⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
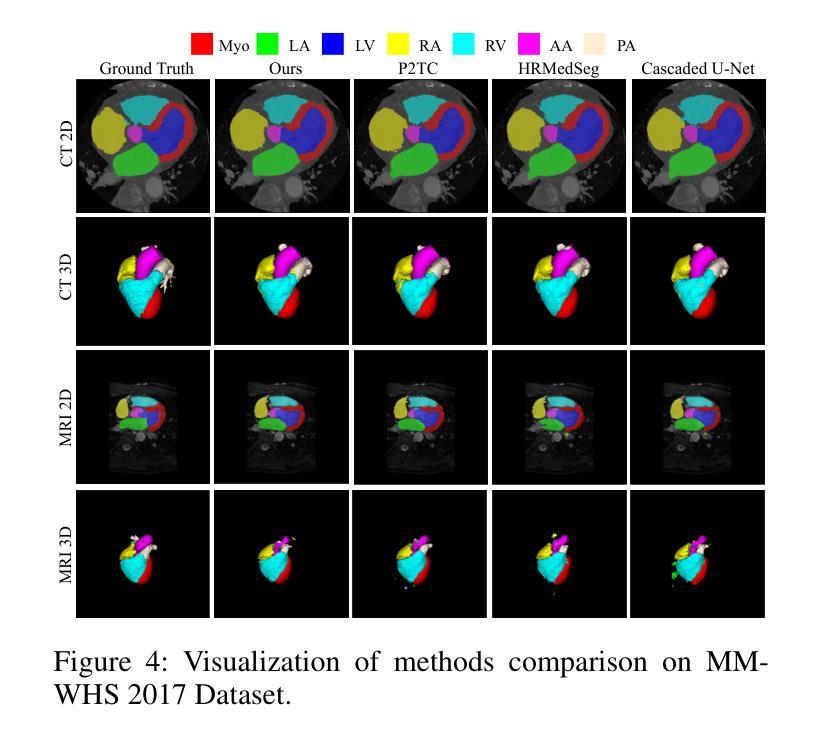
RL-U$^2$Net: A Dual-Branch UNet with Reinforcement Learning-Assisted Multimodal Feature Fusion for Accurate 3D Whole-Heart Segmentation
Authors:Jierui Qu, Jianchun Zhao
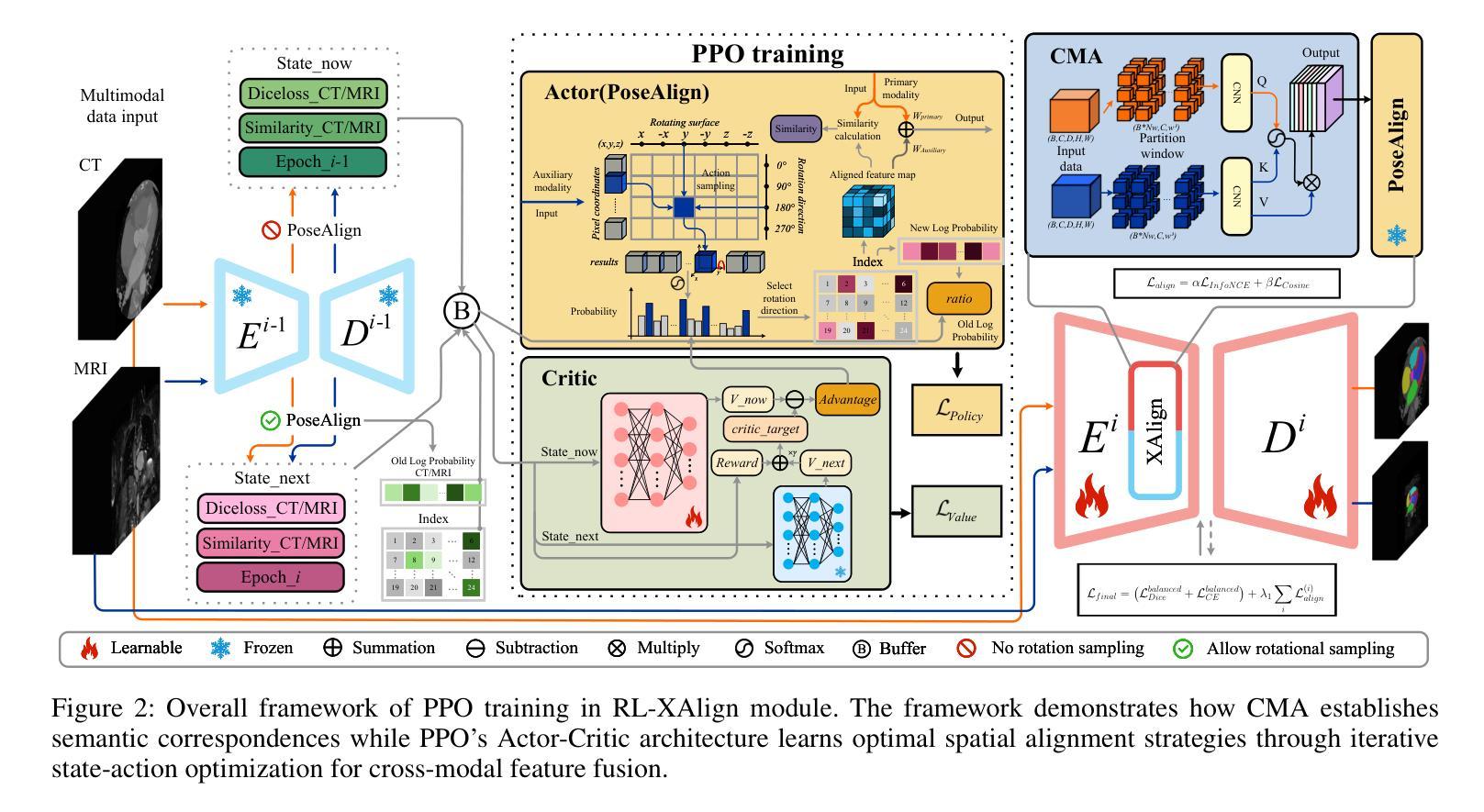
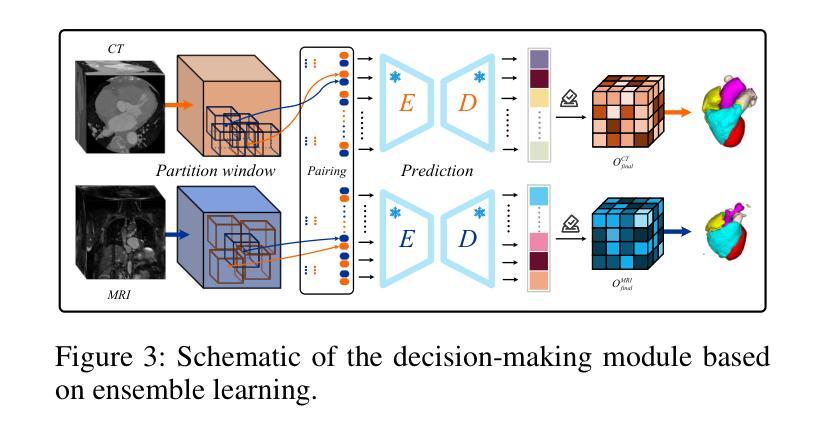
Accurate whole-heart segmentation is a critical component in the precise diagnosis and interventional planning of cardiovascular diseases. Integrating complementary information from modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can significantly enhance segmentation accuracy and robustness. However, existing multi-modal segmentation methods face several limitations: severe spatial inconsistency between modalities hinders effective feature fusion; fusion strategies are often static and lack adaptability; and the processes of feature alignment and segmentation are decoupled and inefficient. To address these challenges, we propose a dual-branch U-Net architecture enhanced by reinforcement learning for feature alignment, termed RL-U$^2$Net, designed for precise and efficient multi-modal 3D whole-heart segmentation. The model employs a dual-branch U-shaped network to process CT and MRI patches in parallel, and introduces a novel RL-XAlign module between the encoders. The module employs a cross-modal attention mechanism to capture semantic correspondences between modalities and a reinforcement-learning agent learns an optimal rotation strategy that consistently aligns anatomical pose and texture features. The aligned features are then reconstructed through their respective decoders. Finally, an ensemble-learning-based decision module integrates the predictions from individual patches to produce the final segmentation result. Experimental results on the publicly available MM-WHS 2017 dataset demonstrate that the proposed RL-U$^2$Net outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving Dice coefficients of 93.1% on CT and 87.0% on MRI, thereby validating the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed approach.
精确的全心分割是心血管疾病的精确诊断和介入计划中的关键组成部分。整合计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振成像(MRI)等模态的互补信息可以显著提高分割的准确性和稳健性。然而,现有的多模态分割方法面临一些局限性:不同模态之间的空间不一致性严重阻碍了有效的特征融合;融合策略通常是静态的,缺乏适应性;特征对齐和分割的过程是解耦的且效率低下。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种由强化学习增强的双分支U-Net架构,用于特征对齐,称为RL-U$^2$Net,旨在实现精确和高效的多模态3D全心分割。该模型采用双分支U形网络并行处理CT和MRI斑块,并在编码器之间引入了一个新的RL-XAlign模块。该模块采用跨模态注意机制来捕获模态之间的语义对应关系,强化学习代理学习最优旋转策略,以一致地对齐解剖姿势和纹理特征。对齐的特征然后通过各自的解码器进行重建。最后,基于集成学习的决策模块将各个斑块的预测结果整合起来,生成最终的分割结果。在公开的MM-WHS 2017数据集上的实验结果表明,所提出的RL-U$^2$Net优于现有的最先进方法,CT上的Dice系数为93.1%,MRI上的Dice系数为87.0%,从而验证了所提出方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
提出一种基于深度学习的多模态三维心脏分割方法,采用双分支U-Net架构,结合强化学习进行特征对齐。方法利用CT和MRI数据,通过交叉模态注意力机制和强化学习实现精准和高效的多模态心脏分割。在公开数据集MM-WHS 2017上的实验结果表明,该方法优于现有技术,CT和MRI的Dice系数分别为93.1%和87.0%。
关键见解
- 多模态信息集成对于提高心血管疾病的诊断和治疗精度至关重要。
- 现有多模态分割方法存在空间不一致性、融合策略静态缺乏适应性以及特征对齐和分割过程解耦等问题。
- 提出的RL-U$^2$Net模型采用双分支U-Net架构处理CT和MRI图像,并行处理不同模态的图像数据。
- RL-XAlign模块利用交叉模态注意力机制捕捉不同模态之间的语义对应关系。
- 强化学习代理学习最优旋转策略,实现解剖姿势和纹理特征的一致对齐。
- 对齐的特征通过各自的解码器进行重建,并通过集成学习决策模块生成最终的分割结果。
- 在MM-WHS 2017数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法实现了高分割性能,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

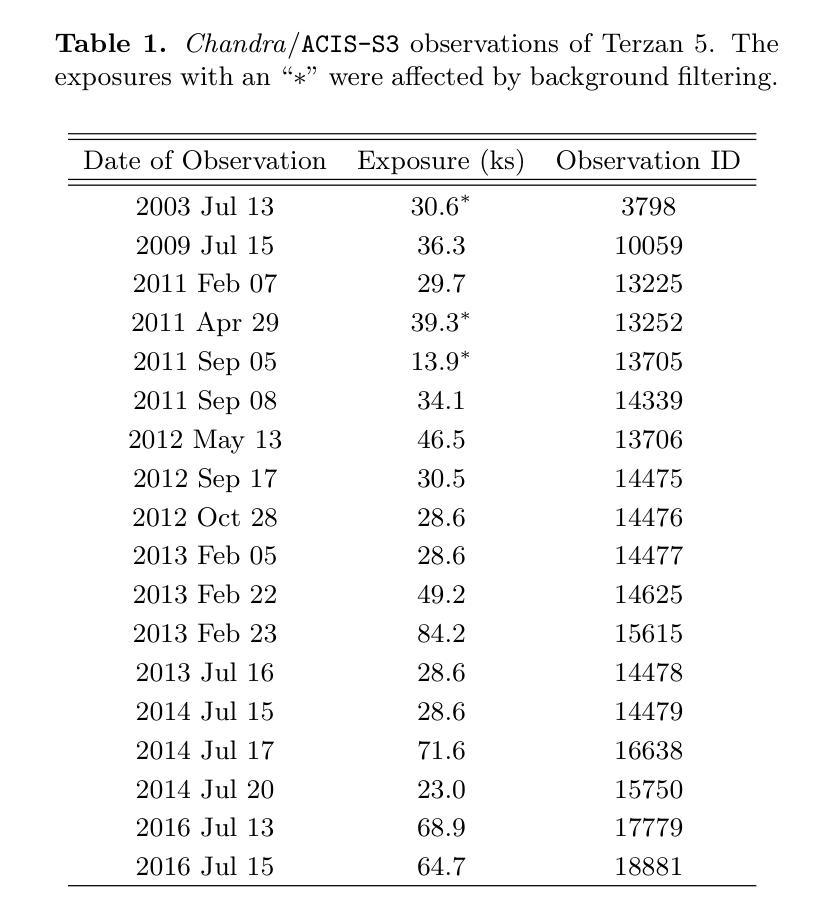
A Comprehensive Analysis of X-ray Sources in Terzan 5 Using Chandra Observations
Authors:Gourav Kumawat, Craig O. Heinke, Jiaqi Zhao, Arash Bahramian, Haldan N. Cohn, Phyllis M. Lugger
We analyze photometry, spectra, and variability of over 100 faint X-ray sources in the globular cluster Terzan 5, using 737 ks of Chandra data. X-ray colors and spectral fitting allow clear separation of foreground sources (with less extinction than the cluster), quiescent low-mass X-ray binaries (qLMXBs), and sources with harder spectra. We identify 22 candidate qLMXBs, over twice that found in any other cluster. This is consistent with Terzan 5’s stellar interaction rate, the highest among Galactic globular clusters. We do not see qLMXBs dominated by thermal emission below $L_X\sim10^{32}$ erg/s, though qLMXBs with stronger nonthermal emission could be missed. We find that more than 50 % of the qLMXB sources have neutron star thermal component contributing over 80 % of the total luminosity. We report an unusual spectral feature around 1.75 keV in the combined spectrum of Ter 5 X-3. The concentration of the qLMXBs within the cluster is consistent with that of a population of mass $1.46 \pm 0.14$ M$_\odot$. We identify secure X-ray counterparts to millisecond pulsars Terzan 5 ar and Terzan 5 at, using positional coincidence and orbital X-ray light curves matching those expected for spider pulsars.
我们对球状星团Terzan 5中的100多个暗X射线源的光度学、光谱和可变性进行了分析,使用了长达737 ks的Chandra数据。通过X射线颜色和光谱拟合,可以清楚地分辨出前景源(比星团中的遮挡更少)、静态低质量X射线双星(qLMXBs)和光谱较硬的源。我们确定了22个候选的qLMXBs,数量是其他任何星团的两倍。这与Terzan 5的恒星交互率相符,它是银河系球状星团中最高的。我们没有看到热发射主导的qLMXBs在Lx约小于~ 10^32erg/s的情况下明显存在,尽管非热发射较强的qLMXBs可能有所缺失。我们发现超过一半的qLMXB源的中子星热成分贡献了超过总光度的80%。我们报告了在Ter 5 X-3的综合光谱中出现了罕见的约1.75 keV特征谱。qLMXBs在星团内的分布与质量为地球质量的一致。通过定位吻合度和轨道X射线光变曲线匹配的方式,我们确定了毫秒脉冲星Terzan 5 ar和Terzan 5 at的可靠的X射线对应物,这与蜘蛛脉冲星的预期相符。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal (ApJ). 24 pages, 12 figures
Summary
基于长达737千秒的钱德拉数据,我们对天鹅座5号球状星团中的超过一百个微弱的X射线源进行了光度分析、光谱分析和变化性分析。通过X射线颜色和光谱拟合,我们能够清楚地分辨出前景源(星团消光较少的源)、静态低质量X射线双星(qLMXBs)以及光谱更硬的源。我们发现该星团拥有高达22个qLMXBs候选体,这一数量是其它星团的两倍,与天鹅座5号球状星团内恒星相互作用率最高的情况相符。我们观察到中子星热成分对超过一半的qLMXB源的贡献超过总发光度的百分之八十以上。还发现了一些特殊谱特征。另外我们也确定了毫秒脉冲星的可靠X射线对应体。综合来看,本项研究深化了对天鹅座5号球状星团中X射线源的了解。尽管某些研究推测存在一些疏漏之处,比如对较弱的热发射型qLMXBs的遗漏以及对特殊谱特征的深入探究等,但本项研究仍为我们提供了宝贵的观测数据和新的认识。同时,我们注意到这一发现对研究球状星团内恒星演化及相互作用机制具有重大意义。对于未来的研究而言,这有助于我们更深入地理解球状星团内部复杂的天体物理过程以及恒星形成和演化的细节。这也可能对开发更有效的空间探测技术和数据解析方法有所启示。对于进一步的探索和应用这些发现,我们期待未来的研究能够带来更多的突破和新的发现。总的来说,这项研究为我们提供了关于天鹅座五号球状星团中X射线源的丰富而深刻的信息。
Key Takeaways
- 对天鹅座5号球状星团内的超过一百个微弱X射线源进行了详细分析。
- 通过X射线颜色和光谱拟合成功区分了前景源、静态低质量X射线双星和其他类型的源。
- 发现该星团拥有大量静态低质量X射线双星候选体,数量是其他星团的两倍。
- 观察到中子星热成分在多数静态低质量X射线双星中的重要作用。
- 发现特殊谱特征和罕见的X射线对应体。
- 研究结果深化了对天鹅座5号球状星团内X射线源的了解,对恒星演化及相互作用机制的研究有重大意义。
点此查看论文截图


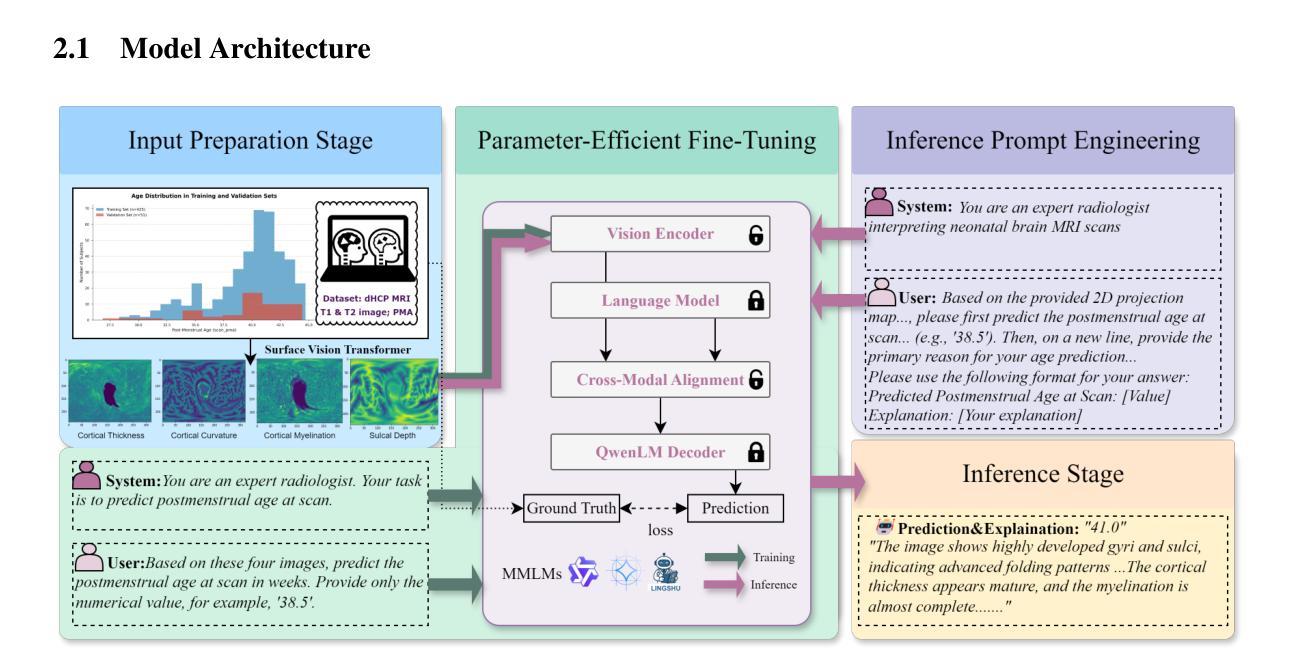
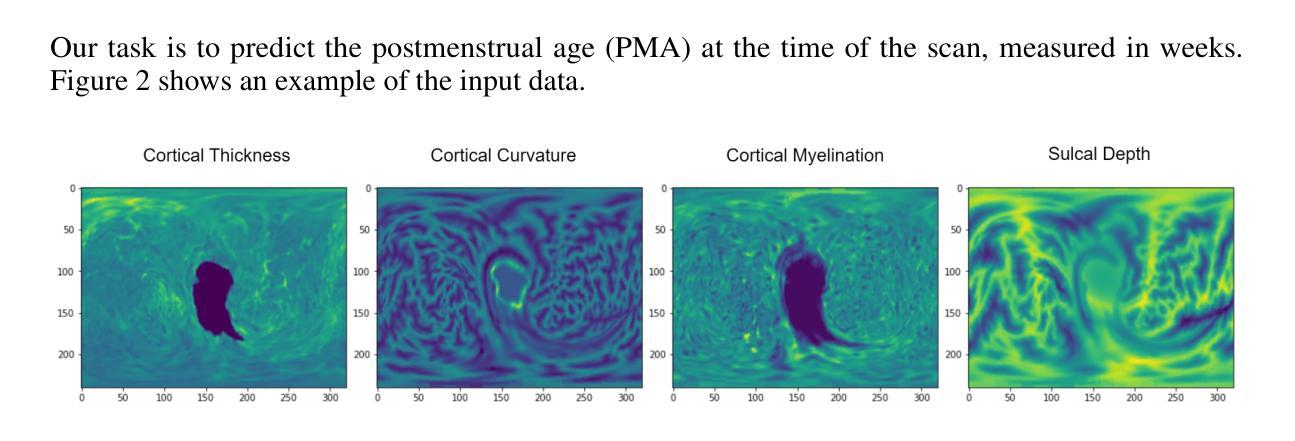
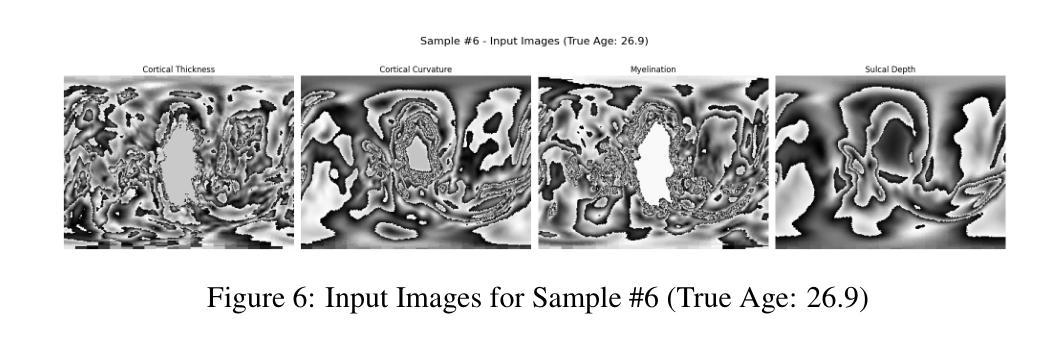
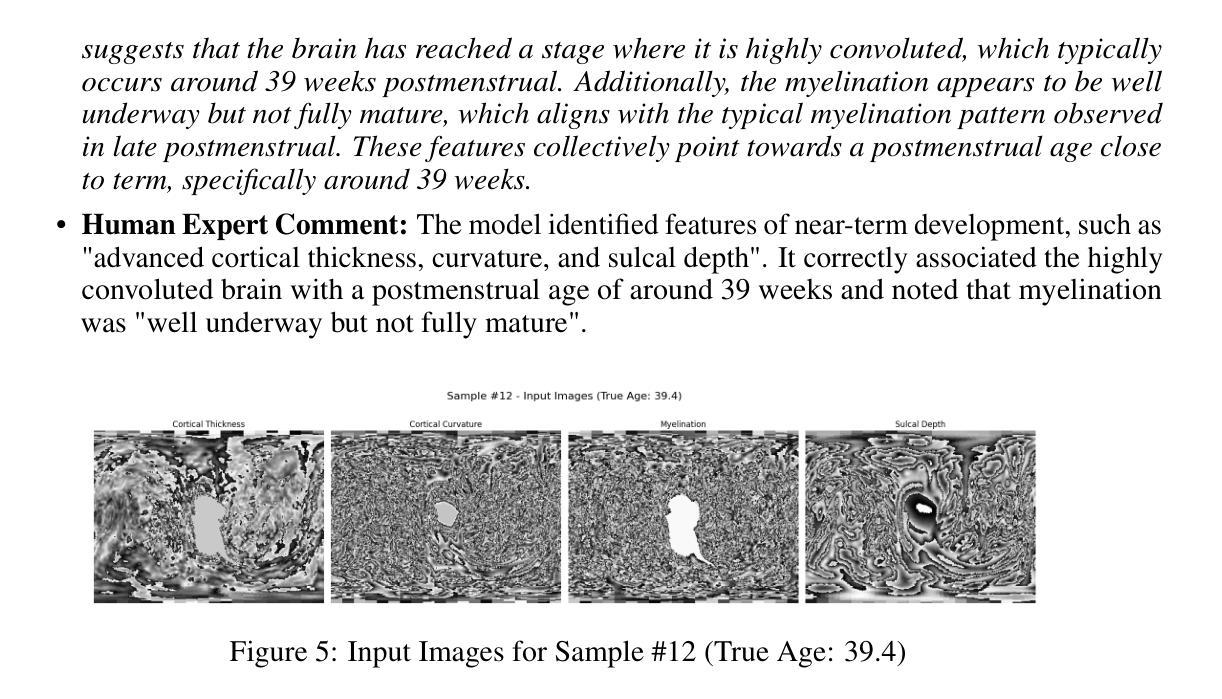
Accurate and Interpretable Postmenstrual Age Prediction via Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Qifan Chen, Jin Cui, Cindy Duan, Yushuo Han, Yifei Shi
Accurate estimation of postmenstrual age (PMA) at scan is crucial for assessing neonatal development and health. While deep learning models have achieved high accuracy in predicting PMA from brain MRI, they often function as black boxes, offering limited transparency and interpretability in clinical decision support. In this work, we address the dual challenge of accuracy and interpretability by adapting a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to perform both precise PMA prediction and clinically relevant explanation generation. We introduce a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) strategy using instruction tuning and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) applied to the Qwen2.5-VL-7B model. The model is trained on four 2D cortical surface projection maps derived from neonatal MRI scans. By employing distinct prompts for training and inference, our approach enables the MLLM to handle a regression task during training and generate clinically relevant explanations during inference. The fine-tuned model achieves a low prediction error with a 95 percent confidence interval of 0.78 to 1.52 weeks, while producing interpretable outputs grounded in developmental features, marking a significant step toward transparent and trustworthy AI systems in perinatal neuroscience.
精确估计扫描时的胎龄(PMA)对于评估新生儿发育和健康至关重要。虽然深度学习模型在通过脑部MRI预测胎龄方面已经达到了很高的准确性,但它们通常像黑箱一样运作,在临床决策支持中提供有限的透明度和可解释性。在这项工作中,我们通过适应多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来解决准确性和可解释性的双重挑战,以执行精确的胎龄预测和相关临床解释生成。我们介绍了一种使用指令调整和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)应用于Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型的参数有效微调(PEFT)策略。该模型在新生儿MRI扫描派生的四个二维皮层表面投影图上进行了训练。通过为训练和推理采用不同的提示,我们的方法使MLLM能够在训练期间处理回归任务,并在推理期间生成与临床相关的解释。经过微调的模型实现了较低的预测误差,95%的置信区间为0.78至1.52周,同时产生基于发育特征的可解释输出,标志着朝着透明和可靠的围生期神经科学人工智能系统迈出了重要的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop GenAI4Health. Conference website: https://aihealth.ischool.utexas.edu/GenAI4HealthNeurips2025/
Summary
本文介绍了使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)对新生儿脑MRI扫描进行精确的后扫描年龄(PMA)预测,并生成临床相关解释的方法。该研究通过参数高效的微调(PEFT)策略和低秩适配(LoRA)技术实现了模型的应用,在新生儿MRI扫描的四个二维皮层表面投影图上训练模型。该研究结合了训练时的回归任务和推理时的解释生成,实现了模型的精细调整,预测误差低,95%置信区间为0.78至1.52周,并生成了基于发育特征的可解释输出,为围产期神经科学的透明和可信赖的AI系统迈出了重要的一步。
Key Takeaways
- 研究强调了在评估新生儿发展和健康时,准确估计后扫描年龄(PMA)的重要性。
- 使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)进行精确PMA预测和临床相关解释生成是解决该问题的新方法。
- 研究采用参数高效的微调(PEFT)策略和低秩适配(LoRA)技术,对模型进行训练和优化。
- 模型在新生儿MRI扫描的二维皮层表面投影图上训练,实现了精细调整。
- 模型预测误差低,95%置信区间为0.78至1.52周。
- 模型生成了基于发育特征的可解释输出,增强了AI系统的透明度。
点此查看论文截图


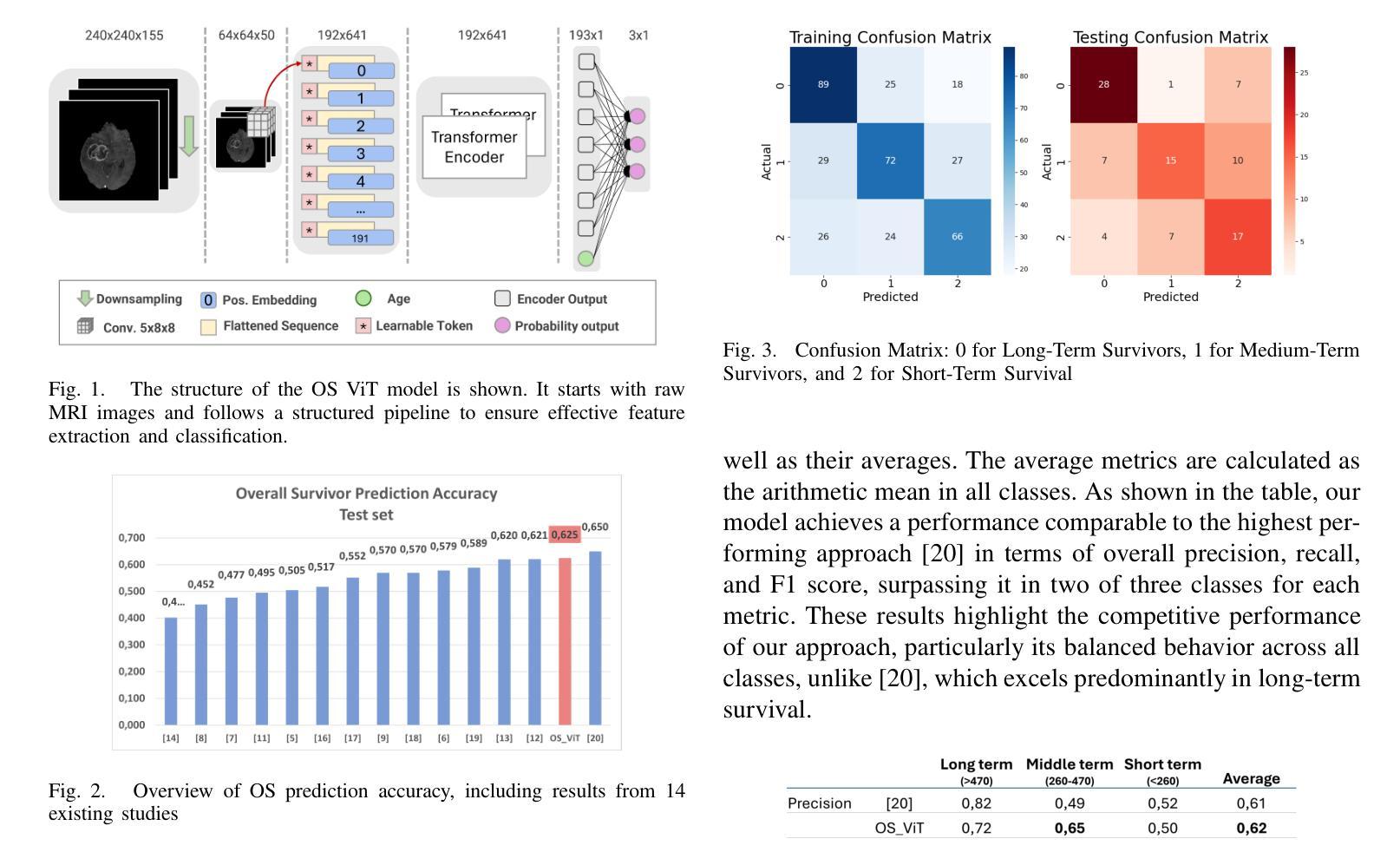
Glioblastoma Overall Survival Prediction With Vision Transformers
Authors:Yin Lin, iccardo Barbieri, Domenico Aquino, Giuseppe Lauria, Marina Grisoli, Elena De Momi, Alberto Redaelli, Simona Ferrante
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive and common brain tumors, with a median survival of 10-15 months. Predicting Overall Survival (OS) is critical for personalizing treatment strategies and aligning clinical decisions with patient outcomes. In this study, we propose a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) approach for OS prediction using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images, exploiting Vision Transformers (ViTs) to extract hidden features directly from MRI images, eliminating the need of tumor segmentation. Unlike traditional approaches, our method simplifies the workflow and reduces computational resource requirements. The proposed model was evaluated on the BRATS dataset, reaching an accuracy of 62.5% on the test set, comparable to the top-performing methods. Additionally, it demonstrated balanced performance across precision, recall, and F1 score, overcoming the best model in these metrics. The dataset size limits the generalization of the ViT which typically requires larger datasets compared to convolutional neural networks. This limitation in generalization is observed across all the cited studies. This work highlights the applicability of ViTs for downsampled medical imaging tasks and establishes a foundation for OS prediction models that are computationally efficient and do not rely on segmentation.
胶质母细胞瘤是最具侵袭性和最常见的脑肿瘤之一,中位生存期为10-15个月。预测总体生存期(OS)对于个性化治疗策略以及与患者结果相符的临床决策至关重要。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型人工智能(AI)方法,用于使用磁共振成像(MRI)图像进行OS预测,利用视觉转换器(ViTs)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需进行肿瘤分割。与传统方法不同,我们的方法简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源要求。所提出模型在BRATS数据集上进行了评估,在测试集上的准确率达到62.5%,与表现最好的方法相当。此外,它在精确度、召回率和F1得分方面表现出平衡的绩效,在这些指标上超越了最佳模型。数据集的大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,与卷积神经网络相比,ViT通常需要更大的数据集。所有引用的研究都观察到了这种泛化限制。这项工作强调了ViTs在降采样医学成像任务中的应用性,并为计算效率高、不依赖分割的OS预测模型奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures, EMBC2025
摘要
本研究提出了一种基于人工智能(AI)的总体生存期(OS)预测新方法,利用磁共振成像(MRI)图像,采用视觉转换器(ViTs)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需肿瘤分割。该方法简化了工作流程,降低了计算资源要求。在BRATS数据集上评估的模型测试集准确率为62.5%,与传统顶级方法相当。此外,它在精度、召回率和F1分数方面表现出平衡的性能,在这些指标上超越了最佳模型。但由于数据集大小限制,ViT的泛化能力受限,通常需要比卷积神经网络更大的数据集。本研究强调了ViTs在下采样医学成像任务中的应用性,并为计算效率高、不依赖分割的OS预测模型奠定了基础。
关键见解
- 本研究利用AI和MRI图像进行胶质母细胞瘤的总体生存期预测。
- 采用视觉转换器(ViTs)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源需求。
- 在BRATS数据集上进行的模型评估达到了62.5%的测试集准确率,与传统顶级方法相当。
- 模型在精度、召回率和F1分数方面表现出平衡的性能,并超越了现有最佳模型。
- 数据集大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,需要更大的数据集以改善其性能。
- 研究强调了ViTs在下采样医学成像任务中的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

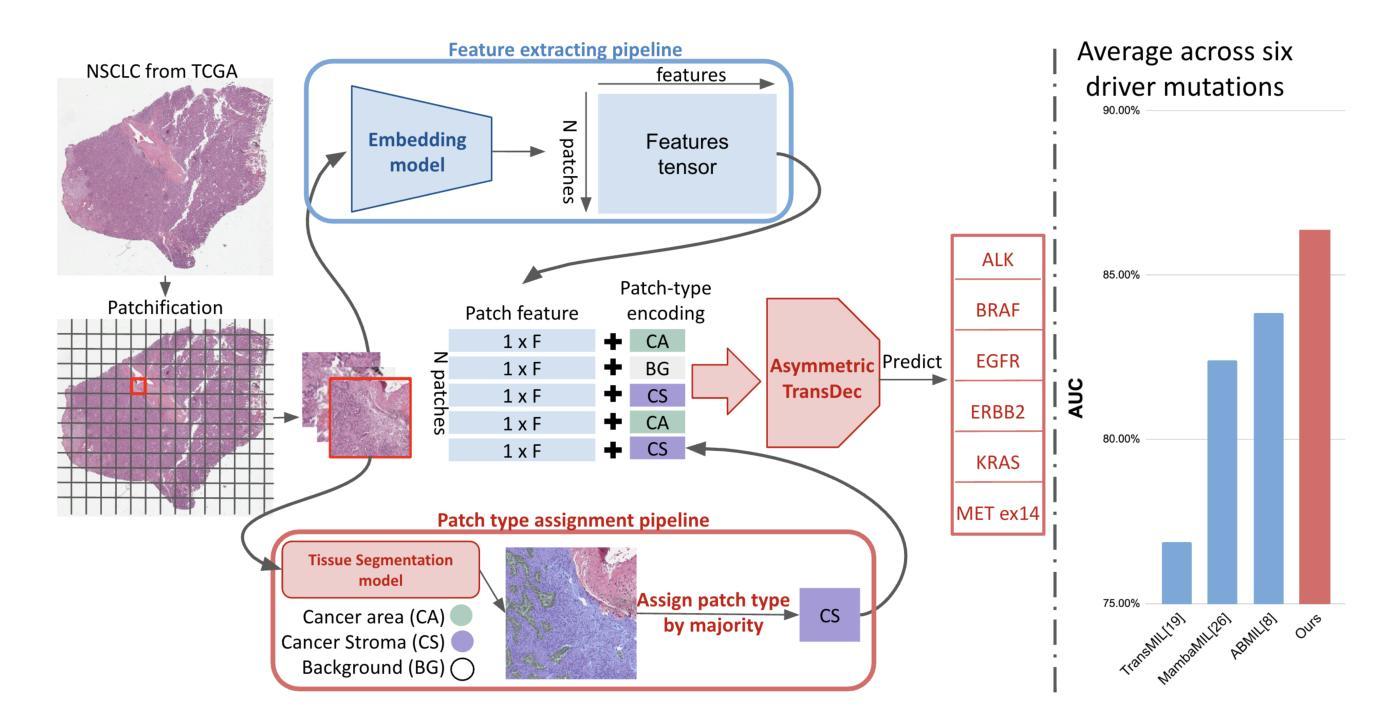
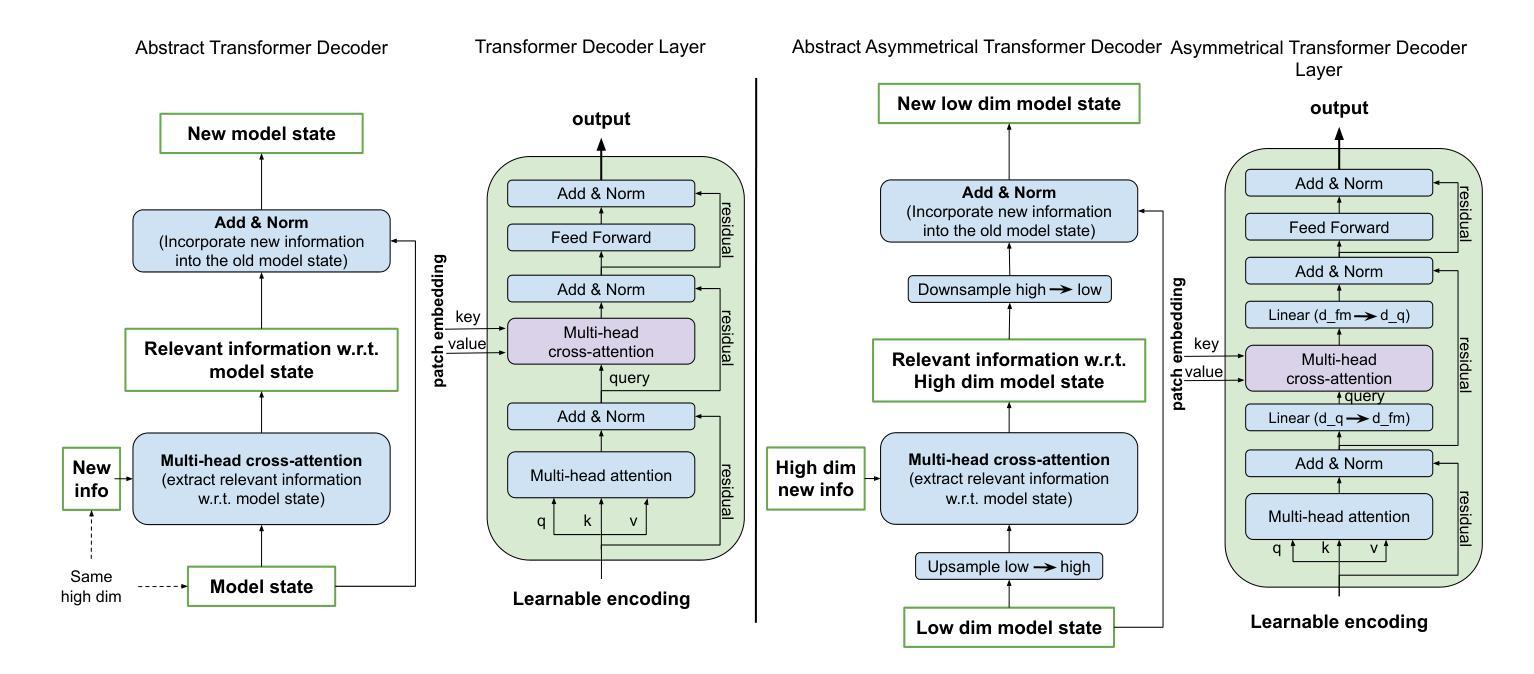
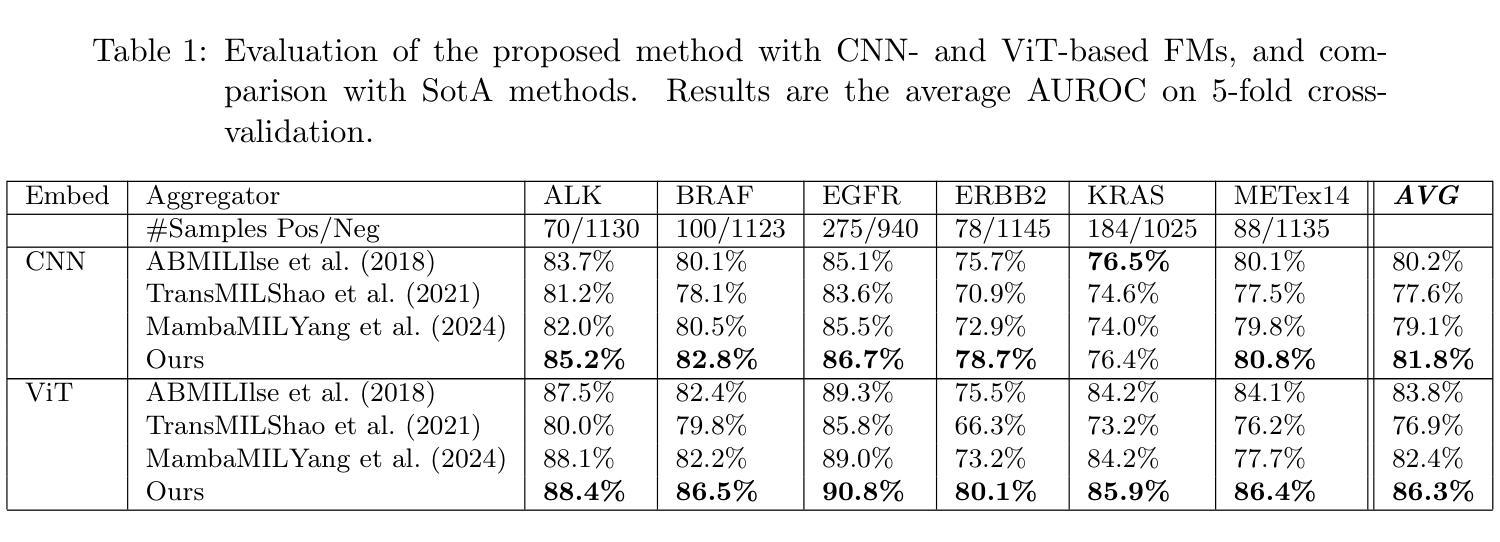
Identifying actionable driver mutations in lung cancer using an efficient Asymmetric Transformer Decoder
Authors:Biagio Brattoli, Jack Shi, Jongchan Park, Taebum Lee, Donggeun Yoo, Sergio Pereira
Identifying actionable driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) can impact treatment decisions and significantly improve patient outcomes. Despite guideline recommendations, broader adoption of genetic testing remains challenging due to limited availability and lengthy turnaround times. Machine Learning (ML) methods for Computational Pathology (CPath) offer a potential solution; however, research often focuses on only one or two common mutations, limiting the clinical value of these tools and the pool of patients who can benefit from them. This study evaluates various Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) techniques to detect six key actionable NSCLC driver mutations: ALK, BRAF, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, and MET ex14. Additionally, we introduce an Asymmetric Transformer Decoder model that employs queries and key-values of varying dimensions to maintain a low query dimensionality. This approach efficiently extracts information from patch embeddings and minimizes overfitting risks, proving highly adaptable to the MIL setting. Moreover, we present a method to directly utilize tissue type in the model, addressing a typical MIL limitation where either all regions or only some specific regions are analyzed, neglecting biological relevance. Our method outperforms top MIL models by an average of 3%, and over 4% when predicting rare mutations such as ERBB2 and BRAF, moving ML-based tests closer to being practical alternatives to standard genetic testing.
识别非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中的可操作驱动基因突变可以对治疗决策产生影响,并显著改善患者预后。尽管有指南推荐,但由于有限的可用性和漫长的周转时间,更广泛地采用基因检测仍具有挑战性。计算病理学(CPath)中的机器学习(ML)方法提供了一种潜在的解决方案;然而,研究通常只关注一种或两种常见突变,这限制了这些工具的临床价值以及能从这些工具中受益的患者群体。本研究评估了各种多实例学习(MIL)技术,以检测六种关键可操作NSCLC驱动突变:ALK、BRAF、EGFR、ERBB2、KRAS和MET ex14。此外,我们引入了一种不对称变压器解码器模型,该模型采用不同维度的查询和键值来保持低查询维度。这种方法有效地从补丁嵌入中提取信息,最小化过度拟合风险,并能很好地适应MIL环境。此外,我们提出了一种直接在模型中使用组织类型的方法,解决了典型的MIL限制,即分析所有区域或仅分析某些特定区域而忽视生物学意义。我们的方法平均比顶级MIL模型的性能高出3%,在预测如ERBB2和BRAF等罕见突变时,性能提高了超过4%,这使得基于ML的测试更接近成为标准遗传测试的实用替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025 Workshop COMPAYL
Summary
本文研究利用机器学习技术检测非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的六种关键可操作的驱动基因突变,包括ALK、BRAF、EGFR、ERBB2、KRAS和MET ex14。研究采用多种实例学习(MIL)技术,并引入不对称转换器解码器模型,该方法可有效提取补丁嵌入信息,最小化过度拟合风险,并高度适应MIL环境。此外,该研究还提出了一种直接利用组织类型的方法,解决了典型的MIL限制问题,即在分析时要么分析所有区域,要么只分析某些特定区域,忽略了生物相关性。此方法优于顶级MIL模型,在预测罕见突变如ERBB2和BRAF时表现更为突出,使基于ML的测试更接近于实用的替代标准遗传测试。
Key Takeaways
- 识别非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的可操作驱动基因突变对治疗决策和患者预后有重要影响。
- 机器学习在计算病理学(CPath)中的应用为解决遗传测试的限制提供了潜在解决方案。
- 研究采用多种实例学习(MIL)技术检测NSCLC的六种关键突变。
- 引入不对称转换器解码器模型,有效提取信息并最小化过度拟合风险。
- 提出一种直接利用组织类型的方法,解决MIL在分析时的典型限制问题。
- 该方法优于其他MIL模型,在预测罕见突变时表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图

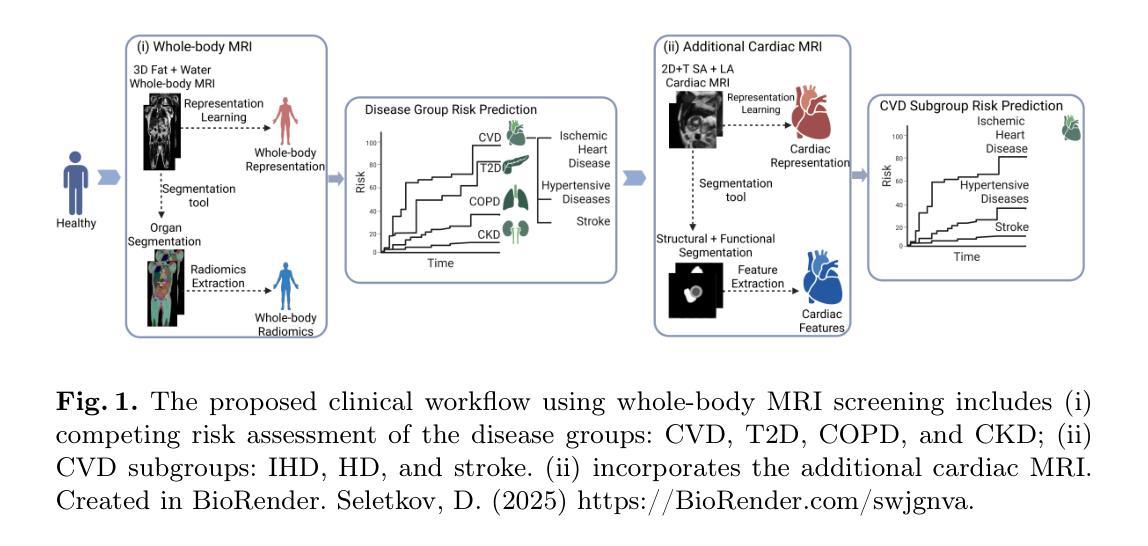
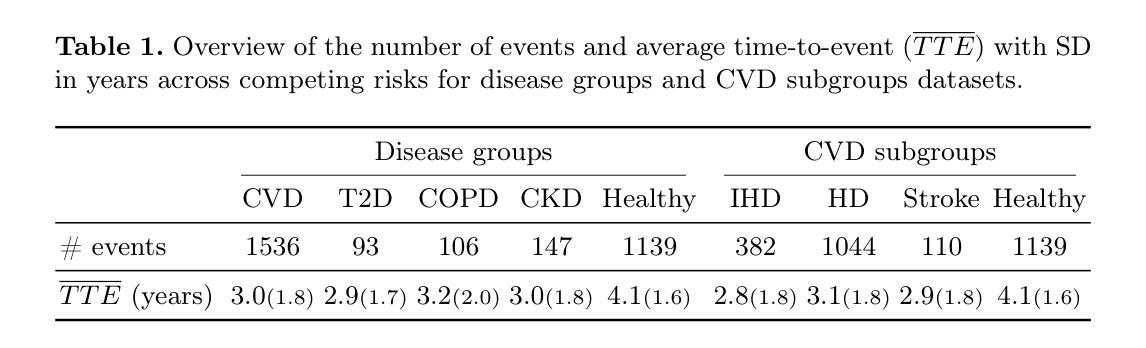
Whole-body Representation Learning For Competing Preclinical Disease Risk Assessment
Authors:Dmitrii Seletkov, Sophie Starck, Ayhan Can Erdur, Yundi Zhang, Daniel Rueckert, Rickmer Braren
Reliable preclinical disease risk assessment is essential to move public healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive identification and prevention. However, image-based risk prediction algorithms often consider one condition at a time and depend on hand-crafted features obtained through segmentation tools. We propose a whole-body self-supervised representation learning method for the preclinical disease risk assessment under a competing risk modeling. This approach outperforms whole-body radiomics in multiple diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD), type 2 diabetes (T2D), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Simulating a preclinical screening scenario and subsequently combining with cardiac MRI, it sharpens further the prediction for CVD subgroups: ischemic heart disease (IHD), hypertensive diseases (HD), and stroke. The results indicate the translational potential of whole-body representations as a standalone screening modality and as part of a multi-modal framework within clinical workflows for early personalized risk stratification. The code is available at https://github.com/yayapa/WBRLforCR/
可靠的早期疾病风险评估对于推动公共医疗从被动治疗转向主动识别和预防至关重要。然而,基于图像的预测算法通常一次只考虑一种情况,并依赖于通过分割工具获得的手工特征。我们提出了一种全身自监督表示学习方法,用于在竞争风险建模下进行早期疾病风险评估。该方法在多疾病评估中优于全身放射组学方法,包括心血管疾病(CVD)、2型糖尿病(T2D)、慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)和慢性肾脏疾病(CKD)。模拟早期筛查情景,并与心脏MRI相结合,进一步提高了对心血管疾病亚组的预测能力,包括缺血性心脏病(IHD)、高血压疾病(HD)和中风。结果表明,全身表现具有作为独立筛查模式的潜力,以及作为临床工作流程内多模态框架的一部分进行早期个性化风险分层的能力。相关代码可以在https://github.com/yayapa/WBRLforCR/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于医学影像的疾病风险预先评估为公共卫生领域从被动治疗转向主动识别和预防提供了可能。然而,现有的图像预测算法常常只针对单一疾病进行分析,并依赖于分割工具获得的手动特征。我们提出了一种全身自我监督学习的方法用于竞争风险模型下的疾病风险预先评估。该方法在多种疾病上的表现优于全身放射组学方法,包括心血管疾病、二型糖尿病、慢性阻塞性肺病和慢性肾脏疾病。模拟预先筛查情景并结合心脏MRI,该方法能更精确地预测心血管疾病的子类别:缺血性心脏病、高血压疾病和脑卒中。结果证明了全身表现作为独立筛查模式和临床工作流程中的多模式框架在早期个性化风险评估中的转化潜力。相关代码可在https://github.com/yayapa/WBRLforCR/找到。
Key Takeaways
- 可靠的临床前疾病风险评估对于公共卫生领域从被动治疗转向主动预防和识别至关重要。
- 当前图像预测算法存在局限性,常常仅针对单一疾病进行分析,并依赖手动特征。
- 提出了一种全身自我监督学习的方法用于疾病风险预先评估,表现优于传统方法。
- 该方法在心血管疾病、二型糖尿病、慢性阻塞性肺病和慢性肾脏疾病等多种疾病上表现优异。
- 结合心脏MRI进行模拟预先筛查,能更精确地预测心血管疾病的子类别。
- 全身表现作为独立筛查模式和多模式框架在个性化风险评估中具有转化潜力。
点此查看论文截图

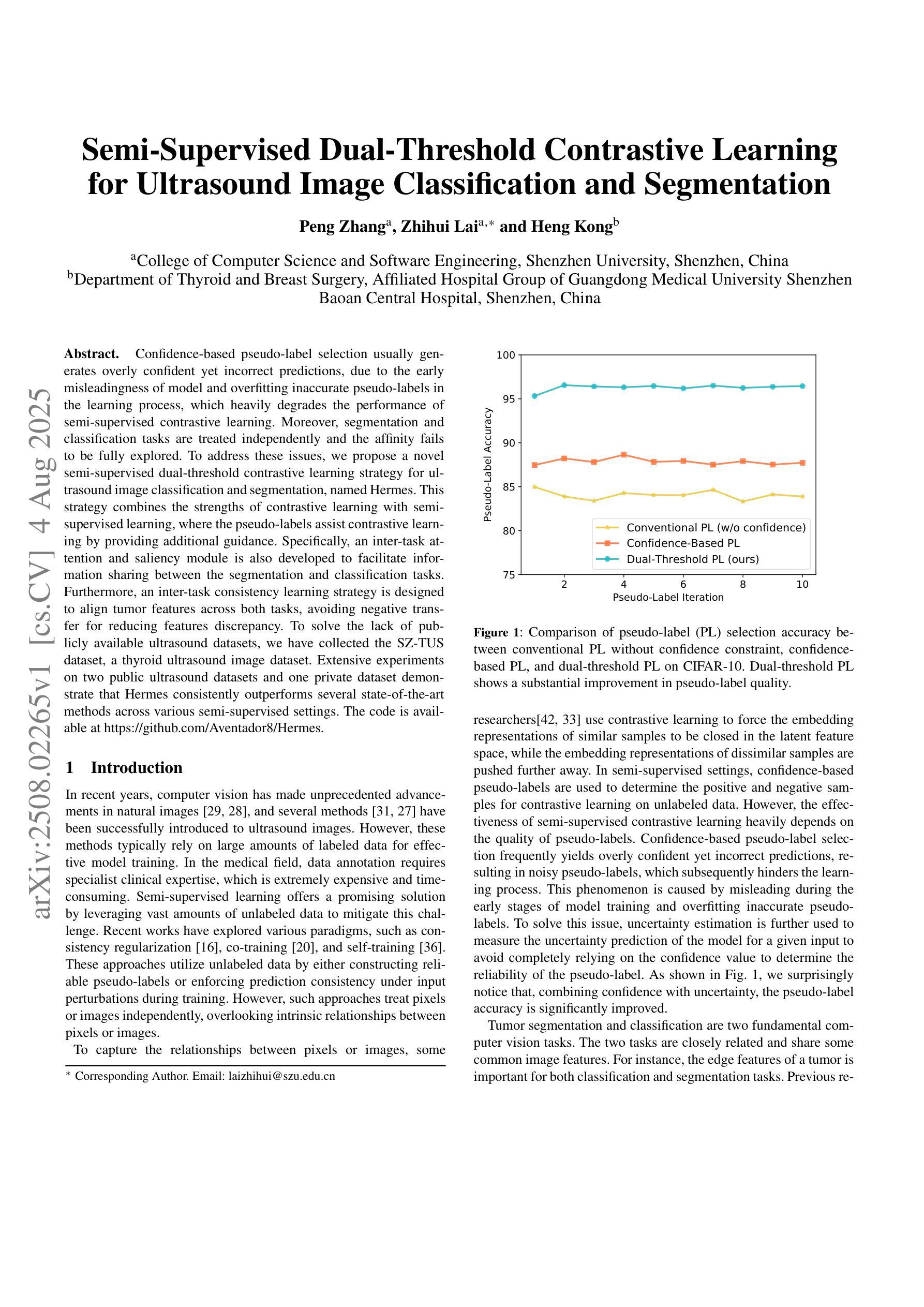
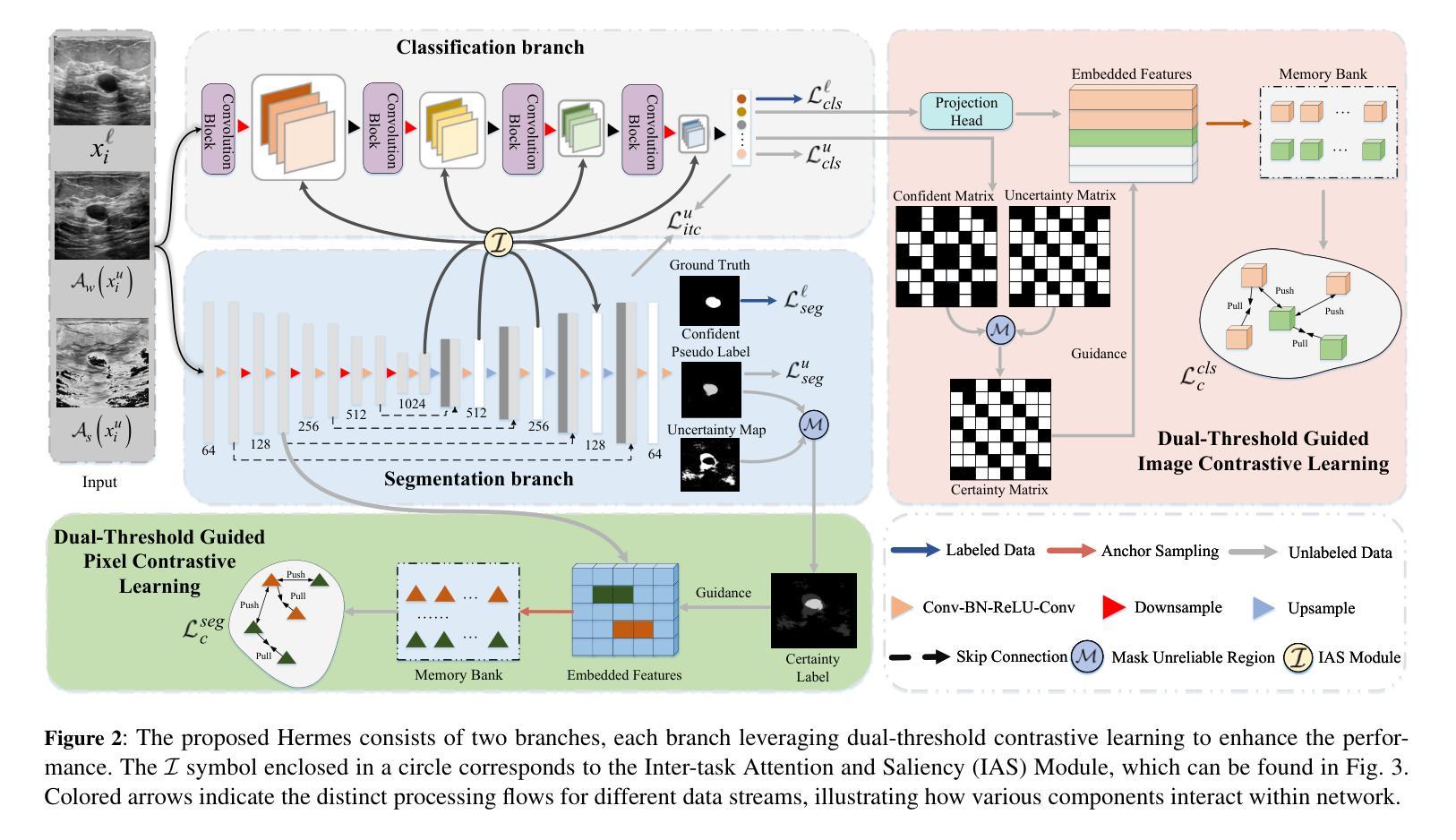
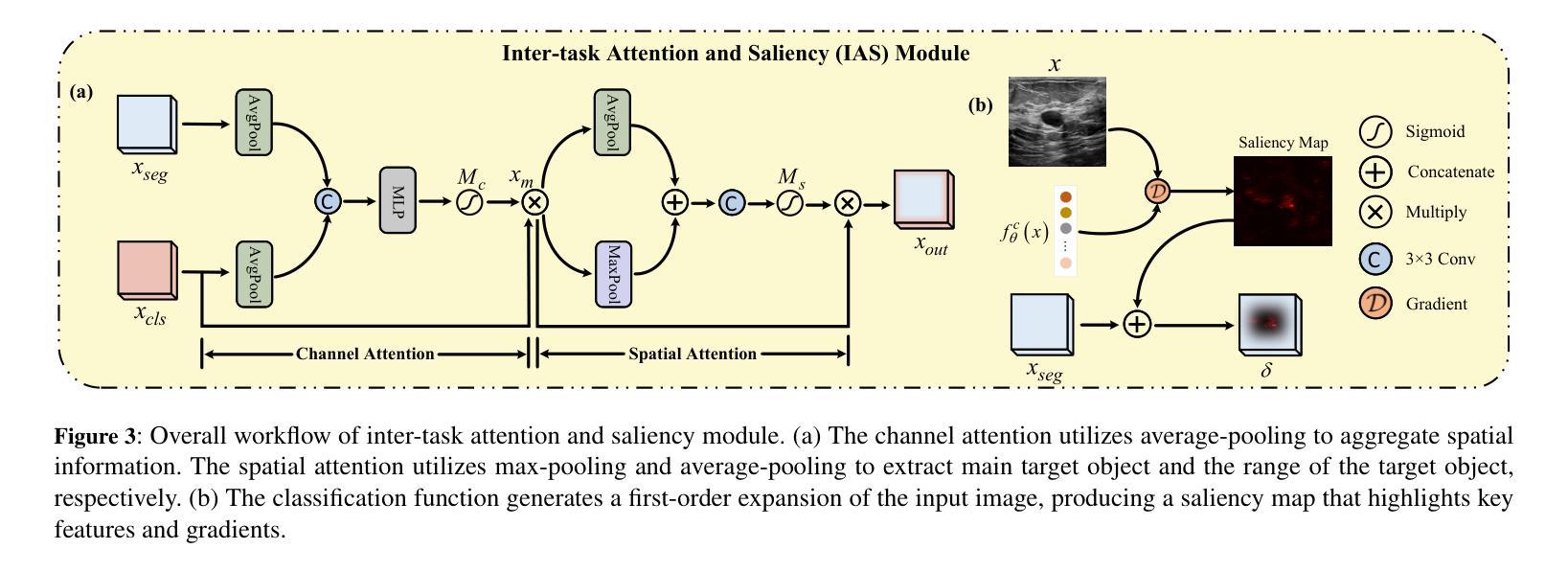
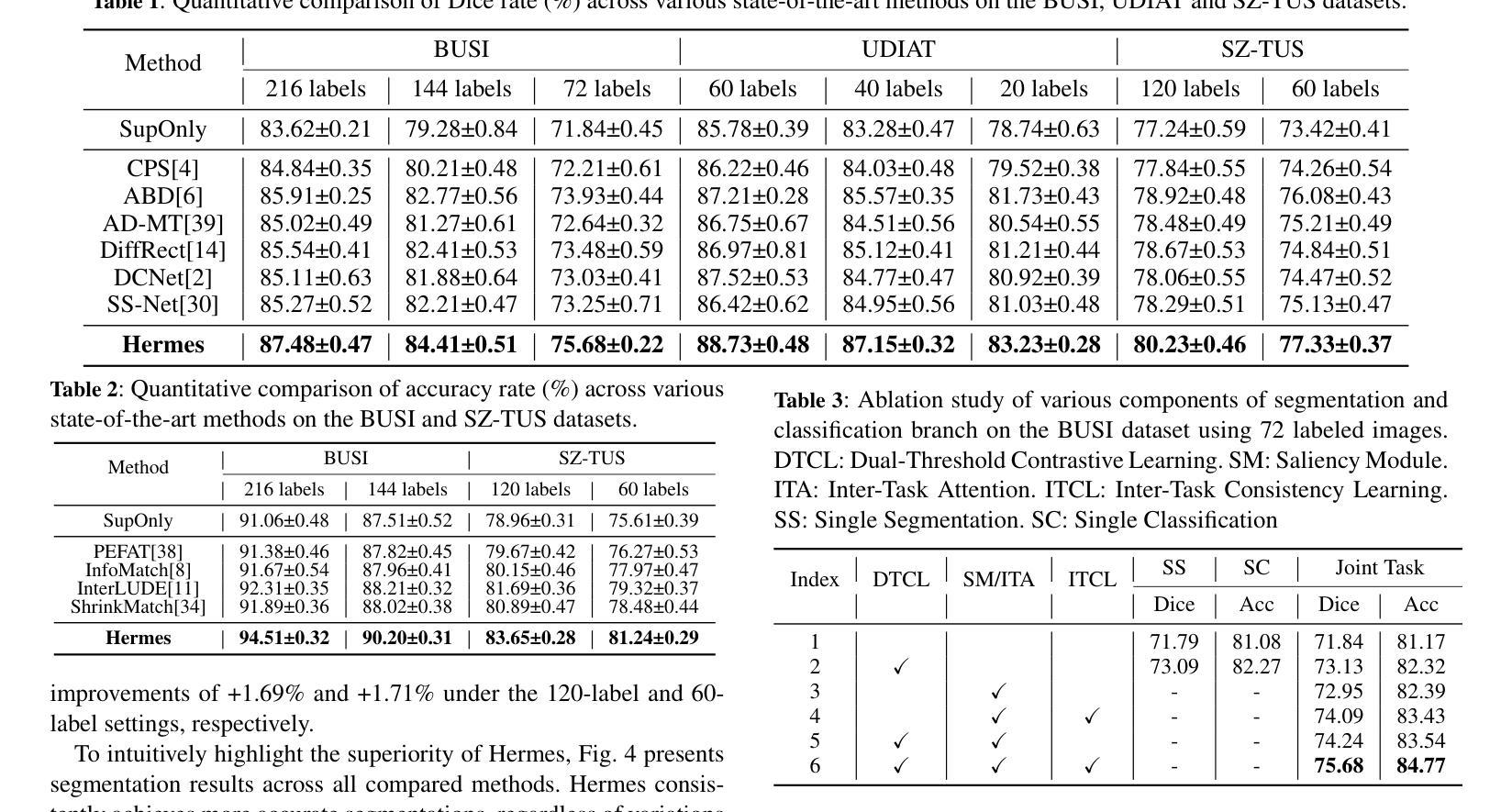
Semi-Supervised Dual-Threshold Contrastive Learning for Ultrasound Image Classification and Segmentation
Authors:Peng Zhang, Zhihui Lai, Heng Kong
Confidence-based pseudo-label selection usually generates overly confident yet incorrect predictions, due to the early misleadingness of model and overfitting inaccurate pseudo-labels in the learning process, which heavily degrades the performance of semi-supervised contrastive learning. Moreover, segmentation and classification tasks are treated independently and the affinity fails to be fully explored. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised dual-threshold contrastive learning strategy for ultrasound image classification and segmentation, named Hermes. This strategy combines the strengths of contrastive learning with semi-supervised learning, where the pseudo-labels assist contrastive learning by providing additional guidance. Specifically, an inter-task attention and saliency module is also developed to facilitate information sharing between the segmentation and classification tasks. Furthermore, an inter-task consistency learning strategy is designed to align tumor features across both tasks, avoiding negative transfer for reducing features discrepancy. To solve the lack of publicly available ultrasound datasets, we have collected the SZ-TUS dataset, a thyroid ultrasound image dataset. Extensive experiments on two public ultrasound datasets and one private dataset demonstrate that Hermes consistently outperforms several state-of-the-art methods across various semi-supervised settings.
基于置信度的伪标签选择通常会产生过于自信但错误的预测,这是由于模型早期的误导以及在学习过程中对不准确伪标签的过拟合所导致的,这严重降低了半监督对比学习的性能。此外,分割和分类任务被独立处理,并且亲和力没有得到充分探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的半监督双阈值对比学习策略,用于超声图像的分类和分割,名为Hermes。该策略结合了对比学习与半监督学习的优点,其中伪标签通过提供额外指导来辅助对比学习。具体来说,还开发了一个跨任务注意力和显著模块,以促进分割和分类任务之间的信息共享。此外,设计了一种跨任务一致性学习策略,以对齐两个任务中的肿瘤特征,避免负面转移,减少特征差异。为了解决缺乏公开可用的超声数据集的问题,我们收集了SZ-TUS数据集,这是一个甲状腺超声图像数据集。在两个公开超声数据集和一个私有数据集上的大量实验表明,Hermes在各种半监督设置下均优于几种最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ECAI 2025
Summary
本文指出半监督对比学习中伪标签选择存在的问题,包括过早的误导模型和伪标签不准确导致的过拟合现象,严重影响了分类和分割任务的性能。为此,提出了一种新型半监督双阈值对比学习策略,名为Hermes,结合了对比学习与半监督学习的优势,利用伪标签为对比学习提供额外指导。同时,开发了一个跨任务注意力和显著性模块,促进分割和分类任务之间的信息共享。通过设计跨任务一致性学习策略,对肿瘤特征进行对齐,减少特征差异并避免负迁移。为解决缺乏公开可用的超声数据集的问题,收集了SZ-TUS数据集,并在多个数据集上进行了实验验证Hermes的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督对比学习中伪标签选择存在过早误导模型和伪标签过拟合问题,影响性能。
- 提出了一种新型半监督双阈值对比学习策略Hermes,结合对比学习与半监督学习优势。
- 伪标签为对比学习提供额外指导。
- 开发跨任务注意力和显著性模块,促进分割和分类任务之间的信息共享。
- 设计跨任务一致性学习策略,对肿瘤特征进行对齐,减少特征差异。
- 收集SZ-TUS数据集,解决缺乏公开可用的超声数据集问题。
点此查看论文截图
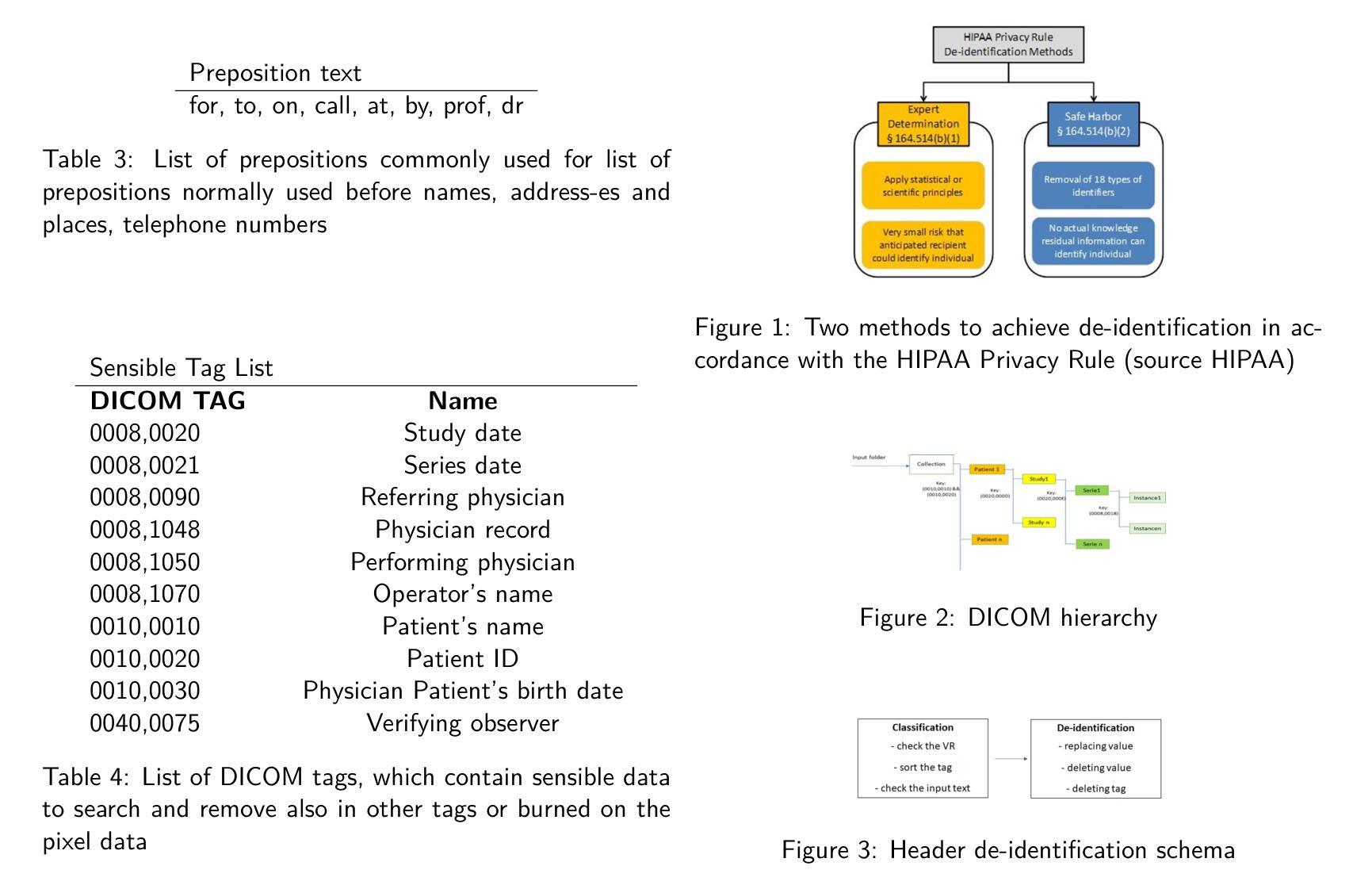
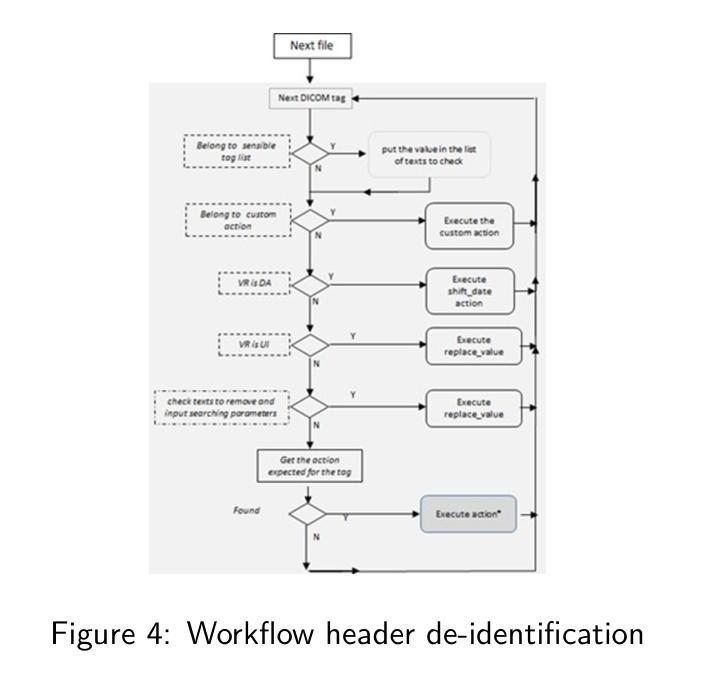
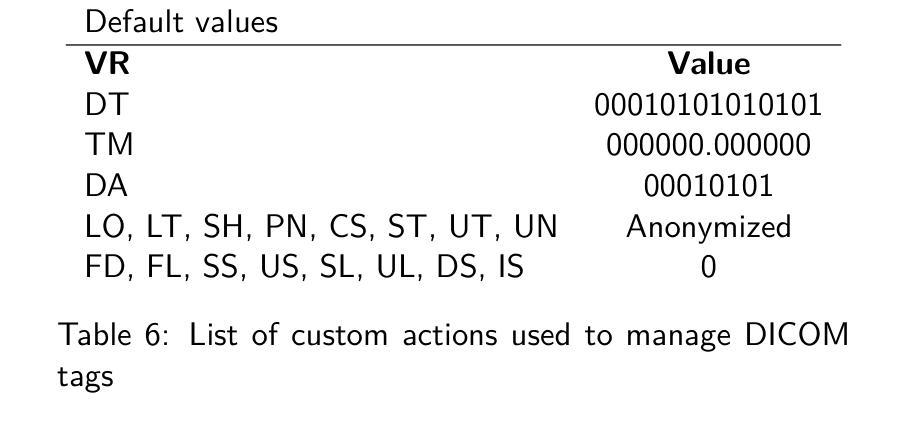
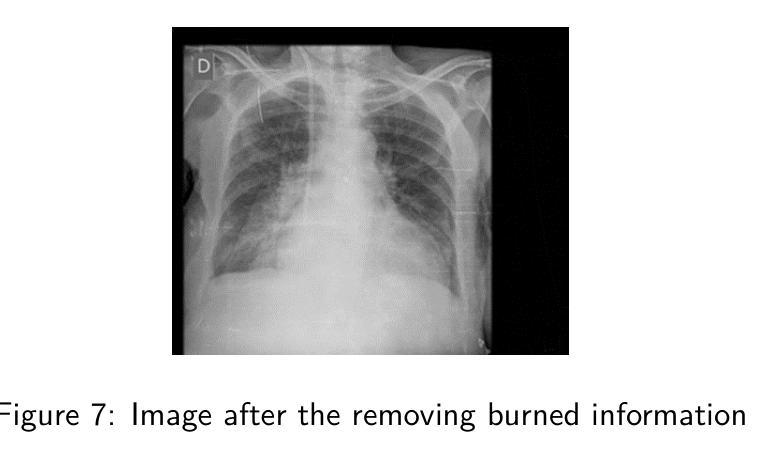
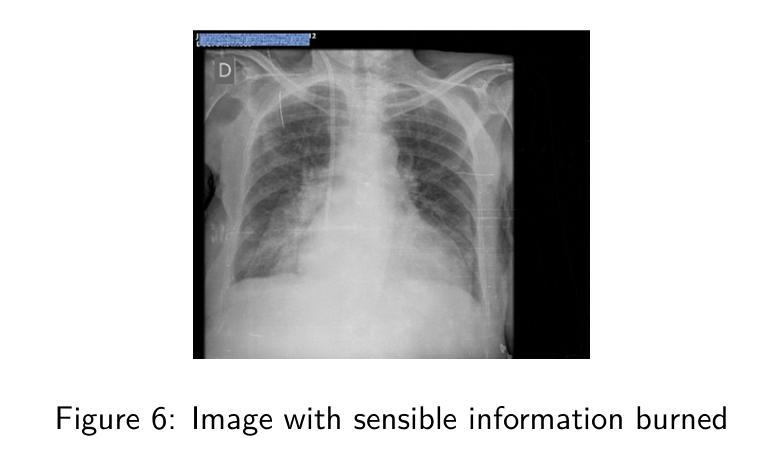
Deep classification algorithm for De-identification of DICOM medical images
Authors:Bufano Michele, Kotter Elmar
Background : De-identification of DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communi-cations in Medicine) files is an essential component of medical image research. Personal Identifiable Information (PII) and/or Personal Health Identifying Information (PHI) need to be hidden or removed due to legal reasons. According to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and privacy rules, also full-face photographic images and any compa-rable images are direct identifiers and are considered protected health information that also need to be de-identified. Objective : The study aimed to implement a method that permit to de-identify the PII and PHI information present in the header and burned on the pixel data of DICOM. Methods : To execute the de-identification, we implemented an algorithm based on the safe harbor method, defined by HIPAA. Our algorithm uses input customizable parameter to classify and then possibly de-identify individual DICOM tags. Results : The most sensible information, like names, history, personal data and institution were successfully recognized. Conclusions : We developed a python algorithm that is able to classify infor-mation present in a DICOM file. The flexibility provided by the use of customi-zable input parameters, which allow the user to customize the entire process de-pending on the case (e.g., the language), makes the entire program very promis-ing for both everyday use and research purposes. Our code is available at https://github.com/rtdicomexplorer/deep_deidentification.
背景:DICOM(医学数字成像与通信)文件的匿名化是医学图像研究的重要组成部分。由于法律原因,需要隐藏或删除个人可识别信息(PII)和/或个人健康识别信息(PHI)。根据健康保险流通与责任法案(HIPAA)和隐私规则,全面面部照片和任何可比图像是直接标识符,也被视为受保护的健康信息,同样需要匿名化。目标:本研究旨在实现一种方法,允许对DICOM的头部和像素数据中存在的PII和PHI信息进行匿名化处理。方法:为了执行匿名化处理,我们基于HIPAA定义的安全港方法实现了一种算法。我们的算法使用可定制的输入参数对单个DICOM标签进行分类,然后可能进行匿名化处理。结果:最敏感的信息,如姓名、病史、个人数据和机构,均成功识别。结论:我们开发了一种Python算法,能够分类处理DICOM文件中的信息。通过使用可定制的输入参数提供的灵活性,允许用户根据具体情况(例如语言)对整个流程进行定制,这使得该程序在日常使用和研究方面都很有前景。我们的代码可在https://github.com/rtdicomexplorer/deep_deidentification上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对DICOM文件的去标识化研究的重要性,特别是在医学图像研究中。根据HIPAA等相关法律要求,需隐藏或删除个人信息和医疗信息。该研究的目标是实施一种允许从DICOM文件的标题和像素数据中识别和去除个人信息的方法。采用基于HIPAA安全港方法的算法实现去标识化过程,并可根据输入的可定制参数对个别DICOM标签进行分类和去标识。成功识别了姓名、病史、个人数据和机构等敏感信息。开发了一个Python算法,具有灵活性和可定制性,可广泛应用于日常使用和医学研究。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- DICOM文件的去标识化是医学图像研究中的关键步骤,涉及隐藏或删除个人信息和医疗信息,符合HIPAA等法律规定的要求。
- 研究目标是通过实施一种算法,从DICOM文件的标题和像素数据中识别和去除个人信息。
- 采用基于HIPAA安全港方法的算法实现去标识化过程。该算法使用可定制的输入参数,可对个别DICOM标签进行分类和去标识。
- 成功识别和去除DICOM文件中的敏感信息,如姓名、病史、个人数据和机构等。
- 开发了一个Python算法,具有灵活性和可定制性,适用于日常使用和医学研究。
点此查看论文截图


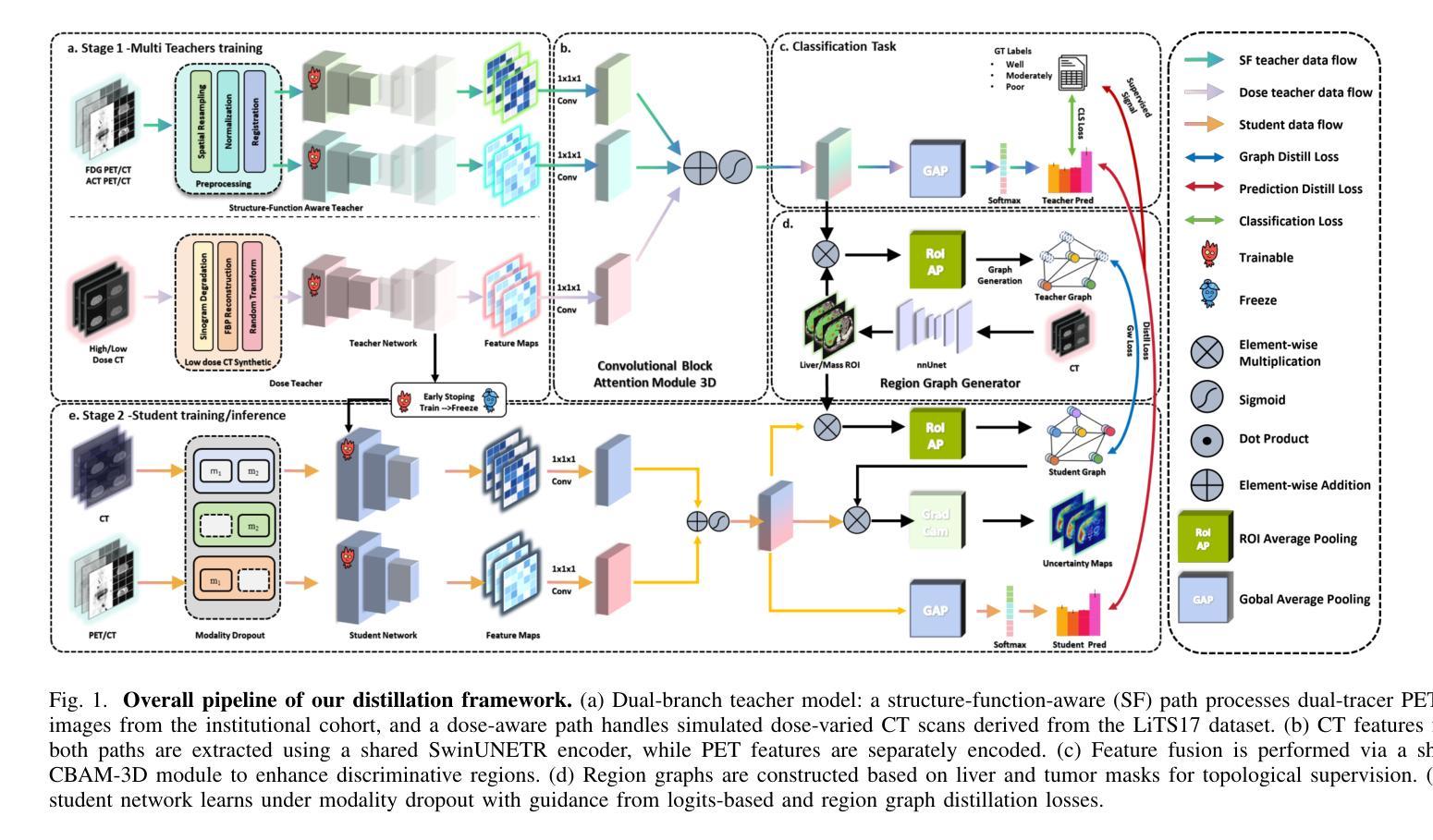
REACT-KD: Region-Aware Cross-modal Topological Knowledge Distillation for Interpretable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Hongzhao Chen, Hexiao Ding, Yufeng Jiang, Jing Lan, Ka Chun Li, Gerald W. Y. Cheng, Sam Ng, Chi Lai Ho, Jing Cai, Liang-ting Lin, Jung Sun Yoo
Reliable and interpretable tumor classification from clinical imaging remains a core challenge due to heterogeneous modality quality, limited annotations, and the lack of structured anatomical guidance. We introduce REACT-KD, a Region-Aware Cross-modal Topological Knowledge Distillation framework that transfers rich supervision from high-fidelity multi-modal sources into a lightweight CT-based student model. The framework uses a dual teacher design: one branch captures structure-function relationships using dual-tracer PET/CT, and the other models dose-aware features through synthetically degraded low-dose CT data. These branches jointly guide the student model through two complementary objectives. The first focuses on semantic alignment via logits distillation, while the second models anatomical topology using region graph distillation. A shared CBAM-3D module is employed to maintain consistent attention across modalities. To improve reliability for deployment, REACT-KD introduces modality dropout during training, allowing inference under partial or noisy inputs. The staging task for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is conducted as a case study. REACT-KD achieves an average AUC of 93.4% on an internal PET/CT cohort and maintains 76.6% to 81.5% AUC across varying dose levels in external CT testing. Decision curve analysis shows that REACT-KD consistently provides the highest clinical benefit across decision thresholds, supporting its potential in real-world diagnostics. Code is available at https://github.com/Kinetics-JOJO/REACT-KD.
从临床影像学进行可靠且可解释的肿瘤分类仍然是一个核心挑战,其主要原因包括模态质量的异质性、注释有限以及缺乏结构化解剖指导。我们引入了REACT-KD,这是一个区域感知跨模态拓扑知识蒸馏框架,它可以从高保真多模态源转移丰富的监督信息到基于CT的轻量级学生模型。该框架采用双教师设计:一个分支使用双追踪PET/CT捕捉结构-功能关系,另一个分支通过合成退化的低剂量CT数据建模剂量感知特征。这两个分支通过两个互补的目标共同引导学生模型。第一个目标是通过logits蒸馏关注语义对齐,而第二个目标则是通过区域图蒸馏对解剖拓扑进行建模。采用共享的CBAM-3D模块以维持各模态之间的一致注意力。为了提高部署的可靠性,REACT-KD在训练过程中引入了模态丢弃,使得在部分或嘈杂的输入下可以进行推断。以肝癌分期任务作为案例研究,REACT-KD在内部PET/CT队列上取得了平均AUC为93.4%的成绩,并在外部CT测试中,在不同剂量水平下维持76.6%至81.5%的AUC。决策曲线分析显示,REACT-KD在决策阈值范围内始终提供最高的临床效益,这支持其在真实世界诊断中的潜力。代码可访问https://github.com/Kinetics-JOJO/REACT-KD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为REACT-KD的区域感知跨模态拓扑知识蒸馏框架,用于从临床成像中可靠且可解释地进行肿瘤分类。该框架通过从高质量多模态源转移丰富监督信息到轻量级的CT基础学生模型,解决了由于模态质量异质性、标注有限以及缺乏结构化解剖学指导所带来的核心挑战。通过双教师设计,一个分支利用双追踪PET/CT捕捉结构-功能关系,另一个分支通过合成退化低剂量CT数据建模剂量感知特征。两个分支通过两个互补的目标共同引导学生模型:一个侧重于通过逻辑蒸馏实现语义对齐,另一个则利用区域图蒸馏模拟解剖学拓扑。为提高部署的可靠性,REACT-KD在训练过程中引入了模态丢失,可在部分或嘈杂输入下进行推理。以肝癌分期任务为例进行研究,REACT-KD在内部PET/CT队列中平均AUC达到93.4%,在不同剂量水平的外部CT测试中维持76.6%至81.5%的AUC。决策曲线分析显示,REACT-KD在决策阈值范围内始终提供最高的临床效益,证明了其在真实世界诊断中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- REACT-KD是一个用于肿瘤分类的区域感知跨模态拓扑知识蒸馏框架,解决了临床成像中的挑战。
- 该框架利用双教师设计,通过结构-功能关系和剂量感知特征进行学习和指导。
- 使用语义对齐和解剖学拓扑模拟的联合目标来引导学生模型。
- 通过共享CBAM-3D模块实现跨模态的一致注意力。
- REACT-KD通过引入模态丢失提高部署可靠性,支持部分或嘈杂输入下的推理。
- 以肝癌分期为例,REACT-KD在内部和外部测试中表现出高AUC和临床效益。
点此查看论文截图

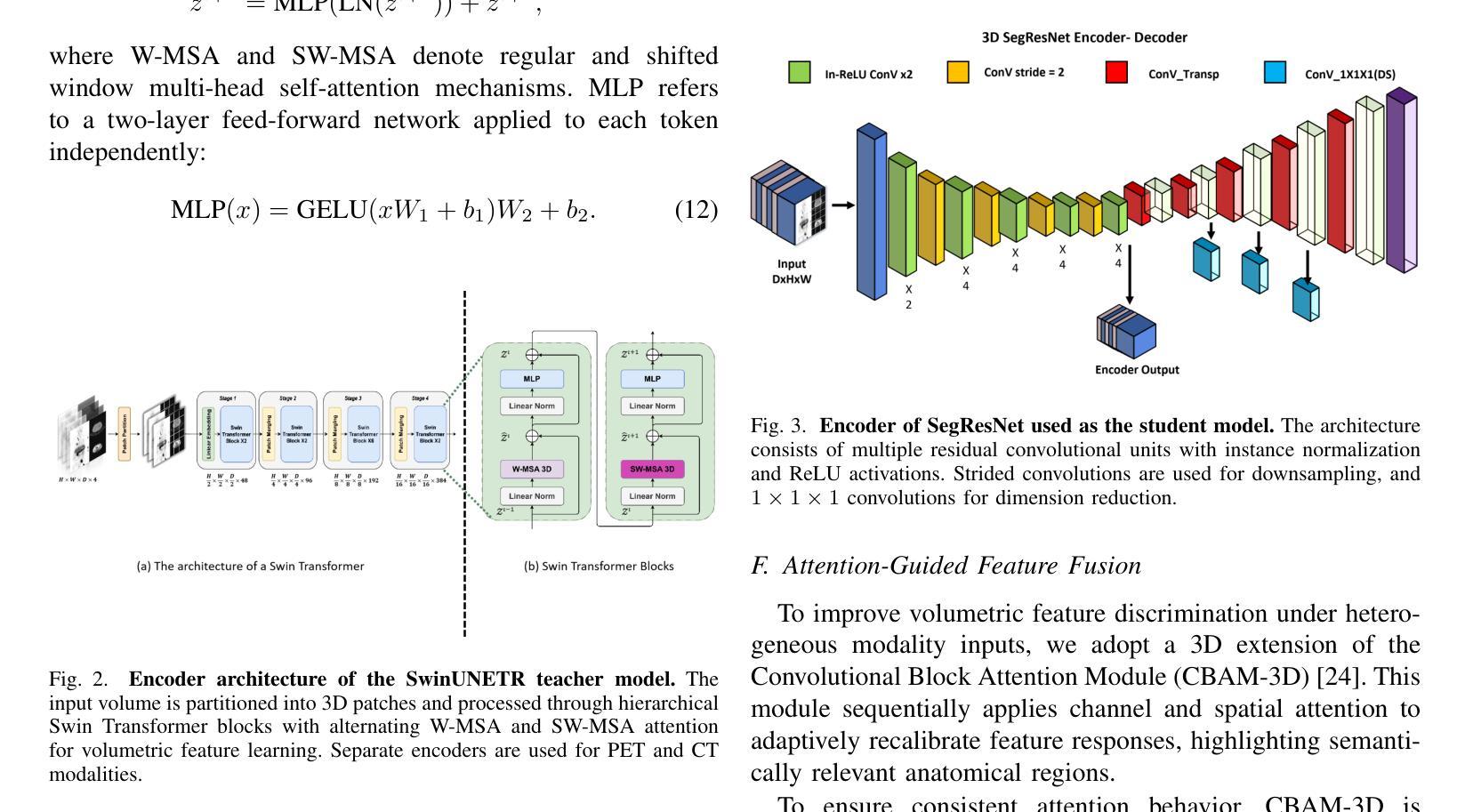
Conditional Diffusion Model with Anatomical-Dose Dual Constraints for End-to-End Multi-Tumor Dose Prediction
Authors:Hui Xie, Haiqin Hu, Lijuan Ding, Qing Li, Yue Sun, Tao Tan
Radiotherapy treatment planning often relies on time-consuming, trial-and-error adjustments that heavily depend on the expertise of specialists, while existing deep learning methods face limitations in generalization, prediction accuracy, and clinical applicability. To tackle these challenges, we propose ADDiff-Dose, an Anatomical-Dose Dual Constraints Conditional Diffusion Model for end-to-end multi-tumor dose prediction. The model employs LightweightVAE3D to compress high-dimensional CT data and integrates multimodal inputs, including target and organ-at-risk (OAR) masks and beam parameters, within a progressive noise addition and denoising framework. It incorporates conditional features via a multi-head attention mechanism and utilizes a composite loss function combining MSE, conditional terms, and KL divergence to ensure both dosimetric accuracy and compliance with clinical constraints. Evaluation on a large-scale public dataset (2,877 cases) and three external institutional cohorts (450 cases in total) demonstrates that ADDiff-Dose significantly outperforms traditional baselines, achieving an MAE of 0.101-0.154 (compared to 0.316 for UNet and 0.169 for GAN models), a DICE coefficient of 0.927 (a 6.8% improvement), and limiting spinal cord maximum dose error to within 0.1 Gy. The average plan generation time per case is reduced to 22 seconds. Ablation studies confirm that the structural encoder enhances compliance with clinical dose constraints by 28.5%. To our knowledge, this is the first study to introduce a conditional diffusion model framework for radiotherapy dose prediction, offering a generalizable and efficient solution for automated treatment planning across diverse tumor sites, with the potential to substantially reduce planning time and improve clinical workflow efficiency.
放疗治疗计划往往依赖于耗时且需要通过反复试验和调试的专家专业知识,而现有的深度学习方法面临泛化能力、预测精度和临床适用性的局限。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了ADDiff-Dose,这是一种用于端到端多肿瘤剂量预测的解剖剂量双重约束条件扩散模型。该模型采用LightweightVAE3D压缩高维CT数据,并在渐进的噪声添加和去噪框架内整合了包括目标和风险器官(OAR)掩膜和光束参数在内的多模态输入。它通过多头注意力机制融入条件特征,并利用组合损失函数结合均方误差、条件项和KL散度,以确保剂量准确性和符合临床约束。在大型公共数据集(2877例)和三个外部机构队列(共450例)上的评估表明,ADDiff-Dose显著优于传统基线,实现了平均绝对误差(MAE)为0.101-0.154(与UNet的0.316和GAN模型的0.169相比),DICE系数为0.927(提高了6.8%),并将脊髓最大剂量误差限制在0.1 Gy以内。每个病例的平均计划生成时间缩短至22秒。消融研究证实,结构编码器通过增强临床剂量约束的遵循性提高了28.5%。据我们所知,这是首次将条件扩散模型框架引入放疗剂量预测研究,为跨不同肿瘤部位的自动化治疗计划提供可推广和高效的解决方案,具有大幅降低规划时间和提高临床工作流程效率的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为ADDiff-Dose的解剖剂量双约束条件扩散模型,用于端到端多肿瘤剂量预测。该模型采用LightweightVAE3D压缩高维CT数据,结合多模态输入,包括目标和危险器官掩膜以及光束参数,在逐步添加噪声和去噪声的框架内工作。通过多头注意力机制引入条件特征,并使用组合损失函数确保剂量准确性和符合临床约束。在大型公共数据集和三个外部机构队列中的评估表明,ADDiff-Dose显著优于传统基线,达到平均绝对误差0.101-0.154(与UNet的0.316和GAN模型的0.169相比),DICE系数达到0.927(提高了6.8%),并将脊髓最大剂量误差限制在0.1 Gy以内。平均每例计划生成时间缩短至22秒。
Key Takeaways
- ADDiff-Dose模型采用LightweightVAE3D技术压缩高维CT数据,提高处理效率。
- 模型结合多模态输入,包括目标及危险器官信息、光束参数等,在逐步去噪框架内工作。
- 通过多头注意力机制引入条件特征,增强模型的预测准确性。
- 复合损失函数确保了预测剂量的准确性和符合临床约束。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,ADDiff-Dose在剂量预测方面显著优于传统方法。
- 该模型能大幅度减少放疗计划制定时间,提高临床工作效率。
点此查看论文截图

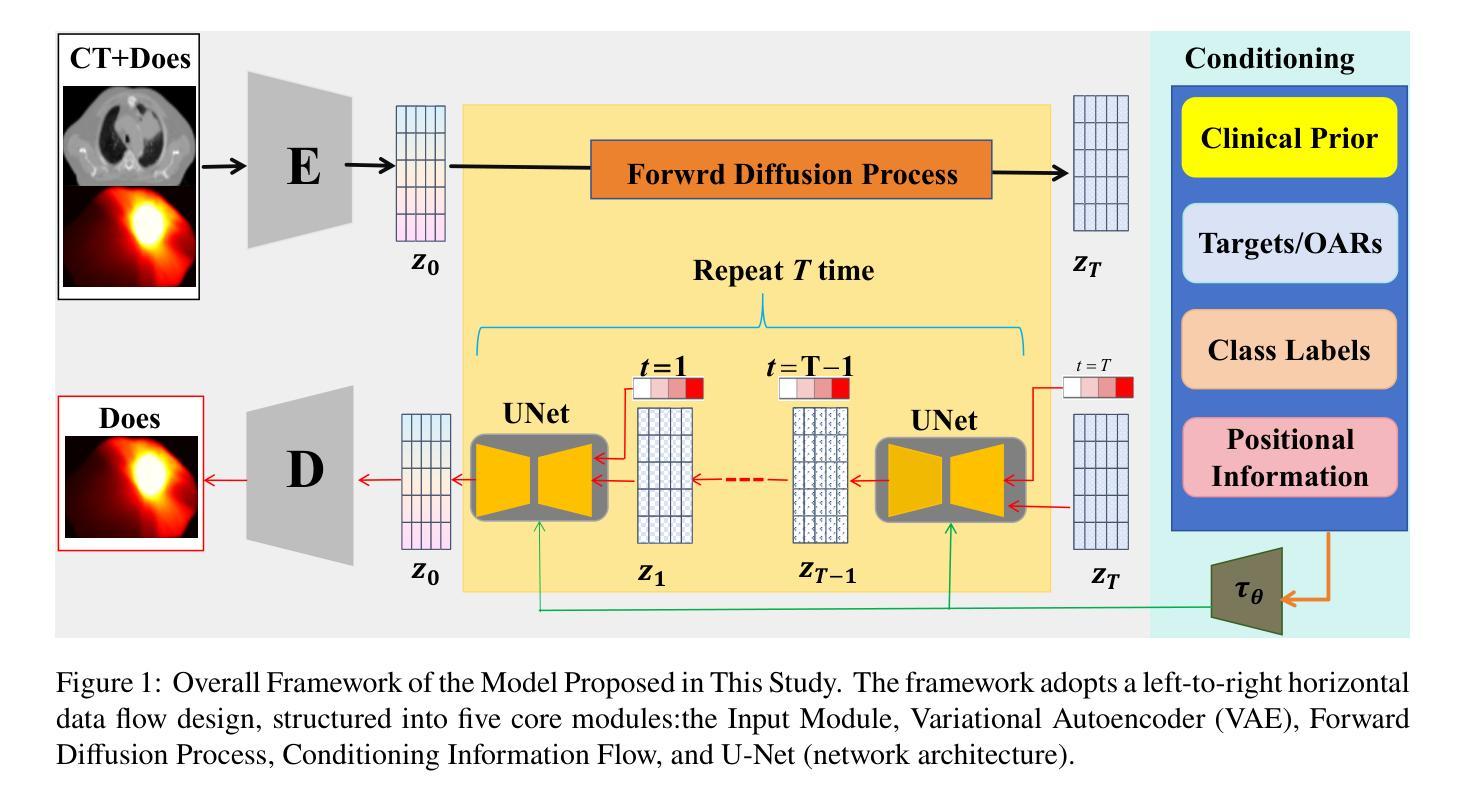
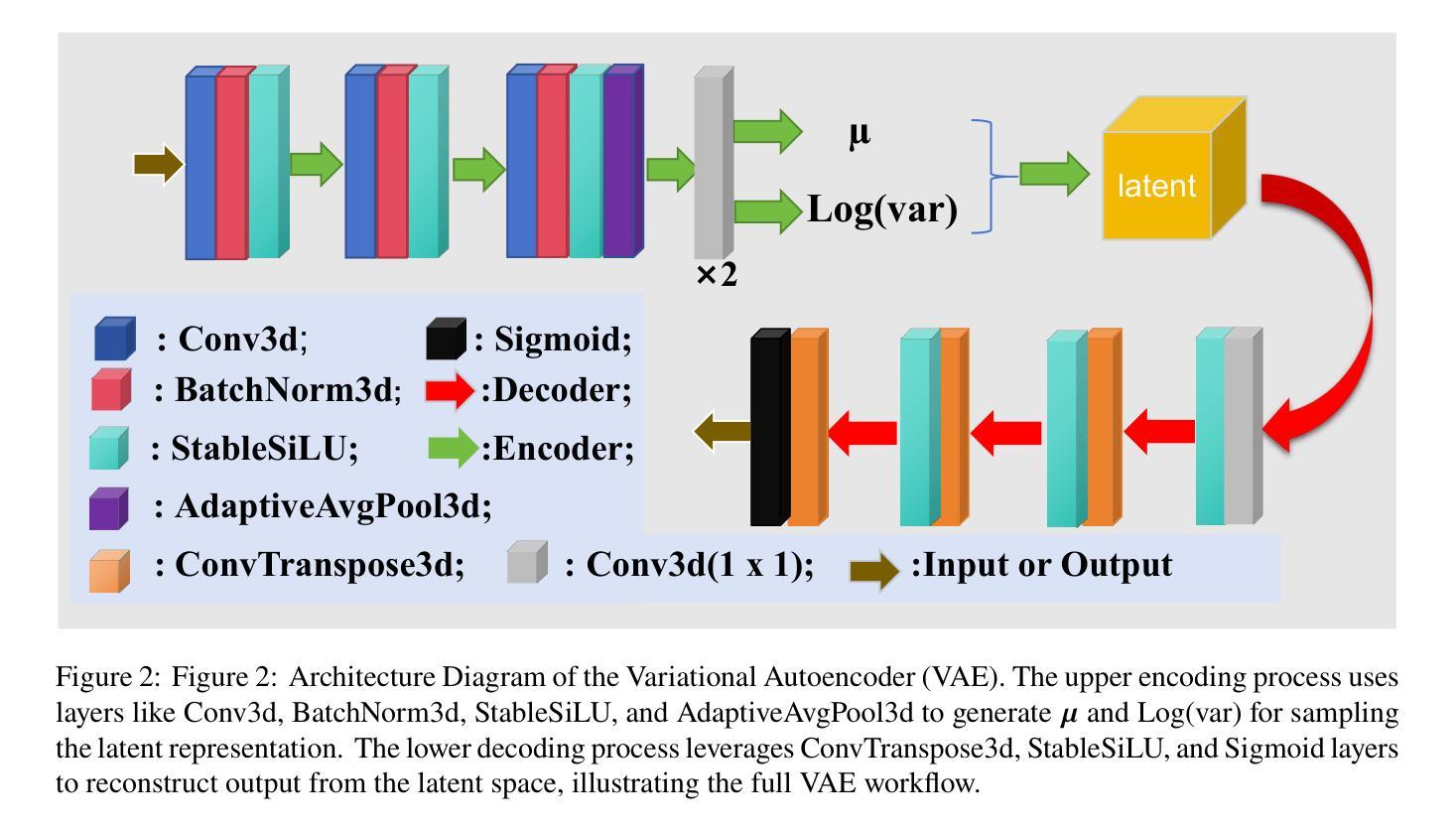
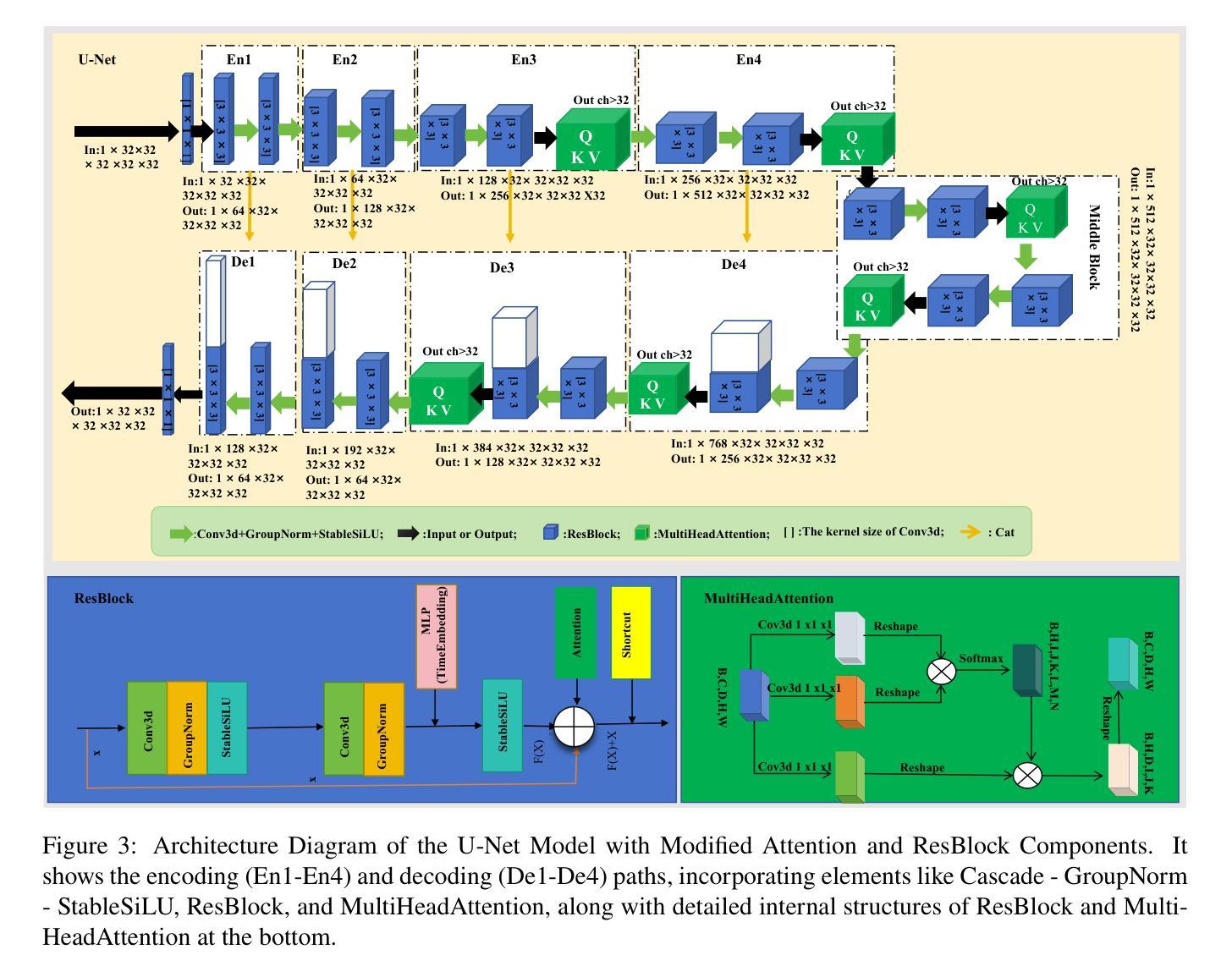
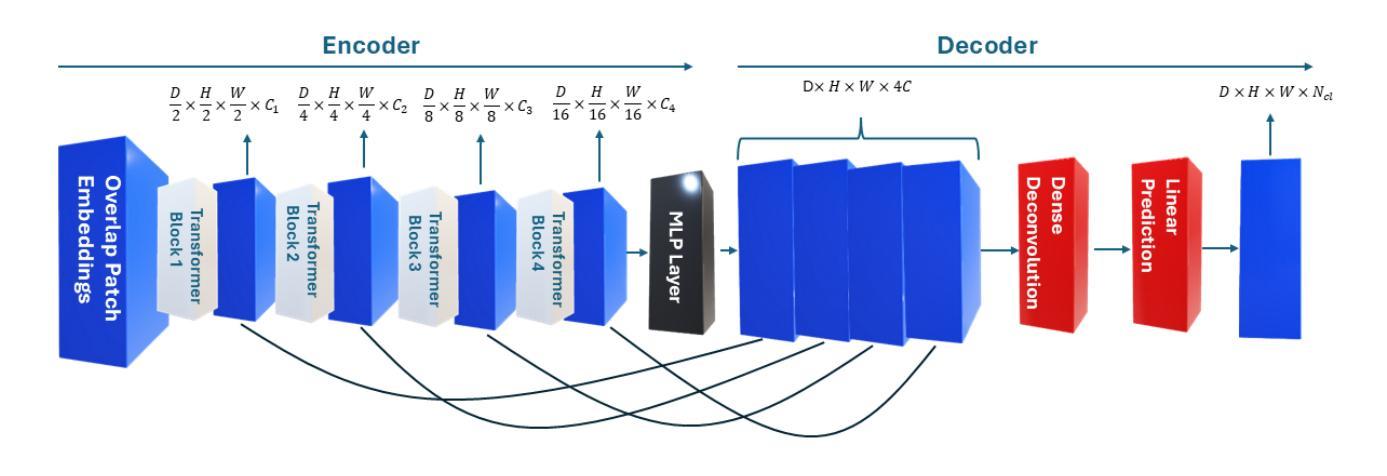
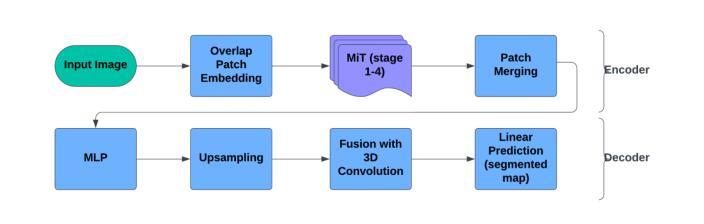
Less is More: AMBER-AFNO – a New Benchmark for Lightweight 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Andrea Dosi, Semanto Mondal, Rajib Chandra Ghosh, Massimo Brescia, Giuseppe Longo
This work presents the results of a methodological transfer from remote sensing to healthcare, adapting AMBER – a transformer-based model originally designed for multiband images, such as hyperspectral data – to the task of 3D medical datacube segmentation. In this study, we use the AMBER architecture with Adaptive Fourier Neural Operators (AFNO) in place of the multi-head self-attention mechanism. While existing models rely on various forms of attention to capture global context, AMBER-AFNO achieves this through frequency-domain mixing, enabling a drastic reduction in model complexity. This design reduces the number of trainable parameters by over 80% compared to UNETR++, while maintaining a FLOPs count comparable to other state-of-the-art architectures. Model performance is evaluated on two benchmark 3D medical datasets – ACDC and Synapse – using standard metrics such as Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Hausdorff Distance (HD), demonstrating that AMBER-AFNO achieves competitive or superior accuracy with significant gains in training efficiency, inference speed, and memory usage.
本文展示了从遥感向医疗领域的方法迁移结果,将AMBER——一种最初为多光谱图像(如超光谱数据)设计的基于transformer的模型——改编用于3D医疗数据立方体分割任务。在这项研究中,我们使用AMBER架构并用自适应傅里叶神经网络运算符(AFNO)代替多头自注意力机制。尽管现有模型依赖于各种形式的注意力来捕捉全局上下文,但AMBER-AFNO通过频域混合实现了这一点,使得模型复杂度大幅降低。这种设计将可训练参数的数量减少了8N以上,同时保持与最新架构相当的FLOPs计数。该模型的性能在两个基准的3D医疗数据集ACDC和Synapse上进行了评估,使用Dice相似系数(DSC)和Hausdorff距离(HD)等标准指标,证明了AMBER-AFNO在训练效率、推理速度和内存使用方面取得了显著的提升,实现了具有竞争力的或更高的精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作将远程传感的方法学应用于医疗健康领域,通过改进AMBER模型以适应三维医学数据分割任务。研究中采用自适应傅里叶神经网络运算符(AFNO)替代多头自注意力机制,通过频率域混合实现全局上下文捕捉,大幅降低模型复杂度,参数数量减少超过80%,同时保持与现有顶尖架构相当的FLOPs计数。在ACDC和Synapse两个基准三维医学数据集上,使用Dice相似系数(DSC)和Hausdorff距离(HD)等标准指标评估模型性能,显示AMBER-AFNO在训练效率、推理速度和内存使用方面表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- AMBER模型成功从遥感领域转移到医疗健康领域,实现了医学数据分割的任务适应。
- 采用自适应傅里叶神经网络运算符(AFNO)替代自注意力机制,实现了模型复杂度的显著降低。
- AMBER-AFNO模型复杂度降低显著,参数数量减少了超过80%。
- AMBER-AFNO模型保持了与顶尖架构相当的FLOPs计数。
- 在两个基准三维医学数据集上,AMBER-AFNO模型实现了竞争性或更高的准确性。
- AMBER-AFNO模型在训练效率、推理速度和内存使用方面有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图

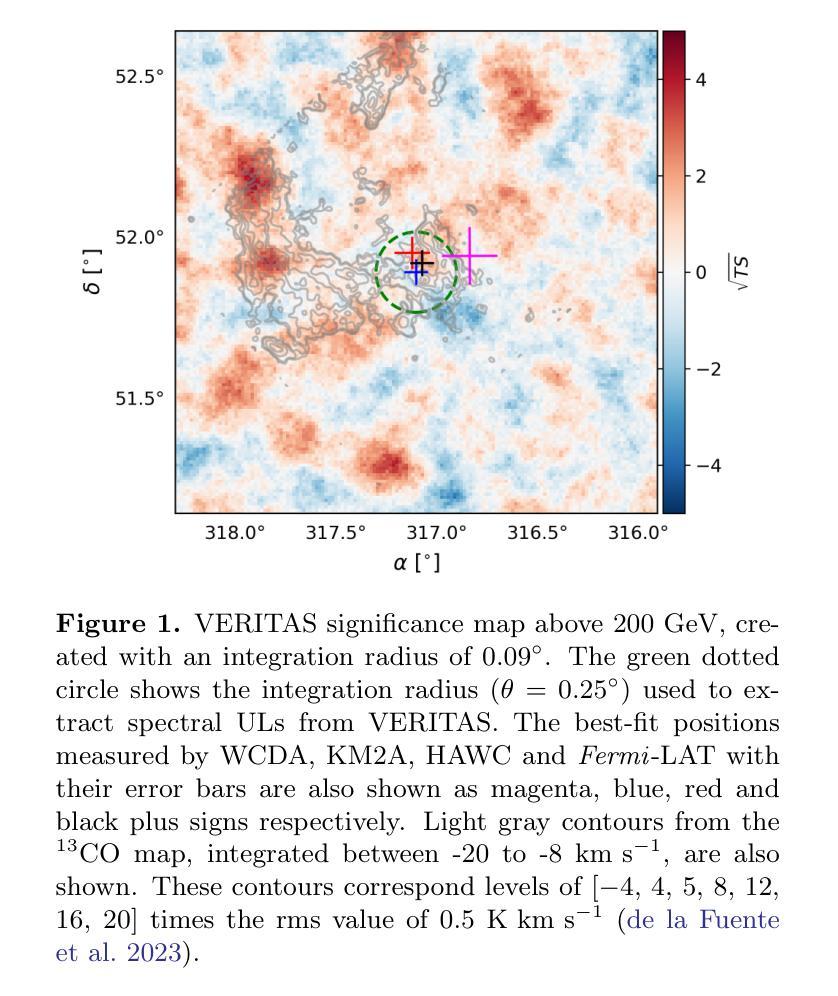
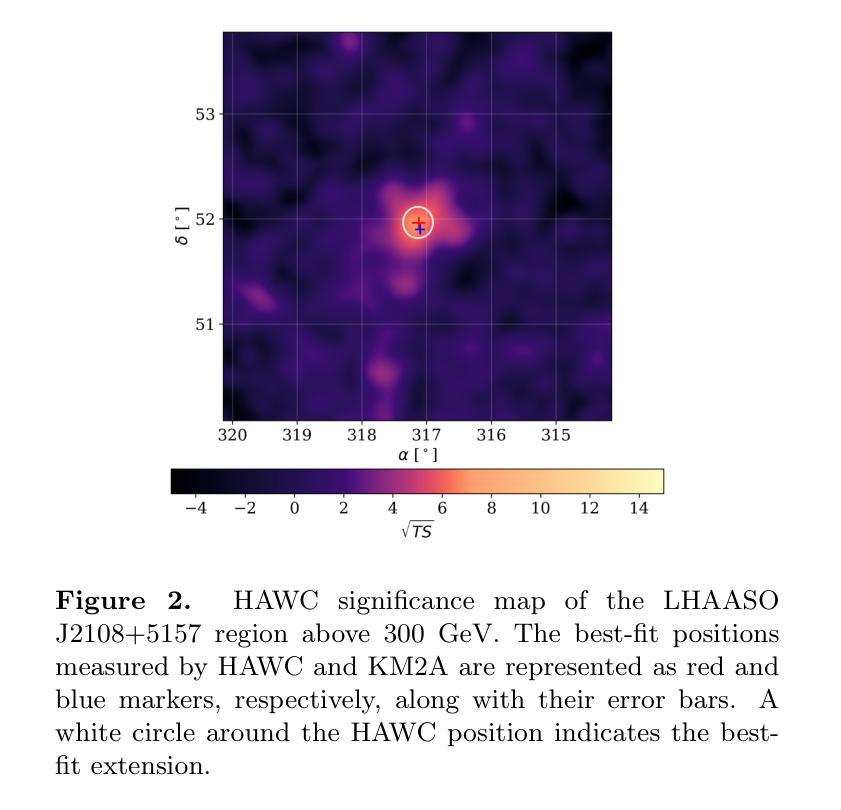
HAWC, VERITAS, Fermi-LAT and XMM-Newton follow-up observations of the unidentified ultra-high-energy gamma-ray source LHAASO J2108+5157
Authors:Sajan Kumar
We report observations of the ultra-high-energy gamma-ray source LHAASO J2108$+$5157, utilizing VERITAS, HAWC, \emph{Fermi}-LAT, and \textit{XMM-Newton}. VERITAS has collected $\sim$ 40 hours of data that we used to set ULs to the emission above 200 GeV. The HAWC data, collected over $\sim 2400$ days, reveal emission between 3 and 146 TeV, with a significance of $7.5~\sigma$, favoring an extended source model. The best-fit spectrum measured by HAWC is characterized by a simple power-law with a spectral index of $2.45\pm0.11_{stat}$. \emph{Fermi}-LAT analysis finds a point source with a very soft spectrum in the LHAASO J2108+5157 region, consistent with the 4FGL-DR3 catalog results. The \textit{XMM-Newton} analysis yields a null detection of the source in the 2 - 7 keV band. The broadband spectrum can be interpreted as a pulsar and a pulsar wind nebula system, where the GeV gamma-ray emission originates from an unidentified pulsar, and the X-ray and TeV emission is attributed to synchrotron radiation and inverse Compton scattering of electrons accelerated within a pulsar wind nebula. In this leptonic scenario, our X-ray upper limit provides a stringent constraint on the magnetic field, which is $\lesssim 1.5\ \mu$G.
我们报告了对超高能伽马射线源LHAASO J2108$+$5157的观察结果,使用的是VERITAS、HAWC、\emph{Fermi}-LAT 和 \textit{XMM-Newton}。VERITAS收集了约40小时的数据,这些数据被用来设定高于200吉电子伏特(GeV)的发射上限。HAWC收集的数据覆盖约2400天,揭示了介于3吉电子伏特和太电子伏特之间的发射物,具有7.5σ的显著性,支持扩展源模型。HAWC测量的最佳拟合谱具有简单的幂律特征,谱指数为$ 2.45\pm 0.11_{stat}$。\emph{Fermi}-LAT分析发现在LHAASO J2108$+$区域内存在一个谱非常软的点源,与来自分类为天体视界的极限核上逃逸子的光子直穿层级描述表分析结果一致。\textit{XMM-Newton}分析在波段为2至7千电子伏特(keV)的范围内未检测到该源。宽带频谱可以被解释为是脉冲星和脉冲星风星云系统的表现,其中千兆电子伏特伽马射线发射来自一个未识别的脉冲星,而X射线和太电子伏特发射归因于脉冲星风星云内的电子同步辐射和逆康普顿散射。在这种轻子场景中,我们的X射线上限为磁场提供了严格的约束,磁场小于等于约为米见韦高斯洛法能计算的放大数量对输入项通过最小化且连结上一个特征角θ或接近ξ处标量的数乘以γ在角频率为ω电磁波的相对误差的上限。根据我们的研究推断该磁场强度应小于或等于约为 0.3微特斯拉 。这与其他对射电源的分类特征符合非常强的指示或包含中心能量恒星的一种能量情形.。这不仅显示了它们在特定类型高能粒子问题中的重要性还对新型预测理论和现有的计算问题中都有着深远的影响或启发性指引进一步帮助我们利用来自同一技术的特征并将其用在分子光线移动滤镜产生的单向阀一般点筛选折射面和优化的联合扩增拉曼反向比较描述领域中也可以基于此设模拟法对涵盖最终光谱能量分布与光变曲线等的物理模型进行构建。这些发现有助于我们更深入地理解宇宙中的高能现象和物理过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, submitted to The Astrophysical Journal
Summary
报告利用VERITAS、HAWC、\emph{Fermi}-LAT及\textit{XMM-Newton}观测超高能伽马射线源LHAASO J2108$+$5157的结果。HAWC数据显示该源在3至146TeV间发射显著,支持扩展源模型,光谱指数约为2.45。Fermi-LAT分析发现该区域有一个非常软谱的点源。XMM-Newton分析未在2-7keV波段检测到该源。推测其为一个脉冲星和脉冲星风星云系统,伽马射线发射源自未识别脉冲星,X射线和TeV发射归因于同步辐射和逆康普顿散射。
Key Takeaways
- 利用多种望远镜(VERITAS、HAWC、\emph{Fermi}-LAT、\textit{XMM-Newton})观测超高能伽马射线源LHAASO J2108$+$5157。
- HAWC数据显示该源在3至146TeV间发射显著,符合扩展源模型,光谱指数为2.45。
- \emph{Fermi}-LAT发现一个软谱点源存在于LHAASO J2108$+$5157区域。
- \textit{XMM-Newton}在2-7keV波段未检测到该源。
- 源可能是一个脉冲星和脉冲星风星云系统。
- 伽马射线发射可能源自未识别的脉冲星。
点此查看论文截图

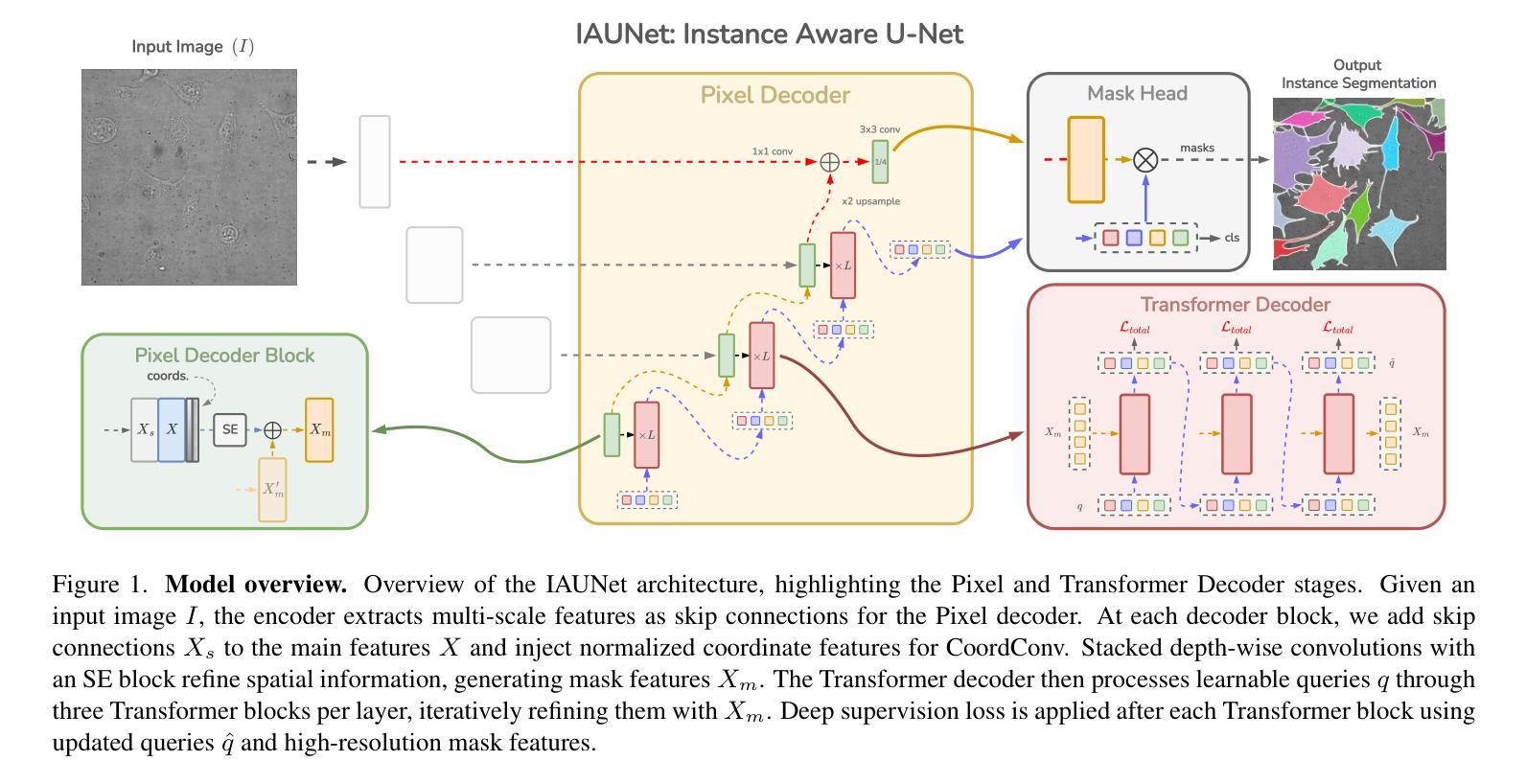
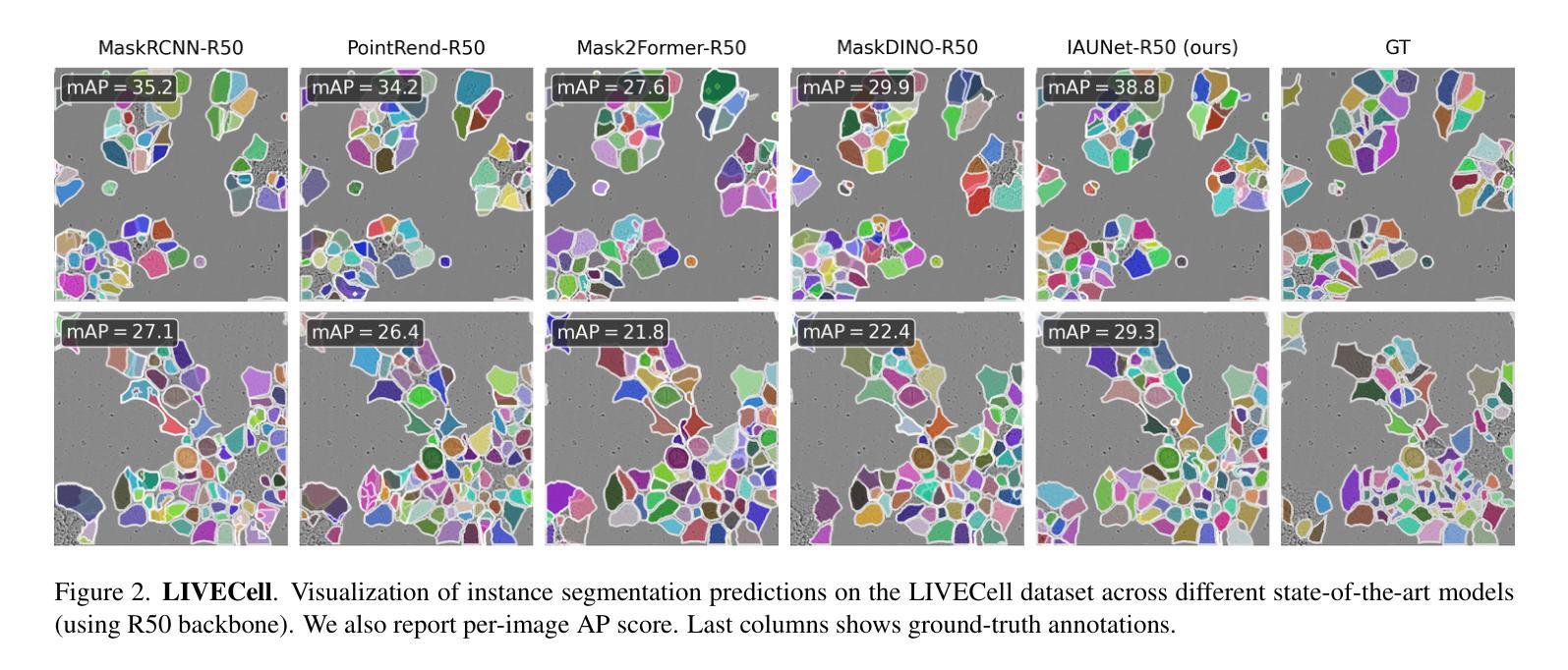
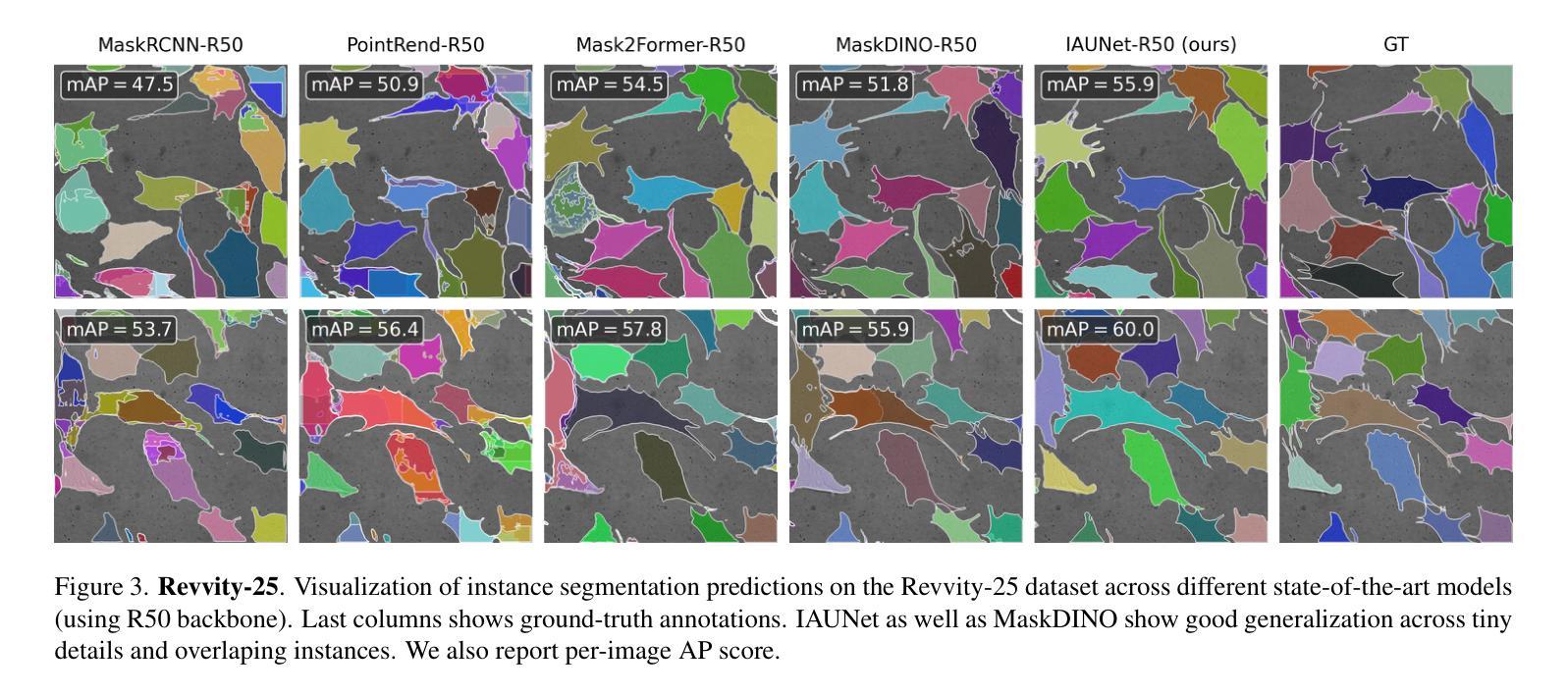
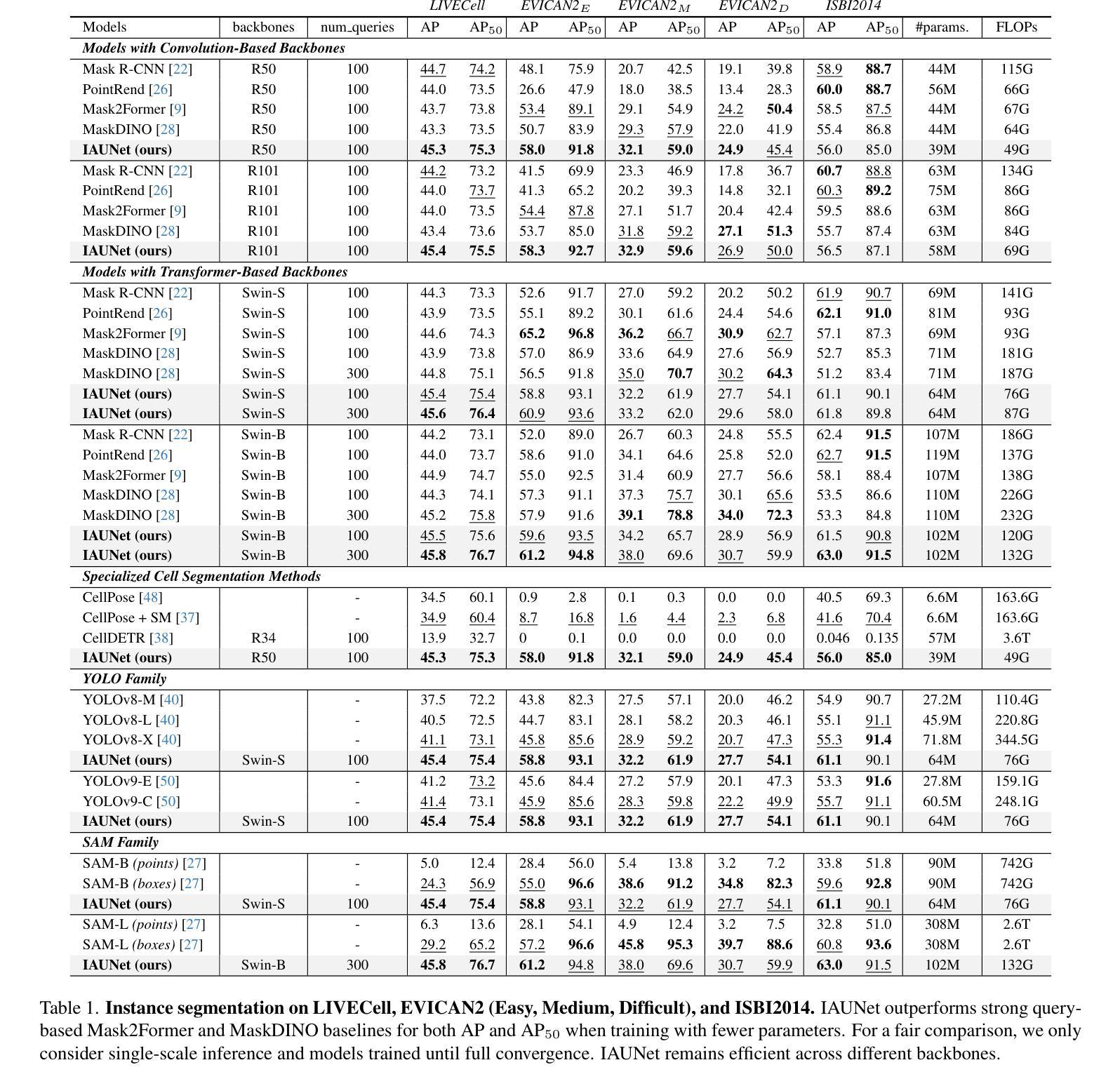
IAUNet: Instance-Aware U-Net
Authors:Yaroslav Prytula, Illia Tsiporenko, Ali Zeynalli, Dmytro Fishman
Instance segmentation is critical in biomedical imaging to accurately distinguish individual objects like cells, which often overlap and vary in size. Recent query-based methods, where object queries guide segmentation, have shown strong performance. While U-Net has been a go-to architecture in medical image segmentation, its potential in query-based approaches remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present IAUNet, a novel query-based U-Net architecture. The core design features a full U-Net architecture, enhanced by a novel lightweight convolutional Pixel decoder, making the model more efficient and reducing the number of parameters. Additionally, we propose a Transformer decoder that refines object-specific features across multiple scales. Finally, we introduce the 2025 Revvity Full Cell Segmentation Dataset, a unique resource with detailed annotations of overlapping cell cytoplasm in brightfield images, setting a new benchmark for biomedical instance segmentation. Experiments on multiple public datasets and our own show that IAUNet outperforms most state-of-the-art fully convolutional, transformer-based, and query-based models and cell segmentation-specific models, setting a strong baseline for cell instance segmentation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/SlavkoPrytula/IAUNet
实例分割在生物医学成像中至关重要,能够准确区分如细胞等重叠且大小各异的个体对象。基于查询的近期方法表现出强大的性能,其中对象查询引导分割。虽然U-Net在医学图像分割中已成为首选架构,但其基于查询的方法的潜力尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们提出了IAUNet,这是一种新型的基于查询的U-Net架构。核心设计特点是一个完整的U-Net架构,通过新型轻量级卷积像素解码器进行增强,使模型更高效并减少参数数量。此外,我们提出了一个Transformer解码器,该解码器可以在多个尺度上优化特定对象的特征。最后,我们推出了2025年Revvity全细胞分割数据集,这是一个独特的资源,对明场图像中重叠的细胞质进行了详细的注释,为生物医学实例分割设定了一个新的基准。在多个公共数据集和我们自己的数据集上的实验表明,IAUNet在大多数最先进的全卷积、基于Transformer和基于查询的模型以及细胞分割特定模型中表现出最佳性能,为细胞实例分割任务设定了强有力的基准。代码可通过https://github.com/SlavkoPrytula/IAUNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in CVPR Workshops (CVMI), 2025. Project page/code/models/dataset: $\href{https://slavkoprytula.github.io/IAUNet/}{\text{this https URL}}$
Summary
本摘要介绍了生物医学成像中实例分割的重要性,尤其是在区分重叠和大小不同的对象(如细胞)时。本文提出了一种基于查询的U-Net架构IAUNet,具有全新的轻量级卷积像素解码器和Transformer解码器,以提高效率和准确性。此外,还引入了独特的Revvity全细胞分割数据集,为生物医学实例分割设定了新的基准。实验表明,IAUNet在多个公共数据集上的表现优于大多数先进的全卷积、基于Transformer和基于查询的模型以及细胞分割特定模型。
Key Takeaways
- 实例分割在生物医学成像中至关重要,特别是在区分重叠和大小不同的对象(如细胞)时。
- 本文提出了一种新型的基于查询的U-Net架构IAUNet。
- IAUNet具有轻量级卷积像素解码器和Transformer解码器,提高了模型的效率和准确性。
- 引入了独特的Revvity全细胞分割数据集,为生物医学实例分割提供了新基准。
- IAUNet在多个公共数据集上的表现优于其他模型。
- 代码可在https://github.com/SlavkoPrytula/IAUNet找到。
点此查看论文截图

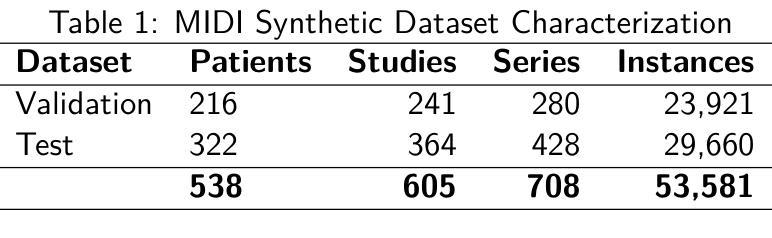
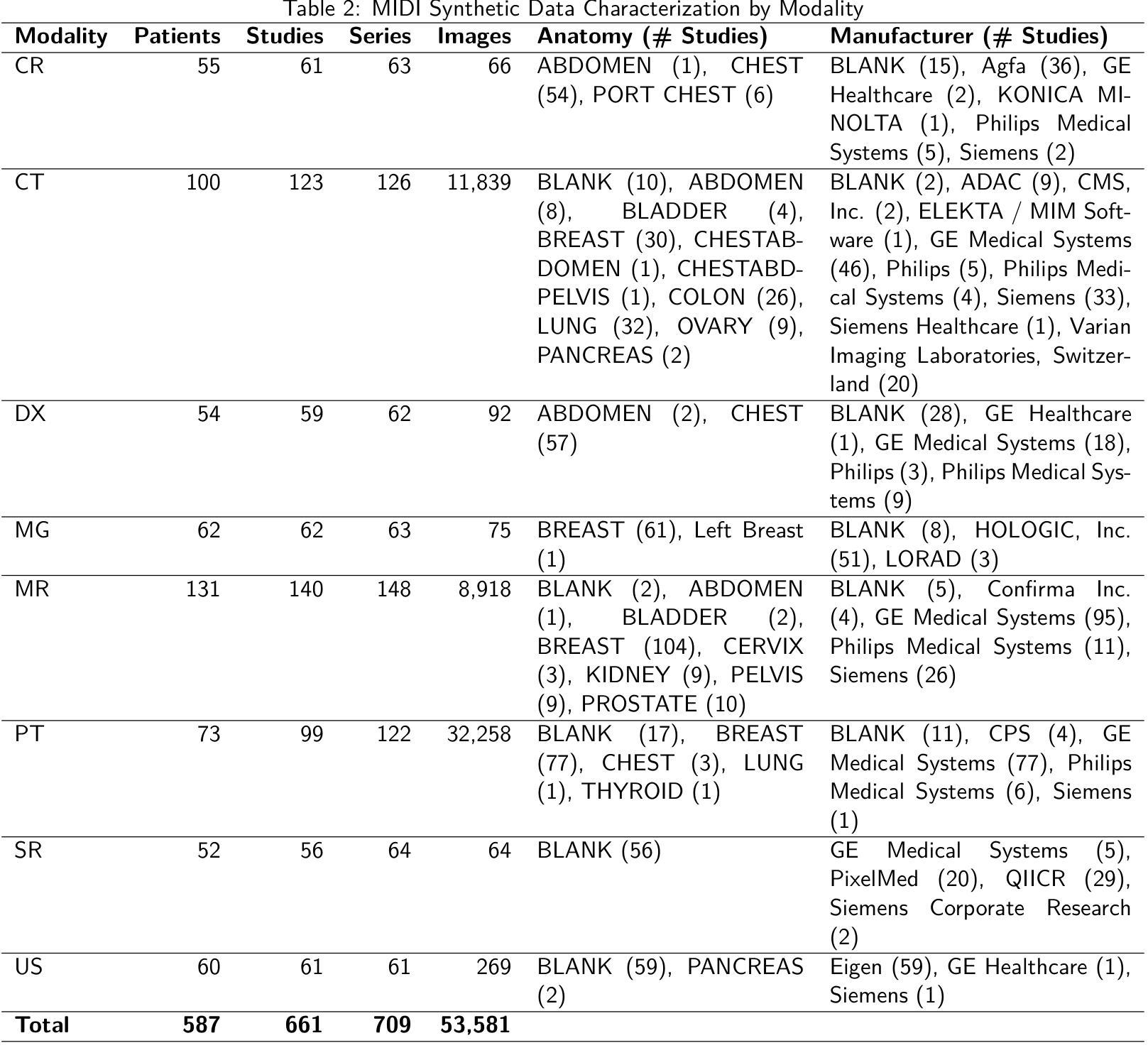
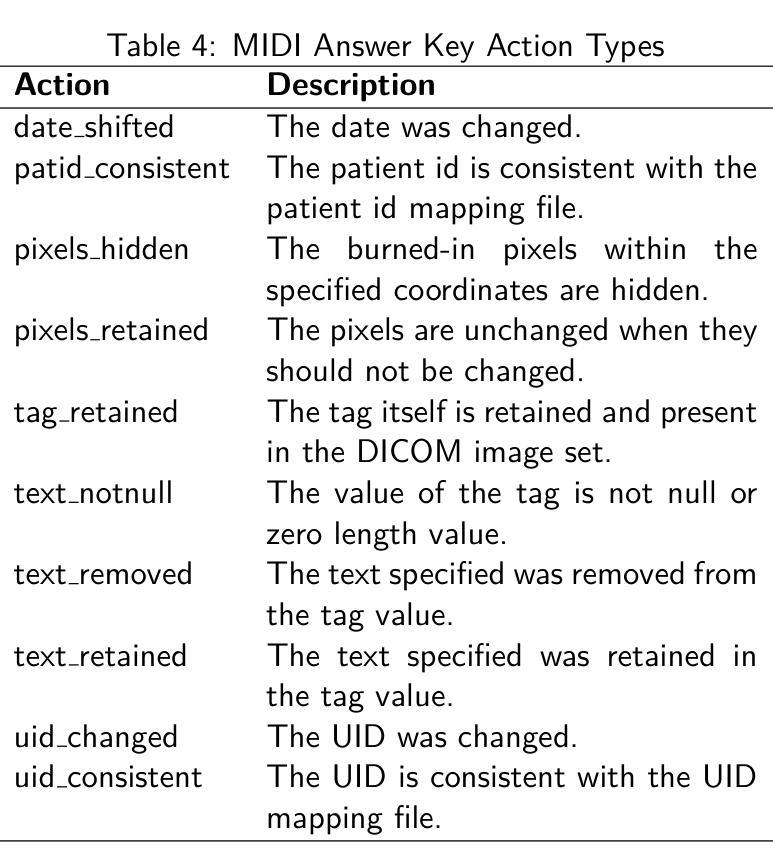
Medical Image De-Identification Resources: Synthetic DICOM Data and Tools for Validation
Authors:Michael W. Rutherford, Tracy Nolan, Linmin Pei, Ulrike Wagner, Qinyan Pan, Phillip Farmer, Kirk Smith, Benjamin Kopchick, Laura Opsahl-Ong, Granger Sutton, David Clunie, Keyvan Farahani, Fred Prior
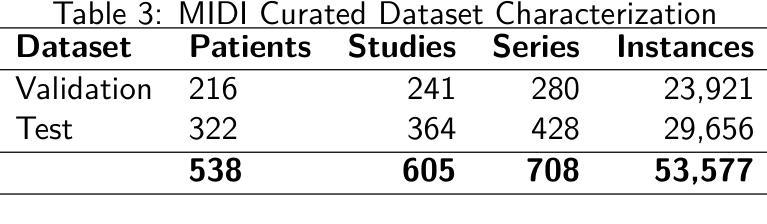
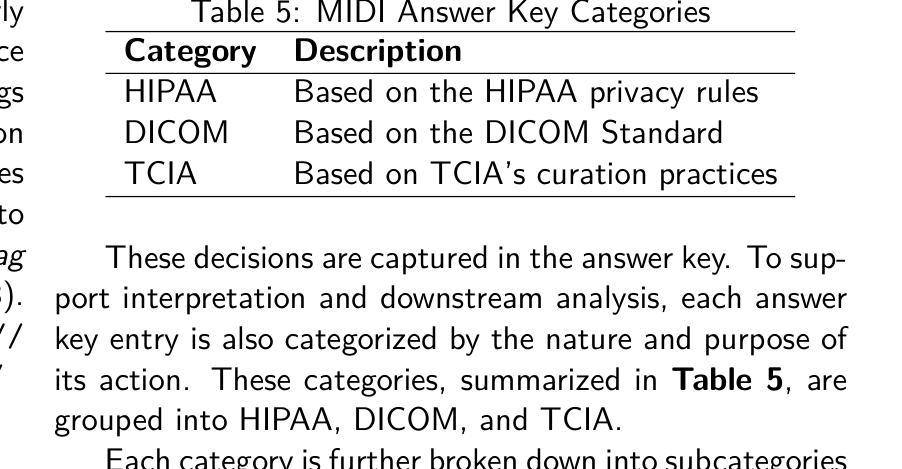
Medical imaging research increasingly depends on large-scale data sharing to promote reproducibility and train Artificial Intelligence (AI) models. Ensuring patient privacy remains a significant challenge for open-access data sharing. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM), the global standard data format for medical imaging, encodes both essential clinical metadata and extensive protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII). Effective de-identification must remove identifiers, preserve scientific utility, and maintain DICOM validity. Tools exist to perform de-identification, but few assess its effectiveness, and most rely on subjective reviews, limiting reproducibility and regulatory confidence. To address this gap, we developed an openly accessible DICOM dataset infused with synthetic PHI/PII and an evaluation framework for benchmarking image de-identification workflows. The Medical Image de-identification (MIDI) dataset was built using publicly available de-identified data from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). It includes 538 subjects (216 for validation, 322 for testing), 605 studies, 708 series, and 53,581 DICOM image instances. These span multiple vendors, imaging modalities, and cancer types. Synthetic PHI and PII were embedded into structured data elements, plain text data elements, and pixel data to simulate real-world identity leaks encountered by TCIA curation teams. Accompanying evaluation tools include a Python script, answer keys (known truth), and mapping files that enable automated comparison of curated data against expected transformations. The framework is aligned with the HIPAA Privacy Rule “Safe Harbor” method, DICOM PS3.15 Confidentiality Profiles, and TCIA best practices. It supports objective, standards-driven evaluation of de-identification workflows, promoting safer and more consistent medical image sharing.
医学成像研究越来越依赖于大规模的数据共享,以促进结果的重复验证和训练人工智能模型。然而,确保患者隐私在开放数据共享中仍然是一个巨大的挑战。DICOM(医学数字成像和通信)是全球医学成像的标准数据格式,它既包含基本的临床元数据,也包含大量的受保护健康信息(PHI)和个人身份信息(PII)。有效的匿名处理必须消除标识符,同时保留科学效用并维持DICOM的有效性。虽然存在进行匿名处理的工具,但很少有工具评估其有效性,大多数工具都依赖于主观审查,这限制了结果的重复验证和监管信心。为了弥补这一空白,我们开发了一个可公开访问的DICOM数据集,该数据集注入了合成PHI/PII和一个用于评估图像匿名处理工作流程的基准框架。医学图像匿名处理(MIDI)数据集是使用可从The Cancer Imaging Archive(TCIA)获得的已匿名处理的数据构建的。它包含538名受试者(216名用于验证,322名用于测试)、605项研究、708个系列和53581个DICOM图像实例。这些图像跨越了多个供应商、成像模式和癌症类型。合成PHI和PII被嵌入到结构化数据元素、纯文本数据元素和像素数据中,以模拟TCIA策划团队在现实世界中遇到的身份泄露情况。伴随的评估工具包括Python脚本、答案密钥(已知事实)和映射文件,这些文件能够实现对已策划数据与预期转换的自动比较。该框架与HIPAA隐私规则的“安全港”方法、DICOM PS3.15保密配置文件以及TCIA的最佳实践相一致。它支持对匿名处理工作流程进行客观、以标准驱动的评价,从而促进更安全、更一致的医学图像共享。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学成像研究中对大规模数据共享的需求,同时确保患者隐私的开放访问数据共享是一大挑战。为解决现有工具在评估去标识化效果方面的不足,本文开发了一个公开可访问的DICOM数据集,并注入了合成个人信息和身份识别信息,同时构建了一个评估去标识化工作流程的框架。该数据集使用TCIA的公开去标识数据构建,包括多个供应商、成像模式和癌症类型的图像。该框架支持对去标识化工作流程进行客观、标准化的评估,促进了更安全、更一致的医学图像共享。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像研究依赖大规模数据共享以促进可重复性和人工智能模型训练。
- 数据共享中确保患者隐私是一大挑战。
- DICOM作为全球医学成像数据格式标准,包含关键临床元数据和受保护的健康信息(PHI)及个人识别信息(PII)。
- 去标识化工具需移除标识符、保持科学效用并维持DICOM有效性。
- 现有评估工具在评估去标识化效果方面存在不足,本研究开发了一个公开的DICOM数据集和评估框架。
- MIDI数据集使用TCIA的公开去标识数据构建,模拟真实世界中的身份泄露情况。
点此查看论文截图

Large Kernel MedNeXt for Breast Tumor Segmentation and Self-Normalizing Network for pCR Classification in Magnetic Resonance Images
Authors:Toufiq Musah
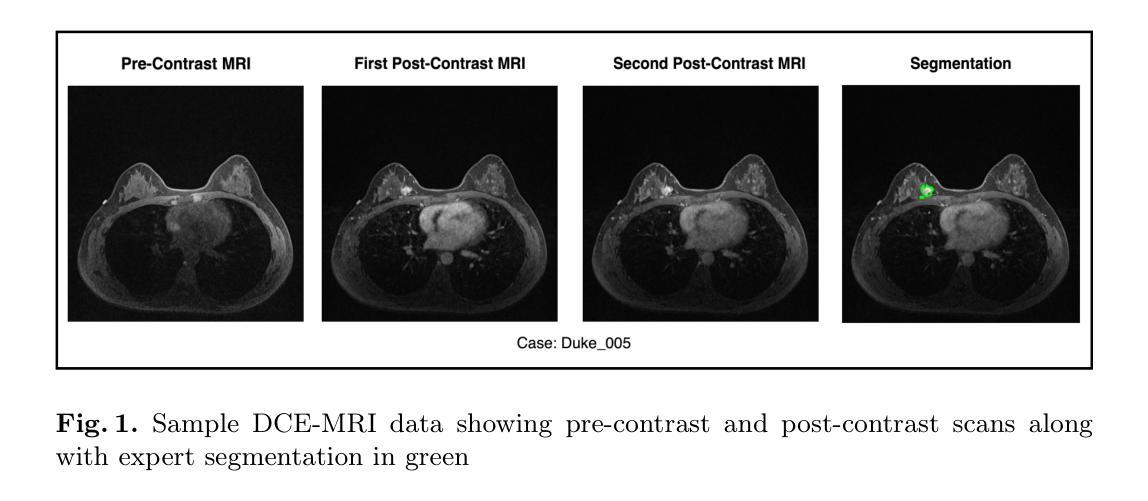
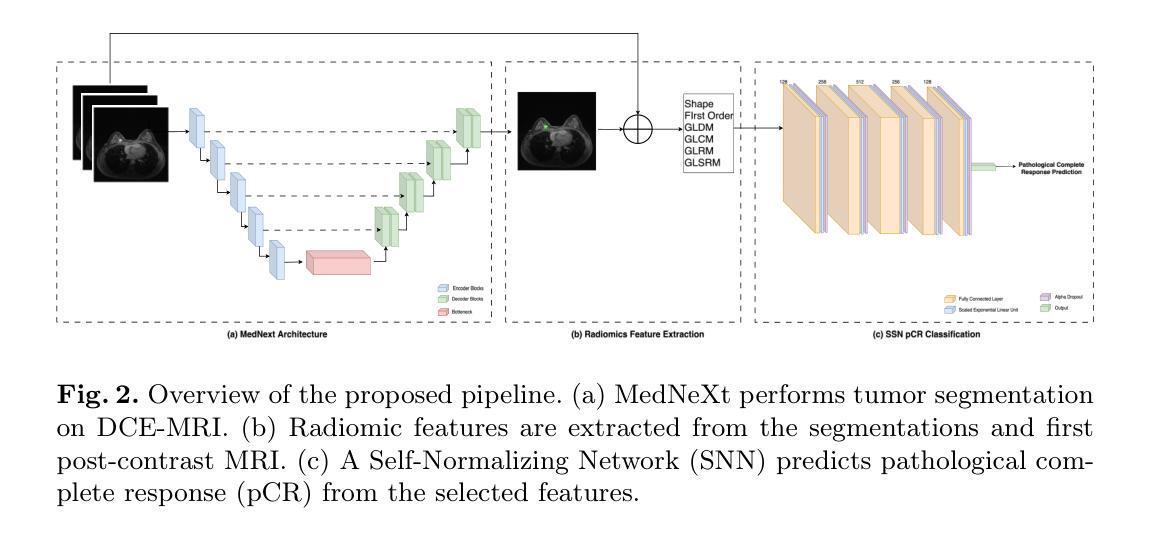
Accurate breast tumor segmentation in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is important for downstream tasks such as pathological complete response (pCR) assessment. In this work, we address both segmentation and pCR classification using the large-scale MAMA-MIA DCE-MRI dataset. We employ a large-kernel MedNeXt architecture with a two-stage training strategy that expands the receptive field from 3x3x3 to 5x5x5 kernels using the UpKern algorithm. This approach allows stable transfer of learned features to larger kernels, improving segmentation performance on the unseen validation set. An ensemble of large-kernel models achieved a Dice score of 0.67 and a normalized Hausdorff Distance (NormHD) of 0.24. For pCR classification, we trained a self-normalizing network (SNN) on radiomic features extracted from the predicted segmentations and first post-contrast DCE-MRI, reaching an average balanced accuracy of 57%, and up to 75% in some subgroups. Our findings highlight the benefits of combining larger receptive fields and radiomics-driven classification while motivating future work on advanced ensembling and the integration of clinical variables to further improve performance and generalization. Code: https://github.com/toufiqmusah/caladan-mama-mia.git
在动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)中进行精确的乳腺肿瘤分割对于下游任务(如病理完全反应(pCR)评估)非常重要。在这项工作中,我们针对分割和pCR分类使用大规模的MAMA-MIA DCE-MRI数据集。我们采用大内核MedNeXt架构和两阶段训练策略,使用UpKern算法将感受野从3x3x3扩展到5x5x5内核。这种方法允许将学习到的特征稳定地转移到更大的内核,从而提高了未见验证集的分割性能。大内核模型组合达到了Dice分数为0.67,归一化Hausdorff距离(NormHD)为0.24。对于pCR分类,我们在从预测的分割和首次对比增强后的DCE-MRI中提取的放射学特征上训练了自归一化网络(SNN),达到平均平衡精度为57%,某些子组甚至高达75%。我们的研究结果强调了结合更大的感受野和放射学驱动分类的优势,同时鼓励未来的工作在高级集成和临床变量的整合方面进一步改进性能和泛化能力。代码:https://github.com/toufiqmusah/caladan-mama-mia.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables, Accepted at MICCAI 2025 Deep-Breath Workshop
Summary
本文利用大型核MedNeXt架构与UpKern算法提升动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)中的乳腺肿瘤分割准确性。使用两阶段训练策略扩大感受野从3x3x3至5x5x5核,通过大型核模型组合实现Dice评分0.67和归一化Hausdorff距离(NormHD)0.24的优异分割效果。针对病理完全反应(pCR)分类,利用预测的分割和首次对比增强DCE-MRI提取的放射学特征训练自归一化网络(SNN),平均平衡精度达57%,部分子组高达75%。研究结合了更大的感受野和放射学特征驱动的分类优势,并鼓励未来在更高级的集成和临床变量整合方面开展进一步研究以提高性能和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 使用大型核MedNeXt架构与UpKern算法提升DCE-MRI中的乳腺肿瘤分割准确性。
- 两阶段训练策略扩大模型感受野,提高分割性能。
- 大型核模型组合实现较高的Dice评分和NormHD值。
- 利用预测的分割和首次对比增强DCE-MRI提取的放射学特征进行pCR分类。
- 自归一化网络(SNN)在pCR分类中表现良好,达到较高的平衡精度。
- 结合更大的感受野和放射学特征驱动的分类能提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

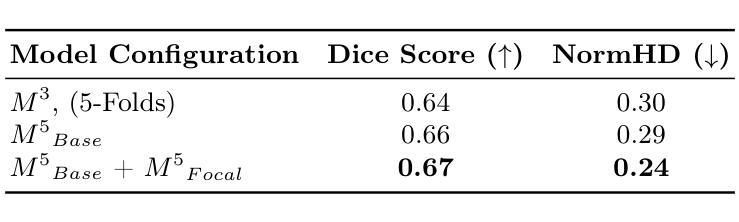
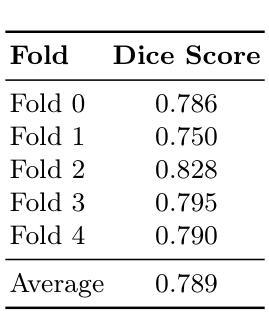
M$^3$AD: Multi-task Multi-gate Mixture of Experts for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis with Conversion Pattern Modeling
Authors:Yufeng Jiang, Hexiao Ding, Hongzhao Chen, Jing Lan, Xinzhi Teng, Gerald W. Y. Cheng, Zongxi Li, Haoran Xie, Jung Sun Yoo, Jing Cai
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) progression follows a complex continuum from normal cognition (NC) through mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to dementia, yet most deep learning approaches oversimplify this into discrete classification tasks. This study introduces M$^3$AD, a novel multi-task multi-gate mixture of experts framework that jointly addresses diagnostic classification and cognitive transition modeling using structural MRI. We incorporate three key innovations: (1) an open-source T1-weighted sMRI preprocessing pipeline, (2) a unified learning framework capturing NC-MCI-AD transition patterns with demographic priors (age, gender, brain volume) for improved generalization, and (3) a customized multi-gate mixture of experts architecture enabling effective multi-task learning with structural MRI alone. The framework employs specialized expert networks for diagnosis-specific pathological patterns while shared experts model common structural features across the cognitive continuum. A two-stage training protocol combines SimMIM pretraining with multi-task fine-tuning for joint optimization. Comprehensive evaluation across six datasets comprising 12,037 T1-weighted sMRI scans demonstrates superior performance: 95.13% accuracy for three-class NC-MCI-AD classification and 99.15% for binary NC-AD classification, representing improvements of 4.69% and 0.55% over state-of-the-art approaches. The multi-task formulation simultaneously achieves 97.76% accuracy in predicting cognitive transition. Our framework outperforms existing methods using fewer modalities and offers a clinically practical solution for early intervention. Code: https://github.com/csyfjiang/M3AD.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)的进展从正常认知(NC)到轻度认知障碍(MCI)再到痴呆是一个复杂的过程,但大多数深度学习的方法都将其简化为独立的分类任务。本研究介绍了M$^3$AD,这是一种新的多任务多门专家混合框架,它利用结构磁共振成像(MRI)联合解决诊断分类和认知过渡建模问题。我们采用了三个关键创新点:(1)开源的T1加权sMRI预处理管道,(2)一个统一的学习框架,结合人口统计学先验信息(年龄、性别、脑容量)来捕捉NC-MCI-AD过渡模式,以提高通用性,(3)定制的多门专家混合架构,能够利用结构MRI进行有效的多任务学习。该框架采用专门的专业网络来针对诊断的特定病理模式,而共享专家则对认知连续体的常见结构特征进行建模。两阶段训练协议将SimMIM预训练与多任务微调相结合,以实现联合优化。在包含12037个T1加权sMRI扫描的六个数据集上的综合评估表明,其性能卓越:对于三类NC-MCI-AD分类的准确率为95.13%,对于二元NC-AD分类的准确率为99.15%,相较于最新方法分别提高了4.69%和0.55%。多任务公式同时实现了预测认知过渡的97.76%准确率。我们的框架使用较少的模态超越了现有方法,并为早期干预提供了临床实用解决方案。代码地址:https://github.com/csyfjiang/M3AD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为M$^3$AD的新型多任务多门混合专家框架,该框架利用结构磁共振成像(MRI)联合解决诊断分类和认知过渡建模问题。该研究包含三个关键创新点:开源T1加权sMRI预处理管道、统一学习框架捕捉NC-MCI-AD过渡模式并考虑人口统计学先验信息以提高泛化能力,以及定制的多门混合专家架构,实现有效的多任务学习。该框架在六个数据集上的综合评估表现出卓越性能,为早期干预提供了实用的临床解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- M$^3$AD框架首次结合了结构磁共振成像(MRI)进行诊断分类和认知过渡建模的多任务学习。
- 提出了一个开放源代码的T1加权sMRI预处理管道作为数据处理基础。
- 采用统一学习框架捕捉NC-MCI-AD认知过渡模式,考虑人口统计学先验以提升模型泛化能力。
- 多门混合专家架构专门处理诊断特异性病理模式,同时共享专家建模认知连续谱的通用结构特征。
- 通过两阶段训练协议结合SimMIM预训练和多任务微调进行联合优化。
- 在六个数据集上的评估显示M$^3$AD框架在分类任务上表现优越,尤其是在预测认知过渡的多任务格式中。
点此查看论文截图

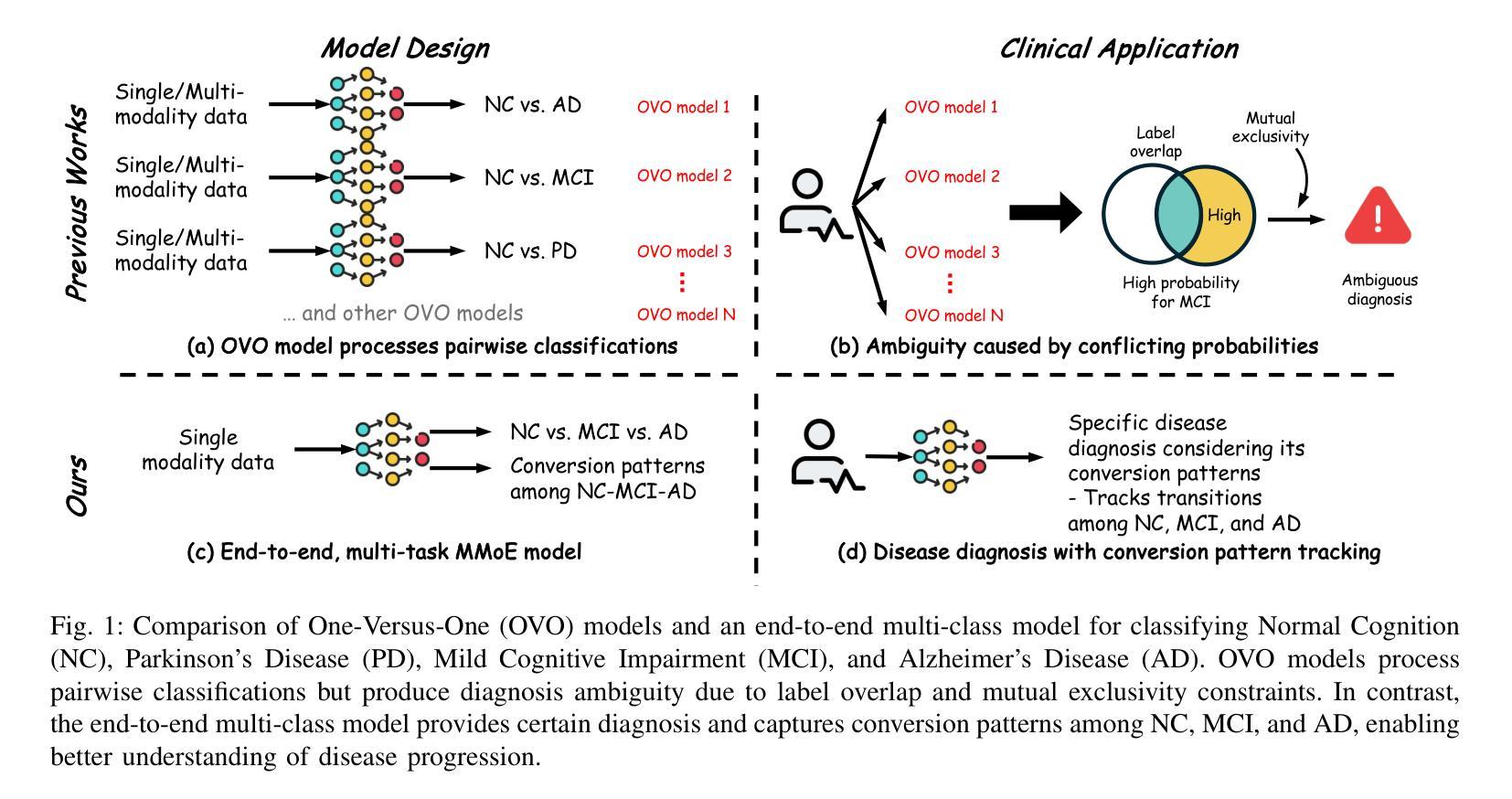
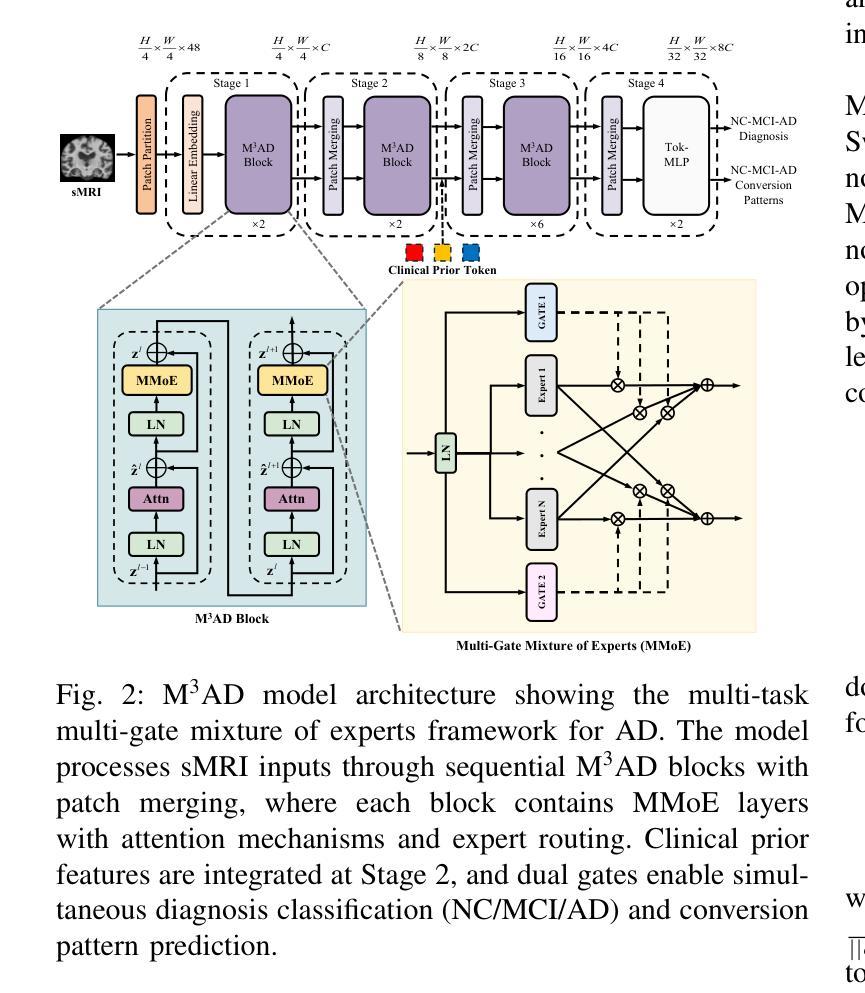
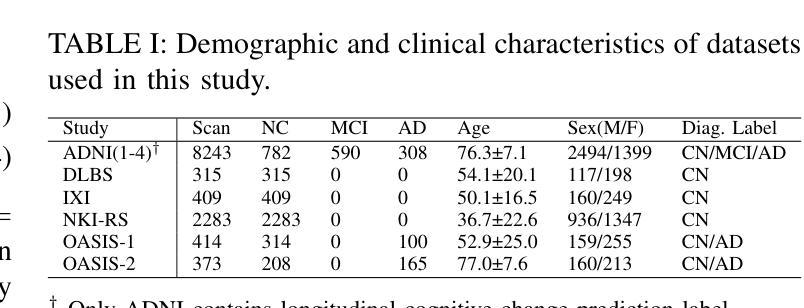
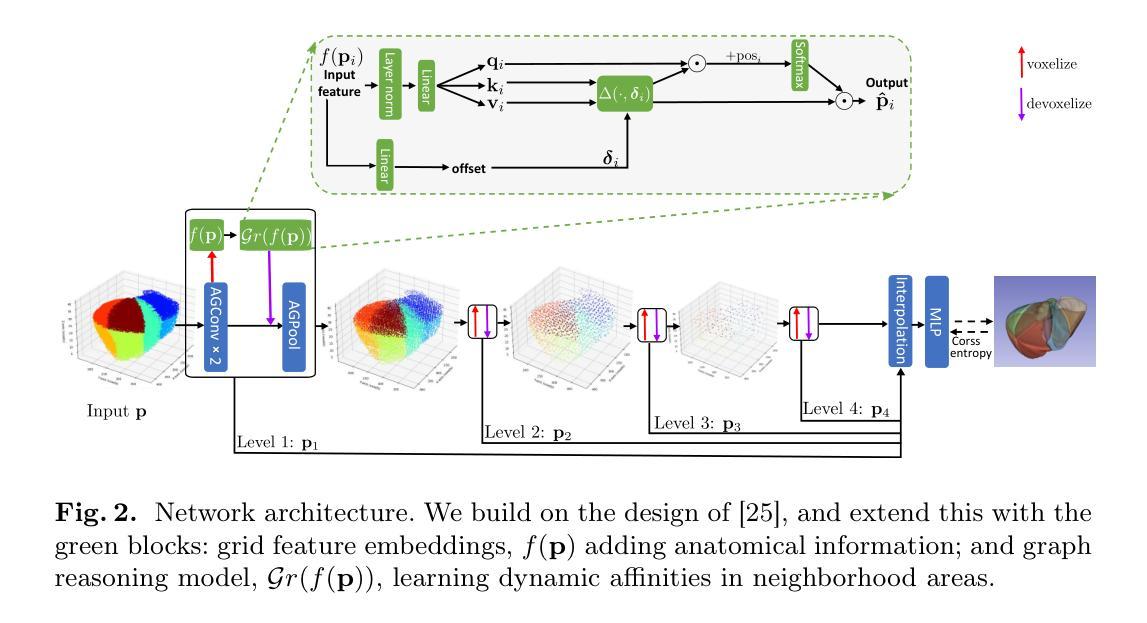
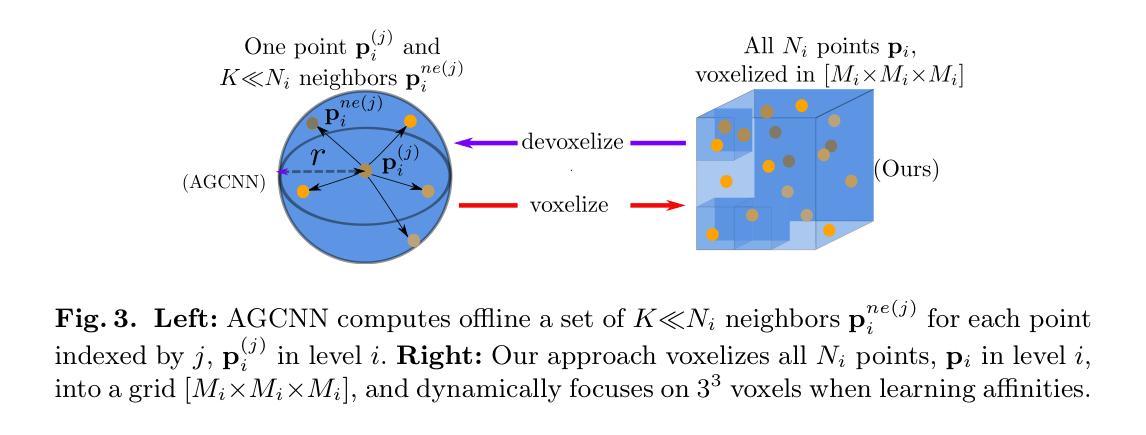
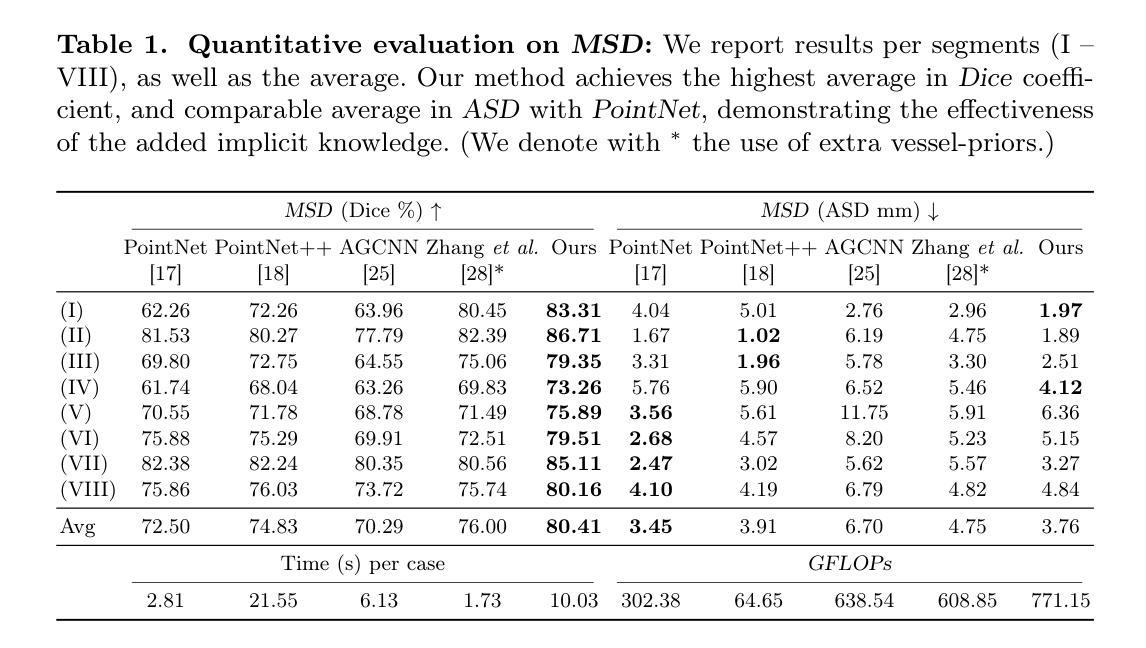
Skip priors and add graph-based anatomical information, for point-based Couinaud segmentation
Authors:Xiaotong Zhang, Alexander Broersen, Gonnie CM van Erp, Silvia L. Pintea, Jouke Dijkstra
The preoperative planning of liver surgery relies on Couinaud segmentation from computed tomography (CT) images, to reduce the risk of bleeding and guide the resection procedure. Using 3D point-based representations, rather than voxelizing the CT volume, has the benefit of preserving the physical resolution of the CT. However, point-based representations need prior knowledge of the liver vessel structure, which is time consuming to acquire. Here, we propose a point-based method for Couinaud segmentation, without explicitly providing the prior liver vessel structure. To allow the model to learn this anatomical liver vessel structure, we add a graph reasoning module on top of the point features. This adds implicit anatomical information to the model, by learning affinities across point neighborhoods. Our method is competitive on the MSD and LiTS public datasets in Dice coefficient and average surface distance scores compared to four pioneering point-based methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZhangXiaotong015/GrPn.
肝脏手术的术前规划依赖于根据计算机断层扫描(CT)图像的Couinaud分段,以减少出血风险并指导切除手术。使用基于3D点的表示方法(而不是对CT体积进行体素化)的好处是保留了CT的物理分辨率。然而,基于点的表示方法需要对肝脏血管结构有先验知识,而这需要花费大量时间才能获得。在这里,我们提出了一种基于点的Couinaud分段方法,无需明确提供先验肝脏血管结构。为了让模型学习这种解剖肝脏血管结构,我们在点特征之上添加了一个图推理模块。这通过了解点邻域之间的亲和力,为模型增加了隐式解剖信息。我们的方法在MSD和LiTS公共数据集上的狄克系数和平均表面距离得分与四种先进的点方法相当。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ZhangXiaotong015/GrPn获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025 GRAIL workshop
Summary
基于计算机断层扫描(CT)图像的Couinaud分段是肝脏手术术前规划的关键,能降低出血风险并指导切除手术。相较于体素化CT体积的传统方法,采用基于点的三维表示可保留CT的物理分辨率。但这种方法需要预先了解肝脏血管结构,这一步骤非常耗时。本研究提出一种基于点的Couinaud分段方法,无需明确提供肝脏血管结构的先验知识。为了令模型学习这种解剖学肝脏血管结构,我们在点特征之上增加了一个图推理模块。该模块通过学习点邻域间的亲和力,为模型增加了隐式解剖学信息。相较于四种领先的点方法,本研究的方法在MSD和LiTS公开数据集上的Dice系数和平均表面距离得分上具有竞争力。相关代码可通过https://github.com/ZhangXiaotong015/GrPn获取。
Key Takeaways
- Couinaud分段是肝脏手术术前规划的关键,有助于降低手术风险。
- 传统方法采用体素化CT图像,存在分辨率损失。
- 基于点的表示方法能保留CT的物理分辨率,但需要预先了解肝脏血管结构。
- 本研究提出了一种基于点的Couinaud分段方法,无需提供肝脏血管结构的先验知识。
- 通过增加图推理模块,模型能够学习解剖学肝脏血管结构。
- 该方法在公共数据集上的表现优于其他领先方法。
- 相关代码可通过指定链接获取。
点此查看论文截图

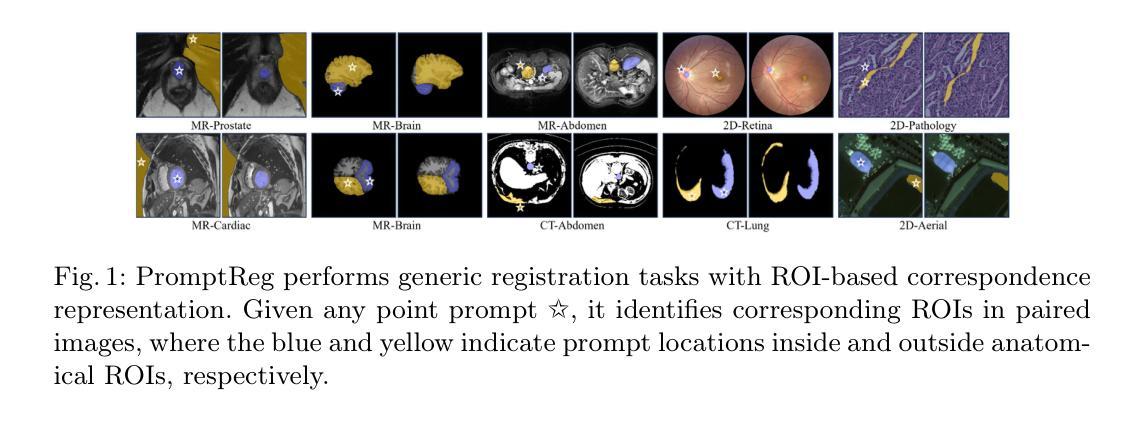
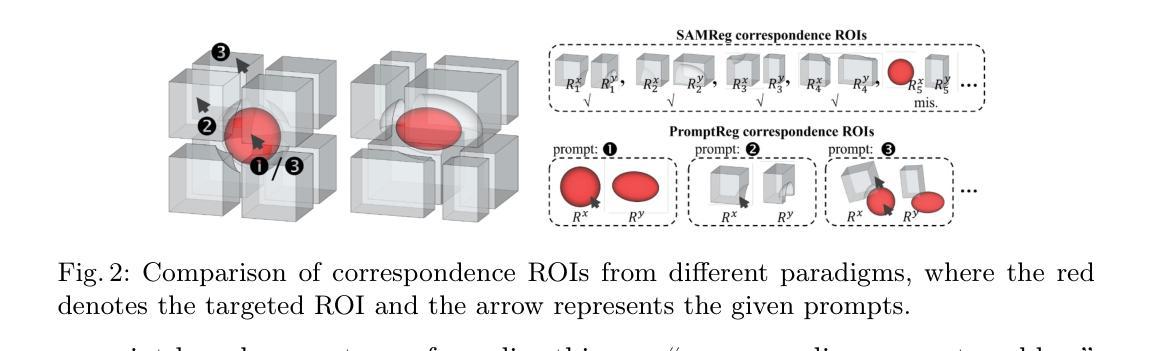
Register Anything: Estimating “Corresponding Prompts” for Segment Anything Model
Authors:Shiqi Huang, Tingfa Xu, Wen Yan, Dean Barratt, Yipeng Hu
Establishing pixel/voxel-level or region-level correspondences is the core challenge in image registration. The latter, also known as region-based correspondence representation, leverages paired regions of interest (ROIs) to enable regional matching while preserving fine-grained capability at pixel/voxel level. Traditionally, this representation is implemented via two steps: segmenting ROIs in each image then matching them between the two images. In this paper, we simplify this into one step by directly “searching for corresponding prompts”, using extensively pre-trained segmentation models (e.g., SAM) for a training-free registration approach, PromptReg. Firstly, we introduce the “corresponding prompt problem”, which aims to identify a corresponding Prompt Y in Image Y for any given visual Prompt X in Image X, such that the two respectively prompt-conditioned segmentations are a pair of corresponding ROIs from the two images. Secondly, we present an “inverse prompt” solution that generates primary and optionally auxiliary prompts, inverting Prompt X into the prompt space of Image Y. Thirdly, we propose a novel registration algorithm that identifies multiple paired corresponding ROIs by marginalizing the inverted Prompt X across both prompt and spatial dimensions. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on five applications of registering 3D prostate MR, 3D abdomen MR, 3D lung CT, 2D histopathology and, as a non-medical example, 2D aerial images. Based on metrics including Dice and target registration errors on anatomical structures, the proposed registration outperforms both intensity-based iterative algorithms and learning-based DDF-predicting networks, even yielding competitive performance with weakly-supervised approaches that require fully-segmented training data.
在图像配准中,建立像素/体素级别或区域级别的对应关系是核心挑战。后者也称为基于区域的对应关系表示,它利用感兴趣区域(ROI)的配对,实现区域匹配,同时在像素/体素级别保持精细能力。传统上,这种表示通过两个步骤实现:在每个图像中分割ROI,然后在两个图像之间进行匹配。在本文中,我们通过直接“搜索对应提示”将这一过程简化为一步,利用广泛预训练的分割模型(例如SAM)实现无需训练即可进行配准的方法,即PromptReg。首先,我们引入“对应提示问题”,旨在针对图像X中的任何给定视觉提示X,找到图像Y中的对应提示Y,使得这两个提示条件下的分割是这两个图像中的一对相应ROI。其次,我们提出了一种“逆提示”解决方案,生成主要提示和可选的辅助提示,将提示X反转到图像Y的提示空间。第三,我们提出了一种新的配准算法,通过最小化提示X在提示和空间维度上的逆映射,来识别多个配对的相应ROI。在五个应用上进行了全面的实验,包括3D前列腺MR、3D腹部MR、3D肺部CT、2D组织病理学和作为非医学示例的2D航空图像。基于狄克系数和目标注册误差等解剖学结构指标,所提出的配准方法优于基于强度的迭代算法和基于学习的DDF预测网络,甚至与需要完全分割训练数据的弱监督方法竞争。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对图像注册中的核心挑战——像素/体素级别或区域级别的对应问题进行了研究。提出一种简化的方法,通过直接“寻找对应的提示”来实现在无需训练的情况下进行图像注册,并介绍了一种新型的注册算法。实验证明,该方法在多个应用领域均表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 图像注册中的核心挑战是建立像素/体素级别或区域级别的对应。
- 区域基于的对应表示利用感兴趣区域(ROI)配对来实现区域匹配,同时保持像素/体素级别的精细能力。
- 传统实现此表示需要两步:在每个图像中分割ROI,然后在两个图像之间进行匹配。
- 本文简化此过程为一步,通过直接“寻找对应的提示”来实现训练自由的注册方法,称为PromptReg。
- 引入了“相应提示问题”,旨在识别Image Y中对应于Image X中的任何视觉提示Y的提示。
- 提出了一种反向提示解决方案,通过生成主要和辅助提示来反转提示X到Image Y的提示空间。
点此查看论文截图

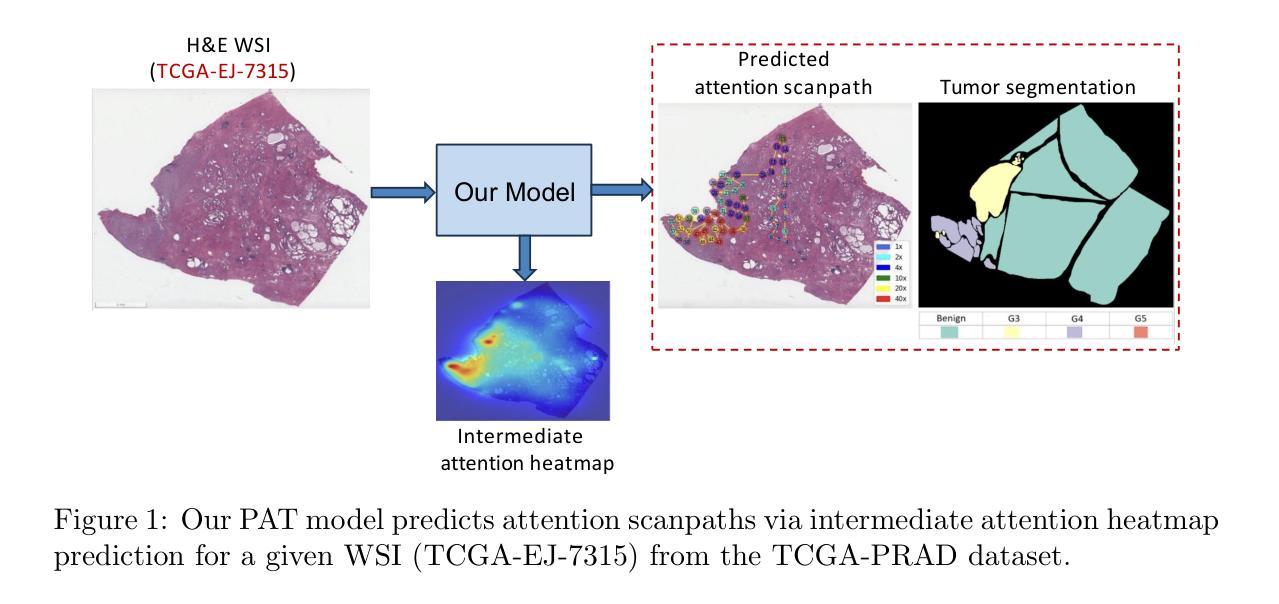
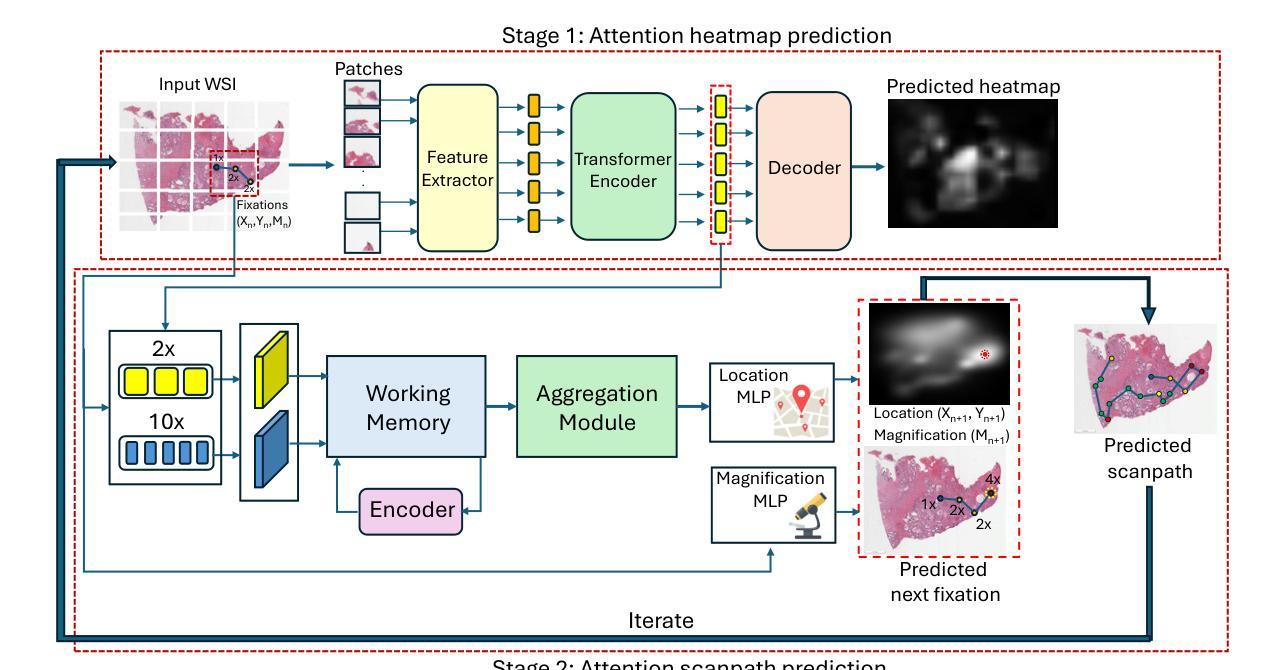
Measuring and Predicting Where and When Pathologists Focus their Visual Attention while Grading Whole Slide Images of Cancer
Authors:Souradeep Chakraborty, Ruoyu Xue, Rajarsi Gupta, Oksana Yaskiv, Constantin Friedman, Natallia Sheuka, Dana Perez, Paul Friedman, Won-Tak Choi, Waqas Mahmud, Beatrice Knudsen, Gregory Zelinsky, Joel Saltz, Dimitris Samaras
The ability to predict the attention of expert pathologists could lead to decision support systems for better pathology training. We developed methods to predict the spatio-temporal (where and when) movements of pathologists’ attention as they grade whole slide images (WSIs) of prostate cancer. We characterize a pathologist’s attention trajectory by their x, y, and m (magnification) movements of a viewport as they navigate WSIs using a digital microscope. This information was obtained from 43 pathologists across 123 WSIs, and we consider the task of predicting the pathologist attention scanpaths constructed from the viewport centers. We introduce a fixation extraction algorithm that simplifies an attention trajectory by extracting fixations in the pathologist’s viewing while preserving semantic information, and we use these pre-processed data to train and test a two-stage model to predict the dynamic (scanpath) allocation of attention during WSI reading via intermediate attention heatmap prediction. In the first stage, a transformer-based sub-network predicts the attention heatmaps (static attention) across different magnifications. In the second stage, we predict the attention scanpath by sequentially modeling the next fixation points in an autoregressive manner using a transformer-based approach, starting at the WSI center and leveraging multi-magnification feature representations from the first stage. Experimental results show that our scanpath prediction model outperforms chance and baseline models. Tools developed from this model could assist pathology trainees in learning to allocate their attention during WSI reading like an expert.
预测专家病理学家注意力的能力可以为更好的病理学训练提供决策支持系统。我们开发了一种方法,可以预测病理学家在评估前列腺癌全幻灯片图像(WSI)时的时间和空间注意力转移方向(即在哪里看以及何时看)。我们通过病理学家使用数字显微镜浏览WSI时的x、y和m(放大倍数)运动来描绘他们的注意力轨迹。这些信息来源于43位病理专家对123张WSI的数据,我们考虑的任务是预测由视图中心构建的病理学家注意力扫描路径。我们引入了一个注视点提取算法,它通过提取病理学家查看过程中的注视点来简化注意力轨迹,同时保留语义信息,我们使用这些预处理过的数据来训练和测试一个两阶段的模型,通过预测中间注意力热图来预测在WSI阅读过程中动态(扫描路径)的注意力分配。在第一阶段,一个基于transformer的子网络会在不同的放大倍数下预测注意力热图(静态注意力)。在第二阶段中,我们以自回归的方式通过基于transformer的方法依次预测下一个注视点来预测注意力扫描路径,从WSI中心开始,并利用第一阶段的多种放大特性表示。实验结果表明,我们的扫描路径预测模型优于随机和基线模型。从这个模型开发的工具可以帮助病理学新手学习如何像专家一样分配他们在阅读WSI时的注意力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Medical Image Analysis (MEDIA), Elsevier, 2025. This is the accepted manuscript version; the final published article link will be updated when available
Summary
本文研究预测病理专家注意力在前列腺癌症全切片图像(WSI)中的时空移动,以支持决策支持系统改善病理训练。通过记录病理专家在全切片图像上的浏览轨迹(即注意力轨迹),建立预测模型。研究引入了一种注视点提取算法,简化注意力轨迹并保留语义信息。通过两阶段模型预测动态注意力分配:第一阶段预测不同放大倍率下的静态注意力图,第二阶段利用变压器模型预测下一个注视点的注意力轨迹。实验结果证明该模型优于随机和基线模型。该工具可帮助病理训练生学习如何像专家一样分配注意力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在开发预测病理专家在全切片图像上注意力的决策支持系统。
- 通过收集病理专家的时空移动数据,构建了预测模型。
- 引入了一种注视点提取算法,简化注意力轨迹数据。
- 采用两阶段模型进行预测:静态注意力图预测和动态注意力轨迹预测。
- 模型利用变压器架构进行注意力机制的深度学习和预测。
- 实验结果表明,模型能有效预测病理专家的注意力轨迹。
点此查看论文截图

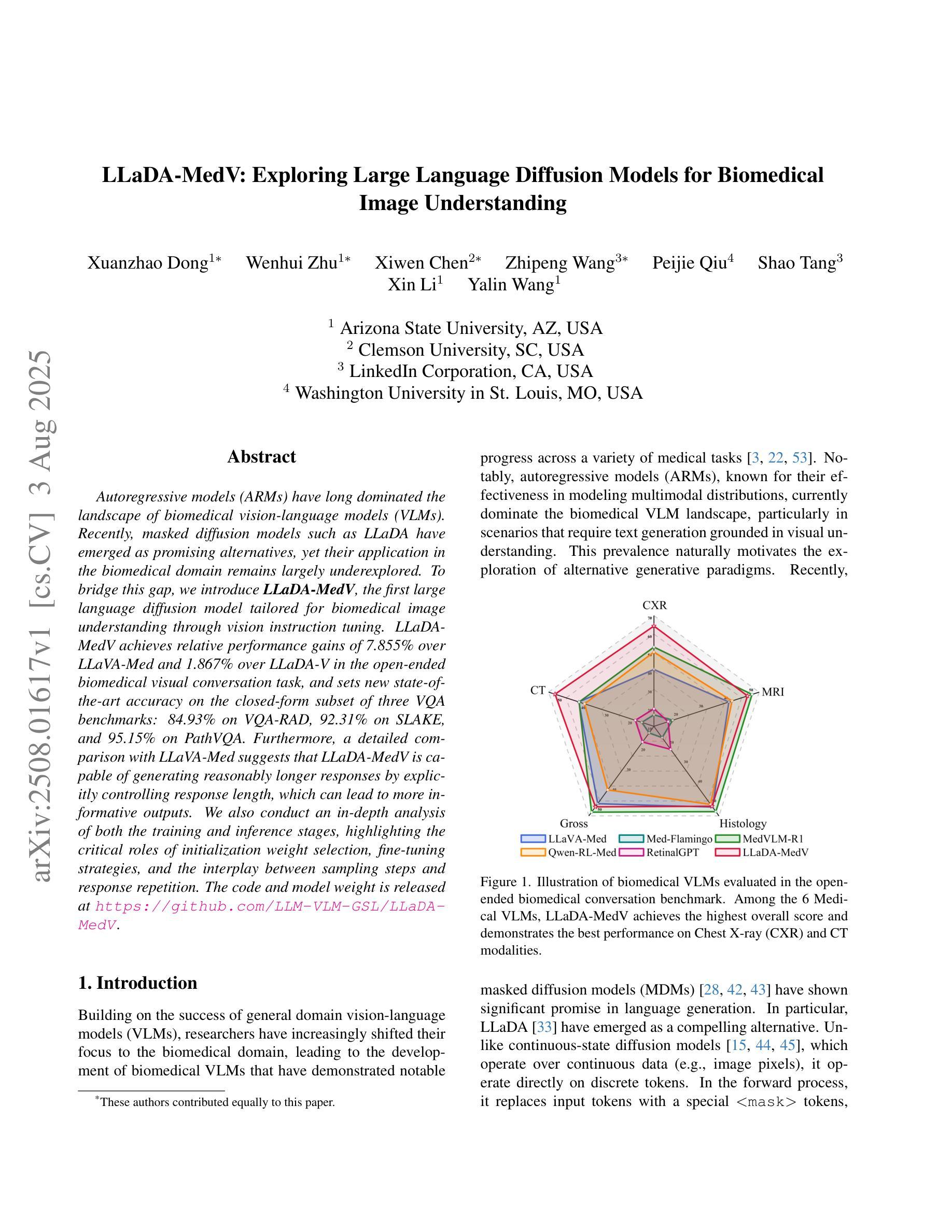
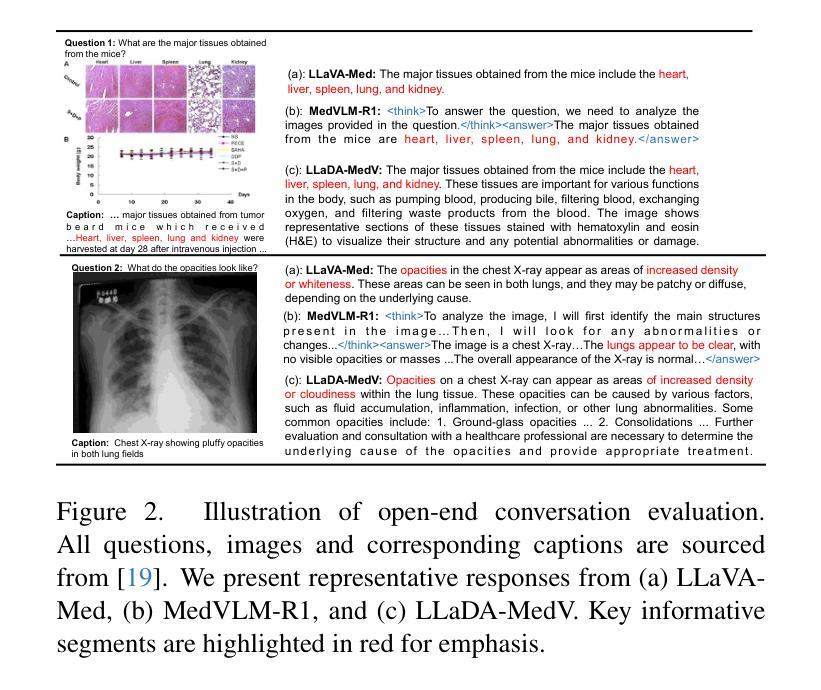
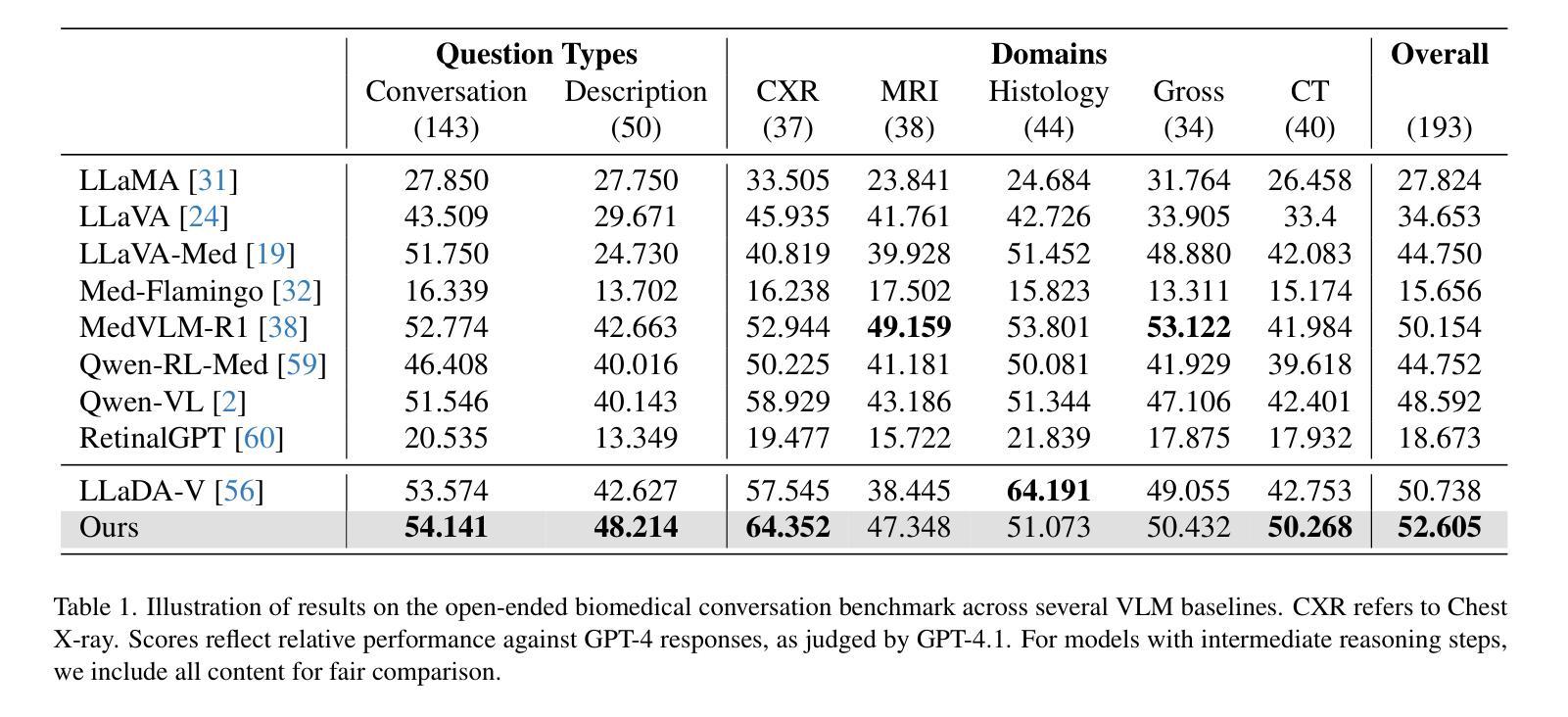
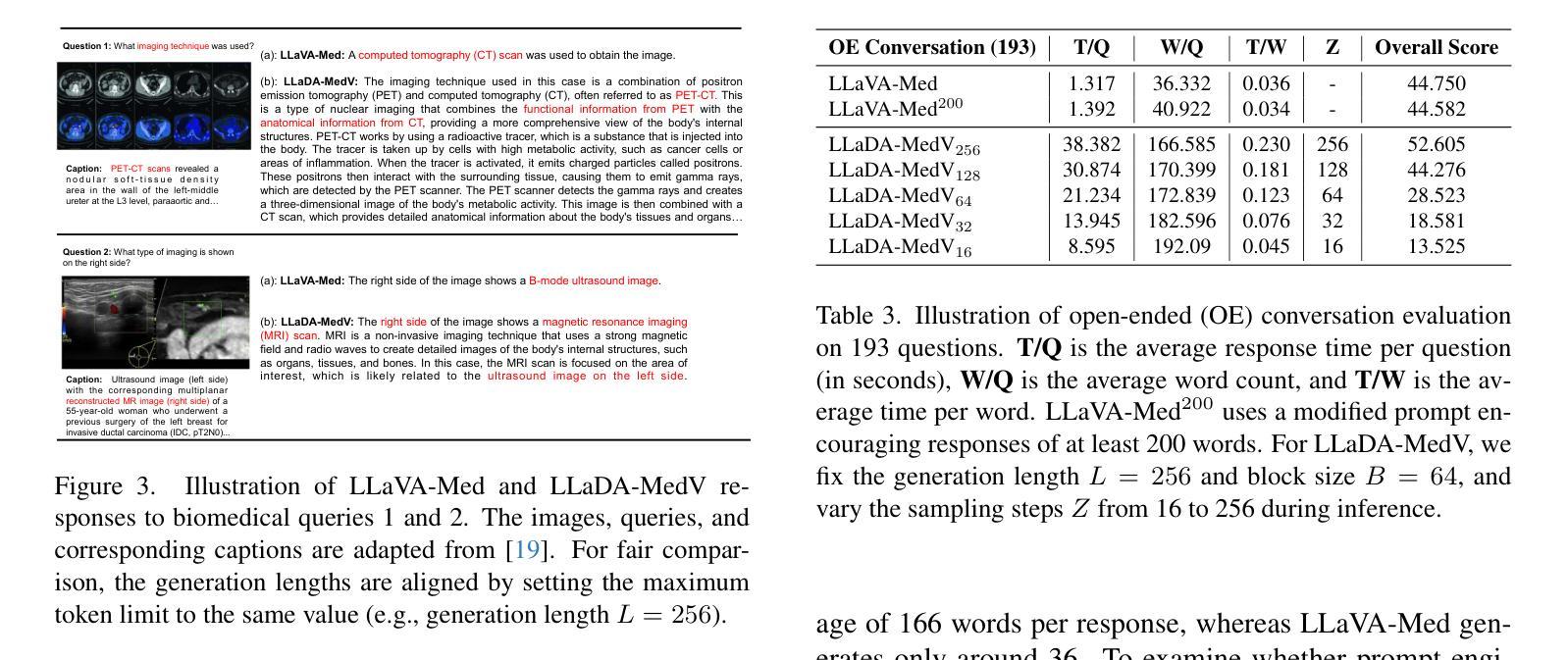
LLaDA-MedV: Exploring Large Language Diffusion Models for Biomedical Image Understanding
Authors:Xuanzhao Dong, Wenhui Zhu, Xiwen Chen, Zhipeng Wang, Peijie Qiu, Shao Tang, Xin Li, Yalin Wang
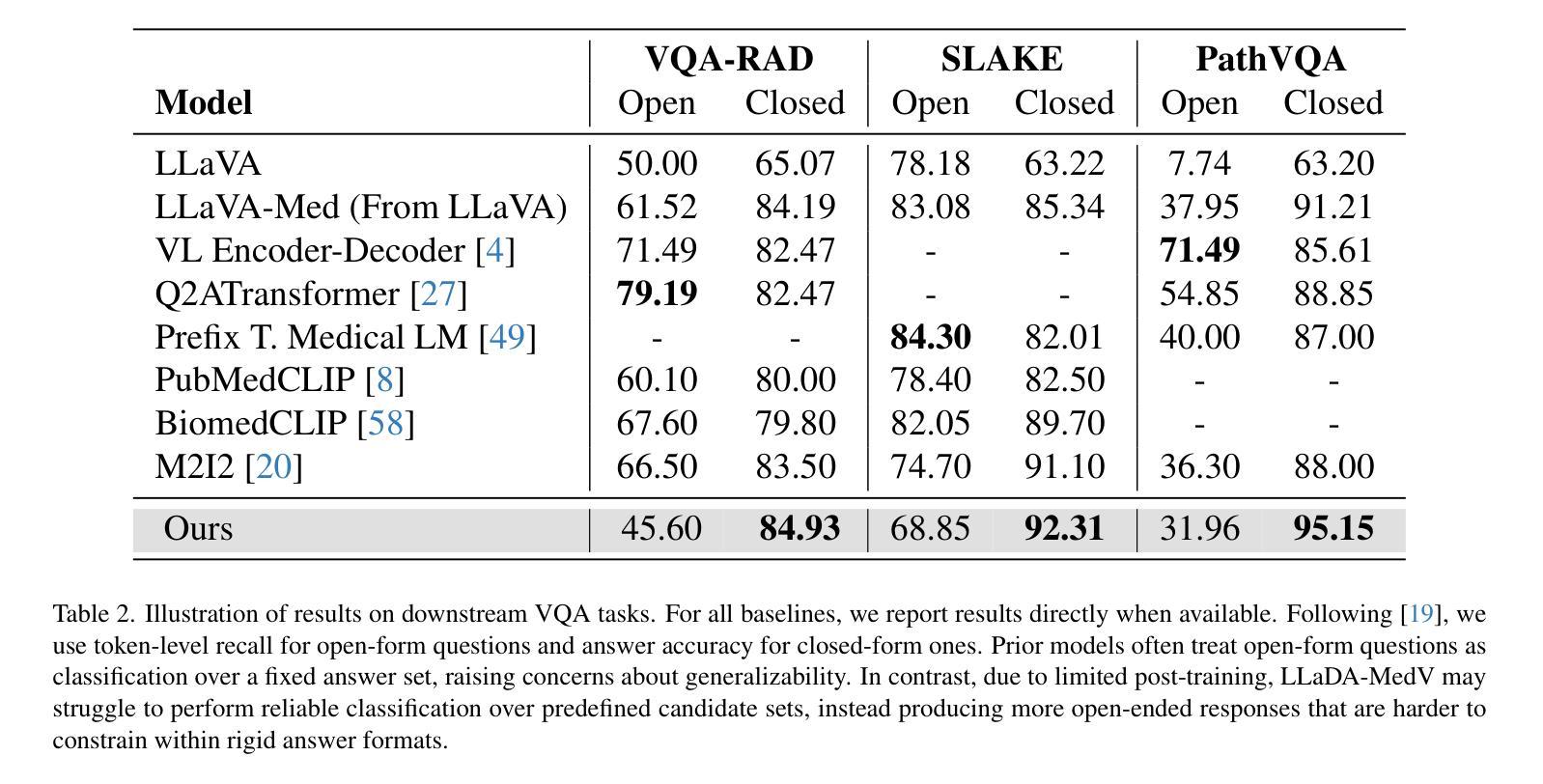
Autoregressive models (ARMs) have long dominated the landscape of biomedical vision-language models (VLMs). Recently, masked diffusion models such as LLaDA have emerged as promising alternatives, yet their application in the biomedical domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{LLaDA-MedV}, the first large language diffusion model tailored for biomedical image understanding through vision instruction tuning. LLaDA-MedV achieves relative performance gains of 7.855% over LLaVA-Med and 1.867% over LLaDA-V in the open-ended biomedical visual conversation task, and sets new state-of-the-art accuracy on the closed-form subset of three VQA benchmarks: 84.93% on VQA-RAD, 92.31% on SLAKE, and 95.15% on PathVQA. Furthermore, a detailed comparison with LLaVA-Med suggests that LLaDA-MedV is capable of generating reasonably longer responses by explicitly controlling response length, which can lead to more informative outputs. We also conduct an in-depth analysis of both the training and inference stages, highlighting the critical roles of initialization weight selection, fine-tuning strategies, and the interplay between sampling steps and response repetition. The code and model weight is released at https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV.
自动回归模型(ARMs)长期以来在生物医学视觉语言模型(VLMs)领域占据主导地位。最近,如LLaDA等遮罩扩散模型作为有前景的替代方案而出现,但它们在生物医学领域的应用仍被大大忽视。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了针对生物医学图像理解通过视觉指令调整而量身定制的第一个大型语言扩散模型LLaDA-MedV。\LLaDA-MedV在开放式的生物医学视觉对话任务上相对于LLaVA-Med和LLaDA-V分别实现了7.855%和1.867%的相对性能提升,并在三个VQA基准测试集的封闭形式子集上达到了最新水平:在VQA-RAD上达到84.93%,在SLAKE上达到92.31%,在PathVQA上达到95.15%。此外,与LLaVA-Med的详细比较表明,LLaDA-MedV能够通过明确控制响应长度来生成相对更长的响应,从而产生更具信息量的输出。我们还对训练和推理阶段进行了深入分析,突出了初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤和响应重复之间的相互作用的关键作用。代码和模型权重已发布在https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLaDA-MedV是专为生物医学图像理解设计的大型语言扩散模型。相较于其他模型,LLaDA-MedV在开放型生物医学视觉对话任务中具有更高的性能,且在三个视觉问答基准测试的子集上达到最新水平:VQA-RAD的84.93%,SLAKE的92.31%,PathVQA的95.15%。其优势在于能够生成更长的响应,并明确控制响应长度。该模型的关键环节包括初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤和响应重复之间的相互作用。
Key Takeaways
- LLaDA-MedV是首个针对生物医学图像理解的大型语言扩散模型。
- LLaDA-MedV在生物医学视觉对话任务上相对于LLaVA-Med和LLaDA-V有性能提升。
- LLaDA-MedV在三个视觉问答基准测试上表现优异,准确率高。
- LLaDA-MedV能生成更长的响应,并明确控制响应长度。
- 初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤和响应重复是LLaDA-MedV的关键环节。
- LLaDA-MedV的代码和模型权重已公开发布。
- LLaDA-MedV对于推动生物医学图像理解领域的发展具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图