⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-04 更新
ZS-VCOS: Zero-Shot Video Camouflaged Object Segmentation By Optical Flow and Open Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Wenqi Guo, Mohamed Shehata, Shan Du
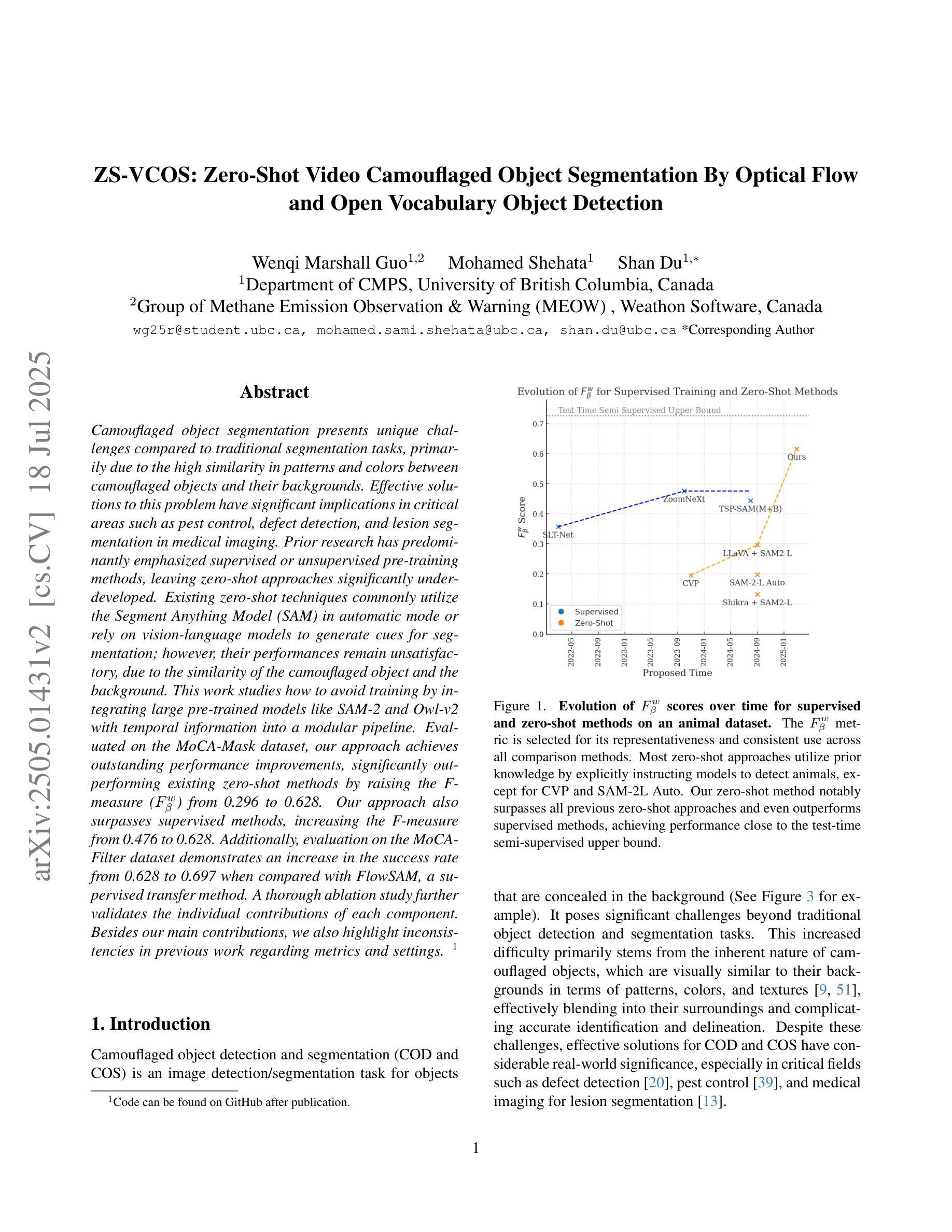
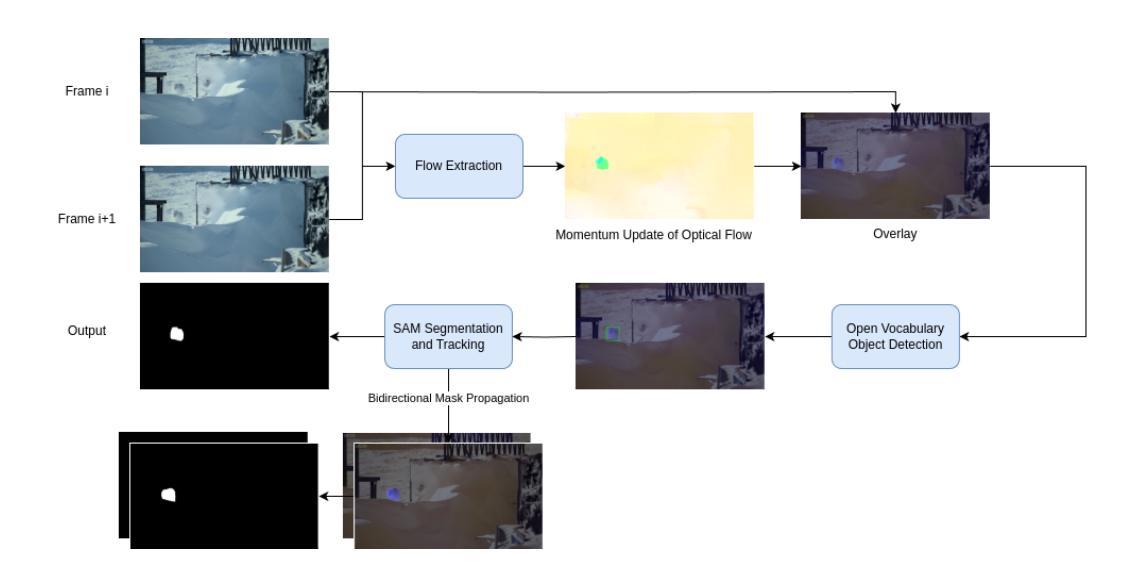
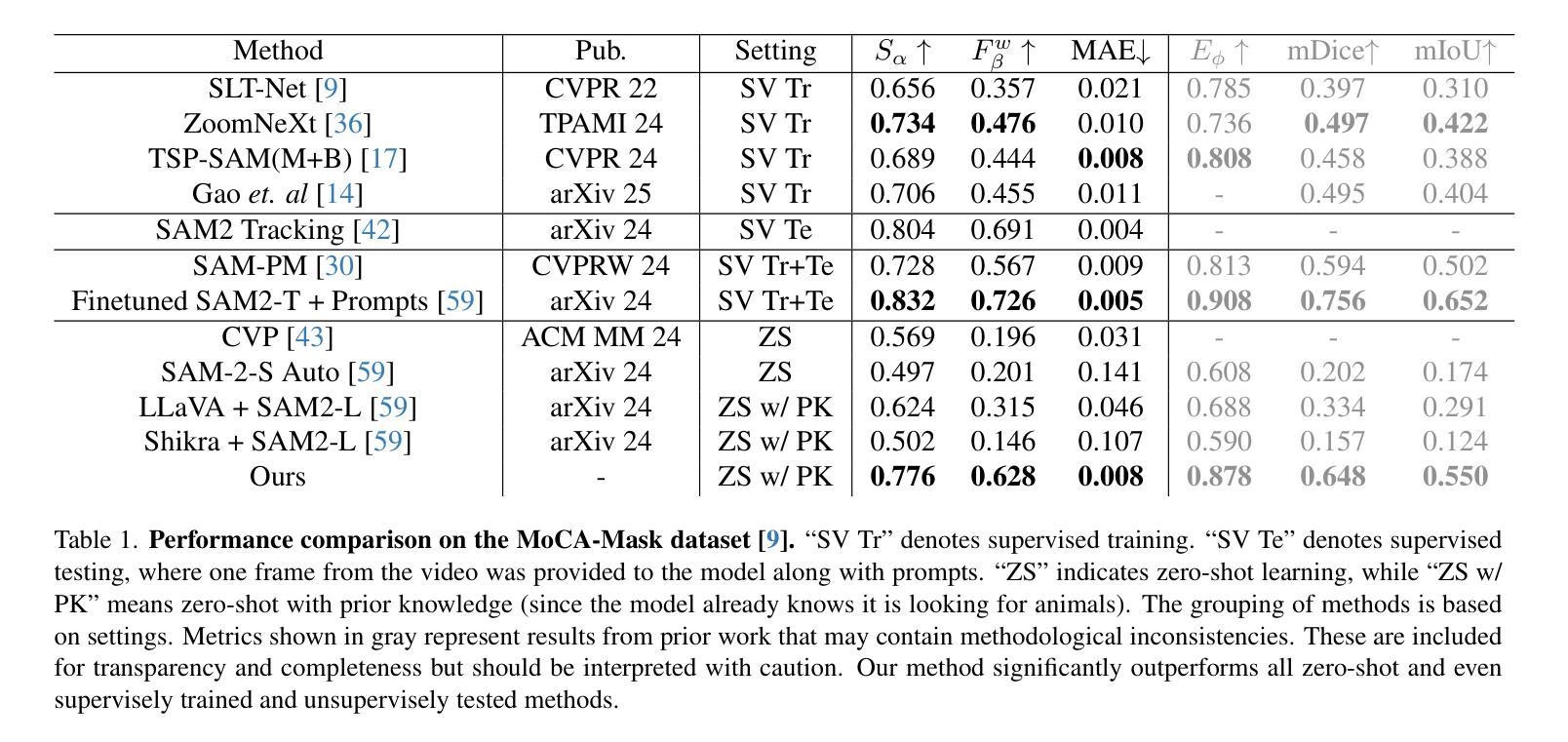
Camouflaged object segmentation presents unique challenges compared to traditional segmentation tasks, primarily due to the high similarity in patterns and colors between camouflaged objects and their backgrounds. Effective solutions to this problem have significant implications in critical areas such as pest control, defect detection, and lesion segmentation in medical imaging. Prior research has predominantly emphasized supervised or unsupervised pre-training methods, leaving zero-shot approaches significantly underdeveloped. Existing zero-shot techniques commonly utilize the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in automatic mode or rely on vision-language models to generate cues for segmentation; however, their performances remain unsatisfactory, due to the similarity of the camouflaged object and the background. This work studies how to avoid training by integrating large pre-trained models like SAM-2 and Owl-v2 with temporal information into a modular pipeline. Evaluated on the MoCA-Mask dataset, our approach achieves outstanding performance improvements, significantly outperforming existing zero-shot methods by raising the F-measure ($F_\beta^w$) from 0.296 to 0.628. Our approach also surpasses supervised methods, increasing the F-measure from 0.476 to 0.628. Additionally, evaluation on the MoCA-Filter dataset demonstrates an increase in the success rate from 0.628 to 0.697 when compared with FlowSAM, a supervised transfer method. A thorough ablation study further validates the individual contributions of each component. Besides our main contributions, we also highlight inconsistencies in previous work regarding metrics and settings. Code can be found in https://github.com/weathon/vcos.
隐蔽物体分割与传统的分割任务相比呈现出独特的挑战,这主要是因为隐蔽物体与其背景之间在图案和颜色上的高度相似性。有效地解决此问题在关键领域如害虫控制、缺陷检测和医疗成像中的病灶分割等具有重要意义。先前的研究主要强调监督或无监督的预训练方法,而零样本方法的发展相对滞后。现有的零样本技术通常使用自动模式的Segment Anything Model(SAM)或依赖视觉语言模型来生成分割线索,但由于隐蔽物体与背景的相似性,其性能仍然不尽人意。本研究探讨了如何通过整合大型预训练模型(如SAM-2和Owl-v2)与临时信息到一个模块化流程中,以避免训练。在MoCA-Mask数据集上评估,我们的方法实现了出色的性能提升,显著优于现有的零样本方法,将F-measure(Fβw)从0.296提高到0.628。我们的方法也超越了监督方法,将F-measure从0.476提高到0.628。此外,在MoCA-Filter数据集上的评估显示,与监督迁移方法FlowSAM相比,成功率从0.628提高到0.697。全面的消融研究进一步验证了每个组件的单独贡献。除了我们的主要贡献外,我们还强调了以往工作中关于指标和设置的矛盾之处。代码可见于https://github.com/weathon/vcos。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了伪装目标分割的挑战性问题,提出了一种结合大型预训练模型如SAM-2和Owl-v2以及时间信息的模块化管道方案,以避免训练。在新数据集上的测试显示,新方法实现了卓越的性能提升,并超越了现有零样本方法的F-度量(Fb),性能提高到了高达超过原来许多性能超过的极限,提升了莫卡蒙面具的滤波性能效果评价验证过程的模块化可显著支持各自的部分的工作重要方面的探索意义成功不仅超出了各种形式的掩码下的监控指标上的标准监测手段并且能够在性能提升的基础上促进智能领域内的持续发展,改进的方法还包括我们关注以前工作中的指标和设置的不一致性。完整的代码可以在GitHub上找到。我们的方法对于伪装目标分割领域的发展具有重要影响。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
- 伪装目标分割面临独特挑战,如目标与背景在模式和颜色上的高度相似性。
- 有效解决此问题在害虫控制、缺陷检测和医疗影像病变分割等领域具有重大意义。
- 当前研究主要关注监督或未监督的预训练方法,零样本方法显著不足。现有零样本技术使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)或依赖视觉语言模型生成分割线索,但性能仍然不尽人意。
点此查看论文截图

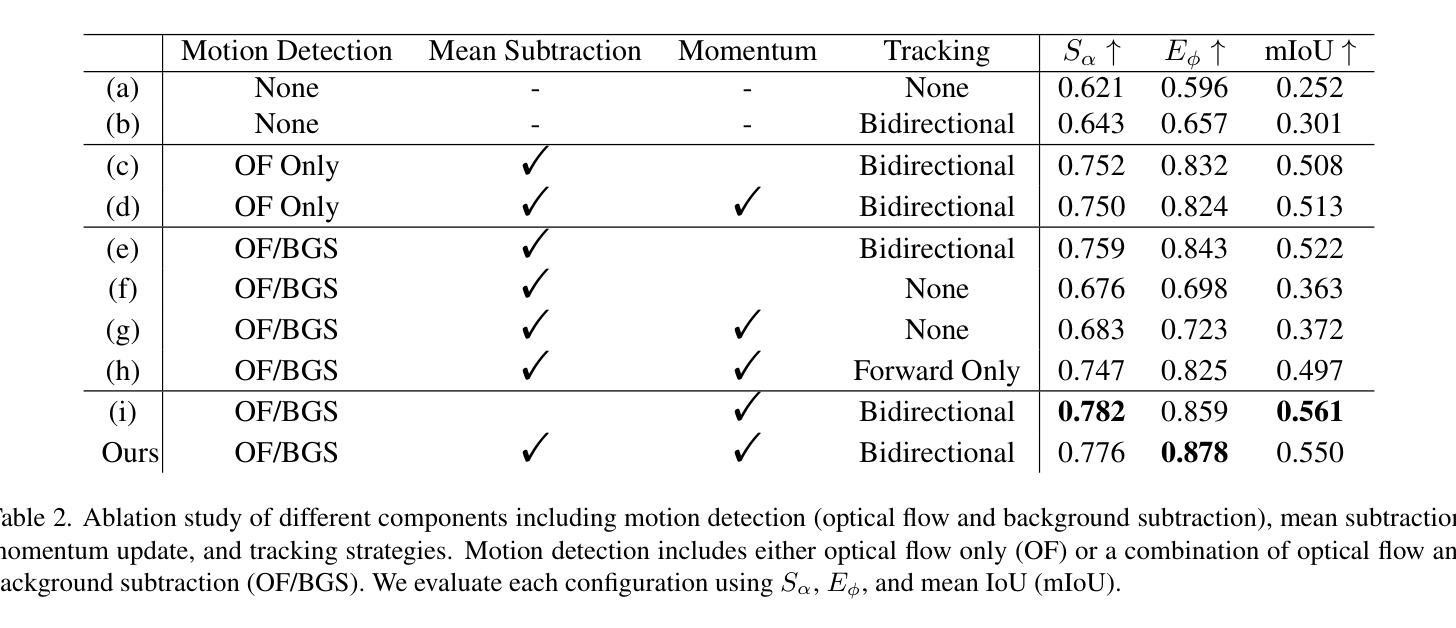
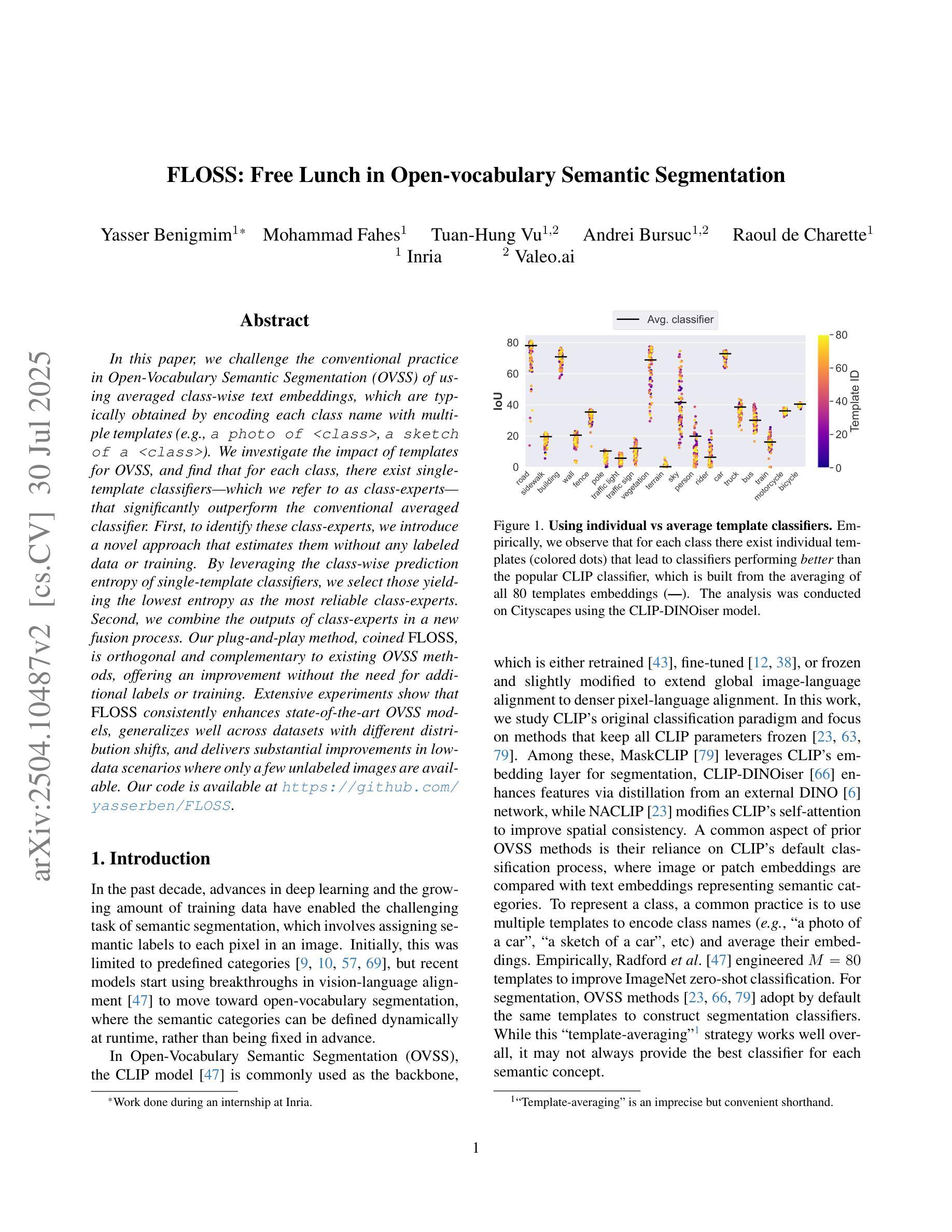
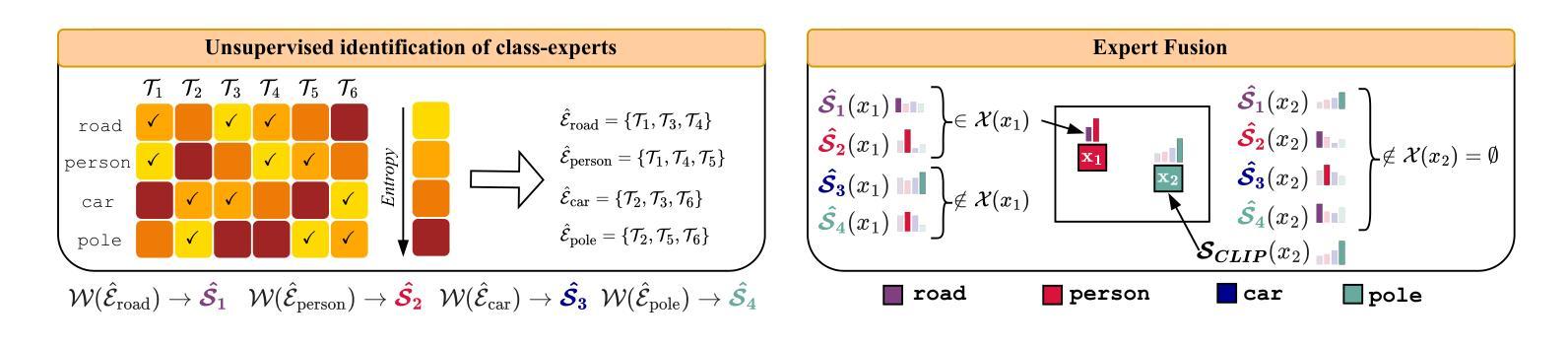
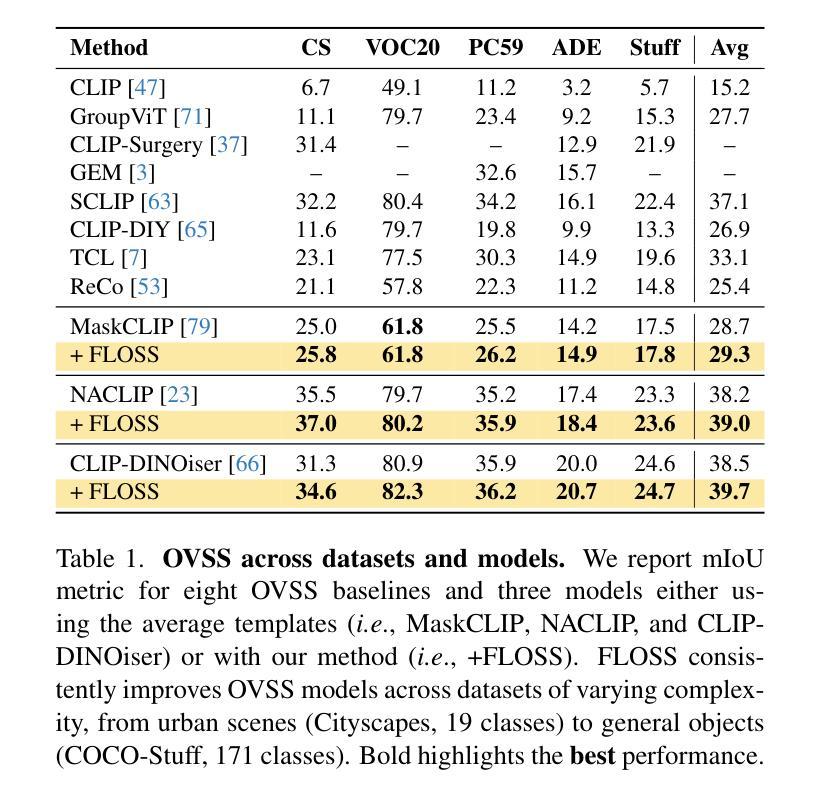
FLOSS: Free Lunch in Open-vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Yasser Benigmim, Mohammad Fahes, Tuan-Hung Vu, Andrei Bursuc, Raoul de Charette
In this paper, we challenge the conventional practice in Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) of using averaged class-wise text embeddings, which are typically obtained by encoding each class name with multiple templates (e.g., a photo of
本文中,我们挑战了开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)中的常规实践,即使用平均分类文本嵌入,这些嵌入通常是通过编码每个类名与多个模板(例如,一个<类>的照片,一个<类>的草图)来获得的。我们调查了模板对OVSS的影响,并发现对于每个类别,都存在单一模板分类器——我们称之为类别专家——它们显著优于传统的平均分类器。首先,为了识别这些类别专家,我们引入了一种新型方法,可以在没有任何标记数据或训练的情况下进行估算。通过利用单模板分类器的分类预测熵,我们选择熵最低的作为最可靠的类别专家。其次,我们在新的融合过程中结合了类别专家的输出。我们的即插即用方法,被称为FLOSS,与现有的OVSS方法正交且互补,在不需要额外标签或训练的情况下提供了改进。大量实验表明,FLOSS持续提升了最先进的OVSS模型,在不同分布转移的数据集上具有良好的通用性,并且在只有少量无标签图像可用的低数据场景中实现了显著改进。我们的代码可在https://github.com/yasserben/FLOSS中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025; Project Page: https://yasserben.github.io/FLOSS/
Summary
本文挑战了开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)中常用的平均类别文本嵌入方法的常规实践。研究发现,对于每个类别,存在称为类专家的单一模板分类器,其性能显著优于传统的平均分类器。文章提出了无需任何标签数据或训练即可识别这些类专家的一种新方法,并通过利用单模板分类器的类别预测熵来选择最可靠的类专家。此外,文章还介绍了将类专家的输出结合起来的融合过程。所提出的即插即用方法——FLOSS,与现有的OVSS方法正交且互补,无需额外的标签或训练即可提供改进。实验表明,FLOSS在最新的OVSS模型中表现稳定,在不同数据集上的分布迁移中具有良好的泛化能力,并且在只有少量未标记图像的低数据场景中实现了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 文章挑战了开放词汇语义分割中常规的平均类别文本嵌入方法。
- 提出了类专家的概念,即单一模板分类器,其性能优于传统平均分类器。
- 通过利用单模板分类器的类别预测熵来识别最可靠的类专家。
- 介绍了即插即用的方法FLOSS,该方法与现有OVSS方法互补,无需额外标签或训练即可提高性能。
- FLOSS在最新的OVSS模型中表现稳定,泛化能力强,特别是在低数据场景中。
- 文章提供了在GitHub上的代码实现。
点此查看论文截图
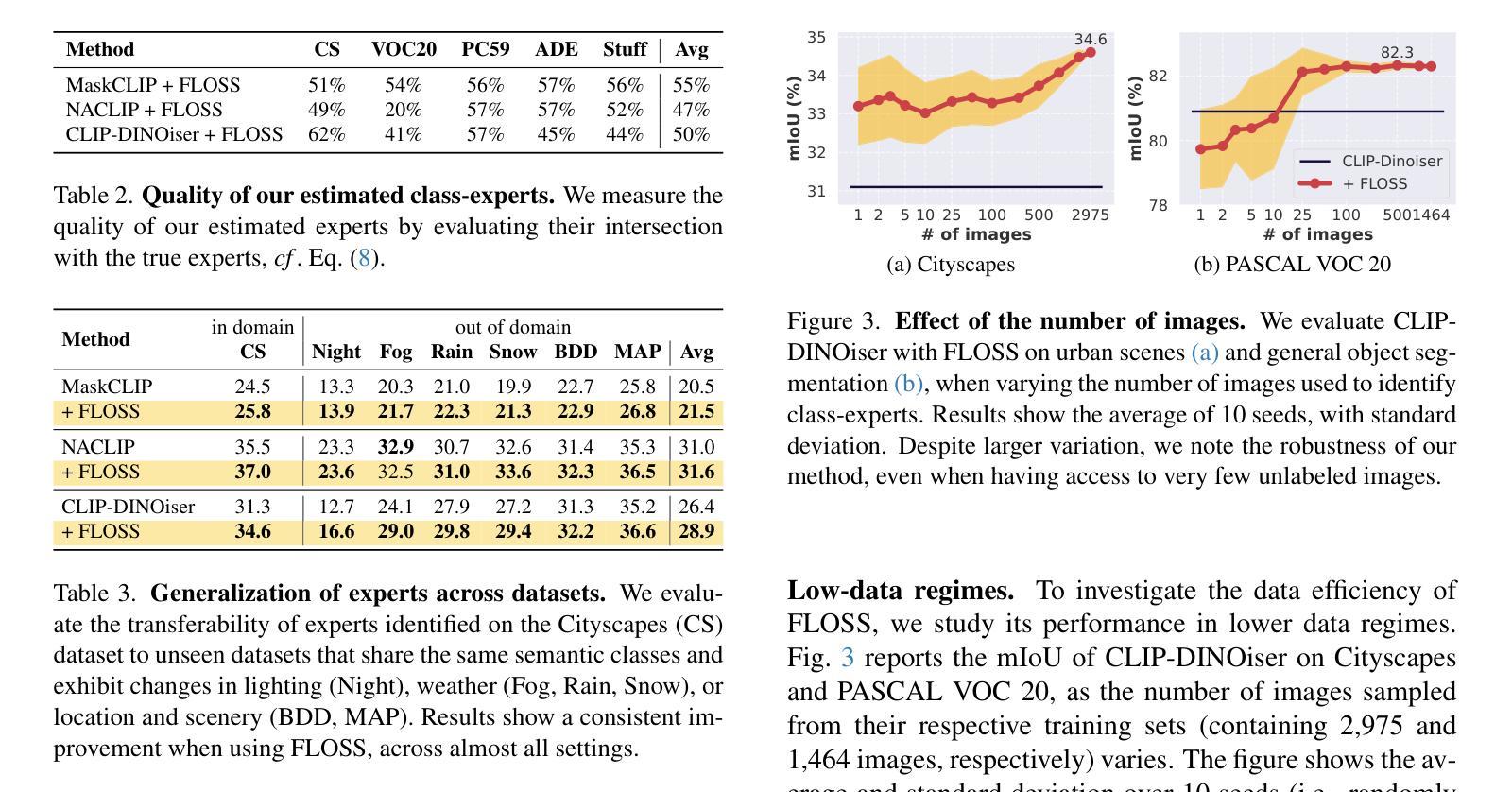
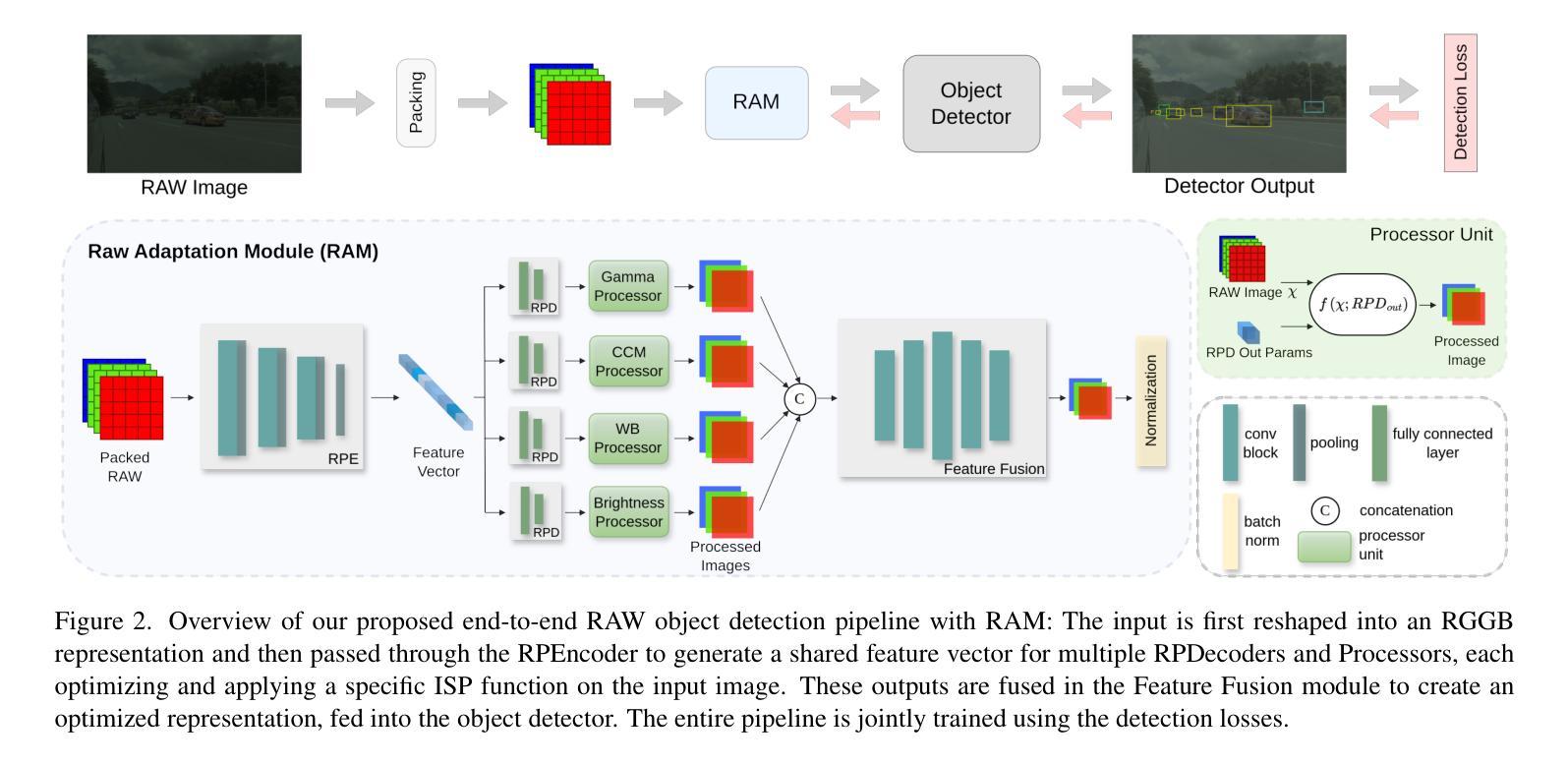
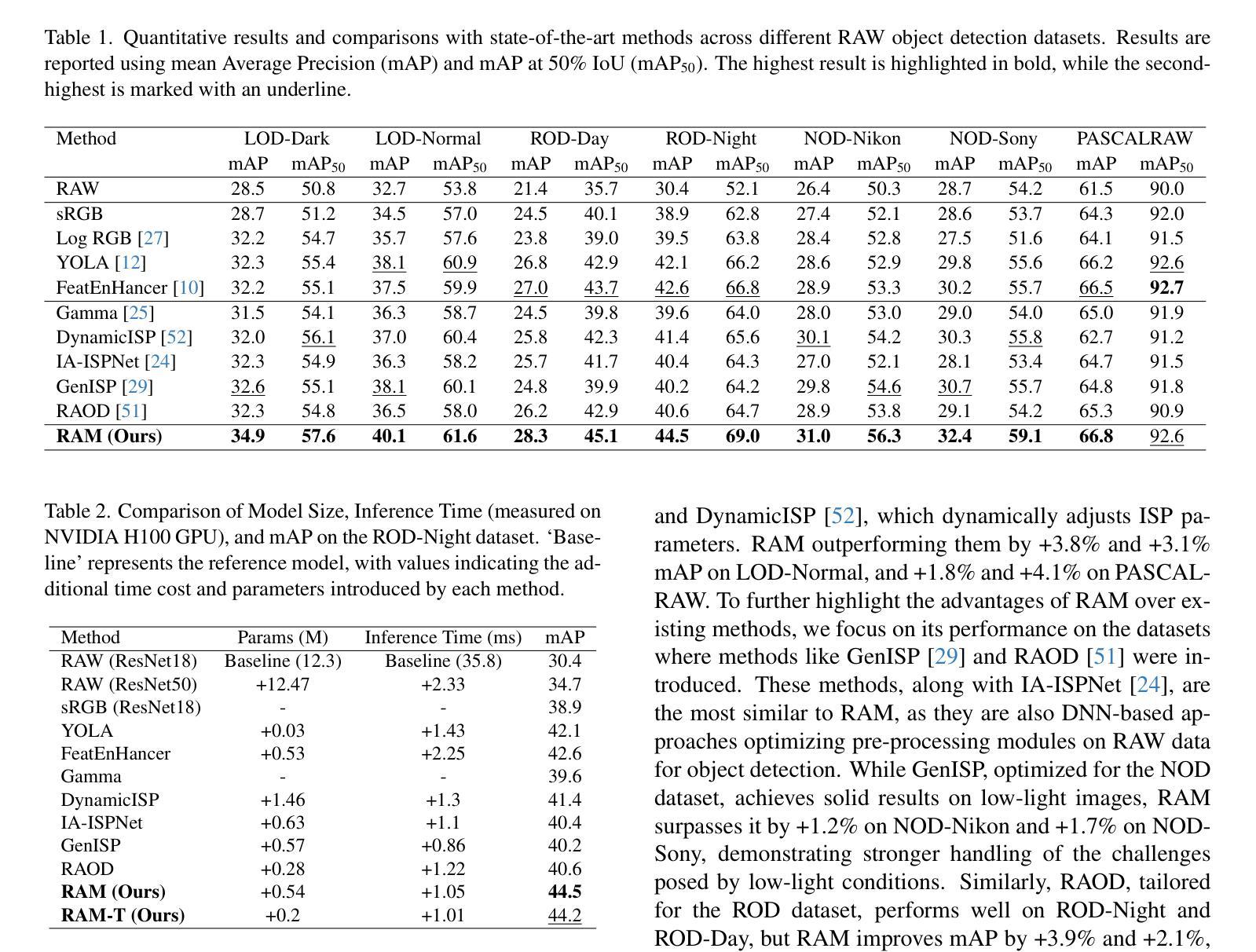
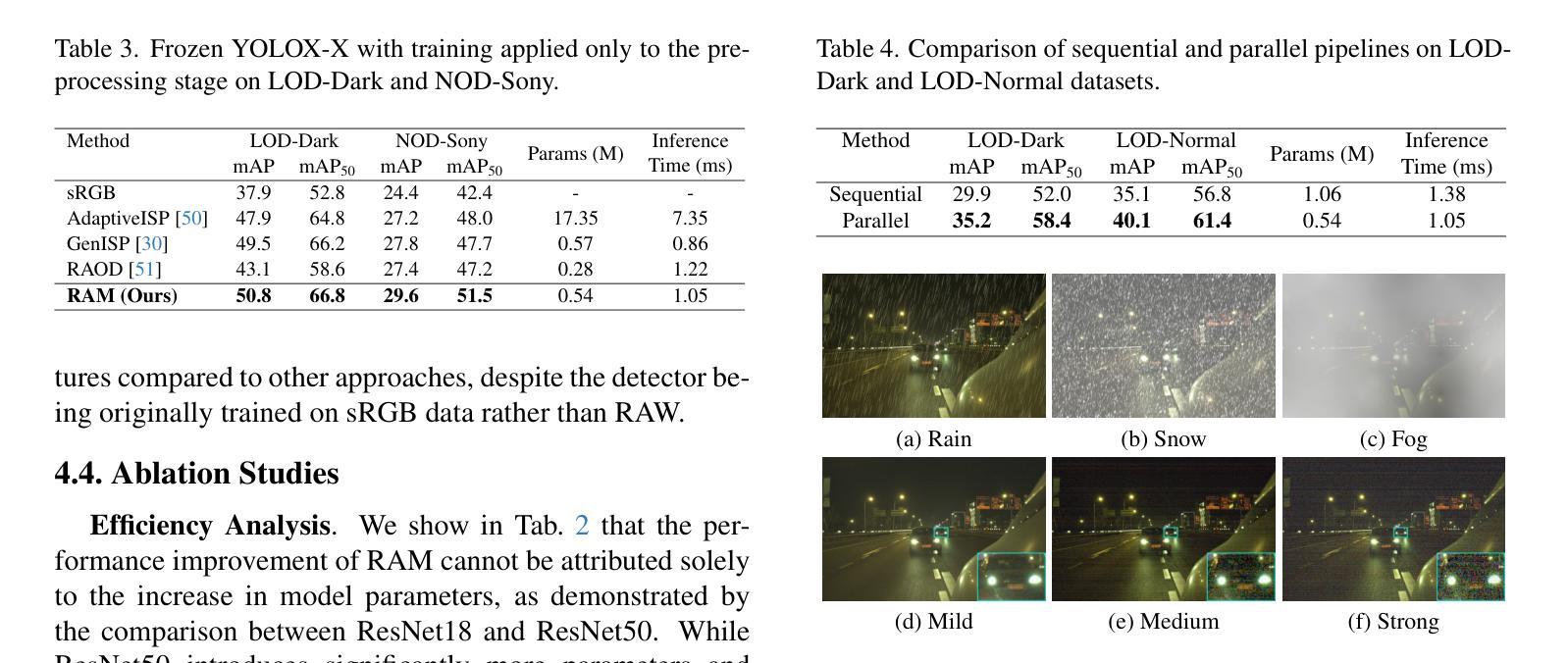
Beyond RGB: Adaptive Parallel Processing for RAW Object Detection
Authors:Shani Gamrian, Hila Barel, Feiran Li, Masakazu Yoshimura, Daisuke Iso
Object detection models are typically applied to standard RGB images processed through Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipelines, which are designed to enhance sensor-captured RAW images for human vision. However, these ISP functions can lead to a loss of critical information that may be essential in optimizing for computer vision tasks, such as object detection. In this work, we introduce Raw Adaptation Module (RAM), a module designed to replace the traditional ISP, with parameters optimized specifically for RAW object detection. Inspired by the parallel processing mechanisms of the human visual system, RAM departs from existing learned ISP methods by applying multiple ISP functions in parallel rather than sequentially, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of image features. These processed representations are then fused in a specialized module, which dynamically integrates and optimizes the information for the target task. This novel approach not only leverages the full potential of RAW sensor data but also enables task-specific pre-processing, resulting in superior object detection performance. Our approach outperforms RGB-based methods and achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse RAW image datasets under varying lighting conditions and dynamic ranges.
对象检测模型通常应用于通过图像信号处理(ISP)管道处理的标准RGB图像,这些管道旨在增强为增强人类视觉而捕获的传感器RAW图像。然而,这些ISP功能可能导致丢失对于优化计算机视觉任务(如对象检测)至关重要的关键信息。在这项工作中,我们引入了原始适配模块(RAM),这是一个旨在替代传统ISP的模块,其参数专为RAW对象检测优化。受人类视觉系统并行处理机制的启发,RAM与传统的学得ISP方法不同,通过并行应用多个ISP功能而不是按顺序应用它们,这允许更全面地捕获图像特征。这些处理过的表示形式随后在一个特殊模块中进行融合,该模块动态地集成并优化针对目标任务的信息。这种新方法不仅充分利用了RAW传感器的全部潜力,而且实现了针对任务的预处理,从而获得了卓越的对象检测性能。我们的方法在多种RAW图像数据集上均表现出优于基于RGB的方法,并在不同的光照条件和动态范围内实现了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在对象检测模型中,传统应用图像信号处理(ISP)管道处理的RGB图像是为人类视觉设计的。但ISP功能可能导致计算机视觉任务中丢失关键信息,如对象检测。本文提出一种名为Raw Adaptation Module(RAM)的模块,旨在替代传统的ISP,并针对RAW对象检测进行优化参数。RAM通过并行应用多个ISP功能,类似于人类视觉系统的并行处理机制,从而更全面地捕获图像特征。这些处理后的表示在专用模块中进行融合,该模块动态集成和优化目标任务的信息。这种方法不仅充分利用了RAW传感器数据的潜力,还实现了针对任务的预处理,从而实现了卓越的对象检测性能。该方法优于基于RGB的方法,并在不同的RAW图像数据集上实现了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 传统ISP管道处理RGB图像设计以人类视觉为主,可能对计算机视觉任务中的对象检测造成信息丢失。
- 提出了一种名为RAM的新型模块,用以替代传统的ISP并特别针对RAW对象检测进行优化。
- RAM模块采用并行处理机制,灵感来源于人类视觉系统,能够更全面地捕获图像特征。
- RAM通过融合多种处理后的图像表示,实现动态集成和优化目标信息。
- 该方法充分利用RAW传感器数据的潜力,实现任务特定的预处理。
- RAM方法优于基于RGB的方法,在各种RAW图像数据集上取得了最佳成果。
点此查看论文截图

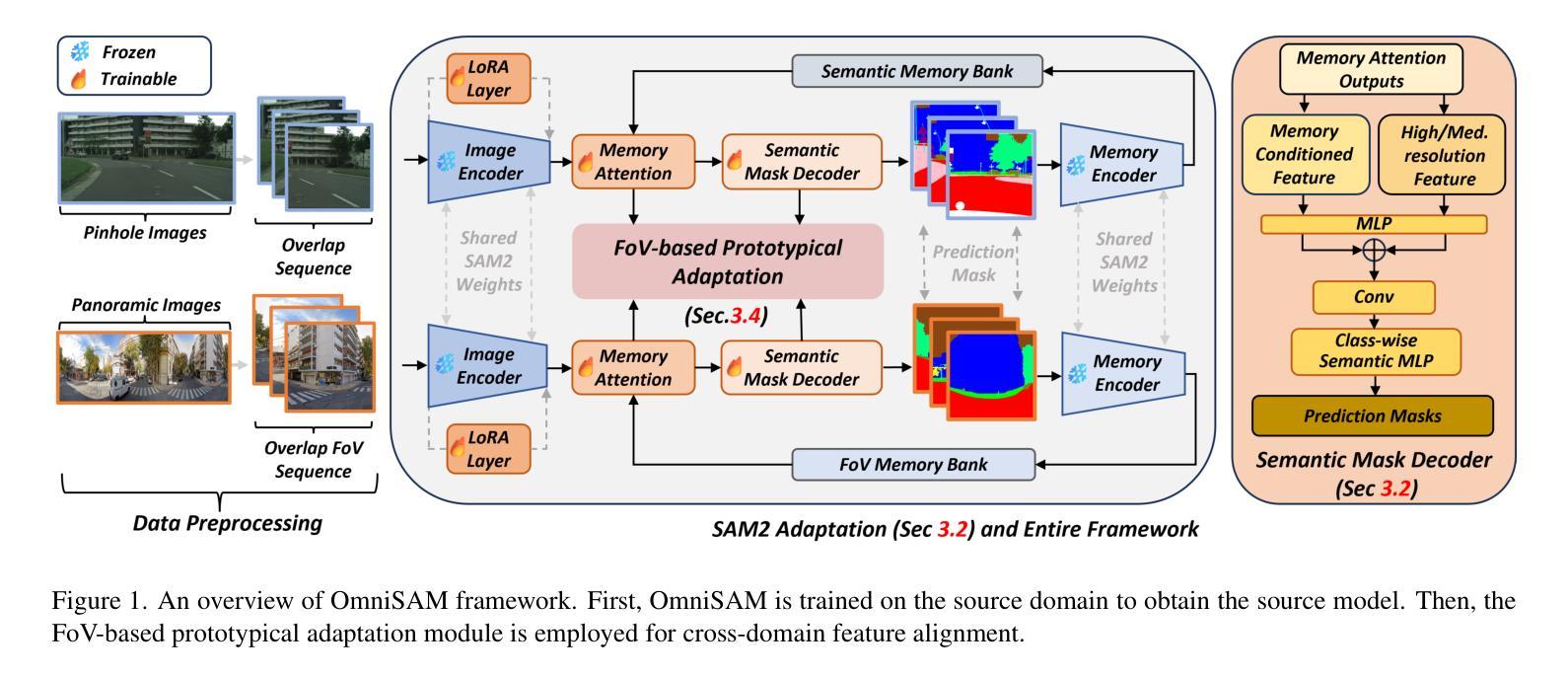
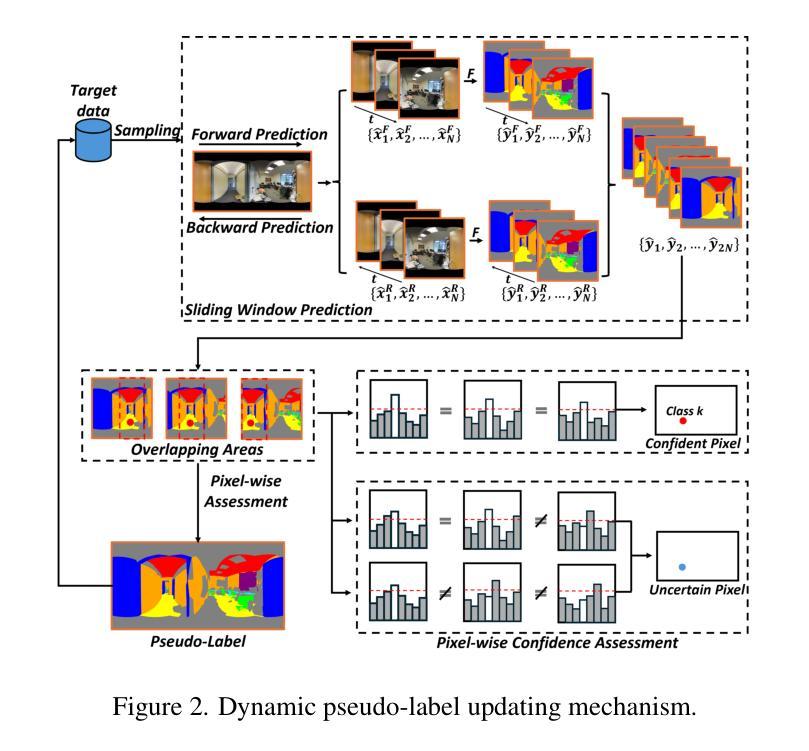
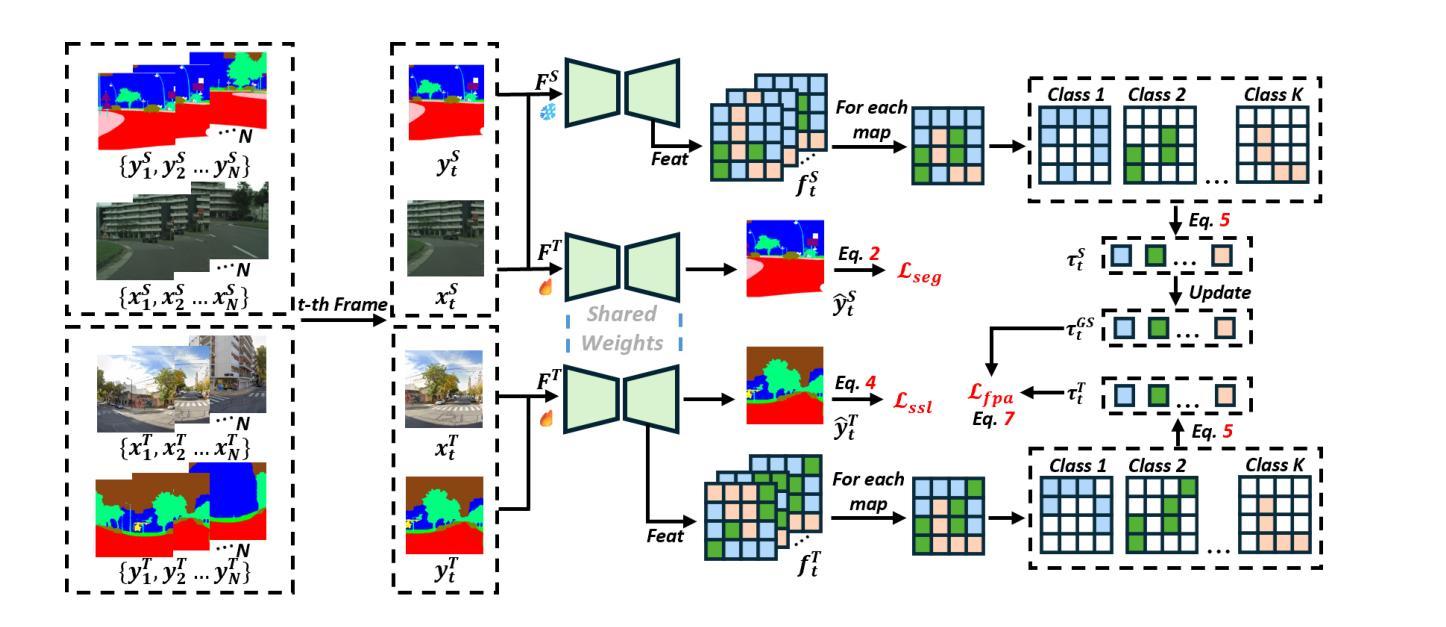
OmniSAM: Omnidirectional Segment Anything Model for UDA in Panoramic Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Ding Zhong, Xu Zheng, Chenfei Liao, Yuanhuiyi Lyu, Jialei Chen, Shengyang Wu, Linfeng Zhang, Xuming Hu
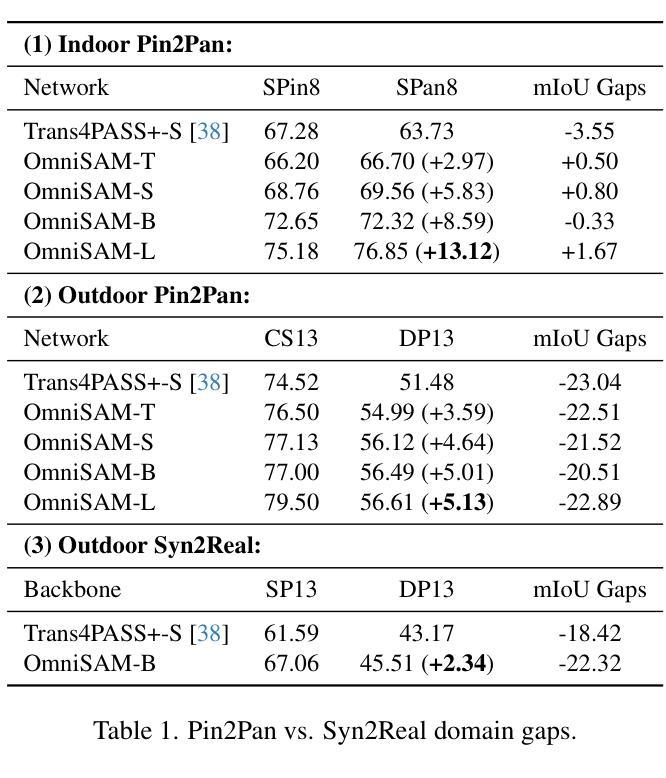
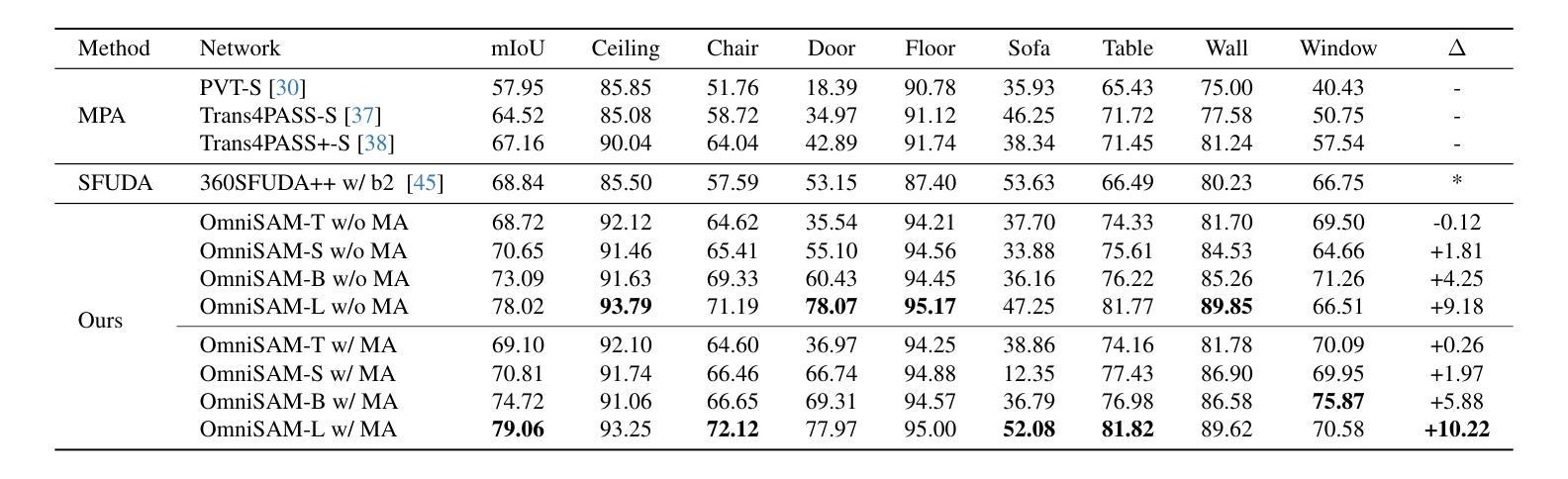
Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) has emerged as a strong base model in various pinhole imaging segmentation tasks. However, when applying it to $360^\circ$ domain, the significant field-of-view (FoV) gap between pinhole ($70^\circ \times 70^\circ$) and panoramic images ($180^\circ \times 360^\circ$) poses unique challenges. Two major concerns for this application includes 1) inevitable distortion and object deformation brought by the large FoV disparity between domains; 2) the lack of pixel-level semantic understanding that the original SAM2 cannot provide. To address these issues, we propose a novel OmniSAM framework, which makes the first attempt to apply SAM2 for panoramic semantic segmentation. Specifically, to bridge the first gap, OmniSAM first divides the panorama into sequences of patches. These patches are then treated as image sequences in similar manners as in video segmentation tasks. We then leverage the SAM2’s memory mechanism to extract cross-patch correspondences that embeds the cross-FoV dependencies, improving feature continuity and the prediction consistency along mask boundaries. For the second gap, OmniSAM fine-tunes the pretrained image encoder and reutilize the mask decoder for semantic prediction. An FoV-based prototypical adaptation module with dynamic pseudo label update mechanism is also introduced to facilitate the alignment of memory and backbone features, thereby improving model generalization ability across different sizes of source models. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that OmniSAM outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by large margins, e.g., 79.06% (+10.22%) on SPin8-to-SPan8, 62.46% (+6.58%) on CS13-to-DP13.
Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)在各种针孔成像分割任务中表现出强大的基础模型能力。然而,当将其应用于$360^\circ$领域时,针孔($70^\circ \times 70^\circ$)与全景图像($180^\circ \times 360^\circ$)之间的视野(FoV)差距巨大,带来了独特的挑战。该应用的主要有两个担忧点:1)由领域间大视野差异带来的不可避免失真和物体变形;2)原始SAM2无法提供的像素级语义理解。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了全新的OmniSAM框架,首次尝试将SAM2应用于全景语义分割。具体来说,为了弥补第一个差距,OmniSAM首先把全景分成一系列的补丁(patches)。这些补丁然后以类似于视频分割任务的方式被当作图像序列来处理。然后,我们利用SAM2的记忆机制来提取跨补丁对应关系,这些关系包含了跨视野的依赖,改善了特征连续性和掩膜边界的预测一致性。对于第二个差距,OmniSAM对预训练图像编码器进行了微调,并重新使用掩膜解码器进行语义预测。我们还引入了一个基于视野的原型适应模块,并带有动态伪标签更新机制,以促进记忆和主干特征的对齐,从而提高模型在不同尺寸源模型上的泛化能力。大量的实验结果证明,OmniSAM大幅超越了最先进的方法,例如在SPin8-to-SPan8上达到79.06%(+10.22%),在CS13-to-DP13上达到62.46%(+6.58%)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对全景语义分割中SAM2模型存在的问题,OmniSAM框架通过划分全景图像为多个补丁,并利用SAM2的内存机制提取跨补丁对应关系,解决了视野差异带来的问题。同时,OmniSAM还通过微调预训练图像编码器并重新利用掩膜解码器进行语义预测,并引入基于视野的原型适应模块和动态伪标签更新机制,提高了模型在不同源模型大小上的泛化能力。实验结果证明OmniSAM大幅优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- SAM2模型在全景成像分割任务中面临视野差异带来的挑战。
- OmniSAM框架通过划分全景图像为补丁,解决了视野差异问题。
- OmniSAM利用SAM2的内存机制提取跨补丁对应关系,提高特征连续性和预测一致性。
- OmniSAM通过微调预训练图像编码器和重新利用掩膜解码器进行语义预测。
- OmniSAM引入基于视野的原型适应模块,提高模型泛化能力。
- 动态伪标签更新机制被用于促进记忆和主干特征的对齐。
点此查看论文截图

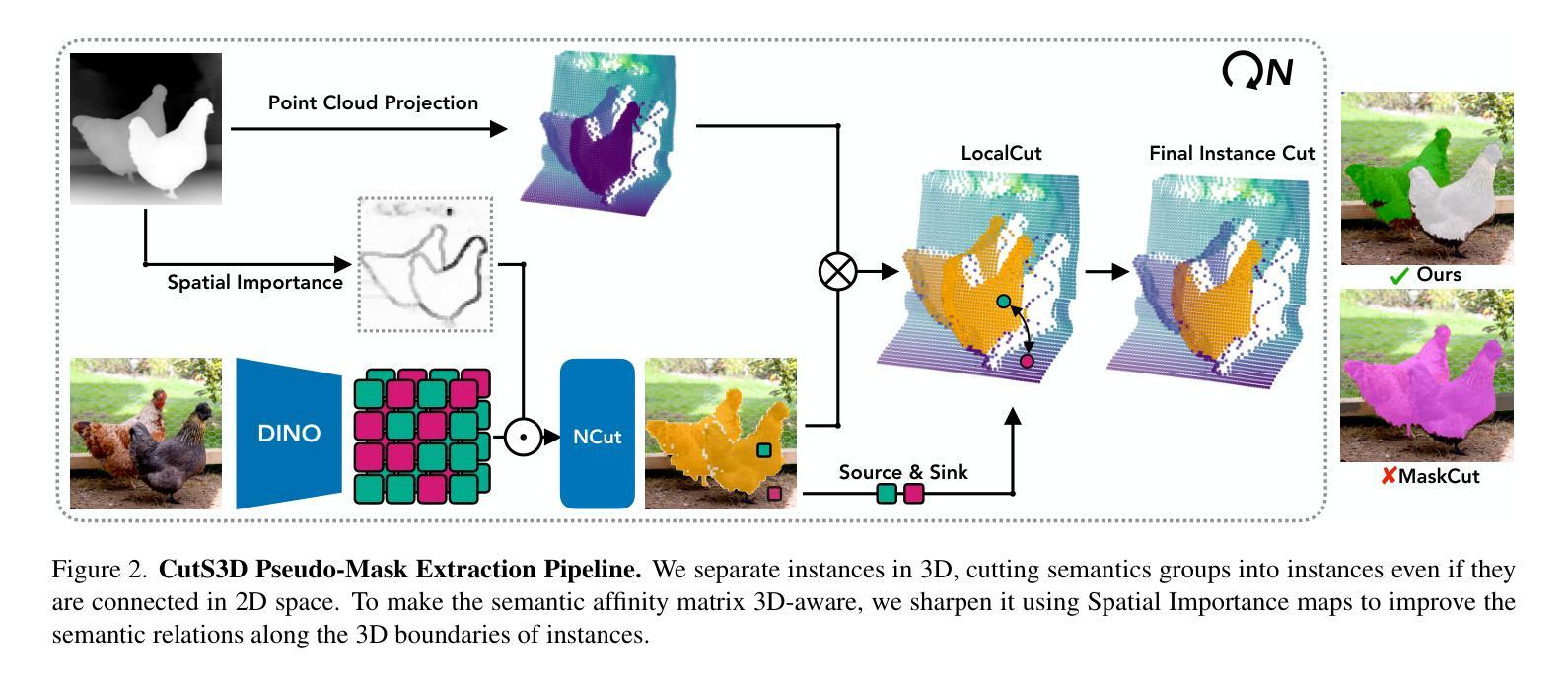
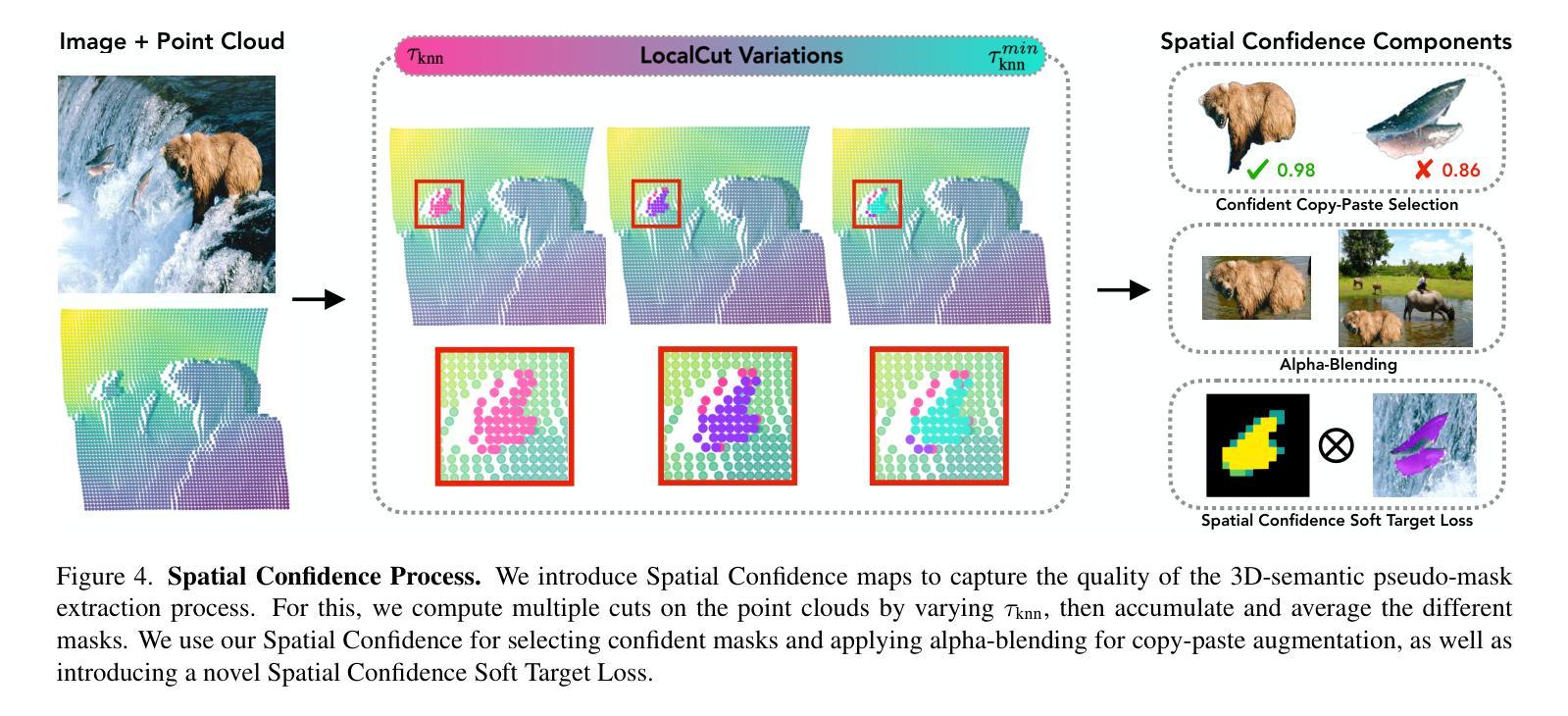
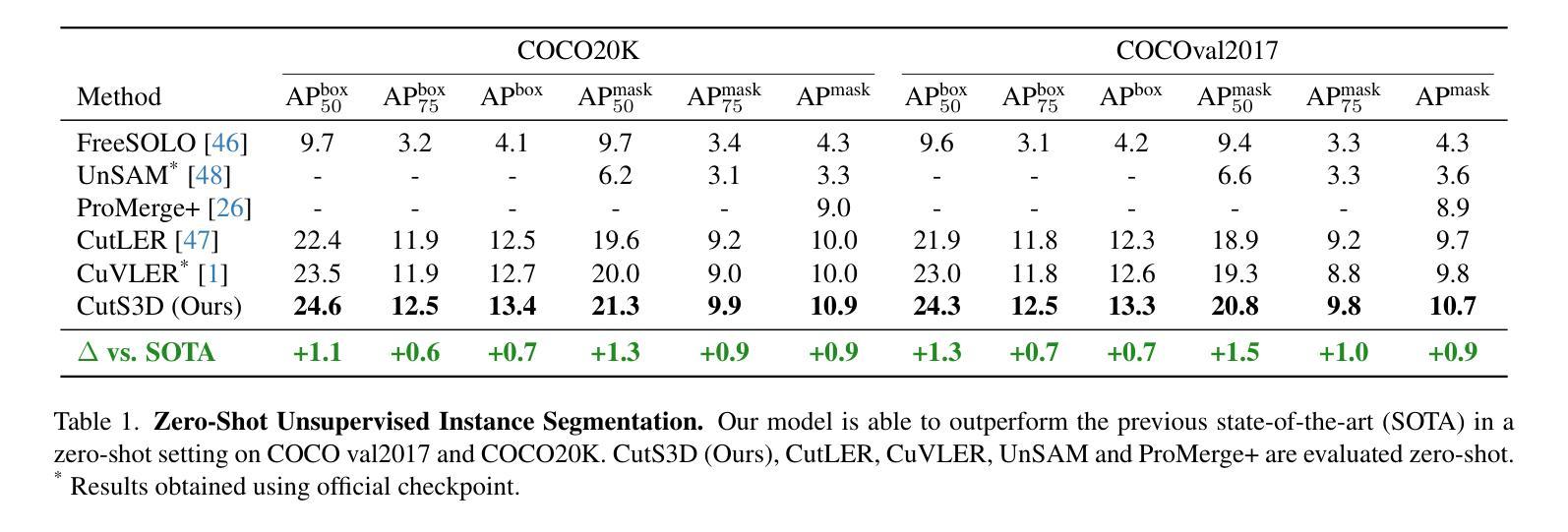
CutS3D: Cutting Semantics in 3D for 2D Unsupervised Instance Segmentation
Authors:Leon Sick, Dominik Engel, Sebastian Hartwig, Pedro Hermosilla, Timo Ropinski
Traditionally, algorithms that learn to segment object instances in 2D images have heavily relied on large amounts of human-annotated data. Only recently, novel approaches have emerged tackling this problem in an unsupervised fashion. Generally, these approaches first generate pseudo-masks and then train a class-agnostic detector. While such methods deliver the current state of the art, they often fail to correctly separate instances overlapping in 2D image space since only semantics are considered. To tackle this issue, we instead propose to cut the semantic masks in 3D to obtain the final 2D instances by utilizing a point cloud representation of the scene. Furthermore, we derive a Spatial Importance function, which we use to resharpen the semantics along the 3D borders of instances. Nevertheless, these pseudo-masks are still subject to mask ambiguity. To address this issue, we further propose to augment the training of a class-agnostic detector with three Spatial Confidence components aiming to isolate a clean learning signal. With these contributions, our approach outperforms competing methods across multiple standard benchmarks for unsupervised instance segmentation and object detection.
传统上,学习在2D图像中分割对象实例的算法主要依赖于大量的人工标注数据。仅近期才出现了采用无监督方法解决此问题的新方法。通常,这些方法首先生成伪掩膜,然后训练类不敏感检测器。虽然这些方法达到了当前最佳水平,但由于只考虑语义,它们往往无法正确分离在2D图像空间中重叠的实例。为了解决这个问题,我们提出将语义掩膜在3D中进行切割,利用场景的点云表示获得最终的2D实例。此外,我们推导出了一个空间重要性函数,我们用它来锐化实例的3D边界上的语义。然而,这些伪掩膜仍然存在掩膜模糊的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们进一步提出使用三种空间置信分量增强类不敏感检测器的训练,旨在获得清晰的学习信号。通过这些贡献,我们的方法在多个用于无监督实例分割和对象检测的基准测试中表现优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025. Project Page with Code, Models & Demo: https://leonsick.github.io/cuts3d/
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的无监督实例分割方法,该方法通过利用三维点云表示场景,在语义掩膜上进行切割以获得最终的二维实例。为解决掩膜模糊问题,提出增强类无关检测器的训练,并加入三个空间置信度组件以隔离清晰的学习信号。此方法在多标准基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 传统实例分割算法依赖大量人工标注数据,近期新兴的无监督方法开始解决此问题。
- 无监督方法通常生成伪掩膜并训练类无关检测器。
- 现有方法在处理二维图像空间中重叠实例时存在问题。
- 提出利用三维点云表示场景,在语义掩膜上进行切割以获取最终二维实例的解决方法。
- 引入空间重要性函数以锐化实例的三维边界语义。
- 伪掩膜仍存在掩膜模糊问题。
点此查看论文截图


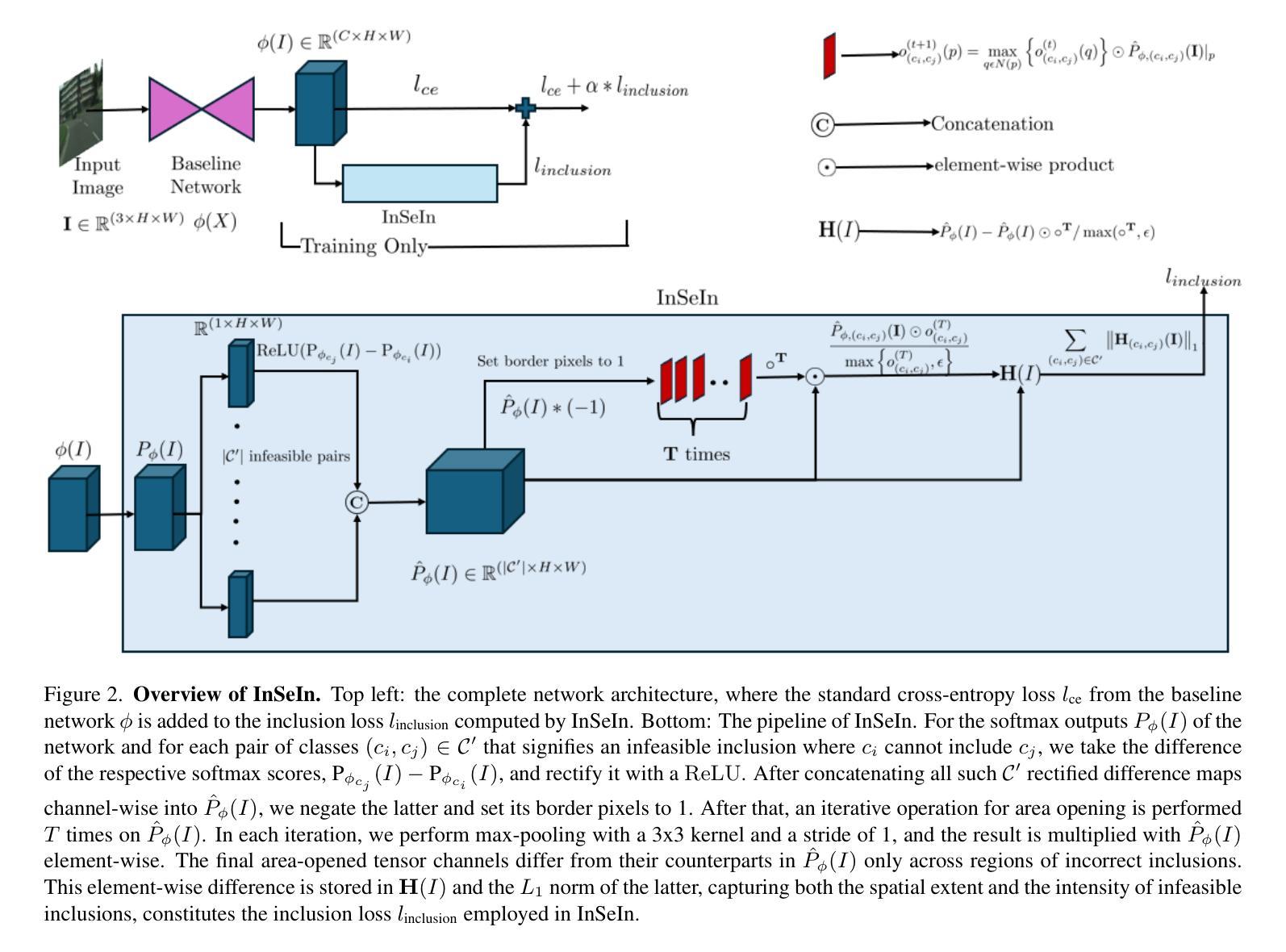
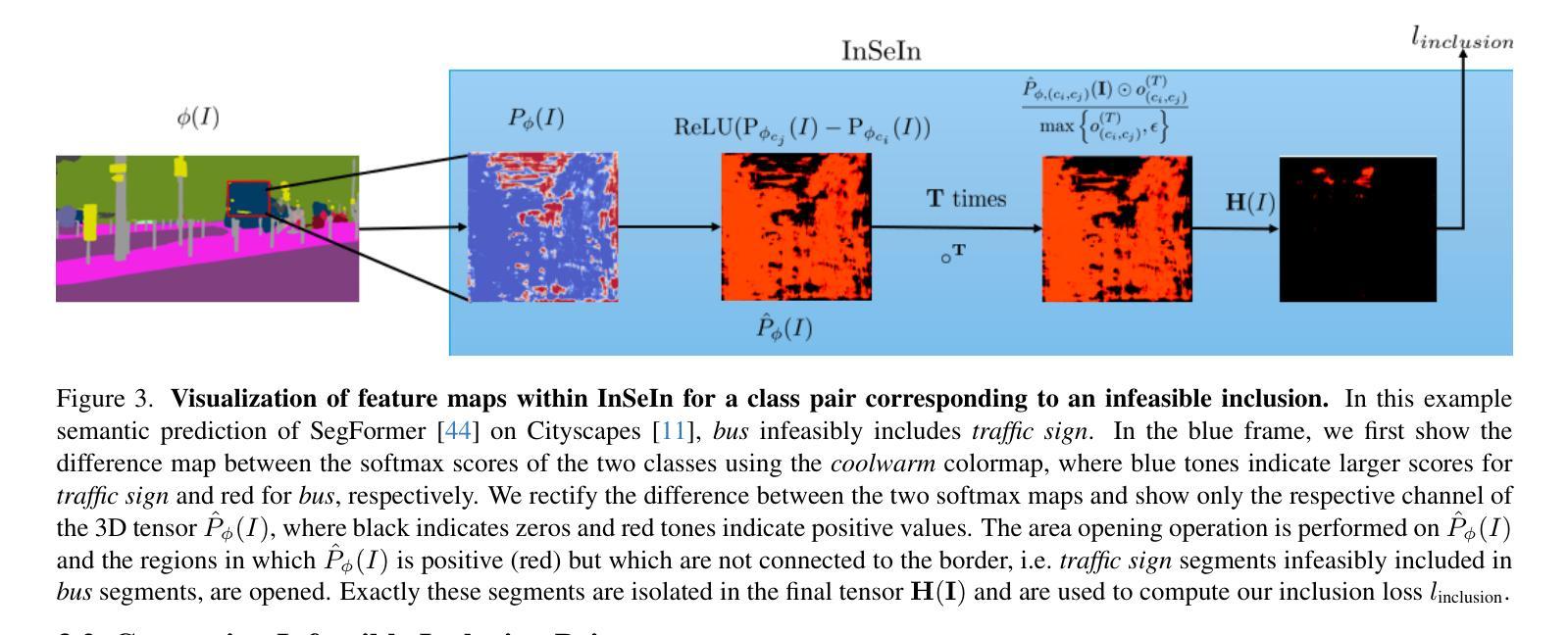
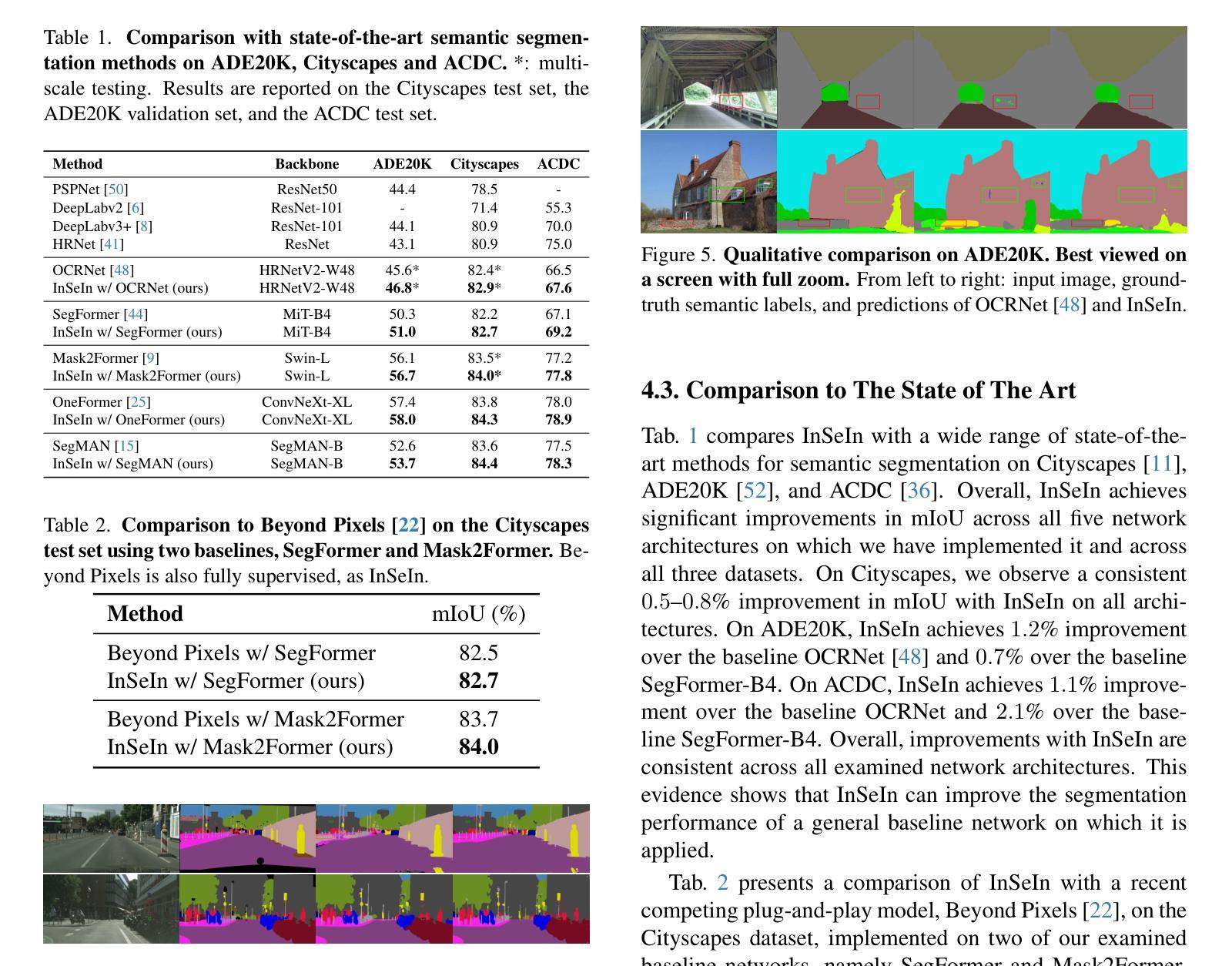
Optimizing against Infeasible Inclusions from Data for Semantic Segmentation through Morphology
Authors:Shamik Basu, Luc Van Gool, Christos Sakaridis
State-of-the-art semantic segmentation models are typically optimized in a data-driven fashion, minimizing solely per-pixel or per-segment classification objectives on their training data. This purely data-driven paradigm often leads to absurd segmentations, especially when the domain of input images is shifted from the one encountered during training. For instance, state-of-the-art models may assign the label “road” to a segment that is included by another segment that is respectively labeled as “sky”. However, the ground truth of the existing dataset at hand dictates that such inclusion is not feasible. Our method, Infeasible Semantic Inclusions (InSeIn), first extracts explicit inclusion constraints that govern spatial class relations from the semantic segmentation training set at hand in an offline, data-driven fashion, and then enforces a morphological yet differentiable loss that penalizes violations of these constraints during training to promote prediction feasibility. InSeIn is a light-weight plug-and-play method, constitutes a novel step towards minimizing infeasible semantic inclusions in the predictions of learned segmentation models, and yields consistent and significant performance improvements over diverse state-of-the-art networks across the ADE20K, Cityscapes, and ACDC datasets. https://github.com/SHAMIK-97/InSeIn
最先进的语义分割模型通常是数据驱动的,仅仅通过最小化其训练数据上的每个像素或每个段的分类目标来进行优化。这种纯粹的数据驱动范式往往会导致荒谬的分割,特别是在输入图像的领域与训练期间遇到的领域不一致时。例如,最先进的模型可能会将一个被标记为“天空”的部分包含的片段标记为“道路”。然而,现有数据集的真相表明,这样的包含是不可能的。我们的方法“不可行的语义包含(InSeIn)”首先以离线、数据驱动的方式从现有的语义分割训练集中提取控制空间类别关系的显式包含约束,然后强制实施一种形态学但可区分的损失,该损失在训练期间对违反这些约束的情况进行处罚,以促进预测的可行性。InSeIn是一种轻量级的即插即用方法,是减少学习分割模型预测中不可行的语义包含的新步骤,在ADE20K、Cityscapes和ACDC数据集上,与各种最先进的网络相比,它产生了持续而显著的性能改进。https://github.com/SHAMIK-97/InSeIn
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了语义分割模型在训练过程中存在的问题,即在面对不同于训练集的数据时会产生荒谬的分割结果。为解决这一问题,提出了一种名为InSeIn的方法,它通过提取语义分割训练集中的空间类关系约束,并在训练过程中强制执行形态学损失以最小化不可行的语义包含情况。此方法能提高不同数据集上的分割模型预测准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割模型面临数据迁移时的挑战,即在不同数据域下的分割结果可能出现荒谬。
- InSeIn方法能从现有的语义分割训练集中提取空间类关系的明确包含约束。
- InSeIn通过强制执行形态学损失来确保模型在训练过程中遵守这些约束。
- 此方法作为一种轻量级的即插即用模块,对于减少学习分割模型预测中的不可行语义包含是一个新的进步。
- InSeIn在ADE20K、Cityscapes和ACDC数据集上相对于其他最先进的网络具有一致且显著的性能改进。
点此查看论文截图

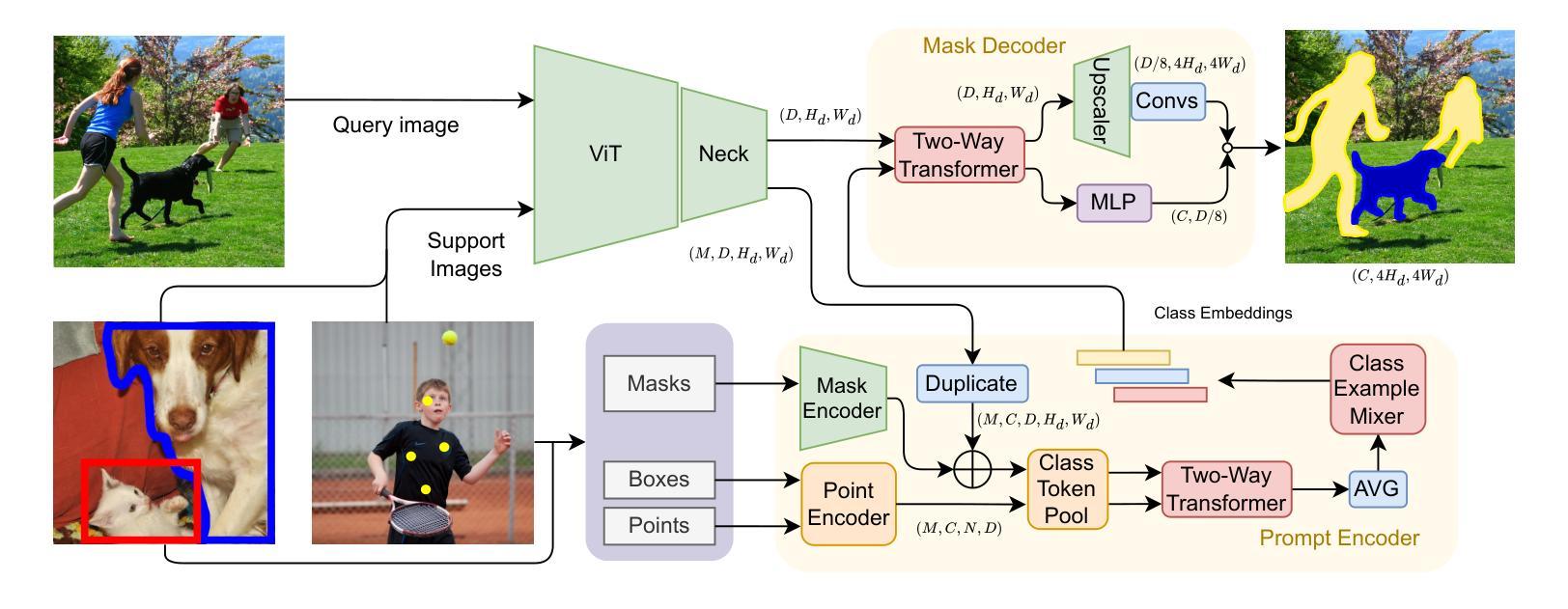
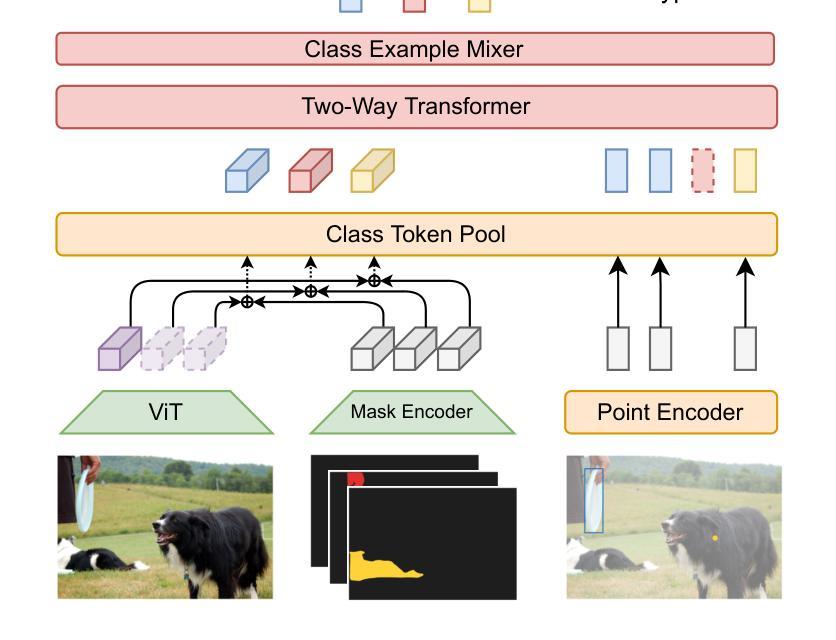
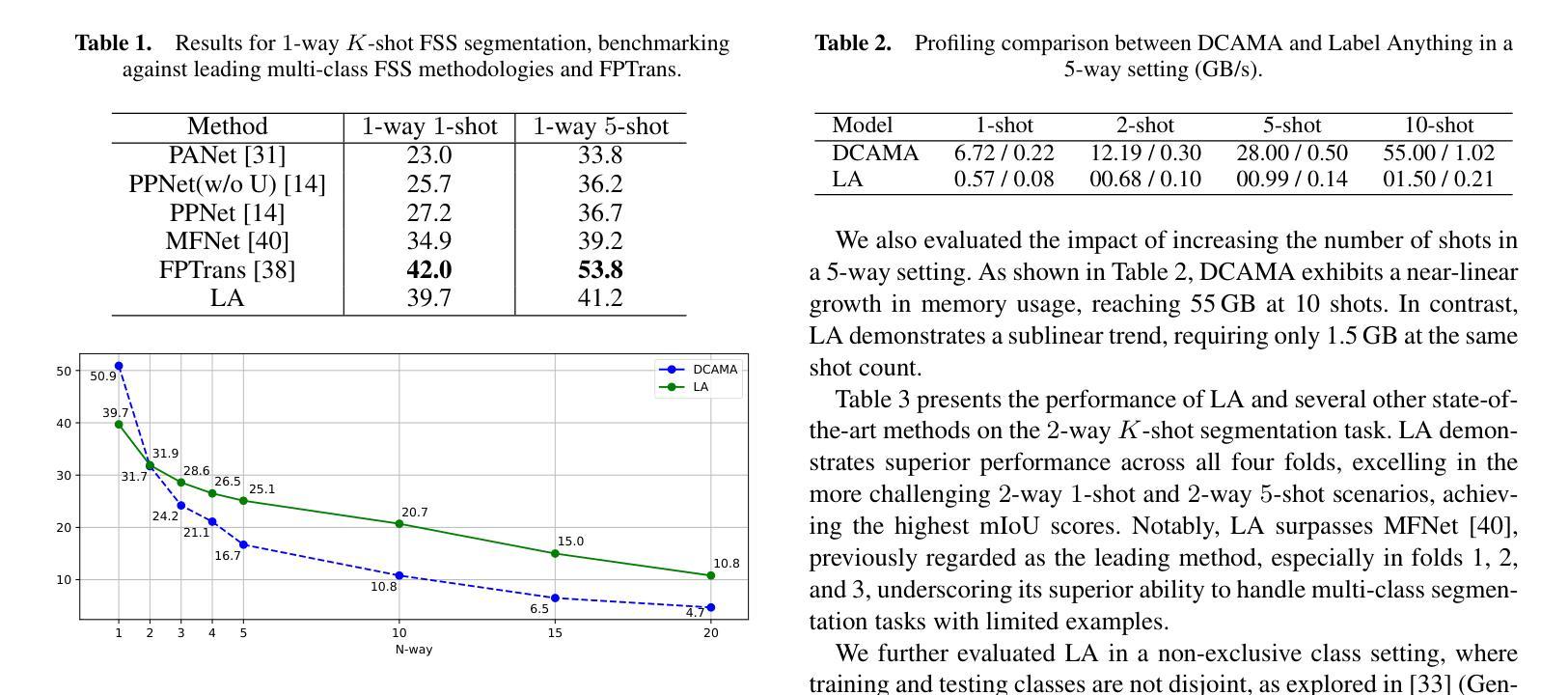
Label Anything: Multi-Class Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation with Visual Prompts
Authors:Pasquale De Marinis, Nicola Fanelli, Raffaele Scaringi, Emanuele Colonna, Giuseppe Fiameni, Gennaro Vessio, Giovanna Castellano
Few-shot semantic segmentation aims to segment objects from previously unseen classes using only a limited number of labeled examples. In this paper, we introduce Label Anything, a novel transformer-based architecture designed for multi-prompt, multi-way few-shot semantic segmentation. Our approach leverages diverse visual prompts – points, bounding boxes, and masks – to create a highly flexible and generalizable framework that significantly reduces annotation burden while maintaining high accuracy. Label Anything makes three key contributions: ($\textit{i}$) we introduce a new task formulation that relaxes conventional few-shot segmentation constraints by supporting various types of prompts, multi-class classification, and enabling multiple prompts within a single image; ($\textit{ii}$) we propose a novel architecture based on transformers and attention mechanisms; and ($\textit{iii}$) we design a versatile training procedure allowing our model to operate seamlessly across different $N$-way $K$-shot and prompt-type configurations with a single trained model. Our extensive experimental evaluation on the widely used COCO-$20^i$ benchmark demonstrates that Label Anything achieves state-of-the-art performance among existing multi-way few-shot segmentation methods, while significantly outperforming leading single-class models when evaluated in multi-class settings. Code and trained models are available at https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything.
少数语义分割旨在使用有限数量的标注示例来对先前未见过的类别进行对象分割。在本文中,我们介绍了Label Anything,这是一种基于transformer的新型架构,专为多提示、多向少数语义分割设计。我们的方法利用多样的视觉提示——点、边界框和掩码,创建一个高度灵活和通用的框架,在保持高准确性的同时,大大减轻了标注负担。Label Anything做出了三项主要贡献:(i)我们引入了一种新的任务公式,通过支持各种提示类型、多类分类以及在单个图像内启用多个提示,放松了传统的少数分割约束;(ii)我们提出了一种基于transformer和注意力机制的新型架构;(iii)我们设计了一种通用训练程序,使我们的模型能够在不同的N路K路以及提示类型配置中使用单个训练模型无缝运行。我们在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试上的大量实验评估表明,Label Anything在现有的多向少数分割方法中实现了最先进的性能,同时在多类设置中显著优于领先的单类模型。代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECAI 2025 - 28th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文介绍了针对多提示、多类别少样本语义分割任务的新型转换器架构Label Anything。它利用点、边界框和遮罩等多种视觉提示,创建一个灵活且可推广的框架,显著减少标注负担的同时保持高准确性。Label Anything的主要贡献包括:引入支持多种提示、多类别分类的新任务形式;提出基于转换器和注意力机制的新型架构;设计一种通用训练程序,使模型能够在不同N路K样本和提示类型配置下灵活操作。在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试中,Label Anything实现了多类别少样本分割方法的最优性能。
Key Takeaways
- Label Anything是一个针对多提示、多类别少样本语义分割的转换器架构。
- 利用多种视觉提示(点、边界框、遮罩)创建灵活且可推广的框架。
- 引入支持多种提示和多类别分类的新任务形式。
- 提出基于转换器和注意力机制的新型架构。
- 设计一种通用训练程序,使模型能够在不同配置下灵活操作。
- 在COCO-20i基准测试中实现了最优性能。
点此查看论文截图