⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
Semi-Supervised Dual-Threshold Contrastive Learning for Ultrasound Image Classification and Segmentation
Authors:Peng Zhang, Zhihui Lai, Heng Kong
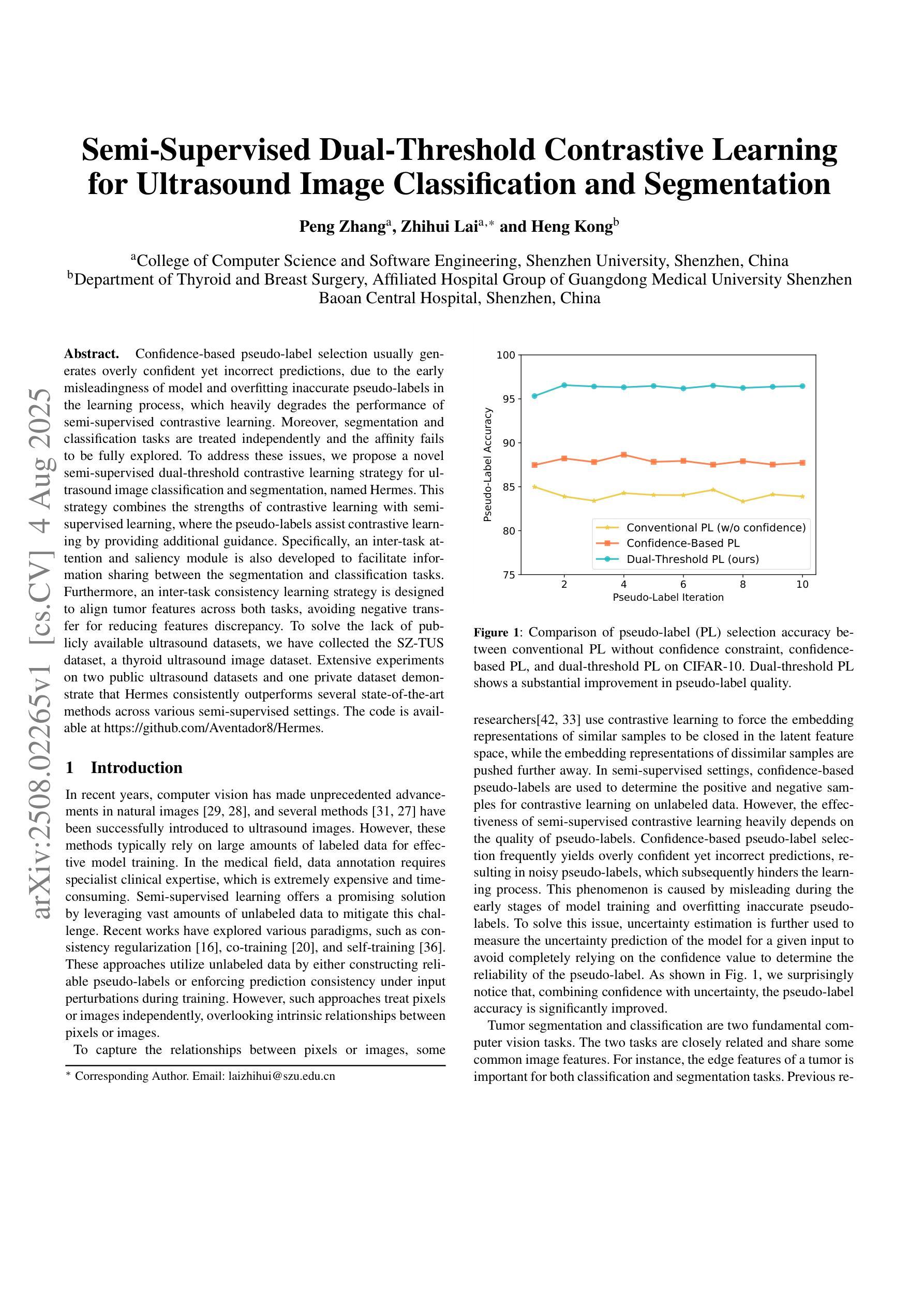
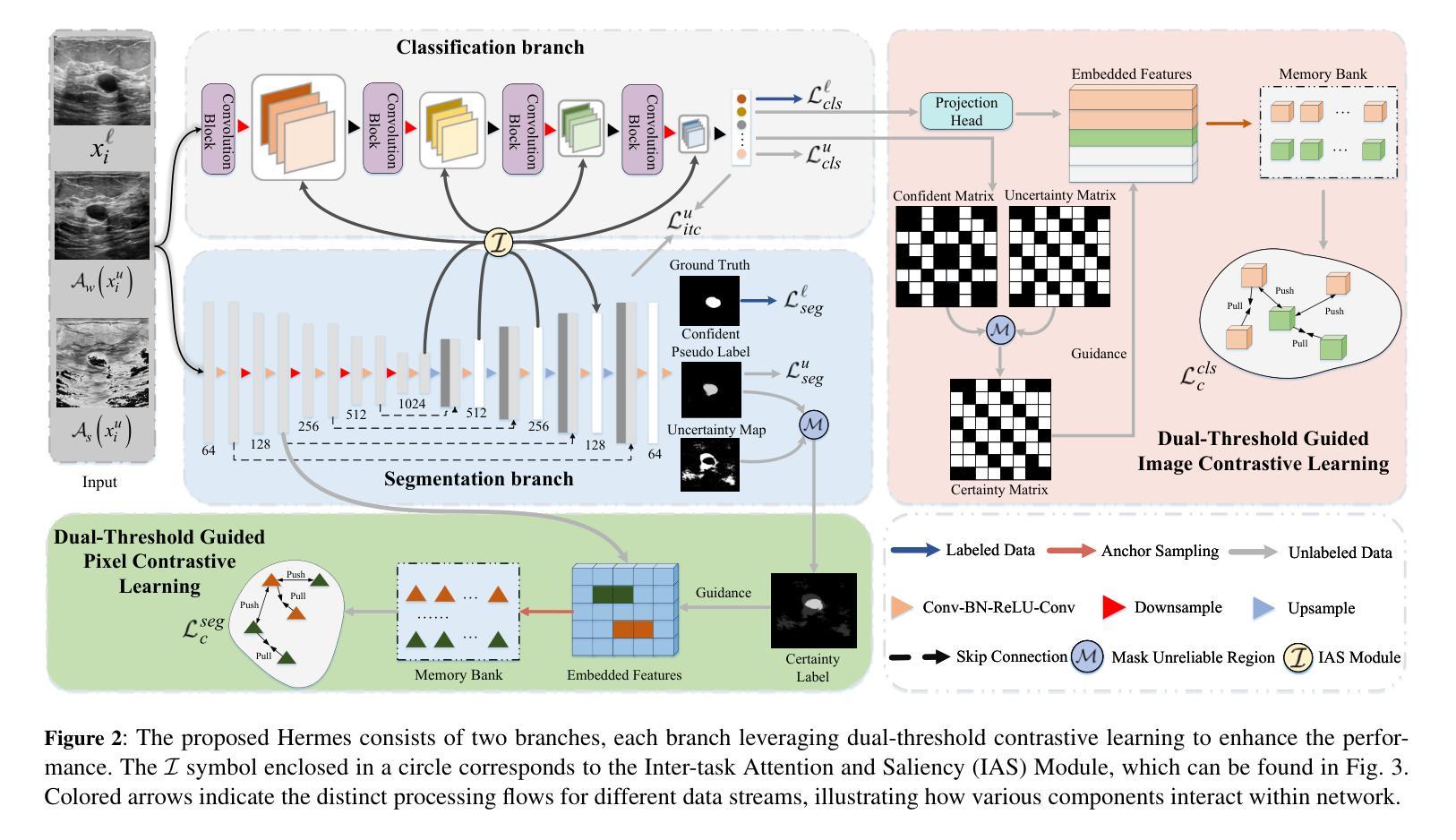
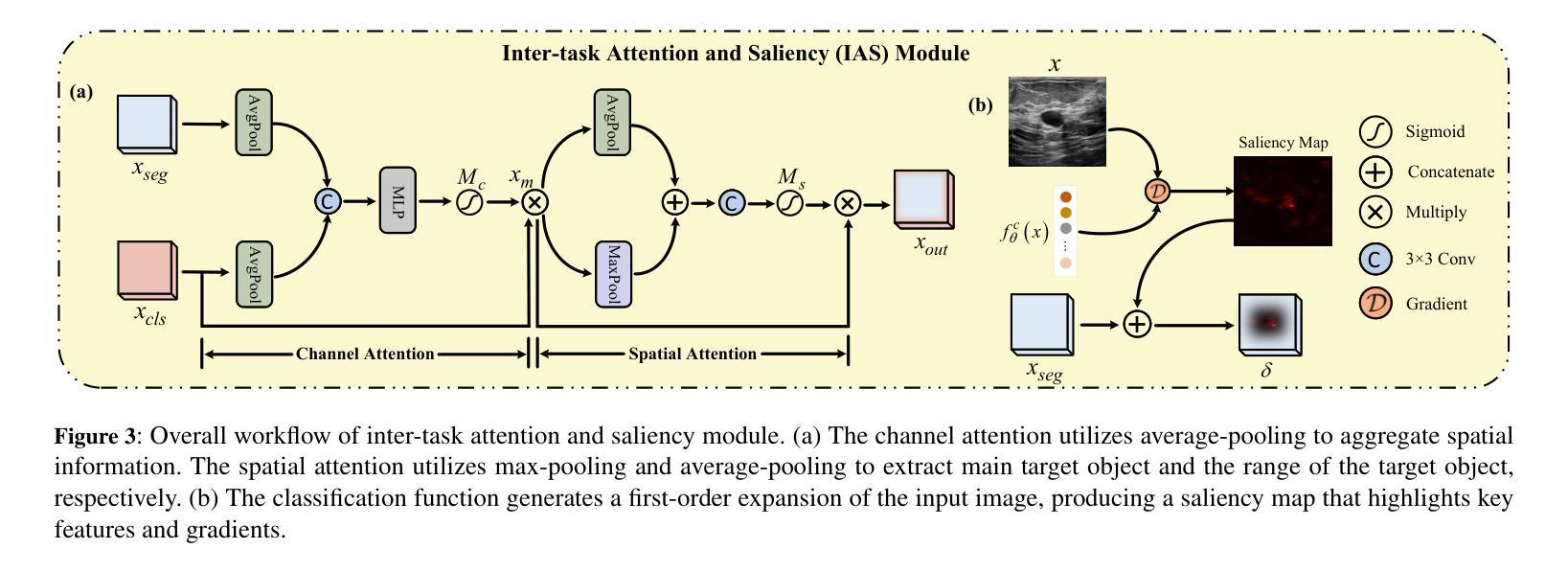
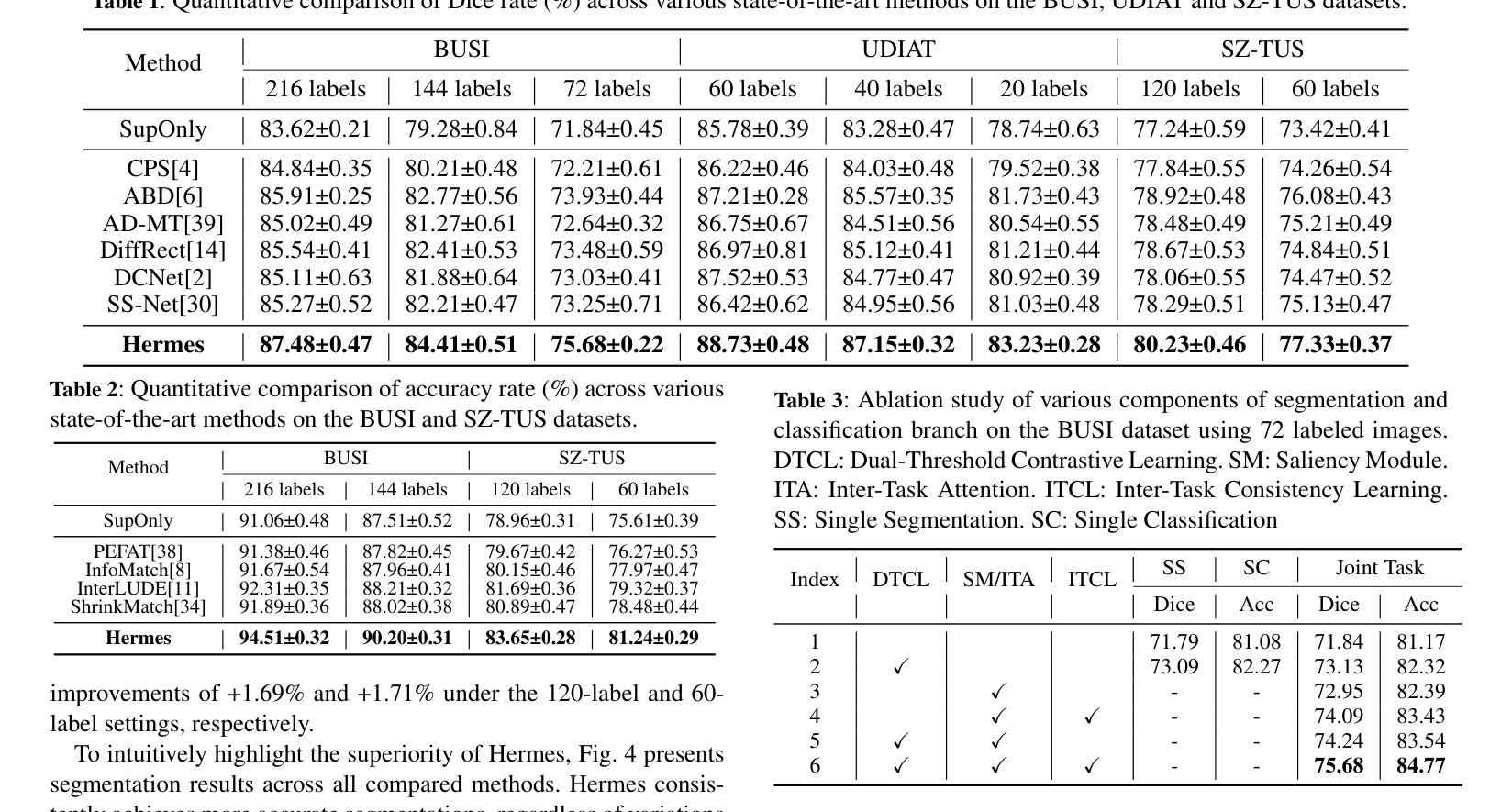
Confidence-based pseudo-label selection usually generates overly confident yet incorrect predictions, due to the early misleadingness of model and overfitting inaccurate pseudo-labels in the learning process, which heavily degrades the performance of semi-supervised contrastive learning. Moreover, segmentation and classification tasks are treated independently and the affinity fails to be fully explored. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised dual-threshold contrastive learning strategy for ultrasound image classification and segmentation, named Hermes. This strategy combines the strengths of contrastive learning with semi-supervised learning, where the pseudo-labels assist contrastive learning by providing additional guidance. Specifically, an inter-task attention and saliency module is also developed to facilitate information sharing between the segmentation and classification tasks. Furthermore, an inter-task consistency learning strategy is designed to align tumor features across both tasks, avoiding negative transfer for reducing features discrepancy. To solve the lack of publicly available ultrasound datasets, we have collected the SZ-TUS dataset, a thyroid ultrasound image dataset. Extensive experiments on two public ultrasound datasets and one private dataset demonstrate that Hermes consistently outperforms several state-of-the-art methods across various semi-supervised settings.
基于置信度的伪标签选择通常会产生过于自信但错误的预测,这是由于模型早期的误导以及在学习过程中对不准确伪标签的过拟合所导致的,这严重降低了半监督对比学习的性能。此外,分割和分类任务被独立处理,亲和力没有得到充分探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型半监督双阈值对比学习策略,用于超声图像分类和分割,名为Hermes。该策略结合了对比学习与半监督学习的优点,其中伪标签通过提供额外指导来辅助对比学习。具体来说,还开发了一个跨任务注意力和显著性模块,以促进分割和分类任务之间的信息共享。此外,还设计了一种跨任务一致性学习策略,以对齐两个任务中的肿瘤特征,避免负面迁移,以减少特征差异。为了解决公共超声数据集缺乏的问题,我们收集了SZ-TUS数据集,这是一个甲状腺超声图像数据集。在两个公共超声数据集和一个私有数据集上的大量实验表明,Hermes在各种半监督设置下均优于几种最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ECAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对超声图像分类和分割的半监督对比学习策略的不足,提出了一种新型的双阈值半监督对比学习策略Hermes。该策略结合了对比学习与半监督学习的优势,利用伪标签为对比学习提供额外指导。同时开发了一种跨任务的注意力和显著性模块,以促进分割和分类任务之间的信息共享。此外,设计了一种跨任务一致性学习策略,以对齐两个任务中的肿瘤特征,减少特征差异,避免负迁移。为解决公开可用的超声数据集缺乏的问题,收集了一个甲状腺超声图像数据集SZ-TUS。在多个公开和私有数据集上的实验表明,Hermes在各种半监督设置下均优于一些最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 当前半监督对比学习在超声图像分类和分割上存在问题,主要是伪标签选择过于自信导致错误预测。
- 提出了一种新型的双阈值半监督对比学习策略Hermes,结合对比学习与半监督学习。
- 利用伪标签为对比学习提供额外指导,开发了一种跨任务的注意力和显著性模块来促进任务间的信息共享。
- 设计了一种跨任务一致性学习策略,以减小分割和分类任务中的肿瘤特征差异。
- 收集了一个甲状腺超声图像数据集SZ-TUS以应对公开可用超声数据集的缺乏。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明Hermes在各种半监督设置下表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
Self-Supervised YOLO: Leveraging Contrastive Learning for Label-Efficient Object Detection
Authors:Manikanta Kotthapalli, Reshma Bhatia, Nainsi Jain
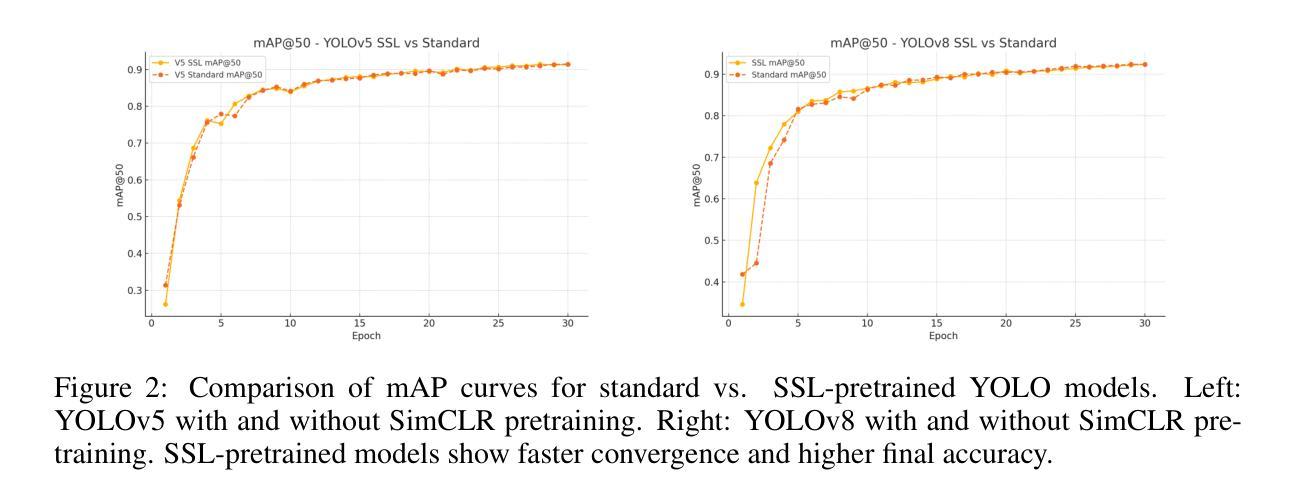
One-stage object detectors such as the YOLO family achieve state-of-the-art performance in real-time vision applications but remain heavily reliant on large-scale labeled datasets for training. In this work, we present a systematic study of contrastive self-supervised learning (SSL) as a means to reduce this dependency by pretraining YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 backbones on unlabeled images using the SimCLR framework. Our approach introduces a simple yet effective pipeline that adapts YOLO’s convolutional backbones as encoders, employs global pooling and projection heads, and optimizes a contrastive loss using augmentations of the COCO unlabeled dataset (120k images). The pretrained backbones are then fine-tuned on a cyclist detection task with limited labeled data. Experimental results show that SSL pretraining leads to consistently higher mAP, faster convergence, and improved precision-recall performance, especially in low-label regimes. For example, our SimCLR-pretrained YOLOv8 achieves a mAP@50:95 of 0.7663, outperforming its supervised counterpart despite using no annotations during pretraining. These findings establish a strong baseline for applying contrastive SSL to one-stage detectors and highlight the potential of unlabeled data as a scalable resource for label-efficient object detection.
一类如YOLO系列的一阶段目标检测器在实时视觉应用中取得了最先进的性能表现,但依然高度依赖于大规模标注数据集进行训练。在这项工作中,我们对对比自监督学习(SSL)进行了一项系统研究,希望通过运用这种学习方式来减少对标注数据集的依赖。具体来说,我们使用SimCLR框架在大量无标签图像上预先训练YOLOv5和YOLOv8的主干网络。我们的方法引入了一条简单有效的流水线,它将YOLO的卷积主干网络作为编码器,采用全局池化和投影头,并使用COCO无标签数据集(包含12万张图像)的增强版本来优化对比损失。随后,在有限的标注数据上,对预训练的主干网络进行微调,以执行骑行者检测任务。实验结果表明,SSL预训练能持续提高mAP值、加快收敛速度并改善精度-召回率性能,特别是在标签数据量较小的情境下尤为明显。例如,我们的SimCLR预训练的YOLOv8在mAP@50:95标准下取得了0.7663的成绩,尽管在预训练过程中没有使用任何注释,但仍优于其有监督训练的对应模型。这些发现为在单阶段检测器中应用对比SSL奠定了坚实基础,并突显出无标签数据作为可扩展资源在标签高效目标检测中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文研究了基于对比学习(Contrastive SSL)的自监督学习在减少YOLOv5和YOLOv8对大规模标注数据集依赖上的应用。该研究通过在未标注图像上预训练YOLO的主干网络,再利用COCO未标注数据集(包含12万张图像)的增强数据优化对比损失,从而引入了一种简单有效的管道。预训练的主干网络在有限的标注数据上进行微调,用于骑行者检测任务。实验结果表明,SSL预训练持续提高了mAP,加快了收敛速度,并改善了精度-召回性能,尤其在低标签条件下表现更为突出。这为对比SSL在一阶段检测器上的应用建立了强有力的基线,并突显未标注数据作为标签有效目标检测的可扩展资源潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 采用对比自监督学习(SSL)减少YOLO对大规模标注数据集的依赖。
- 利用未标注图像预训练YOLO主干网络。
- 使用COCO未标注数据集的增强数据优化对比损失。
- 预训练的主干网络在骑行者检测任务上进行微调。
- SSL预训练提高了mAP,加快了收敛速度,改善了精度-召回性能。
- 在低标签条件下,SSL预训练表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图


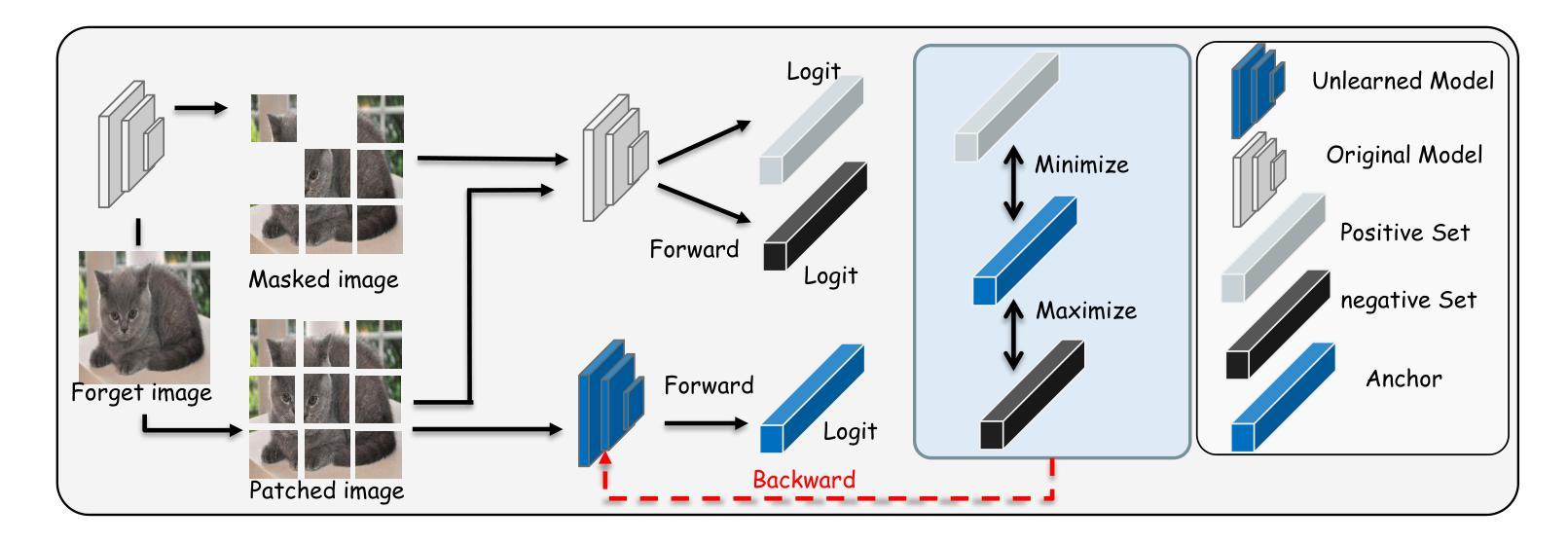
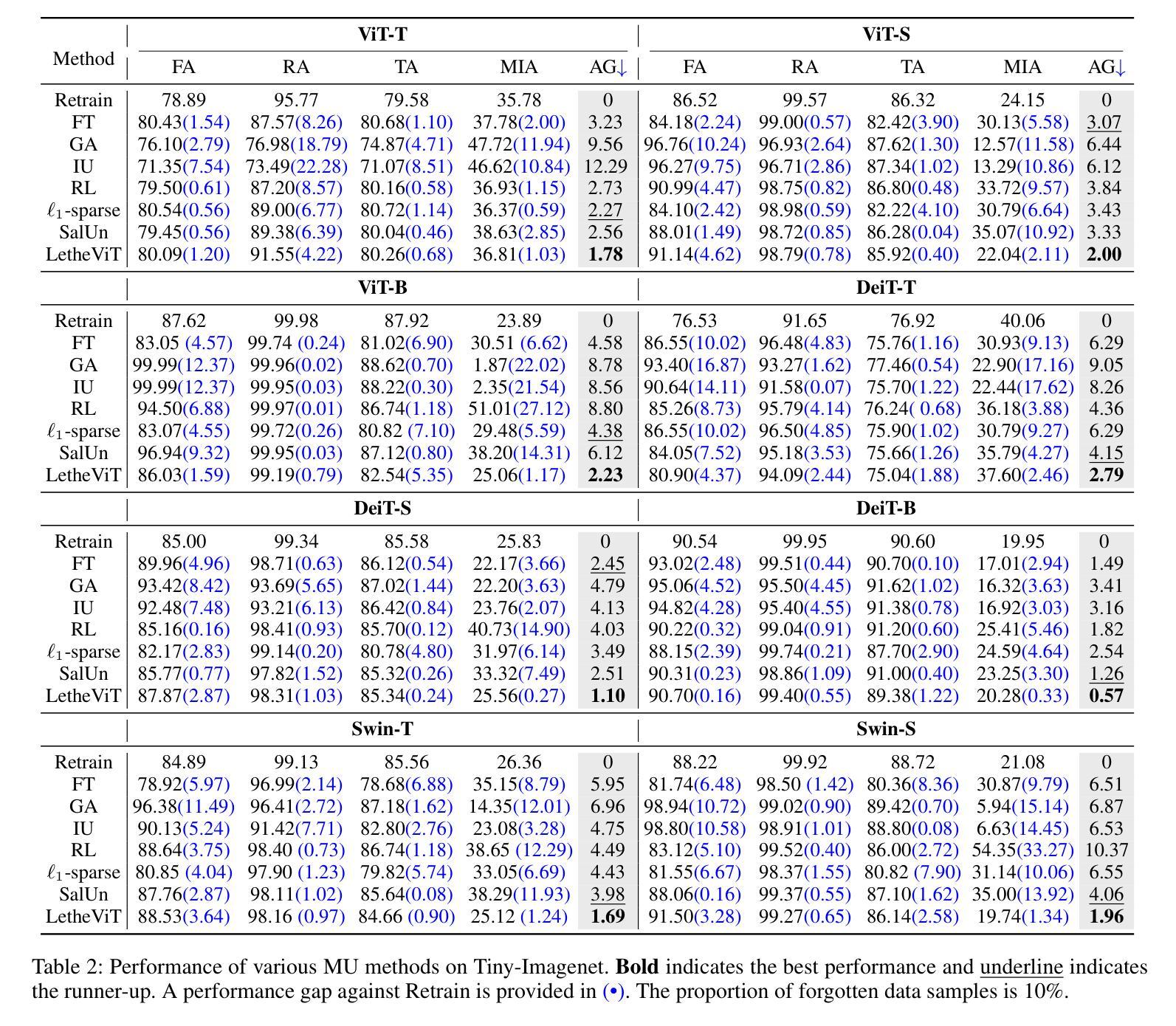
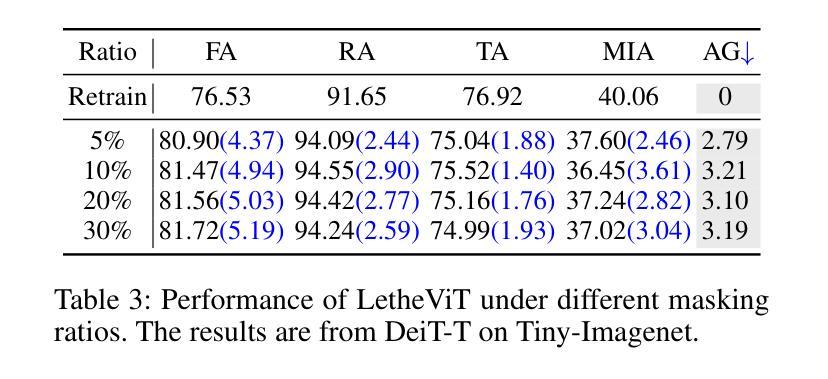
LetheViT: Selective Machine Unlearning for Vision Transformers via Attention-Guided Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yujia Tong, Tian Zhang, Jingling Yuan, Yuze Wang, Chuang Hu
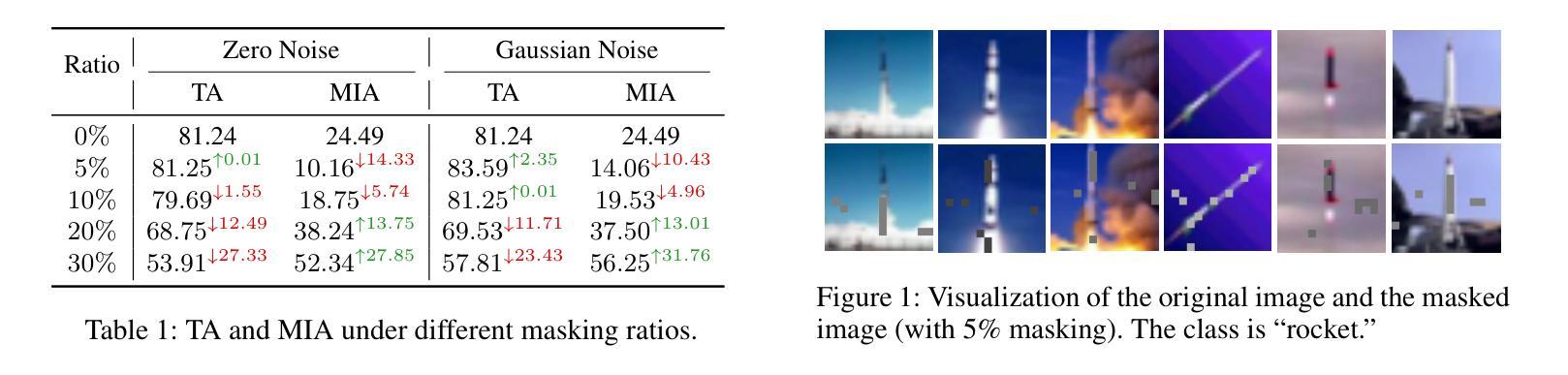
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have revolutionized computer vision tasks with their exceptional performance. However, the introduction of privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA has brought new challenges to them. These laws grant users the right to withdraw their data, necessitating not only the deletion of data but also the complete removal of its influence from trained models. Machine unlearning emerges as a critical solution, with exact unlearning being computationally prohibitive and approximate methods offering a more practical approach. This work addresses the particularly challenging scenario of random data forgetting in ViTs, where the model must forget specific samples while retaining others, even within the same class. We first reveal the core characteristics of ViTs through selective masking experiments: when high-attention areas are masked, the model retains its recognition capability but significantly weakens its memorization ability. Based on the above insights, we propose LetheViT, a contrastive unlearning method tailored for ViTs. LetheViT uses masked image inputs to generate positive logits and original image inputs to generate negative logits, guiding the model to forget specific details while retaining the general cl category outlines. Experimental results demonstrate that LetheViT achieves state-of-the-art performance, effectively balancing privacy compliance with model efficacy.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)以其卓越性能在计算机视觉任务中引发了革命。然而,GDPR和CCPA等隐私法规的出台给它们带来了新的挑战。这些法律赋予用户收回其数据的权利,这不仅要求删除数据,还要求从已训练的模型中完全消除其影响。机器遗忘作为一种关键的解决方案而出现,精确遗忘在计算上是禁止的,而近似方法提供了更实用的方法。这项工作解决了ViTs中随机数据遗忘这一特别具有挑战性的场景,其中模型必须遗忘特定样本,同时保留其他样本,即使在同一类中也是如此.我们首先通过选择性掩蔽实验揭示了ViTs的核心特征:当高注意力区域被掩蔽时,模型的识别能力得以保留,但记忆能力会显著减弱。基于上述见解,我们为ViTs量身定制了一种对比遗忘方法,名为LetheViT。LetheViT使用掩蔽图像输入生成正对数,使用原始图像输入生成负对数,引导模型忘记特定细节,同时保留一般类别轮廓。实验结果表明,LetheViT达到了最先进的性能,有效地平衡了隐私合规性和模型有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ViTs在面对如GDPR和CCPA等隐私法规的挑战时,需要处理用户数据删除的需求。机器遗忘作为一种解决方案,尽管精确遗忘计算上很昂贵,但近似方法更实用。本文研究ViTs中随机数据遗忘这一特殊场景,发现通过选择性遮蔽实验揭示ViTs的核心特性:遮蔽高注意力区域会削弱其记忆能力但保留识别能力。基于此,为ViTs量身定制了对比遗忘方法LetheViT。LetheViT使用遮蔽图像输入生成正向logits和原始图像输入生成负向logits,引导模型遗忘特定细节同时保留类别轮廓。实验证明LetheViT达到最佳性能,有效平衡隐私合规与模型效用。
Key Takeaways
- ViTs在面临隐私法规挑战时,需要应对用户数据删除的需求。
- 机器遗忘是应对这一需求的关键解决方案。
- 精确遗忘在计算上很昂贵,因此近似方法更实用。
- 本文研究发现在ViTs中,遮蔽高注意力区域会显著削弱模型的记忆能力。
- LetheViT是一种针对ViTs的对比遗忘方法,通过生成正向和负向logits来引导模型遗忘特定细节。
- LetheViT在实验中表现出最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

Contrast-Invariant Self-supervised Segmentation for Quantitative Placental MRI
Authors:Xinliu Zhong, Ruiying Liu, Emily S. Nichols, Xuzhe Zhang, Andrew F. Laine, Emma G. Duerden, Yun Wang
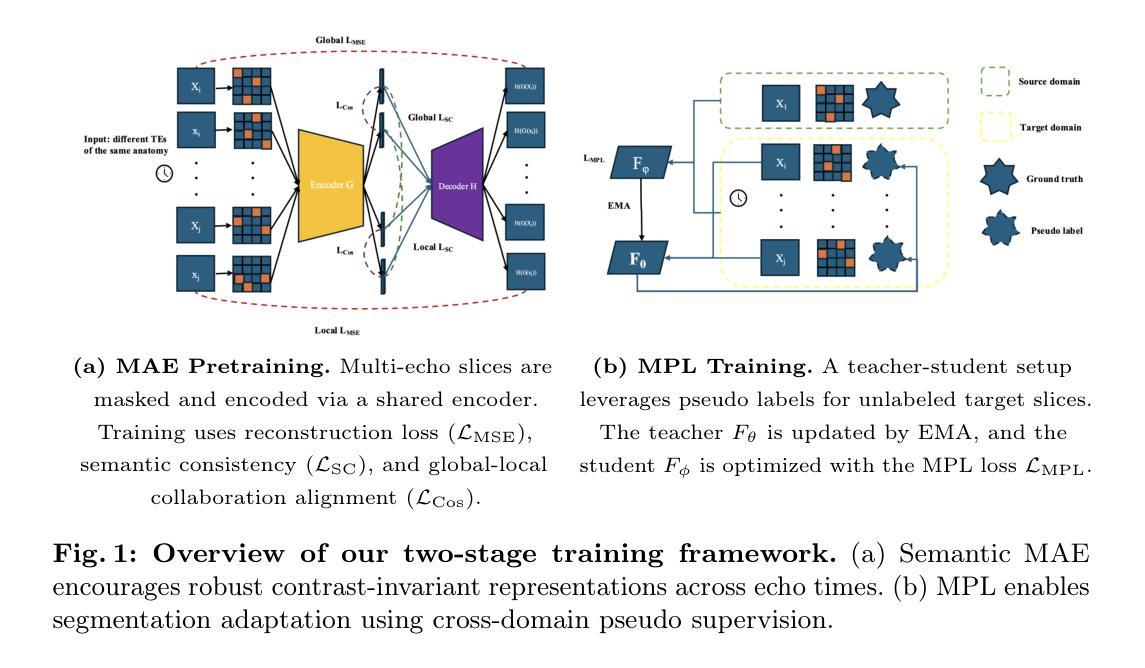
Accurate placental segmentation is essential for quantitative analysis of the placenta. However, this task is particularly challenging in T2*-weighted placental imaging due to: (1) weak and inconsistent boundary contrast across individual echoes; (2) the absence of manual ground truth annotations for all echo times; and (3) motion artifacts across echoes caused by fetal and maternal movement. In this work, we propose a contrast-augmented segmentation framework that leverages complementary information across multi-echo T2*-weighted MRI to learn robust, contrast-invariant representations. Our method integrates: (i) masked autoencoding (MAE) for self-supervised pretraining on unlabeled multi-echo slices; (ii) masked pseudo-labeling (MPL) for unsupervised domain adaptation across echo times; and (iii) global-local collaboration to align fine-grained features with global anatomical context. We further introduce a semantic matching loss to encourage representation consistency across echoes of the same subject. Experiments on a clinical multi-echo placental MRI dataset demonstrate that our approach generalizes effectively across echo times and outperforms both single-echo and naive fusion baselines. To our knowledge, this is the first work to systematically exploit multi-echo T2*-weighted MRI for placental segmentation.
准确的胎盘分割对于胎盘的定量分析至关重要。然而,由于以下因素,这项任务在T2*-加权胎盘成像中尤其具有挑战性:(1)各回声之间边界对比度较弱且不一致;(2)所有回声时间没有手动真实注释;(3)由于胎儿和母亲的移动导致的跨回声运动伪影。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种对比增强分割框架,该框架利用多回声T2*-加权MRI中的互补信息来学习稳健的、对比不变的表示。我们的方法结合了:(i)用于无监督多回声切片预训练的掩码自动编码(MAE);(ii)用于跨回声时间进行无监督域适应的掩码伪标签(MPL);以及(iii)全局-局部协作以将细粒度特征与全局解剖上下文对齐。我们还引入了一种语义匹配损失,以鼓励同一受试者不同回声之间的表示一致性。在临床多回声胎盘MRI数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在不同回声时间之间具有很好的泛化能力,并优于单回声和简单融合基线。据我们所知,这是首次系统地利用多回声T2*-加权MRI进行胎盘分割的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 20 figures
Summary
本文提出一种利用多回声T2*-加权MRI的对比增强分割框架,用于学习稳健、对比不变的表示。该框架集成多种技术,包括用于无监督预训练的掩码自动编码(MAE)、用于跨回声时间的无监督域自适应的掩码伪标签(MPL)、全局局部协作以及语义匹配损失,以鼓励同一主体不同回声之间的表示一致性。实验表明,该方法在跨回声时间具有良好的泛化性能,并优于单回声和简单融合基线。这是首次系统地利用多回声T2*-加权MRI进行胎盘分割的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 准确胎盘分割对胎盘定量分析至关重要。
- T2*-加权胎盘成像中的胎盘分割具有挑战性,主要由于边界对比度弱、不同回声时间缺乏手动真实标注和母子运动引起的运动伪影。
- 提出一种对比增强分割框架,利用多回声T2*-加权MRI的互补信息学习稳健表示。
- 集成掩码自动编码(MAE)进行无监督预训练,用于在未标记的多回声切片上自我学习。
- 采用掩码伪标签(MPL)实现跨回声时间的无监督域自适应。
- 通过全局局部协作将精细特征与全局解剖上下文对齐。
点此查看论文截图