⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
Multi-Agent Game Generation and Evaluation via Audio-Visual Recordings
Authors:Alexia Jolicoeur-Martineau
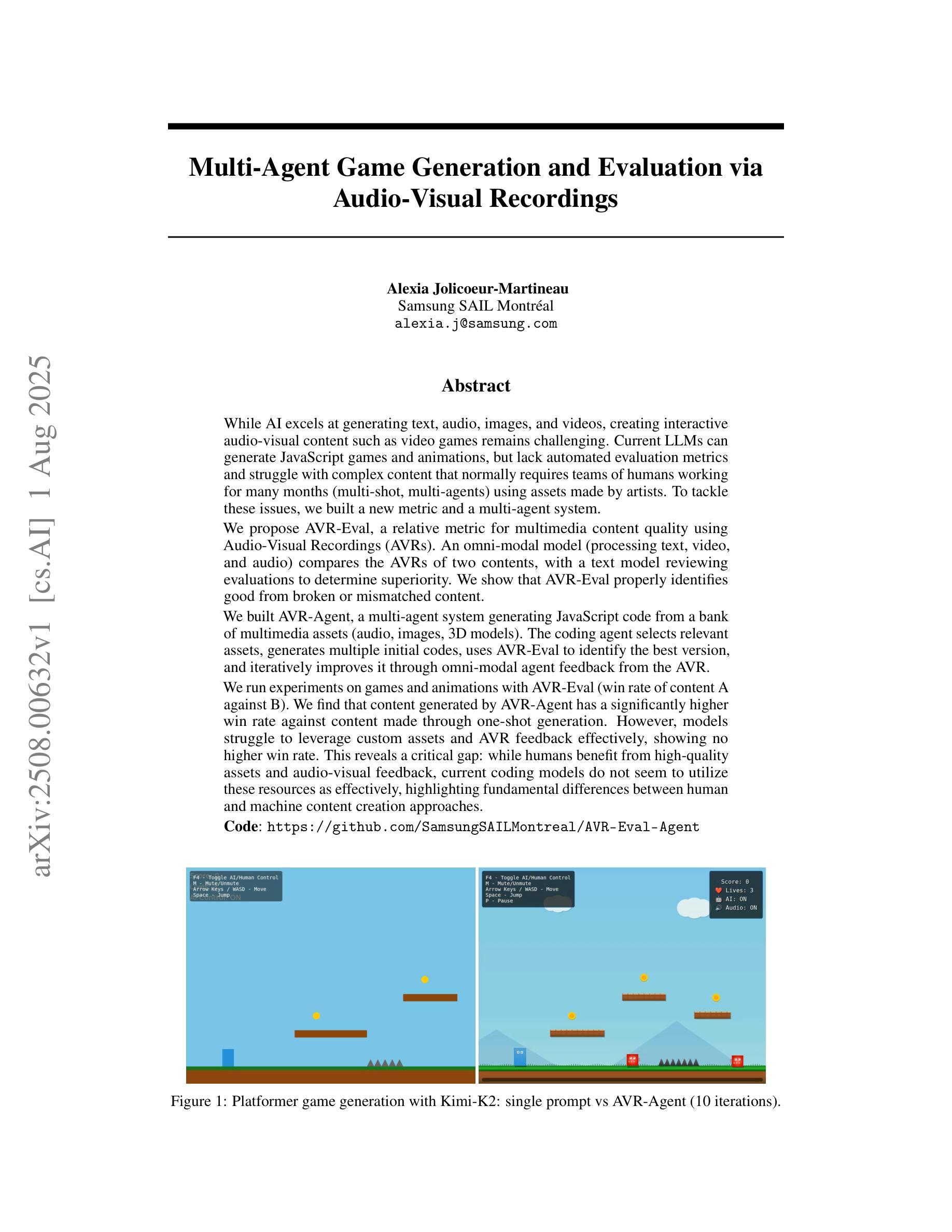
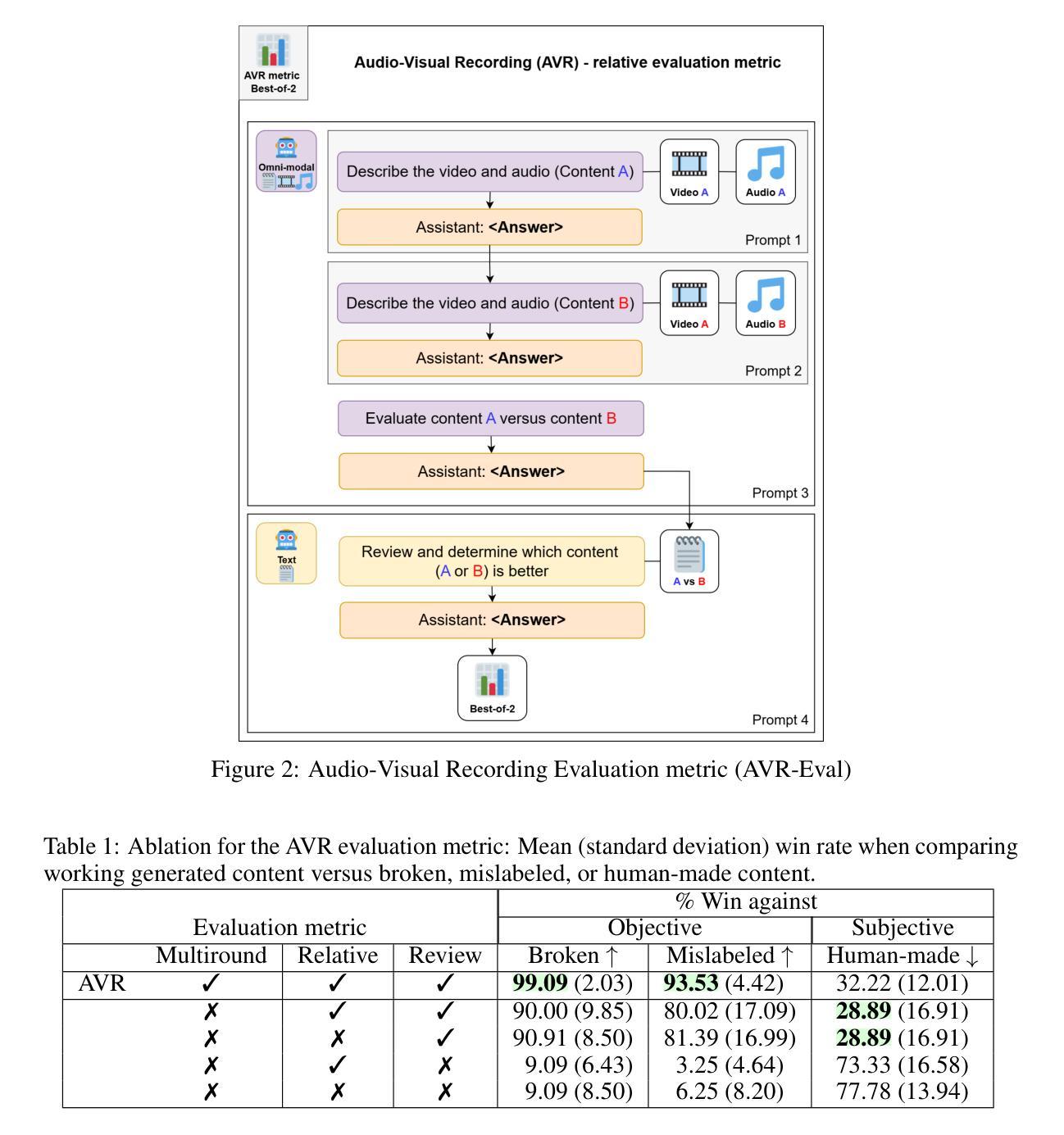
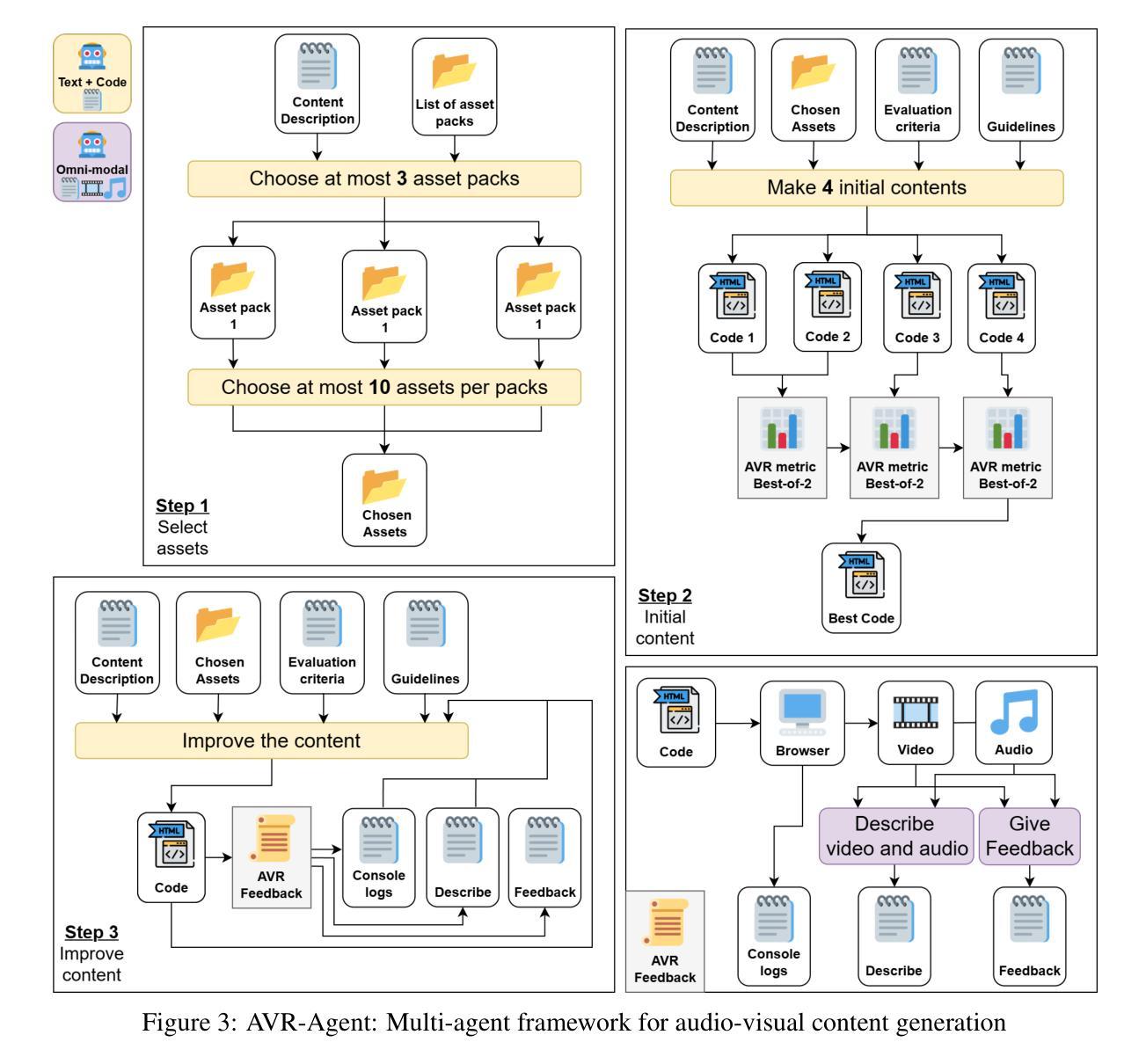
While AI excels at generating text, audio, images, and videos, creating interactive audio-visual content such as video games remains challenging. Current LLMs can generate JavaScript games and animations, but lack automated evaluation metrics and struggle with complex content that normally requires teams of humans working for many months (multi-shot, multi-agents) using assets made by artists. To tackle these issues, we built a new metric and a multi-agent system. We propose AVR-Eval, a relative metric for multimedia content quality using Audio-Visual Recordings (AVRs). An omni-modal model (processing text, video, and audio) compares the AVRs of two contents, with a text model reviewing evaluations to determine superiority. We show that AVR-Eval properly identifies good from broken or mismatched content. We built AVR-Agent, a multi-agent system generating JavaScript code from a bank of multimedia assets (audio, images, 3D models). The coding agent selects relevant assets, generates multiple initial codes, uses AVR-Eval to identify the best version, and iteratively improves it through omni-modal agent feedback from the AVR. We run experiments on games and animations with AVR-Eval (win rate of content A against B). We find that content generated by AVR-Agent has a significantly higher win rate against content made through one-shot generation. However, models struggle to leverage custom assets and AVR feedback effectively, showing no higher win rate. This reveals a critical gap: while humans benefit from high-quality assets and audio-visual feedback, current coding models do not seem to utilize these resources as effectively, highlighting fundamental differences between human and machine content creation approaches.
虽然人工智能在生成文本、音频、图像和视频方面表现出色,但在创建交互式视听内容(如电子游戏)方面仍然面临挑战。当前的LLM(大型语言模型)可以生成JavaScript游戏和动画,但缺乏自动评估指标,并且在需要由人类团队工作数月的复杂内容(多镜头、多代理)方面遇到困境,这些内容的资产通常由艺术家制作。为了解决这些问题,我们开发了一种新的指标和多代理系统。
我们提出AVR-Eval,这是一种使用音频视觉录制(AVR)的多媒体内容质量相对指标。一种多模式模型(处理文本、视频和音频)比较两个内容的AVR,并使用文本模型审查评估来确定优劣。我们证明AVR-Eval能够正确识别优质内容与损坏或不匹配的内容。
我们构建了AVR-Agent,这是一个多代理系统,可以从多媒体资产库(音频、图像、3D模型)生成JavaScript代码。编码代理选择相关资产,生成多个初始代码,使用AVR-Eval来识别最佳版本,并通过AVR的跨模式代理反馈进行迭代改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
当前人工智能在生成文本、音频、图像和视频方面表现出色,但在创建如电子游戏等交互式音视频内容方面仍具挑战。为解决此问题,我们构建了新的度量标准——AVR-Eval,用于评估多媒体内容质量的相对指标,并利用音视频录制(AVRs)进行对比。我们还建立了AVR-Agent多智能体系统,可从多媒体资产库中生成JavaScript代码,通过AVR-Eval选择最佳资产版本并不断改进。实验表明,AVR-Agent生成的内容较一次生成的内容具有更高的胜率,但模型在利用自定义资产和AVR反馈方面存在困难,表明人类与机器的内容创作方式存在根本差异。
Key Takeaways
- 当前人工智能在生成交互式音视频内容如电子游戏方面存在挑战。
- AVR-Eval是一种新的相对度量标准,用于评估多媒体内容质量。
- AVR-Eval通过对比音视频录制(AVRs)来判断内容优劣。
- AVR-Agent是一个多智能体系统,可以从多媒体资产库中生成JavaScript代码。
- 实验显示AVR-Agent生成的内容较一次生成的内容有更高的胜率。
- 模型在利用自定义资产和AVR反馈方面存在困难。
- 人工智能与人类在内容创作方面存在根本差异。
点此查看论文截图
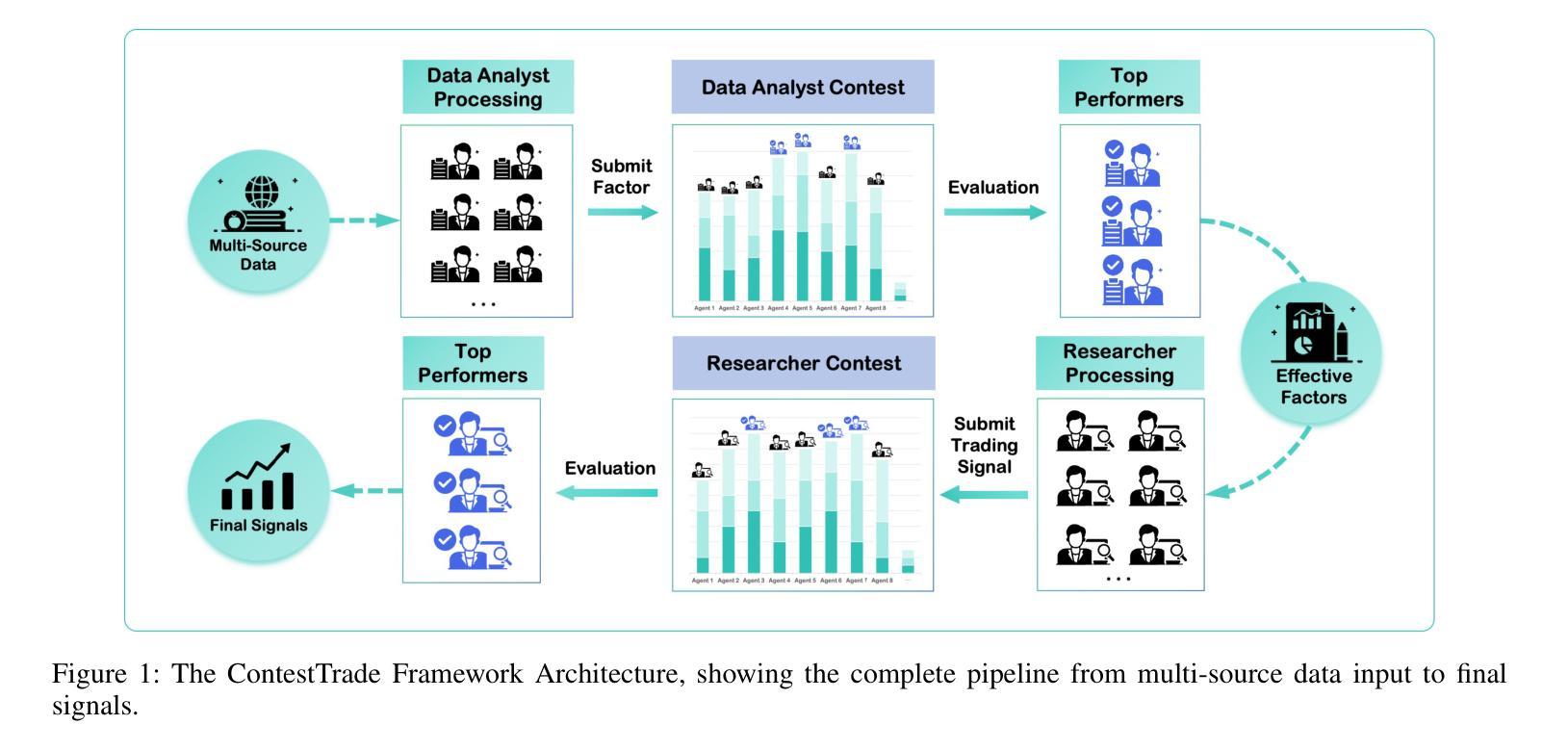
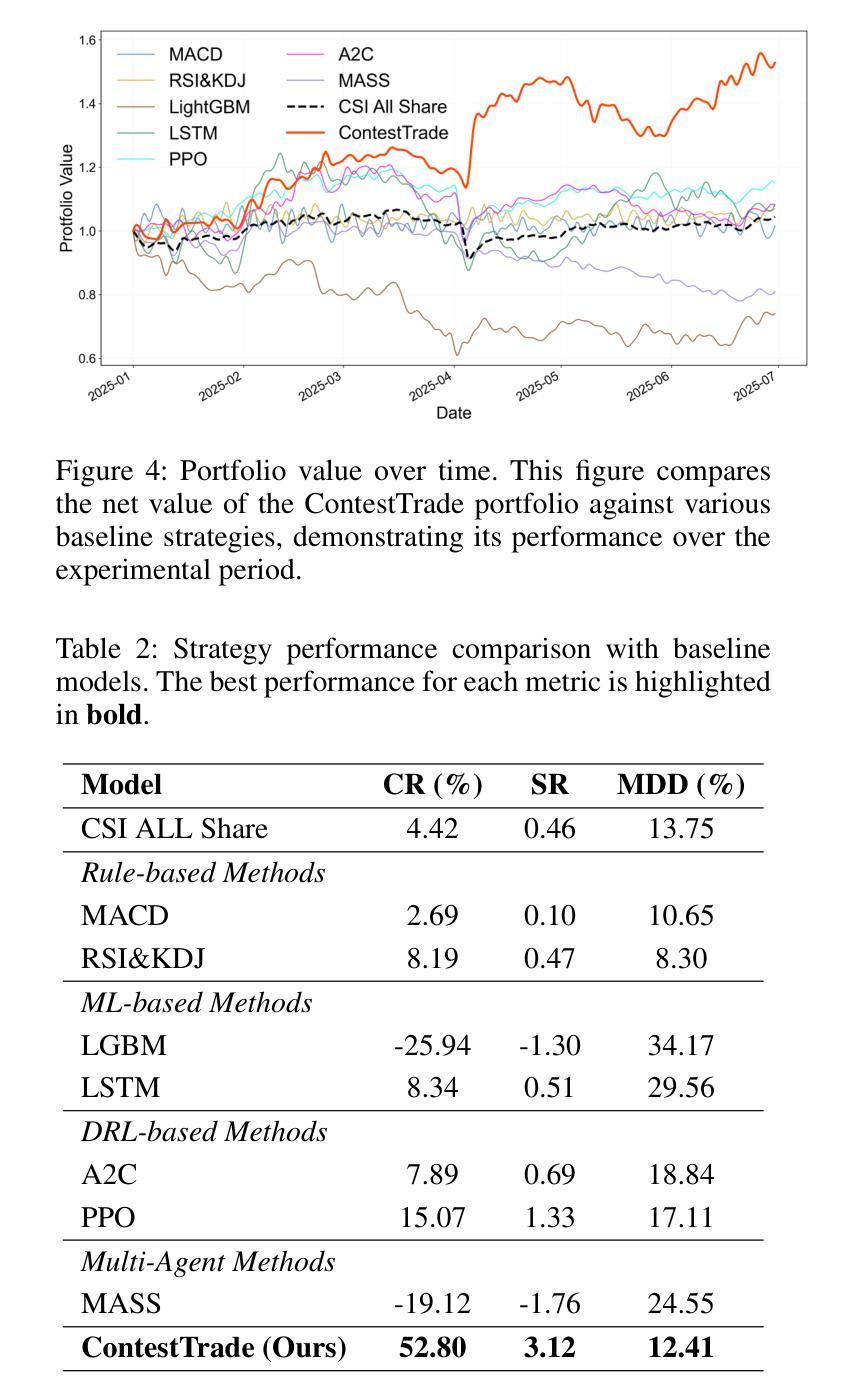
ContestTrade: A Multi-Agent Trading System Based on Internal Contest Mechanism
Authors:Li Zhao, Rui Sun, Zuoyou Jiang, Bo Yang, Yuxiao Bai, Mengting Chen, Xinyang Wang, Jing Li, Zuo Bai
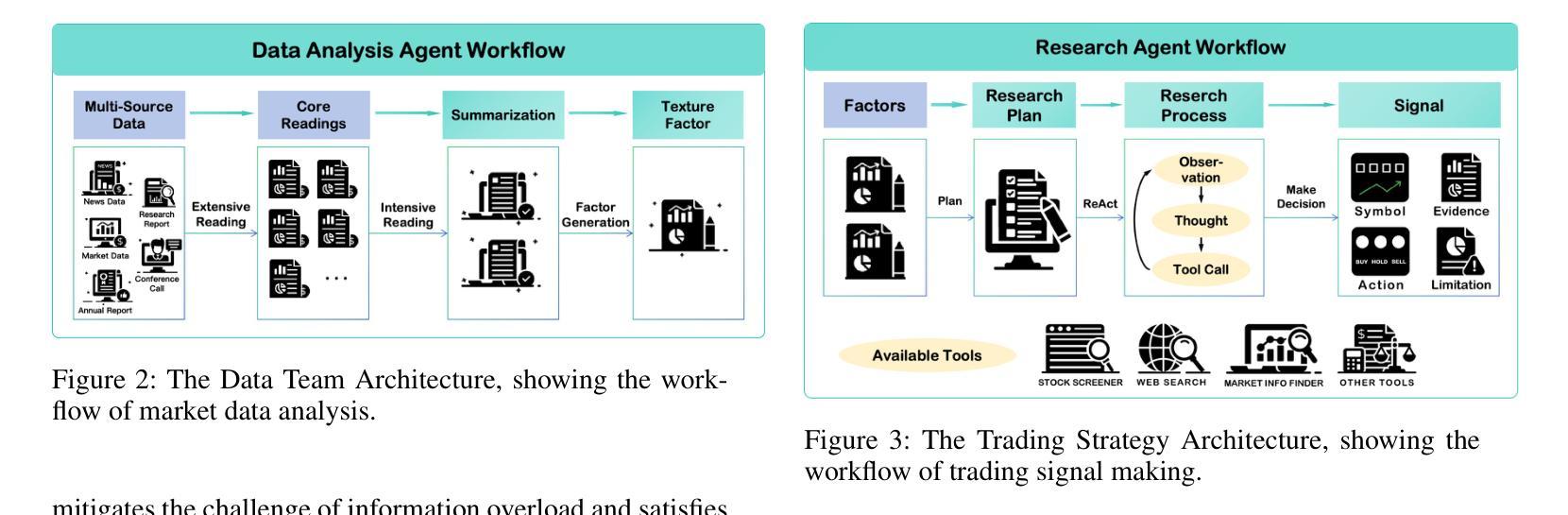
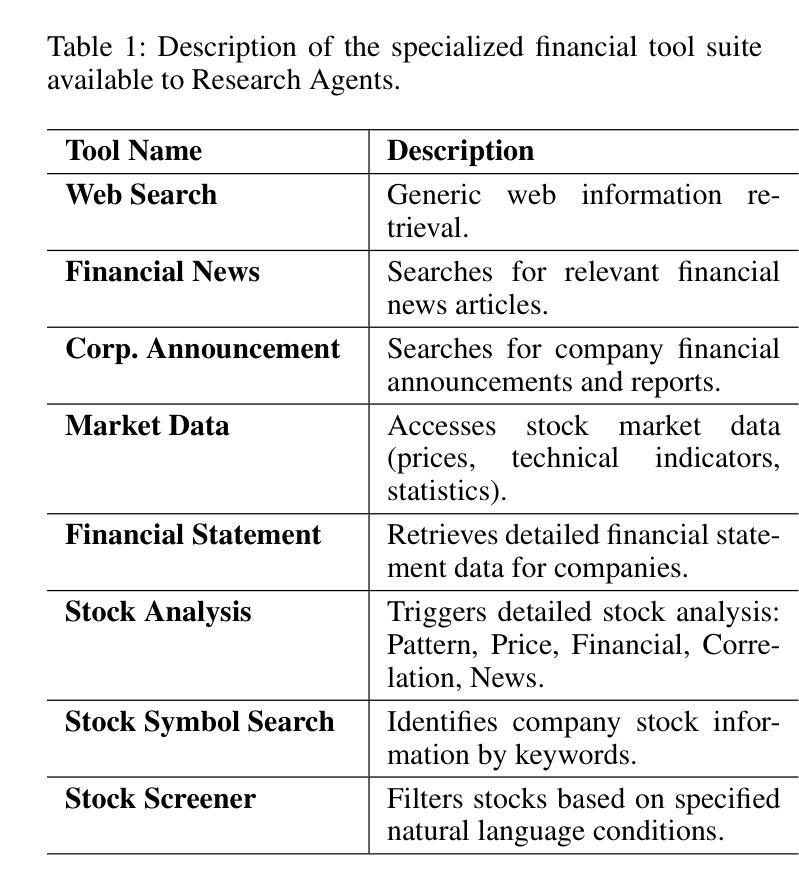
In financial trading, large language model (LLM)-based agents demonstrate significant potential. However, the high sensitivity to market noise undermines the performance of LLM-based trading systems. To address this limitation, we propose a novel multi-agent system featuring an internal competitive mechanism inspired by modern corporate management structures. The system consists of two specialized teams: (1) Data Team - responsible for processing and condensing massive market data into diversified text factors, ensuring they fit the model’s constrained context. (2) Research Team - tasked with making parallelized multipath trading decisions based on deep research methods. The core innovation lies in implementing a real-time evaluation and ranking mechanism within each team, driven by authentic market feedback. Each agent’s performance undergoes continuous scoring and ranking, with only outputs from top-performing agents being adopted. The design enables the system to adaptively adjust to dynamic environment, enhances robustness against market noise and ultimately delivers superior trading performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed system significantly outperforms prevailing multiagent systems and traditional quantitative investment methods across diverse evaluation metrics.
在金融交易领域,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理展现出巨大的潜力。然而,对市场噪声的高度敏感性削弱了LLM交易系统的性能。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型的多代理系统,该系统具有受现代企业管理结构启发的内部竞争机制。该系统由两个专业团队组成:(1)数据团队——负责处理和压缩大量市场数据,将其转化为多样化的文本因素,确保它们符合模型的受限语境。(2)研究团队——负责基于深度研究方法制定并行多路径交易决策。核心创新在于在每个团队内部实施实时评估和排名机制,以真实的市场反馈为驱动。每个代理的表现会进行持续打分和排名,只有表现最佳的代理的输出才会被采用。这一设计使系统能够自适应地调整动态环境,增强对市场噪声的稳健性,并最终实现卓越的交易性能。实验结果表明,我们提出的系统在多种评估指标上显著优于现有的多代理系统和传统的量化投资方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在金融交易领域展现潜力,但对市场噪声的高度敏感性限制了其性能。为解决这一问题,提出了一种新型多智能体系统,采用内部竞争机制,灵感来源于现代企业管理制度。系统包括数据处理和研究团队,分别负责处理市场数据和做出交易决策。核心创新在于实施实时评估和排名机制,根据市场反馈动态调整系统,增强对噪声的稳健性,提高交易性能。实验表明,该系统优于其他多智能体系统和传统量化投资方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在金融交易领域具有显著潜力。
- 市场噪声对大型语言模型性能产生负面影响。
- 新型多智能体系统采用内部竞争机制,类似现代企业管理制度。
- 系统包括数据处理和研究团队,分别负责不同任务。
- 实时评估和排名机制根据市场反馈动态调整系统。
- 该系统增强了系统的适应性和稳健性,提高了交易性能。
点此查看论文截图

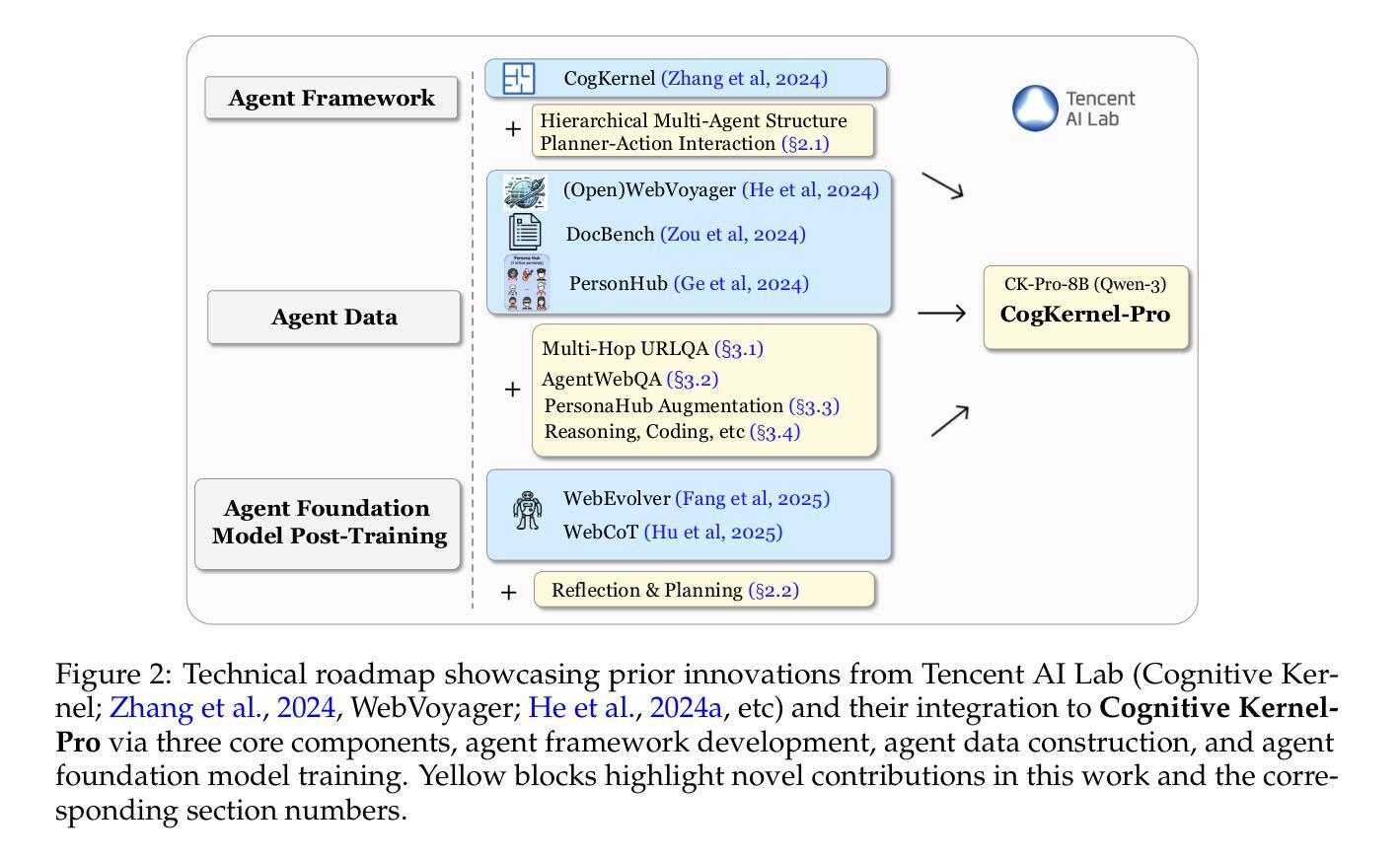
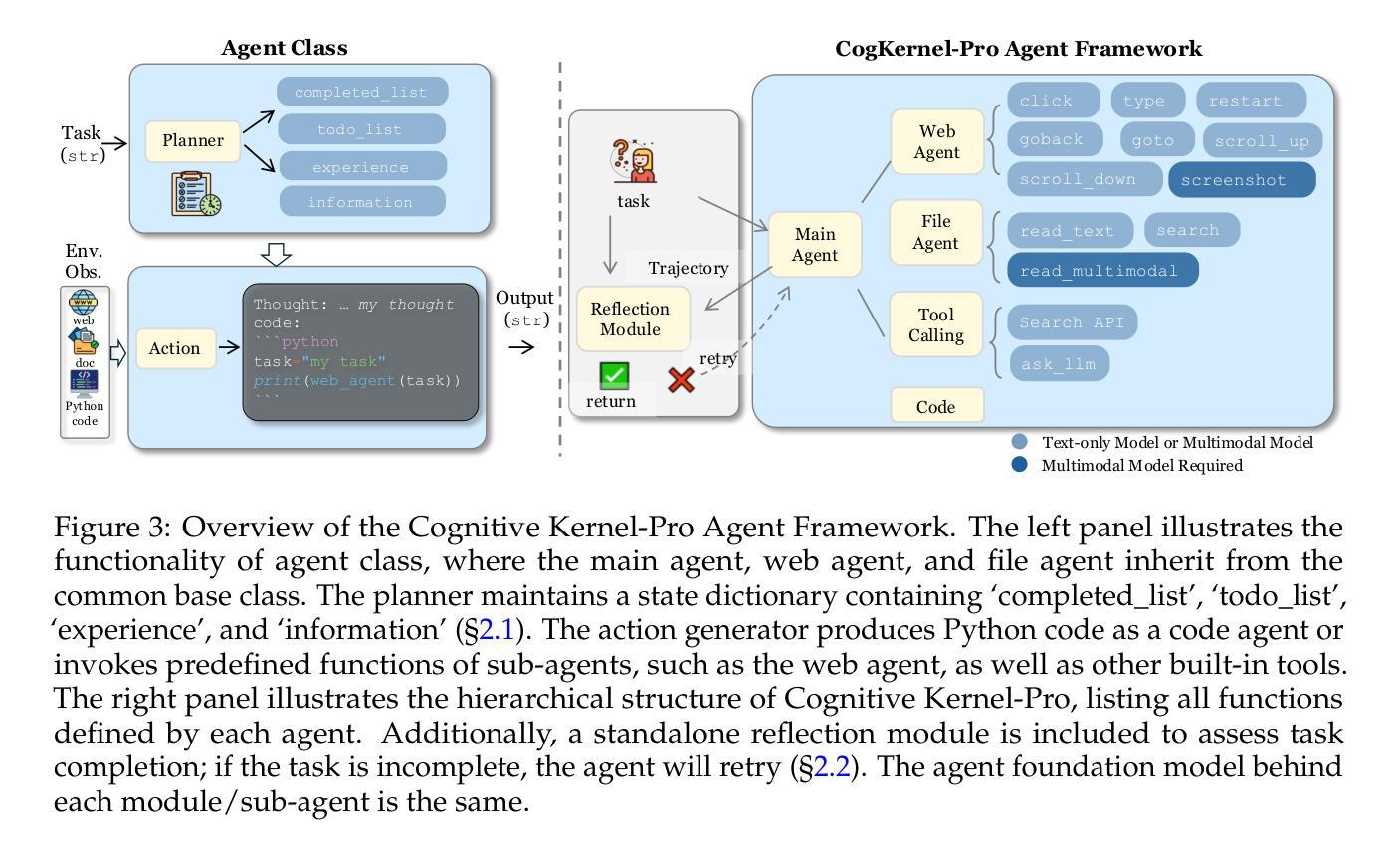
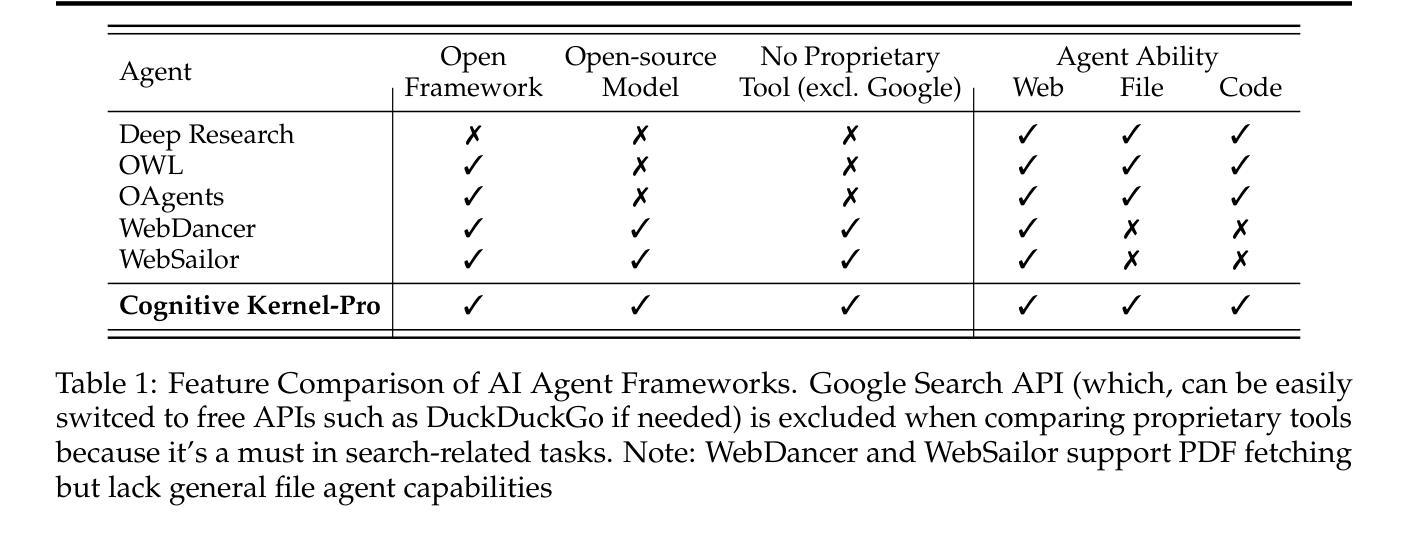
Cognitive Kernel-Pro: A Framework for Deep Research Agents and Agent Foundation Models Training
Authors:Tianqing Fang, Zhisong Zhang, Xiaoyang Wang, Rui Wang, Can Qin, Yuxuan Wan, Jun-Yu Ma, Ce Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Xiyun Li, Hongming Zhang, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
General AI Agents are increasingly recognized as foundational frameworks for the next generation of artificial intelligence, enabling complex reasoning, web interaction, coding, and autonomous research capabilities. However, current agent systems are either closed-source or heavily reliant on a variety of paid APIs and proprietary tools, limiting accessibility and reproducibility for the research community. In this work, we present \textbf{Cognitive Kernel-Pro}, a fully open-source and (to the maximum extent) free multi-module agent framework designed to democratize the development and evaluation of advanced AI agents. Within Cognitive Kernel-Pro, we systematically investigate the curation of high-quality training data for Agent Foundation Models, focusing on the construction of queries, trajectories, and verifiable answers across four key domains: web, file, code, and general reasoning. Furthermore, we explore novel strategies for agent test-time reflection and voting to enhance agent robustness and performance. We evaluate Cognitive Kernel-Pro on GAIA, achieving state-of-the-art results among open-source and free agents. Notably, our 8B-parameter open-source model surpasses previous leading systems such as WebDancer and WebSailor, establishing a new performance standard for accessible, high-capability AI agents. Code is available at https://github.com/Tencent/CognitiveKernel-Pro
通用人工智能代理(AI Agents)越来越多地被认可作为下一代人工智能的基础框架,可实现复杂的推理能力、网页交互能力、编码能力和自主研究能力。然而,当前的大部分代理系统要么是闭源的,要么严重依赖于各种付费的API和专有工具,这给学术界带来了可访问性和再现性的局限性。在此研究中,我们推出了认知核心Pro(Cognitive Kernel-Pro),这是一个完全开源的(在最大程度上)免费的多模块代理框架,旨在推动先进的人工智能代理的开发与评估走向大众化。在认知核心Pro中,我们系统地研究了高质量训练数据的整理,为代理基础模型提供重点支持,特别是在构建查询、轨迹和四大关键领域的可验证答案方面:网络、文件、代码和一般推理。此外,我们还探索了增强代理稳健性和性能的新型策略,包括代理测试时的反思和投票机制。我们在GAIA上对认知核心Pro进行了评估,在开源且免费的代理中取得了最先进的成果。值得注意的是,我们的参数为8B的开源模型超越了之前领先的WebDancer和WebSailor系统,为可访问的高能力人工智能代理建立了新的性能标准。代码可在https://github.com/Tencent/CognitiveKernel-Pro 中获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
通用人工智能代理框架被视为下一代人工智能的基础框架,具有复杂的推理、网络交互、编码和自主研究能力。然而,当前代理系统多为闭源或依赖各种付费API和专有工具,限制了研究社区的可达性和可重复性。本文介绍了一款开源的代理框架Cognitive Kernel-Pro,旨在使高级人工智能代理的开发和评估民主化。框架重点探究高质量训练数据的筛选与采集,实现跨四域的问题提出、轨迹记录和可验证答案。通过测试和反射以及投票技术,提升代理的稳健性和性能。在GAIA上的评估显示,Cognitive Kernel-Pro表现卓越,其开源模型性能超越WebDancer和WebSailor等领先系统。
Key Takeaways
- 通用AI代理框架成为下一代AI的基础,具备复杂推理、网络交互等能力。
- 当前代理系统存在闭源和依赖付费工具的问题,限制研究社区的发展。
- Cognitive Kernel-Pro是一个开源、多模块的代理框架,旨在推进AI代理的民主化开发。
- 该框架注重高质量训练数据的筛选与采集,涉及四域的问题提出和答案构建。
- 通过测试和反射及投票技术提升代理的稳健性和性能。
- Cognitive Kernel-Pro在GAIA上的表现卓越,超越其他领先系统。
点此查看论文截图

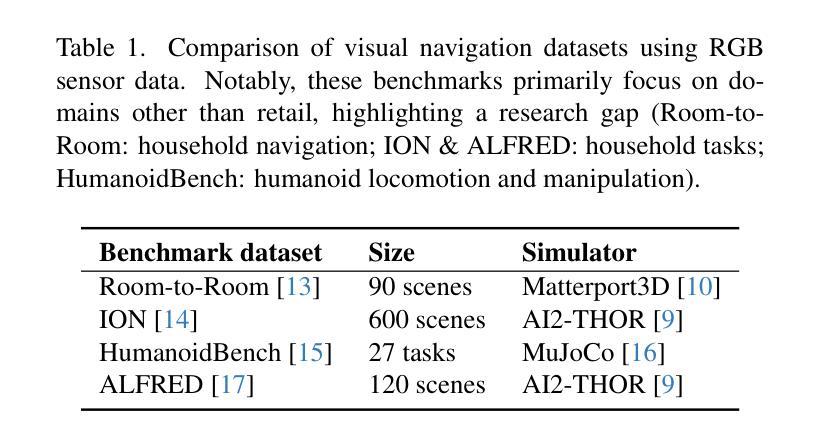
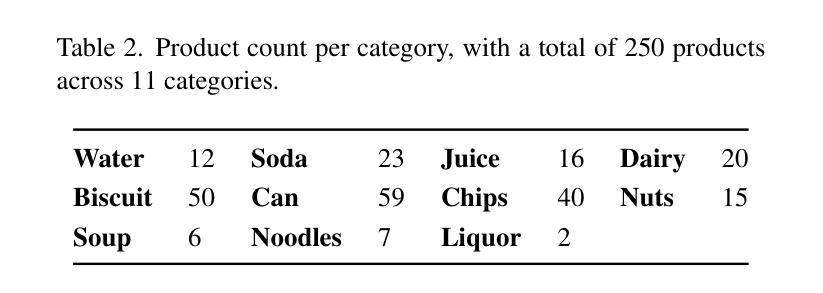
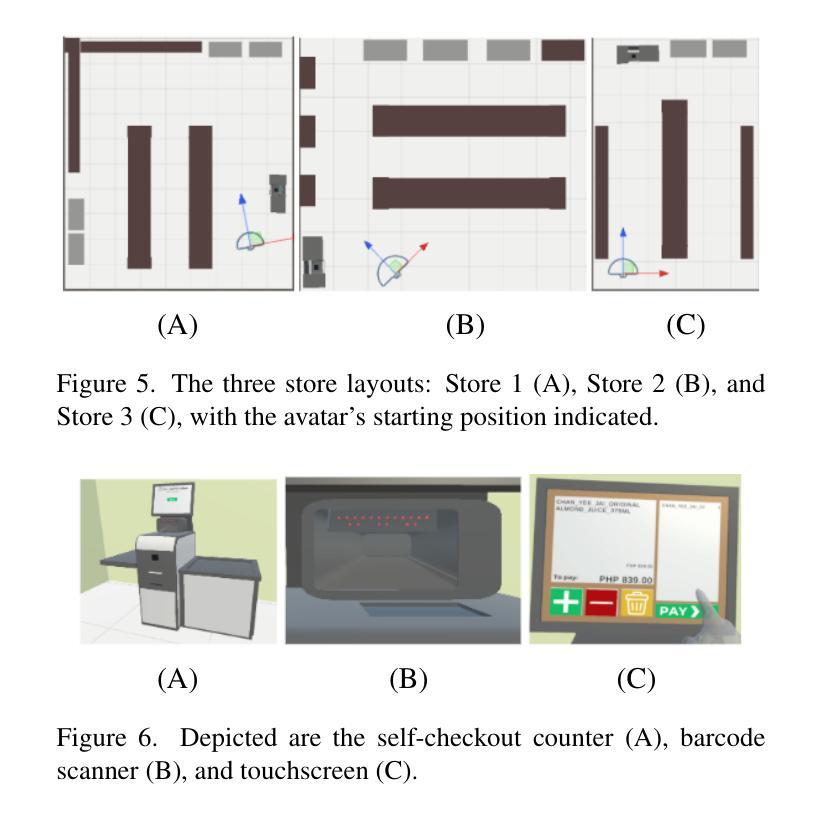
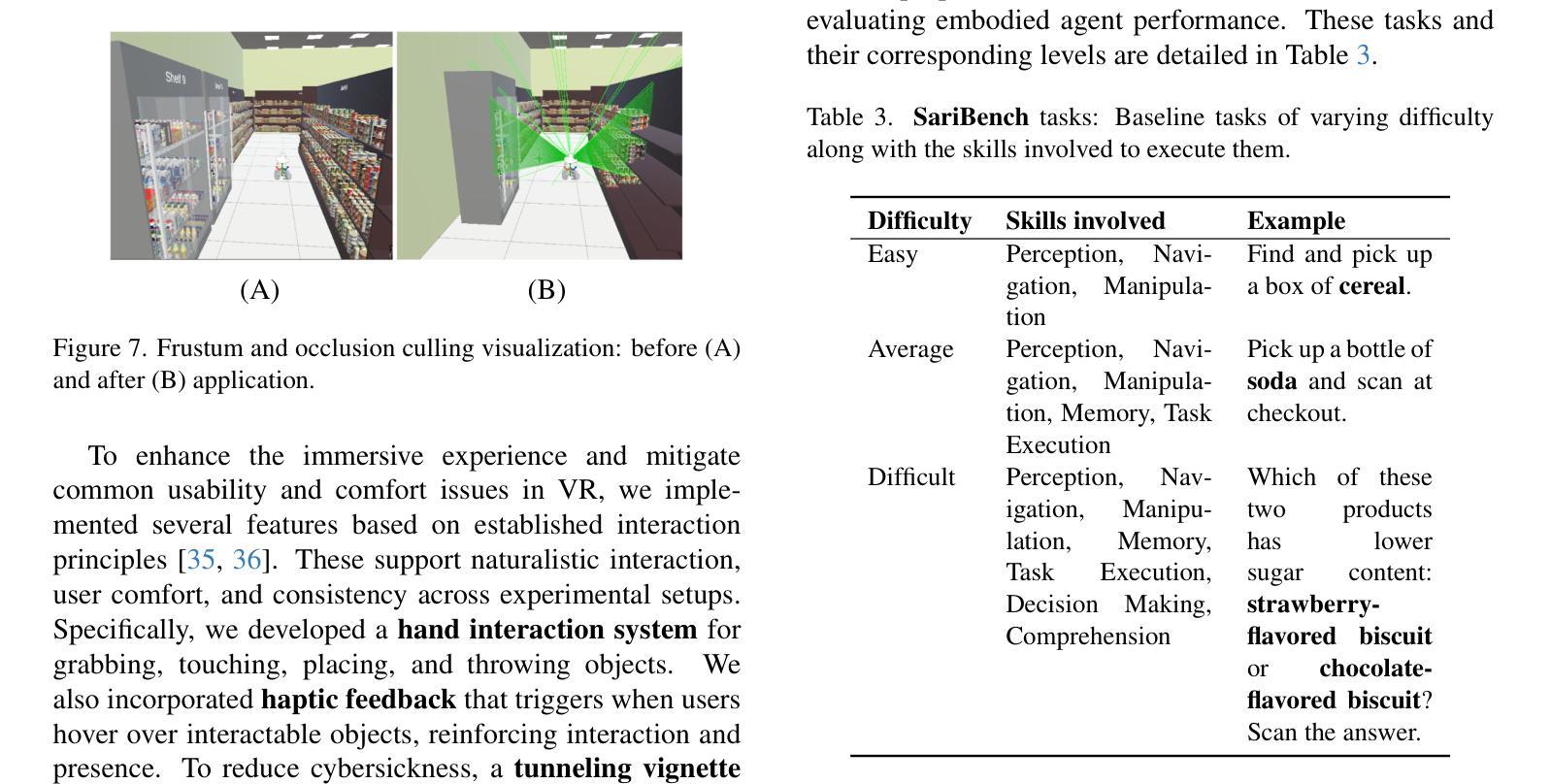
Sari Sandbox: A Virtual Retail Store Environment for Embodied AI Agents
Authors:Janika Deborah Gajo, Gerarld Paul Merales, Jerome Escarcha, Brenden Ashley Molina, Gian Nartea, Emmanuel G. Maminta, Juan Carlos Roldan, Rowel O. Atienza
We present Sari Sandbox, a high-fidelity, photorealistic 3D retail store simulation for benchmarking embodied agents against human performance in shopping tasks. Addressing a gap in retail-specific sim environments for embodied agent training, Sari Sandbox features over 250 interactive grocery items across three store configurations, controlled via an API. It supports both virtual reality (VR) for human interaction and a vision language model (VLM)-powered embodied agent. We also introduce SariBench, a dataset of annotated human demonstrations across varied task difficulties. Our sandbox enables embodied agents to navigate, inspect, and manipulate retail items, providing baselines against human performance. We conclude with benchmarks, performance analysis, and recommendations for enhancing realism and scalability. The source code can be accessed via https://github.com/upeee/sari-sandbox-env.
我们推出Sari Sandbox,这是一个高保真、逼真的3D零售店模拟环境,用于评估实体代理在购物任务中的人类表现基准。为解决针对实体代理训练的零售特定模拟环境中的差距,Sari Sandbox具有超过250种交互式杂货商品,跨越三种店面配置,通过API进行控制。它支持虚拟现实(VR)的人类互动和一个由视觉语言模型(VLM)驱动的实体代理。我们还推出了SariBench数据集,其中包含各种难度任务的注释人类演示。我们的沙盘让实体代理能够浏览、检查并操作零售商品,提供与人类表现基准对比的基准。我们通过基准测试、性能分析和增强现实性和可扩展性的建议来得出结论。源代码可通过https://github.com/upeee/sari-sandbox-env获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, accepted in ICCV 2025 Workshop on RetailVision
Summary
Sari Sandbox是一款高保真、逼真的三维零售店模拟环境,用于评估实体代理在购物任务中的表现与人类表现的基准测试。它弥补了零售特定模拟环境在实体代理训练方面的空白,拥有超过250种交互式杂货商品和三种店面配置,通过API进行控制。它支持虚拟现实(VR)进行人类互动以及通过视觉语言模型(VLM)驱动的实体代理。此外,还推出了SariBench数据集,其中包含各种难度任务的标注人类演示。此模拟环境使实体代理能够导航、检查和操作零售商品,并提供与人类表现的基准测试。有关代码可通过https://github.com/upeee/sari-sandbox-env访问。
Key Takeaways
- Sari Sandbox是一个用于评估实体代理在零售环境中的购物任务性能的高保真模拟环境。
- 它提供了超过250种交互式杂货商品和三种不同的店面配置。
- Sari Sandbox支持虚拟现实交互和通过视觉语言模型的实体代理。
- SariBench数据集包含了各种难度级别的购物任务标注人类演示。
- 此模拟环境允许实体代理进行导航、检查商品和操作商品。
- 提供了与人类表现的基准测试。
点此查看论文截图



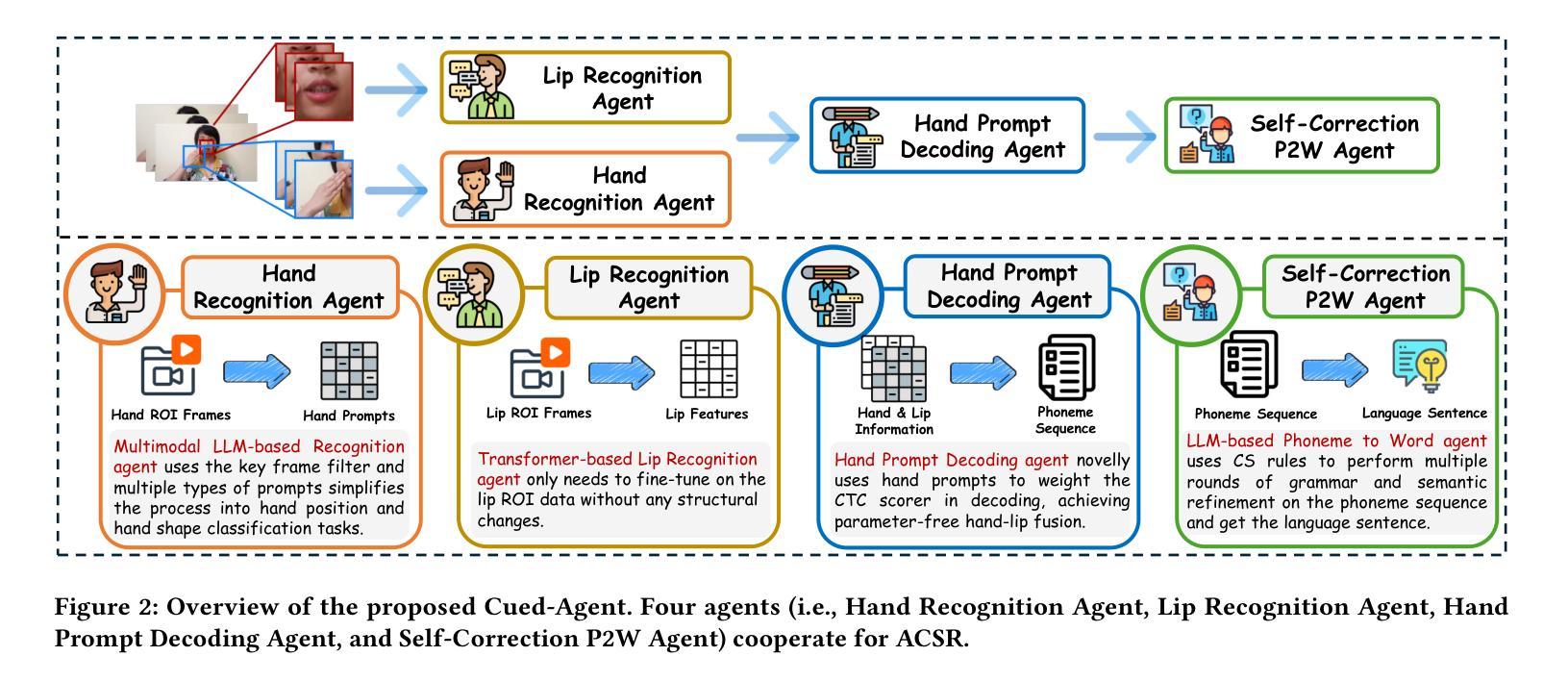
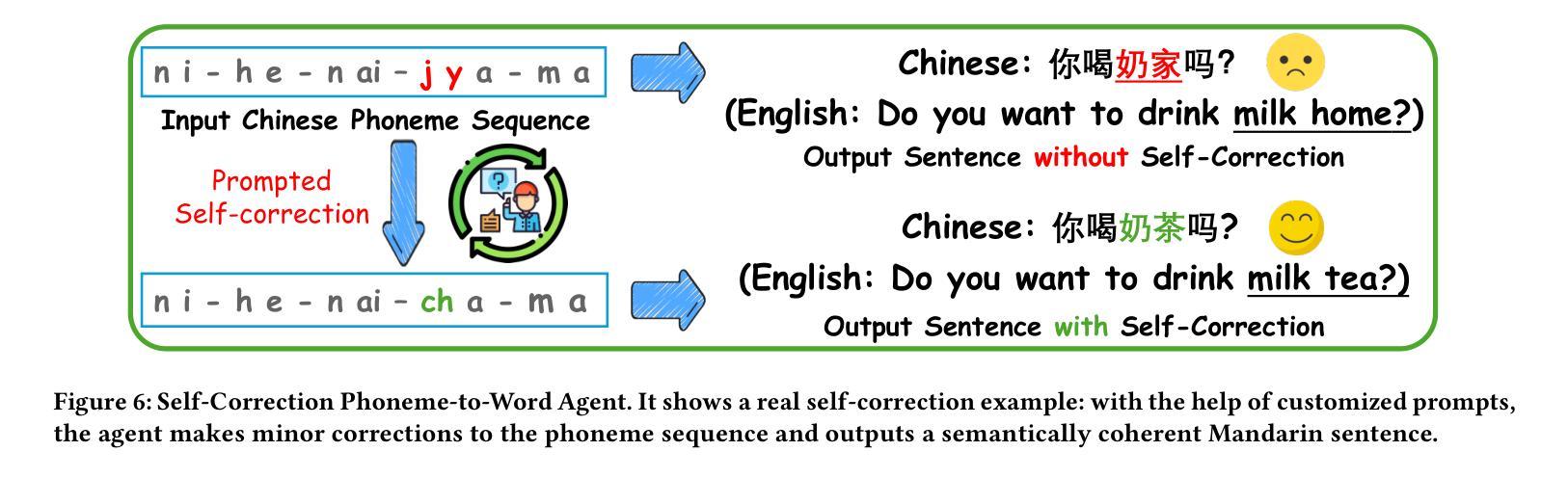
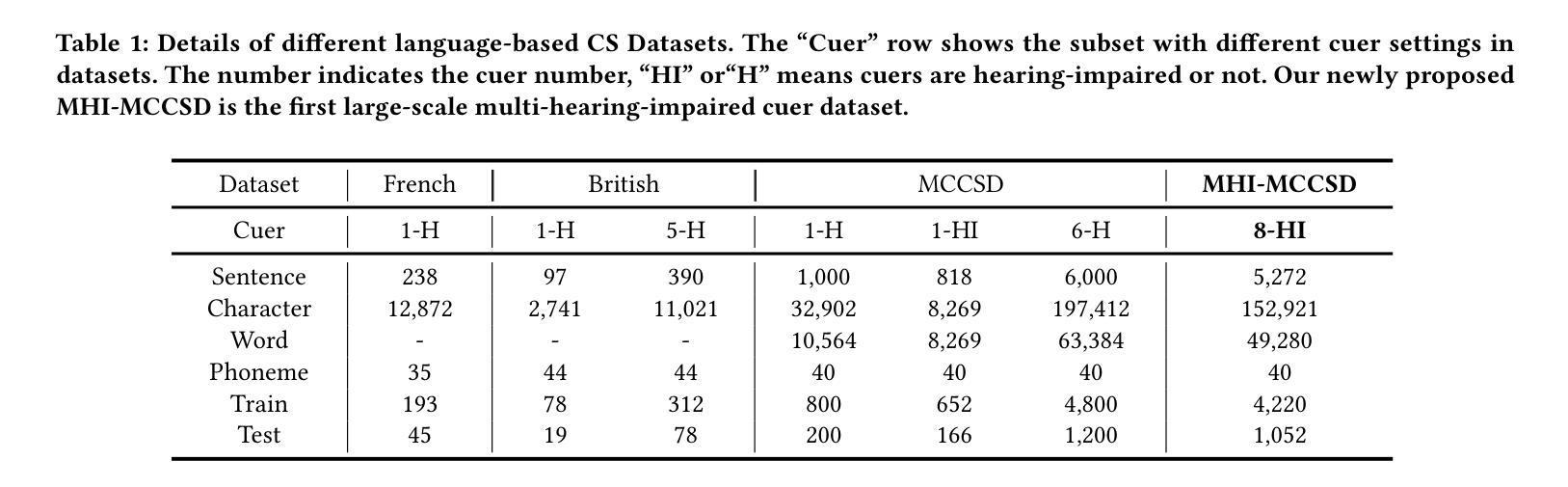
Cued-Agent: A Collaborative Multi-Agent System for Automatic Cued Speech Recognition
Authors:Guanjie Huang, Danny H. K. Tsang, Shan Yang, Guangzhi Lei, Li Liu
Cued Speech (CS) is a visual communication system that combines lip-reading with hand coding to facilitate communication for individuals with hearing impairments. Automatic CS Recognition (ACSR) aims to convert CS hand gestures and lip movements into text via AI-driven methods. Traditionally, the temporal asynchrony between hand and lip movements requires the design of complex modules to facilitate effective multimodal fusion. However, constrained by limited data availability, current methods demonstrate insufficient capacity for adequately training these fusion mechanisms, resulting in suboptimal performance. Recently, multi-agent systems have shown promising capabilities in handling complex tasks with limited data availability. To this end, we propose the first collaborative multi-agent system for ACSR, named Cued-Agent. It integrates four specialized sub-agents: a Multimodal Large Language Model-based Hand Recognition agent that employs keyframe screening and CS expert prompt strategies to decode hand movements, a pretrained Transformer-based Lip Recognition agent that extracts lip features from the input video, a Hand Prompt Decoding agent that dynamically integrates hand prompts with lip features during inference in a training-free manner, and a Self-Correction Phoneme-to-Word agent that enables post-process and end-to-end conversion from phoneme sequences to natural language sentences for the first time through semantic refinement. To support this study, we expand the existing Mandarin CS dataset by collecting data from eight hearing-impaired cuers, establishing a mixed dataset of fourteen subjects. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our Cued-Agent performs superbly in both normal and hearing-impaired scenarios compared with state-of-the-art methods. The implementation is available at https://github.com/DennisHgj/Cued-Agent.
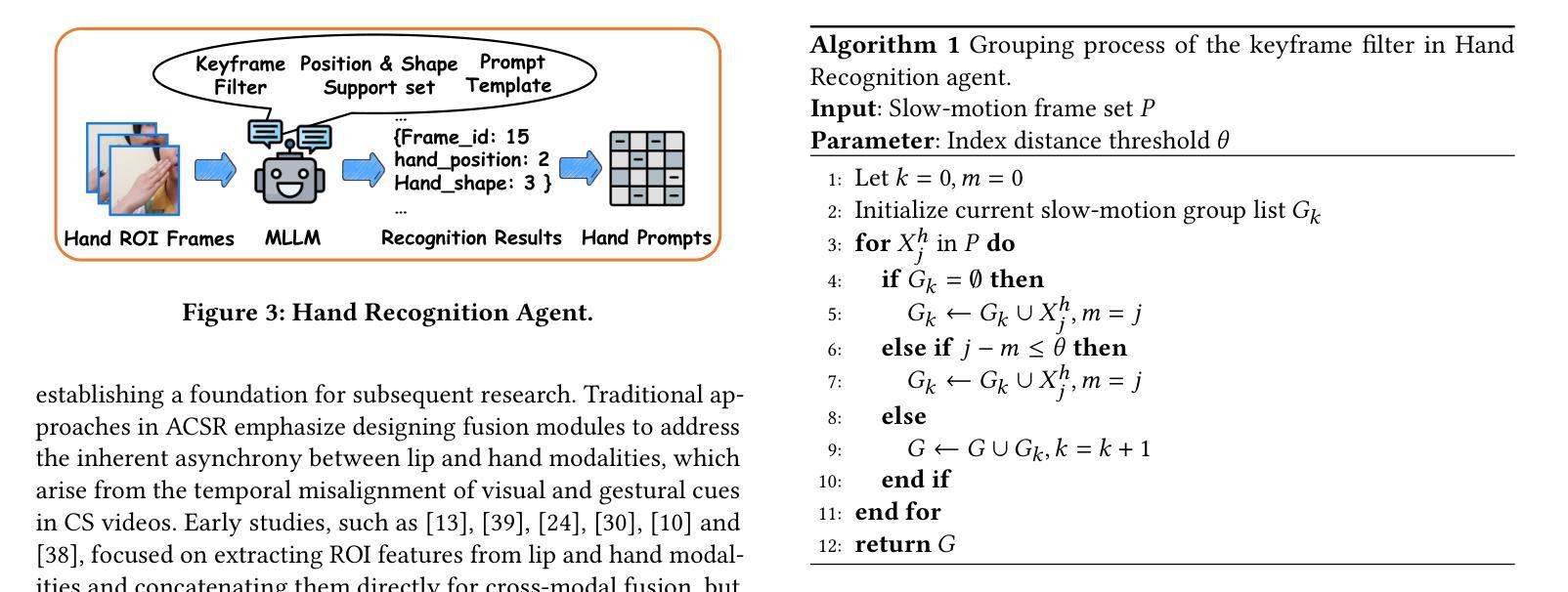
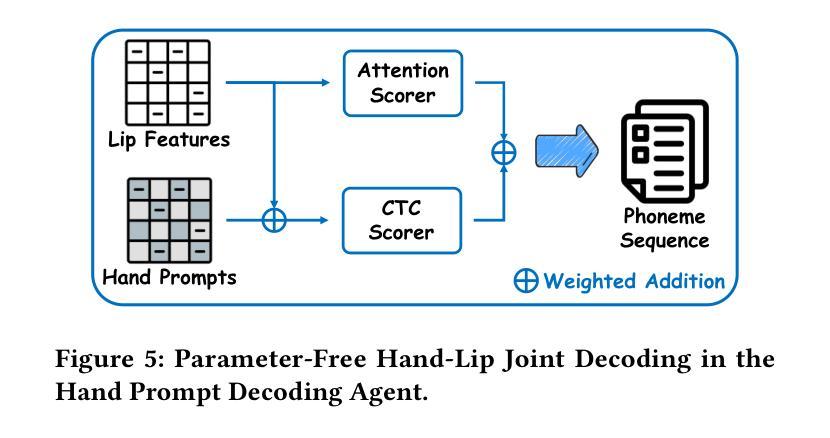
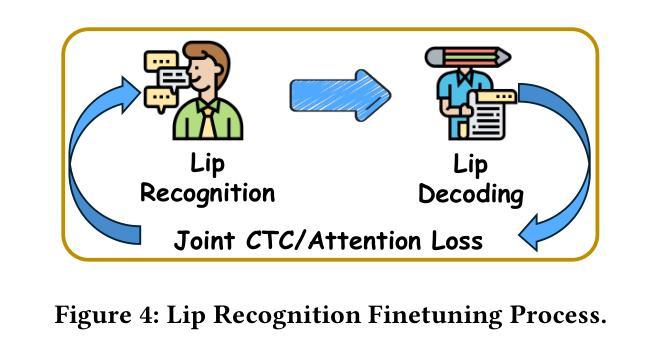
提示语(CS)是一种视觉通信系统,它将唇读与手编码结合起来,为听力障碍者提供交流帮助。自动提示语识别(ACSR)旨在通过人工智能驱动的方法将CS手势和唇部动作转化为文字。传统上,手部和唇部动作之间的时间异步性需要设计复杂的模块以实现有效的多模态融合。然而,受限于数据的可用性,当前的方法在训练这些融合机制方面表现出不足的能力,导致性能不佳。最近,多智能体系统在处理有限数据可用性的复杂任务方面表现出了有前景的能力。为此,我们提出了第一个用于ACSR的协作多智能体系统,名为Cued-Agent。它集成了四个专业子智能体:一个基于多模态大型语言模型的Hand Recognition智能体,它采用关键帧筛选和CS专家提示策略来解码手部动作;一个预训练的基于Transformer的Lip Recognition智能体,它从输入视频中提取唇部特征;一个Hand Prompt Decoding智能体,它以无训练的方式在推理过程中动态整合手部提示和唇部特征;以及一个Self-Correction Phoneme-to-Word智能体,它通过语义细化首次实现从音素序列到自然语言句子的后处理和端到端转换。为了支持这项研究,我们从八名听力受损的cuers中收集数据,建立了一个包含十四名参与者的混合数据集。大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们的Cued-Agent在正常和听力受损场景中表现卓越。实现细节可在https://github.com/DennisHgj/Cued-Agent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
摘要
本文介绍了一种名为Cued-Agent的自动Cued Speech(CS)识别系统。该系统运用多模态语言模型和Transformer模型等技术,结合唇读和手语编码,为听力受损人士提供沟通便利。Cued-Agent包含四个子代理,分别负责手语识别、唇特征提取、手语提示解码和语音到文字的自我修正。研究通过扩展现有的普通话CS数据集,建立了包含十四位主体的混合数据集。实验表明,与现有技术相比,Cued-Agent在正常和听力受损场景下的表现均表现优异。
要点分析
- Cued Speech是一种视觉沟通系统,通过结合唇读和手语编码来促进听力受损人士的沟通。
- 自动CS识别(ACSR)旨在将CS手势和唇动转化为文字,借助AI驱动的方法实现。
- 之前的方法受限于手部和唇部动作的时间异步性,需要设计复杂的模块进行多模态融合,但受限于数据有限,效果并不理想。
- 多代理系统在处理有限数据的复杂任务时表现出潜力。
- Cued-Agent是首个针对ACSR的协作多代理系统,包含四个专门子代理,分别负责手语识别、唇特征提取、手语提示的动态集成和语音到文字的转换。
- 研究通过扩展普通话CS数据集建立了混合数据集,包括来自八名听力受损人士的数据。
- 实验表明,Cued-Agent的表现优于现有技术,无论是在正常还是听力受损的环境下。
点此查看论文截图

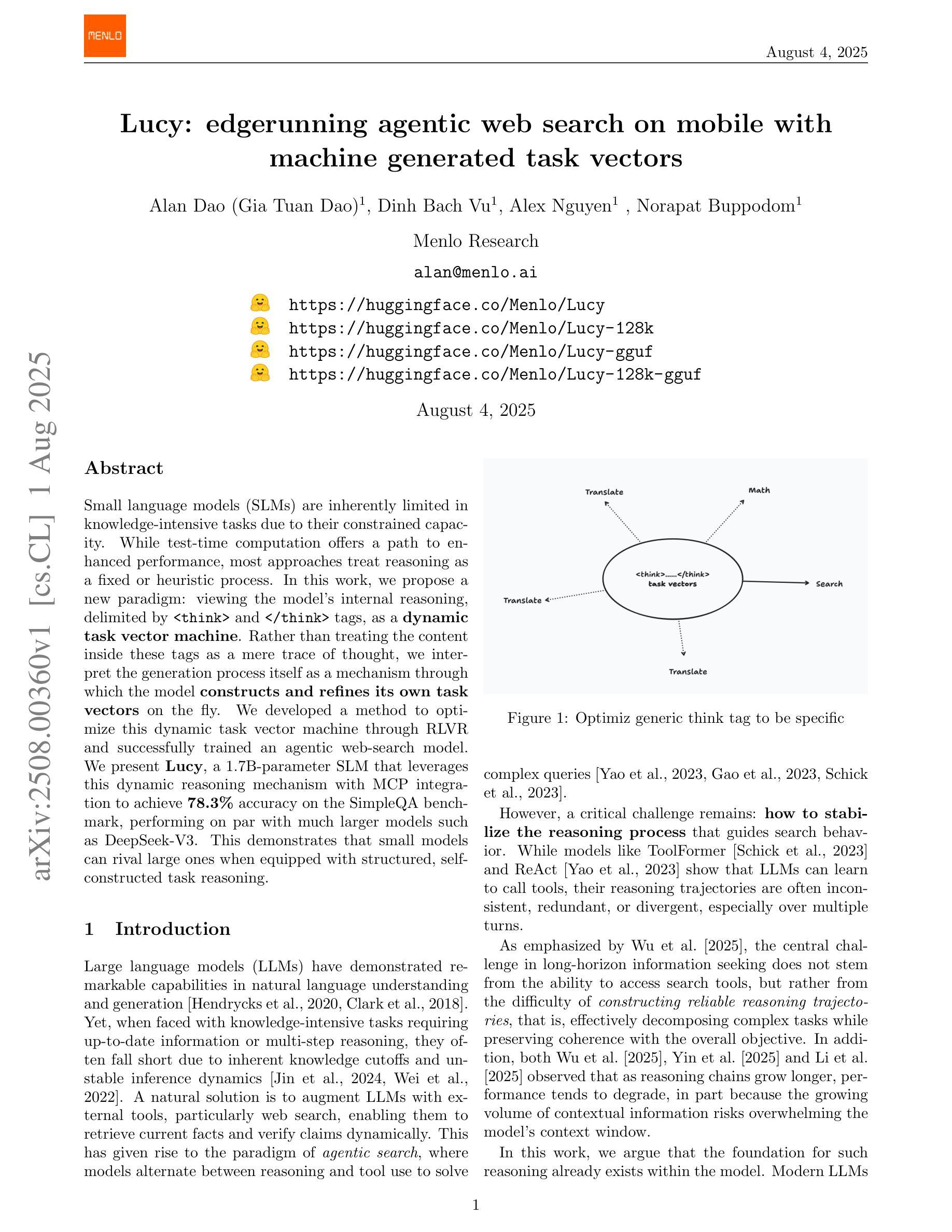
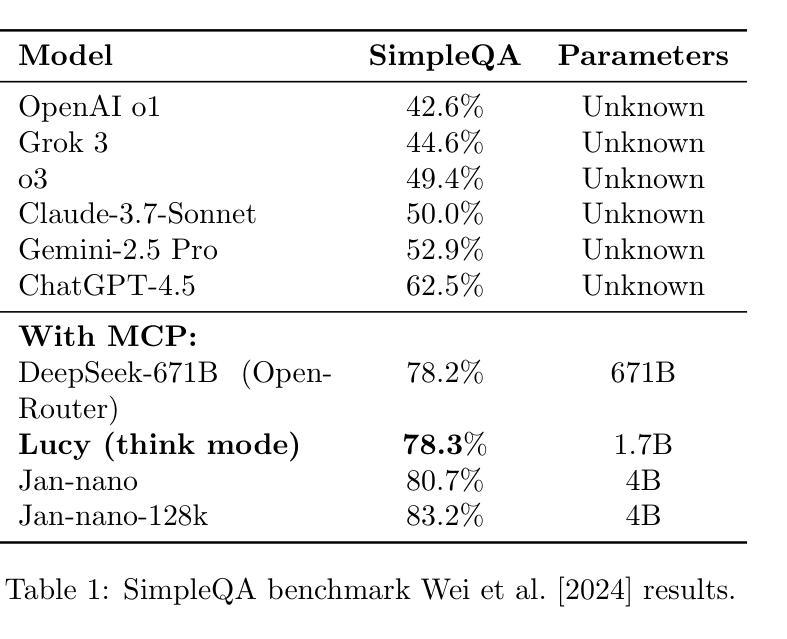
Lucy: edgerunning agentic web search on mobile with machine generated task vectors
Authors:Alan Dao, Dinh Bach Vu, Alex Nguyen, Norapat Buppodom
Small language models (SLMs) are inherently limited in knowledge-intensive tasks due to their constrained capacity. While test-time computation offers a path to enhanced performance, most approaches treat reasoning as a fixed or heuristic process. In this work, we propose a new paradigm: viewing the model’s internal reasoning, delimited by
小型语言模型(SLM)由于其容量有限,在知识密集型任务中存在固有的局限性。虽然测试时的计算提供了提高性能的途径,但大多数方法都将推理视为一个固定或启发式的过程。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个新的范式:将模型内部的推理(由
和 标签限定)视为动态任务向量机。我们不再将这些标签内的内容仅仅视为思考的痕迹,而是将生成过程本身解释为一种机制,通过该机制,模型可以即时地构建和细化自己的任务向量。我们开发了一种通过RLVR优化这种动态任务向量机的方法,并成功训练了一个代理网页搜索模型。我们推出了Lucy,这是一个拥有1.7B参数的SLM,它利用这种动态推理机制和MCP集成,在SimpleQA基准测试上达到了78.3%的准确率,与诸如DeepSeek-V3等大型模型的性能相当。这证明当配备结构化的自我构建任务推理时,小型模型可以与大型模型相抗衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新观点,即将小型语言模型(SLM)的内部推理过程视为动态任务向量机。通过利用
Key Takeaways
- 小型语言模型(SLM)在知识密集型任务上存在局限性。
- 现有方法通常将推理视为固定或启发式过程。
- 本文提出了一种新的观点,即将SLM的内部推理过程视为动态任务向量机。
- 作者利用了
和 标签来定义模型的动态任务向量。 - 作者开发了一种优化方法RLVR,并成功训练了一个名为Lucy的agentic网络搜索模型。
- Lucy在SimpleQA基准测试中实现了78.3%的准确率,与大型模型表现相当。
点此查看论文截图
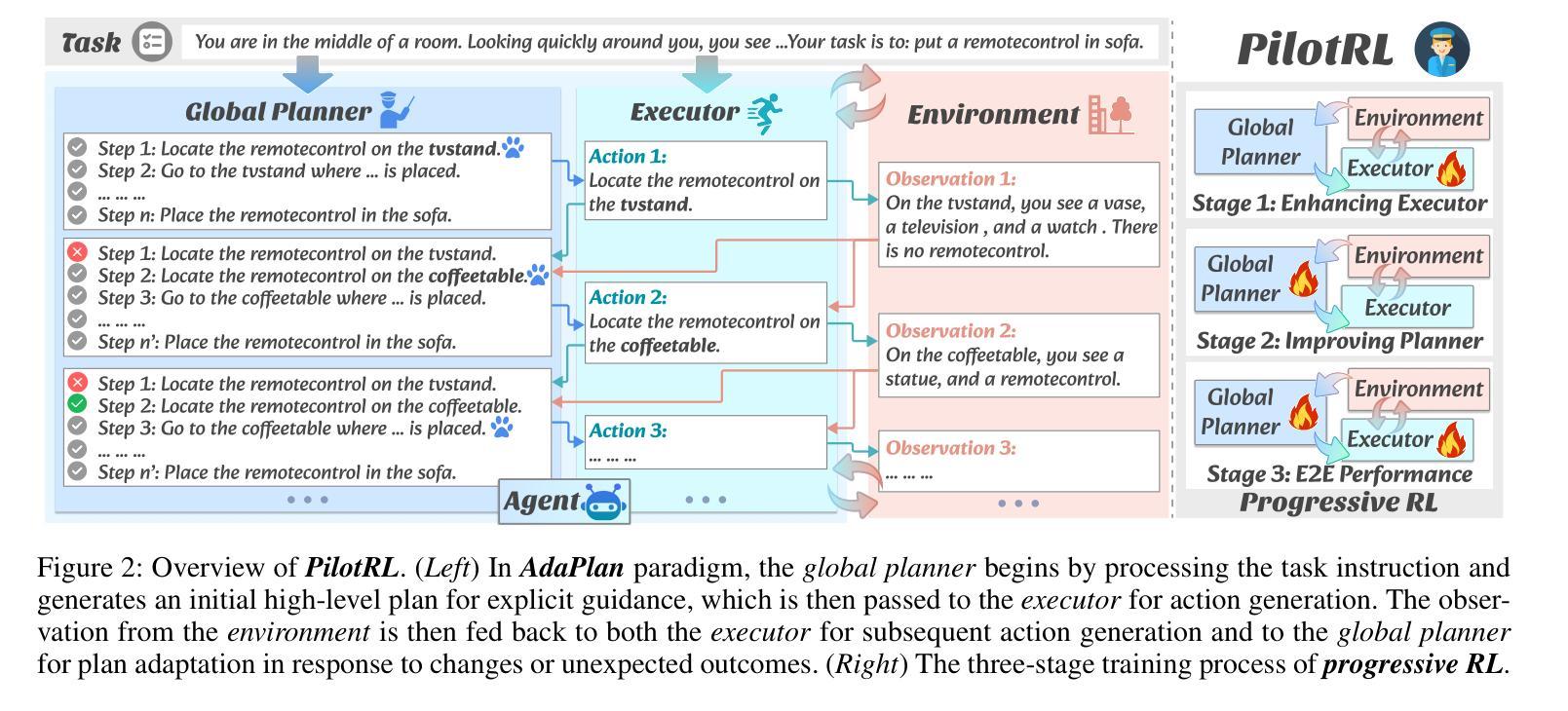
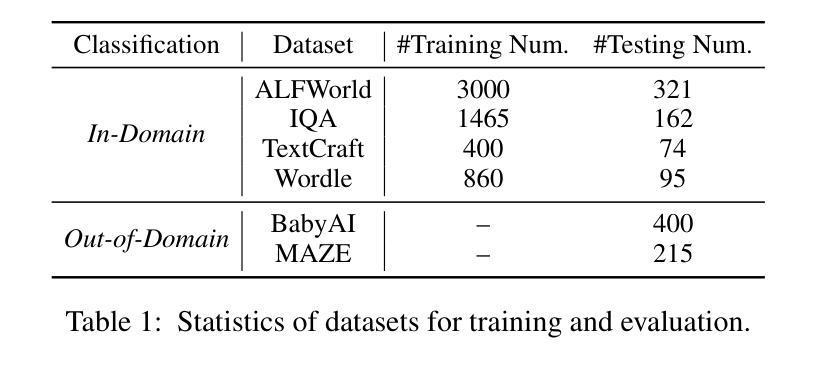
PilotRL: Training Language Model Agents via Global Planning-Guided Progressive Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Keer Lu, Chong Chen, Bin Cui, Huang Leng, Wentao Zhang
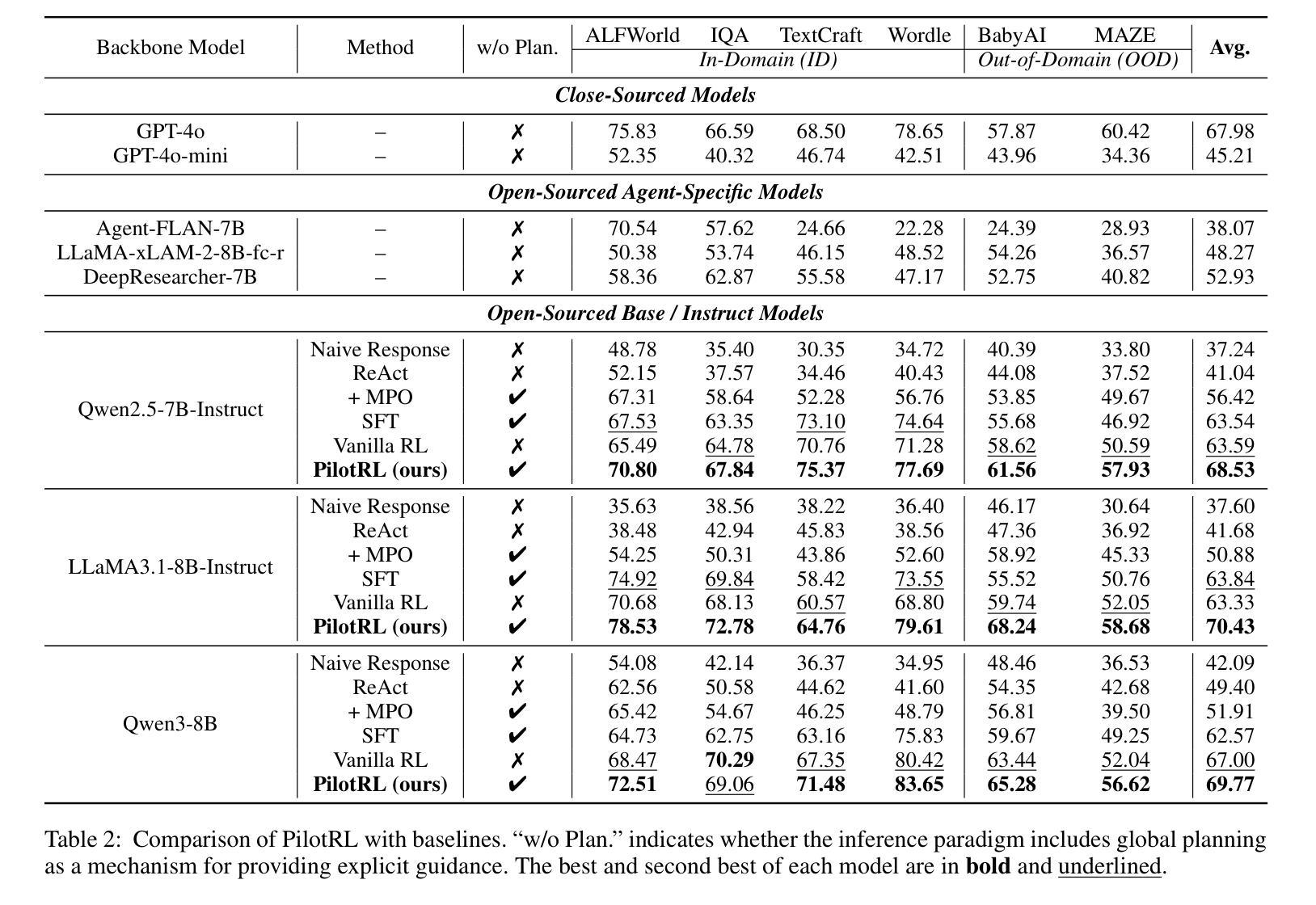
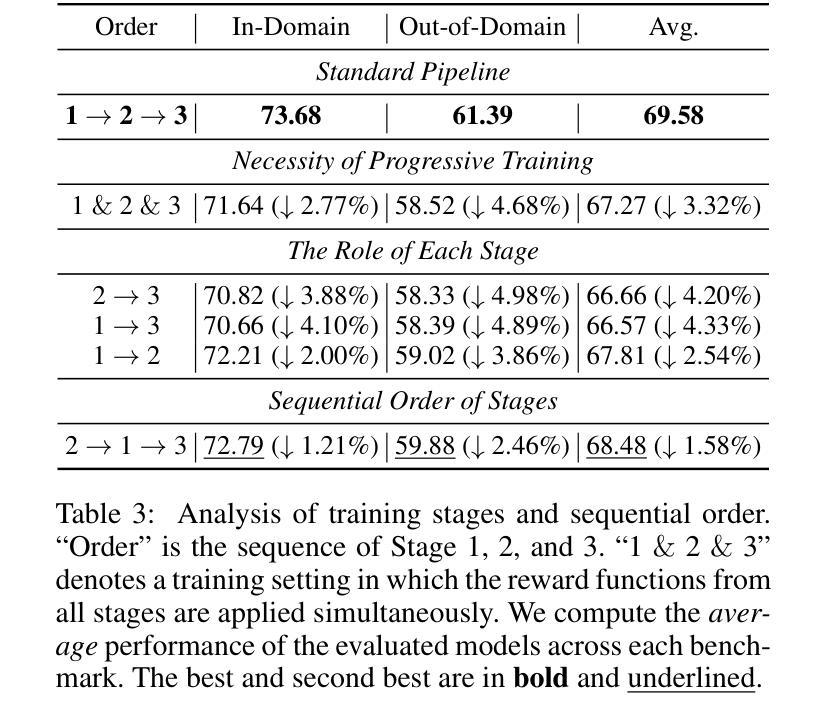
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in tackling agent-oriented tasks. Despite their potential, existing work faces challenges when deploying LLMs in agent-based environments. The widely adopted agent paradigm ReAct centers on integrating single-step reasoning with immediate action execution, which limits its effectiveness in complex tasks requiring long-term strategic planning. Furthermore, the coordination between the planner and executor during problem-solving is also a critical factor to consider in agent design. Additionally, current approaches predominantly rely on supervised fine-tuning, which often leads models to memorize established task completion trajectories, thereby restricting their generalization ability when confronted with novel problem contexts. To address these challenges, we introduce an adaptive global plan-based agent paradigm AdaPlan, aiming to synergize high-level explicit guidance with execution to support effective long-horizon decision-making. Based on the proposed paradigm, we further put forward PilotRL, a global planning-guided training framework for LLM agents driven by progressive reinforcement learning. We first develop the model’s ability to follow explicit guidance from global plans when addressing agent tasks. Subsequently, based on this foundation, we focus on optimizing the quality of generated plans. Finally, we conduct joint optimization of the model’s planning and execution coordination. Experiments indicate that PilotRL could achieve state-of-the-art performances, with LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL surpassing closed-sourced GPT-4o by 3.60%, while showing a more substantial gain of 55.78% comparing to GPT-4o-mini at a comparable parameter scale.
面向代理任务的大型语言模型(LLMs)已经取得了显著的进步。尽管它们具有潜力,但在基于代理的环境中部署LLMs时,现有工作仍面临挑战。广泛采用的ReAct代理范式侧重于将单步推理与即时行动执行相结合,这限制了其在需要长期战略规划的复杂任务中的有效性。此外,在问题解决过程中,规划者和执行者之间的协调也是代理设计中的一个关键因素。另外,当前的方法主要依赖于监督微调,这往往导致模型记忆已建立的任务完成轨迹,从而在面对新的问题上下文时限制其泛化能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了基于自适应全局规划的代理范式AdaPlan,旨在将高级显式指导与执行相结合,以支持有效的长期决策。基于这一范式,我们进一步提出了PilotRL,这是一个由渐进强化学习驱动的LLM代理全局规划引导训练框架。我们首先开发模型在解决代理任务时遵循全局计划显式指导的能力。然后在此基础上,我们专注于优化生成的计划的质量。最后,我们对模型的规划和执行协调进行联合优化。实验表明,PilotRL可以达到最新的性能水平,其中LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL超越封闭源代码的GPT-4o达3.60%,而在相似的参数规模下,与GPT-4o-mini相比则显示出更大的提升,达到55.78%。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理面向代理的任务方面取得了显著进展,但现有工作在将LLM部署在代理环境中时面临挑战。主流代理范式ReAct专注于将即时行动执行与单步推理相结合,这在处理复杂的长远战略计划任务方面有其局限性。此外,代理设计还需要考虑解决问题时规划者和执行者之间的协调问题。当前的方法主要依赖监督微调,这导致模型经常记忆既定的任务完成轨迹,限制了其在面对新情境时的泛化能力。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了自适应全局计划代理范式AdaPlan,旨在实现高级明确指导与执行之间的协同,以支持有效的长期决策。基于这一范式,我们进一步推出了PilotRL,这是一个由全局规划引导的大型语言模型代理训练框架,该框架通过渐进强化学习驱动。实验表明,PilotRL能够实现最先进的性能表现。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在处理面向代理的任务方面取得了进展,但在部署于代理环境中时面临挑战。
- 当前代理范式如ReAct在处理复杂、需要长远规划的任务时存在局限性。
- AdaPlan范式旨在通过实现高级明确指导与执行之间的协同,克服现有挑战,支持有效的长期决策。
- PilotRL是一种基于AdaPlan的新型训练框架,通过渐进强化学习驱动全局规划引导的大型语言模型代理的训练。
- PilotRL模型首先发展遵循全局计划明确指导的能力,然后在此基础上优化生成计划的质量。
- 实验结果显示PilotRL实现了最先进的性能表现,尤其是LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct与PilotRL的结合表现超越了闭源的GPT-4o。
点此查看论文截图

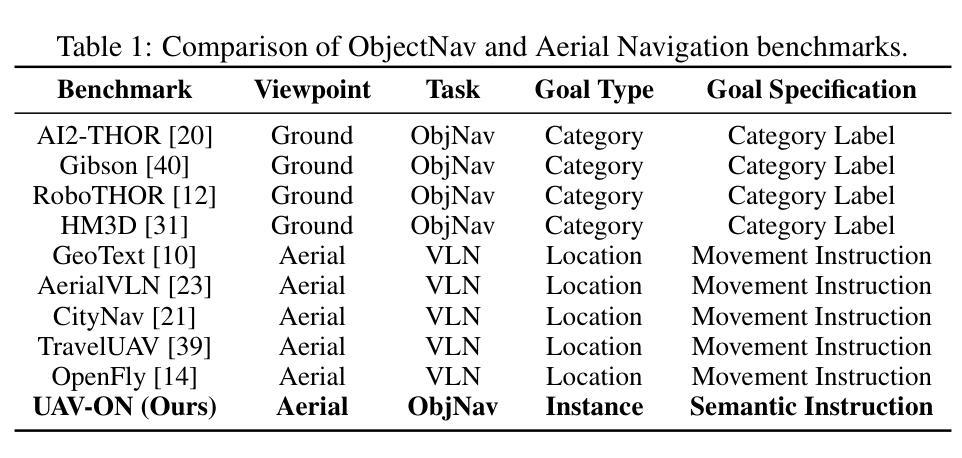
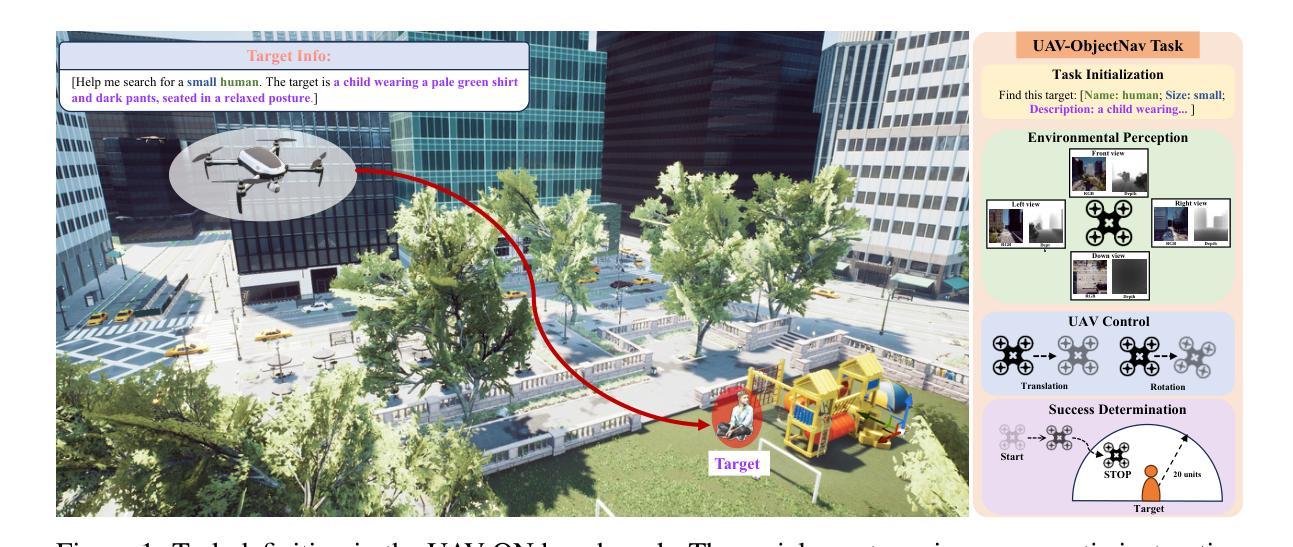
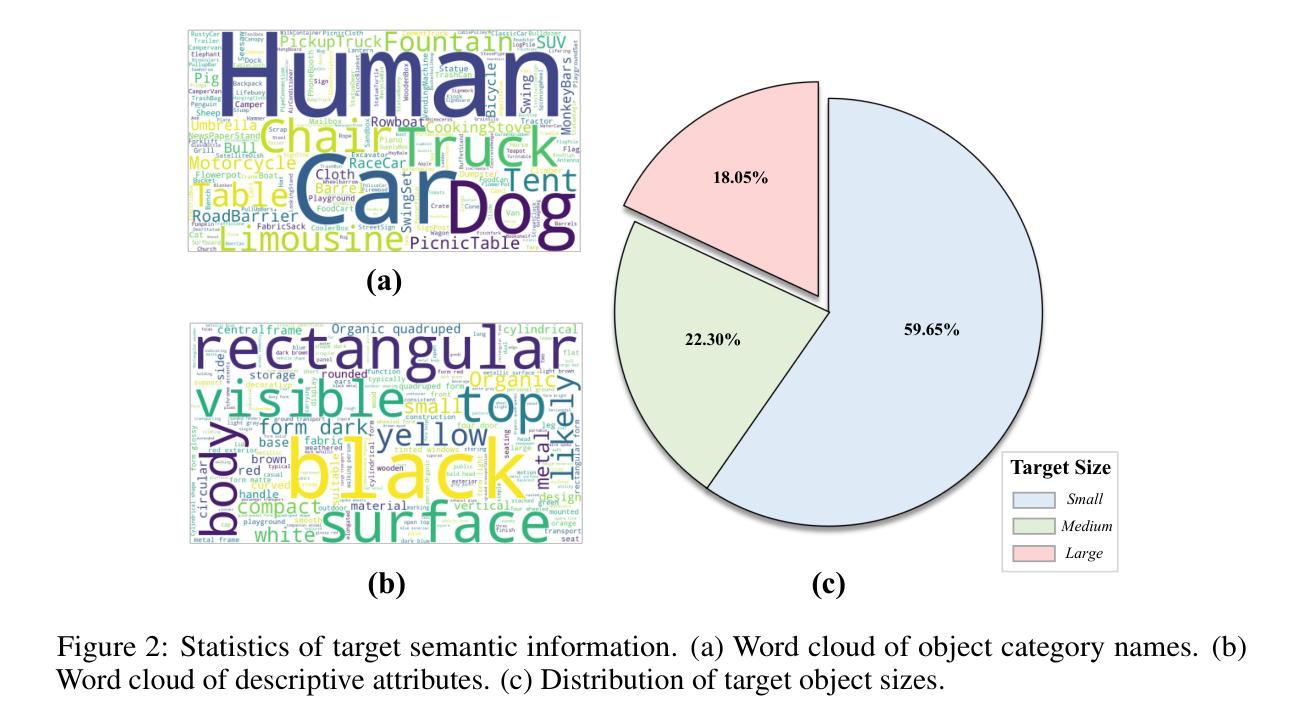
UAV-ON: A Benchmark for Open-World Object Goal Navigation with Aerial Agents
Authors:Jianqiang Xiao, Yuexuan Sun, Yixin Shao, Boxi Gan, Rongqiang Liu, Yanjing Wu, Weili Gua, Xiang Deng
Aerial navigation is a fundamental yet underexplored capability in embodied intelligence, enabling agents to operate in large-scale, unstructured environments where traditional navigation paradigms fall short. However, most existing research follows the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) paradigm, which heavily depends on sequential linguistic instructions, limiting its scalability and autonomy. To address this gap, we introduce UAV-ON, a benchmark for large-scale Object Goal Navigation (ObjectNav) by aerial agents in open-world environments, where agents operate based on high-level semantic goals without relying on detailed instructional guidance as in VLN. UAV-ON comprises 14 high-fidelity Unreal Engine environments with diverse semantic regions and complex spatial layouts, covering urban, natural, and mixed-use settings. It defines 1270 annotated target objects, each characterized by an instance-level instruction that encodes category, physical footprint, and visual descriptors, allowing grounded reasoning. These instructions serve as semantic goals, introducing realistic ambiguity and complex reasoning challenges for aerial agents. To evaluate the benchmark, we implement several baseline methods, including Aerial ObjectNav Agent (AOA), a modular policy that integrates instruction semantics with egocentric observations for long-horizon, goal-directed exploration. Empirical results show that all baselines struggle in this setting, highlighting the compounded challenges of aerial navigation and semantic goal grounding. UAV-ON aims to advance research on scalable UAV autonomy driven by semantic goal descriptions in complex real-world environments.
无人机导航是智能实体中一项基础却尚未被充分探索的能力,它使得代理能够在大规模、非结构化环境中运行,传统的导航模式在这些环境中表现不足。然而,现有的大多数研究都遵循视觉和语言导航(VLN)的模式,该模式严重依赖于连续的语言指令,限制了其可扩展性和自主性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了UAV-ON,这是一个开放世界环境中无人机对象目标导航(ObjectNav)的基准测试,代理可以根据高级语义目标进行操作,而不必依赖VLN中的详细指令指导。UAV-ON包含14个高保真度的Unreal Engine环境,具有多样的语义区域和复杂的空间布局,涵盖城市、自然和混合用途场景。它定义了1270个注释目标对象,每个对象都可以通过实例级别的指令进行表征,这些指令包含类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符,允许基于现实情况的推理。这些指令作为语义目标,为无人机引入了现实模糊性和复杂的推理挑战。为了评估这个基准测试,我们实施了几种基准方法,包括Aerial ObjectNav Agent(AOA),这是一个模块化策略,能够整合指令语义与以自我为中心的观察结果,以实现长期、目标导向的探索。实验结果表明,所有基线在此设置中都面临困难,突显了无人机导航和语义目标定位的挑战性。UAV-ON旨在推动复杂现实环境中基于语义目标描述的无人机自主性研究的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM Dataset Track 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了空中导航在智能体领域中的基本且未被充分探索的能力。传统的导航模式在大型非结构化环境中难以实现空中导航。因此,提出了一种新的大型目标导航任务,称为无人机目标对象导航(UAV-ON)。在此任务中,智能体不再依赖于详细的指令性指导,而是根据高级语义目标进行操作。该任务覆盖了城市、自然和混合用途等不同环境设置。现有方法在此任务上表现不佳,凸显了空中导航和语义目标接地的挑战。UAV-ON的目标是推进在复杂现实环境中实现无人机自主性的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 空中导航是智能体领域中的基本能力,但在大型非结构化环境中存在挑战。
- 传统导航模式在大型非结构化环境中难以实现空中导航。
- UAV-ON是一种新型的大型目标导航任务,智能体基于高级语义目标进行操作。
- UAV-ON任务涵盖了城市、自然和混合用途等不同环境设置。
- UAV-ON引入了目标对象的实例级指令,包括类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符等信息。
- 现有方法在UAV-ON任务上表现不佳,凸显了空中导航和语义目标接地的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

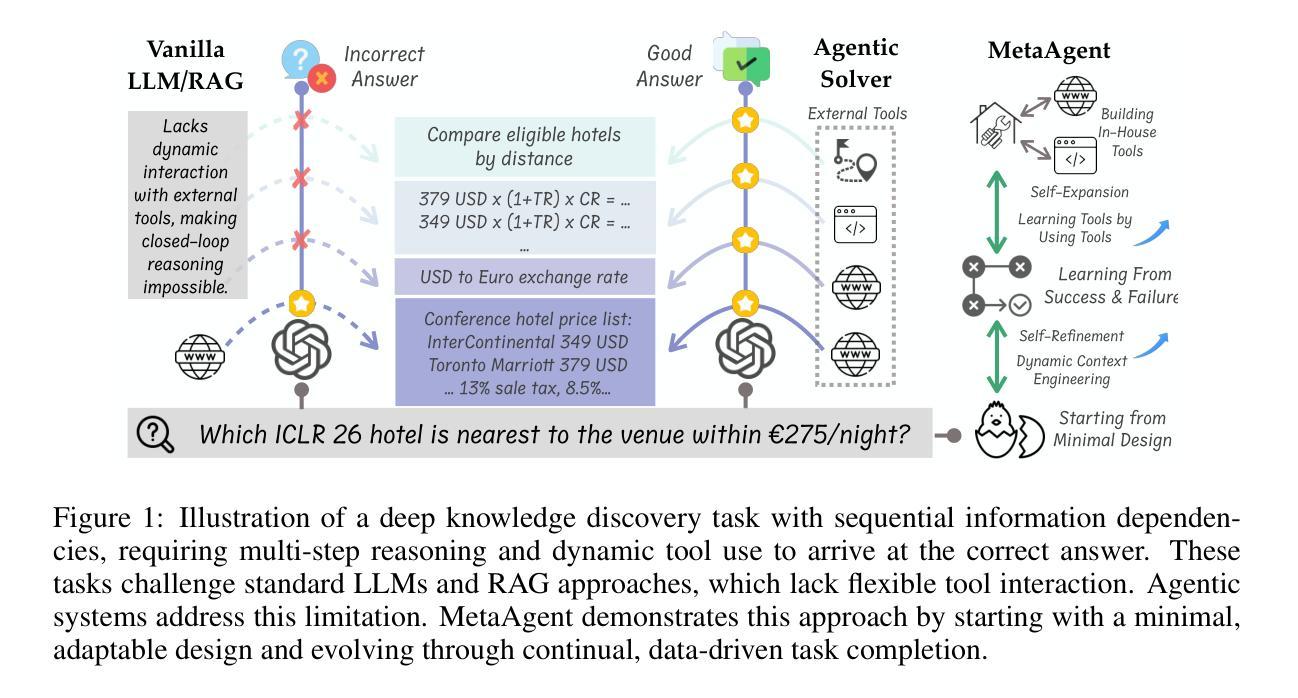
MetaAgent: Toward Self-Evolving Agent via Tool Meta-Learning
Authors:Hongjin Qian, Zheng Liu
In this work, we propose MetaAgent, an agentic paradigm inspired by the principle of learning-by-doing, where expertise is developed through hands-on practice and continual self-improvement. MetaAgent starts with a minimal workflow, equipped only with basic reasoning and adaptive help-seeking abilities. When a knowledge gap is encountered, MetaAgent generates natural language help requests, which are routed to the most suitable external tool by a dedicated tool router. As MetaAgent solves tasks, it continually conducts self-reflection and answer verification, distilling actionable experience into concise texts that are dynamically incorporated into future task contexts. Besides, MetaAgent autonomously builds in-house tools and a persistent knowledge base by organizing its tool-use history, further enhancing its ability to retrieve and integrate relevant information We term this continual, data-driven process as \textit{meta tool learning}, through which MetaAgent incrementally refines its reasoning and tool-use strategies, without changing model parameters or requiring further post-training. Evaluated on challenging knowledge discovery benchmarks, including GAIA, WebWalkerQA, and BrowseCamp, MetaAgent consistently outperforms workflow-based baselines and matches or exceeds end-to-end trained agents, demonstrating the promise of self-evolving agentic systems for robust, general-purpose knowledge discovery. We provide our source codes in https://github.com/qhjqhj00/MetaAgent.
在此工作中,我们提出了MetaAgent,这是一种受实践学习原则启发的代理范式,通过动手实践和持续的自我改进来发展专业知识。MetaAgent从一个最小的工作流程开始,仅具备基本的推理和自适应求助能力。当遇到知识空白时,MetaAgent会生成自然语言求助请求,由专用工具路由器将其路由到最合适的外部工具。随着MetaAgent完成任务,它会持续进行自我反思和答案验证,将可操作的经历提炼成简短的文本,并动态地融入未来的任务上下文。此外,MetaAgent会自主构建内部工具和持久的知识库,通过组织其工具使用历史来进一步提高其检索和整合相关信息的能力。我们将这种持续的数据驱动过程称为“元工具学习”,通过这个过程,MetaAgent能够逐步优化其推理和工具使用策略,无需更改模型参数或需要进行进一步的后续训练。在包括GAIA、WebWalkerQA和BrowseCamp等具有挑战性的知识发现基准测试上,MetaAgent始终优于基于工作流程的基线,并达到或超过了端到端训练的代理水平,证明了自我进化的代理系统在稳健、通用的知识发现方面的潜力。我们在https://github.com/qhjqhj00/MetaAgent提供源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report, 14 pages
Summary
基于学习实践的元代理理念框架设计MetaAgent。具有最小的工作流程,基础推理能力和适应性求助机制,在实践中实现知识的增长和自反更新机制,且能够通过动态精炼的任务上下文自我总结发展出一套通用的实用指南和技巧知识库,同时通过求助生成的场景指导应用自动化检索精准所需知识进而自行进化改善使用工具和知识管理的通用模型方法。我们称之为元工具学习。在多个知识发现基准测试集上的表现证明了其优越性。相关代码已开源。
Key Takeaways
- MetaAgent遵循学习实践的元代理理念框架设计。
- MetaAgent具有最小的工作流程,并具备基础推理和适应性求助机制。
- MetaAgent在实践中通过自我反思和答案验证实现知识的增长和自反更新机制。
- MetaAgent通过精炼的任务上下文总结实用指南和技巧知识库。
- MetaAgent通过元工具学习改善使用工具和知识管理的通用模型方法。
- MetaAgent能够在多个知识发现基准测试集上实现优越表现。
点此查看论文截图

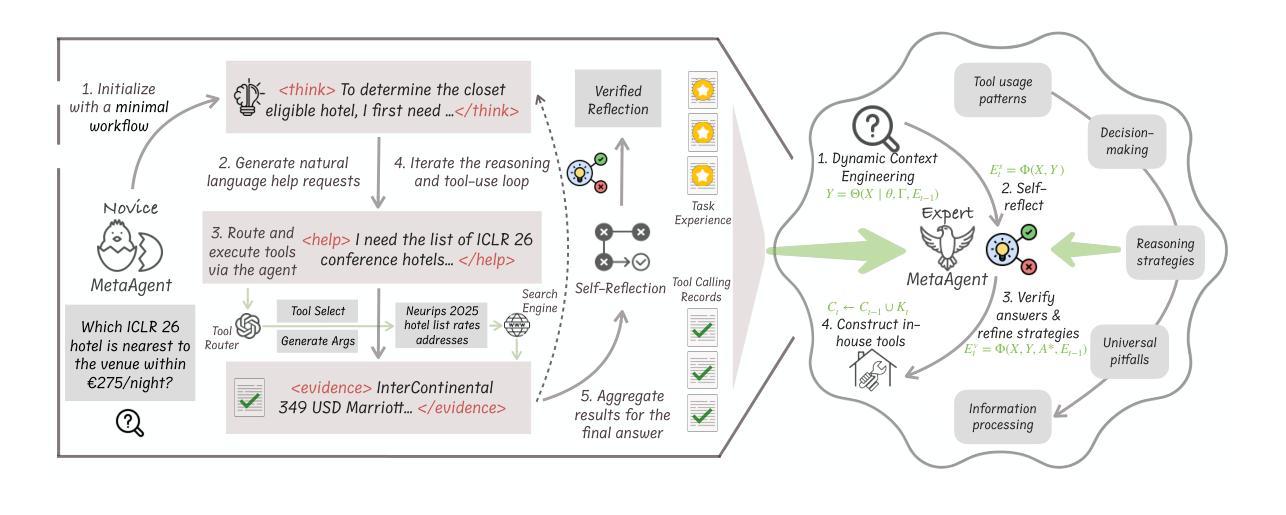
Dynamic Knowledge Exchange and Dual-diversity Review: Concisely Unleashing the Potential of a Multi-Agent Research Team
Authors:Weilun Yu, Shixiang Tang, Yonggui Huang, Nanqing Dong, Li Fan, Honggang Qi, Wei Liu, Xiaoli Diao, Xi Chen, Wanli Ouyang
Scientific progress increasingly relies on effective collaboration among researchers, a dynamic that large language models (LLMs) have only begun to emulate. While recent LLM-based scientist agents show promise in autonomous scientific discovery, they often lack the interactive reasoning and evaluation mechanisms essential to real-world research. We propose IDVSCI (Internal Discussion and Vote SCIentists), a multi-agent framework built on LLMs that incorporates two key innovations: a Dynamic Knowledge Exchange mechanism enabling iterative feedback among agents, and a Dual-Diversity Review paradigm that simulates heterogeneous expert evaluation. These components jointly promote deeper reasoning and the generation of more creative and impactful scientific ideas. To evaluate the effectiveness and generalizability of our approach, we conduct experiments on two datasets: a widely used benchmark in computer science and a new dataset we introduce in the health sciences domain. Results show that IDVSCI consistently achieves the best performance across both datasets, outperforming existing systems such as AI Scientist and VIRSCI. These findings highlight the value of modeling interaction and peer review dynamics in LLM-based autonomous research.
科技进步越来越依赖于研究者之间的有效协作,这一动态是大规模语言模型(LLM)才开始模仿的。虽然基于LLM的科学家代理在自主科学发现方面显示出前景,但它们通常缺乏真实世界研究中必不可少的交互式推理和评估机制。我们提出了IDVSCI(内部讨论与投票科学家),这是一个基于LLM的多代理框架,包含两项关键创新:动态知识交换机制,使代理之间能够进行迭代反馈;以及模拟异质专家评估的双重多样性审查模式。这些组件共同促进了更深入的推理和更具创造力和影响力的科学思想的产生。为了评估我们方法的有效性和通用性,我们在两个数据集上进行了实验:一个在计算机科学中广泛使用的基准测试,以及我们在健康科学领域引入的一个新数据集。结果表明,IDVSCI在两个数据集上均表现最佳,优于现有的AI科学家和VIRSCI系统。这些发现突显了在基于LLM的自主研究中建立互动和同行评审动态的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的科学家代理在自主科学发现方面展现出潜力,但仍缺乏交互式推理和评估机制。本文提出IDVSCI(内部讨论与投票科学家)多代理框架,通过动态知识交换机制和双差异审查范式,模拟专家评估并促进深度推理和创造性科学思想。实验结果表明,IDVSCI在跨学科的基准测试和健康科学领域的新数据集上均表现最佳,优于现有的AI科学家和VIRSCI系统。这凸显了模拟互动和同行评审动态在基于LLM的自主研究中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟科学家间的协作方面显示出潜力,但缺乏真实科研中的交互式推理和评估机制。
- IDVSCI框架包含两个关键创新点:动态知识交换机制和双差异审查范式。
- 动态知识交换机制促进代理间的迭代反馈。
- 双差异审查范式模拟不同专家的评估,提升深度推理和创造性科学想法的产生。
- IDVSCI框架在跨学科基准测试及健康科学新数据集上的实验表现最佳。
- IDVSCI相较于现有系统如AI科学家和VIRSCI具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

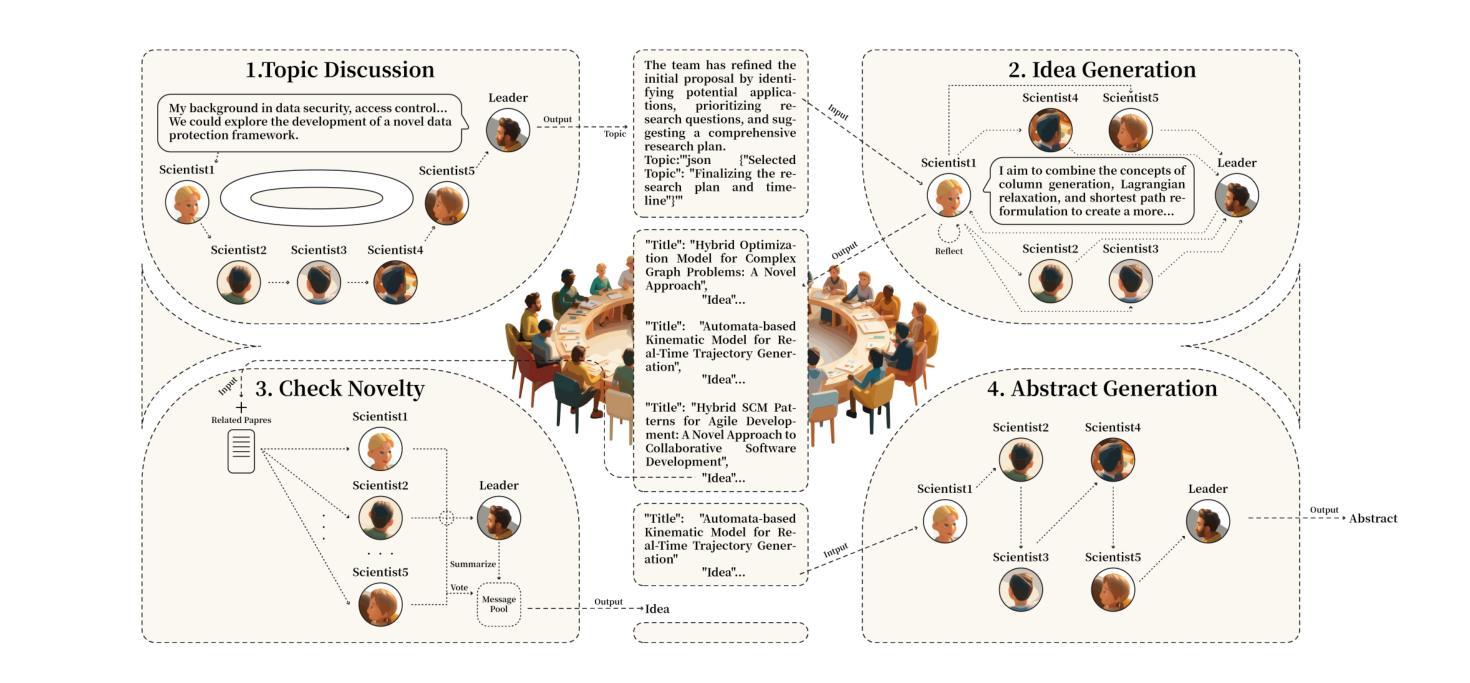
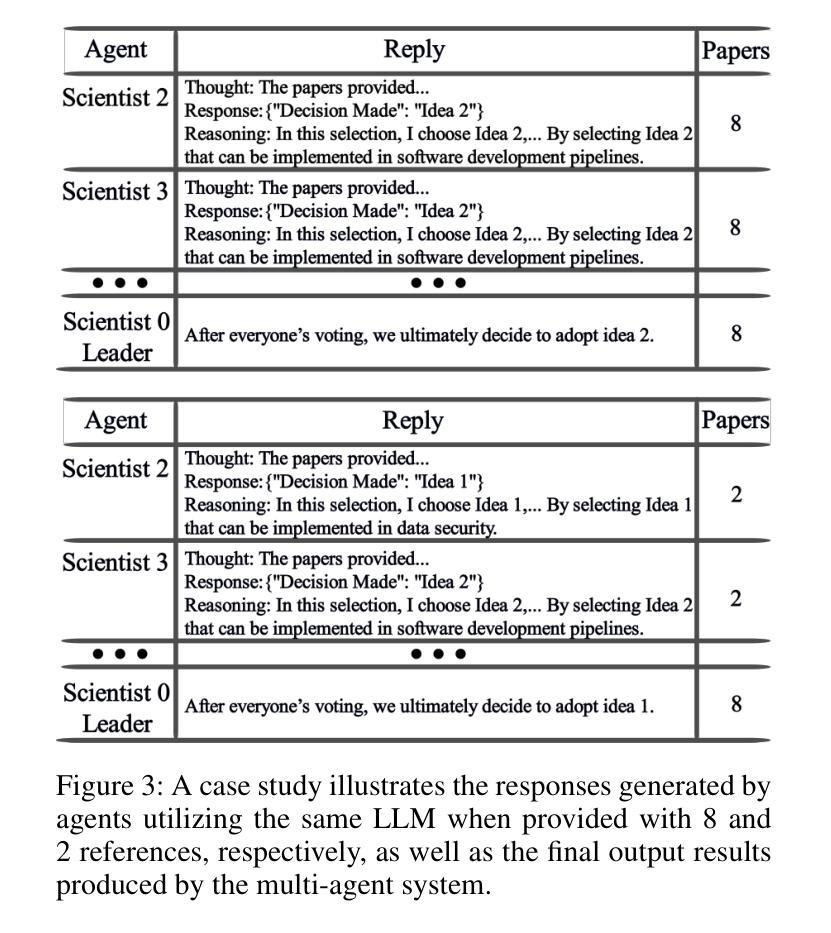
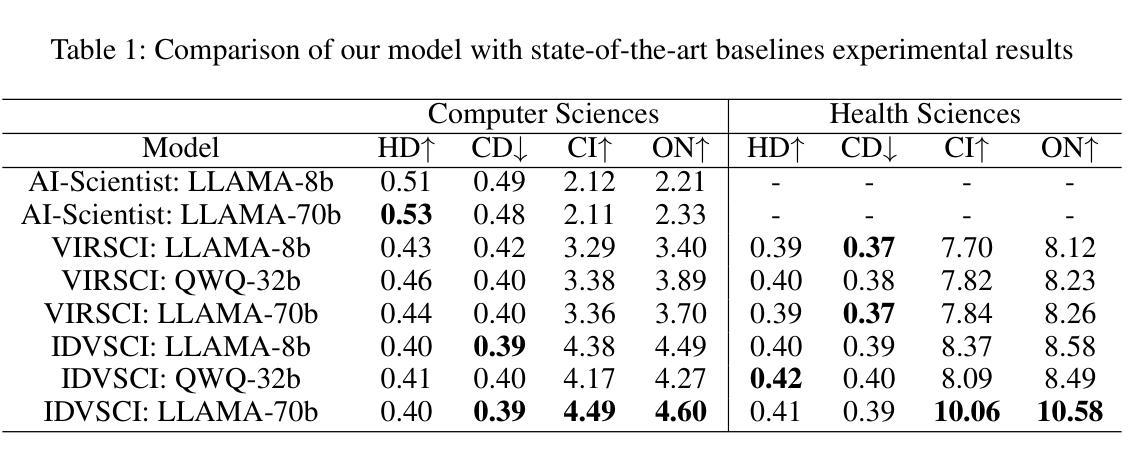
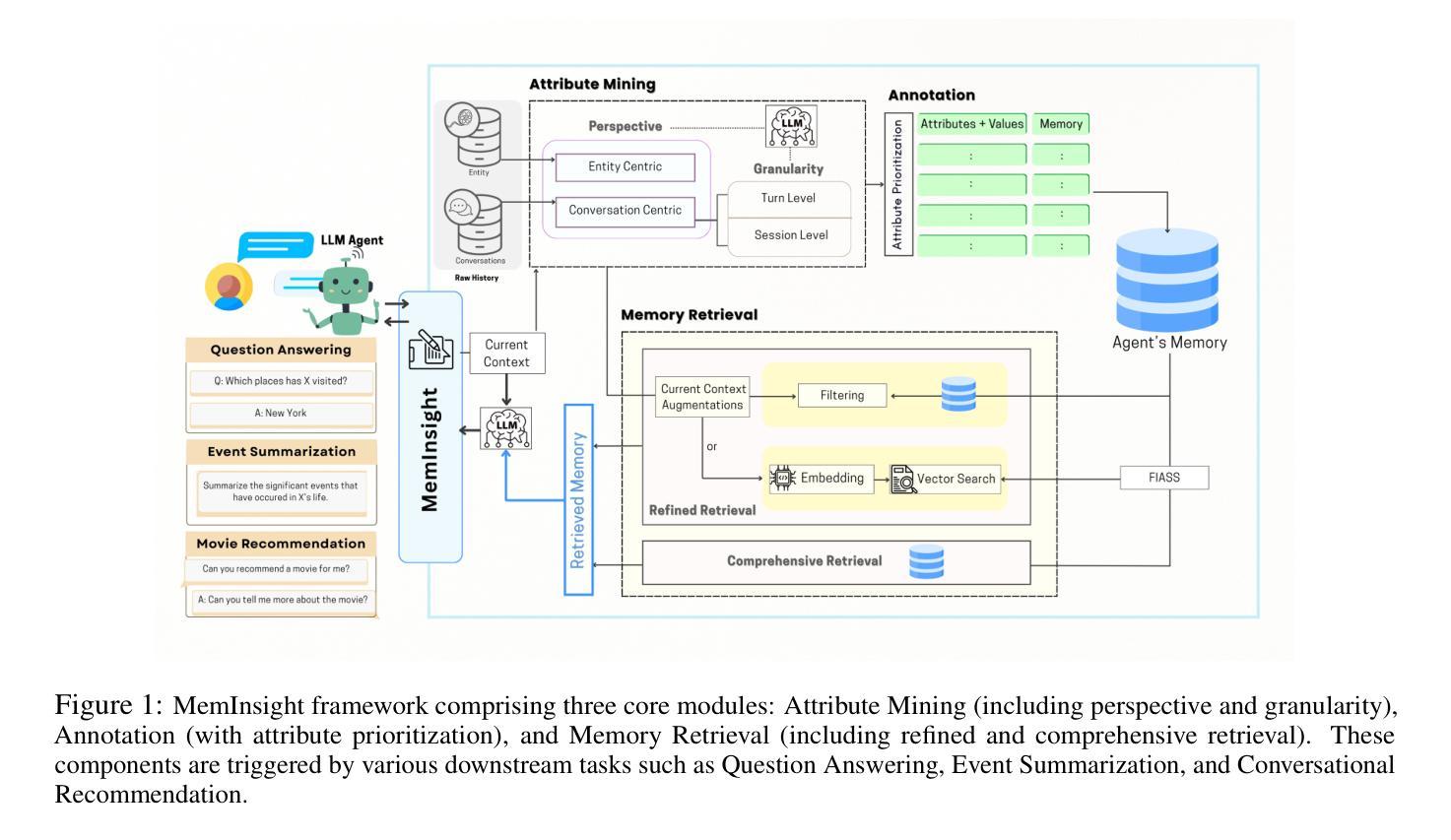
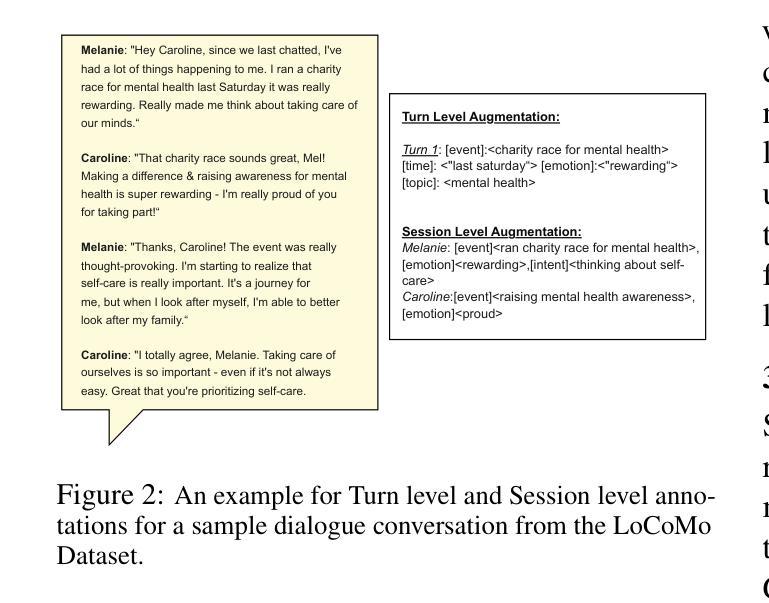
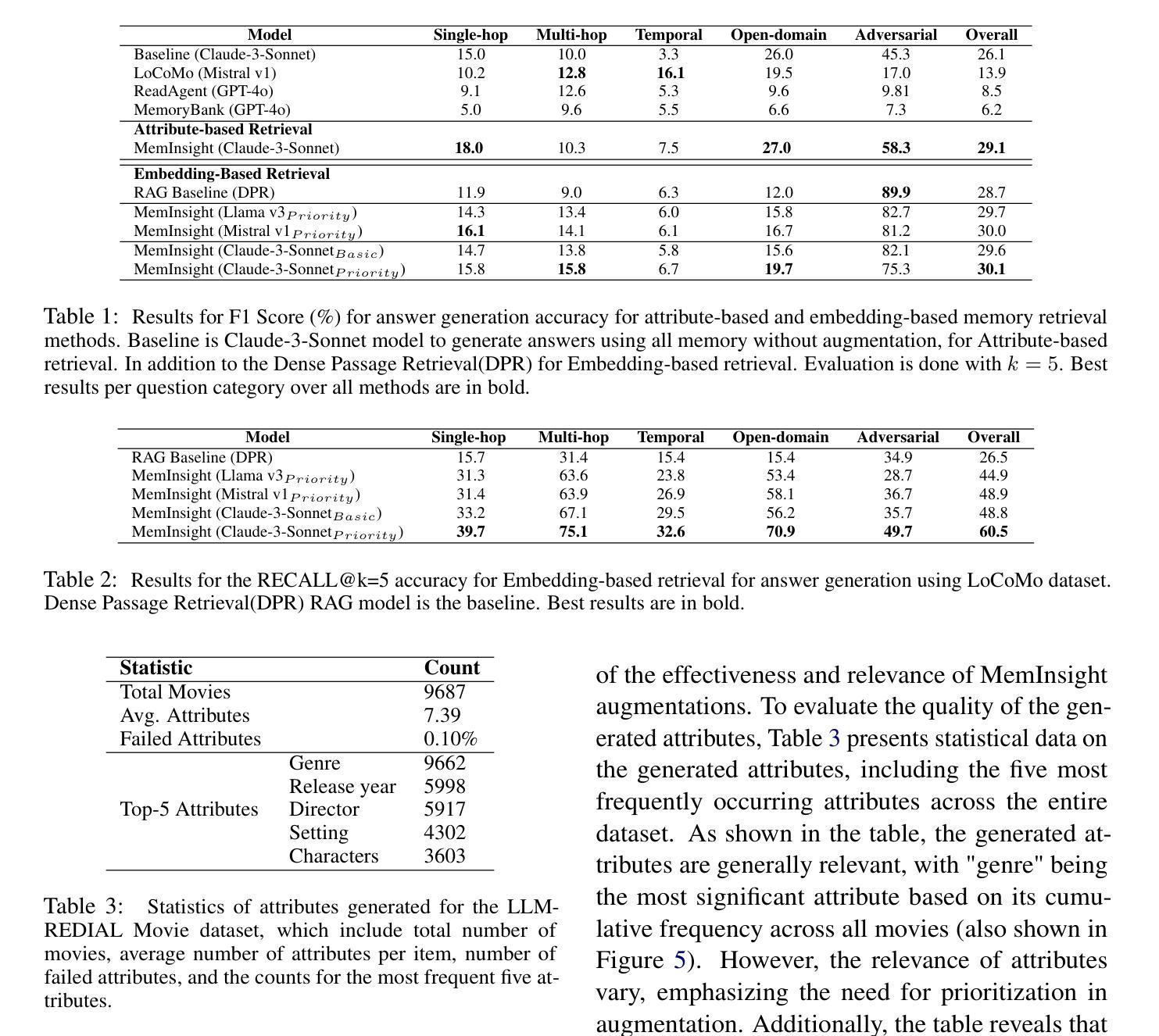
MemInsight: Autonomous Memory Augmentation for LLM Agents
Authors:Rana Salama, Jason Cai, Michelle Yuan, Anna Currey, Monica Sunkara, Yi Zhang, Yassine Benajiba
Large language model (LLM) agents have evolved to intelligently process information, make decisions, and interact with users or tools. A key capability is the integration of long-term memory capabilities, enabling these agents to draw upon historical interactions and knowledge. However, the growing memory size and need for semantic structuring pose significant challenges. In this work, we propose an autonomous memory augmentation approach, MemInsight, to enhance semantic data representation and retrieval mechanisms. By leveraging autonomous augmentation to historical interactions, LLM agents are shown to deliver more accurate and contextualized responses. We empirically validate the efficacy of our proposed approach in three task scenarios; conversational recommendation, question answering and event summarization. On the LLM-REDIAL dataset, MemInsight boosts persuasiveness of recommendations by up to 14%. Moreover, it outperforms a RAG baseline by 34% in recall for LoCoMo retrieval. Our empirical results show the potential of MemInsight to enhance the contextual performance of LLM agents across multiple tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)代理已经进化到可以智能地处理信息、做出决策和与用户或工具进行交互。一个关键的功能是融合了长期记忆能力,使得这些代理能够利用历史交互和知识。然而,不断增长的内存大小和语义结构的需求构成了重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,以增强语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用对历史交互的自主增强,LLM代理能够提供更准确和情境化的响应。我们通过三种任务场景:对话推荐、问答和事件摘要,实证验证了我们的方法的有效性。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight将推荐的说服力提高了1,有助于提高对话的自然度和连贯性;在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面,它比RAG基线高出34%。我们的实验结果表明,MemInsight在多个任务中增强LLM代理的上下文性能方面具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)代理通过集成长期记忆能力,实现了信息的智能处理、决策以及与用户或工具的交互。然而,随着记忆规模的扩大和语义结构的需求增加,挑战也随之增加。本研究提出了一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,以提高语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用自主增强对历史交互的增强,LLM代理可以给出更准确和情境化的响应。我们在三个任务场景中实证验证了所提出方法的有效性,包括对话推荐、问答和事件摘要。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight提高了推荐的说服性达14%。此外,它在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面优于RAG基线34%。结果表明,MemInsight具有增强LLM代理在多个任务中的上下文性能的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)代理通过集成长期记忆能力,实现了智能化处理信息和交互。
- 自主记忆增强方法MemInsight可以提高语义数据表示和检索机制。
- MemInsight利用自主增强技术提高历史交互数据的使用效率,使得LLM代理给出更准确和情境化的响应。
- 在三个任务场景中验证了MemInsight的有效性,包括对话推荐、问答和事件摘要。
- 在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight提高了推荐的说服性达14%。
- MemInsight在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面优于RAG基线34%。
点此查看论文截图