⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-04 更新
A New One-Shot Federated Learning Framework for Medical Imaging Classification with Feature-Guided Rectified Flow and Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Yufei Ma, Hanwen Zhang, Qiya Yang, Guibo Luo, Yuesheng Zhu
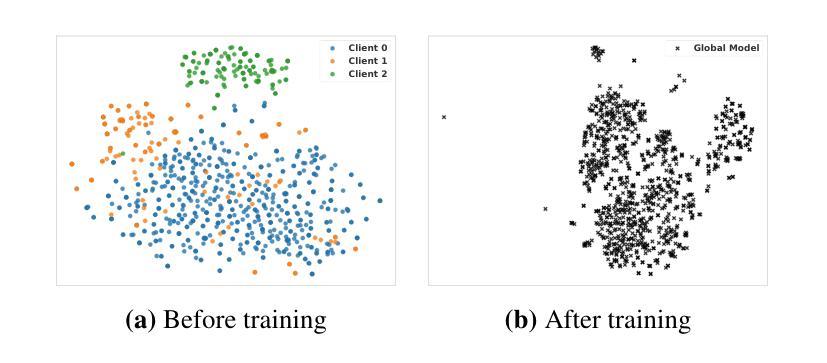
In multi-center scenarios, One-Shot Federated Learning (OSFL) has attracted increasing attention due to its low communication overhead, requiring only a single round of transmission. However, existing generative model-based OSFL methods suffer from low training efficiency and potential privacy leakage in the healthcare domain. Additionally, achieving convergence within a single round of model aggregation is challenging under non-Independent and Identically Distributed (non-IID) data. To address these challenges, in this paper a modified OSFL framework is proposed, in which a new Feature-Guided Rectified Flow Model (FG-RF) and Dual-Layer Knowledge Distillation (DLKD) aggregation method are developed. FG-RF on the client side accelerates generative modeling in medical imaging scenarios while preserving privacy by synthesizing feature-level images rather than pixel-level images. To handle non-IID distributions, DLKD enables the global student model to simultaneously mimic the output logits and align the intermediate-layer features of client-side teacher models during aggregation. Experimental results on three non-IID medical imaging datasets show that our new framework and method outperform multi-round federated learning approaches, achieving up to 21.73% improvement, and exceeds the baseline FedISCA by an average of 21.75%. Furthermore, our experiments demonstrate that feature-level synthetic images significantly reduce privacy leakage risks compared to pixel-level synthetic images.
在多中心场景中,由于只需要一轮传输的低通信开销,一次性联邦学习(OSFL)已经引起了越来越多的关注。然而,现有的基于生成模型的OSFL方法存在训练效率低下和医疗保健领域潜在隐私泄露的问题。此外,在非独立同分布(non-IID)数据下,在单次模型聚合中实现收敛是一个挑战。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了一个改进的OSFL框架,其中开发了一种新的特征引导修正流模型(FG-RF)和双层知识蒸馏(DLKD)聚合方法。客户端的FG-RF加速医疗成像场景中的生成建模,通过合成特征级图像而不是像素级图像来保留隐私。为了处理非IID分布,DLKD使全局学生模型能够在聚合过程中同时模仿输出逻辑并对齐客户端教师模型的中间层特征。在三个非IID医学成像数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的新框架和方法优于多轮联邦学习方法,实现了高达21.73%的改进,并超过基线FedISCA平均21.75%。此外,我们的实验表明,与像素级合成图像相比,特征级合成图像显著降低了隐私泄露风险。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECAI 2025
Summary
论文提出一种改进的一站式联邦学习框架,通过新的特征引导修正流模型和双层知识蒸馏聚合方法,解决了现有生成模型在一站式联邦学习中面临的训练效率低下和隐私泄露问题。新框架在医疗成像场景中加速生成建模,通过合成特征级图像而非像素级图像来保护隐私。同时,双层知识蒸馏技术解决了非独立同分布数据的聚合问题,使全局学生模型在聚合时能够同时模仿输出逻辑和与客户端教师模型的中间层特征对齐。实验证明新框架和方法在非独立同分布医疗成像数据集上的表现优于多轮联邦学习方法,隐私泄露风险也显著降低。
Key Takeaways
- One-Shot Federated Learning (OSFL)具有低通信开销的优点,但在多中心场景中面临训练效率和隐私泄露的挑战。
- 现有基于生成模型的OSFL方法存在不足,论文提出了一种改进的一站式联邦学习框架。
- 框架中引入了新的特征引导修正流模型(FG-RF),加速医疗成像场景中的生成建模。
- FG-RF通过合成特征级图像而不是像素级图像,有助于保护隐私。
- 双层知识蒸馏(DLKD)技术用于处理非独立同分布(non-IID)数据,促进全局学生模型的聚合。
- 实验证明新框架在三个非独立同分布医疗成像数据集上的表现优于多轮联邦学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

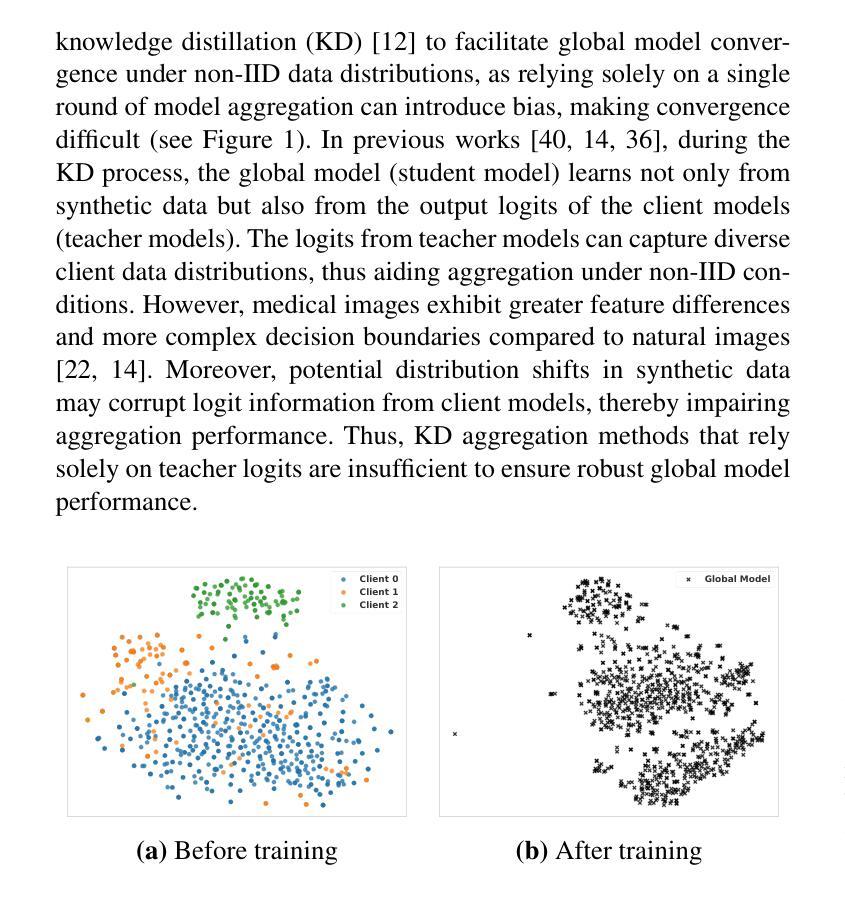
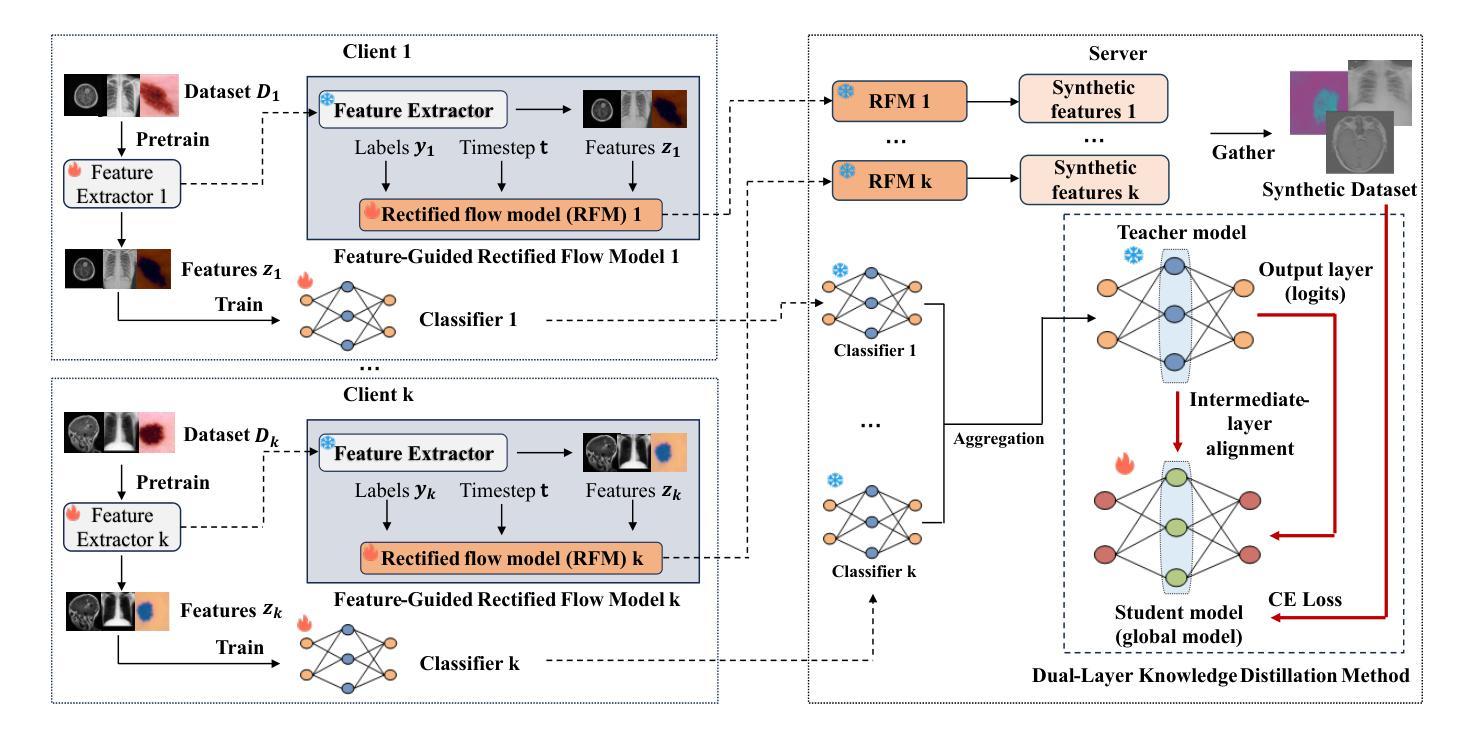
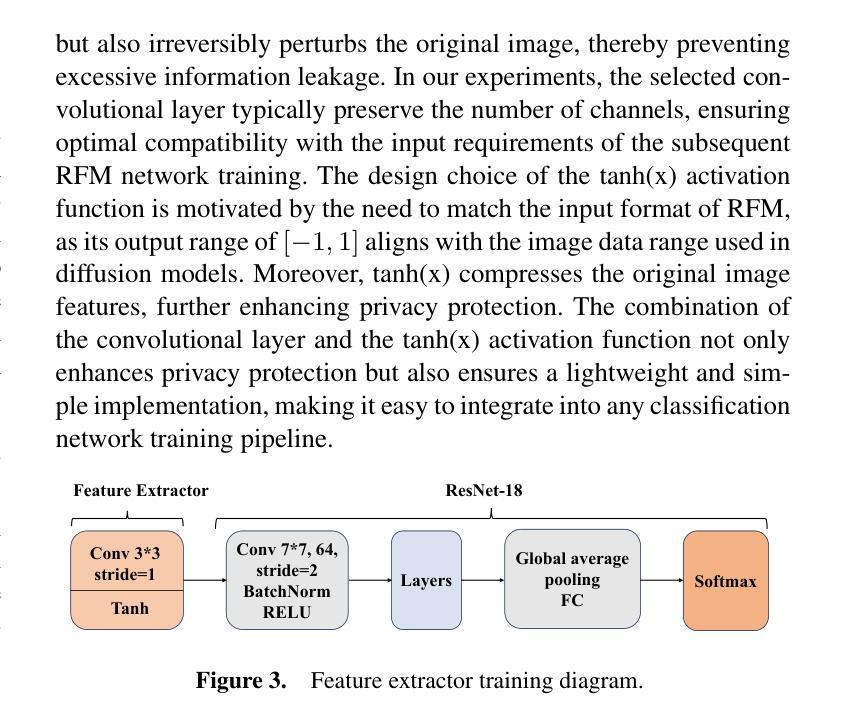
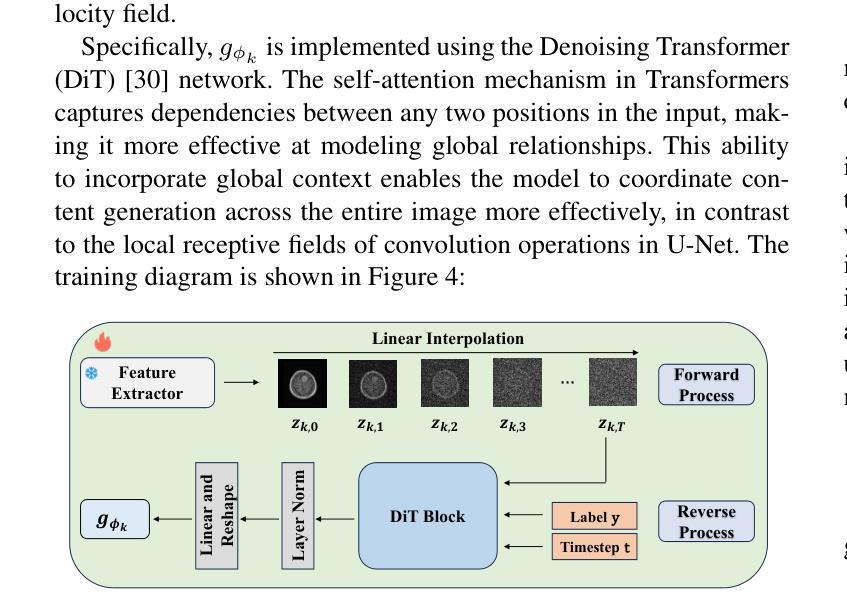
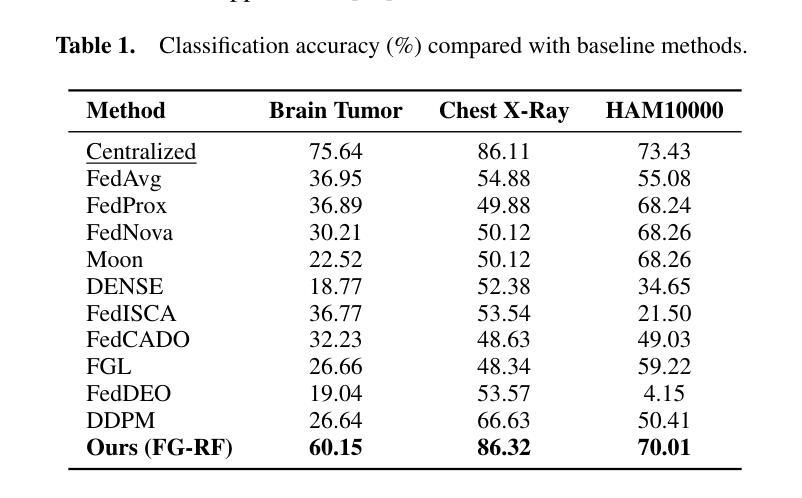
PTCMIL: Multiple Instance Learning via Prompt Token Clustering for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Beidi Zhao, SangMook Kim, Hao Chen, Chen Zhou, Zu-hua Gao, Gang Wang, Xiaoxiao Li
Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) has advanced WSI analysis but struggles with the complexity and heterogeneity of WSIs. Existing MIL methods face challenges in aggregating diverse patch information into robust WSI representations. While ViTs and clustering-based approaches show promise, they are computationally intensive and fail to capture task-specific and slide-specific variability. To address these limitations, we propose PTCMIL, a novel Prompt Token Clustering-based ViT for MIL aggregation. By introducing learnable prompt tokens into the ViT backbone, PTCMIL unifies clustering and prediction tasks in an end-to-end manner. It dynamically aligns clustering with downstream tasks, using projection-based clustering tailored to each WSI, reducing complexity while preserving patch heterogeneity. Through token merging and prototype-based pooling, PTCMIL efficiently captures task-relevant patterns. Extensive experiments on eight datasets demonstrate its superior performance in classification and survival analysis tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Systematic ablation studies confirm its robustness and strong interpretability. The code is released at https://github.com/ubc-tea/PTCMIL.
多实例学习(MIL)在WSI分析方面取得了一定的进展,但在处理WSI的复杂性和异质性方面遇到了困难。现有的MIL方法在将各种补丁信息聚合为稳健的WSI表示方面面临挑战。虽然基于ViT和聚类的方法显示出潜力,但它们计算量大,未能捕获特定任务和特定幻灯片的变异性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了PTCMIL,这是一种基于提示令牌聚类的ViT的新型MIL聚合方法。通过将可学习的提示令牌引入ViT主干,PTCMIL以端到端的方式统一了聚类任务和预测任务。它通过针对每个WSI定制的基于投影的聚类来动态调整聚类与下游任务的对齐方式,在降低复杂性的同时保留补丁的异质性。通过令牌合并和基于原型的池化,PTCMIL有效地捕获了任务相关的模式。在八个数据集上的广泛实验表明,它在分类和生存分析任务中的性能优于其他最新方法。系统的消融研究证实了其稳健性和强大的可解释性。代码已发布在https://github.com/ubc-tea/PTCMIL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PTCMIL方法在多实例学习(MIL)中对WSI分析的改进。针对现有MIL方法在聚合多样补丁信息时面临的挑战,PTCMIL引入了一种基于提示令牌聚类的ViT方法。该方法通过引入可学习的提示令牌,将聚类任务和预测任务统一在端到端的框架内,实现了动态的对下游任务的聚类对齐。PTCMIL采用针对每个WSI量身定制的投影式聚类,降低了复杂性,同时保留了补丁的异质性。通过令牌合并和基于原型的池化,PTCMIL有效地捕获了任务相关的模式。在八个数据集上的广泛实验表明,它在分类和生存分析任务中的性能优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- PTCMIL是一种基于提示令牌聚类的ViT方法,用于改进WSI分析中的多实例学习(MIL)。
- 现有MIL方法在聚合多样补丁信息时面临挑战,PTCMIL旨在解决这一问题。
- PTCMIL引入可学习的提示令牌,将聚类任务和预测任务结合在端到端的框架内。
- PTCMIL采用投影式聚类,针对每个WSI进行定制,以降低复杂性并保留补丁的异质性。
- PTCMIL通过令牌合并和基于原型的池化,有效捕获任务相关模式。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,PTCMIL在分类和生存分析任务中的性能优于现有方法。
- PTCMIL具有稳健性、强可解释性和优秀的性能。
点此查看论文截图

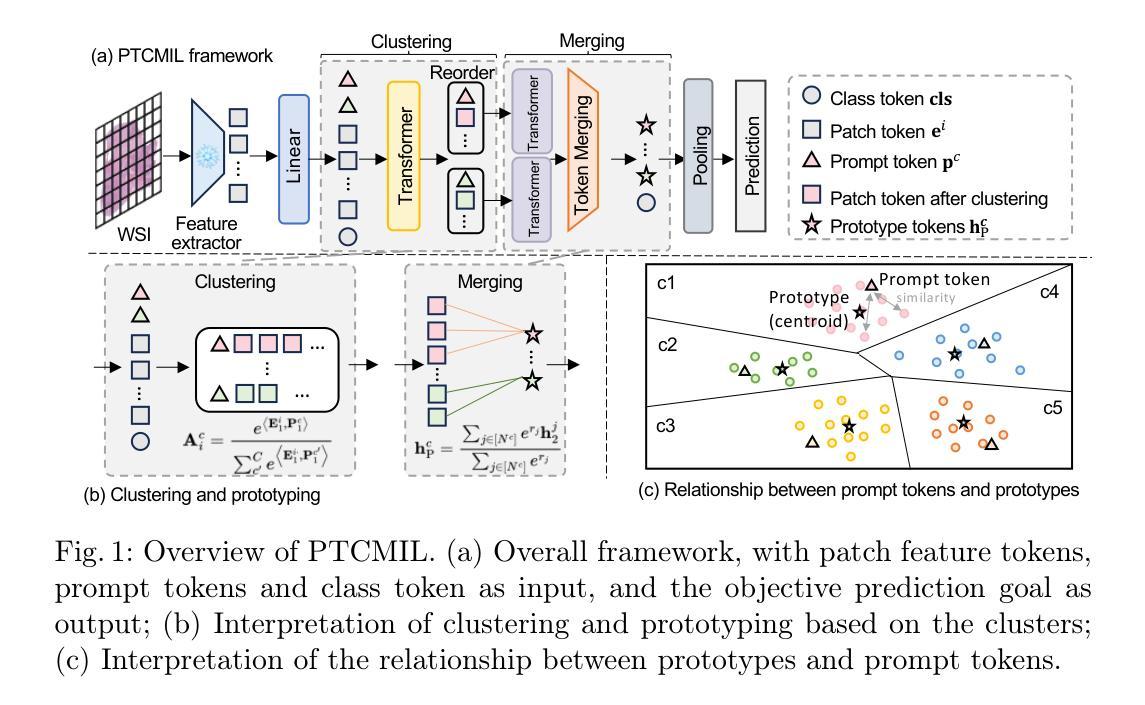
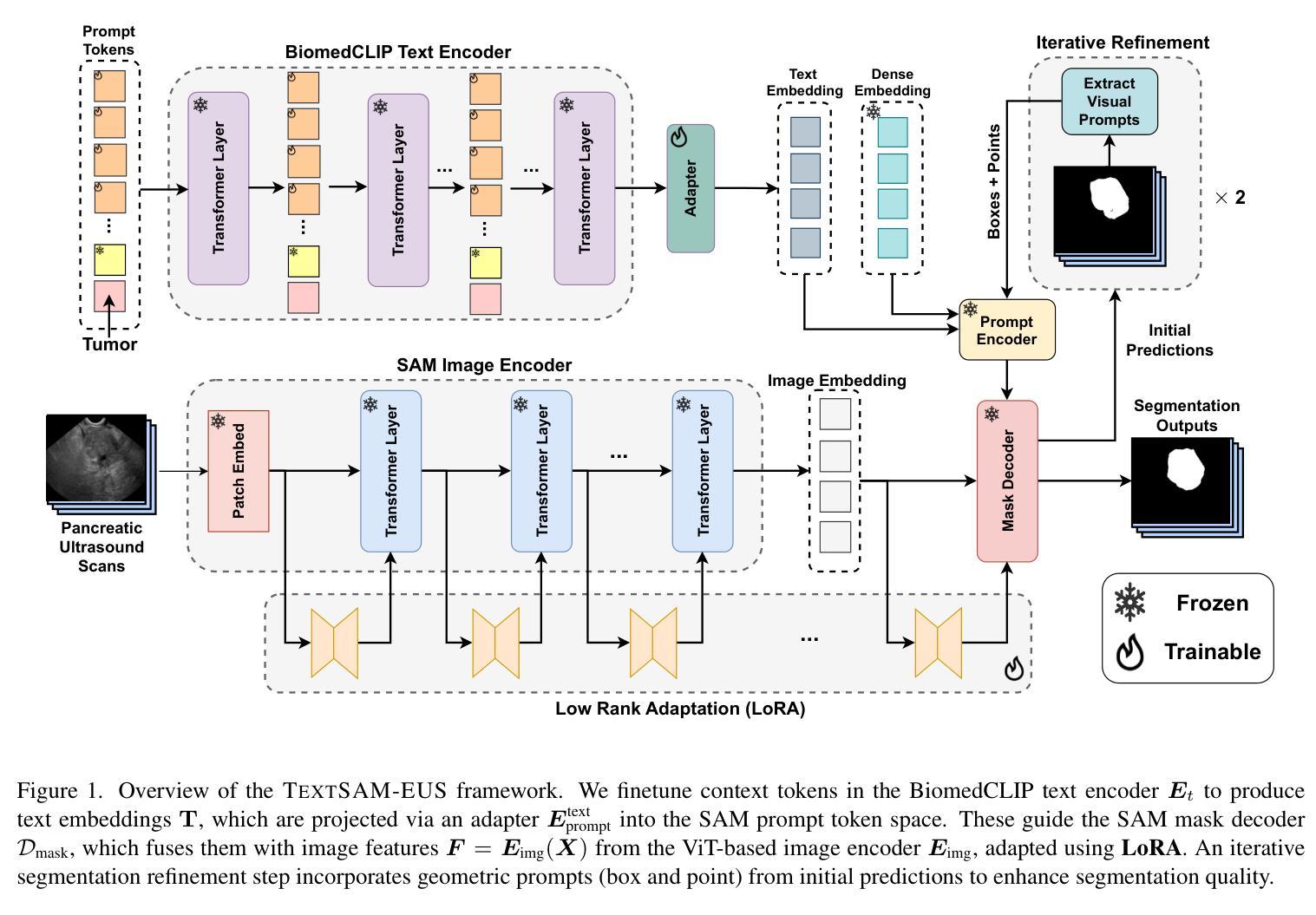
TextSAM-EUS: Text Prompt Learning for SAM to Accurately Segment Pancreatic Tumor in Endoscopic Ultrasound
Authors:Pascal Spiegler, Taha Koleilat, Arash Harirpoush, Corey S. Miller, Hassan Rivaz, Marta Kersten-Oertel, Yiming Xiao
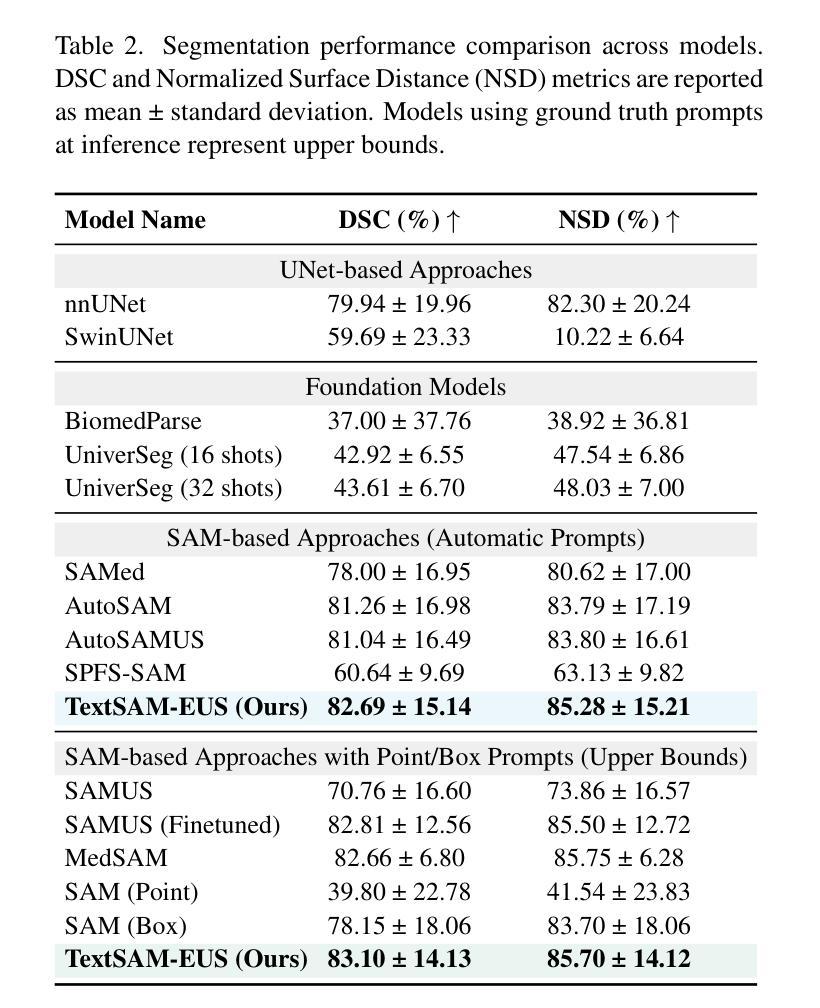
Pancreatic cancer carries a poor prognosis and relies on endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for targeted biopsy and radiotherapy. However, the speckle noise, low contrast, and unintuitive appearance of EUS make segmentation of pancreatic tumors with fully supervised deep learning (DL) models both error-prone and dependent on large, expert-curated annotation datasets. To address these challenges, we present TextSAM-EUS, a novel, lightweight, text-driven adaptation of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) that requires no manual geometric prompts at inference. Our approach leverages text prompt learning (context optimization) through the BiomedCLIP text encoder in conjunction with a LoRA-based adaptation of SAM’s architecture to enable automatic pancreatic tumor segmentation in EUS, tuning only 0.86% of the total parameters. On the public Endoscopic Ultrasound Database of the Pancreas, TextSAM-EUS with automatic prompts attains 82.69% Dice and 85.28% normalized surface distance (NSD), and with manual geometric prompts reaches 83.10% Dice and 85.70% NSD, outperforming both existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) supervised DL models and foundation models (e.g., SAM and its variants). As the first attempt to incorporate prompt learning in SAM-based medical image segmentation, TextSAM-EUS offers a practical option for efficient and robust automatic EUS segmentation. Code is available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/TextSAM-EUS .
胰腺癌预后不良,依赖于内镜超声(EUS)进行靶向活检和放射治疗。然而,内镜超声的斑点噪声、低对比度和非直观外观使得使用全监督深度学习(DL)模型进行胰腺肿瘤分割容易出现错误,并且依赖于大规模的专业注释数据集。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了TextSAM-EUS,这是一种新型的轻量级文本驱动适应性的分段任何东西模型(SAM),在推理过程中无需手动几何提示。我们的方法结合了BiomedCLIP文本编码器的文本提示学习(上下文优化),并使用基于LoRA的SAM架构的适应,以实现EUS中的自动胰腺肿瘤分割,仅调整总参数的0.86%。在公共胰腺内镜超声数据库上,具有自动提示的TextSAM-EUS获得82.69%的Dice系数和85.28%的归一化表面距离(NSD),使用手动几何提示则达到83.10%的Dice系数和85.70%的NSD,超越了现有的最新监督深度学习模型和基础模型(例如SAM及其变体)。作为将提示学习纳入SAM基础医学图像分割的首次尝试,TextSAM-EUS为高效且稳健的自动EUS分割提供了实用的选择。代码可在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/TextSAM-EUS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025 Workshop CVAMD
Summary
针对胰腺癌内镜超声(EUS)图像分割的挑战,提出了一种新型的轻量级文本驱动自适应分段模型TextSAM-EUS。该模型结合文本提示学习和基于LoRA的SAM架构改进,无需手动几何提示即可自动进行胰腺肿瘤分割。在公共胰腺内镜超声数据库上,TextSAM-EUS的自动提示达到82.69%的Dice系数和85.28%的归一化表面距离(NSD),并超越了现有的最先进的监督深度学习模型和基础模型。
Key Takeaways
1. TextSAM-EUS是一个针对内镜超声(EUS)图像分割的新型文本驱动自适应分段模型。
2. 该模型通过结合文本提示学习和基于LoRA的SAM架构改进,增强了模型的分割性能。
3. TextSAM-EUS无需手动几何提示即可自动进行胰腺肿瘤分割。
4. 在公共胰腺内镜超声数据库上,TextSAM-EUS的分割性能超越了现有的最先进的监督深度学习模型和基础模型。
5. TextSAM-EUS的自动提示达到82.69%的Dice系数和85.28%的NSD,表现出良好的性能。
6. 该模型为胰腺肿瘤分割提供了一种实用、高效且稳健的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

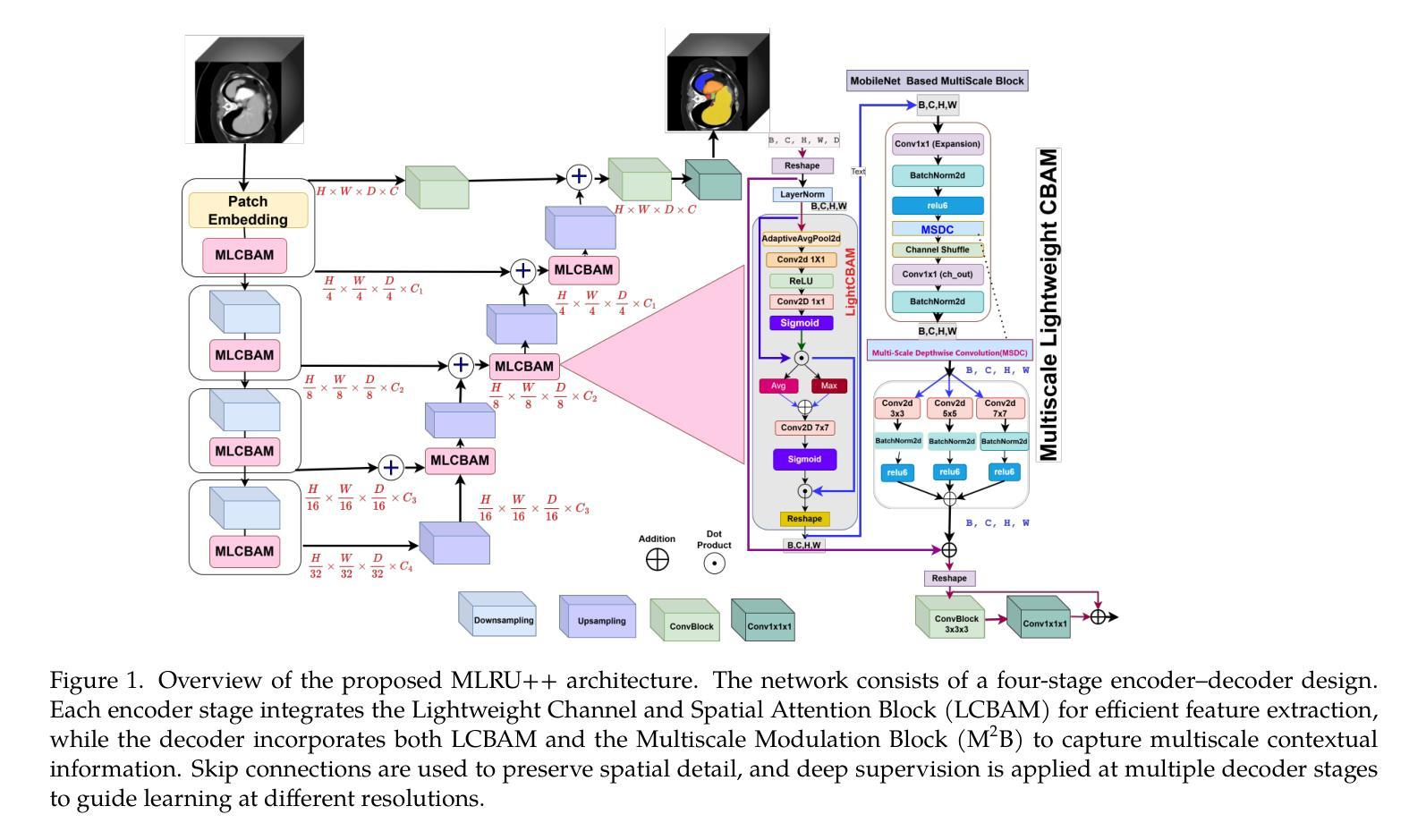
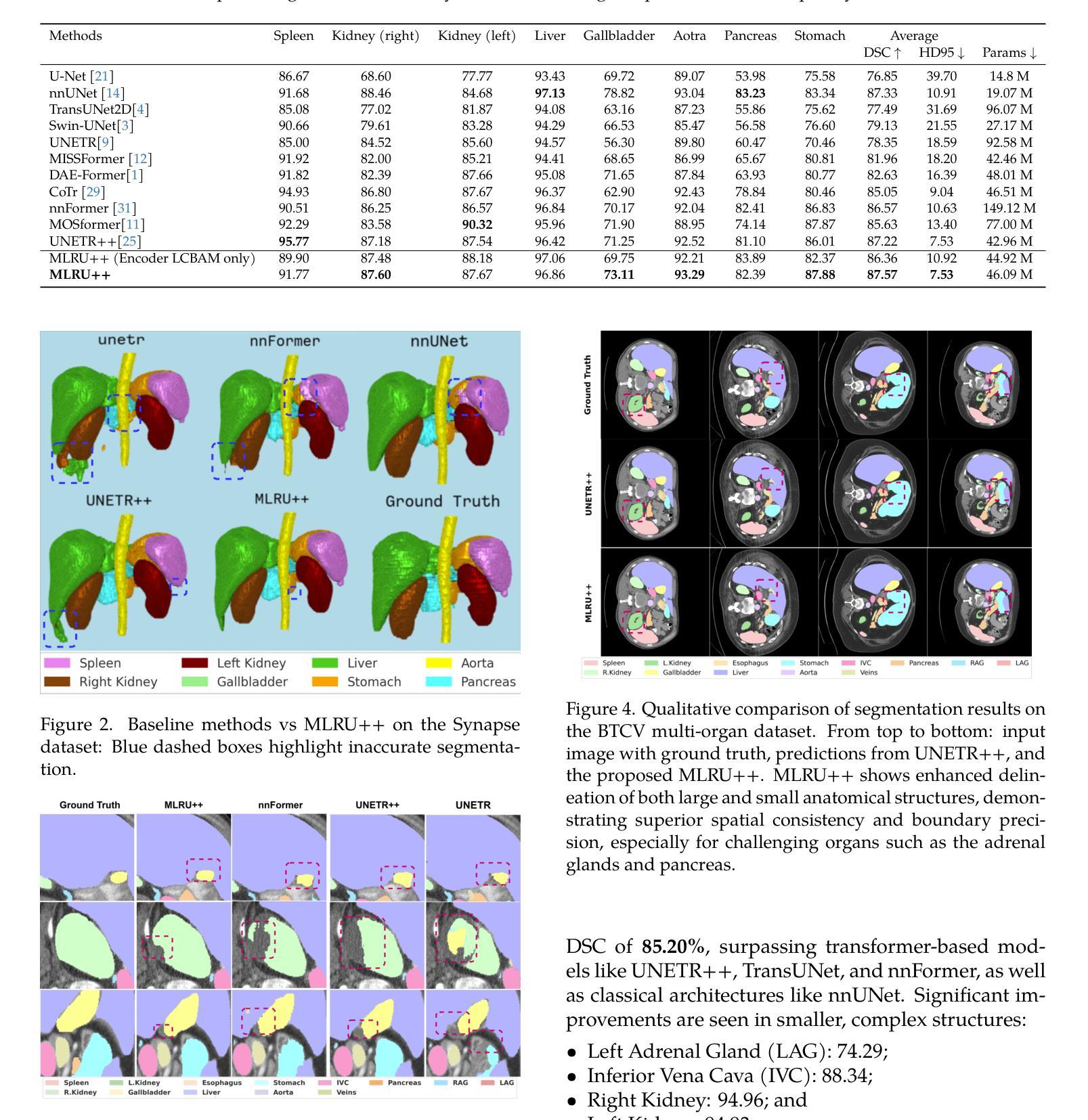
MLRU++: Multiscale Lightweight Residual UNETR++ with Attention for Efficient 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Nand Kumar Yadav, Rodrigue Rizk, William CW Chen, KC Santosh
Accurate and efficient medical image segmentation is crucial but challenging due to anatomical variability and high computational demands on volumetric data. Recent hybrid CNN-Transformer architectures achieve state-of-the-art results but add significant complexity. In this paper, we propose MLRU++, a Multiscale Lightweight Residual UNETR++ architecture designed to balance segmentation accuracy and computational efficiency. It introduces two key innovations: a Lightweight Channel and Bottleneck Attention Module (LCBAM) that enhances contextual feature encoding with minimal overhead, and a Multiscale Bottleneck Block (M2B) in the decoder that captures fine-grained details via multi-resolution feature aggregation. Experiments on four publicly available benchmark datasets (Synapse, BTCV, ACDC, and Decathlon Lung) demonstrate that MLRU++ achieves state-of-the-art performance, with average Dice scores of 87.57% (Synapse), 93.00% (ACDC), and 81.12% (Lung). Compared to existing leading models, MLRU++ improves Dice scores by 5.38% and 2.12% on Synapse and ACDC, respectively, while significantly reducing parameter count and computational cost. Ablation studies evaluating LCBAM and M2B further confirm the effectiveness of the proposed architectural components. Results suggest that MLRU++ offers a practical and high-performing solution for 3D medical image segmentation tasks. Source code is available at: https://github.com/1027865/MLRUPP
准确且高效的医学图像分割至关重要,但由于解剖结构的差异性和对体积数据的计算需求较高,这仍然是一个巨大的挑战。最近的混合CNN-Transformer架构取得了最先进的成果,但增加了复杂性。在本文中,我们提出了MLRU++,这是一种多尺度轻量级剩余UNetr++架构,旨在平衡分割精度和计算效率。它引入了两个关键的创新点:轻量级通道和瓶颈注意力模块(LCBAM),它在最小开销的情况下增强了上下文特征编码;解码器中的多尺度瓶颈块(M2B),它通过多分辨率特征聚合捕获精细的细节。在四个公开的基准数据集(Synapse、BTCV、ACDC和Decathlon Lung)上的实验表明,MLRU++达到了最先进的性能,平均Dice得分分别为Synapse的87.57%、ACDC的93.00%和Lung的81.12%。与现有的领先模型相比,MLRU++在Synapse和ACDC上的Dice得分分别提高了5.38%和2.12%,同时显著减少了参数数量和计算成本。对LCBAM和M2B的消融研究进一步证实了所提出架构组件的有效性。结果表明,MLRU++为三维医学图像分割任务提供了实用且高性能的解决方案。源代码可在:https://github.com/1027865/MLRUPP获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为MLRU++的多尺度轻量级残差UNETR++架构,旨在平衡医学图像分割的准确性和计算效率。它引入了两个关键创新:轻量级通道和瓶颈注意力模块(LCBAM)和多尺度瓶颈块(M2B)。在四个公开基准数据集上的实验表明,MLRU++实现了最先进的性能,平均Dice得分较高。
Key Takeaways
- MLRU++是一个针对医学图像分割的多尺度轻量级残差UNETR++架构。
- 它通过引入LCBAM和M2B两个关键模块来增强特征编码和细节捕捉。
- LCBAM模块以最小的额外计算成本增强上下文特征编码。
- M2B模块在解码器中捕获多尺度特征,从而捕捉更精细的细节。
- MLRU++在四个公开数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
- 与现有模型相比,MLRU++在提高Dice得分的同时,减少了参数数量和计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

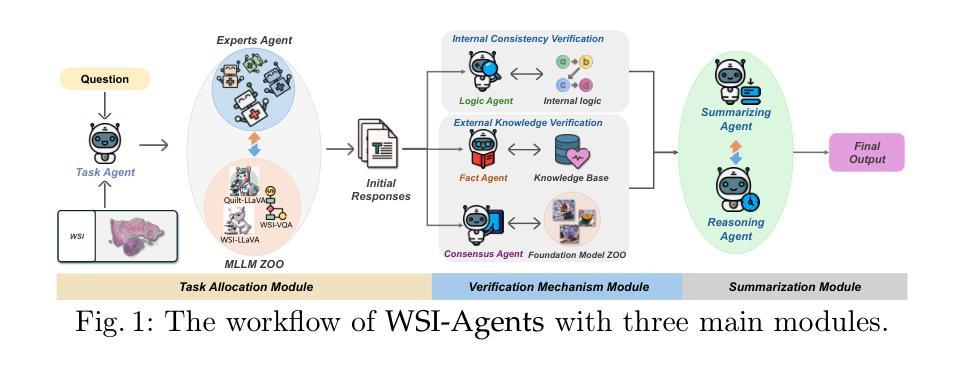
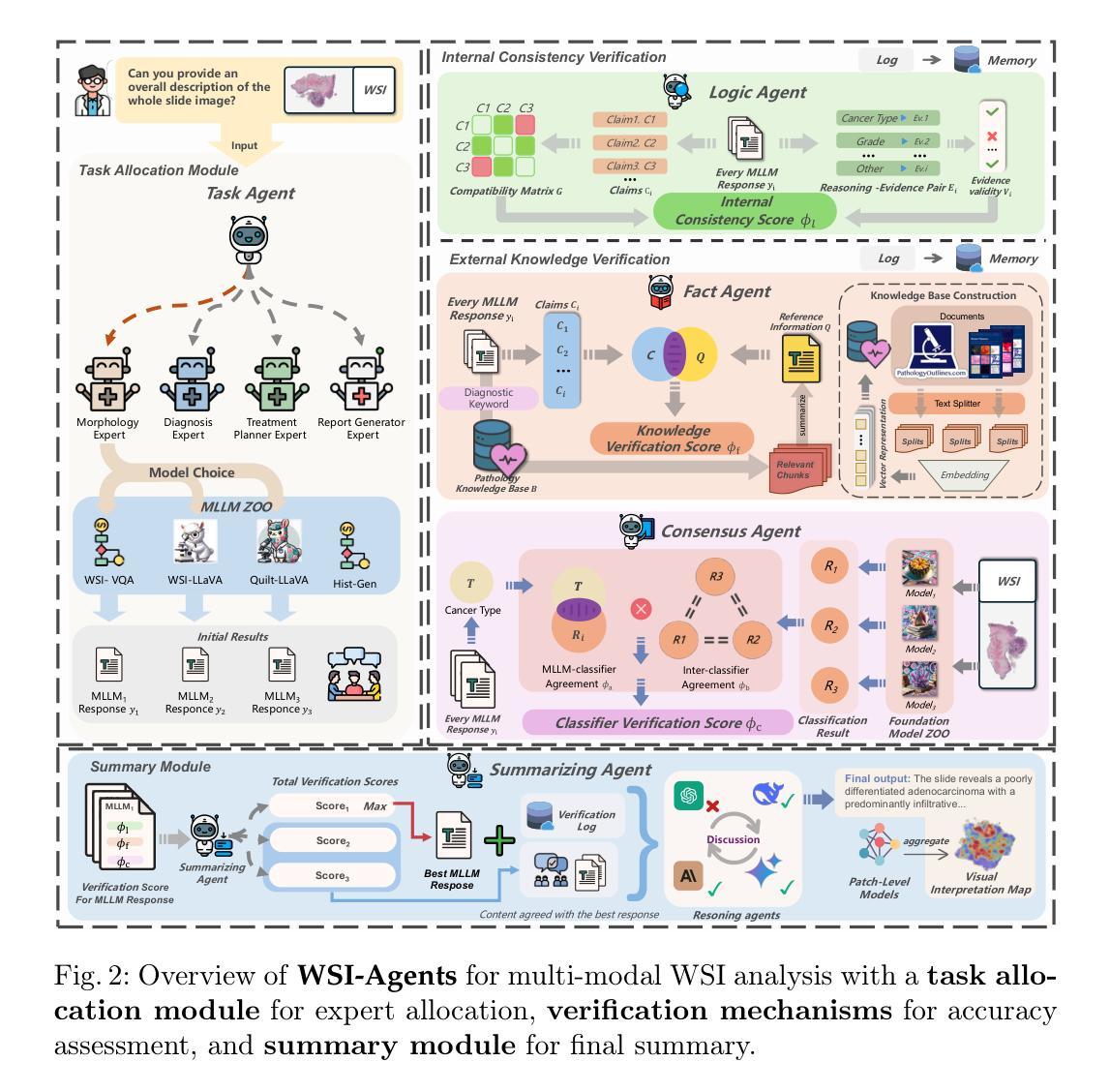
WSI-Agents: A Collaborative Multi-Agent System for Multi-Modal Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Xinheng Lyu, Yuci Liang, Wenting Chen, Meidan Ding, Jiaqi Yang, Guolin Huang, Daokun Zhang, Xiangjian He, Linlin Shen
Whole slide images (WSIs) are vital in digital pathology, enabling gigapixel tissue analysis across various pathological tasks. While recent advancements in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) allow multi-task WSI analysis through natural language, they often underperform compared to task-specific models. Collaborative multi-agent systems have emerged as a promising solution to balance versatility and accuracy in healthcare, yet their potential remains underexplored in pathology-specific domains. To address these issues, we propose WSI-Agents, a novel collaborative multi-agent system for multi-modal WSI analysis. WSI-Agents integrates specialized functional agents with robust task allocation and verification mechanisms to enhance both task-specific accuracy and multi-task versatility through three components: (1) a task allocation module assigning tasks to expert agents using a model zoo of patch and WSI level MLLMs, (2) a verification mechanism ensuring accuracy through internal consistency checks and external validation using pathology knowledge bases and domain-specific models, and (3) a summary module synthesizing the final summary with visual interpretation maps. Extensive experiments on multi-modal WSI benchmarks show WSI-Agents’s superiority to current WSI MLLMs and medical agent frameworks across diverse tasks.
全切片图像(Whole Slide Images,简称WSI)在数字病理学中扮演着至关重要的角色,它可以在不同的病理学任务中实现千兆像素级别的组织分析。虽然最近的多模态大型语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models,简称MLLMs)的进步使得我们可以通过自然语言进行多任务WSI分析,但它们通常相较于特定任务的模型表现较差。协作多智能体系统作为一种在医疗领域中平衡通用性和准确性的有前途的解决方案而出现,但在病理学特定领域,其潜力仍未得到充分探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了WSI-Agents,这是一种用于多模态WSI分析的新型协作多智能体系统。WSI-Agents通过集成专业化功能智能体以及稳健的任务分配和验证机制,通过以下三个组件来提高任务特定的准确性和多任务通用性:(1)任务分配模块使用补丁和WSI级别的MLLM模型库来将任务分配给专业智能体,(2)验证机制通过内部一致性检查和利用病理学知识库和特定领域的模型进行外部验证来确保准确性,(3)摘要模块结合可视化解释地图来总结最终结果。在多模态WSI基准测试上的广泛实验表明,WSI-Agents在多样化任务中的表现优于当前的WSI MLLM和医疗智能体框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多模态大规模语言模型(MLLMs)和全滑片图像(WSI)的重要性,文章提出了一种新的协作多智能体系统——WSI-Agents,用于多模态WSI分析。该系统通过集成专业功能智能体、任务分配模块和验证机制,提高了任务特定准确性和多任务通用性。通过模型库中的补丁和WSI级别MLLMs的任务分配模块进行任务分配,通过内部一致性检查、外部验证以及病理学知识库和特定领域模型确保准确性,并通过摘要模块提供可视化解释图进行综合摘要。实验证明,WSI-Agents在多模态WSI基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- WSI在数字病理学中至关重要,用于进行多吉像素组织分析。
- 多模态大规模语言模型(MLLMs)用于多任务WSI分析,但常常性能不足。
- 协作多智能体系统具有平衡灵活性和准确性的潜力,在医疗领域受到关注。
- WSI-Agents是一个新颖的协作多智能体系统,专为多模态WSI分析设计。
- WSI-Agents集成了专业功能智能体,采用任务分配和验证机制确保准确性与多任务能力。
- 通过模型库中的补丁和WSI级别MLLMs进行任务分配,确保准确性并提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

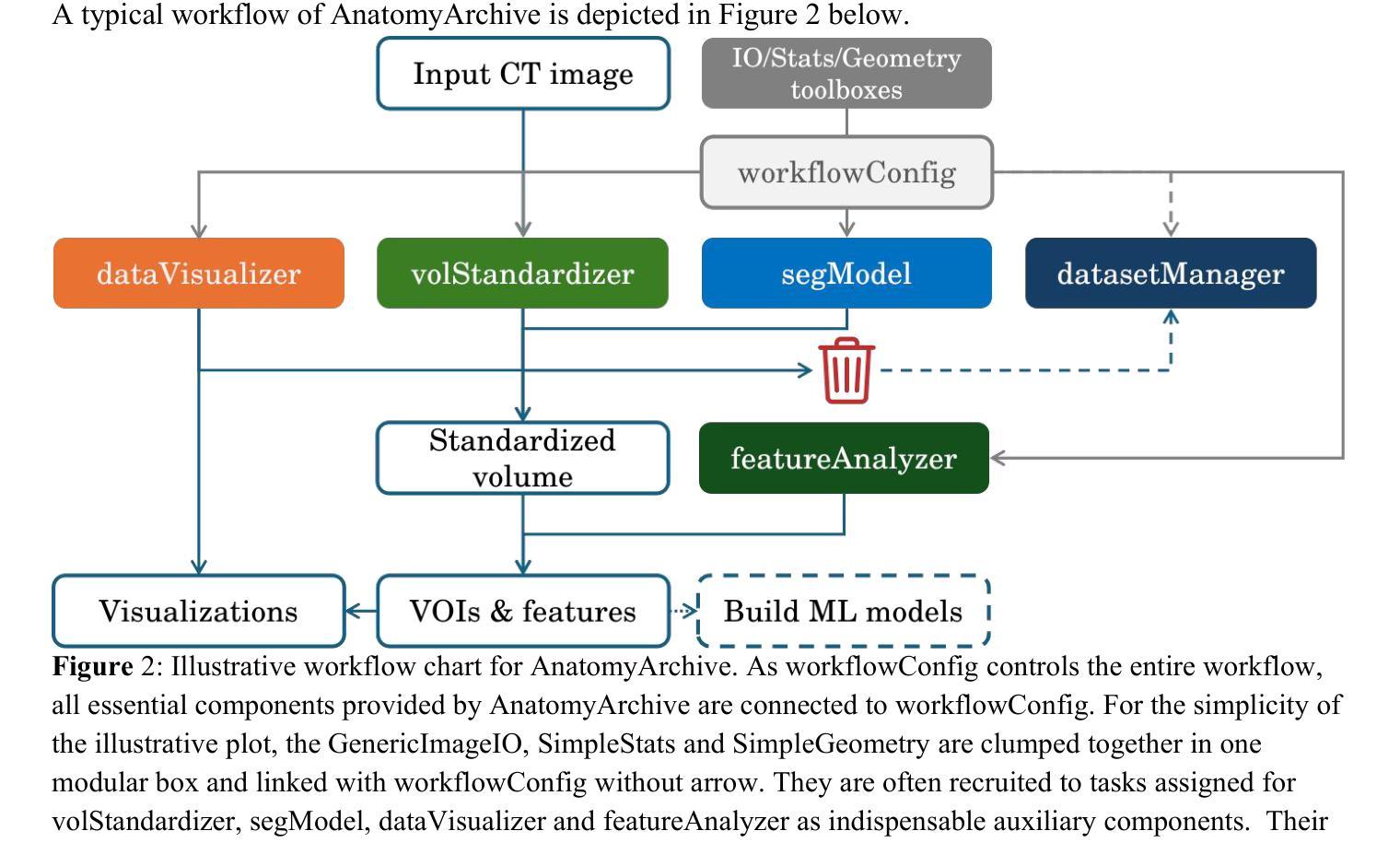
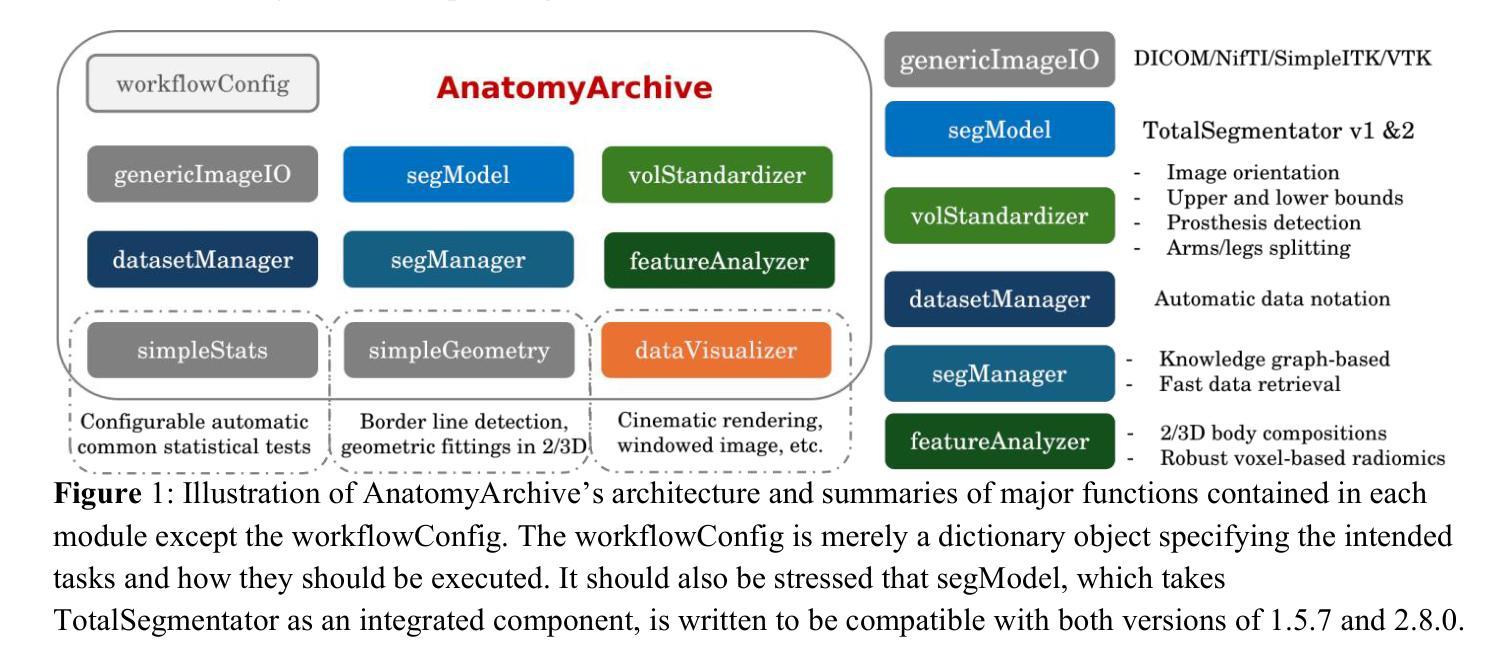
Software architecture and manual for novel versatile CT image analysis toolbox – AnatomyArchive
Authors:Lei Xu, Torkel B Brismar
We have developed a novel CT image analysis package named AnatomyArchive, built on top of the recent full body segmentation model TotalSegmentator. It provides automatic target volume selection and deselection capabilities according to user-configured anatomies for volumetric upper- and lower-bounds. It has a knowledge graph-based and time efficient tool for anatomy segmentation mask management and medical image database maintenance. AnatomyArchive enables automatic body volume cropping, as well as automatic arm-detection and exclusion, for more precise body composition analysis in both 2D and 3D formats. It provides robust voxel-based radiomic feature extraction, feature visualization, and an integrated toolchain for statistical tests and analysis. A python-based GPU-accelerated nearly photo-realistic segmentation-integrated composite cinematic rendering is also included. We present here its software architecture design, illustrate its workflow and working principle of algorithms as well provide a few examples on how the software can be used to assist development of modern machine learning models. Open-source codes will be released at https://github.com/lxu-medai/AnatomyArchive for only research and educational purposes.
我们开发了一种新型的CT图像分析软件包,名为AnatomyArchive,它建立在最新的全身分割模型TotalSegmentator之上。根据用户配置的解剖结构,它提供了自动目标体积选择和取消选择功能,用于体积上限和下限。它拥有基于知识图谱、时间高效的工具,用于解剖分割掩模管理和医学图像数据库维护。AnatomyArchive能够实现自动身体体积裁剪,以及自动检测和排除手臂,以便在2D和3D格式中进行更精确的身体成分分析。它提供了稳健的基于体素的放射学特征提取、特征可视化以及用于统计测试和分析的综合工具链。还包括基于Python的GPU加速、近乎逼真的分割集成复合电影渲染。我们在此介绍其软件架构设计,说明了其工作流程和算法的工作原理,并提供了一些如何使用该软件辅助开发现代机器学习模型的示例。开源代码将仅在研究和教育目的下发布在https://github.com/lxu-medai/AnatomyArchive。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 7 figures
Summary
AnatomyArchive是一款基于TotalSegmentator全身分割模型的CT图像分析软件包,具备自动目标体积选择、解除选择功能,用于体积上下限的设定。它采用知识图谱为基础的工具进行解剖分割掩模管理和医学图像数据库维护,提供自动身体体积裁剪及手臂自动检测和排除功能,用于更精确的2D和3D格式身体组成分析。此外,该软件还包括稳健的基于体素的放射学特征提取、特征可视化以及集成工具链进行统计分析。此外,它还包含基于Python的GPU加速近照片级逼真的分割集成复合电影渲染。该软件旨在辅助现代机器学习模型的开发。
Key Takeaways
- AnatomyArchive是一款新型的CT图像分析软件包,建立在TotalSegmentator全身分割模型之上。
- 提供自动目标体积选择和解除选择功能,可设定体积上下限。
- 采用知识图谱为基础的工具进行解剖分割掩模管理和医学图像数据库维护。
- 能够自动进行身体体积裁剪,并自动检测和排除手臂,提高身体组成分析的精确度。
- 提供基于体素的放射学特征提取、特征可视化以及集成工具链进行统计分析。
- 包含基于Python的GPU加速近照片级渲染,增强分割集成影像的视觉效果。
点此查看论文截图


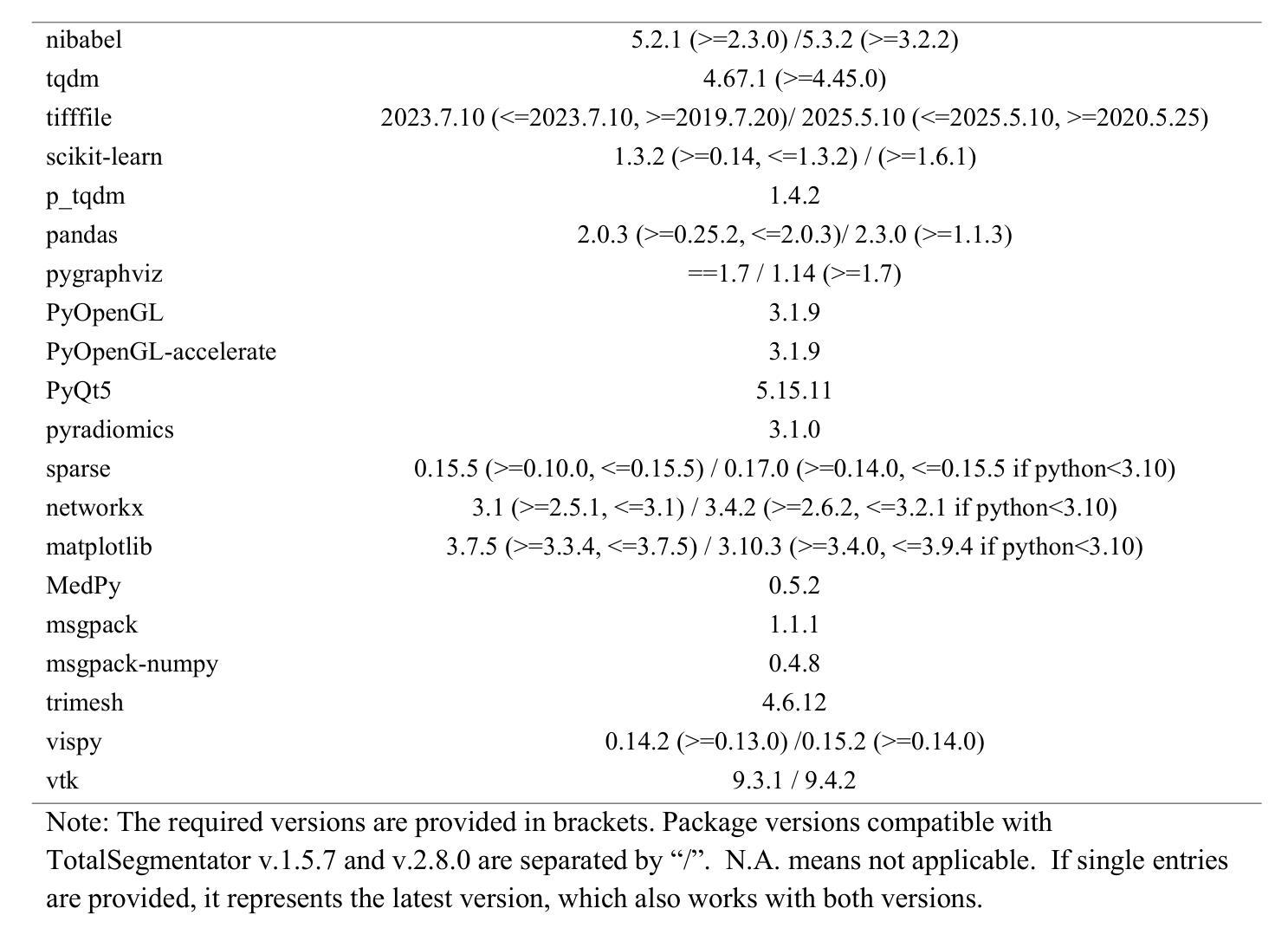
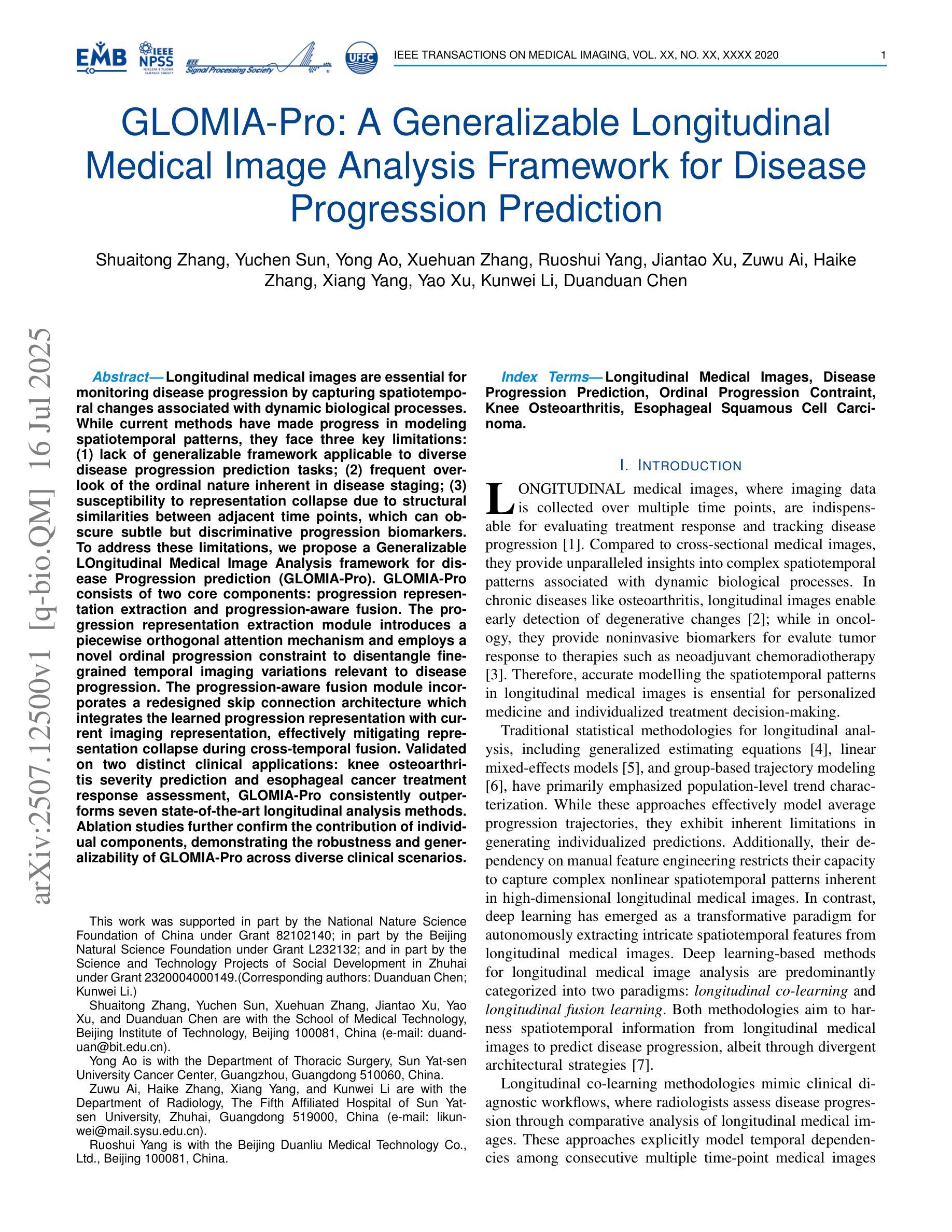
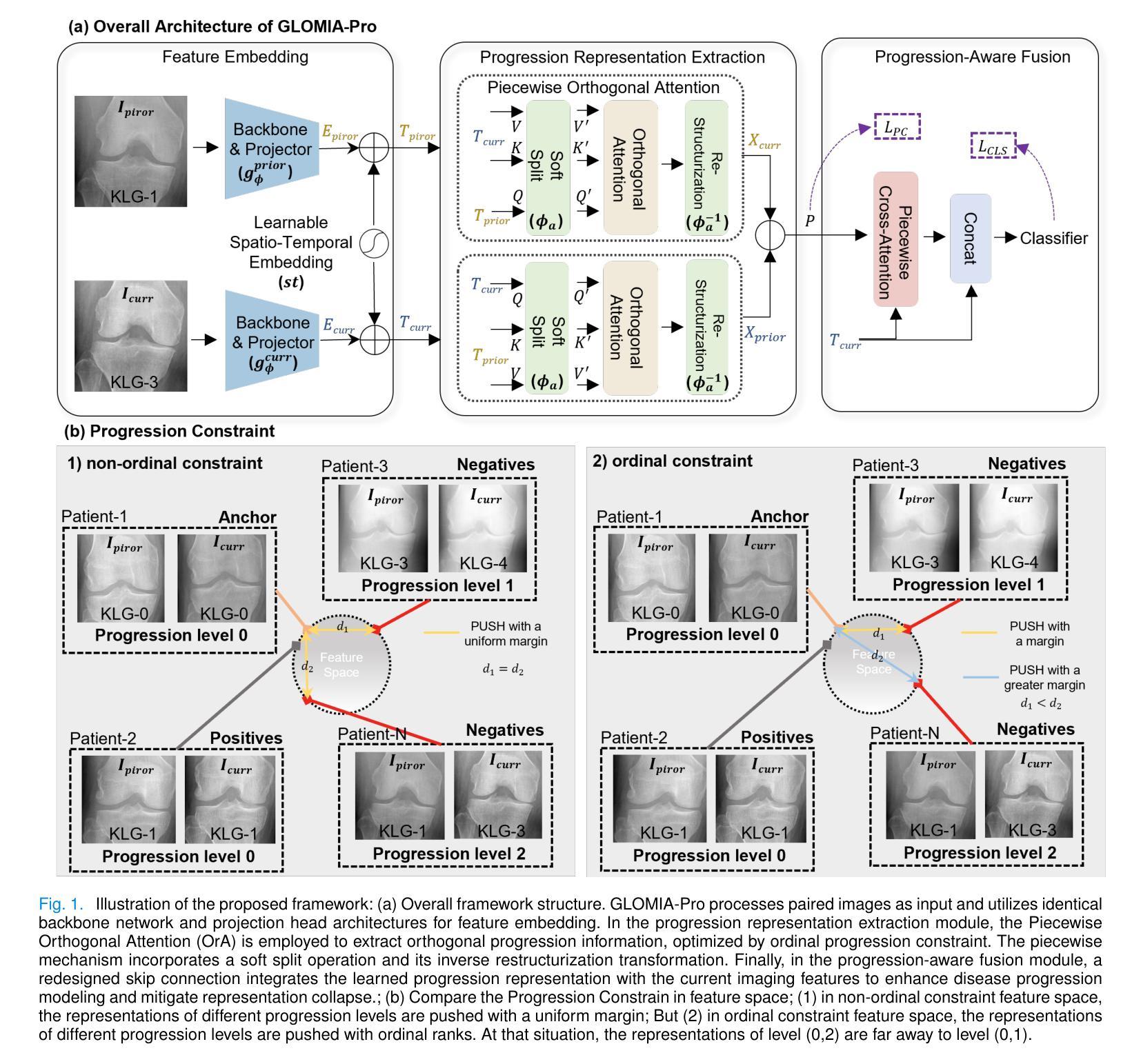
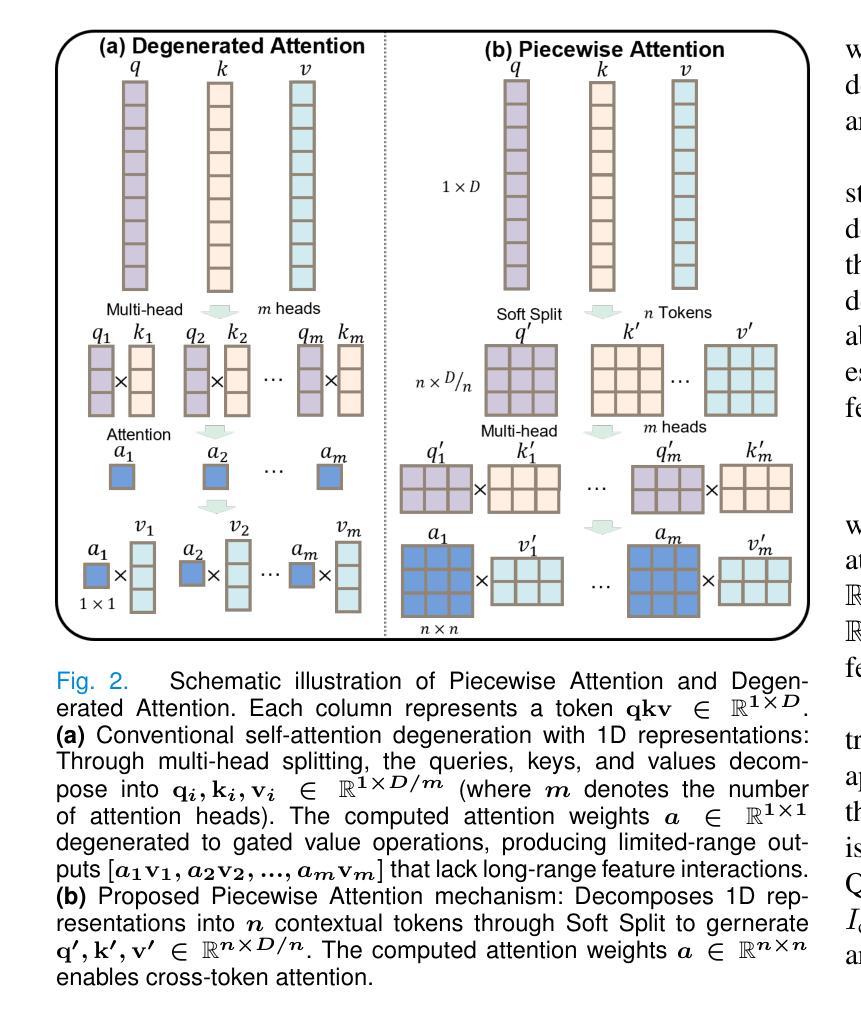
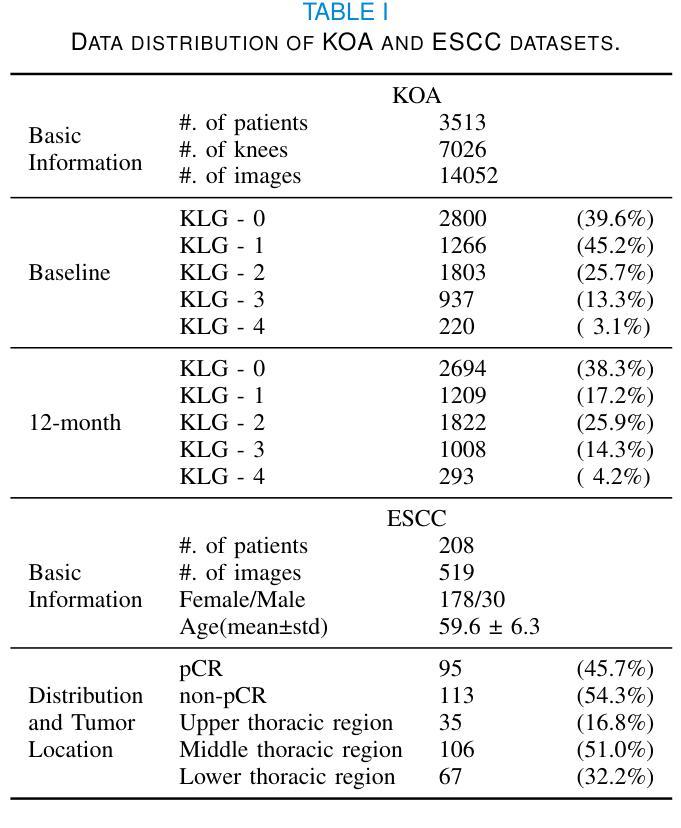
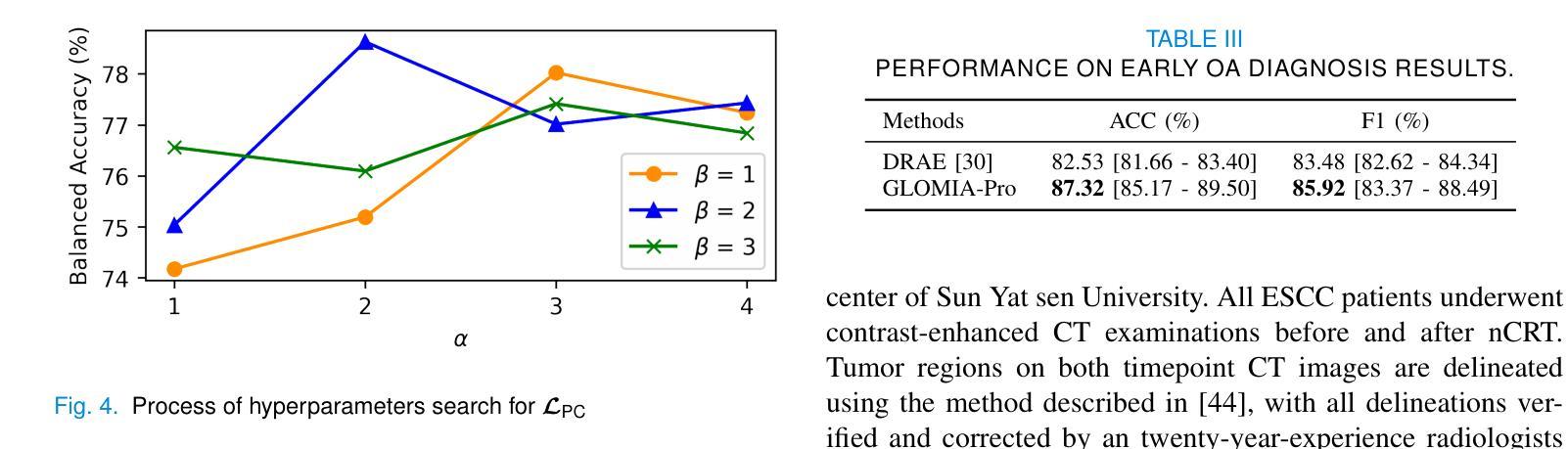
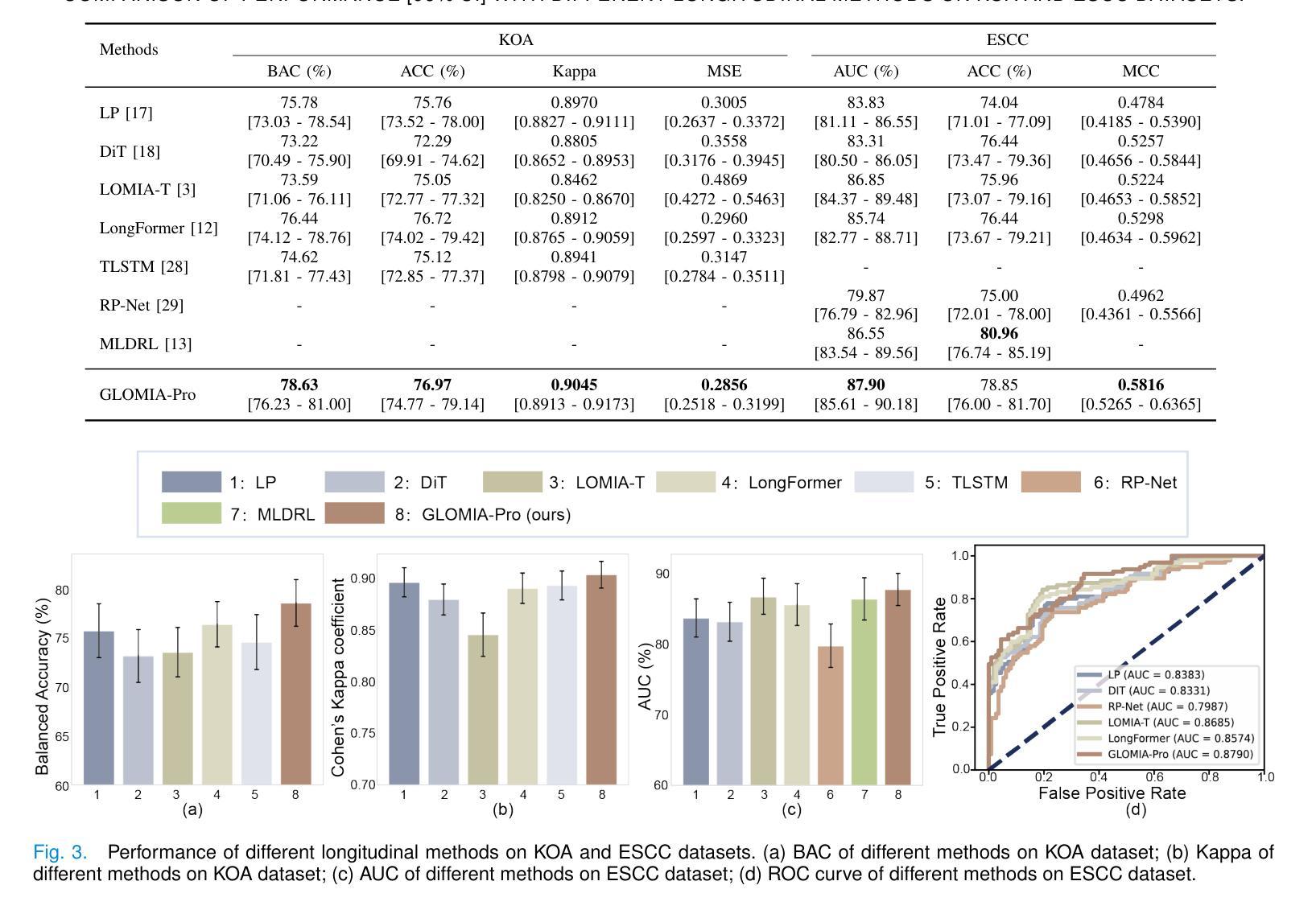
GLOMIA-Pro: A Generalizable Longitudinal Medical Image Analysis Framework for Disease Progression Prediction
Authors:Shuaitong Zhang, Yuchen Sun, Yong Ao, Xuehuan Zhang, Ruoshui Yang, Jiantao Xu, Zuwu Ai, Haike Zhang, Xiang Yang, Yao Xu, Kunwei Li, Duanduan Chen
Longitudinal medical images are essential for monitoring disease progression by capturing spatiotemporal changes associated with dynamic biological processes. While current methods have made progress in modeling spatiotemporal patterns, they face three key limitations: (1) lack of generalizable framework applicable to diverse disease progression prediction tasks; (2) frequent overlook of the ordinal nature inherent in disease staging; (3) susceptibility to representation collapse due to structural similarities between adjacent time points, which can obscure subtle but discriminative progression biomarkers. To address these limitations, we propose a Generalizable LOngitudinal Medical Image Analysis framework for disease Progression prediction (GLOMIA-Pro). GLOMIA-Pro consists of two core components: progression representation extraction and progression-aware fusion. The progression representation extraction module introduces a piecewise orthogonal attention mechanism and employs a novel ordinal progression constraint to disentangle finegrained temporal imaging variations relevant to disease progression. The progression-aware fusion module incorporates a redesigned skip connection architecture which integrates the learned progression representation with current imaging representation, effectively mitigating representation collapse during cross-temporal fusion. Validated on two distinct clinical applications: knee osteoarthritis severity prediction and esophageal cancer treatment response assessment, GLOMIA-Pro consistently outperforms seven state-of-the-art longitudinal analysis methods. Ablation studies further confirm the contribution of individual components, demonstrating the robustness and generalizability of GLOMIA-Pro across diverse clinical scenarios.
纵向医学图像对于捕捉与动态生物过程相关的时空变化以监测疾病进展至关重要。尽管当前的方法在模拟时空模式方面已有所进展,但它们面临三大关键局限:(1)缺乏适用于多种疾病进展预测任务的通用框架;(2)经常忽视疾病分期中固有的有序性质;(3)由于相邻时间点之间的结构相似性,容易导致表示崩溃,从而掩盖了微妙但具有区分力的进展生物标志物。为了解决这些局限,我们提出了用于疾病进展预测的一般化纵向医学图像分析框架(GLOMIA-Pro)。GLOMIA-Pro由两个核心组件构成:进展表示提取和进展感知融合。进展表示提取模块引入了一种分段正交注意力机制,并采用了一种新型序贯进展约束来解开与疾病进展相关的精细时间成像变化。进展感知融合模块采用重新设计的跳跃连接架构,将学习到的进展表示与当前成像表示相结合,有效地减轻了跨时间融合过程中的表示崩溃问题。在膝关节骨关节炎严重程度预测和食管癌治疗反应评估两个独立临床应用上的验证表明,GLOMIA-Pro在性能上始终优于七种最先进的纵向分析方法。消融研究进一步证实了各组件的贡献,证明了GLOMIA-Pro在不同临床场景中的稳健性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
摘要
纵向医学图像通过捕捉与动态生物过程相关的时空变化,对于监测疾病进展至关重要。当前方法虽然已在建模时空模式方面取得进展,但仍存在三个主要局限:一是不适用于多种疾病进展预测任务的通用框架;二是忽视了疾病分期中固有的序数性质;三是由于相邻时间点的结构相似性,容易导致表示崩溃,从而掩盖了微妙但具有区分性的进展生物标志物。为解决这些局限,我们提出了用于疾病进展预测的长周期医学图像分析通用框架(GLOMIA-Pro)。GLOMIA-Pro包括两个核心组件:进展表示提取和进展感知融合。进展表示提取模块引入了一种分段正交注意力机制,并采用了一种新型序进展约束来解开与疾病进展相关的精细时间成像变化。进展感知融合模块采用重新设计的跳过连接架构,将学习到的进展表示与当前成像表示相结合,有效地减轻了跨时间融合时的表示崩溃问题。在两种独特的临床应用——膝关节骨关节炎严重程度预测和食管癌治疗反应评估中,GLOMIA-Pro始终优于七种最先进的纵向分析方法。消融研究进一步证实了各组件的贡献,证明了GLOMIA-Pro在不同临床场景中的稳健性和普遍性。
关键见解
1.纵向医学图像对于监测疾病进展至关重要,捕捉与动态生物过程相关的时空变化。
2.当前方法虽然取得进展,但存在三大局限性:缺乏普适性框架、忽视疾病分期的序数性质和表示崩溃问题。
3.GLOMIA-Pro通过两个核心组件——进展表示提取和进展感知融合,解决上述局限。
4.进展表示提取模块使用分段正交注意力机制和新型序进展约束,捕捉疾病进展相关的精细时间成像变化。
5.进展感知融合模块采用重新设计的跳过连接架构,有效减轻跨时间融合时的表示崩溃问题。
6.在膝关节骨关节炎和食管癌治疗反应评估的临床应用中,GLOMIA-Pro表现优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
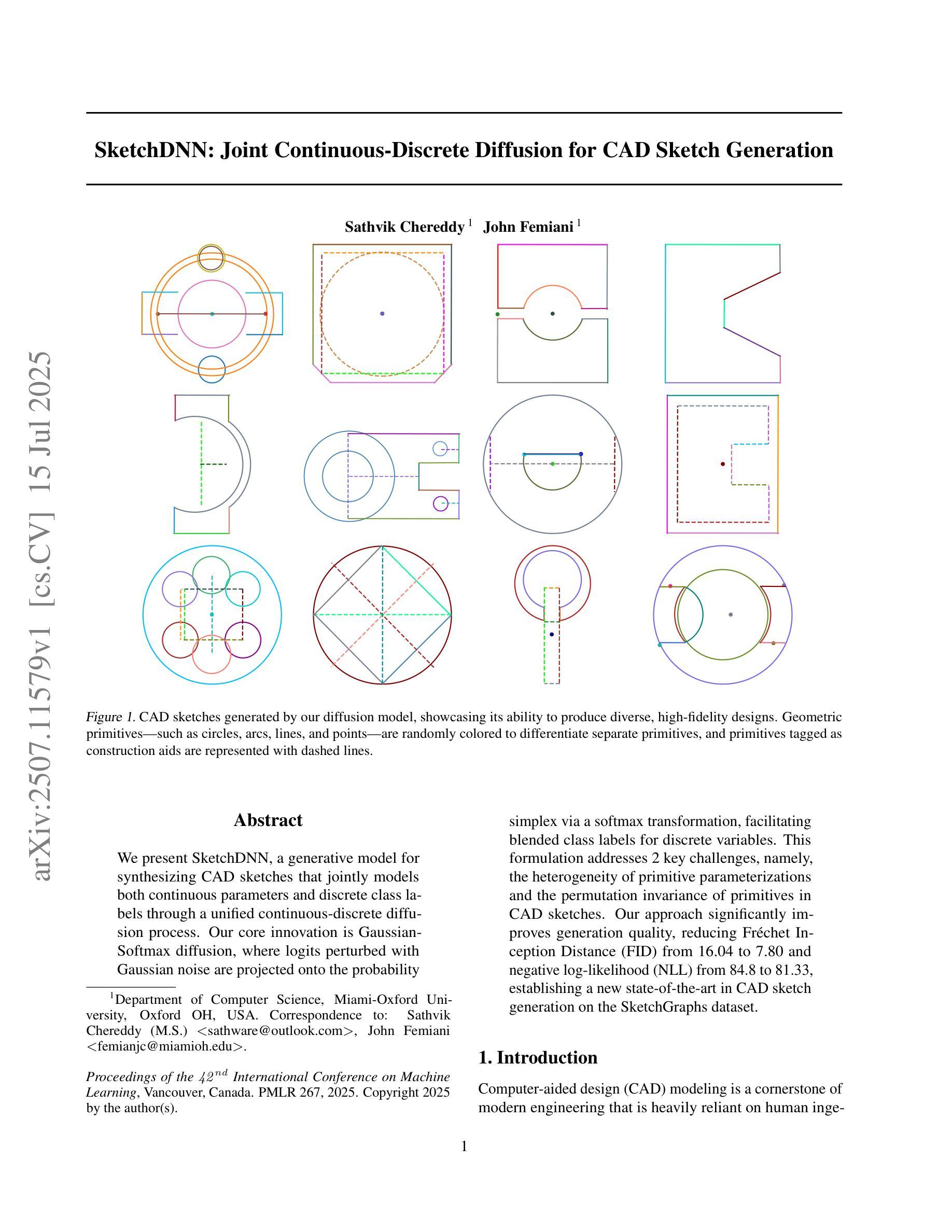
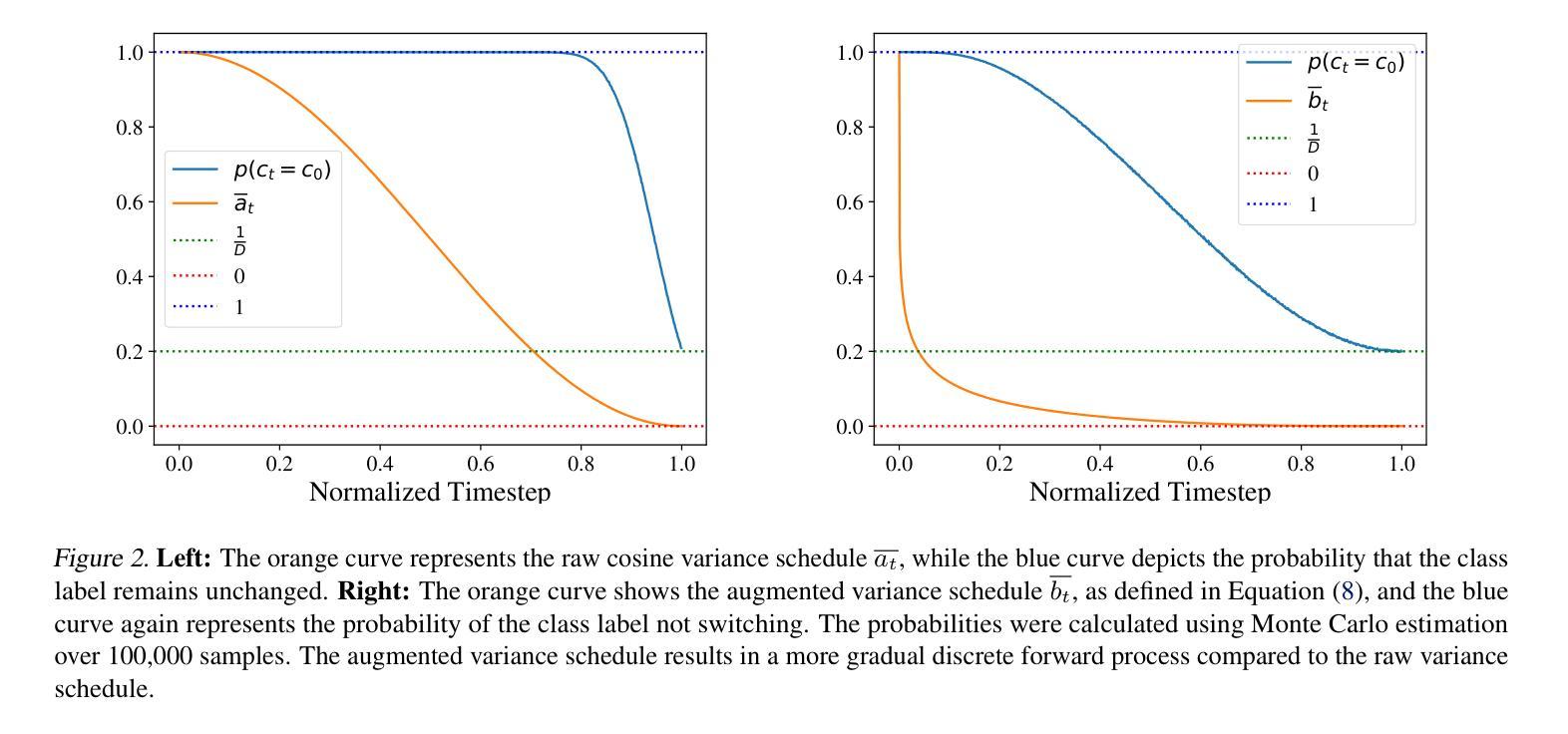
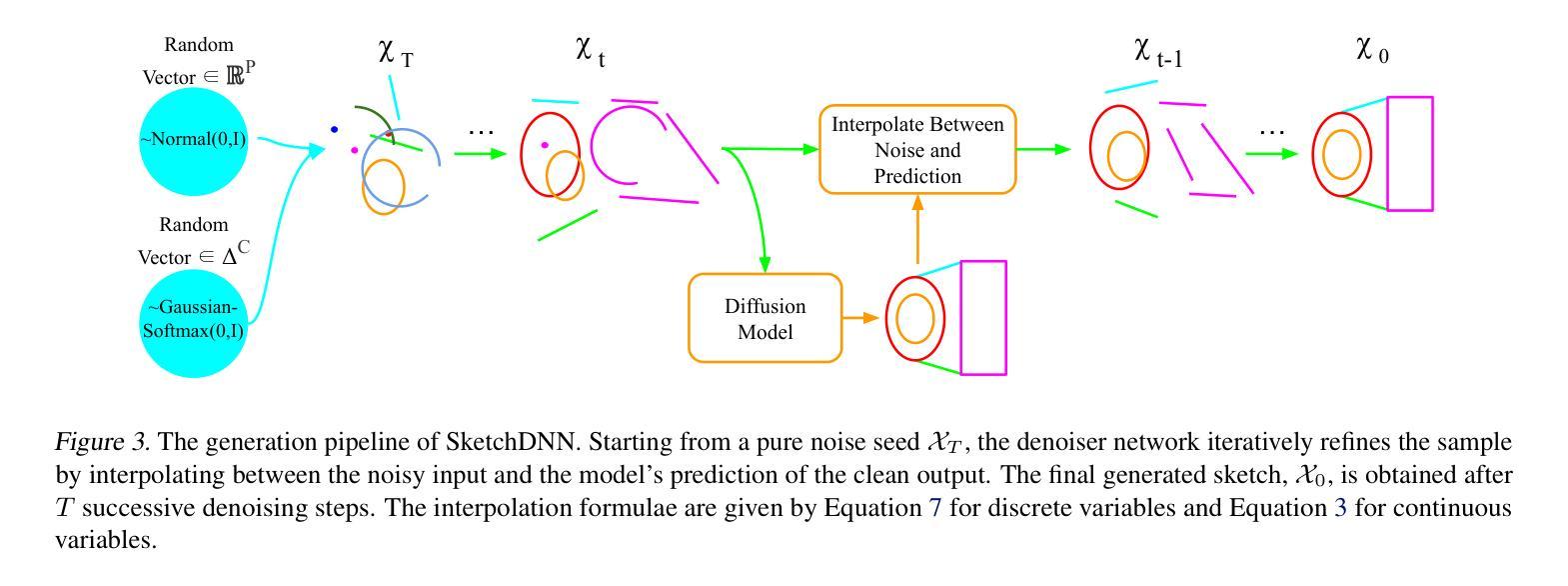
SketchDNN: Joint Continuous-Discrete Diffusion for CAD Sketch Generation
Authors:Sathvik Chereddy, John Femiani
We present SketchDNN, a generative model for synthesizing CAD sketches that jointly models both continuous parameters and discrete class labels through a unified continuous-discrete diffusion process. Our core innovation is Gaussian-Softmax diffusion, where logits perturbed with Gaussian noise are projected onto the probability simplex via a softmax transformation, facilitating blended class labels for discrete variables. This formulation addresses 2 key challenges, namely, the heterogeneity of primitive parameterizations and the permutation invariance of primitives in CAD sketches. Our approach significantly improves generation quality, reducing Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) from 16.04 to 7.80 and negative log-likelihood (NLL) from 84.8 to 81.33, establishing a new state-of-the-art in CAD sketch generation on the SketchGraphs dataset.
我们提出了SketchDNN,这是一个用于合成CAD草图的生成模型。它通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程,对连续参数和离散类标签进行联合建模。我们的核心创新是Gaussian-Softmax扩散,通过高斯噪声扰动的logits被投影到概率单纯形上,通过softmax转换,为离散变量提供混合类标签。这种表述解决了两个关键问题,即原始参数化的异质性和CAD草图中原始图形的排列不变性。我们的方法显著提高了生成质量,将Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)从16.04降低到7.80,将负对数似然(NLL)从84.8降低到81.33,在SketchGraphs数据集上建立了CAD草图生成的新最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 63 figures, Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML2025)
Summary
本文介绍了SketchDNN模型,该模型通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程,对CAD草图进行生成。其核心创新为高斯-Softmax扩散,通过将带有高斯噪声的对数几率映射到概率单纯形上,实现了离散变量的混合类标签。该方法解决了CAD草图参数化的异质性和原始图形的排列不变性两个关键问题。该方法显著提高了生成质量,将Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)从16.04降至7.80,将负对数似然值(NLL)从84.8降至81.33,在SketchGraphs数据集上达到了CAD草图生成的最先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- SketchDNN是一个生成模型,用于合成CAD草图,通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程建模连续参数和离散类标签。
- 模型的核心创新在于高斯-Softmax扩散,解决了CAD草图参数化的异质性问题。
- 模型通过将带有高斯噪声的对数几率映射到概率单纯形上,实现了离散变量的混合类标签。
- 模型解决了原始图形的排列不变性问题。
- SketchDNN显著提高了生成质量,降低了Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)和负对数似然值(NLL)。
- SketchDNN在SketchGraphs数据集上的表现达到了CAD草图生成的最先进水平。
点此查看论文截图
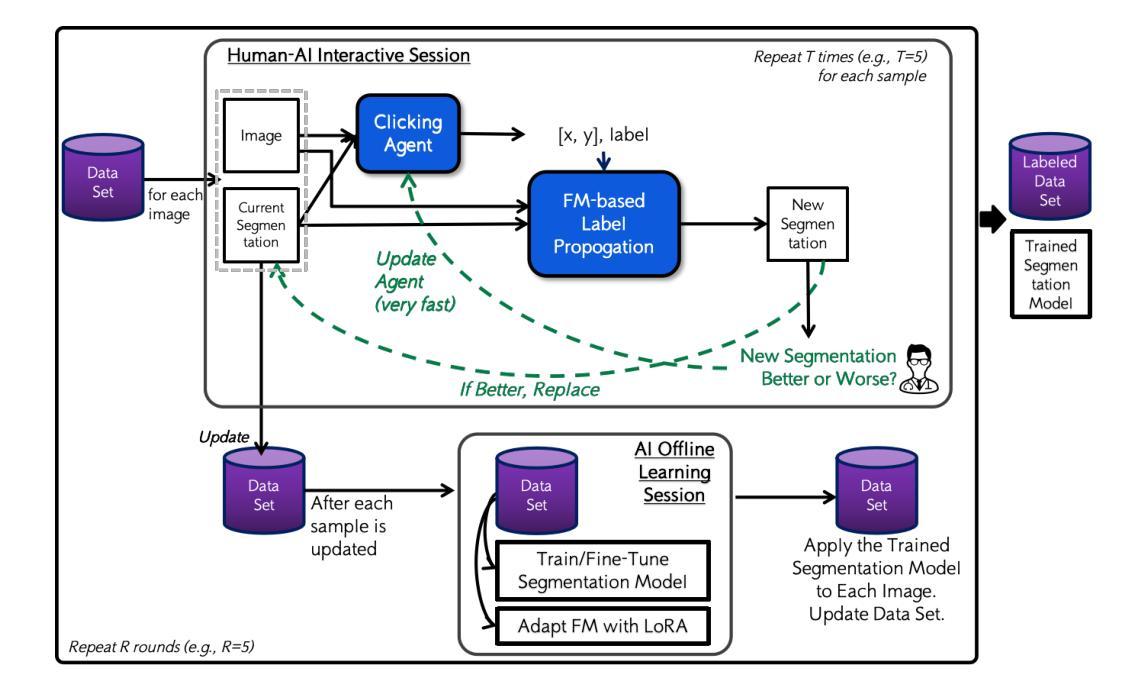
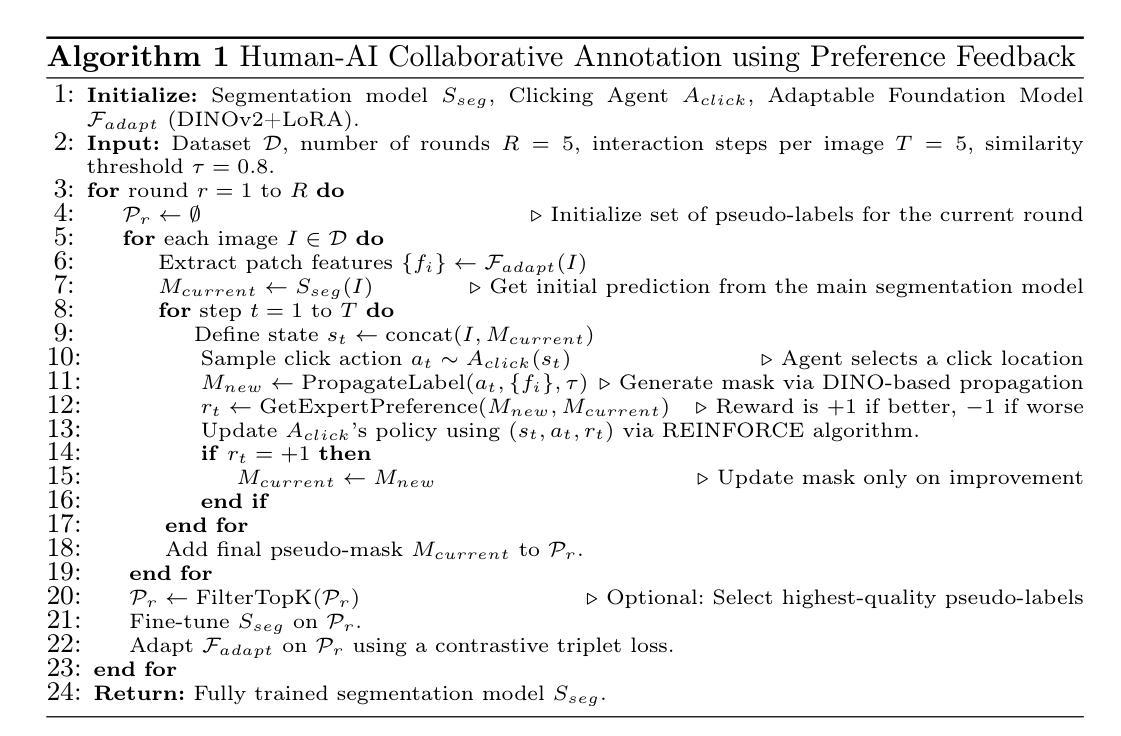
Beyond Manual Annotation: A Human-AI Collaborative Framework for Medical Image Segmentation Using Only “Better or Worse” Expert Feedback
Authors:Yizhe Zhang
Manual annotation of medical images is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, posing a significant bottleneck in the development and deployment of robust medical imaging AI systems. This paper introduces a novel hands-free Human-AI collaborative framework for medical image segmentation that substantially reduces the annotation burden by eliminating the need for explicit manual pixel-level labeling. The core innovation lies in a preference learning paradigm, where human experts provide minimal, intuitive feedback – simply indicating whether an AI-generated segmentation is better or worse than a previous version. The framework comprises four key components: (1) an adaptable foundation model (FM) for feature extraction, (2) label propagation based on feature similarity, (3) a clicking agent that learns from human better-or-worse feedback to decide where to click and with which label, and (4) a multi-round segmentation learning procedure that trains a state-of-the-art segmentation network using pseudo-labels generated by the clicking agent and FM-based label propagation. Experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves competitive segmentation performance using only binary preference feedback, without requiring experts to directly manually annotate the images.
手动标注医学图像是一项劳动强度高且耗时的过程,这成为了稳健的医学成像人工智能系统开发和部署的重大瓶颈。本文介绍了一种新型免手动操作的医学图像分割人机协作框架,通过消除对明确的手动像素级标签的需求,极大地减轻了标注负担。核心创新之处在于偏好学习范式,人类专家提供最少、直观的反馈,只需指示人工智能生成的分割结果是否比之前版本更好或更差。该框架包含四个关键组件:(1)用于特征提取的可适应基础模型(FM),(2)基于特征相似性的标签传播,(3)点击代理能够从人类的更好或更差的反馈中学习,以决定点击的位置和对应的标签,(4)多轮分割学习程序,使用点击代理和基于FM的标签传播生成的伪标签来训练最先进的分割网络。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,该方法仅使用二元偏好反馈就实现了竞争的分割性能,无需专家直接手动标注图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型免手动的人机协作框架,用于医学图像分割,显著减轻了标注负担,无需显式的手动像素级标注。核心创新在于偏好学习范式,人类专家提供最少、直观的反馈,只需指示AI生成的分割是否比之前版本更好或更差。该框架包括四个关键组件:自适应基础模型、基于特征相似性的标签传播、点击代理和多轮分割学习程序。实验表明,该方法仅使用二元偏好反馈即可实现具有竞争力的分割性能,无需专家直接手动标注图像。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像的手动标注是劳动密集且耗时的过程,限制了医疗成像AI系统的发展和部署。
- 新型免手动人机协作框架引入,显著减少标注负担。
- 核心创新在于偏好学习范式,只需人类专家提供简单反馈。
- 框架包括自适应基础模型、标签传播、点击代理和多轮分割学习程序四个关键组件。
- 该方法仅使用二元偏好反馈即可实现具有竞争力的图像分割性能。
- 实验在三个公共数据集上进行,证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

DMCIE: Diffusion Model with Concatenation of Inputs and Errors to Improve the Accuracy of the Segmentation of Brain Tumors in MRI Images
Authors:Sara Yavari, Rahul Nitin Pandya, Jacob Furst
Accurate segmentation of brain tumors in MRI scans is essential for reliable clinical diagnosis and effective treatment planning. Recently, diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in image generation and segmentation tasks. This paper introduces a novel approach to corrective segmentation based on diffusion models. We propose DMCIE (Diffusion Model with Concatenation of Inputs and Errors), a novel framework for accurate brain tumor segmentation in multi-modal MRI scans. We employ a 3D U-Net to generate an initial segmentation mask, from which an error map is generated by identifying the differences between the prediction and the ground truth. The error map, concatenated with the original MRI images, are used to guide a diffusion model. Using multimodal MRI inputs (T1, T1ce, T2, FLAIR), DMCIE effectively enhances segmentation accuracy by focusing on misclassified regions, guided by the original inputs. Evaluated on the BraTS2020 dataset, DMCIE outperforms several state-of-the-art diffusion-based segmentation methods, achieving a Dice Score of 93.46 and an HD95 of 5.94 mm. These results highlight the effectiveness of error-guided diffusion in producing precise and reliable brain tumor segmentations.
在MRI扫描中对脑肿瘤进行准确的分割对于可靠的临床诊断和有效的治疗计划至关重要。最近,扩散模型在图像生成和分割任务中表现出了显著的有效性。本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型修正分割方法。我们提出了DMCIE(输入和误差拼接的扩散模型),这是一种用于多模态MRI扫描中脑肿瘤精确分割的新型框架。我们使用3D U-Net生成初始分割掩膜,通过识别预测与真实标签之间的差异来生成误差图。误差图与原始MRI图像拼接在一起,用于指导扩散模型。使用多模态MRI输入(T1、T1ce、T2、FLAIR),DMCIE通过关注误分类区域,在原始输入的指导下有效地提高了分割精度。在BraTS2020数据集上评估,DMCIE优于几种最先进的基于扩散的分割方法,实现了Dice系数为93.46,HD95为5.94mm。这些结果突显了误差引导扩散在产生精确可靠的脑肿瘤分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型脑肿瘤矫正分割方法——DMCIE。该方法采用3D U-Net生成初始分割掩膜,通过对比预测结果与真实标签生成误差图,并将误差图与原始MRI图像结合,指导扩散模型的运行。使用多模态MRI输入(T1、T1ce、T2、FLAIR),DMCIE能有效提高分割精度,重点关注误分类区域,由原始输入引导。在BraTS2020数据集上的实验结果显示,DMCIE的Dice系数为93.46%,HD95为5.94mm,优于其他先进的扩散分割方法,证明了误差引导扩散在脑肿瘤精确分割中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- DMCIE是一种基于扩散模型的新型脑肿瘤矫正分割方法。
- 采用3D U-Net生成初始分割掩膜,并生成误差图来纠正预测错误。
- 误差图与原始MRI图像结合,为扩散模型提供指导。
- 多模态MRI输入(T1、T1ce、T2、FLAIR)用于提高分割精度。
- DMCIE在BraTS2020数据集上的实验表现出色,Dice系数高达93.46%,HD95为5.94mm。
- DMCIE方法相比其他先进的扩散分割方法具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图

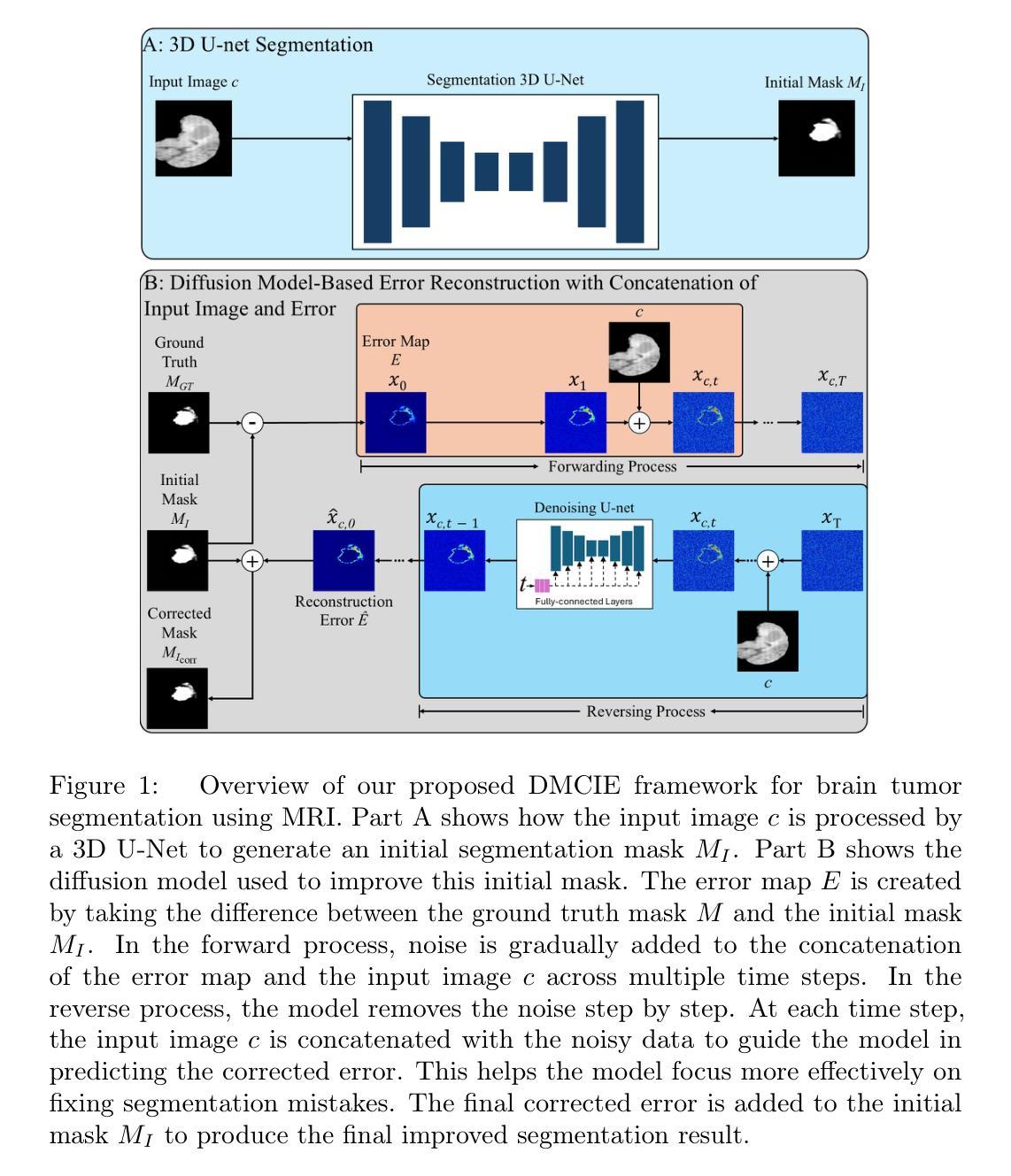
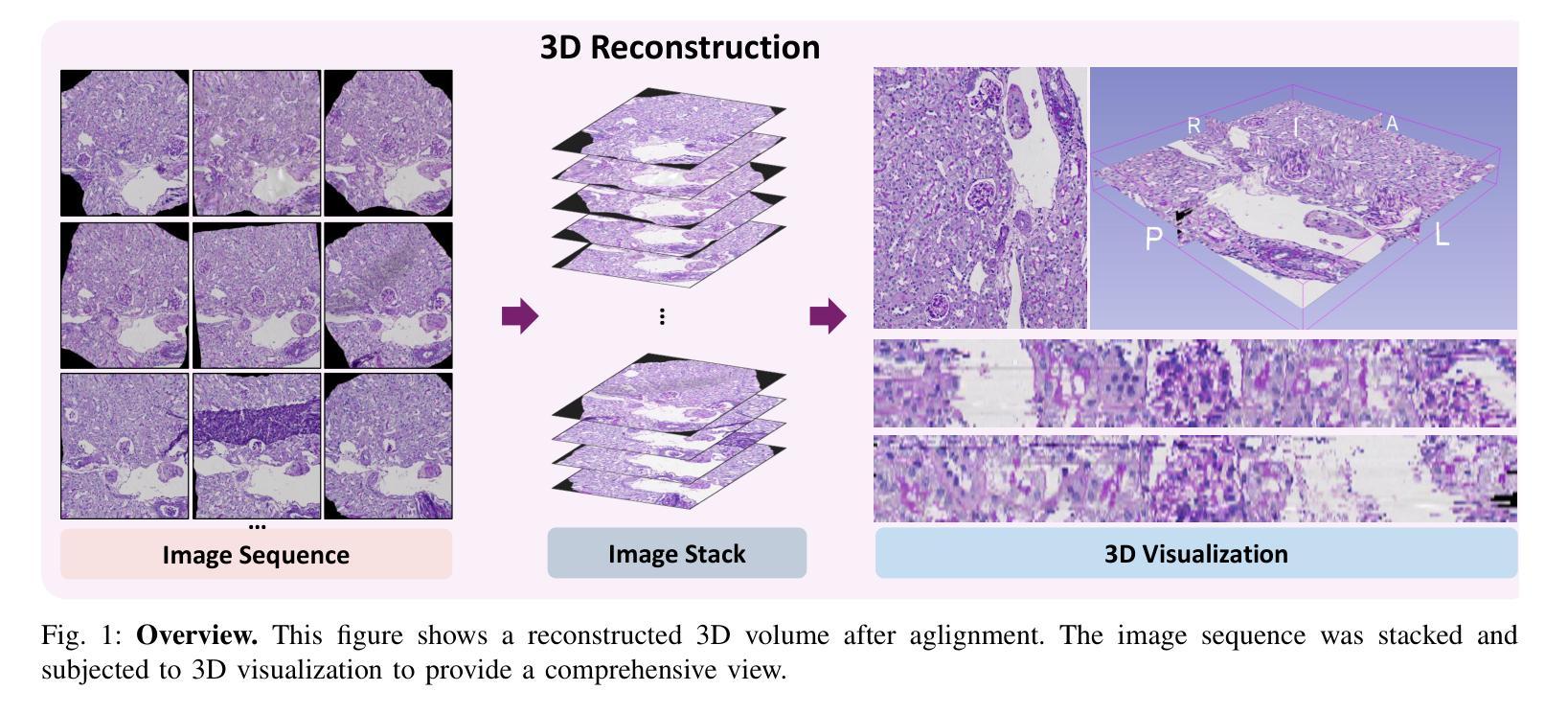
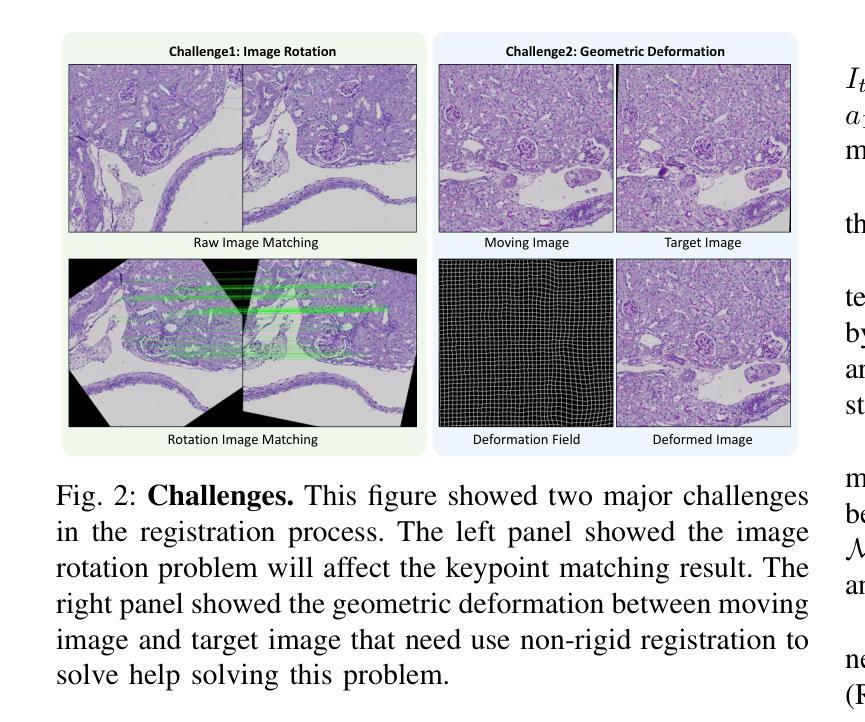
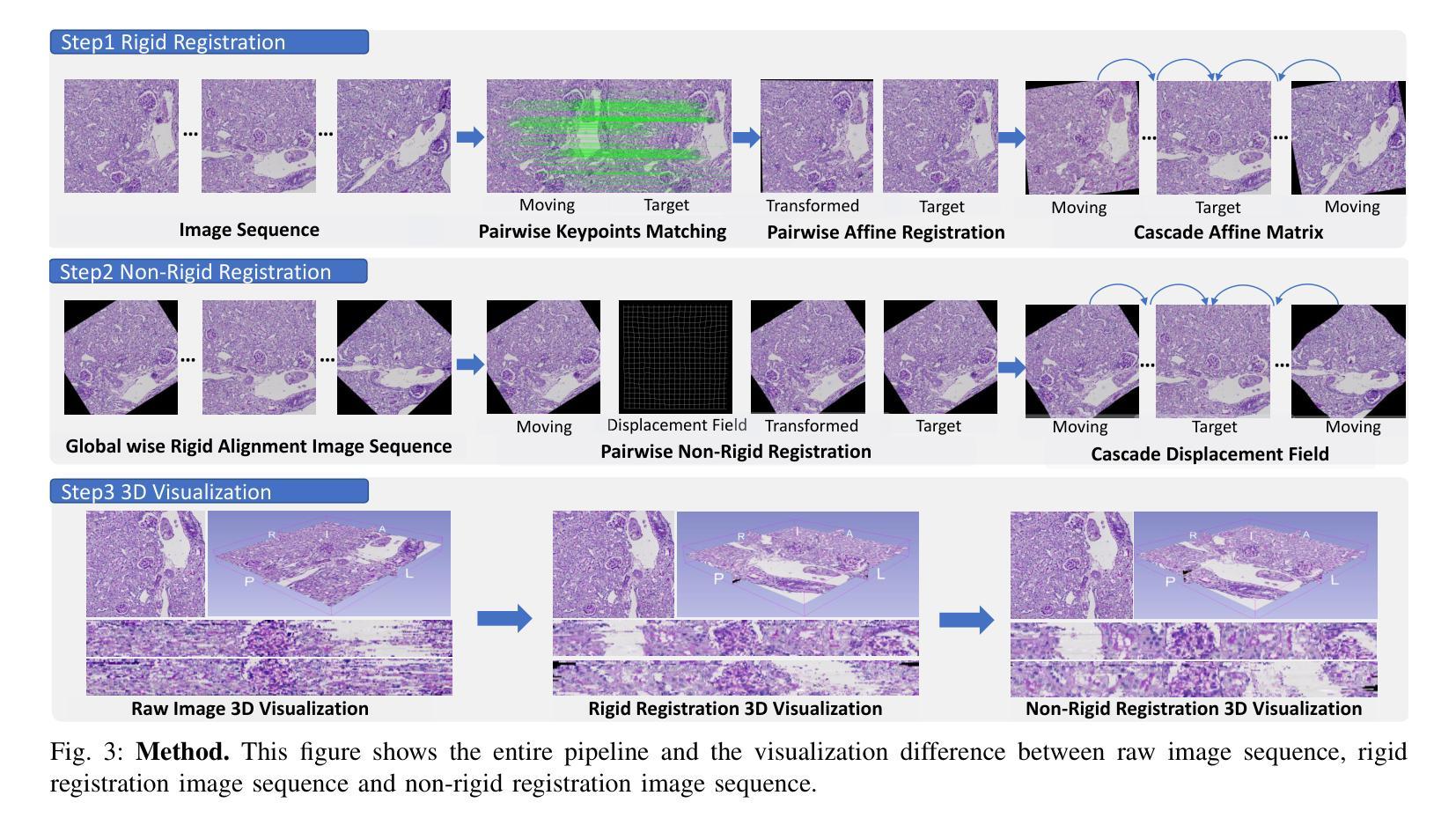
ZeroReg3D: A Zero-shot Registration Pipeline for 3D Consecutive Histopathology Image Reconstruction
Authors:Juming Xiong, Ruining Deng, Jialin Yue, Siqi Lu, Junlin Guo, Marilyn Lionts, Tianyuan Yao, Can Cui, Junchao Zhu, Chongyu Qu, Mengmeng Yin, Haichun Yang, Yuankai Huo
Histological analysis plays a crucial role in understanding tissue structure and pathology. While recent advancements in registration methods have improved 2D histological analysis, they often struggle to preserve critical 3D spatial relationships, limiting their utility in both clinical and research applications. Specifically, constructing accurate 3D models from 2D slices remains challenging due to tissue deformation, sectioning artifacts, variability in imaging techniques, and inconsistent illumination. Deep learning-based registration methods have demonstrated improved performance but suffer from limited generalizability and require large-scale training data. In contrast, non-deep-learning approaches offer better generalizability but often compromise on accuracy. In this study, we introduced ZeroReg3D, a novel zero-shot registration pipeline tailored for accurate 3D reconstruction from serial histological sections. By combining zero-shot deep learning-based keypoint matching with optimization-based affine and non-rigid registration techniques, ZeroReg3D effectively addresses critical challenges such as tissue deformation, sectioning artifacts, staining variability, and inconsistent illumination without requiring retraining or fine-tuning. The code has been made publicly available at https://github.com/hrlblab/ZeroReg3D
组织病理学分析在了解组织结构和病理学方面起着至关重要的作用。虽然最近的注册方法改进了二维组织病理学分析,但它们往往难以保持关键的三维空间关系,限制了其在临床和研究应用中的实用性。具体来说,由于组织变形、切片伪影、成像技术差异和不一致的照明等因素,从二维切片构建准确的三维模型仍然具有挑战性。基于深度学习的注册方法已经显示出改进的性能,但存在通用性有限和需要大量训练数据的问题。相比之下,非深度学习方法提供了更好的通用性,但往往牺牲了准确性。在这项研究中,我们引入了ZeroReg3D,这是一种新型的零样本注册流程,专为从连续组织切片进行准确的三维重建而量身定制。通过结合基于零样本深度学习的关键点匹配和基于优化的仿射和非刚性注册技术,ZeroReg3D有效地解决了组织变形、切片伪影、染色差异和不一致照明等关键问题,无需进行再训练或微调。代码已公开在https://github.com/hrlblab/ZeroReg3D。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学组织分析对理解组织结构和病理学至关重要。当前注册方法虽改进了二维分析,但难以保留重要的三维空间关系,限制了其在临床和研究中的应用。本文提出ZeroReg3D,一种用于从连续组织切片进行准确三维重建的零射击注册流程。它结合了基于深度学习的关键点匹配与优化基础的仿射和非刚性注册技术,有效解决了组织变形、切片伪影、染色变异和照明不一致等关键问题。
Key Takeaways
- 医学组织分析在理解组织结构和病理学方面起着重要作用。
- 当前注册方法在二维分析方面有所改进,但在处理三维空间关系时面临挑战。
- 构建从二维切片到准确三维模型的过程是困难的,原因包括组织变形、切片伪影、成像技术差异和照明不一致等。
- 深度学习方法虽然表现出较高的性能,但其在泛化能力上有限,并需要大量训练数据。
- 非深度学习方法具有较好的泛化能力,但在准确性上有所妥协。
- 本研究介绍了一种新型的零射击注册方法ZeroReg3D,能有效解决上述问题。
点此查看论文截图

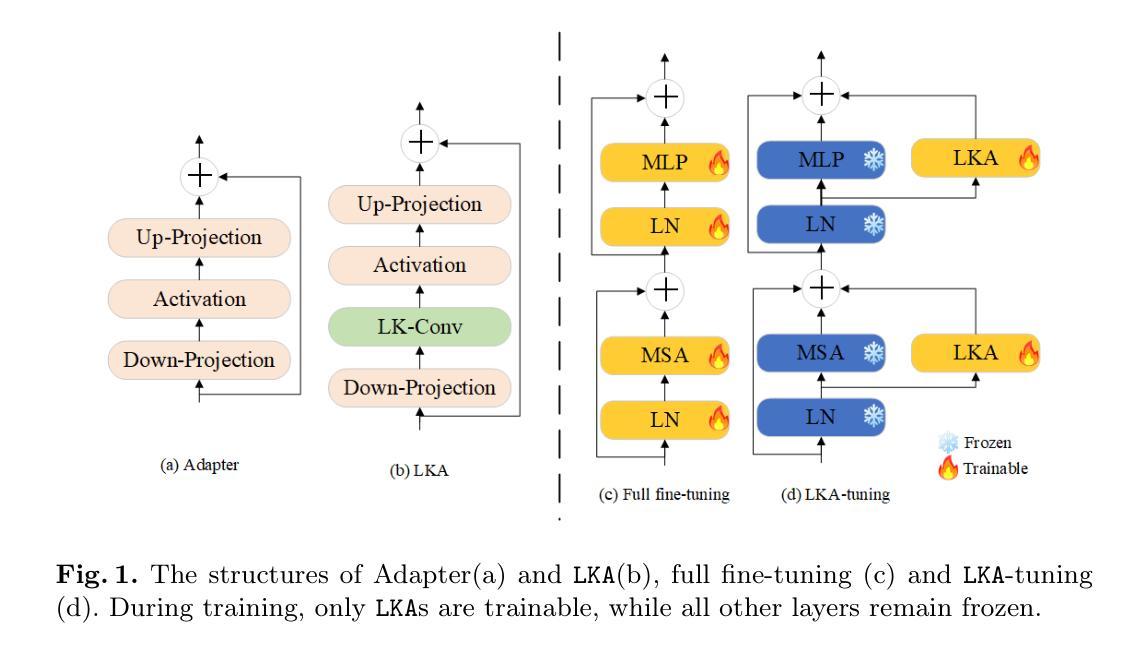
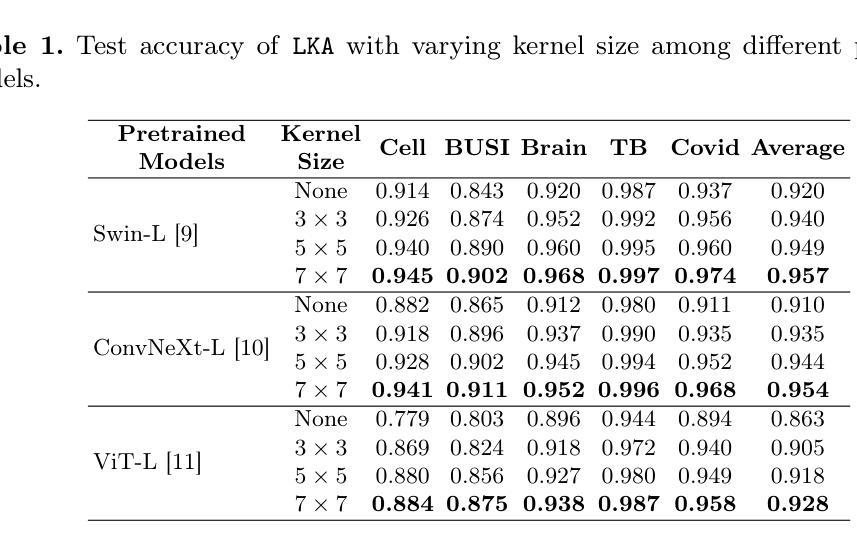
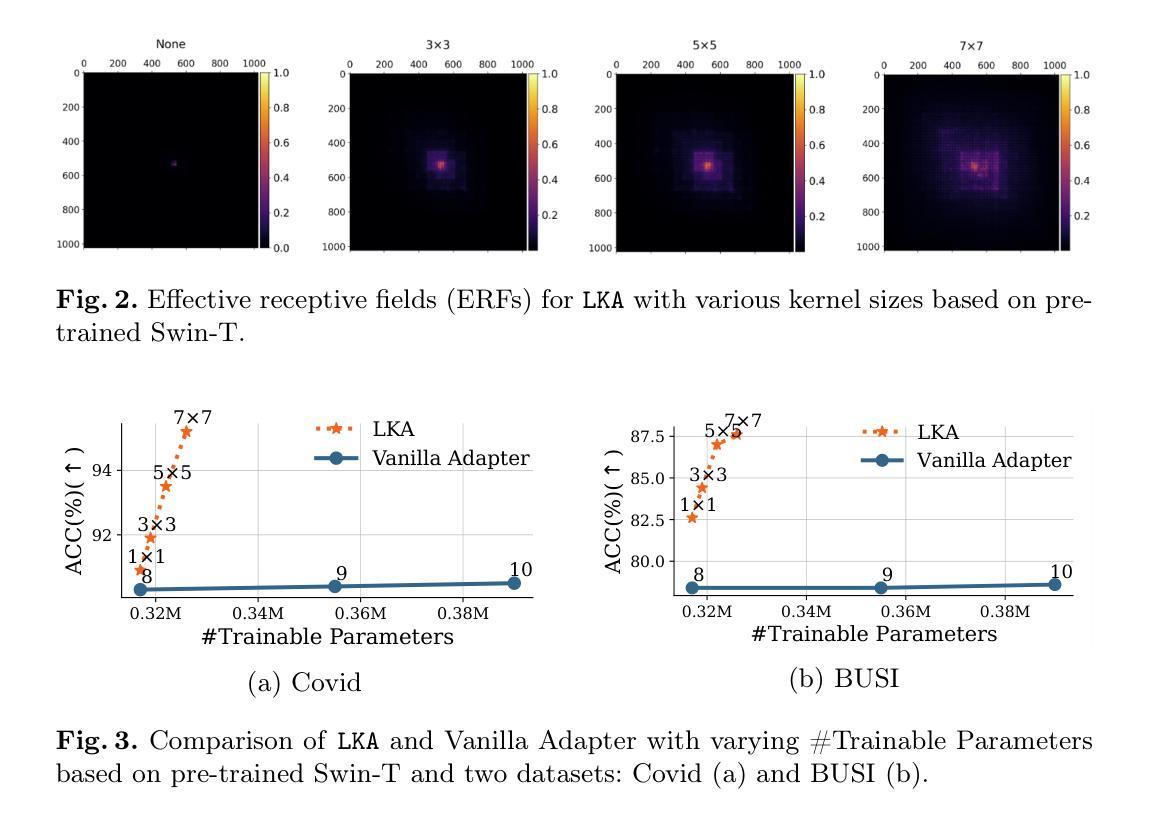
LKA: Large Kernel Adapter for Enhanced Medical Image Classification
Authors:Ziquan Zhu, Si-Yuan Lu, Tianjin Huang, Lu Liu, Zhe Liu
Despite the notable success of current Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods across various domains, their effectiveness on medical datasets falls short of expectations. This limitation arises from two key factors: (1) medical images exhibit extensive anatomical variation and low contrast, necessitating a large receptive field to capture critical features, and (2) existing PEFT methods do not explicitly address the enhancement of receptive fields. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Large Kernel Adapter (LKA), designed to expand the receptive field while maintaining parameter efficiency. The proposed LKA consists of three key components: down-projection, channel-wise large kernel convolution, and up-projection. Through extensive experiments on various datasets and pre-trained models, we demonstrate that the incorporation of a larger kernel size is pivotal in enhancing the adaptation of pre-trained models for medical image analysis. Our proposed LKA outperforms 11 commonly used PEFT methods, surpassing the state-of-the-art by 3.5% in top-1 accuracy across five medical datasets.
尽管当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在不同领域取得了显著的成功,但在医学数据集上的效果却未能达到预期。这一局限性源于两个关键因素:(1)医学图像表现出广泛的解剖变异和低对比度,需要较大的感受野来捕捉关键特征;(2)现有的PEFT方法没有明确解决感受野增强的问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了大型内核适配器(LKA),旨在在保持参数效率的同时扩大感受野。所提出的LKA由三个关键组件组成:下投影、通道大型内核卷积和上投影。通过对各种数据集和预训练模型的广泛实验,我们证明了使用更大的内核尺寸对于增强预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。我们提出的大型内核适配器(LKA)在五个医学数据集上超过了11种常用的PEFT方法,在top-1准确率上超越了最新技术3.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The manuscript has been withdrawn in order to revise key technical components and improve experimental validation. We plan to substantially update the model design and resubmit after further evaluation.
Summary
当前参数有效微调(PEFT)方法在各领域取得了显著成功,但在医学数据集上的效果不尽如人意。主要受限于两点:医学图像存在广泛解剖变异和低对比度,需要大感受野捕捉关键特征;现有PEFT方法未明确解决感受野增强问题。为克服这些挑战,提出Large Kernel Adapter(LKA),旨在扩大感受野同时保持参数效率。LKA由三个关键组件构成:下投影、通道大内核卷积和上投影。在多个数据集和预训练模型上的实验表明,采用更大的内核尺寸对于提高预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。提出的LKA在五个医学数据集上优于11种常用的PEFT方法,在top-1准确率上超过现有技术3.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像具有广泛解剖变异和低对比度特点,需要大感受野捕捉关键特征。
- 当前参数有效微调(PEFT)方法在医学数据集上的效果有限。
- LKA(Large Kernel Adapter)旨在扩大感受野并维持参数效率。
- LKA由下投影、通道大内核卷积和上投影三个关键组件构成。
- 实验证明更大内核尺寸对提高预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。
- LKA在多个医学数据集上表现优于其他PEFT方法,显著提高top-1准确率。
点此查看论文截图

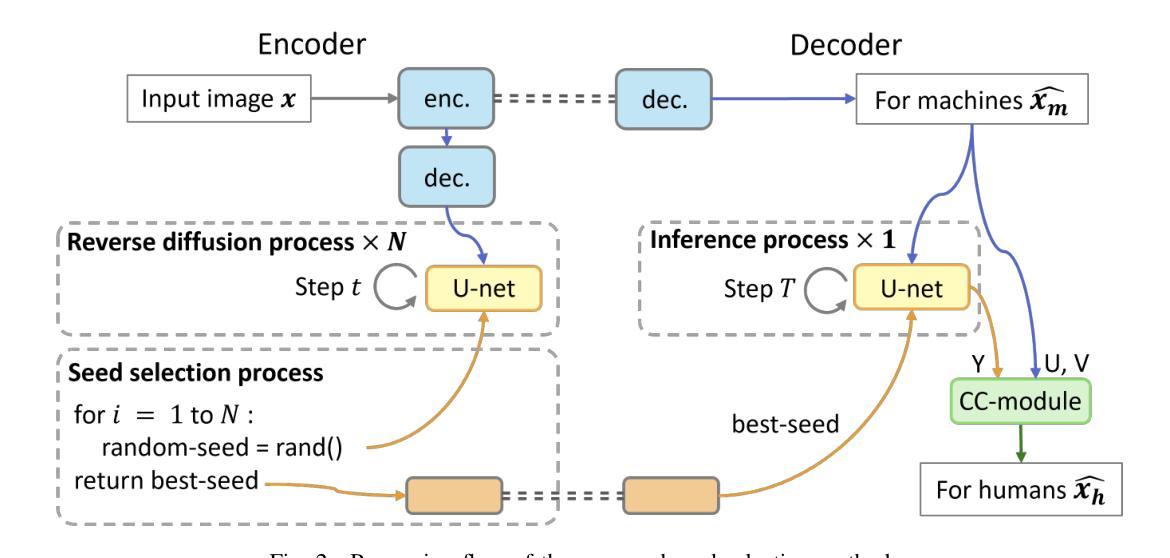
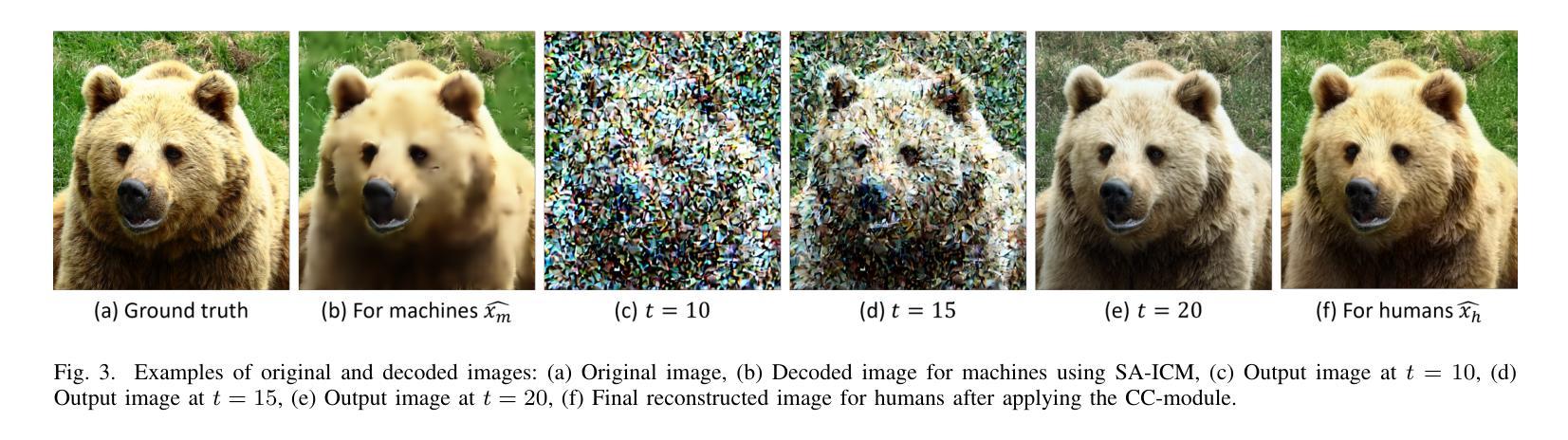
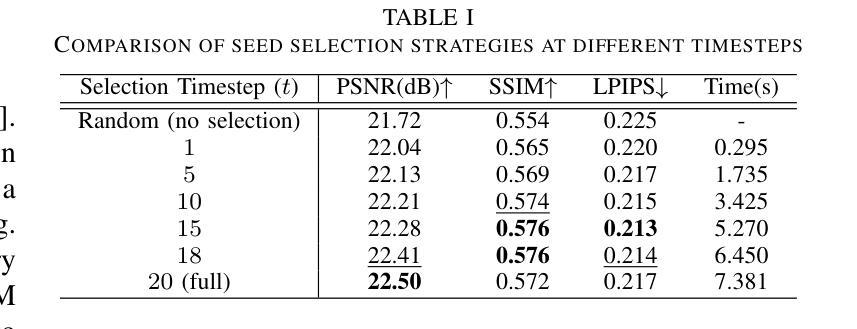
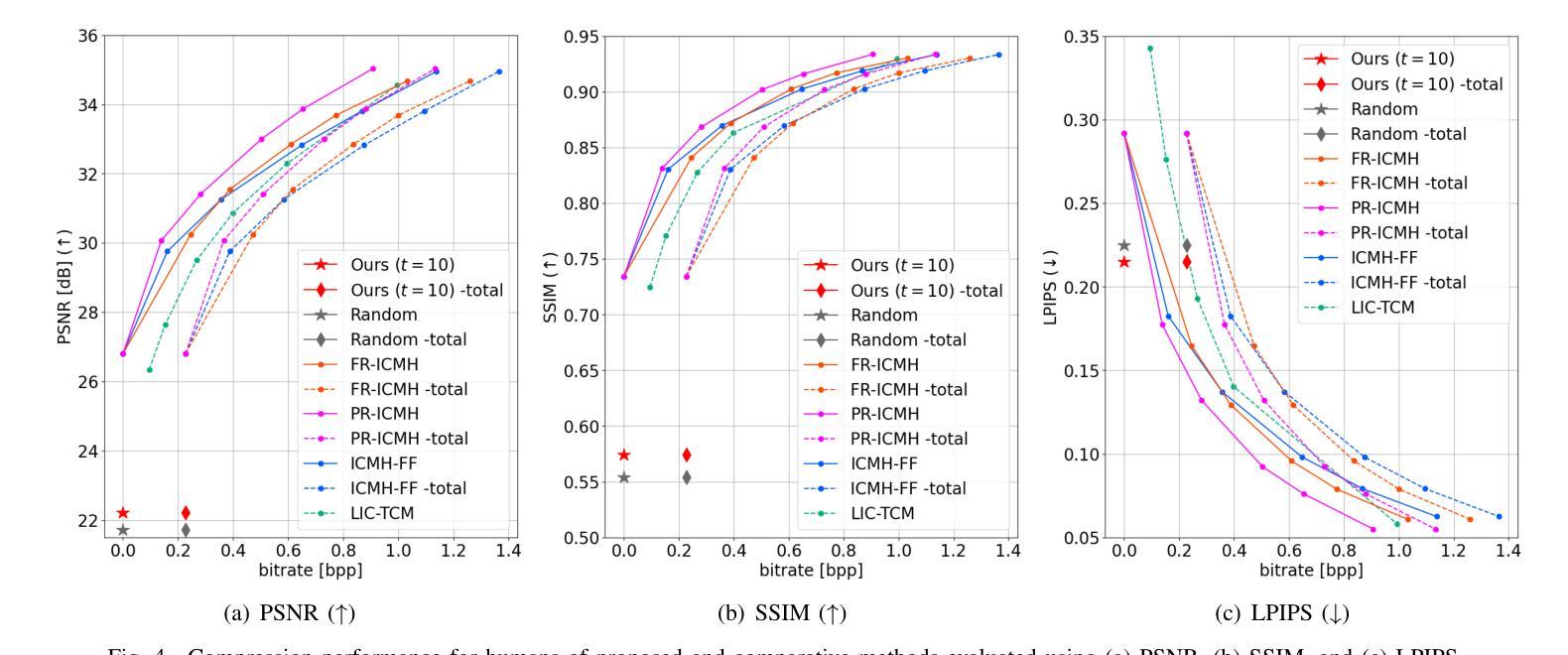
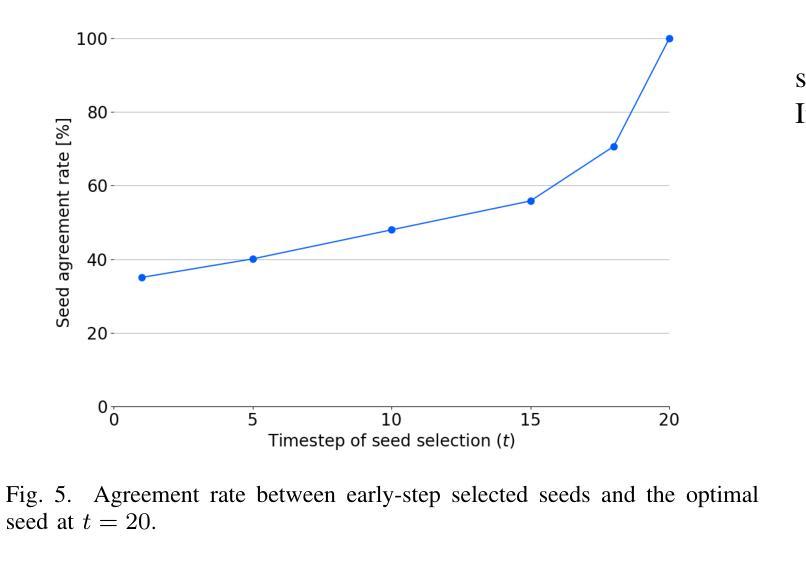
Seed Selection for Human-Oriented Image Reconstruction via Guided Diffusion
Authors:Yui Tatsumi, Ziyue Zeng, Hiroshi Watanabe
Conventional methods for scalable image coding for humans and machines require the transmission of additional information to achieve scalability. A recent diffusion-based approach avoids this by generating human-oriented images from machine-oriented images without extra bitrate. However, it utilizes a single random seed, which may lead to suboptimal image quality. In this paper, we propose a seed selection method that identifies the optimal seed from multiple candidates to improve image quality without increasing the bitrate. To reduce the computational cost, selection is performed based on intermediate outputs obtained from early steps of the reverse diffusion process. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the baseline, which uses a single random seed without selection, across multiple evaluation metrics.
传统的可伸缩图像编码方法和针对人类和机器的编码方法需要传输额外的信息来实现可伸缩性。最近出现的一种基于扩散的方法通过从面向机器的图像生成面向人类的图像,无需额外的比特率。然而,它仅使用一个随机种子,这可能导致图像质量不佳。本文提出了一种种子选择方法,该方法从多个候选种子中识别出最佳种子,旨在提高图像质量而不增加比特率。为了降低计算成本,根据反向扩散过程早期步骤获得的中间输出来进行选择。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多指标评价中均优于使用单一随机种子且不进行选择的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 2025 IEEE 14th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE 2025)
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的图像编码方法,能够从机器导向的图像生成人类导向的图像,无需额外比特率。针对使用单一随机种子可能导致图像质量不佳的问题,提出了一种种子选择方法,从多个候选种子中选择最优种子以提升图像质量,同时不增加比特率。通过早期反向扩散过程的中间输出来降低计算成本。实验结果表明,该方法在多个评估指标上优于使用单一随机种子而不进行选择的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于图像编码,能从机器导向的图像生成人类导向的图像,无需额外比特率。
- 提出了种子选择方法,从多个候选种子中选择最优种子以提升图像质量。
- 种子选择基于早期反向扩散过程的中间输出,以降低计算成本。
- 方法在多个评估指标上优于使用单一随机种子的基线方法。
- 该方法能够避免传统可扩展图像编码方法需要传输额外信息来实现可扩展性的需求。
- 通过优化种子选择,能够在不增加比特率的情况下提高图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

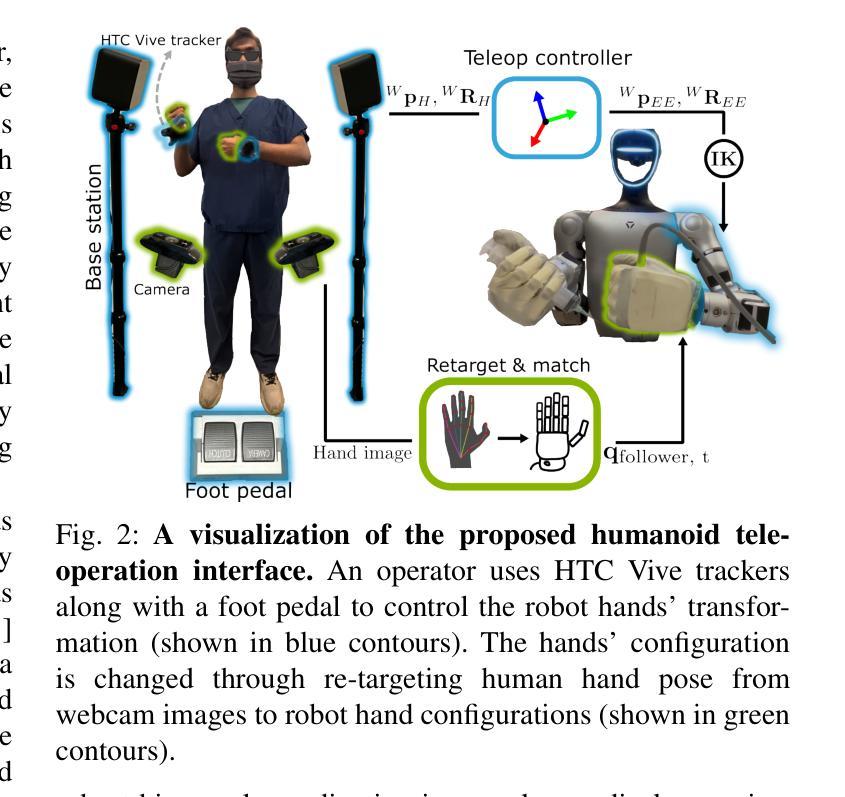
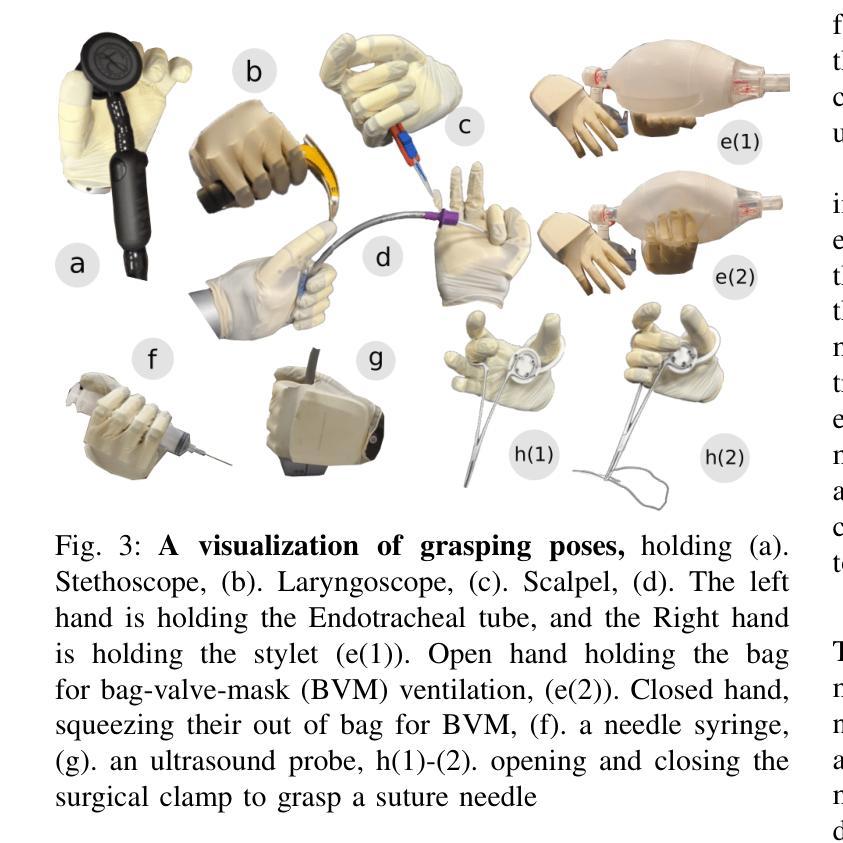
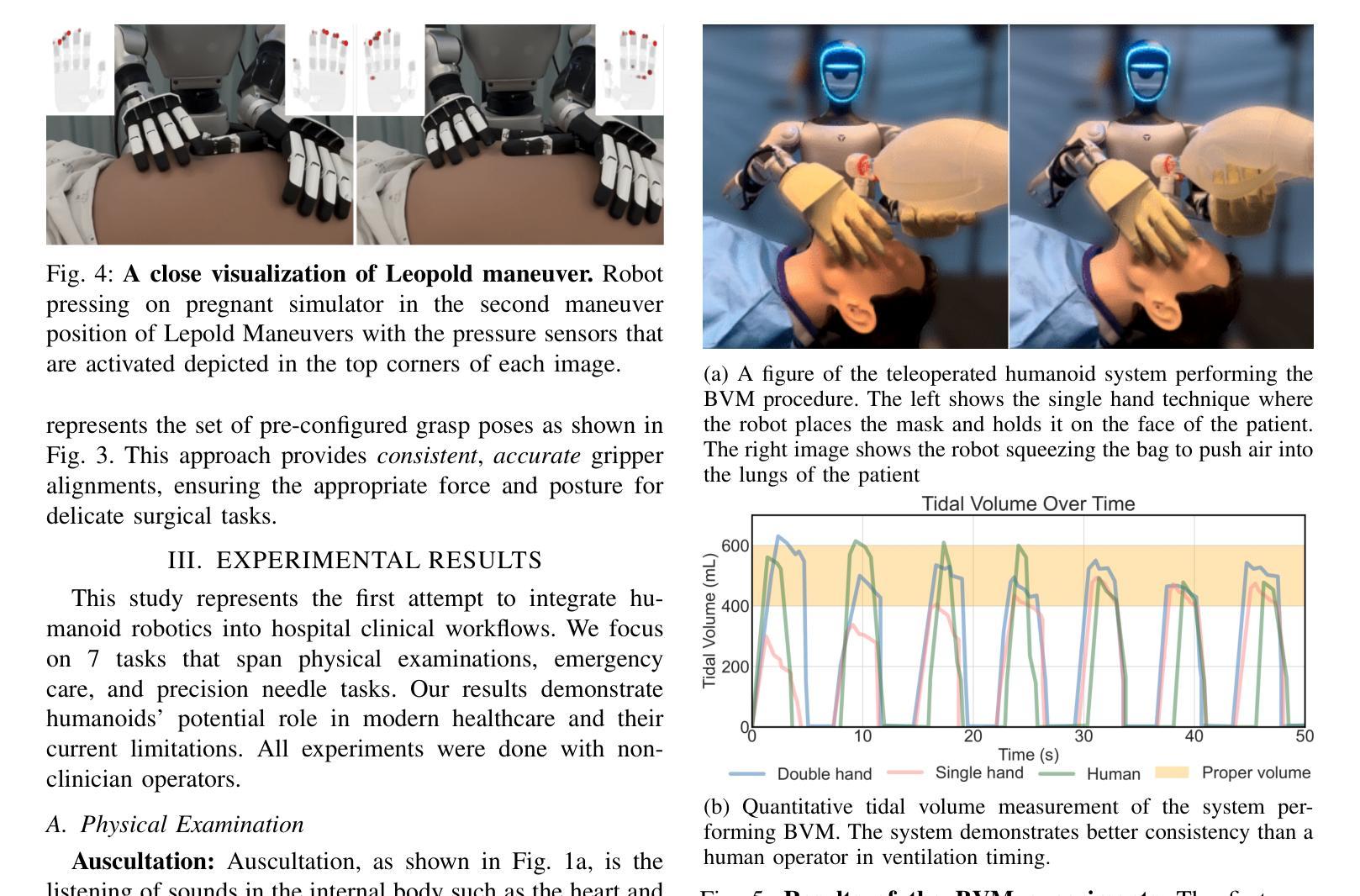
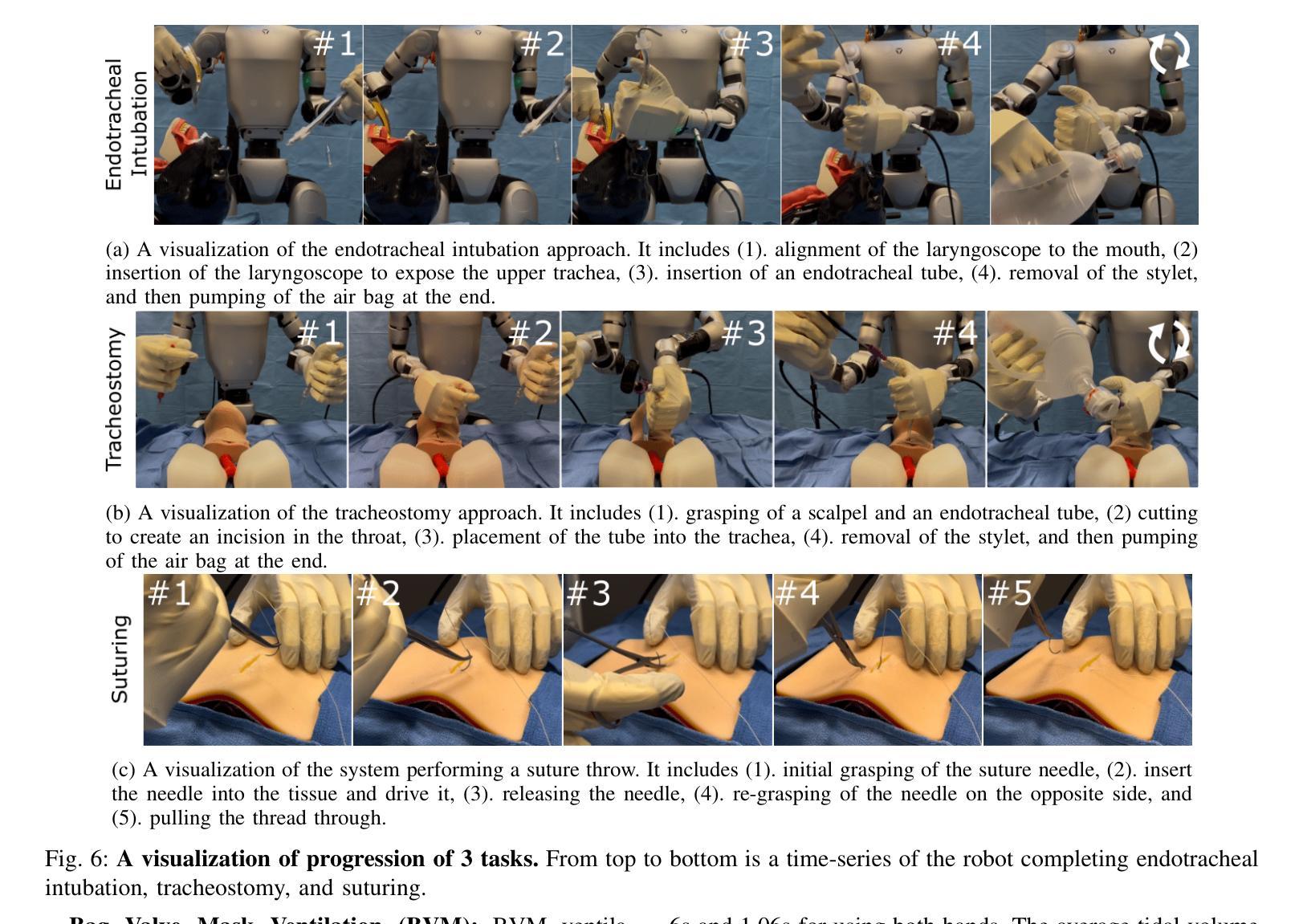
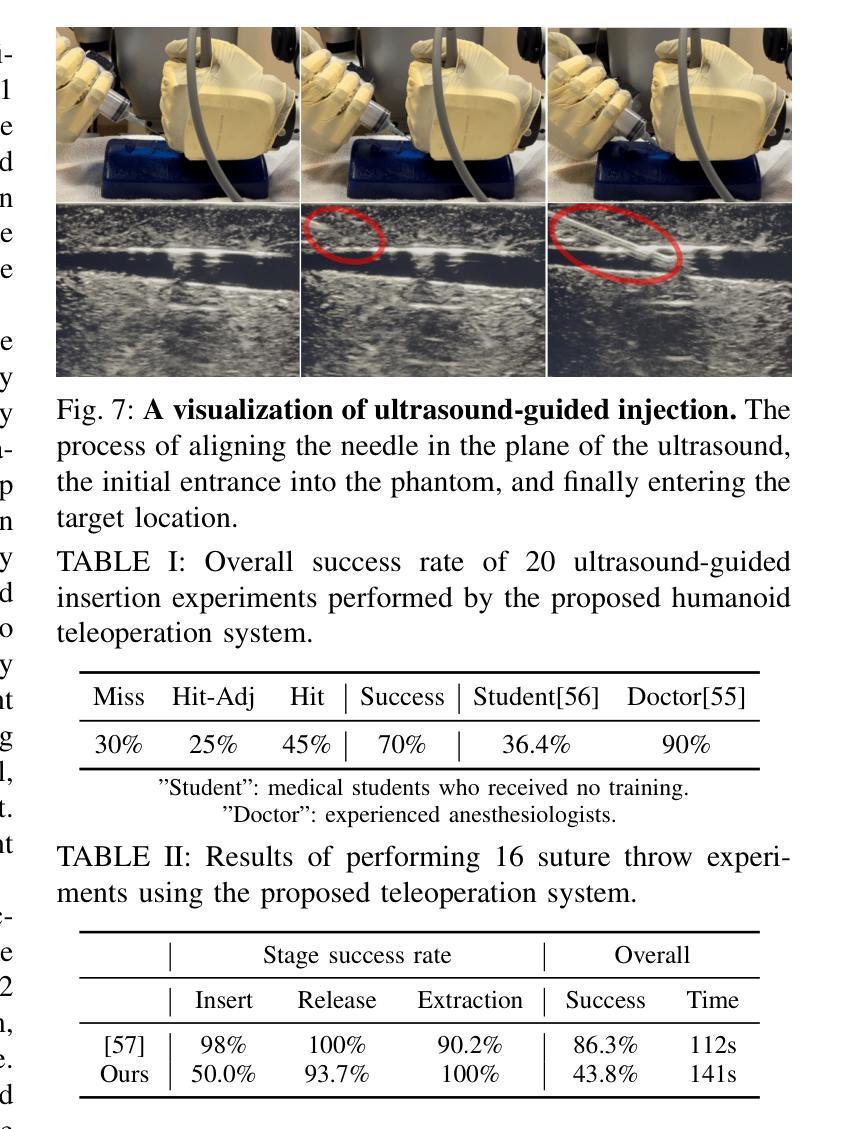
Humanoids in Hospitals: A Technical Study of Humanoid Robot Surrogates for Dexterous Medical Interventions
Authors:Soofiyan Atar, Xiao Liang, Calvin Joyce, Florian Richter, Wood Ricardo, Charles Goldberg, Preetham Suresh, Michael Yip
The increasing demand for healthcare workers, driven by aging populations and labor shortages, presents a significant challenge for hospitals. Humanoid robots have the potential to alleviate these pressures by leveraging their human-like dexterity and adaptability to assist in medical procedures. This work conducted an exploratory study on the feasibility of humanoid robots performing direct clinical tasks through teleoperation. A bimanual teleoperation system was developed for the Unitree G1 Humanoid Robot, integrating high-fidelity pose tracking, custom grasping configurations, and an impedance controller to safely and precisely manipulate medical tools. The system is evaluated in seven diverse medical procedures, including physical examinations, emergency interventions, and precision needle tasks. Our results demonstrate that humanoid robots can successfully replicate critical aspects of human medical assessments and interventions, with promising quantitative performance in ventilation and ultrasound-guided tasks. However, challenges remain, including limitations in force output for procedures requiring high strength and sensor sensitivity issues affecting clinical accuracy. This study highlights the potential and current limitations of humanoid robots in hospital settings and lays the groundwork for future research on robotic healthcare integration.
随着人口老龄化和劳动力短缺的加剧,对医疗工作者的需求不断增加,这给医院带来了重大挑战。类人机器人具有缓解这些压力的潜力,它们可以利用类人的灵巧性和适应性来辅助医疗程序。本研究通过遥操作对人类机器人执行直接临床任务的可能性进行了探索性研究。为Unitree G1类人机器人开发了一个双手遥操作系统,集成了高保真姿态追踪、自定义抓握配置和阻抗控制器,以安全精确地操作医疗工具。该系统在七种不同的医疗程序中进行了评估,包括体检、紧急干预和精确针任务。我们的结果表明,类人机器人能够成功复制人类医学评估和干预的关键方面,在通气和超声引导任务中的定量性能具有前景。然而,仍存在挑战,包括力量输出方面的局限,对于需要高强度的程序以及影响临床准确性的传感器灵敏度问题。该研究突出了类人机器人在医院环境中的潜力和当前局限性,为机器人医疗保健整合的未来研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
人口老龄化及劳动力短缺对医院带来巨大挑战,人类需求医疗工作者的数量不断增加。人形机器人具有人类般的灵巧性和适应性,可协助执行医疗程序,缓解压力。本研究探索了人形机器人通过遥控操作执行直接临床任务的可能性。为Unitree G1人形机器人开发了一个双手动遥控操作系统,集成了高保真姿态追踪、自定义抓握配置和阻抗控制器,可安全精确地操作医疗工具。系统经过七种不同的医疗程序的评估,包括体检、紧急干预和精确针剂任务。结果表明,人形机器人在关键的人类医疗评估和干预方面表现成功,并在通气和超声引导任务中展现出有前景的定量表现。然而仍存在挑战,包括力量输出限制和高强度程序所需的传感器灵敏度问题影响临床准确性。本研究强调了人形机器人在医院环境中的潜力和当前局限性,并为未来机器人医疗保健融合的研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 人口老龄化和劳动力短缺使医院面临巨大挑战,医疗工作者需求增加。
- 人形机器人具备辅助执行医疗程序的潜力,拥有类似人类的灵巧性和适应性。
- 研究探索了人形机器人通过遥控操作执行直接临床任务的可能性。
- 为Unitree G1人形机器人开发的双手动遥控操作系统集成了高保真姿态追踪、自定义抓握和阻抗控制。
- 系统经过多种医疗程序评估,包括体检、紧急干预和针剂任务。
- 人形机器人在医疗评估和干预方面展现成功,特别是在通气和超声引导任务中表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

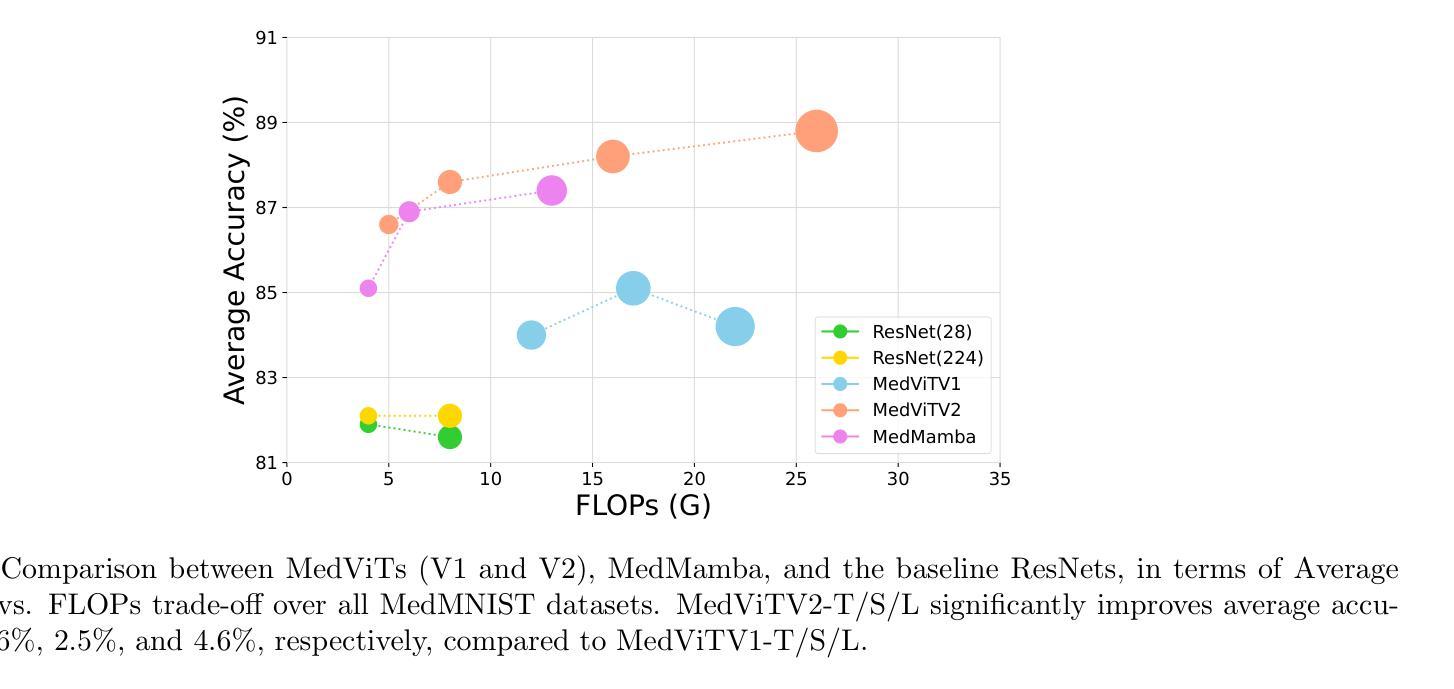
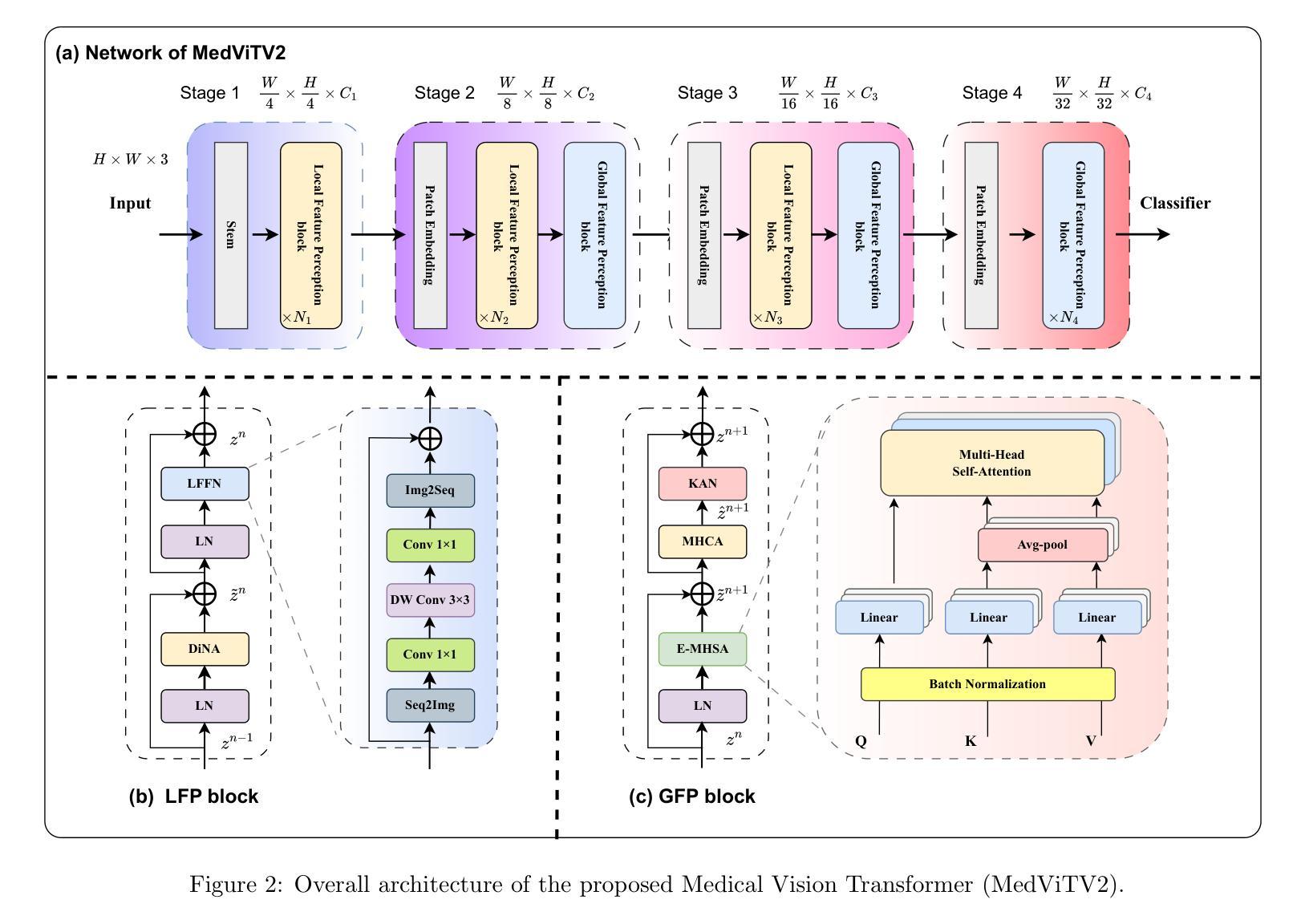
MedViT V2: Medical Image Classification with KAN-Integrated Transformers and Dilated Neighborhood Attention
Authors:Omid Nejati Manzari, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Taha Koleilat, Yiming Xiao, Hassan Rivaz
Convolutional networks, transformers, hybrid models, and Mamba-based architectures have demonstrated strong performance across various medical image classification tasks. However, these methods were primarily designed to classify clean images using labeled data. In contrast, real-world clinical data often involve image corruptions that are unique to multi-center studies and stem from variations in imaging equipment across manufacturers. In this paper, we introduce the Medical Vision Transformer (MedViTV2), a novel architecture incorporating Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) layers into the transformer architecture for the first time, aiming for generalized medical image classification. We have developed an efficient KAN block to reduce computational load while enhancing the accuracy of the original MedViT. Additionally, to counteract the fragility of our MedViT when scaled up, we propose an enhanced Dilated Neighborhood Attention (DiNA), an adaptation of the efficient fused dot-product attention kernel capable of capturing global context and expanding receptive fields to scale the model effectively and addressing feature collapse issues. Moreover, a hierarchical hybrid strategy is introduced to stack our Local Feature Perception and Global Feature Perception blocks in an efficient manner, which balances local and global feature perceptions to boost performance. Extensive experiments on 17 medical image classification datasets and 12 corrupted medical image datasets demonstrate that MedViTV2 achieved state-of-the-art results in 27 out of 29 experiments with reduced computational complexity. MedViTV2 is 44% more computationally efficient than the previous version and significantly enhances accuracy, achieving improvements of 4.6% on MedMNIST, 5.8% on NonMNIST, and 13.4% on the MedMNIST-C benchmark.
卷积网络、变压器、混合模型以及基于Mamba的架构在各种医学图像分类任务中表现出强大的性能。然而,这些方法主要是为了使用标记数据对干净图像进行分类而设计的。相比之下,现实世界中的临床数据通常涉及多中心研究独特的图像腐蚀,并且源于不同制造商的成像设备之间的差异。在本文中,我们介绍了医学视觉变压器(MedViTV2),这是一种新型架构,首次将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)层融入变压器架构中,旨在实现通用医学图像分类。我们开发了一个高效的KAN块,以减少计算负载并提高原始MedViT的准确性。此外,为了抵消我们MedViT在扩大规模时的脆弱性,我们提出了一种增强的膨胀邻域注意力(DiNA),这是对高效融合点积注意力核的适应,能够捕获全局上下文并扩大感受野,以有效地扩展模型并解决特征崩溃问题。此外,还引入了一种分层混合策略,以有效的方式堆叠我们的局部特征感知和全局特征感知块,这可以平衡局部和全局特征感知以提高性能。在17个医学图像分类数据集和12个被腐蚀的医学图像数据集上的大量实验表明,MedViTV2在29次实验中的27次取得了最新技术成果,并且计算复杂度降低。MedViTV2的计算效率比前一个版本提高了44%,并且显著提高了准确性,在MedMNIST上提高了4.6%,在NonMNIST上提高了5.8%,在MedMNIST-C基准测试上提高了13.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了新提出的医疗图像分类模型Medical Vision Transformer(MedViTV2),结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)层和高效Dilated Neighborhood Attention(DiNA)模块。该模型具有全局上下文感知能力和高效的特征提取能力,适用于处理存在图像腐蚀问题的真实世界临床数据。在多个医学图像分类数据集上的实验表明,MedViTV2在计算效率提高的同时,实现了显著的性能提升。相较于之前的版本,MedViTV2计算效率提高了44%,在MedMNIST、NonMNIST和MedMNIST-C基准测试上的准确率分别提高了4.6%、5.8%和13.4%。整体来说,这是一个实现了更高效性能和更全面图像感知的新医学图像分类模型。
Key Takeaways
- MedViTV2结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)层进入transformer架构,旨在实现通用的医学图像分类。
- MedViTV2使用高效的KAN块减少计算负载并增强准确性。
- 为了解决模型规模扩大时的脆弱性问题,引入了增强的Dilated Neighborhood Attention(DiNA)。
- MedViTV2采用局部特征感知与全局特征感知的层次混合策略,平衡了局部和全局特征感知以提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

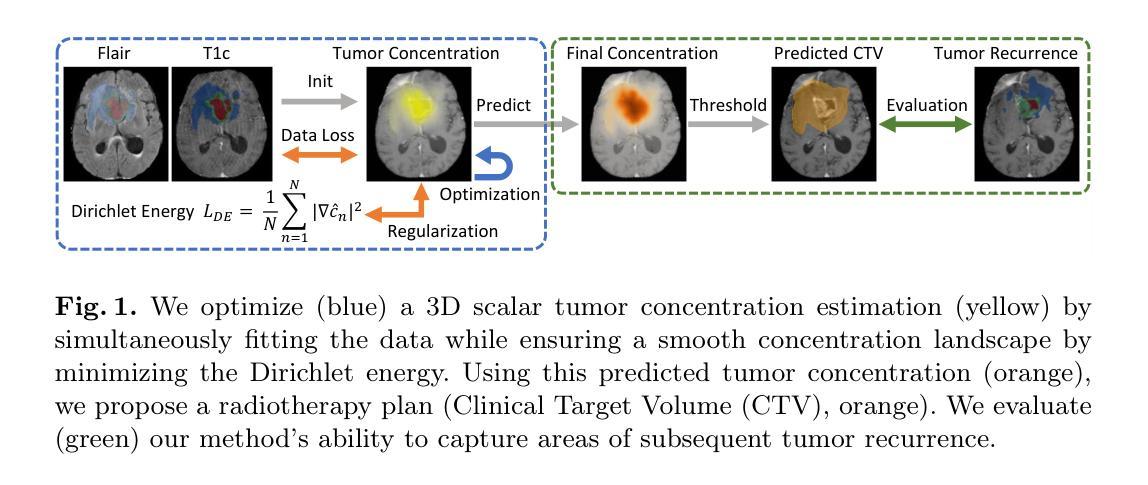
A Lightweight Optimization Framework for Estimating 3D Brain Tumor Infiltration
Authors:Jonas Weidner, Michal Balcerak, Ivan Ezhov, André Datchev, Laurin Lux, Lucas Zimmer, Daniel Rueckert, Björn Menze, Benedikt Wiestler
Glioblastoma, the most aggressive primary brain tumor, poses a severe clinical challenge due to its diffuse microscopic infiltration, which remains largely undetected on standard MRI. As a result, current radiotherapy planning employs a uniform 15 mm margin around the resection cavity, failing to capture patient-specific tumor spread. Tumor growth modeling offers a promising approach to reveal this hidden infiltration. However, methods based on partial differential equations or physics-informed neural networks tend to be computationally intensive or overly constrained, limiting their clinical adaptability to individual patients. In this work, we propose a lightweight, rapid, and robust optimization framework that estimates the 3D tumor concentration by fitting it to MRI tumor segmentations while enforcing a smooth concentration landscape. This approach achieves superior tumor recurrence prediction on 192 brain tumor patients across two public datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines while reducing runtime from 30 minutes to less than one minute. Furthermore, we demonstrate the framework’s versatility and adaptability by showing its ability to seamlessly integrate additional imaging modalities or physical constraints.
胶质母细胞瘤是最具侵袭性的原发性脑肿瘤,由于其弥漫性的微观浸润,在标准MRI上大多无法检测,对临床治疗构成了严峻挑战。因此,目前的放疗计划采用围绕切除腔室均匀15毫米边界的方式,未能捕获患者特定的肿瘤扩散情况。肿瘤增长建模是揭示这种隐蔽浸润的有前途的方法。然而,基于偏微分方程或物理信息神经网络的方法往往计算量大或受到过度约束,限制了其在针对个别患者的临床适应性方面的应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个轻便、快速、稳健的优化框架,它通过拟合MRI肿瘤分割来估计3D肿瘤浓度,同时强制实施平滑的浓度景观。该方法在两个公共数据集的192例脑肿瘤患者身上实现了卓越的肿瘤复发预测效果,优于最先进的基线技术,并将运行时间从30分钟缩短到不到1分钟。此外,我们通过展示该框架无缝集成其他成像模式或物理约束的能力,证明了其通用性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种快速、稳健的优化框架,用于根据MRI肿瘤分割结果估计三维肿瘤浓度,同时实现平滑浓度景观。该框架具有预测肿瘤复发的优越性,能够降低运行时间并展现出良好适应性。这一方法在两种公共数据集上针对192例脑肿瘤患者表现出优越性能。同时展示了框架的灵活性和通用性,可以无缝集成其他成像模式和物理约束。此研究成果为改进放射治疗计划和应对胶质母细胞瘤的临床挑战提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
- 胶质母细胞瘤因其微妙的微观浸润现象而对临床治疗构成严峻挑战。
- 当前放疗计划依赖于统一的安全边界,未能准确捕捉患者特异性肿瘤扩散。
- 肿瘤增长建模成为揭示隐藏浸润的一种有前途的方法。
- 提出的优化框架能迅速估计三维肿瘤浓度,提高肿瘤复发预测准确率。
- 该框架降低了计算时间并展示了良好适应性,对比最先进的方法有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图

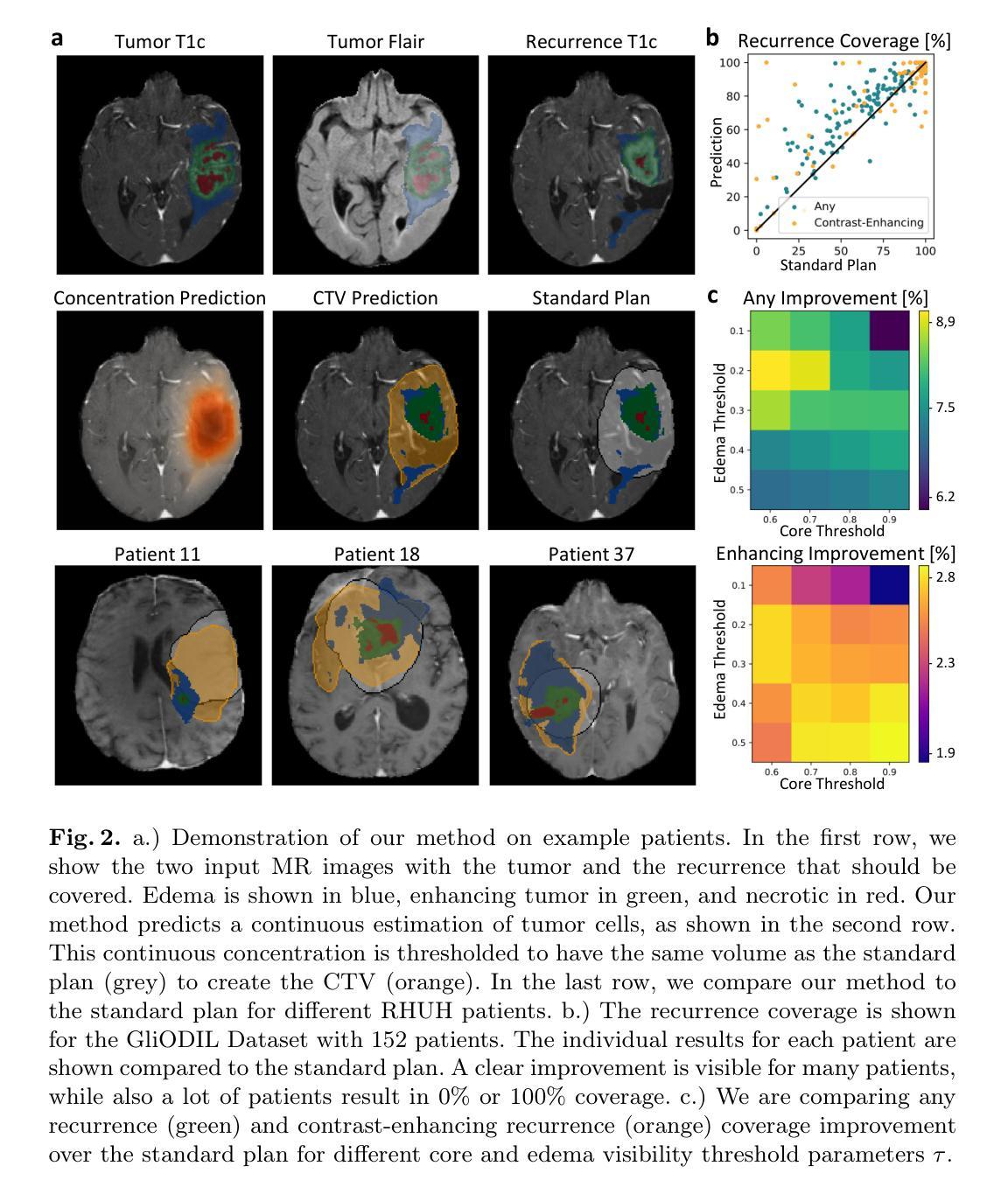
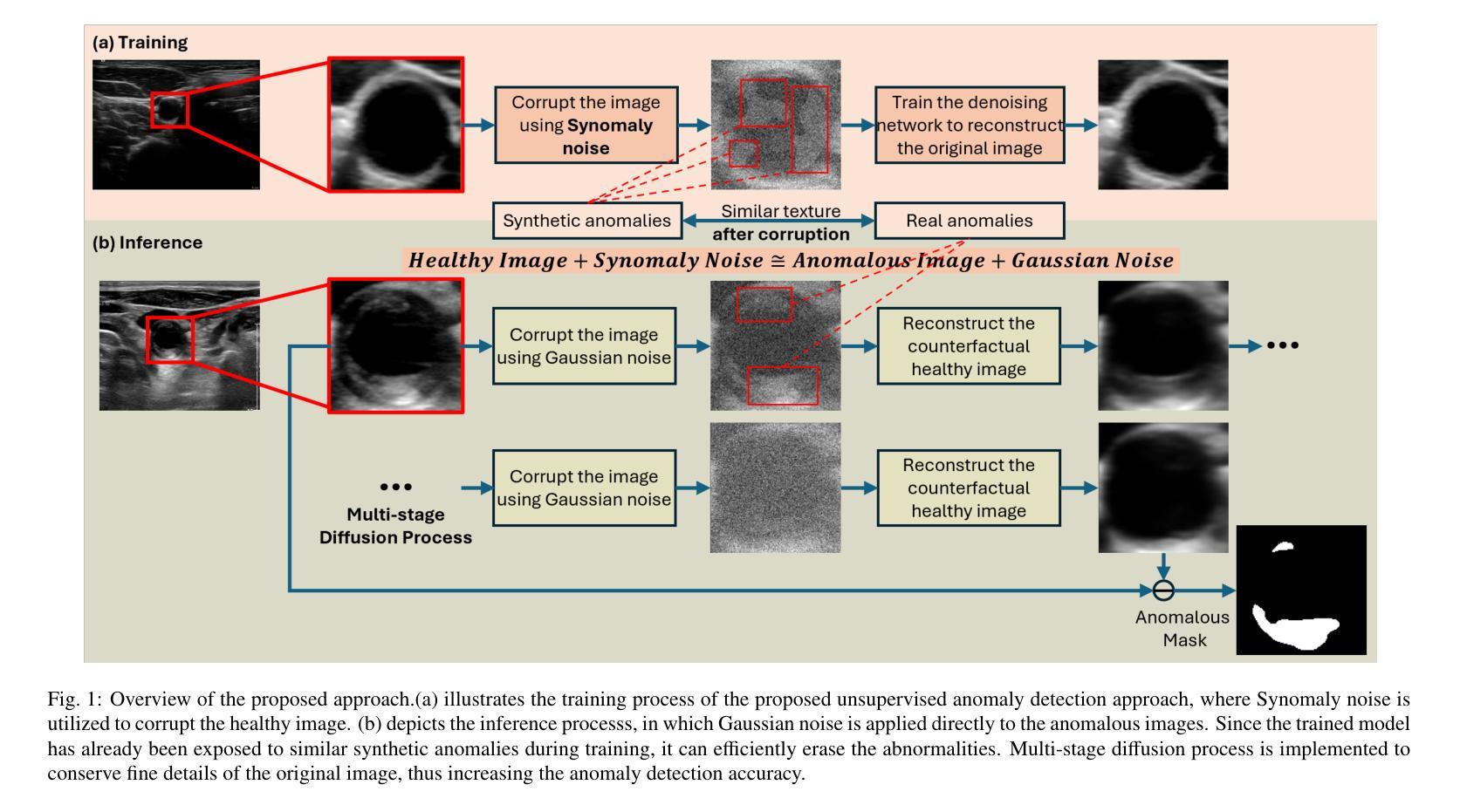
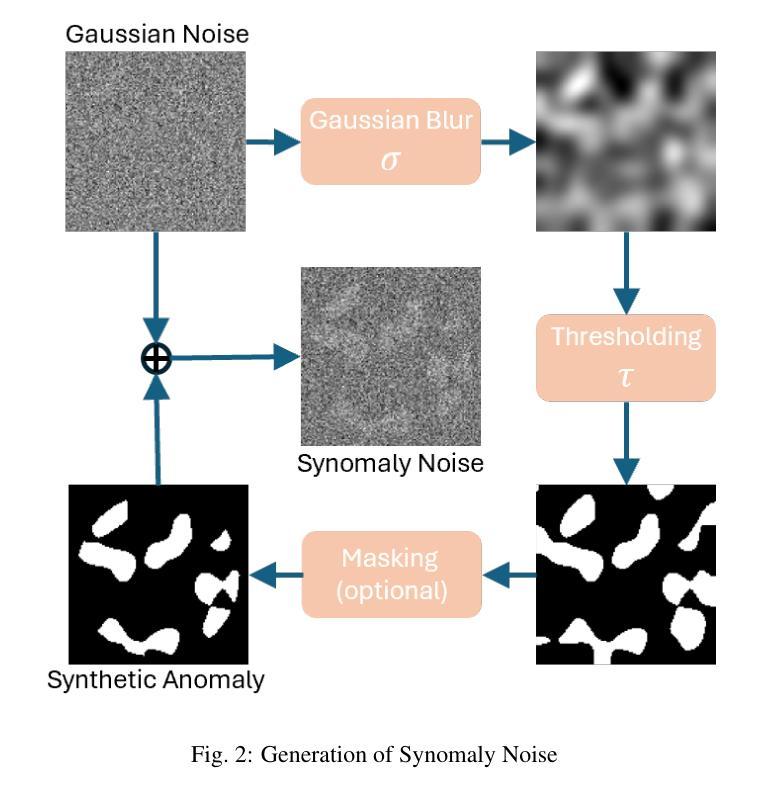
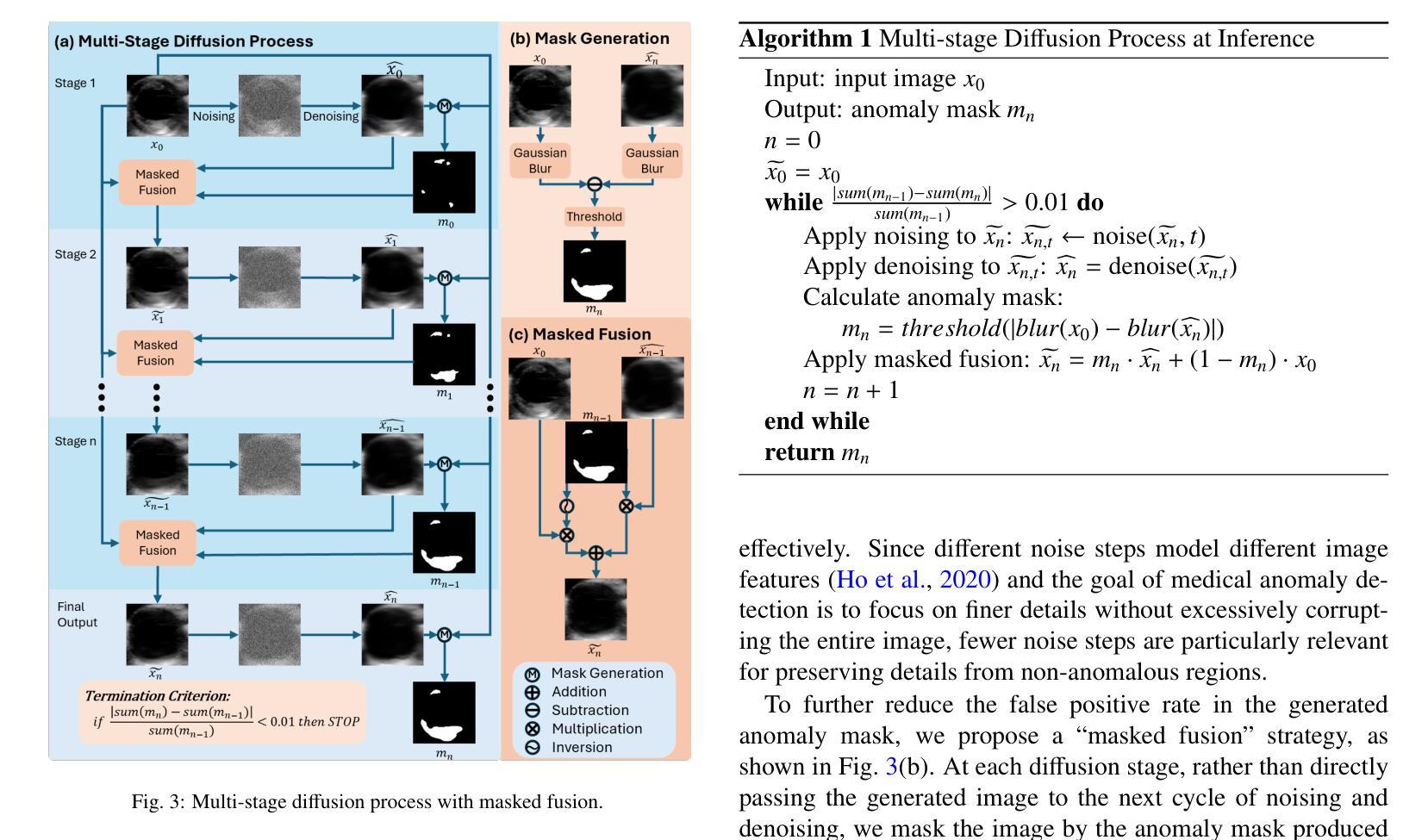
Synomaly Noise and Multi-Stage Diffusion: A Novel Approach for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Medical Images
Authors:Yuan Bi, Lucie Huang, Ricarda Clarenbach, Reza Ghotbi, Angelos Karlas, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
Anomaly detection in medical imaging plays a crucial role in identifying pathological regions across various imaging modalities, such as brain MRI, liver CT, and carotid ultrasound (US). However, training fully supervised segmentation models is often hindered by the scarcity of expert annotations and the complexity of diverse anatomical structures. To address these issues, we propose a novel unsupervised anomaly detection framework based on a diffusion model that incorporates a synthetic anomaly (Synomaly) noise function and a multi-stage diffusion process. Synomaly noise introduces synthetic anomalies into healthy images during training, allowing the model to effectively learn anomaly removal. The multi-stage diffusion process is introduced to progressively denoise images, preserving fine details while improving the quality of anomaly-free reconstructions. The generated high-fidelity counterfactual healthy images can further enhance the interpretability of the segmentation models, as well as provide a reliable baseline for evaluating the extent of anomalies and supporting clinical decision-making. Notably, the unsupervised anomaly detection model is trained purely on healthy images, eliminating the need for anomalous training samples and pixel-level annotations. We validate the proposed approach on brain MRI, liver CT datasets, and carotid US. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing state-of-the-art unsupervised anomaly detection methods, achieving performance comparable to fully supervised segmentation models in the US dataset. Ablation studies further highlight the contributions of Synomaly noise and the multi-stage diffusion process in improving anomaly segmentation. These findings underscore the potential of our approach as a robust and annotation-efficient alternative for medical anomaly detection.
医学成像中的异常检测在识别各种成像模式(如脑部MRI、肝脏CT和颈动脉超声)中的病理区域方面起着至关重要的作用。然而,由于专家标注的稀缺和多种解剖结构的复杂性,完全监督的分割模型训练常常受到限制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型无监督异常检测框架,该框架结合了合成异常(Synomaly)噪声函数和多阶段扩散过程。Synomaly噪声在训练过程中向健康图像中引入合成异常,使模型能够有效地学习异常去除。多阶段扩散过程被用来逐步去噪图像,在保留精细细节的同时提高无异常重建的质量。生成的高保真度反事实健康图像可以进一步增强分割模型的解释性,并提供可靠的基线来评估异常的严重程度和支持临床决策。值得注意的是,无监督的异常检测模型仅使用健康图像进行训练,无需异常训练样本和像素级标注。我们在脑部MRI、肝脏CT数据集和颈动脉超声上对提出的方法进行了验证。实验结果表明,所提出的框架优于现有的最先进的无监督异常检测方法,在超声数据集中实现了与完全监督的分割模型相当的性能。消融研究进一步强调了Synomaly噪声和多阶段扩散过程在提高异常分割中的贡献。这些发现凸显了我们的方法作为稳健且标注效率高的医疗异常检测替代方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的无监督异常检测框架,通过合成异常噪声函数和多阶段扩散过程来解决医学成像中的异常检测问题。该框架能够在无需异常训练样本和像素级注释的情况下,对健康的图像进行训练,有效学习异常移除。多阶段扩散过程能够逐步去噪,保留细节,提高无异常重建的质量。实验结果证明,该框架在脑MRI、肝脏CT和颈动脉超声数据集上表现出优异的性能,可与全监督分割模型相��in比拟。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像中的异常检测对于识别不同成像模态下的病理区域至关重要,如脑MRI、肝脏CT和颈动脉超声。
- 提出的无监督异常检测框架基于扩散模型,包含合成异常噪声函数和多阶段扩散过程。
- 合成异常噪声用于在健康图像中引入合成异常,使模型有效学习异常移除。
- 多阶段扩散过程能够逐步去噪,保留细节,提高图像质量。
- 该框架训练仅需要健康图像,无需异常训练样本和像素级注释。
- 实验结果证明该框架性能优越,可与全监督分割模型相比。
点此查看论文截图

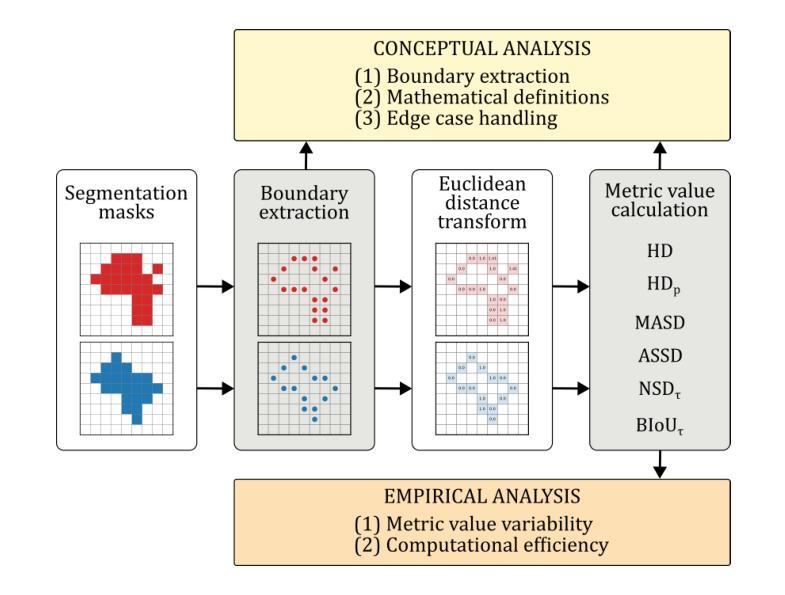
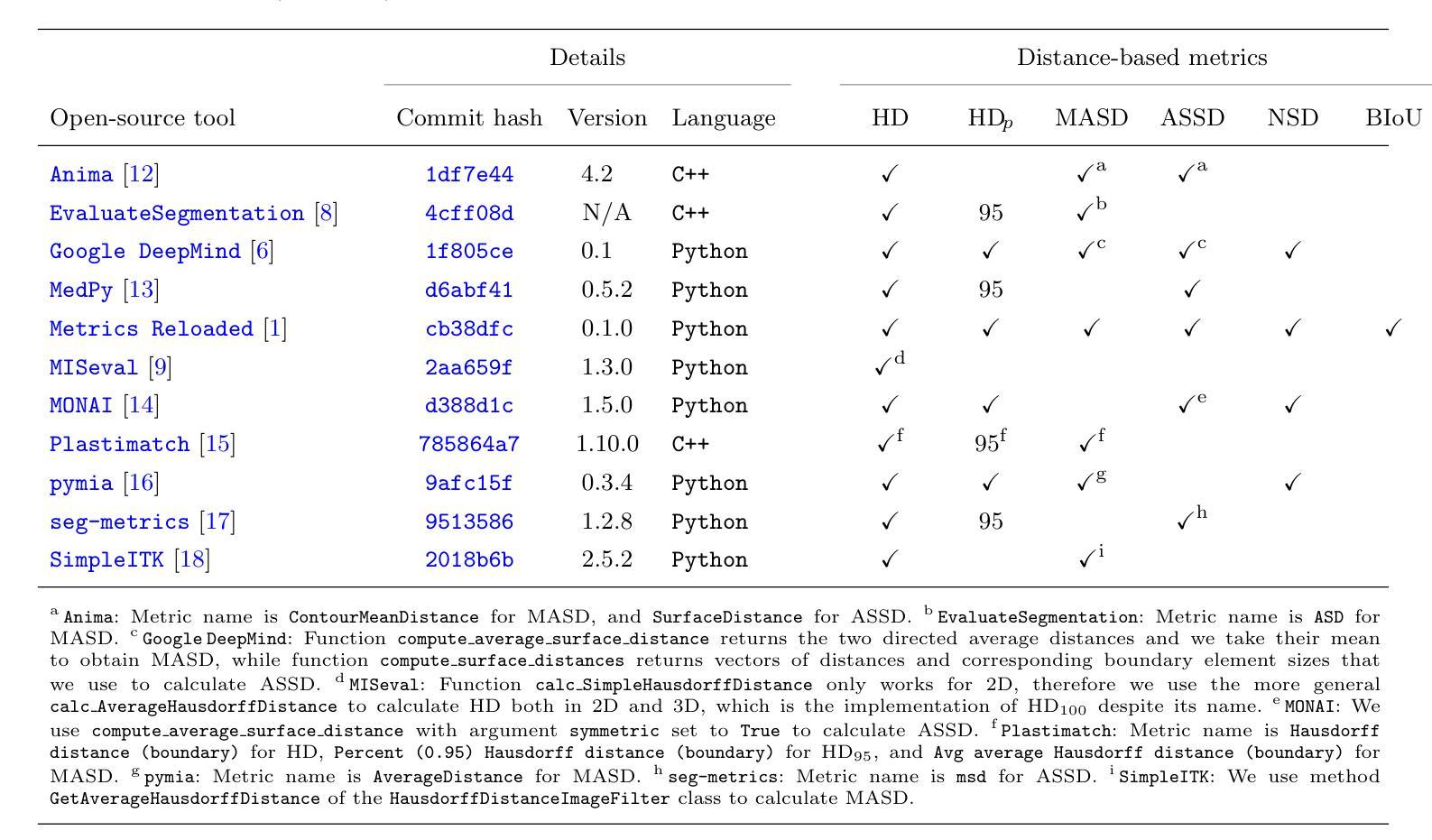
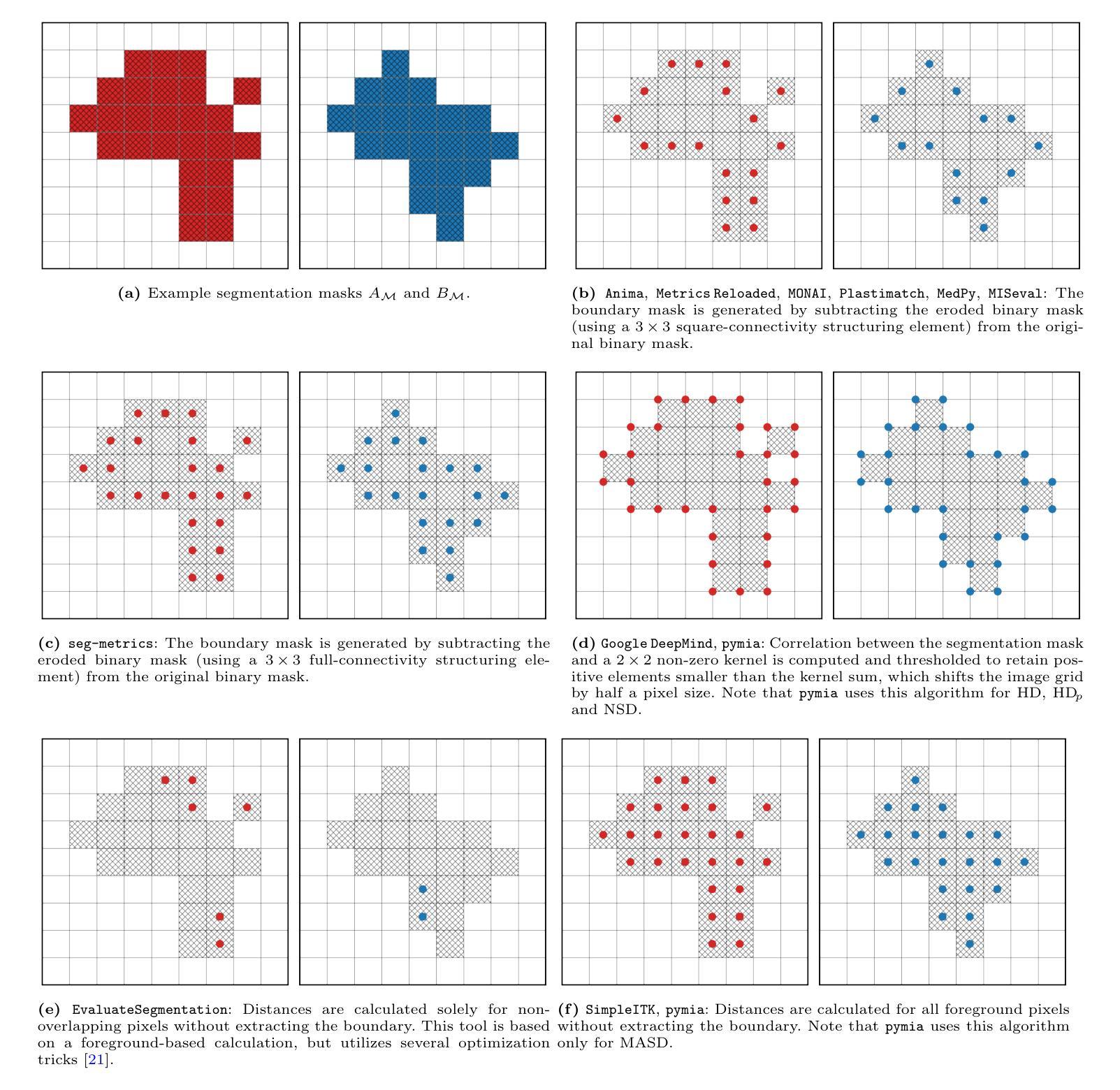
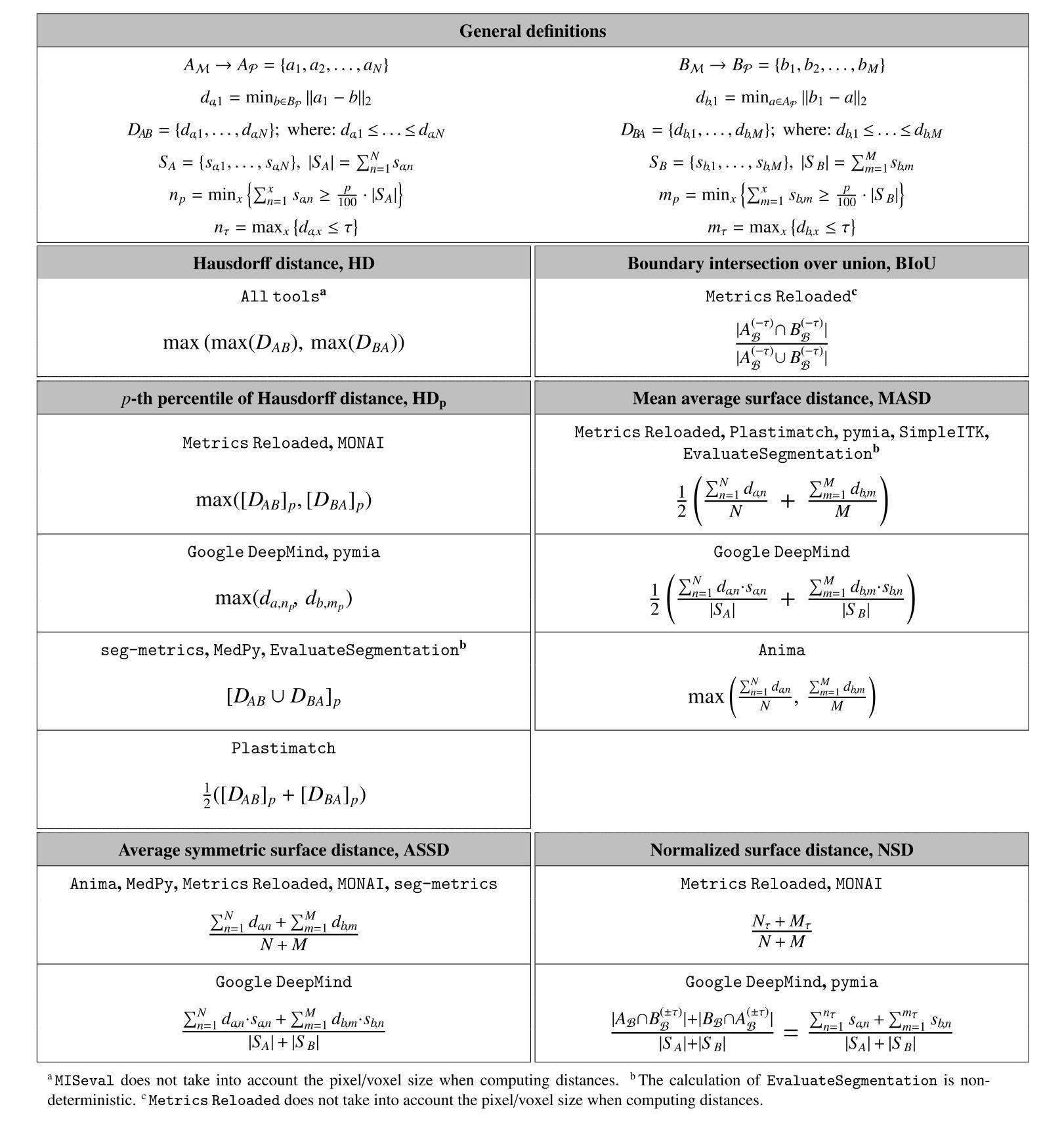
Understanding implementation pitfalls of distance-based metrics for image segmentation
Authors:Gasper Podobnik, Tomaz Vrtovec
Distance-based metrics, such as the Hausdorff distance (HD), are widely used to validate segmentation performance in (bio)medical imaging. However, their implementation is complex, and critical differences across open-source tools remain largely unrecognized by the community. These discrepancies undermine benchmarking efforts, introduce bias in biomarker calculations, and potentially distort medical device development and clinical commissioning. In this study, we systematically dissect 11 open-source tools that implement distance-based metric computation by performing both a conceptual analysis of their computational steps and an empirical analysis on representative two- and three-dimensional image datasets. Alarmingly, we observed deviations in HD exceeding 100 mm and identified multiple statistically significant differences between tools - demonstrating that statistically significant improvements on the same set of segmentations can be achieved simply by selecting a particular implementation. These findings cast doubts on the validity of prior comparisons of results across studies without accounting for the differences in metric implementations. To address this, we provide practical recommendations for tool selection; additionally, our conceptual analysis informs about the future evolution of implementing open-source tools.
基于距离的度量,如豪斯多夫距离(HD),在(生物)医学成像中广泛用于验证分割性能。然而,它们的实现过程复杂,开源工具之间的关键差异在很大程度上仍未得到社区的认可。这些差异破坏了基准测试工作,引入了生物标志物计算中的偏见,并可能扭曲医疗设备开发和临床委托。在本研究中,我们通过对其计算步骤的概念分析和对代表性二维和三维图像数据集的经验分析,系统地分析了实现基于距离的度量计算的11个开源工具。令人担忧的是,我们观察到HD超过100毫米的偏差,并在工具之间发现了多个统计学上的显著差异——这表明通过选择特定的实现方式,可以在同一组分割上实现统计学上的显著改善。这些发现对未考虑度量实现差异的研究结果之间的比较的有效性提出了质疑。为解决这一问题,我们提供了工具选择的实用建议;此外,我们的概念分析为开源工具的未来实施演变提供了信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要讨论了距离度量在生物医学成像领域中的使用,特别指出了距离度量实施中的复杂性和开源工具间的差异。这些差异对基准测试、生物标志物计算以及医疗设备研发和临床委托产生了负面影响。研究通过分析和实证测试了11个开源工具的距离度量计算功能,并指出在选择实现工具时所带来的巨大影响,提出工具选择的实用建议以及对未来工具实施发展的看法。存在的问题可能会导致以前的结果对比变得无效,影响相关研究和决策的制定。这些问题在医疗行业研究中是极具警示意义的关注点。重要的是在实践中要避免不正确的指标计算实施引起的失误,以减少不精确的研究结论导致的误解或潜在损害。在实际的医疗环境中,应采取额外的措施来确保所选指标实施的一致性和准确性。这项研究的结果和推荐可以为生物医学成像的科研和从业者提供宝贵的指导。总体来说,研究人员应对在利用这些开源工具进行计算时的微妙差异进行更多探讨。实施工具选择至关重要,这不仅影响了比较的公平性,也可能对整个研究结果造成偏见和误差的影响。为了实现更准确的评估结果,研究人员需要更加关注工具选择和使用的准确性问题。同时,对于未来的研究来说,需要关注如何改进现有工具并开发新的工具来减少这种差异的影响。总的来说,这项工作旨在推动对距离度量实施一致性的重视和讨论。随着技术的进步和研究的深入,对距离度量的准确性和一致性的要求也越来越高。通过识别现有工具之间的差异并制定相应的解决方案,我们可以推动生物医学成像领域的进步和发展。这将有助于推动更准确、更可靠的生物医学成像研究的开展。此外,这也强调了研究人员在进行相关实验时必须密切关注工具选择和使用的细节问题的重要性。这是保证实验结果的准确性和可靠性的关键步骤之一。这也凸显了在临床决策和研究中需要考虑跨多个开源工具实现的一致性要求的重要性问题的重要性,这对于医学图像的准确性和精确度至关重要。Key Takeaways:关键点概述:
一、距离度量在生物医学成像中的重要性及其广泛用途:用于验证分割性能;然而存在实现复杂性和工具间差异的问题。
二、开源工具间差异的影响:影响基准测试、生物标志物计算以及医疗设备研发和临床委托;可能导致先前研究结果对比失效。
三、研究方法和发现:分析并实证测试了多个开源工具的距离度量计算功能;观察到超过100毫米的Hausdorff距离偏差;不同工具间存在显著差异。
四、关于选择正确工具的实用建议:提出具体建议以解决当前的问题;强调了工具选择的重要性以及它对结果的影响。
五、未来研究方向:改进现有工具和开发新工具的需求;确保未来研究的一致性和准确性对于准确评估至关重要。概念分析为未来的开放源工具发展提供了指导方向。
六、提醒重视一致性讨论的重要性:强调技术进步和研究深入对距离度量准确性和一致性的要求越来越高;推动行业进步和发展需要关注这个问题。
点此查看论文截图

An Effective UNet Using Feature Interaction and Fusion for Organ Segmentation in Medical Image
Authors:Xiaolin Gou, Chuanlin Liao, Jizhe Zhou, Fengshuo Ye, Yi Lin
Nowadays, pre-trained encoders are widely used in medical image segmentation due to their strong capability in extracting rich and generalized feature representations. However, existing methods often fail to fully leverage these features, limiting segmentation performance. In this work, a novel U-shaped model is proposed to address the above issue, including three plug-and-play modules. A channel spatial interaction module is introduced to improve the quality of skip connection features by modeling inter-stage interactions between the encoder and decoder. A channel attention-based module integrating squeeze-and-excitation mechanisms with convolutional layers is employed in the decoder blocks to strengthen the representation of critical features while suppressing irrelevant ones. A multi-level fusion module is designed to aggregate multi-scale decoder features, improving spatial detail and consistency in the final prediction. Comprehensive experiments on the synapse multi-organ segmentation dataset and automated cardiac diagnosis challenge dataset demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving the highest average Dice score of 86.05% and 92.58%, yielding improvements of 1.15% and 0.26%, respectively. In addition, the proposed model provides a balance between accuracy and computational complexity, with only 86.91 million parameters and 23.26 giga floating-point operations.
目前,由于预训练编码器在提取丰富且通用的特征表示方面的强大能力,它已广泛应用于医学图像分割。然而,现有方法往往无法充分利用这些特征,从而限制了分割性能。针对上述问题,本文提出了一种新型的U形模型,包括三个即插即用的模块。引入通道空间交互模块,通过建模编码器与解码器之间的阶段间交互,提高跳过连接特征的质量。在解码器块中采用结合压缩和激发机制与卷积层的通道注意模块,以加强关键特征的表达并抑制无关特征。设计了一种多层次融合模块,用于聚合多尺度解码器特征,提高最终预测中的空间细节和一致性。在突触多器官分割数据集和自动心脏诊断挑战赛数据集上的综合实验表明,该模型优于现有最先进的方法,取得了最高的平均Dice得分,分别为86.05%和92.58%,分别提高了1.15%和0.26%。此外,该模型在准确性与计算复杂度之间达到了平衡,仅有8691万个参数和23.26万亿次浮点运算。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型U型模型,用于解决现有医学图像分割方法未能充分利用预训练编码器提取的特征的问题。模型包括三个即插即用模块,通过引入通道空间交互模块、通道注意力模块和多级融合模块,提高了特征表示的丰富性和质量。实验结果显示,该模型在多个数据集上实现了最佳性能,具有较高的平均Dice得分。同时,该模型具有计算复杂度与准确性之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练编码器在医学图像分割中广泛应用,但现有方法未能充分利用其特征。
- 新型U型模型包括三个即插即用模块,旨在解决此问题。
- 引入通道空间交互模块,改进了跳过连接特征的质量。
- 通道注意力模块结合挤压和激励机制,加强关键特征的表示,同时抑制不相关特征。
- 多级融合模块旨在融合多尺度解码器特征,提高最终预测的准确性和一致性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果显示,该模型性能优于现有方法,具有最高的平均Dice得分。
点此查看论文截图

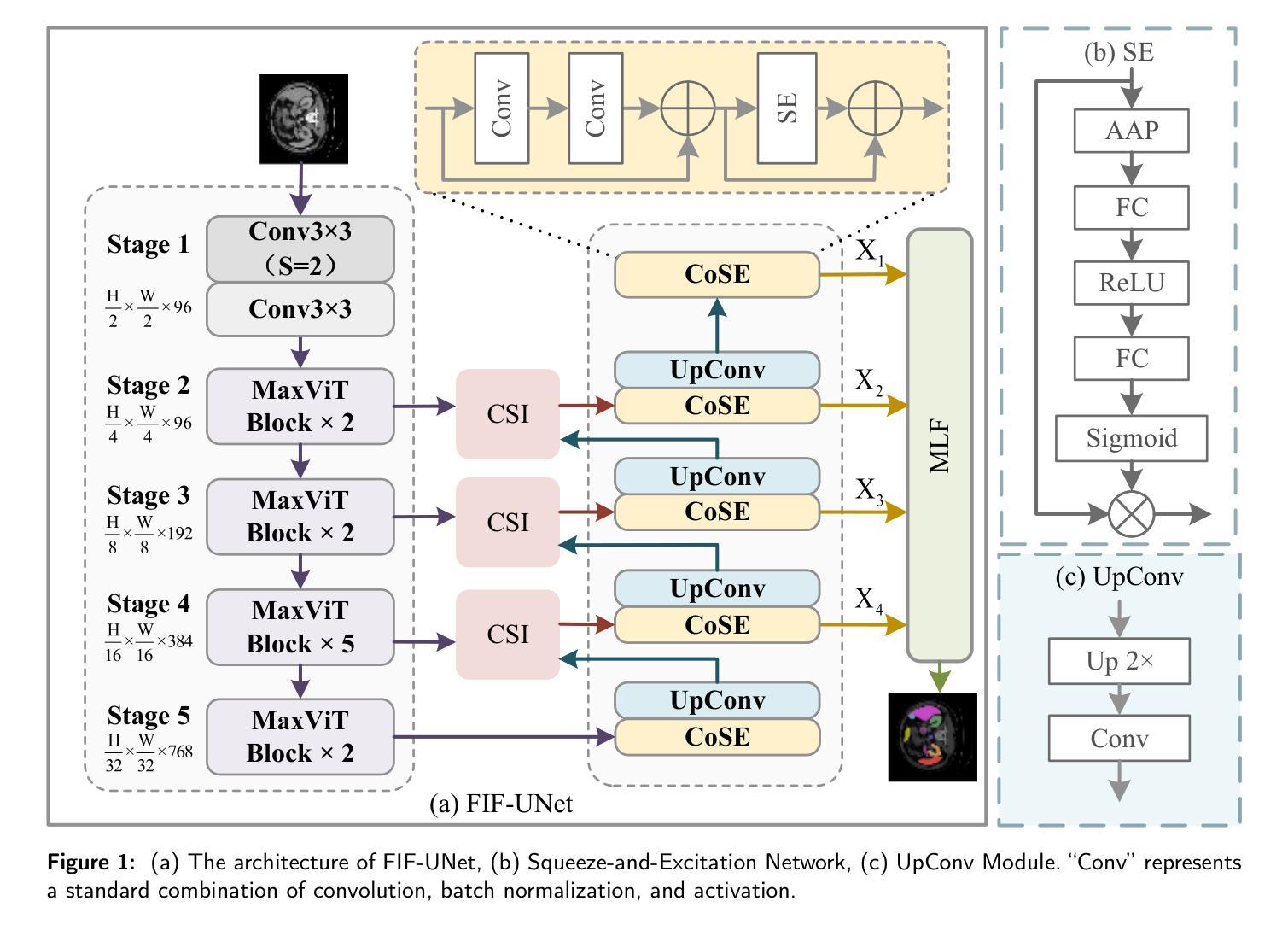
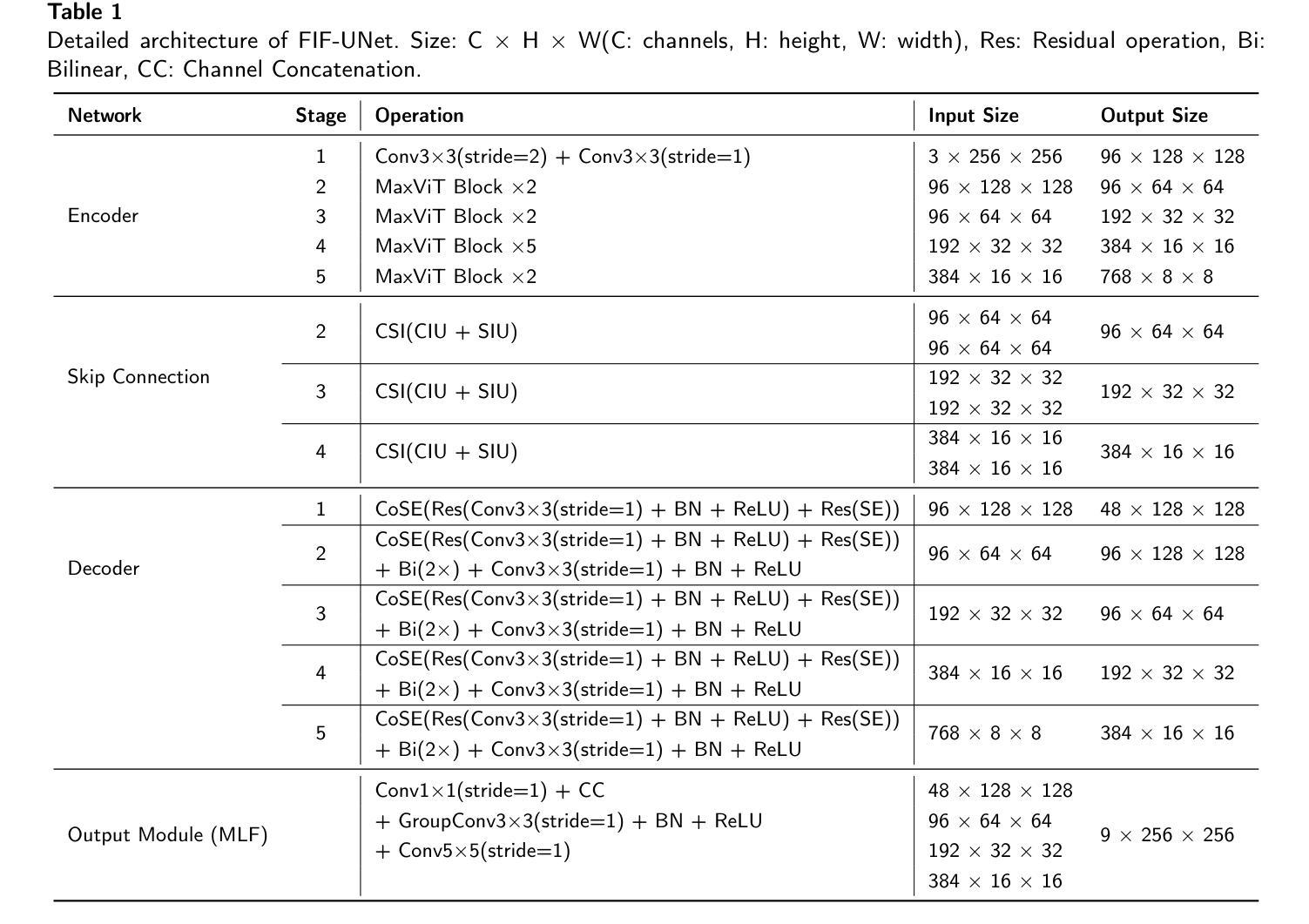
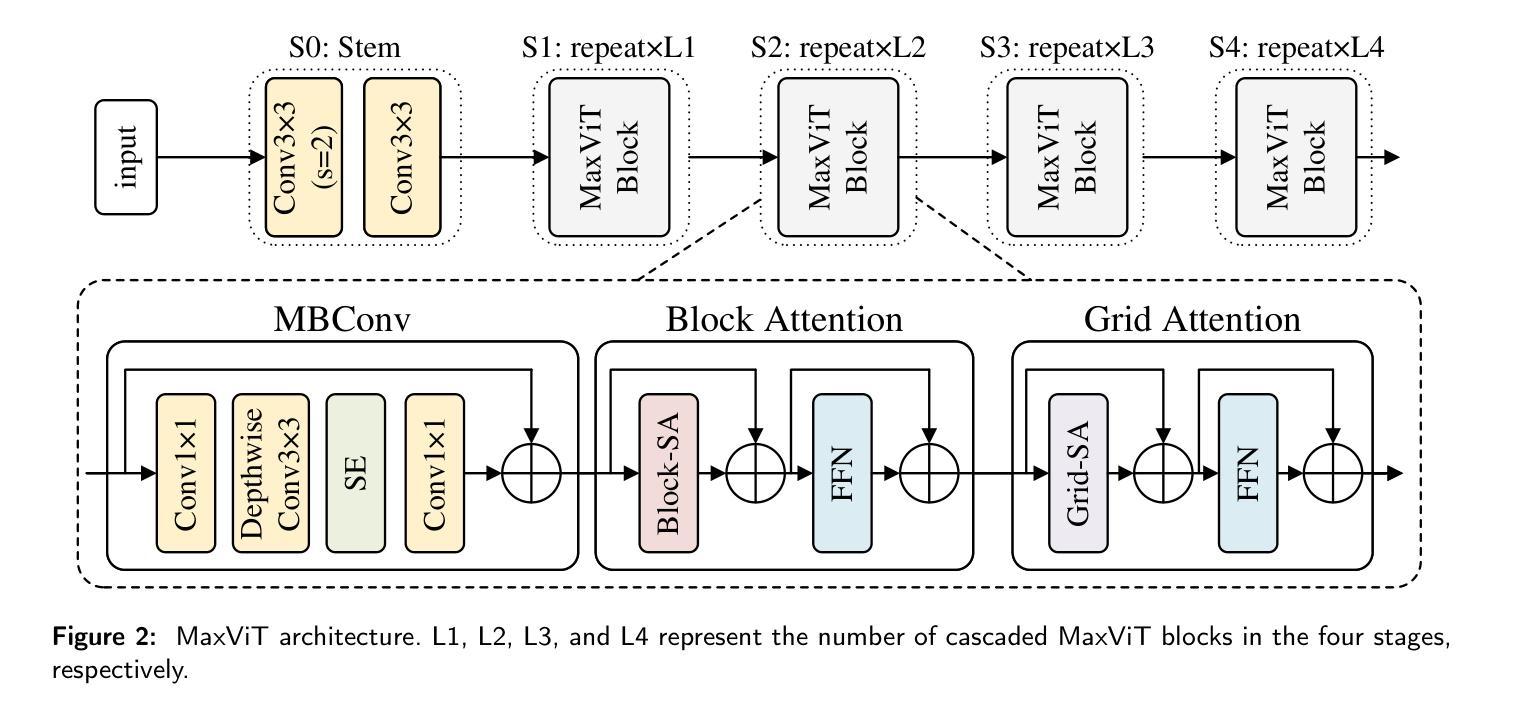
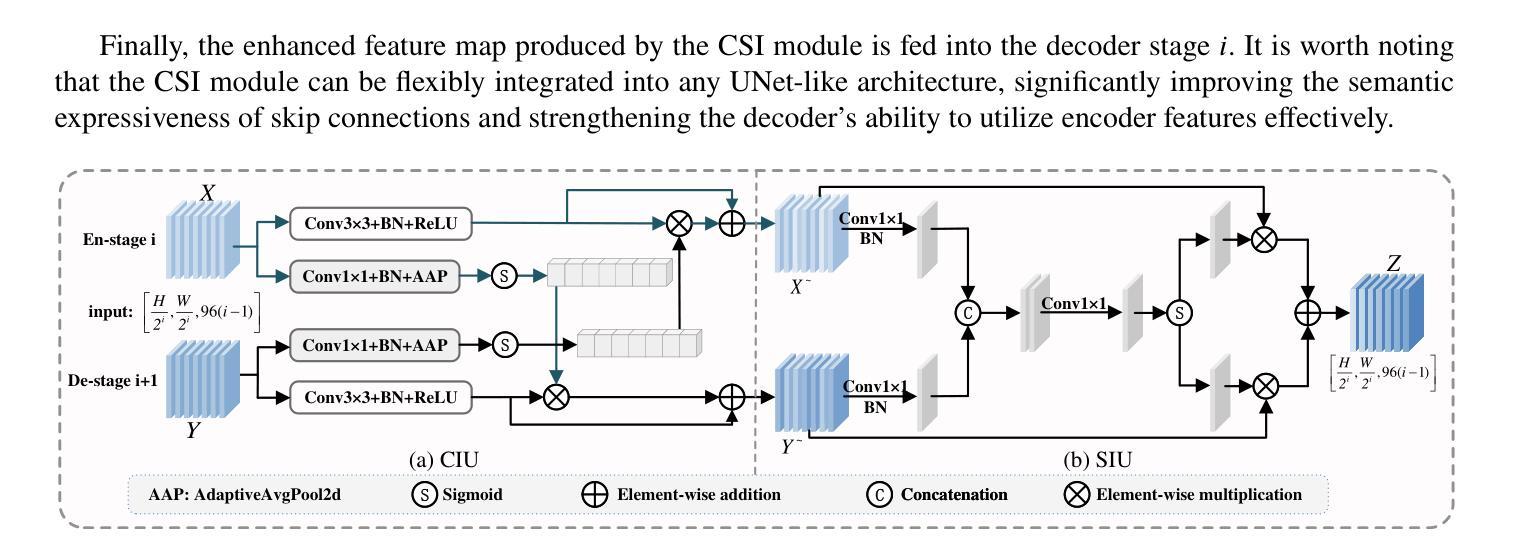
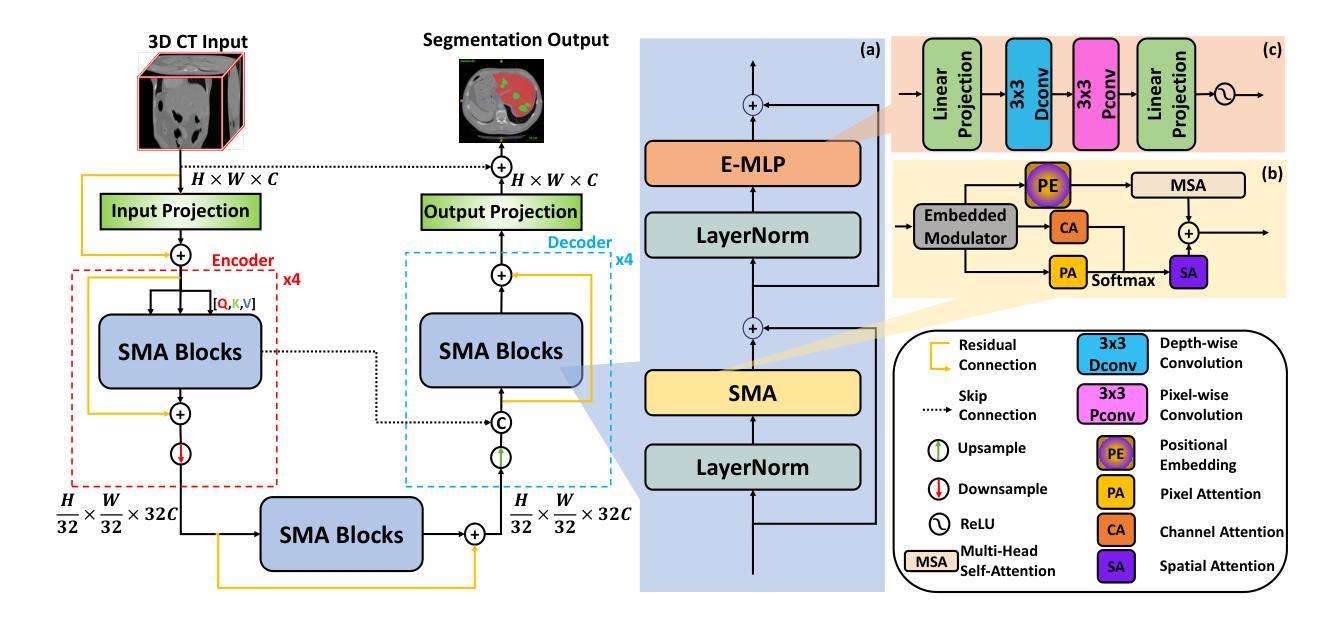
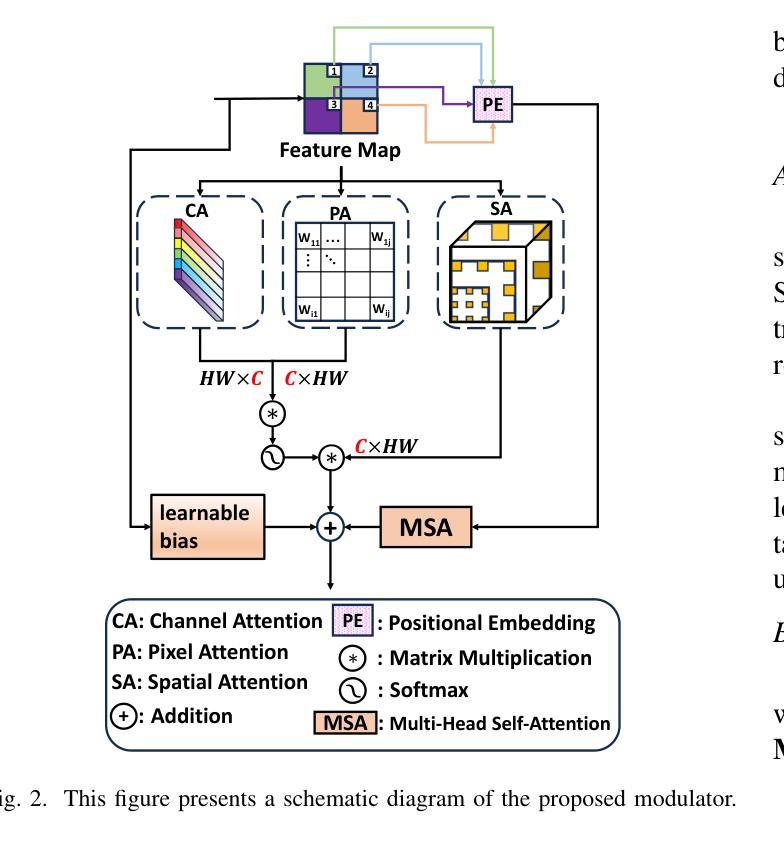
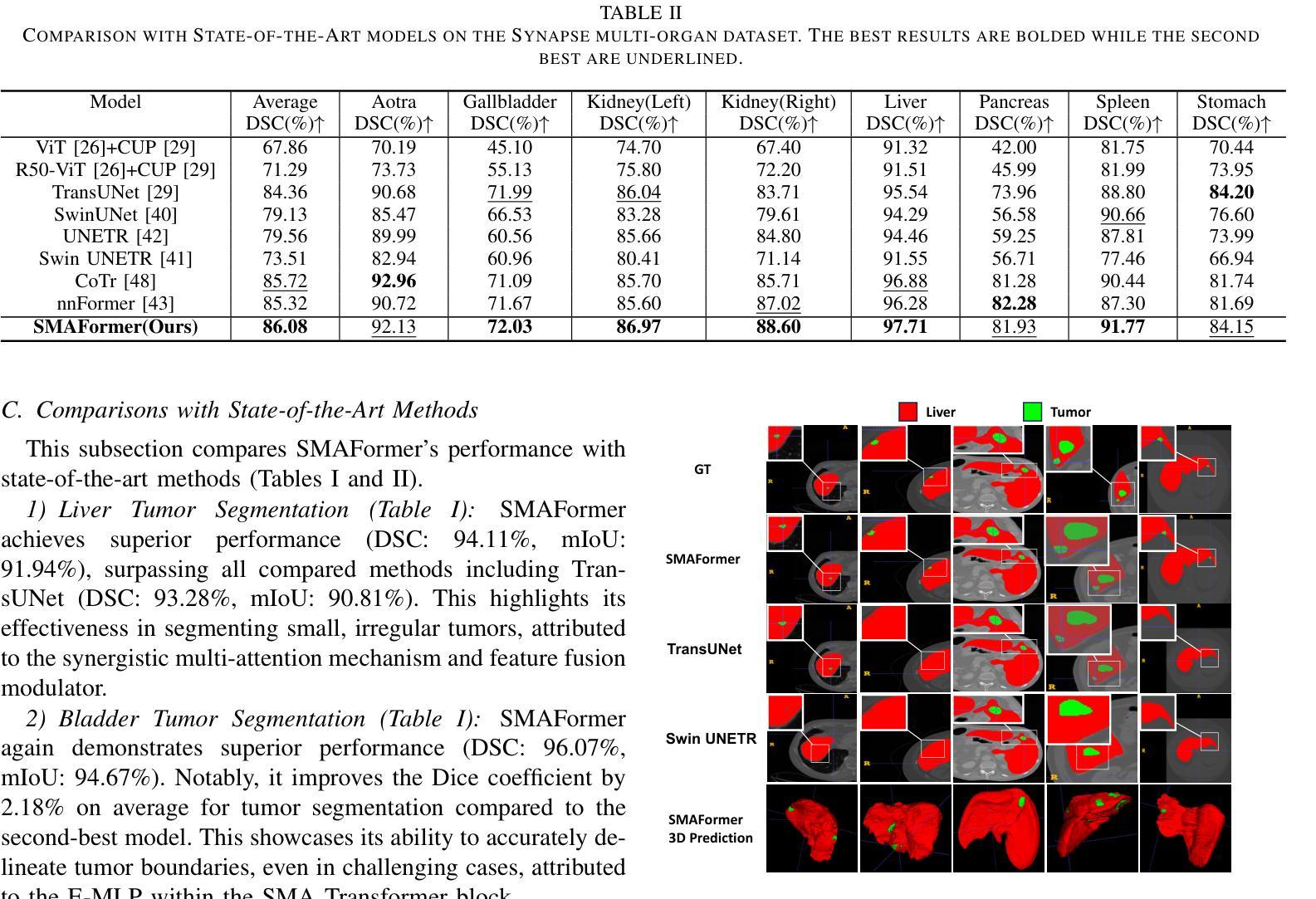
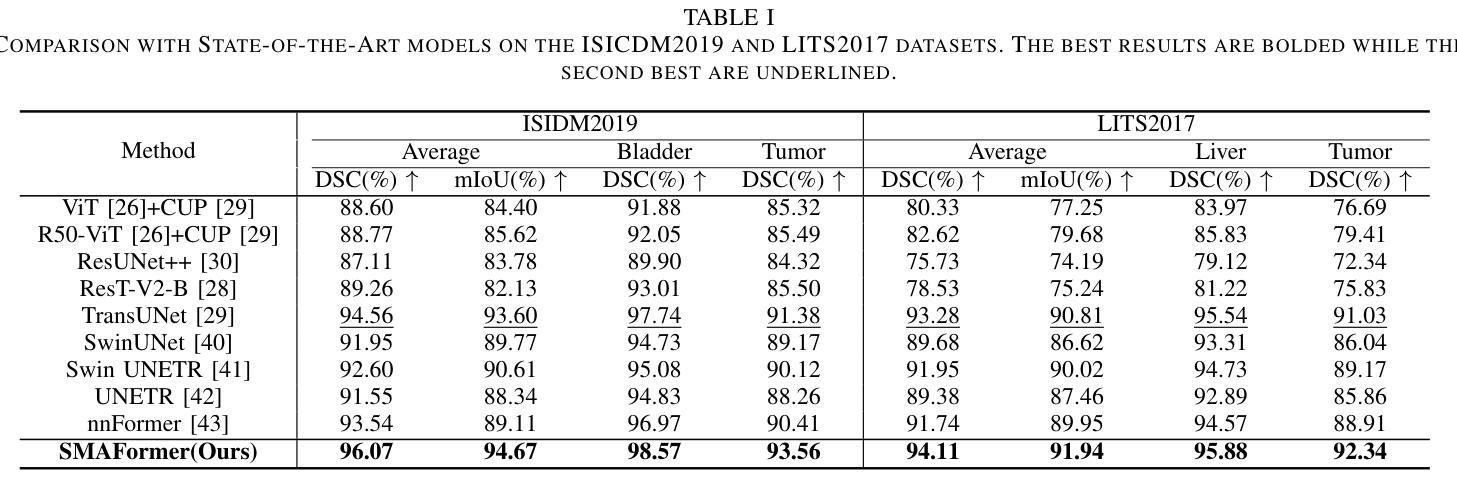
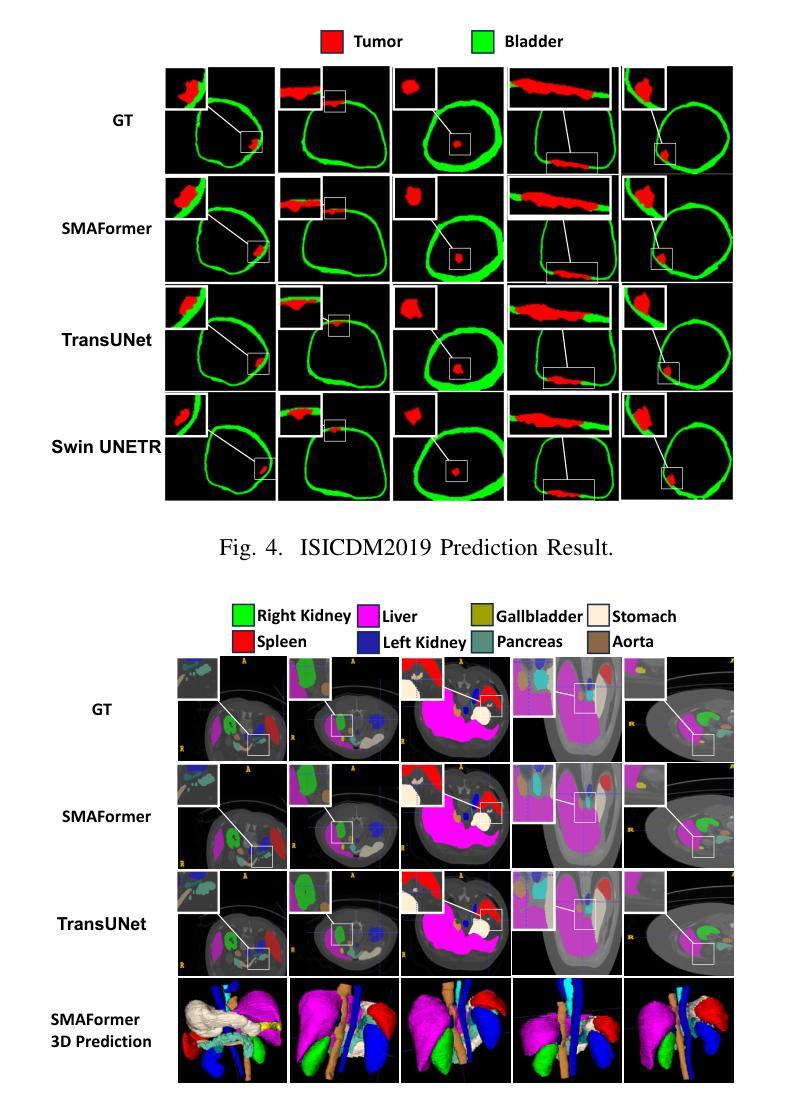
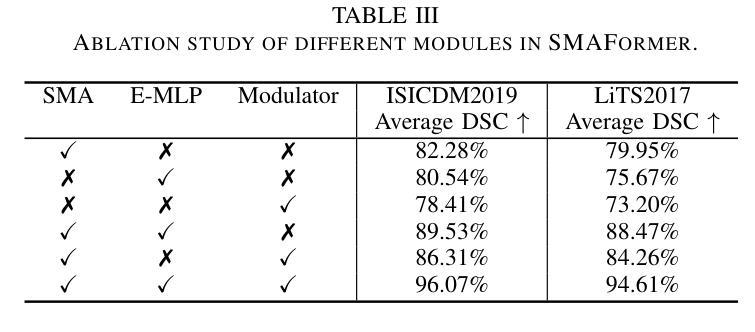
SMAFormer: Synergistic Multi-Attention Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Fuchen Zheng, Xuhang Chen, Weihuang Liu, Haolun Li, Yingtie Lei, Jiahui He, Chi-Man Pun, Shounjun Zhou
In medical image segmentation, specialized computer vision techniques, notably transformers grounded in attention mechanisms and residual networks employing skip connections, have been instrumental in advancing performance. Nonetheless, previous models often falter when segmenting small, irregularly shaped tumors. To this end, we introduce SMAFormer, an efficient, Transformer-based architecture that fuses multiple attention mechanisms for enhanced segmentation of small tumors and organs. SMAFormer can capture both local and global features for medical image segmentation. The architecture comprises two pivotal components. First, a Synergistic Multi-Attention (SMA) Transformer block is proposed, which has the benefits of Pixel Attention, Channel Attention, and Spatial Attention for feature enrichment. Second, addressing the challenge of information loss incurred during attention mechanism transitions and feature fusion, we design a Feature Fusion Modulator. This module bolsters the integration between the channel and spatial attention by mitigating reshaping-induced information attrition. To evaluate our method, we conduct extensive experiments on various medical image segmentation tasks, including multi-organ, liver tumor, and bladder tumor segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/CXH-Research/SMAFormer.
在医学图像分割领域,特殊的计算机视觉技术,特别是基于注意力机制的变压器和采用跳跃连接的残差网络,对于提升性能起到了重要作用。然而,以前的模型在分割小而形状不规则的肿瘤时经常会遇到困难。为此,我们引入了SMAFormer,这是一种高效的基于变压器的架构,融合了多种注意力机制,用于改进小肿瘤和器官的分割。SMAFormer可以捕获医学图像分割的局部和全局特征。该架构包含两个关键组成部分。首先,提出了协同多注意力(SMA)变压器块,具有像素注意力、通道注意力和空间注意力的优点,以丰富特征。其次,为了解决注意力机制转换和特征融合过程中信息损失的问题,我们设计了一个特征融合调制器。该模块通过减轻重塑引起的信息衰减,加强了通道和空间注意力之间的整合。为了评估我们的方法,我们在各种医学图像分割任务上进行了大量实验,包括多器官、肝脏肿瘤和膀胱肿瘤分割,取得了最新结果。代码和模型可在https://github.com/CXH-Research/SMAFormer获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE BIBM 2024
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像分割领域,基于注意力机制的特殊计算机视觉技术,如变压器和残差网络,已经推动了性能的提升。然而,以往模型在分割小型、形状不规则的肿瘤时常常表现不佳。为此,我们引入了SMAFormer,这是一种高效的基于变压器的架构,融合了多种注意力机制,用于改进小型肿瘤和器官的分割。SMAFormer能够捕捉医疗图像分割的局部和全局特征。其架构包括两个关键组件:一是协同多注意力(SMA)变压器块,具有像素注意力、通道注意力和空间注意力的优点,用于特征丰富;二是解决注意力机制转换和特征融合过程中信息损失的问题,我们设计了特征融合调制器。该模块通过缓解重塑引起的信息衰减,加强了通道和空间注意力之间的集成。在多项医学图像分割任务上进行了广泛实验验证,包括多器官、肝脏肿瘤和膀胱肿瘤分割,取得了最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中,基于注意力机制的计算机视觉技术提升了性能。
- 现有模型在分割小型、形状不规则的肿瘤时存在挑战。
- 引入SMAFormer架构,融合多种注意力机制改进小型肿瘤和器官分割。
- SMAFormer包括协同多注意力(SMA)变压器块和特征融合调制器两个关键组件。
- SMA变压器块具有像素、通道和空间注意力的优点。
- 特征融合调制器解决了信息损失的问题,增强了通道与空间注意力的集成。
- 在多个医学图像分割任务上取得最新成果,包括多器官、肝脏和膀胱肿瘤的分割。
点此查看论文截图