⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-03 更新
UPRE: Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation for Object Detection via Unified Prompt and Representation Enhancement
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Fei Wei, Yong Wang, Wenda Zhao, Feiyi Li, Xiangxiang Chu
Zero-shot domain adaptation (ZSDA) presents substantial challenges due to the lack of images in the target domain. Previous approaches leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to tackle this challenge, exploiting their zero-shot learning capabilities. However, these methods primarily address domain distribution shifts and overlook the misalignment between the detection task and VLMs, which rely on manually crafted prompts. To overcome these limitations, we propose the unified prompt and representation enhancement (UPRE) framework, which jointly optimizes both textual prompts and visual representations. Specifically, our approach introduces a multi-view domain prompt that combines linguistic domain priors with detection-specific knowledge, and a visual representation enhancement module that produces domain style variations. Furthermore, we introduce multi-level enhancement strategies, including relative domain distance and positive-negative separation, which align multi-modal representations at the image level and capture diverse visual representations at the instance level, respectively. Extensive experiments conducted on nine benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our framework in ZSDA detection scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE.
零样本域自适应(ZSDA)由于目标域中缺乏图像而面临巨大挑战。之前的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLM)来应对这一挑战,发挥它们的零样本学习能力。然而,这些方法主要解决域分布转移问题,而忽略了检测任务与VLM之间的不匹配,VLM依赖于手工制作的提示。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,该框架联合优化文本提示和视觉表示。具体来说,我们的方法引入了一种多视角域提示,它将语言域先验知识与检测特定知识相结合,以及一个视觉表示增强模块,用于生成域风格变化。此外,我们引入了多级增强策略,包括相对域距离和正负分离,它们分别在图像级别对齐多模式表示,并在实例级别捕获多样化的视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在ZSDA检测场景中具有卓越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了零样本领域自适应检测的新方法,即统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架。它旨在解决使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行零样本学习时出现的文本提示与检测任务不匹配以及领域分布偏移问题。UPRE框架通过优化文本提示和视觉表示,引入多视角领域提示和视觉表示增强模块,并采用多层次增强策略,实现跨领域图像检测的优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- ZSDA面临的主要挑战是目标领域的图像缺失。
- 以往的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行零样本学习来解决这一挑战。
- UPRE框架解决了VLMs与检测任务之间的不匹配问题,同时优化了文本提示和视觉表示。
- UPRE引入了多视角领域提示,结合了语言领域先验知识和检测特定知识。
- 视觉表示增强模块用于生成领域风格变化。
- 多层次增强策略包括相对领域距离和正负分离,用于对齐多模态表示和捕捉实例级别的多种视觉表示。
点此查看论文截图

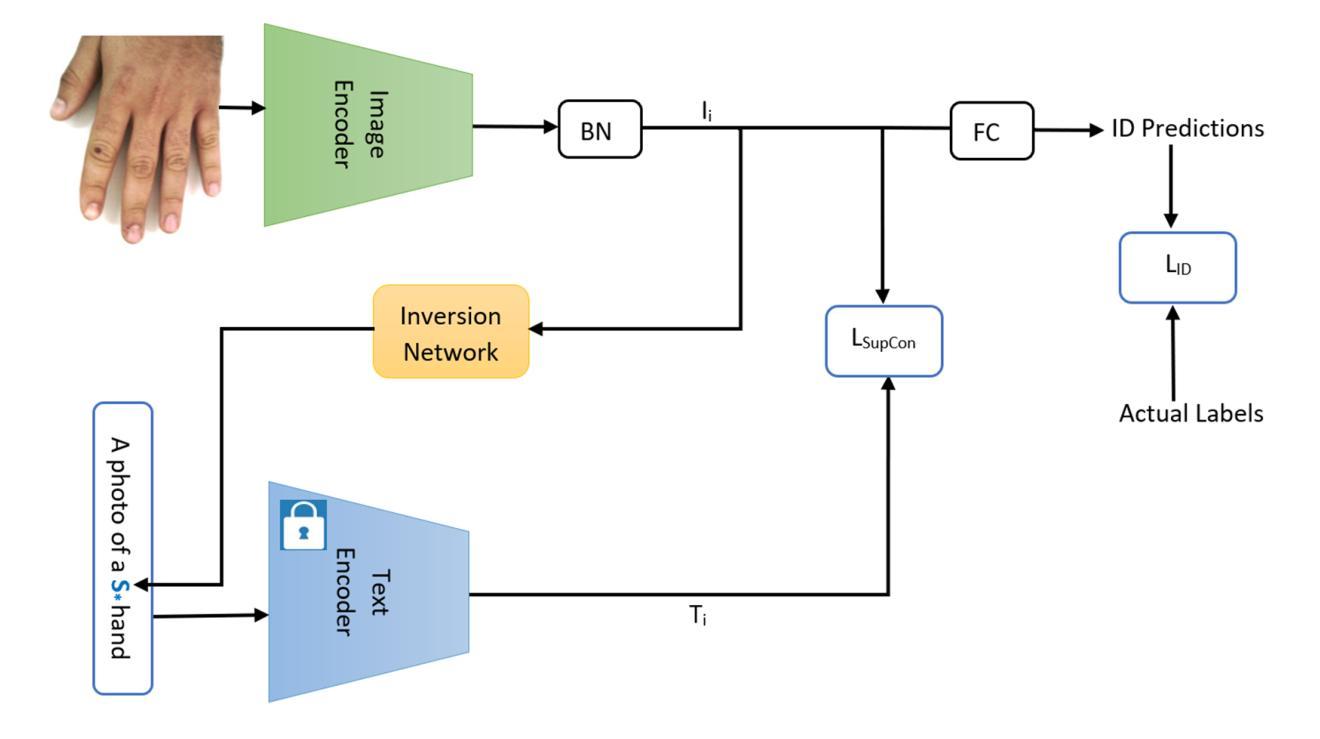
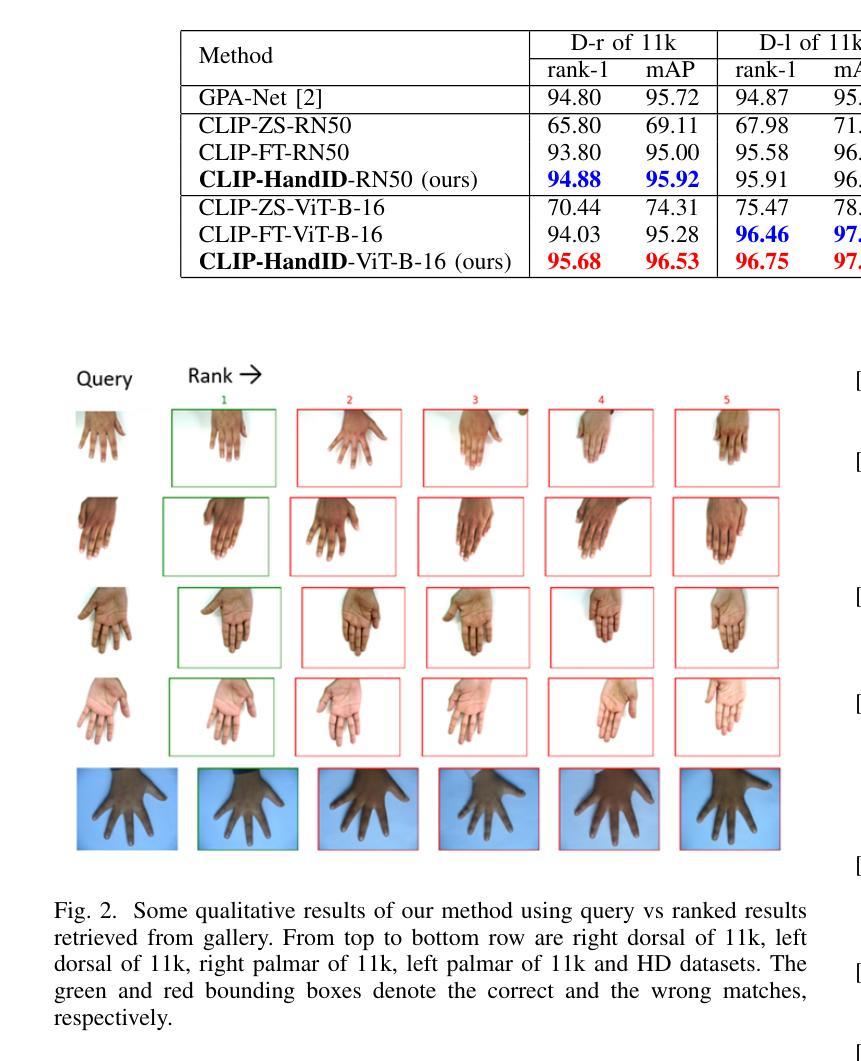
CLIP-HandID: Vision-Language Model for Hand-Based Person Identification
Authors:Nathanael L. Baisa, Babu Pallam, Amudhavel Jayavel
This paper introduces a novel approach to person identification using hand images, designed specifically for criminal investigations. The method is particularly valuable in serious crimes such as sexual abuse, where hand images are often the only identifiable evidence available. Our proposed method, CLIP-HandID, leverages a pre-trained foundational vision-language model - CLIP - to efficiently learn discriminative deep feature representations from hand images (input to CLIP’s image encoder) using textual prompts as semantic guidance. Since hand images are labeled with indexes rather than text descriptions, we employ a textual inversion network to learn pseudo-tokens that encode specific visual contexts or appearance attributes. These learned pseudo-tokens are then incorporated into textual prompts, which are fed into CLIP’s text encoder to leverage its multi-modal reasoning and enhance generalization for identification. Through extensive evaluations on two large, publicly available hand datasets with multi-ethnic representation, we demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
本文介绍了一种利用手部图像进行人员识别的新方法,该方法专为刑事侦查设计。该方法在性虐待等严重犯罪中尤其有价值,在这些情况下,手部图像通常是唯一可用的可识别证据。我们提出的方法CLIP-HandID,利用预训练的视觉语言模型CLIP,通过文本提示作为语义指导,有效地从手部图像(输入CLIP图像编码器)中学习判别深度特征表示。由于手部图像是用索引而不是文本描述来标记的,因此我们采用文本反转网络来学习编码特定视觉上下文或外观属性的伪令牌。然后,这些学习到的伪令牌被纳入文本提示中,这些提示被输入到CLIP的文本编码器中,以利用其多模式推理并增强识别推广。通过对两个包含多种族代表的大型公开手部数据集进行全面评估,我们证明了我们的方法显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于CLIP模型的预训练视觉语言模型,本文提出了一种利用手部图像进行人员识别的新方法,特别是在性虐待等严重犯罪中,手部图像是唯一可识别的证据。通过利用文本提示作为语义指导,CLIP-HandID能够从手部图像中学习具有区分性的深度特征表示。使用索引而不是文本描述来标记手部图像,并通过文本反转网络学习特定视觉上下文或外观属性的伪标记。将这些伪标记纳入文本提示中,以增强CLIP文本编码器的多模态推理和识别泛化能力。在具有多民族代表性的两个大型公开手部数据集上的评估表明,该方法显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种基于CLIP模型的新型手部图像人员识别方法,特别适用于刑事调查中的性虐待等严重犯罪。
- CLIP-HandID利用预训练的视觉语言模型,通过文本提示提高从手部图像中学习特征表示的效率。
- 由于手部图像使用索引而非文本描述进行标记,因此采用文本反转网络学习特定视觉上下文或外观属性的伪标记。
- 伪标记被纳入文本提示中,增强了CLIP的多模态推理和识别泛化能力。
- 该方法在具有多民族代表性的两个大型公开手部数据集上进行了广泛评估。
- 评估结果表明,CLIP-HandID在人员识别方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Single-Channel: Multichannel Signal Imaging for PPG-to-ECG Reconstruction with Vision Transformers
Authors:Xiaoyan Li, Shixin Xu, Faisal Habib, Arvind Gupta, Huaxiong Huang
Reconstructing ECG from PPG is a promising yet challenging task. While recent advancements in generative models have significantly improved ECG reconstruction, accurately capturing fine-grained waveform features remains a key challenge. To address this, we propose a novel PPG-to-ECG reconstruction method that leverages a Vision Transformer (ViT) as the core network. Unlike conventional approaches that rely on single-channel PPG, our method employs a four-channel signal image representation, incorporating the original PPG, its first-order difference, second-order difference, and area under the curve. This multi-channel design enriches feature extraction by preserving both temporal and physiological variations within the PPG. By leveraging the self-attention mechanism in ViT, our approach effectively captures both inter-beat and intra-beat dependencies, leading to more robust and accurate ECG reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing 1D convolution-based approaches, achieving up to 29% reduction in PRD and 15% reduction in RMSE. The proposed approach also produces improvements in other evaluation metrics, highlighting its robustness and effectiveness in reconstructing ECG signals. Furthermore, to ensure a clinically relevant evaluation, we introduce new performance metrics, including QRS area error, PR interval error, RT interval error, and RT amplitude difference error. Our findings suggest that integrating a four-channel signal image representation with the self-attention mechanism of ViT enables more effective extraction of informative PPG features and improved modeling of beat-to-beat variations for PPG-to-ECG mapping. Beyond demonstrating the potential of PPG as a viable alternative for heart activity monitoring, our approach opens new avenues for cyclic signal analysis and prediction.
从PPG重建ECG是一项有前途但具有挑战性的任务。虽然生成模型的最新进展已显着改善了ECG重建,但准确捕获精细波形特征仍然是一个关键挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的PPG-to-ECG重建方法,该方法以视觉变压器(ViT)为核心网络。与依赖单通道PPG的传统方法不同,我们的方法采用四通道信号图像表示形式,结合了原始PPG、其一阶差分、二阶差分和曲线下的面积。这种多通道设计通过保留PPG中的时间和生理变化来丰富特征提取。通过利用ViT中的自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地捕获了心跳间和心跳内的依赖关系,从而实现了更稳健和准确的ECG重建。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于现有的基于一维卷积的方法,在PRD上减少了高达29%,在RMSE上减少了15%。所提出的方法在其他评估指标上也取得了改进,这突显了其在重建ECG信号方面的稳健性和有效性。此外,为了确保临床上相关的评估,我们引入了新的性能指标,包括QRS面积误差、PR间隔误差、RT间隔误差和RT振幅差异误差。我们的研究结果表明,将四通道信号图像表示与ViT的自注意力机制相结合,能够更有效地提取有用的PPG特征,并提高对PPG-to-ECG映射的心跳间变化的建模能力。除了证明PPG作为心脏活动监测的可行替代方案具有潜力外,我们的方法为循环信号分析和预测开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于脉冲波(PPG)的心电图(ECG)重建是一个前景广阔但充满挑战的任务。尽管生成模型领域的最新进展显著改进了ECG重建,但准确捕捉精细波形特征仍是关键挑战。本研究提出了一种新型的PPG到ECG重建方法,该方法以视觉转换器(ViT)为核心网络。与传统的依赖于单通道PPG的方法不同,我们的方法采用四通道信号图像表示,包括原始PPG、其一阶差分、二阶差分和曲线下面积,通过利用ViT中的自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地捕捉到了心跳间和心跳内的依赖关系,实现了更稳健和准确的ECG重建。实验结果表明,我们的方法在一维卷积基方法上持续表现出优势,PRD降低了29%,RMSE降低了15%。此外,为了确保临床相关的评估,我们引入了新的性能指标,包括QRS面积误差、PR间隔误差、RT间隔误差和RT振幅差异误差。研究发现,将四通道信号图像表示与ViT的自注意力机制相结合,能有效提取PPG的信息特征,提高心跳间变化的建模能力,为PPG到ECG的映射提供了新思路。除了证明PPG作为心脏活动监测的可行替代方案具有潜力外,我们的方法还为周期性信号分析和预测开辟了新途径。
关键见解
- PPG-to-ECG重建是一项有前途但具有挑战性的任务。尽管生成模型的最新进展有所改进,但捕捉精细波形特征仍是关键挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的PPG-to-ECG重建方法,使用四通道信号图像表示作为输入,包括原始PPG及其一阶、二阶差值和曲线下面积。
- 利用ViT中的自注意力机制有效捕捉心跳间和心跳内的依赖关系,实现更稳健和准确的ECG重建。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在一维卷积基方法上表现优越,PRD和RMSE等指标有所降低。
- 为了进行临床相关评估,引入了新的性能指标,如QRS面积误差、PR间隔误差等。
- 结合四通道信号图像表示和ViT自注意力机制能有效提取PPG信息特征,提高心跳间变化的建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

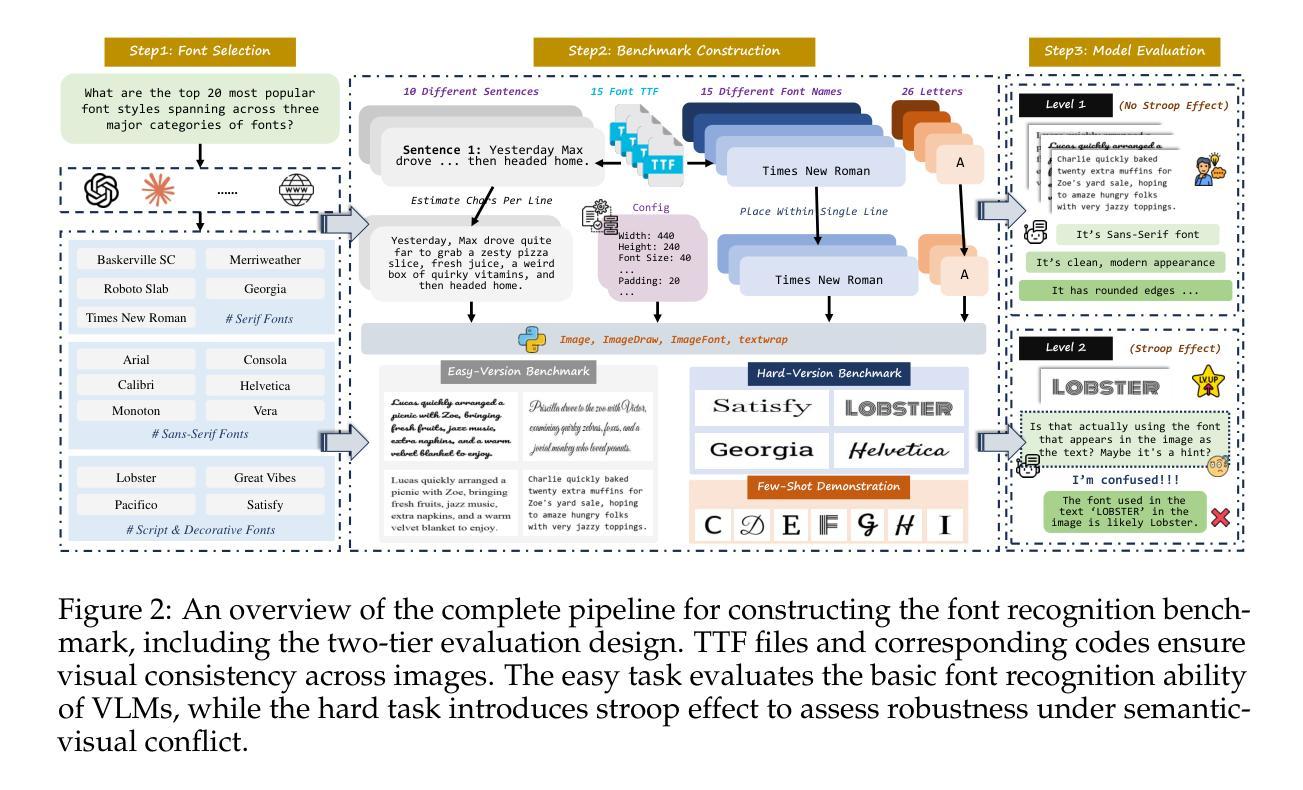
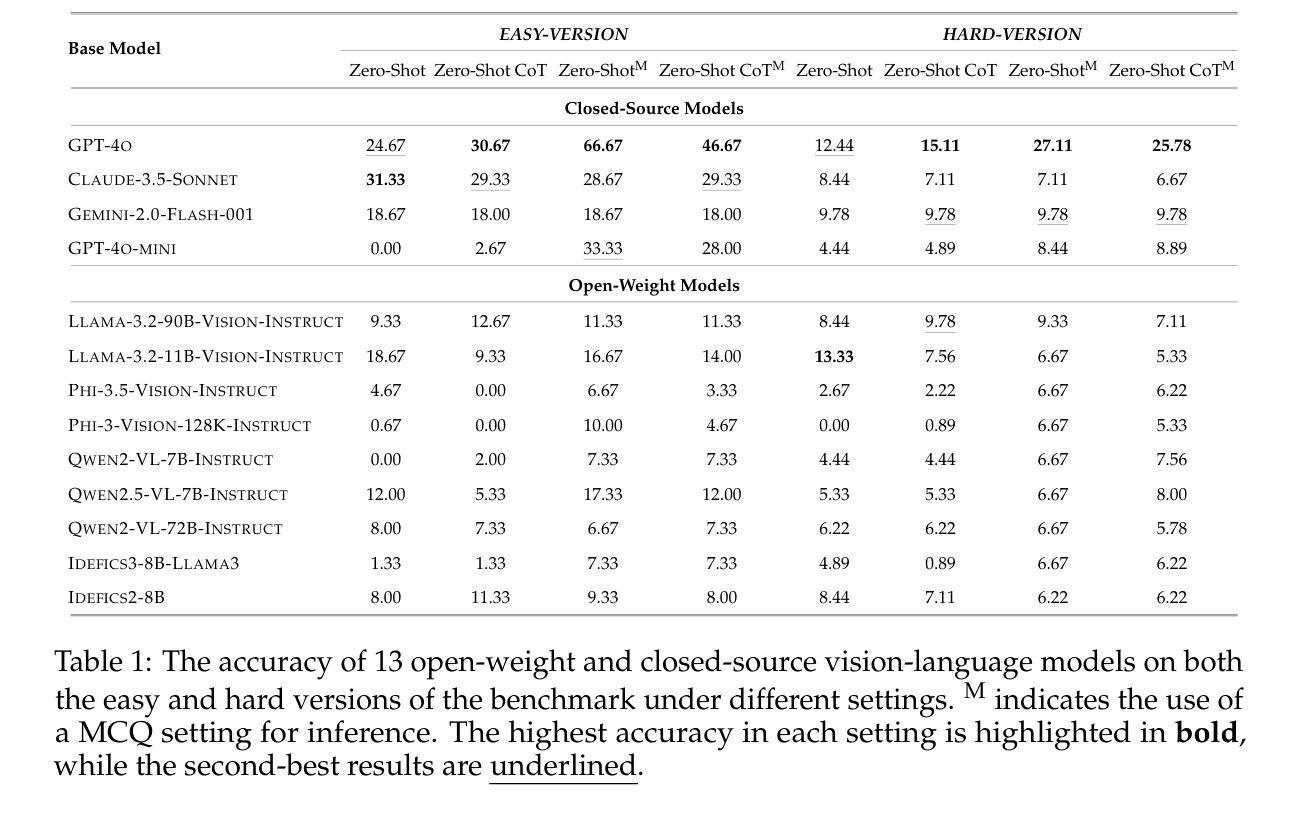
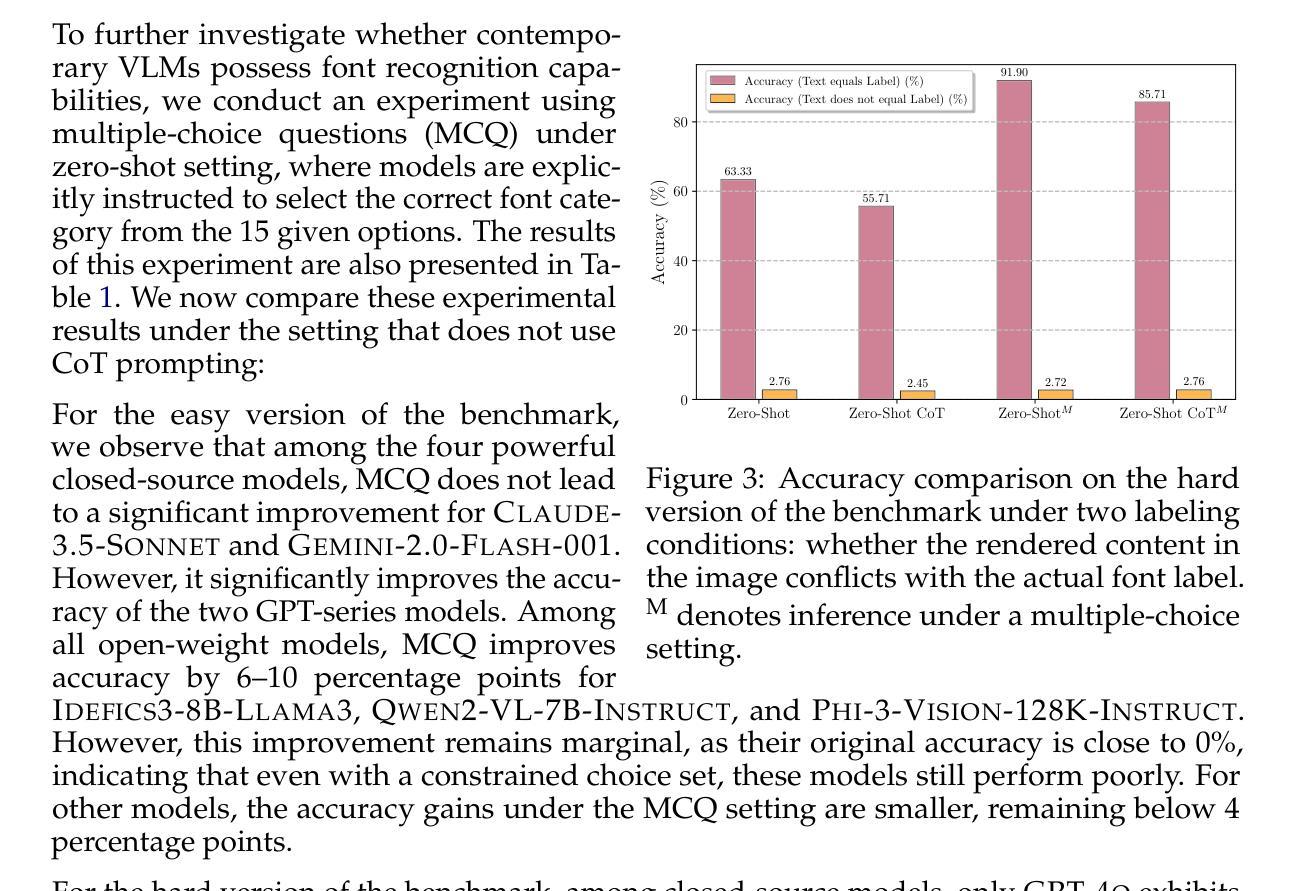
Texture or Semantics? Vision-Language Models Get Lost in Font Recognition
Authors:Zhecheng Li, Guoxian Song, Yujun Cai, Zhen Xiong, Junsong Yuan, Yiwei Wang
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit remarkable visual and linguistic capabilities, achieving impressive performance in various tasks such as image recognition and object localization. However, their effectiveness in fine-grained tasks remains an open question. In everyday scenarios, individuals encountering design materials, such as magazines, typography tutorials, research papers, or branding content, may wish to identify aesthetically pleasing fonts used in the text. Given their multimodal capabilities and free accessibility, many VLMs are often considered potential tools for font recognition. This raises a fundamental question: Do VLMs truly possess the capability to recognize fonts? To investigate this, we introduce the Font Recognition Benchmark (FRB), a compact and well-structured dataset comprising 15 commonly used fonts. FRB includes two versions: (i) an easy version, where 10 sentences are rendered in different fonts, and (ii) a hard version, where each text sample consists of the names of the 15 fonts themselves, introducing a stroop effect that challenges model perception. Through extensive evaluation of various VLMs on font recognition tasks, we arrive at the following key findings: (i) Current VLMs exhibit limited font recognition capabilities, with many state-of-the-art models failing to achieve satisfactory performance and being easily affected by the stroop effect introduced by textual information. (ii) Few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting provide minimal benefits in improving font recognition accuracy across different VLMs. (iii) Attention analysis sheds light on the inherent limitations of VLMs in capturing semantic features.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)表现出显著的视频和语言能力,在各种任务(如图像识别和对象定位)中取得了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,它们在精细任务中的有效性仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在日常场景中,个人遇到设计材料,如杂志、排版教程、研究论文或品牌内容,可能会希望识别文本中视觉上令人愉悦的字体。考虑到它们的多模式能力和自由访问性,许多VLMs通常被认为是字体识别的潜在工具。这引发了一个基本问题:VLMs是否真的具备识别字体的能力?为了调查这一点,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),这是一个由15种常用字体组成的紧凑且结构良好的数据集。FRB包括两个版本:(i)简易版,其中10句话以不同的字体呈现;(ii)困难版,其中每个文本样本由上述的15种字体的名称组成,引入一种斯特鲁普效应,挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLMs在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们得出了以下关键发现:(i)当前VLMs在字体识别方面的能力有限,许多最先进的模型未能取得令人满意的性能,并且很容易受到文本信息引入的斯特鲁普效应的影响。(ii)在VLMs中,少样本学习和思维链提示对改善字体识别精度的好处微乎其微。(iii)注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLM 2025
摘要
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像识别、物体定位等方面表现出强大的视觉和语言能力,但在精细任务上的效果仍有待探讨。针对设计材料中的字体识别问题,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),包含15种常用字体。研究发现,当前VLMs在字体识别方面的能力有限,顶尖模型难以达到满意性能,且易受文本信息干扰。少量学习及Chain-of-Thought提示对提升性能作用有限。注意力分析揭示了VLMs捕捉语义特征的内在局限。
关键见解
- 当前VLMs在字体识别方面的能力有限,难以满足精细任务需求。
- FRB基准测试有效揭示了VLMs在字体识别上的性能短板。
- 顶尖模型在FRB测试中表现不佳,易受文本信息干扰。
- 少量学习对提升VLMs在字体识别任务上的性能作用有限。
- Chain-of-Thought提示策略在改善字体识别准确率方面效果不显著。
- 注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕捉语义特征方面的内在局限。
点此查看论文截图


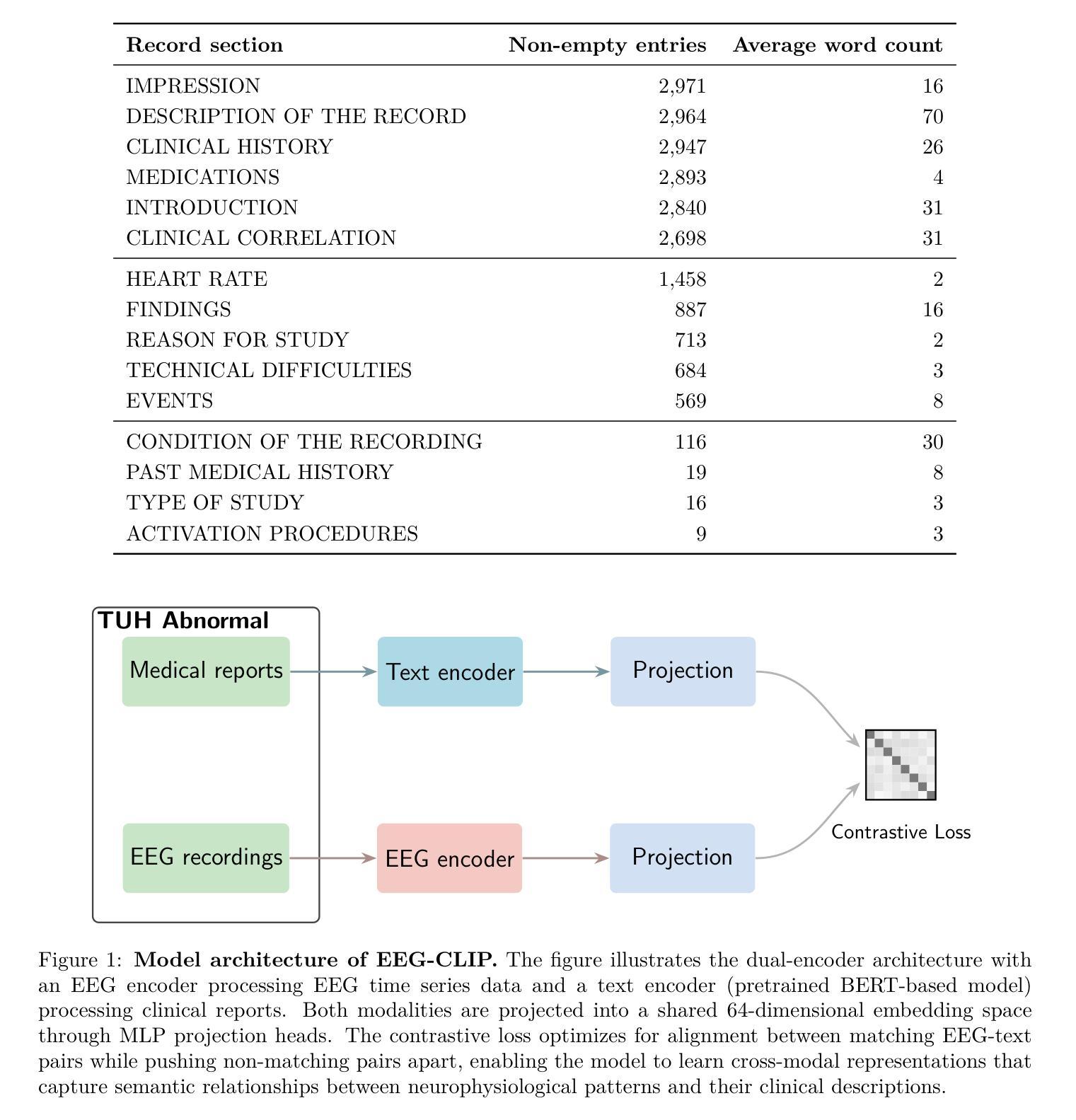
EEG-CLIP : Learning EEG representations from natural language descriptions
Authors:Tidiane Camaret Ndir, Robin Tibor Schirrmeister, Tonio Ball
Deep networks for electroencephalogram (EEG) decoding are often only trained to solve one specific task, such as pathology or age decoding. A more general task-agnostic approach is to train deep networks to match a (clinical) EEG recording to its corresponding textual medical report and vice versa. This approach was pioneered in the computer vision domain matching images and their text captions and subsequently allowed to do successful zero-shot decoding using textual class prompts. In this work, we follow this approach and develop a contrastive learning framework, EEG-CLIP, that aligns the EEG time series and the descriptions of the corresponding clinical text in a shared embedding space. We investigated its potential for versatile EEG decoding, evaluating performance in a range of few-shot and zero-shot settings. Overall, we show that EEG-CLIP manages to non-trivially align text and EEG representations. Our work presents a promising approach to learn general EEG representations, which could enable easier analyses of diverse decoding questions through zero-shot decoding or training task-specific models from fewer training examples. The code for reproducing our results is available at https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip
脑电图(EEG)解码的深度网络通常只被训练用于解决一个特定任务,如病理学或年龄解码。一种更通用的任务无关方法是对深度网络进行训练,使其能够匹配临床脑电图记录及其相应的文本医学报告,反之亦然。这种方法在计算机视觉领域中图像及其文本标题的匹配上开创了先河,随后通过使用文本类别提示实现了成功的零样本解码。在这项工作中,我们遵循这种方法,开发了一个对比学习框架EEG-CLIP,该框架将脑电图时间序列与相应临床文本的描述对齐到一个共享嵌入空间中。我们研究了其在多种脑电图解码中的潜力,评估了在少量样本和零样本设置下的性能。总体而言,我们证明了EEG-CLIP能够非平凡地对齐文本和脑电图表示。我们的工作展示了一种学习通用脑电图表示的有前途的方法,这可能通过零样本解码或使用更少训练样本训练特定任务模型来更容易地分析各种解码问题。重现我们结果的代码可在https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于对比学习的新方法EEG-CLIP,用于将脑电图(EEG)时间序列与相应的临床文本描述对齐,在共享嵌入空间中进行匹配。该方法采用通用任务无关的学习方式,能够应对多种脑电图解码任务,包括少样本和零样本场景。研究结果表明,EEG-CLIP能够实现对文本和脑电图表示的有效对齐,为学习通用的脑电图表示提供了一种有前途的方法,有望通过零样本解码或利用更少训练样本进行特定任务训练,简化对多种解码问题的分析。
Key Takeaways
- EEG-CLIP是一种基于对比学习的新方法,用于匹配EEG记录与相应的文本医疗报告。
- 该方法采用任务无关的学习方式,可应用于多种EEG解码任务。
- EEG-CLIP在共享嵌入空间中对EEG时间序列和临床文本描述进行对齐。
- 研究结果表明EEG-CLIP能有效对齐文本和EEG表示。
- EEG-CLIP方法具有潜力通过零样本解码或利用更少训练样本进行特定任务训练,简化对多种解码问题的分析。
- 代码已公开,方便复现。
点此查看论文截图

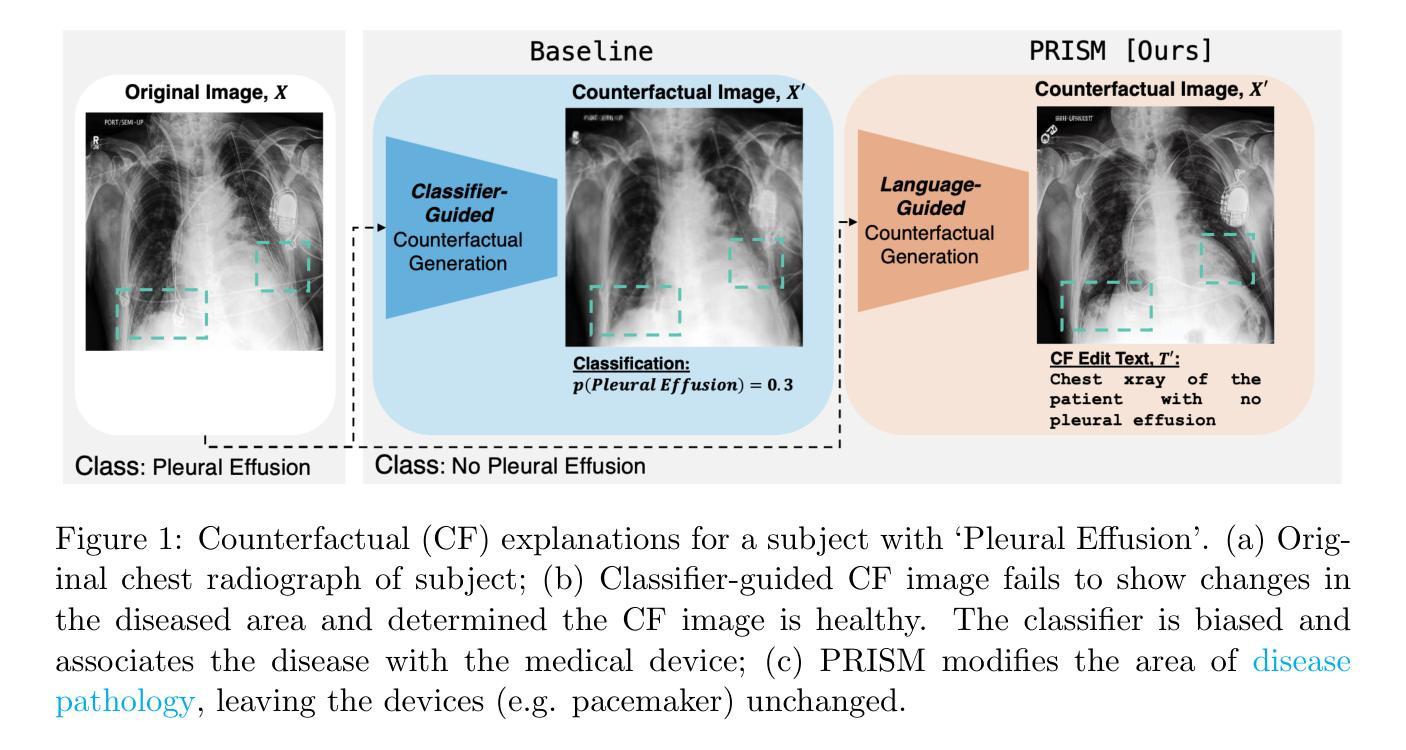
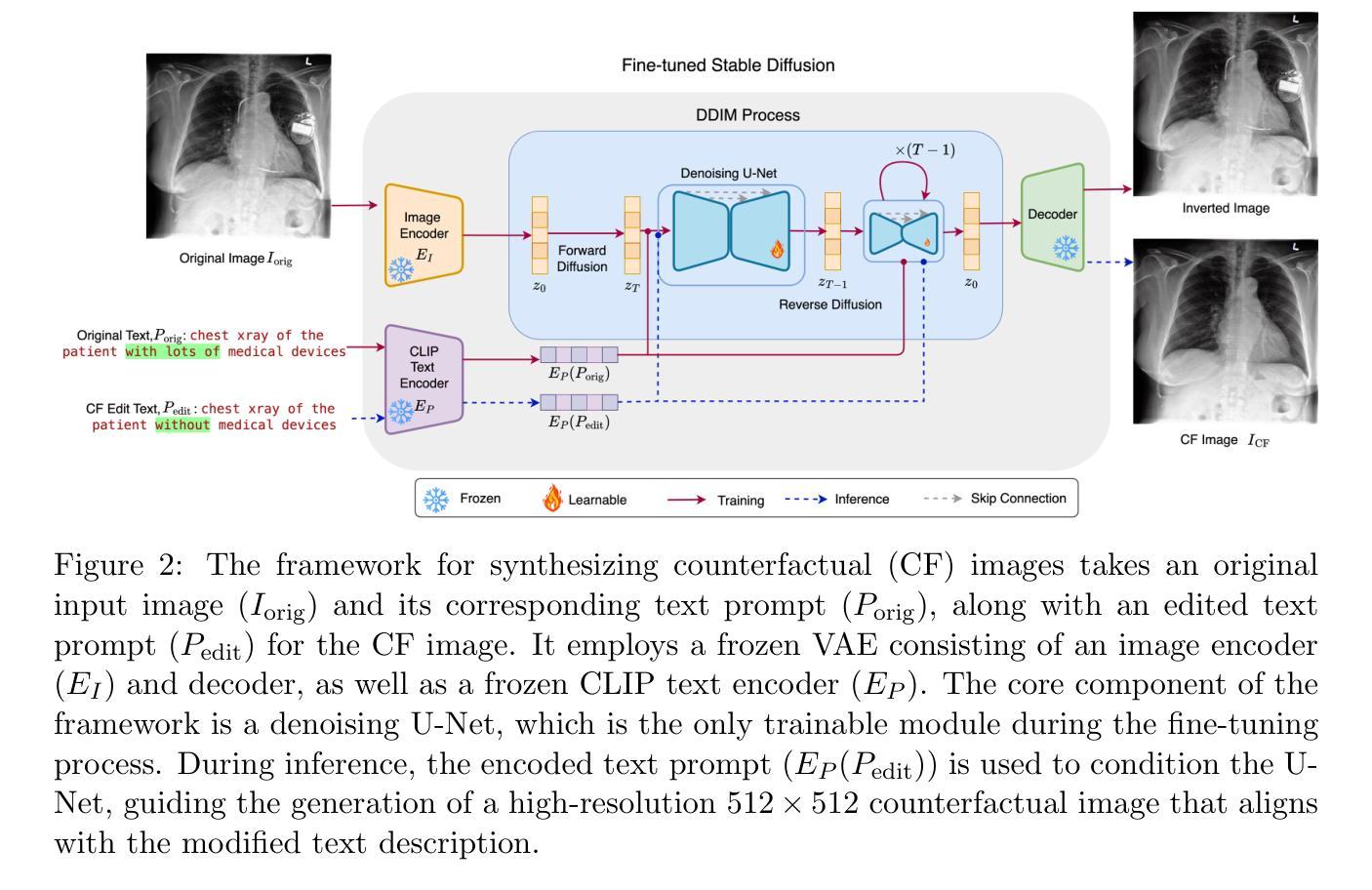
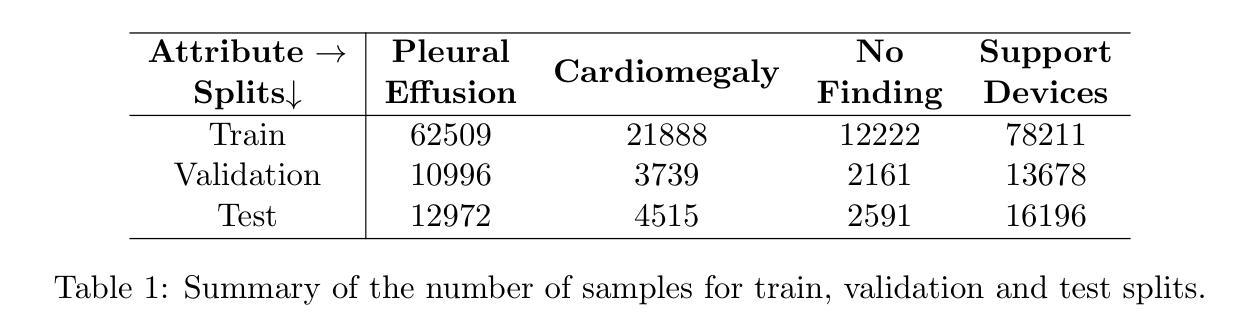
PRISM: High-Resolution & Precise Counterfactual Medical Image Generation using Language-guided Stable Diffusion
Authors:Amar Kumar, Anita Kriz, Mohammad Havaei, Tal Arbel
Developing reliable and generalizable deep learning systems for medical imaging faces significant obstacles due to spurious correlations, data imbalances, and limited text annotations in datasets. Addressing these challenges requires architectures that are robust to the unique complexities posed by medical imaging data. Rapid advancements in vision-language foundation models within the natural image domain prompt the question of how they can be adapted for medical imaging tasks. In this work, we present PRISM, a framework that leverages foundation models to generate high-resolution, language-guided medical image counterfactuals using Stable Diffusion. Our approach demonstrates unprecedented precision in selectively modifying spurious correlations (the medical devices) and disease features, enabling the removal and addition of specific attributes while preserving other image characteristics. Through extensive evaluation, we show how PRISM advances counterfactual generation and enables the development of more robust downstream classifiers for clinically deployable solutions. To facilitate broader adoption and research, we make our code publicly available at https://github.com/Amarkr1/PRISM.
针对医学影像开发可靠且可推广的深度学习系统面临着重大挑战,这主要是由于数据中的虚假关联、数据不平衡以及文本注释有限等问题。要解决这些挑战,需要能够适应医学影像数据独特复杂性的架构。自然图像领域的视觉语言基础模型的快速发展引发了一个问题,即如何将其适应于医学影像任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了PRISM框架,该框架利用基础模型通过Stable Diffusion生成高分辨率、语言引导的医疗影像反事实。我们的方法以前所未有的精度有选择地修改虚假关联(医疗设备和疾病特征),能够在保留其他图像特性的同时移除和添加特定属性。通过广泛的评估,我们展示了PRISM在反事实生成方面的优势,并促进了在临床部署解决方案中开发更稳健的下游分类器。为了更广泛的采用和研究,我们在https://github.com/Amarkr1/PRISM上公开了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MIDL 2025
摘要
本文介绍了PRISM框架,该框架利用基础模型通过Stable Diffusion生成高分辨率、语言引导的医疗图像反事实数据。此方法在选择性修改医疗设备和疾病特征方面的虚假关联方面展现了前所未有的精度,能够在保留其他图像特征的同时移除和添加特定属性。通过广泛评估,表明PRISM推动了反事实生成的发展,并为临床部署解决方案的下游分类器开发提供了更稳健的基础。
要点
- 医疗成像领域在开发可靠且可推广的深度学习系统时面临诸多挑战,如虚假关联、数据不平衡和有限文本注释等问题。
- 需要针对医疗成像数据的独特复杂性构建稳健的架构来解决这些挑战。
- PRISM框架利用基础模型生成高分辨率、语言引导的医疗图像反事实数据,以应对上述挑战。
- PRISM能够在选择性修改医疗设备和疾病特征的虚假关联方面实现高精度。
- PRISM推动了反事实生成的发展,有助于开发更稳健的下游分类器,为临床部署解决方案提供支持。
- PRISM框架的代码已公开可用,便于更广泛的采用和研究。
点此查看论文截图

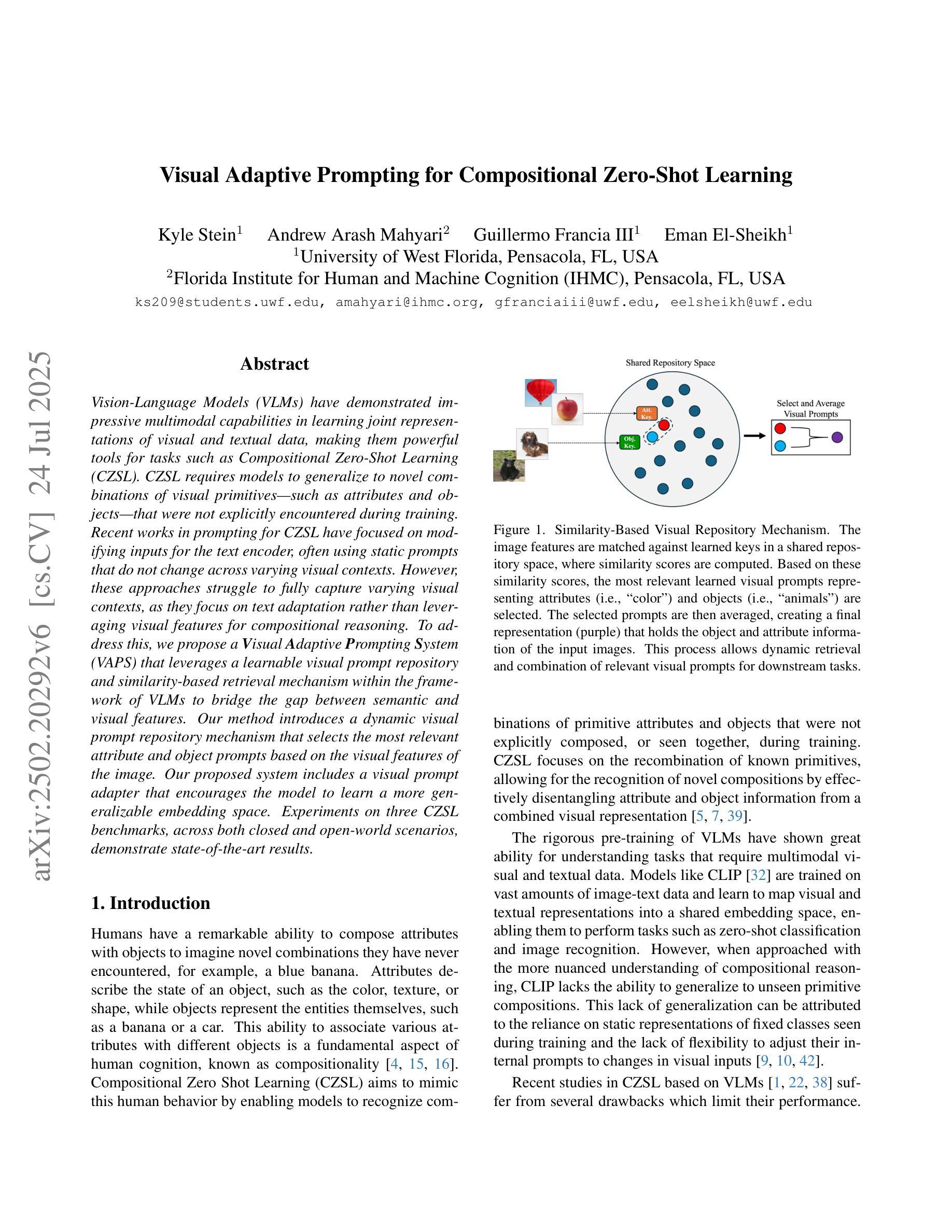
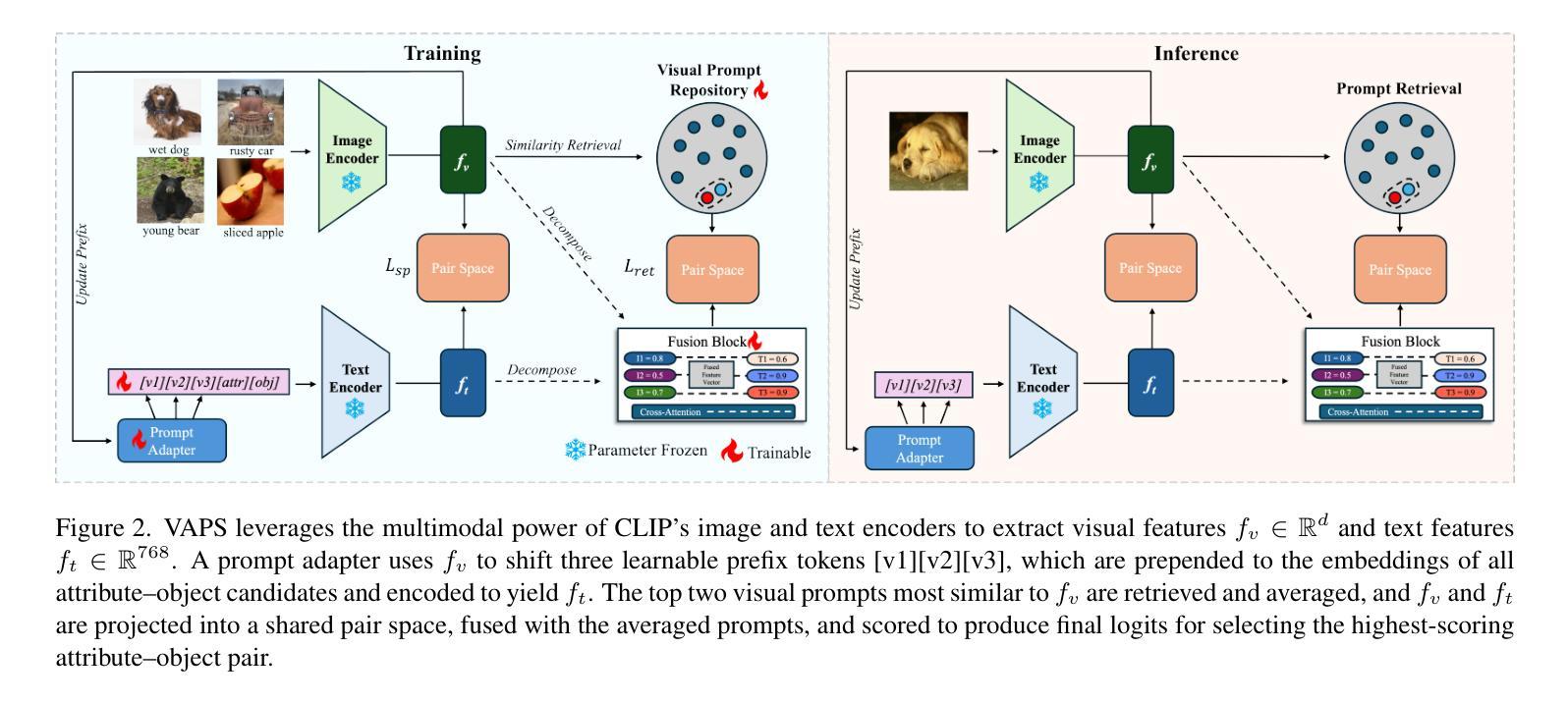
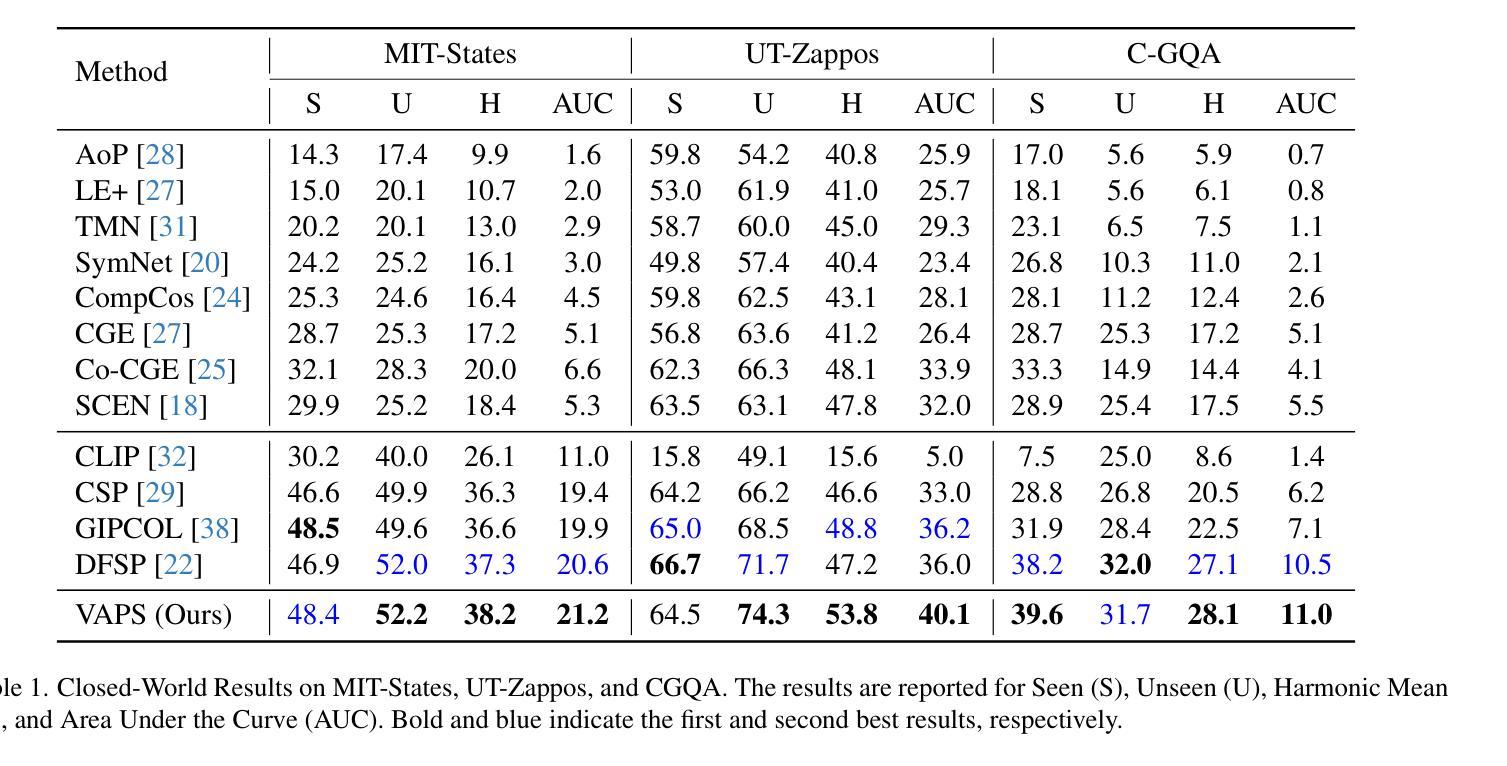
Visual Adaptive Prompting for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia, Eman El-Sheikh
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal capabilities in learning joint representations of visual and textual data, making them powerful tools for tasks such as Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). CZSL requires models to generalize to novel combinations of visual primitives–such as attributes and objects–that were not explicitly encountered during training. Recent works in prompting for CZSL have focused on modifying inputs for the text encoder, often using static prompts that do not change across varying visual contexts. However, these approaches struggle to fully capture varying visual contexts, as they focus on text adaptation rather than leveraging visual features for compositional reasoning. To address this, we propose a Visual Adaptive Prompting System (VAPS) that leverages a learnable visual prompt repository and similarity-based retrieval mechanism within the framework of VLMs to bridge the gap between semantic and visual features. Our method introduces a dynamic visual prompt repository mechanism that selects the most relevant attribute and object prompts based on the visual features of the image. Our proposed system includes a visual prompt adapter that encourages the model to learn a more generalizable embedding space. Experiments on three CZSL benchmarks, across both closed and open-world scenarios, demonstrate state-of-the-art results.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在联合表示视觉和文本数据方面表现出了令人印象深刻的跨模态能力,使其成为完成组合零射击学习(CZSL)等任务的有力工具。CZSL要求模型能够推广到训练期间未明确遇到的新组合的视觉元素,如属性和对象。最近的关于CZSL提示的工作主要集中在修改文本编码器的输入,通常使用静态提示,这些提示在不同的视觉上下文中不会发生变化。然而,这些方法在捕捉不断变化的视觉上下文方面存在困难,因为它们侧重于文本适应,而不是利用视觉特征进行组合推理。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一个视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示仓库和视觉语言模型框架内的基于相似性的检索机制来弥补语义和视觉特征之间的差距。我们的方法引入了一个动态的视觉提示仓库机制,该机制根据图像中的视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。我们提出的系统包括一个视觉提示适配器,它鼓励模型学习一个更具泛化能力的嵌入空间。在三个CZSL基准测试上的实验,无论是封闭还是开放世界场景,都证明了其处于领先地位的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似度的检索机制,在视觉语言模型(VLMs)的框架下,桥接语义和视觉特征之间的鸿沟。VAPS通过动态选择最相关的属性对象提示,以图像视觉特征为基础进行提示,并包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习更通用的嵌入空间。在三个CZSL基准测试(包括封闭和开放世界场景)上的实验表明,该系统取得了最新技术成果。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在多模态学习中表现出强大的能力,特别是在Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL)任务中。
- 现有的提示方法主要关注文本适应,未能充分利用视觉特征进行组合推理。
- 提出的VAPS系统通过利用可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似度的检索机制,桥接语义和视觉特征之间的鸿沟。
- VAPS包括一个动态视觉提示选择机制,根据图像视觉特征选择最相关的属性对象提示。
- VAPS系统包含一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习更通用的嵌入空间。
- 在三个CZSL基准测试上,VAPS系统取得了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图
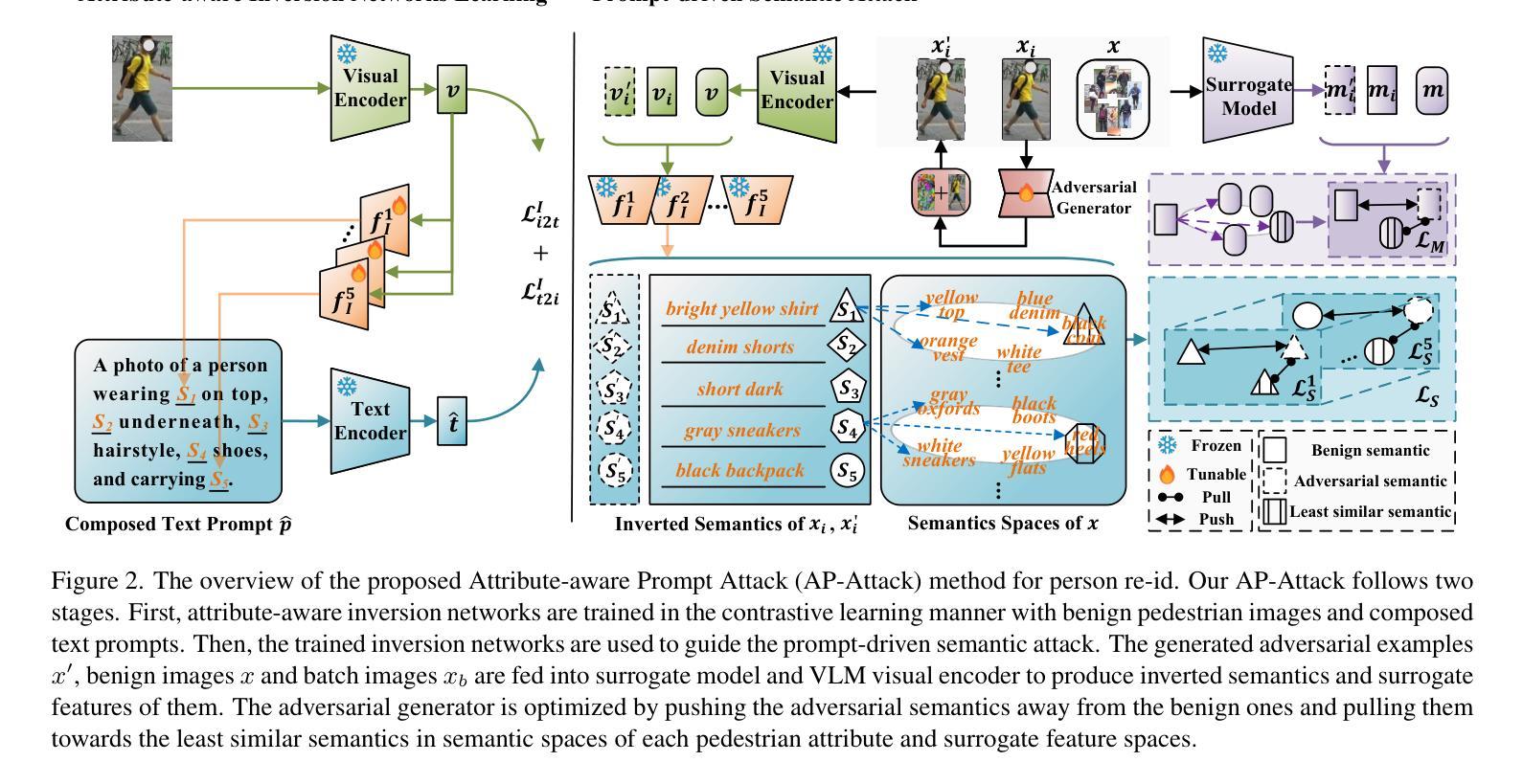
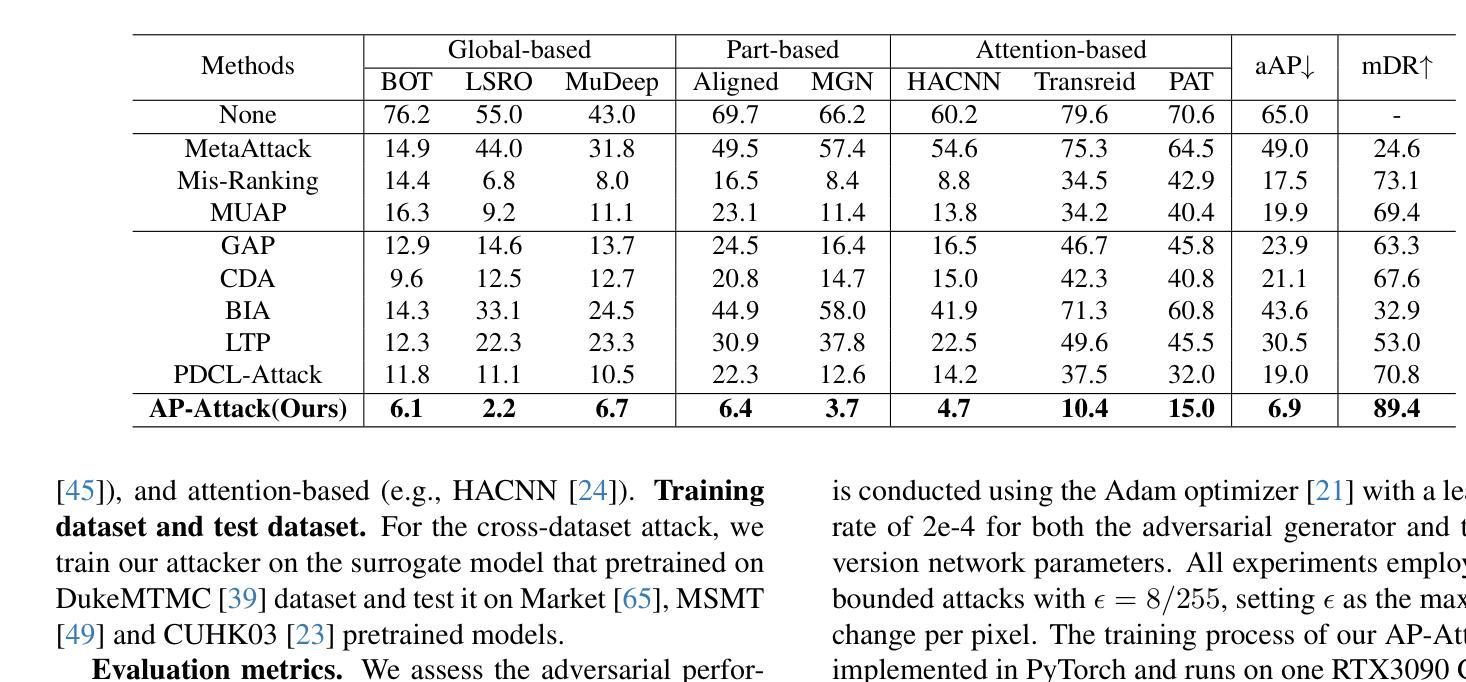
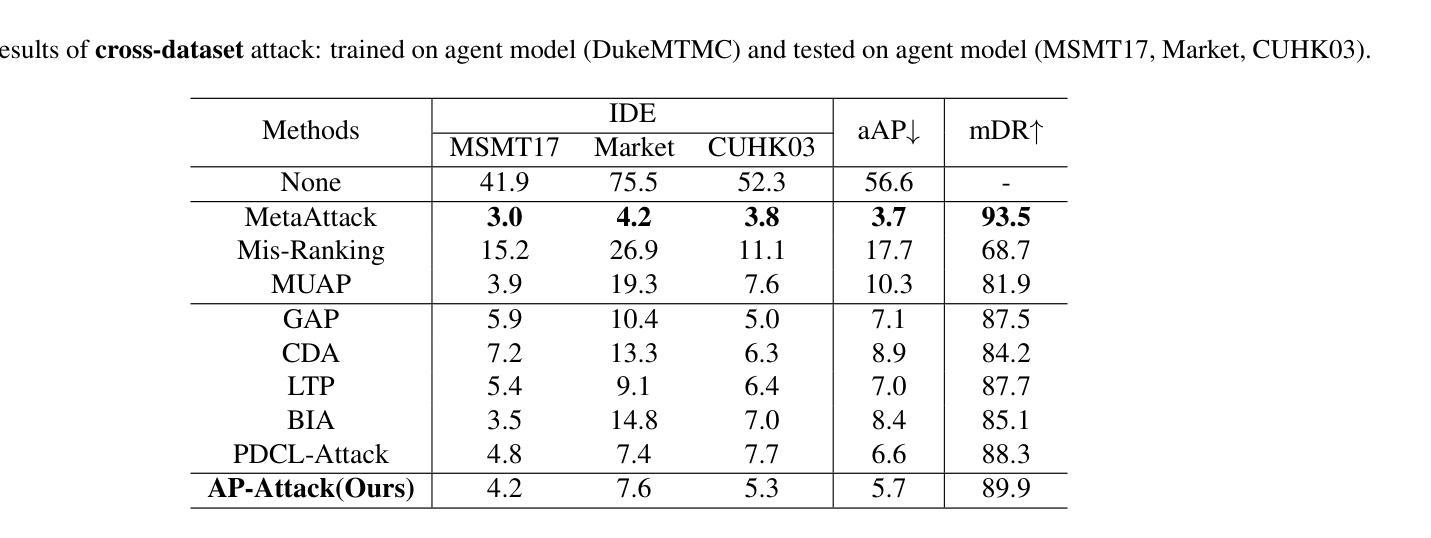
Prompt-driven Transferable Adversarial Attack on Person Re-Identification with Attribute-aware Textual Inversion
Authors:Yuan Bian, Min Liu, Yunqi Yi, Xueping Wang, Yaonan Wang
Person re-identification (re-id) models are vital in security surveillance systems, requiring transferable adversarial attacks to explore the vulnerabilities of them. Recently, vision-language models (VLM) based attacks have shown superior transferability by attacking generalized image and textual features of VLM, but they lack comprehensive feature disruption due to the overemphasis on discriminative semantics in integral representation. In this paper, we introduce the Attribute-aware Prompt Attack (AP-Attack), a novel method that leverages VLM’s image-text alignment capability to explicitly disrupt fine-grained semantic features of pedestrian images by destroying attribute-specific textual embeddings. To obtain personalized textual descriptions for individual attributes, textual inversion networks are designed to map pedestrian images to pseudo tokens that represent semantic embeddings, trained in the contrastive learning manner with images and a predefined prompt template that explicitly describes the pedestrian attributes. Inverted benign and adversarial fine-grained textual semantics facilitate attacker in effectively conducting thorough disruptions, enhancing the transferability of adversarial examples. Extensive experiments show that AP-Attack achieves state-of-the-art transferability, significantly outperforming previous methods by 22.9% on mean Drop Rate in cross-model&dataset attack scenarios.
行人再识别(Re-ID)模型在安防监控系统中扮演关键角色,需要可迁移的对抗性攻击来探索其脆弱性。最近,基于视觉语言模型的攻击(VLM)通过攻击VLM的通用图像和文本特征表现出优越的迁移性,但由于过分强调整体表示中的判别语义,它们缺乏全面的特征破坏。在本文中,我们引入了属性感知提示攻击(AP-Attack),这是一种新方法,利用VLM的图像文本对齐能力,通过破坏特定属性的文本嵌入来明确破坏行人图像的细粒度语义特征。为了获得个别属性的个性化文本描述,设计了文本反转网络,将行人图像映射到代表语义嵌入的伪令牌上,使用对比学习方式与图像和预先定义的提示模板进行训练,该模板明确描述了行人属性。正向和反向的细粒度文本语义有助于攻击者进行有效的全面破坏,提高对抗样本的迁移性。大量实验表明,AP-Attack在迁移性方面达到了最先进的水平,在跨模型和数据集攻击场景中,平均下降率提高了22.9%,显著优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的新型攻击方法——属性感知提示攻击(AP-Attack),该方法利用VLM的图像文本对齐能力,通过破坏行人图像的细粒度语义特征来明确干扰模型。设计文本反演网络将行人图像映射到代表语义嵌入的伪令牌上,借助对比学习的方式与图像和预先定义的描述行人属性的提示模板进行训练。这种新型的攻击方式显著提高了对抗样本的迁移性,在跨模型和跨数据集攻击场景中,平均下降率提高了22.9%。
Key Takeaways
- AP-Attack是一种新型的攻击方法,基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的图像文本对齐能力。
- 该方法通过破坏行人图像的细粒度语义特征来干扰模型。
- 文本反演网络被设计用于将行人图像映射到代表语义嵌入的伪令牌上。
- 通过对比学习的方式,结合图像和预定义的描述行人属性的提示模板进行训练。
- AP-Attack显著提高了对抗样本的迁移性。
- 在跨模型和跨数据集攻击场景中,AP-Attack的平均下降率提高了22.9%,表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

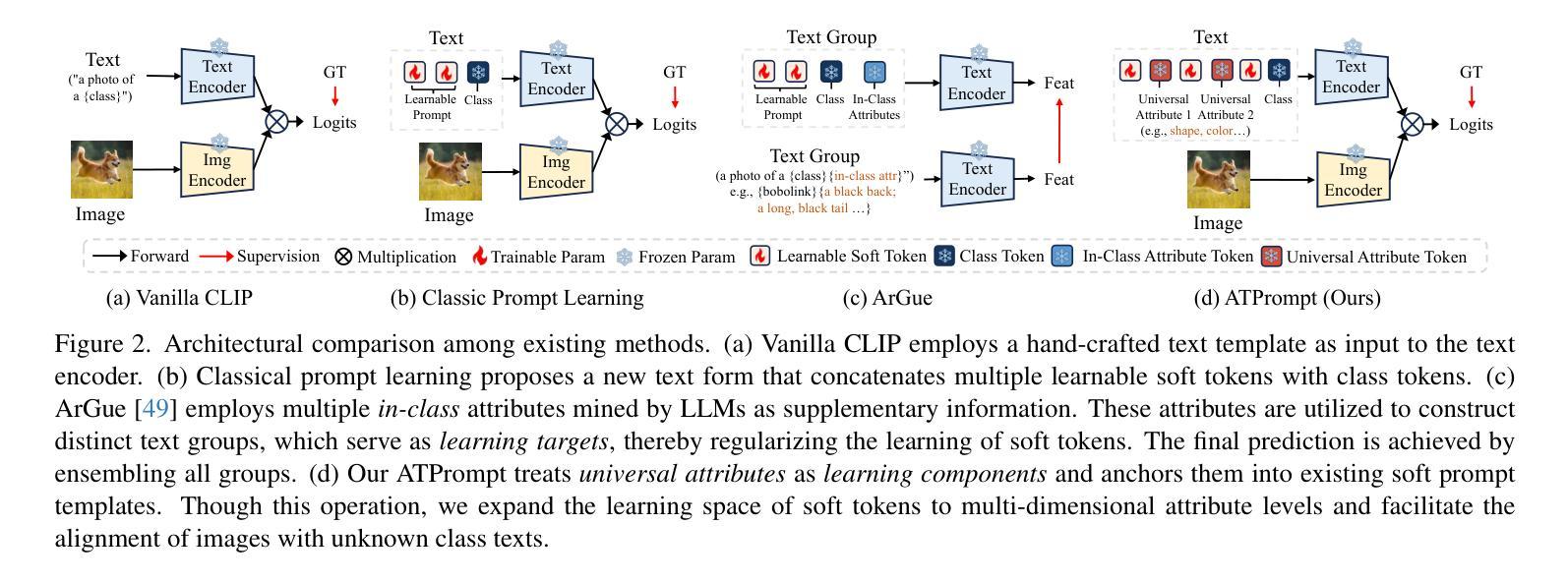
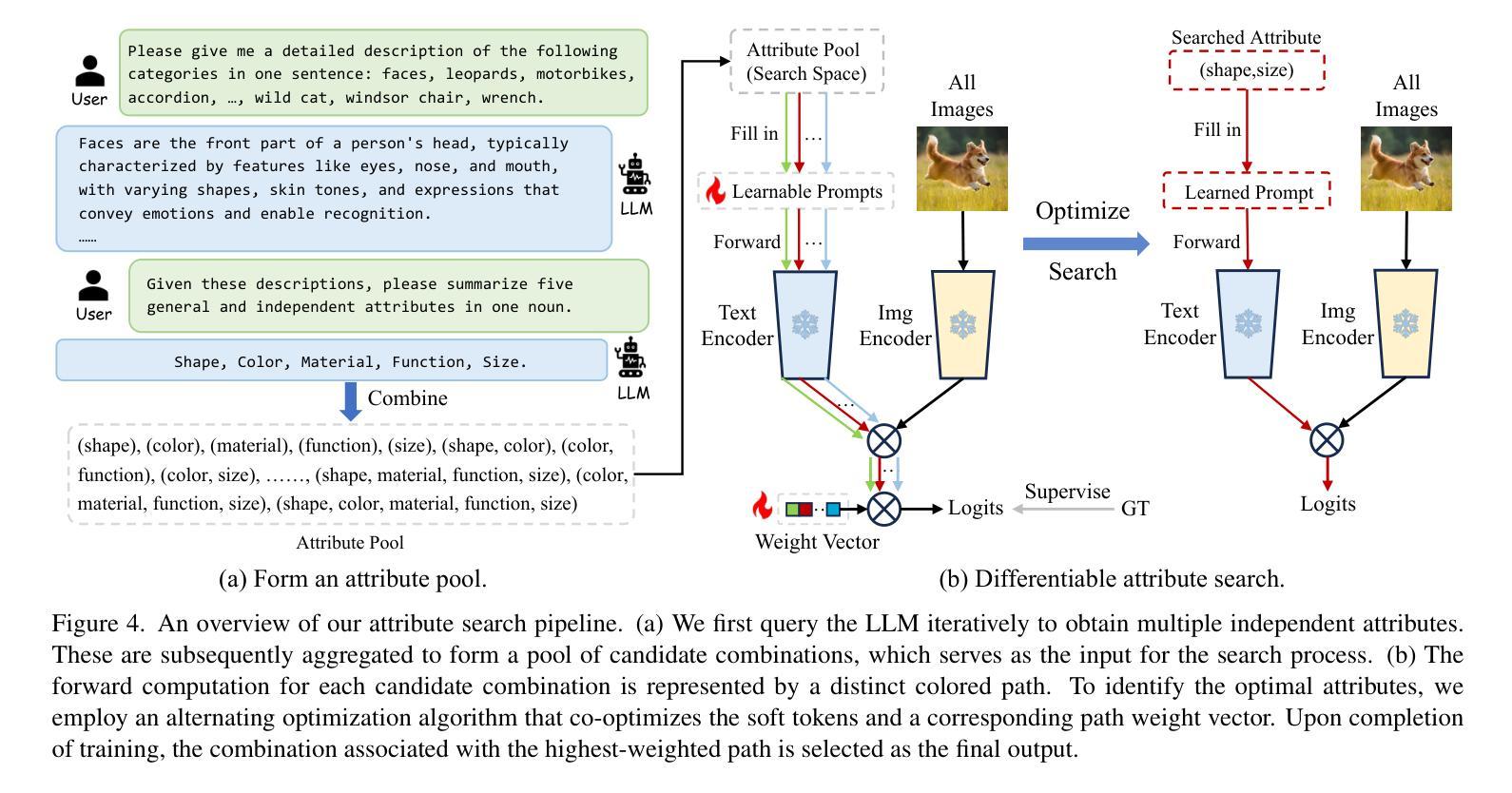
Advancing Textual Prompt Learning with Anchored Attributes
Authors:Zheng Li, Yibing Song, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xiang Li, Jian Yang
Textual-based prompt learning methods primarily employ multiple learnable soft prompts and hard class tokens in a cascading manner as text inputs, aiming to align image and text (category) spaces for downstream tasks. However, current training is restricted to aligning images with predefined known categories and cannot be associated with unknown categories. In this work, we propose utilizing universal attributes as a bridge to enhance the alignment between images and unknown categories. Specifically, we introduce an Attribute-anchored Textual Prompt learning method for vision-language models, named ATPrompt. This approach expands the learning space of soft prompts from the original one-dimensional category level into the multi-dimensional attribute level by incorporating multiple attribute tokens into the learnable soft prompts. Through this modification, we transform the text prompt from a category-centric form to an attribute-category hybrid form. Additionally, we introduce a straightforward differentiable attribute search method to identify representative and suitable attributes for downstream tasks. As an easy-to-use plug-in technique, ATPrompt can seamlessly replace the existing basic prompt format in textual-based methods, providing general improvements at a negligible computational cost. Extensive experiments across 11 datasets validate the effectiveness of our method. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt.
基于文本的提示学习方法主要使用多个可学习的软提示和硬类别令牌以级联方式作为文本输入,旨在对齐图像和文本(类别)空间以供下游任务使用。然而,当前训练仅限于对齐图像与预定义的已知类别,无法与未知类别相关联。在这项工作中,我们提出利用通用属性作为桥梁,增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。具体来说,我们为视觉语言模型引入了一种名为ATPrompt的属性锚定文本提示学习方法。该方法通过将多个属性令牌纳入可学习的软提示中,将软提示的学习空间从原始的一维类别层面扩展到多维属性层面。通过这一改进,我们将文本提示从以类别为中心的形式转变为属性-类别混合形式。此外,我们还引入了一种简单的可区分属性搜索方法,以识别适用于下游任务的代表性属性。作为一种易于使用的插件技术,ATPrompt可以无缝替换基于文本方法中的现有基本提示格式,以微薄的计算成本提供一般性的改进。在11个数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码公开在https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code: https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt. Project Page: https://zhengli97.github.io/ATPrompt/
Summary
该文本介绍了一种基于属性的文本提示学习方法(ATPrompt),通过结合通用属性增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。它将学习空间从单一类别级别扩展到多属性级别,实现了类别与属性的混合文本提示形式。此外,它还引入了一种简洁的可区分属性搜索方法,以识别下游任务的代表性属性。ATPrompt作为易于使用的插件技术,可在文本提示方法中无缝替换现有基本格式,提供通用的改进且计算成本较低。
Key Takeaways
- 该文本介绍了一种新的基于属性的文本提示学习方法(ATPrompt),旨在增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。
- ATPrompt通过将学习空间扩展到多属性级别,实现了文本提示形式的类别与属性的混合。
- ATPrompt引入了可区分属性搜索方法,以识别下游任务的代表性属性。
- 该方法适用于多种数据集,具有广泛的有效性。
- ATPrompt技术能够无缝替换现有文本提示方法中的基本格式。
- ATPrompt提供通用的性能改进,并且计算成本较低。
点此查看论文截图


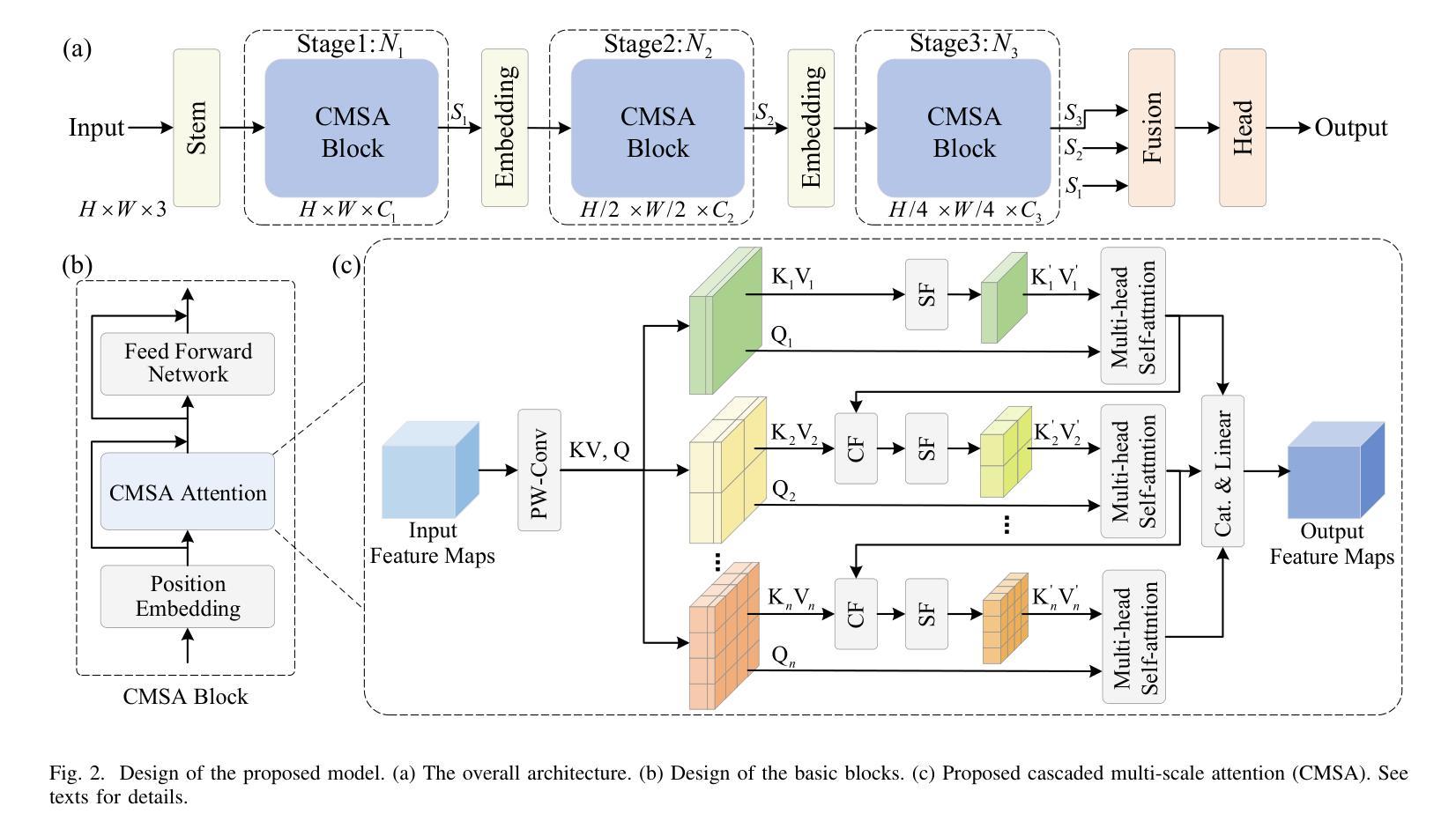
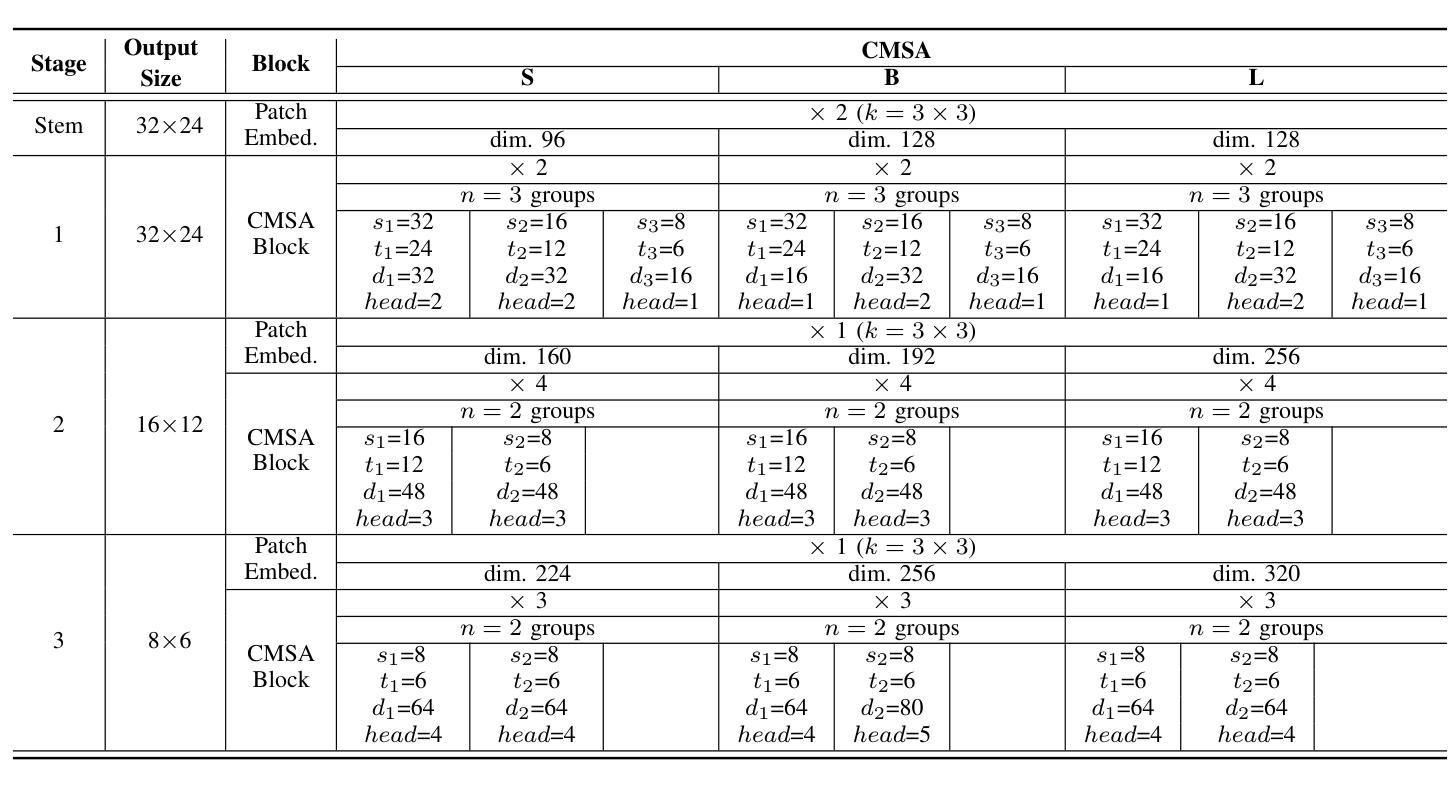
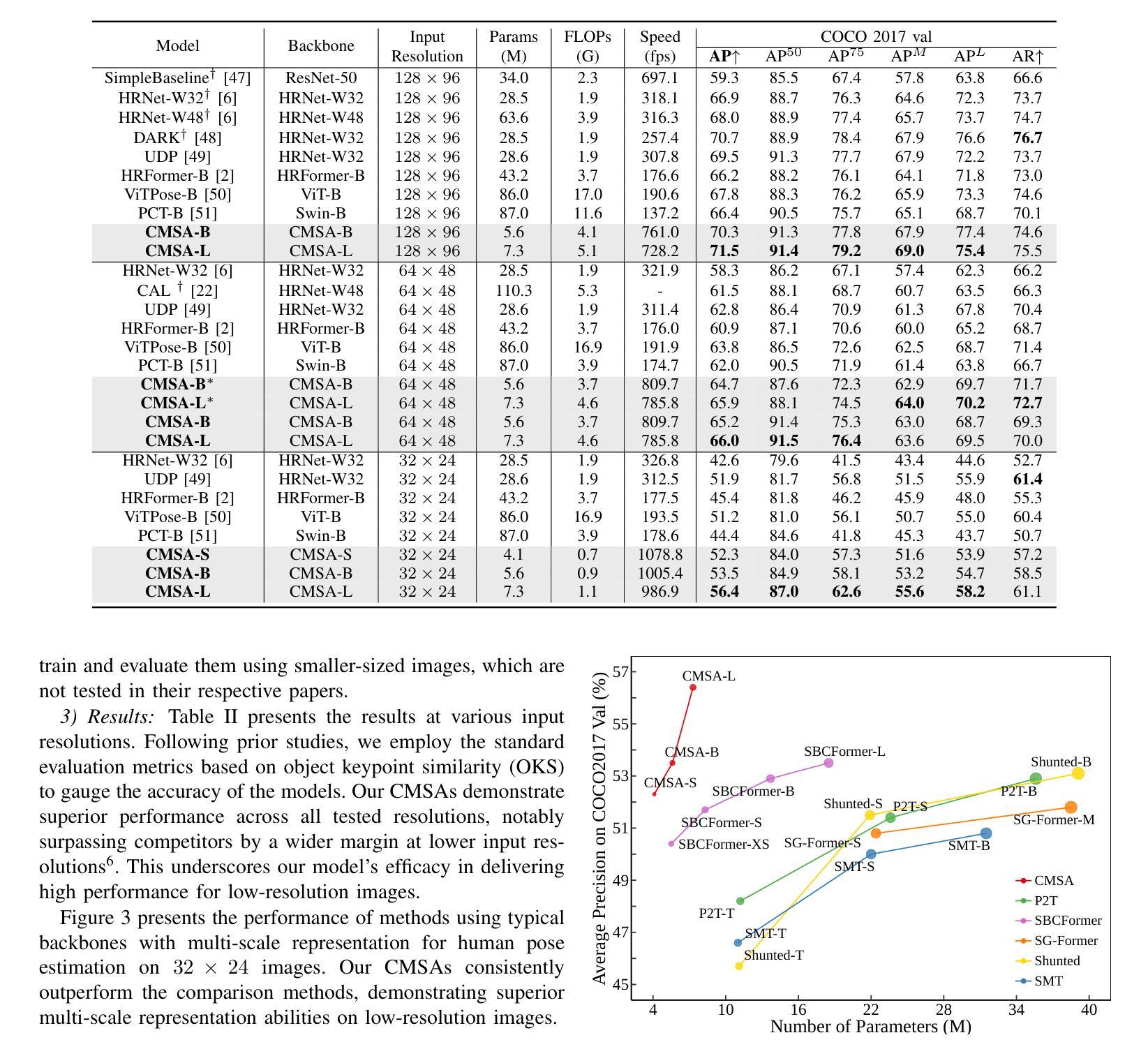
Cascaded Multi-Scale Attention for Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Interaction with Low-Resolution Images
Authors:Xiangyong Lu, Masanori Suganuma, Takayuki Okatani
In real-world applications of image recognition tasks, such as human pose estimation, cameras often capture objects, like human bodies, at low resolutions. This scenario poses a challenge in extracting and leveraging multi-scale features, which is often essential for precise inference. To address this challenge, we propose a new attention mechanism, named cascaded multi-scale attention (CMSA), tailored for use in CNN-ViT hybrid architectures, to handle low-resolution inputs effectively. The design of CMSA enables the extraction and seamless integration of features across various scales without necessitating the downsampling of the input image or feature maps. This is achieved through a novel combination of grouped multi-head self-attention mechanisms with window-based local attention and cascaded fusion of multi-scale features over different scales. This architecture allows for the effective handling of features across different scales, enhancing the model’s ability to perform tasks such as human pose estimation, head pose estimation, and more with low-resolution images. Our experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in these areas with fewer parameters, showcasing its potential for broad application in real-world scenarios where capturing high-resolution images is not feasible. Code is available at https://github.com/xyongLu/CMSA.
在图像识别任务的现实应用(如人体姿态估计)中,相机通常会以低分辨率捕获物体(如人体)。这种情况在提取和利用多尺度特征方面构成了挑战,而对于精确推断,多尺度特征通常是必不可少的。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的注意力机制,名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA),它适用于CNN-ViT混合架构,可有效处理低分辨率输入。CMSA的设计实现了跨不同尺度的特征提取和无缝集成,无需对输入图像或特征图进行降采样。这是通过分组多头自注意力机制与基于窗口的局部注意力相结合,以及在不同尺度上实现多尺度特征的级联融合来实现的。该架构能够有效处理不同尺度的特征,提高模型在低分辨率图像下执行诸如人体姿态估计、头部姿态估计等任务的能力。实验结果表明,该方法在较少的参数下超过了这些领域的最新方法,显示出在高分辨率图像捕获不可行的现实场景中的广泛应用潜力。代码可在https://github.com/xyongLu/CMSA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
针对图像识别任务中常见的低分辨率输入问题,如人体姿态估计等实际应用场景,本文提出了一种名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA)的新型注意力机制。该机制适用于CNN-ViT混合架构,可有效地处理低分辨率输入。CMSA的设计实现了不同尺度特征的提取和无缝集成,无需对输入图像或特征图进行降采样。通过分组多头自注意力机制与基于窗口的局部注意力的新颖结合,以及不同尺度上多尺度特征的级联融合,该架构实现了跨尺度特征的有效处理。实验结果表明,该方法在人体姿态估计、头部姿态估计等领域优于现有最先进的方法,并且参数更少,展示出了在高分辨率图像捕获不可行的现实场景中的广泛应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA)的新型注意力机制,用于处理图像识别任务中的低分辨率输入问题。
- CMSA适用于CNN-ViT混合架构,可实现在不同尺度上特征的提取和无缝集成。
- CMSA设计通过结合分组多头自注意力机制和基于窗口的局部注意力,实现跨尺度特征的有效处理。
- 提出的CMSA架构在人体姿态估计、头部姿态估计等领域优于现有方法,且参数更少。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用潜力,特别是在高分辨率图像捕获不可行的现实场景中。
- 公开可用的代码资源为研究者提供了便利。
点此查看论文截图

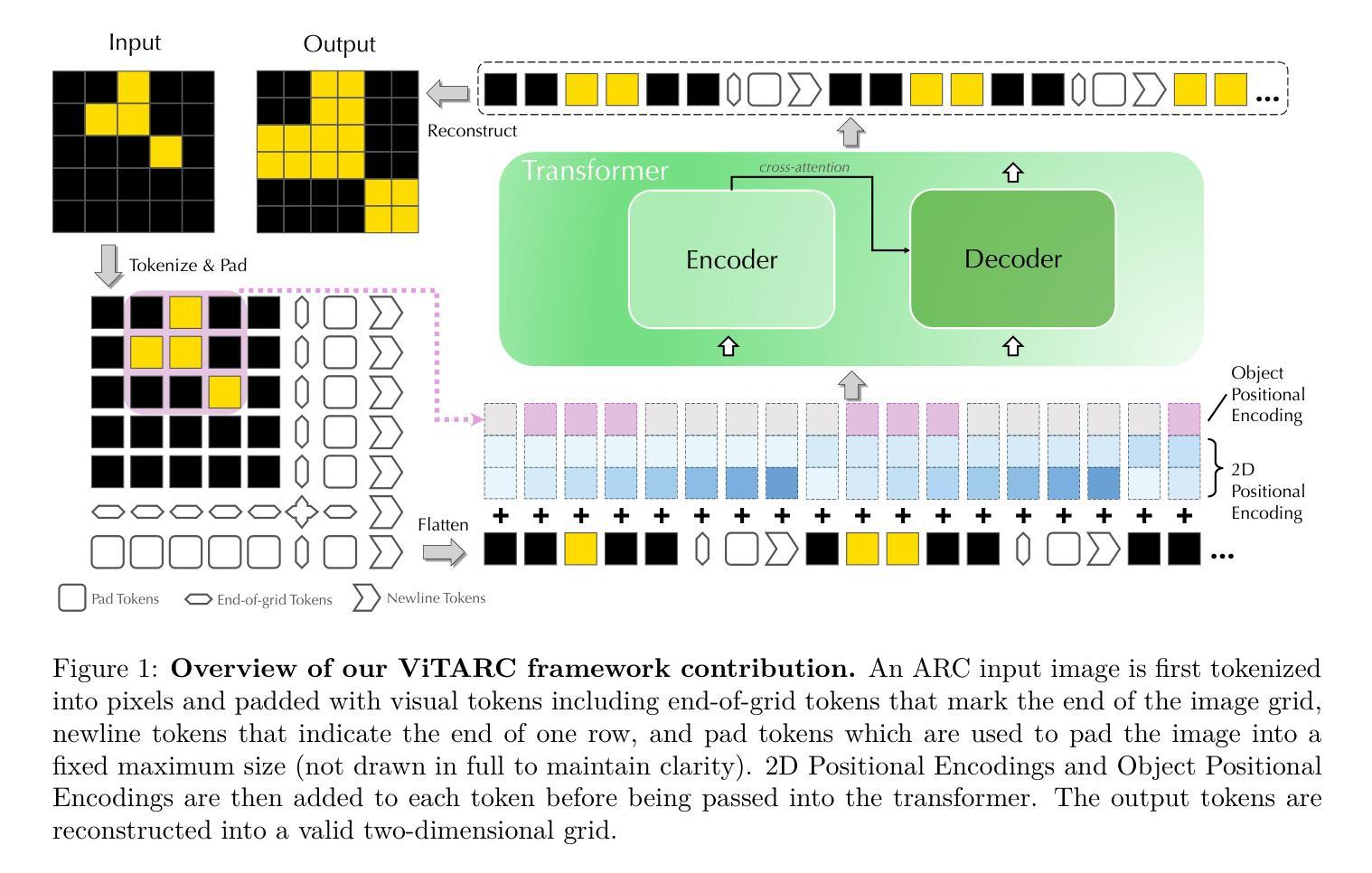
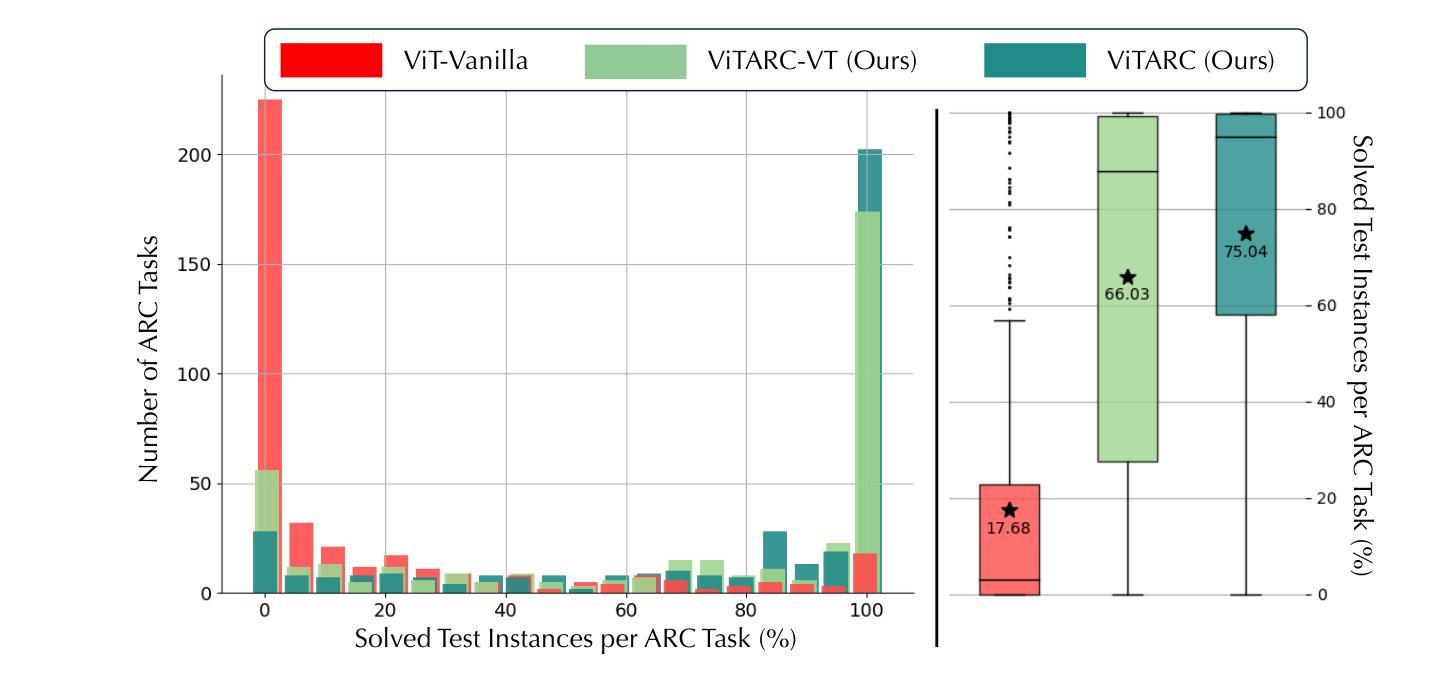
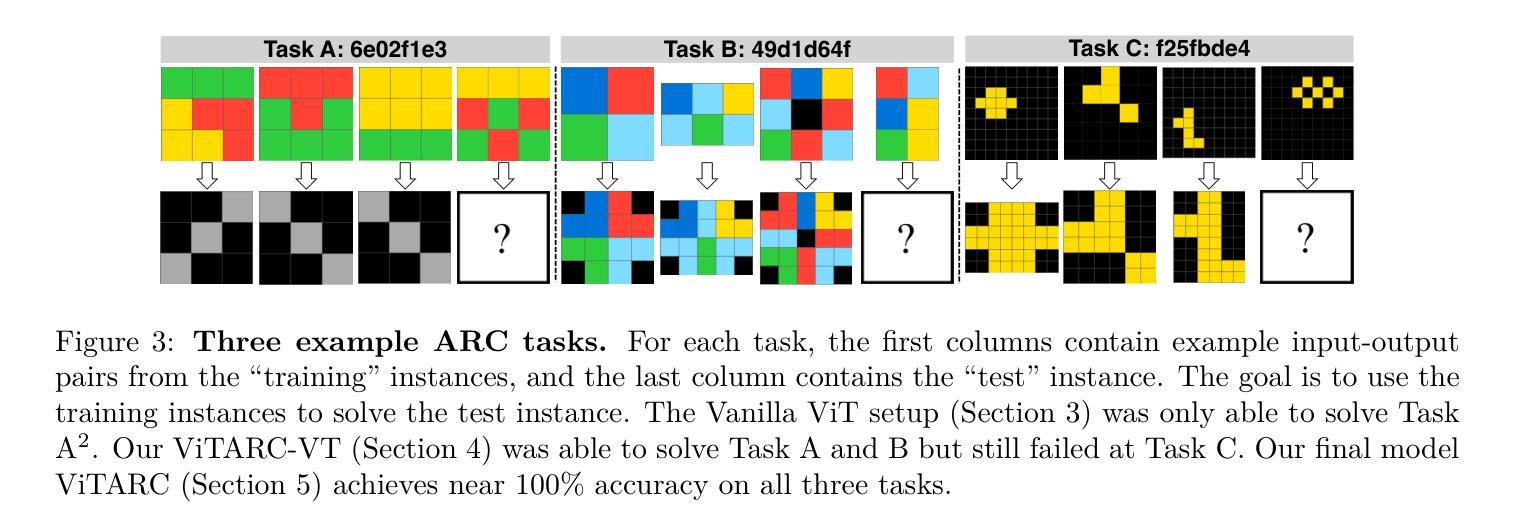
Tackling the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus with Vision Transformers: the Importance of 2D Representation, Positions, and Objects
Authors:Wenhao Li, Yudong Xu, Scott Sanner, Elias Boutros Khalil
The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) is a popular benchmark focused on visual reasoning in the evaluation of Artificial Intelligence systems. In its original framing, an ARC task requires solving a program synthesis problem over small 2D images using a few input-output training pairs. In this work, we adopt the recently popular data-driven approach to the ARC and ask whether a Vision Transformer (ViT) can learn the implicit mapping, from input image to output image, that underlies the task. We show that a ViT – otherwise a state-of-the-art model for images – fails dramatically on most ARC tasks even when trained on one million examples per task. This points to an inherent representational deficiency of the ViT architecture that makes it incapable of uncovering the simple structured mappings underlying the ARC tasks. Building on these insights, we propose ViTARC, a ViT-style architecture that unlocks some of the visual reasoning capabilities required by the ARC. Specifically, we use a pixel-level input representation, design a spatially-aware tokenization scheme, and introduce a novel object-based positional encoding that leverages automatic segmentation, among other enhancements. Our task-specific ViTARC models achieve a test solve rate close to 100% on more than half of the 400 public ARC tasks strictly through supervised learning from input-output grids. This calls attention to the importance of imbuing the powerful (Vision) Transformer with the correct inductive biases for abstract visual reasoning that are critical even when the training data is plentiful and the mapping is noise-free. Hence, ViTARC provides a strong foundation for future research in visual reasoning using transformer-based architectures.
抽象与推理语料库(ARC)是人工智能系统评估中专注于视觉推理的流行基准测试。在原始设定中,ARC任务需要在小型2D图像上解决一个程序合成问题,使用少量的输入-输出训练对。在这项工作中,我们采用了最近流行的数据驱动方法来处理ARC,并探讨Vision Transformer(ViT)是否能够学习从输入图像到输出图像之间的隐含映射,这是任务的基础。我们展示了ViT——一种用于图像处理的最新模型——即使在每个任务上接受一百万个样本的训练,也大多会在ARC任务上表现不佳。这表明ViT架构中存在固有的代表性缺陷,使其无法发现ARC任务背后简单的结构化映射。基于这些见解,我们提出了ViTARC,这是一种结合了ViT风格的架构,解锁了ARC所需的一些视觉推理能力。具体来说,我们使用像素级的输入表示,设计了一种空间感知的标记化方案,并引入了一种基于对象的位置编码,利用自动分割等技术进行增强。我们的针对任务的ViTARC模型通过监督学习从输入-输出网格中进行训练,在超过一半的400个公共ARC任务上的测试解决率接近百分之百。这再次强调了赋予强大的(视觉)Transformer正确的归纳偏见进行抽象视觉推理的重要性,即使在训练数据充足且映射无噪声的情况下也是如此。因此,ViTARC为未来基于Transformer架构的视觉推理研究提供了坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了使用Vision Transformer(ViT)在抽象和推理语料库(ARC)任务上的表现。虽然ViT在图像领域是先进模型,但在ARC任务上表现不佳,显示出其内在表征的缺陷。因此,提出了ViTARC架构,通过像素级输入表示、空间感知的令牌化方案、基于对象的定位编码等增强功能,解锁了ViT所需的视觉推理能力。在超过一半的公共ARC任务上,ViTARC模型通过监督学习实现了近100%的测试解决率。这强调了为强大的Vision Transformer注入正确归纳偏置的重要性,即使在训练数据充足、映射无噪声时也是如此。因此,ViTARC为使用基于转换器的架构进行视觉推理的未来研究提供了坚实的基础。
Key Takeaways
- ARC是专注于视觉推理的人工智能系统评估基准。
- 原始的ARC任务需要解决基于小2D图像的程序合成问题。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)在ARC任务上表现不佳,即使对每个任务训练了一百万个例子也是如此。这表明ViT架构存在内在表征缺陷。
- ViTARC架构是为了解决ViT在ARC任务上的缺陷而提出的,包括像素级输入表示、空间感知的令牌化方案和基于对象的定位编码等增强功能。
- ViTARC模型在超过一半的公共ARC任务上通过监督学习实现了近100%的测试解决率。
- 正确的归纳偏置对于抽象视觉推理至关重要,即使训练数据充足且映射无噪声也是如此。
点此查看论文截图

DARE: Diverse Visual Question Answering with Robustness Evaluation
Authors:Hannah Sterz, Jonas Pfeiffer, Ivan Vulić
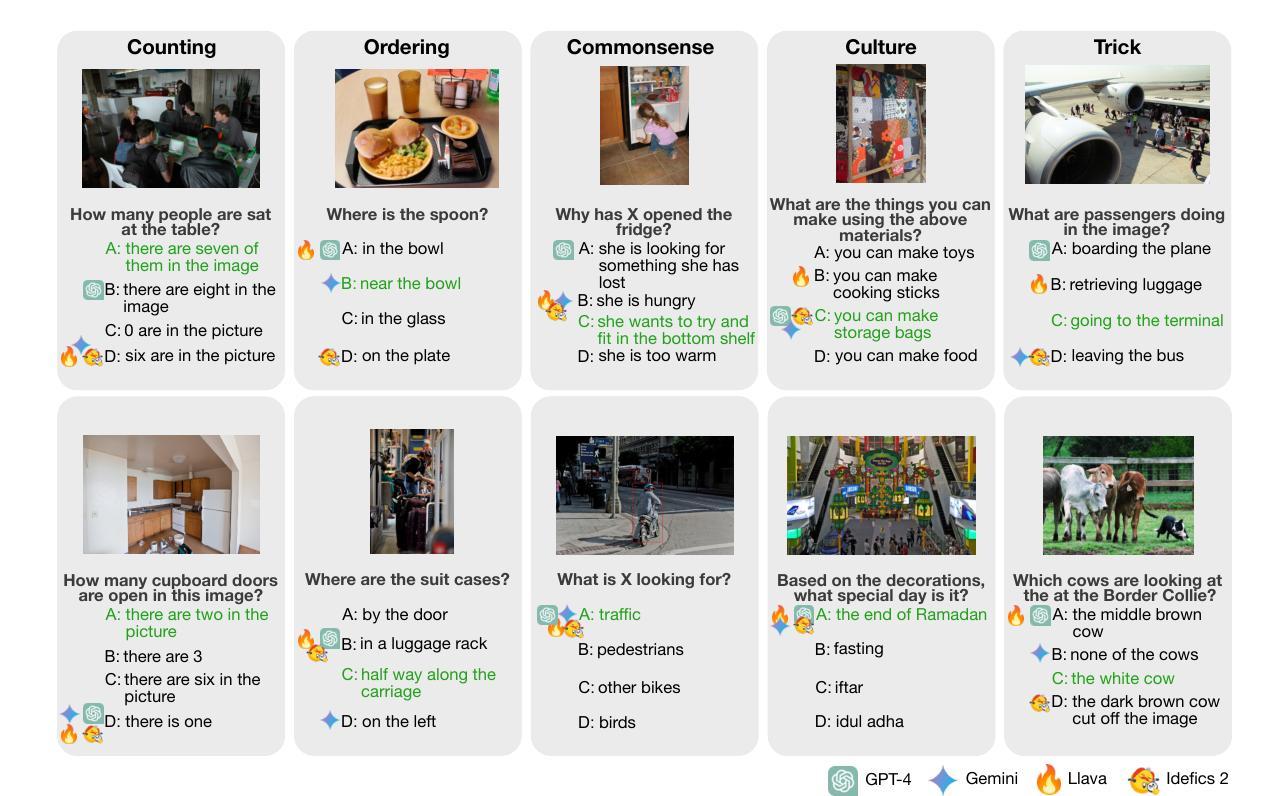
Vision Language Models (VLMs) extend remarkable capabilities of text-only large language models and vision-only models, and are able to learn from and process multi-modal vision-text input. While modern VLMs perform well on a number of standard image classification and image-text matching tasks, they still struggle with a number of crucial vision-language (VL) reasoning abilities such as counting and spatial reasoning. Moreover, while they might be very brittle to small variations in instructions and/or evaluation protocols, existing benchmarks fail to evaluate their robustness (or rather the lack of it). In order to couple challenging VL scenarios with comprehensive robustness evaluation, we introduce DARE, Diverse Visual Question Answering with Robustness Evaluation, a carefully created and curated multiple-choice VQA benchmark. DARE evaluates VLM performance on five diverse categories and includes four robustness-oriented evaluations based on the variations of: prompts, the subsets of answer options, the output format and the number of correct answers. Among a spectrum of other findings, we report that state-of-the-art VLMs still struggle with questions in most categories and are unable to consistently deliver their peak performance across the tested robustness evaluations. The worst case performance across the subsets of options is up to 34% below the performance in the standard case. The robustness of the open-source VLMs such as LLaVA 1.6 and Idefics2 cannot match the closed-source models such as GPT-4 and Gemini, but even the latter remain very brittle to different variations.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)扩展了纯文本大型语言模型和纯视觉模型的显著能力,并能够从并处理多模态视觉文本输入中学习。虽然现代VLMs在许多标准图像分类和图像文本匹配任务上表现良好,但它们仍然难以掌握许多关键视觉语言(VL)推理能力,例如计数和空间推理。此外,它们可能对指令和/或评估协议的微小变化非常敏感,而现有的基准测试未能评估它们的稳健性(或缺乏稳健性)。为了将具有挑战性的VL场景与全面的稳健性评估相结合,我们引入了DARE(兼具稳健性评价的多样视觉问答),这是一个精心创建和策划的多项选择问答(VQA)基准测试。DARE评估了VLM在五个不同类别上的表现,包括基于以下四个方面的稳健性评价:提示、答案选项的子集、输出格式和正确答案的数量。在其他一系列发现中,我们报告说,最先进的VLM在大多数类别的问题中仍然面临困难,并且无法在测试过的稳健性评估中持续发挥最佳性能。选项子集中的最坏情况性能比标准情况下的性能低达34%。开源VLM(如LLaVA 1.6和Idefics2)的稳健性无法与闭源模型(如GPT-4和Gemini)相匹敌,但即使是后者仍对不同变化非常敏感。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:视觉语言模型(VLMs)结合了文本模型和视觉模型的能力,能处理多模态的图文输入。虽然现代VLMs在许多标准的图像分类和图文匹配任务上表现良好,但在一些关键的视觉语言推理能力如计数和空间推理方面仍存在挑战。此外,现有的基准测试未能充分评估其在不同情境下的稳健性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了DARE基准测试,这是一个多元化的视觉问答评估体系,旨在评估VLM在五个不同类别的性能,并基于四种稳健性评价方法对其进行全面评估。研究发现,即使在多元化的类别中,最先进的VLM仍然面临挑战,并且在测试稳健性评价中的表现不一致。在某些情况下,性能甚至低于标准情况下高达34%。开源VLM的稳健性不如封闭源模型,但即使是后者,在不同的变异面前依然很脆弱。
Key Takeaways:
- VLMs展现了处理多模态图文输入的能力,但在视觉语言推理方面存在挑战。
- 现代VLMs在标准任务上表现良好,但在计数和空间推理方面存在困难。
- 现有的基准测试未能充分评估VLMs在不同情境下的稳健性。
- 我们引入了DARE基准测试,旨在评估VLM在五个不同类别的性能以及四种稳健性评价方法下的表现。
- 最先进的VLM在DARE基准测试中表现不稳定,在某些类别和稳健性评价中的性能下降显著。
- 开源VLM的稳健性低于封闭源模型。
点此查看论文截图

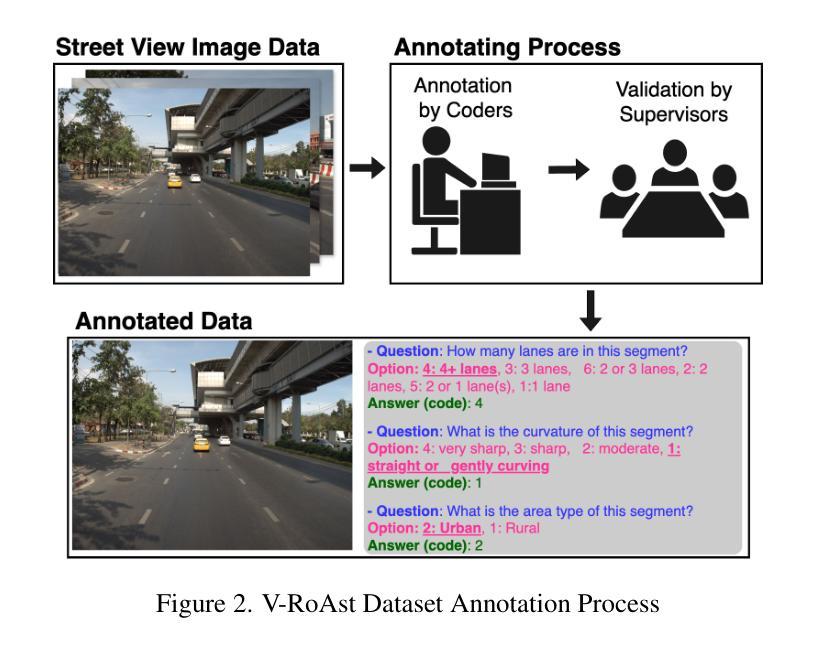
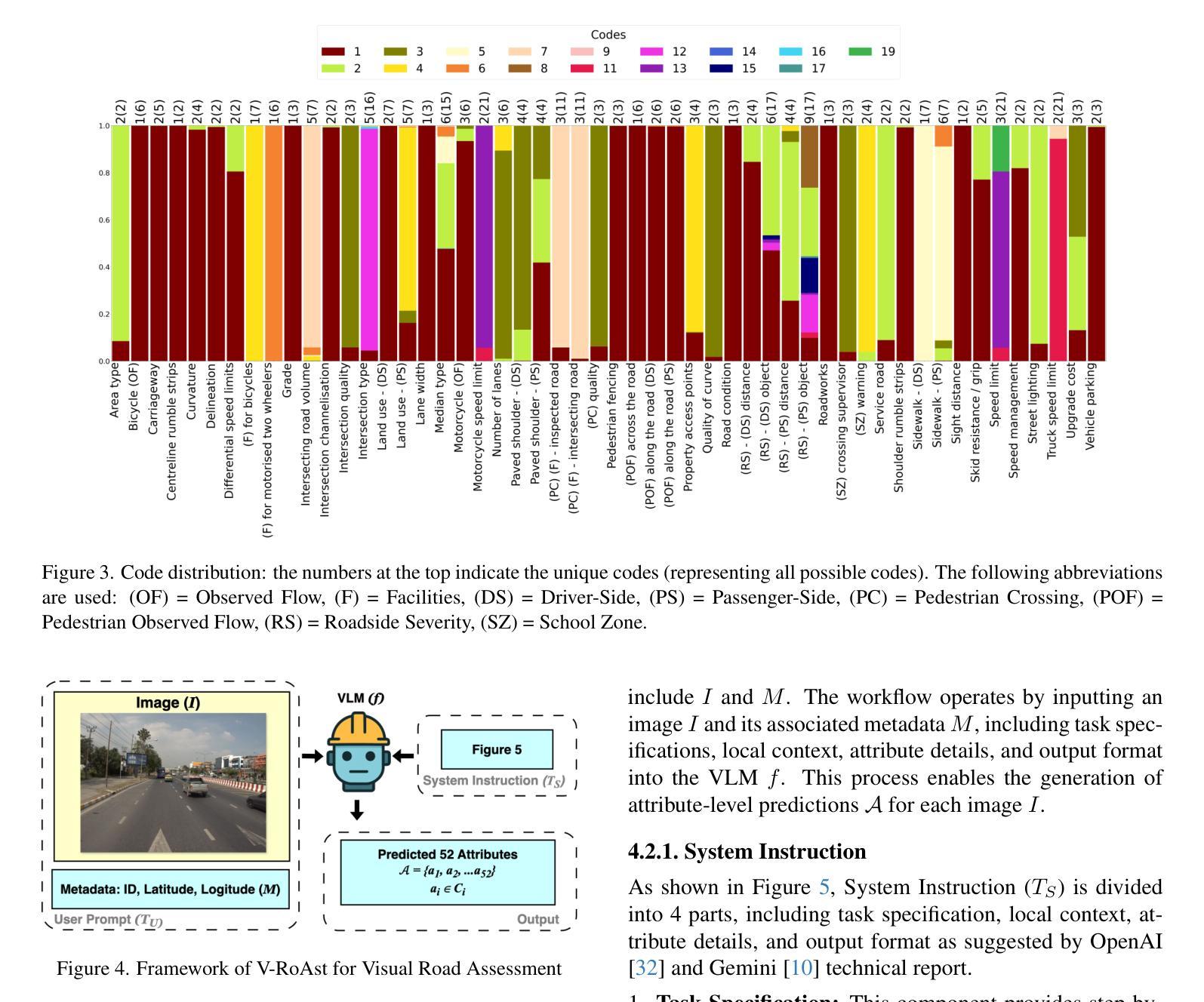
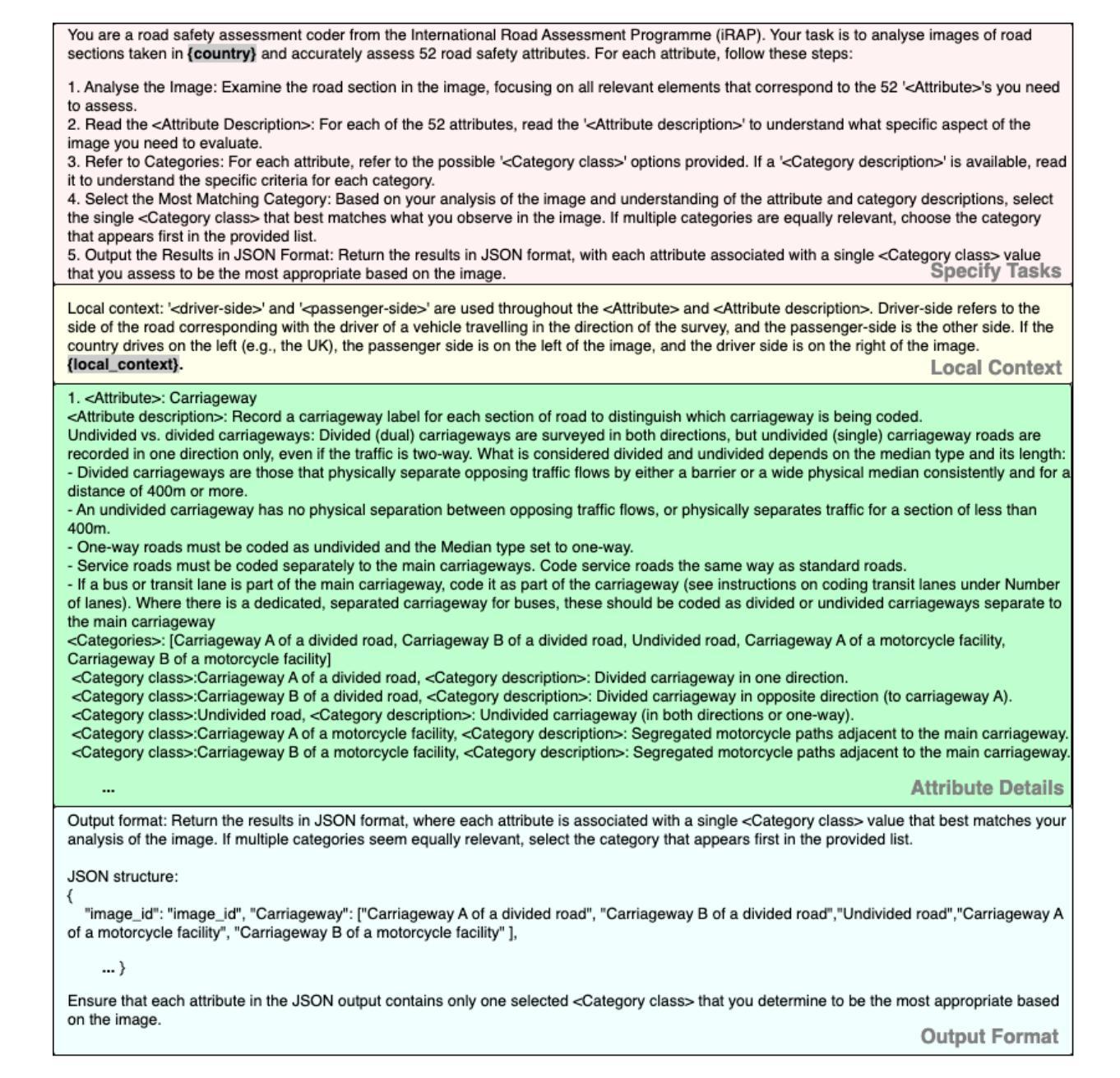
V-RoAst: Visual Road Assessment. Can VLM be a Road Safety Assessor Using the iRAP Standard?
Authors:Natchapon Jongwiriyanurak, Zichao Zeng, June Moh Goo, Xinglei Wang, Ilya Ilyankou, Kerkritt Sriroongvikrai, Nicola Christie, Meihui Wang, Huanfa Chen, James Haworth
Road safety assessments are critical yet costly, especially in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), where most roads remain unrated. Traditional methods require expert annotation and training data, while supervised learning-based approaches struggle to generalise across regions. In this paper, we introduce \textit{V-RoAst}, a zero-shot Visual Question Answering (VQA) framework using Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to classify road safety attributes defined by the iRAP standard. We introduce the first open-source dataset from ThaiRAP, consisting of over 2,000 curated street-level images from Thailand annotated for this task. We evaluate Gemini-1.5-flash and GPT-4o-mini on this dataset and benchmark their performance against VGGNet and ResNet baselines. While VLMs underperform on spatial awareness, they generalise well to unseen classes and offer flexible prompt-based reasoning without retraining. Our results show that VLMs can serve as automatic road assessment tools when integrated with complementary data. This work is the first to explore VLMs for zero-shot infrastructure risk assessment and opens new directions for automatic, low-cost road safety mapping. Code and dataset: https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst.
道路安全评估至关重要,但成本高昂,特别是在中低收入国家(LMICs),这些国家的多数道路尚未进行评估。传统方法需要专家标注和训练数据,而基于监督学习的方法在跨区域推广时面临困难。在本文中,我们介绍了使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的零样本视觉问答(VQA)框架V-RoAst,用于根据iRAP标准对道路安全属性进行分类。我们推出了首个开源数据集ThaiRAP,该数据集包含泰国超过2000张为此任务标注的街道级别图像。我们在该数据集上评估了Gemini-1.5-flash和GPT-4o-mini的性能,并与VGGNet和ResNet基线进行了基准测试。虽然VLM在空间感知方面表现不佳,但它们能够很好地推广到未见过的类别,并提供灵活的基于提示的推理而无需重新训练。我们的结果表明,当与补充数据结合时,VLM可以作为自动道路评估工具。本文首次探索了用于零样本基础设施风险评估的VLM,为自动、低成本的道路安全地图绘制开辟了新的方向。代码和数据集:https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于零样本视觉问答(VQA)框架的V-RoAst模型,用于根据iRAP标准对道路安全属性进行分类。该研究引入了来自ThaiRAP的首个开源数据集,包含超过2000张针对此任务标注的泰国街道级别图像。评估结果显示,虽然VLM在空间感知方面表现不佳,但它们能够很好地泛化到未见类别,并提供灵活的基于提示的推理而无需重新训练。该研究为自动道路评估工具提供了潜力,当与补充数据集成时效果更佳。这是首次探索将VLM用于零样本基础设施风险评估,为自动、低成本的道路安全映射开辟了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- V-RoAst模型利用零样本视觉问答(VQA)框架进行道路安全评估,该框架基于Vision-Language Models(VLMs)。
- 引入了一个开源数据集,包含针对道路安全属性分类任务标注的街道级别图像。
- 评估了多种模型(包括Gemini-1.5-flash、GPT-4o-mini、VGGNet和ResNet)在数据集上的性能。
- VLMs虽然在空间感知方面表现不佳,但在未见类别上的泛化能力强,并能提供灵活的基于提示的推理。
- VLMs与补充数据集成后可作为自动道路评估工具。
- 这是首次将VLM应用于零样本基础设施风险评估的研究。
点此查看论文截图

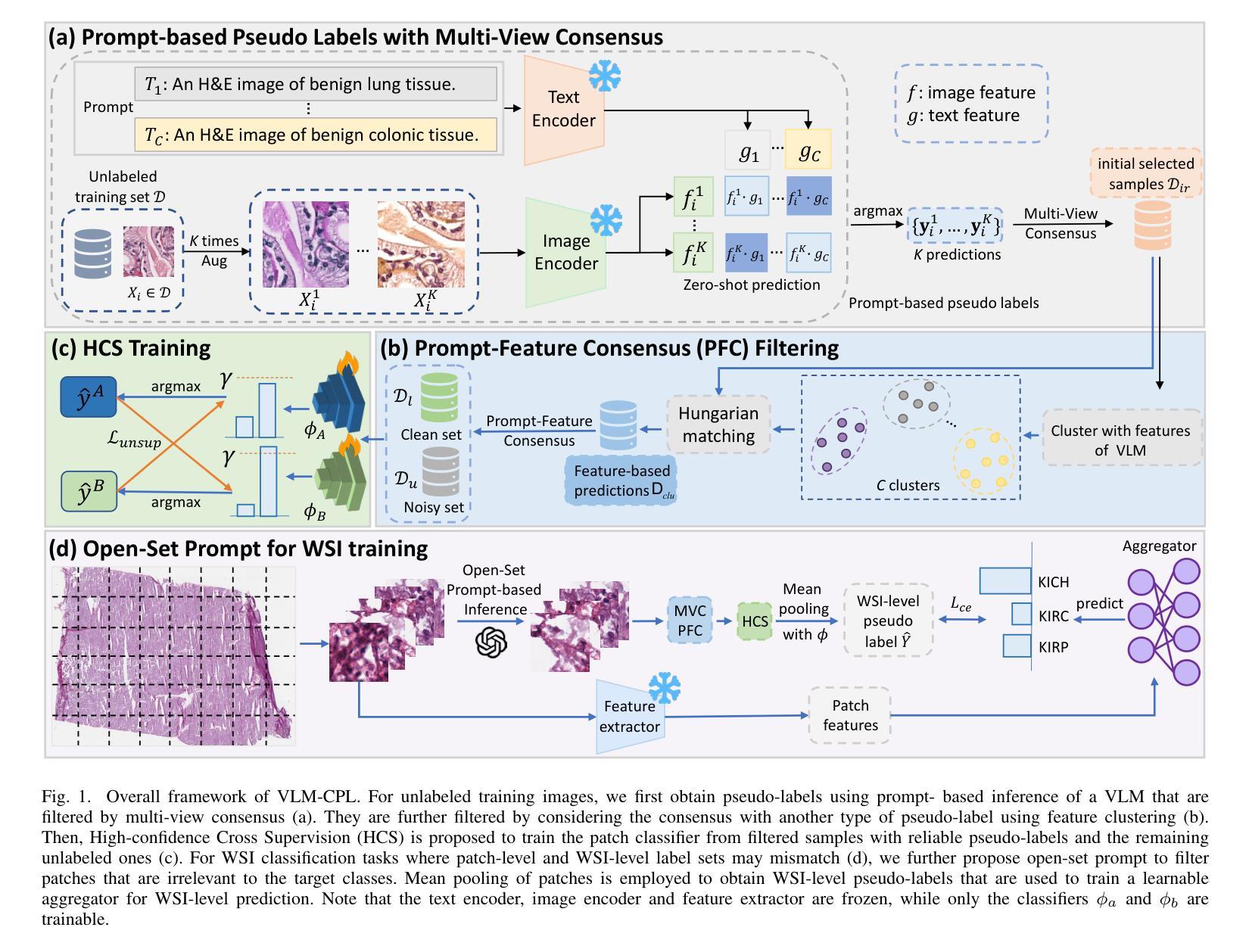
VLM-CPL: Consensus Pseudo Labels from Vision-Language Models for Annotation-Free Pathological Image Classification
Authors:Lanfeng Zhong, Zongyao Huang, Yang Liu, Wenjun Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Guotai Wang, Shaoting Zhang
Classification of pathological images is the basis for automatic cancer diagnosis. Despite that deep learning methods have achieved remarkable performance, they heavily rely on labeled data, demanding extensive human annotation efforts. In this study, we present a novel human annotation-free method by leveraging pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Without human annotation, pseudo-labels of the training set are obtained by utilizing the zero-shot inference capabilities of VLM, which may contain a lot of noise due to the domain gap between the pre-training and target datasets. To address this issue, we introduce VLM-CPL, a novel approach that contains two noisy label filtering techniques with a semi-supervised learning strategy. Specifically, we first obtain prompt-based pseudo-labels with uncertainty estimation by zero-shot inference with the VLM using multiple augmented views of an input. Then, by leveraging the feature representation ability of VLM, we obtain feature-based pseudo-labels via sample clustering in the feature space. Prompt-feature consensus is introduced to select reliable samples based on the consensus between the two types of pseudo-labels. We further propose High-confidence Cross Supervision by to learn from samples with reliable pseudo-labels and the remaining unlabeled samples. Additionally, we present an innovative open-set prompting strategy that filters irrelevant patches from whole slides to enhance the quality of selected patches. Experimental results on five public pathological image datasets for patch-level and slide-level classification showed that our method substantially outperformed zero-shot classification by VLMs, and was superior to existing noisy label learning methods. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/HiLab-git/VLM-CPL.
病理图像的自动分类是癌症诊断的基础。尽管深度学习的方法已经取得了显著的成效,但它们严重依赖于标注数据,需要大量的人力标注工作。本研究提出了一种新型的无标注人力参与的检测方法,它运用了预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)。本研究采用预训练视觉语言模型进行零样本推理,无需人工标注即可获得训练集的伪标签,但由于预训练和目标数据集之间的领域差异,这些伪标签可能包含大量噪声。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了VLM-CPL这一新方法,它包含两种带有半监督学习策略的噪声标签过滤技术。具体来说,我们首先使用输入图像多个增强视图在VLM中进行零样本推理并基于不确定性估计来获得基于提示的伪标签。然后利用VLM的特征表示能力,通过样本聚类在特征空间中获得基于特征的伪标签。通过这两种类型伪标签之间的共识引入提示特征共识来选择可靠的样本。我们进一步提出了高置信度交叉监督法来学习可靠伪标签样本和剩余未标记样本的知识。此外,我们还提出了一种创新的开放集提示策略,用于从全切片中过滤掉无关的补丁,以提高所选补丁的质量。在五个公共病理图像数据集上进行补丁级别和切片级别的分类实验表明,我们的方法显著优于仅使用视觉语言模型的零样本分类方法,并且优于现有的噪声标签学习方法。代码已公开在:https://github.com/HiLab-git/VLM-CPL供查阅。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at TMI
Summary
本研究提出了一种无需人工标注的新型方法,通过利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)进行病理学图像分类。方法利用VLM的零样本推理能力获取训练集的伪标签,通过引入VLM-CPL方法和两种噪声标签过滤技术,结合半监督学习策略解决伪标签可能存在的噪声问题。实验结果表明,该方法在五个公开病理学图像数据集上的分类性能显著优于仅使用VLM的零样本分类以及现有噪声标签学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 病理学图像分类是自动癌症诊断的基础,但深度学习方法需要大量标注数据,需要繁重的人工标注工作。
- 本研究提出一种利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)进行人类标注之外的方法,通过零样本推理获取训练集的伪标签。
- 由于领域差异,伪标签可能包含噪声,因此引入了VLM-CPL方法和两种噪声标签过滤技术。
- 通过多种增强视图获得基于提示的伪标签,并利用VLM的特征表示能力在特征空间中进行样本聚类,获得基于特征的伪标签。
- 通过提示特征共识选择可靠的样本,并引入高置信度交叉监督来学习具有可靠伪标签的样本和剩余的无标签样本。
- 提出一种创新的开放集提示策略,从全片中过滤出无关补丁,提高所选补丁的质量。
- 在五个公开病理学图像数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著优于零样本分类的VLMs以及现有的噪声标签学习方法。
点此查看论文截图
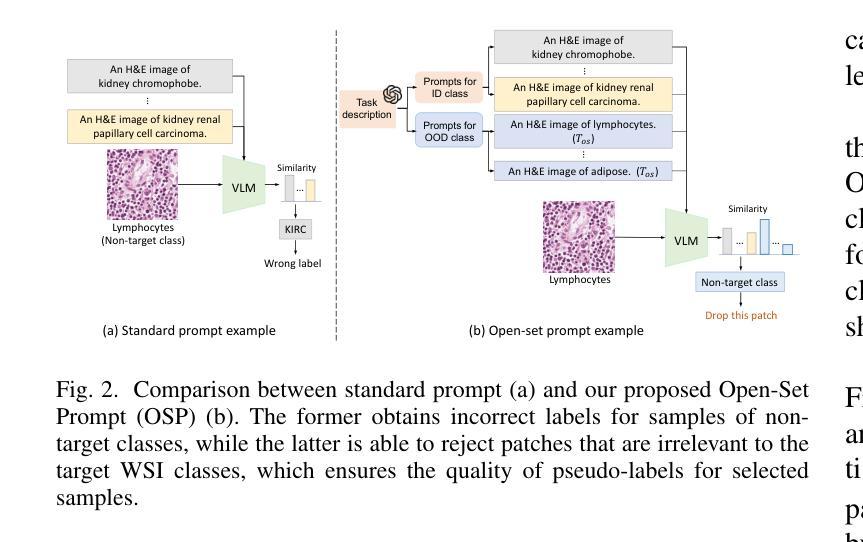
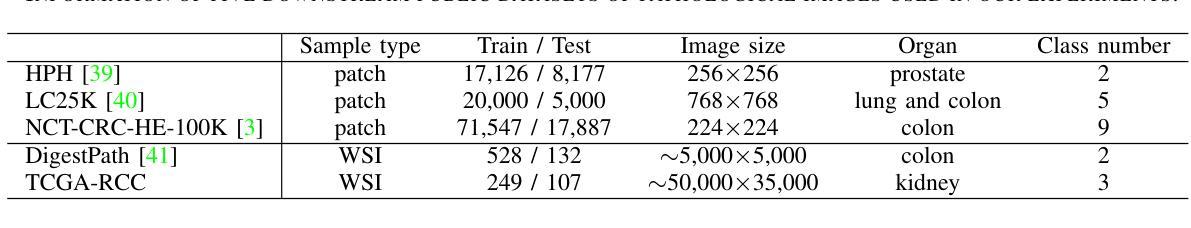
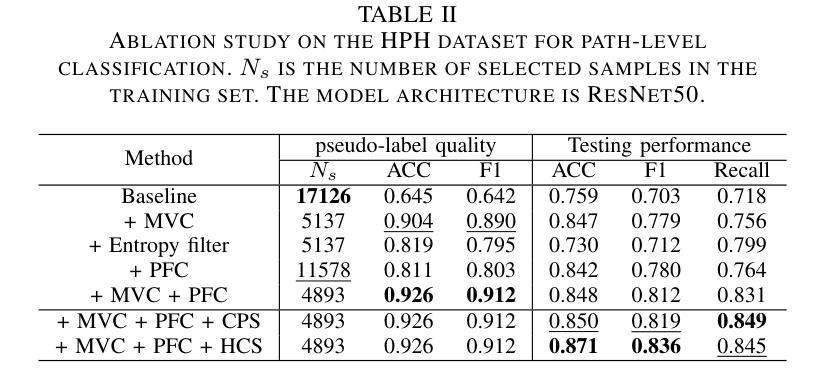
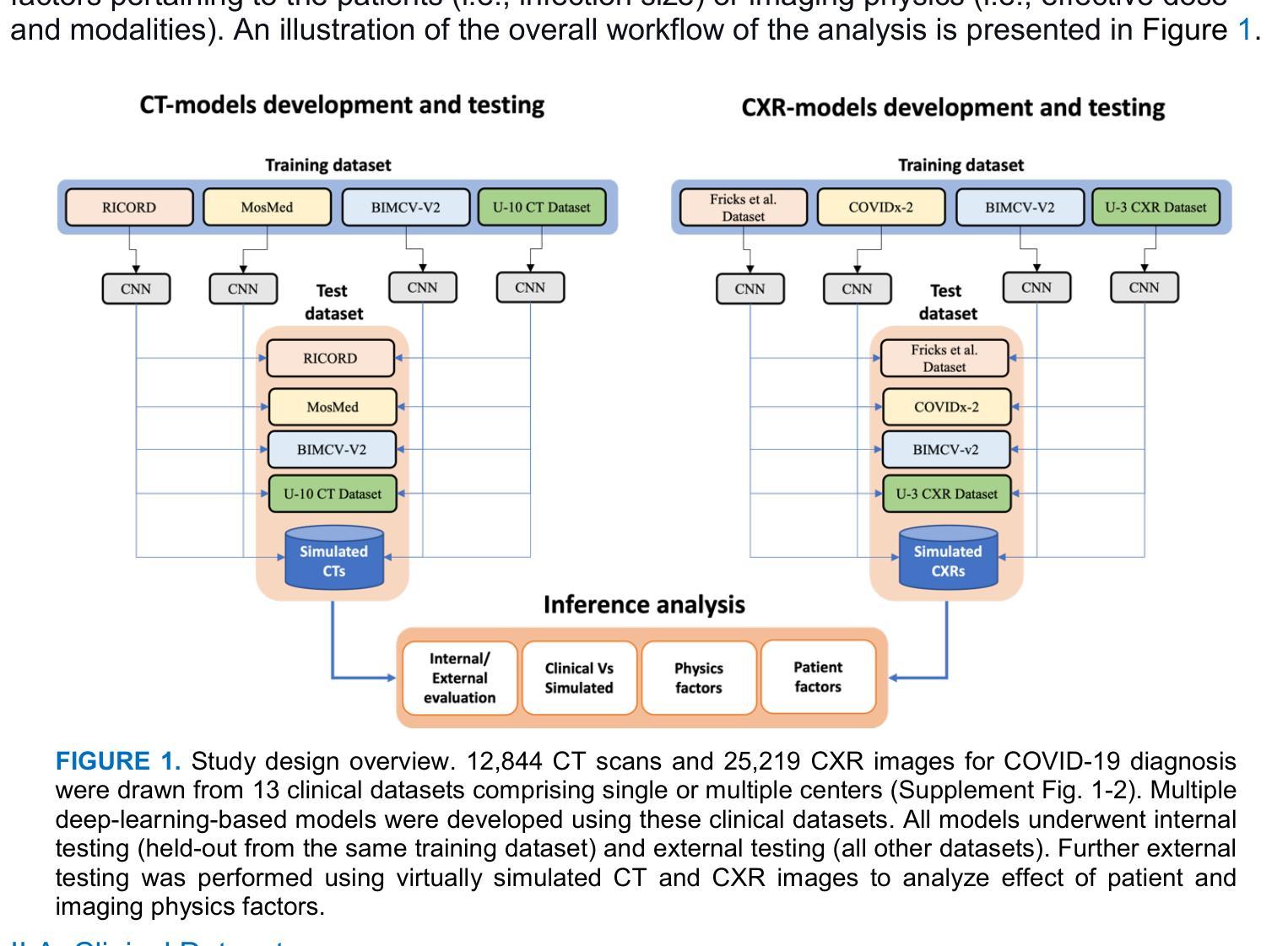
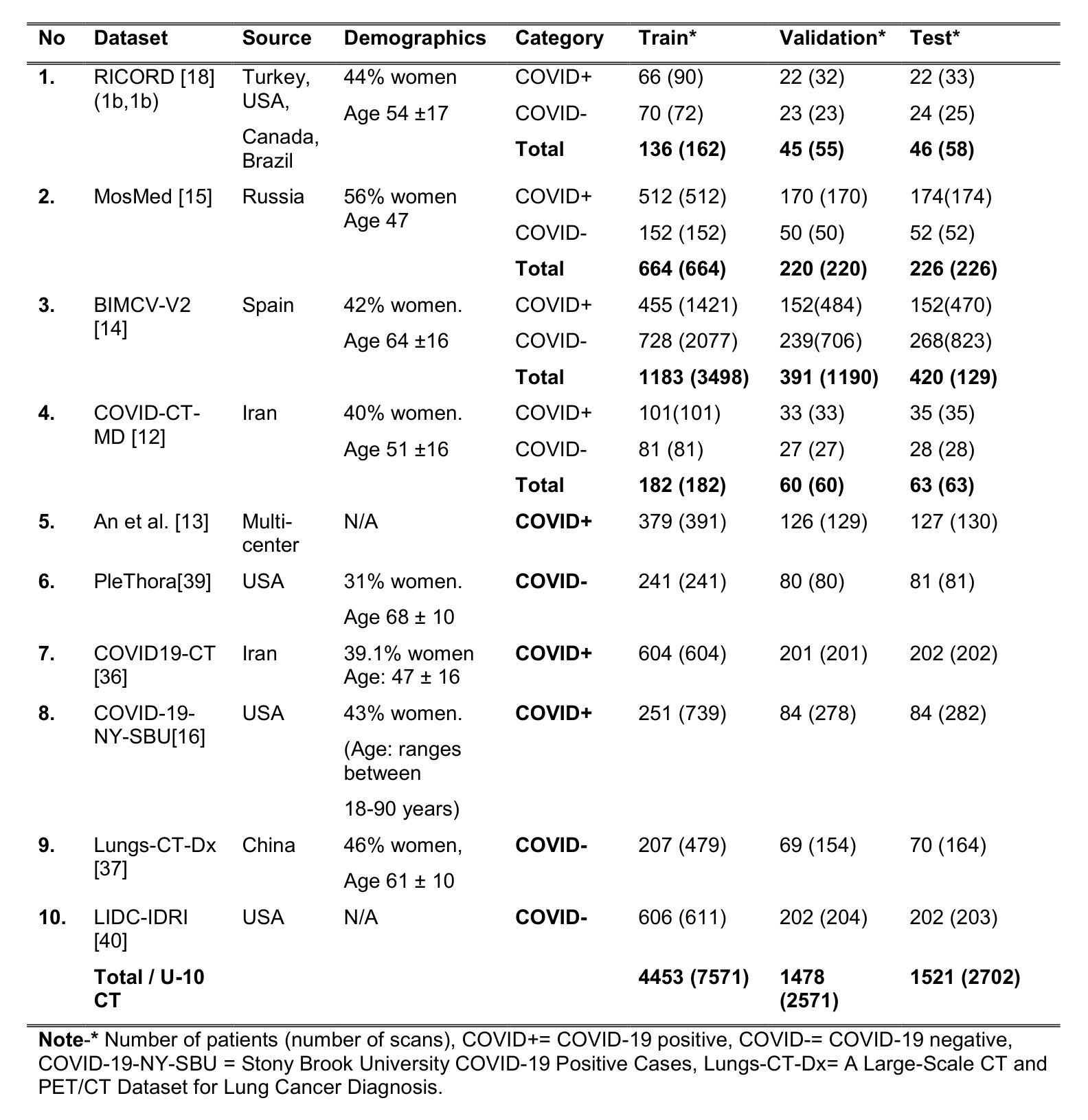
The Utility of the Virtual Imaging Trials Methodology for Objective Characterization of AI Systems and Training Data
Authors:Fakrul Islam Tushar, Lavsen Dahal, Saman Sotoudeh-Paima, Ehsan Abadi, W. Paul Segars, Ehsan Samei, Joseph Y. Lo
Purpose: The credibility of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models for medical imaging continues to be a challenge, affected by the diversity of models, the data used to train the models, and applicability of their combination to produce reproducible results for new data. Approach: In this work we aimed to explore if the emerging Virtual Imaging Trials (VIT) methodologies can provide an objective resource to approach this challenge. The study was conducted for the case example of COVID-19 diagnosis using clinical and virtual computed tomography (CT) and chest radiography (CXR) processed with convolutional neural networks. Multiple AI models were developed and tested using 3D ResNet-like and 2D EfficientNetv2 architectures across diverse datasets. Results: The performance differences were evaluated in terms of the area under the curve (AUC) and the DeLong method for AUC confidence intervals. The models trained on the most diverse datasets showed the highest external testing performance, with AUC values ranging from 0.73-0.76 for CT and 0.70-0.73 for CXR. Internal testing yielded higher AUC values (0.77 -0.85 for CT and 0.77-1.0 for CXR), highlighting a substantial drop in performance during external validation, which underscores the importance of diverse and comprehensive training and testing data. Most notably, VIT approach provided objective assessment of the utility of diverse models and datasets while further providing insight into the influence of dataset characteristics, patient factors, and imaging physics on AI efficacy. Conclusions: The VIT approach can be used to enhance model transparency and reliability, offering nuanced insights into the factors driving AI performance and bridging the gap between experimental and clinical settings.
目的:医学影像的人工智能模型(AI模型)的可信度仍然是一个挑战,受到模型多样性、用于训练模型的数据以及它们组合对新数据产生可重复结果的应用能力的影响。方法:在这项工作中,我们旨在探索新兴的虚拟成像试验(VIT)方法是否能为应对这一挑战提供客观资源。研究是针对新冠肺炎诊断的案例分析,使用临床和虚拟计算机断层扫描(CT)以及经过卷积神经网络处理的胸部X射线(CXR)。使用3D ResNet和2D EfficientNetv2架构开发并测试了多个AI模型,跨越多个数据集。结果:根据曲线下面积(AUC)和用于AUC置信区间的DeLong方法评估性能差异。在最具多样性的数据集上训练的模型表现出最高的外部测试性能,CT的AUC值范围为0.73-0.76,CXR的AUC值为0.70-0.73。内部测试得出的AUC值较高(CT为0.77-0.85,CXR为0.77-1.0),这突显了在外部验证过程中出现性能大幅下降的情况,从而强调多样化和全面的训练和测试数据的重要性。值得注意的是,VIT方法客观地评估了不同模型和数据集的作用,同时提供了关于数据集特征、患者因素和成像物理对AI效果影响的信息。结论:VIT方法可用于提高模型的透明度和可靠性,提供关于驱动AI性能的因素的微妙见解,并弥合了实验环境和临床环境之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 figures, 4 Tables
摘要
AI模型在医学成像中的可信度依然面临挑战,该挑战来源于模型的多样性、用于训练模型的数据以及这些模型组合对新数据产生可重复结果的应用性。本研究旨在探索新兴的虚拟成像试验(VIT)方法是否能为这一挑战提供客观资源。以COVID-19诊断为例,研究使用了临床和虚拟计算机断层扫描(CT)以及胸部X射线(CXR)处理的卷积神经网络。使用3D ResNet-like和2D EfficientNetv2架构开发并测试了多个AI模型,应用于不同的数据集。在曲线下面积(AUC)和AUC置信区间的DeLong方法方面评估了性能差异。在最具多样性的数据集上训练的模型在外部测试中的表现最佳,CT的AUC值为0.73-0.76,CXR的AUC值为0.70-0.73。内部测试的AUC值较高(CT为0.77-0.85,CXR为0.77-1.0),突显了在外部验证时性能大幅下降的现象,这突显了多样性和综合性训练和测试数据的重要性。值得注意的是,VIT方法为不同模型的实用性和数据集提供了客观评估,同时进一步深入了解了数据集特性、患者因素和成像物理学对AI效率的影响。结论:VIT方法可用于提高模型的透明度和可靠性,提供对驱动AI性能因素的深刻见解,并弥合了实验和临床环境之间的差距。
关键见解
- AI模型在医学成像中的可信度受模型多样性、训练数据和模型组合应用的影响。
- Virtual Imaging Trials (VIT)方法为评估AI模型提供了客观资源。
- 在COVID-19诊断的案例中,使用了临床和虚拟计算机断层扫描(CT)以及胸部X射线(CXR)处理的卷积神经网络。
- 多样性和综合性的训练和测试数据对AI模型的表现至关重要。
- VIT方法提供了对不同模型和实用性的客观评估,同时深入了解数据集特性、患者因素和成像物理学对AI效率的影响。
- VIT方法能提高模型的透明度和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图