⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
Learning Potential Energy Surfaces of Hydrogen Atom Transfer Reactions in Peptides
Authors:Marlen Neubert, Patrick Reiser, Frauke Gräter, Pascal Friederich
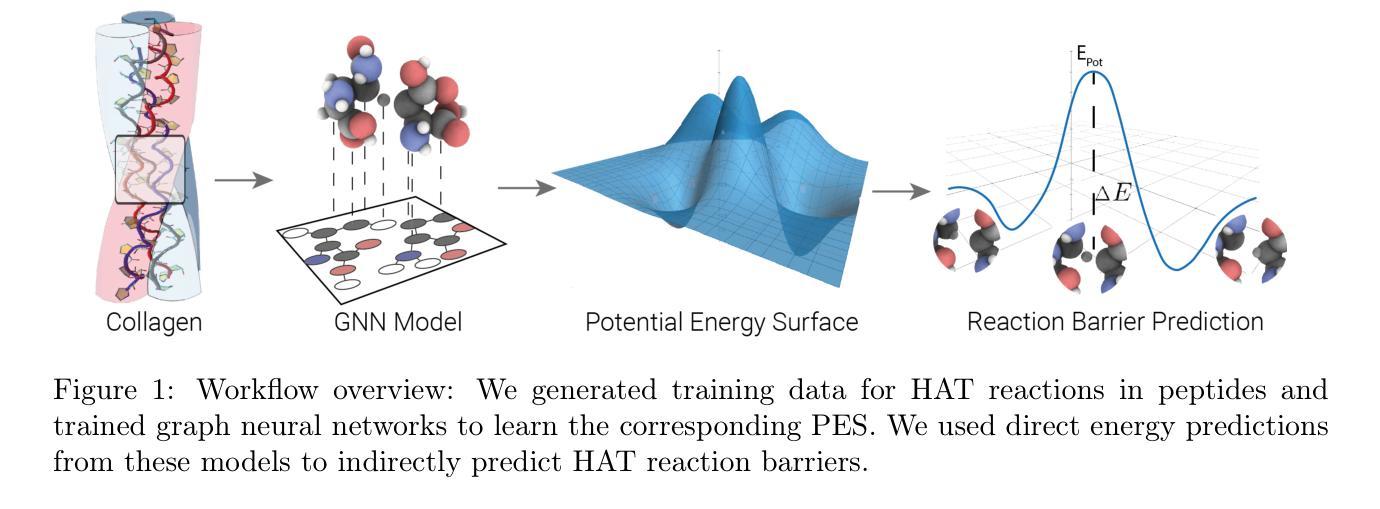
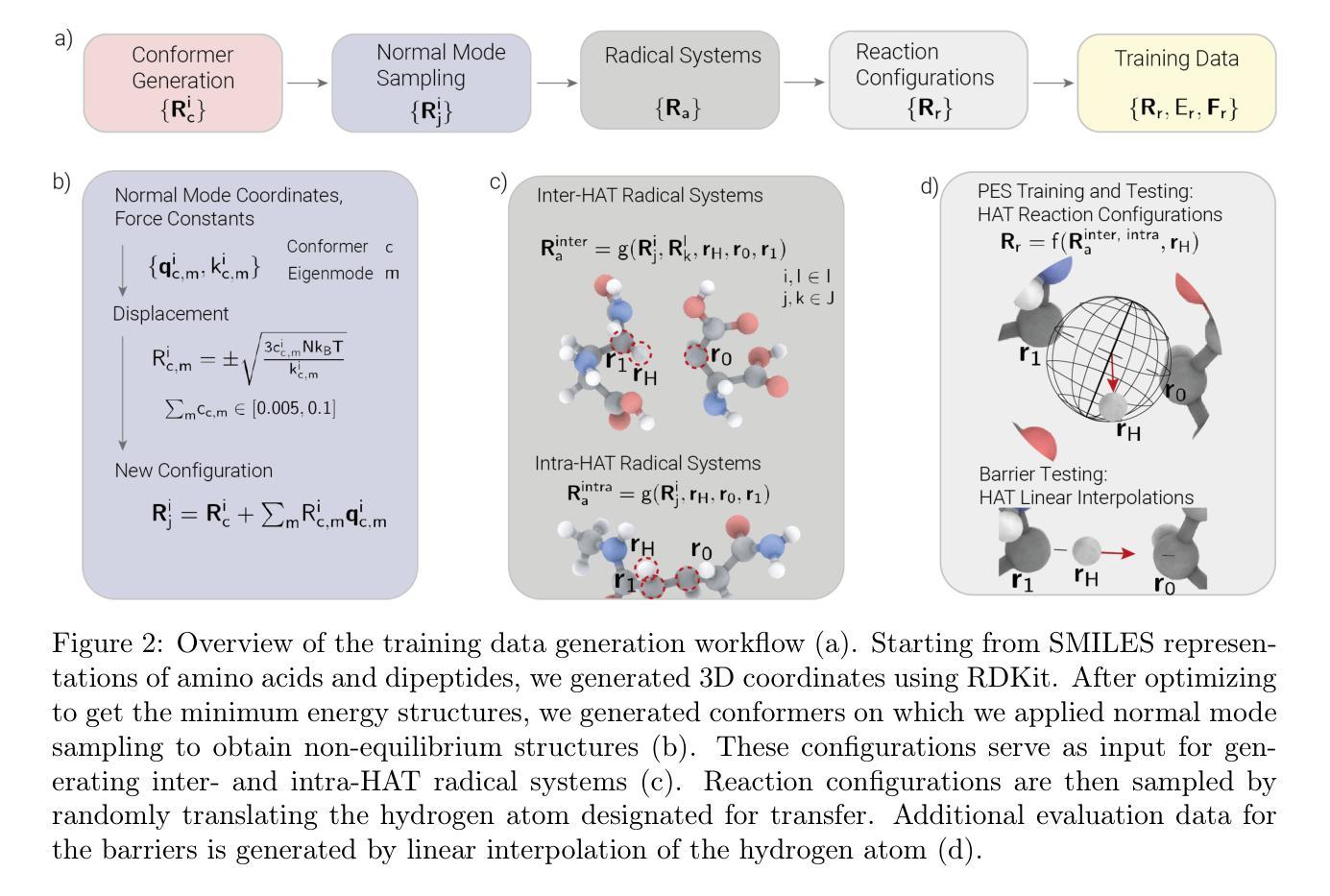
Hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) reactions are essential in many biological processes, such as radical migration in damaged proteins, but their mechanistic pathways remain incompletely understood. Simulating HAT is challenging due to the need for quantum chemical accuracy at biologically relevant scales; thus, neither classical force fields nor DFT-based molecular dynamics are applicable. Machine-learned potentials offer an alternative, able to learn potential energy surfaces (PESs) with near-quantum accuracy. However, training these models to generalize across diverse HAT configurations, especially at radical positions in proteins, requires tailored data generation and careful model selection. Here, we systematically generate HAT configurations in peptides to build large datasets using semiempirical methods and DFT. We benchmark three graph neural network architectures (SchNet, Allegro, and MACE) on their ability to learn HAT PESs and indirectly predict reaction barriers from energy predictions. MACE consistently outperforms the others in energy, force, and barrier prediction, achieving a mean absolute error of 1.13 kcal/mol on out-of-distribution DFT barrier predictions. This accuracy enables integration of ML potentials into large-scale collagen simulations to compute reaction rates from predicted barriers, advancing mechanistic understanding of HAT and radical migration in peptides. We analyze scaling laws, model transferability, and cost-performance trade-offs, and outline strategies for improvement by combining ML potentials with transition state search algorithms and active learning. Our approach is generalizable to other biomolecular systems, enabling quantum-accurate simulations of chemical reactivity in complex environments.
氢原子转移(HAT)反应在许多生物过程中至关重要,例如受损蛋白质中的自由基迁移,但其机制途径仍不完全清楚。由于需要在生物相关规模上达到量子化学的准确性,模拟HAT是一项挑战;因此,基于经典力场或DFT的分子动力学都不适用。机器学习势能提供了一种替代方案,能够以接近量子精度的精度学习势能面(PES)。然而,要训练这些模型以在多样的HAT配置中通用化,特别是在蛋白质中的自由基位置,需要定制的数据生成和谨慎的模型选择。在这里,我们使用半经验方法和DFT在肽中系统地生成HAT配置以构建大型数据集。我们基准测试了三种图神经网络架构(SchNet、Allegro和MACE)在学习HAT PESs的能力以及根据能量预测间接预测反应壁垒的能力。MACE在能量、力和壁垒预测方面表现始终优于其他方法,在非分布DFT壁垒预测上的平均绝对误差为1.13kcal/mol。这种准确性使得可以将ML潜力整合到大规模胶原蛋白模拟中,从预测的障碍计算反应速率,从而推进对肽中HAT和自由基迁移的机制理解。我们分析了规模定律、模型可移植性和成本性能权衡,并概述了通过将ML潜力与过渡态搜索算法和主动学习相结合来改善的策略。我们的方法是可推广到其他生物分子系统,能够实现复杂环境中化学反应的量子精确模拟。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, and 4 tables (references and SI included)
Summary
本文研究了氢原子转移(HAT)反应在生物过程中的重要作用,如受损蛋白质中的自由基迁移。由于需要在生物相关尺度上进行量子化学精确模拟,传统的模拟方法如经典力场和基于DFT的分子动力学并不适用。本研究采用机器学习势能来模拟HAT反应,通过系统生成肽中的HAT构型来构建大型数据集,并对比了三种图神经网络架构(SchNet、Allegro和MACE)在模拟HAT势能面和预测反应壁垒方面的性能。结果显示,MACE在能量、力和壁垒预测方面表现最佳,在分布外的DFT壁垒预测中的平均绝对误差为1.13kcal/mol。这一准确性使得可以将ML势能整合到大规模胶原模拟中,从预测的壁垒计算反应速率,从而促进对HAT和肽中自由基迁移机理的理解。
Key Takeaways
- 氢原子转移(HAT)反应是生物过程中重要的反应类型,如蛋白质中的自由基迁移。
- 传统模拟方法在生物相关尺度上难以达到量子化学精度,因此机器学习势能成为一种替代方案。
- 通过系统生成肽中的HAT构型构建了大型数据集,用于训练机器学习模型。
- 对比了三种图神经网络架构在模拟HAT反应方面的性能,发现MACE表现最佳。
- MACE模型能够准确预测反应壁垒,促进了对HAT反应机理的理解。
- 将ML势能整合到大规模模拟中,可以计算反应速率,进一步了解生物过程中的化学反应性。
点此查看论文截图

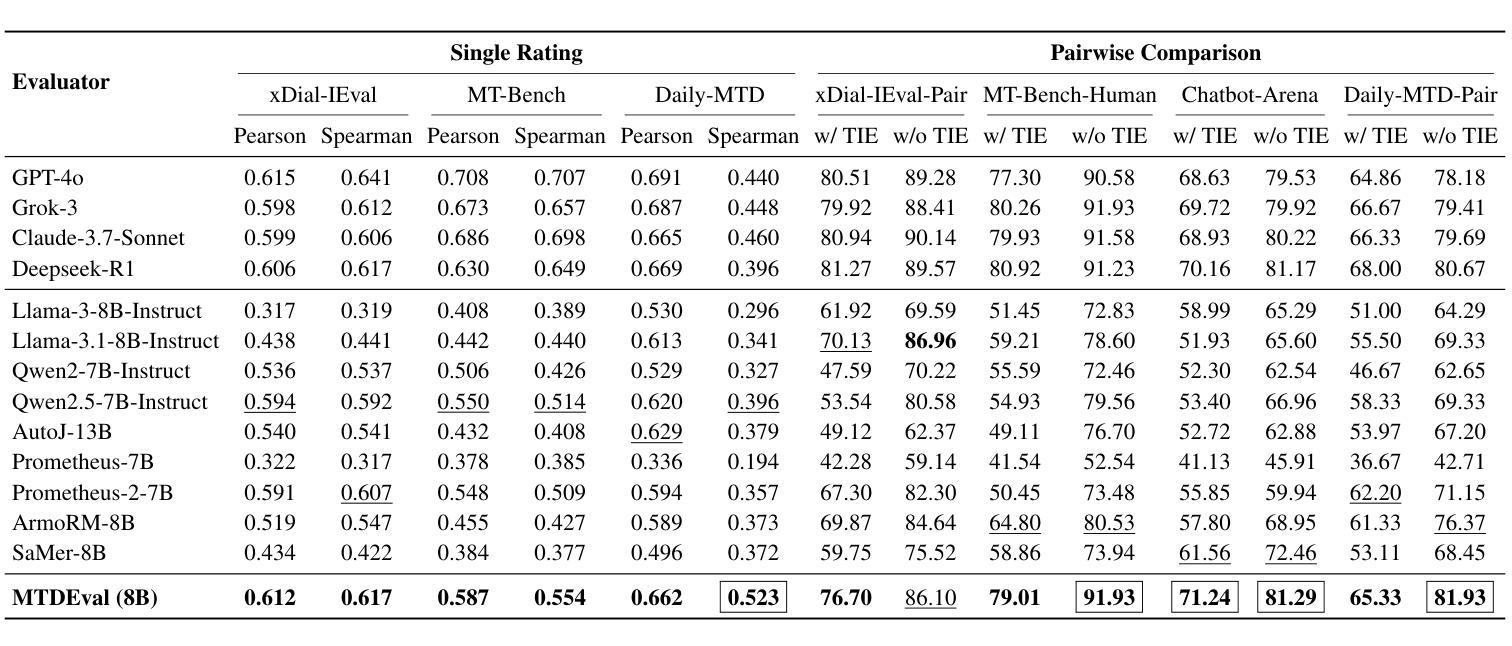
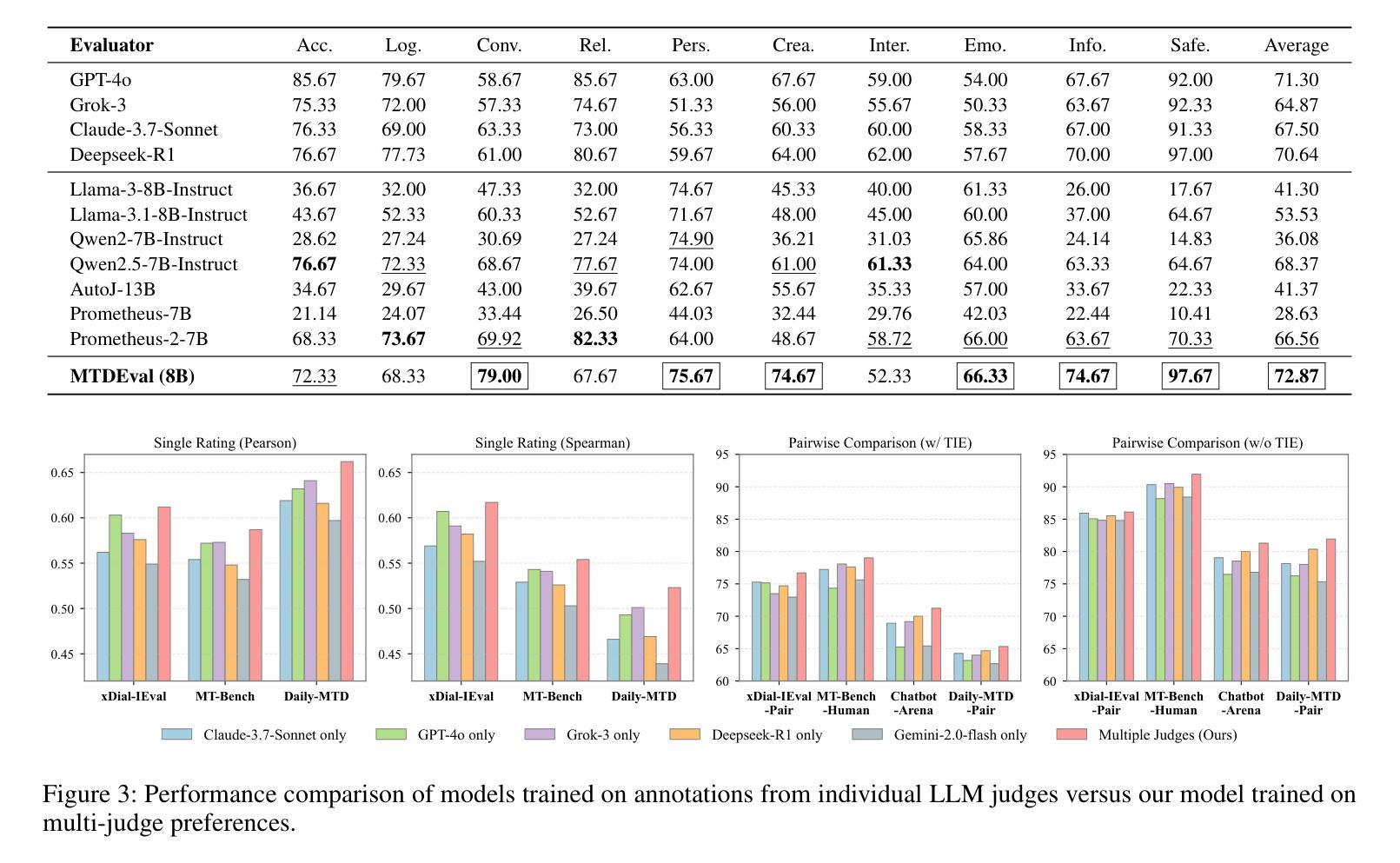
Learning an Efficient Multi-Turn Dialogue Evaluator from Multiple Judges
Authors:Yuqi Tang, Kehua Feng, Yunfeng Wang, Zhiwen Chen, Chengfei Lv, Gang Yu, Qiang Zhang, Keyan Ding
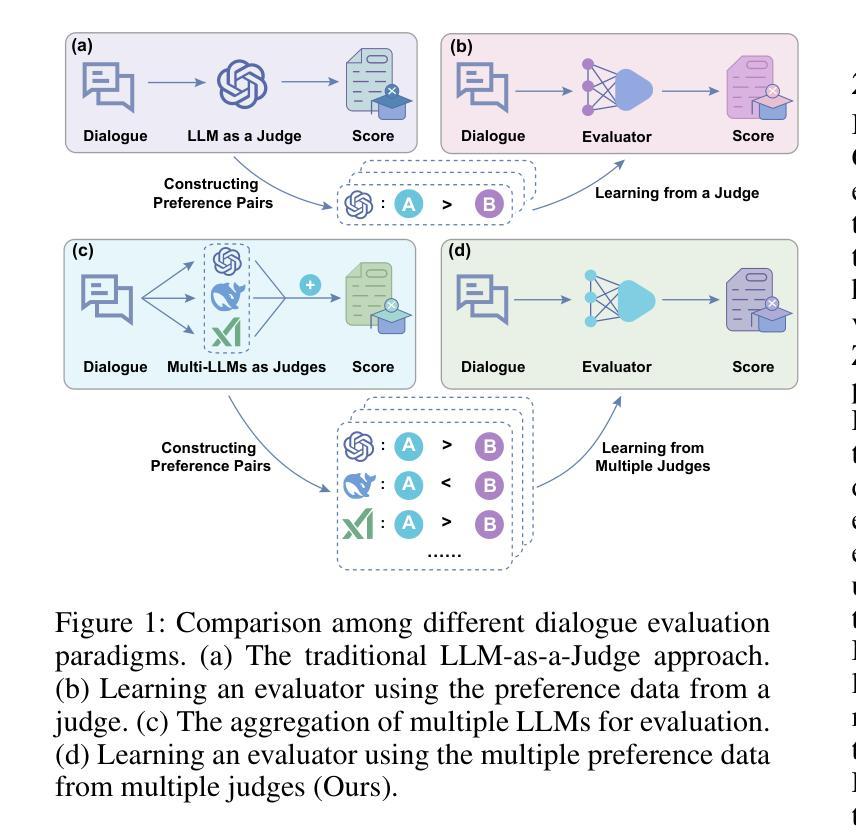
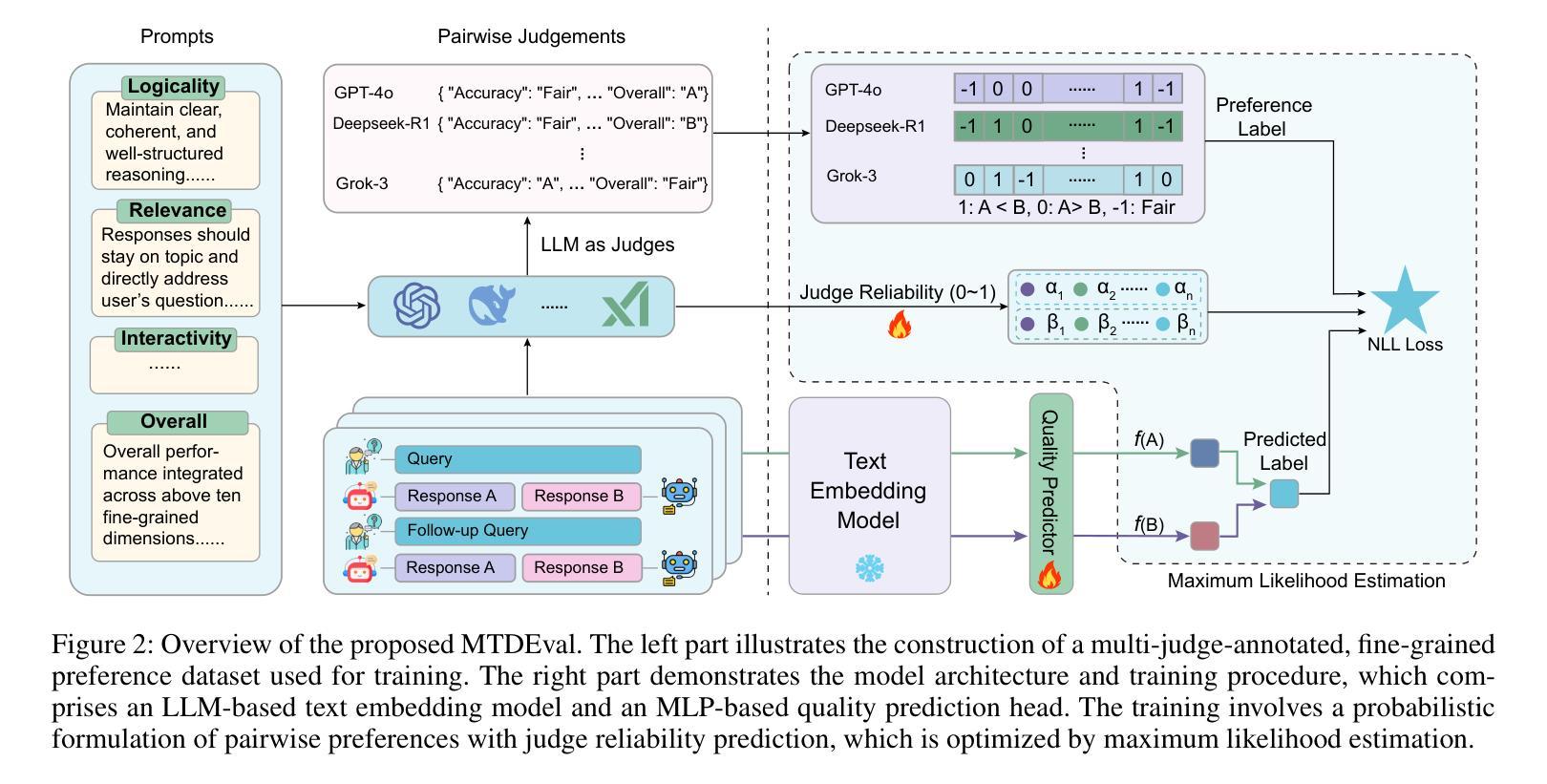
Evaluating the conversational abilities of large language models (LLMs) remains a challenging task. Current mainstream approaches primarily rely on the ``LLM-as-a-judge” paradigm, where an LLM is prompted to serve as an evaluator to assess dialogue quality. However, such methods often suffer from various biases, which undermine the reliability and consistency of the evaluation results. To mitigate these biases, recent methods employ multiple LLMs as judges and aggregate their judgments to select the optimal assessment. Although effective, this multi-judge approach incurs significant computational overhead during inference. In this paper, we propose an efficient multi-turn dialogue evaluator that captures the collective wisdom of multiple LLM judges by aggregating their preference knowledge into a single model. Our approach preserves the advantages of diverse multi-judge feedback while drastically reducing the evaluation cost, enabling fast and flexible dialogue quality assessment. Extensive experiments on seven single rating and pairwise comparison dialogue evaluation benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines across diverse scenarios, showcasing its efficiency and robustness.
评估大型语言模型(LLM)的对话能力仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。当前的主流方法主要依赖于“LLM作为评判员”的模式,即提示LLM作为评估员来评估对话质量。然而,这些方法常常受到各种偏见的影响,从而破坏了评估结果的可靠性和一致性。为了减轻这些偏见,最近的方法采用多个LLM作为评委,并汇总他们的判断来选择最佳评估结果。尽管这种方法有效,但在推理过程中会产生大量的计算开销。在本文中,我们提出了一种高效的多轮对话评估器,它通过将一个模型汇总多个LLM评委的偏好知识来捕捉集体智慧。我们的方法保留了多元评委反馈的优势,同时大大降低了评估成本,实现了快速灵活的对画质量评估。在七个单一评分和成对比较对话评估基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在多种场景下都优于现有基线,展示了其高效性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 2 pages, under review at AAAI 2026
Summary
本论文针对大型语言模型(LLM)的对话能力评估提出了挑战。当前主流方法主要依赖于“LLM作为评判者”的模式,但这种方法存在偏见问题,影响评估结果的可靠性和一致性。为缓解这一问题,本文提出一种高效的多轮对话评估器,通过聚合多个LLM的判断知识到一个单一模型中,捕捉集体智慧,既保留了多元评判的优势,又大幅降低了评估成本,实现了快速灵活的对对话质量进行评估。
Key Takeaways
- 当前评估LLM对话能力的主流方法存在偏见问题。
- 偏见问题影响了评估结果的可靠性和一致性。
- 为缓解偏见问题,可采用多LLM作为评判者并聚合他们的判断。
- 聚合判断知识到一个单一模型中可捕捉集体智慧。
- 该方法实现了快速灵活的对对话质量进行评估。
- 相较于现有基准测试,该方法在多个场景中的表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图

Measurement of production branching ratio after muon nuclear capture reaction of Al and Si isotopes
Authors:R. Mizuno, M. Niikura, T. Y. Saito, T. Matsuzaki, S. Abe, H. Fukuda, M. Hashimoto, A. Hillier, K. Ishida, N. Kawamura, S. Kawase, T. Kawata, K. Kitafuji, F. Minato, M. Oishi, A. Sato, K. Shimomura, P. Strasser, S. Takeshita, D. Tomono, Y. Watanabe
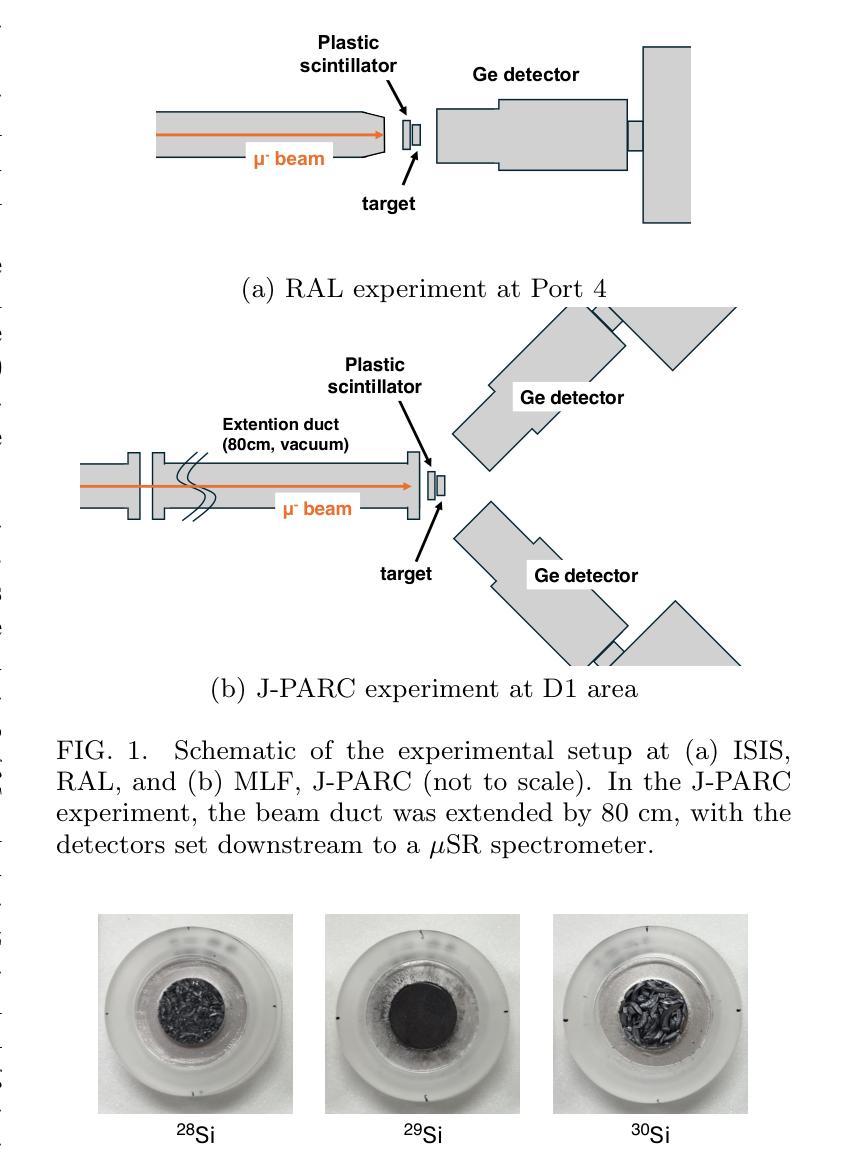
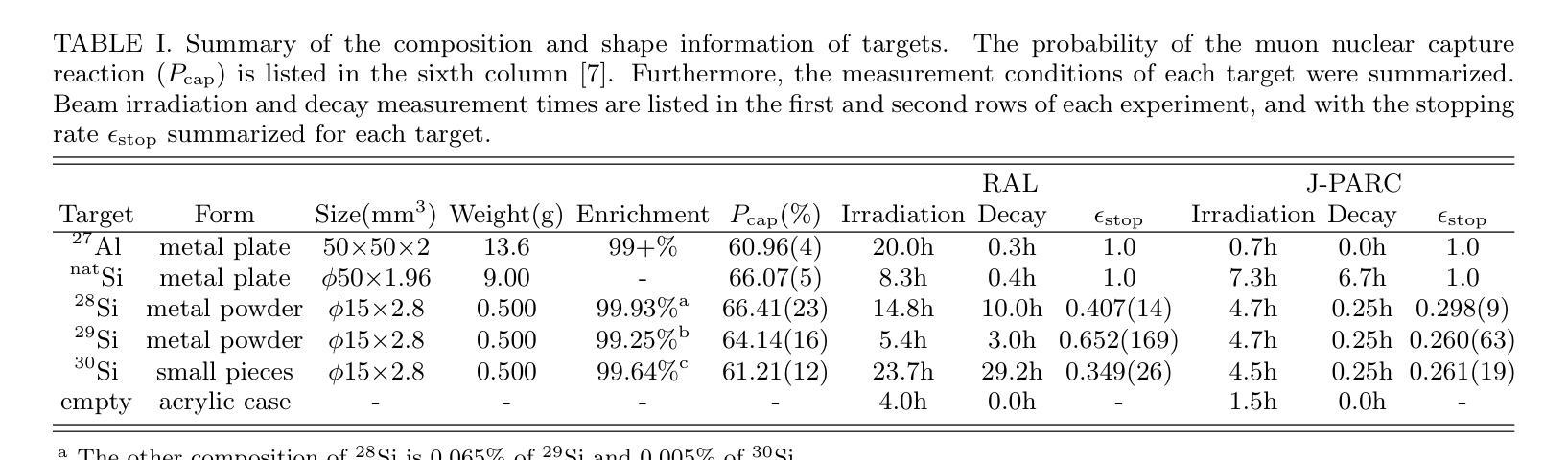
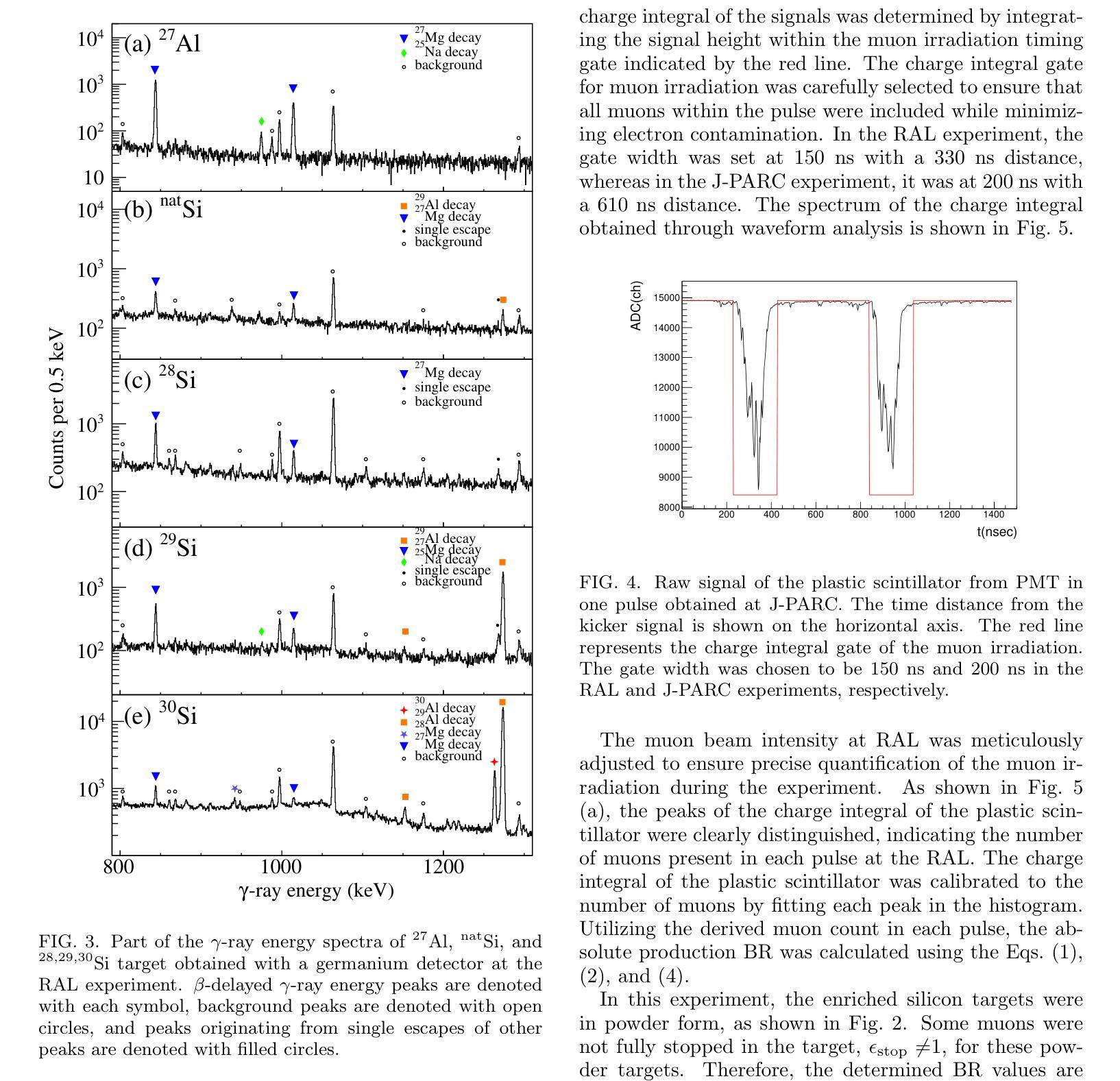
Background: Muon nuclear capture is a reaction between a muon and a proton inside a nucleus through weak interactions. This reaction results in the formation of an excited nucleus, which subsequently de-excites by emitting several particles. Examination of the excited state allows for an investigation of the properties of nuclear excitation and particle emission in highly excited nuclei. Purpose: This study investigates muon nuclear capture of 27Al and 28,29,30Si, focusing on determining the absolute production branching ratio (BR) following muon nuclear capture and subsequent particle emissions. By measuring the absolute production BR, we can collect valuable information on the excitation energy distribution of muon nuclear capture. Methods: Measurements were conducted using the in-beam activation method at two pulsed muon facilities: RIKEN-RAL beamline and MLF at J-PARC. Absolute BRs were determined by measuring the number of muons irradiating the target using a plastic scintillator and the beta-delayed gamma-rays emitted from the produced nuclei using germanium detectors. Results: The absolute production branching ratios of muon nuclear capture on 27Al and 28,29,30Si were obtained with the highest accuracy to date. Predominant neutron emissions, even-odd atomic number dependence of particle emission probabilities, and influence of the neutron excess were observed. These results were compared with previous measurements and theoretical models and discussed regarding the excitation energy distribution, particle emission mechanism, and nuclear properties, such as resonance in the isovector transition. Conclusion: This study emphasizes the importance of considering nuclear structure effects, even-odd effects of proton and neutron numbers, neutron excess, nucleon pairing effect, and particle emission mechanisms, in the context of the muon nuclear capture reaction.
背景:μ子核捕获是μ子和核内质子通过弱相互作用发生的反应。该反应导致形成激发态核,随后通过发射多个粒子来退激。对激发态的研究允许对高度激发核的核激发和粒子发射特性进行研究。目的:本研究调查了μ子在核上的捕获情况,聚焦于测定μ子核捕获以及后续粒子发射后的绝对生产分支比(BR)。通过测量绝对生产分支比,我们可以收集有关μ子核捕获的激发能分布的有价值的信息。方法:实验是在两个脉冲μ子设施(RIKEN-RAL光束线和J-PARC的MLF)上进行的,使用入射束活化法测量。通过使用塑料闪烁体测量照射目标的μ子数量并使用锗探测器测量产生的核发出的延迟β射线γ射线来确定绝对分支比。结果:获得了迄今为止最高精度的μ子在铝和硅上的核捕获的绝对生产分支比。观察到主要的中子发射、粒子发射概率的原子序数的奇偶依赖性以及中子过剩的影响。这些结果与之前的测量和理论模型进行了比较和讨论,涉及激发能分布、粒子发射机制和核属性,例如等矢量跃迁中的共振等。结论:本研究强调了在考虑μ子核捕获反应时,需要考虑核结构效应、质子和中子数量的奇偶效应、中子过剩、核子配对效应和粒子发射机制的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
此研究利用RIKEN-RAL和J-PARC的MLF脉冲μ子设施,通过束内活化法测量了μ子在27Al和28、29、30Si上的核捕获的绝对生产分支比。获得迄今为止最准确的结果,观察到主要的中子发射、粒子发射概率的偶奇原子序数依赖以及中子过剩的影响。对激发能分布、粒子发射机制和核性质如等矢量跃迁的共振进行了讨论。
Key Takeaways
- 研究背景介绍了μ子核捕获反应及其结果,为后续分析提供了基础。
- 目的在于通过测量μ子在27Al和28、29、30Si上的核捕获的绝对生产分支比,了解高度激发态核的激发能量分布信息。
- 采用RIKEN-RAL和J-PARC的MLF脉冲μ子设施的束内活化法进行了测量。
- 获得迄今为止最准确的绝对生产分支比结果。
- 观察到了主要的中子发射现象,以及粒子发射概率与原子序数的偶奇依赖性,以及中子过剩的影响。
- 结果与之前的测量和理论模型进行了比较,讨论了激发能量分布、粒子发射机制和核性质。
点此查看论文截图