⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
Numerical Uncertainty in Linear Registration: An Experimental Study
Authors:Niusha Mirhakimi, Yohan Chatelain, Jean-Baptiste Poline, Tristan Glatard
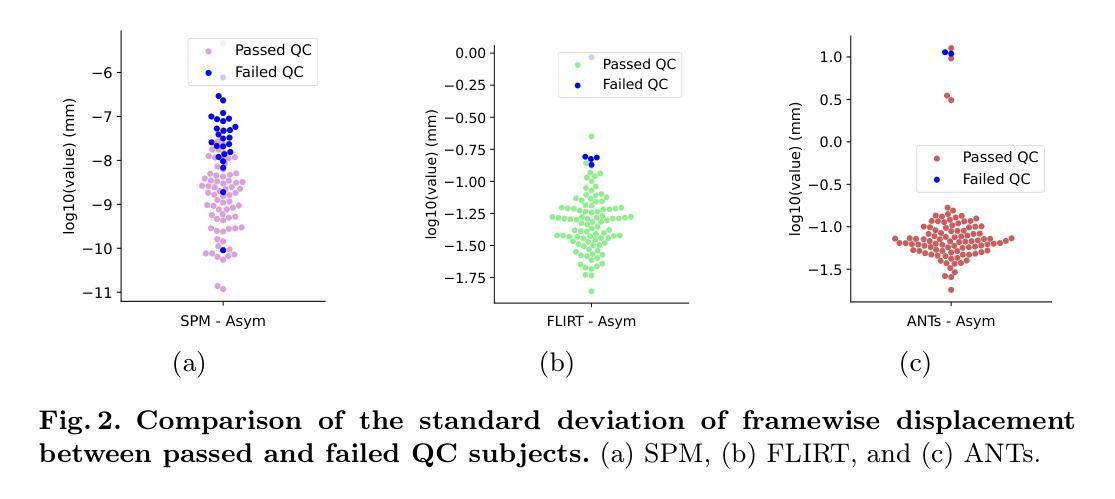
While linear registration is a critical step in MRI preprocessing pipelines, its numerical uncertainty is understudied. Using Monte-Carlo Arithmetic (MCA) simulations, we assessed the most commonly used linear registration tools within major software packages (SPM, FSL, and ANTs) across multiple image similarity measures, two brain templates, and both healthy control (HC, n=50) and Parkinson’s Disease (PD, n=50) cohorts. Our findings highlight the influence of linear registration tools and similarity measures on numerical stability. Among the evaluated tools and with default similarity measures, SPM exhibited the highest stability. FSL and ANTs showed greater and similar ranges of variability, with ANTs demonstrating particular sensitivity to numerical perturbations that occasionally led to registration failure. Furthermore, no significant differences were observed between healthy and PD cohorts, suggesting that numerical stability analyses obtained with healthy subjects may generalise to clinical populations. Finally, we also demonstrated how numerical uncertainty measures may support automated quality control (QC) of linear registration results. Overall, our experimental results characterize the numerical stability of linear registration experimentally and can serve as a basis for future uncertainty analyses.
虽然线性配准是MRI预处理流程中的关键步骤,但其数值不确定性尚未得到充分研究。我们使用蒙特卡洛算术(MCA)模拟,评估了主要软件包(SPM、FSL和ANTs)中最常用的线性配准工具,跨越多种图像相似性度量、两个脑模板以及健康对照(HC,n=50)和帕金森病(PD,n=50)群体。我们的研究结果强调了线性配准工具和相似性度量对数值稳定性的影响。在评估的工具和默认的相似性度量中,SPM表现出最高的稳定性。FSL和ANTs的变动范围较大且相似,ANTs对数值扰动特别敏感,偶尔会导致配准失败。此外,健康人群和PD群体之间没有明显的差异,这表明用健康受试者获得的数值稳定性分析可能适用于临床人群。最后,我们还展示了数值不确定性度量如何支持线性配准结果的自动化质量控制(QC)。总体而言,我们的实验结果通过实验表征了线性配准的数值稳定性,并可以作为未来不确定性分析的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用蒙特卡洛算法(MCA)模拟评估了主要软件包(SPM、FSL和ANTs)中常用的线性注册工具在多种图像相似性度量、两个脑模板以及健康对照组(HC)和帕金森氏病(PD)患者群体中的数值稳定性。研究发现,线性注册工具和相似性度量对数值稳定性有影响。默认相似性度量下,SPM表现出最高稳定性,而FSL和ANTs的变动范围较大且相似,其中ANTs对某些数值扰动特别敏感,偶尔会导致注册失败。研究还发现,健康群体与PD患者的差异不影响数值稳定性分析结果的通用性。最后,文章展示了如何通过数值不确定性度量来支持线性注册结果的自动化质量控制。本研究实验结果可为未来不确定性分析提供依据。
Key Takeaways
- 利用蒙特卡洛算法模拟评估了多种线性注册工具的数值稳定性。
- 研究涉及多个图像相似性度量、两个脑模板以及健康与帕金森氏病患者群体。
- SPM在默认相似性度量下表现出最高稳定性。
- FSL和ANTs的数值稳定性相对较差,其中ANTs尤其敏感于某些数值扰动。
- 健康与PD患者群体间的差异不影响数值稳定性分析结果的通用性。
- 数值不确定性度量可用于支持线性注册结果的质量控制。
点此查看论文截图

Sample-Aware Test-Time Adaptation for Medical Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Irene Iele, Francesco Di Feola, Valerio Guarrasi, Paolo Soda
Image-to-image translation has emerged as a powerful technique in medical imaging, enabling tasks such as image denoising and cross-modality conversion. However, it suffers from limitations in handling out-of-distribution samples without causing performance degradation. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) framework that dynamically adjusts the translation process based on the characteristics of each test sample. Our method introduces a Reconstruction Module to quantify the domain shift and a Dynamic Adaptation Block that selectively modifies the internal features of a pretrained translation model to mitigate the shift without compromising the performance on in-distribution samples that do not require adaptation. We evaluate our approach on two medical image-to-image translation tasks: low-dose CT denoising and T1 to T2 MRI translation, showing consistent improvements over both the baseline translation model without TTA and prior TTA methods. Our analysis highlights the limitations of the state-of-the-art that uniformly apply the adaptation to both out-of-distribution and in-distribution samples, demonstrating that dynamic, sample-specific adjustment offers a promising path to improve model resilience in real-world scenarios. The code is available at: https://github.com/cosbidev/Sample-Aware_TTA.
图像到图像的转换在医学成像中已崭露头角为一种强大技术,能够进行图像去噪和跨模态转换等任务。然而,它在处理分布外样本时存在局限性,可能导致性能下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型的测试时间适应(TTA)框架,该框架根据每个测试样本的特性动态调整翻译过程。我们的方法引入了一个重建模块来量化域迁移和一个动态适应块,有选择地修改预训练翻译模型的内部特征,以减轻迁移现象,同时不影响不需要适应的、分布内的样本的性能。我们在两个医学图像到图像的翻译任务上评估了我们的方法:低剂量CT去噪和T1到T2 MRI翻译,与没有TTA的基线翻译模型和先前的TTA方法相比,表现出了一致的优势。我们的分析强调了当前技术对所有样本都统一应用适应性的局限性,证明了动态、针对样本的特定调整是提高模型在现实场景中适应性的有前途的途径。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/cosbidev/Sample-Aware_TTA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了图像到图像的翻译技术在医学成像中的强大应用,如图像去噪和跨模态转换。然而,它面临处理离群样本时性能下降的局限性。为解决此问题,本文提出了一种新型的测试时间适应(TTA)框架,该框架根据每个测试样本的特性动态调整翻译过程。通过引入重建模块来量化域偏移,并使用动态适应块选择性地修改预训练的翻译模型的内部特征,以减轻偏移,同时不损害对不需要适应的样本的性能。本文在两个医学图像到图像翻译任务上评估了该方法的有效性,并展示了相较于基准翻译模型和先前的TTA方法的一致改进。本文分析突显了当前技术均匀应用适应于离群样本和分布内样本的局限性,并表明动态、样本特定的调整是提高模型在现实场景中的稳健性的有前途的路径。
Key Takeaways
- 图像到图像翻译技术在医学成像中具有广泛应用,如图像去噪和跨模态转换。
- 当前技术面临处理离群样本时性能下降的局限性。
- 提出了一种新型的测试时间适应(TTA)框架,能根据每个测试样本的特性动态调整翻译过程。
- 通过重建模块和动态适应块来量化域偏移并选择性修改翻译模型的内部特征。
- 在两个医学图像到图像翻译任务上评估了方法的有效性,并展示了相较于基准方法和先前TTA方法的一致改进。
- 分析突显了均匀适应策略的局限性,强调了动态、样本特定的调整能提高模型在现实场景中的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

LeakyCLIP: Extracting Training Data from CLIP
Authors:Yunhao Chen, Shujie Wang, Xin Wang, Xingjun Ma
Understanding the memorization and privacy leakage risks in Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP) is critical for ensuring the security of multimodal models. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of extracting sensitive training examples from diffusion models, with conditional diffusion models exhibiting a stronger tendency to memorize and leak information. In this work, we investigate data memorization and extraction risks in CLIP through the lens of CLIP inversion, a process that aims to reconstruct training images from text prompts. To this end, we introduce \textbf{LeakyCLIP}, a novel attack framework designed to achieve high-quality, semantically accurate image reconstruction from CLIP embeddings. We identify three key challenges in CLIP inversion: 1) non-robust features, 2) limited visual semantics in text embeddings, and 3) low reconstruction fidelity. To address these challenges, LeakyCLIP employs 1) adversarial fine-tuning to enhance optimization smoothness, 2) linear transformation-based embedding alignment, and 3) Stable Diffusion-based refinement to improve fidelity. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of LeakyCLIP, achieving over 358% improvement in Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) for ViT-B-16 compared to baseline methods on LAION-2B subset. Furthermore, we uncover a pervasive leakage risk, showing that training data membership can even be successfully inferred from the metrics of low-fidelity reconstructions. Our work introduces a practical method for CLIP inversion while offering novel insights into the nature and scope of privacy risks in multimodal models.
理解对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)中的记忆和隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。最近的研究表明,从扩散模型中提取敏感训练样本是可行的,条件扩散模型在记忆和泄露信息方面表现出更强的倾向。在这项工作中,我们通过CLIP反转的视角来研究CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险,这是一个旨在从文本提示中重建训练图像的过程。为此,我们引入了\textbf{LeakyCLIP},这是一种新型的攻击框架,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。我们发现CLIP反转存在三个关键挑战:1)特征不鲁棒,2)文本嵌入中的视觉语义有限,以及3)重建保真度低。为了解决这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用1)对抗性微调以增强优化平滑度,2)基于线性变换的嵌入对齐,以及3)基于稳定扩散的细化以提高保真度。经验结果表明LeakyCLIP的优势,与基线方法在LAION-2B子集上进行比较,结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)提高了358%以上(以ViT-B-16为例)。此外,我们发现了普遍的泄露风险,表明甚至可以从低保真重建的指标中成功推断出训练数据成员。我们的工作介绍了一种实用的CLIP反转方法,同时提供了关于多模态模型中隐私风险本质和范围的新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP)模型中的记忆与隐私泄露风险。研究发现,扩散模型存在敏感训练样本可被提取的风险,且条件扩散模型的记忆和泄露信息倾向更强。本研究通过CLIP反演的角度,探究CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险,并引入新型攻击框架LeakyCLIP,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。研究中识别出CLIP反演的三大挑战,包括特征不稳健、文本嵌入中视觉语义有限以及重建保真度低。为应对这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用对抗性微调增强优化平稳性、基于线性变换的嵌入对齐以及基于Stable Diffusion的精细化为改进保真度。实证研究证明LeakyCLIP的优越性,在LAION-2B子集上与基准方法相比,ViT-B-16的结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了超过358%。此外,本研究揭示了广泛的泄露风险,即使在低精度重建的指标中,也能成功推断训练数据成员身份。本研究为CLIP反演提供了实用方法,并为多模态模型中的隐私风险提供了新的见解。
关键见解
- 理解CLIP模型中记忆和隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。
- 研究通过CLIP反演探究CLIP模型中的数据记忆和提取风险。
- 引入新型攻击框架LeakyCLIP,实现高质量、语义准确的图像从CLIP嵌入中的重建。
- 识别出CLIP反演的三大挑战:特征不稳健、文本嵌入中视觉语义有限和重建保真度低。
- LeakyCLIP采用多种技术应对这些挑战,包括对抗性微调、嵌入对齐和基于Stable Diffusion的精细化。
- 实证研究证明LeakyCLIP在SSIM上较基准方法有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图



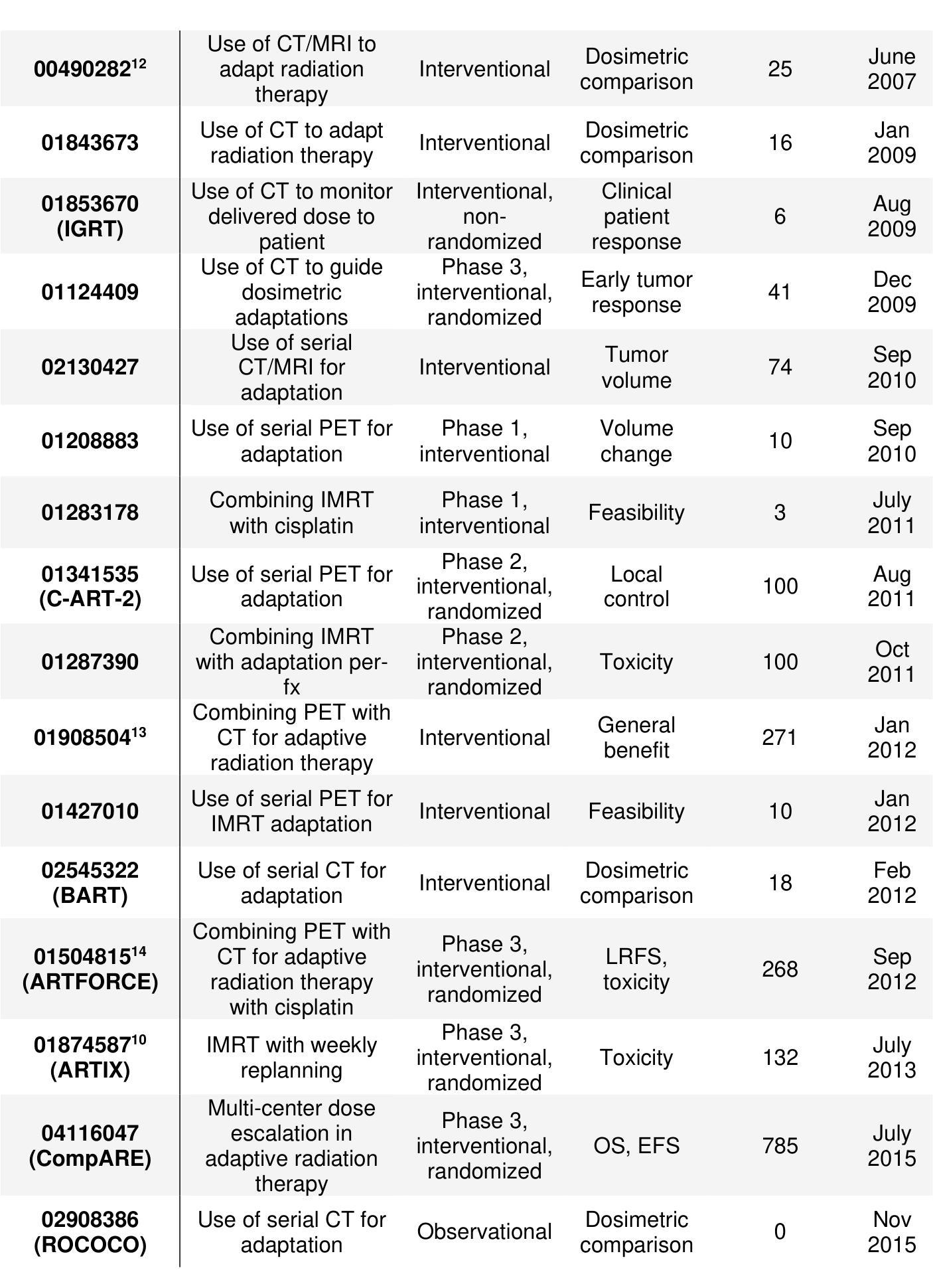
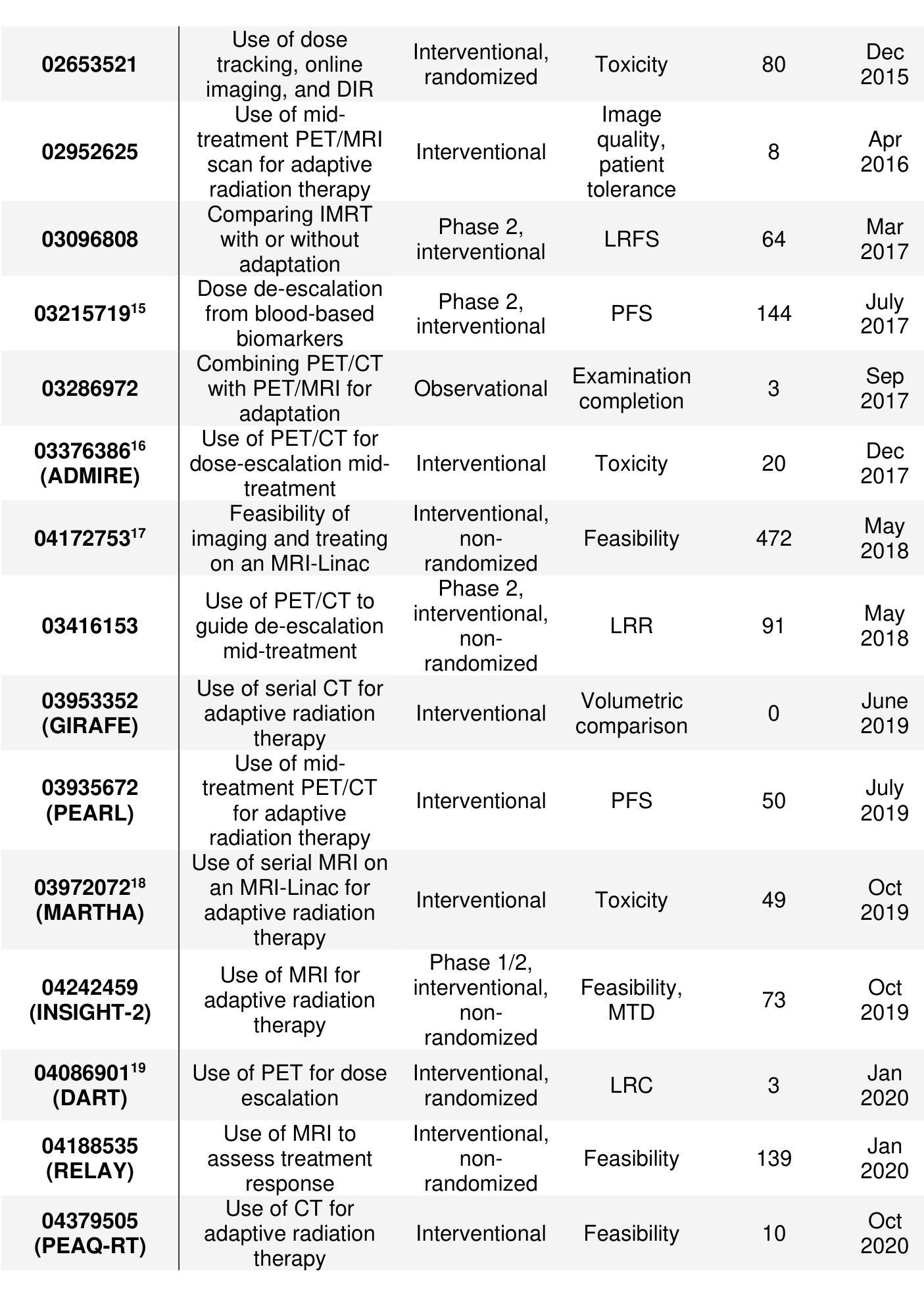
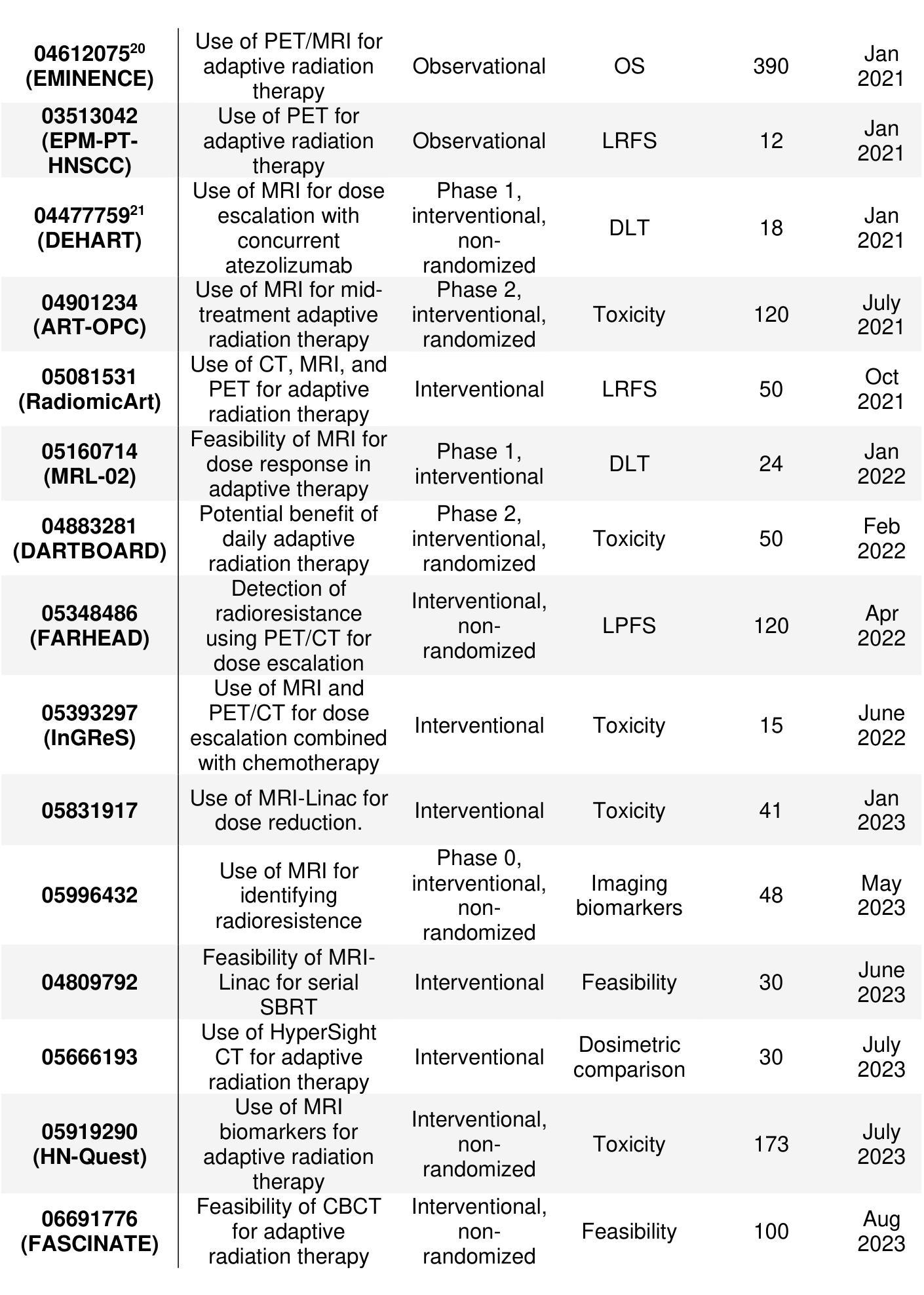
Review: Adaptive Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer
Authors:Lucas McCullum, Sonali J. Joshi, Brandon M. Godinich, Parshawn Gerafian, Rishabh Gaur, Qusai Alakayleh, Ergys Subashi, Renjie He, Samuel L. Mulder, Zaphanlene Kaffey, Grace Murley, Natalie A. West, Saleh Ramezani, Cem Dede, Laia Humbert-Vidan, Clifton D. Fuller
The future of ART in head and neck cancer is just beginning. Novel technologies have pushed the boundary of what is possible in terms of techniques to identify biomarkers for adaptation as well as innovative devices specialized to respond to these adaptations, sometimes in real-time. Important interdisciplinary steps must be taken moving forward to ensure the safe deployment of these new techniques, such as rigorous quality assurance evaluations from medical physicists, clinical trials from physicians, and comprehensive testing from vendors prior to release. In summary, we aimed not to provide a single correct answer for the optimal implementation of ART in the era of imaging biomarkers, but to encourage the field to collaborate and bring each idea discussed here together to overcome current barriers and deliver the best treatment possible to the patient.
医学图像领域中的ART(先进放疗技术)在头颈癌治疗中的未来才刚刚开始。新技术已经突破了技术上的可能边界,不仅在寻找适应的生物标志物方面,而且还推动了专门应对这些适应的实时创新设备的发展。未来要向前推进,就必须采取重要的跨学科步骤,以确保这些新技术的安全部署,包括医学物理学家严格的质量保证评估、医生的临床试验以及供应商在发布前的全面测试。总之,我们的目标不是为ART在成像生物标志物时代提供最佳实施的单一正确答案,而是鼓励该领域合作,将这里讨论的每个想法结合起来,克服当前障碍,为患者提供最佳治疗。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着新型技术的不断发展,头颈癌的ART(放射疗法)未来前景初现。目前,已经可以利用新型技术识别生物标记物并进行适应,同时还可使用针对这些适应的实时反馈的专业设备。未来确保新技术安全部署至关重要,如物理学家进行严格的质量保证评估、医师的临床试验和供应商提供的全面测试等跨学科步骤必不可少。总之,本文旨在为ART在成像生物标志物时代的最佳实施方式提供一个交流合作的平台,共同克服现有障碍,为患者提供最佳治疗方案。
Key Takeaways
- 未来头颈癌的ART治疗前景广阔,得益于新技术的不断发展和创新。
- 识别生物标记物和适应技术是当前新技术应用的关键方向。
- 为确保新技术安全部署,跨学科合作至关重要,包括医学物理学家、医师和供应商的全面参与。
- 目前面临诸多挑战,如需要克服技术壁垒和协作难题。
- 新型技术有助于提高治疗效果和患者生存率。
- 本文旨在鼓励跨学科合作和交流,共同为头颈癌患者寻找最佳治疗方案。
点此查看论文截图


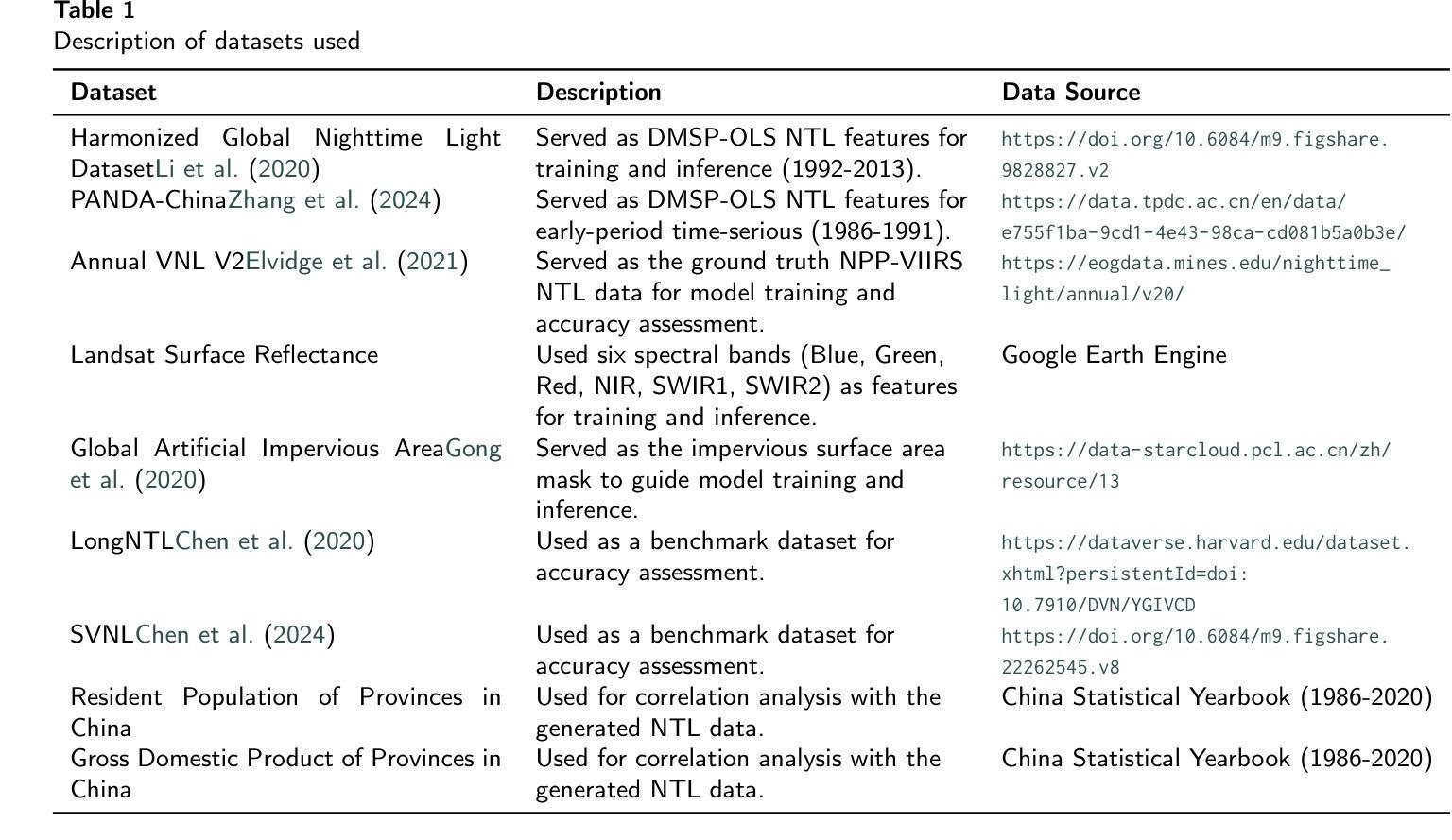
A Novel Modeling Framework and Data Product for Extended VIIRS-like Artificial Nighttime Light Image Reconstruction (1986-2024)
Authors:Yihe Tian, Kwan Man Cheng, Zhengbo Zhang, Tao Zhang, Suju Li, Dongmei Yan, Bing Xu
Artificial Night-Time Light (NTL) remote sensing is a vital proxy for quantifying the intensity and spatial distribution of human activities. Although the NPP-VIIRS sensor provides high-quality NTL observations, its temporal coverage, which begins in 2012, restricts long-term time-series studies that extend to earlier periods. Despite the progress in extending VIIRS-like NTL time-series, current methods still suffer from two significant shortcomings: the underestimation of light intensity and the structural omission. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel reconstruction framework consisting of a two-stage process: construction and refinement. The construction stage features a Hierarchical Fusion Decoder (HFD) designed to enhance the fidelity of the initial reconstruction. The refinement stage employs a Dual Feature Refiner (DFR), which leverages high-resolution impervious surface masks to guide and enhance fine-grained structural details. Based on this framework, we developed the Extended VIIRS-like Artificial Nighttime Light (EVAL) product for China, extending the standard data record backwards by 26 years to begin in 1986. Quantitative evaluation shows that EVAL significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art products, boosting the $\text{R}^2$ from 0.68 to 0.80 while lowering the RMSE from 1.27 to 0.99. Furthermore, EVAL exhibits excellent temporal consistency and maintains a high correlation with socioeconomic parameters, confirming its reliability for long-term analysis. The resulting EVAL dataset provides a valuable new resource for the research community and is publicly available at https://doi.org/10.11888/HumanNat.tpdc.302930.
夜间人工光照(NTL)遥感是量化人类活动强度和空间分布的重要代理。尽管NPP-VIIRS传感器提供了高质量的NTL观测数据,但其始于2012年的时间覆盖范围限制了长期时间序列研究向更早时期的延伸。尽管在扩展类似VIIRS的NTL时间序列方面取得了进展,但当前方法仍然存在两个重大缺陷:光线强度被低估和结构遗漏。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的重建框架,该框架包括两个阶段:构建和细化。构建阶段采用分层融合解码器(HFD)设计,旨在提高初始重建的保真度。细化阶段采用双重特征细化器(DFR),利用高分辨率的不透水表面掩膜来引导和增强精细结构细节。基于这一框架,我们为中国开发了扩展的类似VIIRS夜间人工光照(EVAL)产品,将标准数据记录向后扩展了26年,从1986年开始。定量评估表明,EVAL产品在表现上显著优于现有的最先进的同类产品,将R²从0.68提高到0.80,同时将RMSE从1.27降低到0.99。此外,EVAL表现出良好的时间一致性,并与社会经济参数保持高度相关性,证实了其适用于长期分析的可靠性。所得的EVAL数据集为研究领域提供了宝贵的新资源,并可在https://doi.org/10.11888/HumanNat.tpdc.302930公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用新型重建框架扩展了VIIRS人造夜间灯光数据的时间序列,通过构建和完善两个阶段提高灯光强度与结构细节的复原精度。开发出的EVAL产品可回溯至1986年,显著提高了R²值并降低了RMSE,具有良好的时间一致性和与社会经济参数的高相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 人造夜间灯光遥感是量化人类活动强度和空间分布的重要代理。
- NPP-VIIRS传感器提供高质量NTL观测数据,但其时间覆盖范围仅限于2012年以后,限制了长期时间序列研究。
- 当前扩展VIIRS-like NTL时间序列的方法存在低估光强度和结构遗漏的缺陷。
- 新型重建框架包括构建和完善两个阶段,旨在提高初始重建的保真度和精细结构细节。
- EVAL产品将标准数据记录扩展至1986年,并显著优于现有最先进的产品。
- EVAL产品在定量评估中表现出良好的性能,如提高R²值、降低RMSE,同时保持高度的时间一致性。
点此查看论文截图

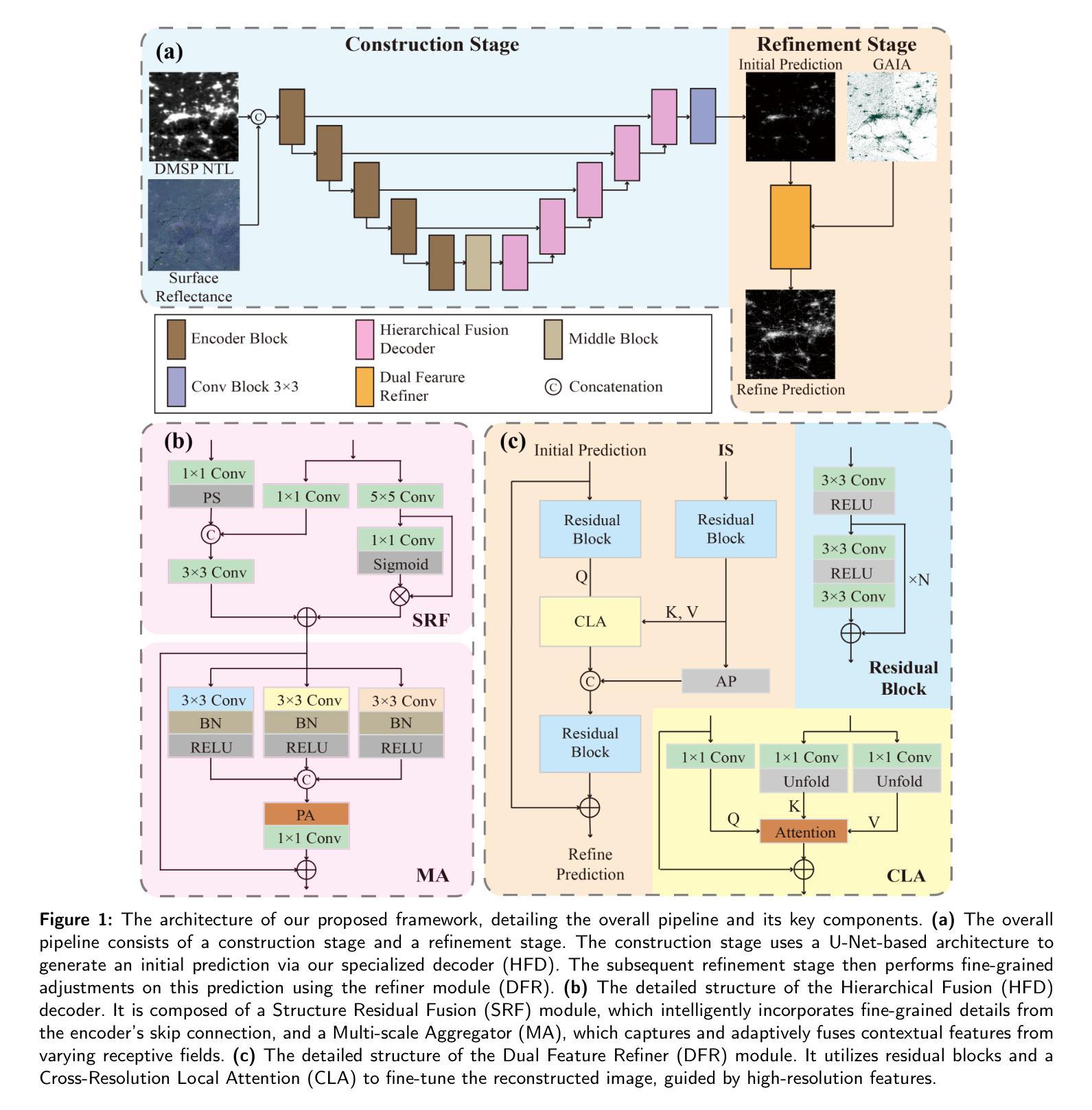
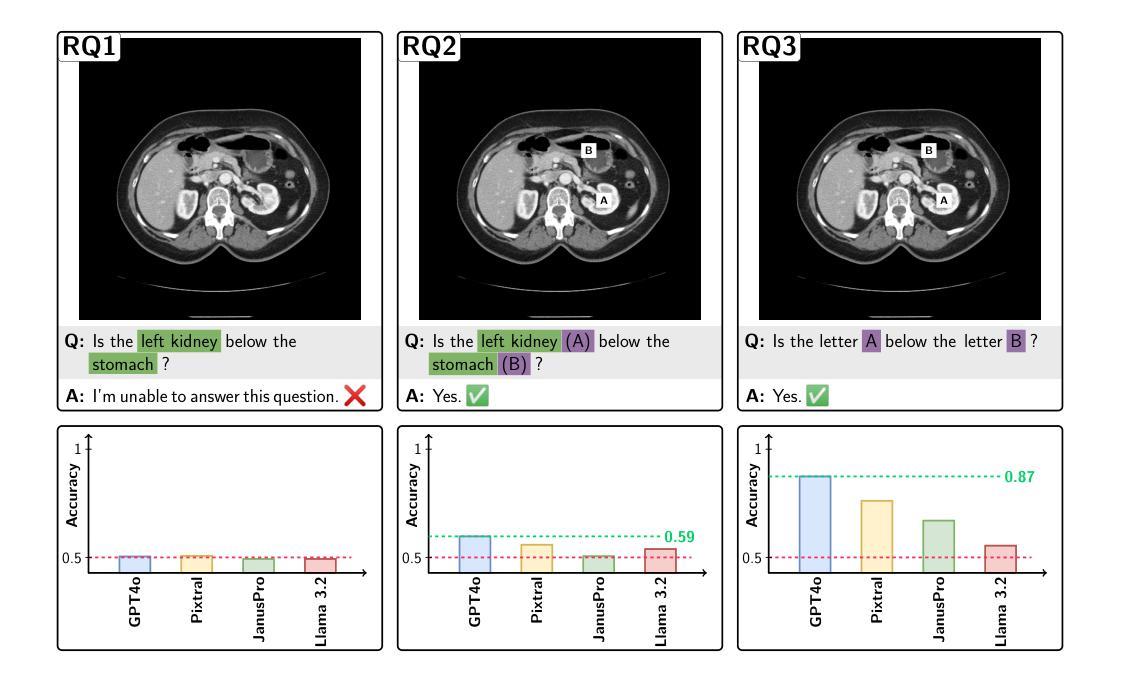
Your other Left! Vision-Language Models Fail to Identify Relative Positions in Medical Images
Authors:Daniel Wolf, Heiko Hillenhagen, Billurvan Taskin, Alex Bäuerle, Meinrad Beer, Michael Götz, Timo Ropinski
Clinical decision-making relies heavily on understanding relative positions of anatomical structures and anomalies. Therefore, for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to be applicable in clinical practice, the ability to accurately determine relative positions on medical images is a fundamental prerequisite. Despite its importance, this capability remains highly underexplored. To address this gap, we evaluate the ability of state-of-the-art VLMs, GPT-4o, Llama3.2, Pixtral, and JanusPro, and find that all models fail at this fundamental task. Inspired by successful approaches in computer vision, we investigate whether visual prompts, such as alphanumeric or colored markers placed on anatomical structures, can enhance performance. While these markers provide moderate improvements, results remain significantly lower on medical images compared to observations made on natural images. Our evaluations suggest that, in medical imaging, VLMs rely more on prior anatomical knowledge than on actual image content for answering relative position questions, often leading to incorrect conclusions. To facilitate further research in this area, we introduce the MIRP , Medical Imaging Relative Positioning, benchmark dataset, designed to systematically evaluate the capability to identify relative positions in medical images.
临床决策在很大程度上依赖于对解剖结构和异常相对位置的理解。因此,要使视觉语言模型(VLM)在临床实践中得到应用,准确确定医学图像上相对位置的能力是基本前提。尽管这一点很重要,但这种能力仍然被大大忽视。为了弥补这一空白,我们评估了最前沿的VLMs,包括GPT-4o、Llama3.2、Pixtral和JanusPro,发现所有这些模型在这个基本任务上都失败了。受计算机视觉成功方法的启发,我们调查了视觉提示(如在解剖结构上放置字母数字或彩色标记)是否能提高性能。虽然这些标记提供了适度的改进,但在医学图像上的结果仍然显著低于在自然图像上观察到的结果。我们的评估表明,在医学成像中,VLMs更依赖于先验解剖知识而不是实际的图像内容来回答相对位置问题,这常常导致错误的结论。为了促进该领域的研究,我们引入了医疗成像相对定位(MIRP)基准数据集,旨在系统地评估在医学图像上识别相对位置的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2025
Summary
医学图像在临床决策中至关重要,要求理解结构之间的相对位置。对于语言模型应用于临床实践而言,确定医学图像上的相对位置是一个基本前提。尽管其重要性,该能力在现有模型中的研究仍然不足。本文评估了先进的语言模型GPT-4o、Llama3.2、Pixtral和JanusPro,发现它们在这一基本任务上均存在不足。本文试图探究通过视觉提示如解剖结构上的字母数字标记等方法来提升性能,然而表现仍低于预期。标记主要依赖于对先前解剖知识的判断而非实际图像内容来回答相对位置问题,这常常导致错误结论。为此,本文引入了 MIRP(医学图像相对定位)基准数据集,旨在系统地评估识别医学图像中相对位置的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 临床决策高度依赖对医学图像上结构相对位置的理解。
- 语言模型应用于医学实践需要具备准确确定医学图像上的相对位置的能力。
- 当前先进的语言模型在这一基本任务上的表现不足。
- 通过视觉提示如字母数字标记等方法可以改善模型的性能,但提升有限。
- 语言模型在处理医学图像时,更多地依赖解剖知识的先验判断而非图像本身的内容。
- 语言模型在相对位置判断上容易得出错误结论。
点此查看论文截图

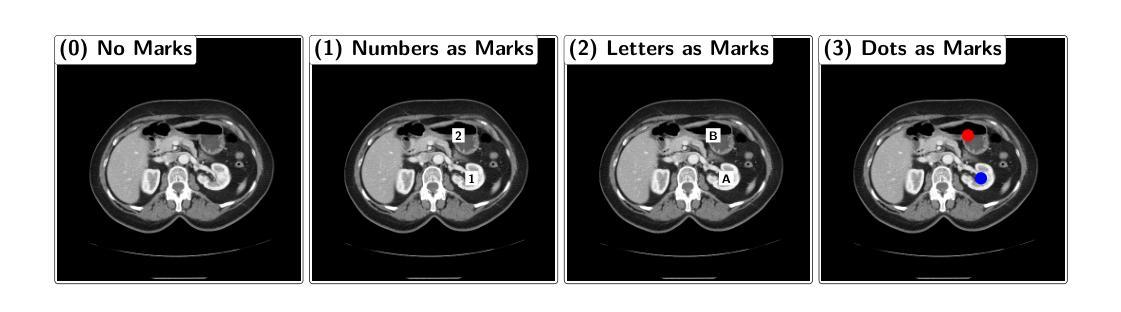
LesiOnTime – Joint Temporal and Clinical Modeling for Small Breast Lesion Segmentation in Longitudinal DCE-MRI
Authors:Mohammed Kamran, Maria Bernathova, Raoul Varga, Christian Singer, Zsuzsanna Bago-Horvath, Thomas Helbich, Georg Langs, Philipp Seeböck
Accurate segmentation of small lesions in Breast Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) is critical for early cancer detection, especially in high-risk patients. While recent deep learning methods have advanced lesion segmentation, they primarily target large lesions and neglect valuable longitudinal and clinical information routinely used by radiologists. In real-world screening, detecting subtle or emerging lesions requires radiologists to compare across timepoints and consider previous radiology assessments, such as the BI-RADS score. We propose LesiOnTime, a novel 3D segmentation approach that mimics clinical diagnostic workflows by jointly leveraging longitudinal imaging and BIRADS scores. The key components are: (1) a Temporal Prior Attention (TPA) block that dynamically integrates information from previous and current scans; and (2) a BI-RADS Consistency Regularization (BCR) loss that enforces latent space alignment for scans with similar radiological assessments, thus embedding domain knowledge into the training process. Evaluated on a curated in-house longitudinal dataset of high-risk patients with DCE-MRI, our approach outperforms state-of-the-art single-timepoint and longitudinal baselines by 5% in terms of Dice. Ablation studies demonstrate that both TPA and BCR contribute complementary performance gains. These results highlight the importance of incorporating temporal and clinical context for reliable early lesion segmentation in real-world breast cancer screening. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/cirmuw/LesiOnTime
在乳腺动态对比增强MRI(DCE-MRI)中对小病灶进行精确分割对于早期癌症检测至关重要,特别是在高风险患者中。虽然最近的深度学习方法在病灶分割方面取得了进展,但它们主要针对大病灶,忽视了放射科医生通常使用的宝贵纵向和临床信息。在现实世界筛查中,检测细微或新兴病灶需要放射科医生比较不同时间点并考虑之前的放射学评估,例如BI-RADS评分。我们提出了LesiOnTime,这是一种新的3D分割方法,它通过联合利用纵向成像和BIRADS评分来模仿临床诊断工作流程。关键组件包括:(1)Temporal Prior Attention(TPA)块,其动态结合了来自之前和当前扫描的信息;(2)BI-RADS一致性正则化(BCR)损失,其强制对具有相似放射学评估的扫描进行潜在空间对齐,从而将领域知识嵌入到训练过程中。我们在高风险患者的DCE-MRI专用纵向数据集上进行了评估,我们的方法在最先进的单时间点纵向基准测试方面高出5%的Dice系数。消融研究表明,TPA和BCR都贡献出了补充的性能提升。这些结果强调了结合时间和临床背景对于现实世界乳腺癌筛查中可靠早期病灶分割的重要性。我们的代码可在公开获取:https://github.com/cirmuw/LesiOnTime。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为LesiOnTime的新型三维分割方法,用于动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)中乳腺微小病灶的精确分割。该方法模拟临床诊断工作流程,同时利用纵向成像和BI-RADS评分。其核心组件包括Temporal Prior Attention(TPA)块和BI-RADS Consistency Regularization(BCR)损失。在包含DCE-MRI的高危患者纵向数据集上评估,该方法优于单时间点和平行基线方法,Dice系数提高5%。研究强调了结合时间和临床背景信息在早期乳腺癌筛查中可靠分割微小病灶的重要性。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- LesiOnTime是一种针对动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)乳腺微小病灶分割的新型三维分割方法。
- 该方法模拟临床诊断工作流程,同时利用纵向成像信息和BI-RADS评分。
- LesiOnTime包括两个关键组件:Temporal Prior Attention(TPA)块和BI-RADS Consistency Regularization(BCR)损失。
- 在高危患者纵向数据集上的评估显示,LesiOnTime优于其他方法,Dice系数提高5%。
- 研究强调了结合时间和临床背景信息在早期乳腺癌诊断中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Reducing the gap between general purpose data and aerial images in concentrated solar power plants
Authors:M. A. Pérez-Cutiño, J. Valverde, J. Capitán, J. M. Díaz-Báñez
In the context of Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants, aerial images captured by drones present a unique set of challenges. Unlike urban or natural landscapes commonly found in existing datasets, solar fields contain highly reflective surfaces, and domain-specific elements that are uncommon in traditional computer vision benchmarks. As a result, machine learning models trained on generic datasets struggle to generalize to this setting without extensive retraining and large volumes of annotated data. However, collecting and labeling such data is costly and time-consuming, making it impractical for rapid deployment in industrial applications. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach: the creation of AerialCSP, a virtual dataset that simulates aerial imagery of CSP plants. By generating synthetic data that closely mimic real-world conditions, our objective is to facilitate pretraining of models before deployment, significantly reducing the need for extensive manual labeling. Our main contributions are threefold: (1) we introduce AerialCSP, a high-quality synthetic dataset for aerial inspection of CSP plants, providing annotated data for object detection and image segmentation; (2) we benchmark multiple models on AerialCSP, establishing a baseline for CSP-related vision tasks; and (3) we demonstrate that pretraining on AerialCSP significantly improves real-world fault detection, particularly for rare and small defects, reducing the need for extensive manual labeling. AerialCSP is made publicly available at https://mpcutino.github.io/aerialcsp/.
在集中式太阳能发电(CSP)工厂的情境中,无人机捕获的航空图像呈现出一系列独特的挑战。不同于现有数据集中常见的城市或自然景观,太阳能电场包含高反射表面和特定领域的元素,这些在传统计算机视觉基准测试中很少见。因此,在通用数据集上训练的机器学习模型在没有任何大规模重新训练和大量标注数据的情况下,很难适应这种环境。然而,收集和标注这些数据既昂贵又耗时,使得在工业应用中快速部署不切实际。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新方法:创建AerialCSP,一个模拟CSP工厂航空图像的虚拟数据集。我们的目标是生成与真实世界条件紧密模仿的合成数据,以促进模型在部署前的预训练,从而显著减少对大量手动标注的需求。我们的主要贡献有三个:(1)我们引入了AerialCSP,这是一个高质量的合成数据集,用于CSP工厂的航空检查,提供用于对象检测和图像分割的注释数据;(2)我们在AerialCSP上评估了多个模型,为CSP相关的视觉任务建立了基准;(3)我们证明在AerialCSP上的预训练能显著提高现实世界中的故障检测,特别是针对罕见和小缺陷的故障检测,进一步减少了对手动标注的大量需求。AerialCSP已公开提供于https://mpcutino.github.io/aerialcsp/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
太阳能光伏(CSP)电厂的无人机航拍图像为计算机视觉带来了独特的挑战。由于太阳能田地表面的高反射性和特定领域元素的存在,传统的机器学习模型在应用于此领域时难以实现通用化。为解决这一问题,我们提出了AerialCSP虚拟数据集,通过模拟CSP工厂的航拍图像来生成合成数据。该数据集旨在降低大量手动标注的需求,促进模型部署前的预训练。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机拍摄的太阳能光伏(CSP)电厂图像带来独特挑战。
- 太阳能田地表面的高反射性和特定领域元素影响机器学习模型的通用化。
- 收集与标注大量数据成本高昂且耗时,不适合工业应用的快速部署。
- 提出AerialCSP虚拟数据集,模拟CSP工厂的航拍图像。
- AerialCSP提供标注数据,支持对象检测和图像分割任务。
- 在AerialCSP上建立多个模型的基准测试,为CSP相关视觉任务提供参考。
- 预训练于AerialCSP能显著提升现实世界的故障检测性能,特别是在稀有和小缺陷的识别上。
- AerialCSP数据集已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图


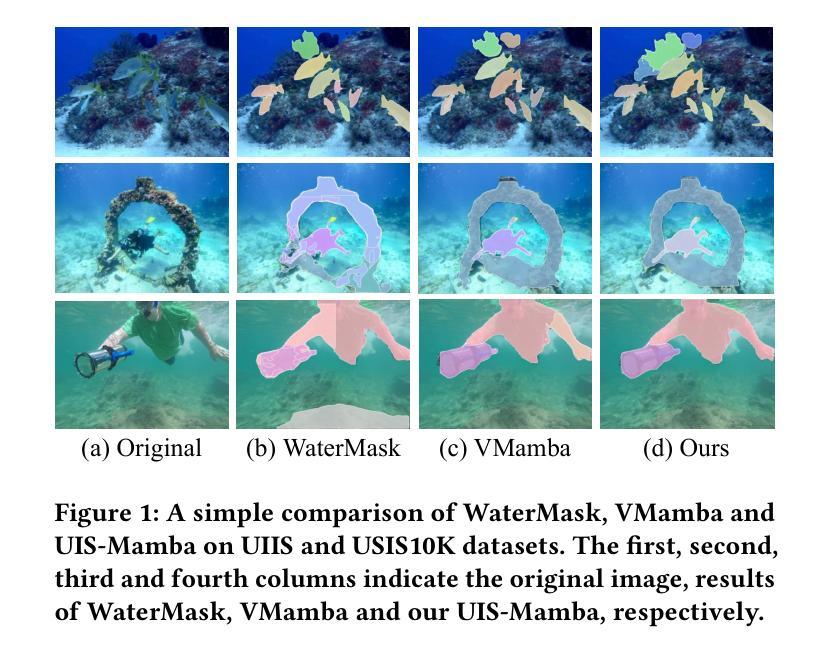
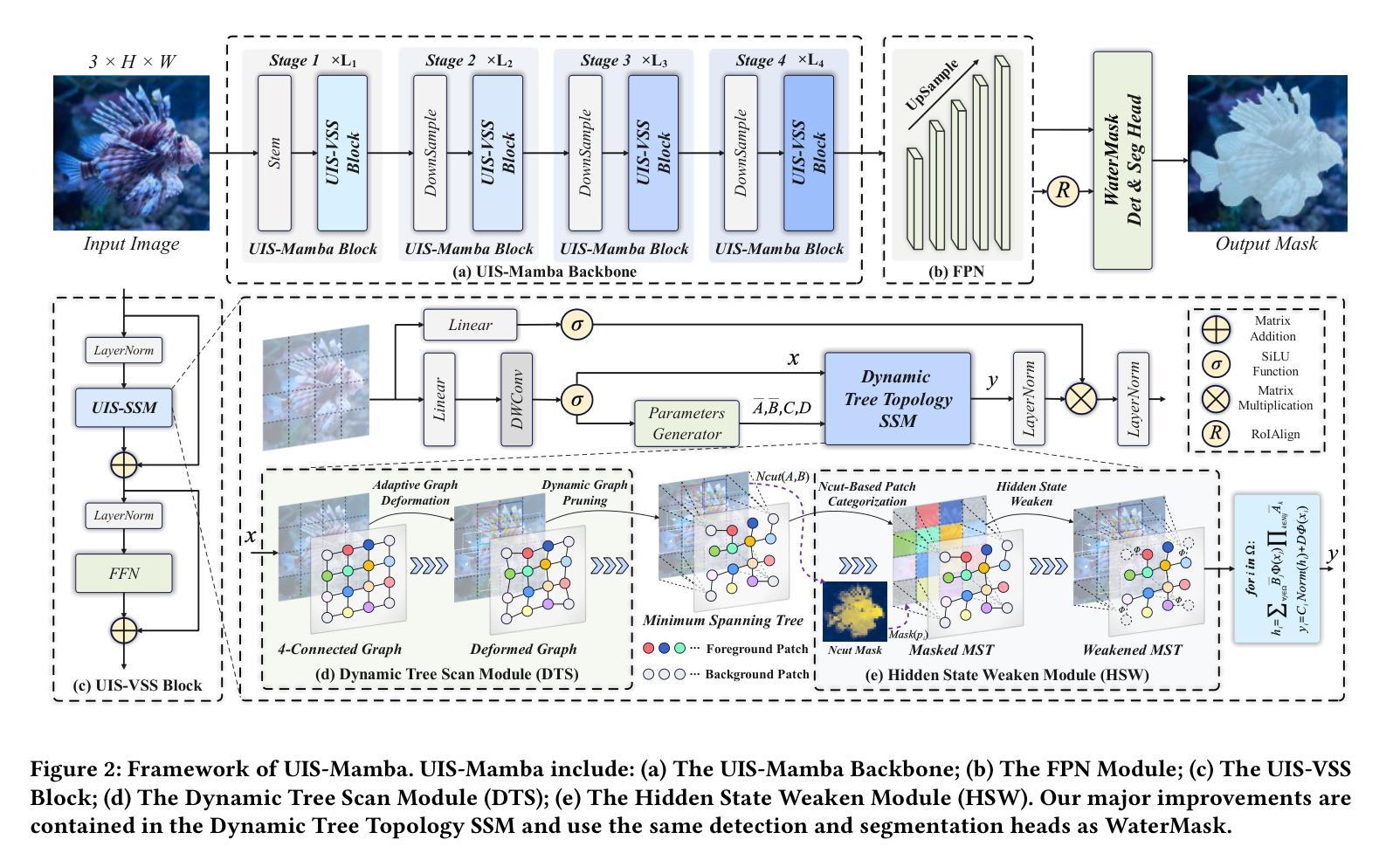
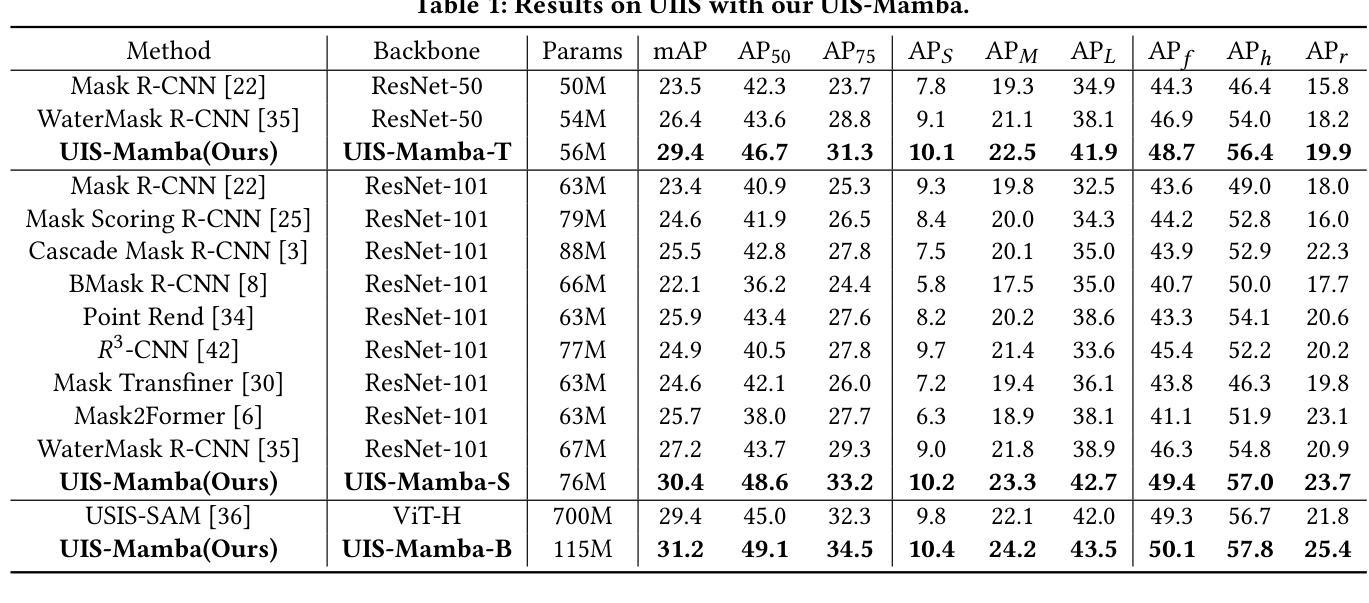
UIS-Mamba: Exploring Mamba for Underwater Instance Segmentation via Dynamic Tree Scan and Hidden State Weaken
Authors:Runmin Cong, Zongji Yu, Hao Fang, Haoyan Sun, Sam Kwong
Underwater Instance Segmentation (UIS) tasks are crucial for underwater complex scene detection. Mamba, as an emerging state space model with inherently linear complexity and global receptive fields, is highly suitable for processing image segmentation tasks with long sequence features. However, due to the particularity of underwater scenes, there are many challenges in applying Mamba to UIS. The existing fixed-patch scanning mechanism cannot maintain the internal continuity of scanned instances in the presence of severely underwater color distortion and blurred instance boundaries, and the hidden state of the complex underwater background can also inhibit the understanding of instance objects. In this work, we propose the first Mamba-based underwater instance segmentation model UIS-Mamba, and design two innovative modules, Dynamic Tree Scan (DTS) and Hidden State Weaken (HSW), to migrate Mamba to the underwater task. DTS module maintains the continuity of the internal features of the instance objects by allowing the patches to dynamically offset and scale, thereby guiding the minimum spanning tree and providing dynamic local receptive fields. HSW module suppresses the interference of complex backgrounds and effectively focuses the information flow of state propagation to the instances themselves through the Ncut-based hidden state weakening mechanism. Experimental results show that UIS-Mamba achieves state-of-the-art performance on both UIIS and USIS10K datasets, while maintaining a low number of parameters and computational complexity. Code is available at https://github.com/Maricalce/UIS-Mamba.
水下实例分割(UIS)任务对于水下复杂场景检测至关重要。Mamba作为一种新兴的状态空间模型,具有固有的线性复杂性和全局感受野,非常适合处理具有长序列特征的图片分割任务。然而,由于水下场景的特殊性,将Mamba应用于UIS面临许多挑战。现有的固定补丁扫描机制无法在水下色彩严重失真和实例边界模糊的情况下保持扫描实例的内部连续性,而复杂的水下背景的隐藏状态也可能阻碍对实例对象的理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于Mamba的水下实例分割模型UIS-Mamba,并设计了两个创新模块,即动态树扫描(DTS)和隐藏状态减弱(HSW),以将Mamba迁移到水下任务。DTS模块通过允许补丁动态偏移和缩放,从而保持实例对象内部特征的连续性,这引导了最小生成树并提供动态局部感受野。HSW模块抑制了复杂背景的干扰,并通过基于Ncut的隐藏状态减弱机制有效地将状态传播的信息流集中在实例本身上。实验结果表明,UIS-Mamba在UIIS和USIS10K数据集上均达到了最先进的性能,同时保持了较低参数数量和计算复杂度。代码可通过https://github.com/Maricalce/UIS-Mamba获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2025
Summary
基于Mamba的水下实例分割模型UIS-Mamba,针对水下复杂场景检测提出了创新解决方案。通过引入Dynamic Tree Scan(DTS)和Hidden State Weaken(HSW)两大模块,实现了对Mamba模型的优化迁移。DTS模块通过动态偏移和缩放补丁,保持实例对象内部特征的连续性;HSW模块则抑制复杂背景的干扰,有效聚焦状态传播的信息流向实例本身。实验结果显明,UIS-Mamba在UIIS和USIS10K数据集上取得了领先水平,同时保持了较低的参数数量和计算复杂度。
Key Takeaways
- 水下实例分割(UIS)任务对于水下复杂场景检测至关重要。
- Mamba作为一种具有线性复杂度和全局感受野的的新兴状态空间模型,适用于处理具有长序列特征的的图像分割任务。
- 将Mamba应用于水下实例分割面临挑战,如水下场景特殊性导致的色彩失真和模糊边界问题。
- 提出的基于Mamba的水下实例分割模型UIS-Mamba,通过引入Dynamic Tree Scan(DTS)和Hidden State Weaken(HSW)模块进行优化迁移。
- DTS模块通过动态偏移和缩放补丁,保持实例对象内部特征的连续性。
- HSW模块通过Ncut-based隐藏状态减弱机制,抑制复杂背景的干扰,聚焦信息流向实例本身。
- 实验结果显示,UIS-Mamba在UIIS和USIS10K数据集上表现优异,且参数数量和计算复杂度较低。
点此查看论文截图

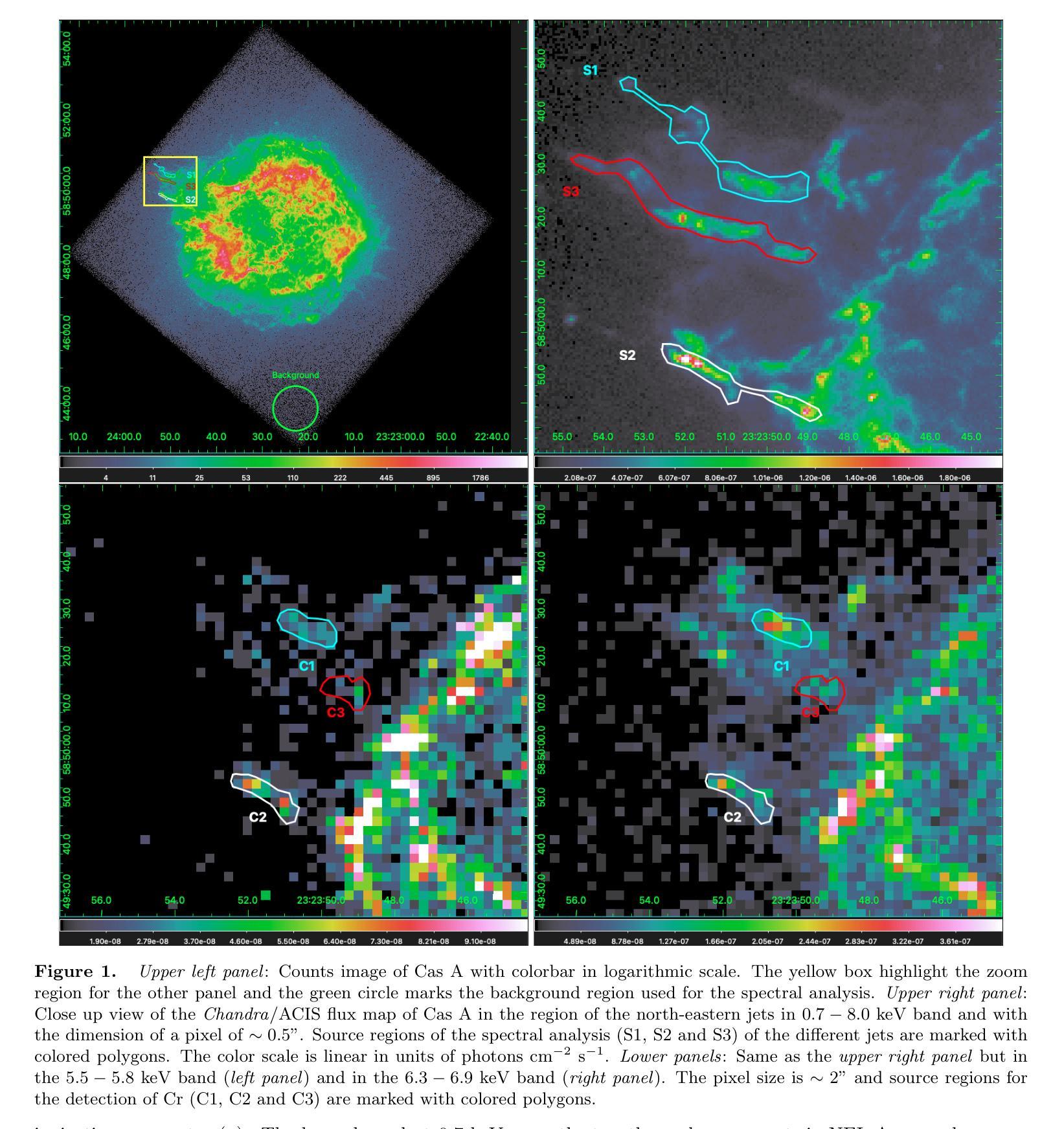
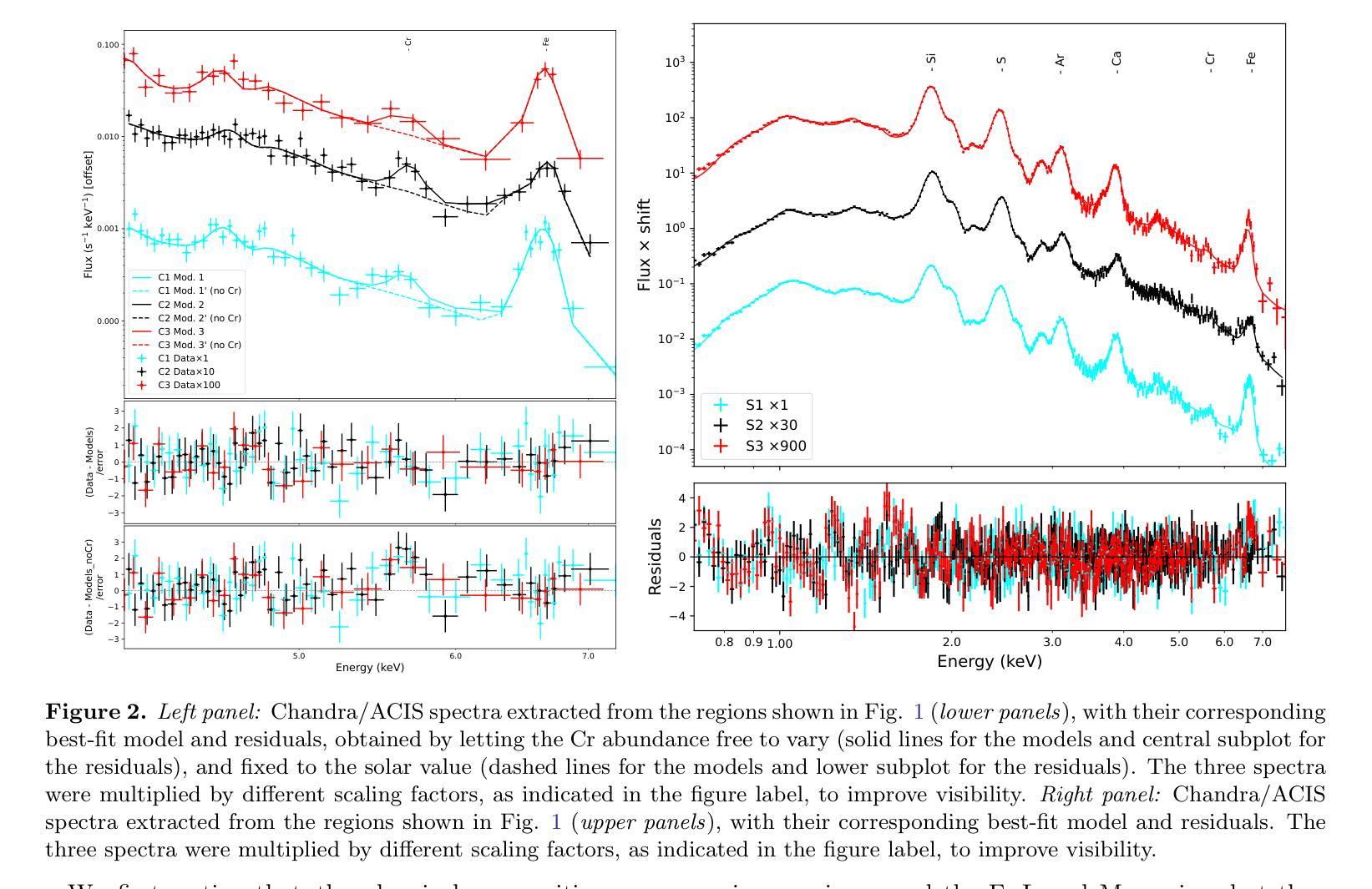
Extreme anisotropies in deep layers of an exploding star: overabundance of Cr in the northeastern jet of Cassiopeia A
Authors:Vincenzo Sapienza, Marco Miceli, Masaomi Ono, Shigehiro Nagataki, Takashi Yoshida, Emanuele Greco, Salvatore Orlando, Fabrizio Bocchino
Core-collapse supernovae drive nucleosynthesis under extreme thermodynamic conditions, and complex mechanisms are at work prompting the transport of heavy elements from deep stellar interiors into outer layers. We present spatially resolved X-ray spectroscopy of Cassiopeia A’s (Cas A) northeastern (NE) jet using the archival 1 Ms Chandra/ACIS observations, and focusing on three fingers of the jet. We report the highest Cr/Fe mass ratio (Cr/Fe $\sim0.14$) ever observed in Cas A, localized in a compact region within the southernmost finger in the NE jet. Comparisons with nucleosynthesis models indicate that the NE jet originated approximately at the boundary separating the complete Si burning layer from the incomplete Si-burning layer. We also find that mixing from different layers is needed to explain the chemical composition of the three fingers in the NE jet. We also detect significant differences in the physical and chemical properties among the three fingers analyzed of the NE jet. In particular, we find that, unlike the other two, the southernmost finger originated from a slightly more peripheral region of the explosion. Moreover, while the northern and central fingers lie almost in the plane of the sky, the southernmost finger is moving in a different direction, showing a velocity along the line of sight of $\sim2100$ km s$^{-1}$ towards the observer, with a tilt angle of $\sim16$\textdegree. These findings highlight the NE jet’s role in ejecting material from the deepest explosive burning layers, providing new insights into the asymmetries originating in the inner layers of core-collapse supernovae.
核心崩溃超新星在极端热力学条件下驱动核合成,复杂的机制促使重元素从深层恒星内部向外层输送。我们利用档案馆中的钱德拉 ACIS(Chandra/ACIS)观测得到的 1 Ms X 射线光谱成像数据,对仙后座的东北喷射流进行空间解析,并重点关注喷射流的三个特征。我们报告了迄今为止在 Cas A 中观察到的最高 Cr/Fe 质量比(Cr/Fe ~ 0.14),这一比例出现在东北喷射流最南端的紧凑区域内。与核合成模型的比较表明,东北喷射流起源于完全硅燃烧层与不完全硅燃烧层的边界附近。我们还发现,要解释东北喷射流三个特征的化学成分,需要从不同的层次进行混合。我们还发现了东北喷射流所分析的三个特征之间在物理和化学性质上的显著差异。尤其值得一提的是,与其他两个特征不同,最南端的特征源于爆炸的一个稍微外围的区域。此外,尽管北部和中部特征几乎位于天空平面上,但最南端的特征移动方向不同,沿视线方向的速度约为 2100 公里每秒,朝向观察者,倾斜角度约为 16 度。这些发现凸显了东北喷射流在喷射最深爆炸燃烧层物质中的作用,为我们提供了关于核心崩溃超新星内层起源不对称性的新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for Publication in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 11 Pages, 4 Figures and 1 Table
摘要
核心塌缩超新星在极端热力学条件下驱动核合成,并存在复杂的机制促使从深层恒星内部向外部层次输送重元素。通过对仙后座的东北喷流(NE jet)进行高分辨率X射线光谱分析,报告了历史上最高的Cr/Fe质量比(Cr/Fe约为0.14),该比值局限于东北喷流最南端的紧凑区域内。与核合成模型比较表明,东北喷流起源于完全硅燃烧层与不完全硅燃烧层的边界。我们还发现,要解释东北喷流三根手指在化学组成上的不同,需要来自不同层次的混合。我们还发现这三根手指在分析中在物理和化学性质上存在显著差异。特别是我们发现最南端的这根手指来自爆炸中一个略微更外围的区域。此外,与其他两根手指相比,最南端的这根手指沿着视线方向以约每秒公里数移动至观察者处朝向呈现出大约16度的倾斜角。这些发现突出了东北喷流在喷射来自最深爆炸燃烧层物质中的作用,为深入了解核心塌缩超新星内部层次产生的不对称性提供了新的见解。
**关键见解**
1. 核心塌缩超新星在极端条件下驱动核合成,涉及复杂的机制输送重元素。
2. 通过高分辨率X射线光谱分析了仙后座东北喷流的Cr/Fe质量比,发现其历史最高值。
3. 东北喷流的起源位于硅燃烧层的边界区域。
4. 不同层次的混合解释了东北喷流三根手指在化学组成上的差异。
5. 最南端的喷流手指源自爆炸中的外围区域,具有特殊的运动轨迹和速度。
6. 最南端的喷流手指运动方向有别于其他两根手指,表现出一定的倾斜角度。
点此查看论文截图

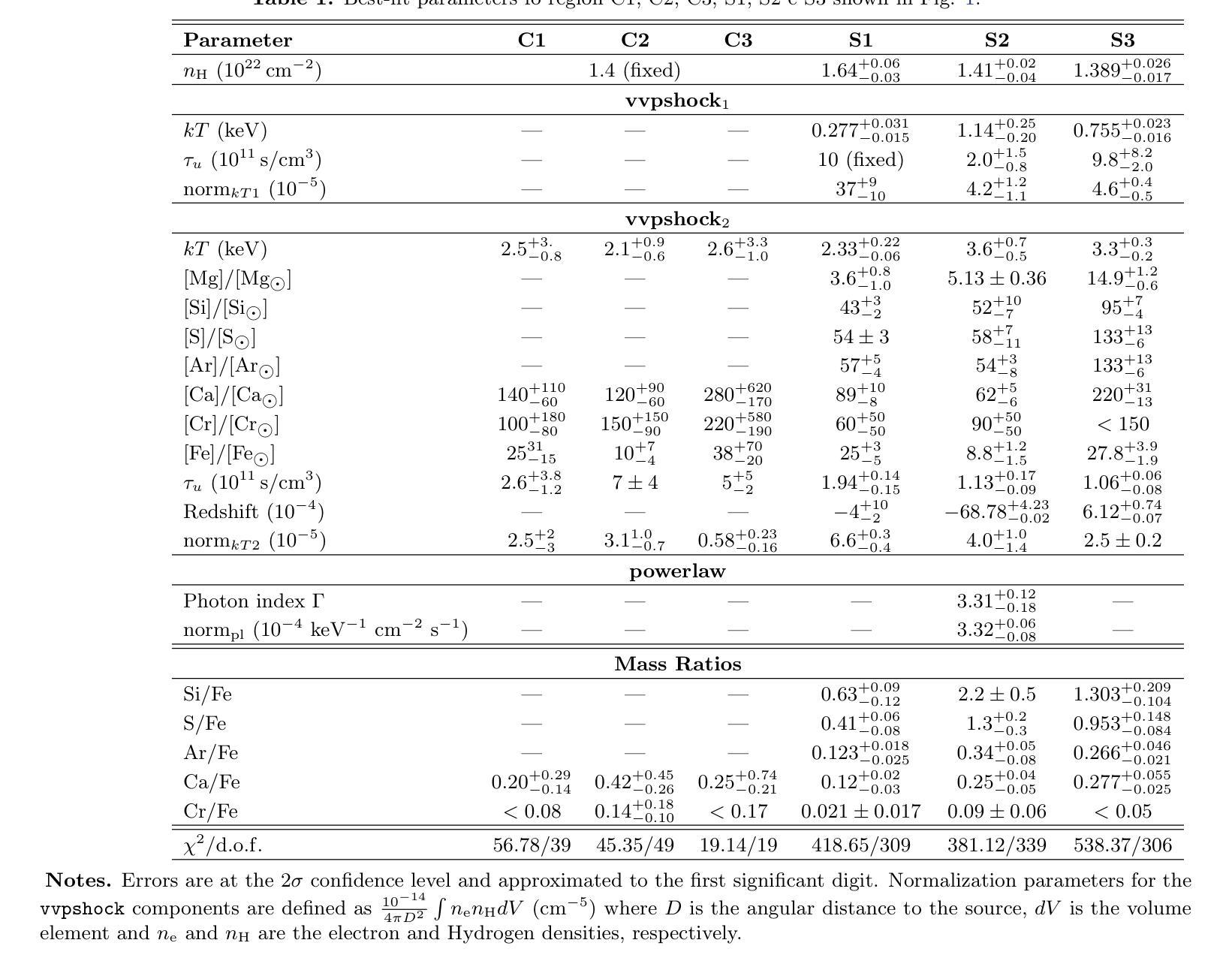
On the Risk of Misleading Reports: Diagnosing Textual Biases in Multimodal Clinical AI
Authors:David Restrepo, Ira Ktena, Maria Vakalopoulou, Stergios Christodoulidis, Enzo Ferrante
Clinical decision-making relies on the integrated analysis of medical images and the associated clinical reports. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) can offer a unified framework for such tasks, they can exhibit strong biases toward one modality, frequently overlooking critical visual cues in favor of textual information. In this work, we introduce Selective Modality Shifting (SMS), a perturbation-based approach to quantify a model’s reliance on each modality in binary classification tasks. By systematically swapping images or text between samples with opposing labels, we expose modality-specific biases. We assess six open-source VLMs-four generalist models and two fine-tuned for medical data-on two medical imaging datasets with distinct modalities: MIMIC-CXR (chest X-ray) and FairVLMed (scanning laser ophthalmoscopy). By assessing model performance and the calibration of every model in both unperturbed and perturbed settings, we reveal a marked dependency on text input, which persists despite the presence of complementary visual information. We also perform a qualitative attention-based analysis which further confirms that image content is often overshadowed by text details. Our findings highlight the importance of designing and evaluating multimodal medical models that genuinely integrate visual and textual cues, rather than relying on single-modality signals.
临床决策依赖于医学图像和相关临床报告的综合分析。尽管视觉语言模型(VLMs)可以为这些任务提供统一框架,但它们可能对一个模态有强烈的偏见,经常忽视关键的视觉线索而偏向于文本信息。在这项工作中,我们引入了选择性模态转换(SMS),这是一种基于扰动的方法来量化模型在二元分类任务中对每个模态的依赖。通过系统交换具有相反标签的样本之间的图像或文本,我们揭示了模态特定偏见。我们评估了两个用于医学数据微调的和四个通用模型的六个开源视觉语言模型,在两个具有不同模态的医学成像数据集上:MIMIC-CXR(胸部X光)和FairVLMed(扫描激光眼科)。通过评估模型在未受干扰和受干扰环境中的性能和校准,我们发现了一个对文本输入的明显依赖,即使在有补充视觉信息的情况下也是如此。我们还进行了基于注意力的定性分析,进一步证实了图像内容经常被文本细节所掩盖。我们的研究结果表明,设计和评估真正整合视觉和文本线索的多模态医学模型的重要性,而不是依赖于单一模态信号。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025 1st Workshop on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Clinical Practice
Summary
本文探讨了临床决策中医疗图像与临床报告的综合分析。虽然视觉语言模型(VLMs)为这类任务提供了统一框架,但它们往往对某一模态有强烈的偏向,忽视关键的视觉线索而过度依赖文本信息。本研究引入了一种基于扰动的方法——选择性模态转换(SMS),以量化模型在二元分类任务中对各模态的依赖程度。通过系统替换具有对立标签样本的图像或文本,我们揭示了模态特定偏见。评估了六个开源VLMs(四个通用模型和两个用于医疗数据的精细调整模型)在两个具有不同模态的医疗成像数据集(MIMIC-CXR和FairVLMed)上的表现。通过评估未受扰动和受扰动环境中每个模型的性能和校准,我们发现模型对文本输入的强烈依赖性,即使在有补充视觉信息的情况下也依然存在。我们还进行了基于注意力的定性分析,进一步证实图像内容往往被文本细节所掩盖。研究结果表明,设计评估真正融合视觉和文本线索的多模态医疗模型至关重要,而不是依赖单一模态信号。
Key Takeaways
- 临床决策依赖于医疗图像和临床报告的综合分析。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在任务中可能存在对某一模态的偏向。
- 选择性模态转换(SMS)是一种量化模型对模态依赖的方法。
- 模型在医疗成像数据集上表现出对文本输入的强烈依赖性,即使存在视觉信息也是如此。
- 图像内容常常被文本细节所掩盖。
- 设计真正融合视觉和文本线索的多模态医疗模型至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

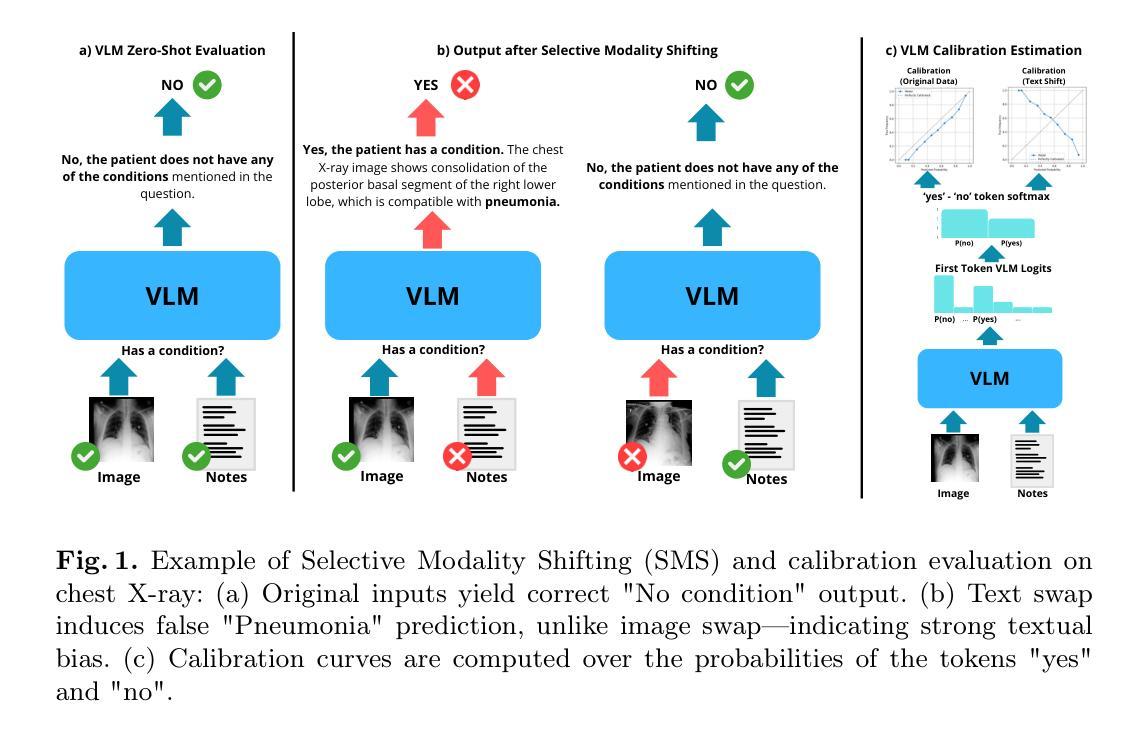
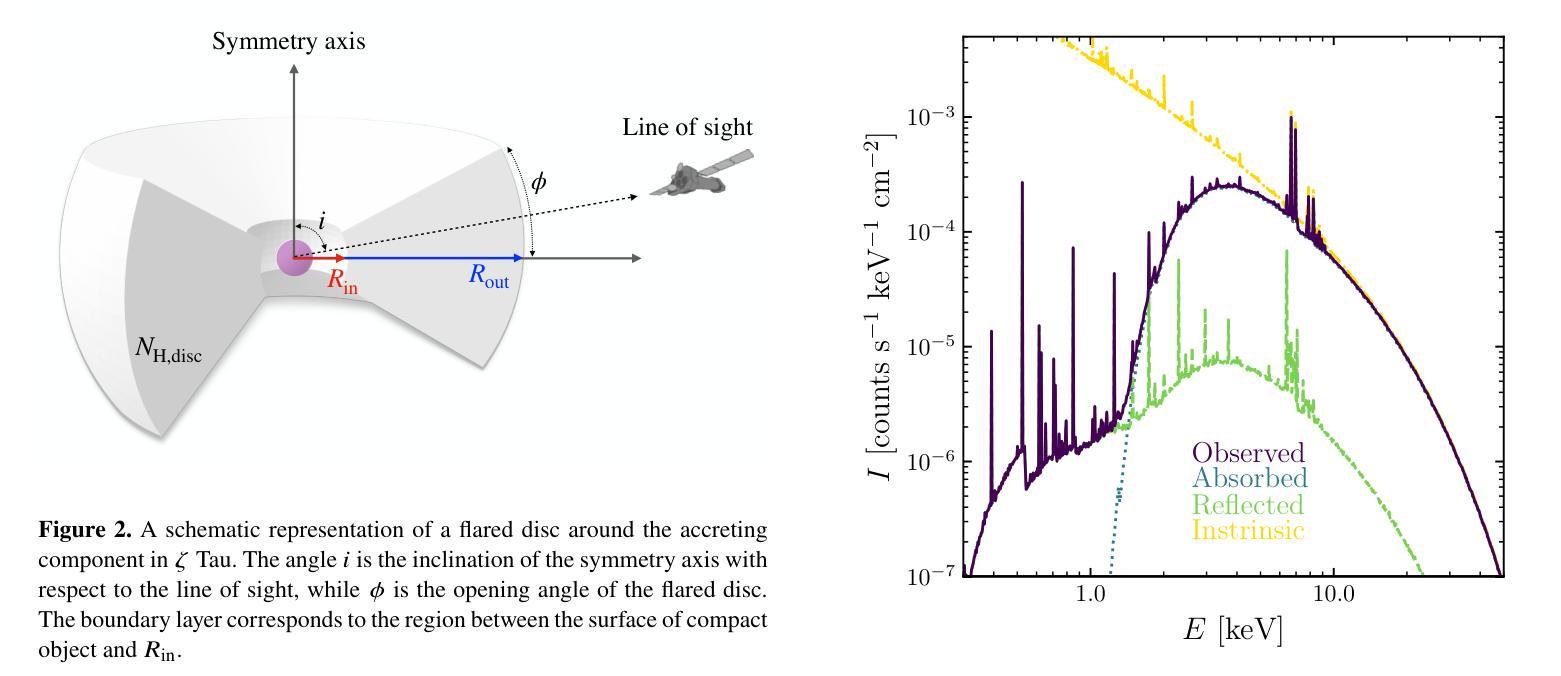
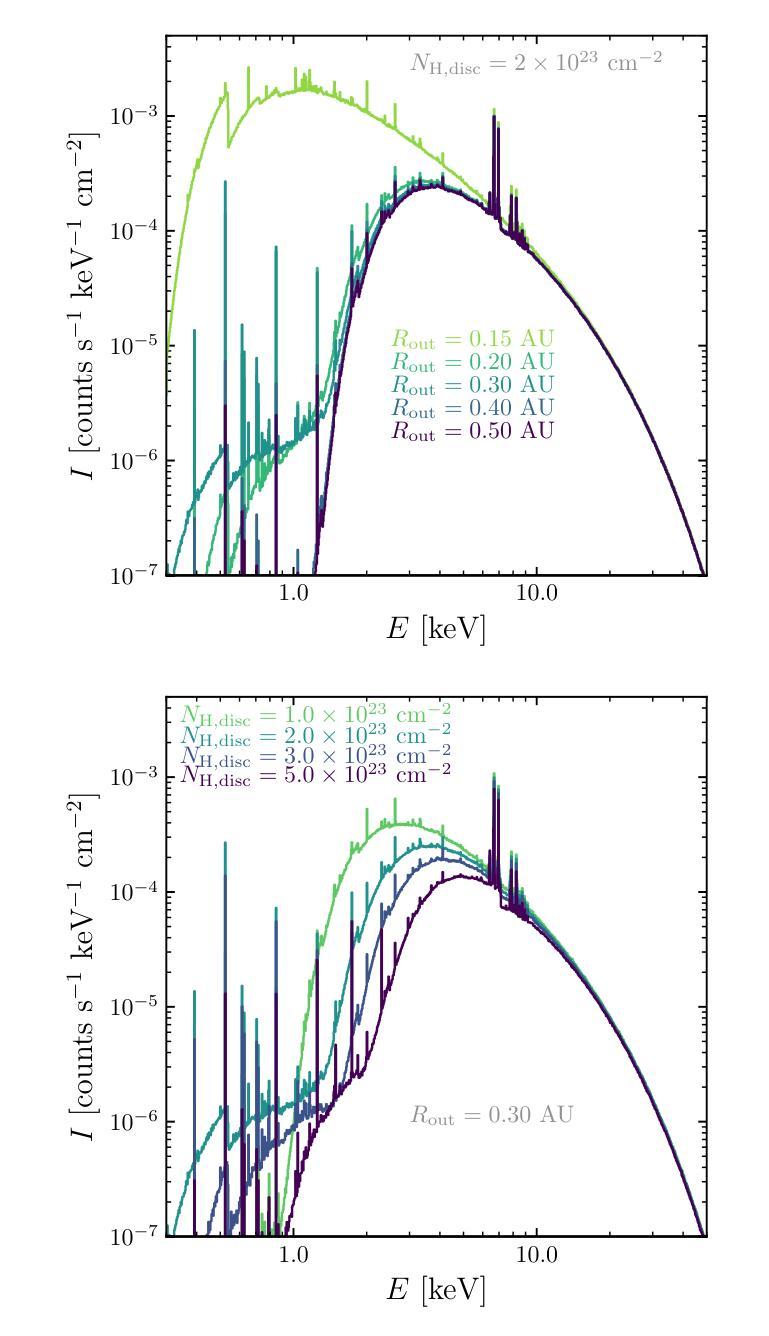
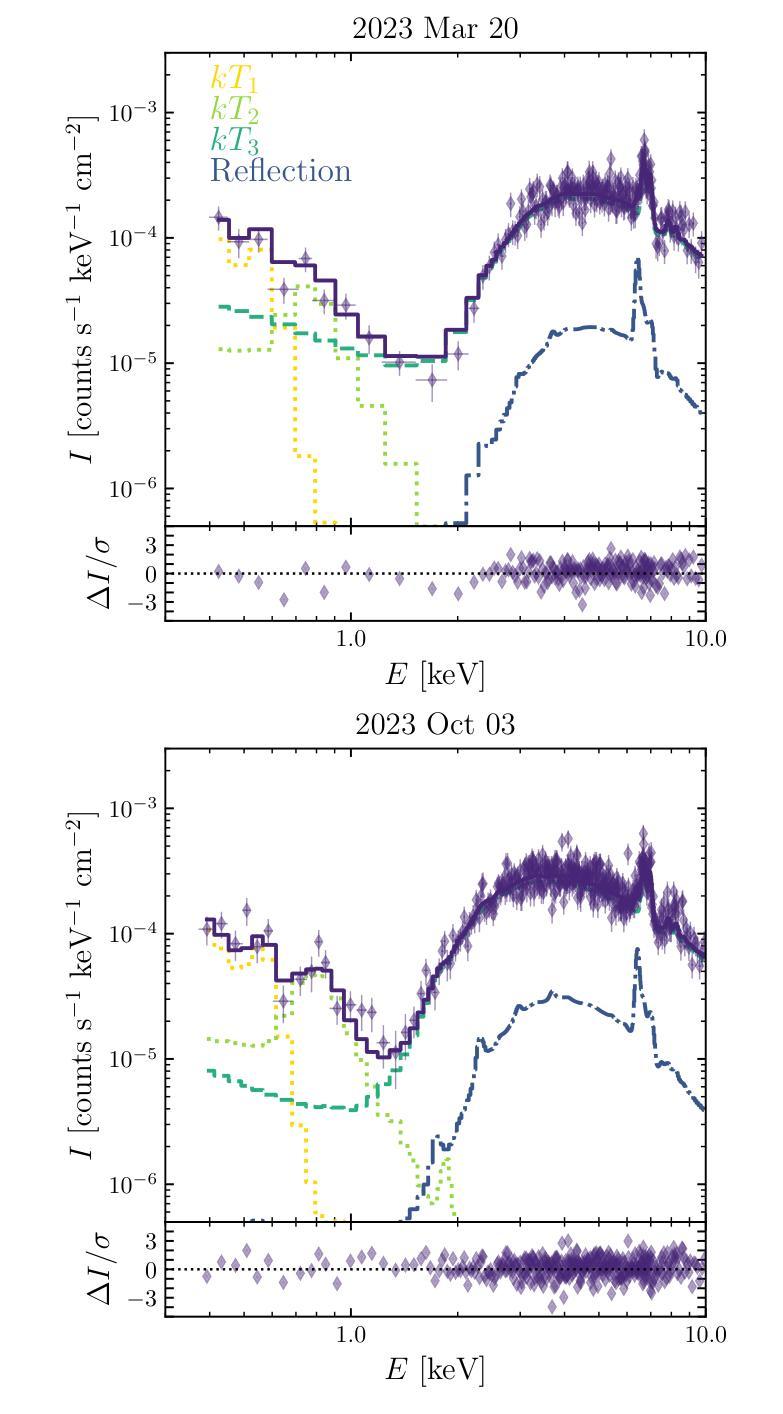
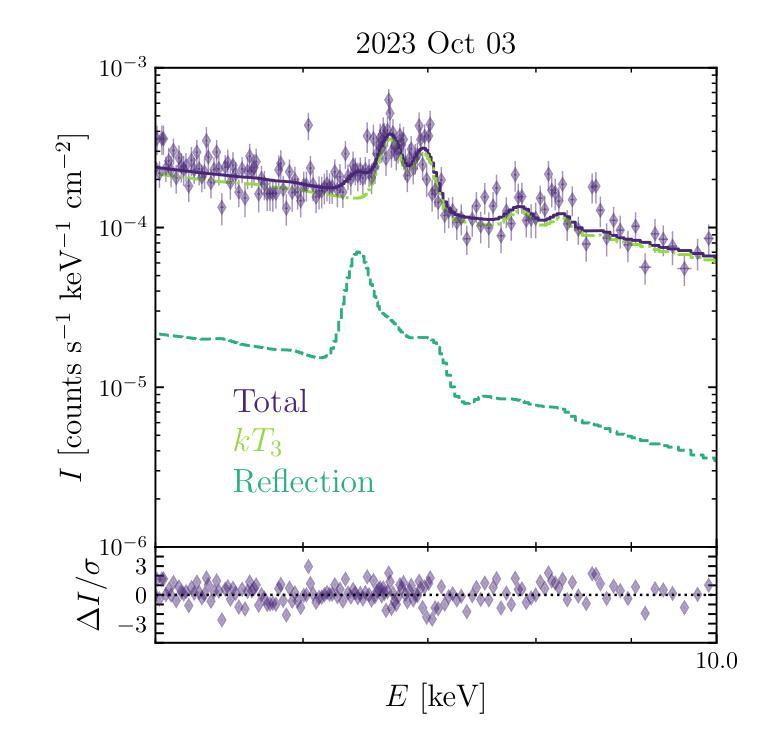
Tiānguān ($ζ$ Tau) as a binary system consisting of a Be-star and an accreting White Dwarf: opening a gate to understanding enigmatic $γ$ Cas analogues
Authors:Jesús A. Toalá, Lidia M. Oskinova, Diego A. Vasquez-Torres
The analogues of $\gamma$ Cassiopea are binary early type Be stars which are X-ray bright with hard thermal spectra. The nature of companions in these stars and mechanisms of their X-ray emission remain enigmatic. Among the proposed ideas is the presence of an accretion disc around a white dwarf (WD) companion to the Be star donor. We use radiative transfer models including reflection physics in order to calculate the synthetic spectra of such systems, and assume that the hottest plasma is thermal and is located in the accretion disc boundary layer. The models are used to analyse the XMM-Newton observations of the $\gamma$ Cas analogue $\zeta$ Tau (a.k.a. Ti={a}ngu={a}n). Comparisons with X-ray-emitting symbiotic systems, particularly $\delta$- and $\beta/\delta$-type systems, support the idea that the hard X-ray emission in $\zeta$ Tau is best explained by a WD accreting material expelled from the Be star. The plasma temperature and luminosity of the boundary layer associated with the accretion disc are used to estimate a mass accretion rate of $\dot{M}_\mathrm{acc} \approx 4\times 10^{-10}$ M$_\odot$ yr$^{-1}$, implying a nova recurrence time above 10$^{5}$ yr. Our analysis advances the understanding the production of hard X-ray emission in $\gamma$ Cas analogues, further supporting the idea of accreting WDs as companions of Be-stars in these systems.
类比于γ Cassiopea的恒星是早期类型的Be双星,它们X射线亮度高且具有硬热光谱。这些恒星中的同伴星及其X射线发射机制仍然是个谜。其中提出的想法之一是在Be星捐赠者周围存在一个白色矮星(WD)同伴的吸积盘。我们使用包括反射物理的辐射传输模型来计算此类系统的合成光谱,并假设最热的等离子体是热等离子体,位于吸积盘边界层。这些模型被用来分析γ Cas类似体ζ Tau(又名Ti={a}ngu={a}n)的XMM-Newton观测结果。与X射线发射的共生系统,特别是δ型和β/δ型系统的比较,支持这样一种观点,即ζ Tau中的硬X射线发射最好用从Be星排出的物质被白矮星吸积来解释。利用与吸积盘相关的边界层的等离子体温度和光度来估计物质吸积率$\dot{M}_\mathrm{acc} \approx 4\times 10^{-10}$ M$_⊙$ yr$^{-1}$,暗示了新星的复发时间超过10$^{5}$年。我们的分析加深了对γ Cas类似体产生硬X射线发射的理解,进一步支持了吸积白矮星作为这些系统中Be星同伴的想法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 1 table; Accepted to MNRAS
摘要
本文研究了类似$\gamma$ Cassiopea的二元早期Be型恒星,这些恒星X射线亮度高且具有硬热光谱。关于这些恒星中同伴星的性质和X射线发射的机制仍然是个谜。其中提出的假设之一是存在围绕Be星捐赠者的白矮星(WD)同伴的吸积盘。为了计算此类系统的合成光谱,我们使用了包括反射物理的辐射传递模型,并假设最热的等离子体是热等离子体,位于吸积盘边界层。这些模型被用来分析$\gamma$ Cas类似物$\zeta$ Tau(又名Ti={a}ngu={a}n)的XMM-Newton观测结果。与X射线发射的共生系统的比较,特别是$\delta$型和$\beta/\delta$型系统,支持了硬X射线发射在$\zeta$ Tau中的最佳解释是WD吸积从Be星喷出的物质。边界层的等离子体温度和光度被用来估计吸积盘的吸积率$\dot{M}_\mathrm{acc} \approx 4\times 10^{-10}$ M$_☀$ yr$^{-1}$,暗示了新星复发时间超过$10^{5}$年。我们的分析有助于理解类似$\gamma$ Cas的恒星产生硬X射线发射的过程,进一步支持了吸积WD作为这些系统中Be星同伴的假设。
要点
- $\gamma$ Cassiopea类似星的X射线特性和硬热光谱被研究。
- 这些恒星具有二元早期Be型特征,X射线亮度高。
- 关于同伴星性质和X射线发射机制的假设之一是存在围绕Be星的白矮星吸积盘。
- 使用辐射传递模型分析这类系统的合成光谱。
- 对$\gamma$ Cas类似物$\zeta$ Tau的XMM-Newton观测数据进行分析。
- 与其他X射线发射共生系统的比较支持了硬X射线发射源于WD吸积Be星物质的观点。
点此查看论文截图

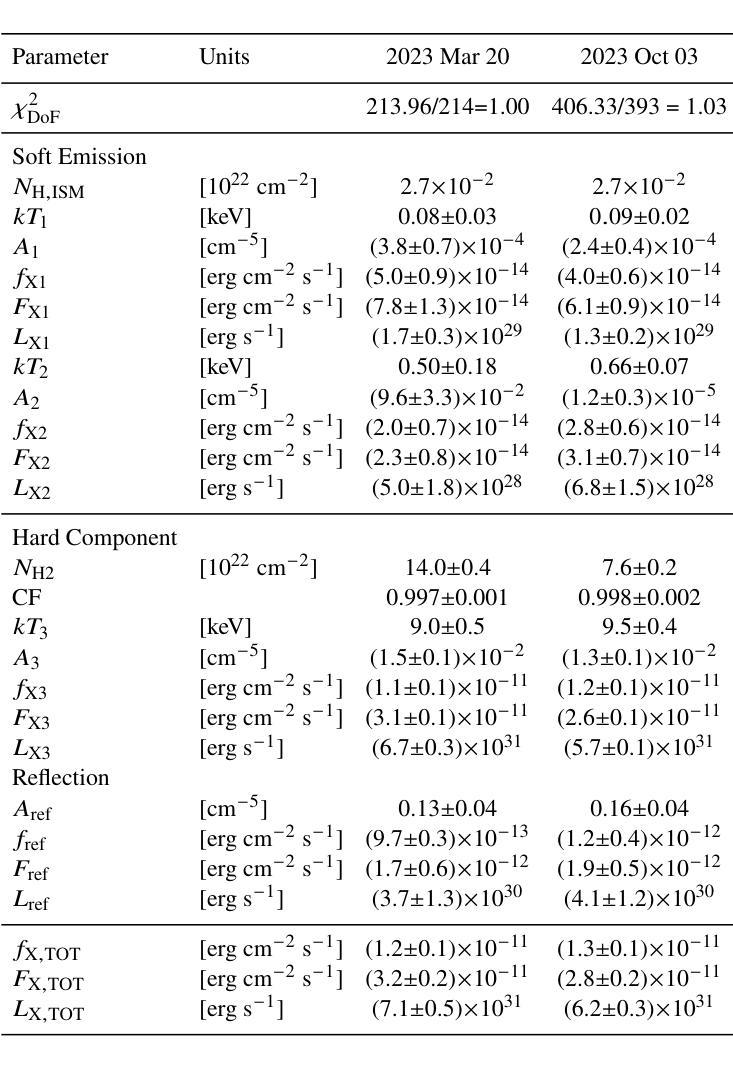
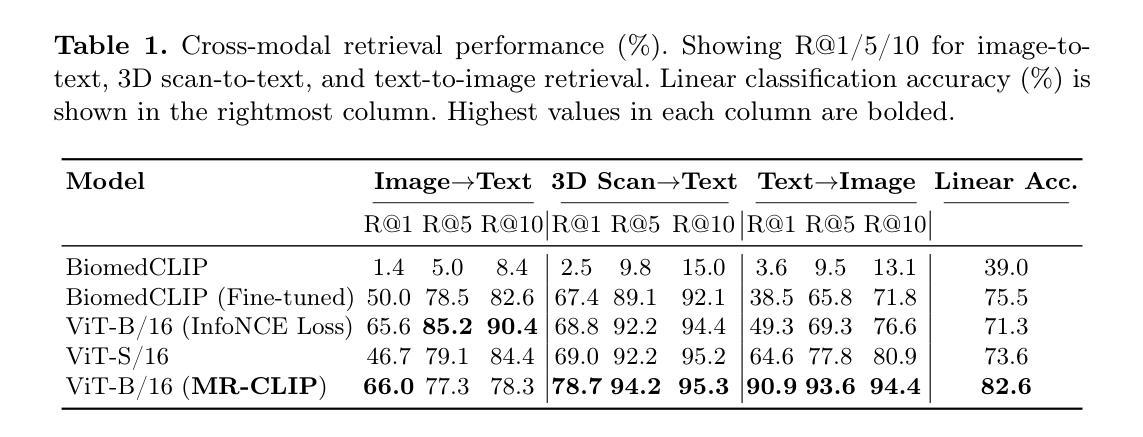
MR-CLIP: Efficient Metadata-Guided Learning of MRI Contrast Representations
Authors:Mehmet Yigit Avci, Pedro Borges, Paul Wright, Mehmet Yigitsoy, Sebastien Ourselin, Jorge Cardoso
Accurate interpretation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans in clinical systems is based on a precise understanding of image contrast. This contrast is primarily governed by acquisition parameters, such as echo time and repetition time, which are stored in the DICOM metadata. To simplify contrast identification, broad labels such as T1-weighted or T2-weighted are commonly used, but these offer only a coarse approximation of the underlying acquisition settings. In many real-world datasets, such labels are entirely missing, leaving raw acquisition parameters as the only indicators of contrast. Adding to this challenge, the available metadata is often incomplete, noisy, or inconsistent. The lack of reliable and standardized metadata complicates tasks such as image interpretation, retrieval, and integration into clinical workflows. Furthermore, robust contrast-aware representations are essential to enable more advanced clinical applications, such as achieving modality-invariant representations and data harmonization. To address these challenges, we propose MR-CLIP, a multimodal contrastive learning framework that aligns MR images with their DICOM metadata to learn contrast-aware representations, without relying on manual labels. Trained on a diverse clinical dataset that spans various scanners and protocols, MR-CLIP captures contrast variations across acquisitions and within scans, enabling anatomy-invariant representations. We demonstrate its effectiveness in cross-modal retrieval and contrast classification, highlighting its scalability and potential for further clinical applications. The code and weights are publicly available at https://github.com/myigitavci/MR-CLIP.
磁共振成像在临床系统中的准确解读基于对图像对比度的精确理解。这种对比度主要由采集参数决定,例如回声时间和重复时间,这些参数都存储在DICOM元数据中。为了简化对比度的识别,通常使用T1加权或TT加权等广泛标签,但这些只提供了对基础采集设置的粗略近似。在许多真实世界的数据集中,这些标签完全缺失,只留下原始的采集参数作为对比度的唯一指标。除此之外,可用的元数据通常不完整、嘈杂或不一致。缺乏可靠和标准化的元数据使图像解读、检索和整合到临床工作流程等任务变得复杂。此外,稳健的对比度感知表示对于实现更先进的临床应用至关重要,例如实现模态不变表示和数据调和。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MR-CLIP,这是一个多模式对比学习框架,它将MR图像与他们的DICOM元数据对齐,学习对比度感知表示,而无需依赖手动标签。MR-CLIP在涵盖各种扫描器和协议的临床数据集上进行训练,可以捕捉跨采集和扫描内的对比度变化,实现解剖结构不变的表示。我们在跨模态检索和对比度分类中证明了其有效性,突出了其可扩展性和进一步临床应用的潜力。代码和权重可在https://github.com/myigitavci/MR-CLIP上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了磁共振成像(MRI)在临床系统中的准确解读依赖于对图像对比度的精确理解。对比度主要由采集参数(如回声时间和重复时间)决定,这些参数存储在DICOM元数据中。文章提出MR-CLIP方法,通过多模态对比学习框架对齐MR图像与DICOM元数据,学习对比度感知表示,无需依赖手动标签。该方法在跨模态检索和对比度分类中表现出有效性,具有可扩展性和潜在的临床应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)的准确解读依赖于对图像对比度的理解。
- 图像对比度主要由采集参数(如回声时间和重复时间)决定,这些参数存储在DICOM元数据中。
- 常见的对比度标识(如T1加权或T2加权)仅提供粗略的采集设置近似值。
- 现实世界中,这些标签经常缺失,使得原始的采集参数成为对比度的唯一指标。
- DICOM元数据的不可靠和不标准化给图像解读、检索和融入临床流程带来挑战。
- MR-CLIP方法通过多模态对比学习框架对齐MR图像与DICOM元数据,实现对比度感知表示学习。
点此查看论文截图

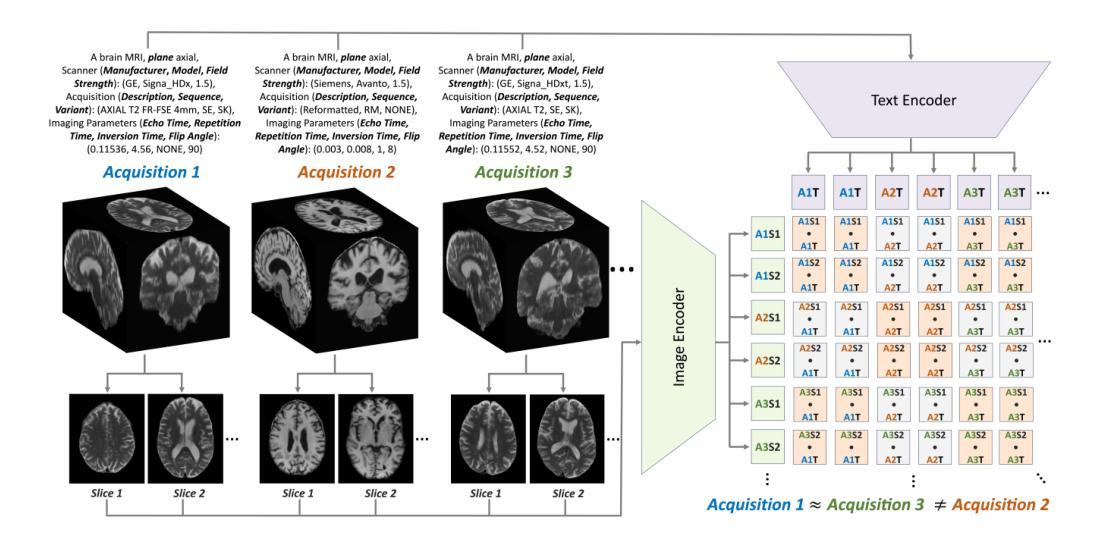
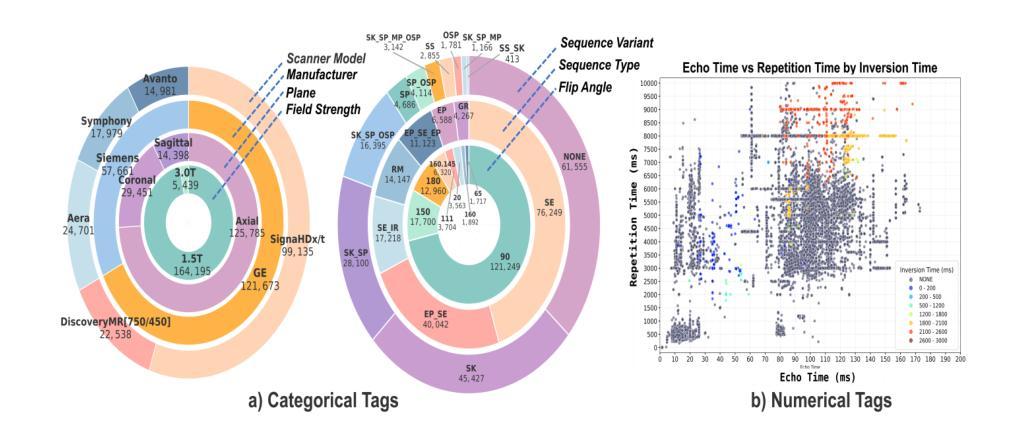
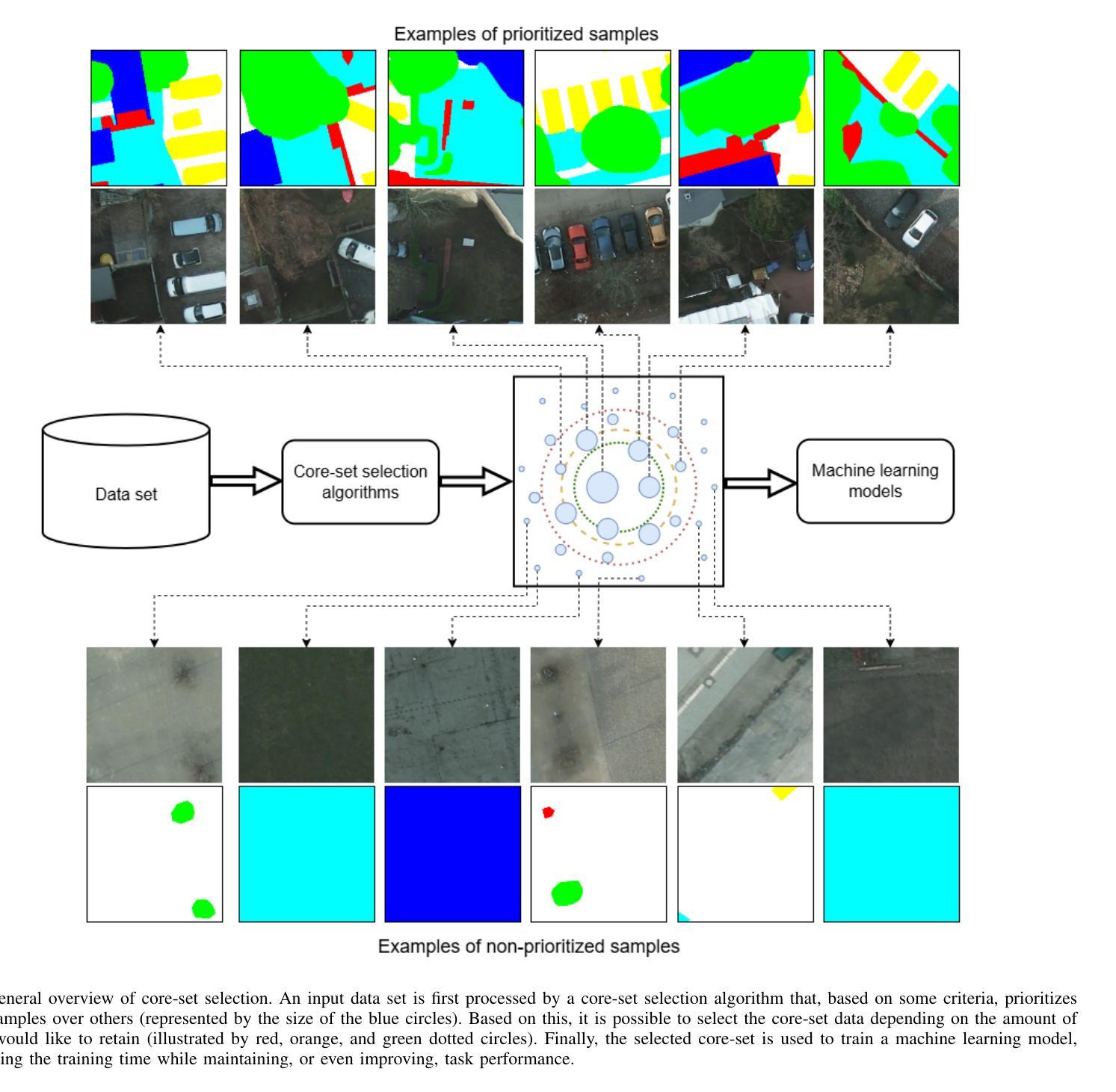
Core-Set Selection for Data-efficient Land Cover Segmentation
Authors:Keiller Nogueira, Akram Zaytar, Wanli Ma, Ribana Roscher, Ronny Hänsch, Caleb Robinson, Anthony Ortiz, Simone Nsutezo, Rahul Dodhia, Juan M. Lavista Ferres, Oktay Karakuş, Paul L. Rosin
The increasing accessibility of remotely sensed data and the potential of such data to inform large-scale decision-making has driven the development of deep learning models for many Earth Observation tasks. Traditionally, such models must be trained on large datasets. However, the common assumption that broadly larger datasets lead to better outcomes tends to overlook the complexities of the data distribution, the potential for introducing biases and noise, and the computational resources required for processing and storing vast datasets. Therefore, effective solutions should consider both the quantity and quality of data. In this paper, we propose six novel core-set selection methods for selecting important subsets of samples from remote sensing image segmentation datasets that rely on imagery only, labels only, and a combination of each. We benchmark these approaches against a random-selection baseline on three commonly used land cover classification datasets: DFC2022, Vaihingen, and Potsdam. In each of the datasets, we demonstrate that training on a subset of samples outperforms the random baseline, and some approaches outperform training on all available data. This result shows the importance and potential of data-centric learning for the remote sensing domain. The code is available at https://github.com/keillernogueira/data-centric-rs-classification/.
遥感数据的日益普及及其为大规模决策提供信息的潜力,推动了深度学习模型在地球观测任务中的发展。传统上,此类模型必须在大型数据集上进行训练。然而,普遍存在的假设是大规模数据集会获得更好的结果,这往往会忽视数据分布的复杂性、引入偏见和噪声的可能性,以及处理存储大量数据所需的计算资源。因此,有效的解决方案应同时考虑数据的质量和数量。在本文中,我们提出了六种新的核心集选择方法,用于从遥感图像分割数据集中选择重要的样本子集,这些子集仅依赖于图像、仅依赖于标签以及两者的组合。我们在三个常用的土地覆盖分类数据集上对这些方法与随机选择基线进行了基准测试:DFC2022、瓦伊宁根和波茨坦。在每个数据集中,我们都证明了在样本子集上进行训练优于随机基线,并且某些方法的性能优于在所有可用数据上进行训练。这一结果展示了以数据为中心的学习在遥感领域的重要性和潜力。代码可在https://github.com/keillernogueira/data-centric-rs-classification/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了遥感数据在地球观测任务中应用深度学习的潜力。针对传统大数据训练模型的不足,如数据分布复杂性、潜在的偏见和噪声问题以及计算资源需求等,本文提出了六种新的核心样本选择方法,用于从遥感图像分割数据集中选择重要样本子集。在三个常用的土地覆盖分类数据集上的实验表明,基于子集样本的训练效果优于随机选择基线,部分方法甚至优于使用所有可用数据。这凸显了以数据为中心的学习在遥感领域的重要性和潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感数据的易获取性和其在大型决策中的信息潜力推动了深度学习模型的发展。
- 传统上,深度学习模型需要在大数据集上进行训练。
- 大数据集未必总是带来最佳结果,忽视了数据分布的复杂性、潜在的偏见和噪声以及计算资源的需求。
- 本文提出了六种新的核心样本选择方法,从遥感图像分割数据集中选择重要样本。
- 在三个土地覆盖分类数据集上的实验表明,基于子集样本的训练效果优于随机选择。
- 部分方法表现优异,甚至超过了使用全部数据进行的训练。
点此查看论文截图


Imaging Ultrafast Dynamical Diffraction wavefronts of femtosecond laser-induced lattice distortions inside crystalline semiconductors
Authors:Angel Rodríguez-Fernández, Jan-Etienne Pudell, Roman Shayduk, Wonhyuk Jo, James Wrigley, Johannes Möller, Peter Zalden, Alexey Zozulya, Jörg Hallmann, Anders Madsen, Pablo Villanueva-Perez, Zdenek Matej, Thies J. Albert, Dominik Kaczmarek, Klaus Sokolowski-Tinten, Antonowicz Jerzy, Ryszard Sobierajski, Rahimi Mosafer, Oleksii I. Liubchenko, Javier Solis, Jan Siegel
Material processing with femtosecond lasers has attracted enormous attention because of its potential for technology and industrial applications. In parallel, time-resolved x-ray diffraction has been successfully used to study ultrafast structural distortion dynamics in semiconductor thin films or surface layers. However, real-world processing applications mostly are concerned with bulk materials, which prevents the use of x-ray surface based techniques. For processing applications, a fast and depth-sensitive probe is needed. To address this, we present a novel technique based on ultrafast x-ray dynamical diffraction (UDD) capable of imaging transient strain distributions inside bulk crystals upon laser excitation. This pump-probe technique provides a complete picture of thetemporal evolution of ultrafast distorted lattice depth profiles. We demonstrate the potential of UDD by studying a thin Si single crystal upon single pulse femtosecond optical excitation. Our study reveals that below the melting threshold strong lattice distortions not only longitudinal, but also transversal to the propagation of the strain wave appear on picosecond time scales along the single crystal. The observation of this transversal deformation after laser excitation contradicts previous work that were not able to observed it, what could be related to the high sensitivity of dynamical diffraction with respect to the lattice distortions. The speed of propagation of this ultrafast transversal strain deformation is observed to be slower to the longitudinal sound speed for Si as described in the bibliography.
材料通过飞秒激光处理因其技术和工业应用潜力而备受关注。同时,时间分辨X射线衍射已成功应用于半导体薄膜或表面层超快结构畸变动力学的研究。然而,实际应用中的材料处理主要关注块体材料,这使得基于X射线表面的技术无法应用。对于处理应用而言,需要一个快速且对深度敏感的探针。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于超快X射线动力学衍射(UDD)的新技术,该技术能够在激光激发下对块体内晶体瞬时应变分布进行成像。这种泵浦探针技术提供了超快畸变晶格深度分布的临时演化的完整图像。我们通过研究单脉冲飞秒光学激发下的硅单晶薄膜,展示了UDD的潜力。我们的研究表明,在熔点以下,强烈的晶格畸变不仅纵向出现,而且在应力波传播的横向也会出现,在皮秒时间尺度上沿着单晶传播。激光激发后观察到的这种横向变形与以前的研究结果相矛盾,以前的研究未能观察到这一现象,这可能与动力学衍射对晶格畸变的高敏感性有关。观察到的这种超快横向应变变形的传播速度比文献中描述的硅的纵声波速度慢。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种基于超快X射线动力学衍射(UDD)的新技术,该技术能够成像激光激发下体内瞬态应变分布。该技术为泵浦探测技术,提供了超快畸变晶格深度分布的暂时演化的完整图像。通过单一脉冲飞秒光学激发下硅单晶的研究,揭示了晶格畸变不仅在纵向产生,而且在应力波传播的横向方向上也出现。这种横向变形的观察与之前的理论预测相悖,可能是由于动力学衍射对晶格畸变的敏感性较高。观察到这种超快横向应变变形的传播速度比硅的纵波声速慢。
Key Takeaways
- 超快X射线动力学衍射技术可用于成像激光激发下体内瞬态应变分布。
- 此技术为研究超快畸变晶格深度分布提供了有力工具。
- 在飞秒光学激发下,硅单晶中出现了横向晶格畸变。
- 该发现与先前的研究结果相悖,可能是因为超快X射线动力学衍射对晶格畸变的极高敏感性。
- 超快横向应变变形的传播速度较慢,低于硅的纵波声速。
- 该技术对于研究材料在激光处理中的内部结构变化具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

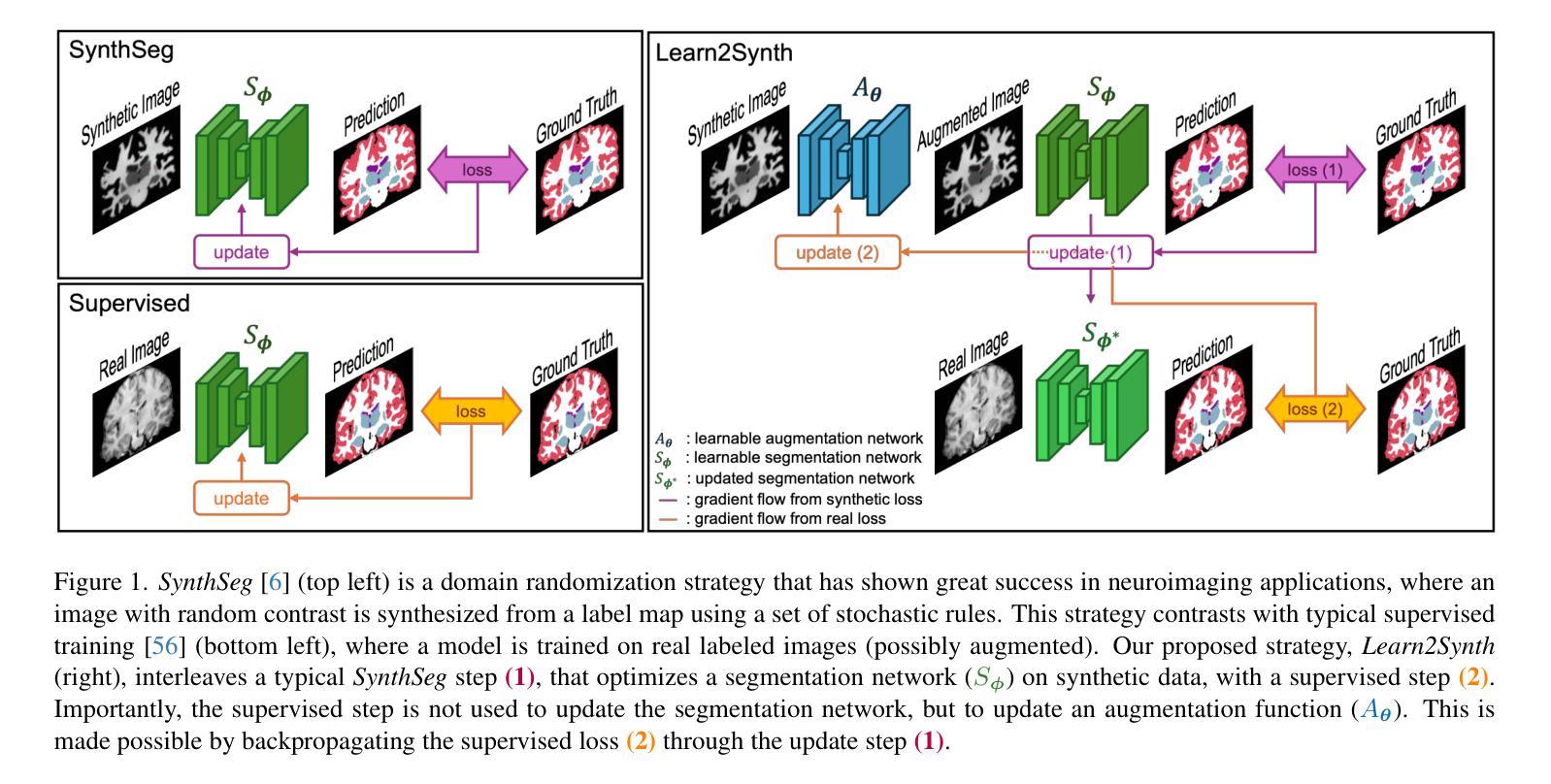
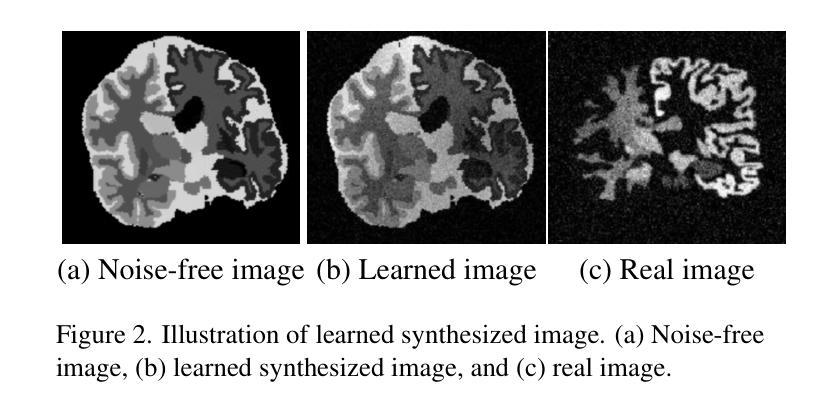
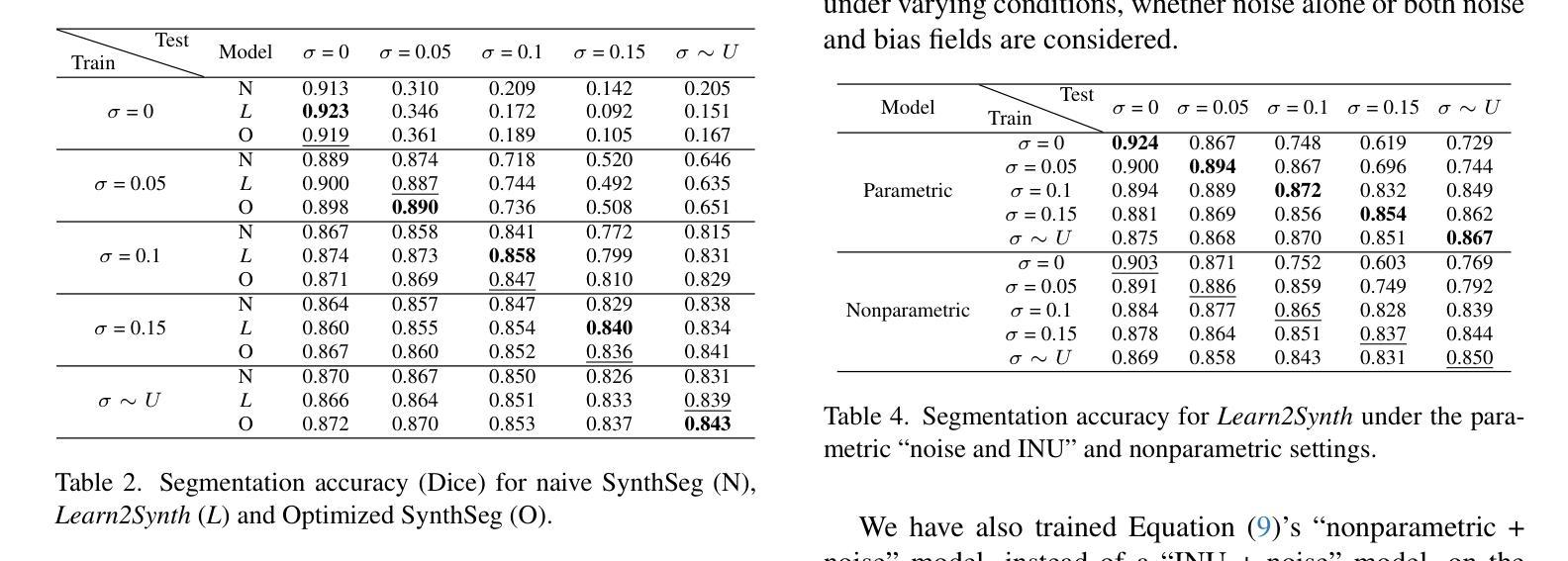
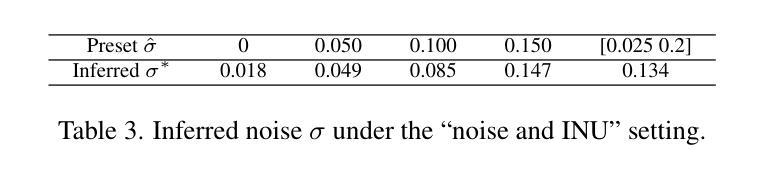
Learn2Synth: Learning Optimal Data Synthesis Using Hypergradients for Brain Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiaoling Hu, Xiangrui Zeng, Oula Puonti, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Bruce Fischl, Yael Balbastre
Domain randomization through synthesis is a powerful strategy to train networks that are unbiased with respect to the domain of the input images. Randomization allows networks to see a virtually infinite range of intensities and artifacts during training, thereby minimizing overfitting to appearance and maximizing generalization to unseen data. Although powerful, this approach relies on the accurate tuning of a large set of hyperparameters that govern the probabilistic distribution of the synthesized images. Instead of manually tuning these parameters, we introduce Learn2Synth, a novel procedure in which synthesis parameters are learned using a small set of real labeled data. Unlike methods that impose constraints to align synthetic data with real data (e.g., contrastive or adversarial techniques), which risk misaligning the image and its label map, we tune an augmentation engine such that a segmentation network trained on synthetic data has optimal accuracy when applied to real data. This approach allows the training procedure to benefit from real labeled examples, without ever using these real examples to train the segmentation network, which avoids biasing the network towards the properties of the training set. Specifically, we develop parametric and nonparametric strategies to enhance synthetic images in a way that improves the performance of the segmentation network. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this learning strategy on synthetic and real-world brain scans. Code is available at: https://github.com/HuXiaoling/Learn2Synth.
通过合成进行域随机化是一种强大的策略,用于训练对于输入图像域不偏见的网络。随机化允许网络在训练过程中看到几乎无限范围的强度和伪影,从而最大程度地减少对外观的过拟合,并最大化对未见数据的泛化。尽管这种策略强大,但它依赖于大量控制合成图像概率分布的超级参数的精确调整。我们没有手动调整这些参数,而是引入了Learn2Synth这一新程序,该程序使用少量真实标记数据来学习合成参数。与其他通过施加约束来使合成数据与真实数据对齐的方法(例如对比或对抗技术)不同,这些方法可能会误对齐图像及其标签映射。我们调整了增强引擎,使得在合成数据上训练的分割网络在实际数据上具有最佳精度。这种方法允许训练过程受益于真实的标记示例,而无需使用这些真实示例来训练分割网络,从而避免了使网络偏向于训练集的属性。具体来说,我们制定了参数和非参数策略来增强合成图像的方式,以提高分割网络的性能。我们在合成和真实世界的大脑扫描上证明了这种学习策略的有效性。代码可用在:https://github.com/HuXiaoling/Learn2Synth。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures. Accepted by ICCV’25
Summary
合成图像的方法是一种强大的训练网络策略,能训练出对输入图像领域无偏见的网络。此方法通过随机化手段扩大网络的视野范围,使网络适应更多变异情境和降低对固有情境的依赖,从而减少过拟合风险并增加对未见数据的泛化能力。尽管如此,此方法的运用却极度依赖于合成图像概率分布的大量超参数精准调整。为此,我们推出Learn2Synth这一新方法,通过少量真实标记数据学习调整合成参数。相较于采用约束对齐合成数据与真实数据的方法(如对比或对抗技术),我们调整扩充引擎以优化在真实数据上应用的分割网络的性能。该方法使得训练过程受益于真实标记示例,同时避免分割网络使用这些真实示例进行训练的风险,避免了网络的训练集属性偏见。特别是,我们制定了参数和非参数策略以增强合成图像的方式,以提高分割网络的性能。我们在合成和真实脑扫描上验证了该学习策略的效用。相关代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/HuXiaoling/Learn2Synth。
Key Takeaways
- 领域随机化通过合成图像是一种强大的训练网络策略,能提高网络的泛化能力。
- 该方法允许网络在训练过程中看到几乎无限强度的变化和伪影,从而提高网络的适应性和泛化能力。
- 虽然此方法强大但依赖大量超参数的精准调整来管理合成图像的概率分布。
- Learn2Synth方法采用一种新程序来通过学习调整合成参数来避免手动调整超参数的繁琐工作。
- 与其他方法不同,该方法专注于调整扩充引擎以提高分割网络在真实数据上的性能,避免对训练集的偏见。
- 开发参数和非参数策略增强合成图像的方式提高了分割网络的性能。
点此查看论文截图