⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
Conan: A Chunkwise Online Network for Zero-Shot Adaptive Voice Conversion
Authors:Yu Zhang, Baotong Tian, Zhiyao Duan
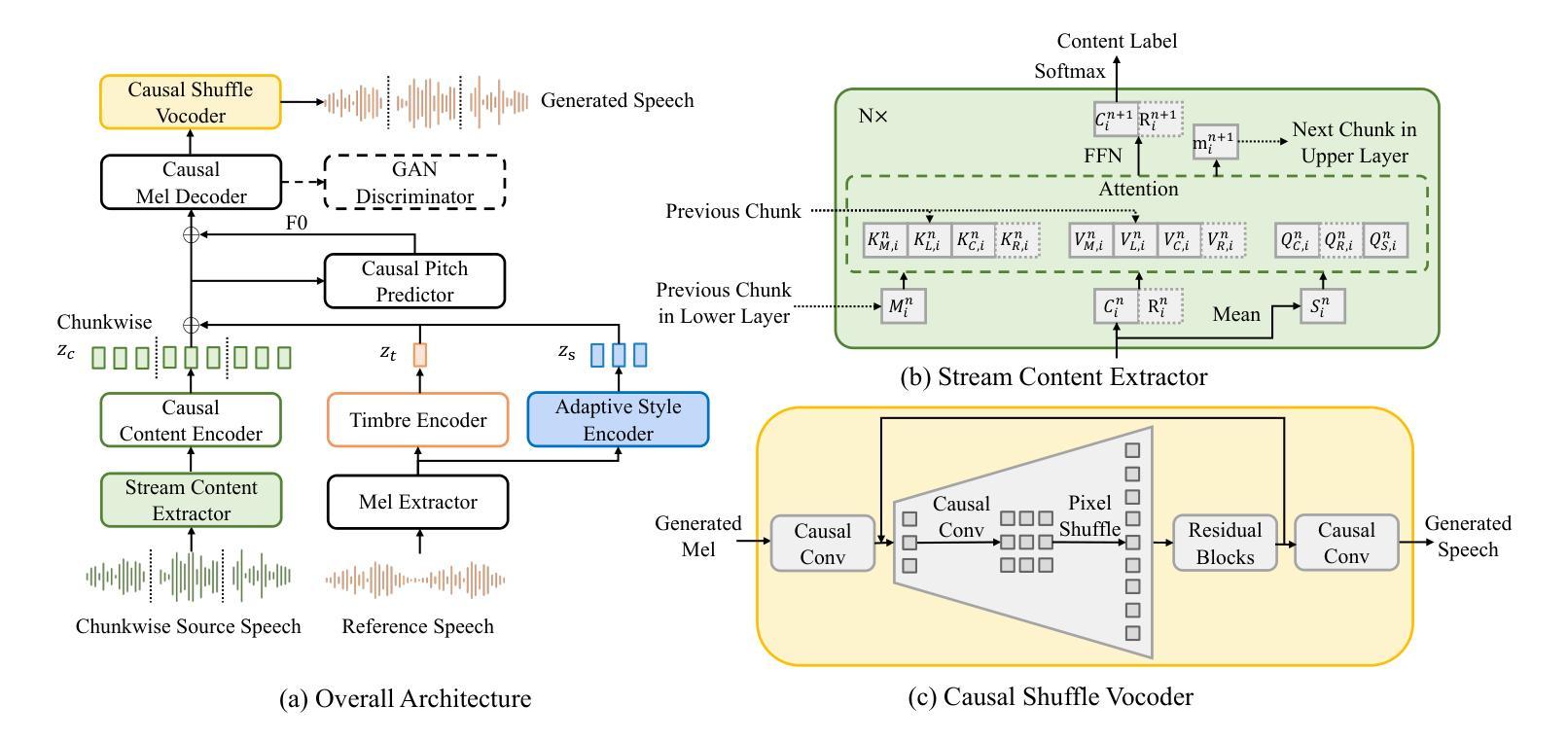
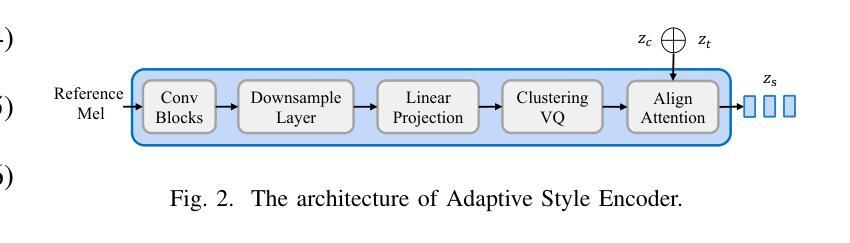
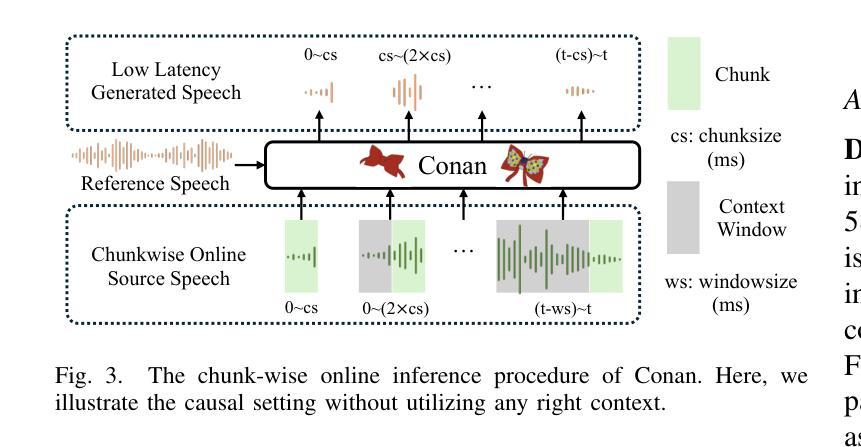
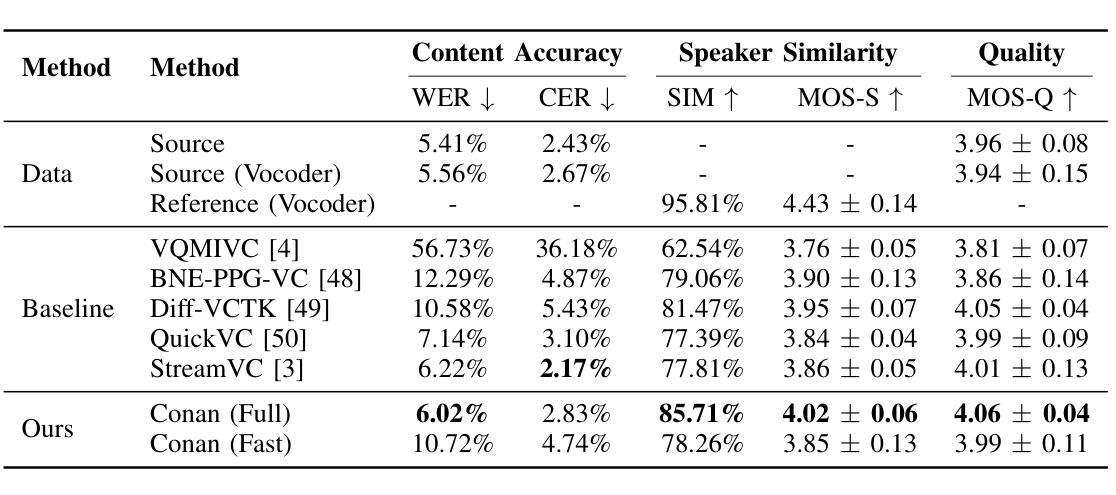
Zero-shot online voice conversion (VC) holds significant promise for real-time communications and entertainment. However, current VC models struggle to preserve semantic fidelity under real-time constraints, deliver natural-sounding conversions, and adapt effectively to unseen speaker characteristics. To address these challenges, we introduce Conan, a chunkwise online zero-shot voice conversion model that preserves the content of the source while matching the voice timbre and styles of reference speech. Conan comprises three core components: 1) a Stream Content Extractor that leverages Emformer for low-latency streaming content encoding; 2) an Adaptive Style Encoder that extracts fine-grained stylistic features from reference speech for enhanced style adaptation; 3) a Causal Shuffle Vocoder that implements a fully causal HiFiGAN using a pixel-shuffle mechanism. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that Conan outperforms baseline models in subjective and objective metrics. Audio samples can be found at https://aaronz345.github.io/ConanDemo.
零样本在线语音转换(VC)在实时通信和娱乐方面有着巨大的潜力。然而,当前的VC模型在实时约束下很难保持语义保真,实现自然转换,并有效地适应未见过的说话人特征。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Conan,这是一种分块在线零样本语音转换模型,能够保留源内容的同时匹配参考语音的音色和风格。Conan包含三个核心组件:1) 流内容提取器,它利用Emformer进行低延迟流内容编码;2) 适应性风格编码器,从参考语音中提取精细的风格特征,以增强风格适应;3) 因果洗牌编解码器,使用像素洗牌机制实现了完全因果的HiFiGAN。实验评估表明,Conan在主观和客观指标上都优于基线模型。音频样本可在https://aaronz345.github.io/ConanDemo找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
零镜头在线语音转换技术对于实时通信和娱乐领域具有巨大潜力。然而,当前模型在实时约束下难以保持语义保真、实现自然的声音转换以及有效适应未见过的说话人特征。为解决这些挑战,我们推出Conan模型,它通过三个核心组件实现分块在线零镜头语音转换:1)利用Emformer进行低延迟流式内容编码的Stream Content Extractor;2)提取参考语音中的精细风格特征的Adaptive Style Encoder,以增强风格适应性;3)使用像素混洗机制的完全因果HiFiGAN实现的Causal Shuffle Vocoder。实验评估显示,Conan在主观和客观指标上均优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 零镜头在线语音转换技术在实时通信和娱乐中具有巨大潜力。
- 当前语音转换模型面临保持语义保真、自然声音转换和适应未见说话人特征的挑战。
- Conan模型通过三个核心组件实现分块在线零镜头语音转换。
- Stream Content Extractor利用Emformer进行低延迟流式内容编码。
- Adaptive Style Encoder提取参考语音中的精细风格特征,增强风格适应性。
- Causal Shuffle Vocoder使用像素混洗机制实现完全因果HiFiGAN。
- 实验评估显示Conan在主观和客观指标上优于基准模型。
点此查看论文截图

AVFSNet: Audio-Visual Speech Separation for Flexible Number of Speakers with Multi-Scale and Multi-Task Learning
Authors:Daning Zhang, Ying Wei
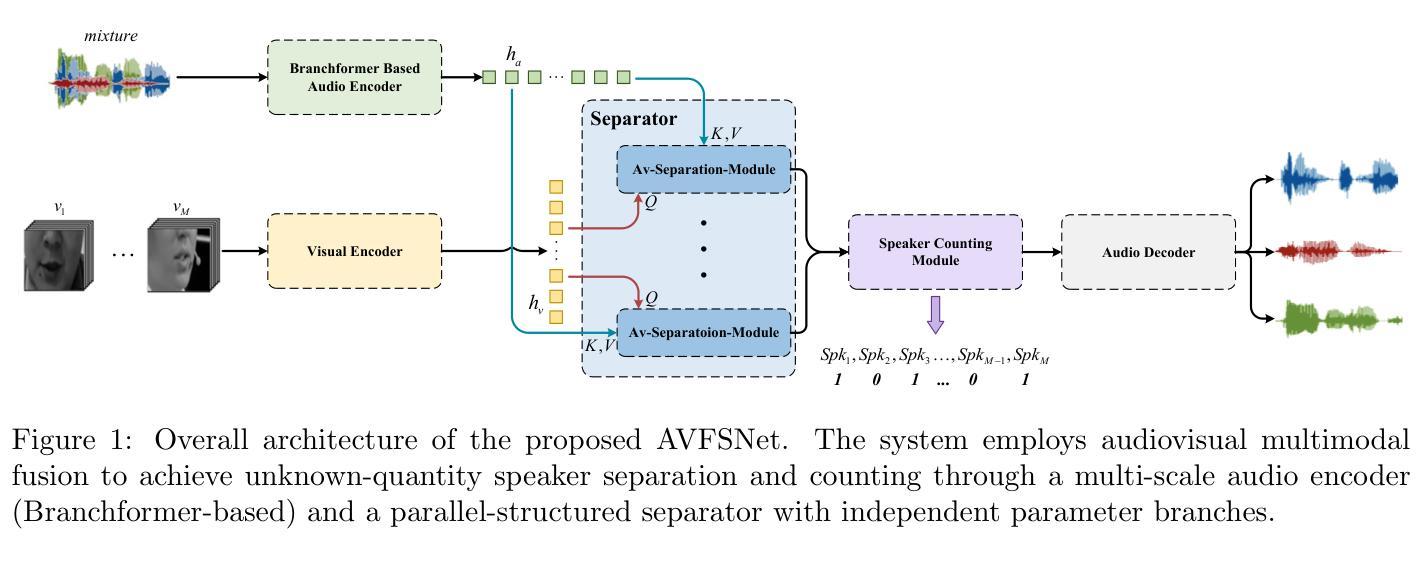
Separating target speech from mixed signals containing flexible speaker quantities presents a challenging task. While existing methods demonstrate strong separation performance and noise robustness, they predominantly assume prior knowledge of speaker counts in mixtures. The limited research addressing unknown speaker quantity scenarios exhibits significantly constrained generalization capabilities in real acoustic environments. To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes AVFSNet – an audio-visual speech separation model integrating multi-scale encoding and parallel architecture – jointly optimized for speaker counting and multi-speaker separation tasks. The model independently separates each speaker in parallel while enhancing environmental noise adaptability through visual information integration. Comprehensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that AVFSNet achieves state-of-the-art results across multiple evaluation metrics and delivers outstanding performance on diverse datasets.
从包含灵活说话人数量的混合信号中分离目标语音是一项具有挑战性的任务。尽管现有方法表现出强大的分离性能和噪声鲁棒性,但它们主要假设混合物中的说话人数量是已知的。解决未知说话人数量场景的研究有限,在真实声学环境中的泛化能力受到显著限制。为了克服这些挑战,本文提出了AVFSNet——一种视听语音分离模型,它融合了多尺度编码和并行架构,并联合优化说话人计数和多说话人分离任务。该模型并行独立地分离每个说话人,同时通过整合视觉信息提高环境噪声适应性。综合实验评估表明,AVFSNet在多个评估指标上达到最新水平,并在不同数据集上表现出卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了从包含可变说话人数量的混合信号中分离目标语音的挑战。现有方法主要假设混合信号中的说话人数量是已知的,而在面对未知说话人数量的场景时,其泛化能力受限。为克服这些挑战,本文提出了AVFSNet——一种集多尺度编码和并行架构于一体的视听语音分离模型。该模型在优化说话人计数和多说话人分离任务时,能并行独立地分离每个说话人,并通过整合视觉信息提高对环境噪声的适应性。实验评估表明,AVFSNet在多个评估指标上达到最新技术水平,并在不同数据集上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 现有语音分离方法在应对包含可变说话人数的混合信号时存在挑战。
- 大部分现有方法假设知道混合信号中的说话人数量,但在真实场景中,这一信息往往是未知的。
- AVFSNet是一种视听语音分离模型,旨在解决上述问题。
- AVFSNet通过多尺度编码和并行架构来独立分离每个说话人。
- 该模型通过整合视觉信息来提高对环境噪声的适应性。
- 实验证明AVFSNet在多个评估指标上表现优秀,达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图

Knowing When to Quit: Probabilistic Early Exits for Speech Separation
Authors:Kenny Falkær Olsen, Mads Østergaard, Karl Ulbæk, Søren Føns Nielsen, Rasmus Malik Høegh Lindrup, Bjørn Sand Jensen, Morten Mørup
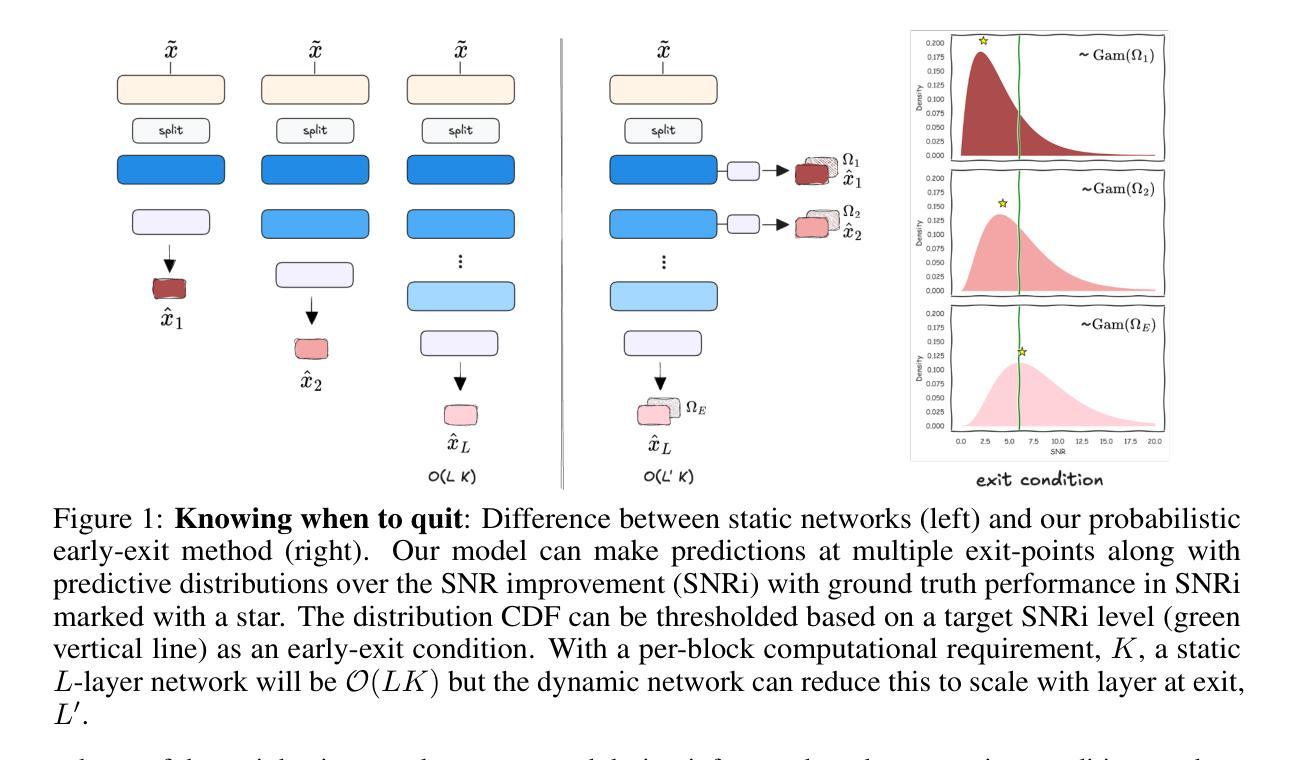
In recent years, deep learning-based single-channel speech separation has improved considerably, in large part driven by increasingly compute- and parameter-efficient neural network architectures. Most such architectures are, however, designed with a fixed compute and parameter budget, and consequently cannot scale to varying compute demands or resources, which limits their use in embedded and heterogeneous devices such as mobile phones and hearables. To enable such use-cases we design a neural network architecture for speech separation capable of early-exit, and we propose an uncertainty-aware probabilistic framework to jointly model the clean speech signal and error variance which we use to derive probabilistic early-exit conditions in terms of desired signal-to-noise ratios. We evaluate our methods on both speech separation and enhancement tasks, and we show that a single early-exit model can be competitive with state-of-the-art models trained at many compute and parameter budgets. Our framework enables fine-grained dynamic compute-scaling of speech separation networks while achieving state-of-the-art performance and interpretable exit conditions.
近年来,基于深度学习的单通道语音分离技术取得了显著的进步,这在很大程度上是由于神经网络架构的计算和参数效率不断提高。然而,大多数这样的架构都是为固定的计算和参数预算设计的,因此无法扩展到不同的计算需求或资源,这限制了它们在嵌入式和异构设备(如手机和可穿戴设备)中的应用。为了支持这些用例,我们设计了一种用于语音分离的神经网络架构,该架构能够实现提前退出,并提出了一种基于不确定性的概率框架,联合对清洁语音信号和误差方差进行建模,我们用其来推导基于所需信噪比的概率提前退出条件。我们在语音分离和增强任务上评估了我们的方法,结果表明,单个提前退出模型可以与在许多计算和参数预算上训练的最新模型相竞争。我们的框架能够在实现最先进的性能的同时,实现语音分离网络的精细动态计算缩放,并提供可解释的退出条件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近年来,基于深度学习的单通道语音分离技术有了显著的进步,这主要得益于计算和参数效率越来越高的神经网络架构。然而,大多数这样的架构都是为固定的计算和参数预算设计的,因此无法适应不同的计算需求或资源,这在嵌入式和异构设备(如手机和可穿戴设备)的使用中造成了限制。为此,我们设计了一种可用于语音分离的神经网络架构,支持提前退出机制,并提出了一种基于不确定性的概率框架,该框架能够联合建模清洁语音信号和误差方差,用于推导符合所需信噪比的概率提前退出条件。我们在语音分离和增强任务上评估了我们的方法,并证明单一提前退出模型可以与非训练时的多种计算和参数预算的最佳模型相竞争。我们的框架在达到最新性能的同时,实现了语音分离网络的精细动态计算缩放,并提供了可解释性的退出条件。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习和神经网络架构的进步显著提升了单通道语音分离技术的性能。
- 当前大多数神经网络架构固定于特定的计算和参数预算,无法适应不同资源环境。
- 提出了一个支持提前退出的神经网络架构用于语音分离。
- 引入了一个基于不确定性的概率框架,联合建模清洁语音信号和误差方差。
- 通过概率模型推导出了符合所需信噪比的提前退出条件。
- 在语音分离和增强任务上的评估显示,提前退出模型具有与非训练时的多种模型相竞争的性能。
点此查看论文截图

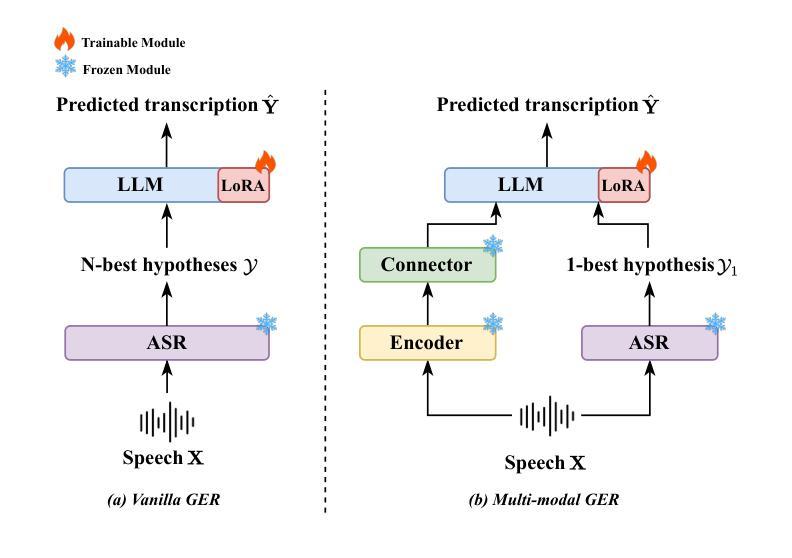
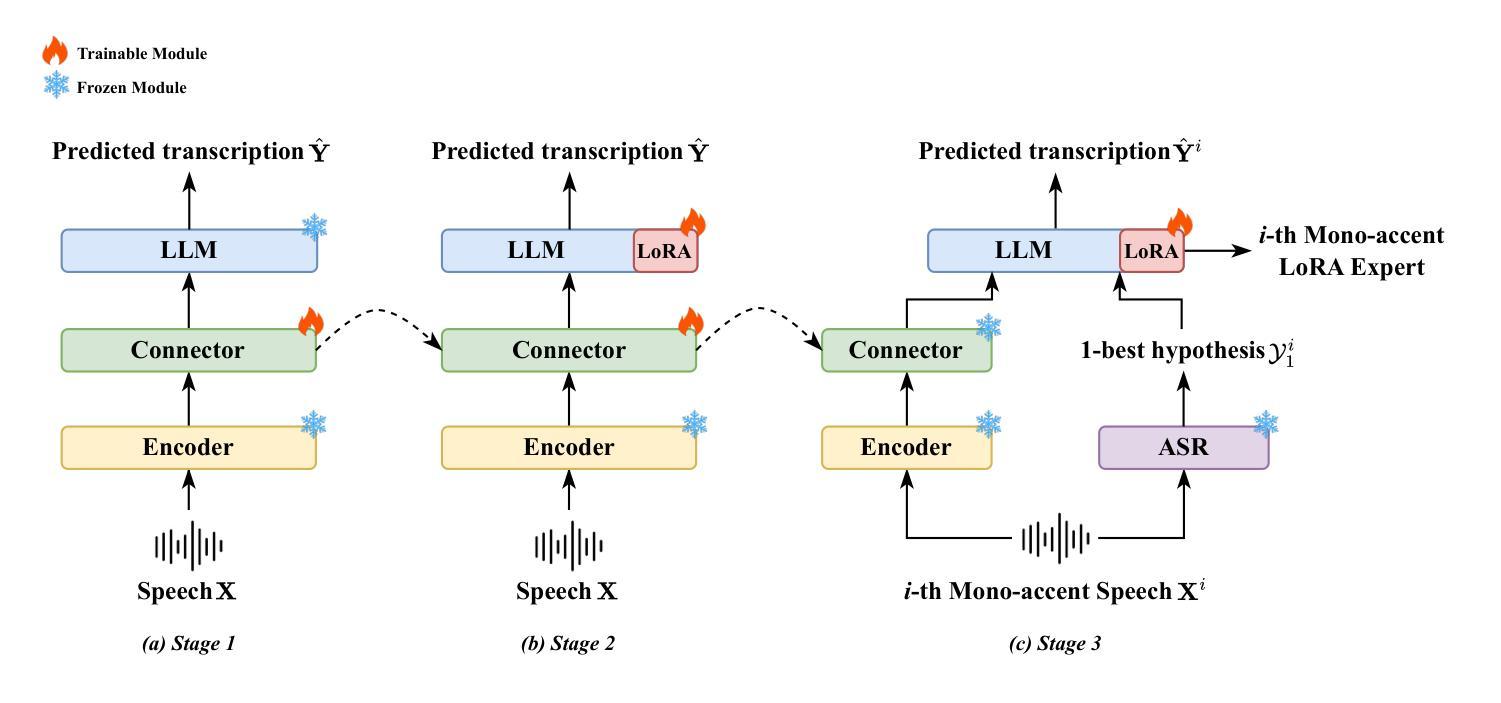
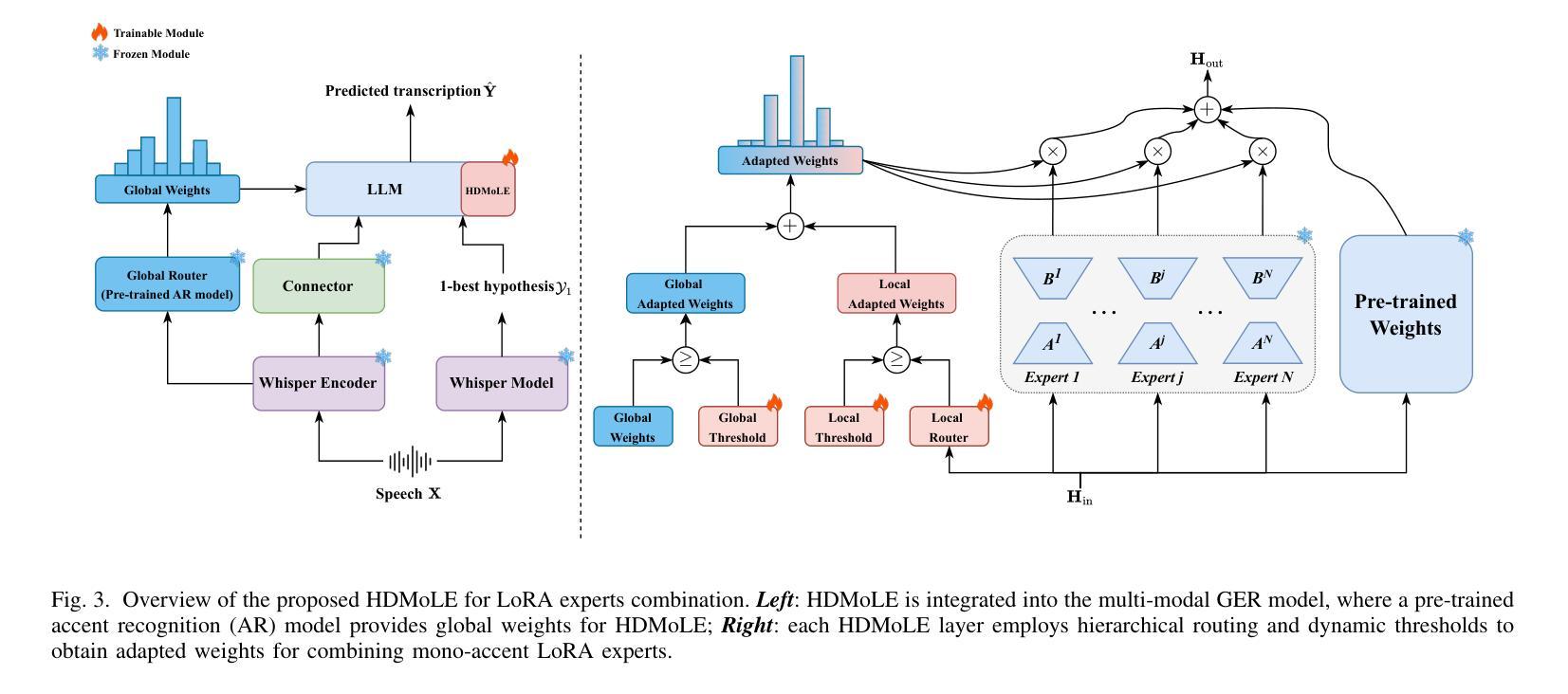
Mixture of LoRA Experts with Multi-Modal and Multi-Granularity LLM Generative Error Correction for Accented Speech Recognition
Authors:Bingshen Mu, Kun Wei, Pengcheng Guo, Lei Xie
Despite improvements in automatic speech recognition, performance drops with accented speech. Generative error correction (GER) leverages the linguistic knowledge of large language models (LLMs), outperforming typical language model methods. However, it lacks specificity in accented speech scenarios. Accents represent deviations from standard pronunciation, making multi-granularity pronunciation and semantic information essential for accented speech recognition. Moreover, accents exhibit considerable diversity, with each accent possessing distinct characteristics. In this study, we leverage GER to improve transcription accuracy by addressing the two primary features. We propose the multi-modal GER, which integrates pronunciation information from the speech modality, and the multi-granularity GER, which incorporates fine-grained phoneme-level pronunciation information. These methods enable the LLM to utilize the pronunciation information of accented speech and the semantic information from word-level hypotheses for accurate transcription predictions through low-rank adaptation (LoRA) fine-tuning. We employ a three-stage strategy to train separate multi-modal GER models for each accent to obtain mono-accent LoRA experts. By adopting our proposed HDMoLE method, which incorporates hierarchical routing and dynamic thresholds within the mixture of LoRA experts, we effectively merge mono-accent LoRA experts within a single multi-modal GER to overcome accent diversity challenges. Furthermore, multi-granularity GER leverages N-best word-level and phoneme-level hypotheses from the HDMoLE model to predict final transcriptions. Experiments on a multi-accent English dataset show that our methods reduce word error rate by 67.35% compared to the baseline vanilla Whisper-large-v3 model.
尽管自动语音识别技术已经得到了改进,但在带有口音的语音方面,其性能仍然会下降。生成式错误修正(GER)利用大型语言模型的语言知识,在自动语音识别方面优于典型的语言模型方法。然而,它在口音语音场景方面的具体性较差。口音代表了与标准发音的偏差,使得多粒度发音和语义信息对于带口音的语音识别至关重要。此外,口音表现出相当大的多样性,每种口音都有其独特的特点。在这项研究中,我们通过解决两个主要特点,利用GER来提高转录准确性。我们提出了多模态GER,它结合了语音模态的发音信息,以及多粒度GER,它结合了精细的音素级发音信息。这些方法使语言模型能够利用带口音语音的发音信息和词级假设的语义信息,通过低秩适应(LoRA)微调进行准确的转录预测。我们采用三阶段策略,针对每种口音训练单独的多模态GER模型,以获得单口音LoRA专家。通过采用我们提出的HDMoLE方法,该方法在LoRA专家的混合体中加入分层路由和动态阈值,我们有效地将单口音LoRA专家合并到一个单一的多模态GER中,以克服口音多样性挑战。此外,多粒度GER利用HDMoLE模型的N个最佳词级和音素级假设来预测最终转录。在多口音英语数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法将词错误率降低了67.35%,与基线Whisper-large-v3模型相比。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing
Summary
针对带口音的语音识别问题,本研究提出多模态生成式错误修正(GER)方法,结合口音的语音信息以及语义信息进行转录预测。通过低秩适应(LoRA)微调技术,训练针对每种口音的多模态GER模型,并采用HDMoLE方法合并这些模型以应对口音多样性挑战。实验表明,该方法较基线模型降低了67.35%的词错误率。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式错误修正(GER)结合了大型语言模型(LLM)的语言知识,用于改善带口音语音的识别性能。
- 多模态GER方法被提出,以结合语音模态的发音信息。
- 多粒度GER方法引入细粒度音素级发音信息,以提高转录准确性。
- 采用低秩适应(LoRA)微调技术,针对每种口音训练多模态GER模型。
- HDMoLE方法通过层次路由和动态阈值在口音专家模型的混合中有效合并单口音LoRA专家,以应对口音多样性。
- 多粒度GER利用N-best的单词级和音素级假设进行最终转录预测。
点此查看论文截图

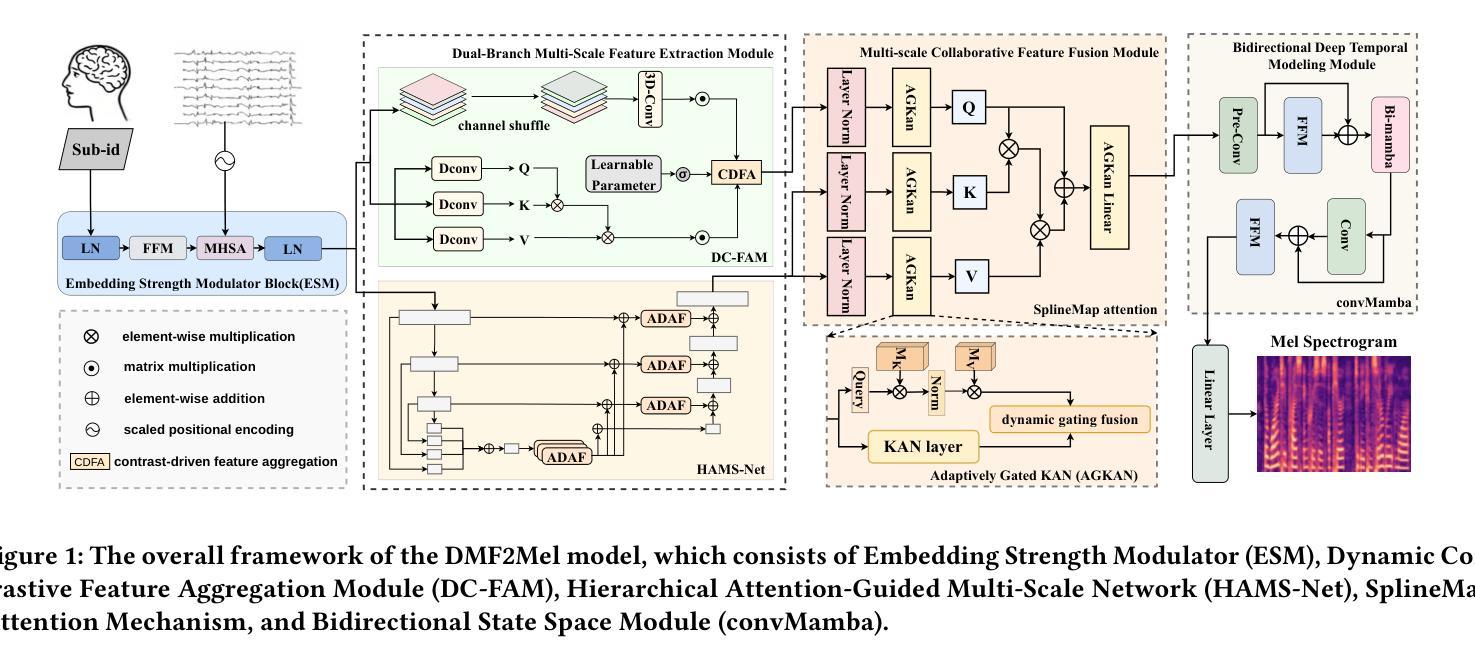
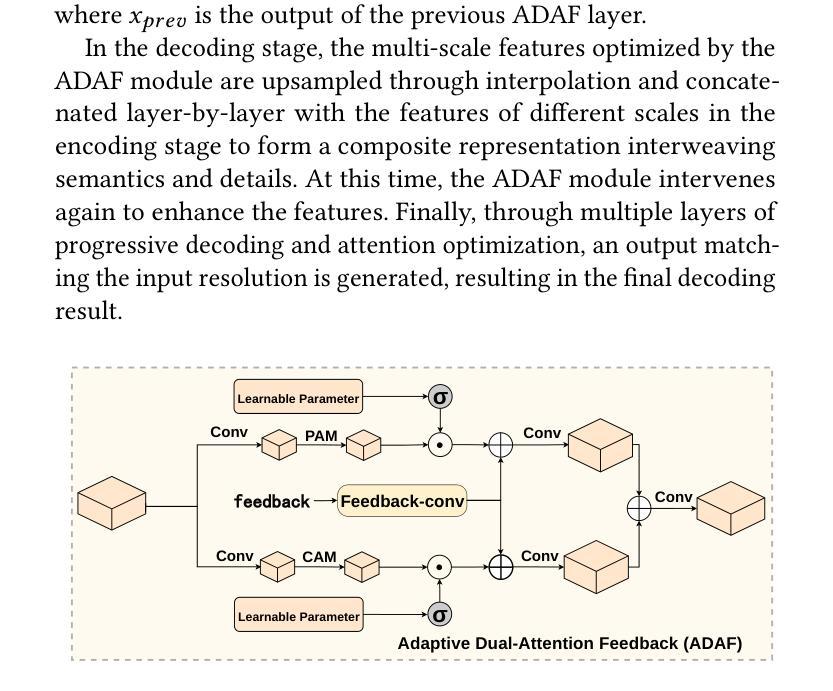
DMF2Mel: A Dynamic Multiscale Fusion Network for EEG-Driven Mel Spectrogram Reconstruction
Authors:Cunhang Fan, Sheng Zhang, Jingjing Zhang, Enrui Liu, Xinhui Li, Minggang Zhao, Zhao Lv
Decoding speech from brain signals is a challenging research problem. Although existing technologies have made progress in reconstructing the mel spectrograms of auditory stimuli at the word or letter level, there remain core challenges in the precise reconstruction of minute-level continuous imagined speech: traditional models struggle to balance the efficiency of temporal dependency modeling and information retention in long-sequence decoding. To address this issue, this paper proposes the Dynamic Multiscale Fusion Network (DMF2Mel), which consists of four core components: the Dynamic Contrastive Feature Aggregation Module (DC-FAM), the Hierarchical Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Network (HAMS-Net), the SplineMap attention mechanism, and the bidirectional state space module (convMamba). Specifically, the DC-FAM separates speech-related “foreground features” from noisy “background features” through local convolution and global attention mechanisms, effectively suppressing interference and enhancing the representation of transient signals. HAMS-Net, based on the U-Net framework,achieves cross-scale fusion of high-level semantics and low-level details. The SplineMap attention mechanism integrates the Adaptive Gated Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (AGKAN) to combine global context modeling with spline-based local fitting. The convMamba captures long-range temporal dependencies with linear complexity and enhances nonlinear dynamic modeling capabilities. Results on the SparrKULee dataset show that DMF2Mel achieves a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.074 in mel spectrogram reconstruction for known subjects (a 48% improvement over the baseline) and 0.048 for unknown subjects (a 35% improvement over the baseline).Code is available at: https://github.com/fchest/DMF2Mel.
从脑电波解码语音是一个具有挑战性的研究课题。尽管现有技术已在重建听觉刺激的梅尔频谱图(如单词或字母级别)方面取得了进展,但在精确重建分钟级别的连续想象中的语音方面仍存在核心挑战:传统模型在平衡时间序列依赖建模的效率和长序列解码中的信息保留方面感到困难。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了动态多尺度融合网络(DMF2Mel),它包含四个核心组件:动态对比特征聚合模块(DC-FAM)、分层注意力引导多尺度网络(HAMS-Net)、SplineMap注意力机制和双向状态空间模块(convMamba)。具体来说,DC-FAM通过局部卷积和全局注意力机制,将语音相关的“前景特征”从嘈杂的“背景特征”中分离出来,有效地抑制了干扰并增强了瞬态信号的表示。HAMS-Net基于U-Net框架,实现了高级语义和低级细节的跨尺度融合。SplineMap注意力机制结合了自适应门控Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(AGKAN),将全局上下文建模与基于样条的局部拟合相结合。convMamba以线性复杂度捕获长期时间依赖关系,并增强了非线性动态建模能力。在SparrKULee数据集上的结果表明,DMF2Mel在已知主题的梅尔频谱图重建中达到了0.074的皮尔逊相关系数(比基线提高了48%),在未知主题上达到了0.048(比基线提高了35%)。代码可用在:https://github.com/fchest/DMF2Mel。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
该文提出了一种动态多尺度融合网络(DMF2Mel),包括四个核心组件,旨在解决从脑信号解码语音中的挑战性问题。该网络能够在不同尺度上融合高低层次的语义和细节,更有效地重建连续的微小想象语音。在SparrKULee数据集上的实验结果显示,DMF2Mel在已知和未知主体上的梅尔频谱图重建方面都取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 动态多尺度融合网络(DMF2Mel)解决了从脑信号解码语音的挑战性问题。
- DMF2Mel包含四个核心组件:动态对比特征聚合模块(DC-FAM)、分层注意力引导多尺度网络(HAMS-Net)、SplineMap注意力机制和双向状态空间模块(convMamba)。
- DC-FAM通过局部卷积和全局注意力机制分离语音相关的“前景特征”和噪声“背景特征”,增强瞬态信号的表示。
- HAMS-Net基于U-Net框架,实现高低层次语义和跨尺度细节融合。
- SplineMap注意力机制结合了全局上下文建模和基于样条的局部拟合。
- convMamba能够捕捉长期时间依赖关系,增强非线性动态建模能力。
- 在SparrKULee数据集上的实验结果显示,DMF2Mel在梅尔频谱图重建方面取得了显著改进,相对于基线方法有大幅度提升。
点此查看论文截图

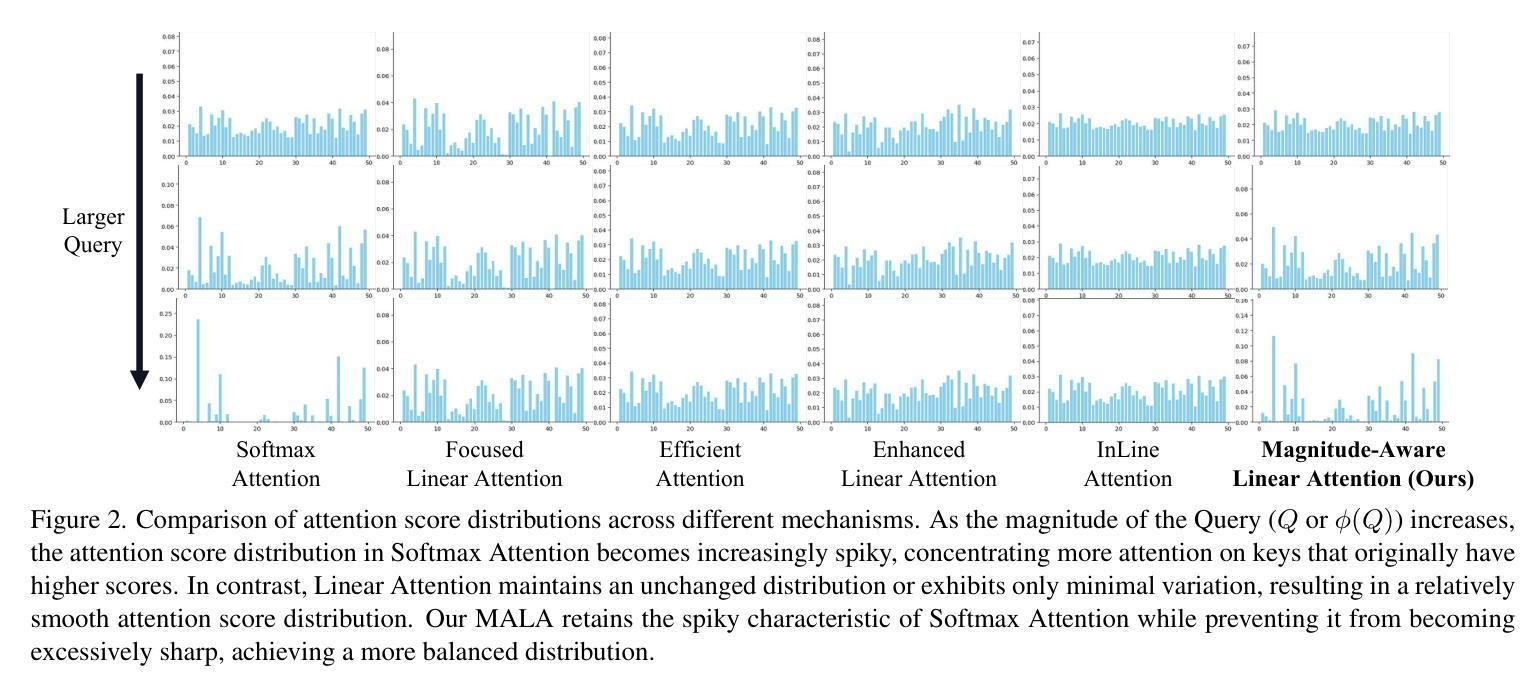
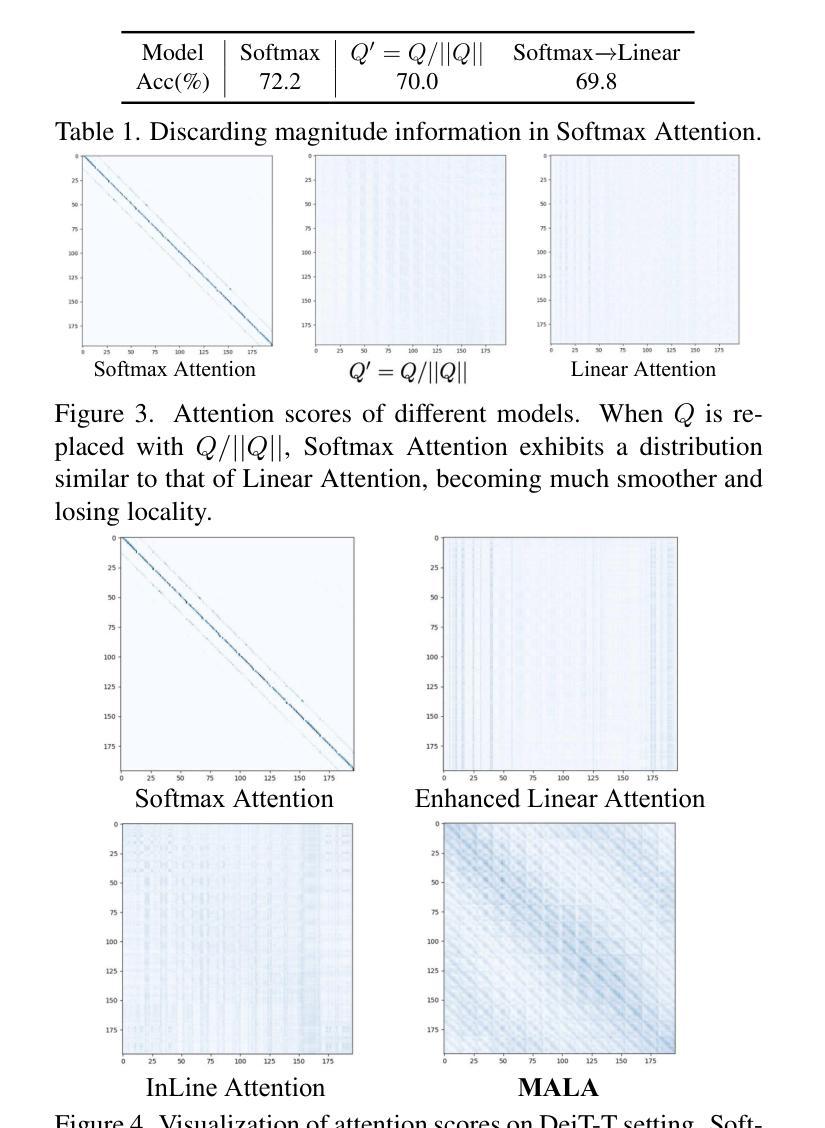
Rectifying Magnitude Neglect in Linear Attention
Authors:Qihang Fan, Huaibo Huang, Yuang Ai, ran He
As the core operator of Transformers, Softmax Attention exhibits excellent global modeling capabilities. However, its quadratic complexity limits its applicability to vision tasks. In contrast, Linear Attention shares a similar formulation with Softmax Attention while achieving linear complexity, enabling efficient global information modeling. Nevertheless, Linear Attention suffers from a significant performance degradation compared to standard Softmax Attention. In this paper, we analyze the underlying causes of this issue based on the formulation of Linear Attention. We find that, unlike Softmax Attention, Linear Attention entirely disregards the magnitude information of the Query. This prevents the attention score distribution from dynamically adapting as the Query scales. As a result, despite its structural similarity to Softmax Attention, Linear Attention exhibits a significantly different attention score distribution. Based on this observation, we propose Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention (MALA), which modifies the computation of Linear Attention to fully incorporate the Query’s magnitude. This adjustment allows MALA to generate an attention score distribution that closely resembles Softmax Attention while exhibiting a more well-balanced structure. We evaluate the effectiveness of MALA on multiple tasks, including image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, natural language processing, speech recognition, and image generation. Our MALA achieves strong results on all of these tasks. Code will be available at https://github.com/qhfan/MALA
Transformer的核心操作器Softmax Attention展现出优秀的全局建模能力。然而,其二次复杂度限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。相比之下,Linear Attention与Softmax Attention有相似的公式,但实现了线性复杂度,能够高效地进行全局信息建模。然而,与标准的Softmax Attention相比,Linear Attention的性能显著下降。在本文中,我们基于Linear Attention的公式分析此问题的根本原因。我们发现,与Softmax Attention不同,Linear Attention完全忽略了Query的幅度信息。这阻止了注意力得分分布在Query缩放时动态适应。因此,尽管其与Softmax Attention的结构相似,但Linear Attention的注意力得分分布却大不相同。基于此观察,我们提出了幅度感知的Linear Attention(MALA),它修改了Linear Attention的计算以充分融入Query的幅度。这一调整使得MALA能够生成与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布,同时展现出更平衡的结构。我们在多个任务上评估了MALA的有效性,包括图像分类、目标检测、实例分割、语义分割、自然语言处理、语音识别和图像生成。我们的MALA在所有任务上都取得了强大的结果。代码将在https://github.com/qhfan/MALA上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025, highlight paper
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer中的核心操作,包括Softmax Attention和Linear Attention。Softmax Attention展现出强大的全局建模能力,但由于其二次复杂性限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。Linear Attention虽然在复杂度上达到了线性级别,但与标准的Softmax Attention相比性能明显下降。原因在于Linear Attention忽略了Query的幅度信息,导致注意力得分分布无法随Query的缩放动态调整。为解决这一问题,本文提出了Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention(MALA),通过修改Linear Attention的计算方法使其能充分利用Query的幅度信息,产生类似于Softmax Attention的注意力得分分布。MALA在各种任务上的表现都非常好。
Key Takeaways
- Softmax Attention具有强大的全局建模能力,但其二次复杂性限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。
- Linear Attention具有线性复杂度,但与Softmax Attention相比性能较差。原因在于其忽略了Query的幅度信息。
- MALA旨在解决Linear Attention的问题,通过修改计算方法以充分利用Query的幅度信息。
点此查看论文截图

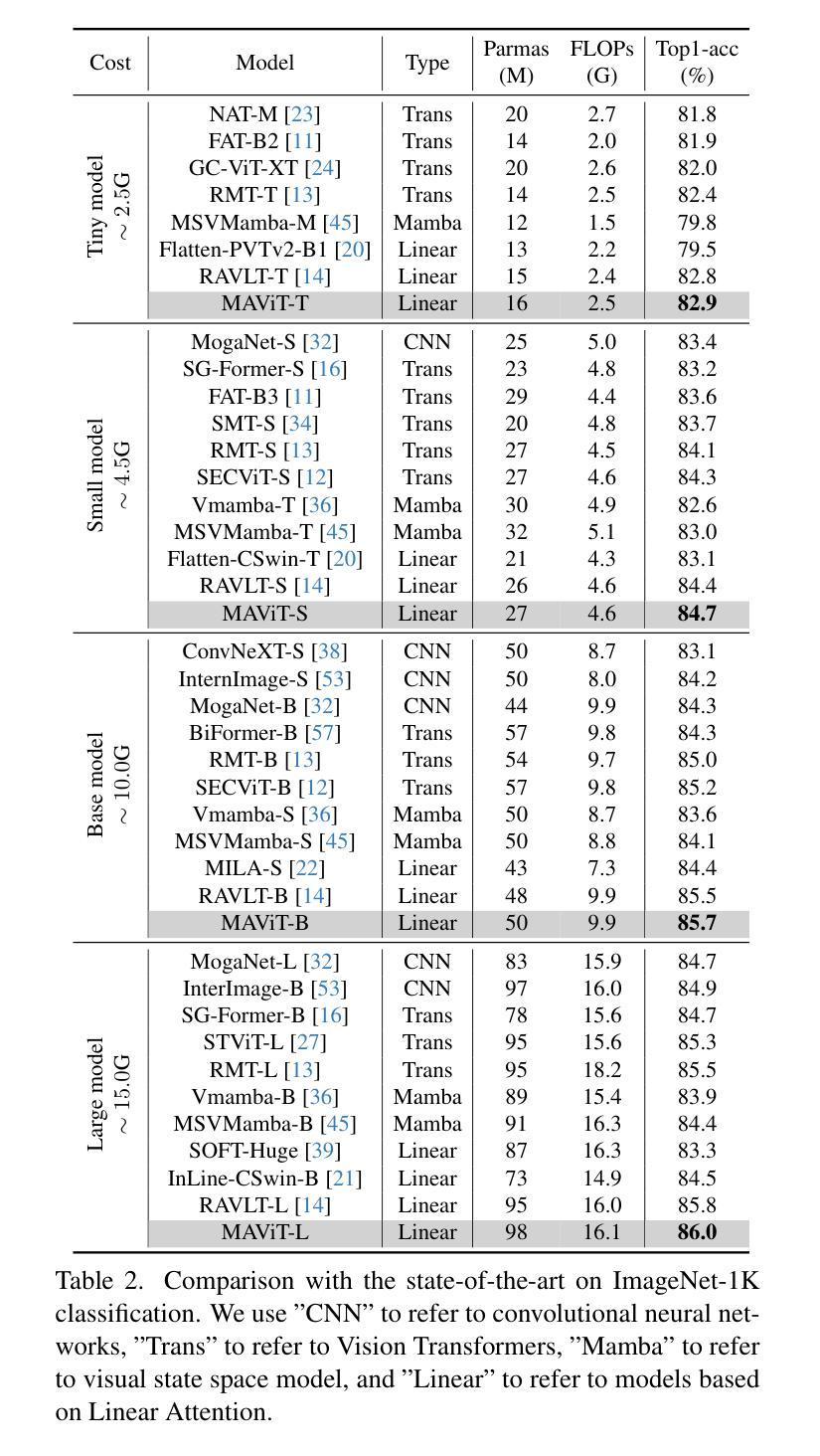
SALM-Duplex: Efficient and Direct Duplex Modeling for Speech-to-Speech Language Model
Authors:Ke Hu, Ehsan Hosseini-Asl, Chen Chen, Edresson Casanova, Subhankar Ghosh, Piotr Żelasko, Zhehuai Chen, Jason Li, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg
Spoken dialogue is an intuitive form of human-computer interaction, yet current speech language models often remain constrained to turn-based exchanges, lacking real-time adaptability such as user barge-in. We propose a novel duplex speech to speech (S2S) architecture featuring continuous user inputs and codec agent outputs with channel fusion that directly models simultaneous user and agent streams. Using a pretrained streaming encoder for user input enables the first duplex S2S model without requiring speech pretrain. Separate architectures for agent and user modeling facilitate codec fine-tuning for better agent voices and halve the bitrate (0.6 kbps) compared to previous works. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms previous duplex models in reasoning, turn-taking, and barge-in abilities. The model requires significantly less speech data, as speech pretrain is skipped, which markedly simplifies the process of building a duplex S2S model from any LLMs. Finally, it is the first openly available duplex S2S model with training and inference code to foster reproducibility.
口语对话是人类与计算机交互的一种直观形式。然而,当前的语音语言模型通常仅限于基于回合的交互,缺乏实时适应性,如用户抢话等。我们提出了一种新型的双语语音到语音(S2S)架构,具有连续用户输入和编解码器代理输出,通过信道融合直接建模用户和代理的并行流。使用预训练的流式编码器进行用户输入,使第一个双语S2S模型无需语音预训练即可实现。对代理和用户建模的单独架构有助于对编解码器进行微调,以产生更好的代理声音,并将比特率与以前的工作相比减半(0.6kbps)。实验结果表明,所提出模型在推理、话轮转换和抢话能力方面优于之前的双语模型。该模型大大减少了所需的语音数据,因为跳过了语音预训练,从而大大简化了从任何大型语言模型构建双语S2S模型的过程。最后,它是第一个公开可用的带有训练和推理代码的双语S2S模型,有利于促进可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的双向语音到语音(Duplex Speech to Speech,简称S2S)架构,该架构支持连续用户输入和编码解码器输出,通过融合通道直接模拟用户和代理的实时交互流。该架构采用预训练的流式编码器对用户输入进行建模,无需语音预训练即可实现首个Duplex S2S模型。实验结果表明,该模型在推理、轮替和打断能力上优于先前的双向模型。此外,该模型对语音数据的需求更少,极大地简化了从任何大型语言模型构建Duplex S2S模型的过程。最后,它是首个公开提供训练和推理代码的Duplex S2S模型,促进了可重复性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新型的Duplex S2S架构,支持连续用户输入和编码解码器输出。
- 通过融合通道直接模拟用户和代理的实时交互流。
- 采用预训练的流式编码器,无需语音预训练即可实现Duplex S2S模型。
- 模型在推理、轮替和打断能力上表现优异。
- 模型对语音数据的需求减少,简化了构建Duplex S2S模型的过程。
- 该模型是首个公开提供训练和推理代码的Duplex S2S模型。
点此查看论文截图

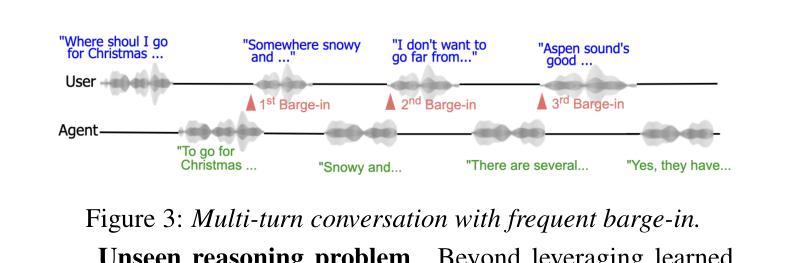
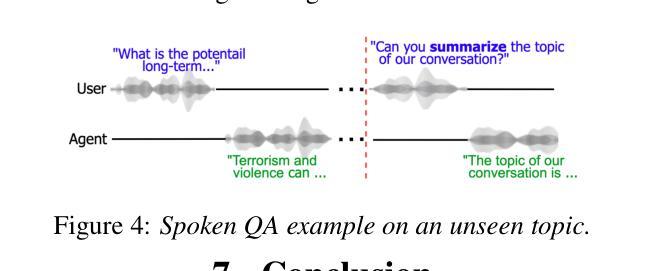
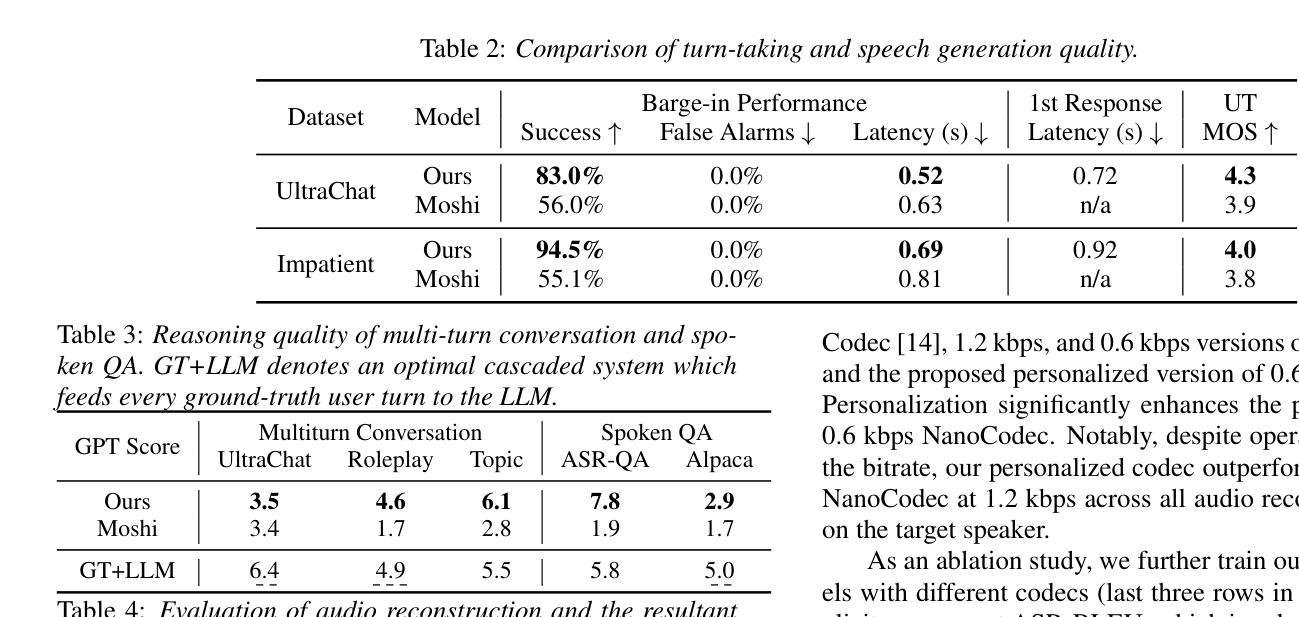
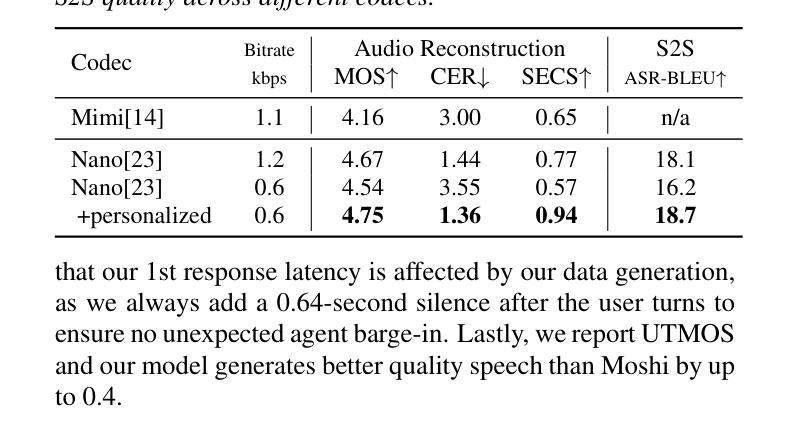
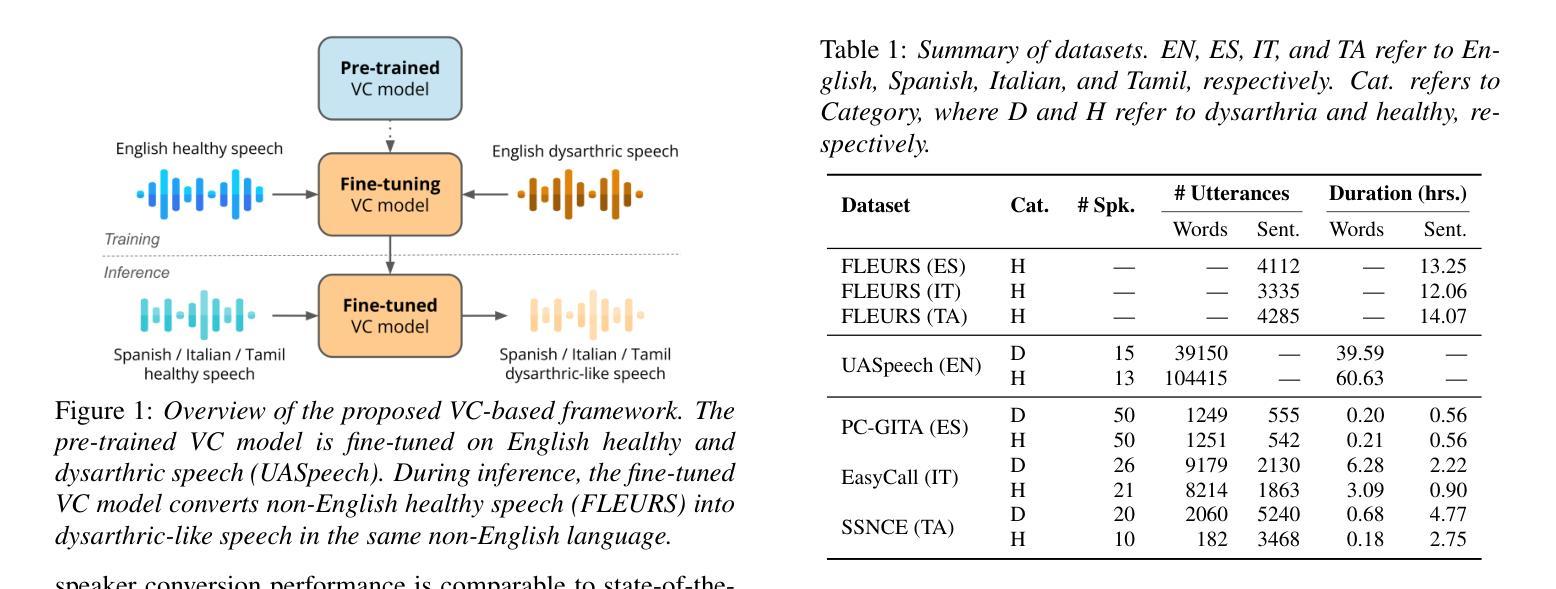
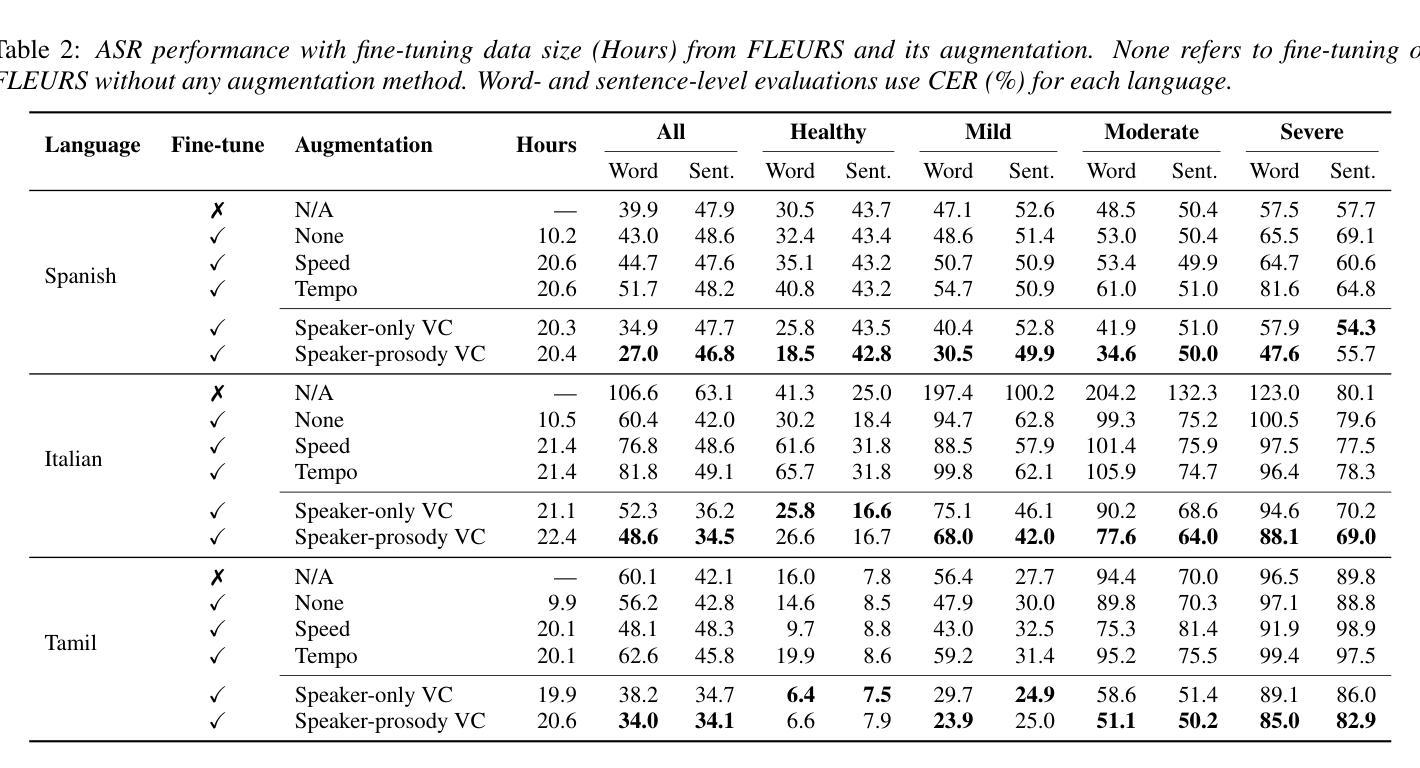
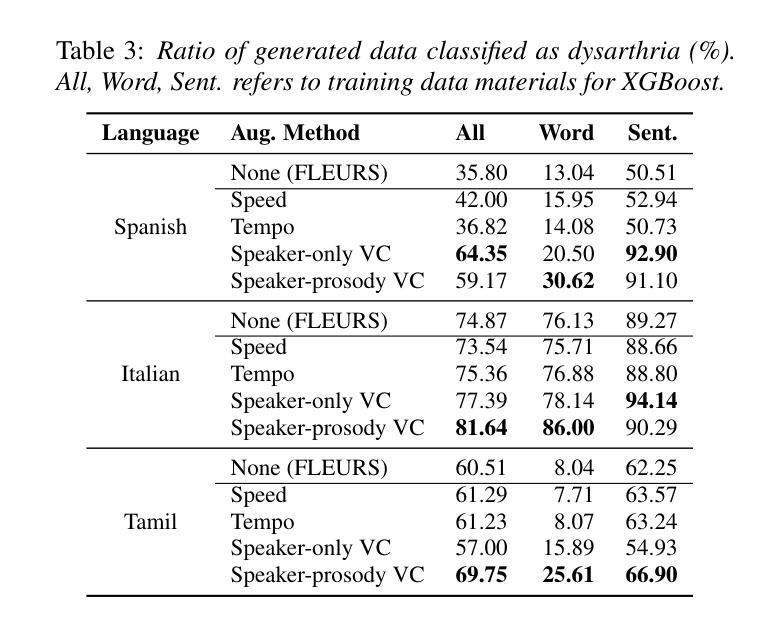
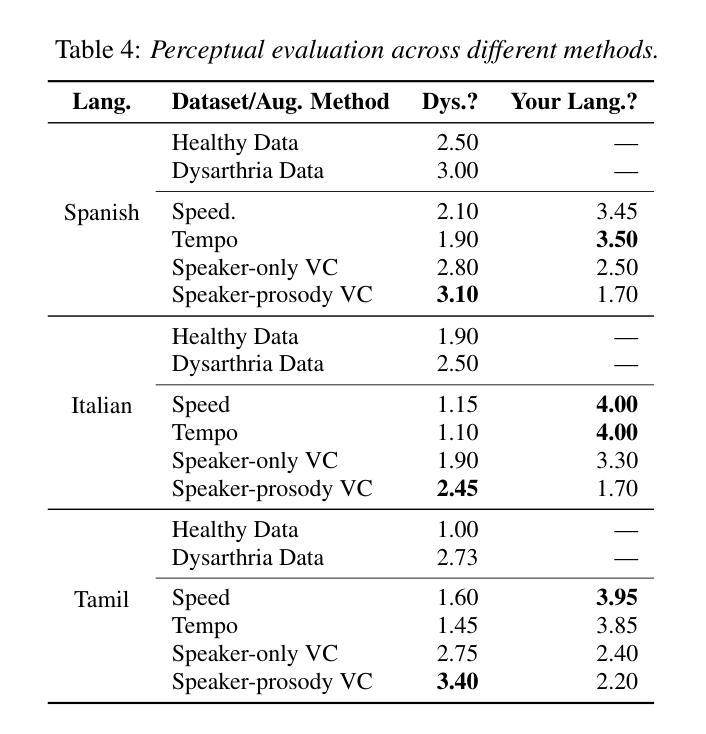
Towards Inclusive ASR: Investigating Voice Conversion for Dysarthric Speech Recognition in Low-Resource Languages
Authors:Chin-Jou Li, Eunjung Yeo, Kwanghee Choi, Paula Andrea Pérez-Toro, Masao Someki, Rohan Kumar Das, Zhengjun Yue, Juan Rafael Orozco-Arroyave, Elmar Nöth, David R. Mortensen
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) for dysarthric speech remains challenging due to data scarcity, particularly in non-English languages. To address this, we fine-tune a voice conversion model on English dysarthric speech (UASpeech) to encode both speaker characteristics and prosodic distortions, then apply it to convert healthy non-English speech (FLEURS) into non-English dysarthric-like speech. The generated data is then used to fine-tune a multilingual ASR model, Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS), for improved dysarthric speech recognition. Evaluation on PC-GITA (Spanish), EasyCall (Italian), and SSNCE (Tamil) demonstrates that VC with both speaker and prosody conversion significantly outperforms the off-the-shelf MMS performance and conventional augmentation techniques such as speed and tempo perturbation. Objective and subjective analyses of the generated data further confirm that the generated speech simulates dysarthric characteristics.
针对发音困难(发音障碍)语音的自动语音识别(ASR)仍具有挑战性,这是由于数据稀缺造成的,特别是在非英语领域尤为明显。为了解决这一问题,我们对英文发音障碍语音(UASpeech)进行微调,以便编码发言人的特征和韵律扭曲。然后将其应用于将健康的非英语语音(FLEURS)转换为非英语发音障碍类似语音。生成的数据随后用于微调多语言自动语音识别模型Massively Multilingual Speech(MMS),以提高对发音障碍语音的识别能力。在PC-GITA(西班牙语)、EasyCall(意大利语)和SSNCE(泰米尔语)上的评估表明,同时实现发言人和韵律转换的语音转换显著优于现成的MMS性能和传统的增强技术,如速度和节奏扰动。对生成数据的客观和主观分析进一步证实,生成的语音模拟了发音障碍的特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure, Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对非英语语言的发音障碍语音自动语音识别(ASR)的挑战性问题。为解决数据稀缺问题,研究团队使用英语发音障碍语音(UASpeech)对语音转换模型进行微调,以编码说话人的特征和韵律扭曲。随后,该模型被应用于将健康的非英语语音(FLEURS)转换为类似发音障碍的语音。生成的语音数据被用于微调多语言ASR模型Massively Multilingual Speech(MMS),以提高对发音障碍语音的识别能力。在西班牙语PC-GITA、意大利语EasyCall和泰米尔语SSNCE上的评估显示,同时实现说话人和韵律转换的语音转换技术显著优于现成的MMS性能和传统的增强技术,如速度和节奏扰动。生成数据的客观和主观分析进一步证实,生成的语音模拟了发音障碍的特征。
Key Takeaways
- 非英语发音障碍语音的自动语音识别(ASR)因数据稀缺而具有挑战性。
- 通过英语发音障碍语音(UASpeech)微调语音转换模型以编码说话人的特征和韵律扭曲。
- 使用该模型将健康的非英语语音转换为类似发音障碍的语音,并用于微调多语言ASR模型。
- 在不同语言的评估中,同时实现说话人和韵律转换的语音转换技术显著提高了ASR性能。
- 与传统的ASR增强技术相比,这种方法的性能更佳。
- 生成的语音数据在客观和主观分析上均模拟了发音障碍的特征。
点此查看论文截图

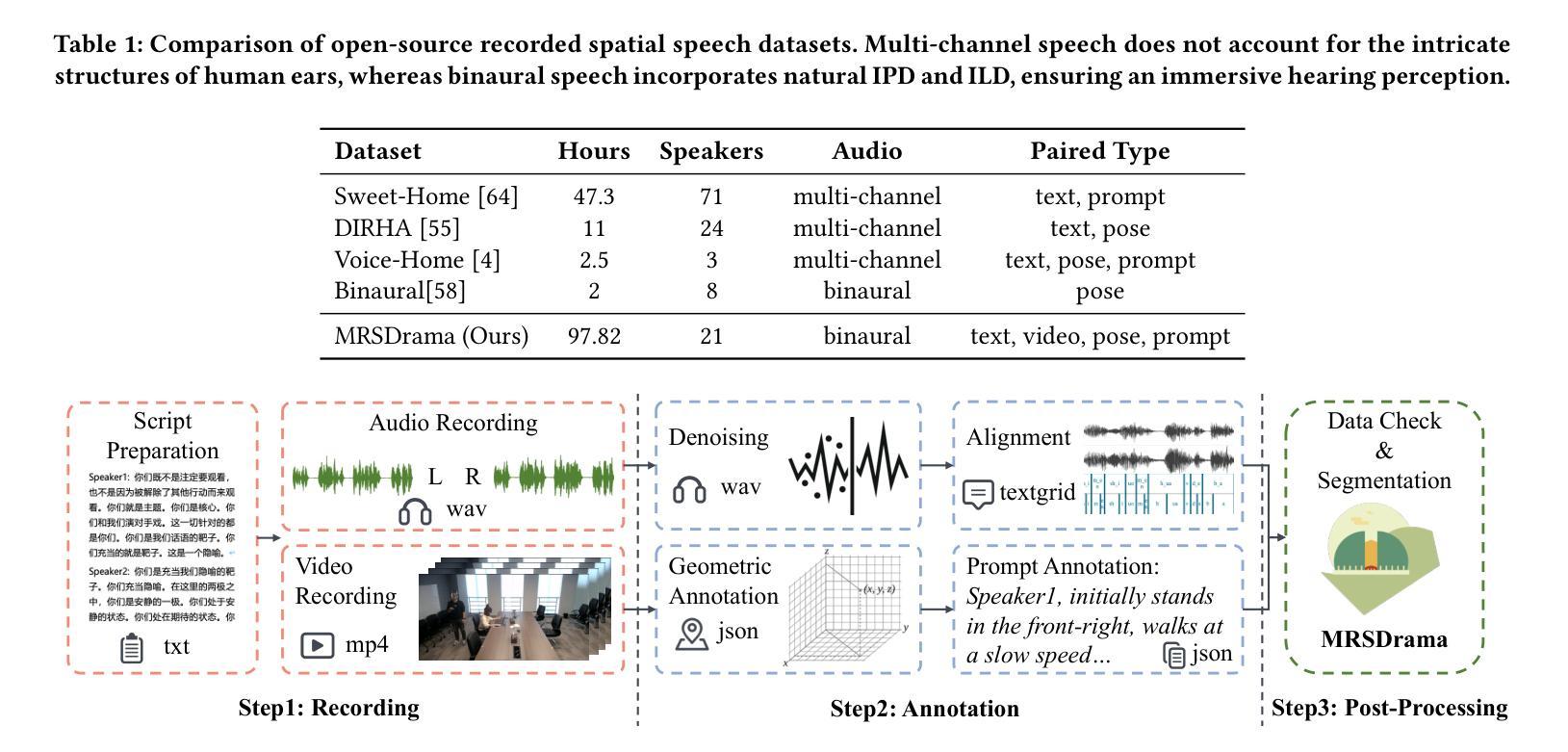
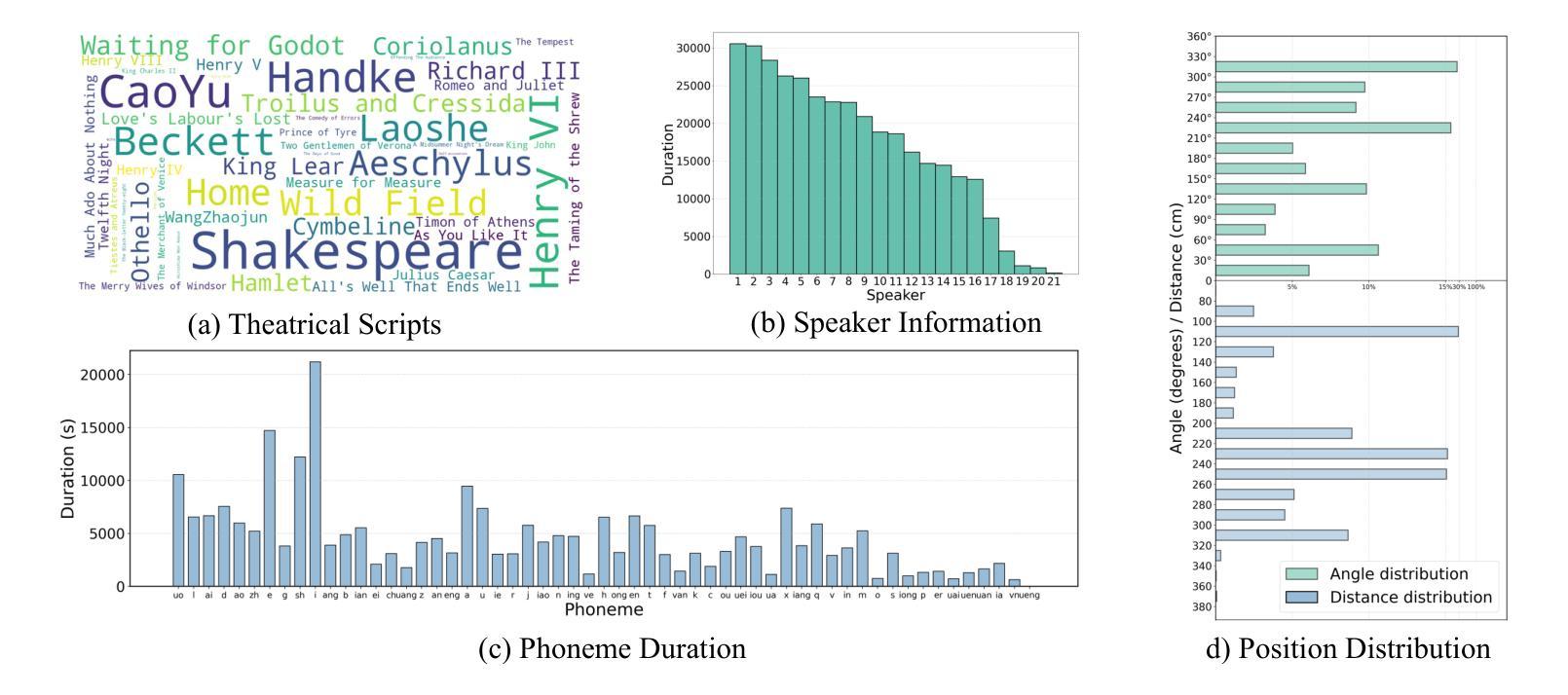
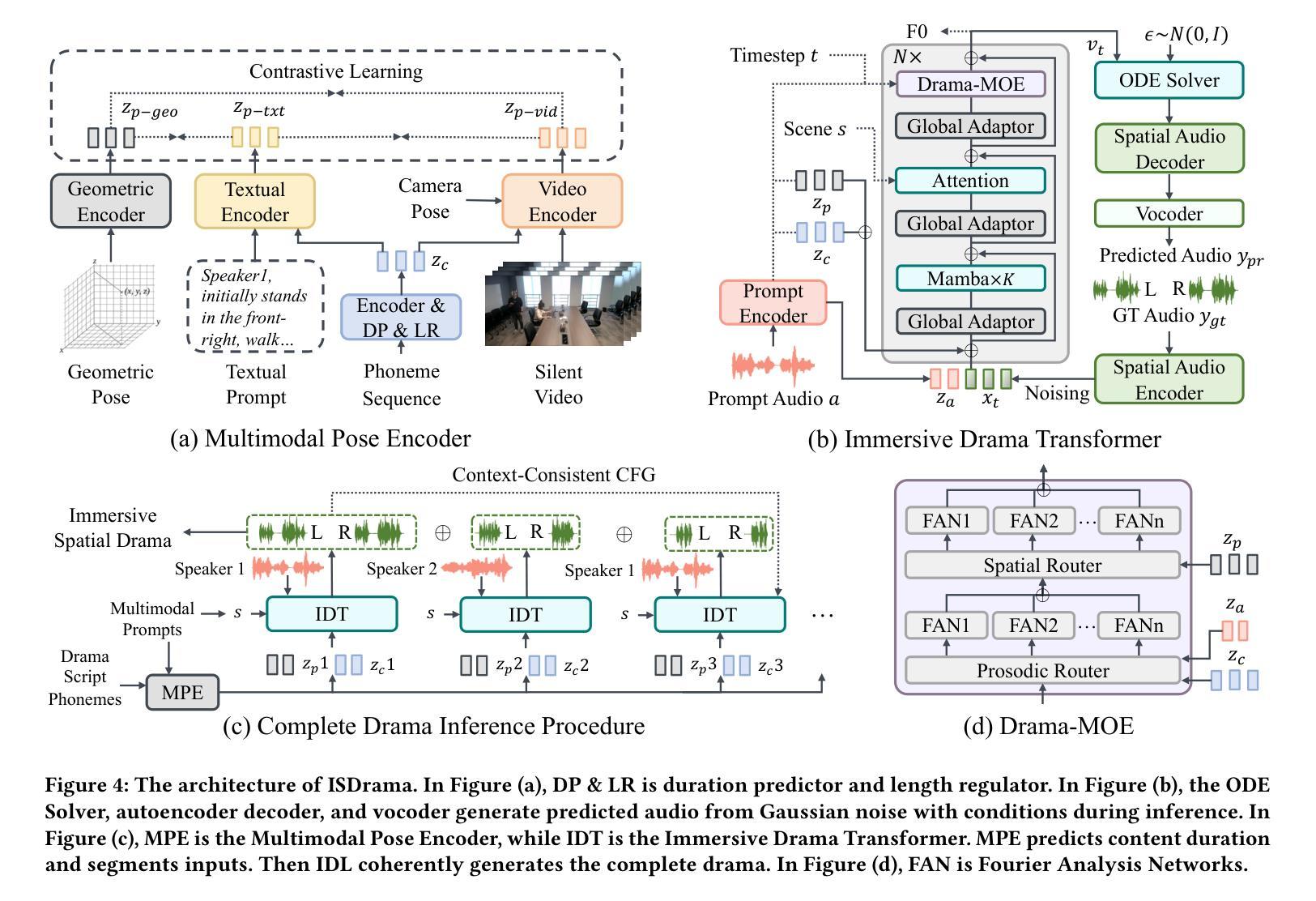
ISDrama: Immersive Spatial Drama Generation through Multimodal Prompting
Authors:Yu Zhang, Wenxiang Guo, Changhao Pan, Zhiyuan Zhu, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao
Multimodal immersive spatial drama generation focuses on creating continuous multi-speaker binaural speech with dramatic prosody based on multimodal prompts, with potential applications in AR, VR, and others. This task requires simultaneous modeling of spatial information and dramatic prosody based on multimodal inputs, with high data collection costs. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first attempt to address these challenges. We construct MRSDrama, the first multimodal recorded spatial drama dataset, containing binaural drama audios, scripts, videos, geometric poses, and textual prompts. Then, we propose ISDrama, the first immersive spatial drama generation model through multimodal prompting. ISDrama comprises these primary components: 1) Multimodal Pose Encoder, based on contrastive learning, considering the Doppler effect caused by moving speakers to extract unified pose information from multimodal prompts. 2) Immersive Drama Transformer, a flow-based mamba-transformer model that generates high-quality drama, incorporating Drama-MOE to select proper experts for enhanced prosody and pose control. We also design a context-consistent classifier-free guidance strategy to coherently generate complete drama. Experimental results show that ISDrama outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective metrics. The demos are available at https://aaronz345.github.io/ISDramaDemo. We provide the dataset and the evaluation code at https://huggingface.co/datasets/AaronZ345/MRSDrama and https://github.com/AaronZ345/ISDrama.
多模态沉浸式空间戏剧生成技术专注于基于多模态提示创建具有戏剧语调的连续多声道双耳语音,在AR、VR等领域具有潜在应用。这项任务需要同时模拟空间信息和戏剧语调,基于多模态输入,并且数据采集成本高昂。据我们所知,我们的工作是首次尝试应对这些挑战。我们构建了MRSDrama,即首个多模态记录的空间戏剧数据集,包含双耳戏剧音频、剧本、视频、几何姿势和文本提示。然后,我们提出了ISDrama,即首个通过多模态提示进行沉浸式空间戏剧生成模型。ISDrama主要包括以下主要组件:1)基于对比学习的多模态姿势编码器,考虑移动扬声器产生的多普勒效应,从多模态提示中提取统一姿势信息。2)沉浸式戏剧转换器,一个基于流的mamba-transformer模型,用于生成高质量戏剧,结合戏剧MOE选择适当的专家以增强语调和姿势控制。我们还设计了一种上下文一致的无分类器引导策略,以连贯地生成完整戏剧。实验结果表明,ISDrama在客观和主观指标上优于基准模型。演示地址为:https://aaronz345.github.io/ISDramaDemo。我们在https://huggingface.co/datasets/AaronZ345/MRSDrama和https://github.com/AaronZ345/ISDrama提供了数据集和评估代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM Multimedia 2025
Summary
基于多模态提示的沉浸式空间戏剧生成,旨在创建连续的多扬声器双耳戏剧语音,具有戏剧性的韵律,并应用于AR、VR等领域。此任务需要同时建模空间信息和戏剧韵律,且数据采集成本高昂。本研究是首次尝试解决这些挑战的工作,构建了首个多模态记录的空间戏剧数据集MRSDrama,并提出首个沉浸式空间戏剧生成模型ISDrama。该模型包括多模态姿态编码器和沉浸式戏剧转换器,能生成高质量戏剧并控制适当的专家进行韵律和姿态选择。实验结果表明,ISDrama在客观和主观指标上均优于基线模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态沉浸式空间戏剧生成集中于创建基于多模态提示的连续多扬声器双耳戏剧语音,具有广泛的应用前景,如AR和VR。
- 该任务需要同时建模空间信息和戏剧韵律,对数据采集的要求较高,成本较大。
- 研究构建了首个多模态记录的空间戏剧数据集MRSDrama,包含双耳戏剧音频、剧本、视频、几何姿态和文本提示。
- 提出了首个沉浸式空间戏剧生成模型ISDrama,包括多模态姿态编码器和沉浸式戏剧转换器。
- ISDrama模型考虑了多普勒效应,能提取统一姿态信息,并采用基于流的mamba-transformer模型生成高质量戏剧。
- 剧中引入Drama-MOE以选择合适的专家增强韵律和姿态控制,并设计了一种上下文一致的无监督指导策略,以连贯地生成完整戏剧。
点此查看论文截图

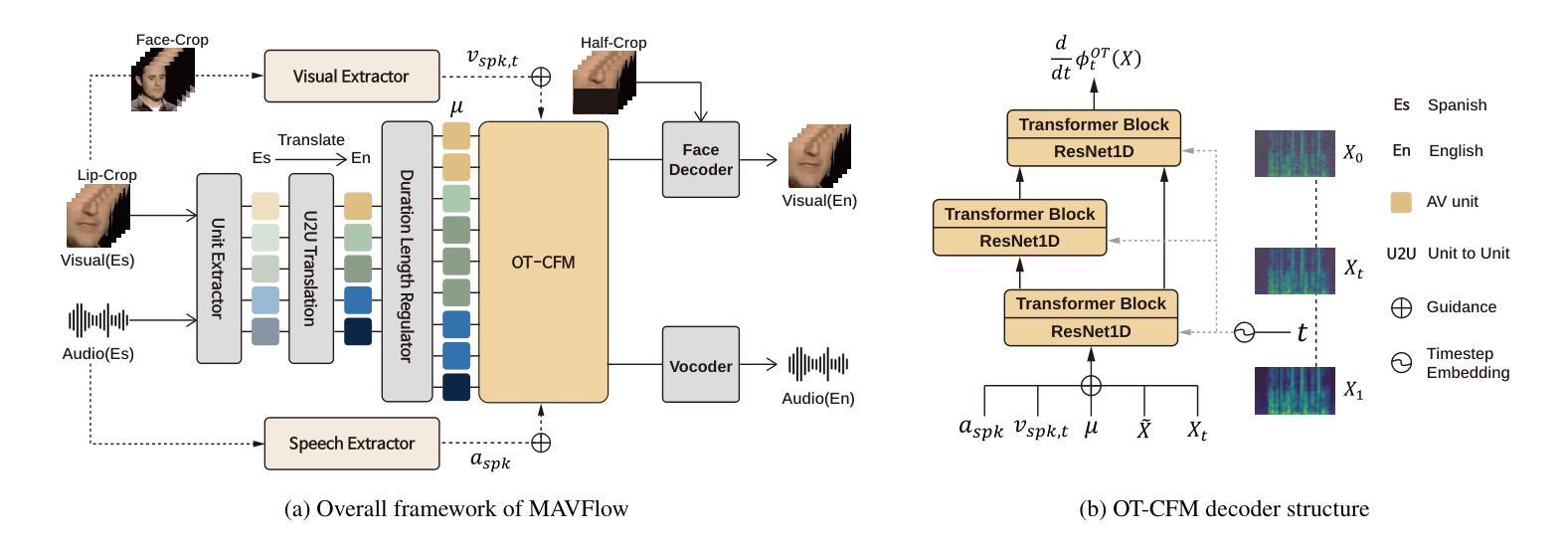
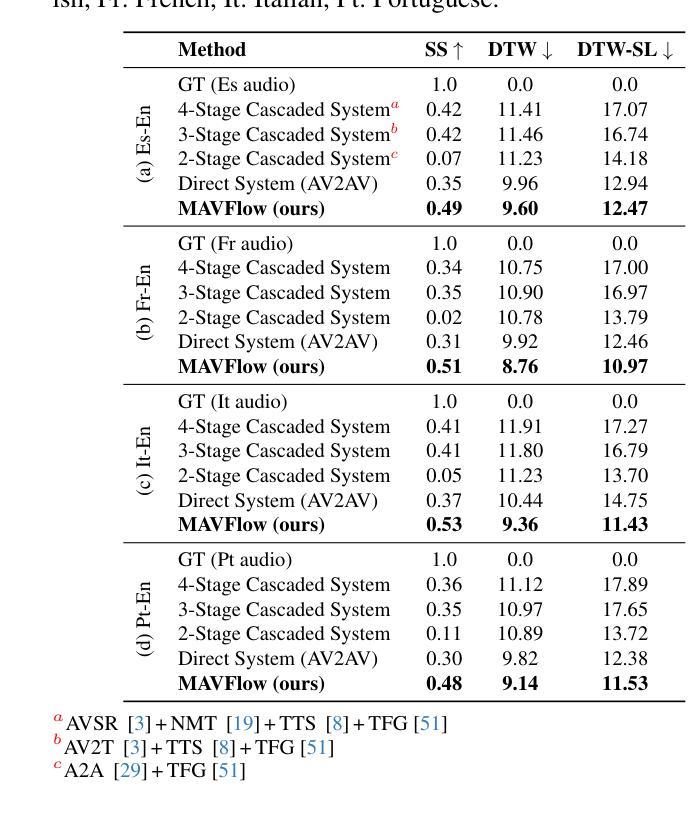
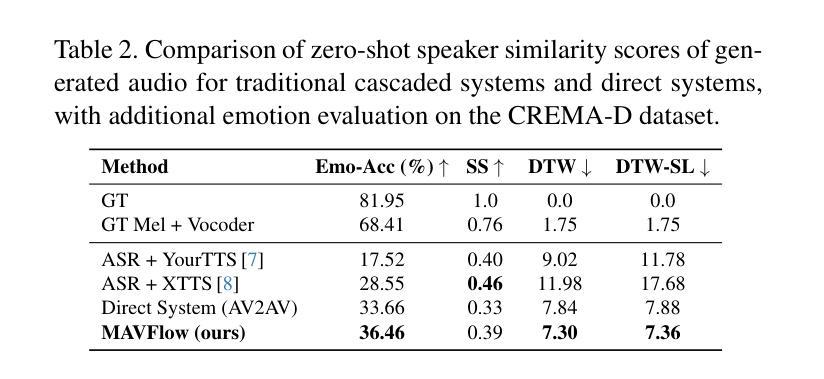
MAVFlow: Preserving Paralinguistic Elements with Conditional Flow Matching for Zero-Shot AV2AV Multilingual Translation
Authors:Sungwoo Cho, Jeongsoo Choi, Sungnyun Kim, Se-Young Yun
Despite recent advances in text-to-speech (TTS) models, audio-visual-to-audio-visual (AV2AV) translation still faces a critical challenge: maintaining speaker consistency between the original and translated vocal and facial features. To address this issue, we propose a conditional flow matching (CFM) zero-shot audio-visual renderer that utilizes strong dual guidance from both audio and visual modalities. By leveraging multimodal guidance with CFM, our model robustly preserves speaker-specific characteristics and enhances zero-shot AV2AV translation abilities. For the audio modality, we enhance the CFM process by integrating robust speaker embeddings with x-vectors, which serve to bolster speaker consistency. Additionally, we convey emotional nuances to the face rendering module. The guidance provided by both audio and visual cues remains independent of semantic or linguistic content, allowing our renderer to effectively handle zero-shot translation tasks for monolingual speakers in different languages. We empirically demonstrate that the inclusion of high-quality mel-spectrograms conditioned on facial information not only enhances the quality of the synthesized speech but also positively influences facial generation, leading to overall performance improvements in LSE and FID score. Our code is available at https://github.com/Peter-SungwooCho/MAVFlow.
尽管近期文本转语音(TTS)模型取得了进展,视听转视听(AV2AV)翻译仍然面临一个关键问题:保持原始和翻译后的语音和面部特征之间的说话人一致性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于条件流匹配(CFM)的零样本视听渲染器,该渲染器利用音频和视觉两种模态的强大双重指导。通过利用多模态指导和CFM,我们的模型能够稳健地保留特定于说话人的特征,并增强零样本AV2AV翻译能力。对于音频模态,我们通过将稳健的说话人嵌入与x向量集成,增强了CFM过程,这有助于加强说话人一致性。此外,我们还向面部渲染模块传达了情感细微差别。由音频和视觉线索提供的指导独立于语义或语言内容,这使得我们的渲染器能够有效地处理不同语言的单语说话人的零样本翻译任务。我们实证表明,面部信息条件下高质量梅尔频谱图的使用不仅提高了合成语音的质量,而且对面部生成产生了积极影响,从而提高了整体性能表现在LSE和FID分数上。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Peter-SungwooCho/MAVFlow。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于条件流匹配(CFM)的零样本音视频渲染器,利用音频和视觉两种模态的强双重指导来解决视听至音视频(AV2AV)翻译中保持发言者一致性的关键挑战。通过整合说话人嵌入和x向量增强CFM过程,同时向面部渲染模块传达情感细微差别,该方法稳健地保留了发言者特定特征并增强了零样本AV2AV翻译能力。该方法独立于语义或语言内容,能有效处理不同语言的单语发言者零样本翻译任务。实验证明,融合高质量梅尔频谱图条件面部信息不仅提高了合成语音的质量,也积极影响了面部生成,提高了整体性能。
Key Takeaways
- 面临AV2AV翻译的挑战:保持原始和翻译后的音视频中的发言者一致性。
- 提出基于条件流匹配(CFM)的零样本音视频渲染器来解决这一挑战。
- 利用音频和视觉两种模态的强双重指导。
- 通过整合说话人嵌入和x向量来增强CFM过程,保留发言者特定特征。
- 面向面部渲染模块传达情感细微差别。
- 方法独立于语义或语言内容,能处理不同语言的单语发言者零样本翻译任务。
点此查看论文截图

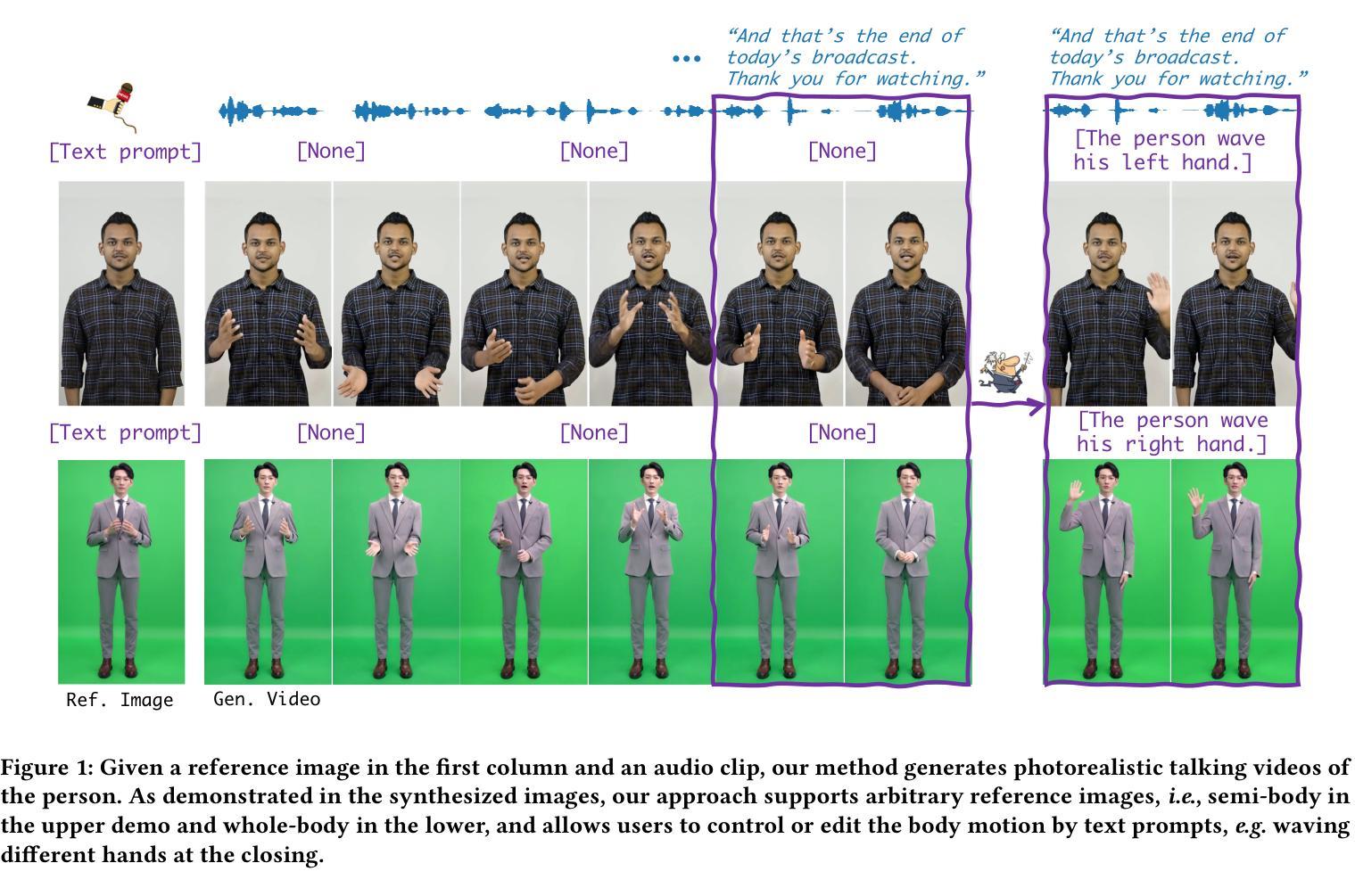
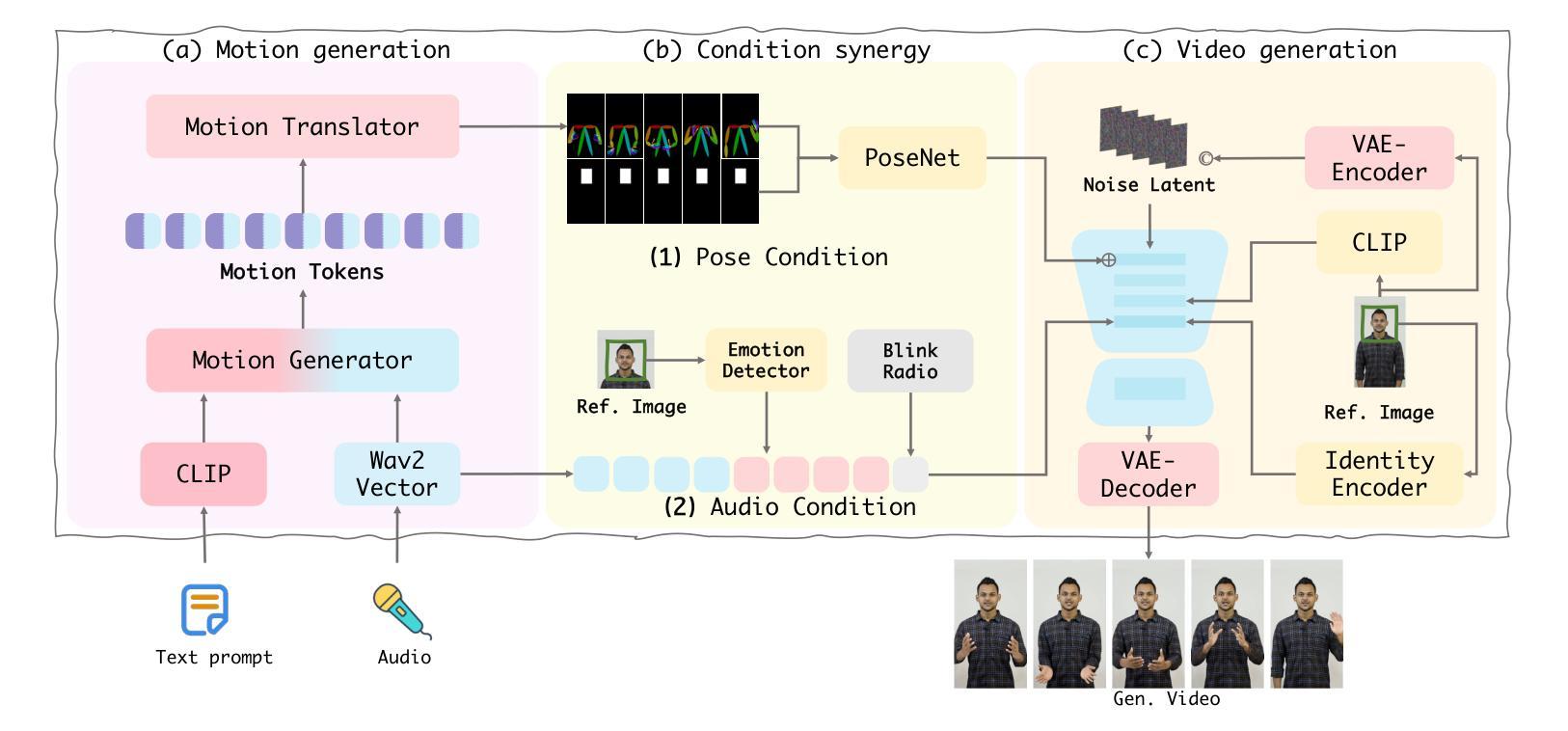
Versatile Multimodal Controls for Expressive Talking Human Animation
Authors:Zheng Qin, Ruobing Zheng, Yabing Wang, Tianqi Li, Zixin Zhu, Sanping Zhou, Ming Yang, Le Wang
In filmmaking, directors typically allow actors to perform freely based on the script before providing specific guidance on how to present key actions. AI-generated content faces similar requirements, where users not only need automatic generation of lip synchronization and basic gestures from audio input but also desire semantically accurate and expressive body movement that can be ``directly guided’’ through text descriptions. Therefore, we present VersaAnimator, a versatile framework that synthesizes expressive talking human videos from arbitrary portrait images. Specifically, we design a motion generator that produces basic rhythmic movements from audio input and supports text-prompt control for specific actions. The generated whole-body 3D motion tokens can animate portraits of various scales, producing talking heads, half-body gestures and even leg movements for whole-body images. Besides, we introduce a multi-modal controlled video diffusion that generates photorealistic videos, where speech signals govern lip synchronization, facial expressions, and head motions while body movements are guided by the 2D poses. Furthermore, we introduce a token2pose translator to smoothly map 3D motion tokens to 2D pose sequences. This design mitigates the stiffness resulting from direct 3D to 2D conversion and enhances the details of the generated body movements. Extensive experiments shows that VersaAnimator synthesizes lip-synced and identity-preserving videos while generating expressive and semantically meaningful whole-body motions.
在影视制作中,导演通常会让演员根据剧本自由发挥,然后再提供关于如何呈现关键动作的具体指导。人工智能生成的内容面临着类似的要求,用户不仅需要自动生成与音频输入同步的嘴唇和基本手势,还希望获得语义准确、富有表现力的身体动作,这些动作可以通过文本描述来“直接指导”。因此,我们推出了VersaAnimator,这是一个通用框架,可以从任意肖像图像中合成富有表现力的谈话人类视频。具体来说,我们设计了一个运动生成器,它可以从音频输入中产生基本的有节奏的运动,并支持通过文本提示来控制特定动作。生成的全身三维运动令牌可以动画化各种规模的肖像,产生谈话头部、半身手势甚至全身图像的下肢动作。此外,我们引入了一种多模式控制的视频扩散技术,生成逼真的视频,其中语音信号控制嘴唇同步、面部表情和头部运动,而身体运动则由二维姿势引导。此外,我们还引入了token2pose转换器,将三维运动令牌平滑地映射到二维姿势序列。这种设计缓解了直接三维到二维转换导致的僵硬问题,并增强了生成的身体动作的细节。大量实验表明,VersaAnimator合成的视频具有唇同步和身份保留特性,同时产生富有表现力和语义上有意义的全身动作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM2025
Summary
VersaAnimator框架能够基于任意肖像图像生成具有表达能力的谈话视频。该框架设计了一个动作生成器,能够从音频输入中产生基本节奏动作并支持通过文本描述进行特定动作的直接指导。它能生成全身三维动作令牌,能够驱动不同规模的肖像图像,产生说话头部、半身姿态和全身图像腿部动作等。此外,引入多模态控制视频扩散技术,通过语音信号控制唇同步、面部表情和头部动作,通过二维姿态引导身体动作。同时,引入token2pose翻译器,将三维动作令牌平滑映射到二维姿态序列,增强生成视频的细节和流畅性。
Key Takeaways
- VersaAnimator是一个通用框架,可以从任意肖像图像合成具有表达能力的谈话视频。
- 该框架包括一个动作生成器,能够从音频输入产生基本节奏动作并支持文本描述对特定动作的直接指导。
- 生成的三维动作令牌可以应用于不同规模的肖像图像,包括头部、半身和全身动作。
- 引入多模态控制视频扩散技术,使语音信号能控制唇同步、面部表情和头部动作,而身体动作则由二维姿态引导。
- token2pose翻译器的设计增强了从三维到二维转换的流畅性,提高了生成视频的细节质量。
- 该框架合成的视频具有唇同步和身份保持的特点。
点此查看论文截图

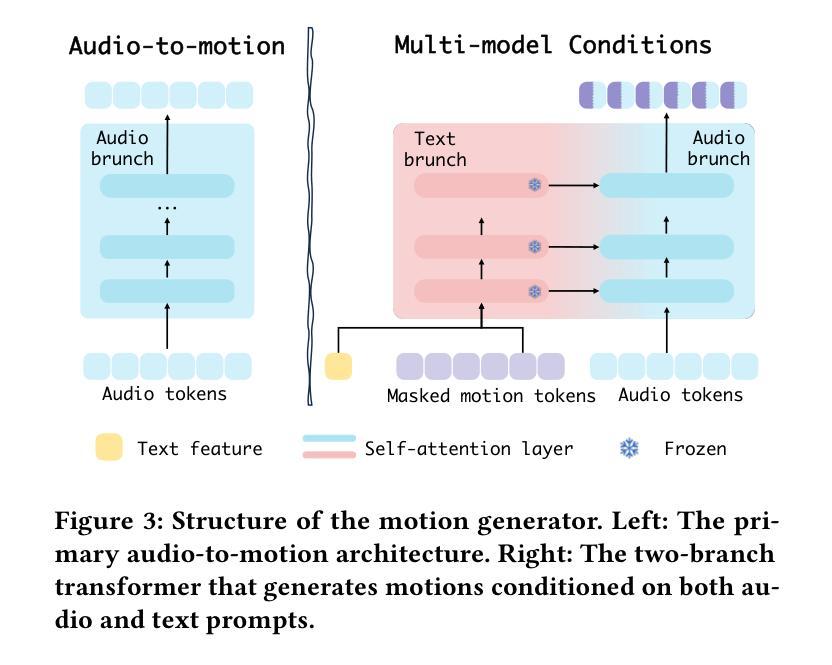


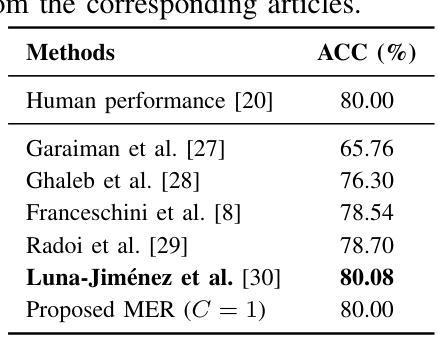
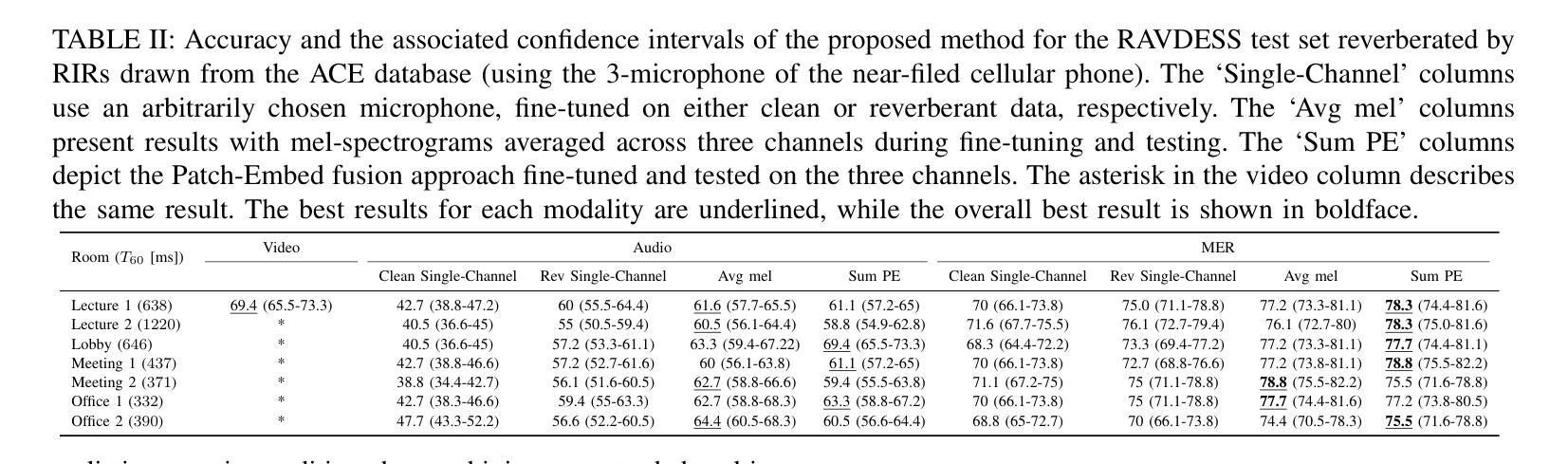
Multi-Microphone and Multi-Modal Emotion Recognition in Reverberant Environment
Authors:Ohad Cohen, Gershon Hazan, Sharon Gannot
This paper presents a Multi-modal Emotion Recognition (MER) system designed to enhance emotion recognition accuracy in challenging acoustic conditions. Our approach combines a modified and extended Hierarchical Token-semantic Audio Transformer (HTS-AT) for multi-channel audio processing with an R(2+1)D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) model for video analysis. We evaluate our proposed method on a reverberated version of the Ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (RAVDESS) dataset using synthetic and real-world Room Impulse Responsess (RIRs). Our results demonstrate that integrating audio and video modalities yields superior performance compared to uni-modal approaches, especially in challenging acoustic conditions. Moreover, we show that the multimodal (audiovisual) approach that utilizes multiple microphones outperforms its single-microphone counterpart.
本文提出了一种多模态情感识别(MER)系统,旨在提高在具有挑战性的声学条件下的情感识别准确性。我们的方法结合了修改和扩展的分层令牌语义音频转换器(HTS-AT)进行多通道音频处理,以及用于视频分析的R(2+1)D卷积神经网络(CNN)模型。我们在瑞尔森视听情感语音和歌曲数据库(RAVDESS)的混响版本数据集上,使用合成和现实世界房间冲击响应(RIRs)评估了我们提出的方法。结果表明,与单模态方法相比,整合音频和视频模态的方法具有更高的性能,特别是在具有挑战性的声学条件下。此外,我们还表明,利用多个麦克风的视听多媒体方法优于其单麦克风对应方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables. Accepted to EUSIPCO 2025
Summary
该论文提出一种多模态情感识别(MER)系统,旨在提高挑战环境下的情感识别准确率。该研究采用改良和扩展的分层令牌语义音频转换器(HTS-AT)进行多通道音频处理,并结合R(2+1)D卷积神经网络(CNN)模型进行视频分析。在瑞尔森音频视觉情感语音和歌曲数据库(RAVDESS)数据集上,使用合成和真实世界房间脉冲响应(RIRs)对该方法进行了评估。结果表明,融合音频和视频模态的方法相较于单模态方法表现更优,特别是在挑战环境下。同时,使用多个麦克风的多模态(视听)方法优于单麦克风方法。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了一种多模态情感识别(MER)系统,用于提高挑战环境下的情感识别准确率。
- 研究结合了分层令牌语义音频转换器(HTS-AT)和R(2+1)D卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,分别处理多通道音频和视频信息。
- 论文在瑞尔森音频视觉情感数据库上进行了实验,使用了合成和真实世界的房间脉冲响应。
- 融合音频和视频模态的方法表现优于单模态方法,特别是在挑战环境下。
- 使用多个麦克风的多模态方法相较于单麦克风方法具有更好的性能。
- 该研究强调了多模态情感识别的潜力,特别是在处理复杂和多变的环境噪声时。
点此查看论文截图

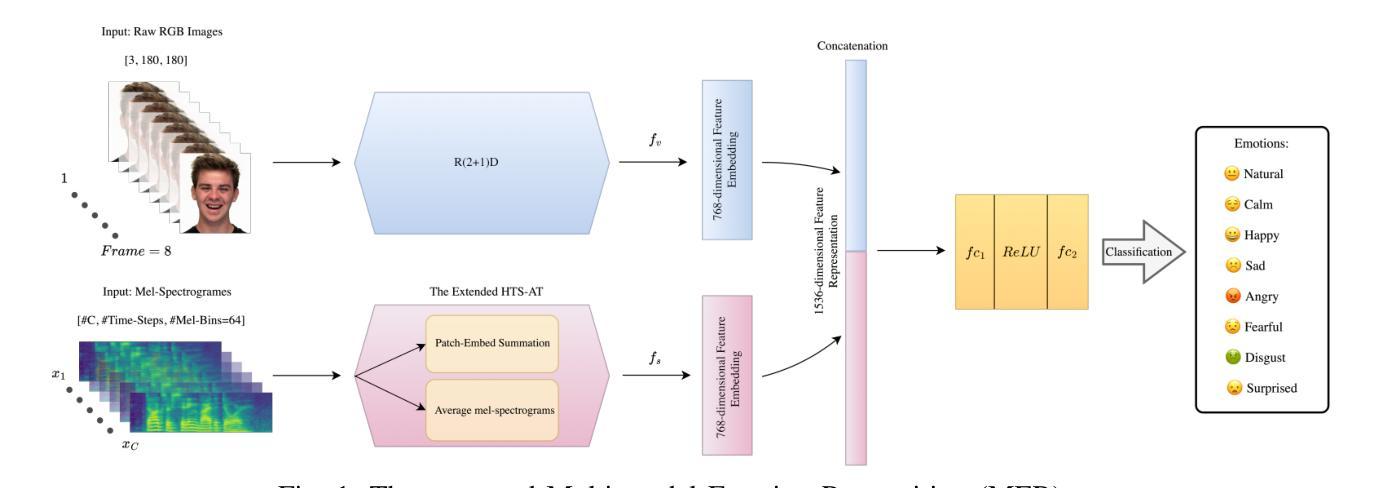
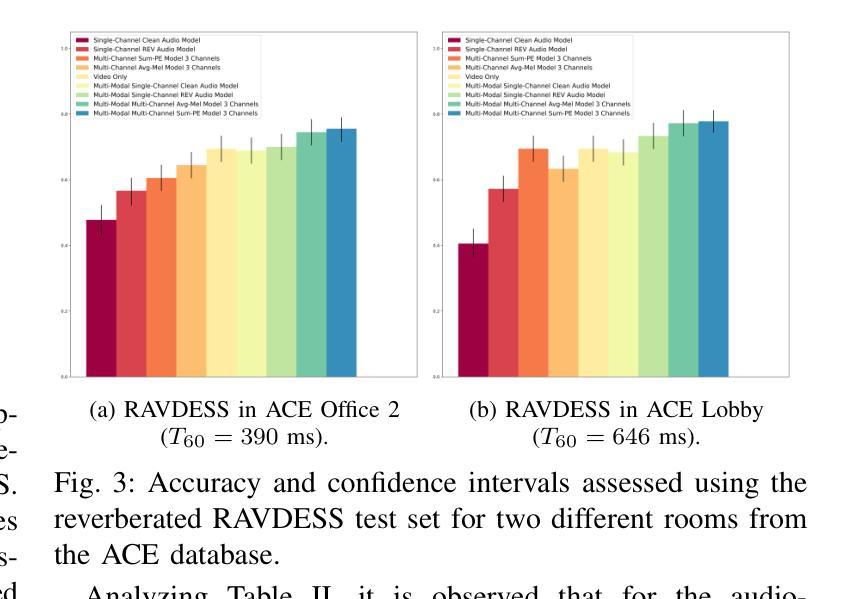
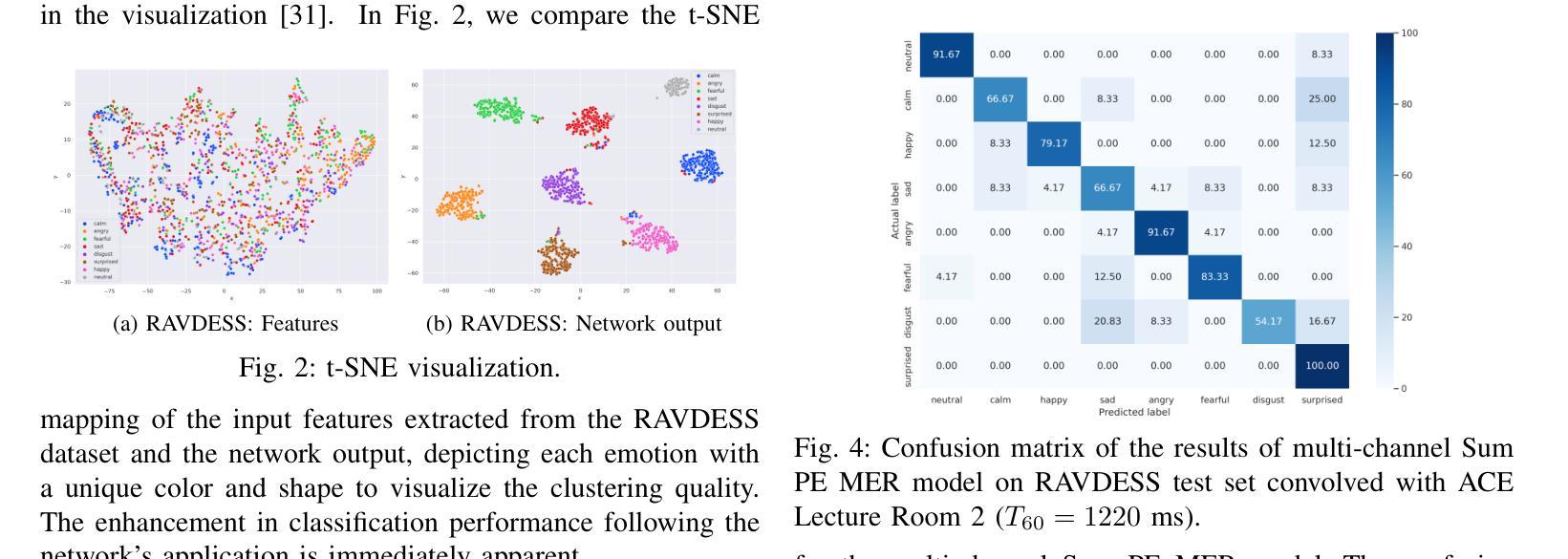
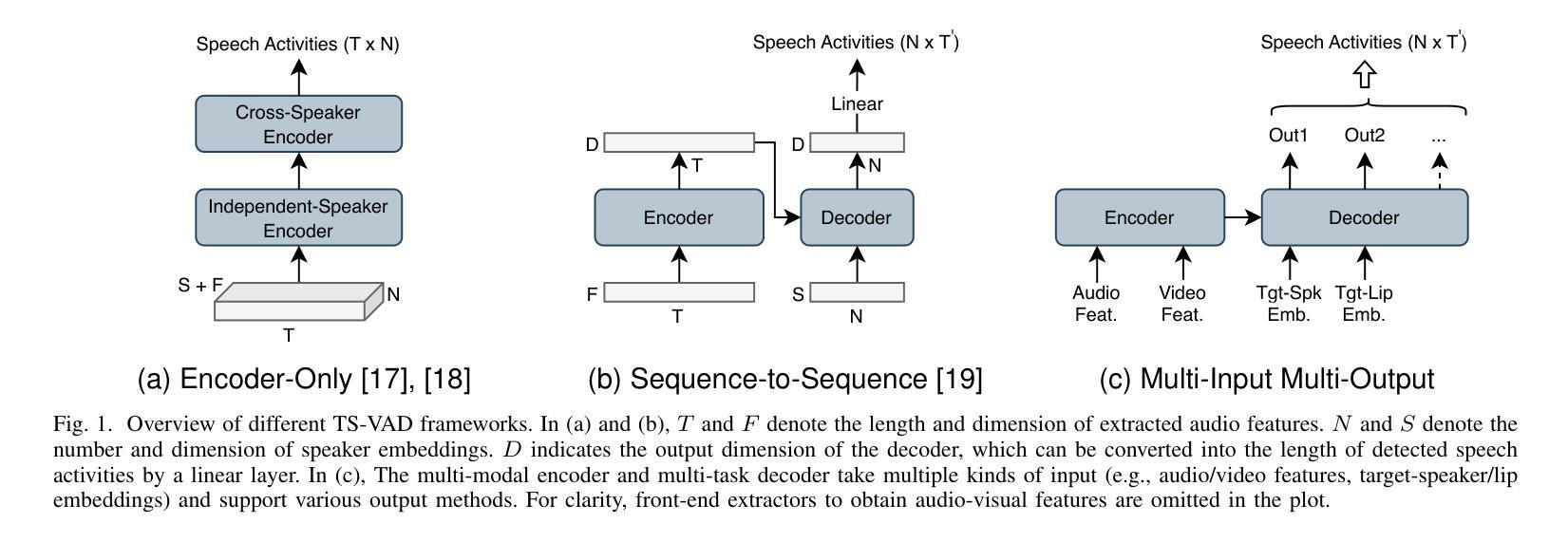
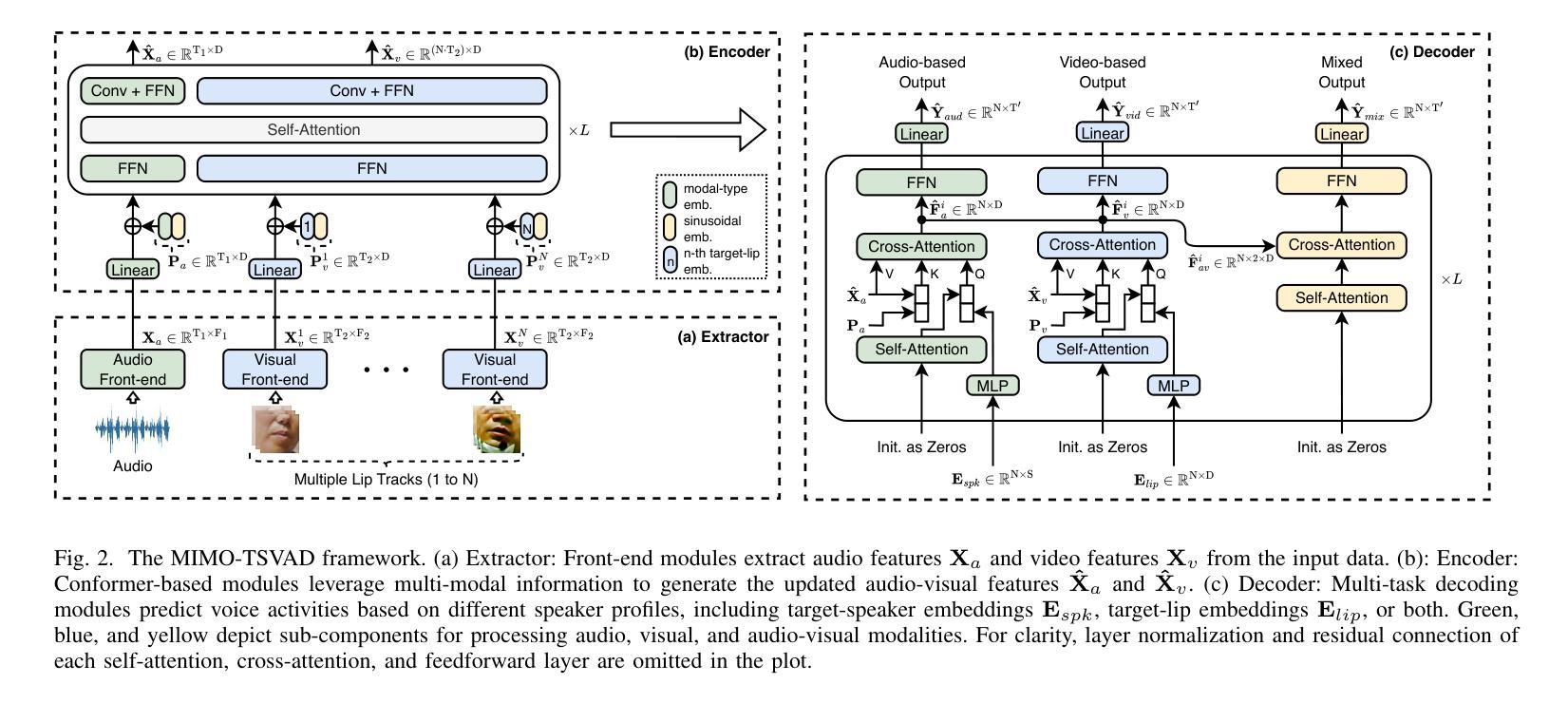
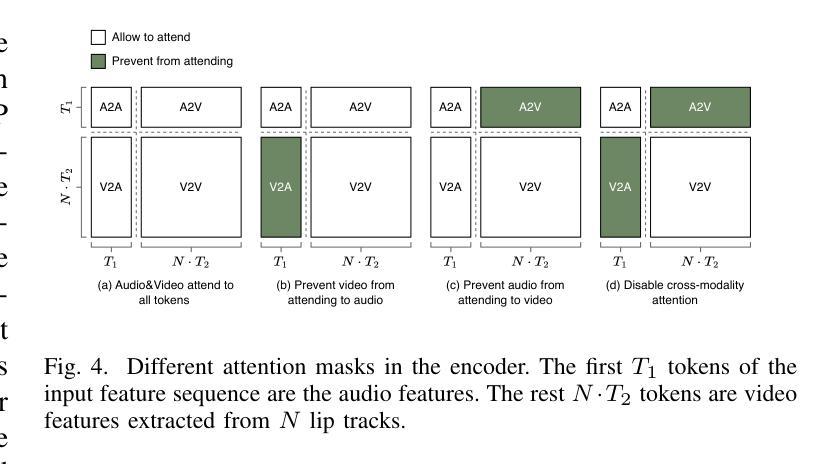
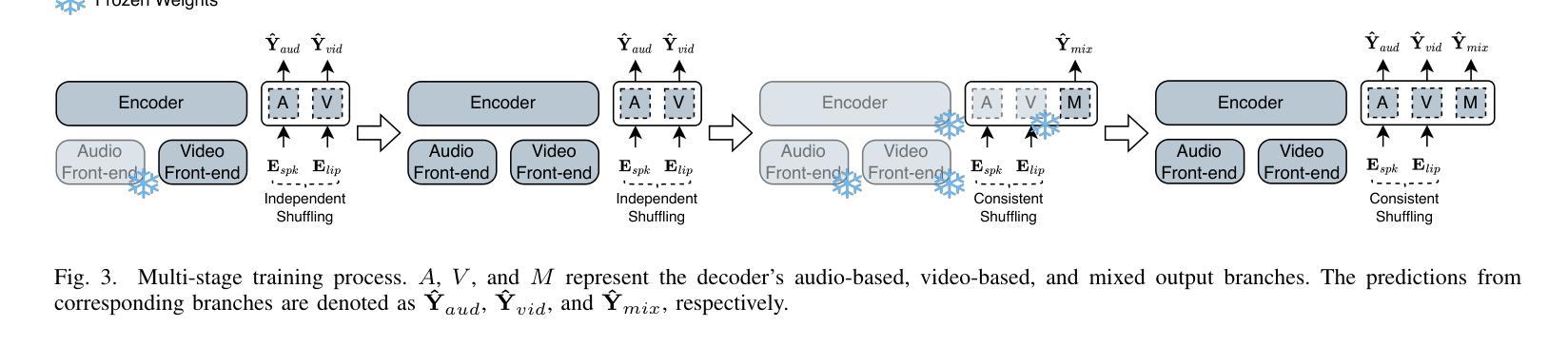
Multi-Input Multi-Output Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection For Unified, Flexible, and Robust Audio-Visual Speaker Diarization
Authors:Ming Cheng, Ming Li
Audio-visual learning has demonstrated promising results in many classical speech tasks (e.g., speech separation, automatic speech recognition, wake-word spotting). We believe that introducing visual modality will also benefit speaker diarization. To date, Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection (TS-VAD) plays an important role in highly accurate speaker diarization. However, previous TS-VAD models take audio features and utilize the speaker’s acoustic footprint to distinguish his or her personal speech activities, which is easily affected by overlapped speech in multi-speaker scenarios. Although visual information naturally tolerates overlapped speech, it suffers from spatial occlusion, low resolution, etc. The potential modality-missing problem blocks TS-VAD towards an audio-visual approach. This paper proposes a novel Multi-Input Multi-Output Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection (MIMO-TSVAD) framework for speaker diarization. The proposed method can take audio-visual input and leverage the speaker’s acoustic footprint or lip track to flexibly conduct audio-based, video-based, and audio-visual speaker diarization in a unified sequence-to-sequence framework. Experimental results show that the MIMO-TSVAD framework demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on the VoxConverse, DIHARD-III, and MISP 2022 datasets under corresponding evaluation metrics, obtaining the Diarization Error Rates (DERs) of 4.18%, 10.10%, and 8.15%, respectively. In addition, it can perform robustly in heavy lip-missing scenarios.
视听学习在多个经典语音任务中展现出有前景的结果,例如语音分离、自动语音识别、唤醒词识别等。我们相信引入视觉模式也将对说话人声音日记有益。迄今为止,目标说话人语音活动检测(TS-VAD)在高度准确的说话人声音日记中发挥着重要作用。然而,之前的TS-VAD模型采用音频特征并利用说话者的声音特征来区分其个人语音活动,这在多说话人场景中的重叠语音下很容易受到影响。虽然视觉信息自然地容忍重叠语音,但它受到空间遮挡、分辨率低等问题的困扰。潜在的模态缺失问题阻碍了TS-VAD向视听方法的转变。本文提出了一种新颖的用于说话人声音日记的多输入多输出目标说话人语音活动检测(MIMO-TSVAD)框架。该方法可以接收视听输入,并利用说话者的声音特征或唇部轨迹在统一的序列到序列框架中进行基于音频、基于视频和视听结合的说话人声音日记。实验结果表明,MIMO-TSVAD框架在VoxConverse、DIHARD-III和MISP 2022数据集上的性能达到了最新水平,在相应的评估指标下,分别获得了4.18%、10.10%和8.15%的日记化错误率(DERs)。此外,它在唇部严重缺失的场景中也能稳健地运行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing
摘要
视听学习在多种经典语音任务中展现出显著成果,如语音分离、自动语音识别和唤醒词识别等。本研究提出一种新颖的针对演讲者分类的多输入多输出目标语音活动检测(MIMO-TSVAD)框架。该框架可融合视听输入,利用演讲者的声学足迹或唇纹进行灵活音频、视频和视听演讲者分类。实验结果显示,MIMO-TSVAD框架在VoxConverse、DIHARD-III和MISP 2022数据集上实现出色性能,对应评价指标下所得聚类错误率分别为4.18%、10.10%和8.15%,且在严重唇缺失场景中表现稳健。
关键见解
- 音频视觉学习在多个语音任务中表现优异,包括语音分离、自动语音识别等。
- 目标语音活动检测(TS-VAD)在精确演讲者分类中起到重要作用。
- 传统TS-VAD模型依赖于音频特征,易受多说话人场景中的语音重叠影响。
- 视觉信息虽然能自然容忍语音重叠,但受到空间遮挡、分辨率低等问题的影响。
- 本研究提出MIMO-TSVAD框架,融合视听输入,进行灵活音频、视频和视听演讲者分类。
- MIMO-TSVAD框架在多个数据集上表现优异,包括VoxConverse、DIHARD-III和MISP 2022。
- MIMO-TSVAD框架在严重唇缺失场景中表现稳健。
点此查看论文截图