⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
StreamAgent: Towards Anticipatory Agents for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Haolin Yang, Feilong Tang, Linxiao Zhao, Xiang An, Ming Hu, Huifa Li, Xinlin Zhuang, Boqian Wang, Yifan Lu, Xiaofeng Zhang, Abdalla Swikir, Junjun He, Zongyuan Ge, Imran Razzak
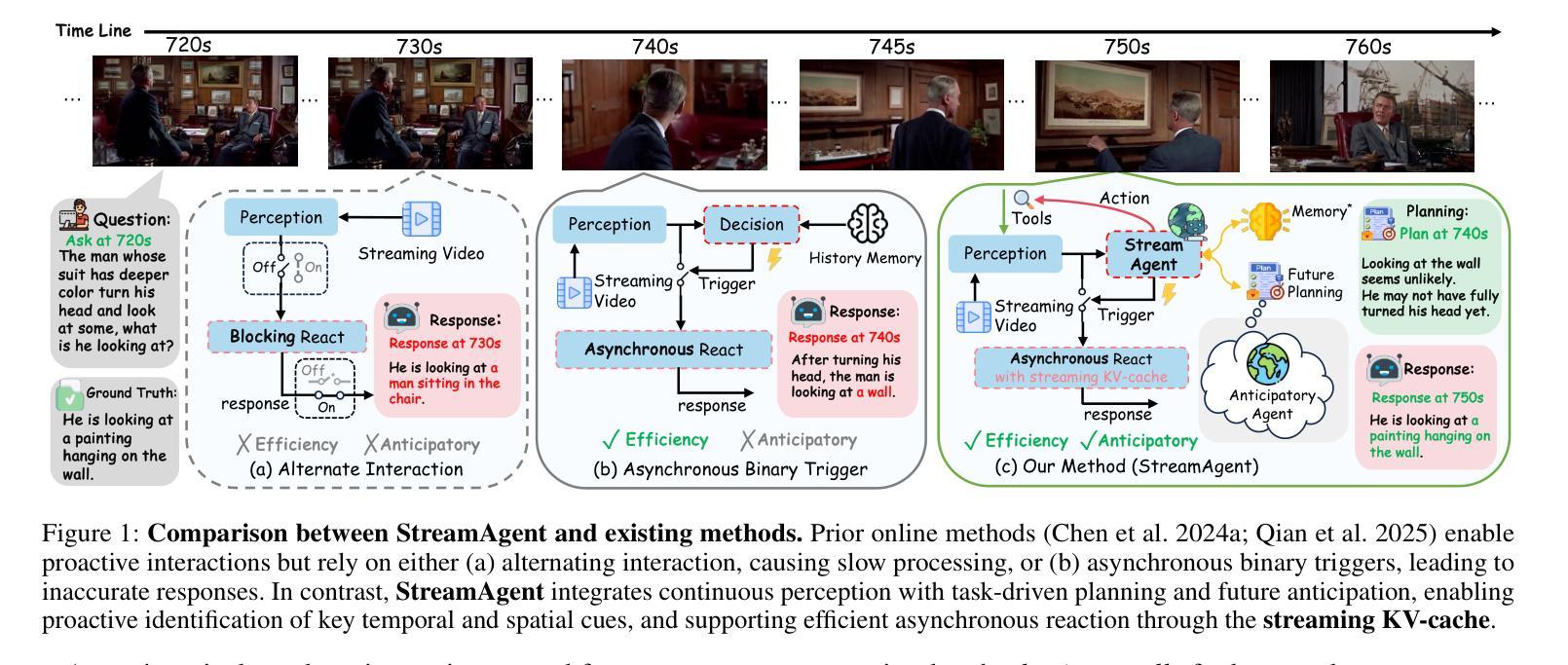
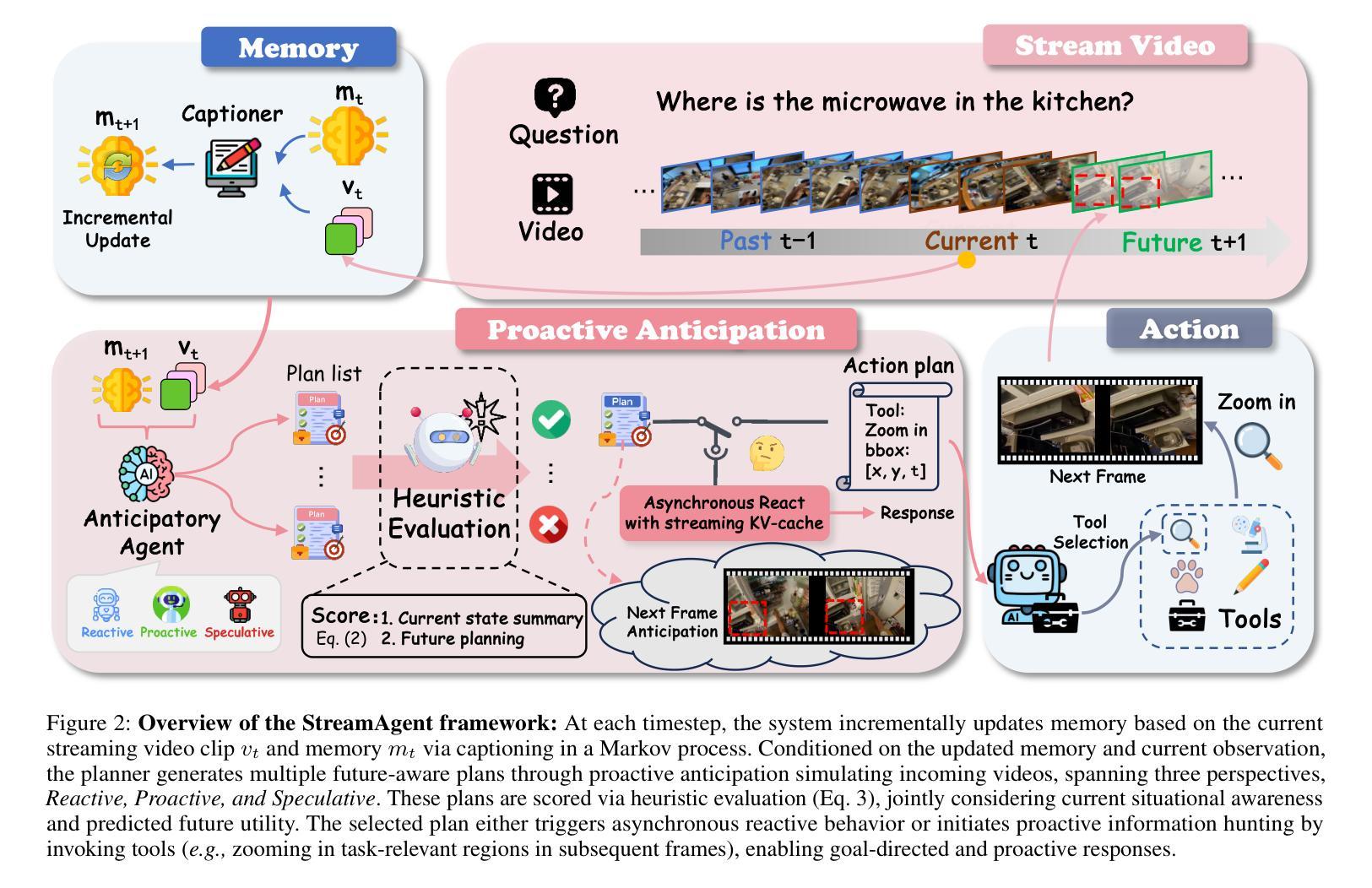
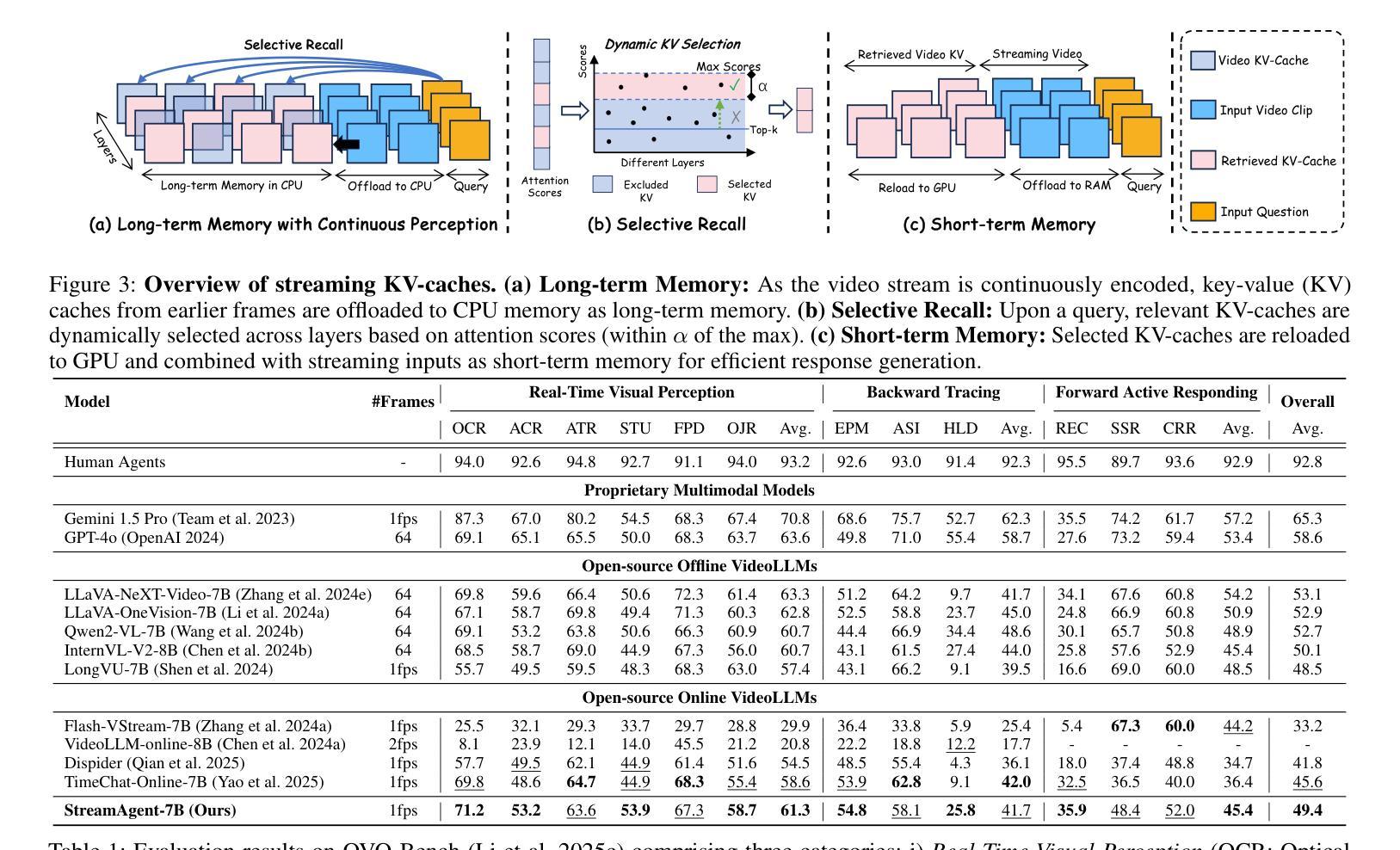
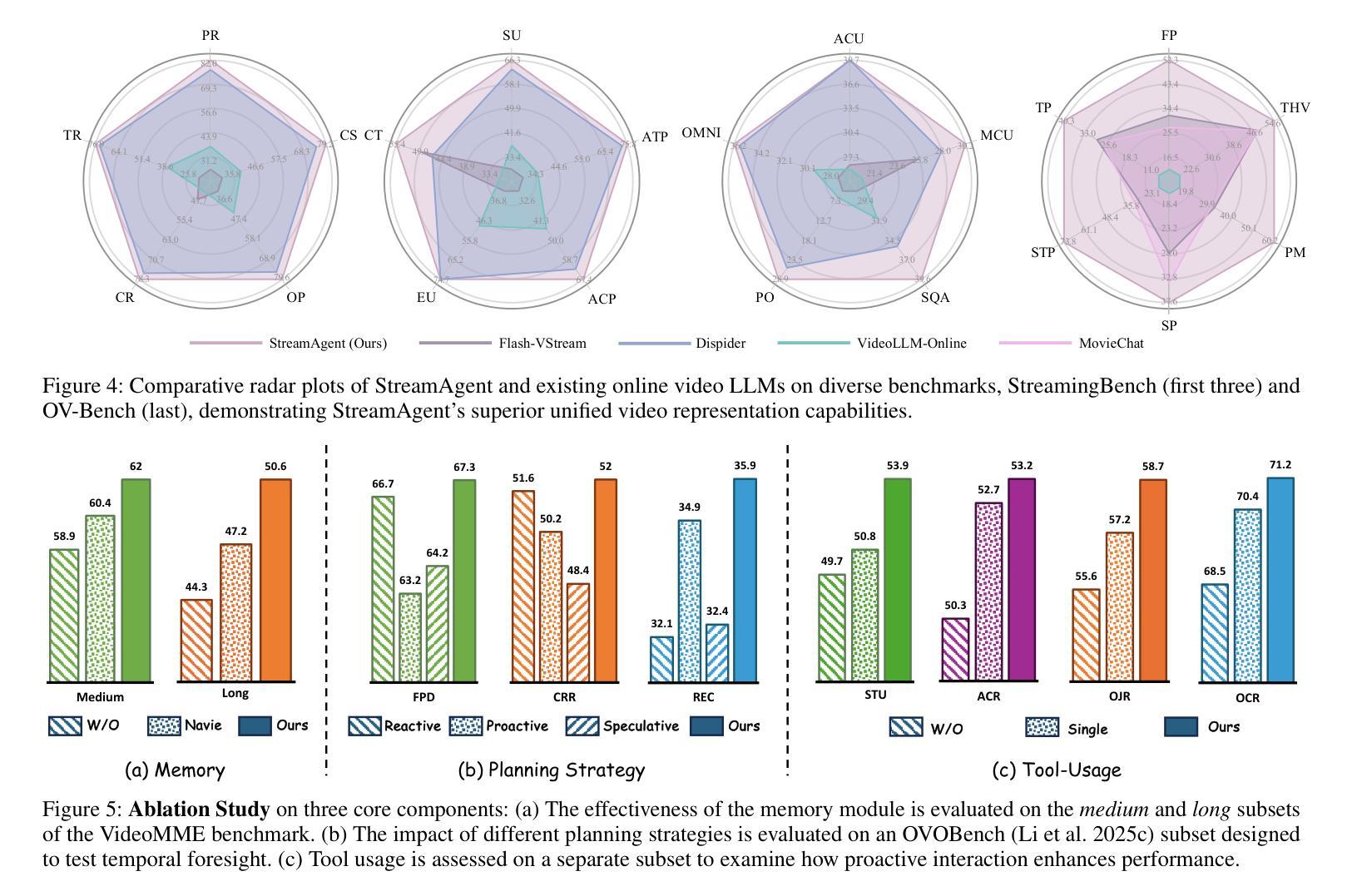
Real-time streaming video understanding in domains such as autonomous driving and intelligent surveillance poses challenges beyond conventional offline video processing, requiring continuous perception, proactive decision making, and responsive interaction based on dynamically evolving visual content. However, existing methods rely on alternating perception-reaction or asynchronous triggers, lacking task-driven planning and future anticipation, which limits their real-time responsiveness and proactive decision making in evolving video streams. To this end, we propose a StreamAgent that anticipates the temporal intervals and spatial regions expected to contain future task-relevant information to enable proactive and goal-driven responses. Specifically, we integrate question semantics and historical observations through prompting the anticipatory agent to anticipate the temporal progression of key events, align current observations with the expected future evidence, and subsequently adjust the perception action (e.g., attending to task-relevant regions or continuously tracking in subsequent frames). To enable efficient inference, we design a streaming KV-cache memory mechanism that constructs a hierarchical memory structure for selective recall of relevant tokens, enabling efficient semantic retrieval while reducing the overhead of storing all tokens in the traditional KV-cache. Extensive experiments on streaming and long video understanding tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods in response accuracy and real-time efficiency, highlighting its practical value for real-world streaming scenarios.
实时流媒体视频理解在自动驾驶和智能监控等领域,给传统离线视频处理带来了挑战。这需要我们进行连续感知、主动决策和基于动态演化视觉内容的响应交互。然而,现有方法依赖于交替感知反应或异步触发,缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预期,这限制了它们在实时流媒体中的响应能力和主动决策制定。为此,我们提出了一种StreamAgent,它能够预测未来包含任务相关信息的时间间隔和空间区域,以实现主动和目标驱动的响应。具体来说,我们通过提示预测代理来整合问题语义和历史观察,预测关键事件的时间进展,将当前观察与预期的未来证据对齐,并随后调整感知行动(例如,关注任务相关区域或在后续帧中进行持续跟踪)。为了实现高效推理,我们设计了一种流KV缓存机制,构建了一种分层内存结构,用于选择性召回相关令牌,实现在减少传统KV缓存中存储所有令牌开销的同时,进行高效语义检索。在流媒体和长视频理解任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在响应准确性和实时效率方面优于现有方法,突显了其在现实流媒体场景中的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
实时流媒体视频理解在自动驾驶和智能监控等领域面临挑战,需要超越传统的离线视频处理,实现连续感知、主动决策和基于动态视觉内容的响应交互。现有方法依赖感知反应或异步触发,缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预测,限制了其在实时流媒体中的响应性和主动决策能力。为此,我们提出StreamAgent,可预测未来任务相关信息的时空间隔区域,实现目标驱动的响应。通过整合问题语义和历史观察,促使预测代理预测关键事件的时间进展,将当前观察与预期的未来证据对齐,并调整感知动作。为提升推理效率,我们设计了一种流式KV缓存机制,构建分层内存结构,实现相关令牌的选择性回忆,从而在减少存储所有令牌的传统KV缓存开销的同时,实现有效的语义检索。在流媒体和长视频理解任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在响应准确性和实时效率方面优于现有方法,突显其在真实流媒体场景中的实用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 实时流媒体视频理解在自动驾驶和智能监控中面临挑战。
- 当前方法依赖感知反应或异步触发,缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预测。
- StreamAgent可预测未来任务相关信息的时空间隔区域。
- 通过整合问题语义和历史观察,实现目标驱动的响应。
- 感知动作可调整以与未来证据对齐。
- 为提升推理效率,设计了一种流式KV缓存机制。
点此查看论文截图

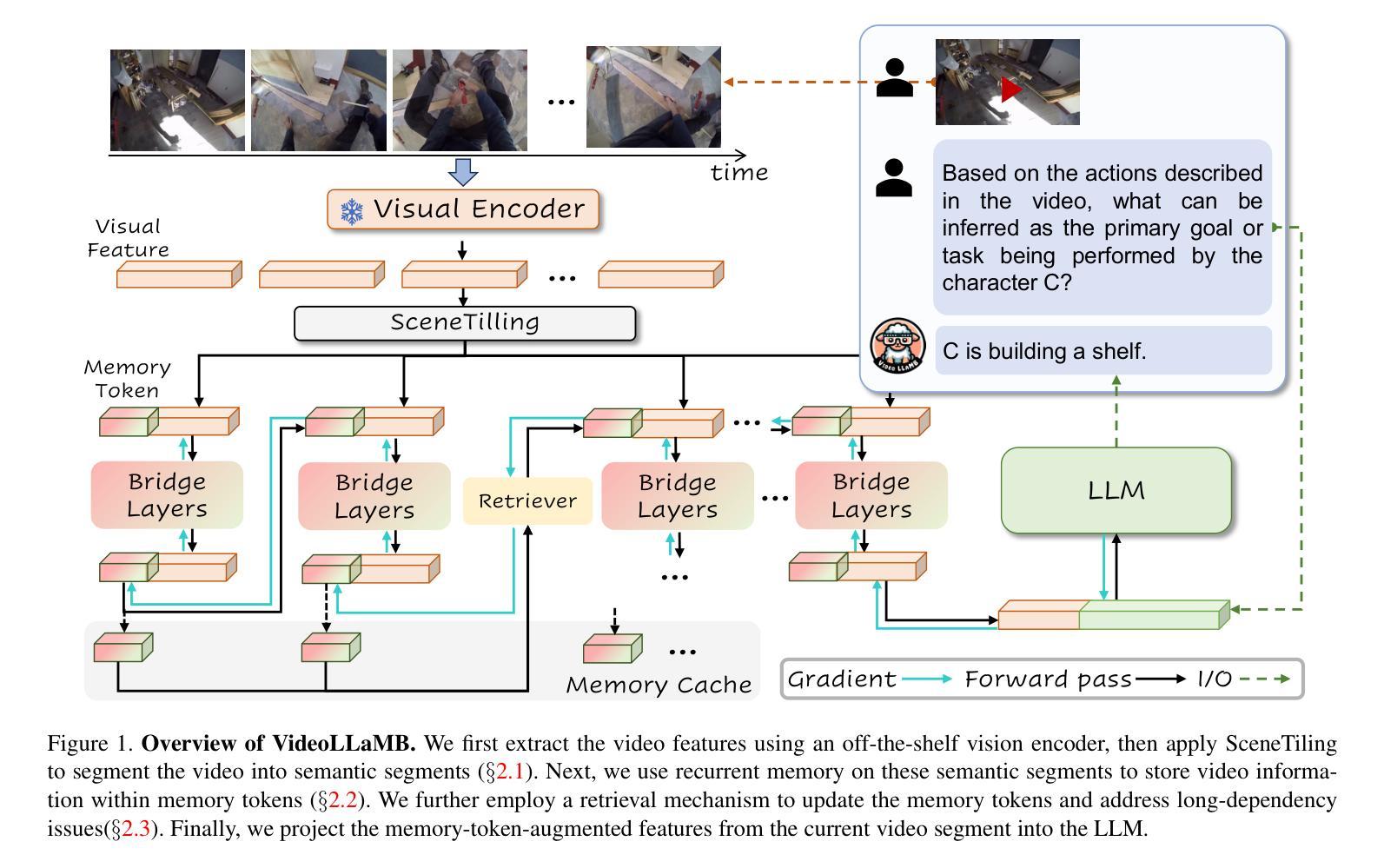
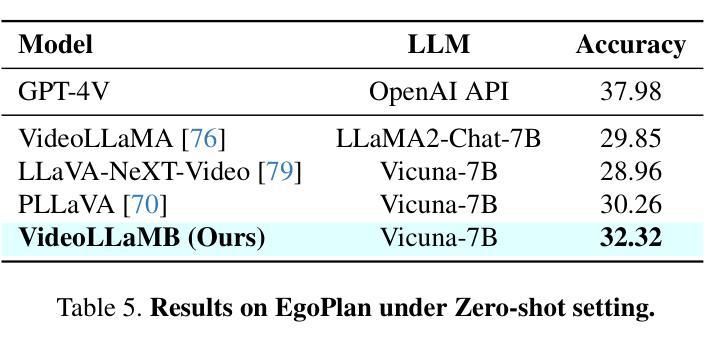
VideoLLaMB: Long Streaming Video Understanding with Recurrent Memory Bridges
Authors:Yuxuan Wang, Yiqi Song, Cihang Xie, Yang Liu, Zilong Zheng
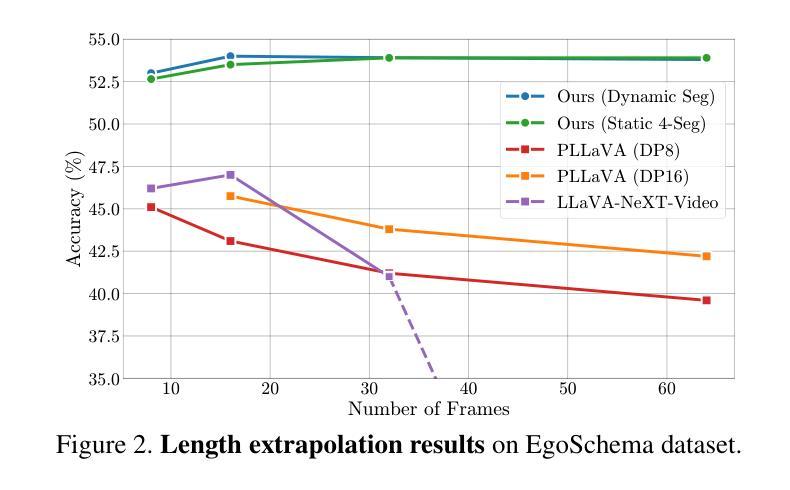
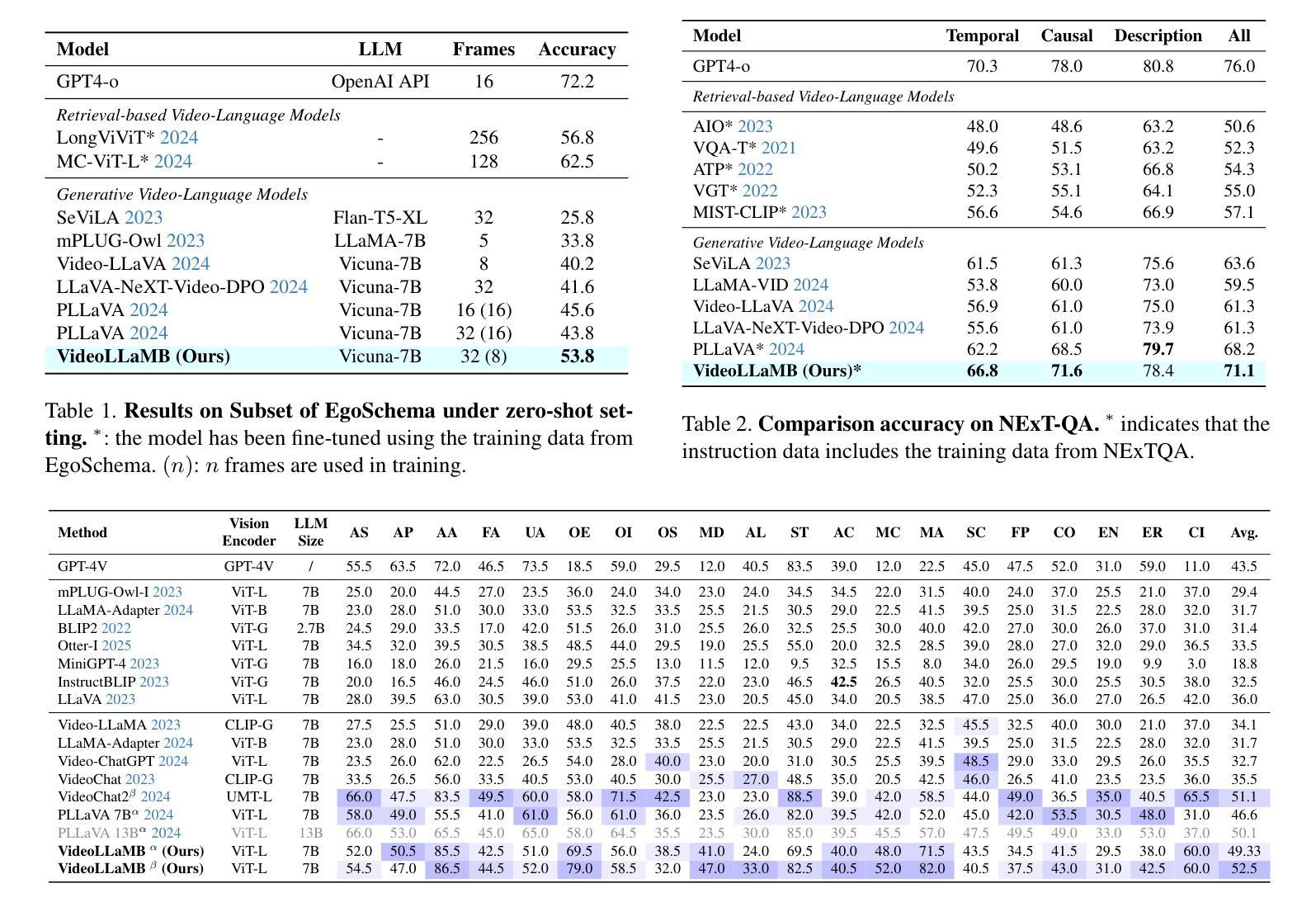
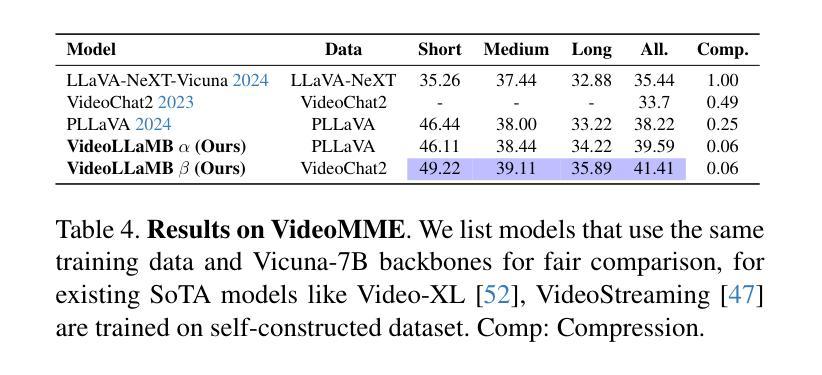
Recent advancements in large-scale video-language models have shown significant potential for real-time planning and detailed interactions. However, their high computational demands and the scarcity of annotated datasets limit their practicality for academic researchers. In this work, we introduce VideoLLaMB, a novel and efficient framework for long video understanding that leverages recurrent memory bridges and temporal memory tokens to enable seamless encoding of entire video sequences with preserved semantic continuity. Central to our approach is a SceneTiling algorithm that segments videos into coherent semantic units, facilitating robust understanding across tasks without requiring additional training. VideoLLaMB achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing models by 4.2 points on four VideoQA benchmarks and by 2.06 points on egocentric planning tasks. Notably, it maintains strong performance under extreme video length scaling (up to 8 times) and excels at fine-grained frame retrieval on our proposed Needle in a Video Haystack (NIAVH) benchmark. With linear GPU memory scaling, VideoLLaMB processes up to 320 frames using a single Nvidia A100 GPU, despite being trained on only 16 frames-offering an unprecedented balance of accuracy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This makes it highly accessible and practical for the academic community.
近期大规模视频语言模型的进展显示出了实时规划和详细交互的巨大潜力。然而,它们的高计算需求和标注数据集的稀缺,限制了学术研究者对其的实际应用。在这项工作中,我们介绍了VideoLLaMB,这是一个用于长视频理解的新型高效框架,它利用递归记忆桥和临时记忆令牌,实现对整个视频序列的无缝编码,同时保持语义连续性。我们的方法的核心是SceneTiling算法,它将视频分割成连贯的语义单元,促进跨任务的稳健理解,而无需额外的训练。VideoLLaMB实现了最先进的性能,在四个VideoQA基准测试上比现有模型高出4.2分,在以自我为中心的任务上高出2.06分。值得注意的是,它在极端视频长度缩放(高达8倍)的情况下保持良好的性能,并在我们提出的“视频中的一根针”(Needle in a Video Haystack, NIAVH)基准测试中精细帧检索方面表现出色。VideoLLaMB具有线性的GPU内存扩展性,即使只在16帧上进行训练,也能使用单个Nvidia A100 GPU处理高达320帧的图像,实现了前所未有的准确性、可扩展性和成本效益之间的平衡。这使得它对于学术界来说高度可用且实用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at ICCV 2025
Summary
视频理解领域的新进展,引入VideoLLaMB框架,利用递归记忆桥和临时记忆令牌实现长视频的无缝编码,具有场景切片算法,可将视频分割成连贯的语义单元,无需额外训练即可实现跨任务稳健理解。在多个基准测试中表现优异,可在极端视频长度缩放下保持性能,并在细粒度帧检索方面表现出色。具有线性GPU内存缩放特性,使用单个Nvidia A100 GPU处理高达320帧,在仅使用16帧进行训练的情况下,实现了准确性、可扩展性和成本效益之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- VideoLLaMB是一个用于长视频理解的框架,通过递归记忆桥和临时记忆令牌实现无缝编码。
- 场景切片算法将视频分割成连贯的语义单元,促进跨任务的稳健理解。
- VideoLLaMB在多个视频问答基准测试中达到或超越了现有模型的表现。
- 该框架在极端视频长度缩放下仍能保持强大的性能。
- VideoLLaMB在细粒度帧检索方面表现出色,特别是在提出的“视频中的一根针”(Needle in a Video Haystack)基准测试中。
- VideoLLaMB具有线性GPU内存缩放特性,可在单个Nvidia A100 GPU上处理大量帧。
点此查看论文截图