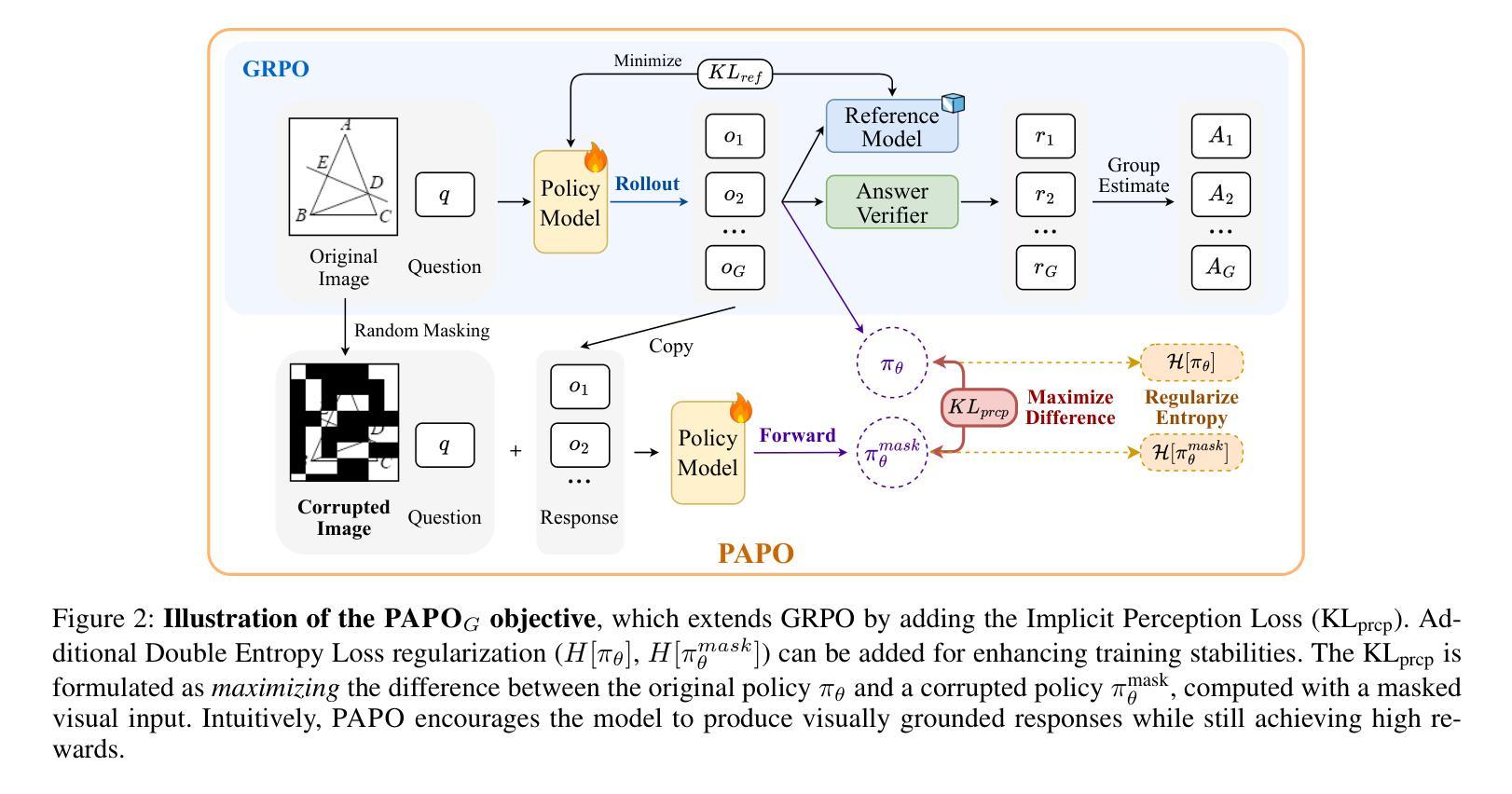
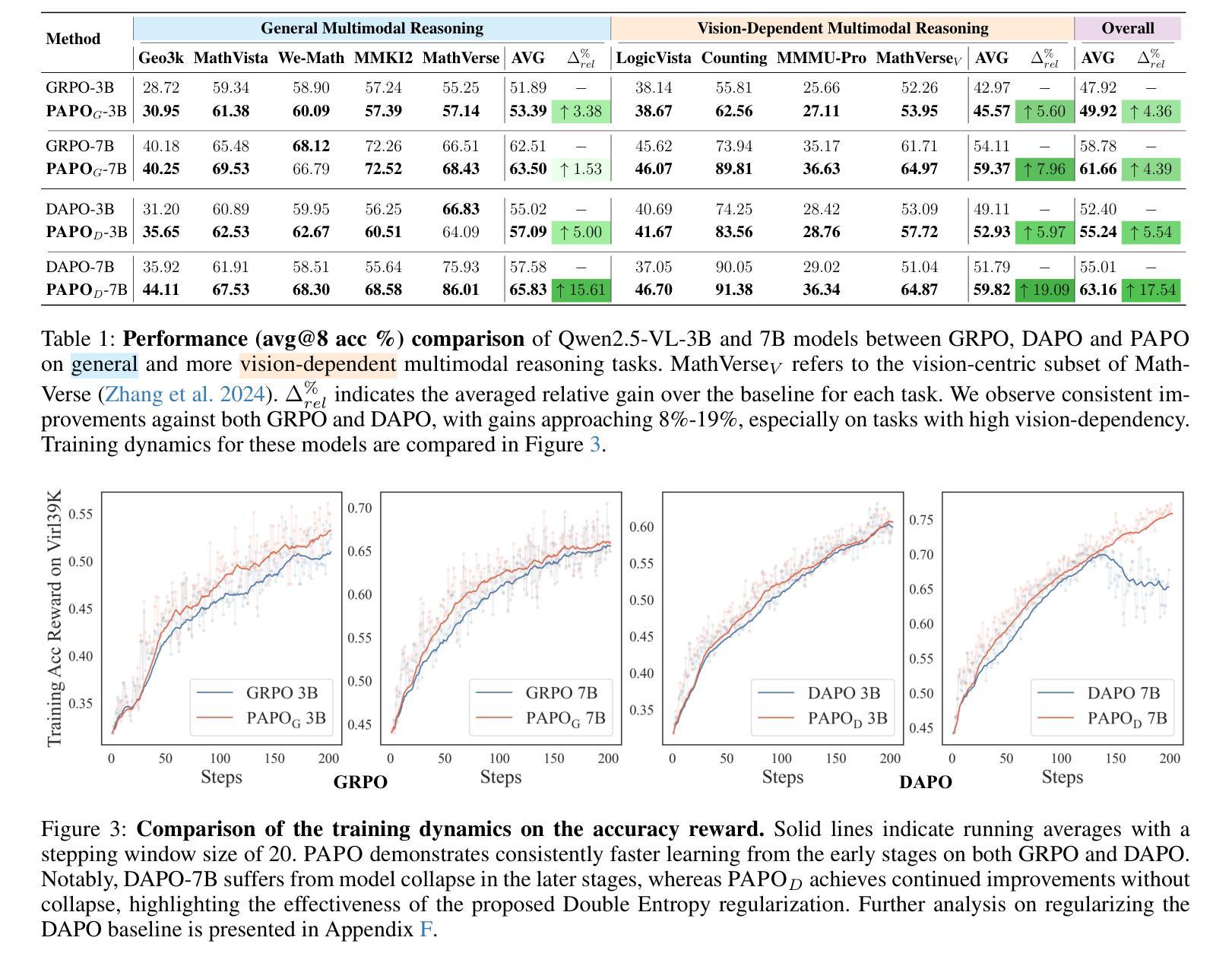
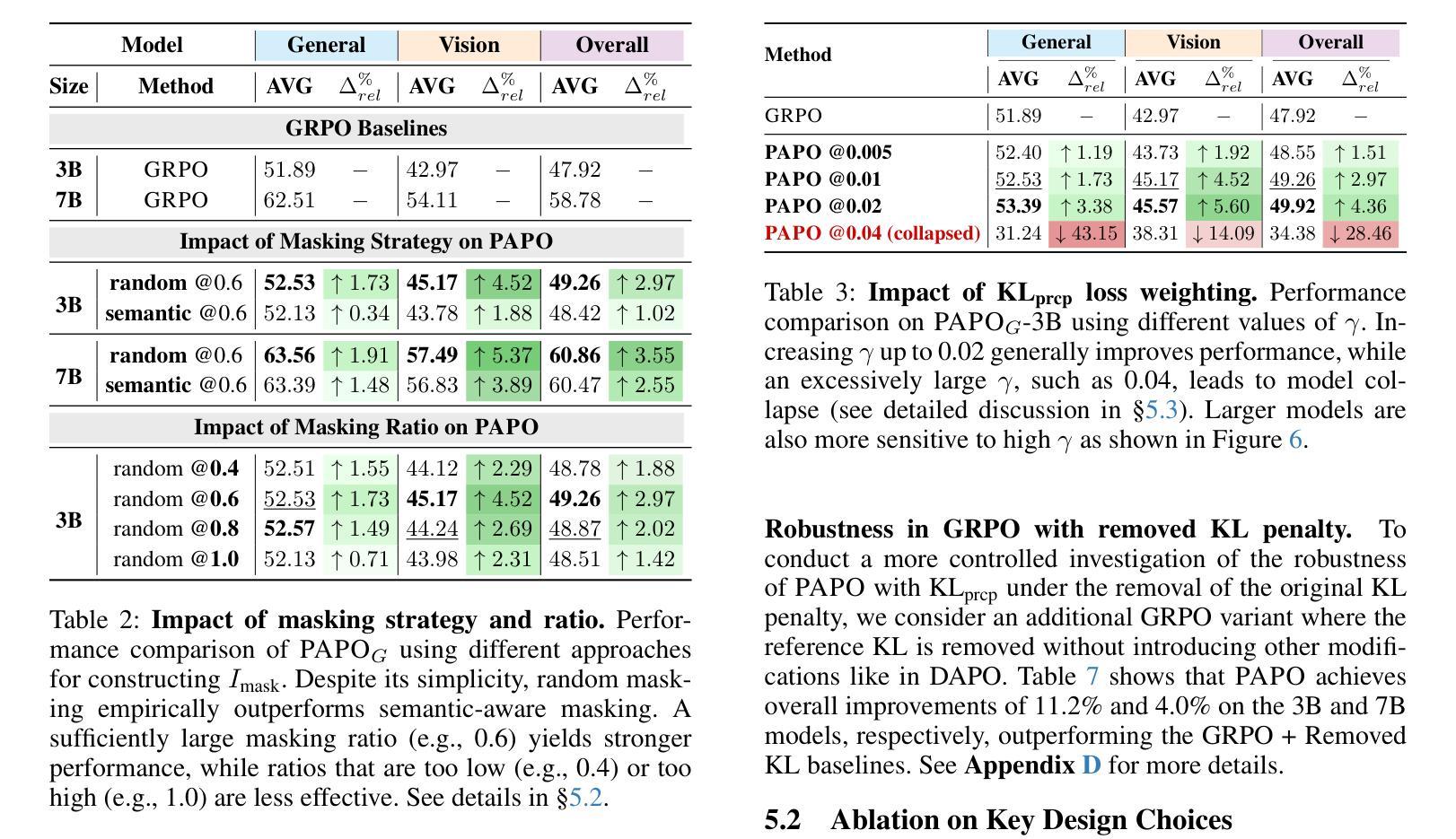
Perception-Aware Policy Optimization for Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Zhenhailong Wang, Xuehang Guo, Sofia Stoica, Haiyang Xu, Hongru Wang, Hyeonjeong Ha, Xiusi Chen, Yangyi Chen, Ming Yan, Fei Huang, Heng Ji
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has proven to be a highly effective strategy for endowing Large Language Models (LLMs) with robust multi-step reasoning abilities. However, its design and optimizations remain tailored to purely textual domains, resulting in suboptimal performance when applied to multimodal reasoning tasks. In particular, we observe that a major source of error in current multimodal reasoning lies in the perception of visual inputs. To address this bottleneck, we propose PAPO, a novel policy gradient algorithm that encourages the model to learn to perceive while learning to reason. Specifically, we introduce the Implicit Perception Loss in the form of a KL divergence term, which can be seamlessly plugged into mainstream RLVR algorithms such as GRPO and DAPO. Notably, PAPO does not rely on additional data curation, reward models, or stronger teacher models. To further enhance the training stability of PAPO, we introduce the Double Entropy Loss, which effectively regularizes the new KL objective without compromising performance. Despite its simplicity, PAPO yields significant overall improvements of 4.4%-17.5% on diverse multimodal benchmarks. The improvements are more pronounced, approaching 8.0%-19.1%, on tasks with high vision dependency. We also observe a substantial reduction of 30.5% in perception errors, indicating improved perceptual capabilities with PAPO. Overall, our work introduces a deeper integration of perception-aware supervision into core learning objectives and lays the groundwork for a new RL framework that encourages visually grounded reasoning. Code and data will be made publicly available for research purposes. Project page: https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/PAPO.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)已被证明是赋予大型语言模型(LLM)强大的多步推理能力的一种高度有效的策略。然而,其设计和优化仍然针对纯文本领域,在应用于多模态推理任务时表现不佳。我们观察到,当前多模态推理中的误差主要来源于视觉输入的感知。为了解决这一瓶颈,我们提出了PAPO,这是一种新型的策略梯度算法,鼓励模型在学习的过程中学会感知。具体来说,我们以KL散度项的形式引入隐感知损失,它可以无缝地插入主流的RLVR算法,如GRPO和DAPO。值得注意的是,PAPO不依赖额外的数据整理、奖励模型或更强大的教师模型。为了进一步提高PAPO的训练稳定性,我们引入了双重熵损失,它有效地规范了新的KL目标,而不会影响性能。尽管PAPO简单,但在多种多模态基准测试中,它实现了4.4%~17.5%的显著总体改进。在高视觉依赖的任务上,改进更为显著,达到了8.0%~19.1%。我们还观察到感知错误率降低了30.5%,这表明PAPO提高了感知能力。总的来说,我们的工作将感知感知监督更深入地集成到核心学习目标中,并为鼓励视觉基础推理的新型RL框架奠定了基础。代码和数据将公开发布以供研究之用。项目页面:https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/PAPO。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)为大型语言模型(LLM)赋予稳健的多步推理能力提供了有效策略。然而,其设计与优化仅限于纯文本领域,在应用于多模态推理任务时表现不佳。针对当前多模态推理中误差的主要来源——视觉输入的感知问题,我们提出了PAPO这一新型策略优化梯度算法。它通过引入隐式感知损失(以KL散度形式)来鼓励模型在推理中学习感知,可无缝集成到主流RLVR算法如GRPO和DAPO中。值得注意的是,PAPO不依赖额外数据整理、奖励模型或更强教师模型。为进一步增强PAPO的训练稳定性,我们引入了双重熵损失,有效正则化新的KL目标而不损害性能。尽管简单,PAPO在多样化多模态基准测试中整体改进了4.4%-17.5%的成绩,在高视觉依赖任务上的改进更为显著,达到8.0%-19.1%。同时观察到感知错误率显著下降30.5%,表明PAPO提高了感知能力。总体而言,我们的工作将感知感知监督更深入地集成到核心学习目标中,并为鼓励视觉感知推理的新型RL框架奠定了基础。
关键见解
- RLVR在赋予LLM多步推理能力方面高度有效,但在多模态推理任务中表现不佳。
- 当前多模态推理的主要误差来源于视觉输入的感知问题。
- PAPO是一种新型策略优化梯度算法,通过引入隐式感知损失解决这一问题。
- PAPO能够无缝集成到主流RLVR算法中,且不依赖额外数据、奖励模型或教师模型。
- 通过引入双重熵损失,增强了PAPO的训练稳定性。
- PAPO在多种多模态基准测试中取得了显著的性能改进,特别是在高视觉依赖任务上。
点此查看论文截图
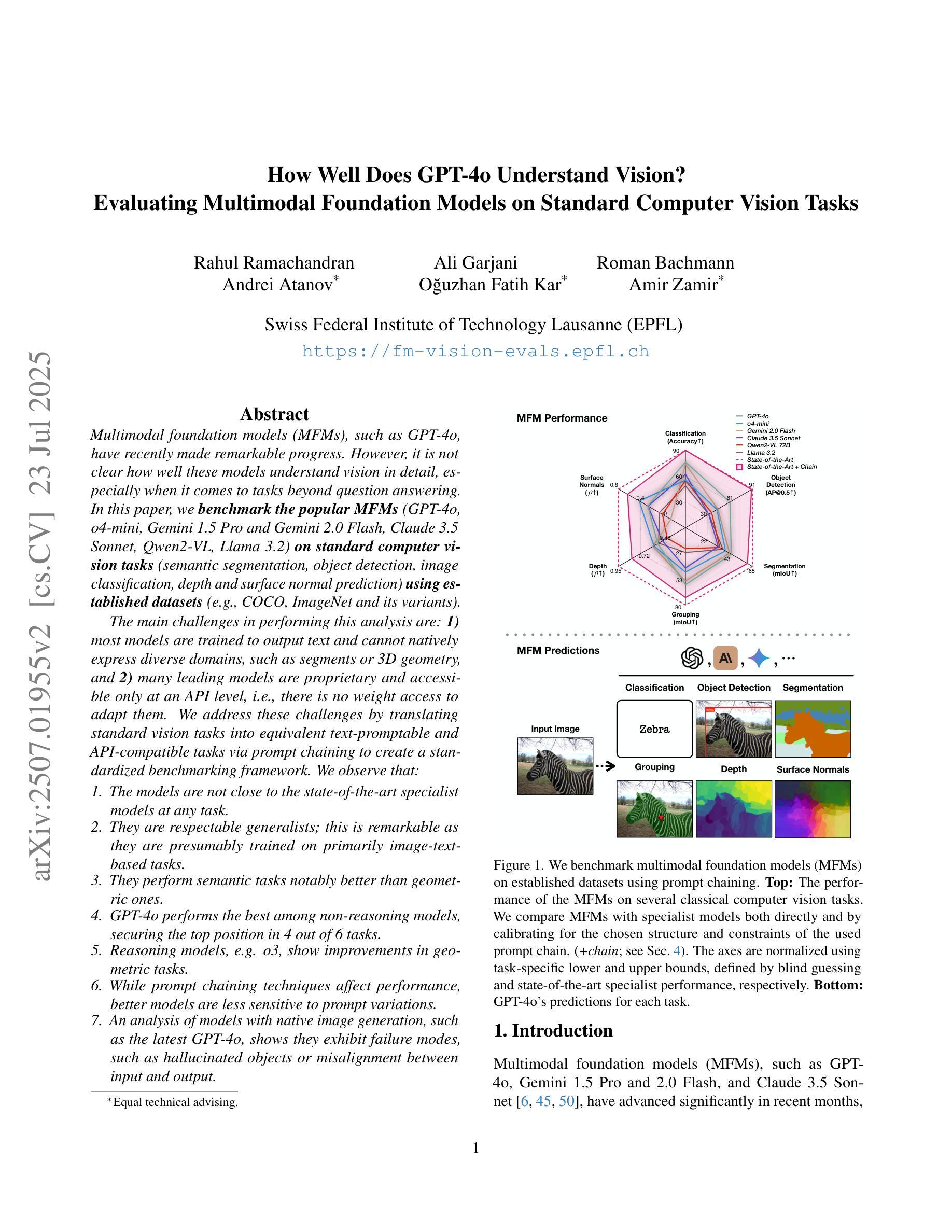
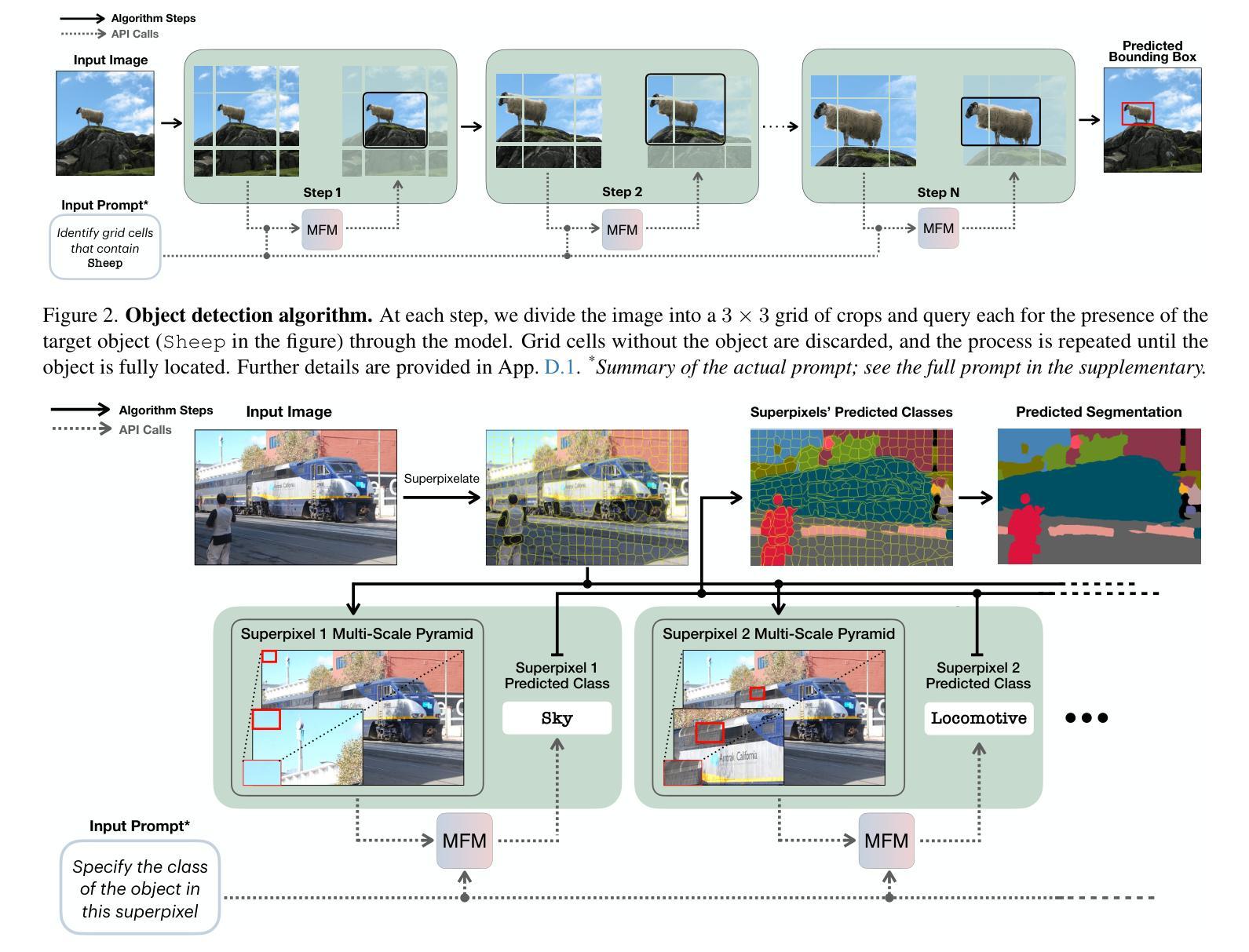
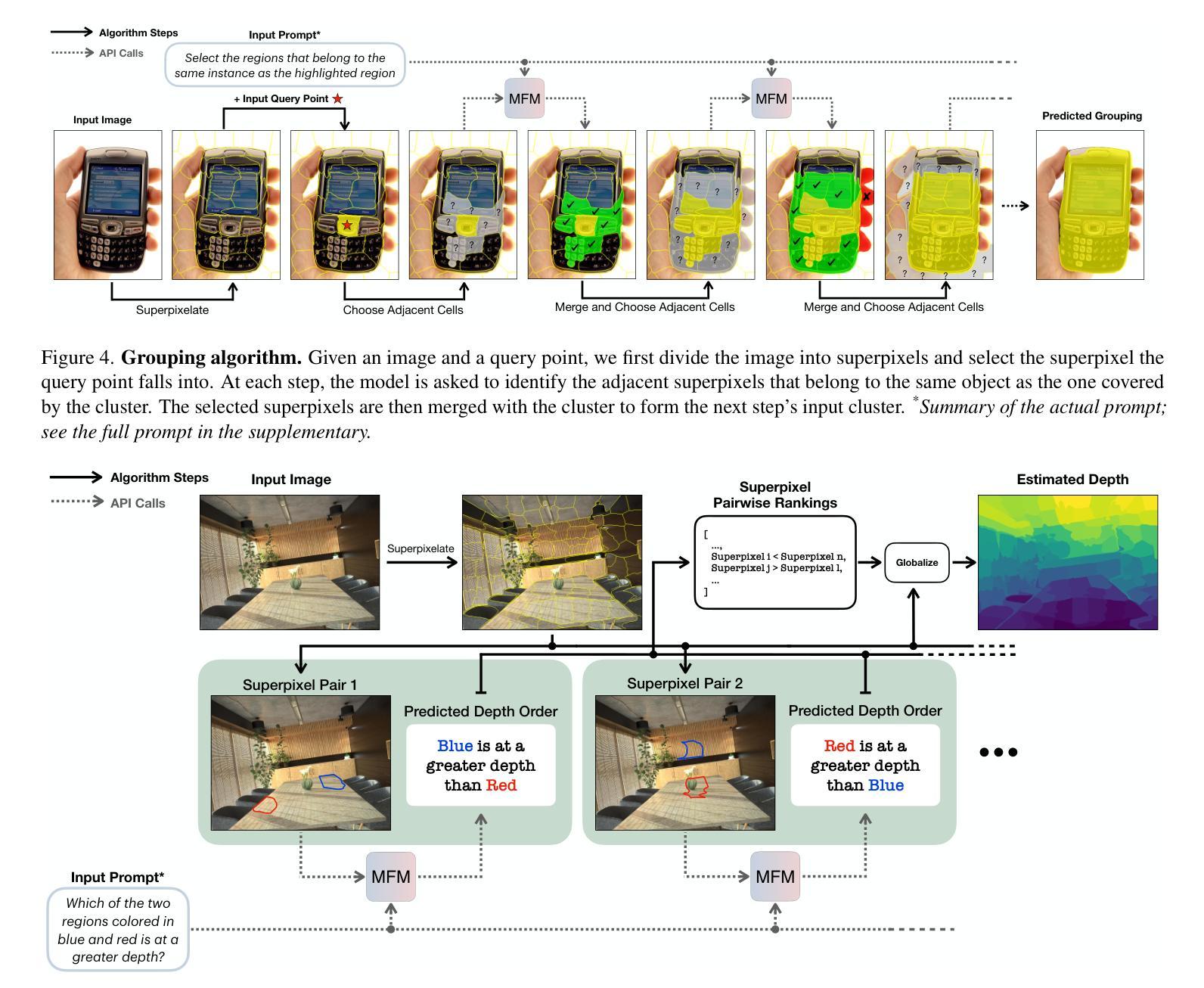
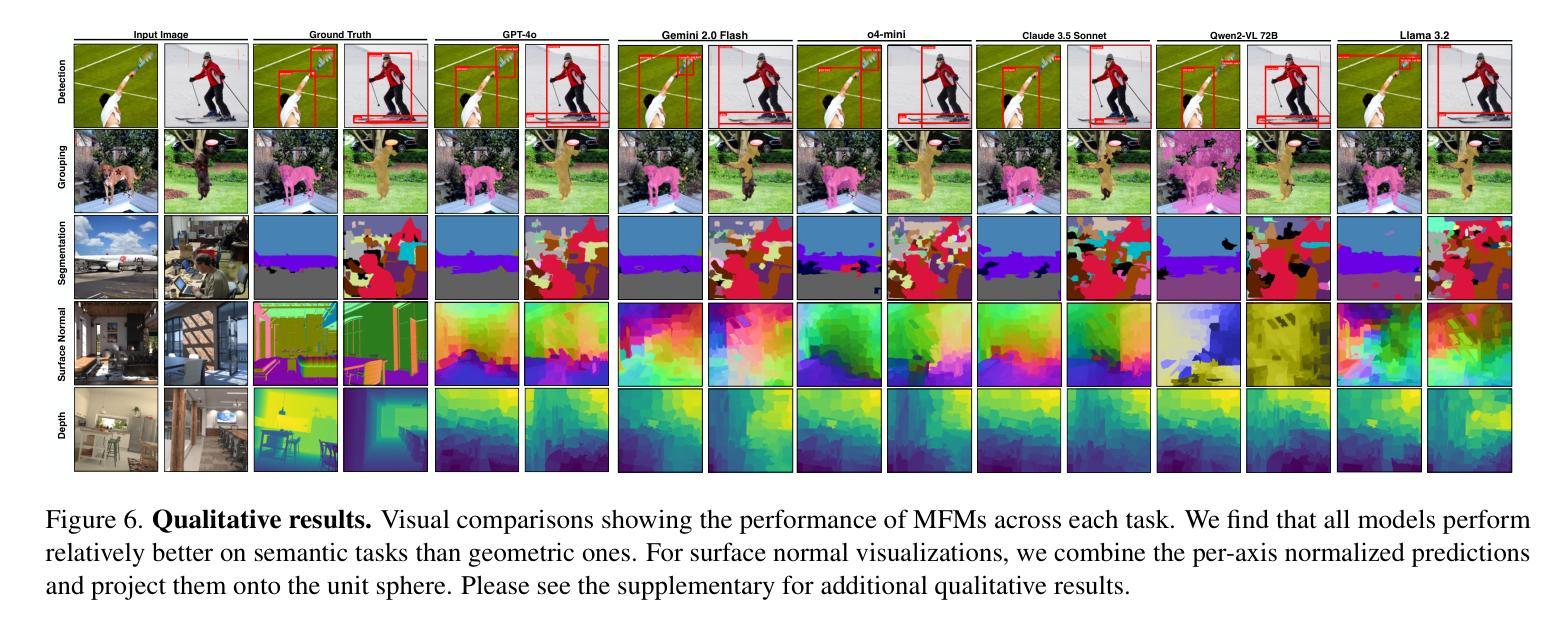
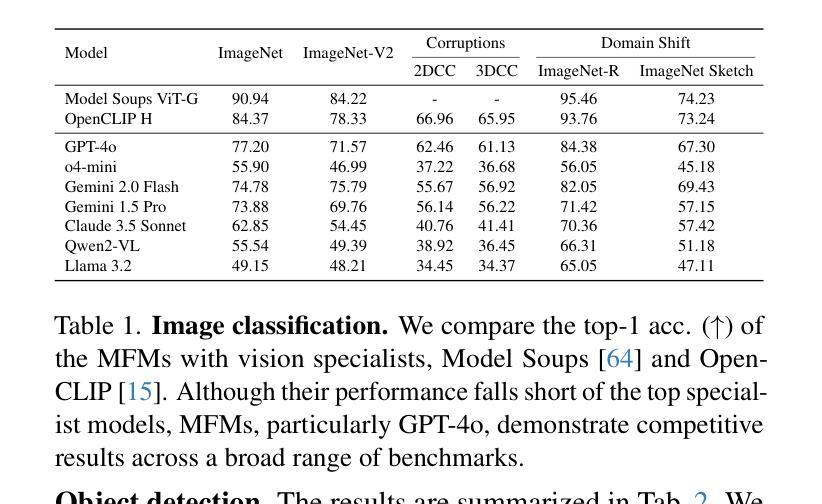
How Well Does GPT-4o Understand Vision? Evaluating Multimodal Foundation Models on Standard Computer Vision Tasks
Authors:Rahul Ramachandran, Ali Garjani, Roman Bachmann, Andrei Atanov, Oğuzhan Fatih Kar, Amir Zamir
Multimodal foundation models, such as GPT-4o, have recently made remarkable progress, but it is not clear where exactly these models stand in terms of understanding vision. In this paper, we benchmark the performance of popular multimodal foundation models (GPT-4o, o4-mini, Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemini 2.0 Flash, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Qwen2-VL, Llama 3.2) on standard computer vision tasks (semantic segmentation, object detection, image classification, depth and surface normal prediction) using established datasets (e.g., COCO, ImageNet and its variants, etc). The main challenges to performing this are: 1) most models are trained to output text and cannot natively express versatile domains, such as segments or 3D geometry, and 2) many leading models are proprietary and accessible only at an API level, i.e., there is no weight access to adapt them. We address these challenges by translating standard vision tasks into equivalent text-promptable and API-compatible tasks via prompt chaining to create a standardized benchmarking framework. We observe that 1) the models are not close to the state-of-the-art specialist models at any task. However, 2) they are respectable generalists; this is remarkable as they are presumably trained on primarily image-text-based tasks. 3) They perform semantic tasks notably better than geometric ones. 4) While the prompt-chaining techniques affect performance, better models exhibit less sensitivity to prompt variations. 5) GPT-4o performs the best among non-reasoning models, securing the top position in 4 out of 6 tasks, 6) reasoning models, e.g. o3, show improvements in geometric tasks, and 7) a preliminary analysis of models with native image generation, like the latest GPT-4o, shows they exhibit quirks like hallucinations and spatial misalignments.
最近,像GPT-4o这样的多模态基础模型取得了显著的进步,但在视觉理解方面,这些模型的确切表现尚不清楚。在本文中,我们在标准计算机视觉任务(如语义分割、目标检测、图像分类、深度和表面法线预测)上,使用已建立的数据集(例如COCO、ImageNet及其变体等)对流行的多模态基础模型(GPT-4o、o4-mini、Gemini 1.5 Pro和Gemini 2.0 Flash、Claude 3.5 Sonnet、Qwen2-VL、Llama 3.2)进行了基准测试。执行此操作的主要挑战是:1)大多数模型被训练用于输出文本,无法原生表达诸如片段或3D几何等多样领域;2)许多领先的模型是专有模型,只能通过API级别访问,即无法获取其权重以进行适应。我们通过将标准视觉任务通过提示链转化为等效的文本提示和API兼容的任务,来创建标准化的基准测试框架,以解决这些挑战。我们的观察是:1)这些模型在任何任务上都未接近最先进的专家模型;然而,2)它们是相当不错的通用模型;这尤为显著,因为它们的训练主要集中在基于图像文本的任务上。3)它们执行语义任务明显比几何任务更好。4)虽然提示链技术会影响性能,但更好的模型对提示变化的敏感性较低。5)GPT-4o在非推理模型中表现最佳,在6个任务中的4个中位居榜首。6)推理模型(例如o3)在几何任务中显示出改进,7)对具有原生图像生成的模型(如最新的GPT-4o)的初步分析显示,它们具有诸如幻觉和空间错位等特性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page at https://fm-vision-evals.epfl.ch/
Summary
本文评估了多款流行的多模态基础模型(如GPT-4o、o4-mini、Gemini系列等)在标准计算机视觉任务上的表现。通过采用特定的提示链技术,将标准的视觉任务转化为文本提示和API兼容的任务,从而建立了一个标准化的评估框架。研究结果显示,这些模型虽在各项任务上均未达到最佳状态,但在多项任务上表现出较好的通用性能。其中GPT-4o在非推理模型中表现最佳,并在四项任务中位列第一。同时,具有原生图像生成功能的模型存在诸如幻觉和空间错位等问题。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态基础模型在计算机视觉任务上的表现被评估,涉及语义分割、目标检测、图像分类、深度预测和表面法线预测等任务。
- 面临的主要挑战是模型原生表达能力的局限性和专有模型的权重不可访问性。
- 通过提示链技术,将标准视觉任务转化为文本提示和API兼容的任务,建立了标准化的评估框架。
- 这些模型虽未接近专业模型的表现,但在多项任务上展现出良好的通用性能。
- GPT-4o在非推理模型中表现最佳,在四项任务中位列第一。
- 推理模型在几何任务上有所改善。
点此查看论文截图
Unable to Forget: Proactive Interference Reveals Working Memory Limits in LLMs Beyond Context Length
Authors:Chupei Wang, Jiaqiu Vince Sun
Information retrieval in Large Language Models (LLMs) is increasingly recognized as intertwined with generation capabilities rather than mere lookup. While longer contexts are often assumed to improve retrieval, the effects of intra-context interference remain understudied. To address this, we adapt the proactive interference (PI) paradigm from cognitive science, where earlier information disrupts recall of newer updates. In humans, susceptibility to such interference is inversely linked to working memory capacity. We introduce PI-LLM, an evaluation that sequentially streams semantically related key-value updates and queries only the final values. Although these final values are clearly positioned just before the query, LLM retrieval accuracy declines log-linearly toward zero as interference accumulates; errors arise from retrieving previously overwritten values. Attempts to mitigate interference via prompt engineering (e.g., instructing models to ignore earlier input) yield limited success. These findings reveal a fundamental constraint on LLMs’ ability to disentangle interference and flexibly manipulate information, suggesting a working memory bottleneck beyond mere context access. This calls for approaches that strengthen models’ ability to suppress irrelevant content during retrieval.
在大型语言模型(LLM)中,信息检索与生成能力的相互交织越来越被人们所认识,而不仅仅是简单的查找。虽然常常假设较长的上下文环境可以提高检索效果,但关于语境内部干扰的影响研究仍然不足。为了解决这个问题,我们从认知科学中采用了主动干扰(PI)范式,其中早期信息会干扰对更新的回忆。在人类中,对这种干扰的敏感性是与工作记忆容量成反比的。我们引入了PI-LLM评估方法,该方法按顺序流式传输语义相关的键值更新,并仅查询最终值。尽管这些最终值明确地定位在查询之前,但随着干扰的累积,LLM的检索准确率以对数线性方式下降到零;错误源自于检索先前覆盖的值。尝试通过提示工程(例如指导模型忽略早期输入)来减轻干扰取得了有限的成功。这些发现揭示了LLM在解开干扰和灵活操作信息方面的基本约束,表明存在一个工作记忆瓶颈,超出了简单的上下文访问。这要求采用加强模型在检索过程中抑制无关内容的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025 Workshop on Long Context Foundation Models (ICFM). Code: https://github.com/zhuangziGiantfish/Unable-to-Forget
摘要
LLM中的信息检索不再仅仅是查找,而是与生成能力紧密相连。尽管长文本背景通常被认为能提高检索效果,但关于内部上下文干扰的影响尚缺乏研究。为了解决这个问题,我们从认知科学中引入了主动干扰(PI)的概念,即早期信息会干扰对最新更新的回忆。在人类中,对这类干扰的敏感性是与工作记忆容量成反比的。我们提出了PI-LLM评估方法,该方法按顺序流式传输语义相关的键值更新,并仅查询最终值。尽管这些最终值明确地位于查询之前,但随着干扰的累积,LLM的检索准确率会以对数线性方式降低到零;错误来自于检索到先前被覆盖的值。尝试通过提示工程(例如指导模型忽略早期输入)来减轻干扰的效果有限。这些发现揭示了一个基本限制:LLM在分离干扰和灵活操纵信息方面存在工作记忆瓶颈,这不仅仅是访问上下文的问题。这要求采用加强模型在检索过程中抑制无关内容的方法。
关键见解
- 信息检索在LLM中不再仅是查找,而是与生成能力紧密相连。
- 长文本背景虽有助于提高检索效果,但内部上下文干扰的影响尚待研究。
- 主动干扰(PI)概念对于理解LLM的检索能力很重要,特别是在处理新信息和旧信息之间的干扰时。
- 人类对主动干扰的敏感性与工作记忆容量成反比。
- LLM在应对干扰信息时存在工作记忆瓶颈,这影响了其检索准确性。
- 尝试通过提示工程来减轻干扰的效果有限。
点此查看论文截图

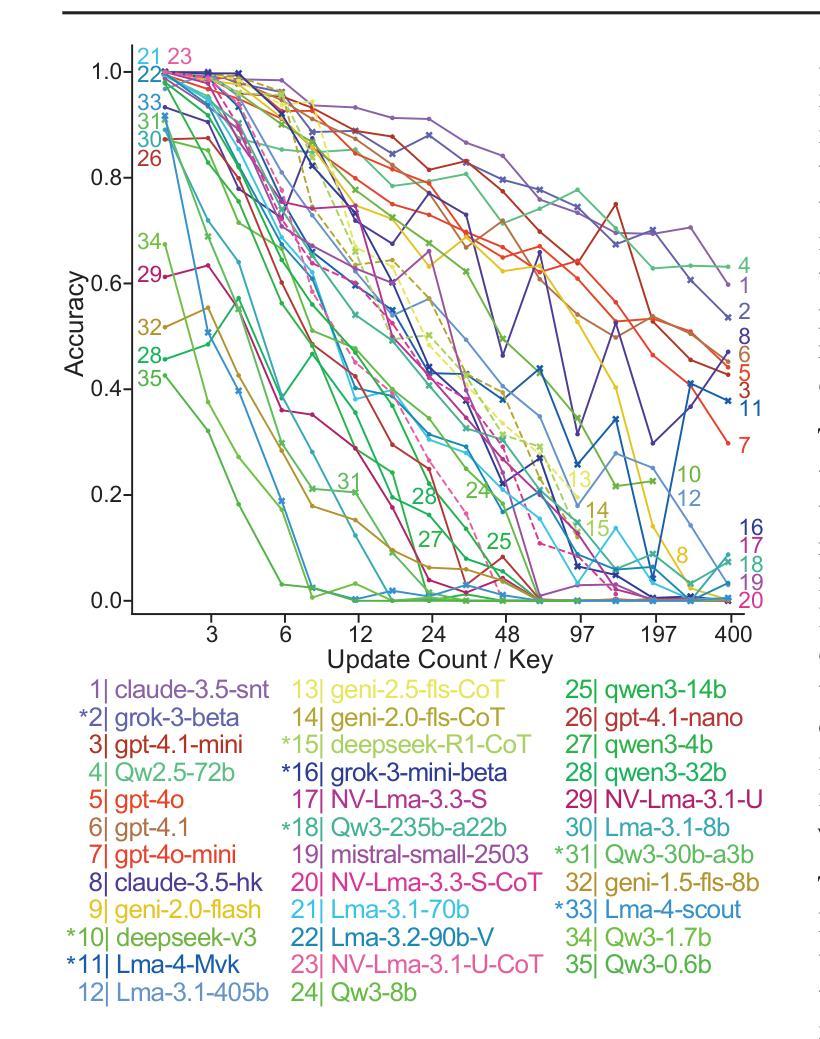

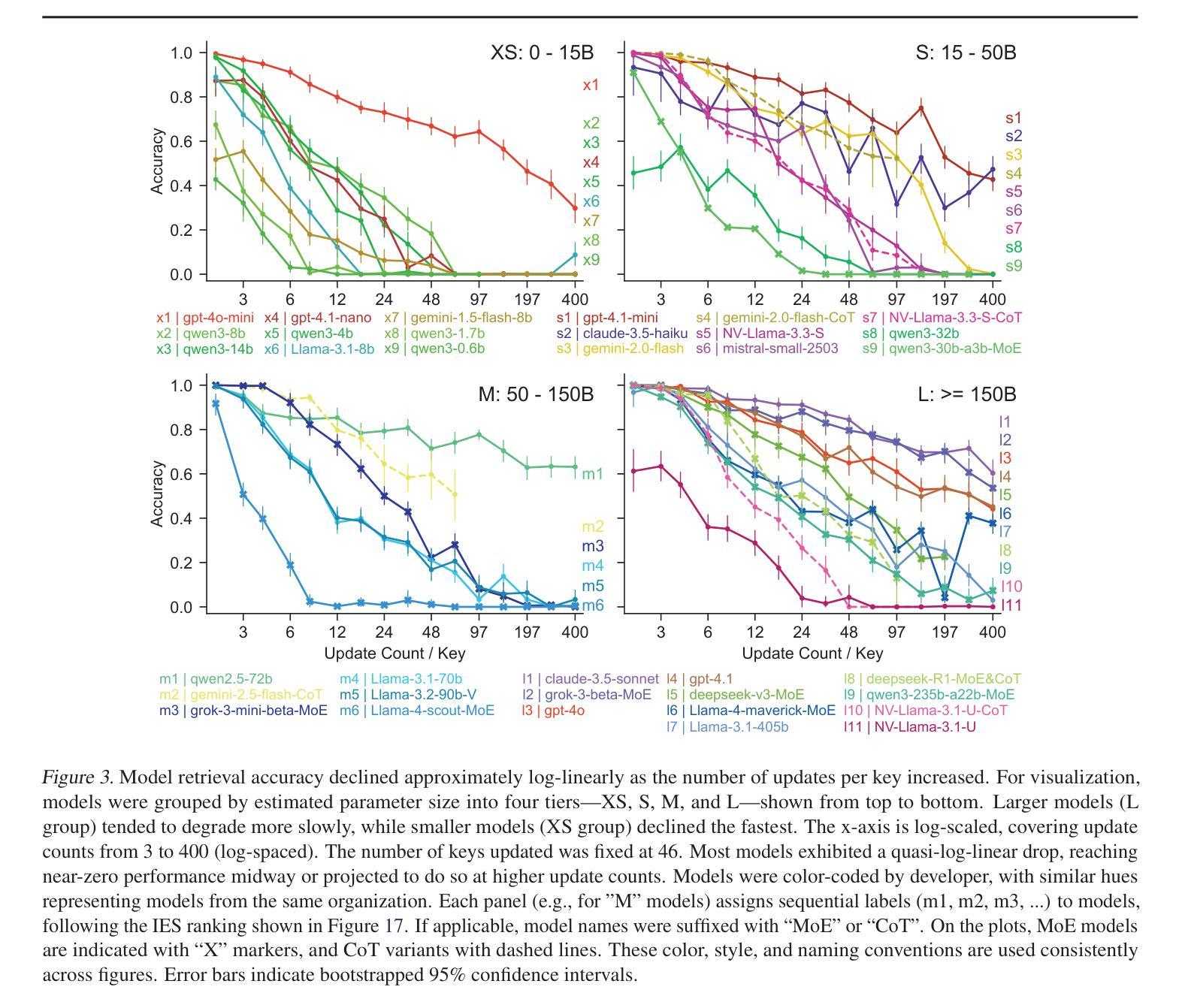
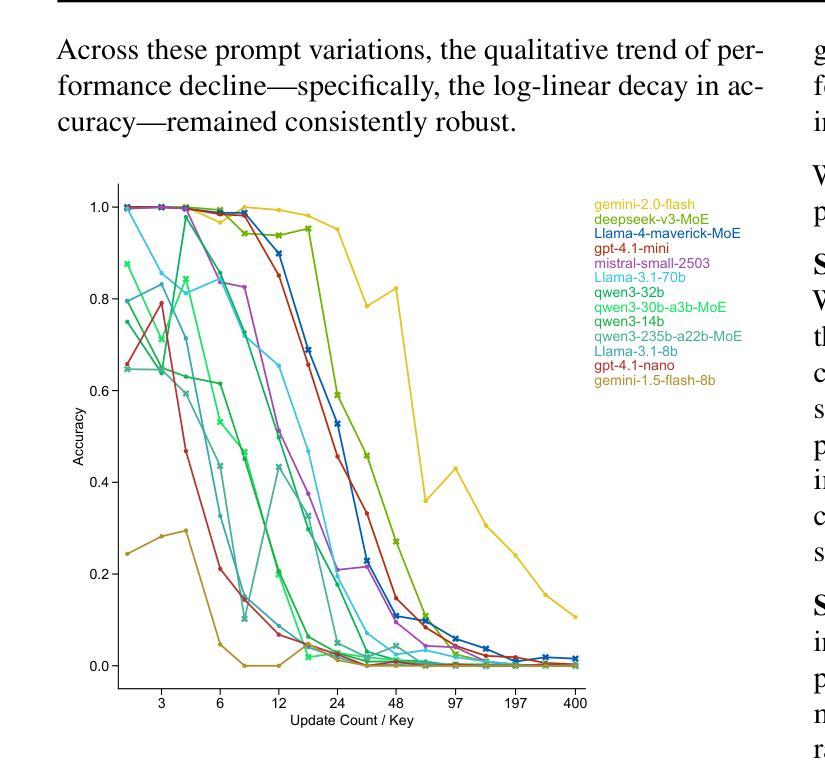
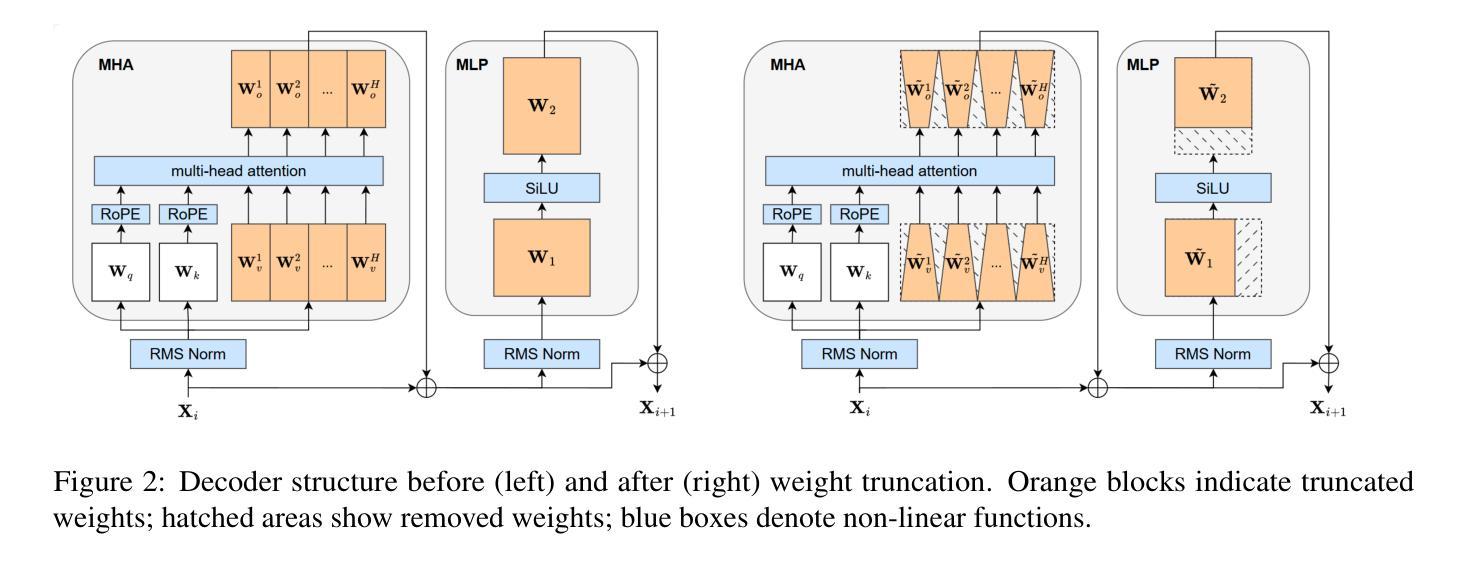
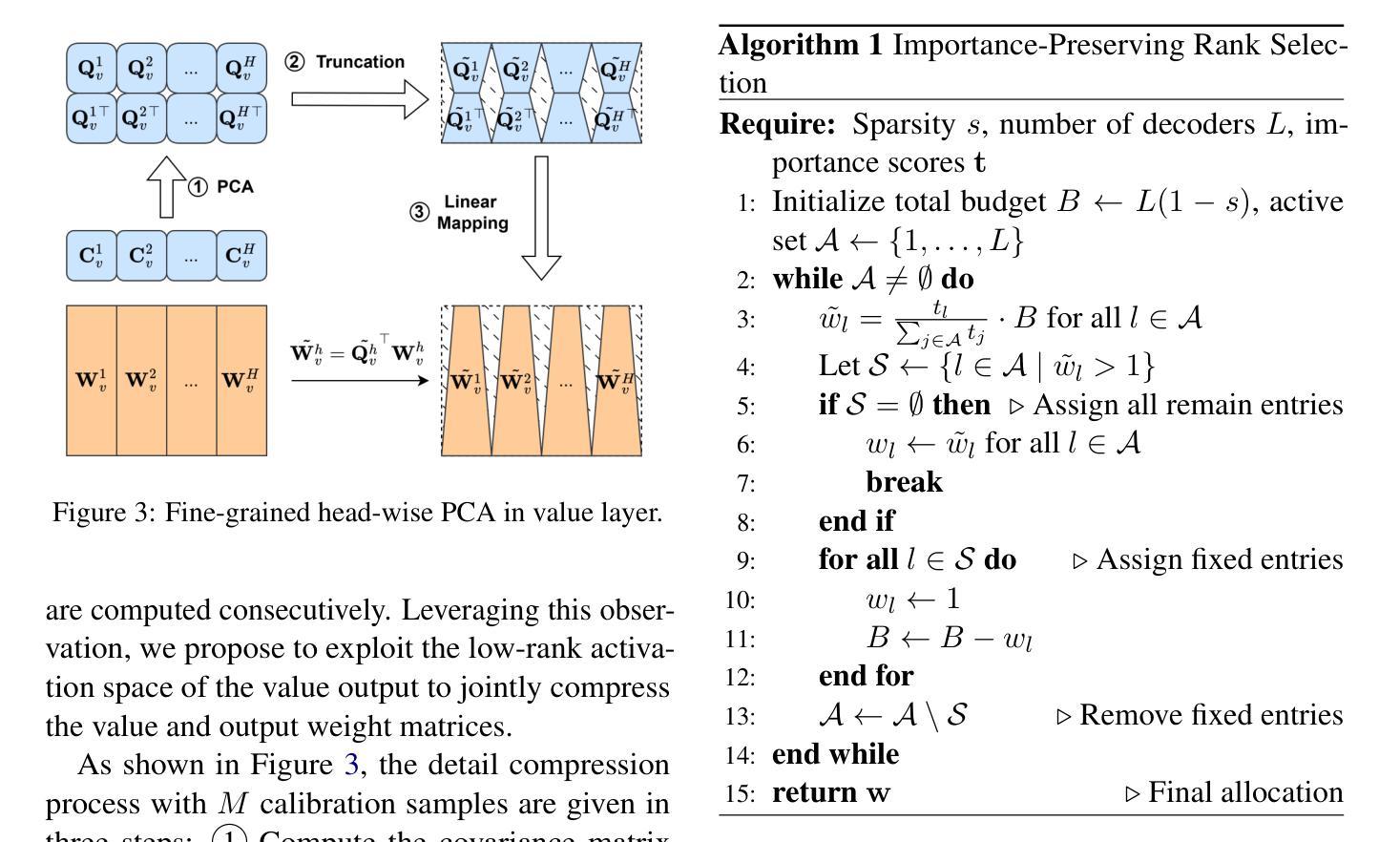
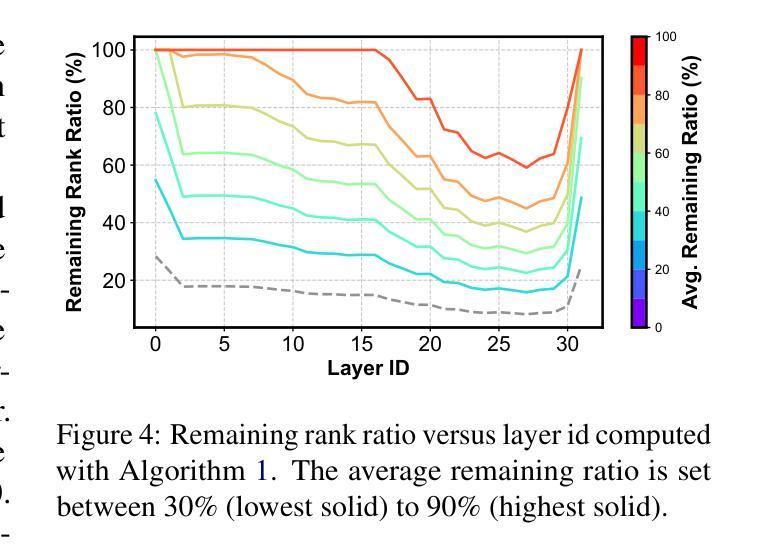
FLAT-LLM: Fine-grained Low-rank Activation Space Transformation for Large Language Model Compression
Authors:Jiayi Tian, Ryan Solgi, Jinming Lu, Yifan Yang, Hai Li, Zheng Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled remarkable progress in natural language processing, yet their high computational and memory demands pose challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments. Although recent low-rank decomposition methods offer a promising path for structural compression, they often suffer from accuracy degradation, expensive calibration procedures, and result in inefficient model architectures that hinder real-world inference speedups. In this paper, we propose FLAT-LLM, a fast and accurate, training-free structural compression method based on fine-grained low-rank transformations in the activation space. Specifically, we reduce the hidden dimension by transforming the weights using truncated eigenvectors computed via head-wise Principal Component Analysis, and employ a greedy budget redistribution strategy to adaptively allocate ranks across decoders. FLAT-LLM achieves efficient and effective weight compression without recovery fine-tuning, which could complete the calibration within a few minutes. Evaluated across 5 models and 11 datasets, FLAT-LLM outperforms structural pruning baselines in generalization and downstream performance, while delivering inference speedups over decomposition-based methods.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理方面取得了显著的进步,然而它们对计算和内存的高需求给资源受限环境中的部署带来了挑战。尽管最近的低秩分解方法为结构压缩提供了一条有前景的道路,但它们往往存在精度下降、校准程序昂贵的问题,并导致模型架构效率低下,阻碍了现实世界中的推理速度提升。在本文中,我们提出了FLAT-LLM,这是一种快速且准确的无训练结构压缩方法,基于激活空间中的精细低秩转换。具体来说,我们通过头主成分分析计算得到的截断特征向量来转换权重,降低隐藏维度,并采用贪婪预算再分配策略来自适应地在解码器之间分配等级。FLAT-LLM实现了高效有效的权重压缩,无需恢复微调,可以在几分钟内完成校准。在5个模型和11个数据集上的评估表明,FLAT-LLM在通用性和下游性能方面的表现优于结构剪枝基线,同时在基于分解的方法上实现了推理速度的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理领域取得了显著进展,但其高计算需求和内存需求使其在资源受限的环境中部署面临挑战。本文提出一种基于精细粒度低秩转换的激活空间快速准确的无训练结构压缩方法FLAT-LLM。通过利用头主成分分析计算截断特征向量来转换权重,并采用贪婪预算重新分配策略自适应地调整解码器之间的等级,实现了无需恢复微调的有效权重压缩。在5个模型和11个数据集上的评估表明,FLAT-LLM在泛化和下游性能上优于结构剪枝基线,并且在基于分解的方法上实现了推理速度的提升。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在自然语言处理上取得显著进展,但资源受限环境的部署存在挑战。
- FLAT-LLM是一种基于激活空间的快速准确的无训练结构压缩方法。
- FLAT-LLM利用头主成分分析进行权重转换,并采用贪婪预算重新分配策略。
- FLAT-LLM实现了无需恢复细调的权重压缩。
- FLAT-LLM在多个模型和数据集上的性能优于结构剪枝基线。
- FLAT-LLM提升了推理速度,相比基于分解的方法有优势。
点此查看论文截图
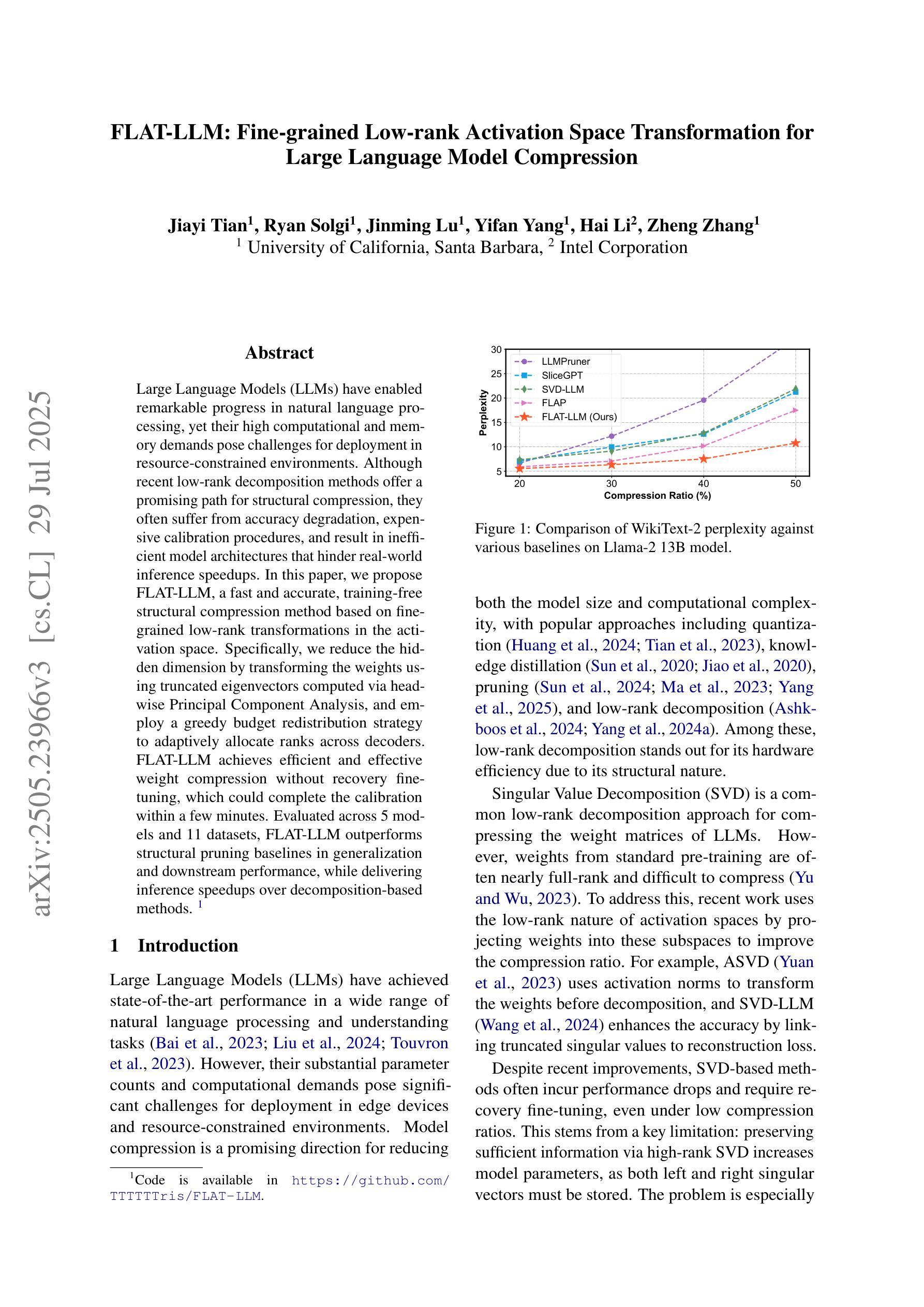
How Can I Publish My LLM Benchmark Without Giving the True Answers Away?
Authors:Takashi Ishida, Thanawat Lodkaew, Ikko Yamane
Publishing a large language model (LLM) benchmark on the Internet risks contaminating future LLMs: the benchmark may be unintentionally (or intentionally) used to train or select a model. A common mitigation is to keep the benchmark private and let participants submit their models or predictions to the organizers. However, this strategy will require trust in a single organization and still permits test-set overfitting through repeated queries. To overcome this issue, we propose a way to publish benchmarks without completely disclosing the ground-truth answers to the questions, while still maintaining the ability to openly evaluate LLMs. Our main idea is to inject randomness to the answers by preparing several logically correct answers, and only include one of them as the solution in the benchmark. This reduces the best possible accuracy, i.e., Bayes accuracy, of the benchmark. Not only is this helpful to keep us from disclosing the ground truth, but this approach also offers a test for detecting data contamination. In principle, even fully capable models should not surpass the Bayes accuracy. If a model surpasses this ceiling despite this expectation, this is a strong signal of data contamination. We present experimental evidence that our method can detect data contamination accurately on a wide range of benchmarks, models, and training methodologies.
在互联网上发布大型语言模型(LLM)的基准测试存在一定的风险,可能会污染未来的LLM:该基准测试可能会被无意中(或故意)用于训练或选择模型。一种常见的缓解方法是保持基准测试私密,让参与者向组织者提交他们的模型或预测。然而,这种策略需要信任单一组织,并且仍然允许通过重复查询来进行测试集过度拟合。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种发布基准测试的方法,而无需完全披露问题的真实答案,同时仍能够公开评估LLM。我们的主要想法是通过准备几个逻辑上正确的答案并引入随机性,然后将其中只有一个作为基准测试中的解决方案。这降低了基准测试的最佳可能精度,即贝叶斯精度。这不仅有助于我们避免透露真实答案,而且这种方法还提供了一种检测数据污染的方法。原则上,即使是非常完善的模型也不应超过贝叶斯精度。如果一个模型超出了这个上限,尽管有这样的预期,这也是数据污染的一个强烈信号。我们提供的实验证据表明,我们的方法可以在广泛的基准测试、模型和训练方法论中准确地检测数据污染。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended version of the paper presented as an Oral at the ICML 2025 Workshop on the Impact of Memorization on Trustworthy Foundation Models
Summary
本文讨论了在互联网上发布大型语言模型(LLM)基准测试的风险,可能会污染未来的LLM。为解决这个问题,提出了一种新的基准测试发布方法,该方法通过准备多个逻辑正确的答案并随机选择其中之一作为解决方案来注入随机性,以维持公开评估LLM的能力的同时不透露问题的真实答案。这种方法不仅有助于不透露真实答案,而且还为检测数据污染提供了一个测试。实验证明,该方法能在各种基准测试、模型和训练方法论中准确检测数据污染。
Key Takeaways
- 发布LLM基准测试可能存在污染未来LLM的风险。
- 常用的缓解策略是保持基准测试私有,但这种方法需要信任单一组织并可能允许通过重复查询进行过度拟合。
- 提出了一种新的基准测试发布方法,通过注入随机性来公开评估LLM,同时不透露问题的真实答案。
- 该方法通过准备多个逻辑正确的答案,只选择其中之一作为解决方案来实现随机性。
- 该方法不仅有助于防止透露真实答案,而且提供了一个检测数据污染的信号:模型的表现如果超越了根据贝叶斯准确率预期的水平,则可能是数据污染的信号。
- 实验证明该方法可在广泛的基准测试、模型和训练方法论中准确检测数据污染。
- 该方法有助于保持基准测试的公正性和透明度,同时减少数据污染的风险。
点此查看论文截图


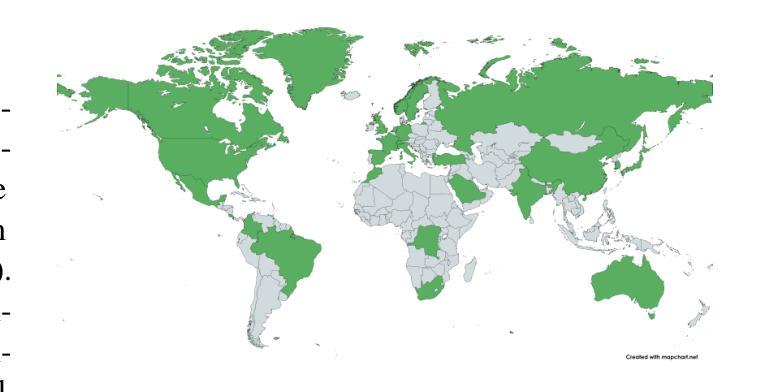
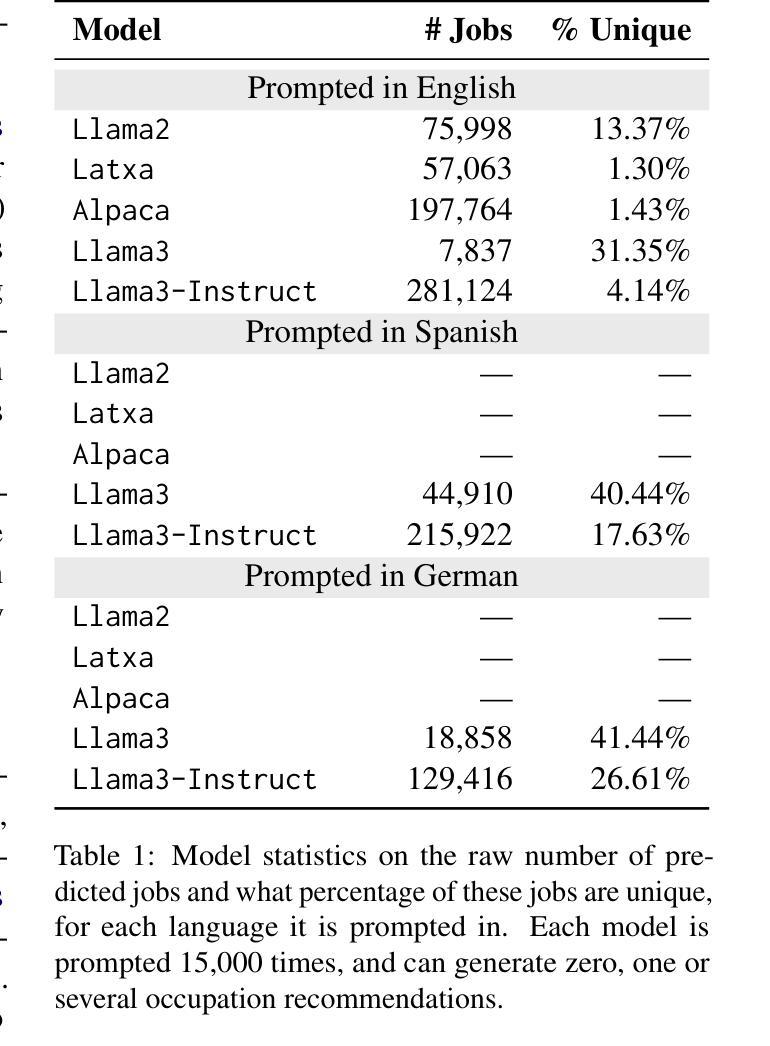
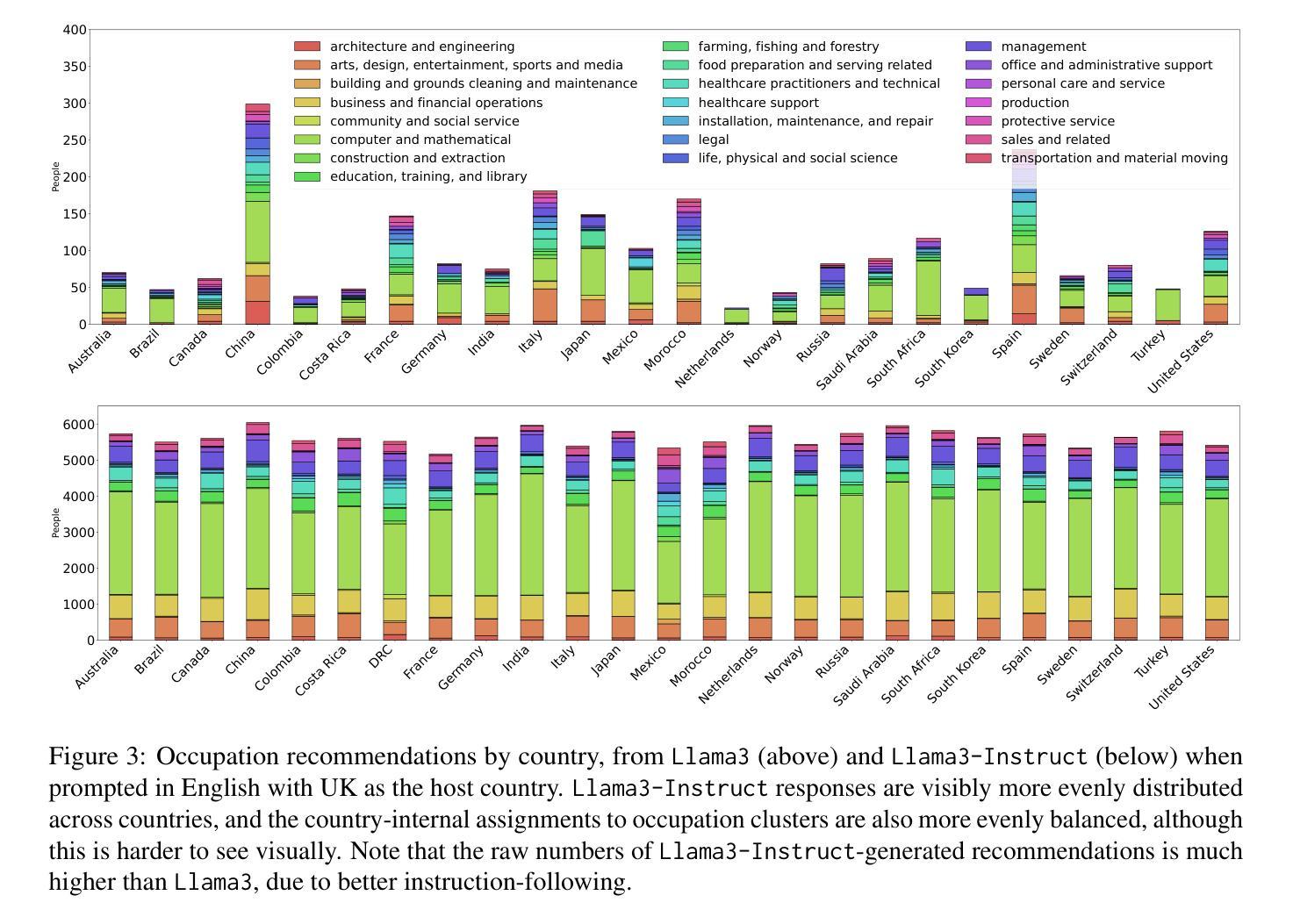
Colombian Waitresses y Jueces canadienses: Gender and Country Biases in Occupation Recommendations from LLMs
Authors:Elisa Forcada Rodríguez, Olatz Perez-de-Viñaspre, Jon Ander Campos, Dietrich Klakow, Vagrant Gautam
One of the goals of fairness research in NLP is to measure and mitigate stereotypical biases that are propagated by NLP systems. However, such work tends to focus on single axes of bias (most often gender) and the English language. Addressing these limitations, we contribute the first study of multilingual intersecting country and gender biases, with a focus on occupation recommendations generated by large language models. We construct a benchmark of prompts in English, Spanish and German, where we systematically vary country and gender, using 25 countries and four pronoun sets. Then, we evaluate a suite of 5 Llama-based models on this benchmark, finding that LLMs encode significant gender and country biases. Notably, we find that even when models show parity for gender or country individually, intersectional occupational biases based on both country and gender persist. We also show that the prompting language significantly affects bias, and instruction-tuned models consistently demonstrate the lowest and most stable levels of bias. Our findings highlight the need for fairness researchers to use intersectional and multilingual lenses in their work.
自然语言处理(NLP)的公平性研究的目标之一是衡量和减轻由NLP系统传播的刻板偏见。然而,这类工作往往侧重于单一偏见轴(通常是性别)和英语语言。为了解决这个问题,我们对多语言交叉国家与性别偏见进行了首次研究,重点研究大型语言模型生成的职业推荐。我们在英语、西班牙语和德语中构建了基准提示,系统地改变国家和性别,使用25个国家和四组代词。然后,我们在这一基准上对五个基于Llama的模型进行了评估,发现大型语言模型包含了重要的性别和国家偏见。值得注意的是,即使模型在单独考虑性别或国家时表现出公平性,基于国家和性别的交叉职业偏见仍然存在。我们还表明,提示语言对偏见有很大影响,而指令调整模型则始终表现出最低且最稳定的偏见水平。我们的研究结果强调,公平研究人员需要在工作中使用交叉和多语言的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Workshop on Gender Bias in Natural Language Processing at ACL 2025
Summary
在这个研究中,作者衡量并减轻了由自然语言处理系统传播的职业偏见问题。他们首次进行了多语言交叉国家与性别偏见的研究,重点关注大型语言模型生成的职业推荐偏见。研究通过英语、西班牙语和德语的系统化测试,发现大型语言模型存在显著的性别和国籍偏见,即使模型在单一维度上表现出公平性,基于国家和性别的交叉偏见仍然存在。研究还显示提示语言显著影响偏见,而指令训练模型表现出的偏见程度最低且最稳定。这项研究强调公平性研究人员需要在工作中使用交叉和多语言视角。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究衡量并减轻了自然语言处理系统中的职业偏见问题。
- 研究首次进行了多语言交叉国家与性别偏见的研究。
- 研究发现大型语言模型存在显著的性别和国籍偏见。
- 即使模型在单一维度上表现出公平性,基于国家和性别的交叉偏见仍然存在。
- 提示语言显著影响偏见。
- 指令训练模型在职业推荐偏见问题上表现最佳,偏见程度最低且最稳定。
点此查看论文截图