⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
LeakyCLIP: Extracting Training Data from CLIP
Authors:Yunhao Chen, Shujie Wang, Xin Wang, Xingjun Ma
Understanding the memorization and privacy leakage risks in Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP) is critical for ensuring the security of multimodal models. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of extracting sensitive training examples from diffusion models, with conditional diffusion models exhibiting a stronger tendency to memorize and leak information. In this work, we investigate data memorization and extraction risks in CLIP through the lens of CLIP inversion, a process that aims to reconstruct training images from text prompts. To this end, we introduce \textbf{LeakyCLIP}, a novel attack framework designed to achieve high-quality, semantically accurate image reconstruction from CLIP embeddings. We identify three key challenges in CLIP inversion: 1) non-robust features, 2) limited visual semantics in text embeddings, and 3) low reconstruction fidelity. To address these challenges, LeakyCLIP employs 1) adversarial fine-tuning to enhance optimization smoothness, 2) linear transformation-based embedding alignment, and 3) Stable Diffusion-based refinement to improve fidelity. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of LeakyCLIP, achieving over 358% improvement in Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) for ViT-B-16 compared to baseline methods on LAION-2B subset. Furthermore, we uncover a pervasive leakage risk, showing that training data membership can even be successfully inferred from the metrics of low-fidelity reconstructions. Our work introduces a practical method for CLIP inversion while offering novel insights into the nature and scope of privacy risks in multimodal models.
理解对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)中的记忆和隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。最近的研究已经证明了从扩散模型中提取敏感训练样本的可行性,条件扩散模型表现出更强的记忆和泄露信息的趋势。在这项工作中,我们通过CLIP反转的视角来研究CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险,这是一个旨在从文本提示重建训练图像的过程。为此,我们引入了\textbf{LeakyCLIP},这是一种新的攻击框架,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。我们发现CLIP反转面临三个关键挑战:1)特征不稳健,2)文本嵌入中的视觉语义有限,以及3)重建保真度低。为了解决这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用1)对抗微调增强优化平滑度,2)基于线性变换的嵌入对齐,以及3)基于稳定扩散的细化以提高保真度。经验结果表明LeakyCLIP的优越性,在LAION-2B子集上与基线方法相比,ViT-B-16的结构相似性指数测量(SSIM)提高了358%以上。此外,我们发现了普遍的泄露风险,表明甚至可以从低保真重建的指标中成功推断出训练数据成员。我们的工作介绍了一种实用的CLIP反转方法,同时提供了对多模态模型中隐私风险性质和范围的新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Contrastive Language--Image Pretraining(CLIP)模型中的记忆与隐私泄露风险。研究者通过CLIP反演的角度研究数据记忆与提取风险,并引入了一种名为LeakyCLIP的新型攻击框架,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。研究识别了三个关键挑战并提供了解决方案,最终实现了高效的图像重建。此外,还发现即使低质量的图像重建也存在数据泄露风险。本文提供了实用的CLIP反演方法,并对多模态模型的隐私风险提供了新的见解。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型中存在记忆和隐私泄露风险,尤其是条件扩散模型。
- LeakyCLIP攻击框架用于从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量图像重建。
- CLIP反演面临三个关键挑战:非稳健特征、文本嵌入中有限的视觉语义和低重建保真度。
- LeakyCLIP通过对抗性微调、基于线性变换的嵌入对齐和基于Stable Diffusion的细化来解决这些挑战。
- LeakyCLIP在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)上实现了超过ViT-B-16基线方法358%的改进。
- 即使是低质量的图像重建也存在数据泄露风险。
点此查看论文截图



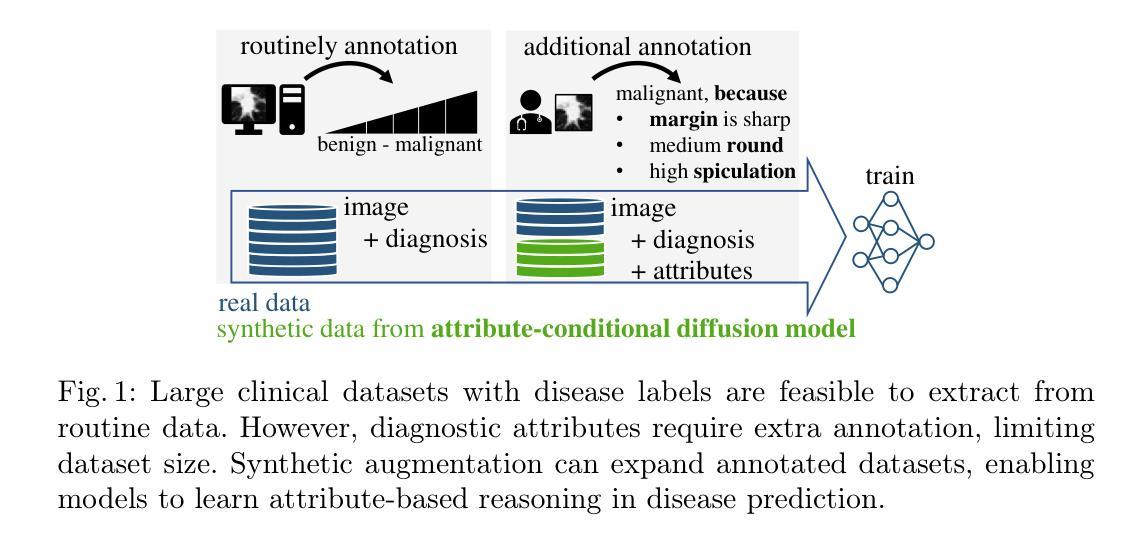
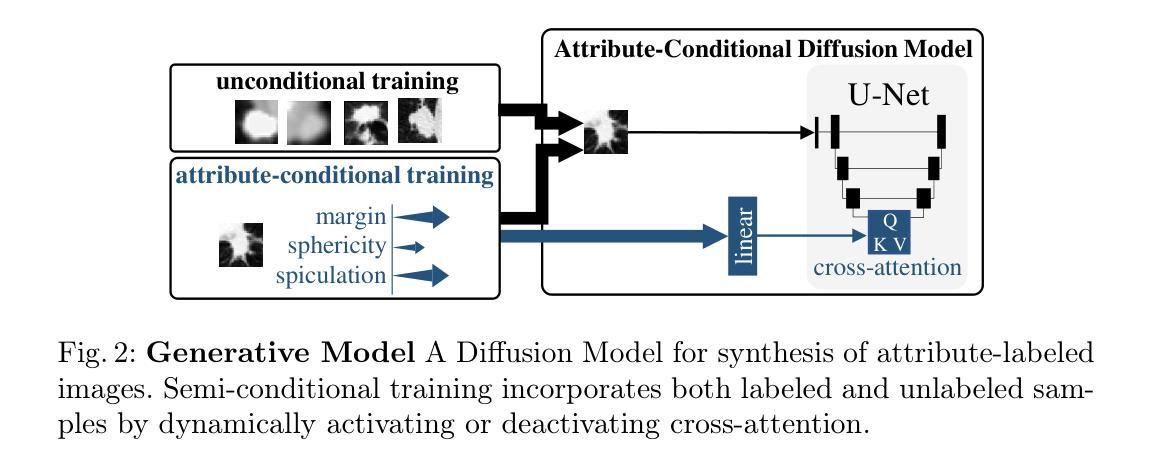
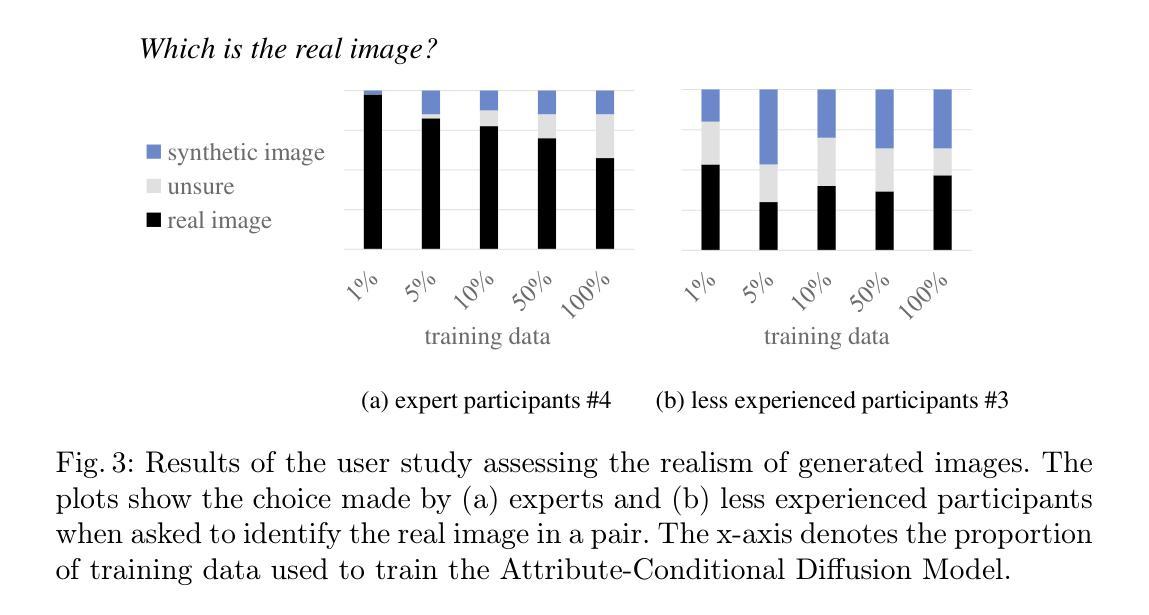
Minimum Data, Maximum Impact: 20 annotated samples for explainable lung nodule classification
Authors:Luisa Gallée, Catharina Silvia Lisson, Christoph Gerhard Lisson, Daniela Drees, Felix Weig, Daniel Vogele, Meinrad Beer, Michael Götz
Classification models that provide human-interpretable explanations enhance clinicians’ trust and usability in medical image diagnosis. One research focus is the integration and prediction of pathology-related visual attributes used by radiologists alongside the diagnosis, aligning AI decision-making with clinical reasoning. Radiologists use attributes like shape and texture as established diagnostic criteria and mirroring these in AI decision-making both enhances transparency and enables explicit validation of model outputs. However, the adoption of such models is limited by the scarcity of large-scale medical image datasets annotated with these attributes. To address this challenge, we propose synthesizing attribute-annotated data using a generative model. We enhance the Diffusion Model with attribute conditioning and train it using only 20 attribute-labeled lung nodule samples from the LIDC-IDRI dataset. Incorporating its generated images into the training of an explainable model boosts performance, increasing attribute prediction accuracy by 13.4% and target prediction accuracy by 1.8% compared to training with only the small real attribute-annotated dataset. This work highlights the potential of synthetic data to overcome dataset limitations, enhancing the applicability of explainable models in medical image analysis.
提供人类可解释的解释的分类模型增强了临床医生对医学图像诊断的信任和可用性。一个研究重点是整合和预测病理相关的视觉属性,这些属性被放射科医生用于诊断,使AI决策与临床推理相一致。放射科医生使用形状和纹理等属性作为既定的诊断依据,并在AI决策中反映这些依据,既提高了透明度,又能够明确验证模型输出。然而,由于缺乏大规模医学图像数据集,这些属性被标注的数据集稀缺,因此这种模型的采用受到限制。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出使用生成模型合成属性标注数据。我们通过对扩散模型进行属性条件增强,仅使用LIDC-IDRI数据集的20个属性标注的肺结节样本进行训练。将其生成的图像纳入可解释模型的训练,提高了性能,与仅使用小型真实属性标注数据集进行训练相比,属性预测精度提高了13.4%,目标预测精度提高了1.8%。这项工作突出了合成数据在克服数据集限制方面的潜力,增强了可解释模型在医学图像分析中的应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at iMIMIC - Interpretability of Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Computing workshop MICCAI 2025 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention
Summary
分类模型提供可解释的解释,增强临床医生对医学影像诊断的信任和使用性。研究重点是整合并预测放射科医生使用的病理相关视觉属性,使AI决策与临床推理相一致。使用形状和纹理等属性作为诊断标准,在AI决策中体现这些标准提高了透明度和模型输出的明确验证性。然而,由于缺乏大规模标注有这些属性的医学图像数据集,这些模型的应用受到限制。为解决这一挑战,我们提出使用生成模型合成属性标注数据。我们增强了扩散模型并对其进行属性条件训练,仅使用LIDC-IDRI数据集的20个属性标注的肺结节样本。将其生成的图像纳入可解释模型的训练中,提高了性能,与仅使用小型真实属性标注数据集进行训练相比,属性预测准确率提高13.4%,目标预测准确率提高1.8%。这项工作突显了合成数据在克服数据集限制方面的潜力,提高了可解释模型在医学图像分析中的应用性。
Key Takeaways
- 分类模型提供解释性可以增强临床医生对医学影像诊断的信任和使用性。
- AI决策与临床推理的整合是研究的重点,包括预测病理相关的视觉属性。
- 放射科医生使用的属性如形状和纹理被纳入AI决策中,以提高透明度和模型验证性。
- 缺乏大规模标注医学图像数据集是应用这些模型的主要挑战。
- 提出使用生成模型(如扩散模型)合成属性标注数据作为解决方案。
- 合成数据在医学图像分析中的使用提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

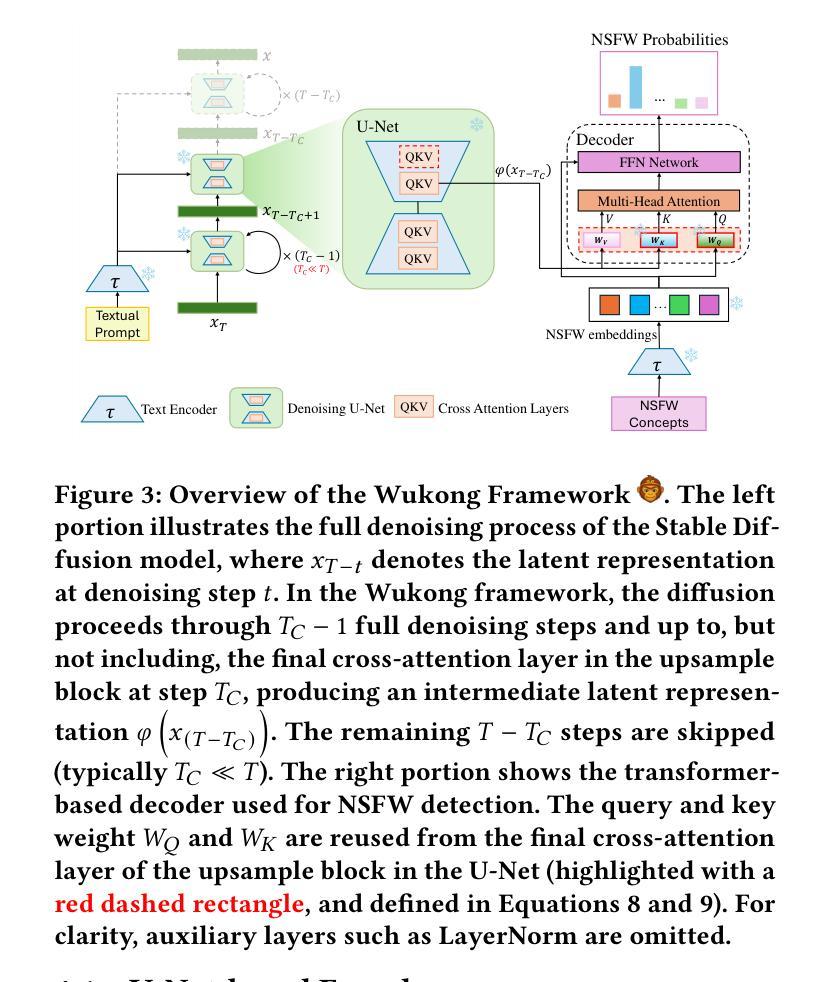
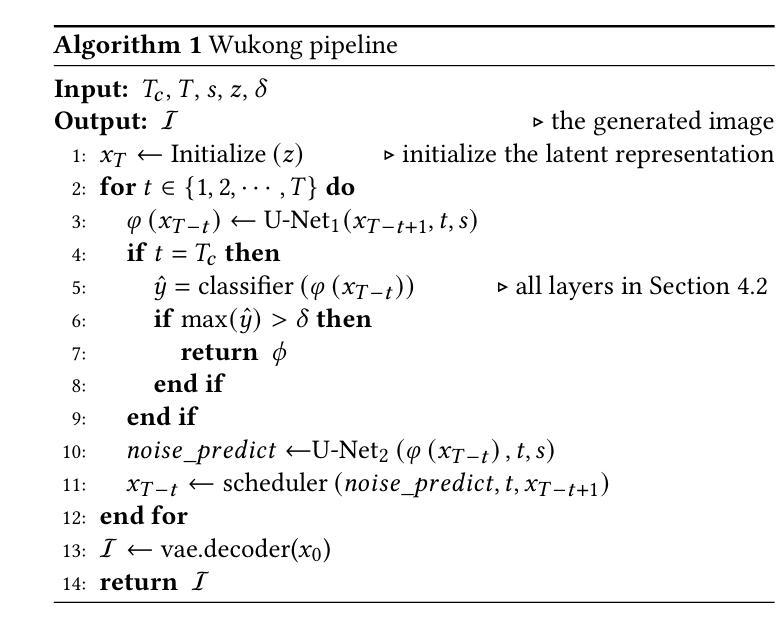
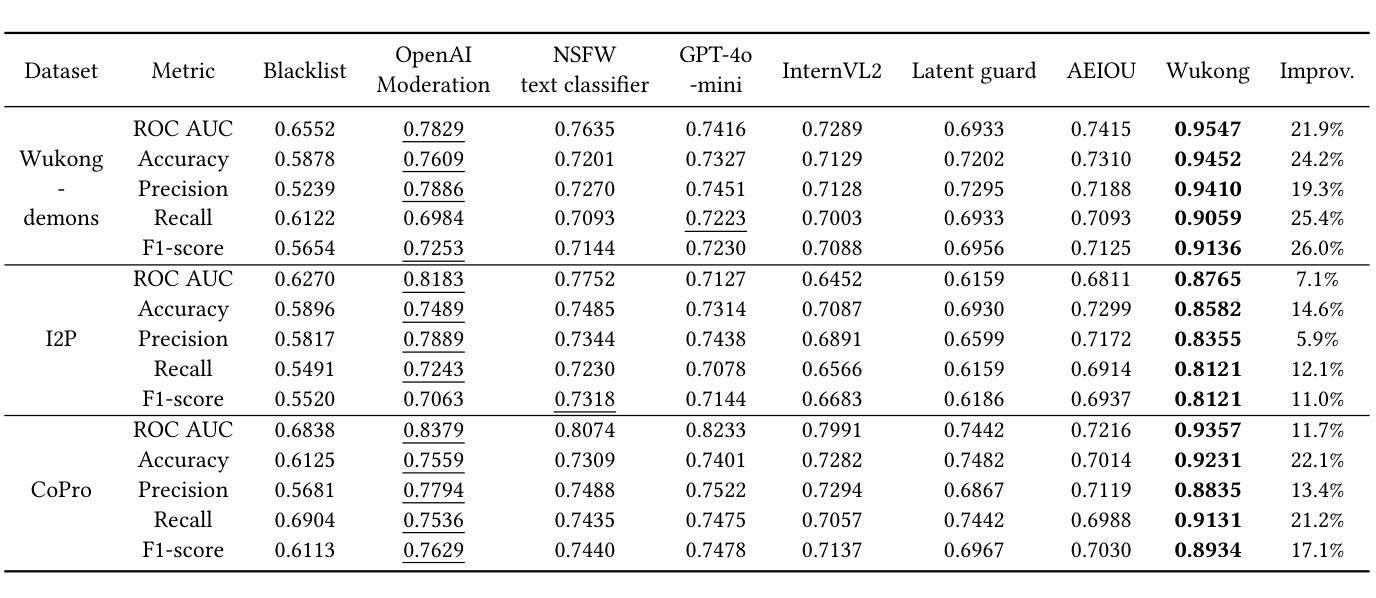
Wukong Framework for Not Safe For Work Detection in Text-to-Image systems
Authors:Mingrui Liu, Sixiao Zhang, Cheng Long
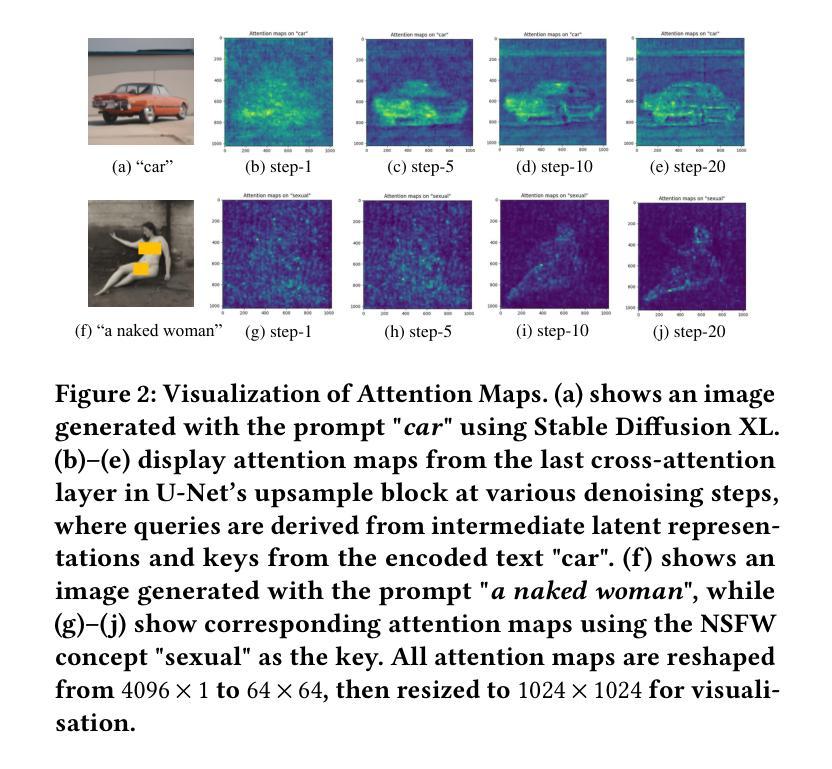
Text-to-Image (T2I) generation is a popular AI-generated content (AIGC) technology enabling diverse and creative image synthesis. However, some outputs may contain Not Safe For Work (NSFW) content (e.g., violence), violating community guidelines. Detecting NSFW content efficiently and accurately, known as external safeguarding, is essential. Existing external safeguards fall into two types: text filters, which analyze user prompts but overlook T2I model-specific variations and are prone to adversarial attacks; and image filters, which analyze final generated images but are computationally costly and introduce latency. Diffusion models, the foundation of modern T2I systems like Stable Diffusion, generate images through iterative denoising using a U-Net architecture with ResNet and Transformer blocks. We observe that: (1) early denoising steps define the semantic layout of the image, and (2) cross-attention layers in U-Net are crucial for aligning text and image regions. Based on these insights, we propose Wukong, a transformer-based NSFW detection framework that leverages intermediate outputs from early denoising steps and reuses U-Net’s pre-trained cross-attention parameters. Wukong operates within the diffusion process, enabling early detection without waiting for full image generation. We also introduce a new dataset containing prompts, seeds, and image-specific NSFW labels, and evaluate Wukong on this and two public benchmarks. Results show that Wukong significantly outperforms text-based safeguards and achieves comparable accuracy of image filters, while offering much greater efficiency.
文本到图像(T2I)生成是一种流行的AI生成内容(AIGC)技术,能够实现多样化和创意性的图像合成。然而,一些输出可能包含不宜在工作场合展示(NSFW)的内容(例如暴力),这违反了社区准则。高效且准确地检测NSFW内容,被称为外部安全保障,是至关重要的。现有的外部安全保障措施分为两种:文本过滤器,它分析用户提示,但忽略了T2I模型特定的变化,并容易受到对抗性攻击;图像过滤器,它分析最终生成的图像,但计算成本高昂并引入延迟。扩散模型是现代T2I系统(如Stable Diffusion)的基础,通过迭代去噪生成图像,使用带有ResNet和Transformer块的U-Net架构。我们观察到:(1)早期的去噪步骤定义了图像语义布局,(2)U-Net中的交叉注意层对于对齐文本和图像区域至关重要。基于此洞察,我们提出了基于变压器的Wukong NSFW检测框架,该框架利用早期去噪步骤的中间输出并重新使用U-Net的预训练交叉注意参数。Wukong在扩散过程中运行,能够实现无需等待完整图像生成的早期检测。我们还引入了一个包含提示、种子和图像特定NSFW标签的新数据集,并在该数据集和两个公共基准测试上对Wukong进行了评估。结果表明,Wukong在文本保障措施方面表现出显著优势,并实现了与图像过滤器相当的准确性,同时提供了更高的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
文本提出一种基于扩散模型的名为“悟空”的NSFW检测框架,利用扩散模型早期去噪步骤中的中间输出来检测图像内容的安全性。悟空能在扩散过程中运行,无需等待完整的图像生成就能实现早期检测,既准确又高效。同时引入新数据集用于评估性能。
Key Takeaways
- T2I生成技术是一种流行的AIGC技术,可以生成多样且有创意的图像,但可能包含NSFW内容。
- 检测NSFW内容对于遵守社区准则至关重要,现有外部保障措施存在缺陷。
- 扩散模型是T2I系统的基石,通过迭代去噪生成图像。
- 早期去噪步骤定义了图像语义布局,U-Net中的跨注意力层对于文本和图像区域的对齐至关重要。
- 悟空检测框架基于扩散模型,利用早期去噪步骤的中间输出来检测NSFW内容。
- 悟空能在扩散过程中进行早期检测,无需等待完整图像生成。
点此查看论文截图

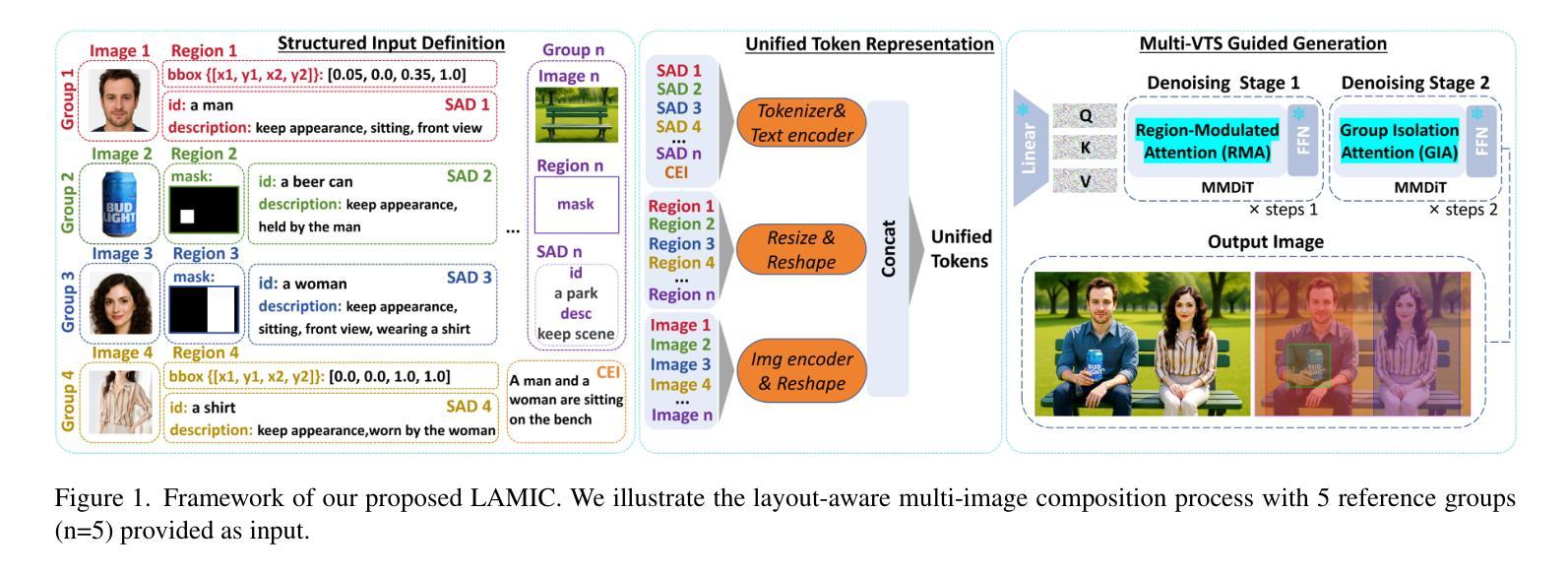
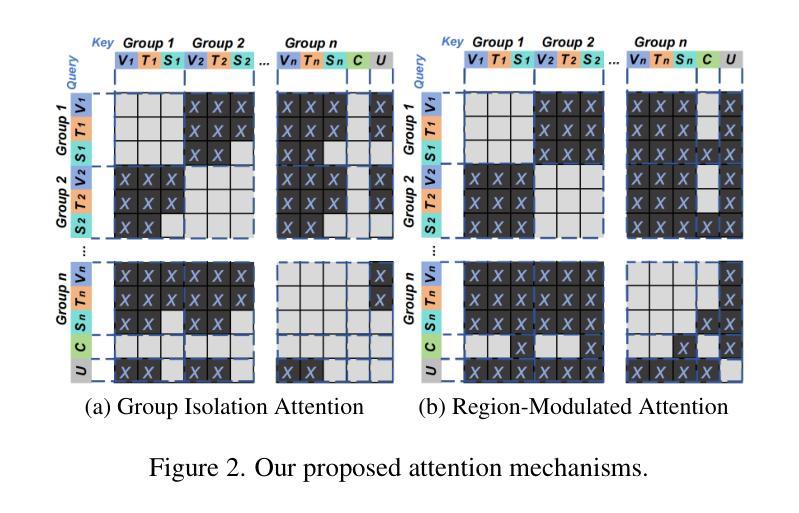
LAMIC: Layout-Aware Multi-Image Composition via Scalability of Multimodal Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Yuzhuo Chen, Zehua Ma, Jianhua Wang, Kai Kang, Shunyu Yao, Weiming Zhang
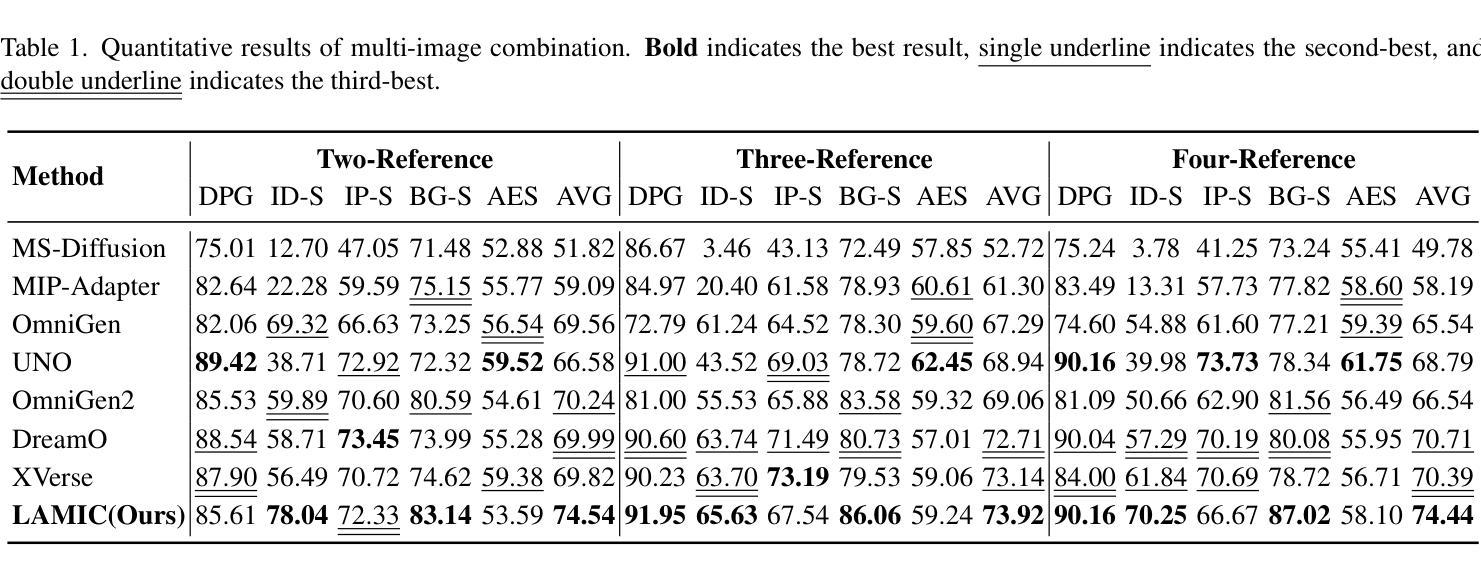
In controllable image synthesis, generating coherent and consistent images from multiple references with spatial layout awareness remains an open challenge. We present LAMIC, a Layout-Aware Multi-Image Composition framework that, for the first time, extends single-reference diffusion models to multi-reference scenarios in a training-free manner. Built upon the MMDiT model, LAMIC introduces two plug-and-play attention mechanisms: 1) Group Isolation Attention (GIA) to enhance entity disentanglement; and 2) Region-Modulated Attention (RMA) to enable layout-aware generation. To comprehensively evaluate model capabilities, we further introduce three metrics: 1) Inclusion Ratio (IN-R) and Fill Ratio (FI-R) for assessing layout control; and 2) Background Similarity (BG-S) for measuring background consistency. Extensive experiments show that LAMIC achieves state-of-the-art performance across most major metrics: it consistently outperforms existing multi-reference baselines in ID-S, BG-S, IN-R and AVG scores across all settings, and achieves the best DPG in complex composition tasks. These results demonstrate LAMIC’s superior abilities in identity keeping, background preservation, layout control, and prompt-following, all achieved without any training or fine-tuning, showcasing strong zero-shot generalization ability. By inheriting the strengths of advanced single-reference models and enabling seamless extension to multi-image scenarios, LAMIC establishes a new training-free paradigm for controllable multi-image composition. As foundation models continue to evolve, LAMIC’s performance is expected to scale accordingly. Our implementation is available at: https://github.com/Suchenl/LAMIC.
在可控图像合成中,从多个参考图像生成具有空间布局意识的连贯和一致图像仍然是一个开放挑战。我们提出了LAMIC,一个基于布局感知的多图像组合框架,它首次以无训练的方式将单参考扩散模型扩展到多参考场景。基于MMDiT模型,LAMIC引入了两种即插即用的注意力机制:1)群组隔离注意力(GIA)以增强实体解纠缠;和2)区域调制注意力(RMA)以实现布局感知生成。为了全面评估模型能力,我们进一步引入了三项指标:1)包含率(IN-R)和填充率(FI-R)以评估布局控制;和2)背景相似性(BG-S)以衡量背景一致性。大量实验表明,LAMIC在大多数主要指标上达到了最新性能水平:它在所有设置下的ID-S、BG-S、IN-R和AVG分数方面一直优于现有的多参考基线,并在复杂组合任务中获得了最佳DPG。这些结果证明了LAMIC在身份保留、背景保留、布局控制和提示遵循方面的卓越能力,这些都无需任何训练或微调,展示了强大的零样本泛化能力。通过继承先进单参考模型的优势,并能够实现无缝扩展到多图像场景,LAMIC为可控多图像组合建立了新的无训练范式。随着基础模型的不断发展,LAMIC的性能预计也会相应提升。我们的实现可访问于:https://github.com/Suchenl/LAMIC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一个无需训练的多参考扩散模型框架LAMIC,可合成具有空间布局意识的连贯且一致的多张图像。它通过引入集团隔离注意力和区域调制注意力两种插件式注意力机制,实现了在多个图像上的多参考图像合成。此外,为了全面评估模型的能力,本文引入了三项新指标用于评估布局控制、背景一致性等能力。实验表明,LAMIC在大多数主要指标上达到了最佳性能,展示了强大的零样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- LAMIC是一个无需训练的多参考扩散模型框架,用于合成具有空间布局意识的连贯且一致的多张图像。
- 它通过引入Group Isolation Attention (GIA)和Region-Modulated Attention (RMA)来处理多参考图像。
- 为了评估模型的能力,引入了三项新指标:Inclusion Ratio (IN-R)、Fill Ratio (FI-R)和Background Similarity (BG-S)。
- 实验结果显示LAMIC在多个指标上达到最佳性能,特别是在身份保持、背景保留、布局控制和提示遵循方面。
- LAMIC具有强大的零样本泛化能力,并展示了先进单参考模型的优点以及无缝扩展到多图像场景的能力。
点此查看论文截图
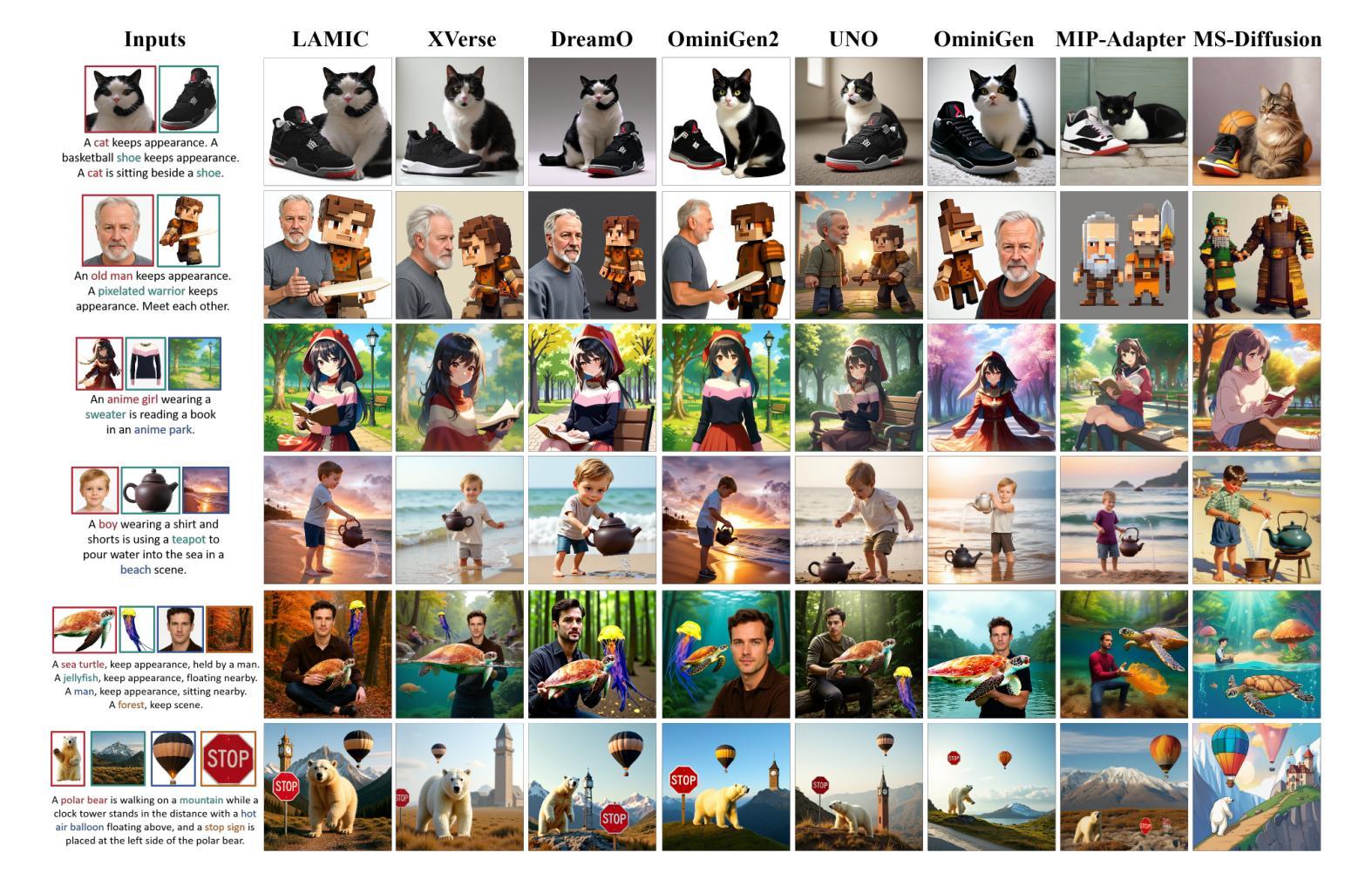

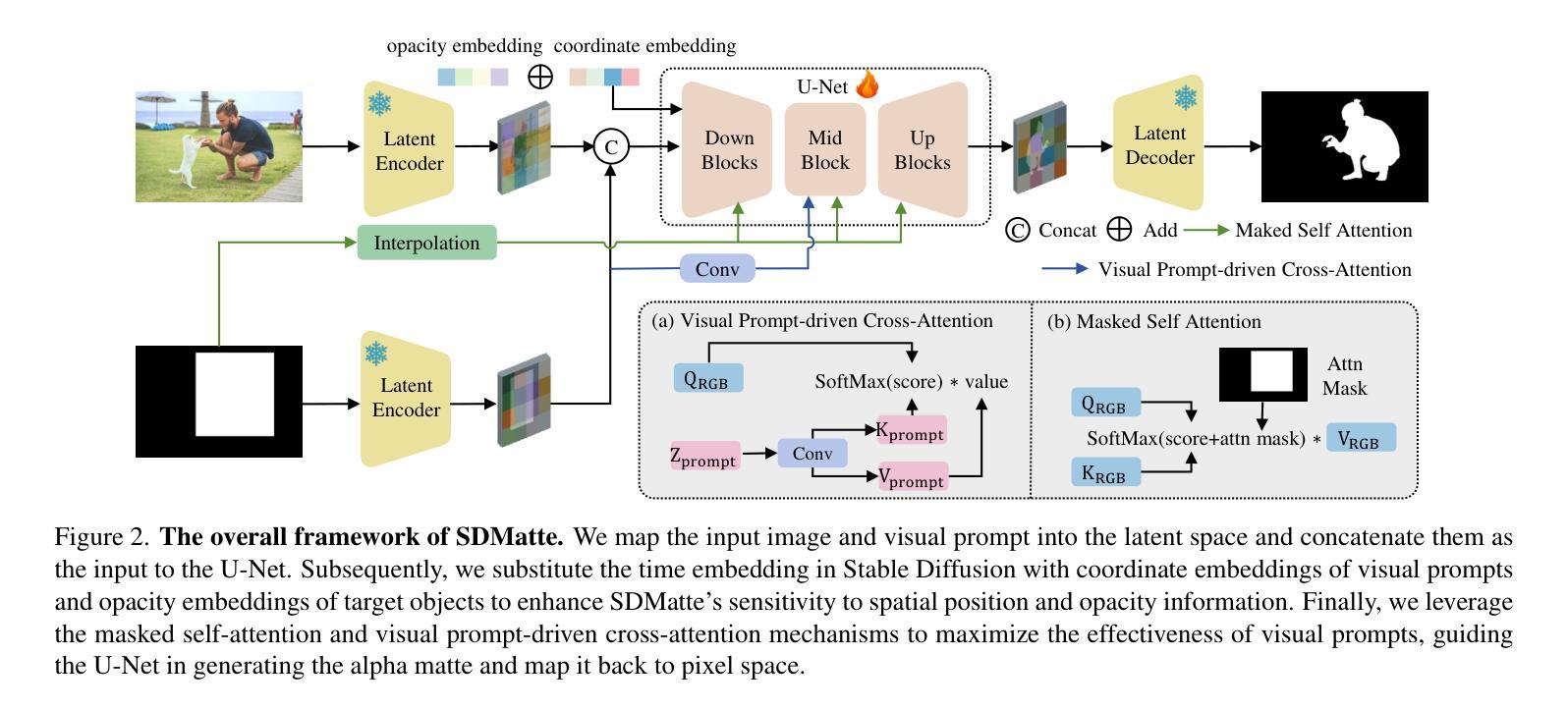
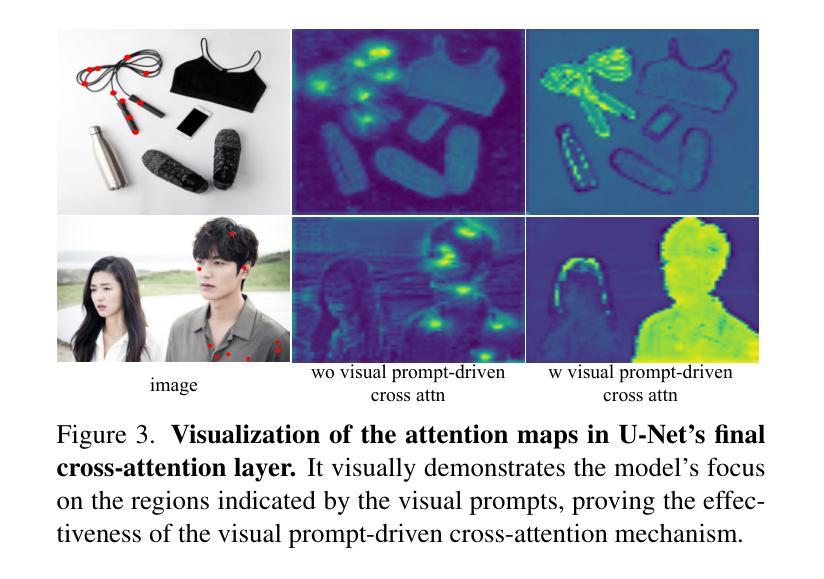
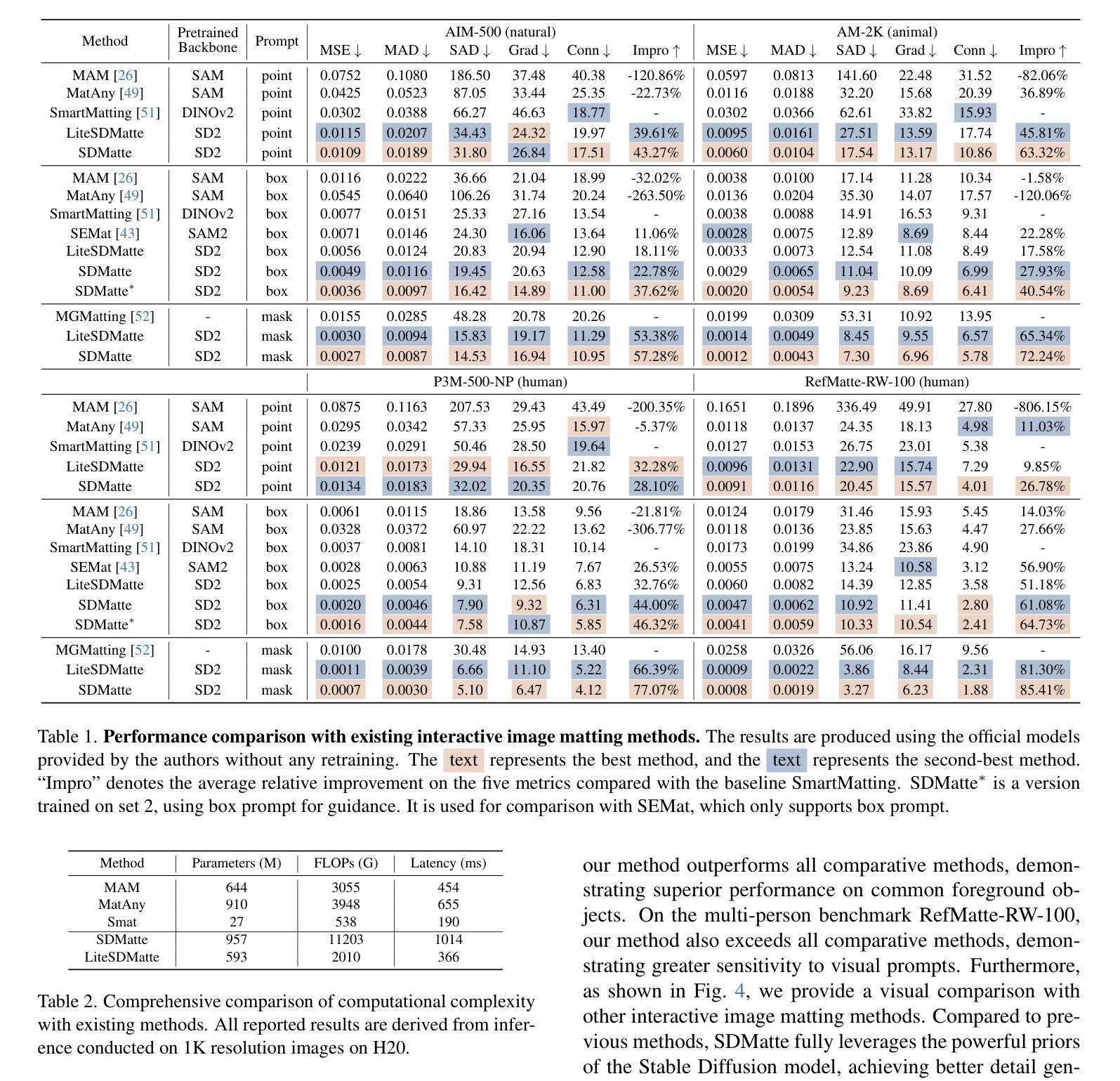
SDMatte: Grafting Diffusion Models for Interactive Matting
Authors:Longfei Huang, Yu Liang, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Wei Dong, Lunde Chen, Wanyu Liu, Bo Li, Pengtao Jiang
Recent interactive matting methods have shown satisfactory performance in capturing the primary regions of objects, but they fall short in extracting fine-grained details in edge regions. Diffusion models trained on billions of image-text pairs, demonstrate exceptional capability in modeling highly complex data distributions and synthesizing realistic texture details, while exhibiting robust text-driven interaction capabilities, making them an attractive solution for interactive matting. To this end, we propose SDMatte, a diffusion-driven interactive matting model, with three key contributions. First, we exploit the powerful priors of diffusion models and transform the text-driven interaction capability into visual prompt-driven interaction capability to enable interactive matting. Second, we integrate coordinate embeddings of visual prompts and opacity embeddings of target objects into U-Net, enhancing SDMatte’s sensitivity to spatial position information and opacity information. Third, we propose a masked self-attention mechanism that enables the model to focus on areas specified by visual prompts, leading to better performance. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method, validating its effectiveness in interactive matting. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/vivoCameraResearch/SDMatte.
近期交互式拔毛(matting)方法已经显示出捕捉物体主要区域的满意性能,但在边缘区域提取精细细节方面存在不足。在数十亿图像文本对上训练的扩散模型,在模拟高度复杂的数据分布和合成逼真的纹理细节方面表现出卓越的能力,同时展现出稳健的文本驱动交互能力,使其成为交互式拔毛的理想解决方案。为此,我们提出了SDMatte,一种基于扩散的交互式拔毛模型,有三个主要贡献。首先,我们利用扩散模型的强大先验,将文本驱动的交互能力转化为视觉提示驱动的交互能力,以实现交互式拔毛。其次,我们将视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入整合到U-Net中,提高了SDMatte对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感度。第三,我们提出了一种掩膜自注意力机制,使模型能够关注视觉提示指定的区域,从而提高性能。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法性能优越,验证了其在交互式拔毛中的有效性。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/vivoCameraResearch/SDMatte上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025, 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的交互式抠图技术。该技术利用扩散模型的强大先验信息,将文本驱动交互能力转化为视觉提示驱动交互能力,实现了交互式抠图。通过整合视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入到U-Net中,并引入掩膜自注意力机制,提高了模型对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感度,实现了更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在捕获对象主要区域方面表现出良好的性能,但在边缘区域提取精细细节方面存在挑战。
- 扩散模型具有对高度复杂数据分布进行建模和合成逼真纹理细节的能力,同时展现出强大的文本驱动交互能力。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的交互式抠图技术SDMatte,该技术将文本驱动交互能力转化为视觉提示驱动交互能力。
- SDMatte通过整合视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入到U-Net中,提高了对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感度。
- SDMatte引入了一种掩膜自注意力机制,使模型能够关注视觉提示指定的区域,从而实现更好的性能。
- 在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,SDMatte方法具有卓越的性能,验证了其在交互式抠图中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

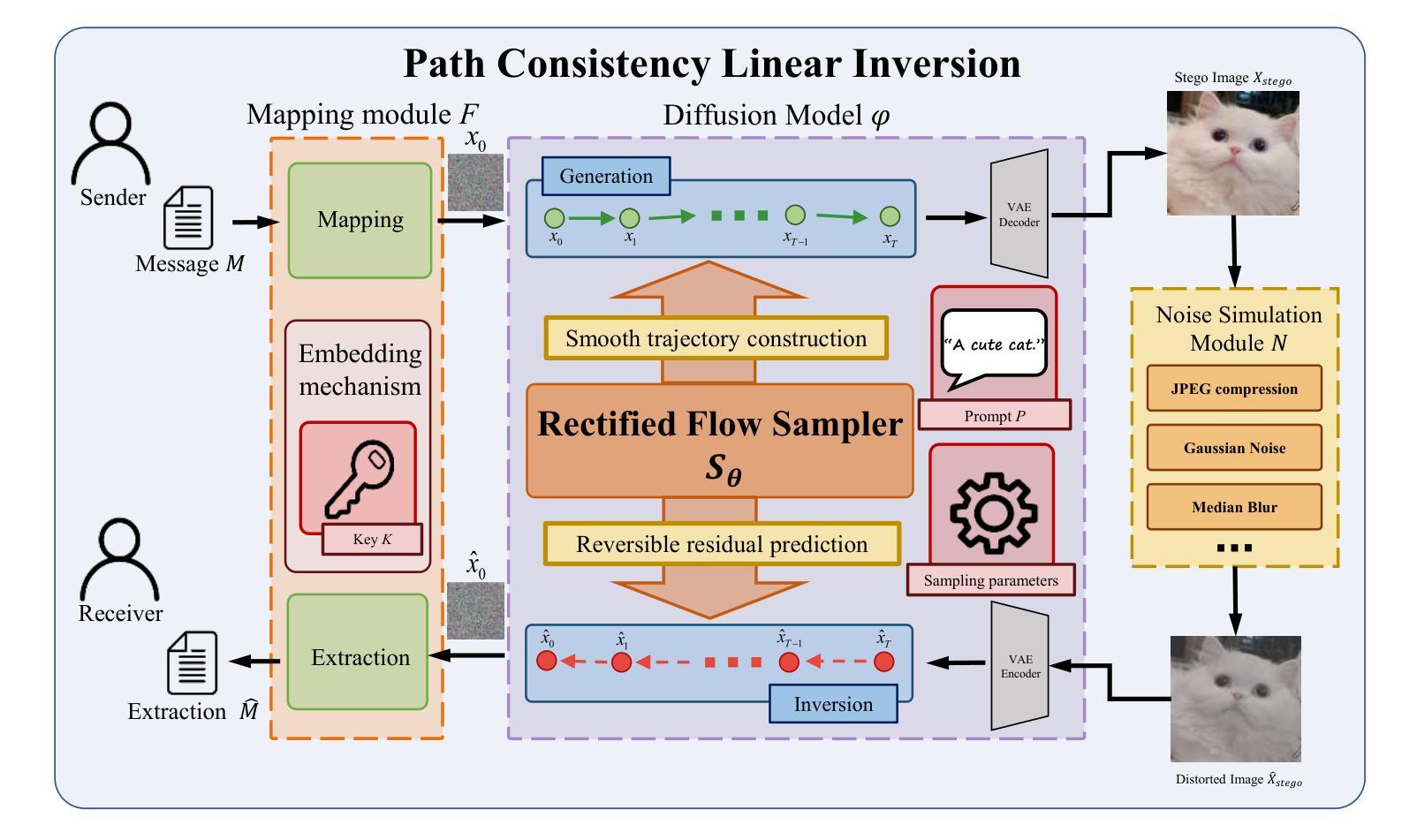
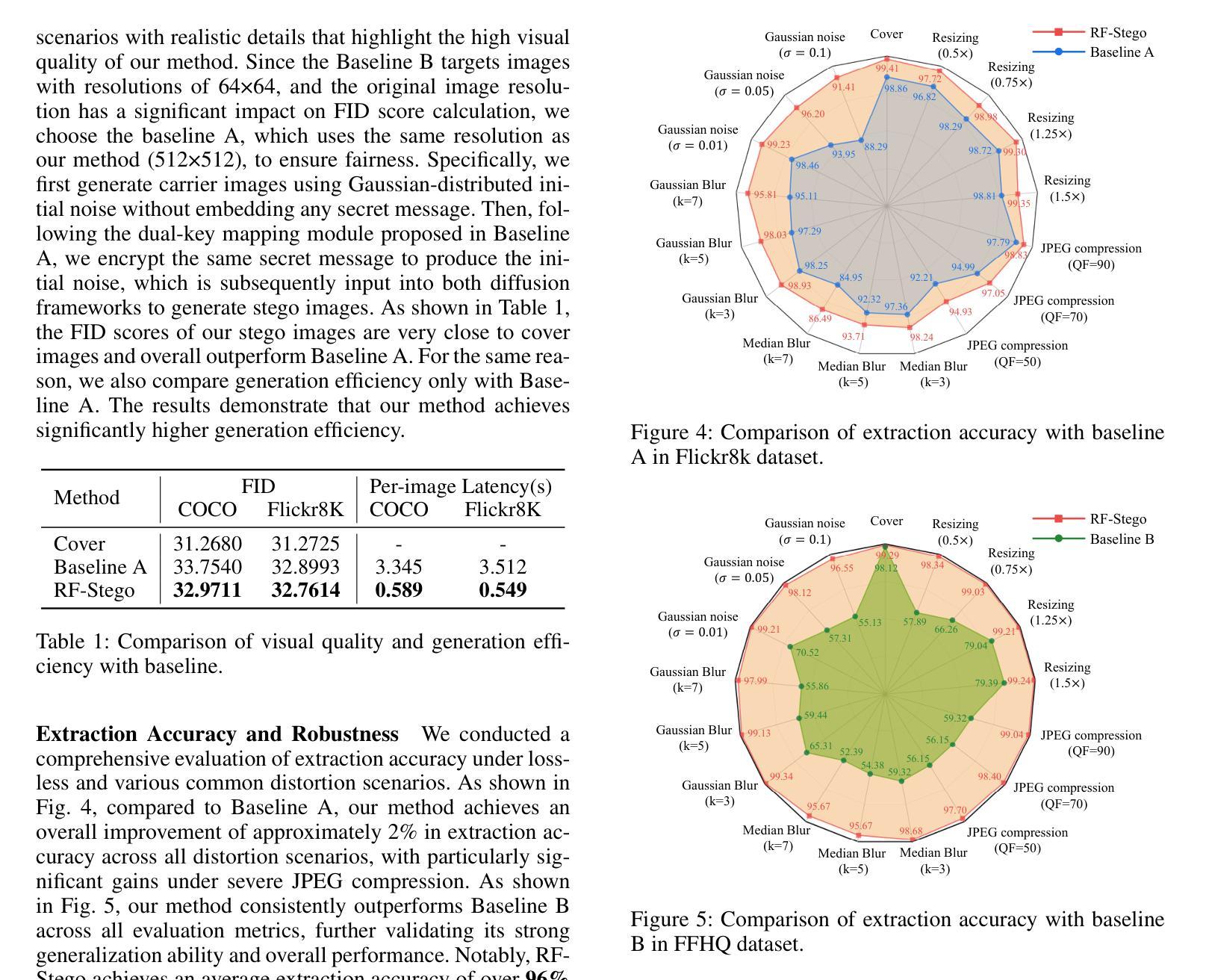
Accurate Latent Inversion for Generative Image Steganography via Rectified Flow
Authors:Yuqi Qian, Yun Cao, Meiyang Lv, Haocheng Fu
Steganography based on diffusion models has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to generate high-quality images and exhibit strong robustness. In such approaches, the secret message is first embedded into the initial latent variable, and then the stego image is generated through the forward process. To extract the message, an inversion process is required to reconstruct the latent variables from the received image. However, inaccurate latent inversion leads to significant discrepancies between the reconstructed and original latent variables, rendering message extraction infeasible. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{RF-Stego}, a novel generative image steganography method that enables accurate latent inversion and significantly improves extraction accuracy. First, we develop the \textbf{P}ath \textbf{C}onsistency \textbf{L}inear \textbf{I}nversion (\textbf{PCLI}), which imposes formal constraints on the inversion process. By explicitly aligning it with the forward generation path and modeling both directions along a shared linear path, PCLI eliminates path mismatch and ensures path consistency throughout the steganographic process. Second, through rigorous theoretical proof, we demonstrate that \textbf{R}ectified \textbf{F}low \textbf{(RF)} offers both theoretical reversibility and numerical stability in the inversion process. Based on this, we replace traditional unstable samplers with RF sampler which effectively improves the numerical precision of the inversion process. Experimental results show RF-Stego outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of extraction accuracy, image quality, robustness, security and generation efficiency.
基于扩散模型的隐写术因其能够生成高质量图像并表现出强大的稳健性而越来越受到关注。在这种方法中,首先将秘密信息嵌入到初始潜在变量中,然后通过前向过程生成隐写图像。为了提取信息,需要进行反向过程来从接收到的图像中重建潜在变量。然而,不准确的潜在变量反向会导致重建的潜在变量与原始变量之间存在显著差异,从而使信息提取变得不可行。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型生成图像隐写术方法,名为RF-Stego,该方法能够实现准确的潜在变量反向,并显著提高提取精度。首先,我们开发了路径一致性线性反向(PCLI),对反向过程施加正规约束。PCLI通过明确将其与前向生成路径对齐,并对两个方向进行共享线性路径建模,消除了路径不匹配,确保了隐写术过程中的路径一致性。其次,通过严格的理论证明,我们证明了校正流(RF)在反向过程中提供了理论上的可逆性和数值稳定性。基于此,我们用RF采样器替换了传统的不稳定采样器,有效提高反向过程的数值精度。实验结果表明,RF-Stego在提取精度、图像质量、稳健性、安全性和生成效率等方面均优于现有先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的隐写术因其能生成高质量图像并展现出强大的稳健性而备受关注。通过将秘密信息嵌入初始潜在变量,生成隐写图像,再通过正向过程进行传输。提取信息时,需要逆向过程重建潜在变量。然而,不准确的潜在变量逆向会导致重建与原始潜在变量之间的显著差异,使得信息提取变得不可能。为解决这一问题,我们提出一种新型生成图像隐写术方法——RF-Stego,能实现准确的潜在变量逆向并显著提高提取精度。首先,我们开发出路径一致性线性逆向(PCLI),对逆向过程施加正式约束。其次,通过严格的理论证明,我们发现整流流(RF)在理论上具有可逆性和数值稳定性。基于此,我们采用RF采样器替代传统的不稳定采样器,有效提高逆向过程的数值精度。实验结果表明,RF-Stego在提取精度、图像质量、稳健性、安全性和生成效率方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在隐写术领域受到关注,因其能生成高质量图像并展现稳健性。
- 现有隐写术在潜在变量逆向时存在不准确问题,导致信息提取困难。
- RF-Stego通过PCLI技术实现路径一致性,确保隐写过程中的路径匹配。
- RF流具有理论上的可逆性和数值稳定性,能提高逆向过程的精度。
- 采用RF采样器替代传统不稳定采样器,提高数值精度。
- RF-Stego在提取精度、图像质量、稳健性、安全性及生成效率方面超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图


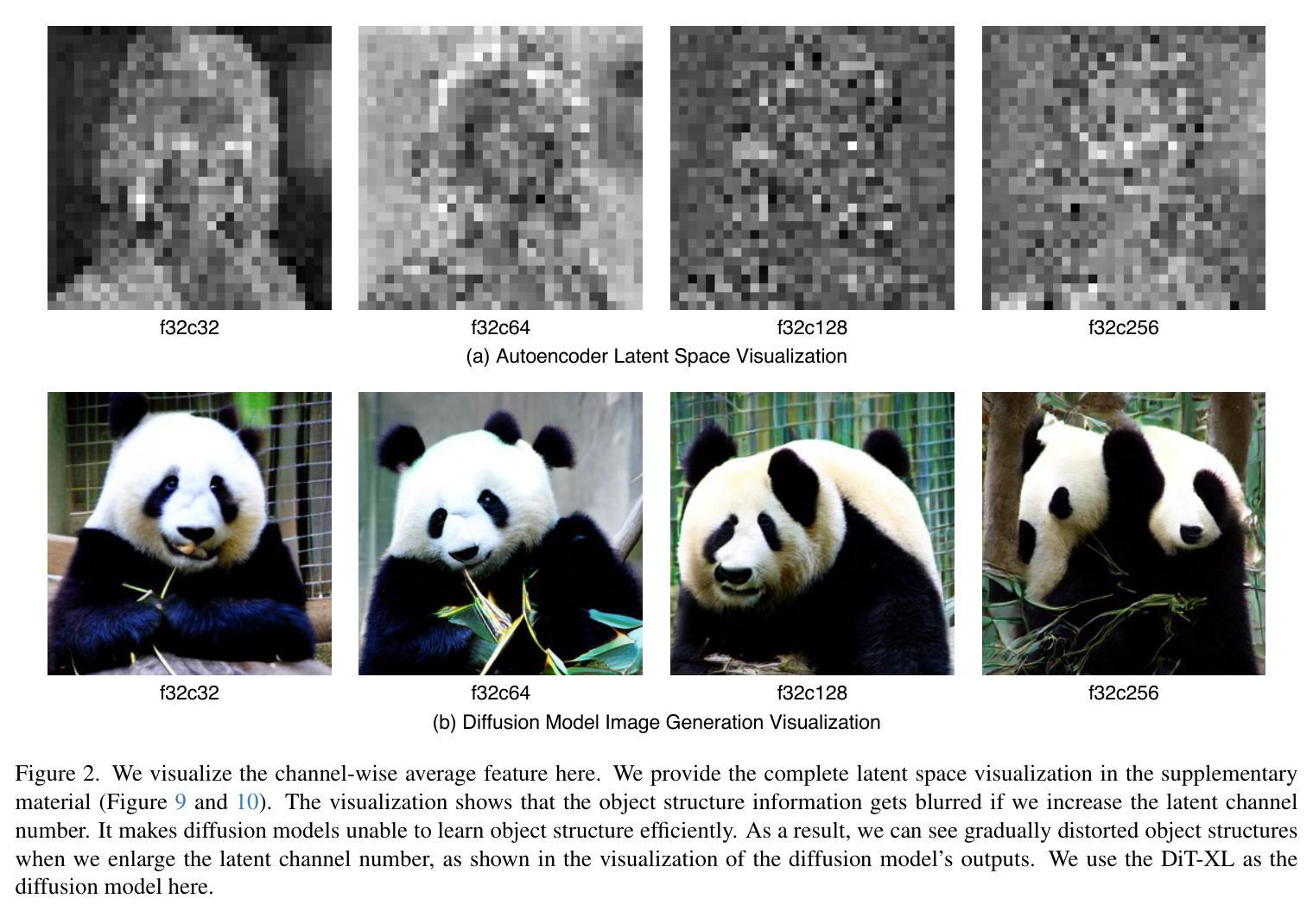
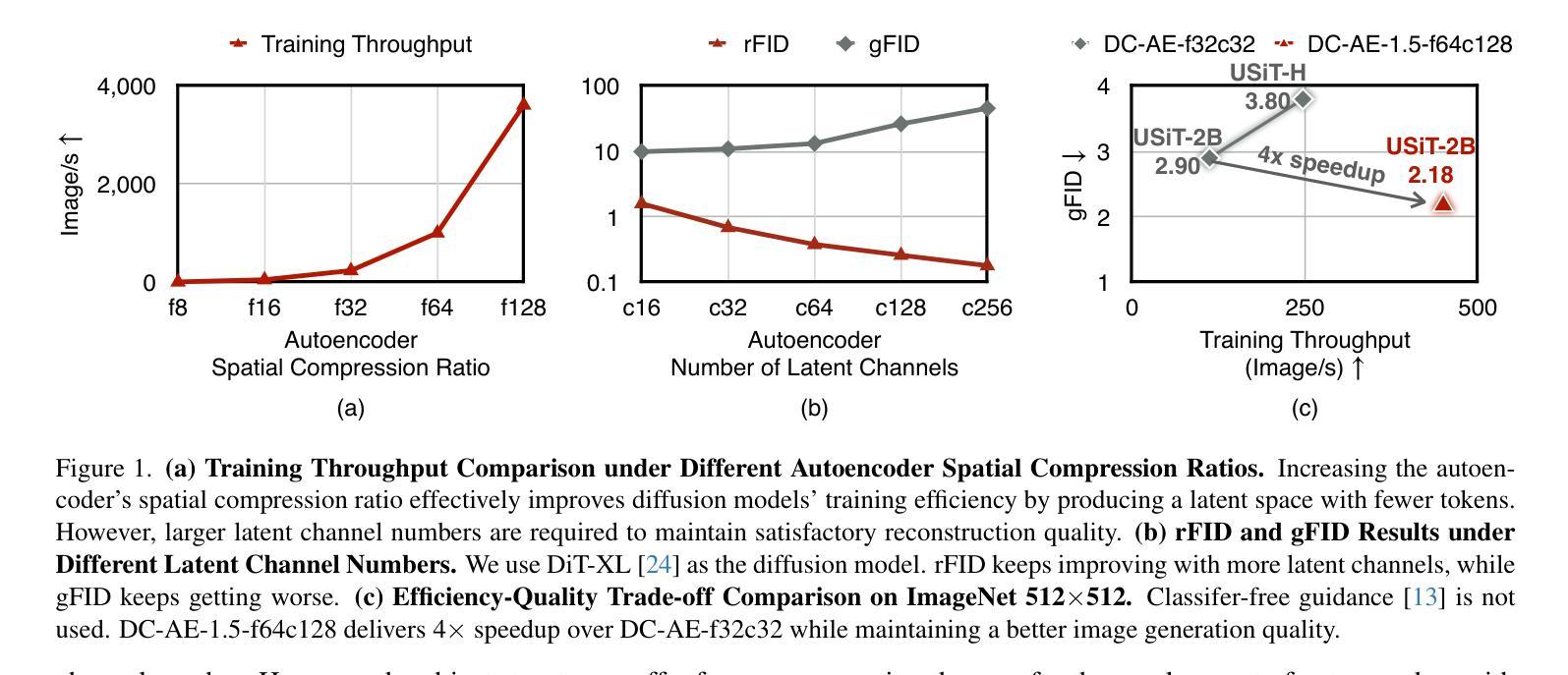
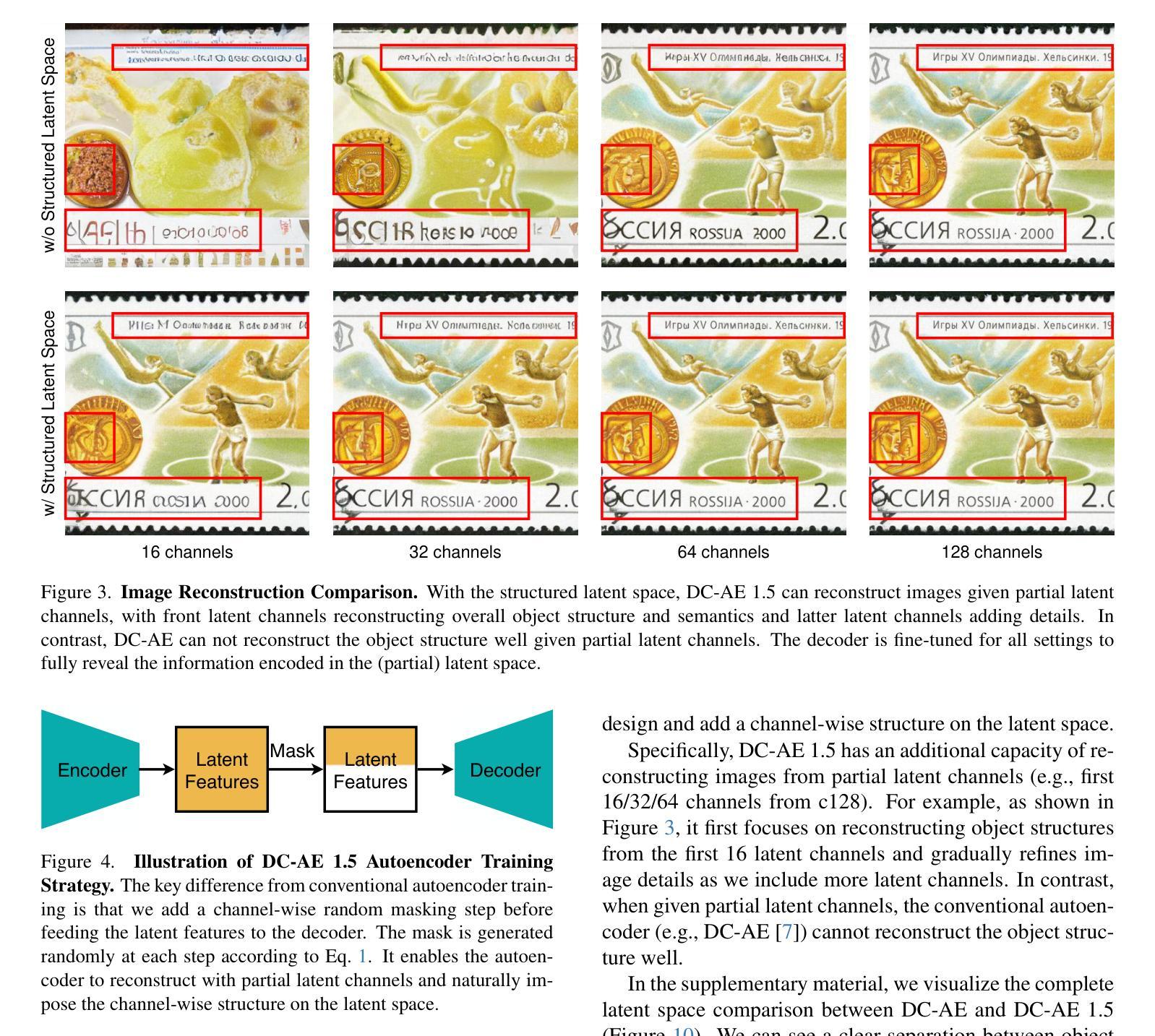
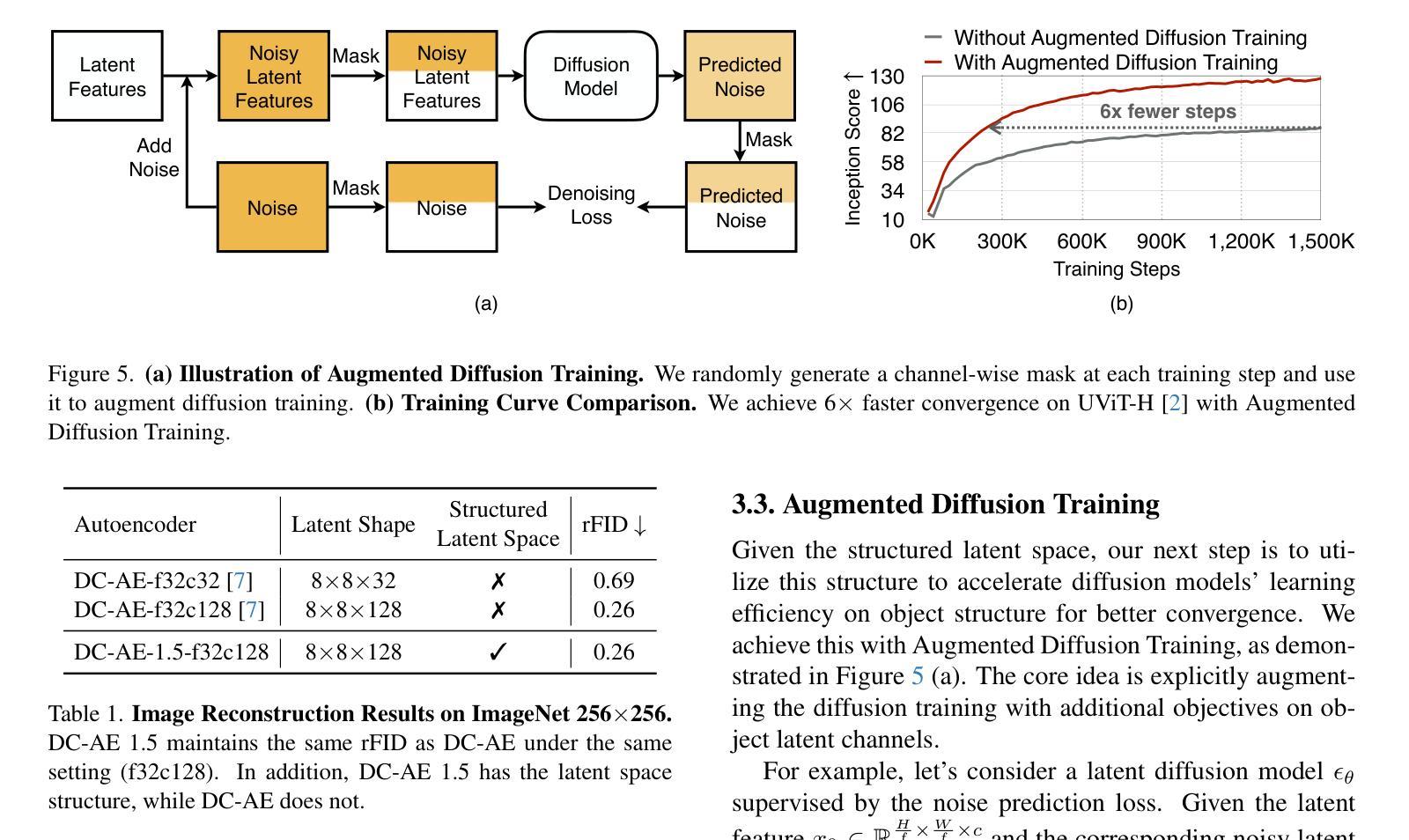
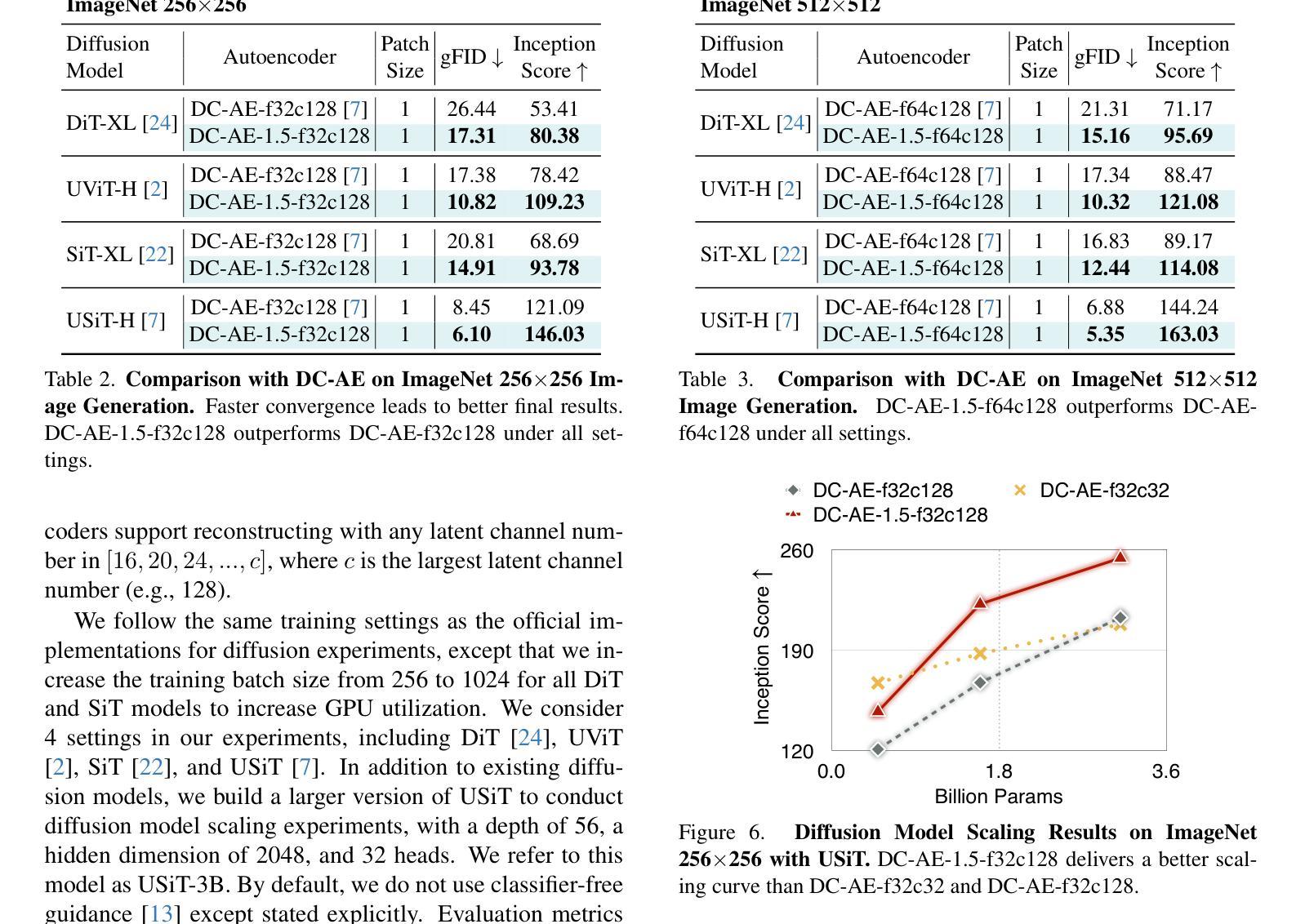
DC-AE 1.5: Accelerating Diffusion Model Convergence with Structured Latent Space
Authors:Junyu Chen, Dongyun Zou, Wenkun He, Junsong Chen, Enze Xie, Song Han, Han Cai
We present DC-AE 1.5, a new family of deep compression autoencoders for high-resolution diffusion models. Increasing the autoencoder’s latent channel number is a highly effective approach for improving its reconstruction quality. However, it results in slow convergence for diffusion models, leading to poorer generation quality despite better reconstruction quality. This issue limits the quality upper bound of latent diffusion models and hinders the employment of autoencoders with higher spatial compression ratios. We introduce two key innovations to address this challenge: i) Structured Latent Space, a training-based approach to impose a desired channel-wise structure on the latent space with front latent channels capturing object structures and latter latent channels capturing image details; ii) Augmented Diffusion Training, an augmented diffusion training strategy with additional diffusion training objectives on object latent channels to accelerate convergence. With these techniques, DC-AE 1.5 delivers faster convergence and better diffusion scaling results than DC-AE. On ImageNet 512x512, DC-AE-1.5-f64c128 delivers better image generation quality than DC-AE-f32c32 while being 4x faster. Code: https://github.com/dc-ai-projects/DC-Gen.
我们介绍了DC-AE 1.5,这是一种用于高分辨率扩散模型的新型深度压缩自编码器家族。增加自编码器的潜在通道数量是提高其重建质量的一种非常有效的方法。然而,这会导致扩散模型的收敛速度变慢,结果是在重建质量提高的情况下生成质量较差。这个问题限制了潜在扩散模型的质量上限,并阻碍了使用更高空间压缩比的自编码器。我们引入了两个关键创新来解决这一挑战:i)结构化潜在空间,这是一种基于训练的方法,对潜在空间施加所需的通道结构,前面的潜在通道捕获对象结构,后面的潜在通道捕获图像细节;ii)增强扩散训练,这是一种增强扩散训练策略,在对象潜在通道上增加扩散训练目标以加速收敛。通过这些技术,DC-AE 1.5在收敛速度和扩散规模结果方面优于DC-AE。在ImageNet 512x512上,DC-AE-1.5-f64c128在图像生成质量上优于DC-AE-f32c32,同时速度更快,为原来的四倍。代码:https://github.com/dc-ai-projects/DC-Gen。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
深度压缩自编码器DC-AE 1.5在高分辨率扩散模型中的应用介绍。通过增加自编码器的潜在通道数量可提高重建质量,但会导致扩散模型收敛速度减慢,影响生成质量。为解决此问题,引入两项关键技术:结构化潜在空间和增强扩散训练。DC-AE 1.5通过这两项技术实现了更快的收敛速度和更好的扩散尺度结果。在ImageNet 512x512上,DC-AE 1.5的f64c128版本在保持更好图像生成质量的同时,速度比DC-AE的f32c32版本快四倍。
Key Takeaways
- DC-AE 1.5是深度压缩自编码器的新版本,用于高分辨率扩散模型。
- 增加自编码器的潜在通道数量可以提高重建质量,但会导致扩散模型收敛速度减慢。
- 结构化潜在空间是一种基于训练的方法,可以在潜在空间上施加所需的通道结构。
- 增强扩散训练是一种加速收敛的策略,通过额外的扩散训练目标在对象潜在通道上实现。
- DC-AE 1.5通过应用上述两项技术,实现了比DC-AE更快的收敛速度和更好的扩散尺度结果。
- 在ImageNet 512x512上,DC-AE 1.5的f64c128版本在图像生成质量和速度上均表现更优。
点此查看论文截图


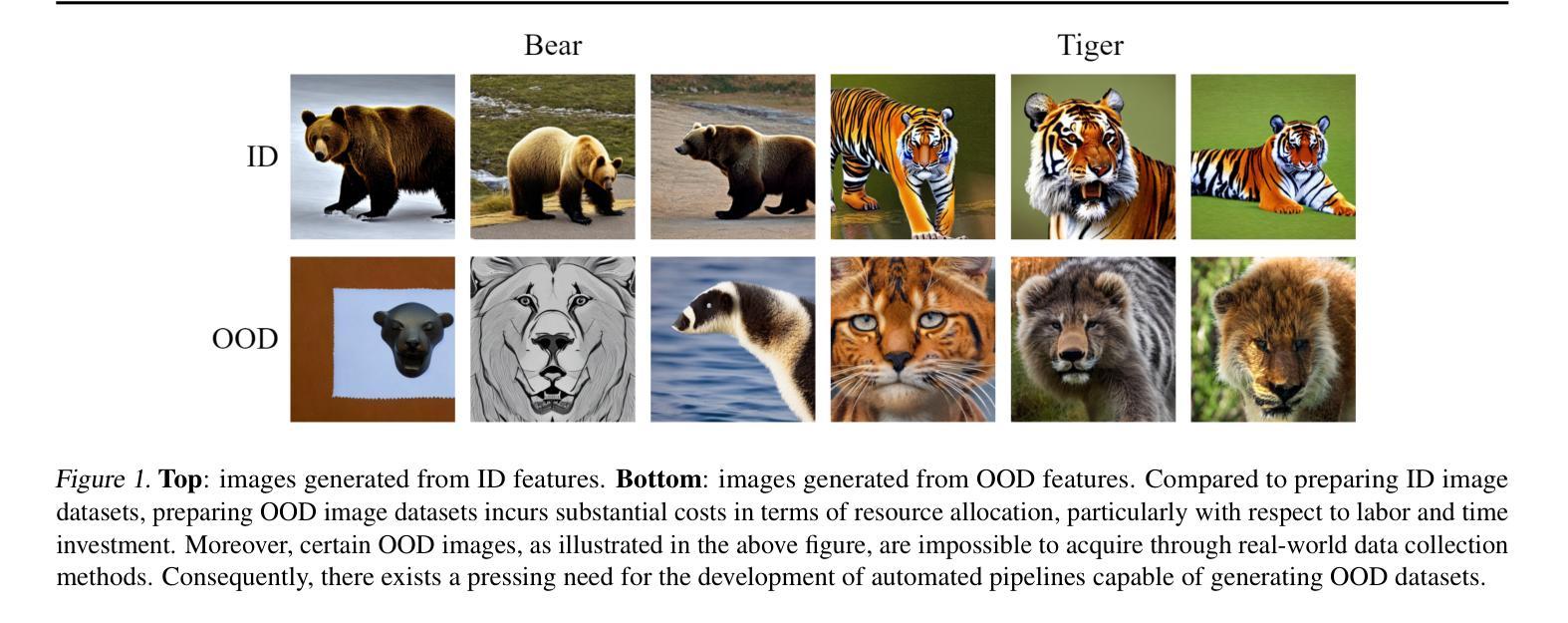
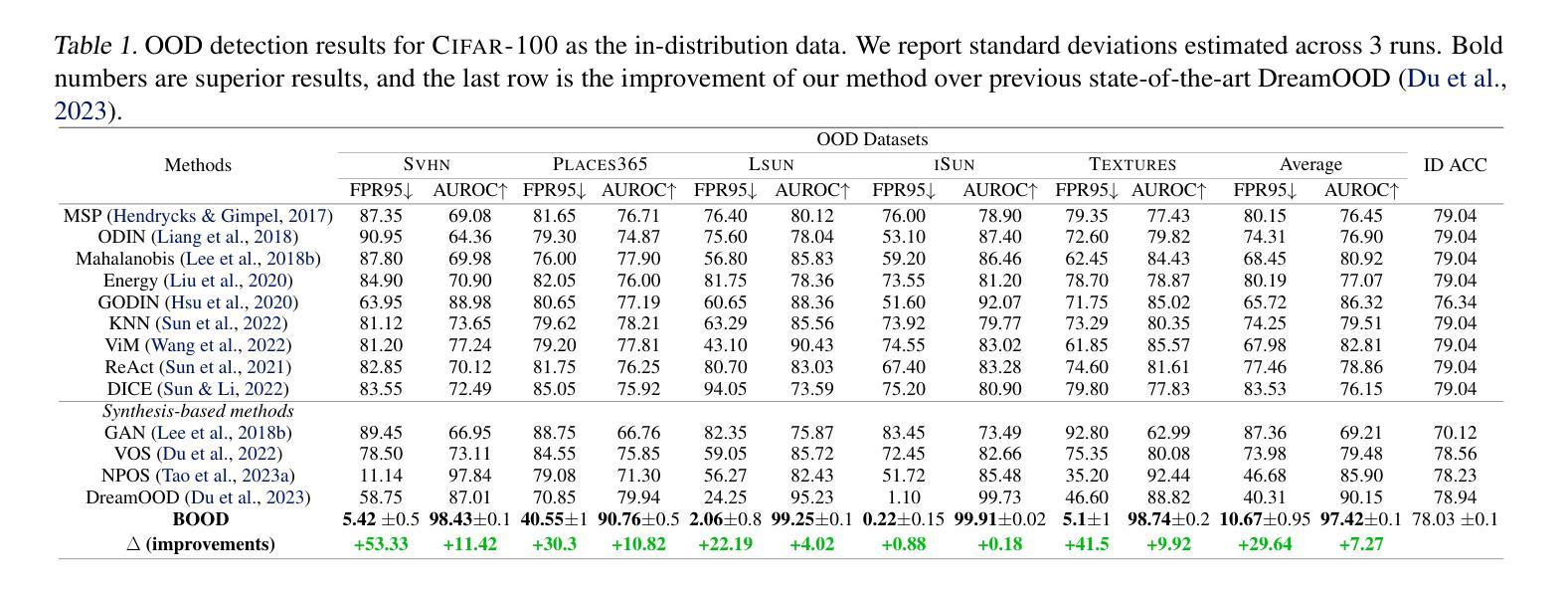
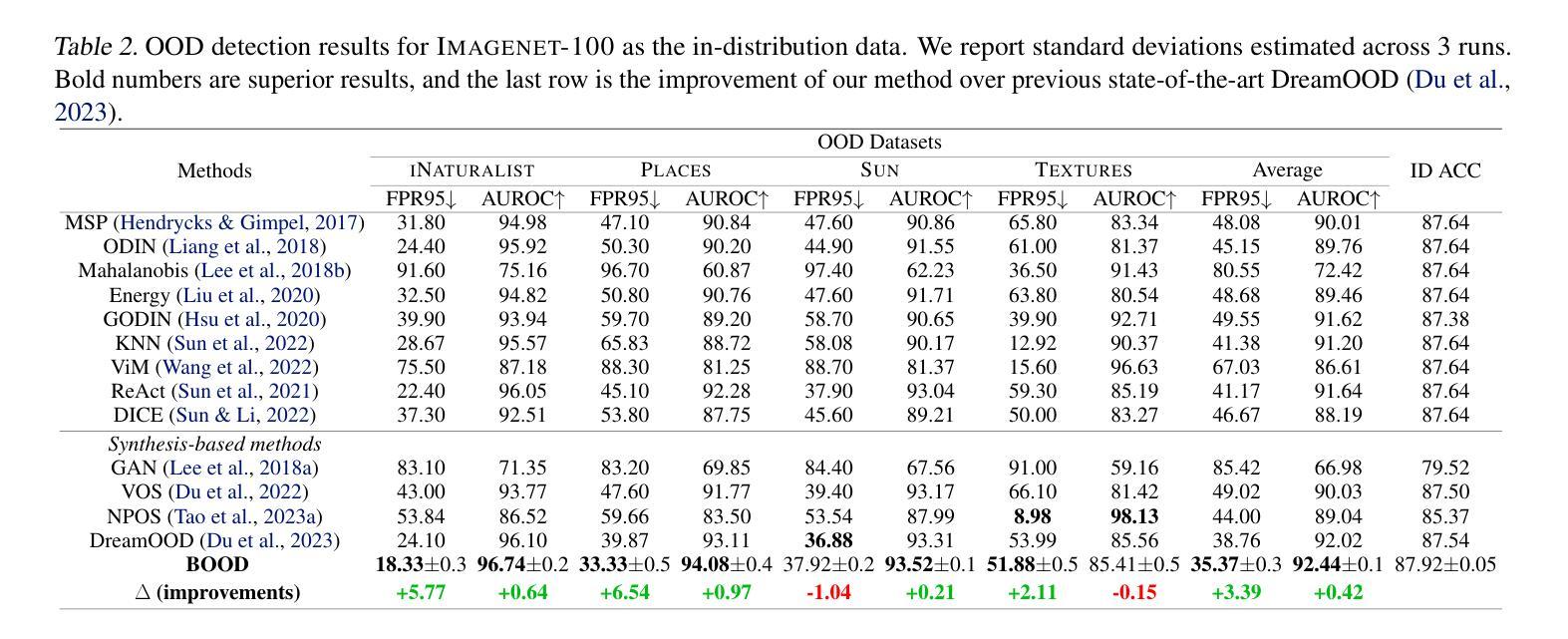
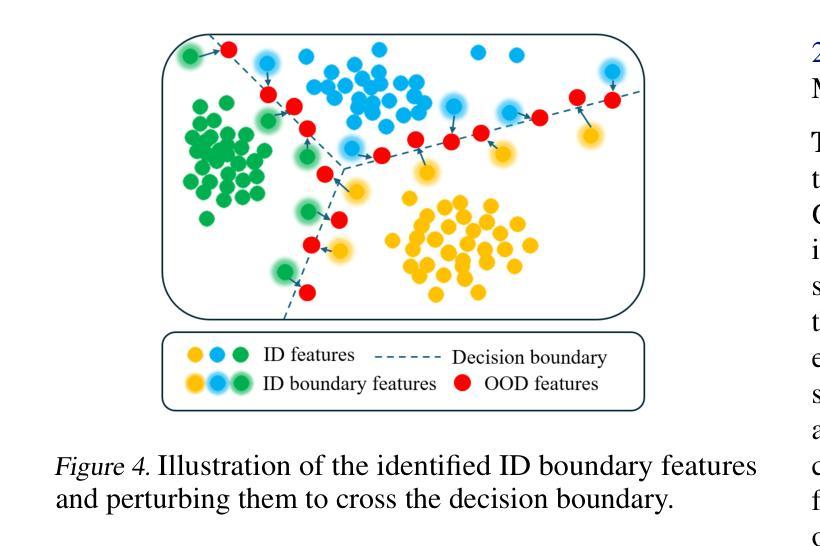
BOOD: Boundary-based Out-Of-Distribution Data Generation
Authors:Qilin Liao, Shuo Yang, Bo Zhao, Ping Luo, Hengshuang Zhao
Harnessing the power of diffusion models to synthesize auxiliary training data based on latent space features has proven effective in enhancing out-of-distribution (OOD) detection performance. However, extracting effective features outside the in-distribution (ID) boundary in latent space remains challenging due to the difficulty of identifying decision boundaries between classes. This paper proposes a novel framework called Boundary-based Out-Of-Distribution data generation (BOOD), which synthesizes high-quality OOD features and generates human-compatible outlier images using diffusion models. BOOD first learns a text-conditioned latent feature space from the ID dataset, selects ID features closest to the decision boundary, and perturbs them to cross the decision boundary to form OOD features. These synthetic OOD features are then decoded into images in pixel space by a diffusion model. Compared to previous works, BOOD provides a more training efficient strategy for synthesizing informative OOD features, facilitating clearer distinctions between ID and OOD data. Extensive experimental results on common benchmarks demonstrate that BOOD surpasses the state-of-the-art method significantly, achieving a 29.64% decrease in average FPR95 (40.31% vs. 10.67%) and a 7.27% improvement in average AUROC (90.15% vs. 97.42%) on the CIFAR-100 dataset.
利用扩散模型合成辅助训练数据,基于潜在空间特征提升离群分布(OOD)检测性能已经得到了证实。然而,在潜在空间中,由于难以确定类之间的决策边界,在分布内(ID)边界之外提取有效特征仍然具有挑战性。本文提出了一种基于边界的离群数据生成(BOOD)新型框架,该框架使用扩散模型合成高质量OOD特征并生成人类兼容的异常图像。BOOD首先学习来自ID数据集的文本条件潜在特征空间,选择最接近决策边界的ID特征,并通过扰动它们来跨越决策边界以形成OOD特征。这些合成的OOD特征随后通过扩散模型在像素空间中解码为图像。与以前的工作相比,BOOD为合成信息丰富的OOD特征提供了更有效的训练策略,有助于更清楚地区分ID和OOD数据。在常用基准测试上的大量实验结果表明,BOOD显著超过了现有最先进的算法,在CIFAR-10O数据集上实现了平均FPR95降低29.64%(从40.31%降至到低至低至为特低到仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至仅低至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降至至降低至的降至至10.67%),平均AUROC提高了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升了提升到了了了了了了了了了了了了了提升到高7.27%(从提高了提升到到提升到提升到高达达到提高提高提高了从到总计的提到了达到提升至总共是总提高到总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计是总计提高了总计为从高达达到从90.15%提高到达到97.42%)。整体表现性能大幅度提升表明了BOOD方法的显著优势及潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, To be published in the Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
利用扩散模型合成辅助训练数据,基于潜在空间特征提高检测性能。本文提出一种基于边界的外部数据生成(BOOD)框架,利用扩散模型合成高质量外部特征并生成人类兼容的异常图像。BOOD学习文本条件下的潜在特征空间,选择最接近决策边界的内部特征,通过扰动形成外部特征。合成外部特征在像素空间解码为图像。与以前的工作相比,BOOD为合成信息性外部特征提供了更有效的训练策略,更清晰地区分内部和外部数据。在公共基准测试上的实验结果表明,BOOD显著优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于合成辅助训练数据,能提高检测性能。
- 提出一种名为BOOD的框架,用于生成高质量的外部分布特征。
- BOOD利用扩散模型将合成的外部特征解码为图像。
- BOOD学习文本条件下的潜在特征空间并选择接近决策边界的内部特征。
- 通过扰动内部特征来形成外部特征并跨越决策边界。
- BOOD策略能更清晰地区分内部和外部数据,提高区分能力。
点此查看论文截图



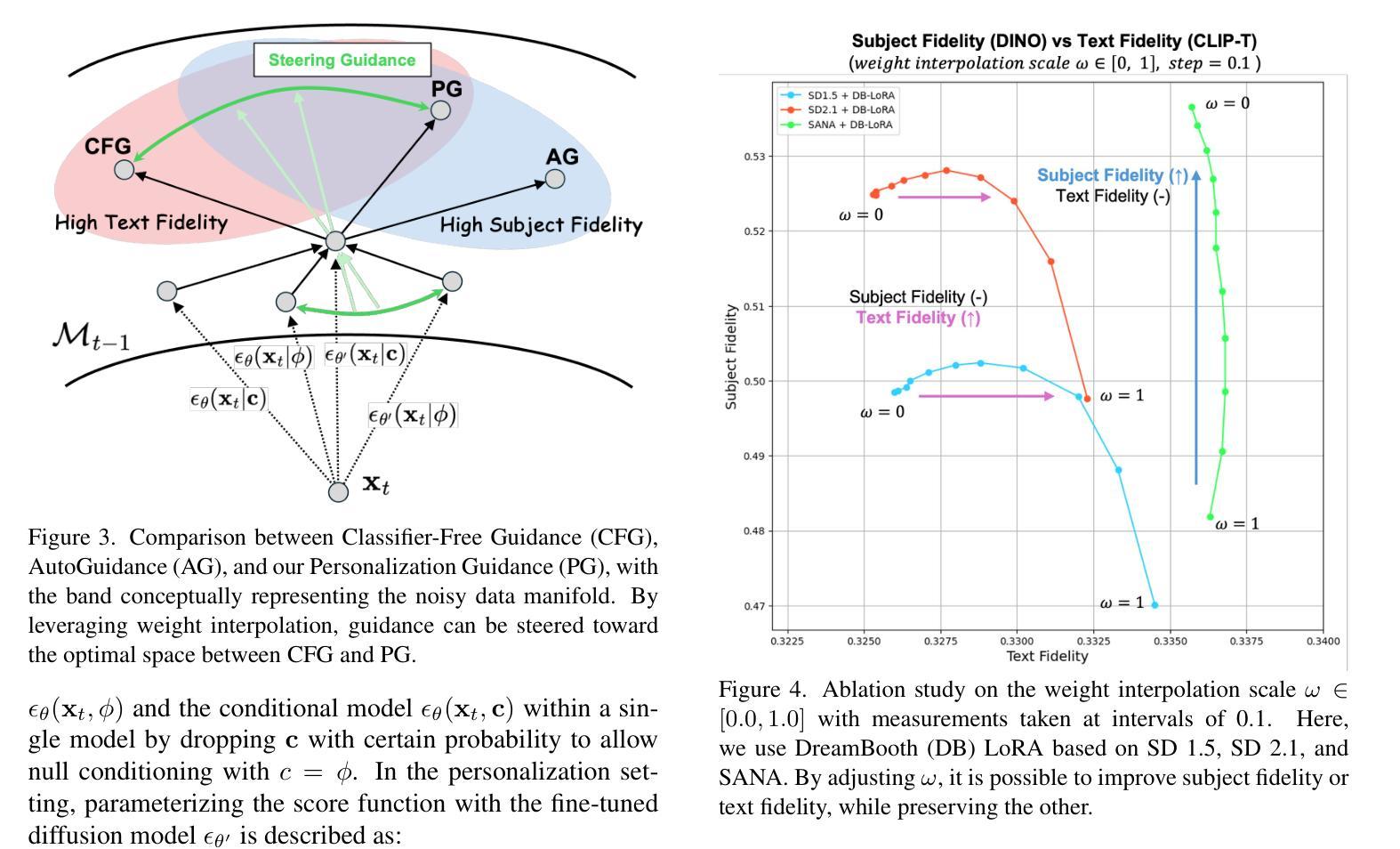
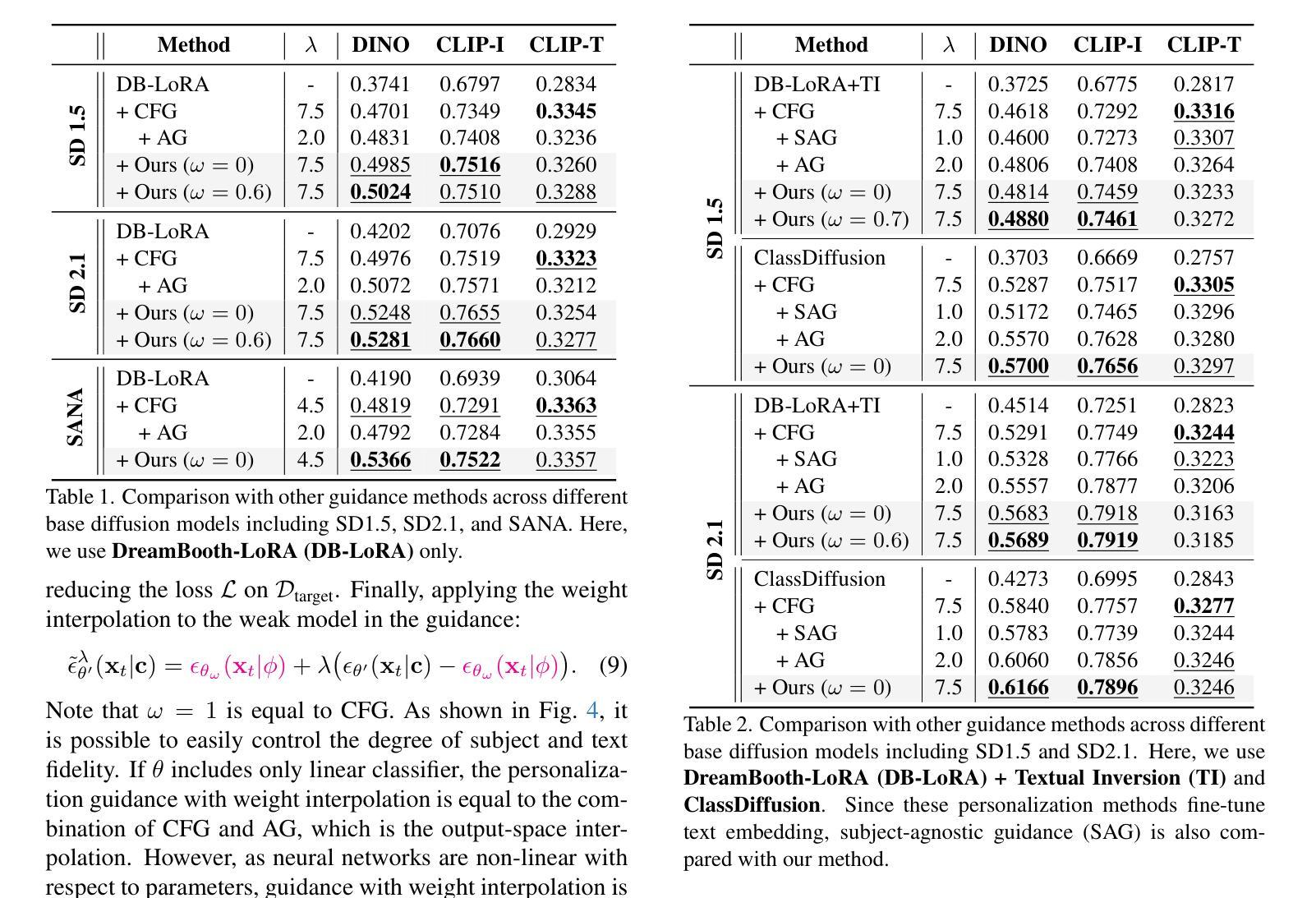
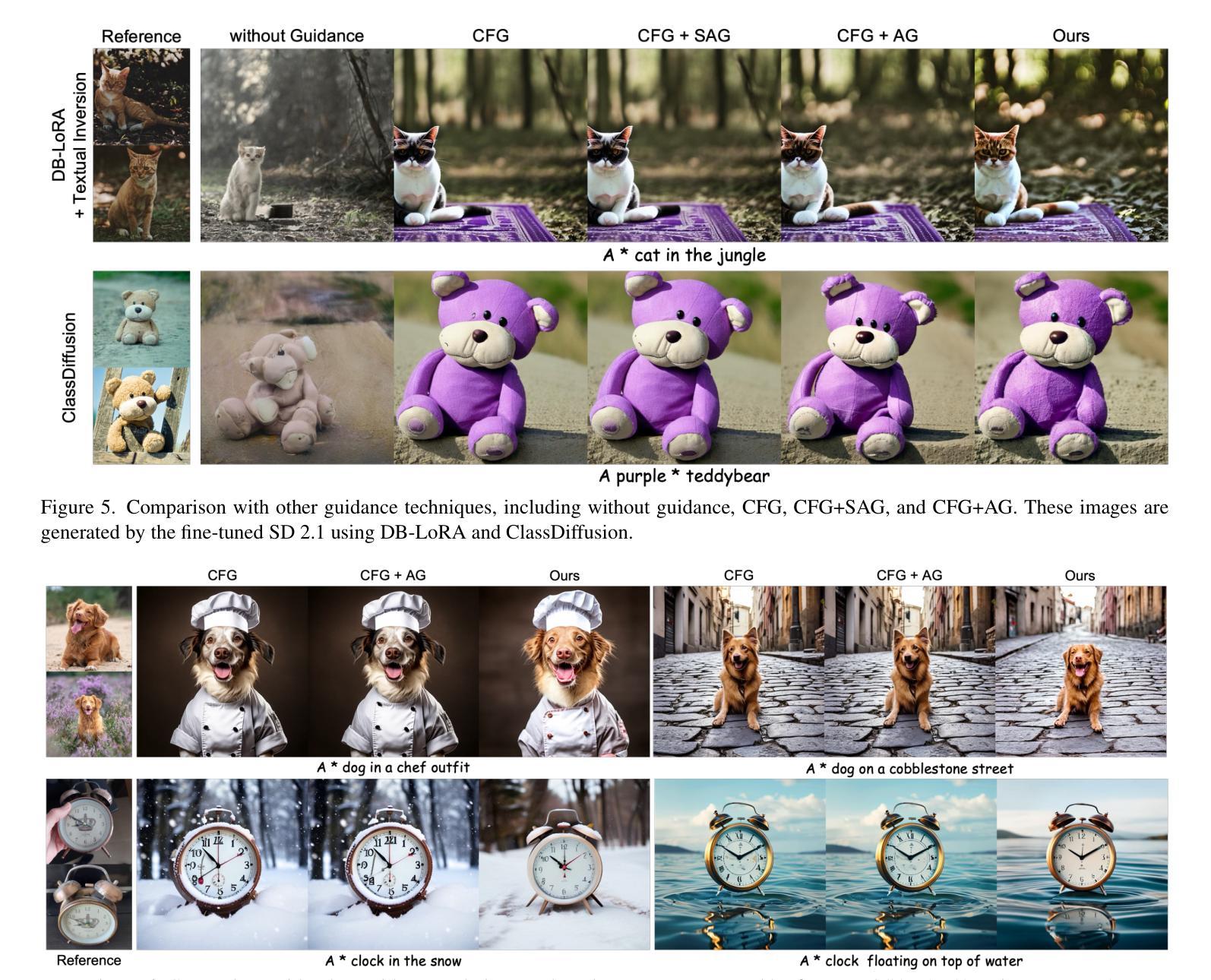
Steering Guidance for Personalized Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Sunghyun Park, Seokeon Choi, Hyoungwoo Park, Sungrack Yun
Personalizing text-to-image diffusion models is crucial for adapting the pre-trained models to specific target concepts, enabling diverse image generation. However, fine-tuning with few images introduces an inherent trade-off between aligning with the target distribution (e.g., subject fidelity) and preserving the broad knowledge of the original model (e.g., text editability). Existing sampling guidance methods, such as classifier-free guidance (CFG) and autoguidance (AG), fail to effectively guide the output toward well-balanced space: CFG restricts the adaptation to the target distribution, while AG compromises text alignment. To address these limitations, we propose personalization guidance, a simple yet effective method leveraging an unlearned weak model conditioned on a null text prompt. Moreover, our method dynamically controls the extent of unlearning in a weak model through weight interpolation between pre-trained and fine-tuned models during inference. Unlike existing guidance methods, which depend solely on guidance scales, our method explicitly steers the outputs toward a balanced latent space without additional computational overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed guidance can improve text alignment and target distribution fidelity, integrating seamlessly with various fine-tuning strategies.
个性化文本到图像扩散模型对于将预训练模型适应于特定目标概念至关重要,这能够实现多样化的图像生成。然而,使用少量图像进行微调会在适应目标分布(例如主题保真度)和保留原始模型的广泛知识(例如文本可编辑性)之间引入固有的权衡。现有的采样指导方法,如无分类器指导(CFG)和自动指导(AG),无法有效地将输出导向平衡的空间:CFG限制了目标分布的适应,而AG则妥协了文本对齐。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了个性化指导方法,这是一种简单而有效的方法,利用未学习的弱模型以空文本提示为条件。此外,我们的方法通过推断期间在预训练模型和微调模型之间进行权重插值,动态控制弱模型的未学习程度。与现有依赖指导尺度的指导方法不同,我们的方法能够明确地将输出导向平衡潜在空间,而无需额外的计算开销。实验结果表明,我们提出的指导方法能够改进文本对齐和目标分布保真度,无缝集成各种微调策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对文本到图像扩散模型的个性化需求,指出在适应预训练模型到特定目标概念时面临的挑战。文章提出一种新型的个人化指导方法,利用未学习的弱模型并对其进行动态控制,以在推理过程中实现平衡输出空间。此方法通过权重插值实现预训练模型和微调模型之间的平衡,从而提高文本对齐和目标分布保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型的个性化是关键,尤其在适应预训练模型到特定目标概念时。
- 现存的采样指导方法如无分类器指导(CFG)和自动指导(AG)难以有效实现目标分布对齐与保持原始知识之间的平衡。
- 提出的个人化指导方法利用未学习的弱模型,通过权重插值在预训练模型和微调模型间动态控制输出空间。
- 与现有指导方法不同,新方法可以在不增加计算开销的情况下,明确引导输出达到平衡潜在空间。
- 实验结果表明,新提出的指导方法可以提高文本对齐和目标分布保真度。
- 该方法可以无缝集成到各种微调策略中。
点此查看论文截图


Jet Image Generation in High Energy Physics Using Diffusion Models
Authors:Victor D. Martinez, Vidya Manian, Sudhir Malik
This article presents, for the first time, the application of diffusion models for generating jet images corresponding to proton-proton collision events at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The kinematic variables of quark, gluon, W-boson, Z-boson, and top quark jets from the JetNet simulation dataset are mapped to two-dimensional image representations. Diffusion models are trained on these images to learn the spatial distribution of jet constituents. We compare the performance of score-based diffusion models and consistency models in accurately generating class-conditional jet images. Unlike approaches based on latent distributions, our method operates directly in image space. The fidelity of the generated images is evaluated using several metrics, including the Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID), which demonstrates that consistency models achieve higher fidelity and generation stability compared to score-based diffusion models. These advancements offer significant improvements in computational efficiency and generation accuracy, providing valuable tools for High Energy Physics (HEP) research.
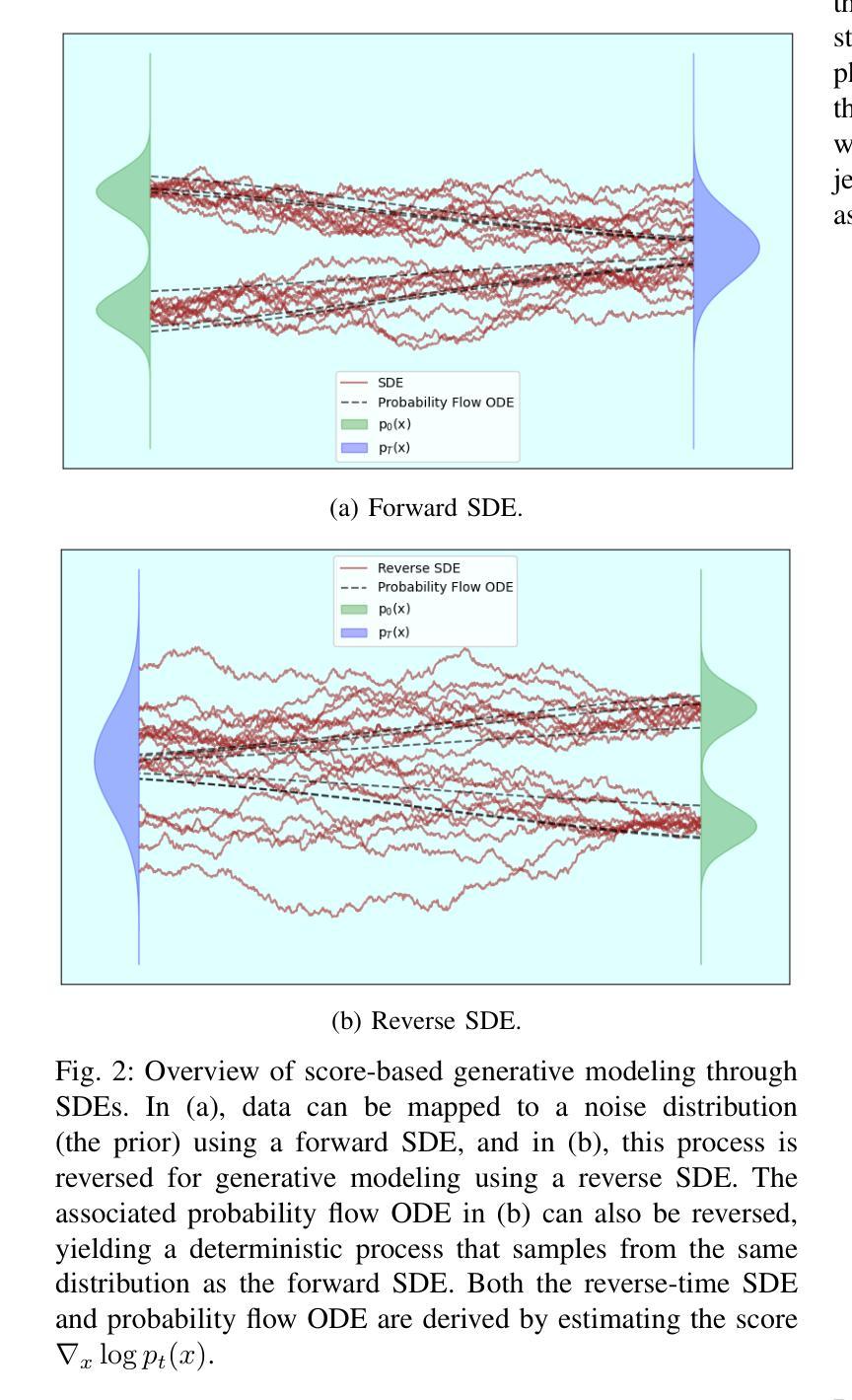
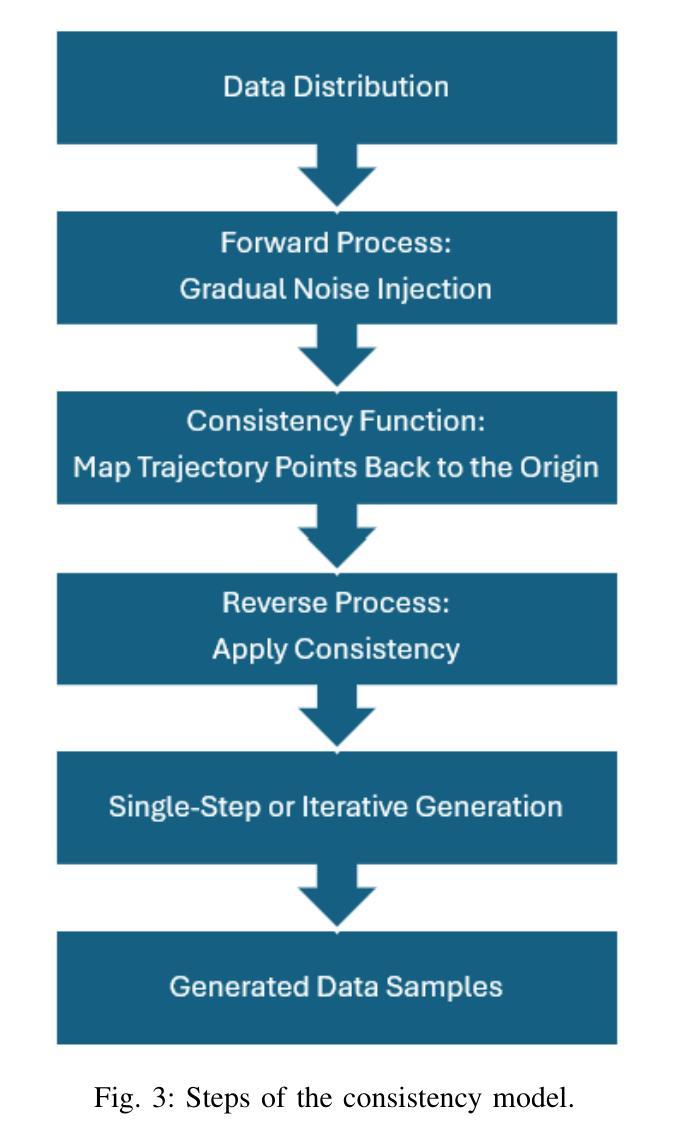
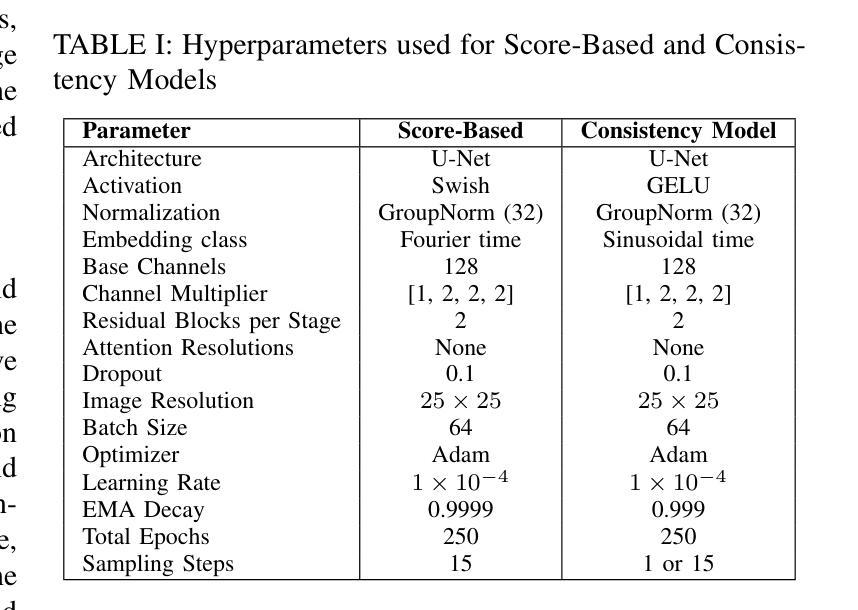
本文首次介绍了扩散模型在生成大型强子对撞机(LHC)质子-质子碰撞事件对应的喷射图像中的应用。JetNet模拟数据集中的夸克、胶子、W玻色子、Z玻色子和顶级夸克喷射的运动学变量被映射到二维图像表示。扩散模型在这些图像上进行训练,学习喷射成分的空间分布。我们比较了基于分数的扩散模型和一致性模型在准确生成类条件喷射图像方面的性能。不同于基于潜在分布的方法,我们的方法直接在图像空间中进行操作。生成的图像的保真度通过包括Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)在内的多个指标进行评估,证明一致性模型在保真度和生成稳定性方面优于基于分数的扩散模型。这些进步在计算效率和生成准确性方面提供了重大改进,为高能物理学(HEP)研究提供了有价值的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper is under review at IEEE Transactions in Nuclear Science
Summary
本文首次展示了扩散模型在大型强子对撞机(LHC)质子-质子碰撞事件中的喷射图像生成应用。文章利用JetNet模拟数据集将夸克、胶子、W玻色子、Z玻色子和顶级喷射物的运动变量映射成二维图像表示。扩散模型在这些图像上进行训练,学习喷射成分的空间分布。文章比较了基于分数的扩散模型和一致性模型在生成类条件喷射图像方面的准确性。与基于潜在分布的方法不同,该方法直接在图像空间中进行操作。生成的图像的保真度通过包括Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)在内的多个指标进行评估,证明一致性模型相较于基于分数的扩散模型具有更高的保真度和生成稳定性。这些进展在计算效率和生成准确性方面提供了重大改进,为高能物理学(HEP)研究提供了有价值的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 首次将扩散模型应用于大型强子对撞机的质子-质子碰撞事件的喷射图像生成。
- 利用JetNet模拟数据集将运动变量映射成二维图像。
- 扩散模型在图像空间上进行训练,学习喷射成分的空间分布。
- 比较了基于分数的扩散模型和一致性模型在生成类条件喷射图像方面的性能。
- 一致性模型相较于基于分数的扩散模型具有更高的图像生成保真度和稳定性。
- 该研究为高能物理学研究提供了重要的工具,特别是在计算效率和生成准确性方面。
点此查看论文截图

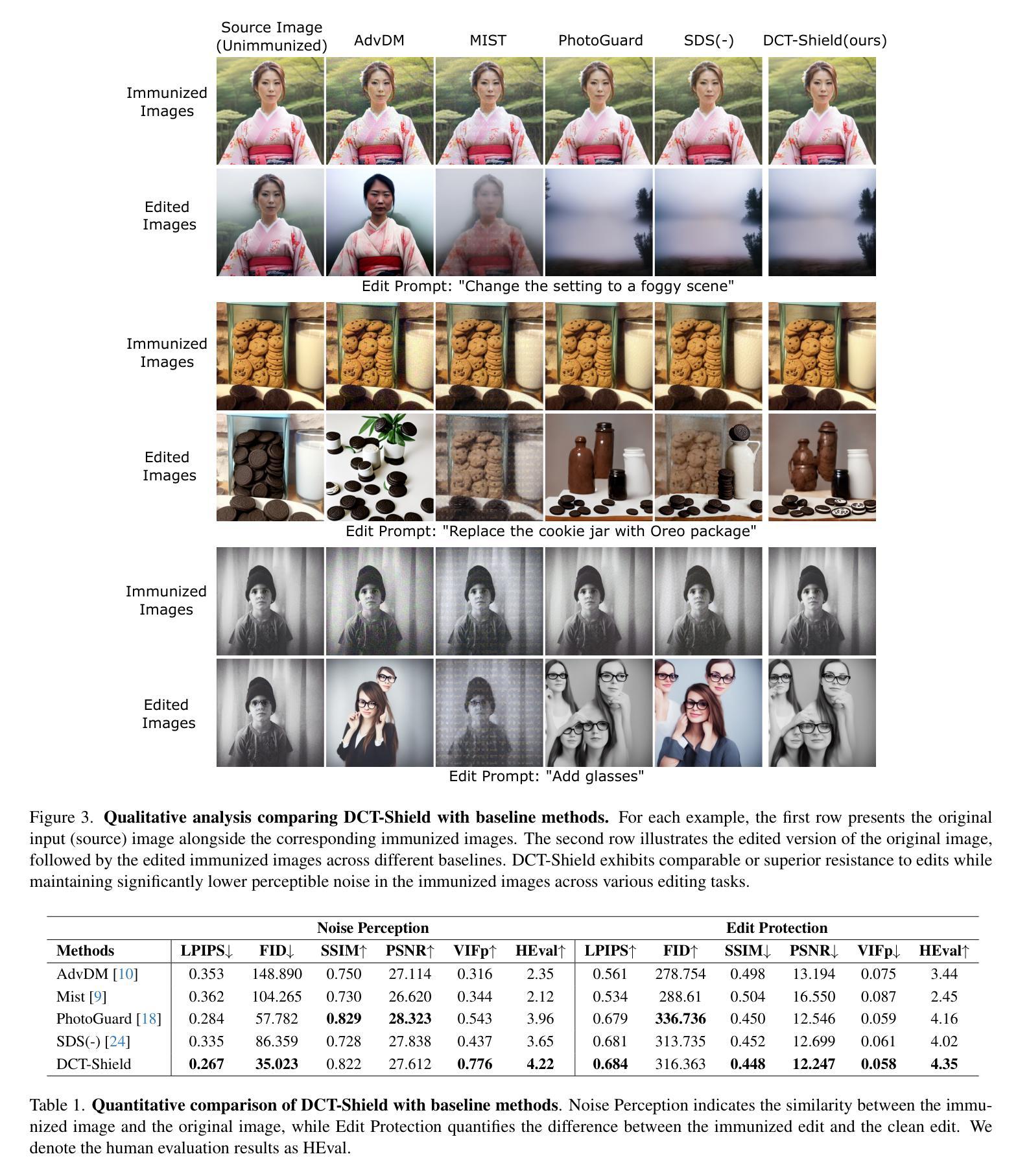
DCT-Shield: A Robust Frequency Domain Defense against Malicious Image Editing
Authors:Aniruddha Bala, Rohit Chowdhury, Rohan Jaiswal, Siddharth Roheda
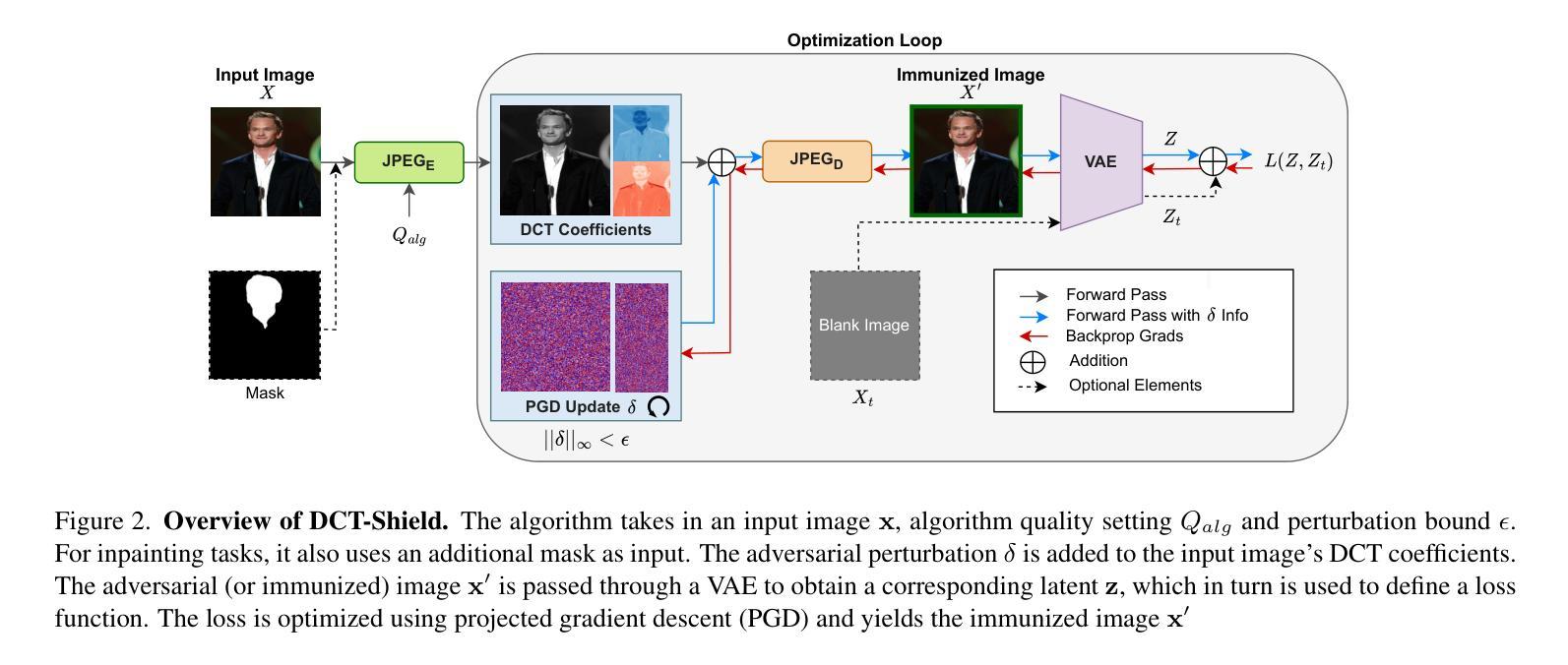
Advancements in diffusion models have enabled effortless image editing via text prompts, raising concerns about image security. Attackers with access to user images can exploit these tools for malicious edits. Recent defenses attempt to protect images by adding a limited noise in the pixel space to disrupt the functioning of diffusion-based editing models. However, the adversarial noise added by previous methods is easily noticeable to the human eye. Moreover, most of these methods are not robust to purification techniques like JPEG compression under a feasible pixel budget. We propose a novel optimization approach that introduces adversarial perturbations directly in the frequency domain by modifying the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) coefficients of the input image. By leveraging the JPEG pipeline, our method generates adversarial images that effectively prevent malicious image editing. Extensive experiments across a variety of tasks and datasets demonstrate that our approach introduces fewer visual artifacts while maintaining similar levels of edit protection and robustness to noise purification techniques.
扩散模型的进步使得通过文本提示进行简单的图像编辑成为可能,但同时也引发了人们对图像安全的担忧。能够访问用户图像的攻击者可能会利用这些工具进行恶意编辑。最近的防御方法试图通过在像素空间添加有限噪声来保护图像,以破坏基于扩散的编辑模型的功能。然而,以前方法添加的对抗性噪声很容易被人眼察觉。此外,这些方法中的大多数在可行的像素预算下对JPEG压缩等净化技术并不稳健。我们提出了一种新的优化方法,通过在输入图像的离散余弦变换(DCT)系数中引入对抗性扰动,直接在频域进行扰动。我们的方法利用JPEG管道生成对抗性图像,有效防止恶意图像编辑。在多种任务和数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在引入较少视觉伪影的同时,保持了类似的编辑保护水平和对抗噪声净化技术的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
摘要
随着扩散模型技术的进步,通过文本提示进行图像编辑变得更加轻松,这也引发了人们对图像安全的担忧。攻击者可能会利用这些工具对用户图像进行恶意编辑。最近的防御方法试图通过添加像素空间中的有限噪声来保护图像,从而破坏基于扩散的编辑模型的功能。然而,以前方法添加的对抗性噪声很容易被人眼察觉。此外,这些方法中的大多数在可行的像素预算下并不适用于净化技术,如JPEG压缩。我们提出了一种新的优化方法,通过在频率域中直接修改输入图像的离散余弦变换(DCT)系数来引入对抗性扰动。通过利用JPEG管道,我们的方法生成对抗性图像,有效防止恶意图像编辑。在多种任务和数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法引入的视觉伪影更少,同时保持了类似的编辑保护水平和对抗噪声净化技术的稳健性。
关键见解
- 扩散模型进步使得通过文本提示进行图像编辑变得轻松,引发对图像安全的担忧。
- 攻击者可能利用这些工具进行恶意图像编辑。
- 现有防御方法通过添加像素空间中的噪声来保护图像,但这种方法容易被察觉并不够稳健。
- 提出的优化方法在频率域引入对抗性扰动,通过修改输入图像的离散余弦变换(DCT)系数来防御恶意编辑。
- 该方法生成的对抗性图像能有效防止恶意图像编辑。
- 方法在广泛实验下表现出较少的视觉伪影和较高的编辑保护水平及稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

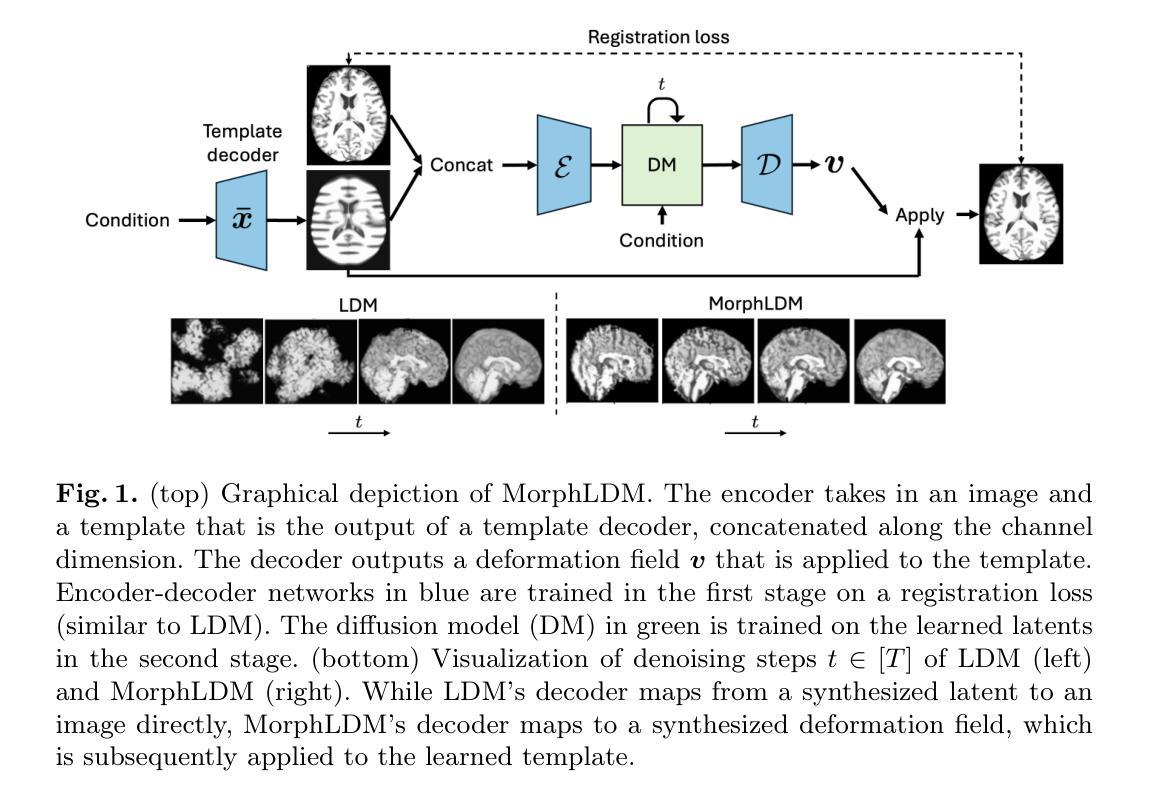
Generating Novel Brain Morphology by Deforming Learned Templates
Authors:Alan Q. Wang, Fangrui Huang, Bailey Trang, Wei Peng, Mohammad Abbasi, Kilian Pohl, Mert Sabuncu, Ehsan Adeli
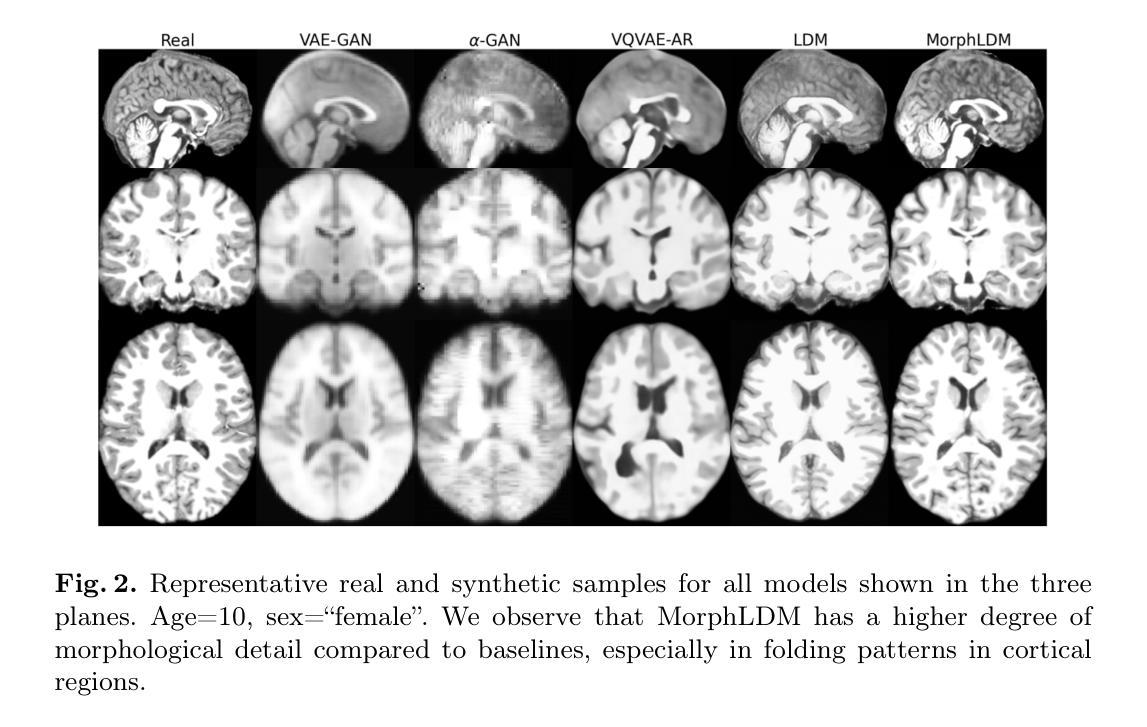
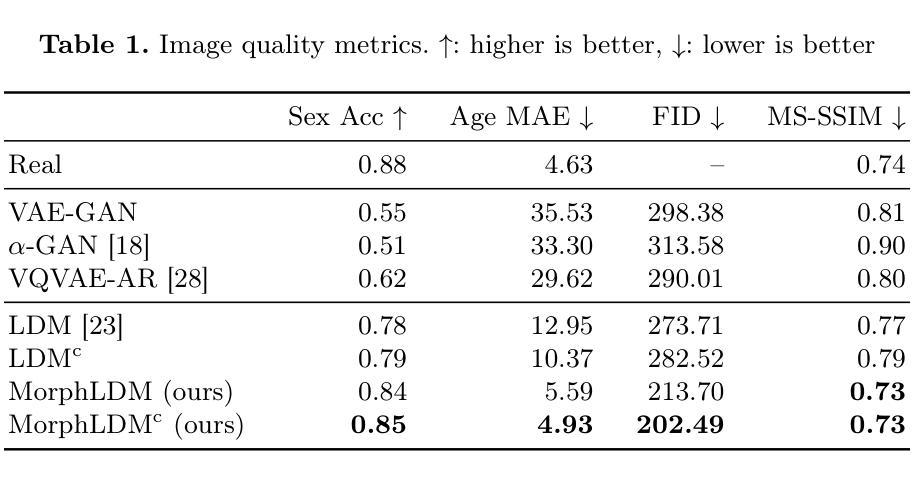
Designing generative models for 3D structural brain MRI that synthesize morphologically-plausible and attribute-specific (e.g., age, sex, disease state) samples is an active area of research. Existing approaches based on frameworks like GANs or diffusion models synthesize the image directly, which may limit their ability to capture intricate morphological details. In this work, we propose a 3D brain MRI generation method based on state-of-the-art latent diffusion models (LDMs), called MorphLDM, that generates novel images by applying synthesized deformation fields to a learned template. Instead of using a reconstruction-based autoencoder (as in a typical LDM), our encoder outputs a latent embedding derived from both an image and a learned template that is itself the output of a template decoder; this latent is passed to a deformation field decoder, whose output is applied to the learned template. A registration loss is minimized between the original image and the deformed template with respect to the encoder and both decoders. Empirically, our approach outperforms generative baselines on metrics spanning image diversity, adherence with respect to input conditions, and voxel-based morphometry. Our code is available at https://github.com/alanqrwang/morphldm.
设计针对3D结构脑MRI的生成模型,以合成形态上合理且具有特定属性(例如年龄、性别、疾病状态)的样本是一个活跃的研究领域。现有基于GAN或扩散模型等框架的方法直接合成图像,这可能限制了它们捕捉复杂形态细节的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于最新潜在扩散模型(LDM)的3D脑MRI生成方法,称为MorphLDM。它通过应用合成变形场到一个学习到的模板来生成新的图像。我们的编码器输出的潜在嵌入来源于图像和学习到的模板本身,这个模板是模板解码器的输出;这个潜在嵌入被传递给变形场解码器,其输出应用于学习到的模板。通过最小化原始图像和变形模板之间的注册损失,关于编码器和两个解码器的损失被最小化。经验上,我们的方法在图像多样性、对输入条件的遵循性以及基于体素的形态测量等指标上的表现都超过了基准生成模型。我们的代码可在https://github.com/alanqrwang/morphldm上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Provisional Acceptance at MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的3D脑MRI生成方法MorphLDM,通过应用合成变形场于学习模板,生成新的图像。该方法使用不同于典型LDM的重建式自编码器,其编码器输出的是来自图像和学习模板的潜在嵌入,该潜在嵌入传递给变形场解码器,其输出应用于学习模板。通过最小化原始图像与变形模板之间的注册损失,关于编码器和两个解码器的评估指标,该方法在图像多样性、符合输入条件以及体素形态测量方面优于基准生成模型。相关代码可在链接找到。
Key Takeaways
- 研究设计生成模型以合成具有形态合理性和特定属性(如年龄、性别、疾病状态)的3D结构脑MRI样本。
- 当前基于GAN或扩散模型的方法可能无法捕捉复杂的形态细节。
- 提出了一种基于最新潜在扩散模型(LDM)的3D脑MRI生成方法,名为MorphLDM。
- MorphLDM通过应用合成变形场到学习模板生成新图像。
- 该方法使用不同于典型的LDM的编码器结构,结合了图像和学习模板的潜在嵌入。
- 通过最小化原始图像和变形模板之间的注册损失来优化模型性能。
- 该方法在图像多样性、遵循输入条件以及基于体素的形态测量方面超过了基准生成模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

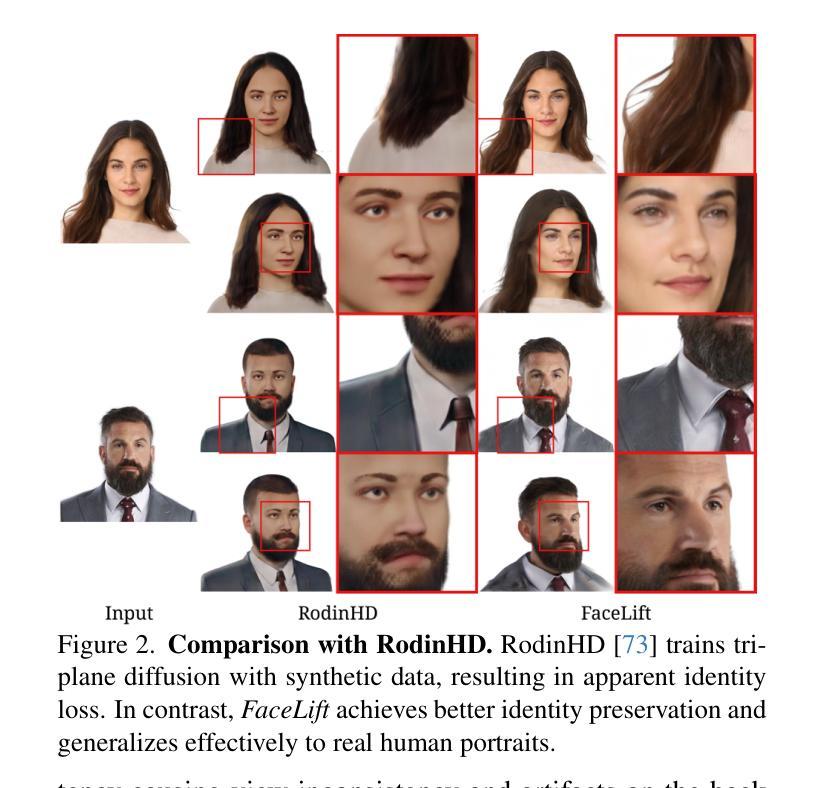
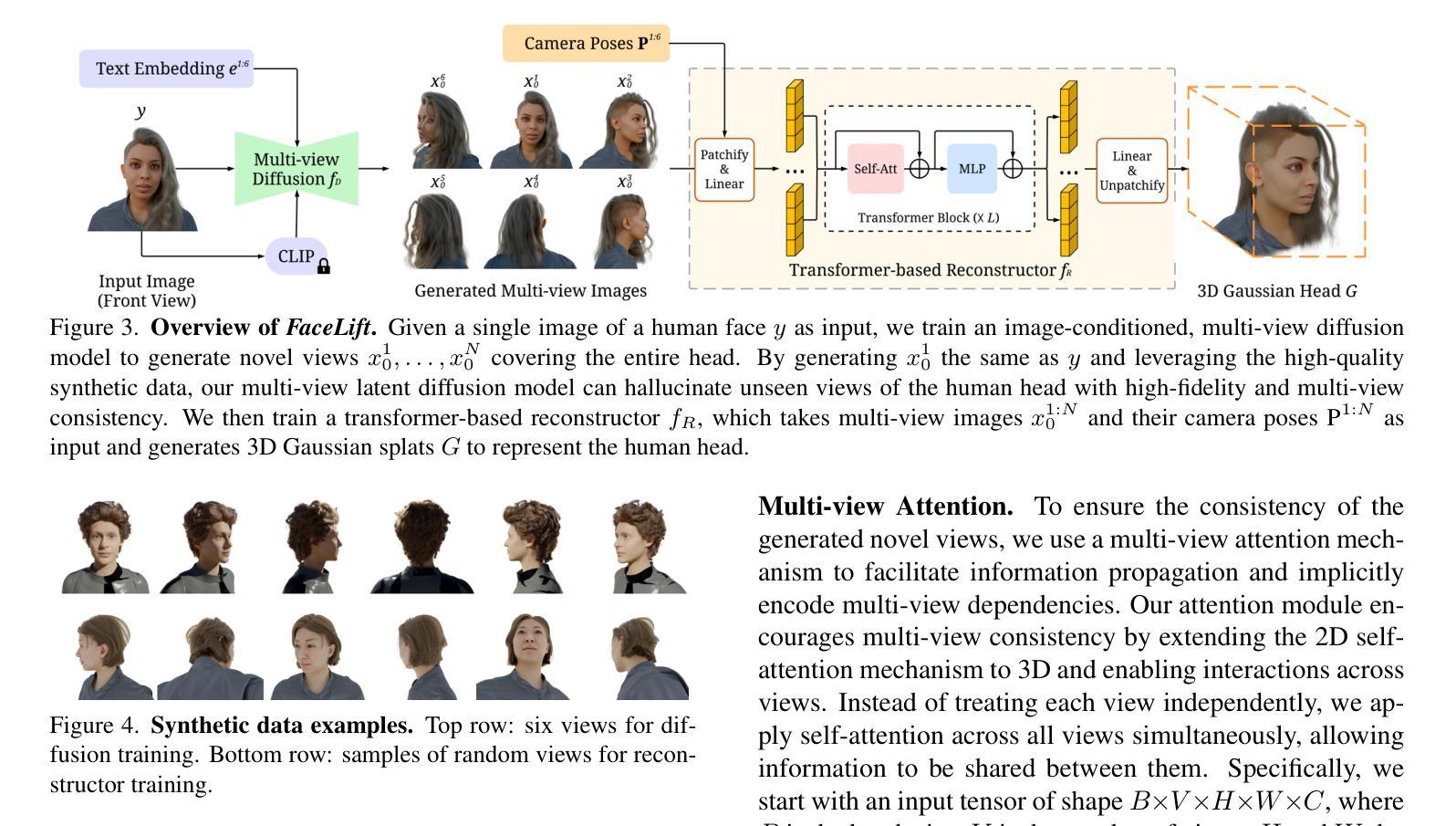
FaceLift: Learning Generalizable Single Image 3D Face Reconstruction from Synthetic Heads
Authors:Weijie Lyu, Yi Zhou, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Zhixin Shu
We present FaceLift, a novel feed-forward approach for generalizable high-quality 360-degree 3D head reconstruction from a single image. Our pipeline first employs a multi-view latent diffusion model to generate consistent side and back views from a single facial input, which then feeds into a transformer-based reconstructor that produces a comprehensive 3D Gaussian splats representation. Previous methods for monocular 3D face reconstruction often lack full view coverage or view consistency due to insufficient multi-view supervision. We address this by creating a high-quality synthetic head dataset that enables consistent supervision across viewpoints. To bridge the domain gap between synthetic training data and real-world images, we propose a simple yet effective technique that ensures the view generation process maintains fidelity to the input by learning to reconstruct the input image alongside the view generation. Despite being trained exclusively on synthetic data, our method demonstrates remarkable generalization to real-world images. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we show that FaceLift outperforms state-of-the-art 3D face reconstruction methods on identity preservation, detail recovery, and rendering quality.
我们提出了FaceLift,这是一种新型的前馈方法,用于从单一图像进行可泛化的高质量360度3D头部重建。我们的管道首先采用多视角潜在扩散模型,从单个面部输入生成一致的侧面和背面视图,然后将其输入基于变压器的重建器,生成全面的3D高斯splat表示。以前的方法在单目3D面部重建中常常缺乏全视角覆盖或视角一致性,因为缺乏足够的多视角监督。我们通过创建高质量合成头部数据集来解决这个问题,该数据集可以在不同视角进行一致监督。为了缩小合成训练数据和真实世界图像之间的领域差距,我们提出了一种简单有效的技术,确保视图生成过程通过学习与视图生成一起重建输入图像来保持对输入的保真度。尽管我们的方法仅在合成数据上进行训练,但在真实世界图像上却表现出了惊人的泛化能力。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,我们证明了FaceLift在身份保留、细节恢复和渲染质量方面优于最新的3D面部重建方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Camera-Ready Version. Project Page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift
Summary
FaceLift是一种新型前馈方法,用于从单一图像实现可泛化的高质量360度3D头部重建。它通过多视角潜在扩散模型生成一致的侧面和背面视角,然后利用基于变压器的重建器生成全面的3D高斯splat表示。该方法解决了因缺乏多视角监督而导致的前视图覆盖不足或视角不一致的问题。通过创建高质量合成头部数据集实现跨视角的一致监督。同时提出简单有效的技术,确保视图生成过程保持对输入的忠实度,并在视图生成的同时进行重建输入图像的学习。尽管仅在合成数据上进行训练,但该方法在真实图像上表现出卓越的泛化能力,并在身份保留、细节恢复和渲染质量方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- FaceLift是一种用于从单一图像进行3D头部重建的新方法。
- 通过多视角潜在扩散模型和基于变压器的重建器生成全面且高质量的3D头部表示。
- 解决了因缺乏多视角监督而导致的前视图覆盖不足或视角不一致的问题。
- 利用合成头部数据集进行训练,实现了跨视角的一致监督。
- 提出了一种简单有效的技术,确保视图生成过程忠实于输入。
- 方法在真实图像上具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图