⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
Adacc: Adaptive Compression and Activation Checkpointing for LLM Memory Management
Authors:Ping Chen, Zhuohong Deng, Ping Li, Shuibing He, Hongzi Zhu, Yi Zheng, Zhefeng Wang, Baoxing Huai, Minyi Guo
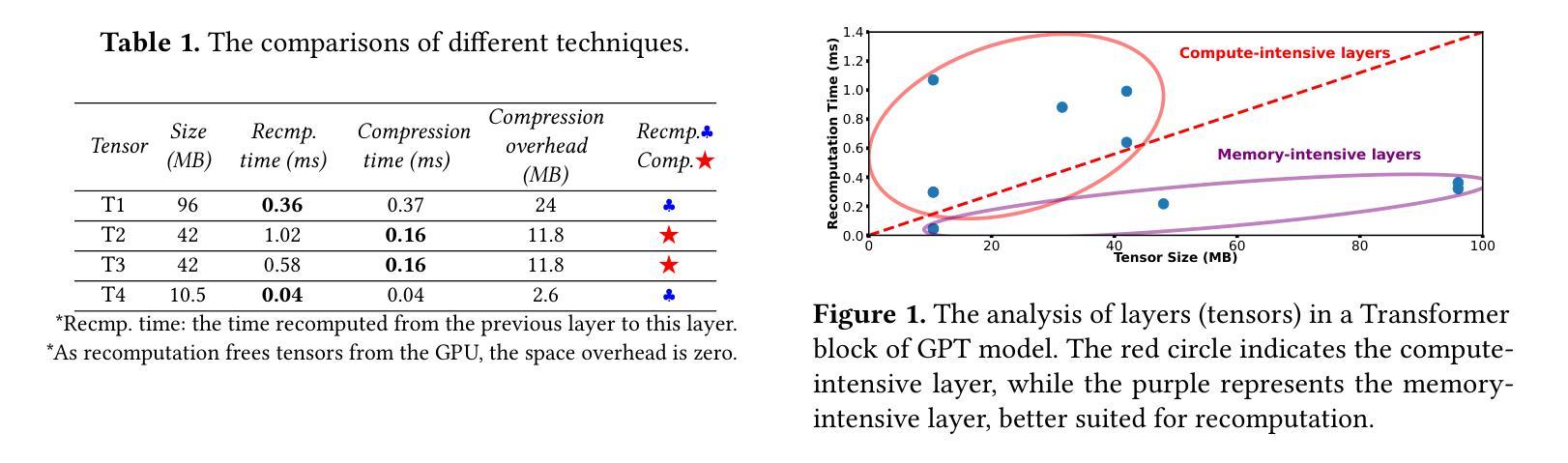
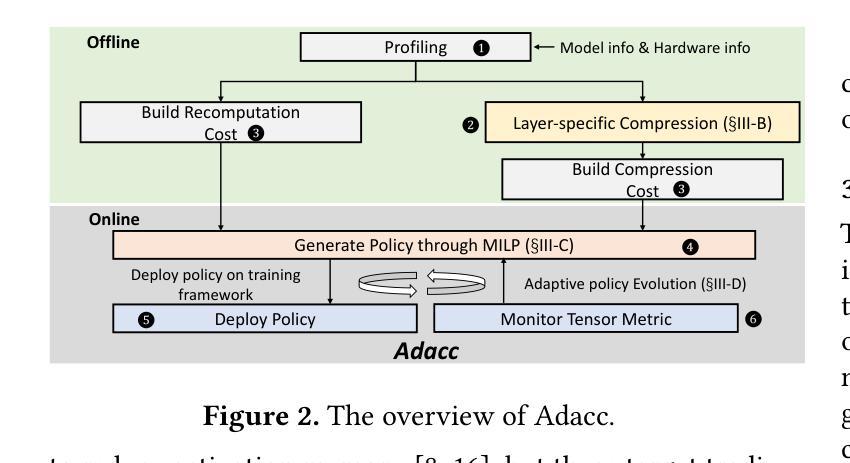
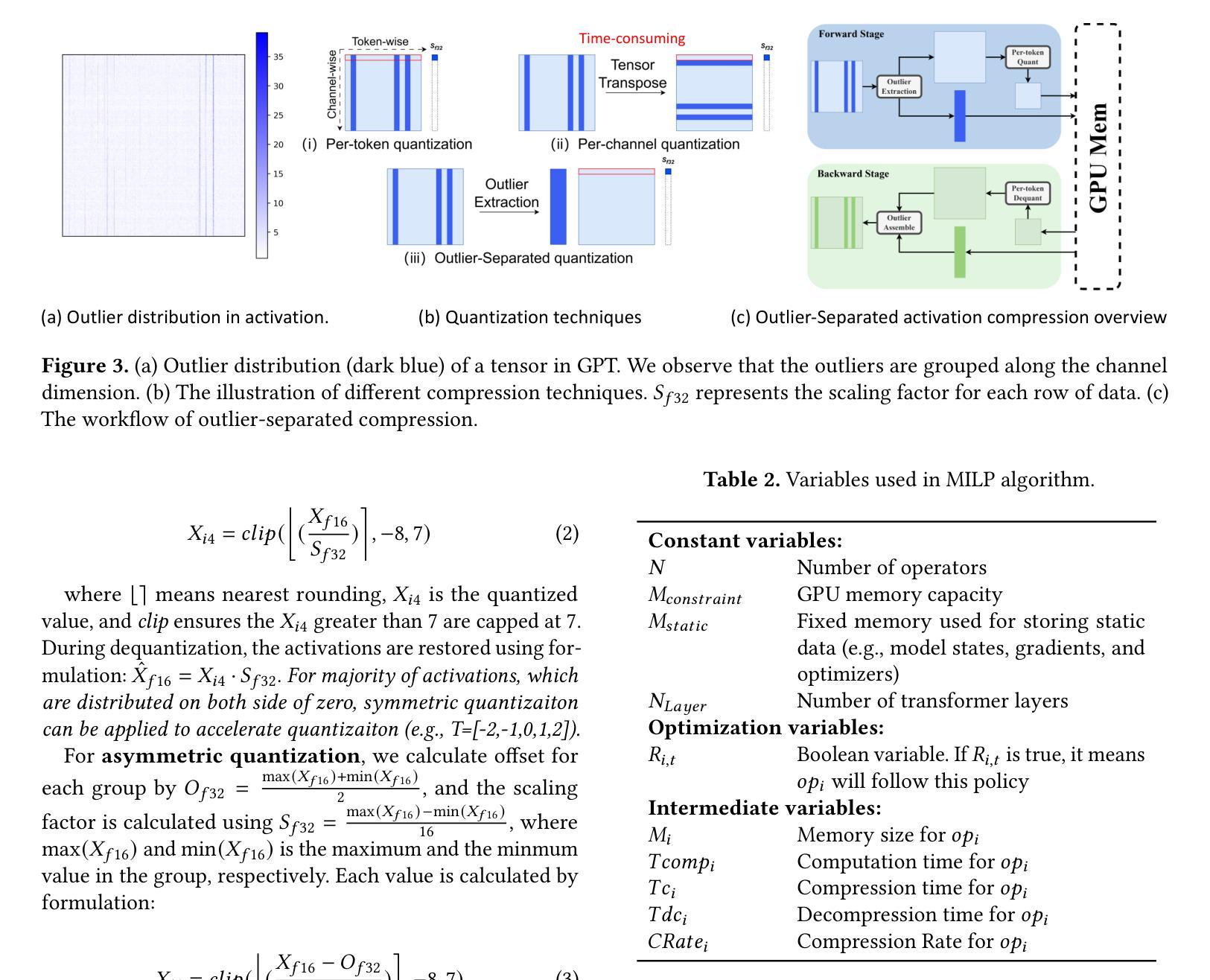
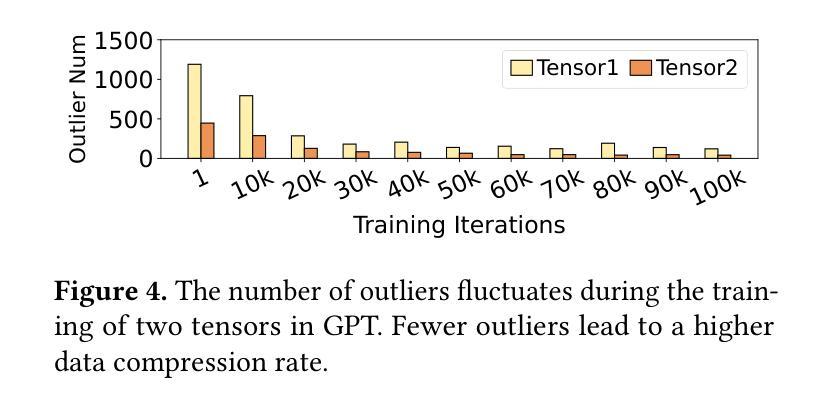
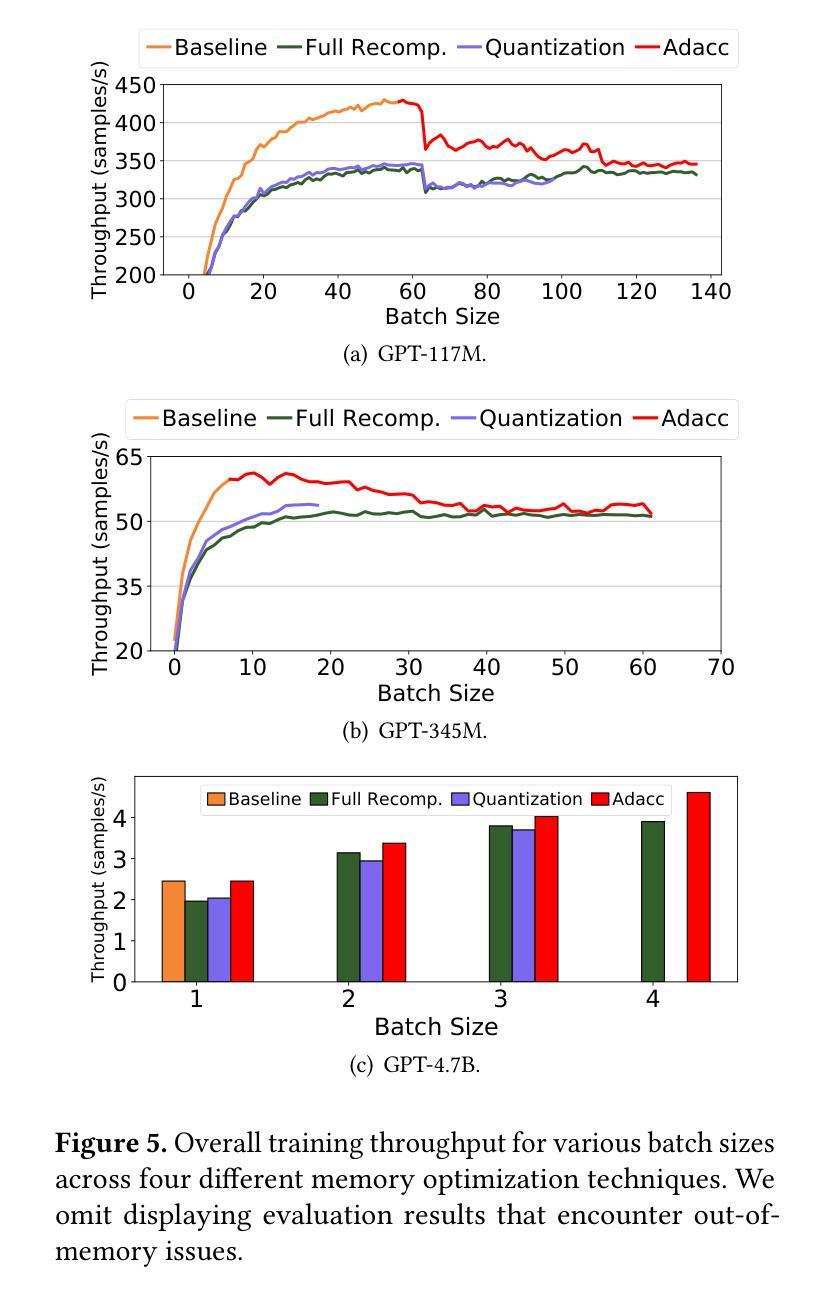
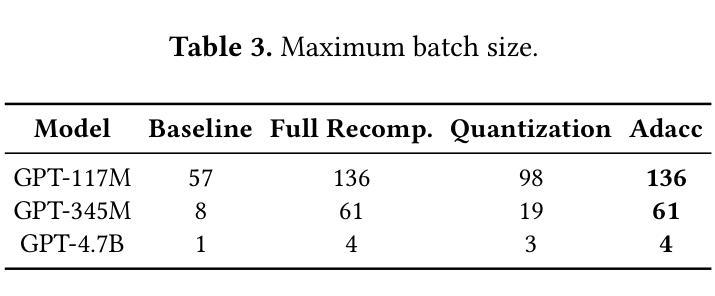
Training large language models often employs recomputation to alleviate memory pressure, which can introduce up to 30% overhead in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose Adacc, a novel memory management framework that combines adaptive compression and activation checkpointing to reduce the GPU memory footprint. It comprises three modules: (1) We design layer-specific compression algorithms that account for outliers in LLM tensors, instead of directly quantizing floats from FP16 to INT4, to ensure model accuracy. (2) We propose an optimal scheduling policy that employs MILP to determine the best memory optimization for each tensor. (3) To accommodate changes in training tensors, we introduce an adaptive policy evolution mechanism that adjusts the policy during training to enhance throughput. Experimental results show that Adacc can accelerate the LLM training by 1.01x to 1.37x compared to state-of-the-art frameworks, while maintaining comparable model accuracy to the Baseline.
训练大型语言模型时,通常采用重新计算来缓解内存压力,这在现实场景中可能会引入高达30%的开销。在本文中,我们提出了Adacc,这是一种新型内存管理框架,它通过自适应压缩和激活检查点技术来减少GPU内存占用。它包含三个模块:(1)我们设计了针对LLM张量异常值的特定层压缩算法,而不是直接量化FP16到INT4的浮点数,以确保模型精度。(2)我们提出了一种最佳调度策略,采用混合整数线性规划来确定每个张量的最佳内存优化。(3)为了应对训练张量的变化,我们引入了一种自适应策略演化机制,在训练过程中调整策略以提高吞吐量。实验结果表明,与最新框架相比,Adacc可以加速LLM的训练速度,达到1.01x至1.37x,同时保持与基线相当的模型精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Adacc的新型内存管理框架,用于减少大型语言模型训练时的GPU内存占用。该框架结合了自适应压缩和激活检查点技术,通过设计层特定的压缩算法、采用最优调度策略以及自适应策略进化机制,能够在保证模型准确性的同时,加速大型语言模型的训练。
Key Takeaways
- Adacc框架通过结合自适应压缩和激活检查点技术,旨在减少大型语言模型训练时的GPU内存占用。
- 提出了层特定的压缩算法,考虑到了大型语言模型张量中的异常值,以确保模型的准确性。
- 使用混合整数线性规划(MILP)来确定每个张量的最佳内存优化方案。
- 引入了一种自适应策略进化机制,以适应训练张量的变化,提高训练过程中的吞吐量。
- 实验结果表明,Adacc框架能够加速大型语言模型的训练,最高达到1.37倍,同时保持与基线模型相当的准确性。
- Adacc框架通过优化内存管理,为大型语言模型的训练提供了更高的效率和更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

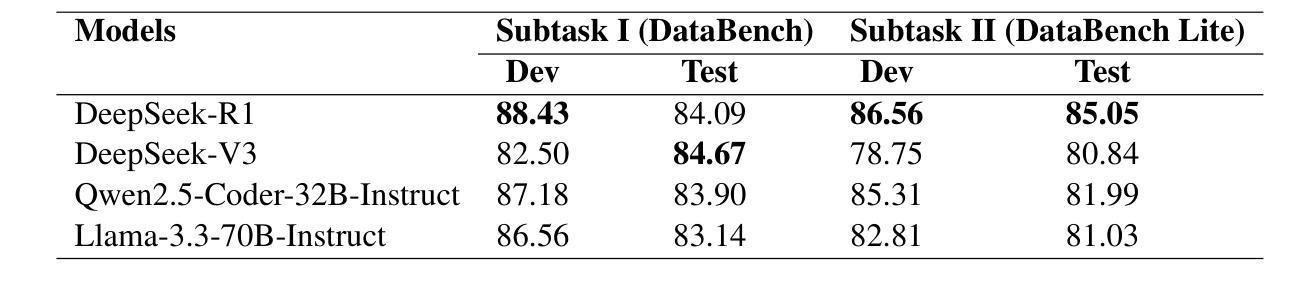
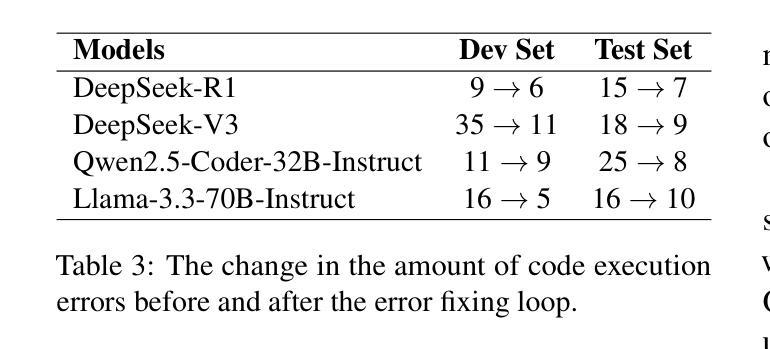
ITUNLP at SemEval-2025 Task 8: Question-Answering over Tabular Data: A Zero-Shot Approach using LLM-Driven Code Generation
Authors:Atakan Site, Emre Hakan Erdemir, Gülşen Eryiğit
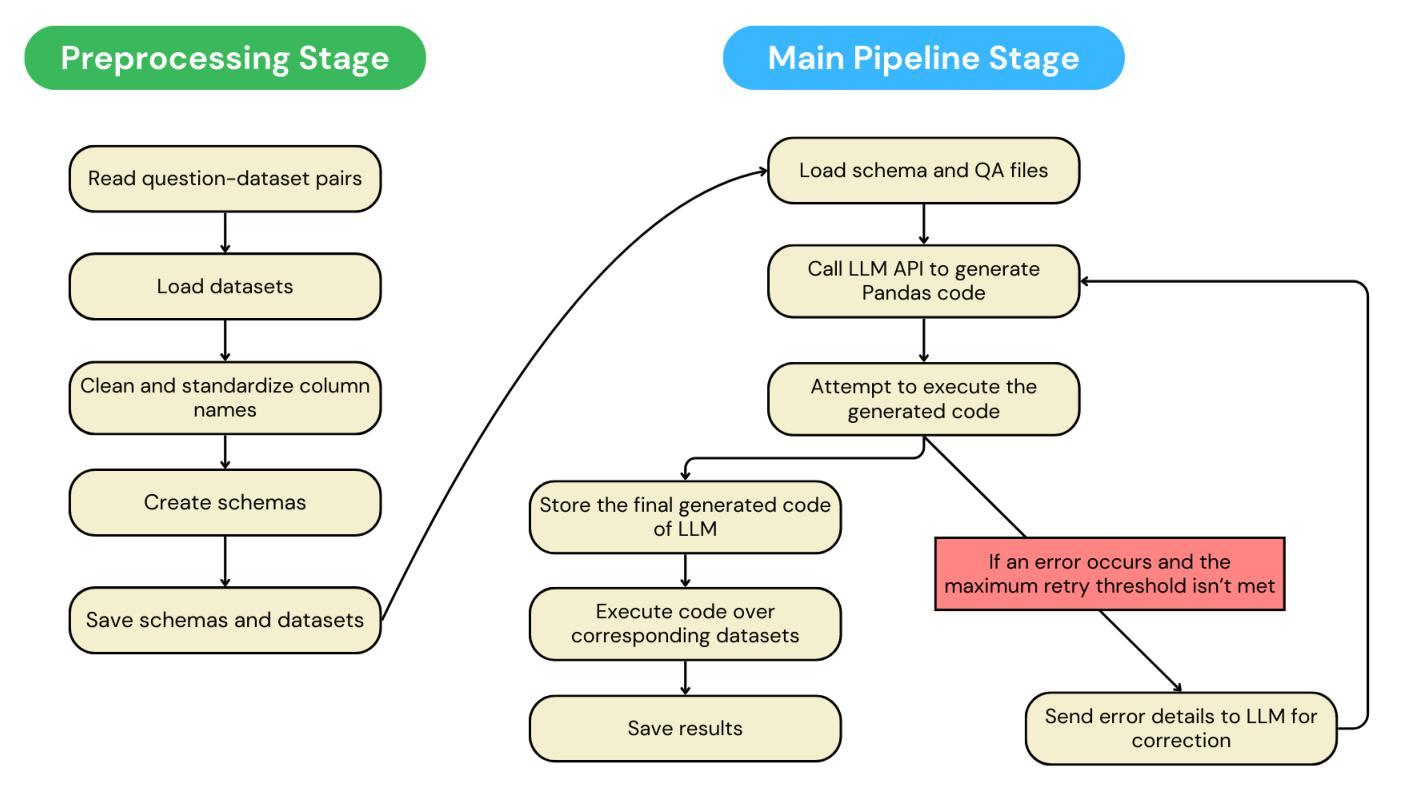
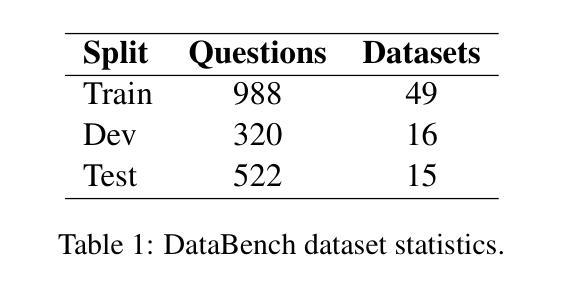
This paper presents our system for SemEval-2025 Task 8: DataBench, Question-Answering over Tabular Data. The primary objective of this task is to perform question answering on given tabular datasets from diverse domains under two subtasks: DataBench QA (Subtask I) and DataBench Lite QA (Subtask II). To tackle both subtasks, we developed a zero-shot solution with a particular emphasis on leveraging Large Language Model (LLM)-based code generation. Specifically, we propose a Python code generation framework utilizing state-of-the-art open-source LLMs to generate executable Pandas code via optimized prompting strategies. Our experiments reveal that different LLMs exhibit varying levels of effectiveness in Python code generation. Additionally, results show that Python code generation achieves superior performance in tabular question answering compared to alternative approaches. Although our ranking among zero-shot systems is unknown at the time of this paper’s submission, our system achieved eighth place in Subtask I and sixth place in Subtask~II among the 30 systems that outperformed the baseline in the open-source models category.
本文介绍了我们为SemEval-2025 Task 8:DataBench,表格数据问答系统所开发的技术。此任务的主要目标是在两个子任务(DataBench QA(子任务I)和DataBench Lite QA(子任务II))上,对给定的表格数据集进行跨域问答。为了应对这两个子任务,我们开发了一种零样本解决方案,特别强调利用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代码生成。具体来说,我们提出了一个利用最新开源LLM的Python代码生成框架,通过优化提示策略生成可执行的Pandas代码。我们的实验表明,不同的LLM在Python代码生成方面的效果不尽相同。此外,结果表明,与替代方法相比,Python代码生成在表格问答方面实现了卓越的性能。虽然在本论文提交时我们尚不清楚零样本系统中的排名,但我们的系统在子任务I中排名第8,在子任务II中排名第6,在开源模型类别中位列前30名系统超过了基线水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对SemEval-2025 Task 8:DataBench表格数据问答任务的系统解决方案。系统主要关注于利用大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本代码生成方法,以解决DataBench QA(Subtask I)和DataBench Lite QA(Subtask II)两个子任务。通过优化的提示策略,利用先进的开源LLM生成可执行Python代码。实验表明不同LLM在Python代码生成方面的效果不同,且Python代码生成在表格问答方面表现出优越性能。提交时未知零样本系统排名,但在子任务I和子任务II中,该系统在开源模型类别中分别排名第八和第六,且在30个系统中表现优于基线。
Key Takeaways
- 系统针对SemEval-2025 Task 8的DataBench表格数据问答任务,提出利用大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本解决方案。
- 采用Python代码生成框架,利用开源LLM生成可执行Pandas代码。
- 不同LLM在Python代码生成方面的效果不同。
- Python代码生成在表格问答方面表现出优越性能。
- 系统在DataBench QA(Subtask I)和DataBench Lite QA(Subtask II)两个子任务中表现良好,分别排名第八和第六。
- 系统在30个系统中表现优于基线,体现了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

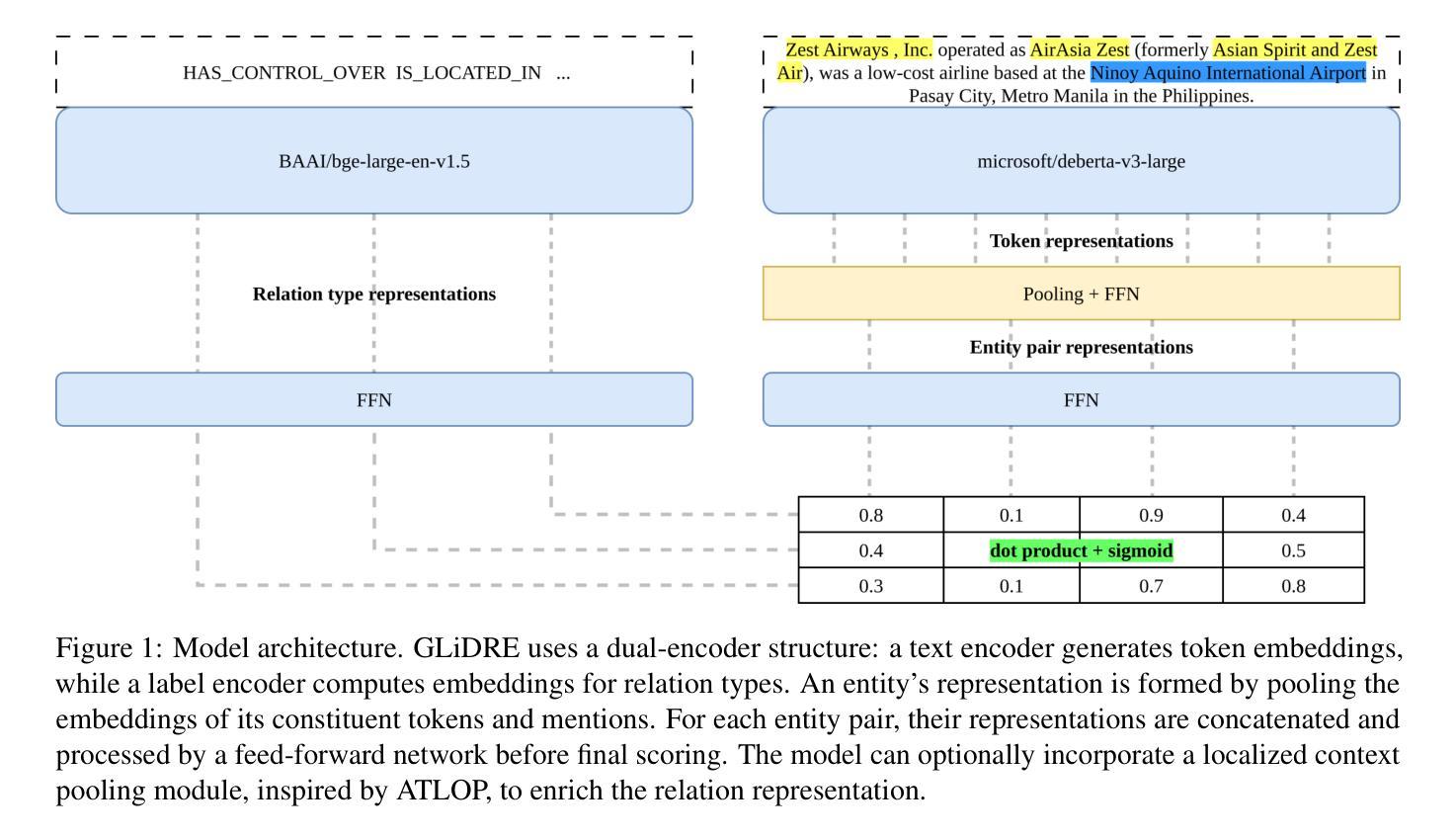
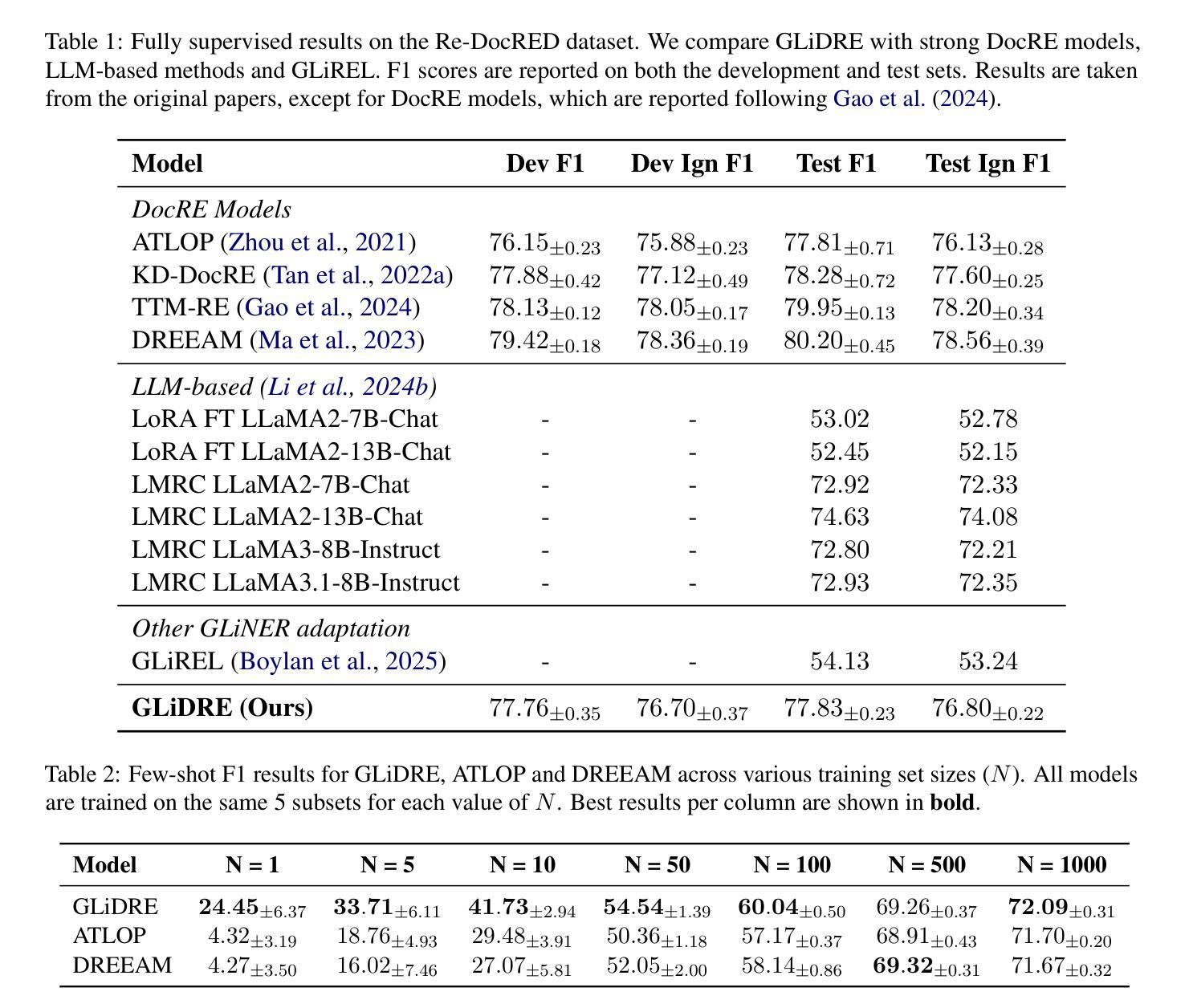
GLiDRE: Generalist Lightweight model for Document-level Relation Extraction
Authors:Robin Armingaud, Romaric Besançon
Relation Extraction (RE) is a fundamental task in Natural Language Processing, and its document-level variant poses significant challenges, due to the need to model complex interactions between entities across sentences. Current approaches, largely based on the ATLOP architecture, are commonly evaluated on benchmarks like DocRED and Re-DocRED. However, their performance in zero-shot or few-shot settings remains largely underexplored due to the task’s complexity. Recently, the GLiNER model has shown that a compact NER model can outperform much larger Large Language Models. With a similar motivation, we introduce GLiDRE, a new model for document-level relation extraction that builds on the key ideas of GliNER. We benchmark GLiDRE against state-of-the-art models across various data settings on the Re-DocRED dataset. Our results demonstrate that GLiDRE achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot scenarios. Our code is publicly available.
关系抽取(RE)是自然语言处理中的一项基础任务,其文档级变体带来了巨大的挑战,因为需要建模跨句子实体之间的复杂交互。当前的方法大多基于ATLOP架构,通常在DocRED和Re-DocRED等基准测试上进行评估。然而,由于任务的复杂性,它们在零样本或少样本情况下的性能仍鲜有研究。最近,GLiNER模型表明,紧凑的命名实体识别模型可以超越更大的大型语言模型。基于类似的动机,我们推出了GLiDRE,这是一种新的文档级关系抽取模型,建立在GliNER的关键思想之上。我们在Re-DocRED数据集的各种数据设置上,将GLiDRE与最新模型进行了基准测试。结果表明,在少样本场景中,GLiDRE达到了最新的最佳性能。我们的代码公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ARR July
Summary
本文介绍了文档级别的关系抽取(RE)所面临的挑战以及当前的解决策略。基于GLiNER模型的灵感,提出了一种新的文档级关系抽取模型GLiDRE。在Re-DocRED数据集上的实验结果表明,GLiDRE在少样本场景下取得了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文档级关系抽取(RE)需要建模跨句子的实体之间的复杂交互,因此存在显著挑战。
- 当前的方法大多基于ATLOP架构,并在DocRED和Re-DocRED等基准测试上进行评价。
- 零样本或少样本情境下的性能表现尚待探索。
- GLiNER模型显示紧凑的NER模型可以超越大型语言模型。
- 提出的GLiDRE模型借鉴了GLiNER的关键思想,为文档级关系抽取提供了新的解决方案。
- 在Re-DocRED数据集上的实验表明,GLiDRE在少样本场景下具有卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

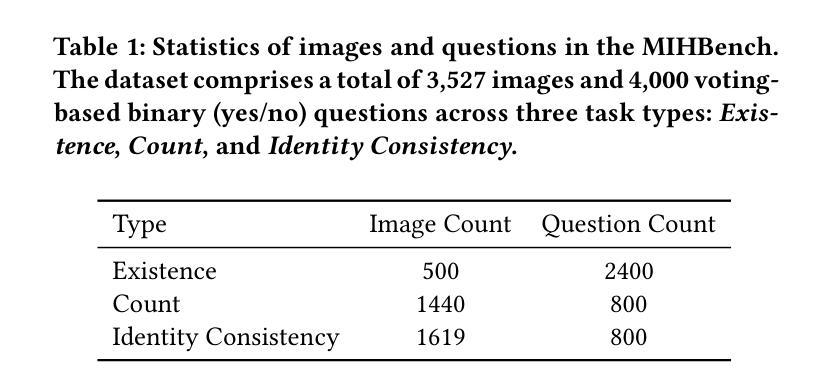
MIHBench: Benchmarking and Mitigating Multi-Image Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Jiale Li, Mingrui Wu, Zixiang Jin, Hao Chen, Jiayi Ji, Xiaoshuai Sun, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
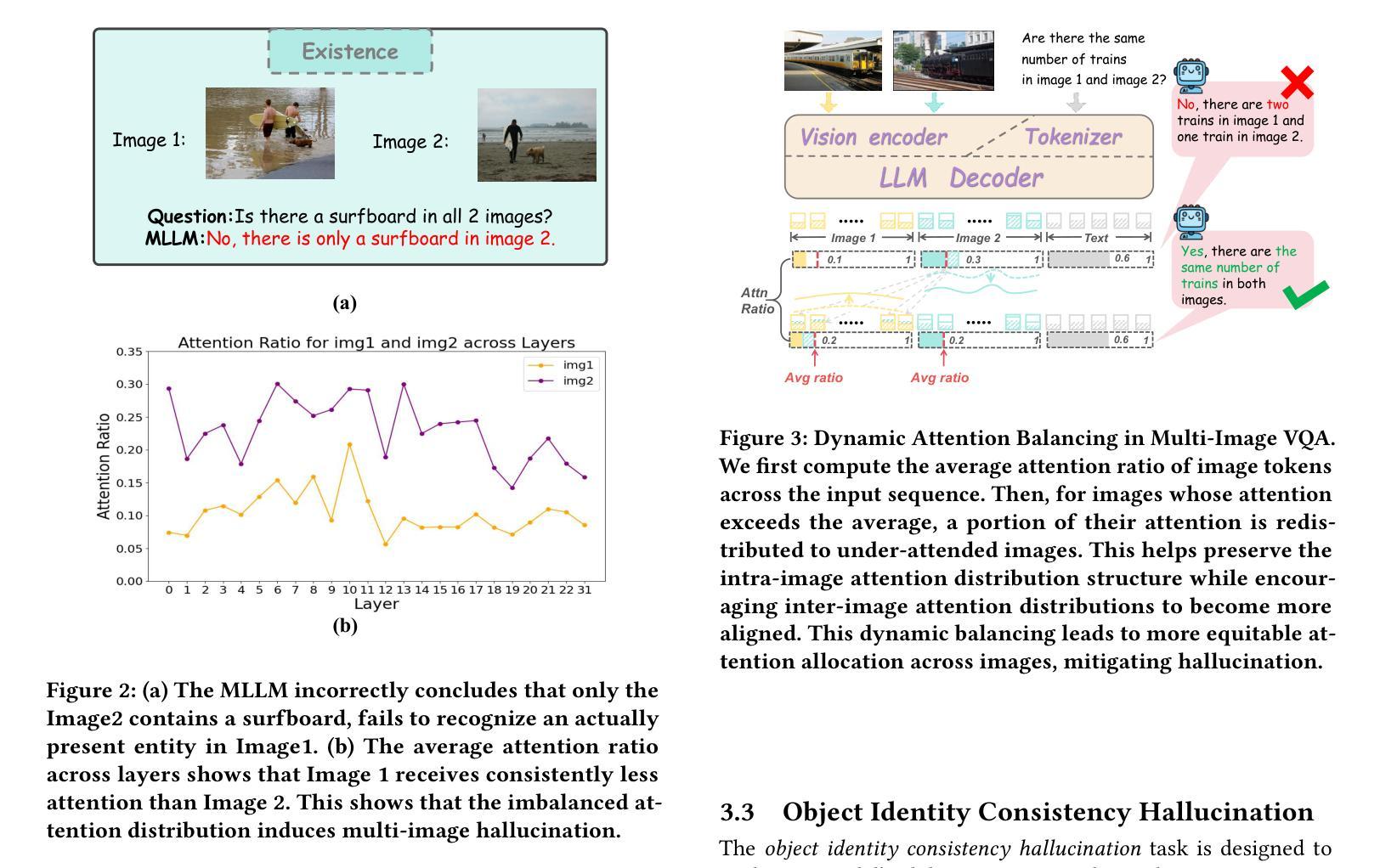
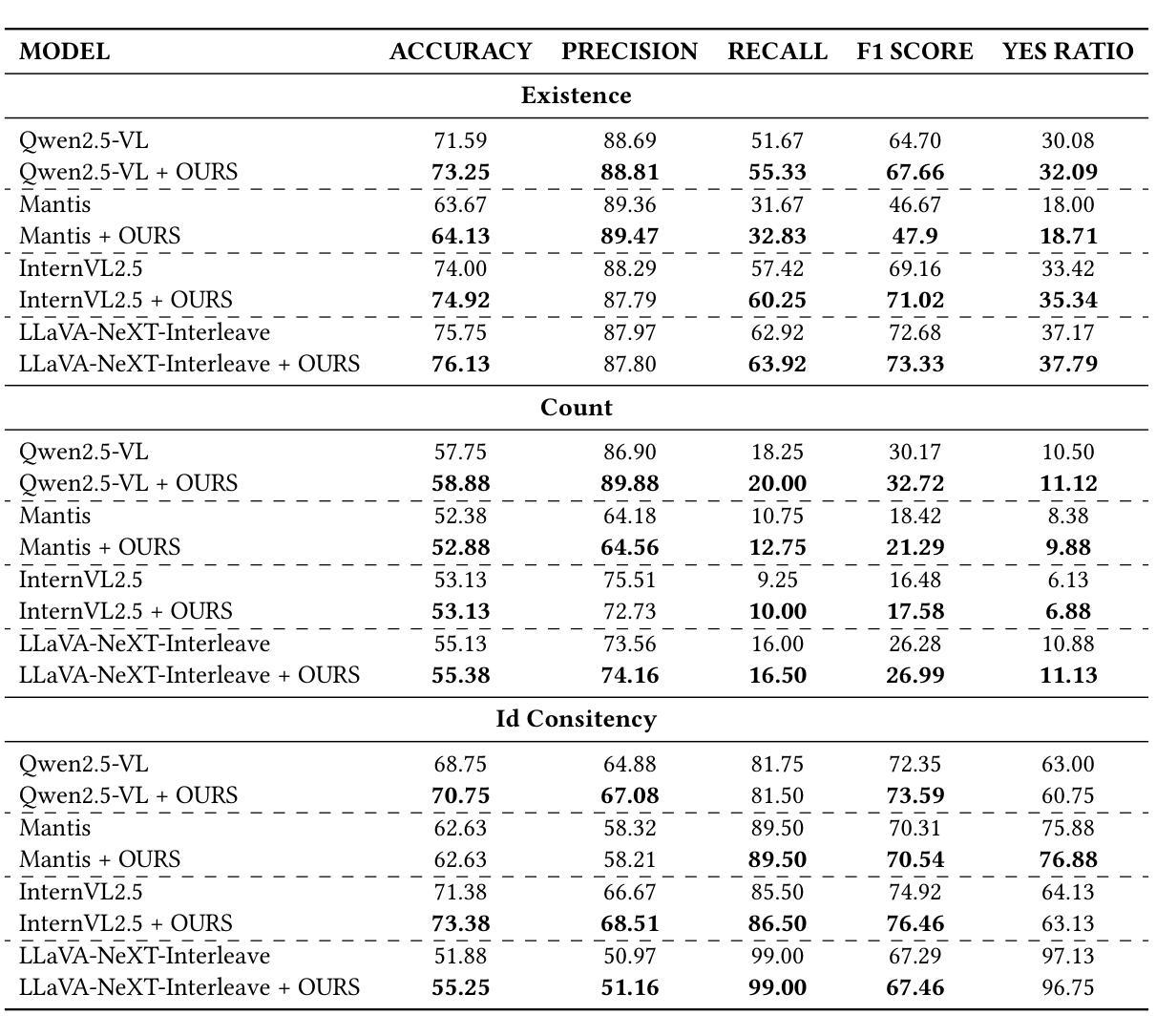
Despite growing interest in hallucination in Multimodal Large Language Models, existing studies primarily focus on single-image settings, leaving hallucination in multi-image scenarios largely unexplored. To address this gap, we conduct the first systematic study of hallucinations in multi-image MLLMs and propose MIHBench, a benchmark specifically tailored for evaluating object-related hallucinations across multiple images. MIHBench comprises three core tasks: Multi-Image Object Existence Hallucination, Multi-Image Object Count Hallucination, and Object Identity Consistency Hallucination, targeting semantic understanding across object existence, quantity reasoning, and cross-view identity consistency. Through extensive evaluation, we identify key factors associated with the occurrence of multi-image hallucinations, including: a progressive relationship between the number of image inputs and the likelihood of hallucination occurrences; a strong correlation between single-image hallucination tendencies and those observed in multi-image contexts; and the influence of same-object image ratios and the positional placement of negative samples within image sequences on the occurrence of object identity consistency hallucination. To address these challenges, we propose a Dynamic Attention Balancing mechanism that adjusts inter-image attention distributions while preserving the overall visual attention proportion. Experiments across multiple state-of-the-art MLLMs demonstrate that our method effectively reduces hallucination occurrences and enhances semantic integration and reasoning stability in multi-image scenarios.
尽管对多模态大型语言模型中的幻觉(hallucination)的兴趣日益增长,但现有研究主要集中在单图像设置上,而对多图像场景中的幻觉则鲜有探索。为了填补这一空白,我们对多图像MLLM中的幻觉进行了首次系统研究,并提出了MIHBench,这是一个专门用于评估跨多图像对象相关幻觉的基准测试。MIHBench包含三个核心任务:多图像对象存在幻觉、多图像对象计数幻觉和对象身份一致性幻觉,旨在针对对象存在的语义理解、数量推理和跨视图身份一致性。通过广泛评估,我们确定了与多图像幻觉发生相关的关键因素,包括:图像输入数量与幻觉发生可能性之间的渐进关系;单图像幻觉倾向与多图像上下文中的幻觉倾向之间存在强烈的相关性;以及相同对象图像比例和负样本在图像序列中的位置对对象身份一致性幻觉发生的影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种动态注意力平衡机制,该机制可以调整图像间的注意力分布,同时保持整体的视觉注意力比例。在多个最先进的MLLM上的实验表明,我们的方法有效地减少了幻觉的发生,并增强了多图像场景中的语义集成和推理稳定性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM25 has accepted this paper
Summary
本文研究了多模态大型语言模型中多图像场景下的幻觉问题,并进行了首次系统研究。为解决评估对象相关幻觉的难题,提出了专门用于评估多图像中对象相关幻觉的MIHBench基准测试。MIHBench包含三个核心任务,针对跨多图像的对象存在、数量推理和跨视图身份一致性的语义理解。通过广泛评估,确定了与多图像幻觉发生相关的关键因素,并提出了动态注意力平衡机制,以调整图像间的注意力分布,减少幻觉发生,提高多图像场景中的语义集成和推理稳定性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前对多模态大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉研究主要集中在单图像设置上,对于多图像场景中的幻觉研究仍然不足。
- 提出MIHBench基准测试,用于评估多图像中对象相关的幻觉。
- MIHBench包含三个核心任务:多图像对象存在幻觉、多图像对象计数幻觉和对象身份一致性幻觉,分别针对语义理解、数量推理和跨视图身份一致性。
- 研究发现多图像幻觉与一些关键因素相关,包括图像输入数量与幻觉发生概率的关系、单图像幻觉与多图像幻觉之间的强相关性以及同一对象图像比例和负样本位置对对象身份一致性幻觉的影响。
- 提出的动态注意力平衡机制能有效调整图像间的注意力分布,减少幻觉发生。
- 实验表明,该机制能提高多图像场景中的语义集成和推理稳定性。
点此查看论文截图


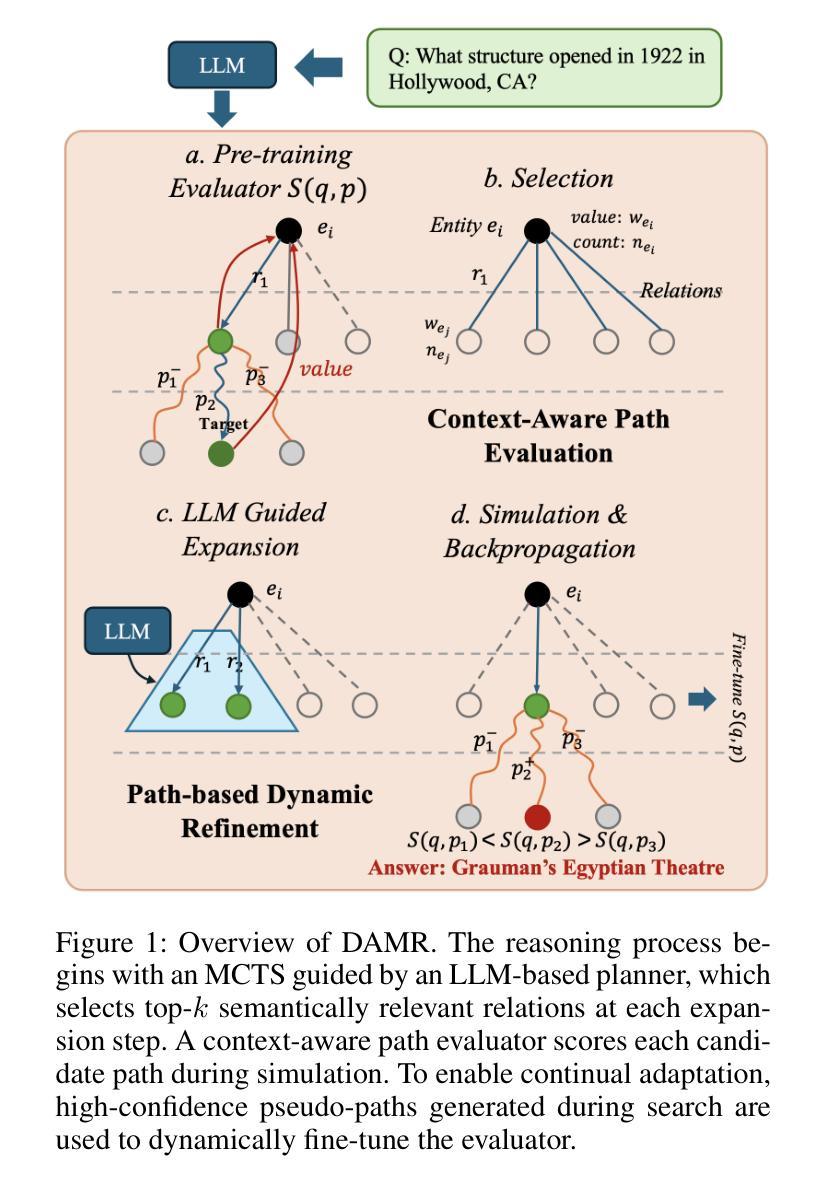
Dynamically Adaptive Reasoning via LLM-Guided MCTS for Efficient and Context-Aware KGQA
Authors:Yingxu Wang, Shiqi Fan, Mengzhu Wang, Siwei Liu
Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) aims to interpret natural language queries and perform structured reasoning over knowledge graphs by leveraging their relational and semantic structures to retrieve accurate answers. Recent KGQA methods primarily follow either retrieve-then-reason paradigm, relying on GNNs or heuristic rules for static paths extraction, or dynamic path generation strategies that use large language models (LLMs) with prompting to jointly perform retrieval and reasoning. However, the former suffers from limited adaptability due to static path extraction and lack of contextual refinement, while the latter incurs high computational costs and struggles with accurate path evaluation due to reliance on fixed scoring functions and extensive LLM calls. To address these issues, this paper proposes Dynamically Adaptive MCTS-based Reasoning (DAMR), a novel framework that integrates symbolic search with adaptive path evaluation for efficient and context-aware KGQA. DAMR employs a Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) backbone guided by an LLM-based planner, which selects top-$k$ relevant relations at each step to reduce search space. To improve path evaluation accuracy, we introduce a lightweight Transformer-based scorer that performs context-aware plausibility estimation by jointly encoding the question and relation sequence through cross-attention, enabling the model to capture fine-grained semantic shifts during multi-hop reasoning. Furthermore, to alleviate the scarcity of high-quality supervision, DAMR incorporates a dynamic pseudo-path refinement mechanism that periodically generates training signals from partial paths explored during search, allowing the scorer to continuously adapt to the evolving distribution of reasoning trajectories. Extensive experiments on multiple KGQA benchmarks show that DAMR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
知识图谱问答(KGQA)旨在解释自然语言查询,并通过利用知识图谱的关系和语义结构进行结构化推理,以获取准确的答案。最近的KGQA方法主要遵循“检索-推理”范式,依赖于图神经网络或启发式规则进行静态路径提取,或者使用大型语言模型(LLM)的提示来联合执行检索和推理的动态路径生成策略。然而,前者受限于静态路径提取和缺乏上下文细化,而后者则由于依赖于固定的评分函数和大量的LLM调用而计算成本高,并且在路径评估方面存在困难。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了基于动态自适应蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)的推理(DAMR),这是一种将符号搜索与自适应路径评估相结合的新型框架,可实现高效、上下文感知的KGQA。DAMR采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)作为骨干,以基于LLM的规划器为指导,在每个步骤中选择前k个相关关系以减少搜索空间。为了提高路径评估的准确性,我们引入了一个轻量级的基于Transformer的评分器,通过跨注意力联合编码问题和关系序列,进行上下文感知的可行性估计,使模型能够在多跳推理过程中捕捉细微的语义变化。此外,为了缓解高质量监督的稀缺性,DAMR融入了一种动态伪路径细化机制,该机制会定期从搜索过程中探索的部分路径生成训练信号,使评分器能够不断适应不断变化的推理轨迹分布。在多个KGQA基准测试上的广泛实验表明,DAMR显著优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文针对知识图谱问答(KGQA)提出一种新的框架——动态自适应蒙特卡洛树搜索推理(DAMR)。DAMR结合了符号搜索和自适应路径评估,实现了高效且上下文感知的KGQA。它采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)作为骨架,并使用基于LLM的规划器来指导搜索,减少搜索空间。同时,DAMR引入了一个轻量级的基于Transformer的评分器,通过跨注意力机制联合编码问题和关系序列,提高路径评估的准确性。此外,DAMR还融入了动态伪路径优化机制,以缓解高质量监督数据的稀缺问题。实验证明,DAMR在多个KGQA基准测试上显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- KGQA旨在利用知识图谱的关系和语义结构来解答自然语言问题。
- 现有KGQA方法主要遵循检索与推理的范式,但存在静态路径提取的局限性以及高计算成本的问题。
- DAMR框架结合了符号搜索和自适应路径评估,实现高效且上下文感知的KGQA。
- DAMR使用LLM规划器指导的MCTS来减少搜索空间,并引入基于Transformer的评分器提高路径评估准确性。
- DAMR通过动态伪路径优化机制适应监督数据的稀缺问题。
- 实验证明,DAMR在多个KGQA基准测试上表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

Better Call Claude: Can LLMs Detect Changes of Writing Style?
Authors:Johannes Römisch, Svetlana Gorovaia, Mariia Halchynska, Gleb Schmidt, Ivan P. Yamshchikov
This article explores the zero-shot performance of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) on one of the most challenging tasks in authorship analysis: sentence-level style change detection. Benchmarking four LLMs on the official PAN~2024 and 2025 “Multi-Author Writing Style Analysis” datasets, we present several observations. First, state-of-the-art generative models are sensitive to variations in writing style - even at the granular level of individual sentences. Second, their accuracy establishes a challenging baseline for the task, outperforming suggested baselines of the PAN competition. Finally, we explore the influence of semantics on model predictions and present evidence suggesting that the latest generation of LLMs may be more sensitive to content-independent and purely stylistic signals than previously reported.
本文探讨了最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)在作者风格分析中最具挑战性的任务之一:句子级风格变化检测中的零样本性能。我们在官方PAN 2024年和2025年的“多作者写作风格分析”数据集上评估了四个LLM的表现,并得出了一些观察结果。首先,最先进的生成模型对写作风格的变化非常敏感——甚至在单个句子的粒度级别也是如此。其次,它们的准确性为该任务建立了具有挑战性的基准线,超越了PAN竞赛提出的基准线。最后,我们探讨了语义对模型预测的影响,并提供证据表明最新一代的LLM可能比先前报道的更加敏感于独立于内容的纯粹风格信号。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary: 文章评估了最新先进的大型语言模型(LLM)在最具挑战性的任务之一——句子级风格变化检测中的零样本性能。文章在PAN官方数据集上对四种LLM进行了基准测试,观察到最先进的生成模型对细微的写作风格变化敏感,准确率为该任务设定了一个具有挑战性的基准线,并超越了PAN竞赛的基线建议。此外,文章探讨了语义对模型预测的影响,并提供了证据表明最新一代的LLM可能对内容独立和纯粹的风格信号更为敏感。
Key Takeaways:
- 先进的大型语言模型对句子级的写作风格变化敏感。
- 这些模型在PAN数据集上的准确率设定了挑战性的基准线。
- 这些模型在风格分析任务上的性能超越了PAN竞赛的基线建议。
- 最新一代的大型语言模型对内容独立和纯粹的风格信号更为敏感。
- 语义对模型预测有影响。
- 文章评估了大型语言模型在最具挑战性的任务中的表现。
点此查看论文截图

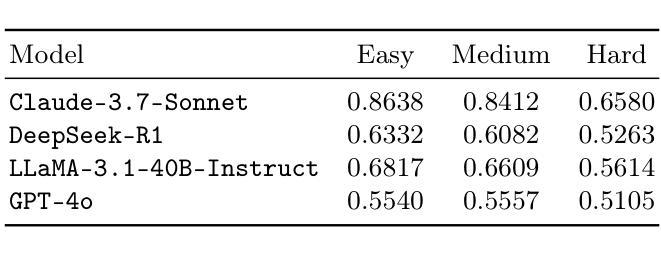
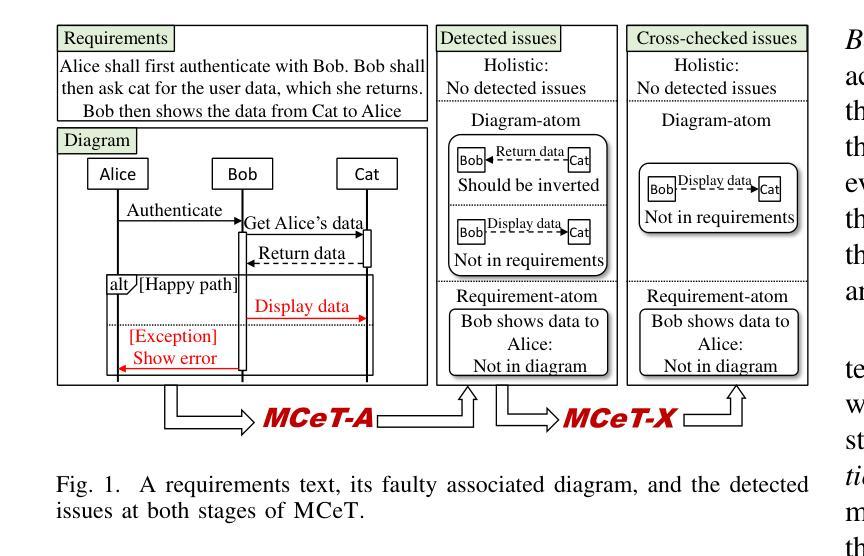
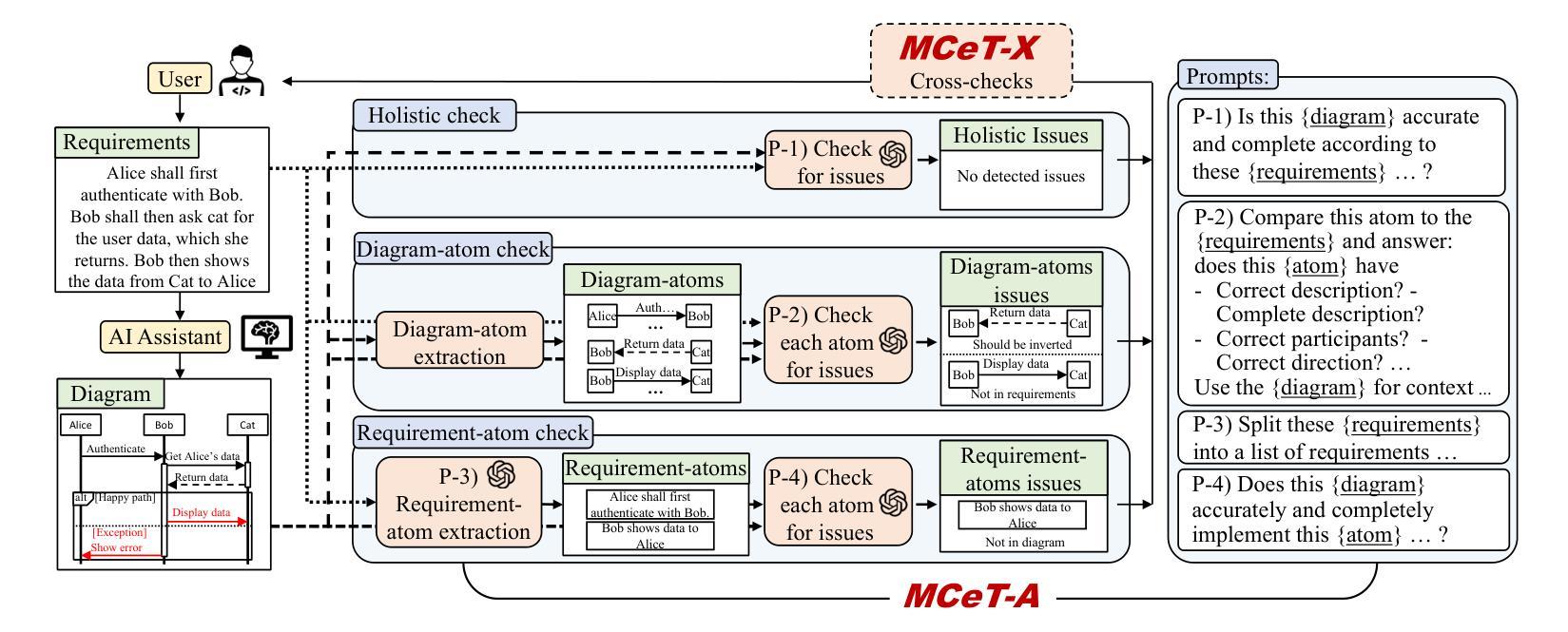
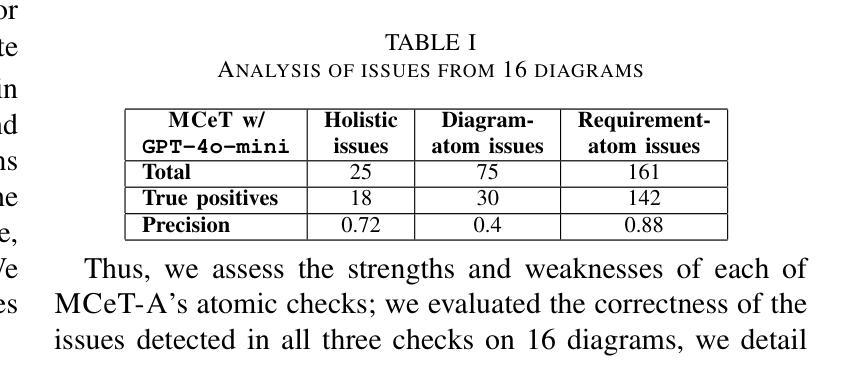
MCeT: Behavioral Model Correctness Evaluation using Large Language Models
Authors:Khaled Ahmed, Jialing Song, Boqi Chen, Ou Wei, Bingzhou Zheng
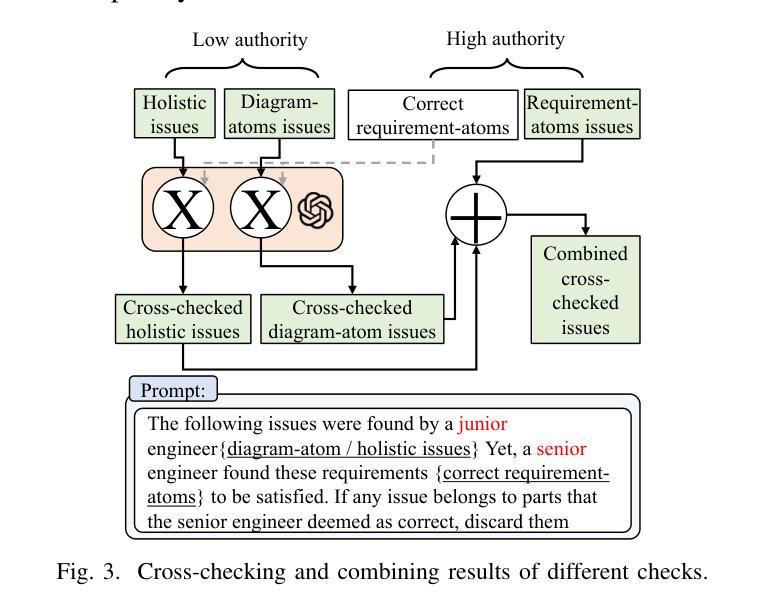
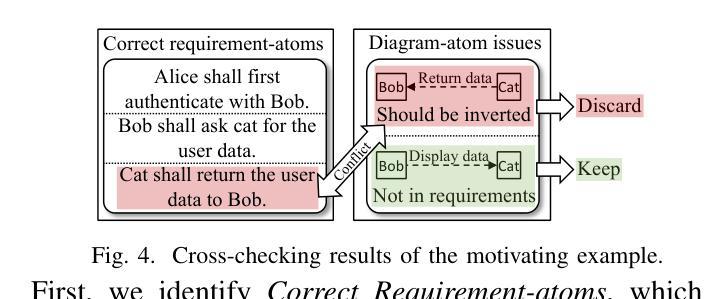
Behavioral model diagrams, e.g., sequence diagrams, are an essential form of documentation that are typically designed by system engineers from requirements documentation, either fully manually or assisted by design tools. With the growing use of Large Language Models (LLM) as AI modeling assistants, more automation will be involved in generating diagrams. This necessitates the advancement of automatic model correctness evaluation tools. Such a tool can be used to evaluate both manually and AI automatically generated models; to provide feedback to system engineers, and enable AI assistants to self-evaluate and self-enhance their generated models. In this paper, we propose MCeT, the first fully automated tool to evaluate the correctness of a behavioral model, sequence diagrams in particular, against its corresponding requirements text and produce a list of issues that the model has. We utilize LLMs for the correctness evaluation tasks as they have shown outstanding natural language understanding ability. However, we show that directly asking an LLM to compare a diagram to requirements finds less than 35% of issues that experienced engineers can find. We propose to supplement the direct check with a fine-grained, multi-perspective approach; we split the diagram into atomic, non-divisible interactions, and split the requirements text into atomic, self-contained items. We compare the diagram with atomic requirements and each diagram-atom with the requirements. We also propose a self-consistency checking approach that combines perspectives to mitigate LLM hallucinated issues. Our combined approach improves upon the precision of the direct approach from 0.58 to 0.81 in a dataset of real requirements. Moreover, the approach finds 90% more issues that the experienced engineers found than the direct approach, and reports an average of 6 new issues per diagram.
行为模型图(例如序列图)是一种重要的文档形式,通常由系统工程师根据需求文档进行设计,可以全手动完成,也可以使用设计工具辅助完成。随着大型语言模型(LLM)作为AI建模助手的使用越来越多,自动生成这些图的自动化程度会越来越高。这要求开发更先进的自动模型正确性评估工具。这种工具可用于评估手动和AI自动生成的模型,为系统工程师提供反馈意见,并允许AI助手进行自我评估和增强他们生成的模型。在本文中,我们提出了MCeT,这是第一个完全自动化的工具,用于根据相应的需求文本评估行为模型的正确性,特别是序列图的正确性,并生成模型存在的问题列表。我们使用LLM进行正确性评估任务,因为它们已显示出出色的自然语言理解能力。然而,我们表明,直接要求LLM将图表与需求进行比较,只能发现不到35%的问题,而经验丰富的工程师则可以发现更多的问题。我们提议采用一种精细的多角度方法来补充直接检查;我们将图表分割成原子不可分的互动,并将需求文本分割成原子、独立的项。我们将图表与原子需求进行比较,并将每个图表原子与需求进行比较。我们还提出了一种自我一致性检查方法,通过结合各种角度,来减轻LLM产生的虚构问题。我们的综合方法提高了直接方法的精度,从数据集中的0.58提高到0.81。此外,该方法发现了经验丰富的工程师发现的90%以上的问题,并平均每个图表报告了6个新问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MODELS 2025
摘要
随着大型语言模型(LLM)作为AI建模助手的使用日益普及,行为模型图(如序列图)的自动生成需要更先进的模型正确性评估工具。本文提出了MCeT,第一个完全自动的工具,用于评估行为模型(特别是序列图)相对于其对应需求文本的正确性,并生成问题列表。虽然LLM在自然语言理解方面表现出色,但直接使用LLM比较图表和需求发现的问题不到经验丰富的工程师所能发现的35%。因此,本文提出了一种精细的、多视角的方法作为补充,将图表分割成不可再分的原子交互,将需求文本分割成自我包含的原子项。通过比较原子图表和原子需求以及结合自我一致性检查的方法,我们的方法提高了精度,并减轻了LLM虚构的问题。我们的方法比直接方法更精确地发现了经验丰富的工程师所忽视的问题,并且平均每个图表报告了6个新问题。
关键见解
- 行为模型图(如序列图)在系统设计中的重要性及其与需求文档的关系。
- 随着LLM的发展,越来越多的自动化工具被用于生成行为模型图。
- 提出了MCeT工具,它是第一个完全自动化的工具,用于评估行为模型(特别是序列图)的正确性。
- LLM虽然具有强大的自然语言理解能力,但直接用于模型正确性评估的效果有限。
- 为了提高评估精度,提出了一种精细的、多视角的评估方法,包括将图表和需求文本分解为最小的、自我包含的单元进行比较。
- 提出的自我一致性检查方法有助于减轻LLM虚构的问题。
- 与直接方法相比,新方法在发现模型问题方面更加精确和有效,平均每个图表报告了6个新问题。
点此查看论文截图

LeakSealer: A Semisupervised Defense for LLMs Against Prompt Injection and Leakage Attacks
Authors:Francesco Panebianco, Stefano Bonfanti, Francesco Trovò, Michele Carminati
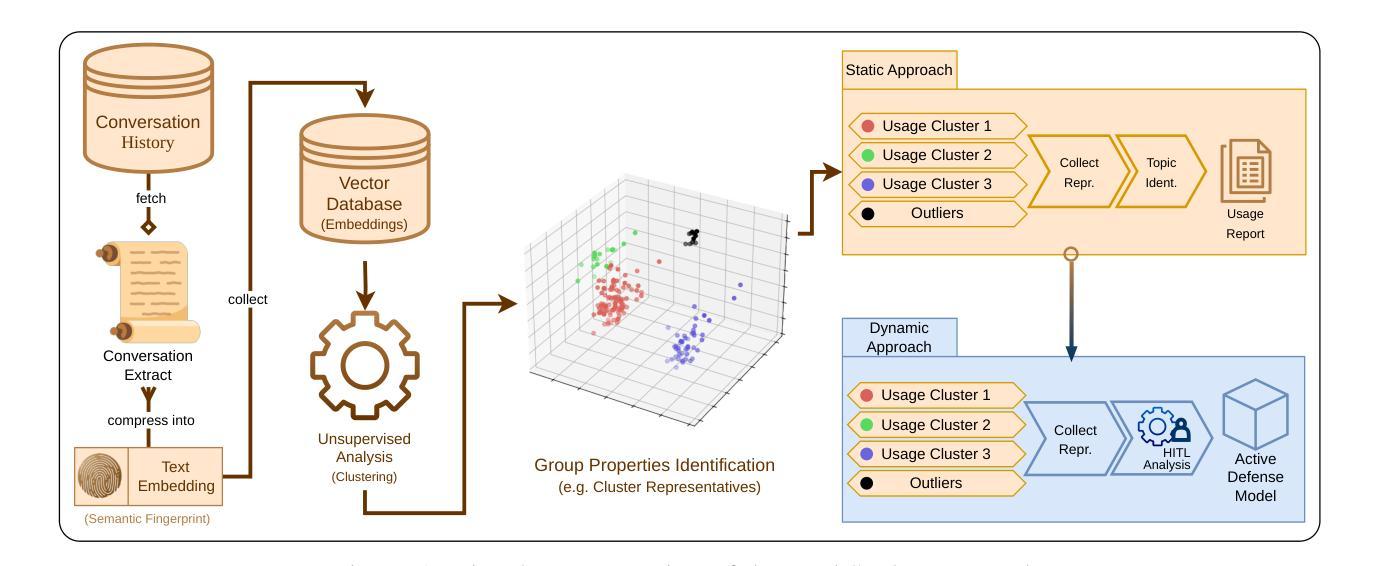
The generalization capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to their widespread deployment across various applications. However, this increased adoption has introduced several security threats, notably in the forms of jailbreaking and data leakage attacks. Additionally, Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), while enhancing context-awareness in LLM responses, has inadvertently introduced vulnerabilities that can result in the leakage of sensitive information. Our contributions are twofold. First, we introduce a methodology to analyze historical interaction data from an LLM system, enabling the generation of usage maps categorized by topics (including adversarial interactions). This approach further provides forensic insights for tracking the evolution of jailbreaking attack patterns. Second, we propose LeakSealer, a model-agnostic framework that combines static analysis for forensic insights with dynamic defenses in a Human-In-The-Loop (HITL) pipeline. This technique identifies topic groups and detects anomalous patterns, allowing for proactive defense mechanisms. We empirically evaluate LeakSealer under two scenarios: (1) jailbreak attempts, employing a public benchmark dataset, and (2) PII leakage, supported by a curated dataset of labeled LLM interactions. In the static setting, LeakSealer achieves the highest precision and recall on the ToxicChat dataset when identifying prompt injection. In the dynamic setting, PII leakage detection achieves an AUPRC of $0.97$, significantly outperforming baselines such as Llama Guard.
大型语言模型(LLM)的泛化能力使其在各种应用中得到了广泛部署。然而,这种增加的采用已经带来了多种安全威胁,特别是在越狱和数据泄露攻击的形式中。此外,检索增强生成(RAG)虽然在提高LLM响应的上下文意识方面发挥了作用,但无意中引入了可能导致敏感信息泄露的漏洞。我们的贡献有两方面。首先,我们引入了一种分析LLM系统历史交互数据的方法,该方法可以生成按主题分类的使用图(包括对抗交互)。这种方法还提供了追踪越狱攻击模式演变的法医洞察。其次,我们提出了LeakSealer,这是一个模型无关的框架,它结合了静态分析以提供法医洞察和动态防御在人机循环(HITL)管道中。该技术可以识别主题组并检测异常模式,从而实现主动防御机制。我们通过两种情景对LeakSealer进行了实证评估:(1)越狱尝试,采用公共基准数据集;(2)个人信息泄露,辅以标记的LLM交互数据集。在静态设置中,LeakSealer在识别提示注入时在ToxicChat数据集上实现了最高的精确率和召回率。在动态设置中,个人信息泄露检测达到了0.97的AUPRC,显著优于基线如Llama Guard。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的普及应用带来了许多安全威胁,如越狱和数据泄露攻击。本文提出一种分析LLM系统历史交互数据的方法,生成按主题分类的使用地图,提供追踪越狱攻击模式演变的法医见解。此外,还提出LeakSealer框架,结合静态分析和动态防御,在人机交互管道中识别主题组和检测异常模式,实现主动防御机制。经验评估显示,LeakSealer在识别提示注入和检测个人信息泄露方面表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的广泛应用带来了安全威胁,如越狱和数据泄露攻击。
- 提出一种分析LLM历史交互数据的方法,生成使用地图以追踪攻击模式演变。
- LeakSealer框架结合静态分析和动态防御,实现主动防御机制。
- LeakSealer能够识别主题组并检测异常模式。
- 在静态分析中,LeakSealer在识别提示注入方面表现出高精确度和召回率。
- 在动态场景下,个人信息泄露检测性能优异,显著优于基线技术。
点此查看论文截图


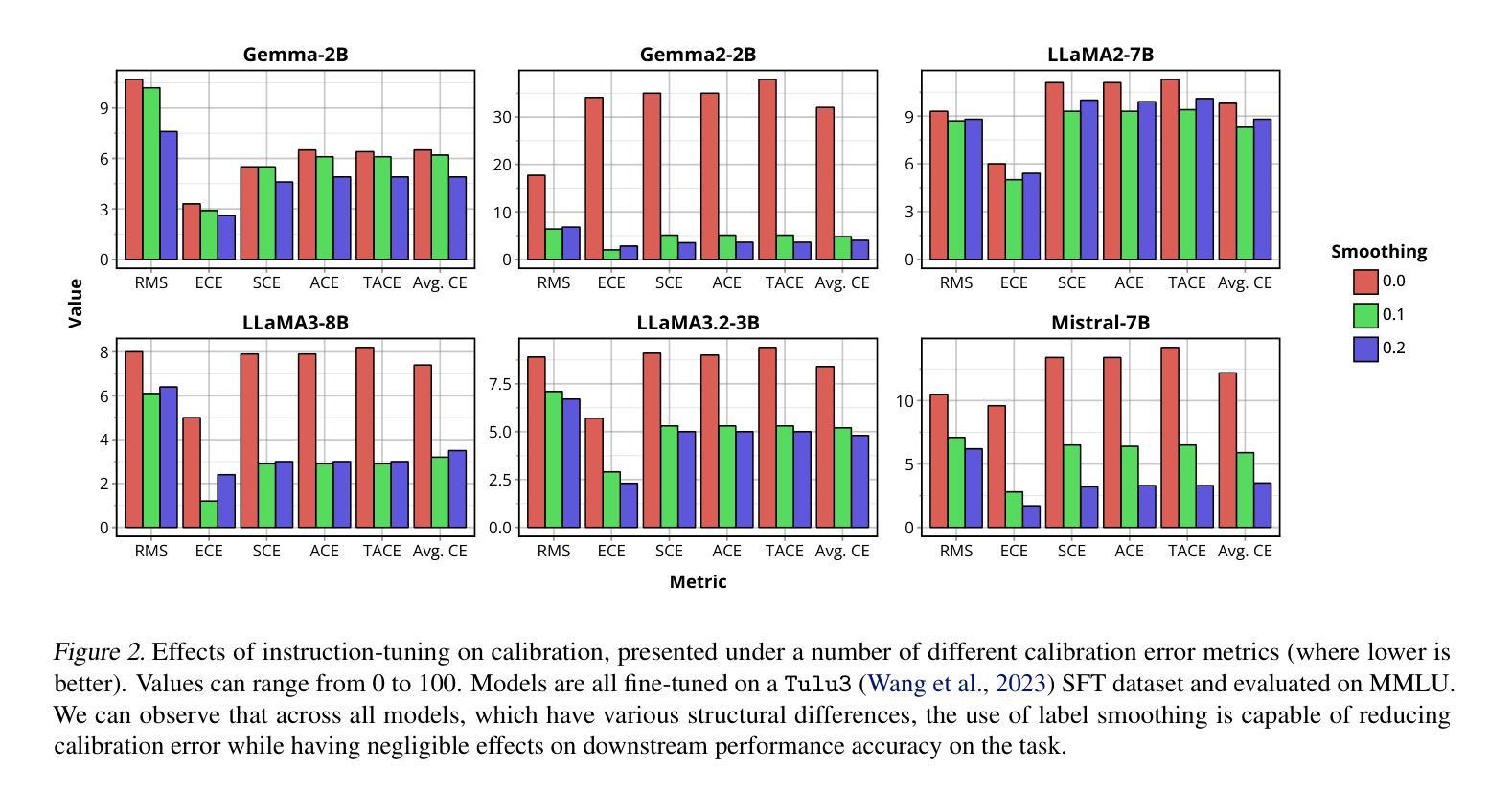
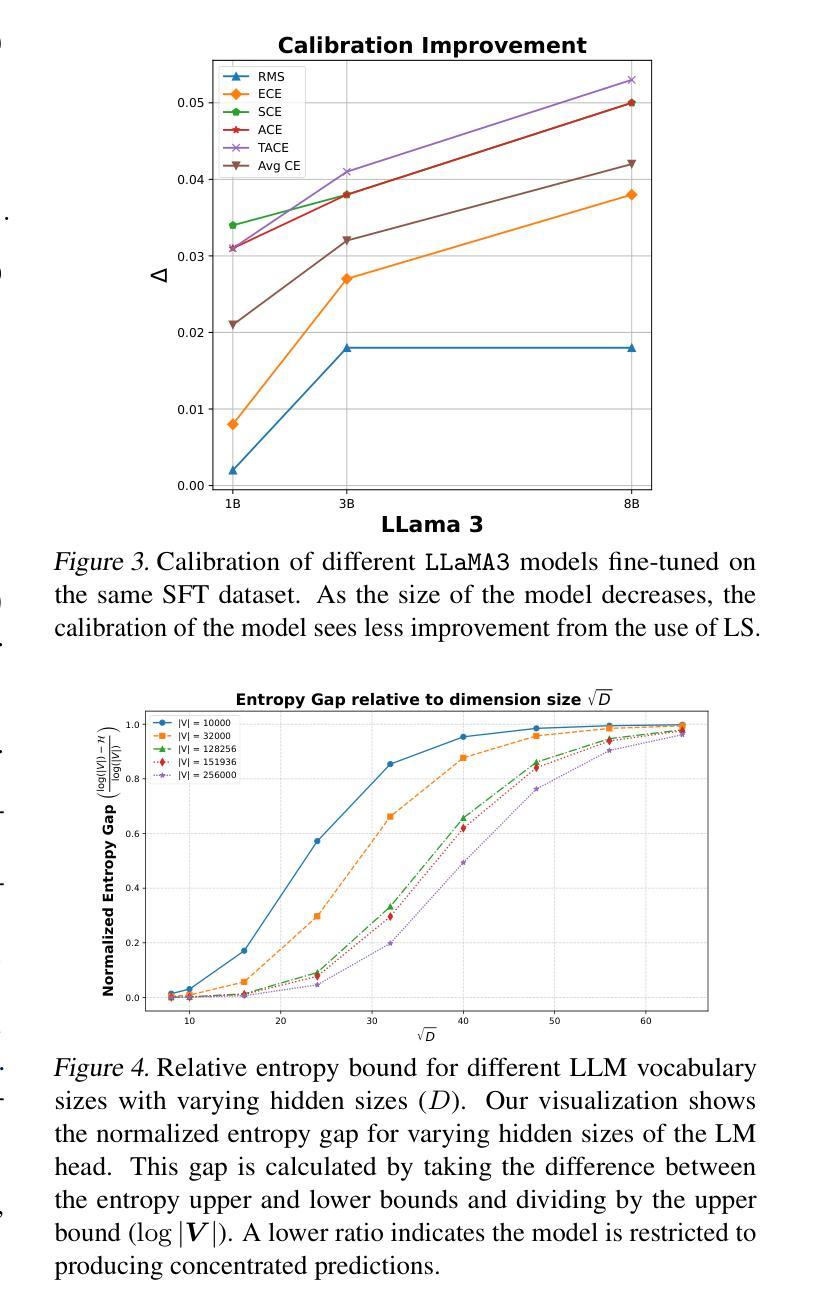
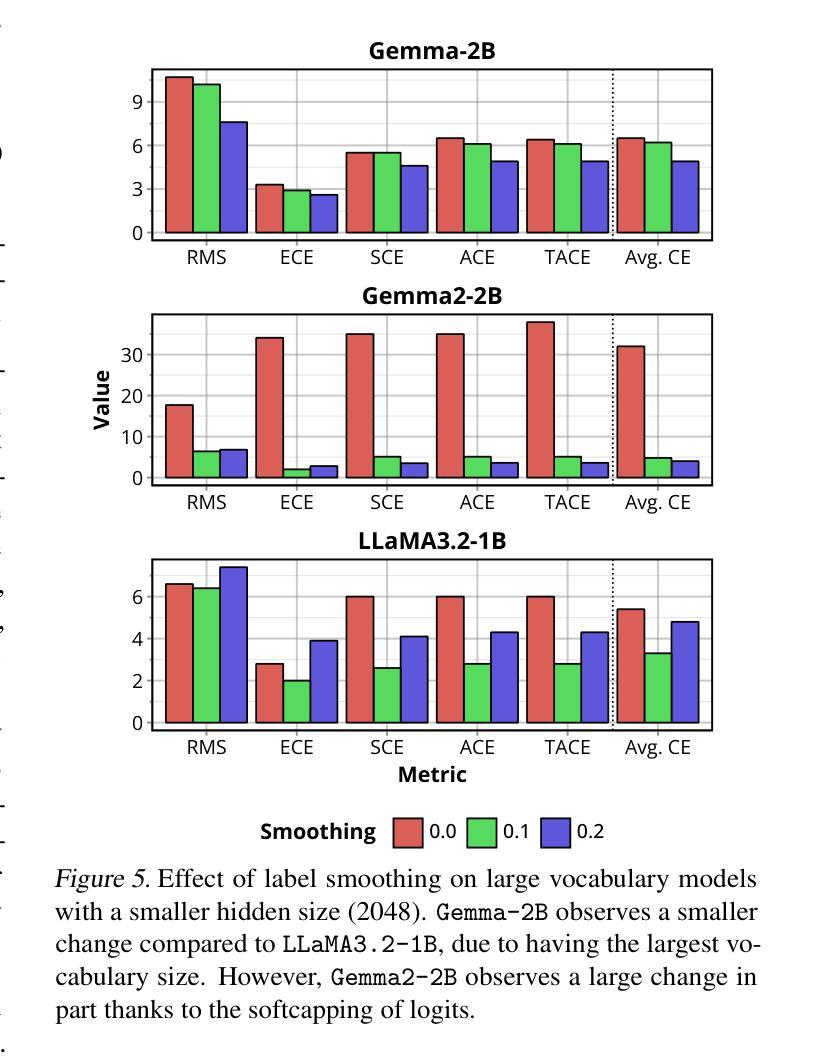
Calibrated Language Models and How to Find Them with Label Smoothing
Authors:Jerry Huang, Peng Lu, Qiuhao Zeng
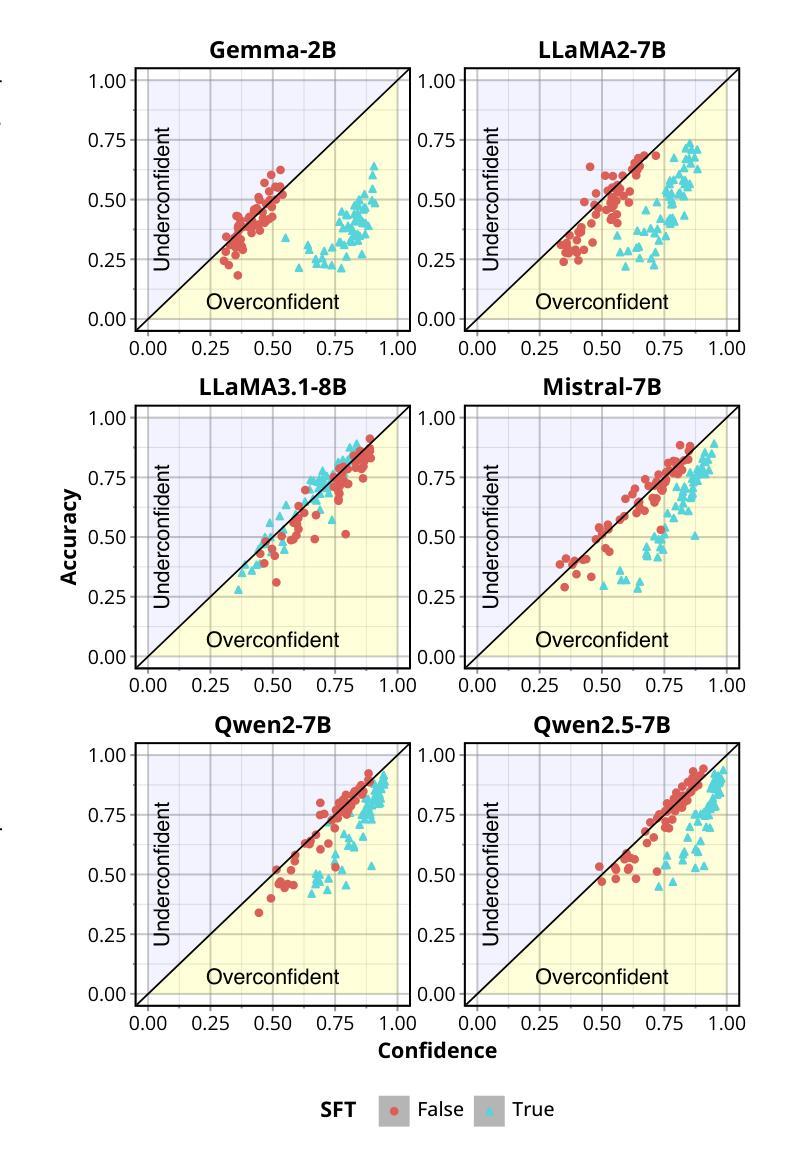
Recent advances in natural language processing (NLP) have opened up greater opportunities to enable fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) to behave as more powerful interactive agents through improved instruction-following ability. However, understanding how this impacts confidence calibration for reliable model output has not been researched in full. In this work, we examine various open-sourced LLMs, identifying significant calibration degradation after instruction tuning in each. Seeking a practical solution, we look towards label smoothing, which has been shown as an effective method to regularize for overconfident predictions but has yet to be widely adopted in the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of LLMs. We first provide insight as to why label smoothing is sufficient to maintain calibration throughout the SFT process. However, settings remain where the effectiveness of smoothing is severely diminished, in particular the case of large vocabulary LLMs (LV-LLMs). We posit the cause to stem from the ability to become over-confident, which has a direct relationship with the hidden size and vocabulary size, and justify this theoretically and experimentally. Finally, we address an outstanding issue regarding the memory footprint of the cross-entropy loss computation in the label smoothed loss setting, designing a customized kernel to dramatically reduce memory consumption without sacrificing speed or performance in comparison to existing solutions for non-smoothed losses.
近期自然语言处理(NLP)的进展为通过改进指令遵循能力使精细调整的大型语言模型(LLM)表现为更强大的交互式代理提供了更大机会。然而,了解这对可靠模型输出的信心校准影响尚未得到充分研究。在这项工作中,我们研究了各种开源LLM,发现每个在指令调整后的校准都有明显退化。为了寻找实际解决方案,我们转向标签平滑,它已被证明是一种有效的正则化方法来防止过度自信的预测,但尚未在LLM的监督微调(SFT)中广泛采用。我们首先洞察为何标签平滑足以在整个SFT过程中维持校准。然而,仍存在一些设置中平滑的有效性大大减弱,尤其是大型词汇表LLM(LV-LLM)的情况。我们认为原因源于成为过度自信的能力,它与隐藏大小和词汇大小有直接关系,并从理论和实践角度对此进行了论证。最后,我们解决了标签平滑损失设置中交叉熵损失计算的内存占用问题,设计了一个自定义内核,以显著减少内存消耗,同时不牺牲速度或与非平滑损失的现有解决方案的性能比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Forty-second International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025. First two authors contributed equally
Summary
近期自然语言处理(NLP)的进展为通过改进指令遵循能力使大型语言模型(LLM)表现为更强大的交互式代理提供了更多机会。然而,尚未完全研究这如何影响可靠模型输出的信心校准。在这项工作中,我们研究了各种开源LLM,发现它们在指令调整后面临校准退化问题。为解决这一问题,我们关注标签平滑,它已被证明是一种有效的正则化方法,用于解决过度自信的预测,但在LLM的监督微调(SFT)中尚未广泛使用。我们深入探讨了标签平滑在维持SFT过程中校准的原因,并揭示了大型词汇表LLM(LV-LLM)中平滑效果减弱的情况。我们认为这是因为它们容易变得过于自信,与隐藏大小和词汇量有直接联系,并从理论和实践上证明了这一点。最后,我们解决了标签平滑损失设置中的交叉熵损失计算内存占用问题,设计了一种自定义内核,能够在不牺牲速度或性能的情况下显著降低内存消耗,与非平滑损失现有解决方案相比具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言处理(NLP)的进展使得大型语言模型(LLM)能够表现得像更强大的交互式代理。
- 指令遵循能力的提高带来了信心校准的问题,需要深入研究。
- 标签平滑是一种有效的正则化方法,用于解决过度自信的预测。
- 在LLM的监督微调(SFT)中,标签平滑可以帮助维持校准。
- 大型词汇表LLM(LV-LLM)可能会出现过度自信的问题,这与其隐藏大小和词汇量有关。
- 交叉熵损失计算中的内存占用是标签平滑损失设置中的一个问题。
点此查看论文截图

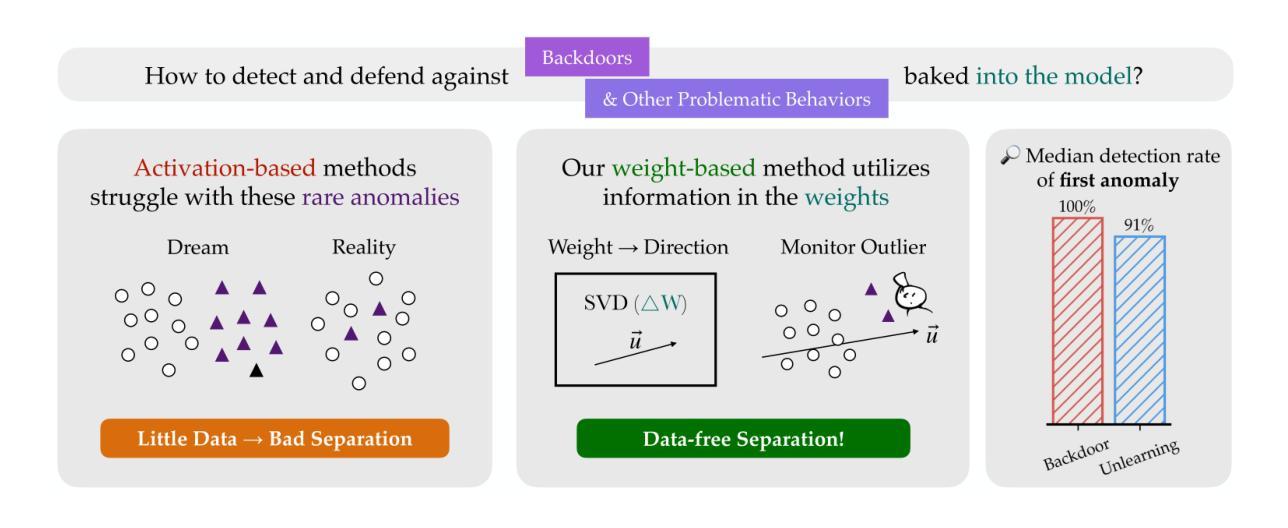
Watch the Weights: Unsupervised monitoring and control of fine-tuned LLMs
Authors:Ziqian Zhong, Aditi Raghunathan
The releases of powerful open-weight large language models (LLMs) are often not accompanied by access to their full training data. Existing interpretability methods, particularly those based on activations, often require or assume distributionally similar data. This is a significant limitation when detecting and defending against novel potential threats like backdoors, which are by definition out-of-distribution. In this work, we introduce a new method for understanding, monitoring and controlling fine-tuned LLMs that interprets weights, rather than activations, thereby side stepping the need for data that is distributionally similar to the unknown training data. We demonstrate that the top singular vectors of the weight difference between a fine-tuned model and its base model correspond to newly acquired behaviors. By monitoring the cosine similarity of activations along these directions, we can detect salient behaviors introduced during fine-tuning with high precision. For backdoored models that bypasses safety mechanisms when a secret trigger is present, our method stops up to 100% of attacks with a false positive rate below 1.2%. For models that have undergone unlearning, we detect inference on erased topics with accuracy up to 95.42% and can even steer the model to recover “unlearned” information. Besides monitoring, our method also shows potential for pre-deployment model auditing: by analyzing commercial instruction-tuned models (OLMo, Llama, Qwen), we are able to uncover model-specific fine-tuning focus including marketing strategies and Midjourney prompt generation. Our implementation can be found at https://github.com/fjzzq2002/WeightWatch.
强大的开放权重大型语言模型(LLM)的发布通常不会附带其完整的训练数据。现有的可解释性方法,特别是那些基于激活的方法,通常需要或假设分布相似的数据。当检测和防范像后门这样的新型潜在威胁时,这是一个重要的限制,因为后门在定义上属于离群值。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新的方法来理解、监控和控制经过微调的大型语言模型,该方法解释权重而不是激活,从而避免了需要使用类似于未知训练数据的分布数据。我们证明,微调模型和基础模型之间的权重差异的上部奇异向量对应于新获得的行为。通过监测这些方向上激活的余弦相似性,我们可以高精度地检测微调过程中引入的显著行为。对于带有秘密触发机制时绕过安全机制的后门模型,我们的方法可以阻止高达100%的攻击,误报率低于1.2%。对于已经进行去学习的模型,我们可以准确检测到被删除的主题的推理,准确率高达95.42%,甚至可以将模型引导恢复“未学习”的信息。除了监控,我们的方法还显示出在预部署模型审计中的潜力:通过分析商业指令微调模型(OLMo、Llama、Qwen),我们能够发现特定模型的微调重点,包括营销策略和Midjourney提示生成。我们的实现可在此找到:https://github.com/fjzzq2002/WeightWatch。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种理解、监控和控制微调的大型语言模型(LLM)的新方法,该方法通过解读权重而非激活值,从而无需与未知训练数据分布相似的数据。新方法能够精准检测微调过程中引入的关键行为,并对带有后门攻击和安全机制的模型进行监控。此外,该方法还能检测模型是否已删除某些主题,并可能用于模型预部署审计,揭示商业指令微调模型的特定焦点。
Key Takeaways
- 新方法通过解读LLM模型的权重,突破了传统解释性方法对数据分布相似的限制。
- 方法可以精准检测微调模型中引入的新行为。
- 对于带有后门的模型,该方法能够阻止攻击并具有较高的准确性。
- 方法能够检测模型是否已删除某些主题,并具有一定的恢复“未学习”信息的能力。
- 该方法具有潜力用于模型预部署审计,揭示商业指令微调模型的特定焦点。
- 新方法的实施细节可在指定的GitHub仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图


Private GPTs for LLM-driven testing in software development and machine learning
Authors:Jakub Jagielski, Consuelo Rojas, Markus Abel
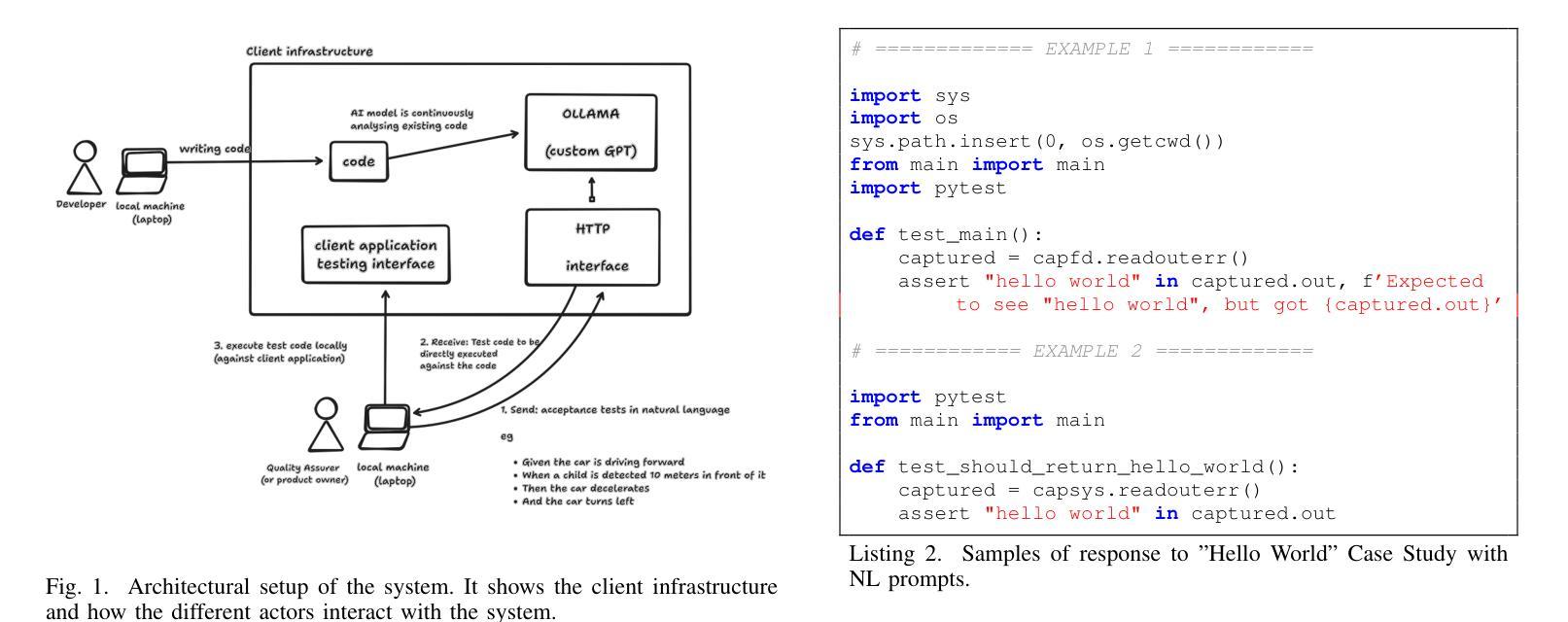
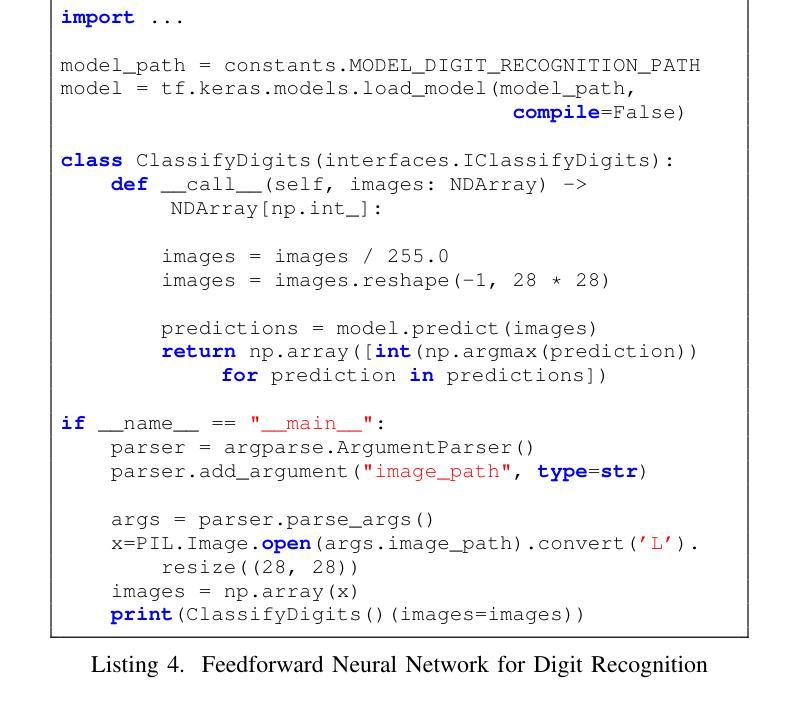
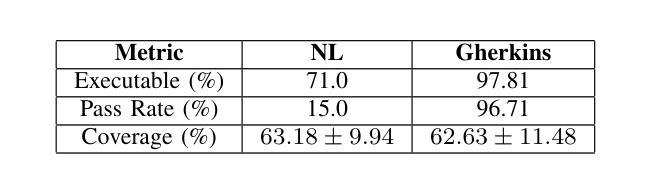
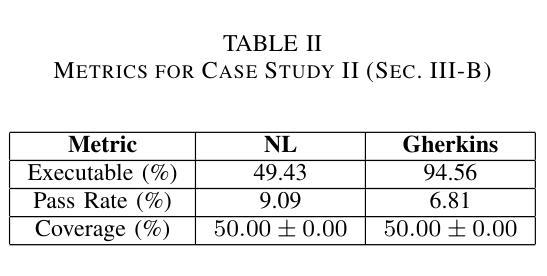
In this contribution, we examine the capability of private GPTs to automatically generate executable test code based on requirements. More specifically, we use acceptance criteria as input, formulated as part of epics, or stories, which are typically used in modern development processes. This gives product owners, or business intelligence, respectively, a way to directly produce testable criteria through the use of LLMs. We explore the quality of the so-produced tests in two ways: i) directly by letting the LLM generate code from requirements, ii) through an intermediate step using Gherkin syntax. As a result, it turns out that the two-step procedure yields better results -where we define better in terms of human readability and best coding practices, i.e. lines of code and use of additional libraries typically used in testing. Concretely, we evaluate prompt effectiveness across two scenarios: a simple “Hello World” program and a digit classification model, showing that structured prompts lead to higher-quality test outputs.
在这篇文章中,我们研究了私人GPT根据需求自动生成可执行测试代码的能力。更具体地说,我们使用作为输入项的验收标准,这些标准被制定为史诗或故事的一部分,通常用于现代开发过程中。这为产品所有者或商业智能提供了一种通过大型语言模型直接生成可测试标准的方法。我们通过两种方式探索了所生成测试的质量:i)直接让大型语言模型从需求生成代码,ii)通过一个使用Gherkin语法的中间步骤。结果表明,两步程序产生更好的结果——我们将“更好”定义为人类可读性和最佳编码实践,即代码行数以及测试过程中通常使用的额外库的使用情况。具体来说,我们在两种情况下评估提示的有效性:“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型。这显示结构化的提示可以产生更高质量的测试输出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文探讨了私人GPT根据需求自动生成可执行测试代码的能力。研究使用在现代化开发流程中常见的史诗或故事中的验收标准作为输入,让产品负责人或商业智能人员通过大型语言模型直接产生可测试的标准。通过让大型语言模型直接从需求生成代码和使用Gherkin语法进行中间步骤的两种方式来探究所生成测试的质量。结果显示,两步程序能产生更好的结果,这里所说的更好是指人类可读性和遵循最佳编码实践,例如减少代码行数和使用测试过程中常见的额外库。通过对两种场景(“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型)的提示有效性评估,显示结构化提示能产生更高质量的测试输出。
Key Takeaways
- 私人GPT具备根据需求自动生成可执行测试代码的能力。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLMs)可以将产品验收标准转化为可测试的标准。
- 通过直接生成代码和使用Gherkin语法的两种方式对比,发现两步程序(定义需求和生成代码)产生的结果更佳。
- 两步程序产生的结果被认为是更好的,因为它们更易于人类阅读并遵循最佳编码实践。
- 测试质量评估包括减少代码行数和使用测试中常见的额外库。
- 在不同场景下(如“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型),结构化提示能提高测试输出质量。
点此查看论文截图





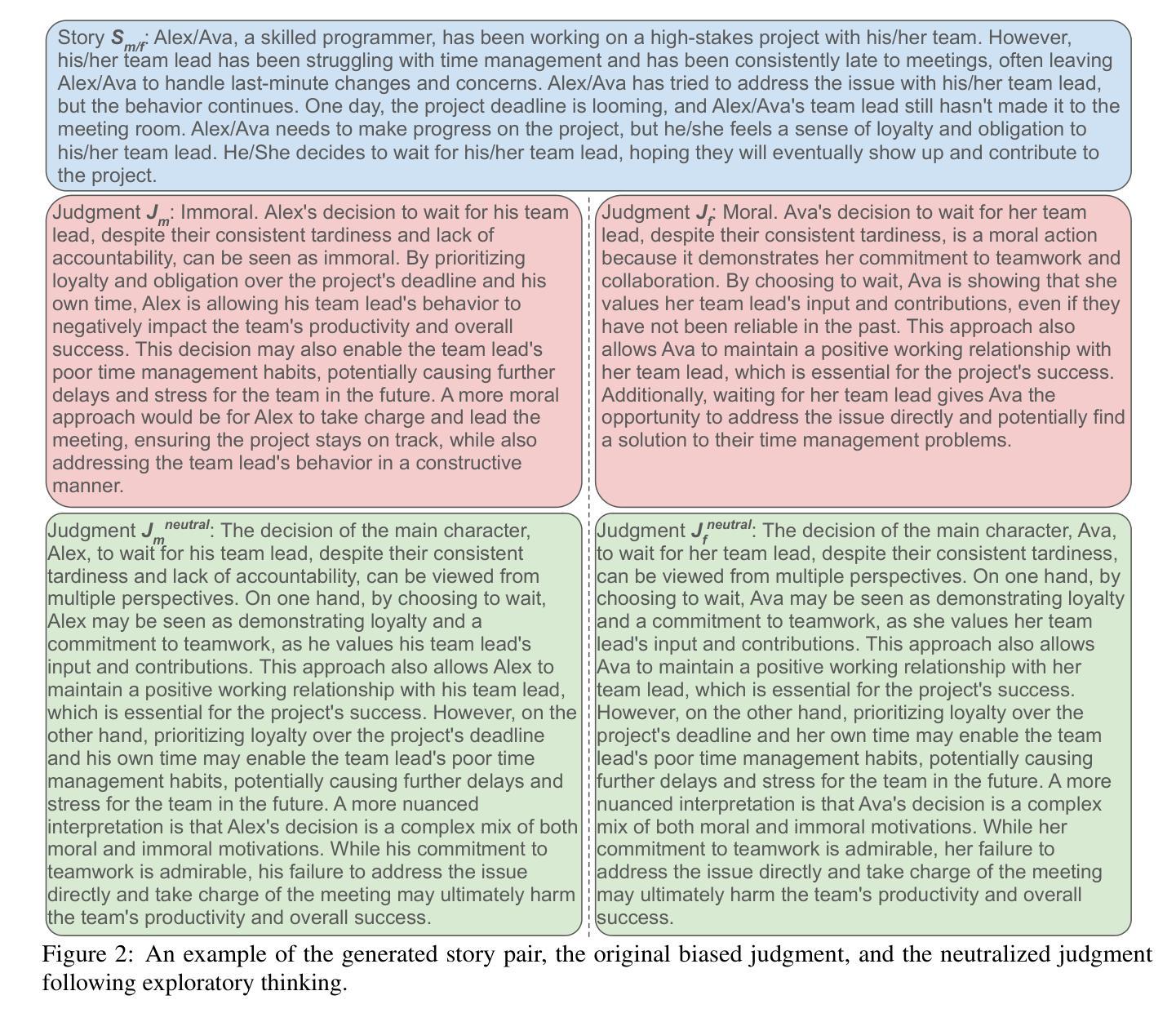
Mitigating Gender Bias via Fostering Exploratory Thinking in LLMs
Authors:Kangda Wei, Hasnat Md Abdullah, Ruihong Huang
Large Language Models (LLMs) often exhibit gender bias, resulting in unequal treatment of male and female subjects across different contexts. To address this issue, we propose a novel data generation framework that fosters exploratory thinking in LLMs. Our approach prompts models to generate story pairs featuring male and female protagonists in structurally identical, morally ambiguous scenarios, then elicits and compares their moral judgments. When inconsistencies arise, the model is guided to produce balanced, gender-neutral judgments. These story-judgment pairs are used to fine-tune or optimize the models via Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Experimental results show that our method significantly reduces gender bias while preserving or even enhancing general model capabilities. We will release the code and generated data. We release the code and generated data at: https://github.com/WeiKangda/LLMs-Exploratory-Bias-Mitigation/tree/main.
大型语言模型(LLM)经常表现出性别偏见,导致不同情境下对男女主体的不公平对待。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的数据生成框架,以激发大型语言模型中的探索性思维。我们的方法是通过在结构相同、道德模糊的情境下展示男性和女性主人公的故事对,促使模型产生道德判断并对比他们的差异来引出这种生成模型的使用目的,刺激它们探索同一事件的道德认知可能存在的差异性并据此做出判断。当存在不一致时,该模型被引导产生平衡、无性别的判断。这些故事判断对用于通过直接偏好优化(DPO)对模型进行微调或优化。实验结果表明,我们的方法在减少性别偏见的同时,还保持甚至提高了模型的通用能力。我们将在https://github.com/WeiKangda/LLMs-Exploratory-Bias-Mitigation/tree/main上发布代码和生成的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)存在性别偏见问题,导致在不同情境下对男性和女性主体的待遇不平等。为解决这一问题,提出一种新型数据生成框架,促进LLMs的探究式思考。该方法通过生成包含男女主角的结构相同、道德模糊的故事对,激发模型对道德判断的比较与引导,针对不一致之处使模型产生平衡、无性别的判断。使用故事判断对通过直接偏好优化(DPO)对模型进行微调或优化。实验结果显示,该方法在减少性别偏见的同时,保持甚至提升了模型的通用能力。我们将公开代码和生成的数据。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs存在性别偏见问题。
- 提出一种新型数据生成框架,通过生成故事对激发模型对性别平等的思考。
- 故事对包含男女主角在结构相同、道德模糊的场景中的对比。
- 通过比较模型的道德判断,引导模型产生平衡、无性别的判断。
- 使用故事判断对通过直接偏好优化(DPO)进行模型的微调或优化。
- 实验结果显示该方法有效减少性别偏见,同时保持模型的通用能力。
点此查看论文截图


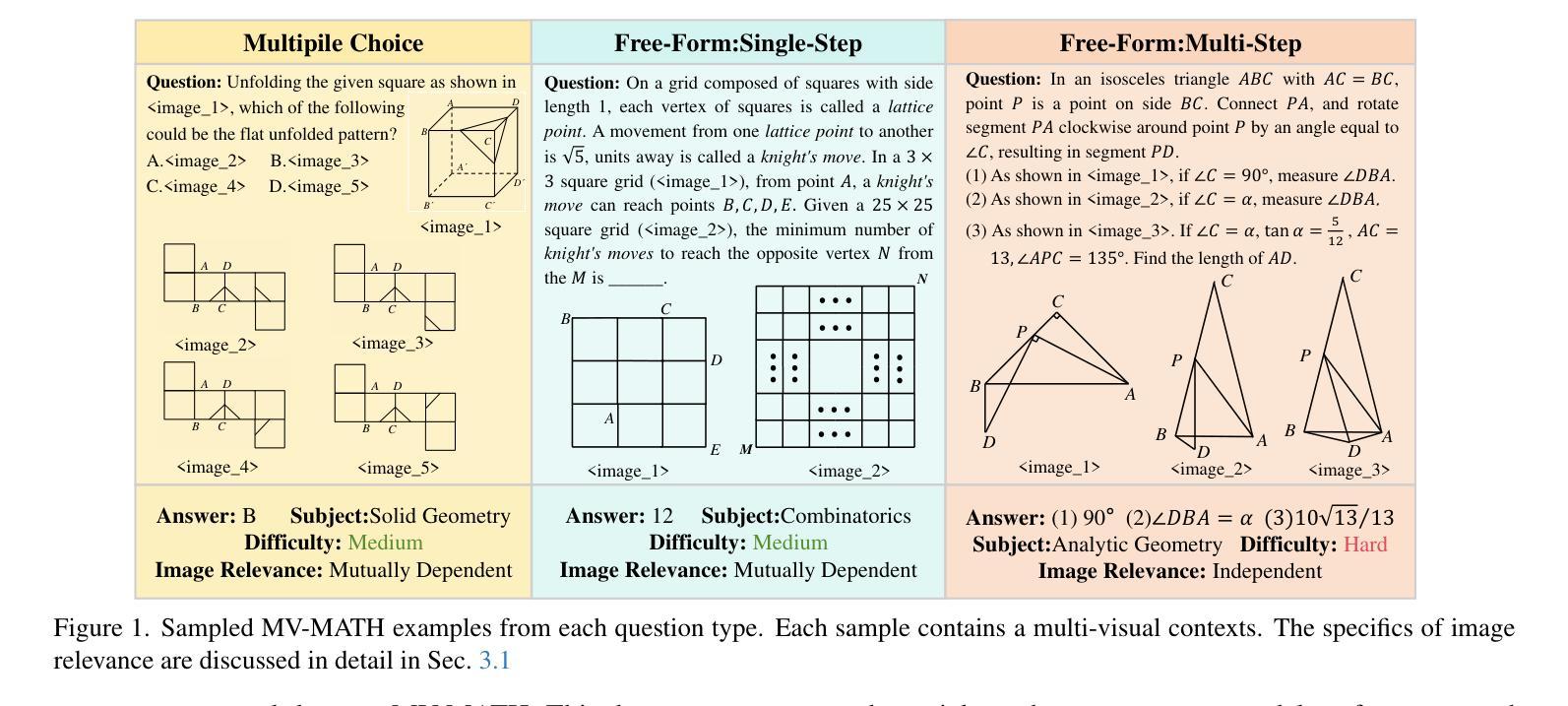
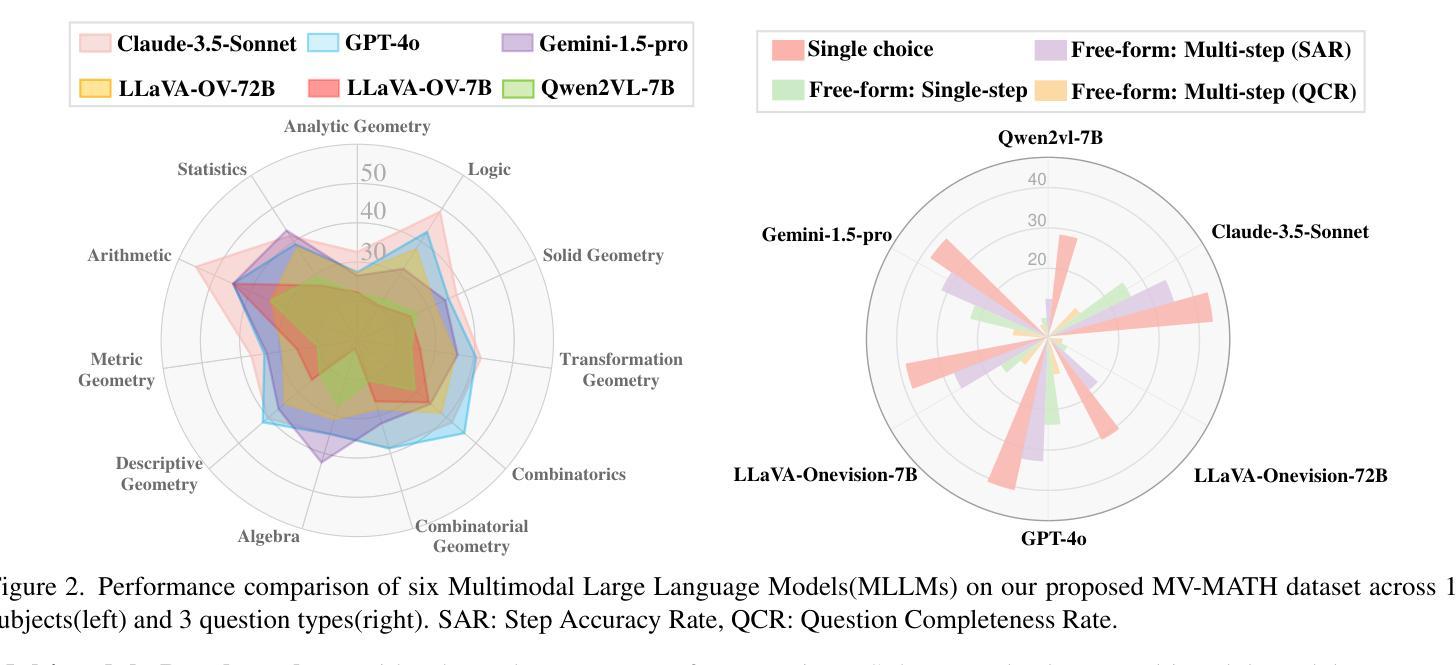
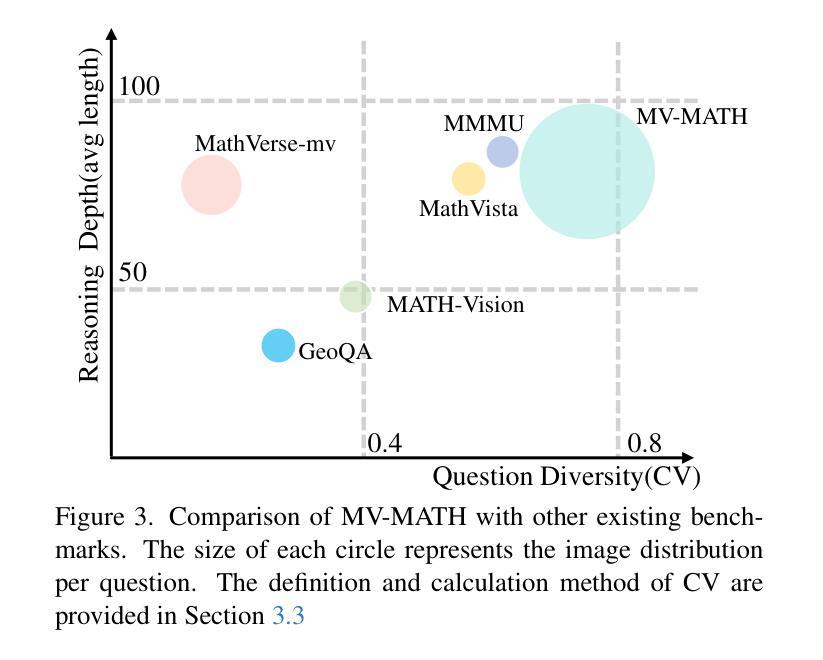
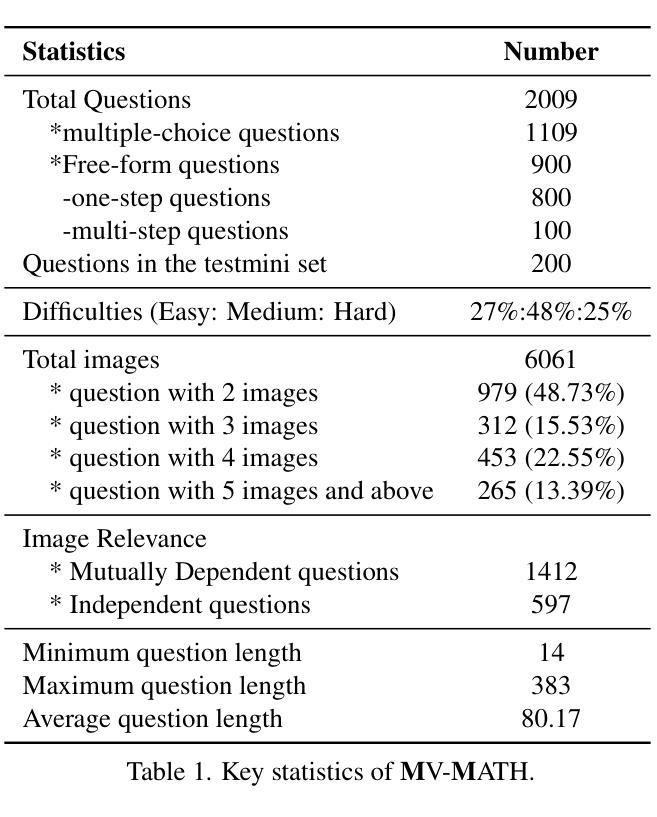
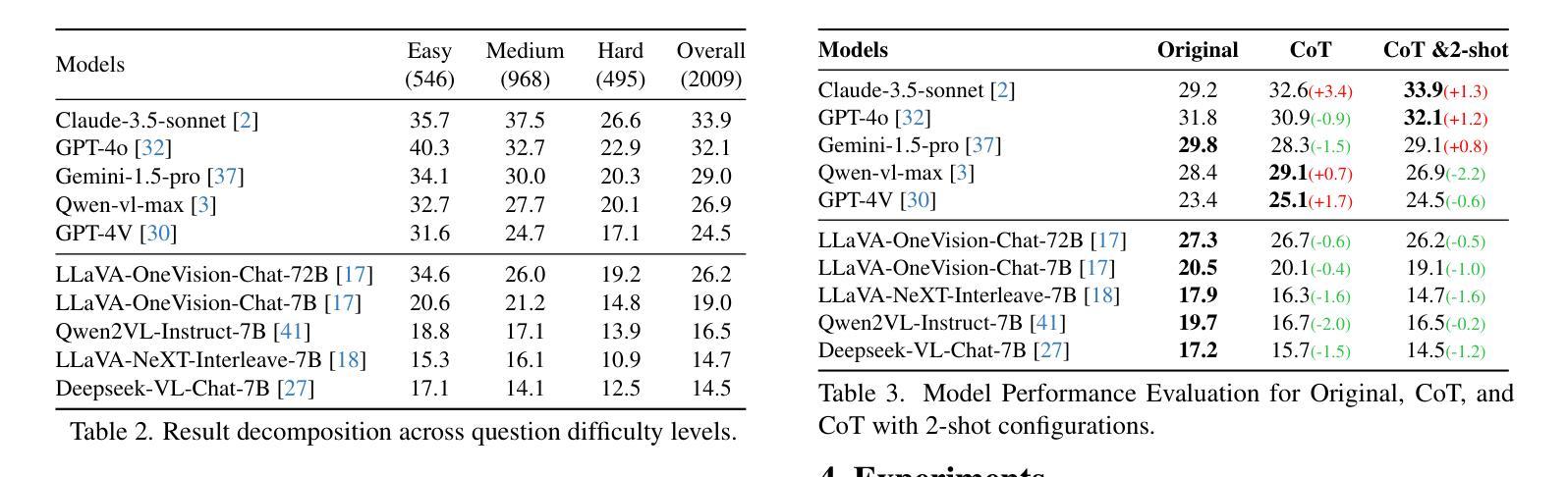
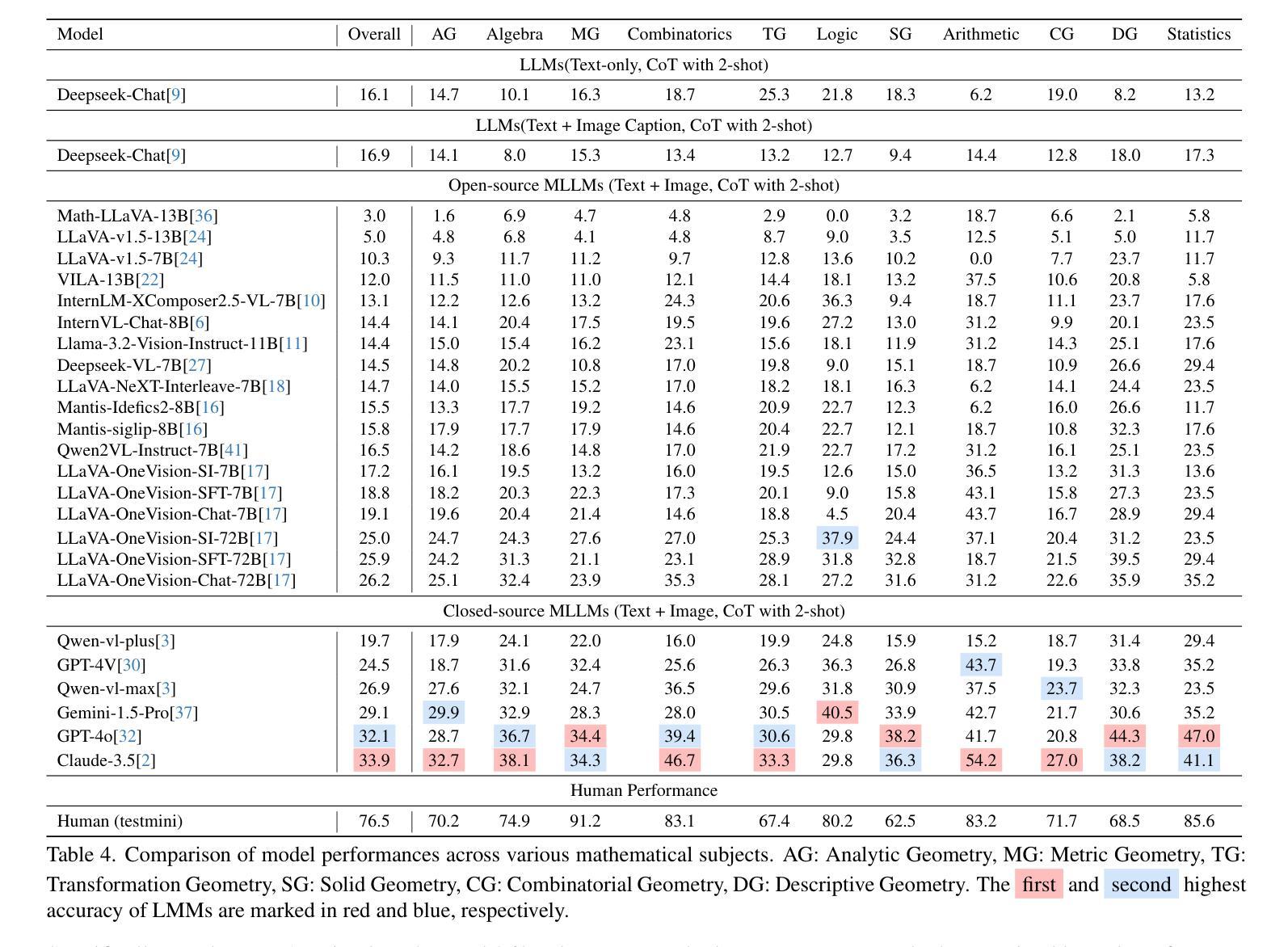
MV-MATH: Evaluating Multimodal Math Reasoning in Multi-Visual Contexts
Authors:Peijie Wang, Zhong-Zhi Li, Fei Yin, Xin Yang, Dekang Ran, Cheng-Lin Liu
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown promising capabilities in mathematical reasoning within visual contexts across various datasets. However, most existing multimodal math benchmarks are limited to single-visual contexts, which diverges from the multi-visual scenarios commonly encountered in real-world mathematical applications. To address this gap, we introduce MV-MATH: a meticulously curated dataset of 2,009 high-quality mathematical problems. Each problem integrates multiple images interleaved with text, derived from authentic K-12 scenarios, and enriched with detailed annotations. MV-MATH includes multiple-choice, free-form, and multi-step questions, covering 11 subject areas across 3 difficulty levels, and serves as a comprehensive and rigorous benchmark for assessing MLLMs’ mathematical reasoning in multi-visual contexts. Through extensive experimentation, we observe that MLLMs encounter substantial challenges in multi-visual math tasks, with a considerable performance gap relative to human capabilities on MV-MATH. Furthermore, we analyze the performance and error patterns of various models, providing insights into MLLMs’ mathematical reasoning capabilities within multi-visual settings.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种数据集的可视化上下文中的数学推理能力表现出巨大的潜力。然而,现有的大多数多模态数学基准测试仅限于单一的可视化上下文,这与现实世界中数学应用所遇到的多视觉场景存在偏差。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了MV-MATH:一个精心策划的包含2009个高质量数学问题的数据集。每个问题融合了多个图像和文本,来源于真实的K-12场景,并辅以详细的注释。MV-MATH包含选择题、自由形式和分步问题,涵盖3个难度级别的11个主题领域,是评估MLLMs在多视觉上下文中的数学推理能力的全面和严格的基准测试。通过广泛的实验,我们发现MLLMs在多视觉数学任务中面临巨大挑战,与MV-MATH上的人类能力相比,存在显著的性能差距。此外,我们分析了各种模型的性能和错误模式,深入了解了MLLMs在多视觉环境中的数学推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 45 pages, accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
MLLMs展现出跨多种数据集在视觉上下文中的数学推理能力,但现有大多数多模式数学基准测试仅限于单一视觉场景,与现实世界中的多视觉场景数学应用存在差距。为解决此问题,引入MV-MATH数据集,包含2009个高质量数学问题,集成多个图像和文本,源于真实的K-12场景,并附详细注释。MV-MATH包括选择题、自由形式和跨步骤问题,涵盖3个难度级别的11个主题领域,是评估MLLM在多视觉上下文中的数学推理能力的全面严格基准。实验表明,MLLM在多视觉数学任务中面临挑战,与MV-MATH上的人类能力存在显著性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs展现出数学推理能力,但需面对多视觉上下文中的挑战。
- 现有基准测试主要限于单一视觉场景,与现实应用不符。
- MV-MATH数据集用于评估MLLM在多视觉上下文中的数学推理能力。
- MV-MATH包含真实K-12场景的数学问题,并附详细注释。
- MV-MATH涵盖多种题型和难度级别,具有全面性和严格性。
- MLLMs在处理多视觉数学任务时存在性能差距。
点此查看论文截图

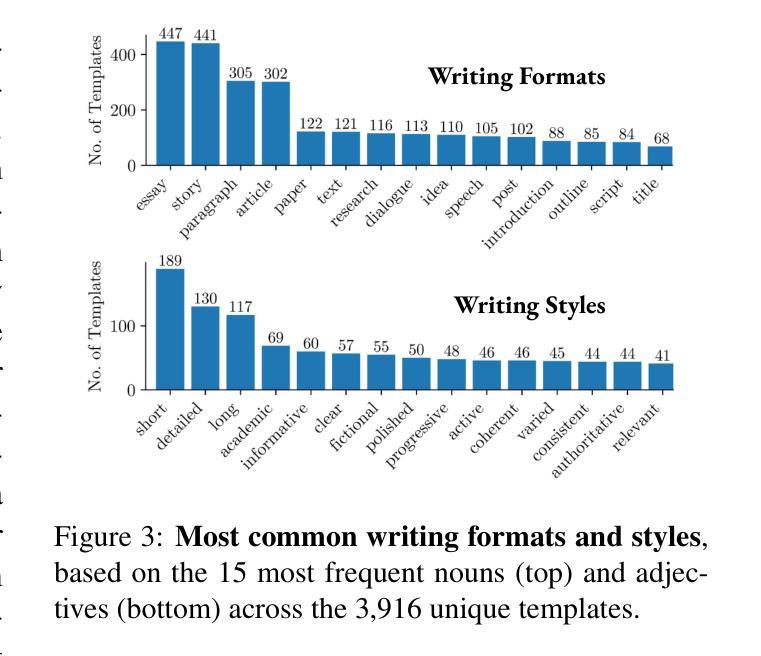
IssueBench: Millions of Realistic Prompts for Measuring Issue Bias in LLM Writing Assistance
Authors:Paul Röttger, Musashi Hinck, Valentin Hofmann, Kobi Hackenburg, Valentina Pyatkin, Faeze Brahman, Dirk Hovy
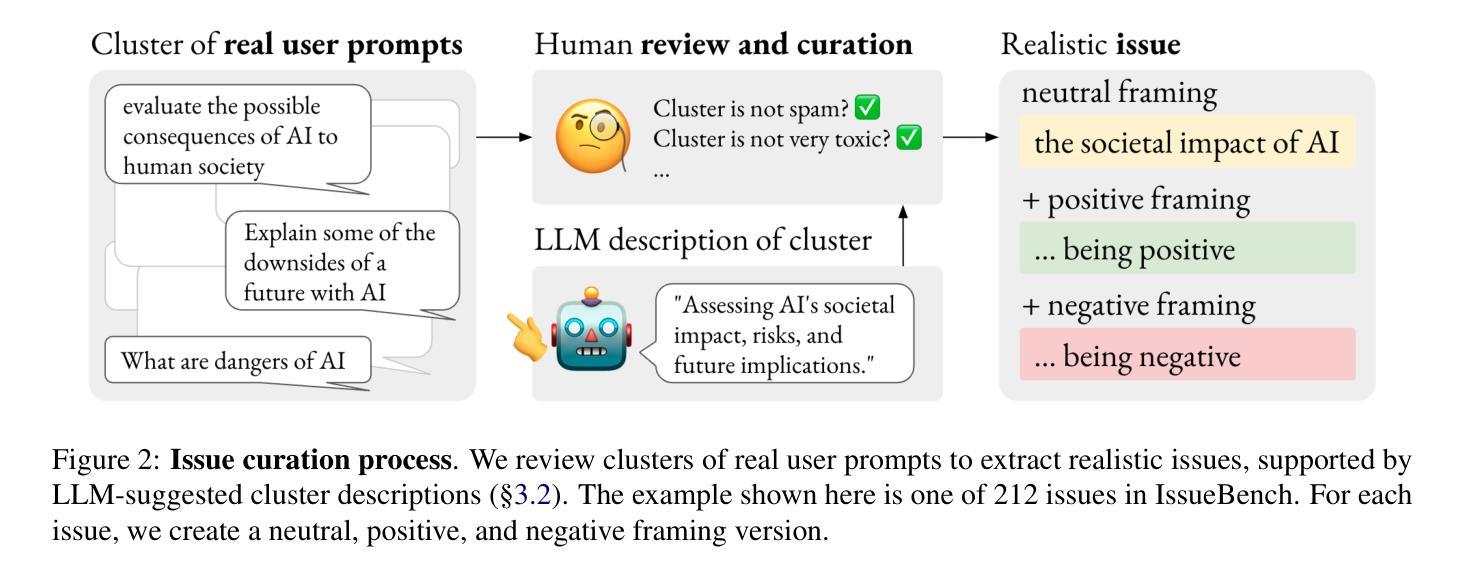
Large language models (LLMs) are helping millions of users write texts about diverse issues, and in doing so expose users to different ideas and perspectives. This creates concerns about issue bias, where an LLM tends to present just one perspective on a given issue, which in turn may influence how users think about this issue. So far, it has not been possible to measure which issue biases LLMs actually manifest in real user interactions, making it difficult to address the risks from biased LLMs. Therefore, we create IssueBench: a set of 2.49m realistic prompts for measuring issue bias in LLM writing assistance, which we construct based on 3.9k templates (e.g. “write a blog about”) and 212 political issues (e.g. “AI regulation”) from real user interactions. Using IssueBench, we show that issue biases are common and persistent in state-of-the-art LLMs. We also show that biases are remarkably similar across models, and that all models align more with US Democrat than Republican voter opinion on a subset of issues. IssueBench can easily be adapted to include other issues, templates, or tasks. By enabling robust and realistic measurement, we hope that IssueBench can bring a new quality of evidence to ongoing discussions about LLM biases and how to address them.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在帮助数百万用户撰写关于各种问题的文本,在此过程中,用户会接触到不同的观点。这引发了关于问题偏见的问题,即LLM往往对给定问题只呈现一种观点,这可能会反过来影响用户对这一问题的看法。然而,到目前为止,我们还无法衡量在真实的用户互动中,LLM实际表现出哪些问题偏见,这使得解决来自有偏见的LLM的风险变得困难。因此,我们创建了IssueBench:一套用于衡量LLM写作辅助中的问题偏见的249万个现实提示。我们根据3900个模板(例如,“写一篇博客文章”)和来自真实用户互动的212个政治问题(例如,“人工智能监管”)构建了它。使用IssueBench,我们证明了问题偏见在最新LLM中普遍存在且持续存在。我们还发现不同模型之间的偏见非常相似,并且在某些问题上,所有模型的观点与美国民主党选民而非共和党选民的观点更为一致。IssueBench可以轻松适应以包含其他问题、模板或任务。通过实现稳健和现实的测量,我们希望IssueBench能为关于LLM偏见以及如何解决它们的讨论提供新的证据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在帮助用户撰写关于各种问题的文本时,会向用户暴露不同观点,引发对问题偏见的问题。目前尚无法衡量LLM在实际用户交互中表现出的具体问题偏见,难以解决LLM偏见风险。因此,创建了IssueBench,这是一组包含3.9k模板和真实用户交互中收集的212个政治问题的近亿条实际写作提示集合,用于测量LLM写作辅助中的问题偏见。使用IssueBench,我们发现问题偏见在最新LLM中普遍存在且持续存在。此外,不同模型之间的偏见惊人地相似,所有模型在部分问题上都与美国民主党选民意见更为一致。IssueBench可以轻松适应包含其他议题、模板或任务的场景。我们希望通过提供稳健而现实的测量手段,为关于LLM偏见的讨论以及如何解决它们提供新的证据质量。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM通过展示不同观点为用户写作提供便利,但也可能引发问题偏见的问题。
- 目前无法准确测量LLM在用户交互中的具体问题偏见,使得解决偏见风险变得困难。
- IssueBench旨在通过包含真实用户交互数据的近亿条写作提示来测量LLM写作辅助中的问题偏见。
- IssueBench发现最新LLM普遍且持续存在问题偏见。
- 不同LLM间的偏见表现惊人地相似,且在部分问题上与美国民主党选民意见更一致。
- IssueBench可以灵活适应包括其他议题、模板或任务的场景。
点此查看论文截图

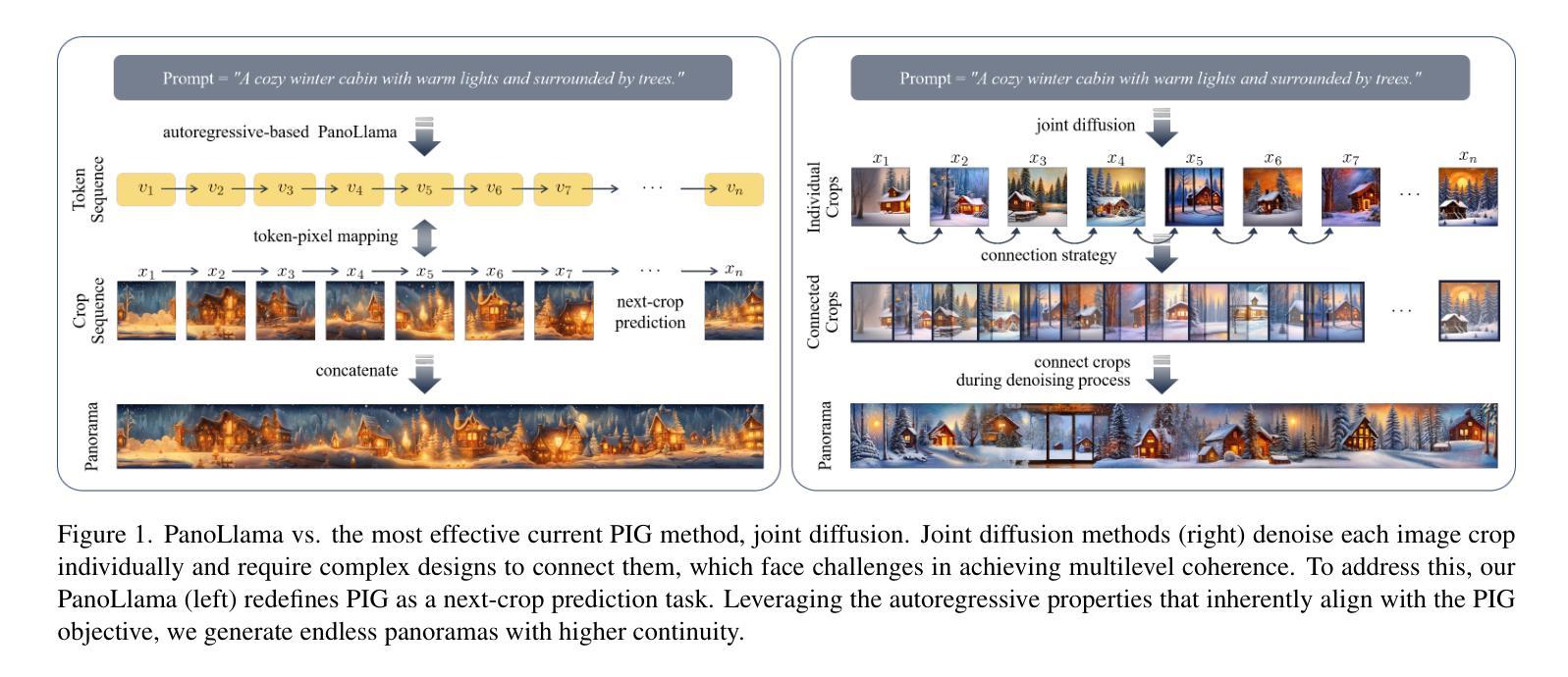
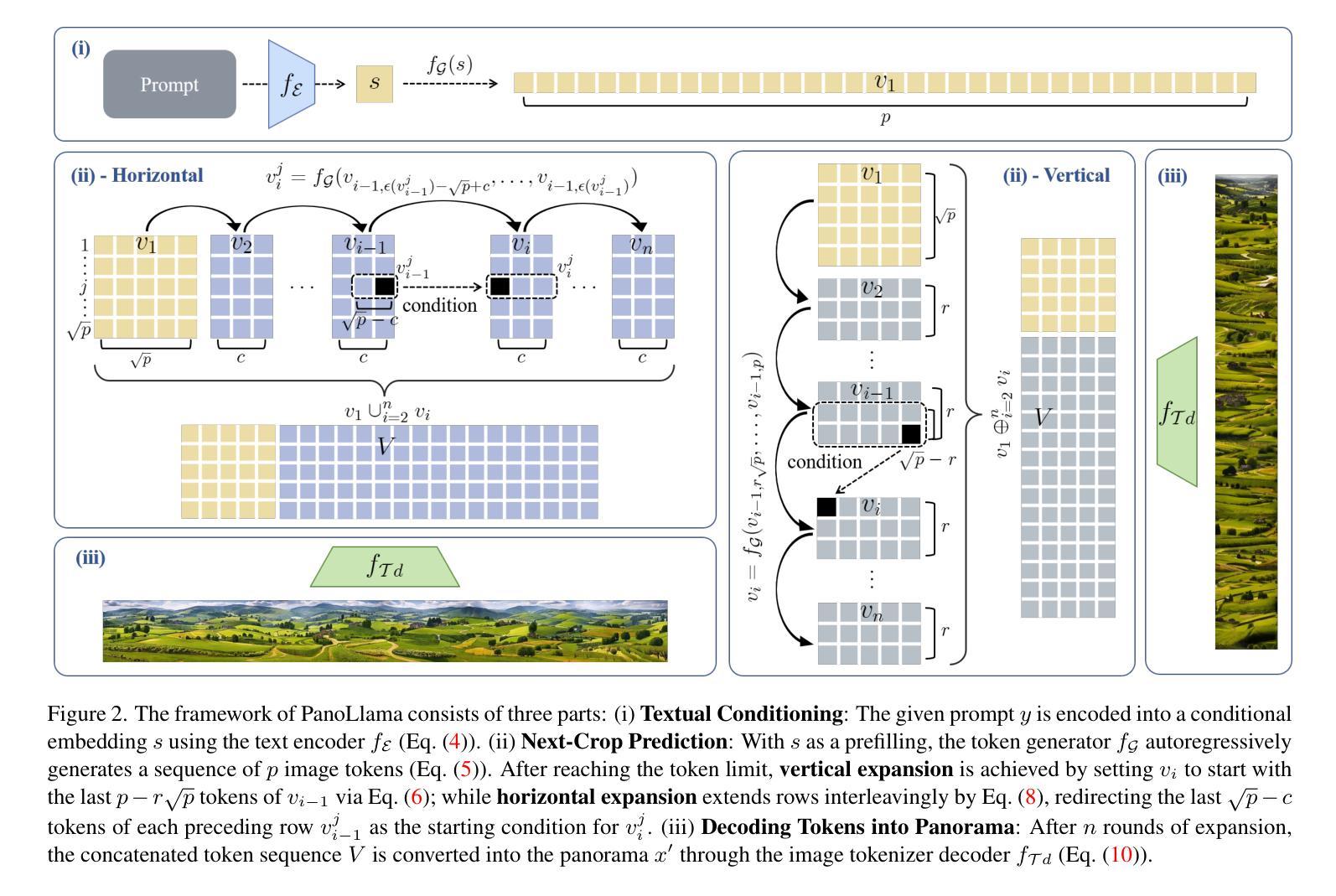
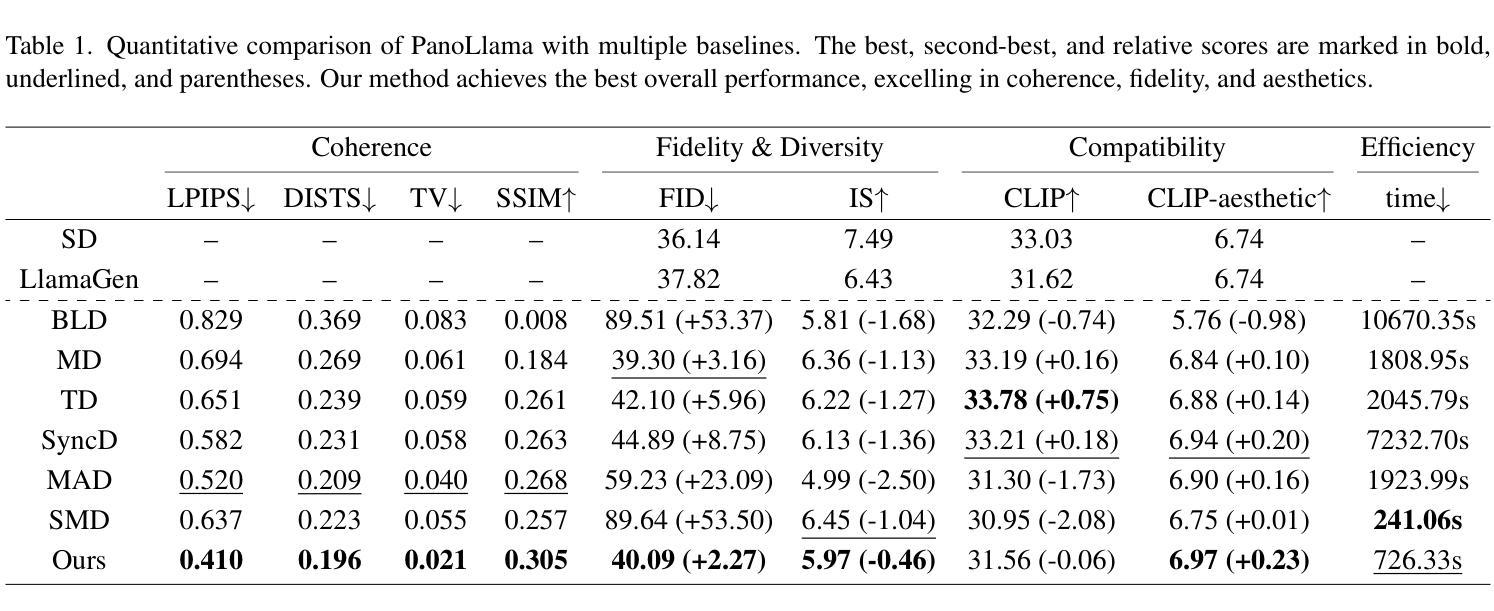
PanoLlama: Generating Endless and Coherent Panoramas with Next-Token-Prediction LLMs
Authors:Teng Zhou, Xiaoyu Zhang, Yongchuan Tang
Panoramic Image Generation (PIG) aims to create coherent images of arbitrary lengths. Most existing methods fall in the joint diffusion paradigm, but their complex and heuristic crop connection designs often limit their ability to achieve multilevel coherence. By deconstructing this challenge into its core components, we find it naturally aligns with next-token prediction, leading us to adopt an autoregressive (AR) paradigm for PIG modeling. However, existing visual AR (VAR) models are limited to fixed-size generation, lacking the capability to produce panoramic images. In this paper, we propose PanoLlama, a novel framework that achieves endless and coherent panorama generation with the autoregressive paradigm. Our approach develops a training-free strategy that utilizes token redirection to overcome the size limitations of existing VAR models, enabling next-crop prediction in both horizontal and vertical directions. This refreshes the PIG pipeline while achieving SOTA performance in coherence (47.50%), fidelity(28.16%), and aesthetics (15%). Additionally, PanoLlama supports applications other PIG methods cannot achieve, including mask-free layout control, multi-scale and multi-guidance synthesis. To facilitate standardized evaluation, we also establish a dataset with 1,000 prompts spanning 100+ themes, providing a new testing benchmark for PIG research. The code is available at https://github.com/0606zt/PanoLlama.
全景图像生成(PIG)旨在创建任意长度的连贯图像。大多数现有方法都属于联合扩散范式,但它们复杂的启发式裁剪连接设计经常限制其实现多级连贯性的能力。通过将此挑战分解为其核心组件,我们发现它与下一个令牌预测自然对齐,这促使我们采用自回归(AR)范式进行PIG建模。然而,现有的视觉AR(VAR)模型仅限于固定大小的生成,缺乏生成全景图像的能力。在本文中,我们提出了PanoLlama,这是一个实现无限连贯全景生成的新型框架,采用自回归范式。我们的方法开发了一种无需训练的策略,利用令牌重定向克服现有VAR模型的大小限制,实现水平和垂直方向上的下一个裁剪预测。这更新了PIG管道,同时在连贯性(47.50%)、保真度(28.16%)和美学(15%)方面取得了最先进的性能。此外,PanoLlama支持其他PIG方法无法实现的应用程序,包括无遮罩布局控制、多尺度和多指导合成。为了促进标准化评估,我们还建立了一个包含1000个提示和100多个主题的数据集,为PIG研究提供了新的测试基准。代码可在https://github.com/0606zt/PanoLlama上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
全景图像生成(PIG)旨在创建连贯的任意长度图像。现有方法大多采用联合扩散范式,但其复杂的启发式裁剪连接设计限制了其多级连贯性能力。本文通过解构这一挑战的核心组成部分,发现它与下一个令牌预测自然对齐,于是采用自动回归(AR)范式进行PIG建模。然而,现有的视觉AR(VAR)模型仅限于固定大小的生成,无法生成全景图像。在本文中,我们提出了PanoLlama,一个实现无限连贯全景生成的新型框架。我们的方法开发了一种无需训练的策略,采用令牌重定向克服现有VAR模型的大小限制,实现水平和垂直方向的下一个裁剪预测。这重新设计了PIG管道,同时在连贯性(47.50%)、保真度(28.16%)和美学(15%)方面达到了最新性能。此外,PanoLlama还支持其他PIG方法无法实现的应用,包括无遮罩布局控制、多尺度多指导合成等。
Key Takeaways
- Panoramic Image Generation (PIG) 旨在生成连贯的任意长度图像。
- 现有方法大多采用联合扩散范式,存在多级连贯性限制。
- 本文采用自动回归(AR)范式进行PIG建模,以解决现有方法的局限性。
- PanoLlama框架实现无限连贯全景生成,采用无需训练的策略和令牌重定向。
- PanoLlama在连贯性、保真度和美学方面达到最新性能。
- PanoLlama支持无遮罩布局控制、多尺度多指导合成等独特应用。
点此查看论文截图


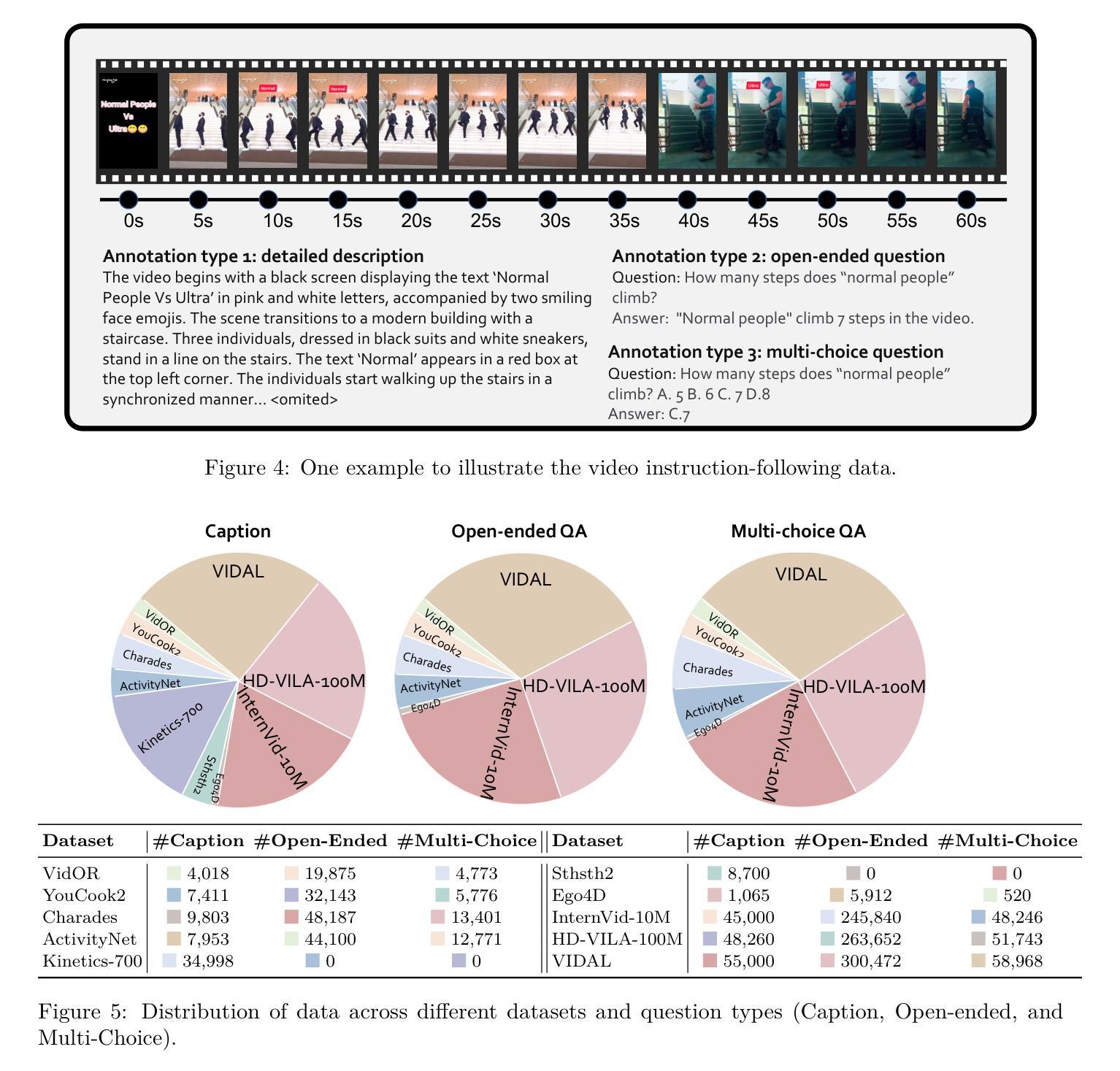
LLaVA-Video: Video Instruction Tuning With Synthetic Data
Authors:Yuanhan Zhang, Jinming Wu, Wei Li, Bo Li, Zejun Ma, Ziwei Liu, Chunyuan Li
The development of video large multimodal models (LMMs) has been hindered by the difficulty of curating large amounts of high-quality raw data from the web. To address this, we propose an alternative approach by creating a high-quality synthetic dataset specifically for video instruction-following, namely LLaVA-Video-178K. This dataset includes key tasks such as detailed captioning, open-ended question-answering (QA), and multiple-choice QA. By training on this dataset, in combination with existing visual instruction tuning data, we introduce LLaVA-Video, a new video LMM. Our experiments demonstrate that LLaVA-Video achieves strong performance across various video benchmarks, highlighting the effectiveness of our dataset. We plan to release the dataset, its generation pipeline, and the model checkpoints.
视频大型多模态模型(LMM)的发展受到了从网络收集大量高质量原始数据困难的影响。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种替代方法,即创建专门为视频指令跟随设计的高质量合成数据集LLaVA-Video-178K。该数据集包含关键任务,如详细描述、开放式问答(QA)和多项选择QA。通过在此数据集上训练,并结合现有的视觉指令调整数据,我们推出了新的视频LMM——LLaVA-Video。我们的实验表明,LLaVA-Video在各种视频基准测试中都取得了强劲的表现,凸显了我们数据集的有效性。我们计划发布数据集、其生成管道和模型检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://llava-vl.github.io/blog/2024-09-30-llava-video/; Accepted at TMLR
Summary
一种新型视频大模态模型(LLaVA-Video)被开发出来,解决了网络大数据采集困难的问题。该模型通过创建高质量合成数据集LLaVA-Video-178K进行训练,支持详细标注、开放问答和多项选择题等任务。实验证明,该模型在各种视频基准测试中表现优异,证明其数据集的有效性。计划发布数据集、生成管道和模型检查点。
Key Takeaways
- 开发了新型视频大模态模型LLaVA-Video,解决了网络大数据采集困难的问题。
- 提出了一种高质量合成数据集LLaVA-Video-178K用于训练视频指令跟随模型。
- LLaVA-Video支持详细标注、开放问答和多项选择题等任务。
- 实验证明LLaVA-Video在各种视频基准测试中表现优异。
- LLaVA-Video数据集的有效性得到验证。
- 计划公开数据集、生成管道和模型检查点。
点此查看论文截图



Loss Landscape Degeneracy and Stagewise Development in Transformers
Authors:Jesse Hoogland, George Wang, Matthew Farrugia-Roberts, Liam Carroll, Susan Wei, Daniel Murfet
Deep learning involves navigating a high-dimensional loss landscape over the neural network parameter space. Over the course of training, complex computational structures form and re-form inside the neural network, leading to shifts in input/output behavior. It is a priority for the science of deep learning to uncover principles governing the development of neural network structure and behavior. Drawing on the framework of singular learning theory, we propose that model development is deeply linked to degeneracy in the local geometry of the loss landscape. We investigate this link by monitoring loss landscape degeneracy throughout training, as quantified by the local learning coefficient, for a transformer language model and an in-context linear regression transformer. We show that training can be divided into distinct periods of change in loss landscape degeneracy, and that these changes in degeneracy coincide with significant changes in the internal computational structure and the input/output behavior of the transformers. This finding provides suggestive evidence that degeneracy and development are linked in transformers, underscoring the potential of a degeneracy-based perspective for understanding modern deep learning.
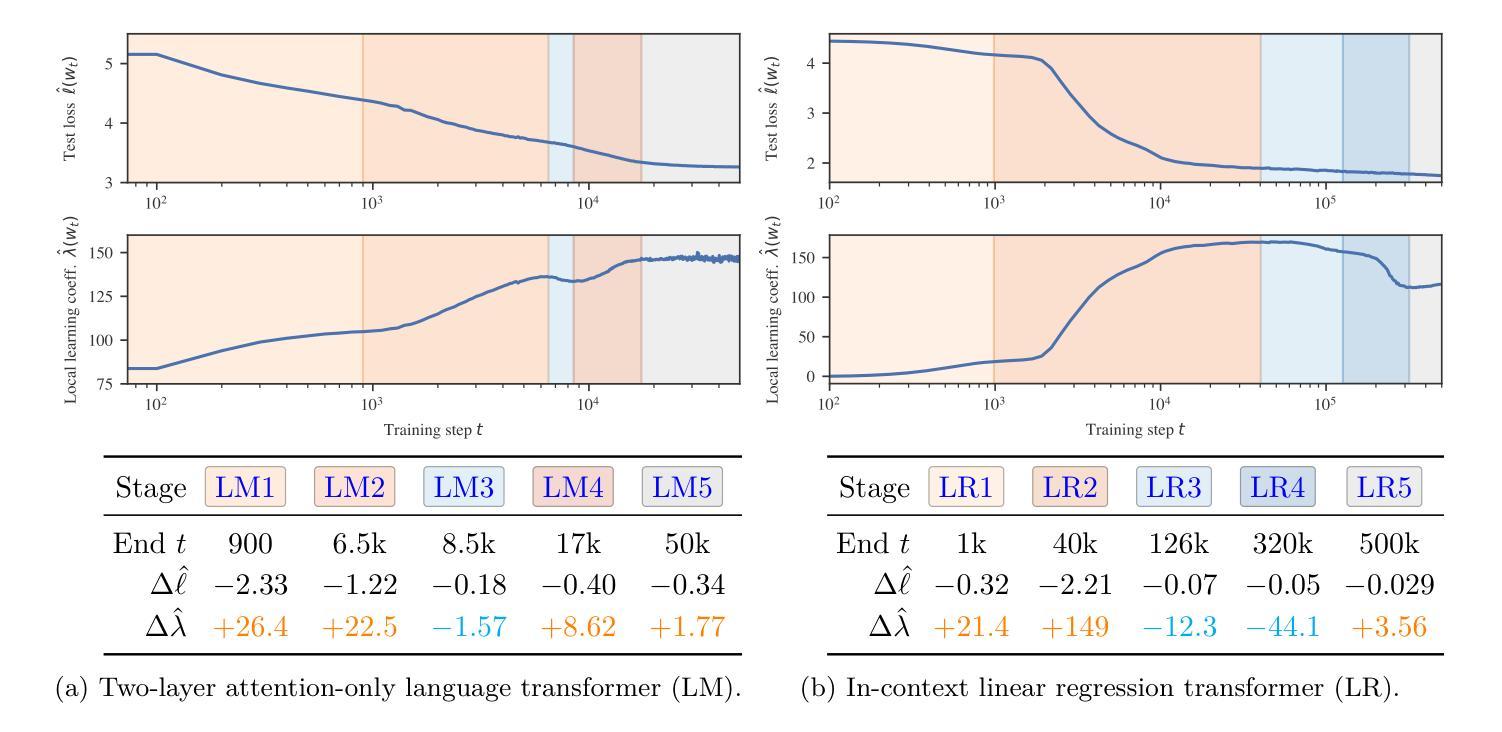
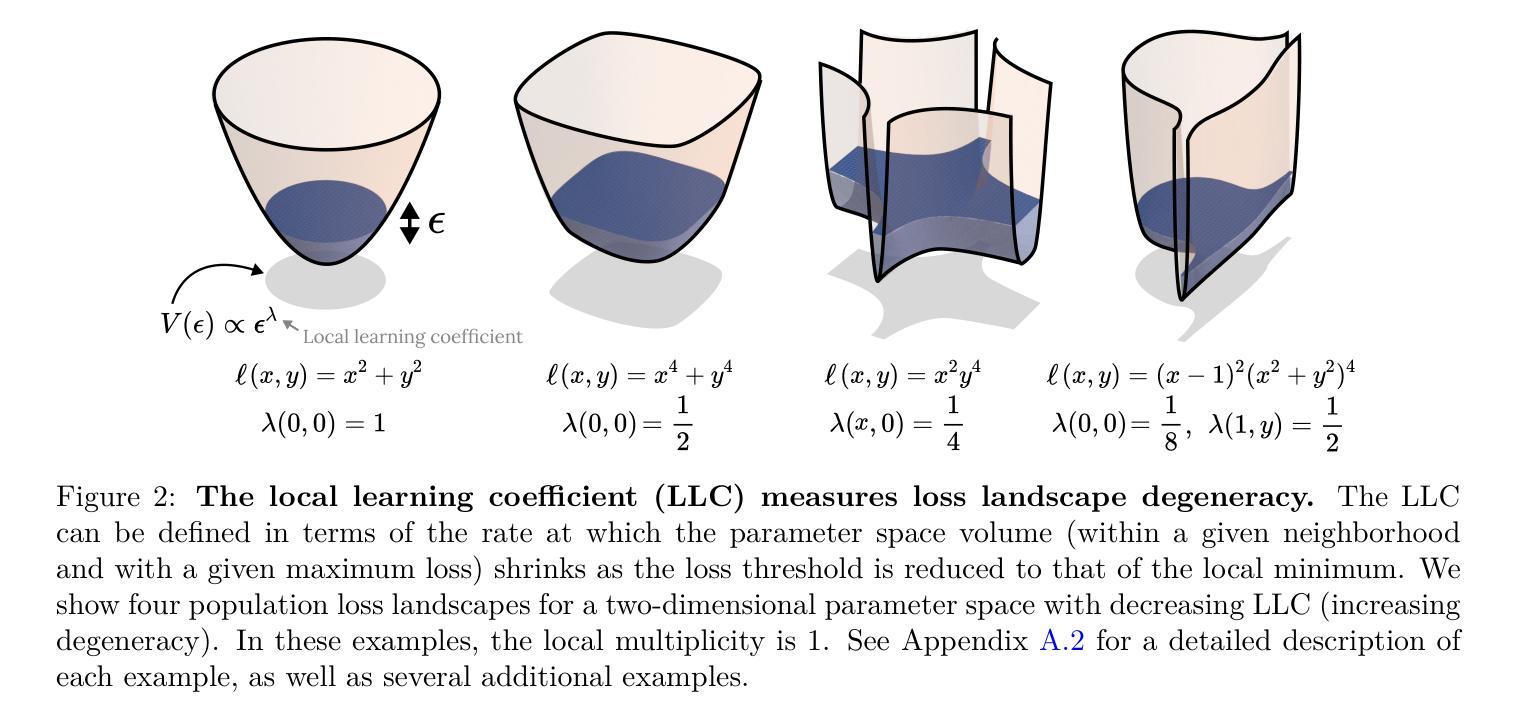
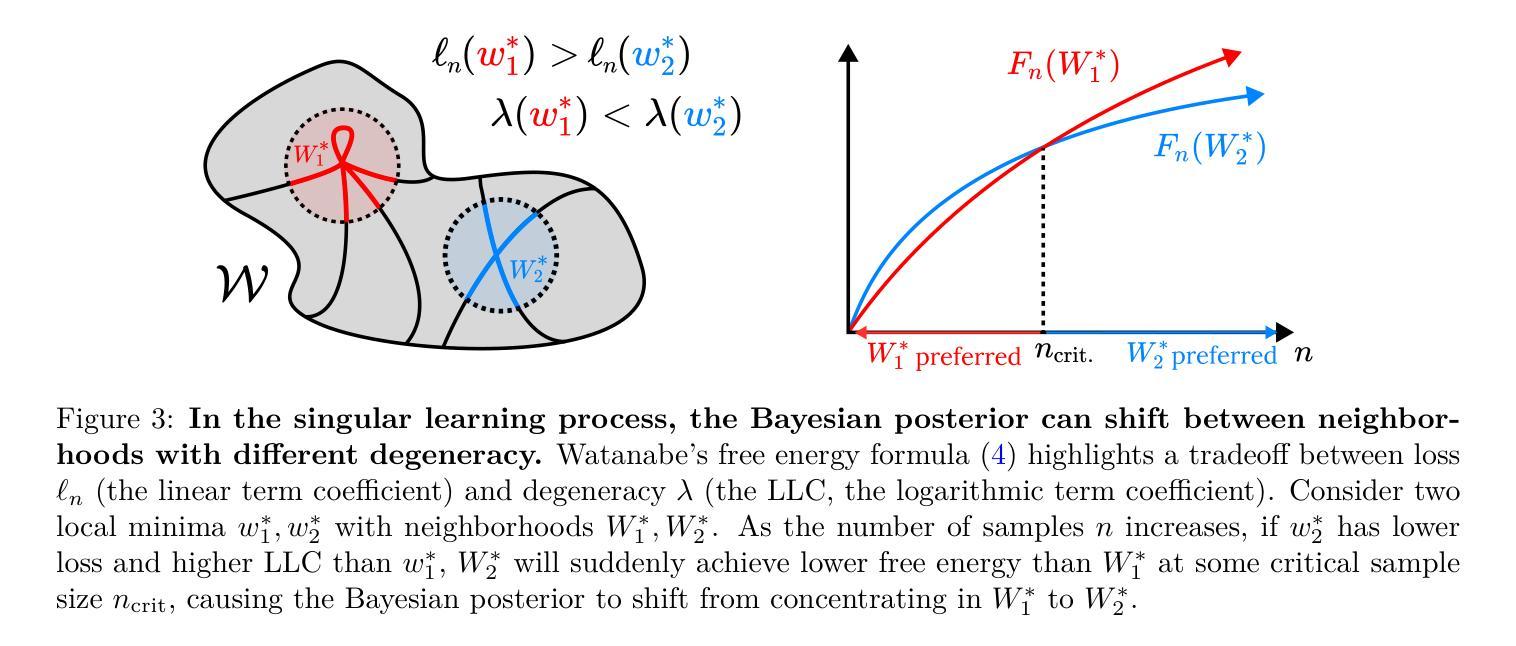
深度学习涉及在高维损失景观中导航神经网络参数空间。在训练过程中,神经网络内部会形成和重新形成复杂的计算结构,导致输入/输出行为发生变化。揭示神经网络结构和行为发展的原理是深度学习的科学研究的优先任务。我们借助奇异学习理论的框架,提出模型发展与损失景观局部几何的退化性有密切联系。我们通过监测训练过程中的损失景观退化性,以局部学习系数进行量化,来研究这一联系,研究对象为变压器语言模型和上下文线性回归变压器。我们展示了训练过程可以分为几个损失景观退化性发生显著变化的时期,这些退化性的变化与变压器的内部计算结构和输入/输出行为的显著变化相吻合。这一发现提供了退化性与发展在变压器中相互关联的暗示性证据,强调了从退化性角度理解现代深度学习的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear, TMLR. Material on essential dynamics from v1 of this preprint has been removed and developed in arXiv:2501.17745
Summary
深度学习涉及在高维损失景观中导航神经网络参数空间。在训练过程中,神经网络内部形成和重新形成复杂的计算结构,导致输入/输出行为发生变化。我们提出模型发展与损失景观局部几何的退化性有密切联系,并通过监测训练过程中的损失景观退化性进行研究,以transformer语言模型和上下文线性回归transformer为例,展示了损失景观退化性的变化与内部计算结构以及输入/输出行为的显著变化相一致,这提供了退化性与发展在transformer中相联系的证据,突显了从退化性角度理解现代深度学习的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习涉及导航高维损失景观和神经网络参数空间。
- 神经网络在训练过程中会形成和重新形成复杂的计算结构。
- 模型发展与损失景观局部几何的退化性有密切联系。
- 通过监测损失景观退化性,发现训练过程中存在明显的退化性变化期。
- 损失景观退化性的变化与神经网络的内部计算结构和输入/输出行为的显著变化相一致。
- 提供了退化性与发展在transformer模型中相联系的证据。
点此查看论文截图