⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
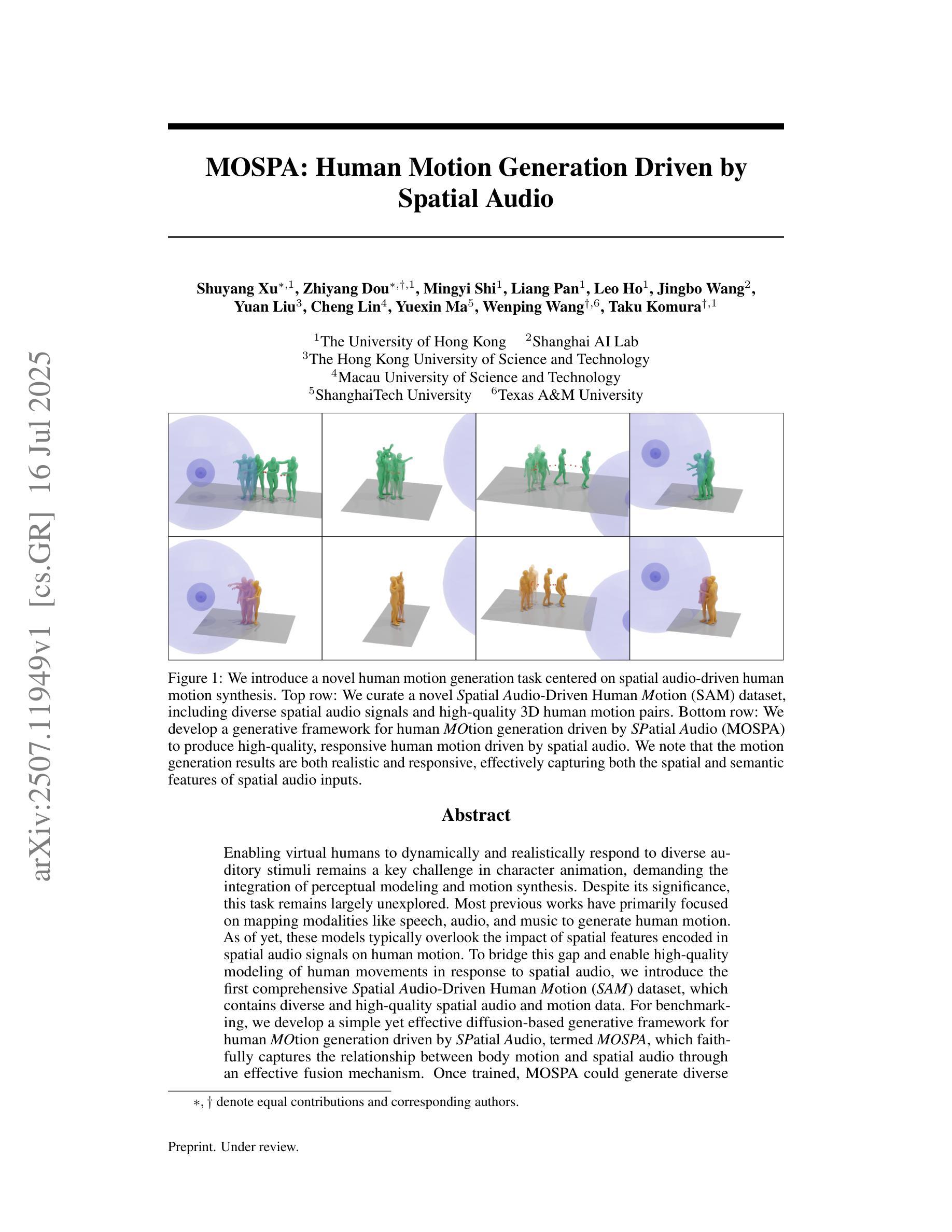
MOSPA: Human Motion Generation Driven by Spatial Audio
Authors:Shuyang Xu, Zhiyang Dou, Mingyi Shi, Liang Pan, Leo Ho, Jingbo Wang, Yuan Liu, Cheng Lin, Yuexin Ma, Wenping Wang, Taku Komura
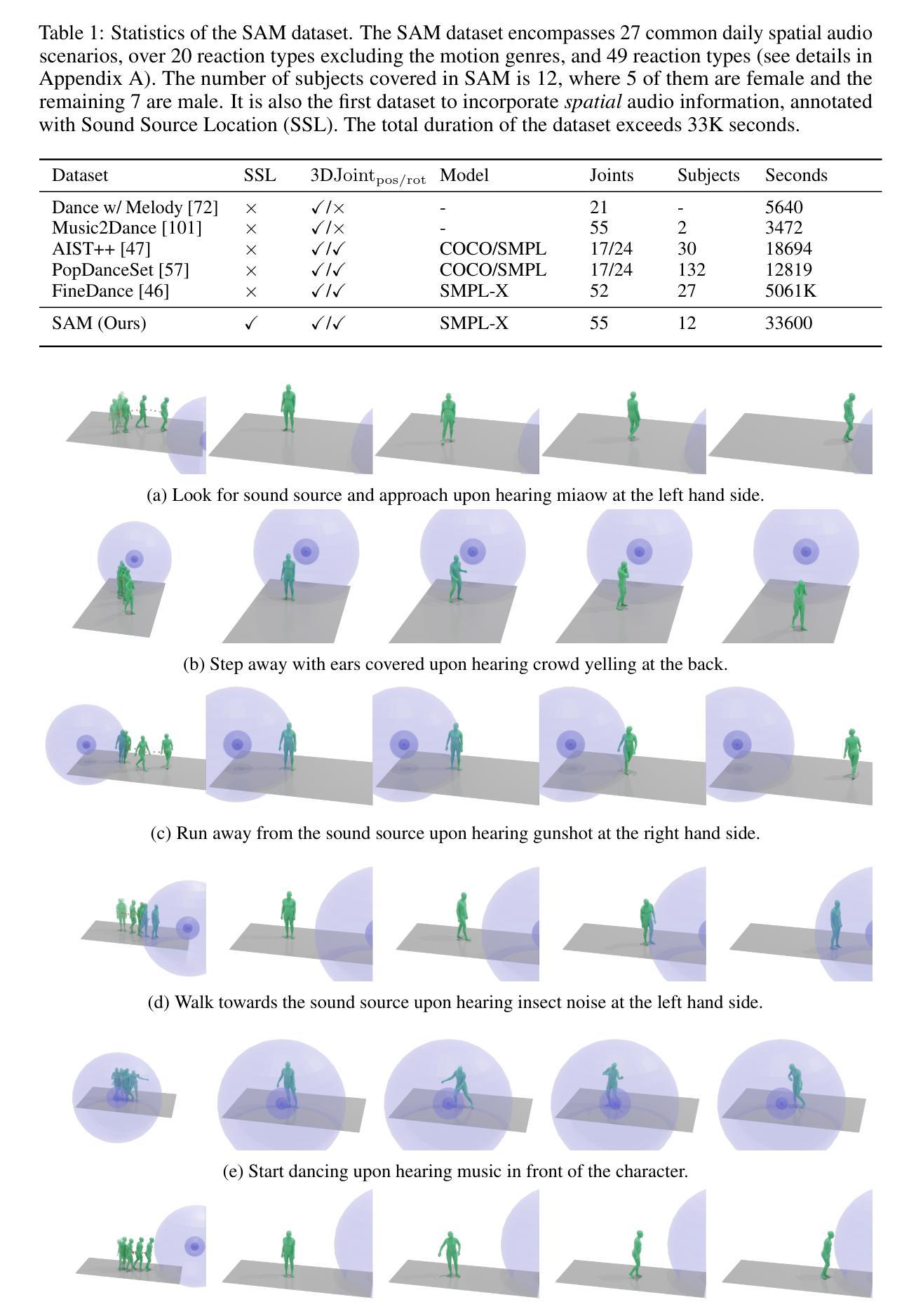
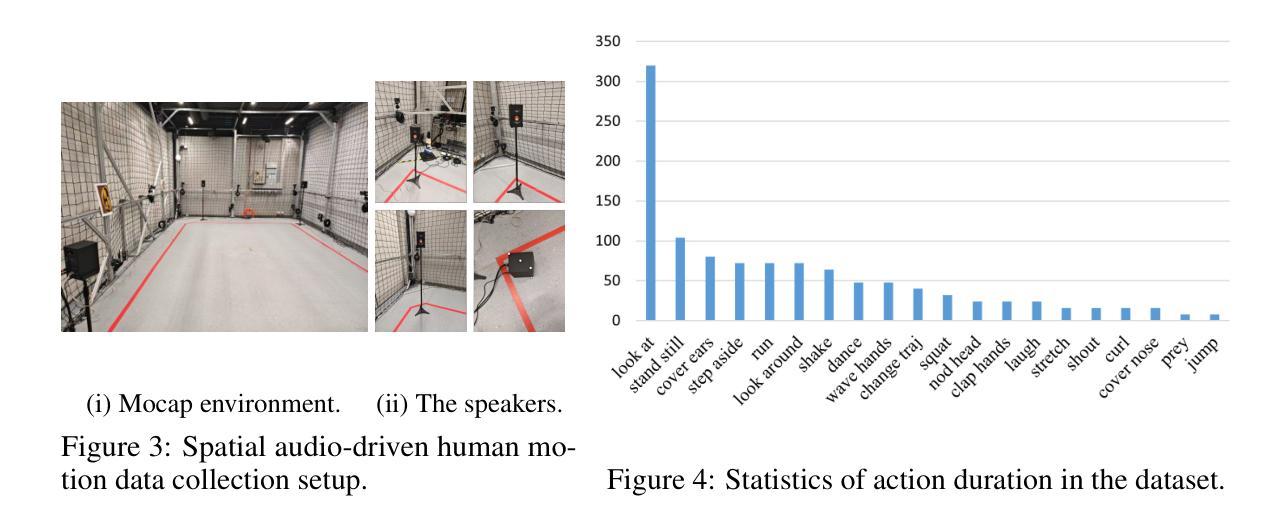
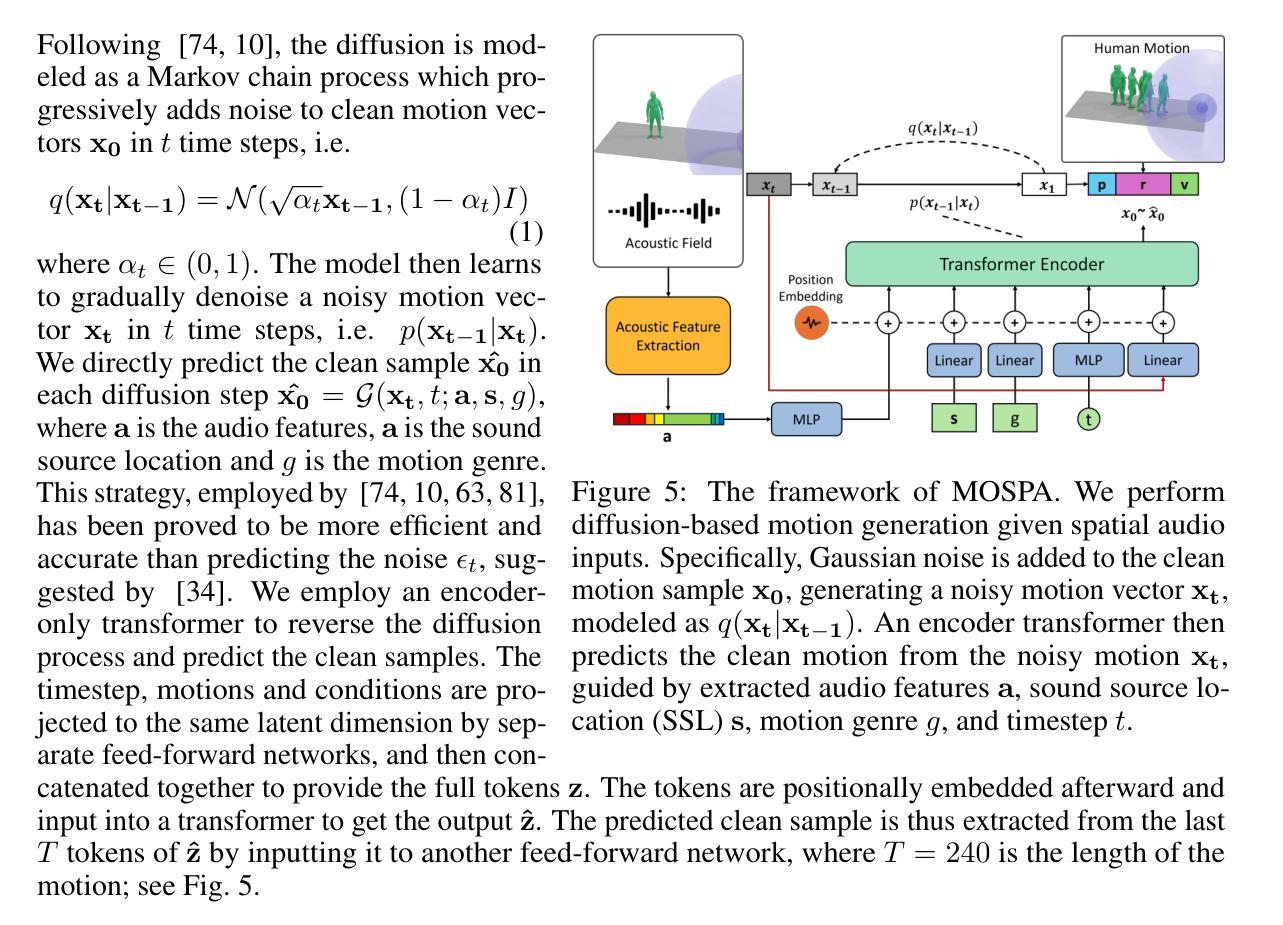
Enabling virtual humans to dynamically and realistically respond to diverse auditory stimuli remains a key challenge in character animation, demanding the integration of perceptual modeling and motion synthesis. Despite its significance, this task remains largely unexplored. Most previous works have primarily focused on mapping modalities like speech, audio, and music to generate human motion. As of yet, these models typically overlook the impact of spatial features encoded in spatial audio signals on human motion. To bridge this gap and enable high-quality modeling of human movements in response to spatial audio, we introduce the first comprehensive Spatial Audio-Driven Human Motion (SAM) dataset, which contains diverse and high-quality spatial audio and motion data. For benchmarking, we develop a simple yet effective diffusion-based generative framework for human MOtion generation driven by SPatial Audio, termed MOSPA, which faithfully captures the relationship between body motion and spatial audio through an effective fusion mechanism. Once trained, MOSPA could generate diverse realistic human motions conditioned on varying spatial audio inputs. We perform a thorough investigation of the proposed dataset and conduct extensive experiments for benchmarking, where our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on this task. Our model and dataset will be open-sourced upon acceptance. Please refer to our supplementary video for more details.
让虚拟人类动态且真实地响应各种听觉刺激仍是角色动画中的关键挑战,这需要感知建模和运动合成的融合。尽管其意义重大,但这个任务仍未得到充分探索。以前的大多数工作主要集中在将语音、音频和音乐等映射模式映射到人类运动生成上。然而,迄今为止,这些模型通常忽视了空间音频信号中编码的空间特征对人类运动的影响。为了弥补这一差距,实现对空间音频响应的人类运动高质量建模,我们首次推出了全面的空间音频驱动人类运动(SAM)数据集,其中包含多样且高质量的空间音频和运动数据。为了基准测试,我们开发了一个基于扩散的简单而有效的人类运动生成驱动框架MOSPA,它通过有效的融合机制忠实捕捉身体运动和空间音频之间的关系。一旦训练完成,MOSPA可以根据不同的空间音频输入生成多样且真实的人类运动。我们对提出的数据集进行了全面调查,并进行了广泛的基准测试实验,我们的方法在该任务上取得了最先进的性能。我们的模型和数据集将在接受后开源。更多详细信息请参阅我们的补充视频。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对空间音频驱动的人物动作模拟的综合数据集,该数据集包含多样且高质量的空间音频和运动数据。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种基于扩散的生成框架MOSPA,它能够有效地将空间音频和人物动作相融合,从而生成逼真的人物动作。通过实验验证,MOSPA在任务上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 空间音频对人物动作模拟的影响被忽视,需要新的数据集和模型来弥补这一差距。
- 引入首个全面的空间音频驱动人物运动(SAM)数据集,包含多样且高质量的数据。
- 提出了一种基于扩散的生成框架MOSPA,用于根据空间音频生成人物动作。
- MOSPA通过有效的融合机制,捕捉空间音频和人物动作之间的关系。
- MOSPA能够生成多样化的、逼真的人物动作,根据不同的空间音频输入进行条件生成。
- 实验结果表明,MOSPA在任务上实现了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图
MEDTalk: Multimodal Controlled 3D Facial Animation with Dynamic Emotions by Disentangled Embedding
Authors:Chang Liu, Ye Pan, Chenyang Ding, Susanto Rahardja, Xiaokang Yang
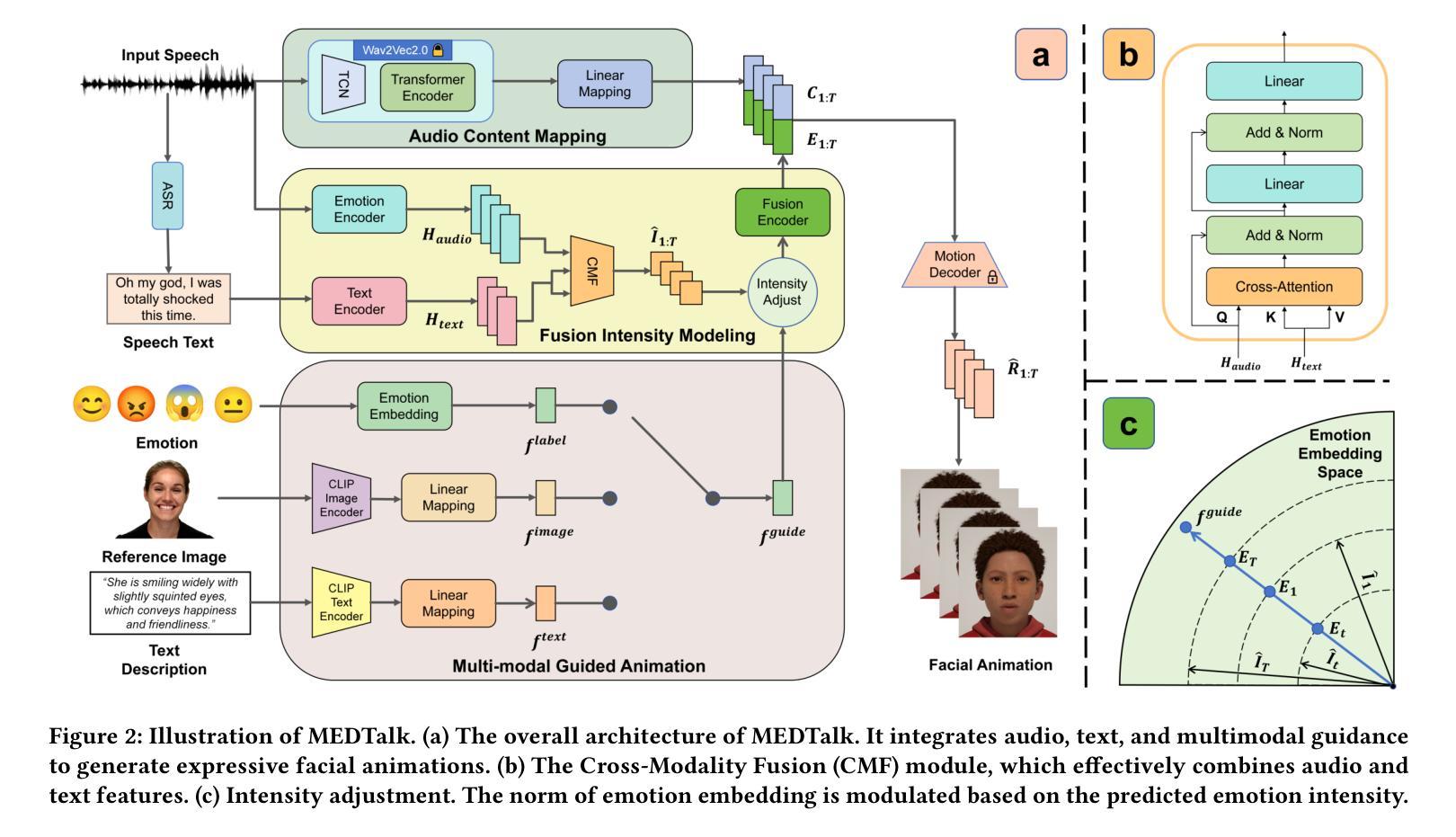
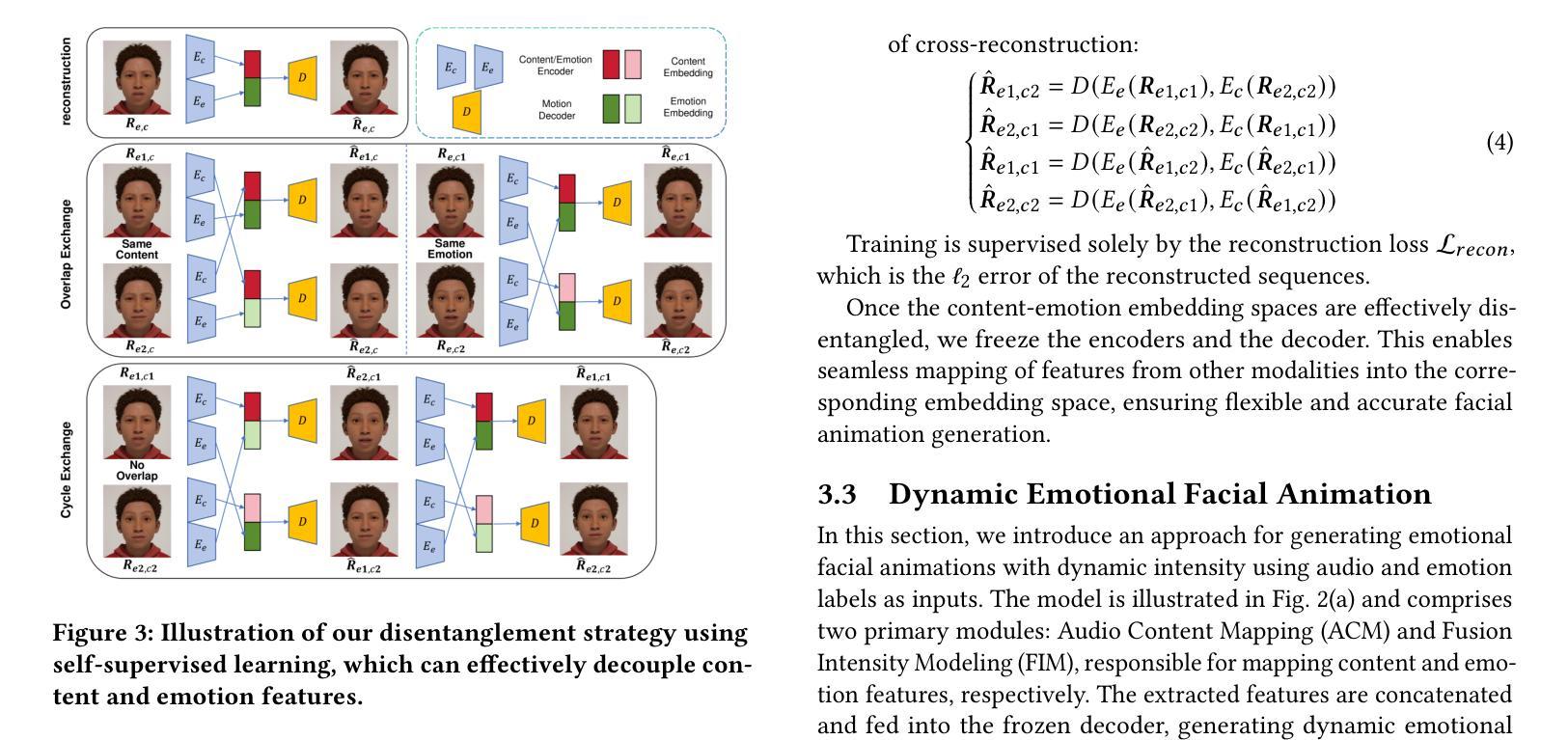
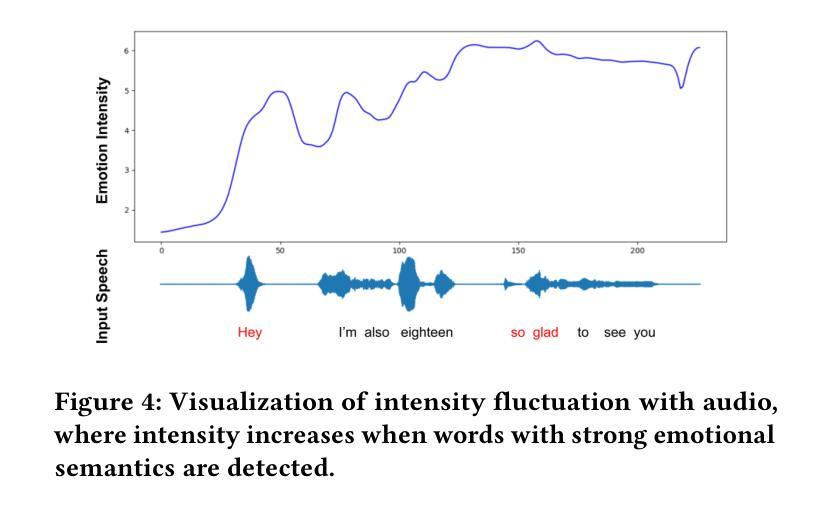
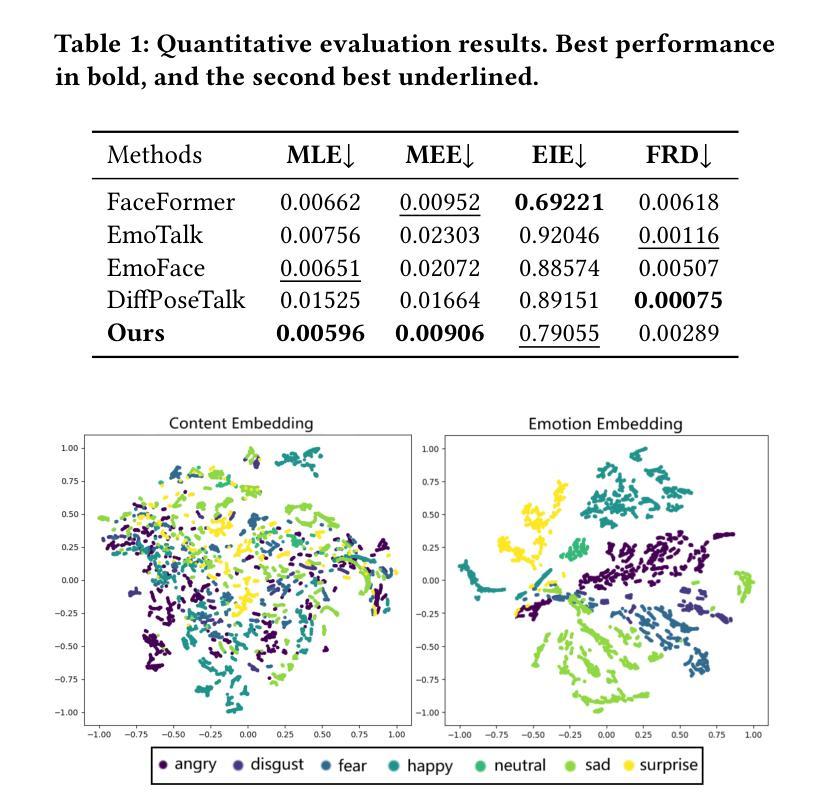
Audio-driven emotional 3D facial animation aims to generate synchronized lip movements and vivid facial expressions. However, most existing approaches focus on static and predefined emotion labels, limiting their diversity and naturalness. To address these challenges, we propose MEDTalk, a novel framework for fine-grained and dynamic emotional talking head generation. Our approach first disentangles content and emotion embedding spaces from motion sequences using a carefully designed cross-reconstruction process, enabling independent control over lip movements and facial expressions. Beyond conventional audio-driven lip synchronization, we integrate audio and speech text, predicting frame-wise intensity variations and dynamically adjusting static emotion features to generate realistic emotional expressions. Furthermore, to enhance control and personalization, we incorporate multimodal inputs-including text descriptions and reference expression images-to guide the generation of user-specified facial expressions. With MetaHuman as the priority, our generated results can be conveniently integrated into the industrial production pipeline. The code is available at: https://github.com/SJTU-Lucy/MEDTalk.
音频驱动的情感3D面部动画旨在生成同步的唇部运动和生动的面部表情。然而,大多数现有方法主要关注静态和预定义的情感标签,这限制了其多样性和自然性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MEDTalk,这是一个用于精细粒度和动态情感对话头部生成的新型框架。我们的方法首先通过使用精心设计的跨重建过程,从运动序列中分离内容和情感嵌入空间,实现对唇部运动和面部表情的独立控制。除了传统的音频驱动唇同步外,我们还整合了音频和语音文本,预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征,以生成逼真的情感表达。此外,为了提高控制和个性化,我们结合了多种模式输入,包括文本描述和参考表情图像,以指导用户指定的面部表情的生成。以MetaHuman为优先,我们生成的结果可以方便地集成到工业生产流程中。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/SJTU-Lucy/MEDTalk。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了MEDTalk框架,它是一个针对精细化和动态情绪交谈头部生成的全新框架。它通过解开内容和情感嵌入空间,实现独立控制唇动和面部表情。它整合音频、语音文本,预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征以生成真实情感表达。MEDTalk结合多种模式输入如文本描述和参考表情图像来引导生成用户指定的面部表情,能方便地集成到工业生产流程中。
Key Takeaways
- MEDTalk是一个用于精细化情绪交谈头部生成的全新框架,能够克服现有方法多样性不足的局限。
- MEDTalk实现了独立控制唇动和面部表情,通过解开内容和情感嵌入空间的方式。
- MEDTalk不仅依赖音频驱动唇同步,还整合音频和语音文本,预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征。
- MEDTalk能够结合多种模式输入如文本描述和参考表情图像来引导生成用户指定的面部表情。
- MEDTalk生成的虚拟头部可以在工业生产流程中轻松集成,使得生成内容更为多样化和真实。
- MEDTalk以MetaHuman为重点应用,可以在其基础上产生具有现实感的情绪表达结果。
点此查看论文截图

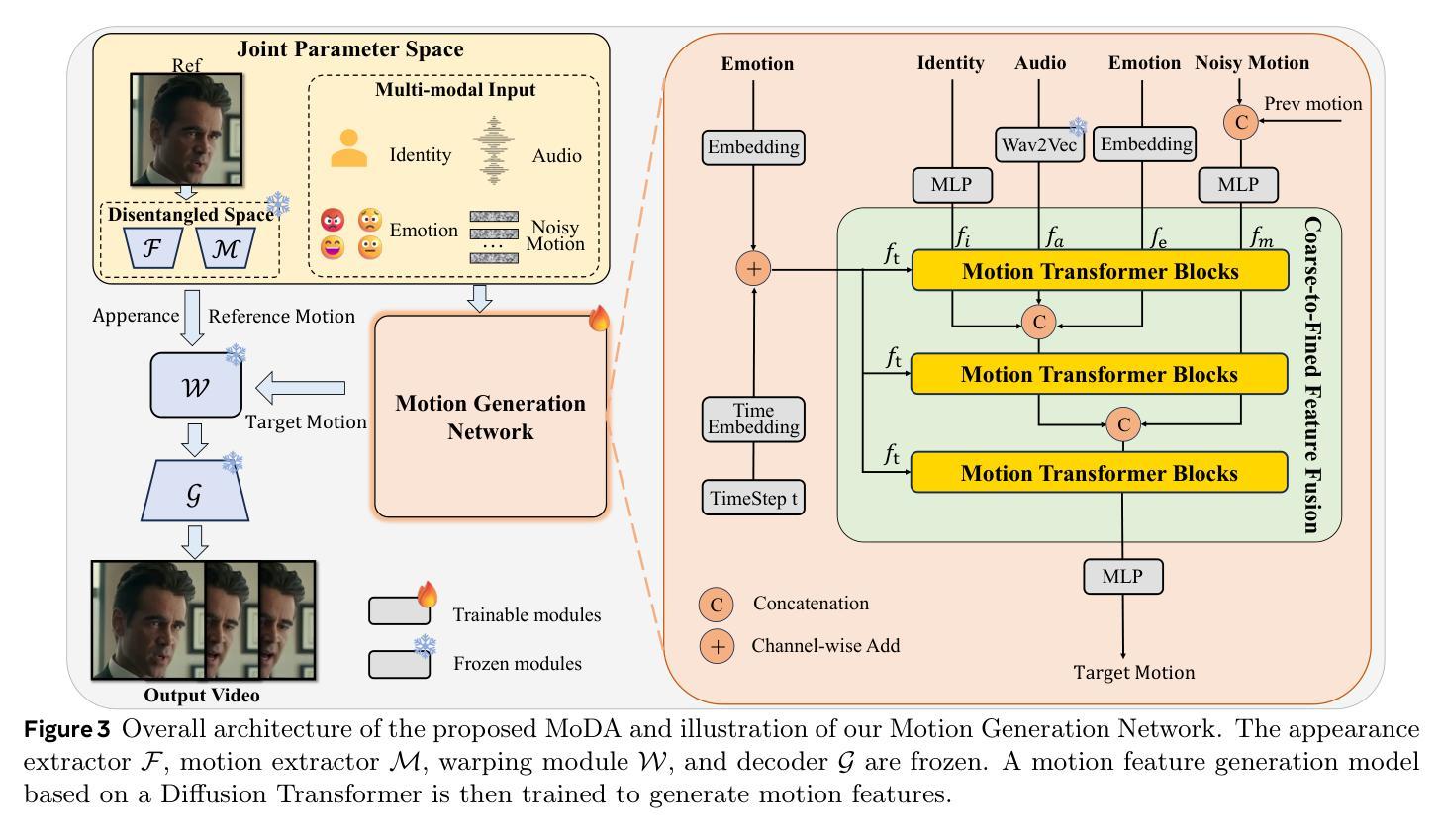
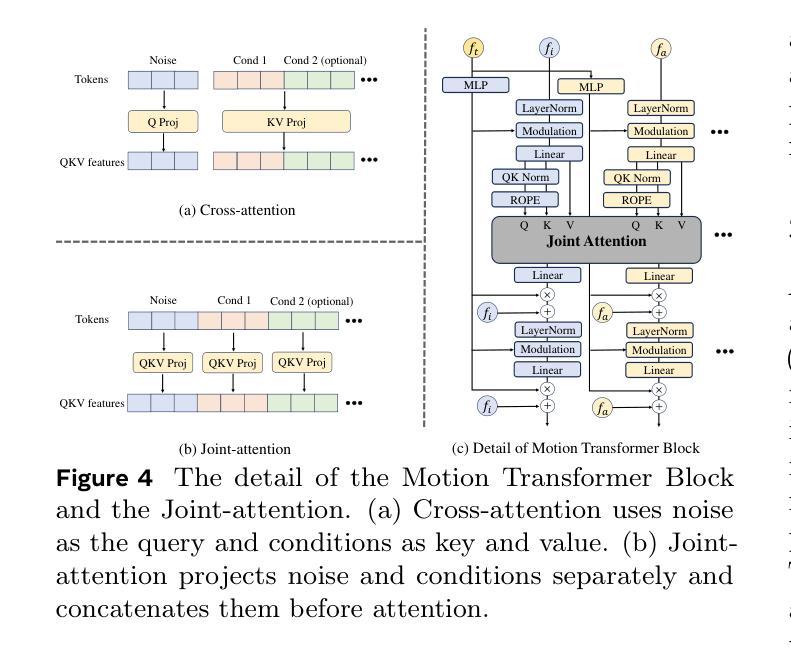
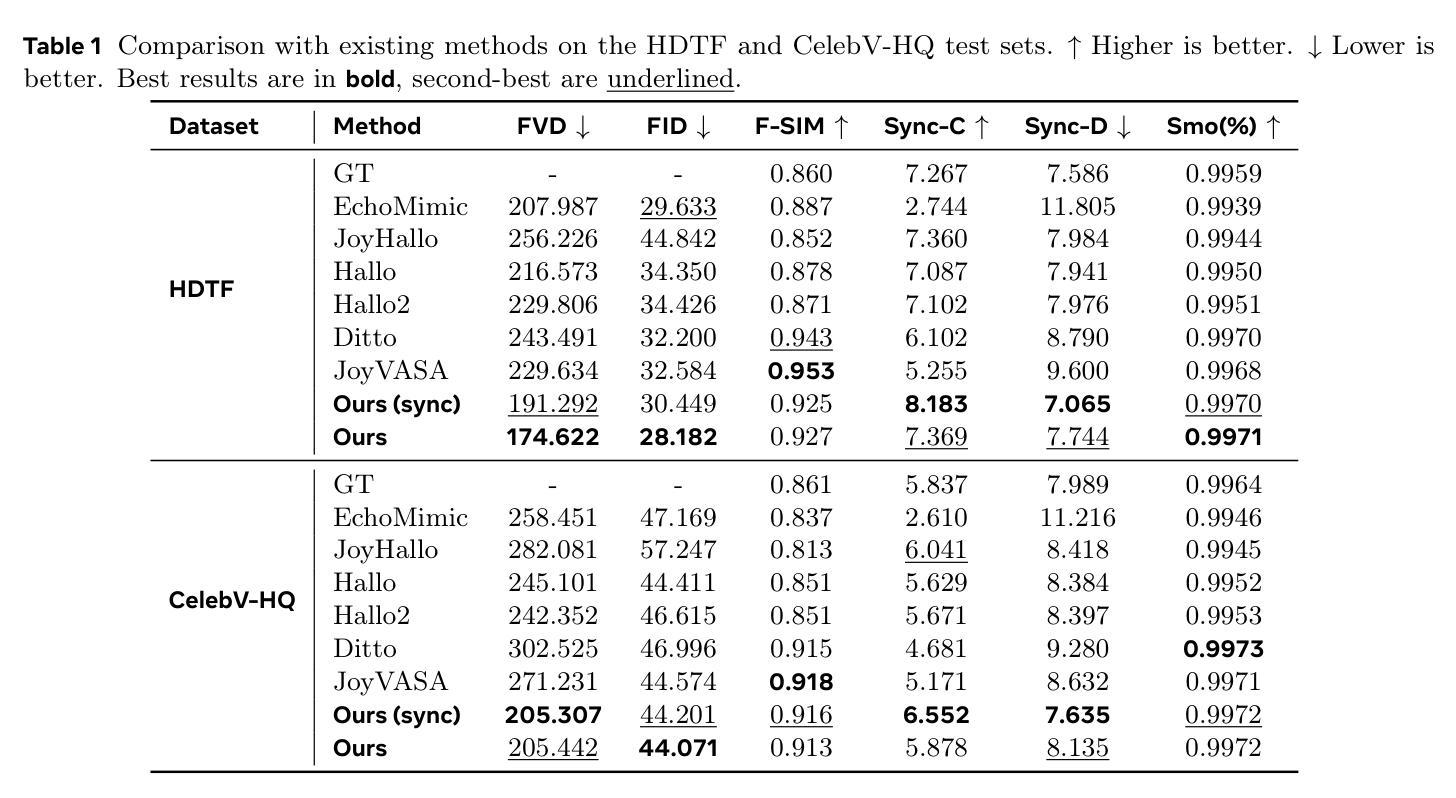
MoDA: Multi-modal Diffusion Architecture for Talking Head Generation
Authors:Xinyang Li, Gen Li, Zhihui Lin, Yichen Qian, GongXin Yao, Weinan Jia, Aowen Wang, Weihua Chen, Fan Wang
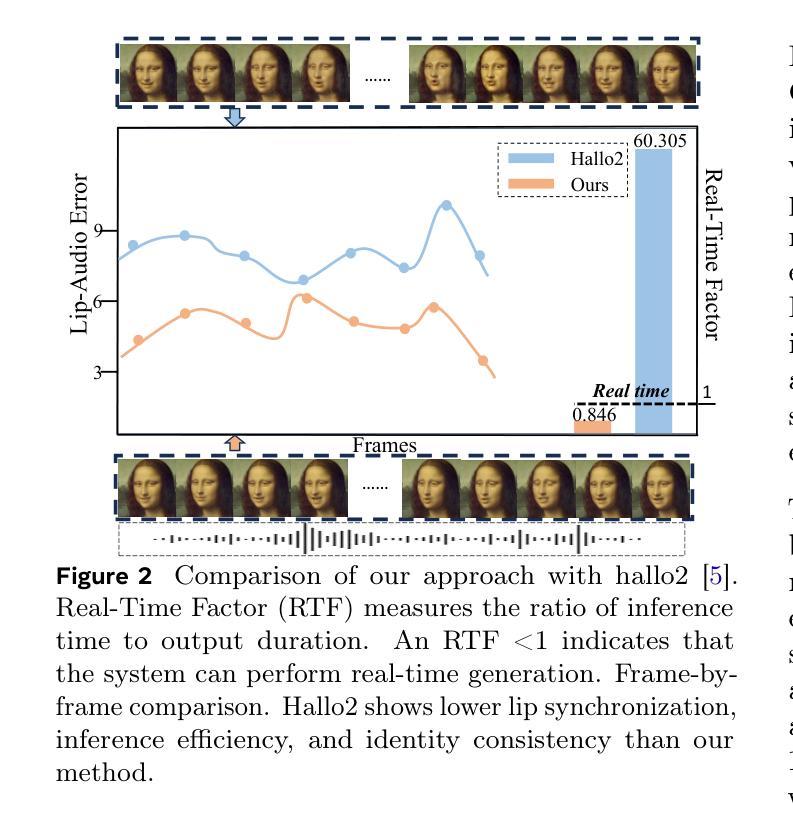
Talking head generation with arbitrary identities and speech audio remains a crucial problem in the realm of the virtual metaverse. Recently, diffusion models have become a popular generative technique in this field with their strong generation capabilities. However, several challenges remain for diffusion-based methods: 1) inefficient inference and visual artifacts caused by the implicit latent space of Variational Auto-Encoders (VAE), which complicates the diffusion process; 2) a lack of authentic facial expressions and head movements due to inadequate multi-modal information fusion. In this paper, MoDA handles these challenges by: 1) defining a joint parameter space that bridges motion generation and neural rendering, and leveraging flow matching to simplify diffusion learning; 2) introducing a multi-modal diffusion architecture to model the interaction among noisy motion, audio, and auxiliary conditions, enhancing overall facial expressiveness. In addition, a coarse-to-fine fusion strategy is employed to progressively integrate different modalities, ensuring effective feature fusion. Experimental results demonstrate that MoDA improves video diversity, realism, and efficiency, making it suitable for real-world applications. Project Page: https://lixinyyang.github.io/MoDA.github.io/
虚拟元宇宙领域中的头部说话人生成具有任意身份和语音音频仍然是一个关键问题。最近,扩散模型凭借其强大的生成能力,已成为该领域的一种流行的生成技术。然而,基于扩散的方法仍存在几个挑战:1)由于变分自动编码器(VAE)的隐式潜在空间复杂,导致扩散过程出现低效推理和视觉伪影;2)由于缺乏多模态信息融合,导致面部表情和头部动作不真实。本文中,MoDA通过以下方法应对这些挑战:1)定义连接运动生成和神经渲染的联合参数空间,并利用流匹配简化扩散学习;2)引入多模态扩散架构,对含噪运动、音频和辅助条件之间的交互进行建模,从而提高面部的整体表现力。此外,采用从粗到细的融合策略,逐步融合不同的模式,确保有效的特征融合。实验结果表明,MoDA提高了视频的多样性、真实性和效率,适合在现实世界应用。项目页面:https://lixinyyang.github.io/MoDA.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures
Summary
虚拟元宇宙中的头部生成问题依然存在,扩散模型成为当前主流技术。然而,扩散模型面临诸多挑战,如推理效率低下和视觉伪影等。MoDA方法通过定义联合参数空间和引入多模态扩散架构来解决这些问题,提高了视频多样性和现实感。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟元宇宙中的头部生成问题仍然重要,扩散模型成为解决此问题的主流技术。
- 扩散模型面临推理效率低下和视觉伪影等挑战。
- MoDA方法通过定义联合参数空间解决了这些问题,简化了扩散学习过程。
- MoDA引入了多模态扩散架构,对噪声运动、音频和辅助条件进行建模,增强了面部表现力。
- 采用从粗到细的融合策略,逐步整合不同模态,确保特征融合有效。
点此查看论文截图


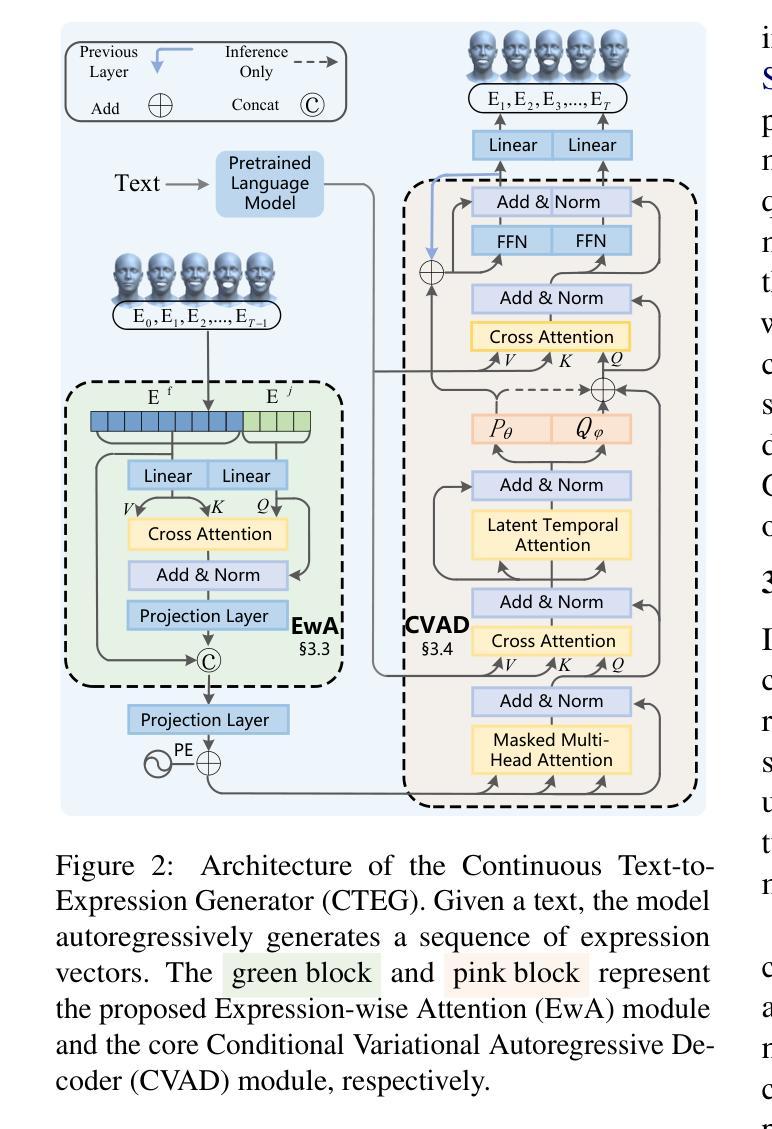
When Words Smile: Generating Diverse Emotional Facial Expressions from Text
Authors:Haidong Xu, Meishan Zhang, Hao Ju, Zhedong Zheng, Erik Cambria, Min Zhang, Hao Fei
Enabling digital humans to express rich emotions has significant applications in dialogue systems, gaming, and other interactive scenarios. While recent advances in talking head synthesis have achieved impressive results in lip synchronization, they tend to overlook the rich and dynamic nature of facial expressions. To fill this critical gap, we introduce an end-to-end text-to-expression model that explicitly focuses on emotional dynamics. Our model learns expressive facial variations in a continuous latent space and generates expressions that are diverse, fluid, and emotionally coherent. To support this task, we introduce EmoAva, a large-scale and high-quality dataset containing 15,000 text-3D expression pairs. Extensive experiments on both existing datasets and EmoAva demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms baselines across multiple evaluation metrics, marking a significant advancement in the field.
使数字人类能够表达丰富的情绪,在对话系统、游戏和其他交互场景中具有重要应用。尽管最近在说话人头部合成方面取得了令人印象深刻的唇同步结果,但它们往往忽视了面部表情的丰富性和动态性。为了填补这一关键空白,我们引入了一种端到端的文本到表情模型,该模型明确专注于情感动态。我们的模型在连续的潜在空间学习表情面部变化,并生成多样、流畅、情感连贯的表达式。为了支持此任务,我们介绍了EmoAva,这是一个包含15000个文本-3D表情对的大规模高质量数据集。在现有数据集和EmoAva上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个评估指标上显著优于基线,标志着该领域的一个重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages. Resources: https://github.com/WalkerMitty/EmoAva
Summary
本文介绍了一种端到端的文本到表情模型,该模型专注于情感动力学,可以生成丰富、流畅、情感连贯的面部表情。为支持此任务,引入了EmoAva数据集,包含15,000个文本-3D表情对。实验证明,该方法在多个评估指标上显著优于基准测试,标志着该领域的重要进展。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新的文本到表情模型,该模型能够生成丰富、动态的表情。
- 模型的焦点是情感动力学,能够生成情感连贯的面部表情。
- 引入了一个名为EmoAva的大规模高质量数据集,用于支持该任务。
- 该模型在多个评估指标上显著优于现有方法。
- 该技术可用于对话系统、游戏和其他交互场景。
- 模型在连续潜在空间学习面部表情变化。
点此查看论文截图