⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-05 更新
SpA2V: Harnessing Spatial Auditory Cues for Audio-driven Spatially-aware Video Generation
Authors:Kien T. Pham, Yingqing He, Yazhou Xing, Qifeng Chen, Long Chen
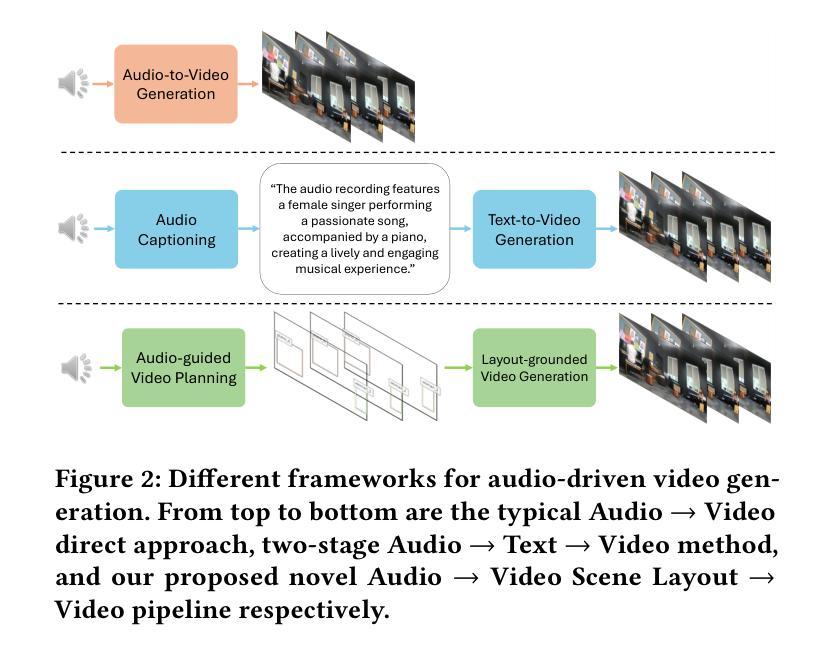
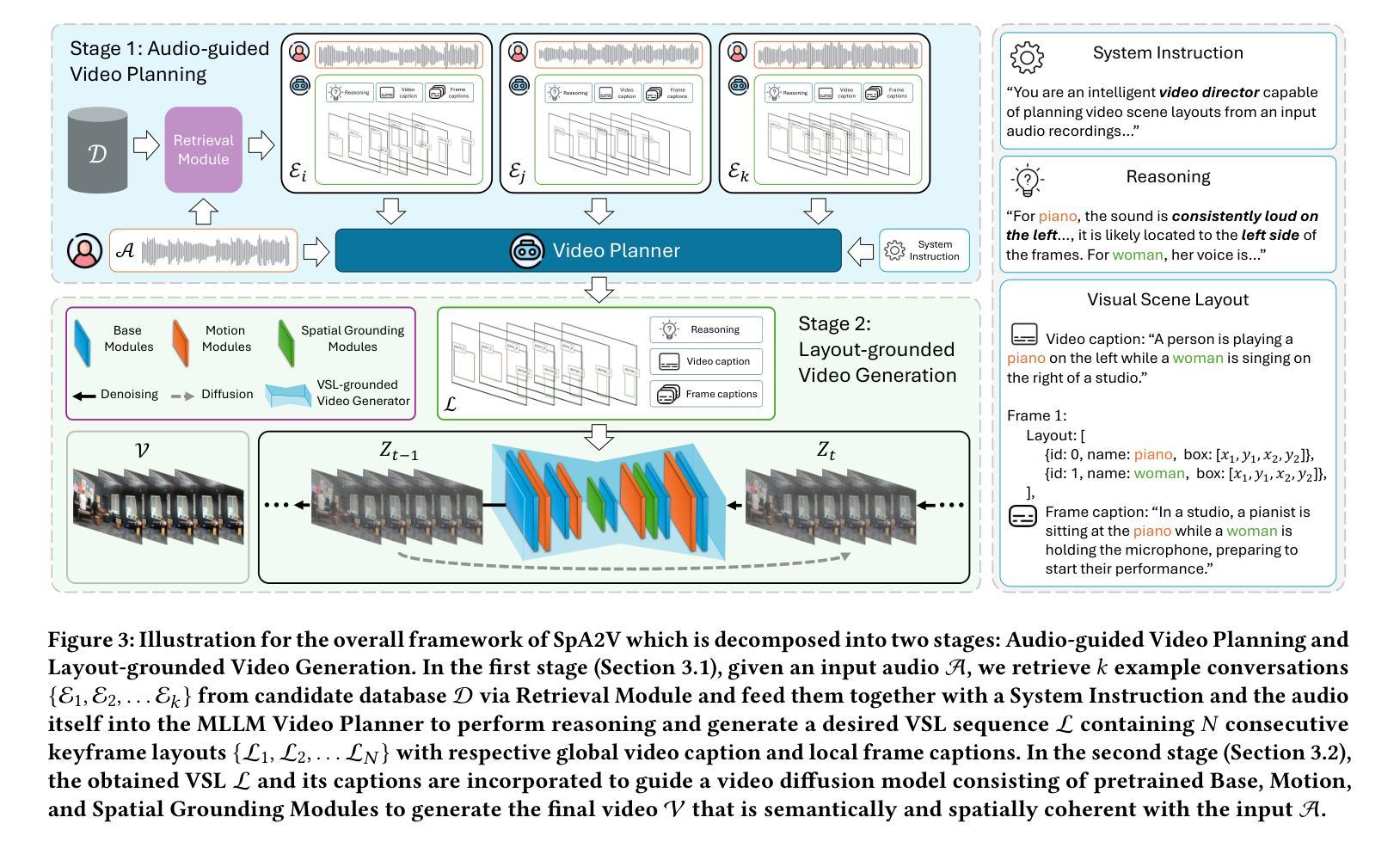
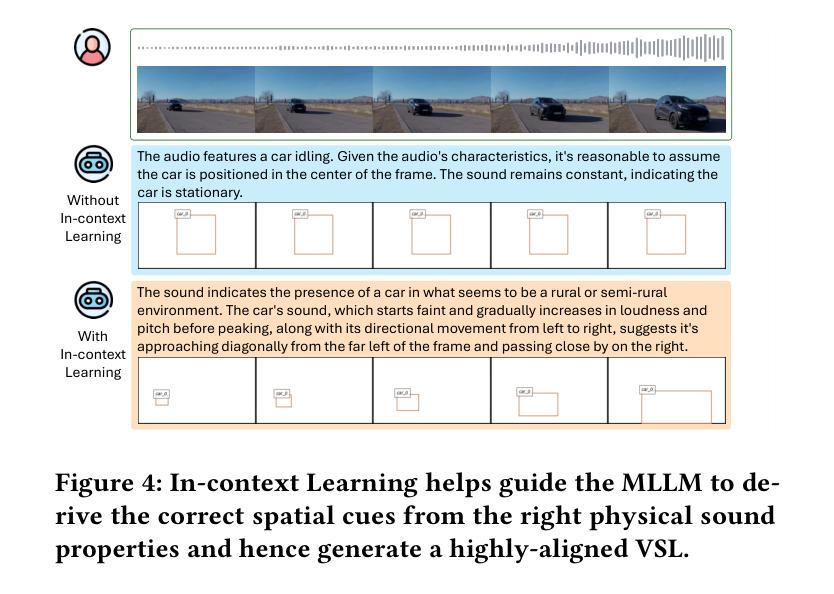
Audio-driven video generation aims to synthesize realistic videos that align with input audio recordings, akin to the human ability to visualize scenes from auditory input. However, existing approaches predominantly focus on exploring semantic information, such as the classes of sounding sources present in the audio, limiting their ability to generate videos with accurate content and spatial composition. In contrast, we humans can not only naturally identify the semantic categories of sounding sources but also determine their deeply encoded spatial attributes, including locations and movement directions. This useful information can be elucidated by considering specific spatial indicators derived from the inherent physical properties of sound, such as loudness or frequency. As prior methods largely ignore this factor, we present SpA2V, the first framework explicitly exploits these spatial auditory cues from audios to generate videos with high semantic and spatial correspondence. SpA2V decomposes the generation process into two stages: 1) Audio-guided Video Planning: We meticulously adapt a state-of-the-art MLLM for a novel task of harnessing spatial and semantic cues from input audio to construct Video Scene Layouts (VSLs). This serves as an intermediate representation to bridge the gap between the audio and video modalities. 2) Layout-grounded Video Generation: We develop an efficient and effective approach to seamlessly integrate VSLs as conditional guidance into pre-trained diffusion models, enabling VSL-grounded video generation in a training-free manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SpA2V excels in generating realistic videos with semantic and spatial alignment to the input audios.
音频驱动的视频生成旨在合成与输入音频记录相匹配的逼真视频,类似于人类从听觉输入中可视化场景的能力。然而,现有方法主要关注探索语义信息,如音频中存在的声音源类别,这限制了它们生成具有准确内容和空间构图的能力。相比之下,我们人类不仅可以自然地识别声音源的语义类别,还可以确定其深度编码的空间属性,包括位置和移动方向。通过考虑从声音固有物理属性派生的特定空间指标(如响度或频率),可以阐明这些有用信息。由于先前的方法大多忽略了这一因素,我们推出了SpA2V,这是第一个明确利用音频中的空间听觉线索来生成具有高度语义和空间对应关系的视频的框架。SpA2V将生成过程分为两个阶段:1)音频引导的视频规划:我们精心采用最先进的MLLM,用于一项新任务,即从输入音频中提取空间和语义线索来构建视频场景布局(VSL)。这作为连接音频和视频模态之间的桥梁的中间表示。2)布局为基础的视频生成:我们开发了一种高效且有效的方法,无缝地将VSL作为条件指导集成到预训练的扩散模型中,以无训练的方式实现基于VSL的视频生成。大量实验表明,SpA2V在生成与输入音频语义和空间对齐的逼真视频方面表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The 33rd ACM Multimedia Conference (MM ‘25)
Summary
本文提出一种名为SpA2V的音频驱动视频生成框架,该框架利用音频中的空间听觉线索生成与音频高度语义和空间对应的视频。它通过两个阶段实现:首先是音频引导的视频规划,利用先进的MLLM从音频中提取空间和时间线索来构建视频场景布局(VSL),作为音频和视频模态之间的桥梁;其次是布局为基础的视频生成,将VSL作为条件指导融入预训练的扩散模型,实现无需训练的视频生成。
Key Takeaways
- SpA2V框架利用音频中的空间听觉线索来生成视频,与现有方法主要关注语义信息不同。
- SpA2V通过两个阶段实现视频生成:音频引导的视频规划阶段和布局为基础的视频生成阶段。
- 音频引导的视频规划阶段利用MLLM从音频中提取空间和时间线索,构建视频场景布局(VSL)。
- 布局为基础的视频生成阶段将VSL作为条件指导融入预训练的扩散模型,实现无需训练的视频生成。
- SpA2V能够生成与输入音频在语义和空间上高度对应的视频。
- 人类能够从音频中自然地识别声音源的语义类别和深度编码的空间属性,这启发了SpA2V的设计。
点此查看论文截图


Is It Really You? Exploring Biometric Verification Scenarios in Photorealistic Talking-Head Avatar Videos
Authors:Laura Pedrouzo-Rodriguez, Pedro Delgado-DeRobles, Luis F. Gomez, Ruben Tolosana, Ruben Vera-Rodriguez, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
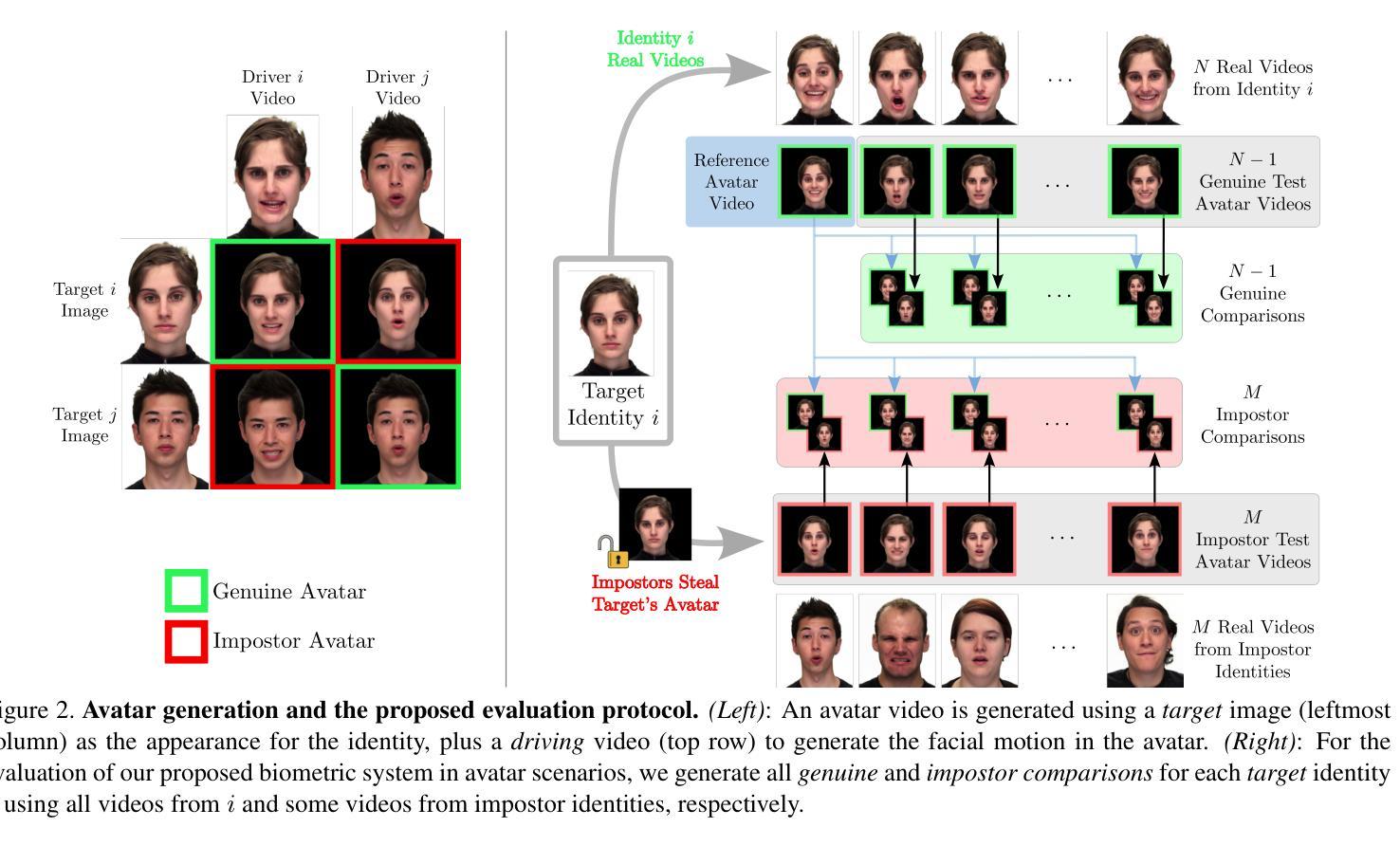
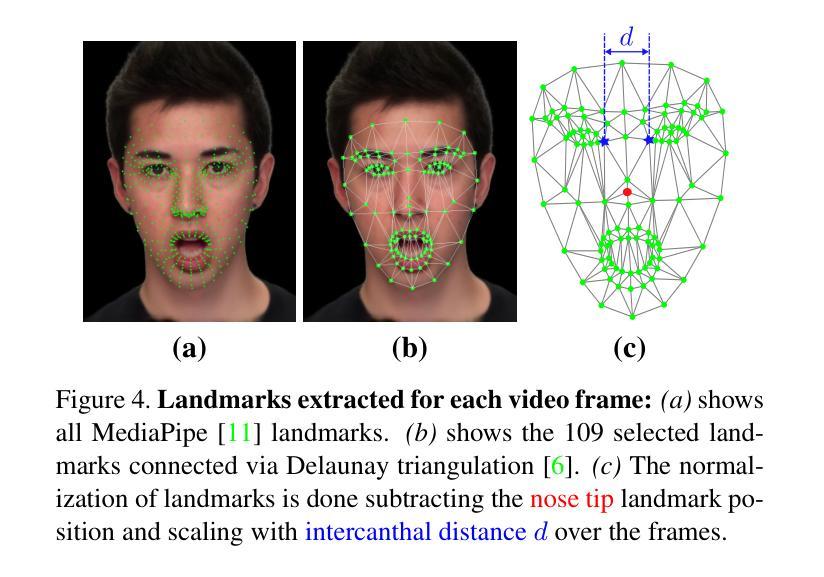
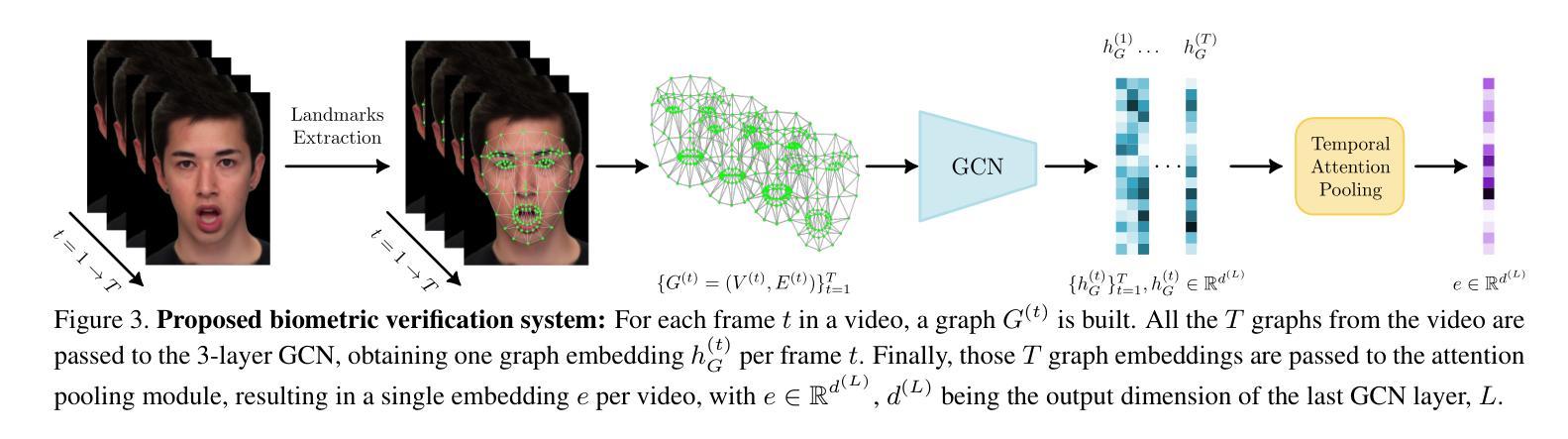
Photorealistic talking-head avatars are becoming increasingly common in virtual meetings, gaming, and social platforms. These avatars allow for more immersive communication, but they also introduce serious security risks. One emerging threat is impersonation: an attacker can steal a user’s avatar-preserving their appearance and voice-making it nearly impossible to detect its fraudulent usage by sight or sound alone. In this paper, we explore the challenge of biometric verification in such avatar-mediated scenarios. Our main question is whether an individual’s facial motion patterns can serve as reliable behavioral biometrics to verify their identity when the avatar’s visual appearance is a facsimile of its owner. To answer this question, we introduce a new dataset of realistic avatar videos created using a state-of-the-art one-shot avatar generation model, GAGAvatar, with genuine and impostor avatar videos. We also propose a lightweight, explainable spatio-temporal Graph Convolutional Network architecture with temporal attention pooling, that uses only facial landmarks to model dynamic facial gestures. Experimental results demonstrate that facial motion cues enable meaningful identity verification with AUC values approaching 80%. The proposed benchmark and biometric system are available for the research community in order to bring attention to the urgent need for more advanced behavioral biometric defenses in avatar-based communication systems.
高保真数字人头在虚拟会议、游戏以及社交平台上的使用正变得越来越普遍。这些数字人头让沟通变得更加沉浸,但同时也带来了严重的安全风险。其中一个新兴威胁是伪装:攻击者可以盗取用户的数字人头并保留其外观和声音,仅仅通过视觉或听觉很难检测出其欺诈性使用。在这篇论文中,我们探讨了这种数字人头介导场景中的生物识别挑战。我们的主要问题是,当数字人头的外观是其所有者的复制品时,个体的面部运动模式能否作为可靠的行为生物识别来验证其身份。为了回答这个问题,我们使用最先进的单镜头数字人头生成模型GAGAvatar制作了真实的数字人头视频,并制作了包含真实和假冒数字人头的新数据集来解答该问题。我们还提出了一种轻量级、可解释的时空图卷积网络架构,该架构具有时间注意力池化功能,仅使用面部特征点来模拟动态面部表情。实验结果表明,面部运动线索能够实现有意义的身份验证,AUC值接近80%。所提出的基准测试和生物识别系统可供研究界使用,旨在提醒人们注意在基于数字人头的通信系统中对更先进的生物识别防御手段的迫切需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB 2025)
Summary
本文探讨了虚拟会议、游戏和社交平台中越来越常见的逼真式头像所带来的安全风险问题。文章聚焦于身份伪造威胁,攻击者可以利用用户的头像进行模仿,仅通过视觉和声音难以识别其欺诈行为。本文旨在研究在这种头像介导的场景下生物识别验证的挑战,特别是探讨面部运动模式能否作为可靠的行为生物识别方式来验证身份。为此,文章引入了一个新数据集,并利用最先进的单镜头头像生成模型GAGAvatar创建了真实头像视频。同时,提出了一种轻量级、可解释的时空图卷积网络架构,该架构仅使用面部特征点来模拟动态面部表情,并通过实验验证了面部运动线索对于身份验证的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 逼真式头像在虚拟会议、游戏和社交平台中的普及带来了严重的安全风险,尤其是身份伪造问题。
- 攻击者可以通过模仿用户的头像进行欺诈行为,使得仅通过视觉和声音难以识别其真实性。
- 面部运动模式可以作为可靠的行为生物识别方式来验证身份。
- 文章引入了一个新数据集,用于研究头像介导场景下的生物识别验证挑战。
- 使用先进的单镜头头像生成模型GAGAvatar创建真实头像视频数据集。
- 提出了一种轻量级、可解释的时空图卷积网络架构,该架构仅使用面部特征点进行动态面部表情模拟。
- 实验结果显示,面部运动线索对于身份验证具有重要意义,AUC值接近80%。
点此查看论文截图

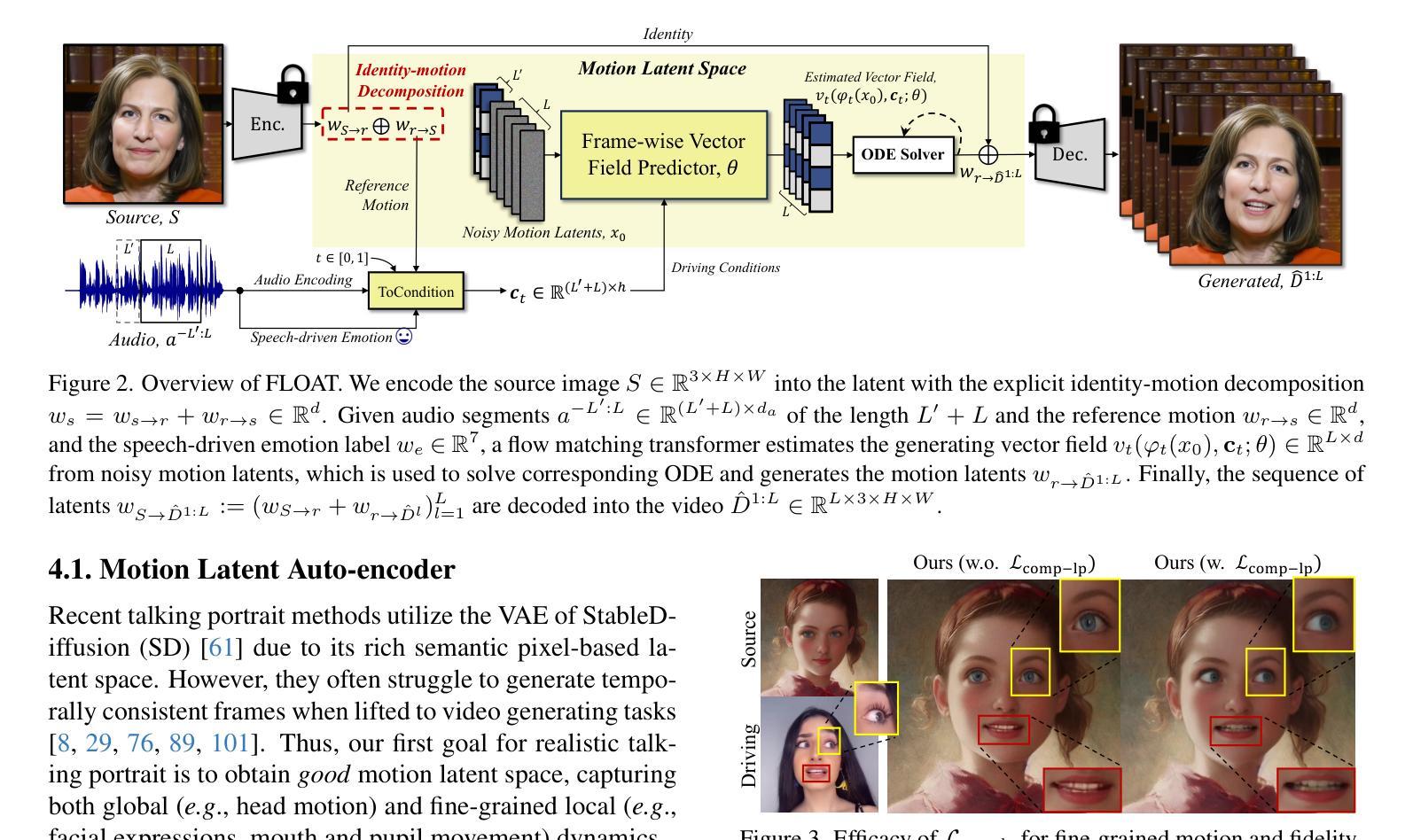
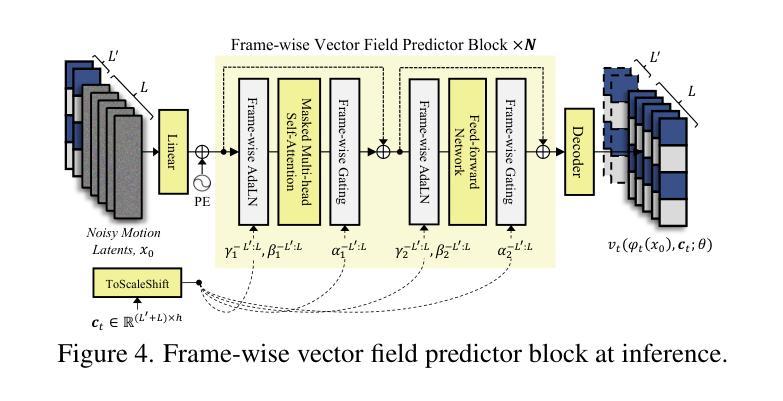
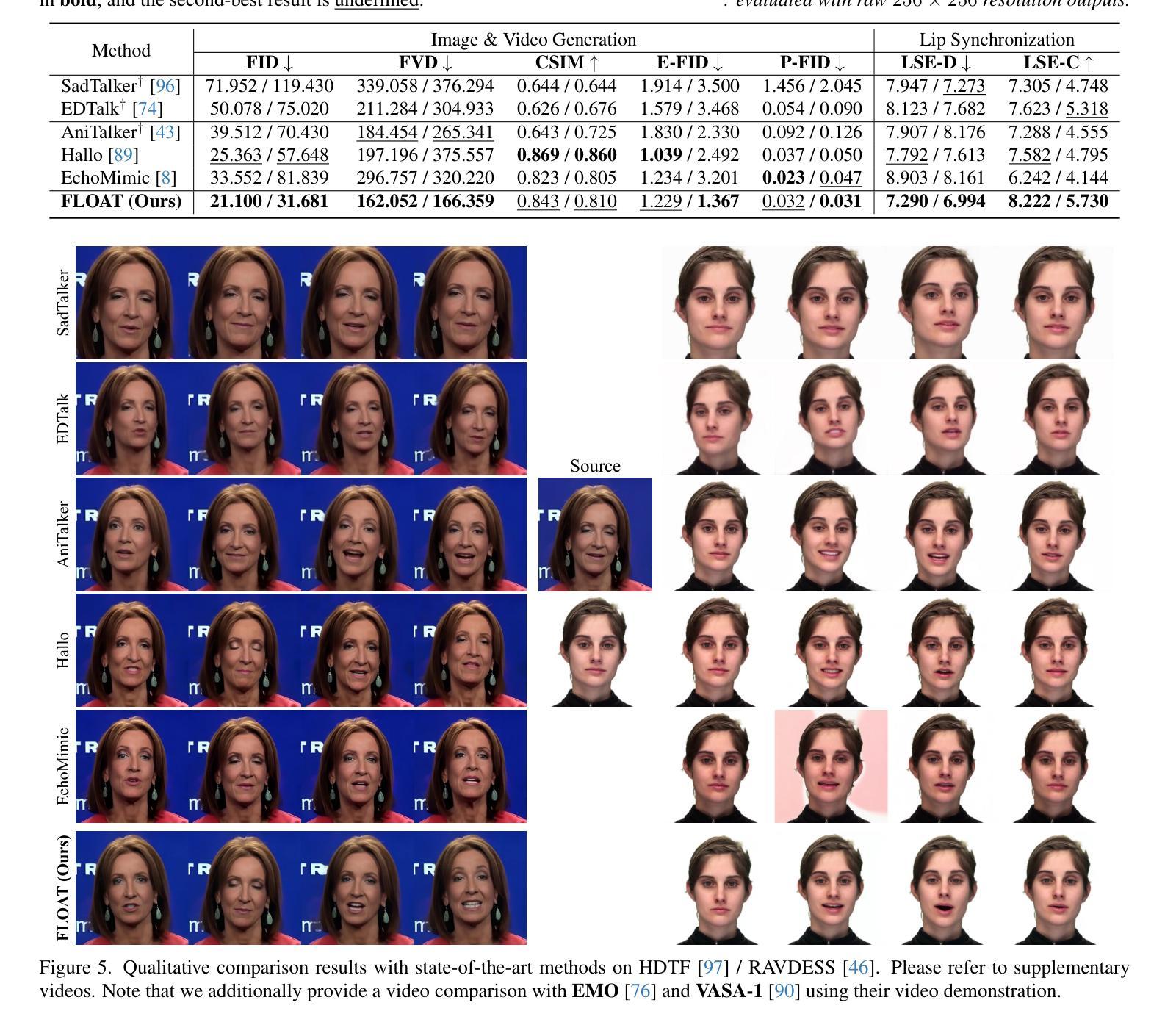
FLOAT: Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait
Authors:Taekyung Ki, Dongchan Min, Gyeongsu Chae
With the rapid advancement of diffusion-based generative models, portrait image animation has achieved remarkable results. However, it still faces challenges in temporally consistent video generation and fast sampling due to its iterative sampling nature. This paper presents FLOAT, an audio-driven talking portrait video generation method based on flow matching generative model. Instead of a pixel-based latent space, we take advantage of a learned orthogonal motion latent space, enabling efficient generation and editing of temporally consistent motion. To achieve this, we introduce a transformer-based vector field predictor with an effective frame-wise conditioning mechanism. Additionally, our method supports speech-driven emotion enhancement, enabling a natural incorporation of expressive motions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art audio-driven talking portrait methods in terms of visual quality, motion fidelity, and efficiency.
随着基于扩散的生成模型的快速发展,肖像图像动画已经取得了显著成果。然而,由于其迭代采样的性质,它在时间一致的视频生成和快速采样方面仍然面临挑战。本文提出了FLOAT,这是一种基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动式肖像视频生成方法。我们利用学习得到的正交运动潜在空间,而不是基于像素的潜在空间,实现了高效的时间一致运动的生成和编辑。为此,我们引入了一种基于变压器的向量场预测器,并设计了一种有效的帧条件机制。此外,我们的方法支持语音驱动的情感增强,能够实现表达性动作的自然融合。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面优于最先进的音频驱动式肖像动画方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://deepbrainai-research.github.io/float/
Summary
随着扩散生成模型的快速发展,肖像动画在图像生成领域取得了显著成果,但仍面临视频生成中的时序一致性和快速采样挑战。本文提出了基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法FLOAT。该方法采用学习到的正交运动潜在空间,实现了高效且时序一致的生成与编辑。通过引入基于变压器的矢量场预测器及有效的帧条件机制,实现了语音驱动的情感增强,使动作表达更加自然。实验证明,该方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面均优于现有音频驱动肖像方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在肖像动画领域取得显著进展。
- FLOAT方法基于流匹配生成模型,实现音频驱动的肖像视频生成。
- 采用正交运动潜在空间,实现高效且时序一致的生成与编辑。
- 引入基于变压器的矢量场预测器,提高运动预测准确性。
- 有效的帧条件机制,使动作表达更加自然。
- 支持语音驱动的情感增强。
点此查看论文截图