⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
Uncertainty Estimation for Novel Views in Gaussian Splatting from Primitive-Based Representations of Error and Visibility
Authors:Thomas Gottwald, Edgar Heinert, Matthias Rottmann
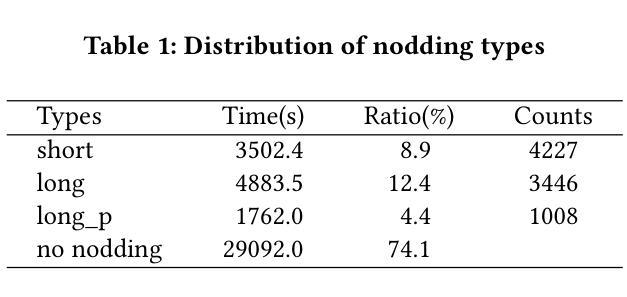
In this work, we present a novel method for uncertainty estimation (UE) in Gaussian Splatting. UE is crucial for using Gaussian Splatting in critical applications such as robotics and medicine. Previous methods typically estimate the variance of Gaussian primitives and use the rendering process to obtain pixel-wise uncertainties. Our method establishes primitive representations of error and visibility of trainings views, which carries meaningful uncertainty information. This representation is obtained by projection of training error and visibility onto the primitives. Uncertainties of novel views are obtained by rendering the primitive representations of uncertainty for those novel views, yielding uncertainty feature maps. To aggregate these uncertainty feature maps of novel views, we perform a pixel-wise regression on holdout data. In our experiments, we analyze the different components of our method, investigating various combinations of uncertainty feature maps and regression models. Furthermore, we considered the effect of separating splatting into foreground and background. Our UEs show high correlations to true errors, outperforming state-of-the-art methods, especially on foreground objects. The trained regression models show generalization capabilities to new scenes, allowing uncertainty estimation without the need for holdout data.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于高斯涂抹(Gaussian Splatting)中的不确定性估计(UE)的新方法。不确定性估计是使用高斯涂抹于机器人和医学等关键应用中的关键。以前的方法通常估计高斯基元(Gaussian primitives)的方差,并使用渲染过程获得像素级的不确定性。我们的方法建立了训练视图误差和可见性的基元表示,其中包含有意义的不确定性信息。这种表示是通过将训练误差和可见性投影到基元上获得的。新型视图的不确定性是通过渲染这些新型视图的基元不确定性表示而获得的,从而产生不确定性特征图。为了聚合这些新型视图的不确定性特征图,我们在预留数据上进行像素级回归。在我们的实验中,我们分析了我们方法的不同组成部分,研究了不确定性特征图和回归模型的各种组合。此外,我们还考虑了将涂抹分为前景和背景的影响。我们的不确定性估计与真实误差高度相关,尤其是在前景对象上,优于最新方法。经过训练的回归模型对新场景具有通用性,允许在没有预留数据的情况下进行不确定性估计。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种用于高斯混合模型中的不确定性估计(UE)的新方法。该方法对于在机器人和医学等关键应用中使用高斯混合模型至关重要。与之前的方法相比,我们的方法建立了训练视图的误差和可见性的原始表示,包含有意义的不确定性信息。通过投影训练误差和可见性来获得这种表示。通过渲染这些新颖视图的不确定性原始表示,我们获得了不确定性特征图。为了汇总这些不确定性特征图,我们对保留数据执行像素级回归。实验表明,我们的方法在分析不同组件和考虑前景与背景的分离效果时表现出优越性,与真实误差高度相关,并优于现有方法,特别是在前景对象上。训练的回归模型具有对新场景的泛化能力,无需保留数据即可进行不确定性估计。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了用于高斯混合模型中的不确定性估计的新方法。
- 建立了训练视图的误差和可见性的原始表示,包含有意义的不确定性信息。
- 通过渲染新颖视图的不确定性原始表示获得不确定性特征图。
- 通过像素级回归汇总不确定性特征图。
- 实验表明,该方法与真实误差高度相关,优于现有方法。
- 训练的回归模型具有对新场景的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

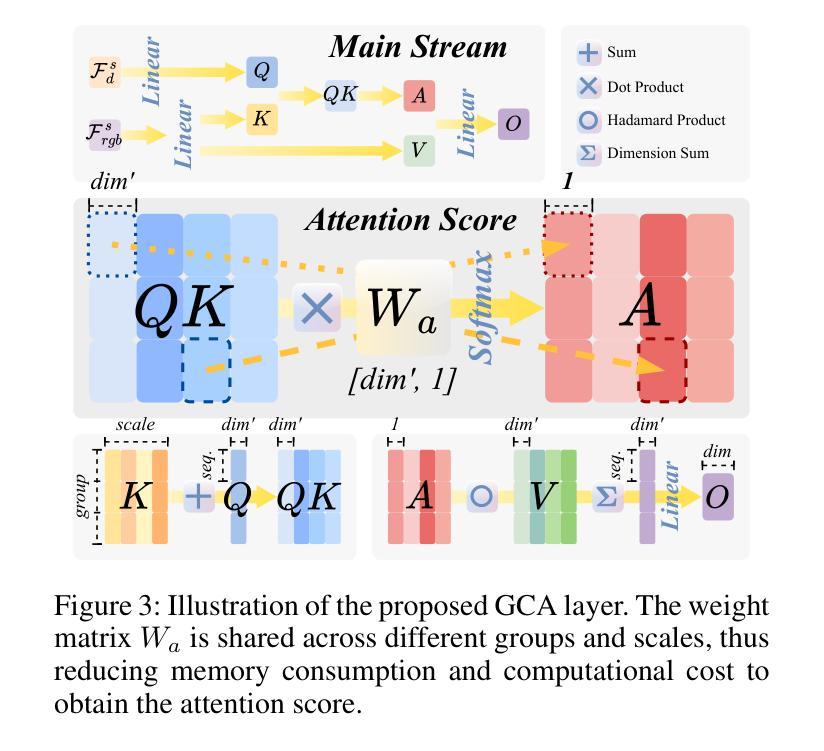
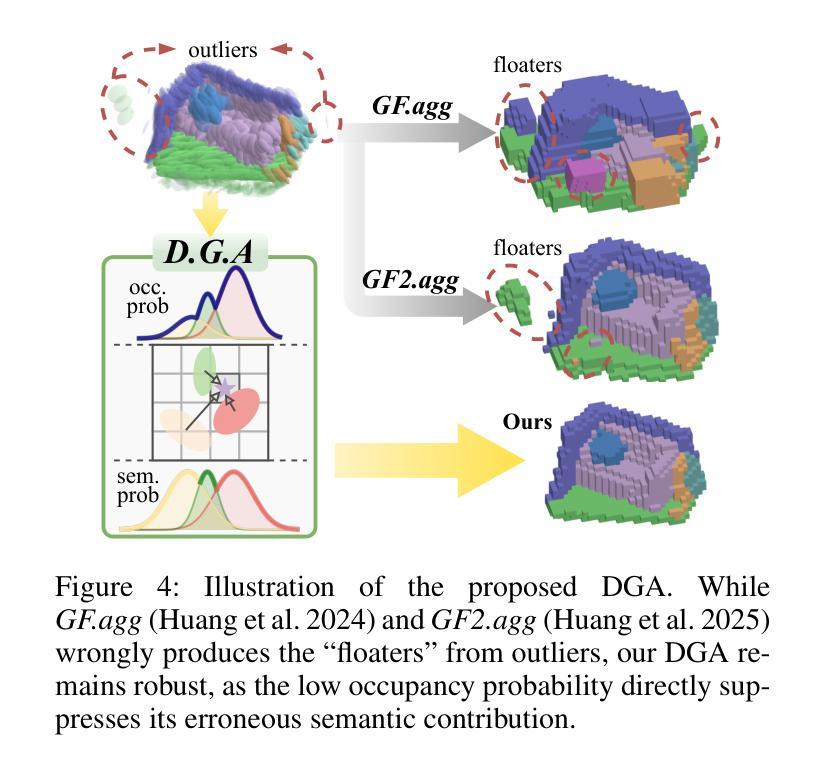
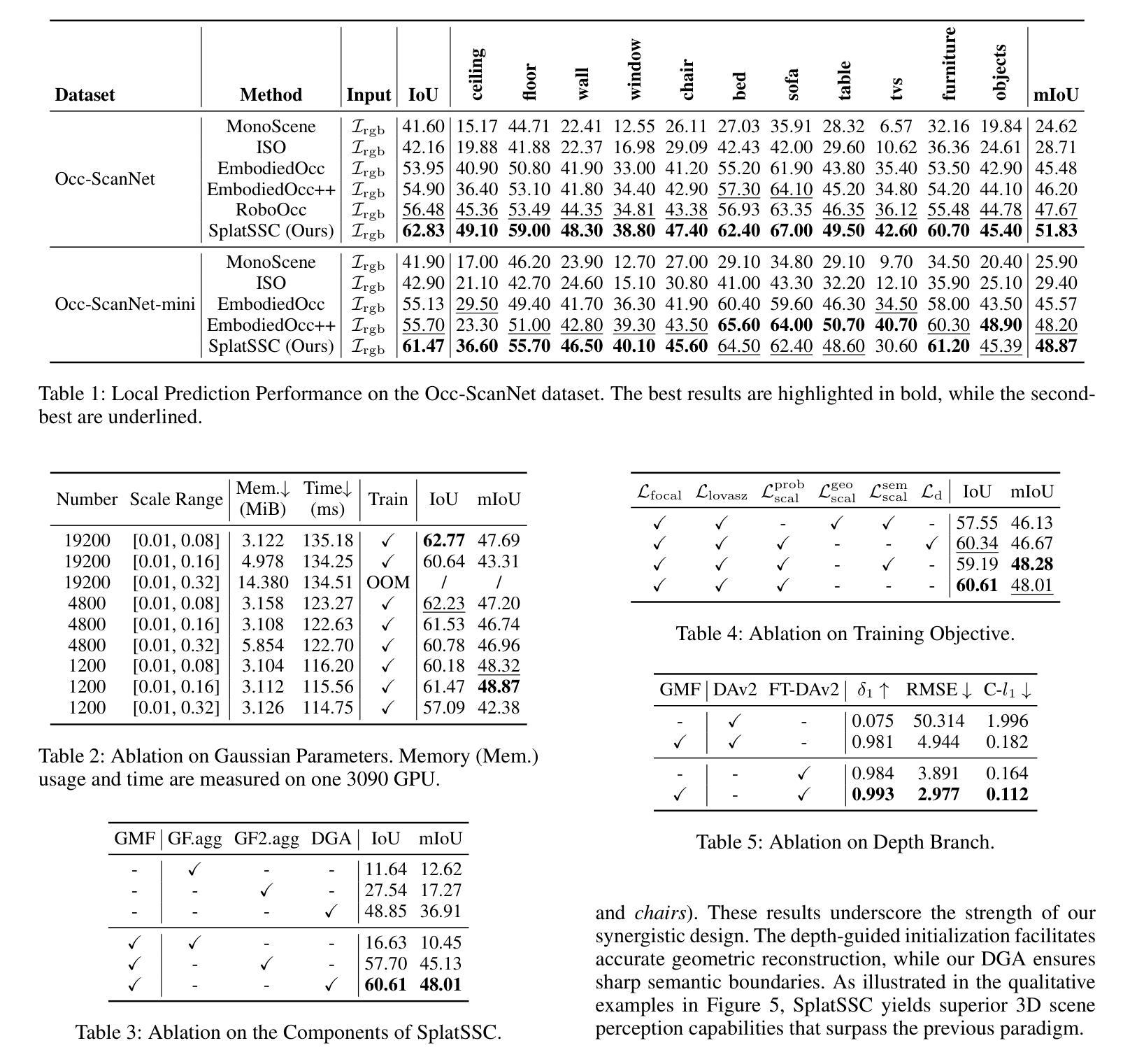
SplatSSC: Decoupled Depth-Guided Gaussian Splatting for Semantic Scene Completion
Authors:Rui Qian, Haozhi Cao, Tianchen Deng, Shenghai Yuan, Lihua Xie
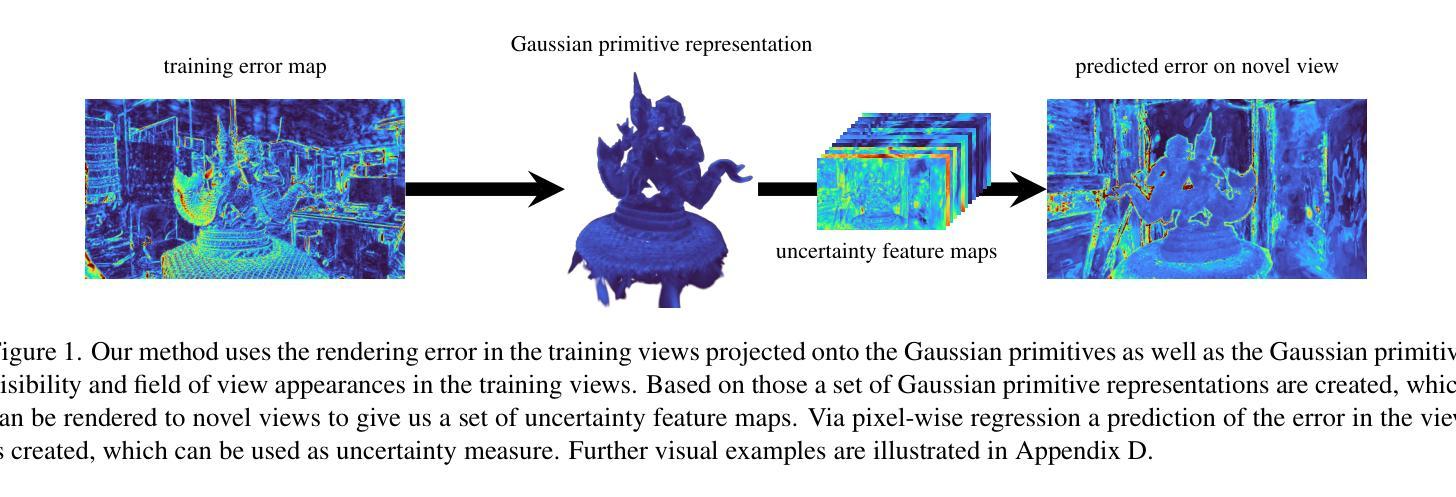
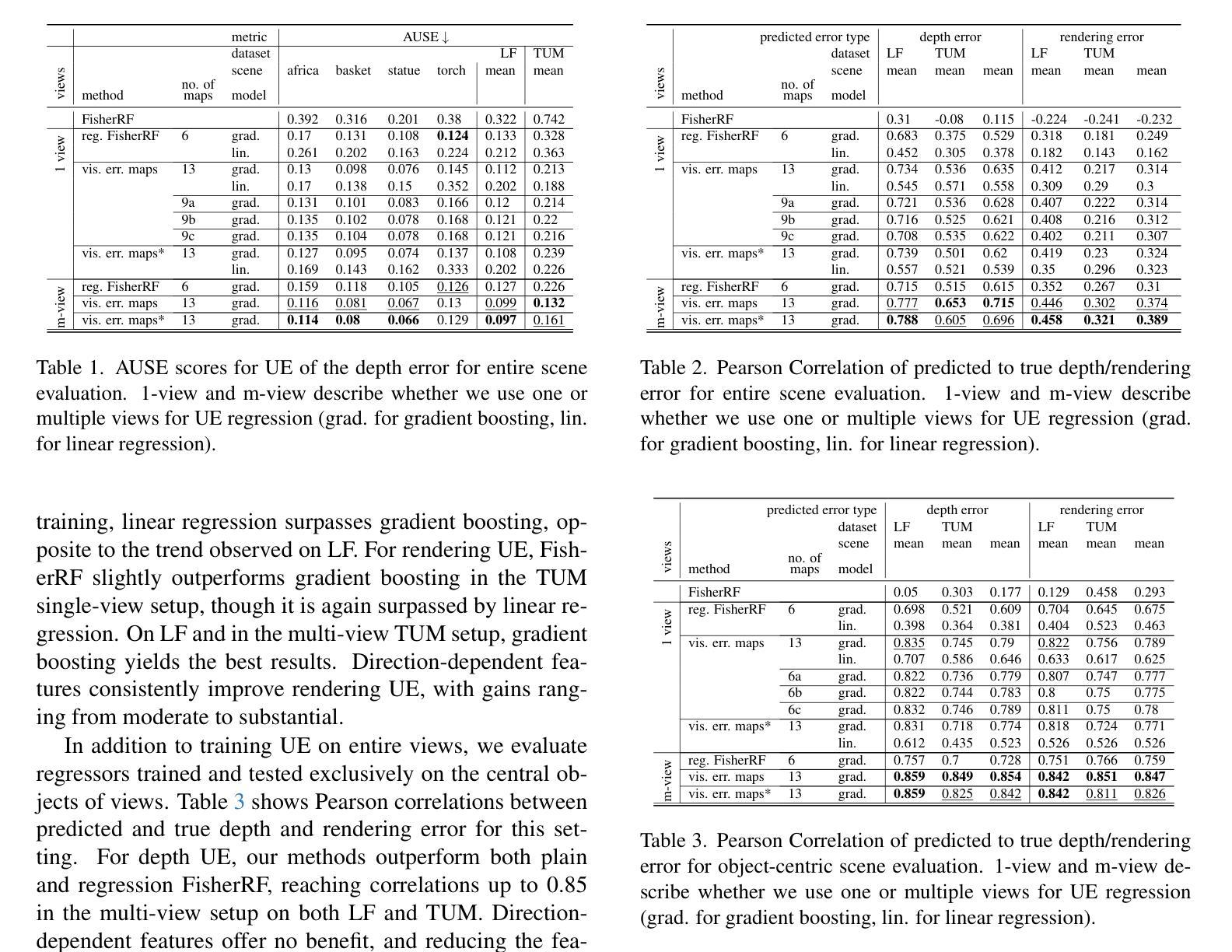
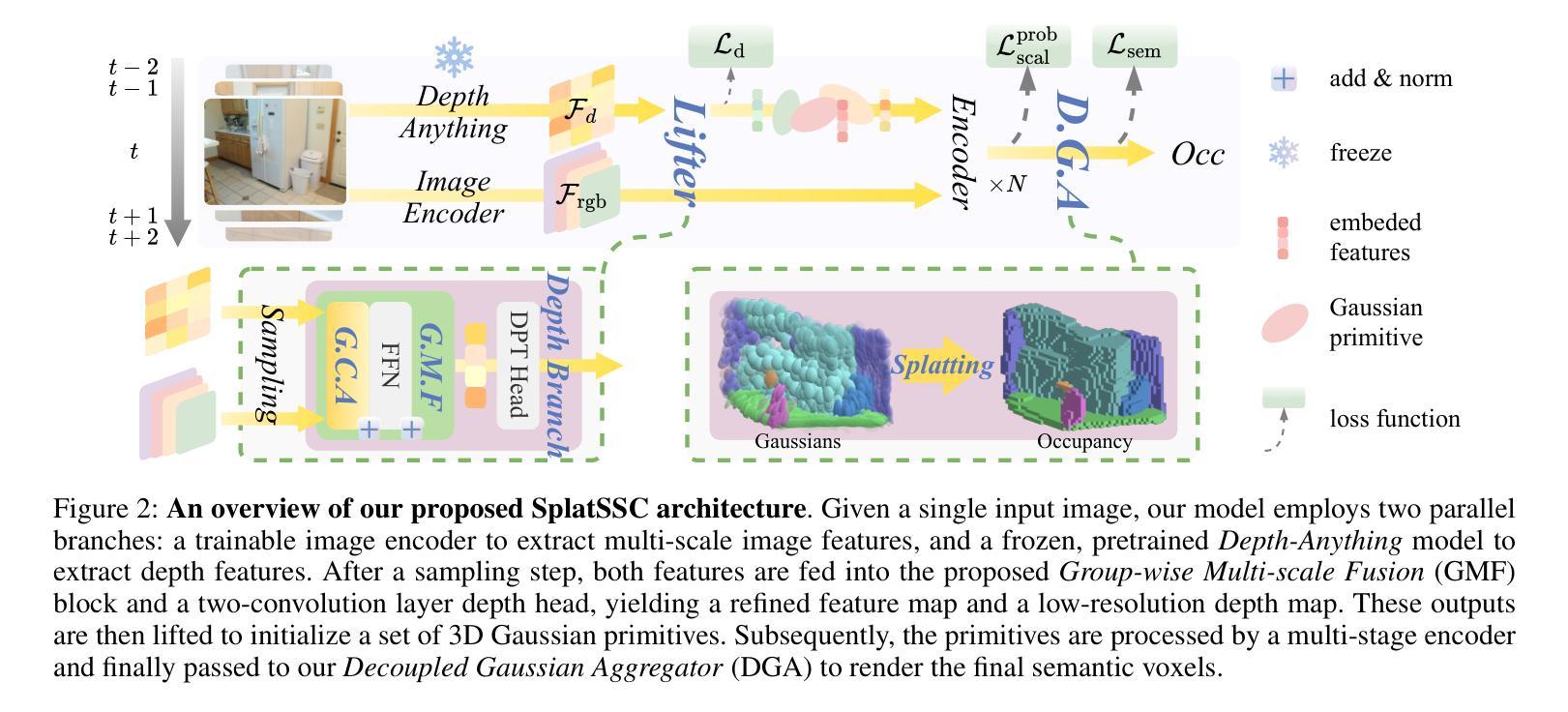
Monocular 3D Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) is a challenging yet promising task that aims to infer dense geometric and semantic descriptions of a scene from a single image. While recent object-centric paradigms significantly improve efficiency by leveraging flexible 3D Gaussian primitives, they still rely heavily on a large number of randomly initialized primitives, which inevitably leads to 1) inefficient primitive initialization and 2) outlier primitives that introduce erroneous artifacts. In this paper, we propose SplatSSC, a novel framework that resolves these limitations with a depth-guided initialization strategy and a principled Gaussian aggregator. Instead of random initialization, SplatSSC utilizes a dedicated depth branch composed of a Group-wise Multi-scale Fusion (GMF) module, which integrates multi-scale image and depth features to generate a sparse yet representative set of initial Gaussian primitives. To mitigate noise from outlier primitives, we develop the Decoupled Gaussian Aggregator (DGA), which enhances robustness by decomposing geometric and semantic predictions during the Gaussian-to-voxel splatting process. Complemented with a specialized Probability Scale Loss, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Occ-ScanNet dataset, outperforming prior approaches by over 6.3% in IoU and 4.1% in mIoU, while reducing both latency and memory consumption by more than 9.3%. The code will be released upon acceptance.
单目3D语义场景补全(SSC)是一项具有挑战性但前景光明的任务,旨在从单张图像中推断场景的密集几何和语义描述。虽然最近的以对象为中心的模式通过利用灵活的3D高斯原始数据显著提高了效率,但它们仍然严重依赖于大量随机初始化的原始数据,这不可避免地导致1)原始数据初始化效率低下和2)异常原始数据引入错误伪影。在本文中,我们提出了SplatSSC,这是一种解决这些限制的新颖框架,采用深度引导初始化策略和有原则的高斯聚合器。SplatSSC不是进行随机初始化,而是利用由组级多尺度融合(GMF)模块组成的专用深度分支,该模块融合多尺度图像和深度特征来生成稀疏但有代表性的初始高斯原始数据集。为了减轻异常原始数据带来的噪声,我们开发了去耦高斯聚合器(DGA),通过在高斯到体素贴图过程中分解几何和语义预测,提高了方法的稳健性。结合专用的概率尺度损失,我们的方法在Occ-ScanNet数据集上实现了最新性能,在IoU和mIoU上分别超越了先前的方法6.3%和4.1%,同时降低了超过9.3%的延迟和内存消耗。代码在接受后将予以发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SplatSSC的新型框架,用于解决单目三维语义场景完成(SSC)任务中遇到的原始初始化效率低下和异常原始引入错误伪影的问题。通过深度引导的初始化和原则性的高斯聚集策略,SplatSSC改善了传统随机初始化方法,实现了高效且准确的场景描述。在Occ-ScanNet数据集上,该方法实现了最先进的性能,提高了交并比(IoU)和平均交并比(mIoU)超过先前的方法,同时降低了延迟和内存消耗。
Key Takeaways
- 单目三维语义场景完成(SSC)旨在从单一图像中推断场景的密集几何和语义描述,是一个具有挑战但前景广阔的任务。
- 现有对象中心范式虽然通过灵活的3D高斯原始提高了效率,但仍存在原始初始化效率低下和异常原始引入错误伪影的问题。
- SplatSSC框架通过深度引导的初始化和原则性的高斯聚集策略解决了这些问题。
- SplatSSC使用专门的深度分支和Group-wise Multi-scale Fusion(GMF)模块生成稀疏但有代表性的初始高斯原始。
- Decoupled Gaussian Aggregator(DGA)的开发减轻了异常原始带来的噪声,通过在高斯到体素溅出过程中分解几何和语义预测增强了稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

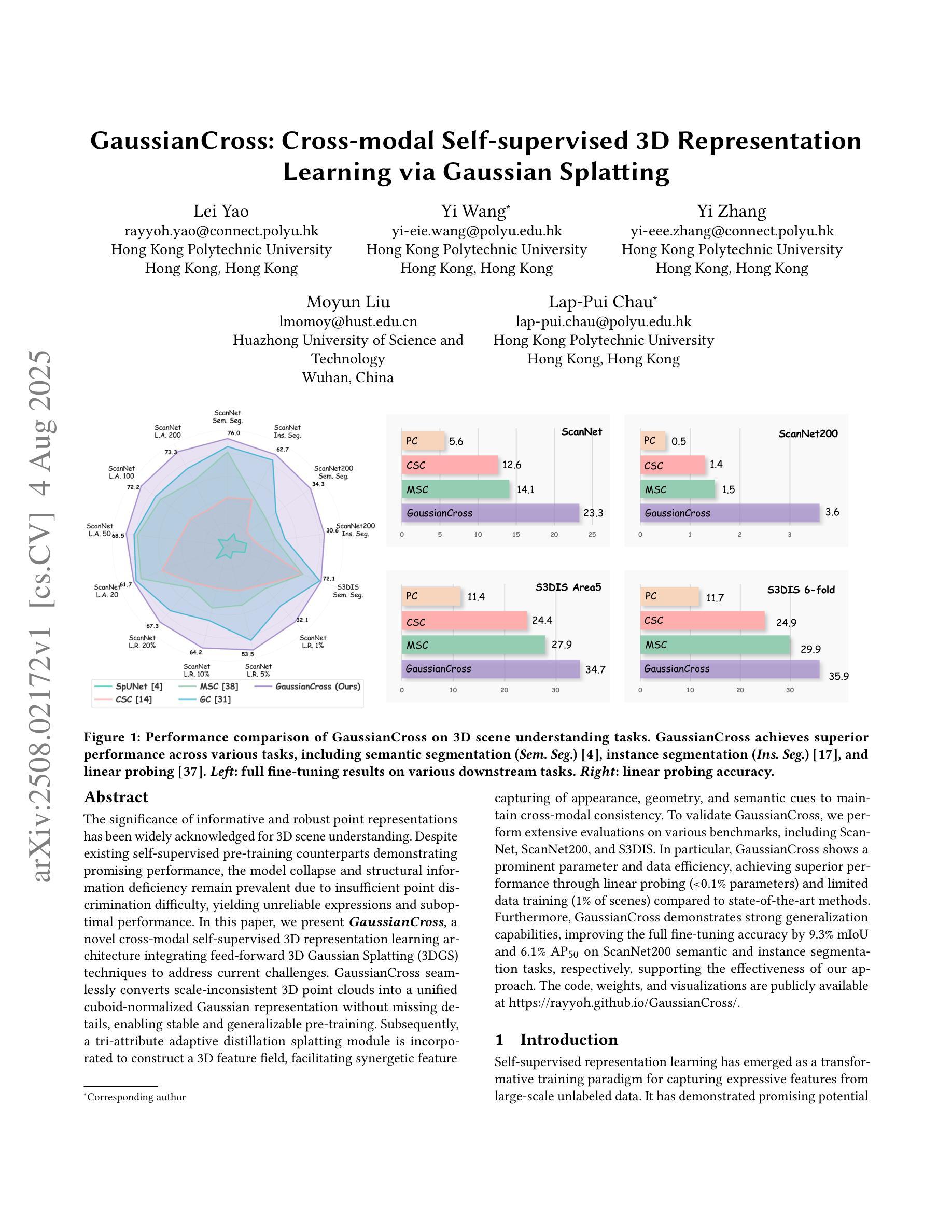
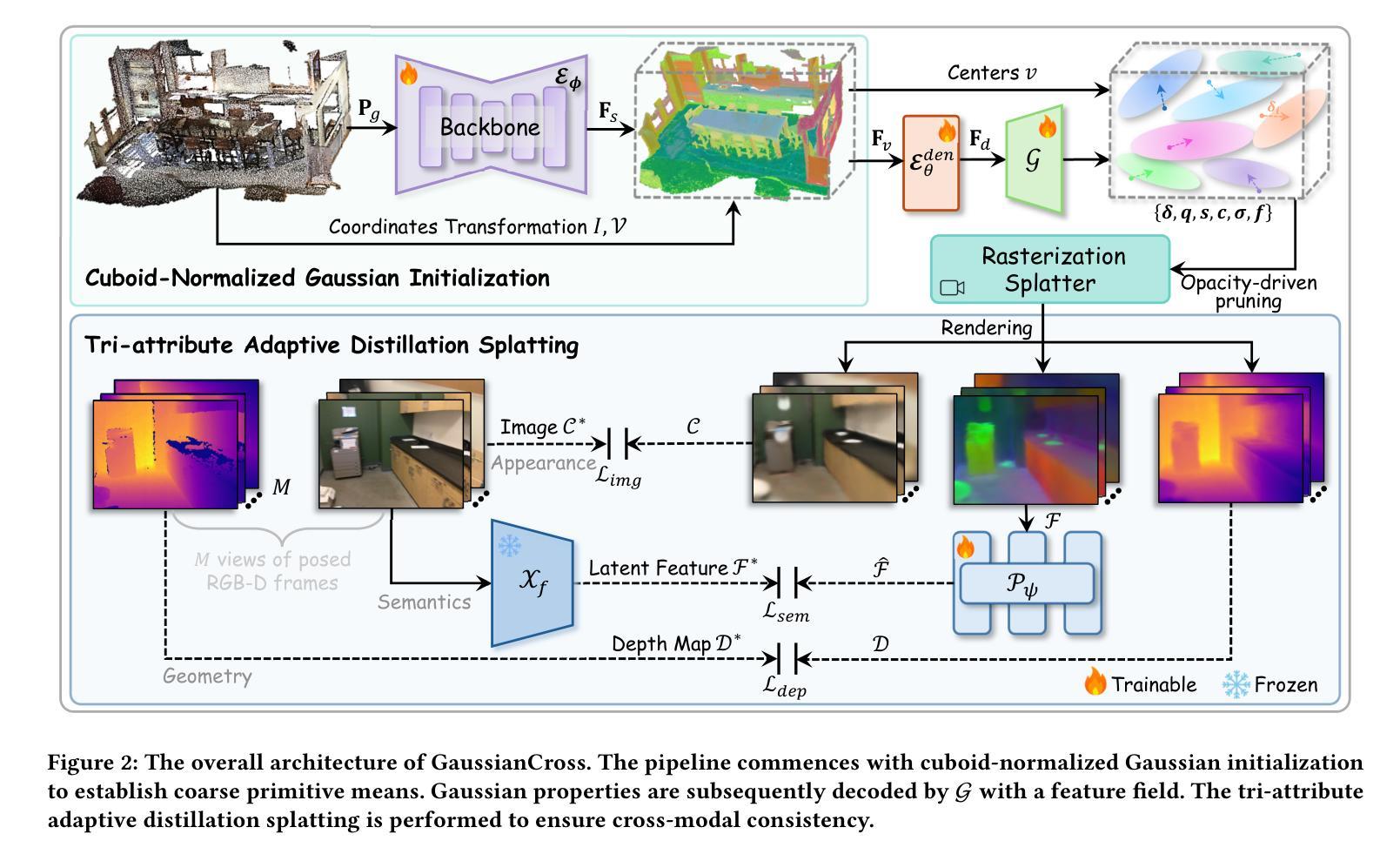
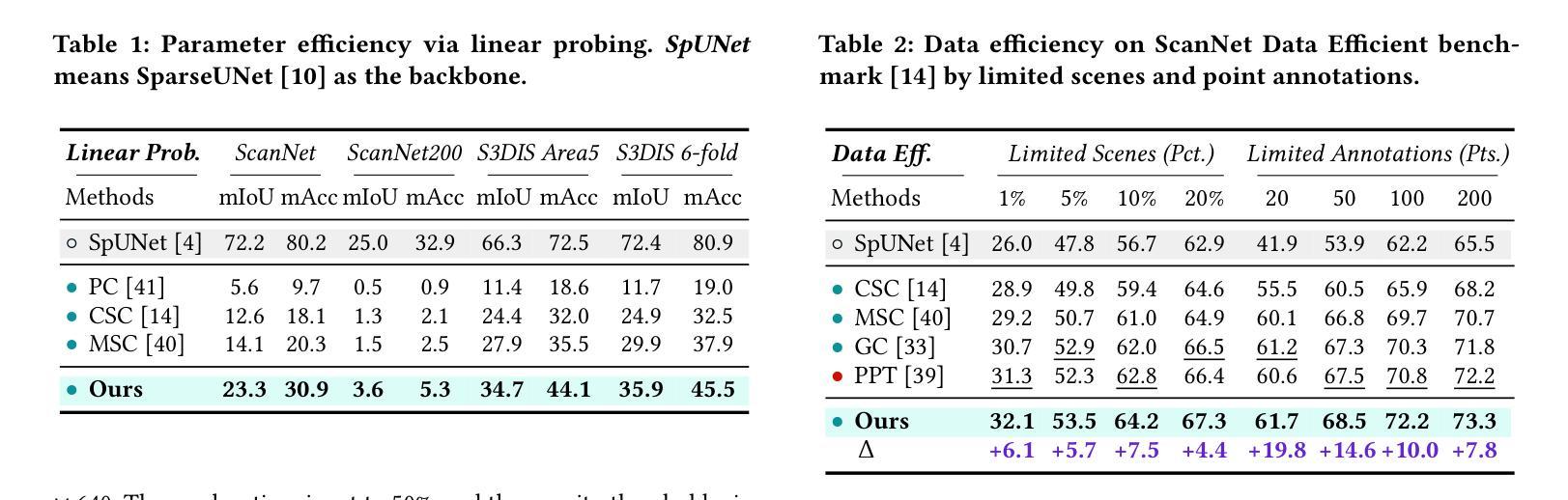
GaussianCross: Cross-modal Self-supervised 3D Representation Learning via Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lei Yao, Yi Wang, Yi Zhang, Moyun Liu, Lap-Pui Chau
The significance of informative and robust point representations has been widely acknowledged for 3D scene understanding. Despite existing self-supervised pre-training counterparts demonstrating promising performance, the model collapse and structural information deficiency remain prevalent due to insufficient point discrimination difficulty, yielding unreliable expressions and suboptimal performance. In this paper, we present GaussianCross, a novel cross-modal self-supervised 3D representation learning architecture integrating feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques to address current challenges. GaussianCross seamlessly converts scale-inconsistent 3D point clouds into a unified cuboid-normalized Gaussian representation without missing details, enabling stable and generalizable pre-training. Subsequently, a tri-attribute adaptive distillation splatting module is incorporated to construct a 3D feature field, facilitating synergetic feature capturing of appearance, geometry, and semantic cues to maintain cross-modal consistency. To validate GaussianCross, we perform extensive evaluations on various benchmarks, including ScanNet, ScanNet200, and S3DIS. In particular, GaussianCross shows a prominent parameter and data efficiency, achieving superior performance through linear probing (<0.1% parameters) and limited data training (1% of scenes) compared to state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, GaussianCross demonstrates strong generalization capabilities, improving the full fine-tuning accuracy by 9.3% mIoU and 6.1% AP$_{50}$ on ScanNet200 semantic and instance segmentation tasks, respectively, supporting the effectiveness of our approach. The code, weights, and visualizations are publicly available at \href{https://rayyoh.github.io/GaussianCross/}{https://rayyoh.github.io/GaussianCross/}.
点云信息的表达和稳健性对于3D场景理解具有重要意义。尽管现有的自监督预训练模型表现出有前景的性能,但由于点云辨别难度不足,模型崩溃和结构信息缺失的问题仍然普遍存在,导致表达不可靠和性能不佳。针对这些挑战,本文提出了GaussianCross,这是一种新型跨模态自监督3D表示学习架构,它集成了前馈3D高斯喷射(3DGS)技术。GaussianCross能够无缝地将尺度不一致的3D点云转换为统一的立方体归一化高斯表示,而不损失任何细节,从而实现稳定和可泛化的预训练。随后,融入了一个三属性自适应蒸馏喷射模块,以构建3D特征场,这有助于协同捕获外观、几何和语义线索的特征,以保持跨模态一致性。为了验证GaussianCross的有效性,我们在各种基准测试集上进行了广泛评估,包括ScanNet、ScanNet200和S3DIS。尤其值得一提的是,GaussianCross在参数和数据效率方面表现出色,通过线性探测(<0.1%的参数)和有限数据训练(1%的场景)实现了卓越的性能,超过了最先进的方法。此外,GaussianCross显示出强大的泛化能力,在ScanNet200的语义和实例分割任务上,全精细调整准确度提高了9.3% mIoU和6.1% AP50,这支持了我们方法的有效性。代码、权重和可视化结果可在[https://rayyoh.github.io/GaussianCross/]公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, accepted by MM’25
Summary
本文提出一种名为GaussianCross的新型跨模态自监督三维表示学习架构,集成前馈三维高斯塑形技术(3DGS),解决现有模型在点云处理中的坍塌和结构信息缺失问题。GaussianCross可将尺度不一致的三维点云转换为统一的立方体归一化高斯表示,同时保留细节,实现稳定和可泛化的预训练。此外,通过引入三属性自适应蒸馏塑形模块构建三维特征场,融合外观、几何和语义线索,保持跨模态一致性。在ScanNet、ScanNet200和S3DIS等多个基准测试上,GaussianCross展现出卓越的性能和参数、数据效率。其强大的泛化能力在ScanNet200语义和实例分割任务上分别提高了9.3% mIoU和6.1% AP50。代码、权重和可视化已公开。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianCross是一种新型跨模态自监督三维表示学习架构,集成3DGS技术解决模型坍塌和信息缺失问题。
- GaussianCross可将尺度不一致的点云转换为统一的高斯表示,实现稳定且可泛化的预训练。
- 三属性自适应蒸馏塑形模块用于构建三维特征场,融合多种线索,保持跨模态一致性。
- GaussianCross在多个基准测试上表现优越,参数和数据效率高。
- GaussianCross在语义和实例分割任务上表现出强大的泛化能力。
- 代码、权重和可视化已公开供公众访问。
点此查看论文截图
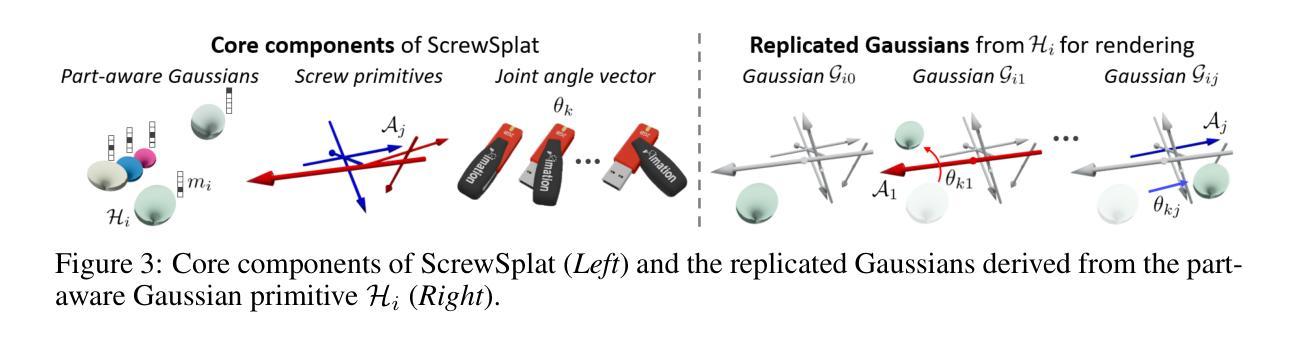
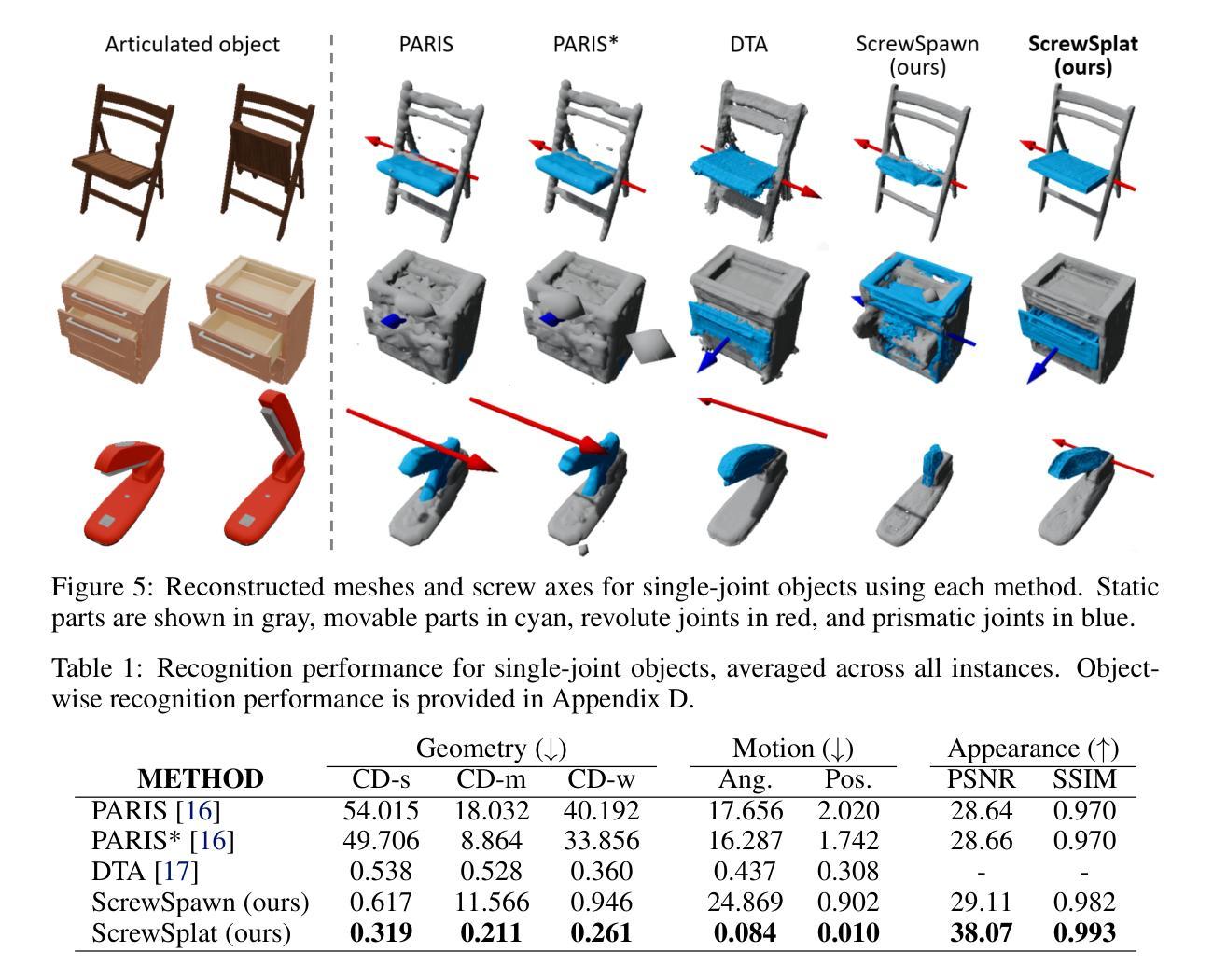
ScrewSplat: An End-to-End Method for Articulated Object Recognition
Authors:Seungyeon Kim, Junsu Ha, Young Hun Kim, Yonghyeon Lee, Frank C. Park
Articulated object recognition – the task of identifying both the geometry and kinematic joints of objects with movable parts – is essential for enabling robots to interact with everyday objects such as doors and laptops. However, existing approaches often rely on strong assumptions, such as a known number of articulated parts; require additional inputs, such as depth images; or involve complex intermediate steps that can introduce potential errors – limiting their practicality in real-world settings. In this paper, we introduce ScrewSplat, a simple end-to-end method that operates solely on RGB observations. Our approach begins by randomly initializing screw axes, which are then iteratively optimized to recover the object’s underlying kinematic structure. By integrating with Gaussian Splatting, we simultaneously reconstruct the 3D geometry and segment the object into rigid, movable parts. We demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art recognition accuracy across a diverse set of articulated objects, and further enables zero-shot, text-guided manipulation using the recovered kinematic model.
关节对象识别——识别具有可动部件的对象的几何形状和运动关节的任务——是实现机器人与门、笔记本电脑等日常对象交互的关键。然而,现有方法通常依赖于强大的假设,例如已知关节部件的数量;需要额外的输入,如深度图像;或涉及可能引入潜在错误的复杂中间步骤——这限制了它们在现实世界的实用性。在本文中,我们介绍了ScrewSplat,这是一种简单的端到端方法,仅使用RGB观察结果。我们的方法通过随机初始化螺杆轴开始,然后对其进行迭代优化,以恢复对象的底层运动学结构。通过与高斯拼贴相结合,我们同时重建了对象的3D几何形状,并将其分割成刚性可移动部件。我们证明我们的方法在多种关节对象上实现了最先进的识别精度,并进一步使用恢复的运动学模型实现了零样本、文本引导的操控。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 12 figures, Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL) 2025
摘要
机器人对带有活动部件的日常物体的互动识别至关重要,包括对物体的几何形状和活动关节的识别。然而,现有的方法往往依赖于强烈的假设,如已知的活动部件数量;需要额外的输入,如深度图像;或者涉及可能引入错误的复杂中间步骤,这在现实世界的实际应用中受到限制。本文介绍了一种名为ScrewSplat的简单端到端方法,它仅使用RGB观察结果进行操作。我们的方法通过随机初始化螺丝轴开始,然后对其进行迭代优化,以恢复物体的底层运动学结构。通过与高斯贴图技术的结合,我们同时重建了物体的三维几何形状,并将物体分割成刚性、可移动的部分。我们证明,我们的方法在多种活动物体上实现了最先进的识别精度,并进一步利用恢复的运动学模型实现了零样本文本指导操作。
要点
- 机器人对日常物体的互动识别非常重要,涉及识别物体的几何形状和活动关节。
- 现有方法存在局限性,如强烈假设、需要额外输入和复杂中间步骤。
- 本文介绍了一种名为ScrewSplat的简洁端到端方法,仅使用RGB观察结果。
- ScrewSplat通过随机初始化螺丝轴并迭代优化,以恢复物体的底层运动学结构。
- 结合高斯贴图技术,ScrewSplat同时重建了三维几何形状并将物体分割成可移动部分。
- ScrewSplat在多种活动物体上实现了最先进的识别精度。
点此查看论文截图

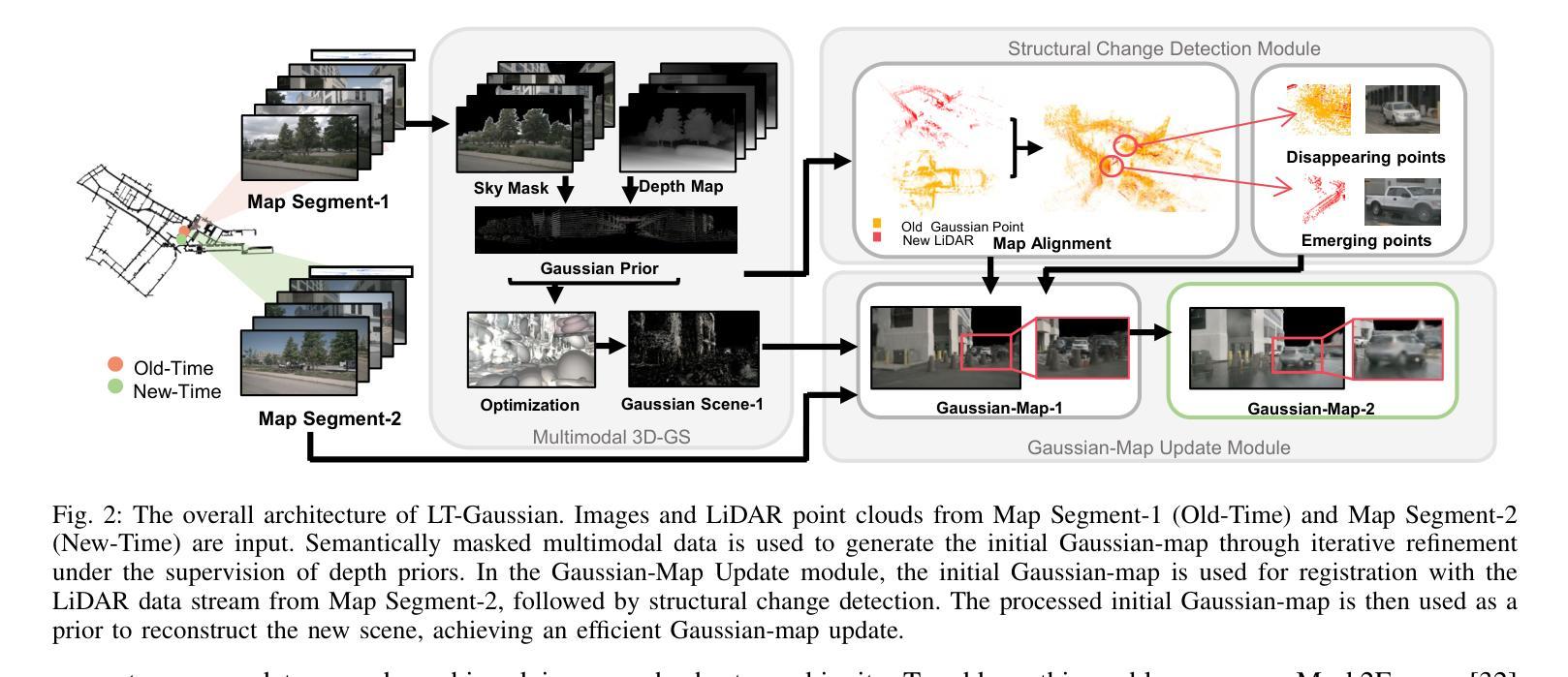
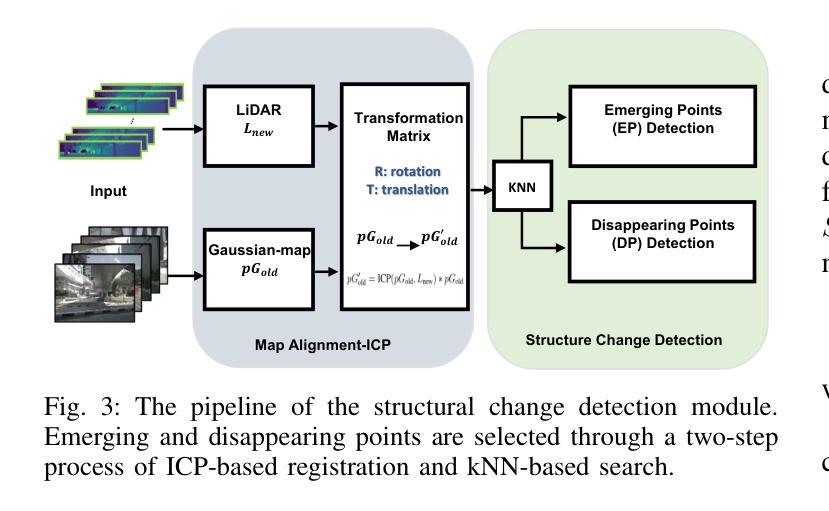
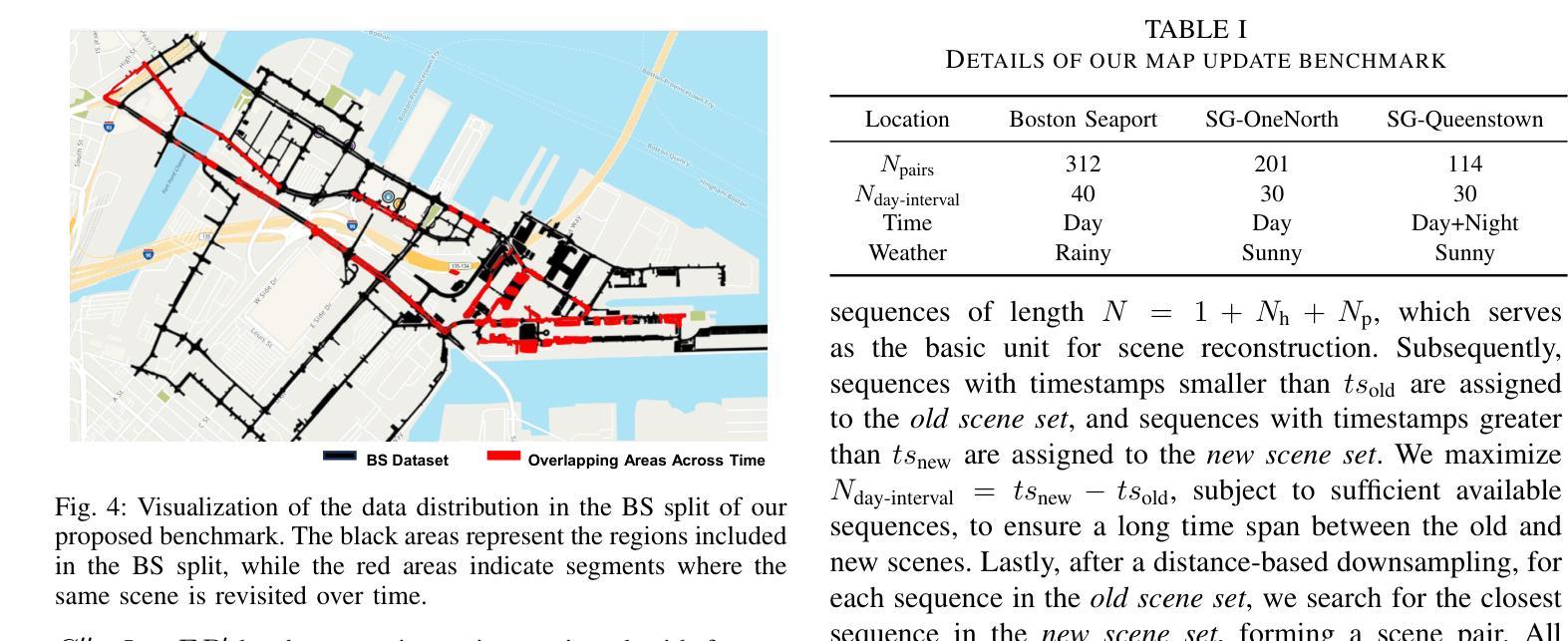
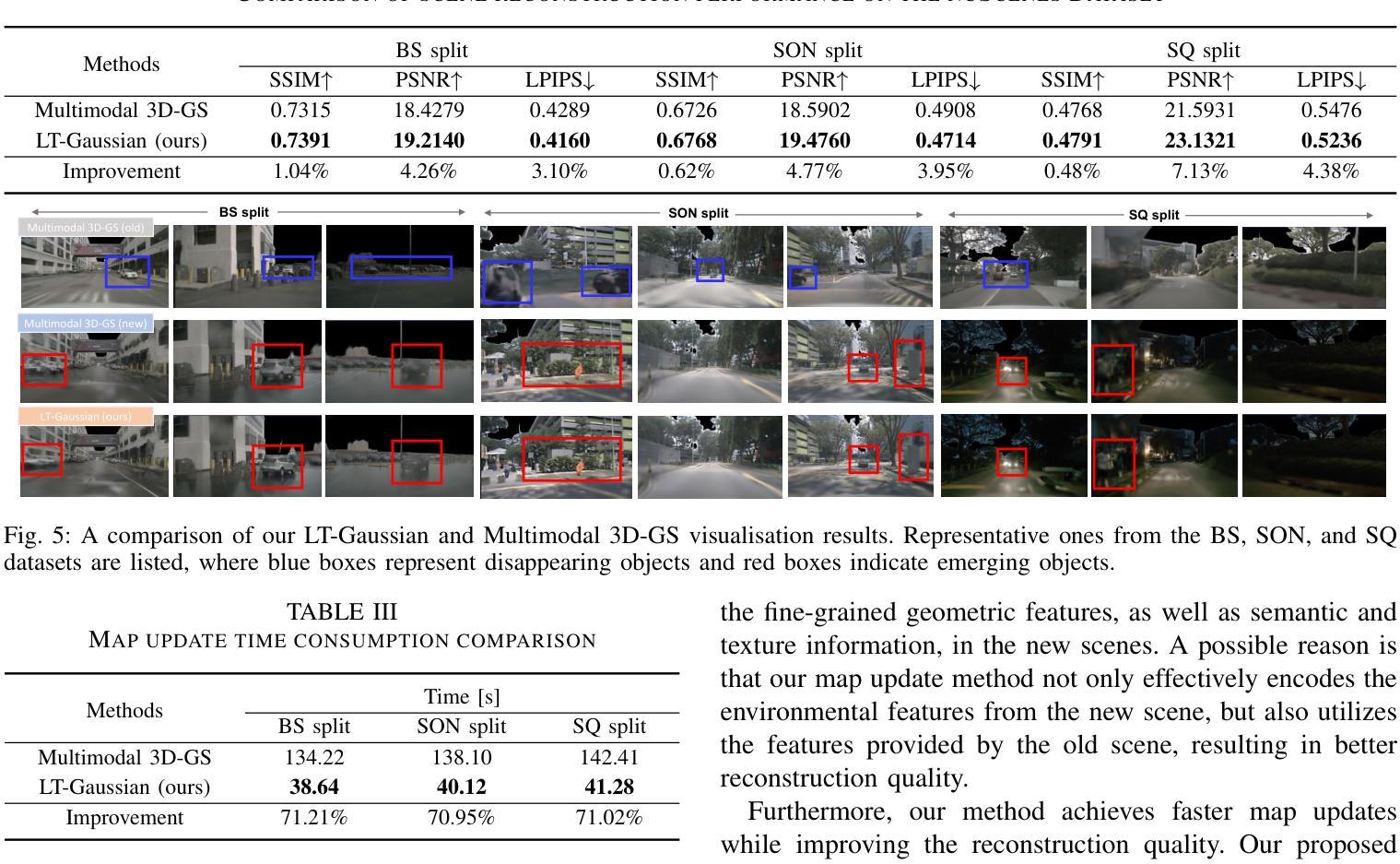
LT-Gaussian: Long-Term Map Update Using 3D Gaussian Splatting for Autonomous Driving
Authors:Luqi Cheng, Zhangshuo Qi, Zijie Zhou, Chao Lu, Guangming Xiong
Maps play an important role in autonomous driving systems. The recently proposed 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) produces rendering-quality explicit scene reconstruction results, demonstrating the potential for map construction in autonomous driving scenarios. However, because of the time and computational costs involved in generating Gaussian scenes, how to update the map becomes a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose LT-Gaussian, a map update method for 3D-GS-based maps. LT-Gaussian consists of three main components: Multimodal Gaussian Splatting, Structural Change Detection Module, and Gaussian-Map Update Module. Firstly, the Gaussian map of the old scene is generated using our proposed Multimodal Gaussian Splatting. Subsequently, during the map update process, we compare the outdated Gaussian map with the current LiDAR data stream to identify structural changes. Finally, we perform targeted updates to the Gaussian-map to generate an up-to-date map. We establish a benchmark for map updating on the nuScenes dataset to quantitatively evaluate our method. The experimental results show that LT-Gaussian can effectively and efficiently update the Gaussian-map, handling common environmental changes in autonomous driving scenarios. Furthermore, by taking full advantage of information from both new and old scenes, LT-Gaussian is able to produce higher quality reconstruction results compared to map update strategies that reconstruct maps from scratch. Our open-source code is available at https://github.com/ChengLuqi/LT-gaussian.
地图在自动驾驶系统中扮演着重要角色。最近提出的3D高斯展布(3D-GS)技术能够产生高质量的渲染效果,展现出在自动驾驶场景构建地图的潜力。然而,由于生成高斯场景所需的时间和计算成本,如何更新地图成为了一大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于3D-GS地图的地图更新方法LT-Gaussian。LT-Gaussian主要包括三个组成部分:多模态高斯展布、结构变化检测模块和高斯地图更新模块。首先,我们使用提出的多模态高斯展布生成旧场景的高斯地图。随后,在地图更新过程中,我们将过时的高斯地图与当前的激光雷达数据流进行比较,以识别结构变化。最后,我们对高斯地图进行有针对性的更新,以生成最新的地图。我们在nuScenes数据集上建立了地图更新的基准测试,以定量评估我们的方法。实验结果表明,LT-Gaussian能够有效且高效地更新高斯地图,处理自动驾驶场景中常见的环境变化。此外,通过充分利用新旧场景的信息,LT-Gaussian能够产生比那些从头开始重建的地图更新策略更高质量的重建结果。我们的开源代码可在https://github.com/ChengLuqi/LT-gaussian找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IV 2025
Summary
基于三维高斯映射的地图更新方法对于自动驾驶系统至关重要。本文提出的LT-Gaussian算法针对地图更新提供了新的解决方案。通过引入三个核心组件,包括多模态高斯拼贴、结构变化检测模块和高斯地图更新模块,LT-Gaussian能够高效且有效地更新高斯地图,并处理自动驾驶场景中的常见环境变化。此外,该算法利用新旧场景的信息优势,生成高质量的重建结果。
Key Takeaways
- LT-Gaussian针对基于三维高斯映射的地图更新提出了一种新的解决方案。
- LT-Gaussian包含三个核心组件:多模态高斯拼贴、结构变化检测模块和高斯地图更新模块。
- 多模态高斯拼贴被用来生成旧的场景的高斯地图。
- 在地图更新过程中,通过与当前激光雷达数据流的对比,检测结构变化。
- 针对变化部分进行的高斯地图更新能够生成更新的地图。
- 在nuScenes数据集上建立的地图更新基准测试证明LT-Gaussian能有效且高效地更新高斯地图。
点此查看论文截图

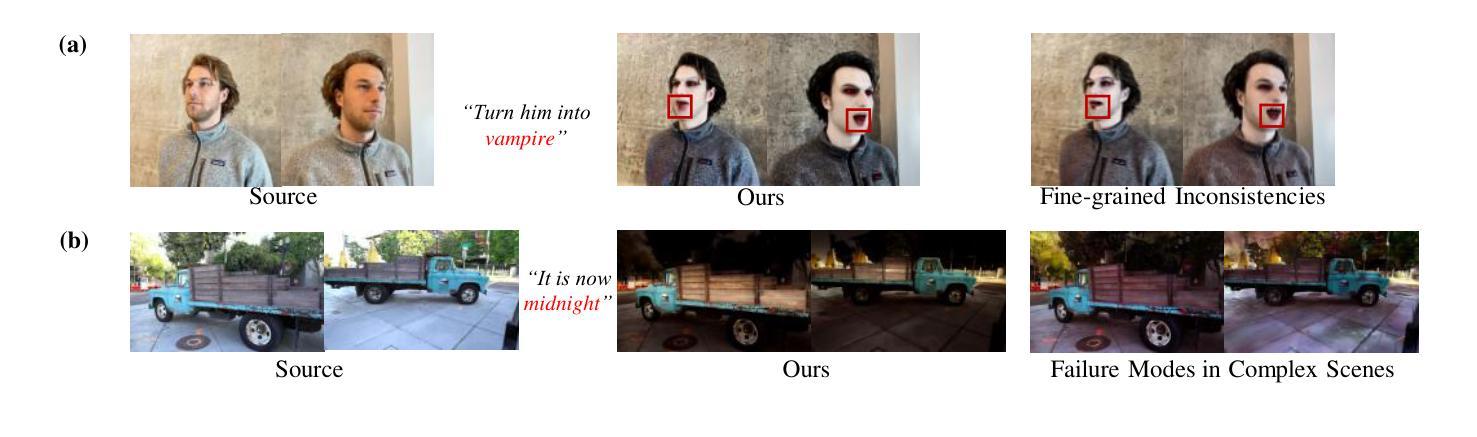
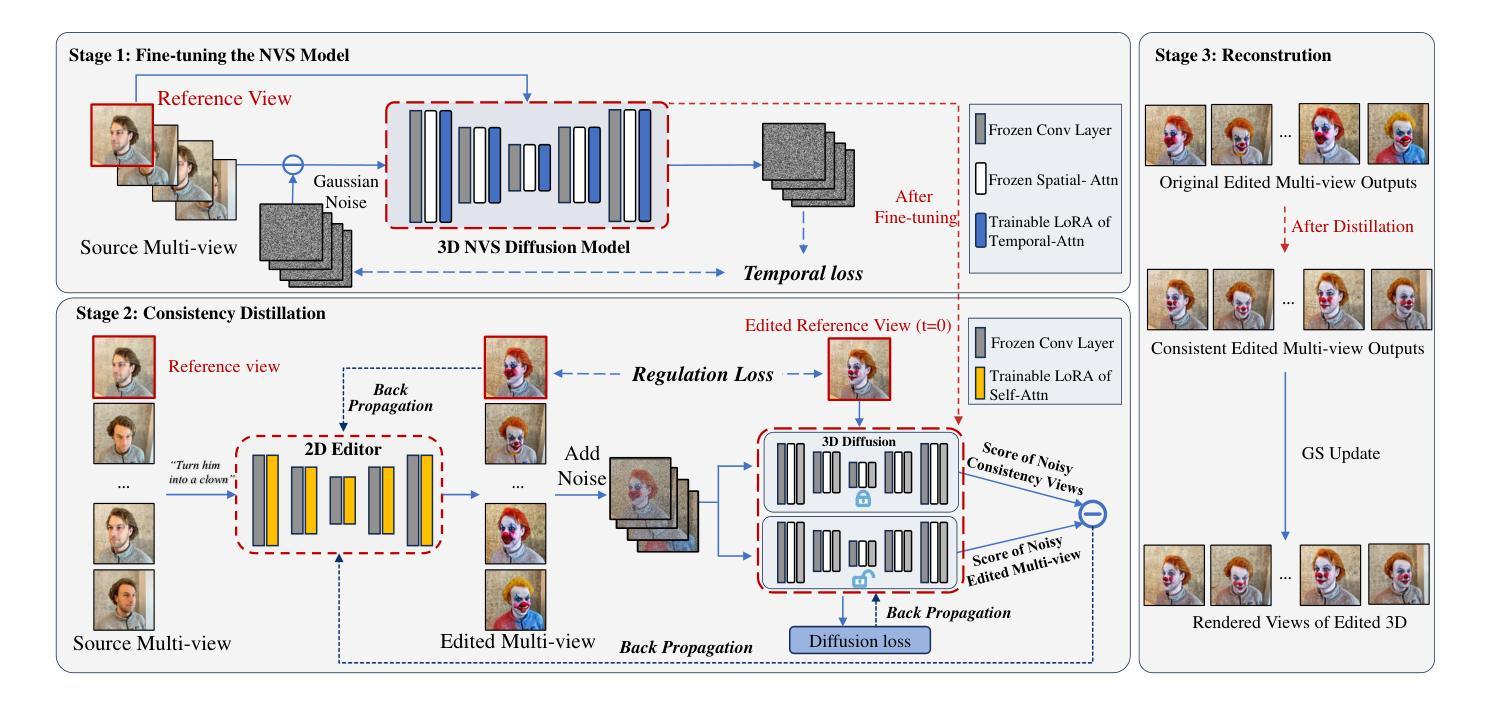
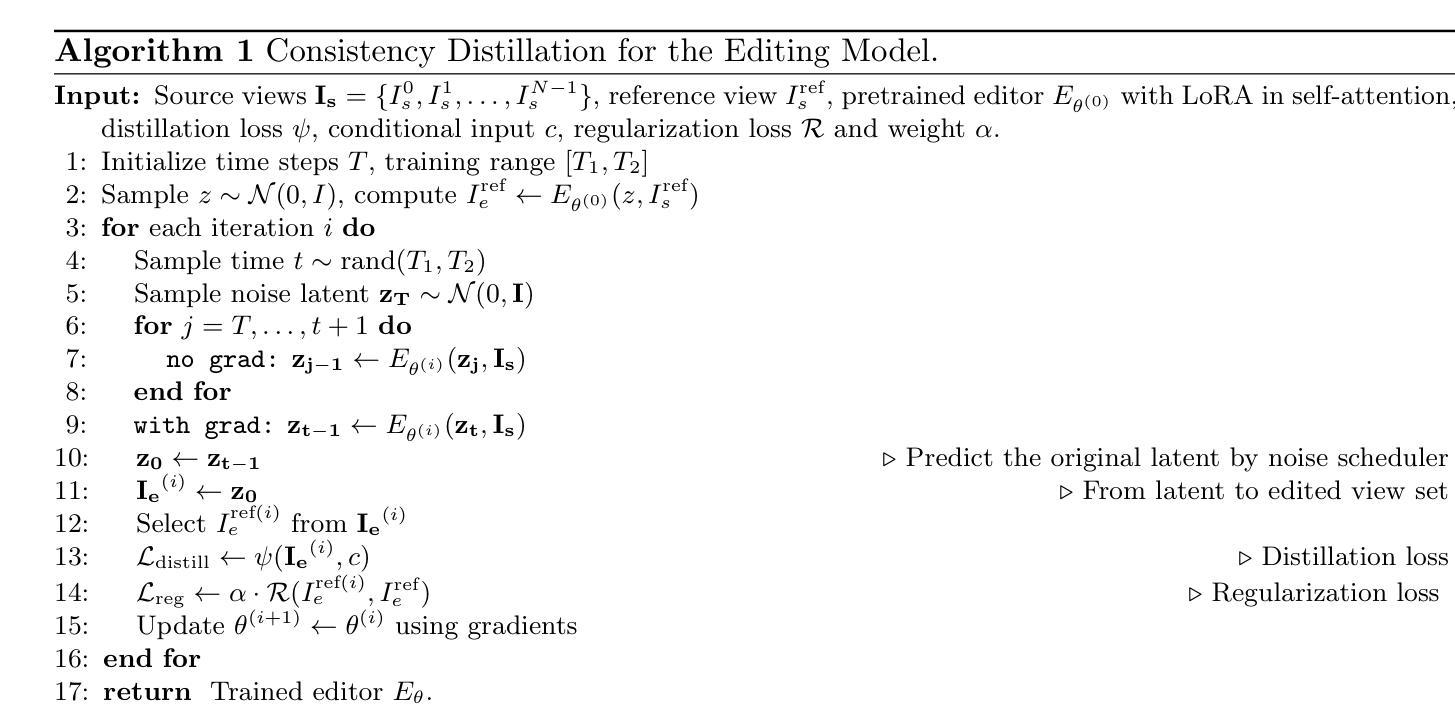
DisCo3D: Distilling Multi-View Consistency for 3D Scene Editing
Authors:Yufeng Chi, Huimin Ma, Kafeng Wang, Jianmin Li
While diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable progress in 2D image generation and editing, extending these capabilities to 3D editing remains challenging, particularly in maintaining multi-view consistency. Classical approaches typically update 3D representations through iterative refinement based on a single editing view. However, these methods often suffer from slow convergence and blurry artifacts caused by cross-view inconsistencies. Recent methods improve efficiency by propagating 2D editing attention features, yet still exhibit fine-grained inconsistencies and failure modes in complex scenes due to insufficient constraints. To address this, we propose \textbf{DisCo3D}, a novel framework that distills 3D consistency priors into a 2D editor. Our method first fine-tunes a 3D generator using multi-view inputs for scene adaptation, then trains a 2D editor through consistency distillation. The edited multi-view outputs are finally optimized into 3D representations via Gaussian Splatting. Experimental results show DisCo3D achieves stable multi-view consistency and outperforms state-of-the-art methods in editing quality.
虽然扩散模型在二维图像生成和编辑方面取得了显著的进步,但将其能力扩展到三维编辑仍然具有挑战性,特别是在保持多视图一致性方面。传统的方法通常基于单个编辑视图通过迭代优化来更新三维表示。然而,这些方法通常遭受慢收敛和由跨视图不一致导致的模糊伪影的困扰。最近的方法通过传播二维编辑注意力特征来提高效率,但由于约束不足,在复杂场景中仍然存在细微的不一致性和失败模式。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了DisCo3D这一新颖框架,它将三维一致性先验知识蒸馏到二维编辑器中。我们的方法首先使用多视图输入对三维生成器进行微调,以适应场景,然后通过一致性蒸馏训练二维编辑器。最后,将编辑后的多视图输出通过高斯平铺优化为三维表示。实验结果表明,DisCo3D实现了稳定的多视图一致性,并在编辑质量方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文介绍了将扩散模型应用于3D编辑的挑战,尤其是保持多视角一致性方面。为解决此问题,提出了一种新型框架DisCo3D,它通过蒸馏3D一致性先验知识到2D编辑器中,通过微调3D生成器并使用多视角输入进行场景适应,然后训练2D编辑器进行一致性蒸馏。编辑后的多视角输出通过高斯投影优化为3D表示。实验结果表明,DisCo3D实现了稳定的多视角一致性,并在编辑质量方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在3D编辑中面临多视角一致性维持的挑战。
- 现有方法通过单一编辑视角的迭代优化来更新3D表示,但存在速度慢、易出现模糊伪影的问题。
- 最近的方法通过传播2D编辑注意力特征提高了效率,但仍存在细微不一致性以及在复杂场景中的失败模式。
- DisCo3D框架通过蒸馏3D一致性先验知识到2D编辑器中来解决这些问题。
- DisCo3D首先通过多视角输入微调3D生成器进行场景适应。
- 然后训练2D编辑器进行一致性蒸馏,编辑后的多视角输出通过高斯投影优化为3D表示。
点此查看论文截图

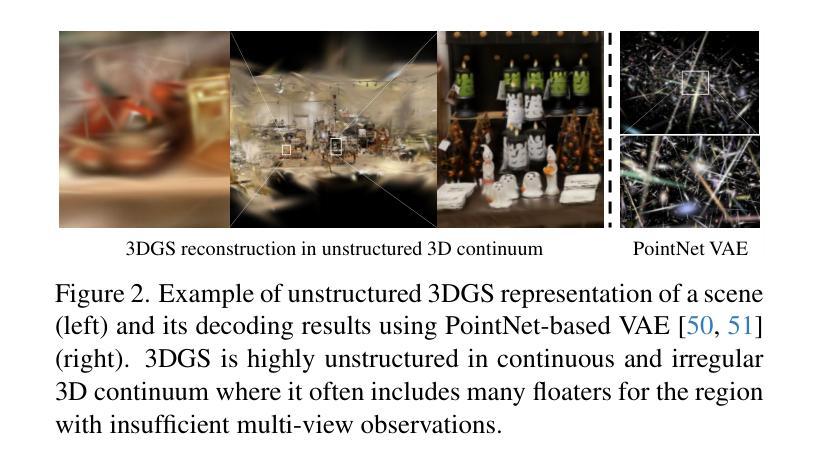
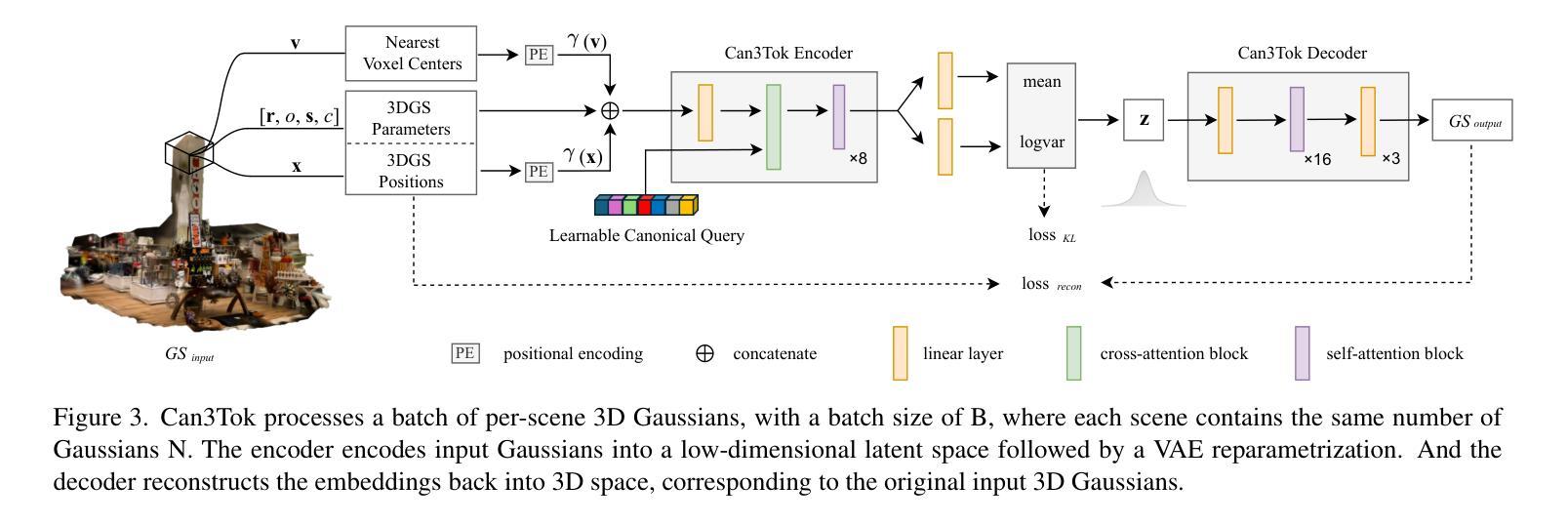
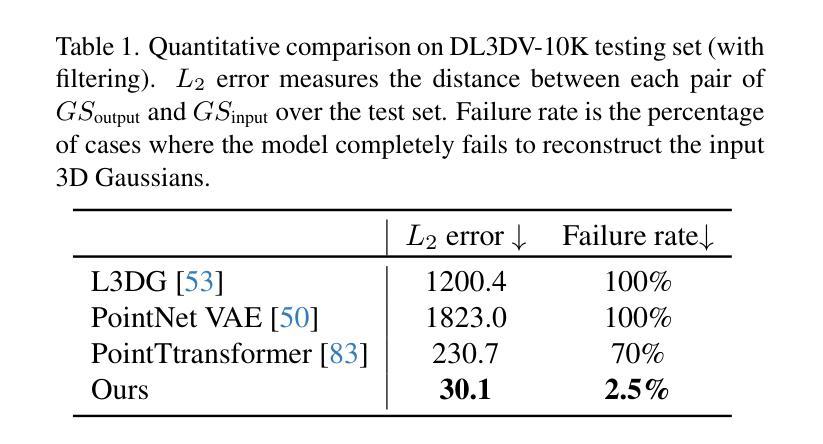
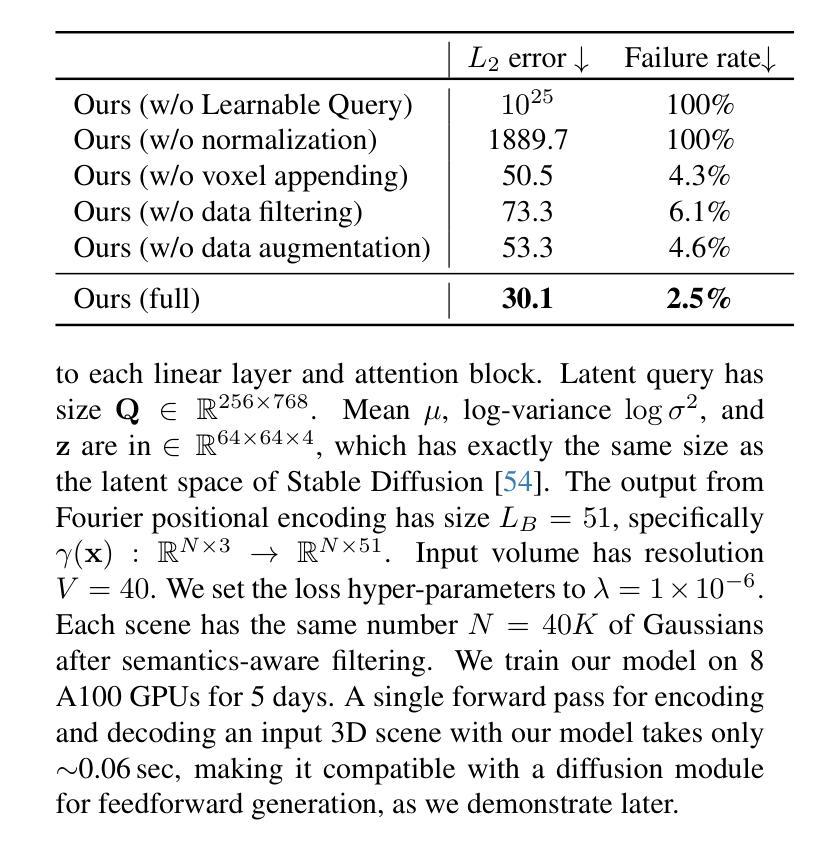
Can3Tok: Canonical 3D Tokenization and Latent Modeling of Scene-Level 3D Gaussians
Authors:Quankai Gao, Iliyan Georgiev, Tuanfeng Y. Wang, Krishna Kumar Singh, Ulrich Neumann, Jae Shin Yoon
3D generation has made significant progress, however, it still largely remains at the object-level. Feedforward 3D scene-level generation has been rarely explored due to the lack of models capable of scaling-up latent representation learning on 3D scene-level data. Unlike object-level generative models, which are trained on well-labeled 3D data in a bounded canonical space, scene-level generations with 3D scenes represented by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) are unbounded and exhibit scale inconsistency across different scenes, making unified latent representation learning for generative purposes extremely challenging. In this paper, we introduce Can3Tok, the first 3D scene-level variational autoencoder (VAE) capable of encoding a large number of Gaussian primitives into a low-dimensional latent embedding, which effectively captures both semantic and spatial information of the inputs. Beyond model design, we propose a general pipeline for 3D scene data processing to address scale inconsistency issue. We validate our method on the recent scene-level 3D dataset DL3DV-10K, where we found that only Can3Tok successfully generalizes to novel 3D scenes, while compared methods fail to converge on even a few hundred scene inputs during training and exhibit zero generalization ability during inference. Finally, we demonstrate image-to-3DGS and text-to-3DGS generation as our applications to demonstrate its ability to facilitate downstream generation tasks.
虽然三维生成技术已经取得了显著进展,但它仍然主要停留在对象级别。由于缺乏能够在三维场景级别数据上扩展潜在表示学习的模型,前馈三维场景级别生成的研究很少。与在有限规范空间中训练的对象级生成模型不同,以三维高斯贴图(3DGS)表示的三维场景的场景级生成是无界的,并且在不同场景之间表现出尺度不一致性,这使得用于生成目的的统一潜在表示学习极具挑战性。在本文中,我们介绍了Can3Tok,这是一款首款能够在大规模的三维场景级别上使用变分自编码器(VAE)编码大量高斯原语到一个低维度潜在嵌入物的三维场景级模型。它能有效地捕获输入数据的语义和空间信息。除了模型设计之外,我们还提出了针对三维场景数据处理的一般流程来解决尺度不一致的问题。我们在最新的场景级三维数据集DL3DV-10K上验证了我们的方法,发现只有Can3Tok能够成功推广到新的三维场景,而相比之下其他方法甚至在数百个场景输入的训练过程中无法收敛,并且在推理过程中没有泛化能力。最后,我们展示了图像到3DGS和文本到3DGS的应用来展示它促进下游生成任务的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Can3Tok模型,这是一种针对三维场景数据的场景级变分自编码器(VAE)。该模型能够编码大量的高斯基本体到一个低维度的潜在嵌入空间,有效捕捉输入的场景语义和空间信息。此外,为了解决规模不一致性问题,还提出了针对三维场景数据处理的通用流程。相较于其他方法,Can3Tok成功推广到新型三维场景,并在DL3DV-10K数据集上验证了其有效性。最后,展示了图像到三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)和文字到三维高斯喷溅的生成应用。
Key Takeaways
- 3D generation目前主要停留在物体级别,场景级别的生成研究较少。
- 缺乏能够在三维场景级别数据上进行规模化潜在表示学习的模型是主要原因。
- Can3Tok是首个针对三维场景数据的场景级变分自编码器(VAE)。
- Can3Tok模型能将大量高斯基本体编码进低维潜在嵌入空间,捕捉场景的语义和空间信息。
- 提出了一种针对三维场景数据处理的通用流程来解决规模不一致性问题。
- 在DL3DV-10K数据集上验证了Can3Tok的有效性,相比其他方法具有更好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


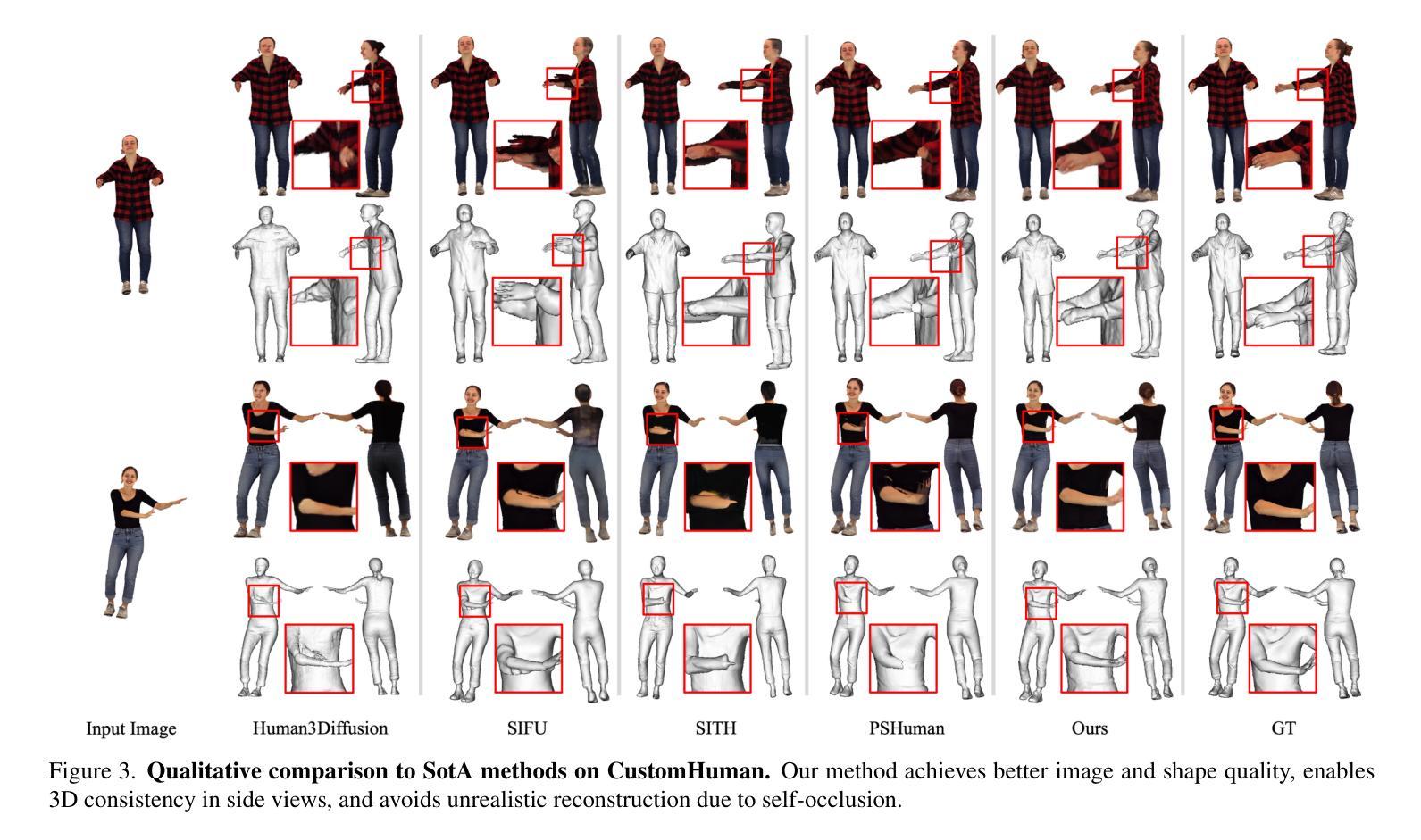
MoGA: 3D Generative Avatar Prior for Monocular Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction
Authors:Zijian Dong, Longteng Duan, Jie Song, Michael J. Black, Andreas Geiger
We present MoGA, a novel method to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D Gaussian avatars from a single-view image. The main challenge lies in inferring unseen appearance and geometric details while ensuring 3D consistency and realism. Most previous methods rely on 2D diffusion models to synthesize unseen views; however, these generated views are sparse and inconsistent, resulting in unrealistic 3D artifacts and blurred appearance. To address these limitations, we leverage a generative avatar model, that can generate diverse 3D avatars by sampling deformed Gaussians from a learned prior distribution. Due to limited 3D training data, such a 3D model alone cannot capture all image details of unseen identities. Consequently, we integrate it as a prior, ensuring 3D consistency by projecting input images into its latent space and enforcing additional 3D appearance and geometric constraints. Our novel approach formulates Gaussian avatar creation as model inversion by fitting the generative avatar to synthetic views from 2D diffusion models. The generative avatar provides an initialization for model fitting, enforces 3D regularization, and helps in refining pose. Experiments show that our method surpasses state-of-the-art techniques and generalizes well to real-world scenarios. Our Gaussian avatars are also inherently animatable. For code, see https:// zj-dong.github.io/ MoGA/.
我们提出了MoGA这一新方法,它能够从单视图图像重建出高保真度的三维高斯头像。主要挑战在于在保障三维一致性和真实感的同时推断出看不见的外观和几何细节。过去的大多数方法都依赖于二维扩散模型来合成看不见的视图,然而这些生成的视图稀疏且不一致,导致三维人工制品不真实和外观模糊。为了解决这些局限,我们利用生成头像模型,通过从学习到的先验分布中采样变形的高斯函数来生成多样化的三维头像。由于三维训练数据有限,仅使用这样的三维模型无法捕获未见过身份的所有图像细节。因此,我们将其整合为先验,通过将输入图像投影到其潜在空间并施加额外的三维外观和几何约束来确保三维一致性。我们的新方法将高斯头像创建公式化为模型反演,通过将生成的头像拟合到二维扩散模型的合成视图来实现。生成的头像为模型拟合提供了初始化,强制实施三维正则化,并有助于细化姿态。实验表明,我们的方法超越了最先进的技术并在现实世界场景中具有良好的通用性。我们的高斯头像本质上是可动画的。有关代码,请参见:[https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 (Highlight), Project Page: https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/
Summary
提出了一种名为MoGA的新方法,可从单视图图像重建高保真3D高斯化身。该方法主要挑战在于推断出未见的外观和几何细节,同时确保3D一致性和逼真性。与大多数先前方法不同,MoGA采用生成化身模型,通过从学习到的先验分布中采样变形高斯来生成多样化的3D化身。通过将生成化身模型作为先验,并将输入图像投影到其潜在空间并施加额外的3D外观和几何约束来确保3D一致性。MoGA将高斯化身创建公式化为模型反演问题,通过将生成化身拟合到来自2D扩散模型的合成视图来实现。实验表明,该方法优于最新技术并在真实场景中具有良好泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- MoGA是一种从单视图图像重建高保真3D高斯化身的新方法。
- 该方法主要解决如何推断未见的外观和几何细节,并确保3D一致性和逼真性。
- MoGA采用生成化身模型,通过采样变形高斯来生成多样化的3D化身。
- 为了确保3D一致性,将生成化身模型作为先验,并施加额外的约束。
- MoGA通过将生成化身拟合到来自2D扩散模型的合成视图来实现模型反演。
- 实验证明MoGA优于现有技术,并在真实场景中具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

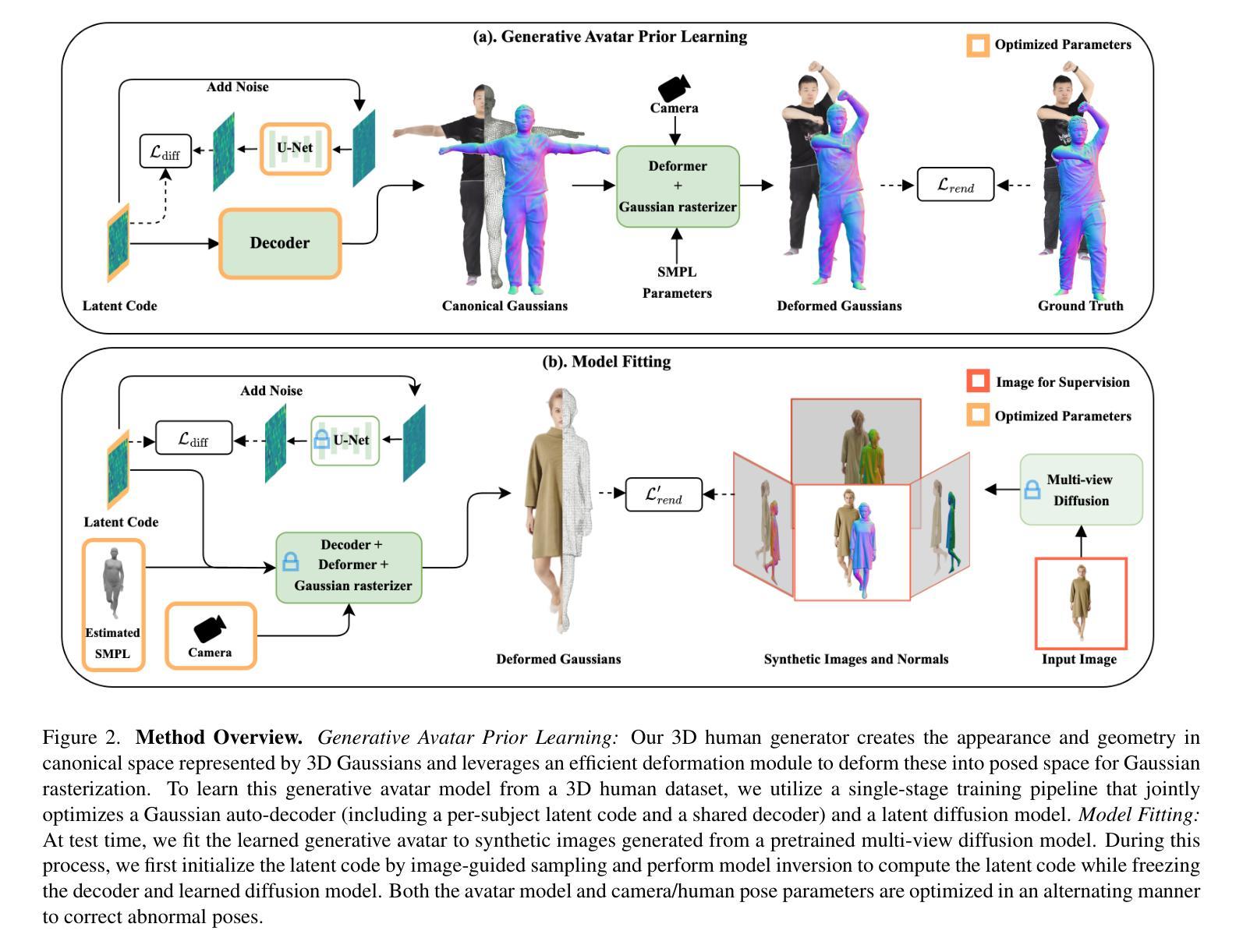

GSCache: Real-Time Radiance Caching for Volume Path Tracing using 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:David Bauer, Qi Wu, Hamid Gadirov, Kwan-Liu Ma
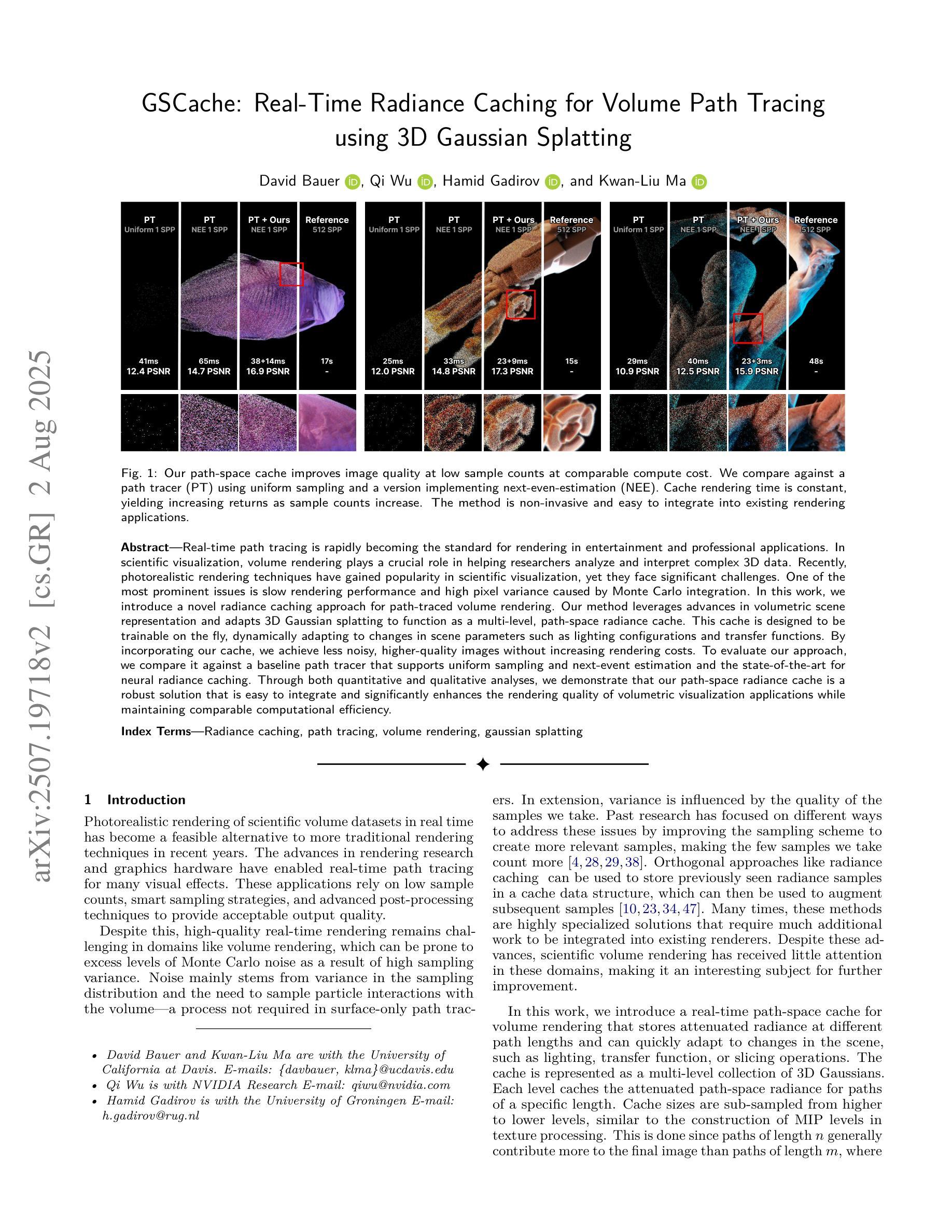
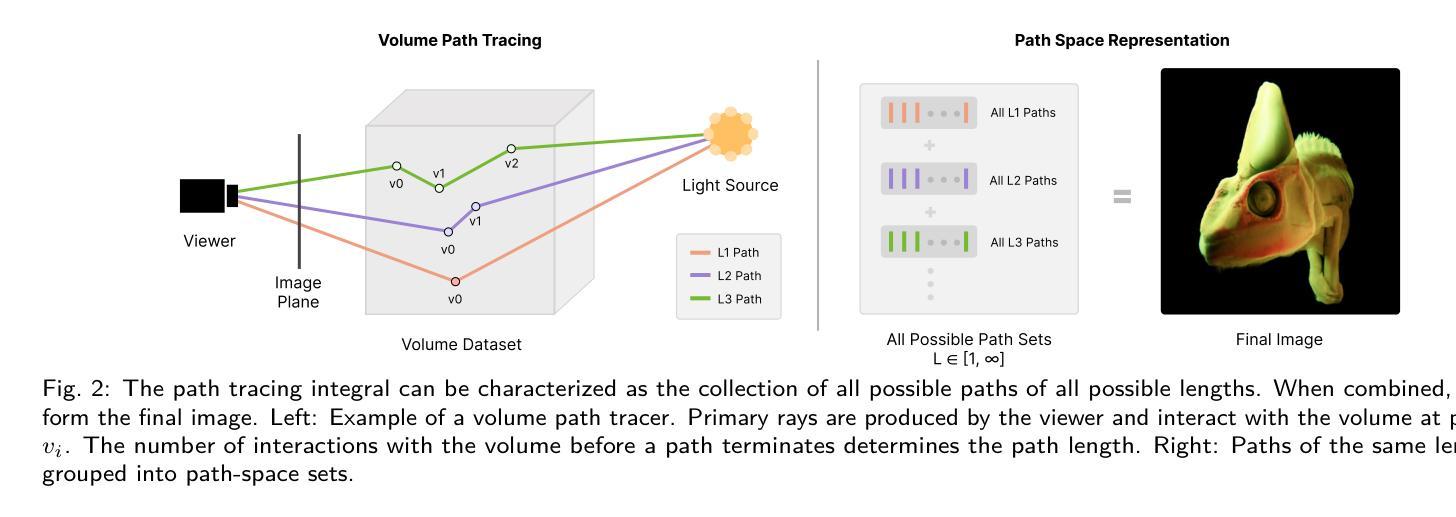
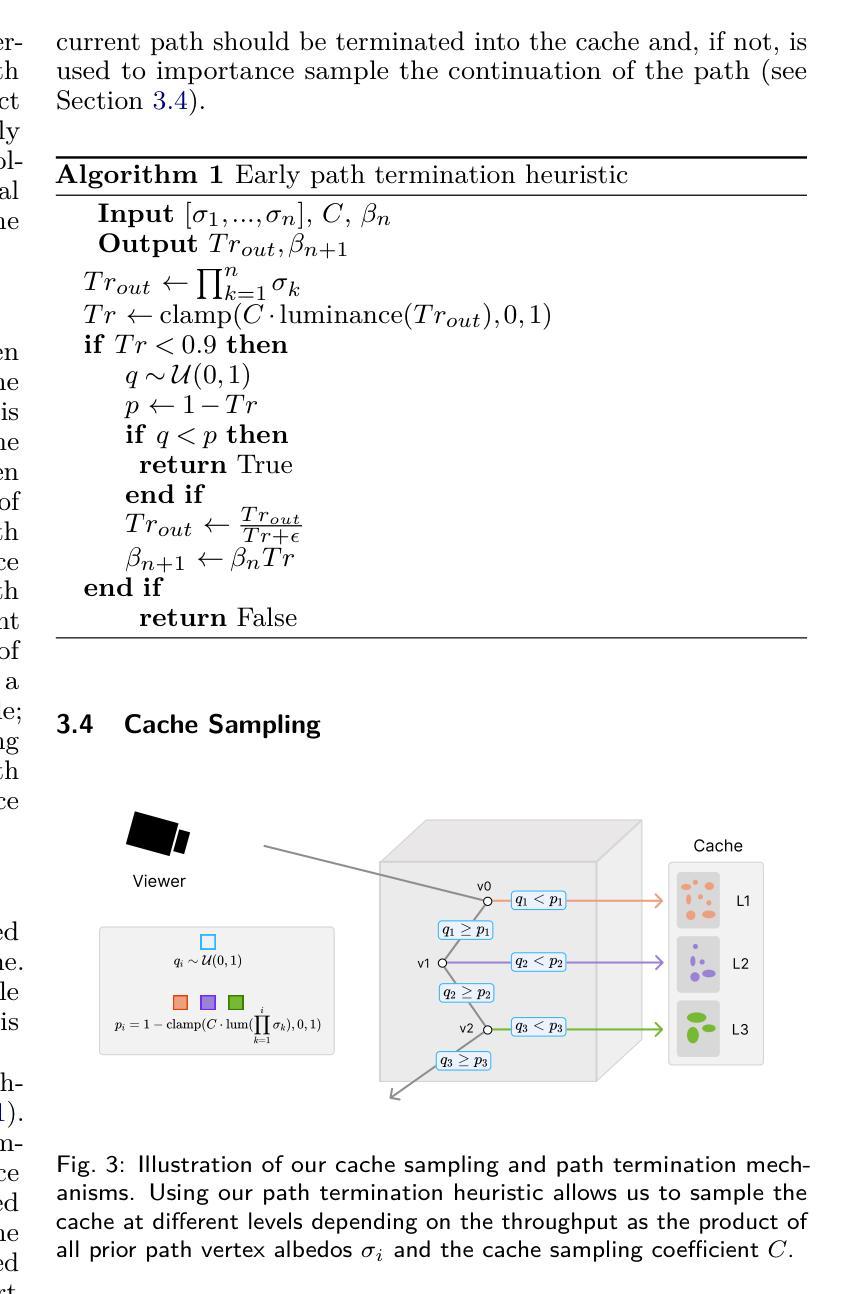
Real-time path tracing is rapidly becoming the standard for rendering in entertainment and professional applications. In scientific visualization, volume rendering plays a crucial role in helping researchers analyze and interpret complex 3D data. Recently, photorealistic rendering techniques have gained popularity in scientific visualization, yet they face significant challenges. One of the most prominent issues is slow rendering performance and high pixel variance caused by Monte Carlo integration. In this work, we introduce a novel radiance caching approach for path-traced volume rendering. Our method leverages advances in volumetric scene representation and adapts 3D Gaussian splatting to function as a multi-level, path-space radiance cache. This cache is designed to be trainable on the fly, dynamically adapting to changes in scene parameters such as lighting configurations and transfer functions. By incorporating our cache, we achieve less noisy, higher-quality images without increasing rendering costs. To evaluate our approach, we compare it against a baseline path tracer that supports uniform sampling and next-event estimation and the state-of-the-art for neural radiance caching. Through both quantitative and qualitative analyses, we demonstrate that our path-space radiance cache is a robust solution that is easy to integrate and significantly enhances the rendering quality of volumetric visualization applications while maintaining comparable computational efficiency.
实时路径追踪正在迅速成为娱乐和专业应用渲染的标准。在科学可视化中,体渲染在研究分析复杂三维数据时扮演着至关重要的角色。近年来,虽然写实渲染技术在科学可视化中越来越受欢迎,但它们面临着巨大的挑战。最突出的问题之一是Monte Carlo积分导致的渲染性能缓慢和高像素方差。在这项工作中,我们为路径追踪体积渲染引入了一种新型辐射缓存方法。我们的方法利用体积场景表示的进展,并适应三维高斯溅射作为多级路径空间辐射缓存。该缓存被设计为可即时训练,动态适应场景参数的变化,如照明配置和传输函数。通过采用我们的缓存,我们可以在不增加渲染成本的情况下实现噪声更少、质量更高的图像。为了评估我们的方法,我们将它与支持均匀采样和下一个事件估计的基本路径追踪器以及最新的神经辐射缓存技术进行了比较。通过定量和定性分析,我们证明我们的路径空间辐射缓存是一种稳健的解决方案,易于集成,在保持相当的计算效率的同时,显著提高了体积可视化应用的渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
实时路径追踪正在迅速成为娱乐和专业应用中渲染的标准。在科学可视化中,体积渲染扮演着帮助研究人员分析和解释复杂3D数据的重要角色。尽管最近光栅化渲染技术在科学可视化中受到欢迎,但它们面临着巨大的挑战。其中最突出的问题是渲染性能缓慢和由蒙特卡洛积分引起的高像素方差。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的辐射缓存路径追踪体积渲染方法。我们的方法利用了体积场景表示的进展,并将三维高斯涂抹技术适应于作为多层次路径空间辐射缓存工作。该缓存设计能够在飞行时进行训练,动态适应场景参数的变化,如照明配置和传输功能。通过结合我们的缓存,我们可以在不增加渲染成本的情况下实现更少的噪声和更高质量的图像。我们通过将其与基线路径追踪器和支持均匀采样和下一个事件估计的最先进技术进行比较,来评估我们的方法。通过定量和定性分析,我们证明了我们的路径空间辐射缓存是一种可靠的解决方案,易于集成,并能显著提高体积可视化应用程序的渲染质量,同时保持相当的计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- 实时路径追踪已成为娱乐和专业应用中渲染的主流技术。
- 科学可视化中体积渲染在分析复杂3D数据方面起着关键作用。
- 蒙特卡洛积分在光栅化渲染技术中引发高像素方差和渲染性能缓慢的问题。
- 引入了一种新型的路径空间辐射缓存方法用于体积渲染。
- 该方法利用体积场景表示的进展,并采用三维高斯涂抹技术作为多层次路径空间辐射缓存。
- 缓存设计能动态适应场景参数变化,提高渲染质量并减少噪声。
点此查看论文截图
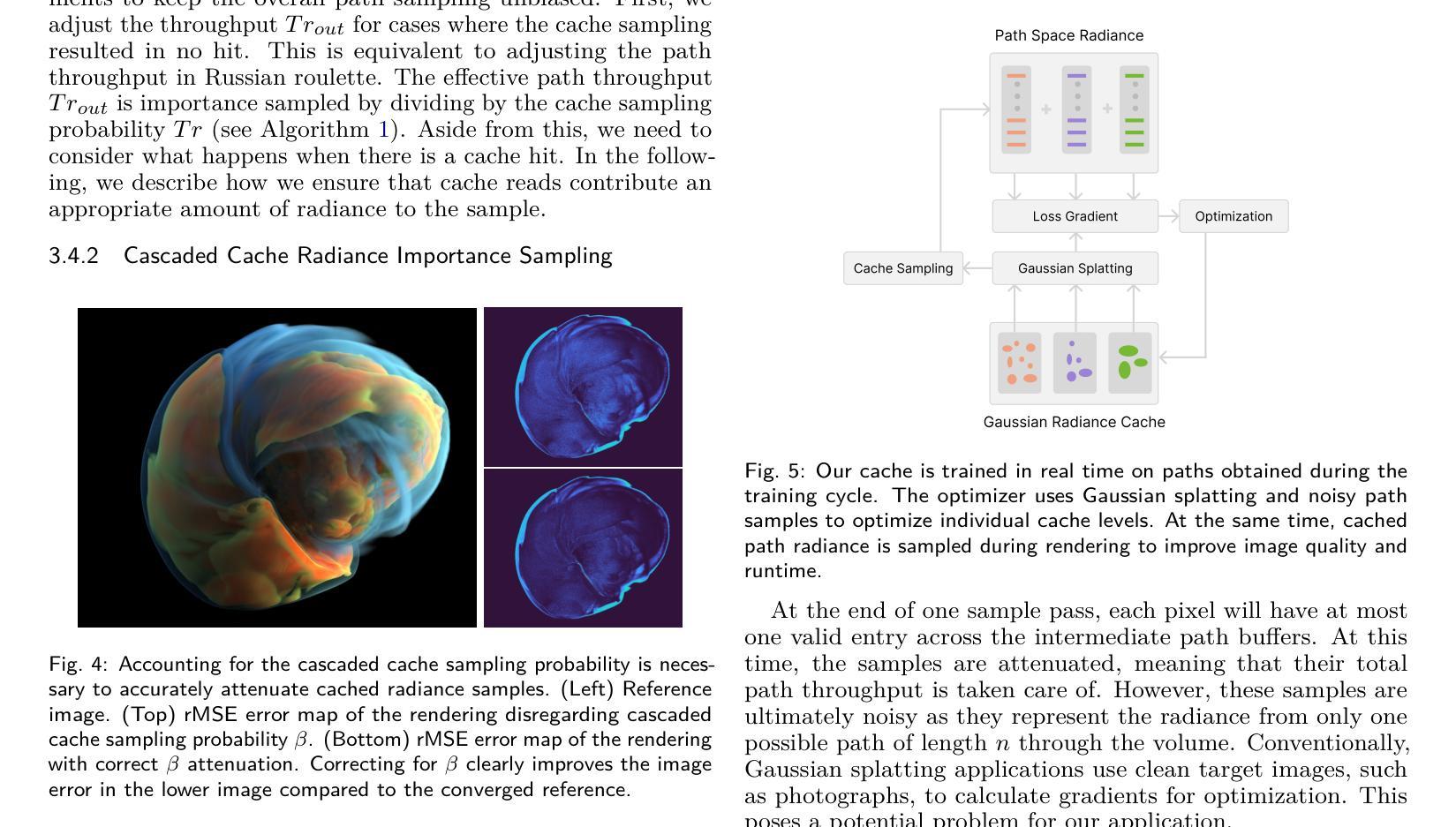
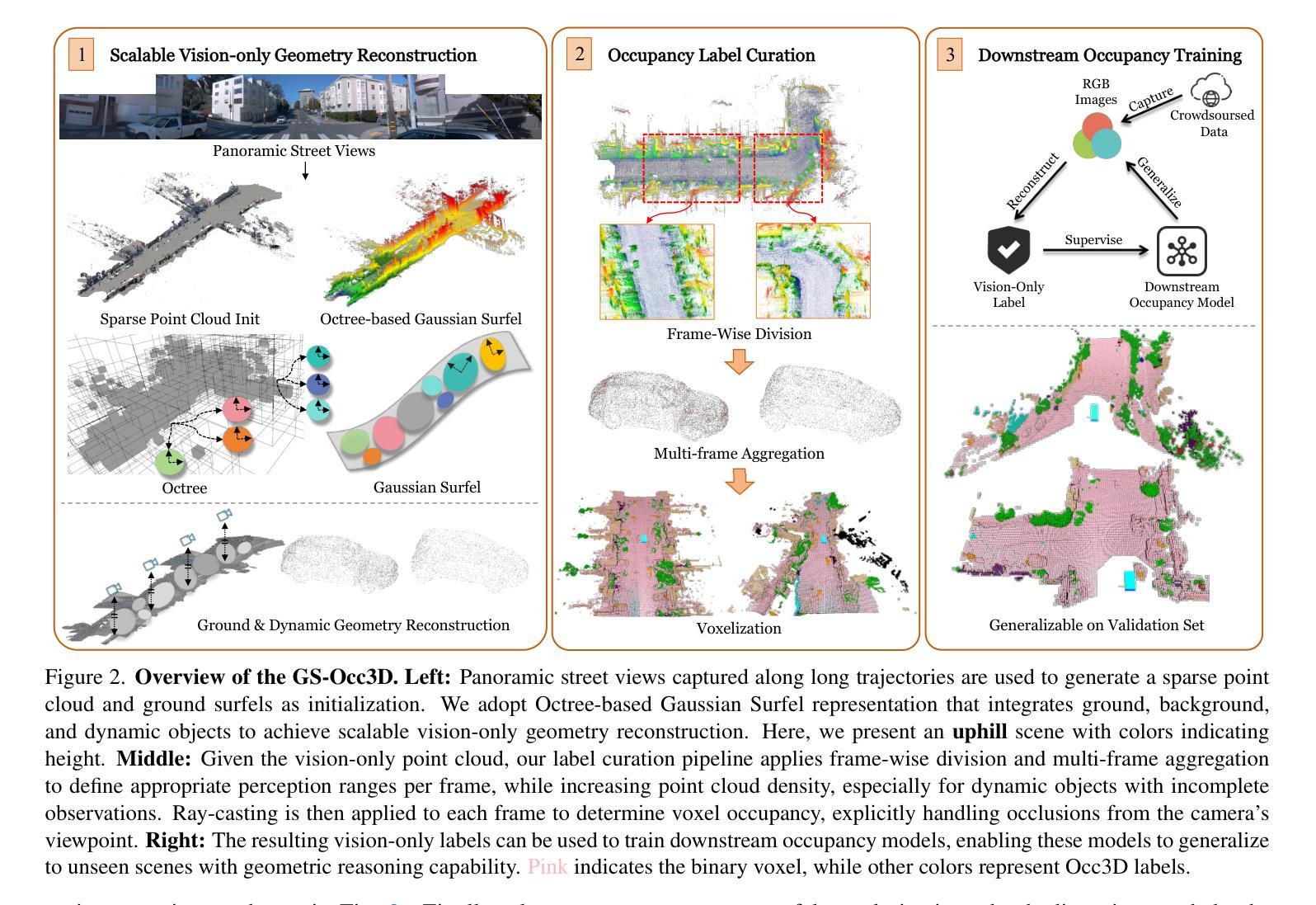
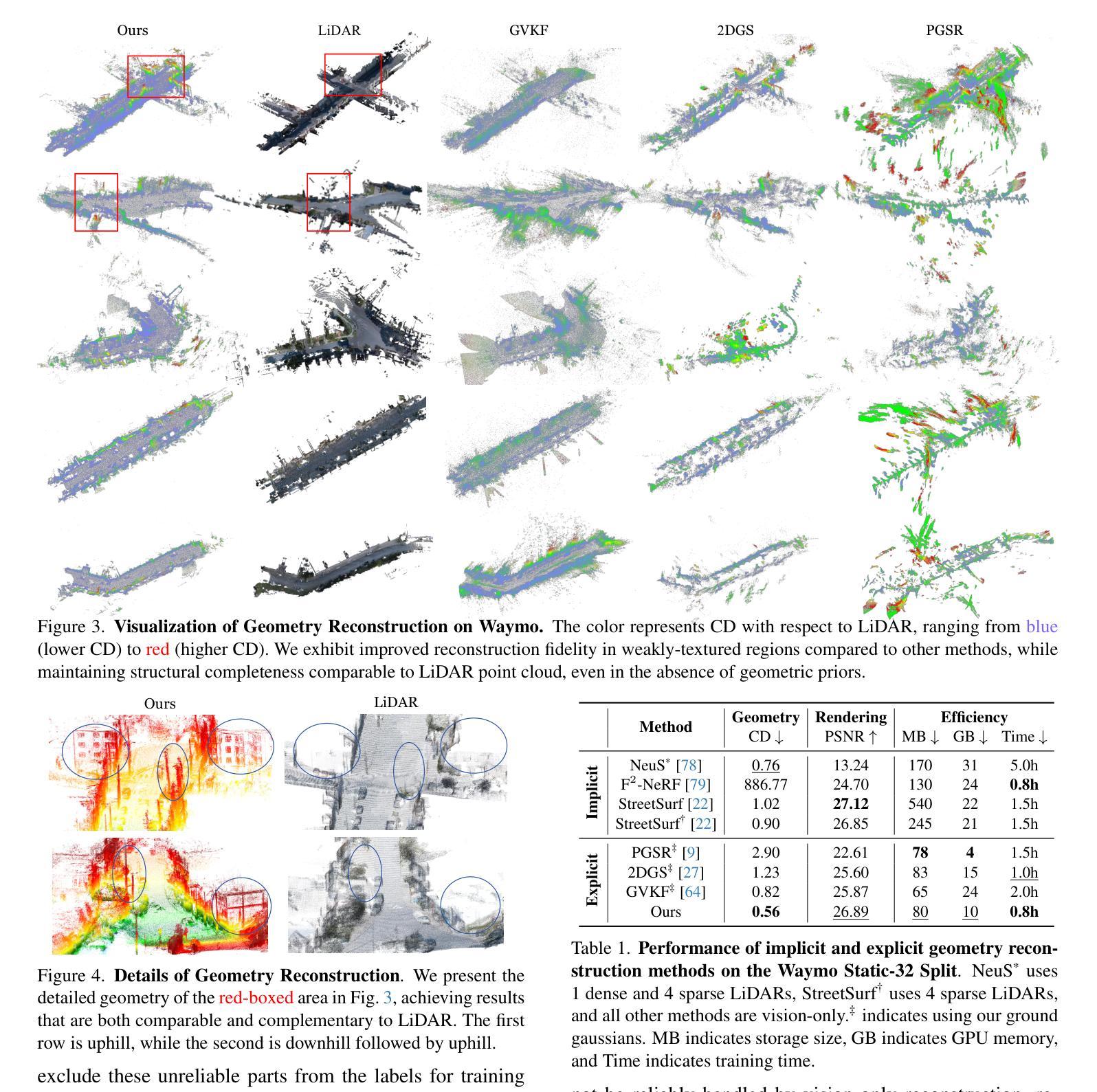
GS-Occ3D: Scaling Vision-only Occupancy Reconstruction with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Baijun Ye, Minghui Qin, Saining Zhang, Moonjun Gong, Shaoting Zhu, Zebang Shen, Luan Zhang, Lu Zhang, Hao Zhao, Hang Zhao
Occupancy is crucial for autonomous driving, providing essential geometric priors for perception and planning. However, existing methods predominantly rely on LiDAR-based occupancy annotations, which limits scalability and prevents leveraging vast amounts of potential crowdsourced data for auto-labeling. To address this, we propose GS-Occ3D, a scalable vision-only framework that directly reconstructs occupancy. Vision-only occupancy reconstruction poses significant challenges due to sparse viewpoints, dynamic scene elements, severe occlusions, and long-horizon motion. Existing vision-based methods primarily rely on mesh representation, which suffer from incomplete geometry and additional post-processing, limiting scalability. To overcome these issues, GS-Occ3D optimizes an explicit occupancy representation using an Octree-based Gaussian Surfel formulation, ensuring efficiency and scalability. Additionally, we decompose scenes into static background, ground, and dynamic objects, enabling tailored modeling strategies: (1) Ground is explicitly reconstructed as a dominant structural element, significantly improving large-area consistency; (2) Dynamic vehicles are separately modeled to better capture motion-related occupancy patterns. Extensive experiments on the Waymo dataset demonstrate that GS-Occ3D achieves state-of-the-art geometry reconstruction results. By curating vision-only binary occupancy labels from diverse urban scenes, we show their effectiveness for downstream occupancy models on Occ3D-Waymo and superior zero-shot generalization on Occ3D-nuScenes. It highlights the potential of large-scale vision-based occupancy reconstruction as a new paradigm for scalable auto-labeling. Project Page: https://gs-occ3d.github.io/
占用信息对于自动驾驶至关重要,它为感知和规划提供了必要的几何先验知识。然而,现有方法主要依赖于基于激光雷达的占用注释,这限制了可扩展性,并阻止了大量潜在的众包数据用于自动标注。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GS-Occ3D,这是一个可扩展的仅视觉框架,可直接重建占用信息。仅使用视觉的占用信息重建由于稀疏的视点、动态的场景元素、严重的遮挡和长距离运动而面临重大挑战。现有的基于视觉的方法主要依赖于网格表示,这会导致几何不完整和额外的后处理,从而限制了可扩展性。为了克服这些问题,GS-Occ3D使用基于八叉树的高斯曲面片(Gaussian Surfel)优化显式占用表示,确保效率和可扩展性。此外,我们将场景分解为静态背景、地面和动态物体,以实现定制建模策略:(1)地面被明确重建为主要的结构元素,这显著提高了大面积的一致性;(2)动态车辆则进行单独建模,以更好地捕捉与运动相关的占用模式。在Waymo数据集上的广泛实验表明,GS-Occ3D达到了最新的几何重建效果。我们从各种城市场景中整理出仅使用视觉的二进制占用标签,并展示了它们在Occ3D-Waymo上的下游占用模型的有效性,以及在Occ3D-nuScenes上的出色零样本泛化能力。这凸显了大规模基于视觉的占用信息重建作为新的可扩展自动标注模式潜力。项目页面:https://gs-occ3d.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://gs-occ3d.github.io/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为GS-Occ3D的仅视觉感知的可扩展框架,用于直接重建占用空间。该框架解决了仅依靠LiDAR的占用标注方法存在的可扩展性问题,并能够利用大量的潜在众包数据进行自动标注。GS-Occ3D采用基于Octree的Gaussian Surfel公式优化占用表示,解决了现有视觉方法在处理稀疏视点、动态场景元素、严重遮挡和长距离运动时的挑战。通过分解场景为静态背景、地面和动态物体,实现了针对性的建模策略,显著提高了占用重建的效果。实验结果表明,GS-Occ3D在Waymo数据集上实现了最先进的几何重建效果,并展示了大规模视觉感知占用重建作为新的可扩展自动标注方法的前景。
Key Takeaways
- GS-Occ3D是一个仅视觉感知的框架,用于直接重建占用空间,解决了依赖LiDAR的占用标注方法的局限性。
- 该框架能够利用大量的潜在众包数据进行自动标注,提高了可扩展性。
- GS-Occ3D采用基于Octree的Gaussian Surfel公式优化占用表示,解决了现有视觉方法在处理各种场景挑战时的问题。
- 场景被分解为静态背景、地面和动态物体,以实现针对性的建模策略。
- 地面作为主导结构元素被显式重建,提高了大区域的一致性。
- 动态车辆被单独建模,以更好地捕捉运动相关的占用模式。
点此查看论文截图

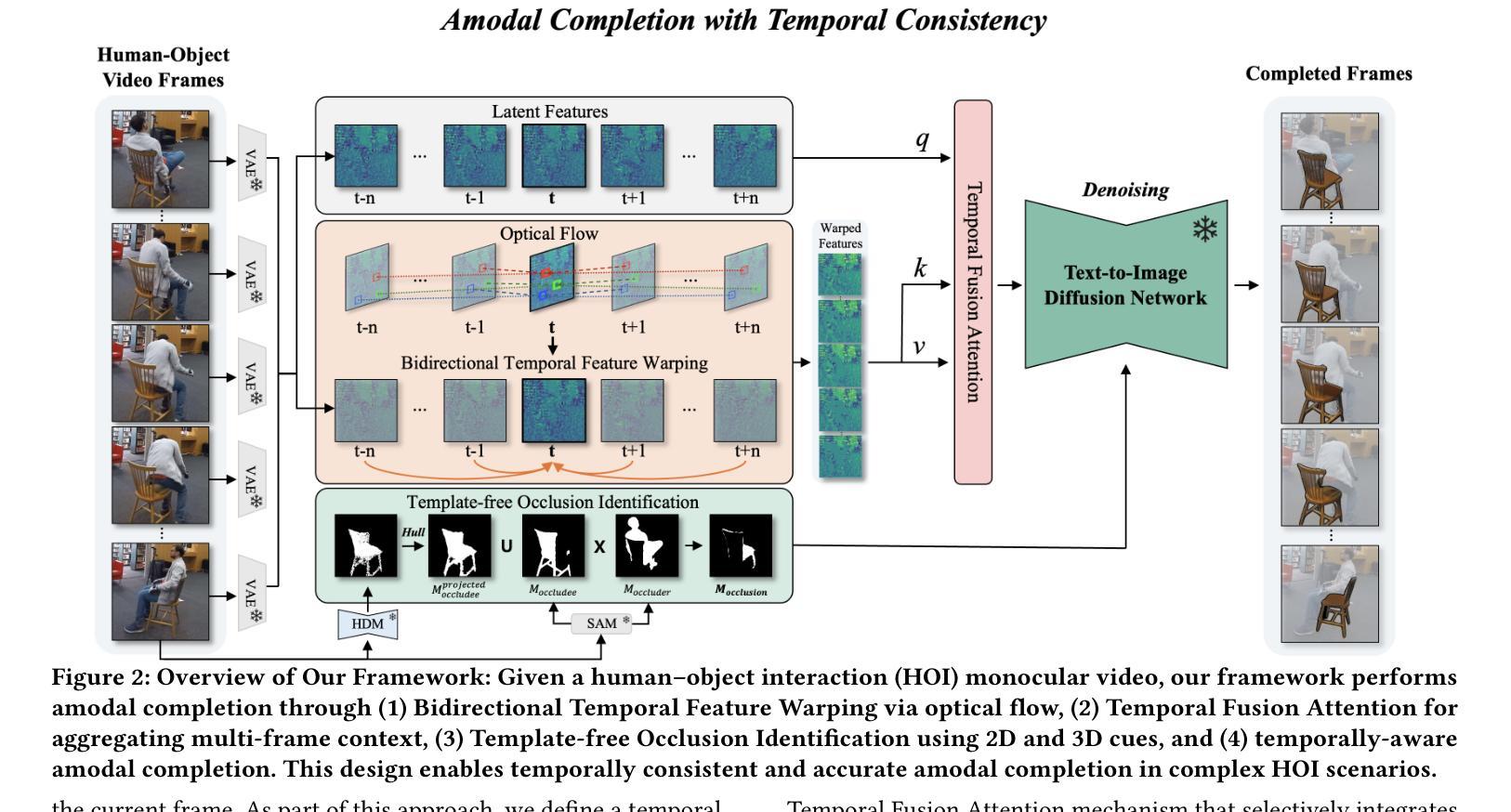
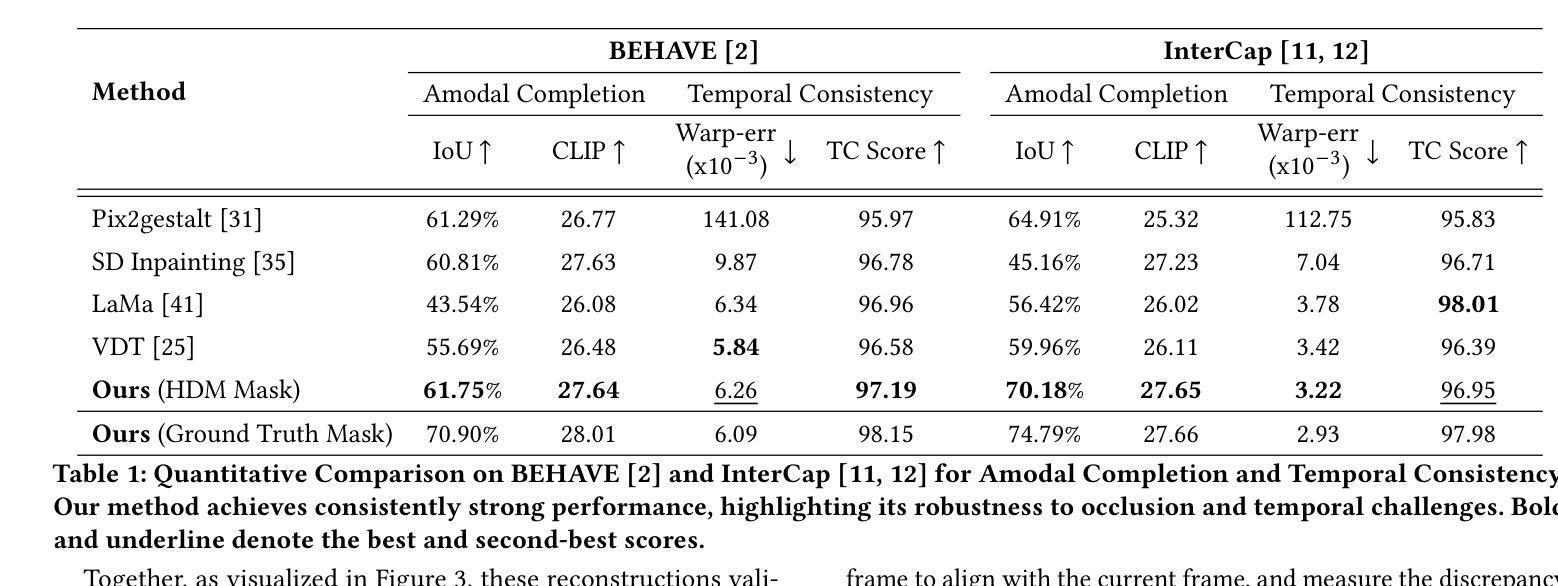
Occlusion-Aware Temporally Consistent Amodal Completion for 3D Human-Object Interaction Reconstruction
Authors:Hyungjun Doh, Dong In Lee, Seunggeun Chi, Pin-Hao Huang, Kwonjoon Lee, Sangpil Kim, Karthik Ramani
We introduce a novel framework for reconstructing dynamic human-object interactions from monocular video that overcomes challenges associated with occlusions and temporal inconsistencies. Traditional 3D reconstruction methods typically assume static objects or full visibility of dynamic subjects, leading to degraded performance when these assumptions are violated-particularly in scenarios where mutual occlusions occur. To address this, our framework leverages amodal completion to infer the complete structure of partially obscured regions. Unlike conventional approaches that operate on individual frames, our method integrates temporal context, enforcing coherence across video sequences to incrementally refine and stabilize reconstructions. This template-free strategy adapts to varying conditions without relying on predefined models, significantly enhancing the recovery of intricate details in dynamic scenes. We validate our approach using 3D Gaussian Splatting on challenging monocular videos, demonstrating superior precision in handling occlusions and maintaining temporal stability compared to existing techniques.
我们引入了一种新的从单目视频中重建动态人机交互的框架,该框架克服了与遮挡和时间不一致相关的挑战。传统的3D重建方法通常假设物体是静态的或动态主体完全可见,当这些假设被违反时,特别是在发生相互遮挡的场景中,会导致性能下降。为了解决这一问题,我们的框架利用模态完成来推断部分遮挡区域的完整结构。与在单个帧上运行的传统方法不同,我们的方法结合了时间上下文,强制视频序列之间的连贯性,以逐步优化和稳定重建。这种无模板的策略能够适应不同的条件,而不依赖于预定义的模型,从而显著提高了动态场景中细节的恢复。我们使用单目视频上的三维高斯拼贴法验证了我们的方法,该方法在处理遮挡和保持时间稳定性方面表现出较高的精度,优于现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种从单目视频中重建动态人-物体交互的新型框架,该框架克服了与遮挡和暂时不一致相关的挑战。传统3D重建方法通常假设物体静态或动态主体的完全可见性,当这些假设不成立时,特别是在发生相互遮挡的场景中,性能会下降。为解决这一问题,我们的框架利用模态完成法推断部分遮挡区域的完整结构。与传统在单个帧上操作的方法不同,我们的方法结合了时间上下文,强制视频序列之间的连贯性,以逐步精细和调整重建。这种无模板的策略适应于各种条件,而不依赖于预设模型,显著提高了在动态场景中恢复细节的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 新型框架能够重建单目视频中的动态人-物体交互。
- 该框架克服了遮挡和暂时不一致的挑战。
- 传统3D重建方法通常假设物体静态或完全可见,但在实际场景中这些假设可能不成立。
- 框架利用模态完成法推断部分遮挡区域的完整结构。
- 与只在单个帧上操作的方法不同,该框架结合了时间上下文,保持视频序列之间的连贯性。
- 无模板策略使其适应各种条件,无需依赖预设模型。
点此查看论文截图


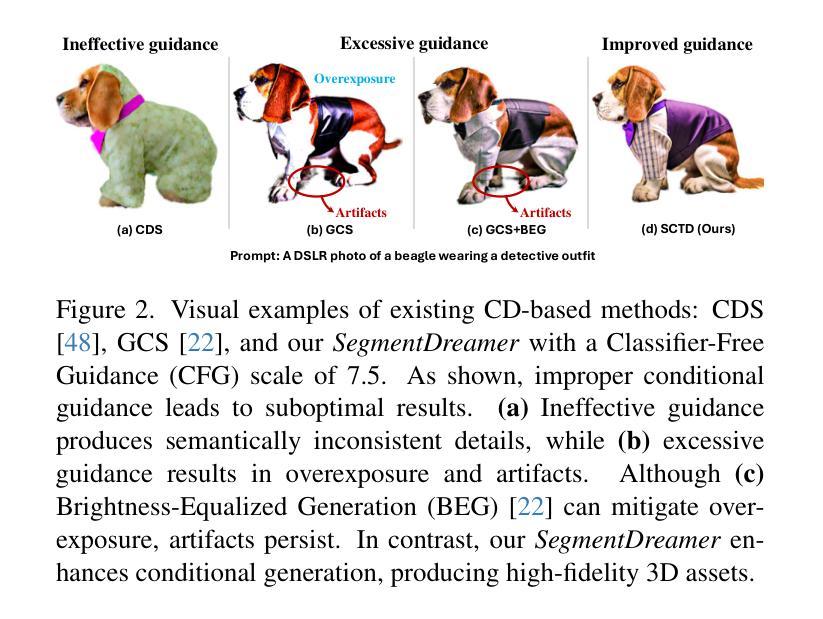
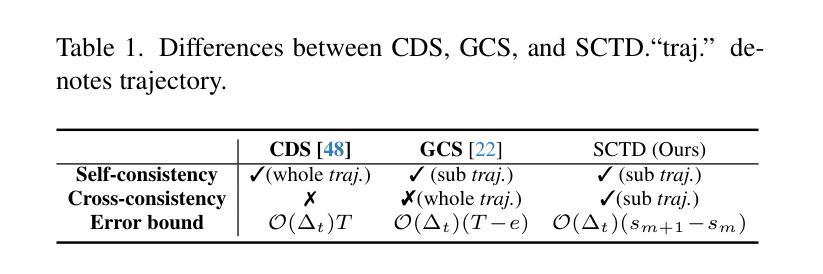
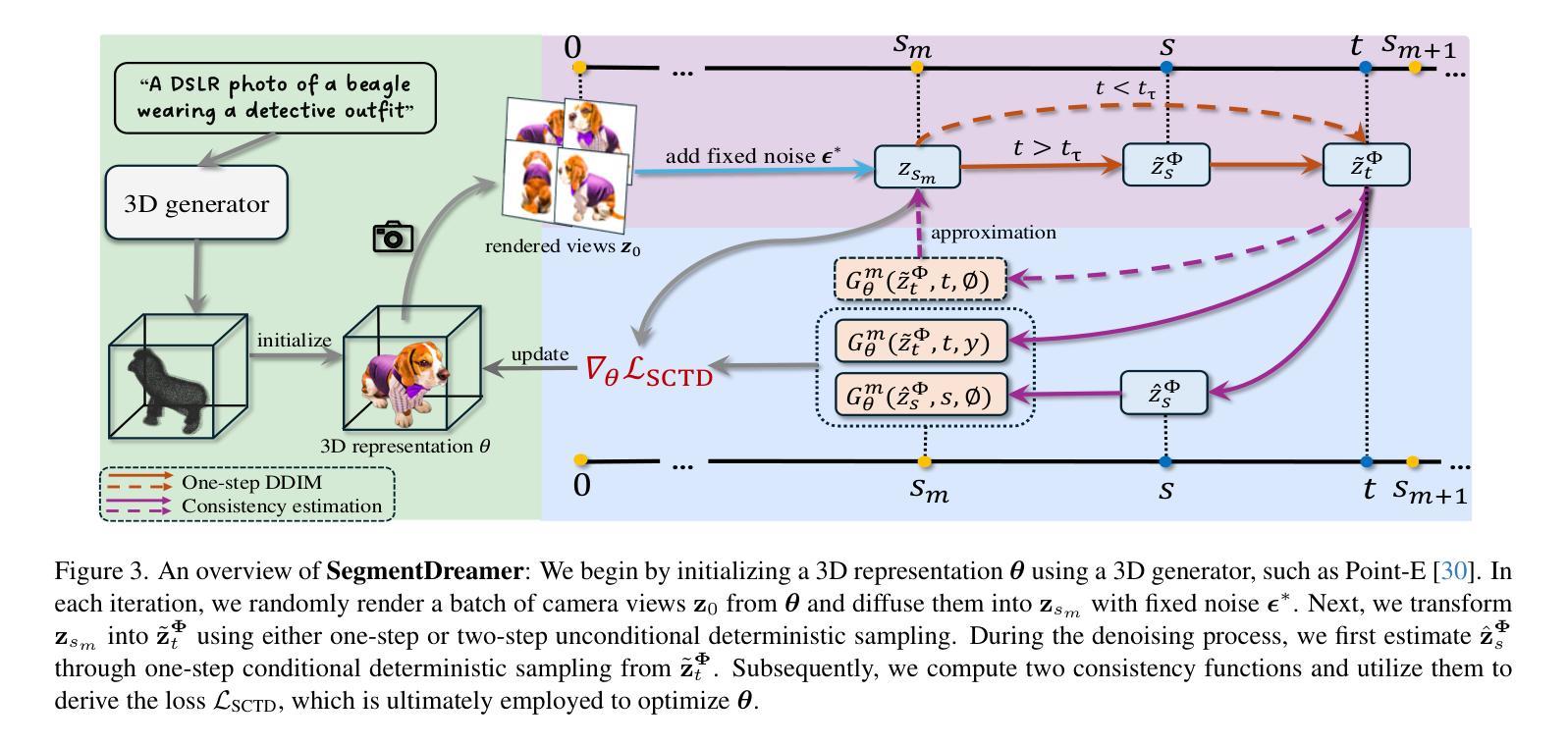
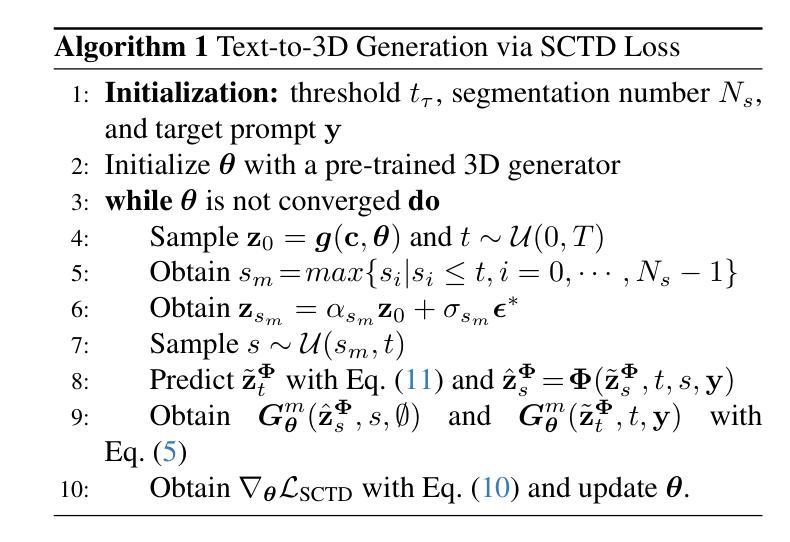
SegmentDreamer: Towards High-fidelity Text-to-3D Synthesis with Segmented Consistency Trajectory Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Zhu, Zixuan Chen, Guangcong Wang, Xiaohua Xie, Yi Zhou
Recent advancements in text-to-3D generation improve the visual quality of Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) and its variants by directly connecting Consistency Distillation (CD) to score distillation. However, due to the imbalance between self-consistency and cross-consistency, these CD-based methods inherently suffer from improper conditional guidance, leading to sub-optimal generation results. To address this issue, we present SegmentDreamer, a novel framework designed to fully unleash the potential of consistency models for high-fidelity text-to-3D generation. Specifically, we reformulate SDS through the proposed Segmented Consistency Trajectory Distillation (SCTD), effectively mitigating the imbalance issues by explicitly defining the relationship between self- and cross-consistency. Moreover, SCTD partitions the Probability Flow Ordinary Differential Equation (PF-ODE) trajectory into multiple sub-trajectories and ensures consistency within each segment, which can theoretically provide a significantly tighter upper bound on distillation error. Additionally, we propose a distillation pipeline for a more swift and stable generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our SegmentDreamer outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, enabling high-fidelity 3D asset creation through 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS).
近期文本到3D生成的进展通过直接将一致性蒸馏(CD)与得分蒸馏相联系,提高了得分蒸馏采样(SDS)及其变体的视觉质量。然而,由于自一致性和跨一致性之间的不平衡,这些基于CD的方法不可避免地存在不当的条件指导,导致生成结果不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SegmentDreamer,这是一个旨在充分释放一致性模型潜力的高保真文本到3D生成的新型框架。具体来说,我们通过提出的分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)重新定义了SDS,通过明确自一致性和跨一致性之间的关系,有效地缓解了不平衡问题。此外,SCTD将概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE)轨迹划分为多个子轨迹,确保每个段内的一致性,这在理论上可以为蒸馏误差提供更紧密的上界。我们还提出了一种更快速稳定的蒸馏管道。大量实验表明,我们的SegmentDreamer在视觉质量上超过了最先进的方法,通过3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)实现了高保真3D资产创建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, project page: https://zjhjojo.github.io/segmentdreamer/
Summary
文本描述了最新进展在文本到三维生成的技术,介绍了Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)及其变体的视觉质量提升方法。文章指出CD(一致性蒸馏)技术与其他技术相结合的优势,但由于自我一致性和跨一致性之间的不平衡问题,这些基于CD的方法存在潜在的性能障碍。为解决这个问题,文章提出了SegmentDreamer框架,通过分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)技术重新定义了SDS,有效解决了不平衡问题,并优化了概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE)轨迹的多个子轨迹,确保每个分段内的一致性。此外,文章还提出了更快速稳定的生成蒸馏管道。实验证明,SegmentDreamer在视觉质量上超过了现有方法,并通过三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)实现了高保真三维资产创建。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到三维生成技术有所提升,通过Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)及其变体改进视觉质量。
- 一致性蒸馏(CD)技术在提升文本到三维生成效果方面具有优势。
- CD-based方法存在自我一致性和跨一致性不平衡问题,导致条件指导不当和生成结果不佳。
- SegmentDreamer框架通过分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)解决了CD方法的不平衡问题。
- SCTD技术重新定义了SDS,优化了概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE)轨迹的子轨迹。
- SegmentDreamer提出更快速稳定的生成蒸馏管道。
点此查看论文截图

TSGS: Improving Gaussian Splatting for Transparent Surface Reconstruction via Normal and De-lighting Priors
Authors:Mingwei Li, Pu Pang, Hehe Fan, Hua Huang, Yi Yang
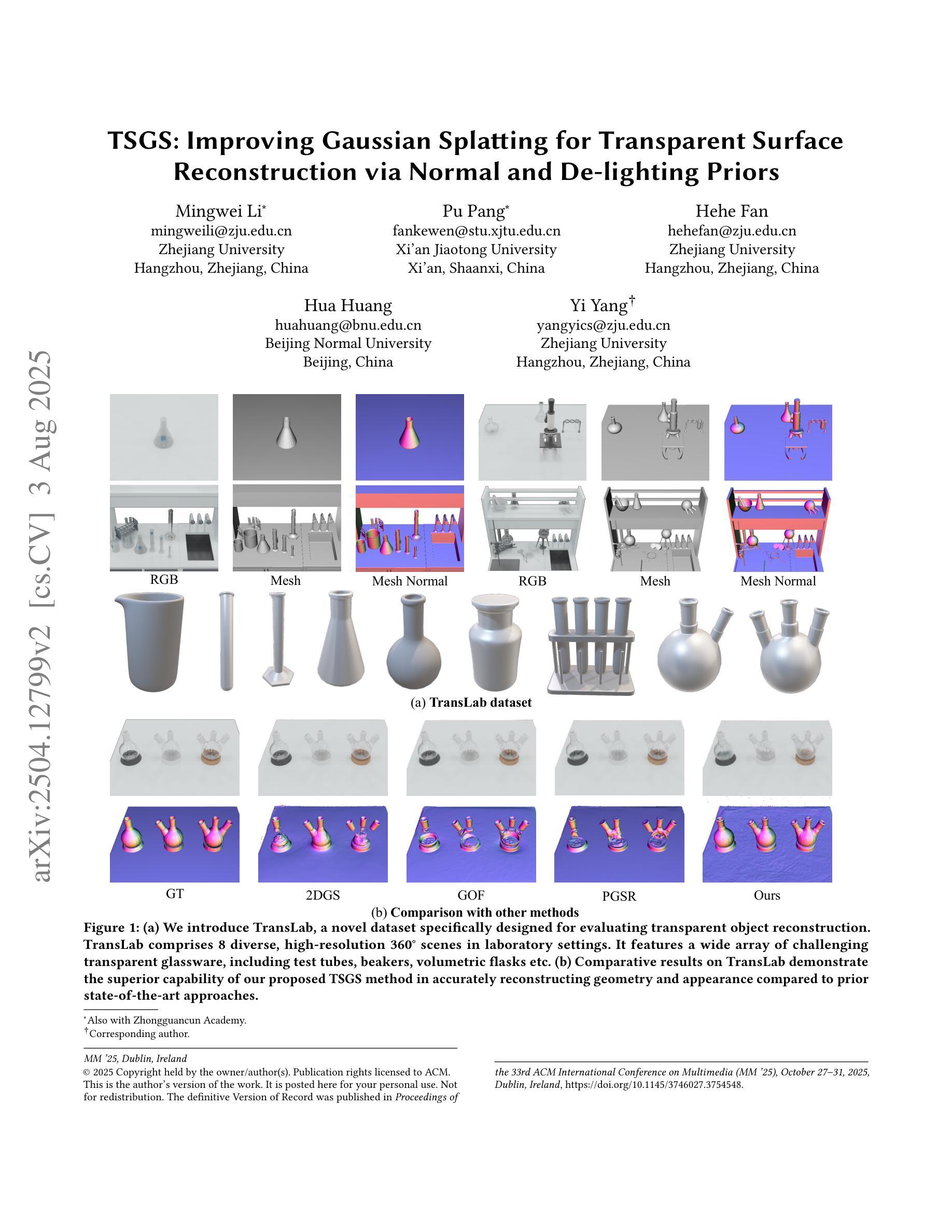
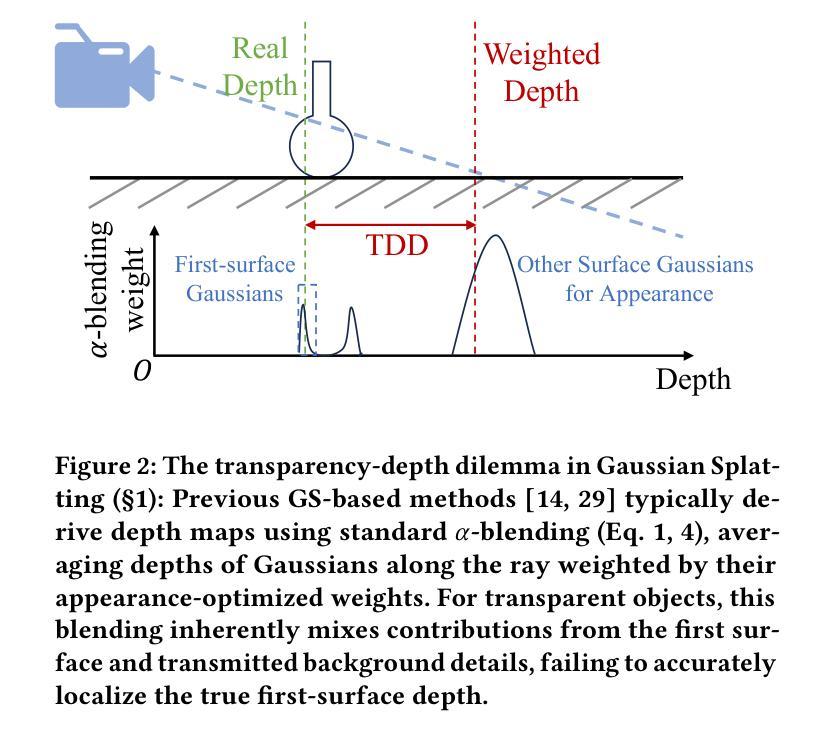
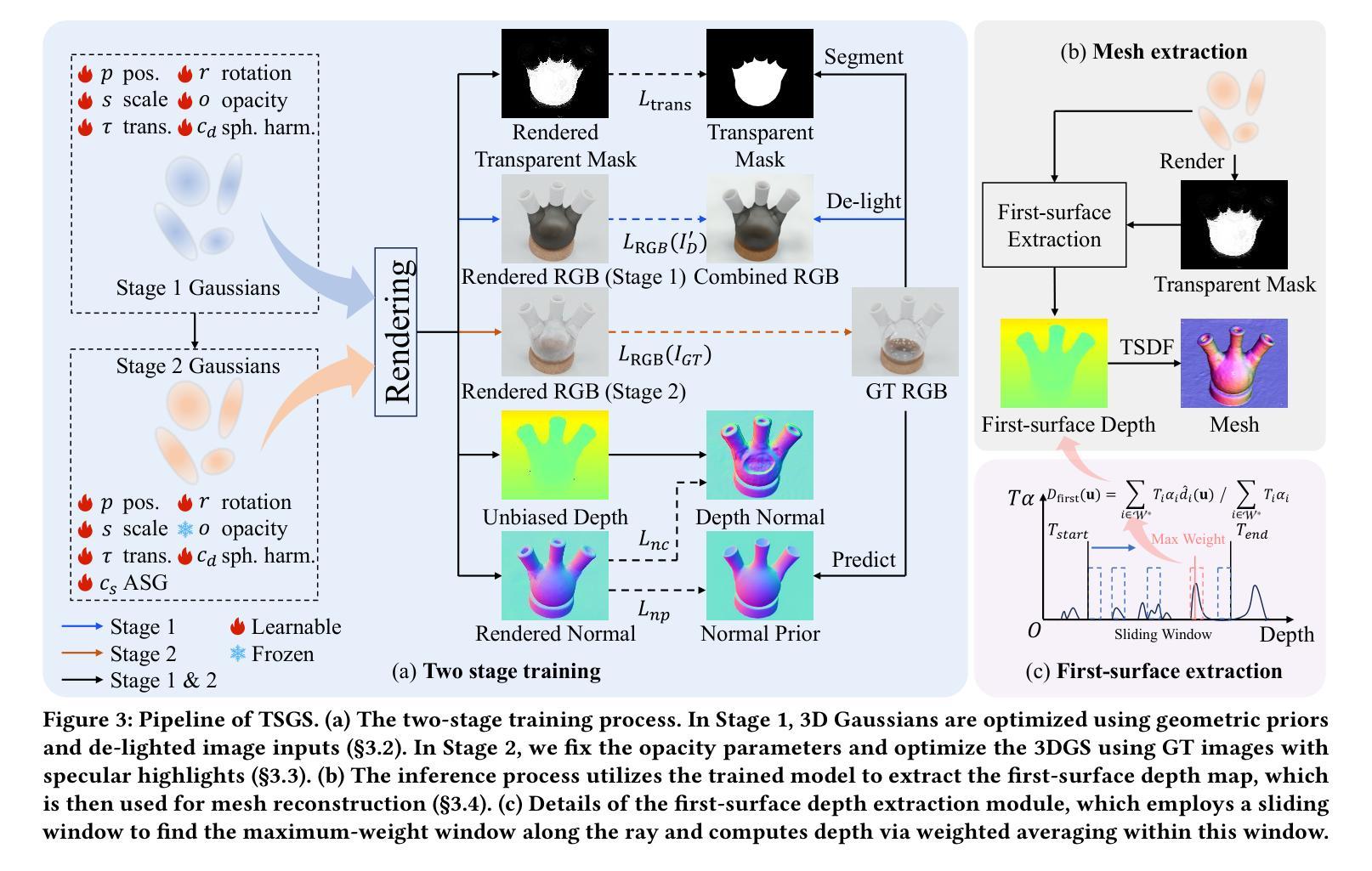
Reconstructing transparent surfaces is essential for tasks such as robotic manipulation in labs, yet it poses a significant challenge for 3D reconstruction techniques like 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). These methods often encounter a transparency-depth dilemma, where the pursuit of photorealistic rendering through standard $\alpha$-blending undermines geometric precision, resulting in considerable depth estimation errors for transparent materials. To address this issue, we introduce Transparent Surface Gaussian Splatting (TSGS), a new framework that separates geometry learning from appearance refinement. In the geometry learning stage, TSGS focuses on geometry by using specular-suppressed inputs to accurately represent surfaces. In the second stage, TSGS improves visual fidelity through anisotropic specular modeling, crucially maintaining the established opacity to ensure geometric accuracy. To enhance depth inference, TSGS employs a first-surface depth extraction method. This technique uses a sliding window over $\alpha$-blending weights to pinpoint the most likely surface location and calculates a robust weighted average depth. To evaluate the transparent surface reconstruction task under realistic conditions, we collect a TransLab dataset that includes complex transparent laboratory glassware. Extensive experiments on TransLab show that TSGS achieves accurate geometric reconstruction and realistic rendering of transparent objects simultaneously within the efficient 3DGS framework. Specifically, TSGS significantly surpasses current leading methods, achieving a 37.3% reduction in chamfer distance and an 8.0% improvement in F1 score compared to the top baseline. The code and dataset are available at https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/.
重建透明表面对于实验室的机器人操作等任务至关重要,然而,它为3D重建技术(例如3D高斯拼贴(3DGS))带来了重大挑战。这些方法经常面临透明度与深度之间的两难困境,其中通过标准alpha混合追求逼真的渲染会破坏几何精度,导致对透明材料的深度估计出现重大误差。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了透明表面高斯拼贴(TSGS)这一新框架,它将几何学习与外观优化分离。在几何学习阶段,TSGS通过使用抑制镜面反射的输入来准确表示表面。在第二阶段,TSGS通过各向异性镜面建模提高视觉保真度,关键的是保持已建立的透明度以确保几何精度。为了提高深度推断能力,TSGS采用了一种基于首表面深度提取方法的技术。该技术通过alpha混合权重上的滑动窗口来精确定位表面位置,并计算一个稳健的加权平均深度。为了在实际条件下评估透明表面重建任务,我们收集了一个TransLab数据集,其中包含复杂的透明实验室玻璃器皿。在TransLab上的广泛实验表明,TSGS能够在高效的3DGS框架内实现透明物体的准确几何重建和逼真渲染。具体来说,TSGS大大超越了当前的主流方法,与顶级基线相比,车身距离减少了37.3%,F1分数提高了8.0%。代码和数据集可在[https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://longxiang-ai.github.io/TSGS/ . Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
透明表面重建是实验室机器人操作等任务的关键,但对于3D重建技术(如3D高斯贴片技术)而言是一项挑战。标准的融合方法会损害几何精度,导致深度估计错误。为解决这一问题,我们提出透明表面高斯贴片技术(TSGS),该技术将几何学习与外观优化分开。首先,TSGS使用抑制镜面反射的图像来准确表示表面几何结构;接着,通过各向异性镜面模型提高视觉保真度并维持透明度保证几何精度。为增强深度推断,TSGS采用首表面深度提取方法。我们在具有复杂透明实验室器皿的TransLab数据集上进行了广泛实验,证明TSGS在透明物体准确几何重建和真实感渲染方面具有卓越性能,相较于现有顶尖方法有明显提升。
Key Takeaways
- 透明表面重建是实验室机器人操作等任务的关键挑战。
- 传统3D重建技术在处理透明物体时面临透明度与深度估计的困境。
- TSGS技术通过分离几何学习与外观优化来解决这一问题。
- TSGS使用抑制镜面反射的图像进行几何学习,确保准确表示表面结构。
- TSGS采用各向异性镜面模型提高视觉质量并保持透明度以维持几何精度。
- TSGS采用首表面深度提取技术以增强深度推断。
点此查看论文截图
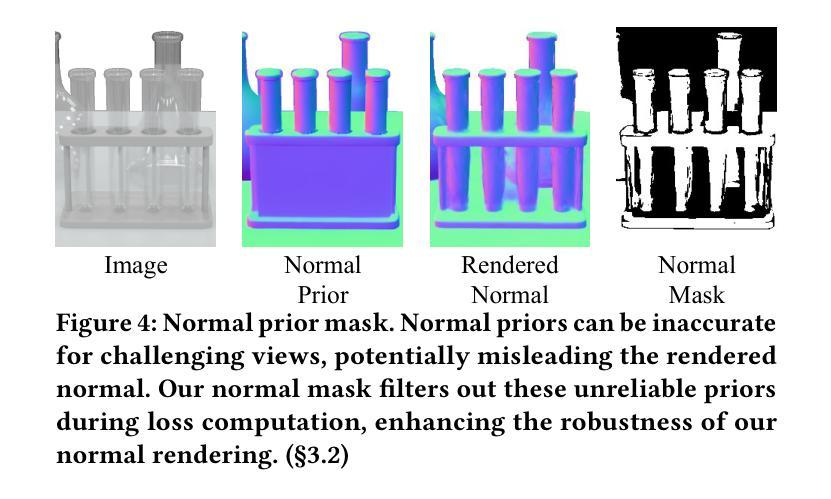
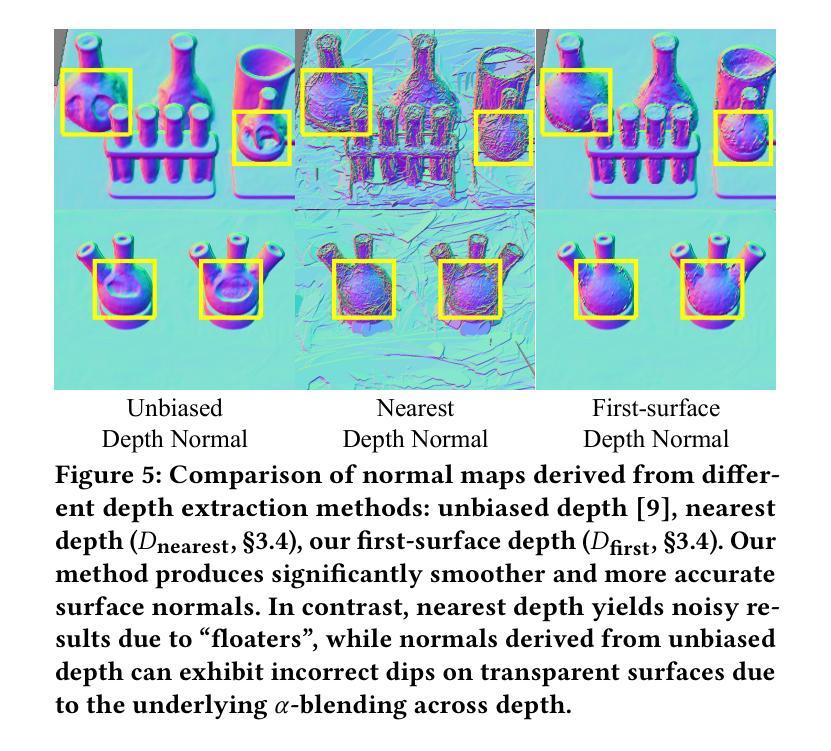
Embracing Dynamics: Dynamics-aware 4D Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Authors:Zhicong Sun, Jacqueline Lo, Jinxing Hu
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology has recently achieved photorealistic mapping capabilities thanks to the real-time, high-fidelity rendering enabled by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). However, due to the static representation of scenes, current 3DGS-based SLAM encounters issues with pose drift and failure to reconstruct accurate maps in dynamic environments. To address this problem, we present D4DGS-SLAM, the first SLAM method based on 4DGS map representation for dynamic environments. By incorporating the temporal dimension into scene representation, D4DGS-SLAM enables high-quality reconstruction of dynamic scenes. Utilizing the dynamics-aware InfoModule, we can obtain the dynamics, visibility, and reliability of scene points, and filter out unstable dynamic points for tracking accordingly. When optimizing Gaussian points, we apply different isotropic regularization terms to Gaussians with varying dynamic characteristics. Experimental results on real-world dynamic scene datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both camera pose tracking and map quality.
同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)技术最近由于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)所实现的实时高保真渲染而获得了逼真的映射能力。然而,由于场景静态表示,当前基于3DGS的SLAM在动态环境中遇到了姿态漂移和无法重建准确地图的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了D4DGS-SLAM,这是基于4DGS地图表示的用于动态环境的第一个SLAM方法。通过将时间维度融入场景表示,D4DGS-SLAM能够实现动态场景的高质量重建。通过使用动力学感知的InfoModule,我们可以获得场景点的动力学、可见性和可靠性,并相应地过滤出不稳定动态点进行跟踪。在优化高斯点时,我们对具有不同动态特征的高斯应用不同的等距正则化项。在真实世界动态场景数据集上的实验结果证明,我们的方法在相机姿态追踪和地图质量方面均优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IROS 2025
Summary
基于三维高斯融合(3DGS)技术的实时渲染能力,同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)技术已实现了逼真的映射功能。然而,由于场景静态表示的限制,当前基于3DGS的SLAM在动态环境中存在姿态漂移和无法准确重建地图的问题。为解决此问题,我们提出了基于四维高斯融合(4DGS)地图表示的SLAM方法——D4DGS-SLAM。通过引入时间维度进行场景表示,D4DGS-SLAM可实现动态场景的高质量重建。利用动力学感知的InfoModule,我们可以获取场景的动态性、可见性和可靠性信息,并据此过滤出不稳定动态点进行跟踪。在优化高斯点时,我们对具有不同动态特性的高斯应用不同的等距正则化项。在真实世界动态场景数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在相机姿态跟踪和地图质量方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 基于三维高斯融合(3DGS)技术的同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)技术已实现了逼真的映射功能。
- 当前基于3DGS的SLAM在动态环境中存在姿态漂移和地图精度问题。
- 为解决动态环境下的姿态漂移问题,首次提出了基于四维高斯融合(4DGS)地图表示的SLAM方法——D4DGS-SLAM。
- D4DGS-SLAM通过引入时间维度,实现了动态场景的高质量重建。
- D4DGS-SLAM利用动力学感知的InfoModule过滤不稳定动态点,并优化高斯点以改善性能。
- D4DGS-SLAM在相机姿态跟踪和地图质量方面表现出优异性能,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

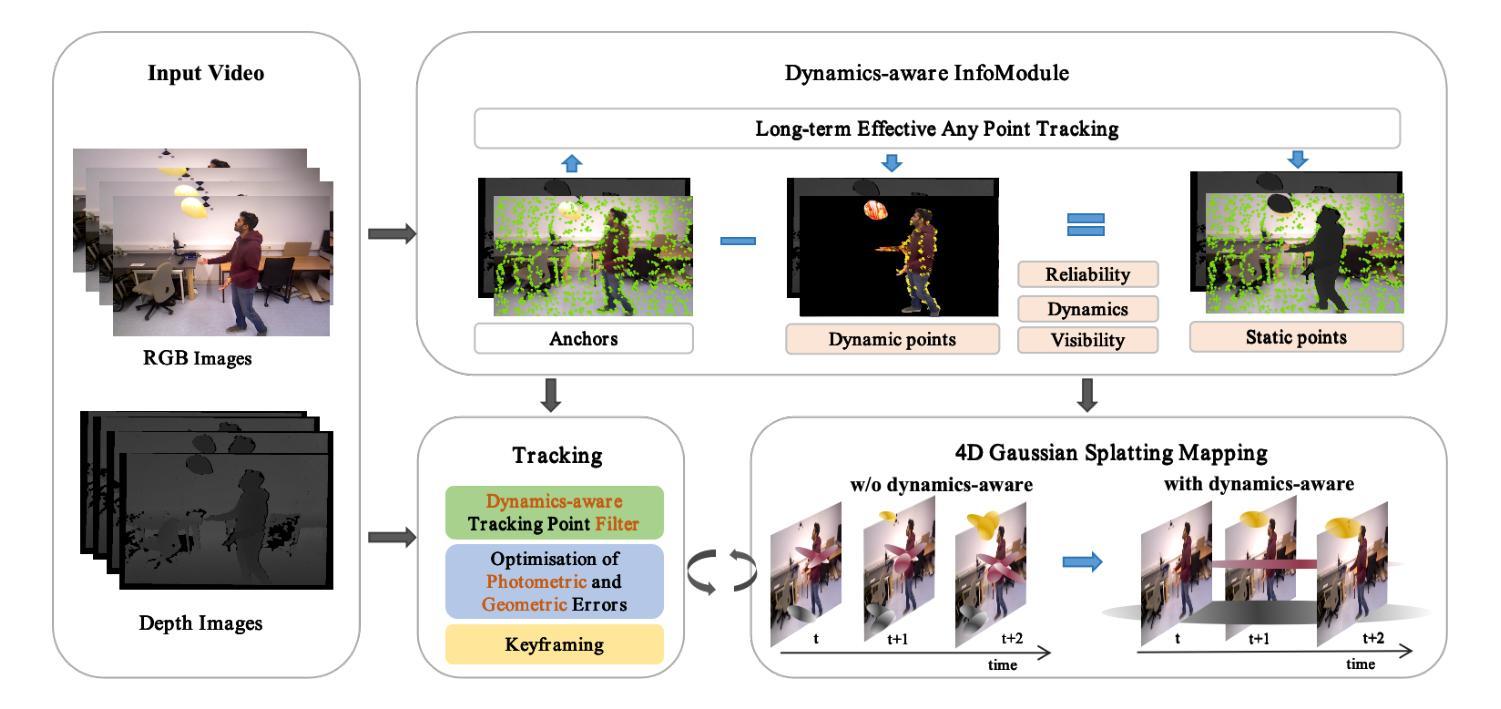


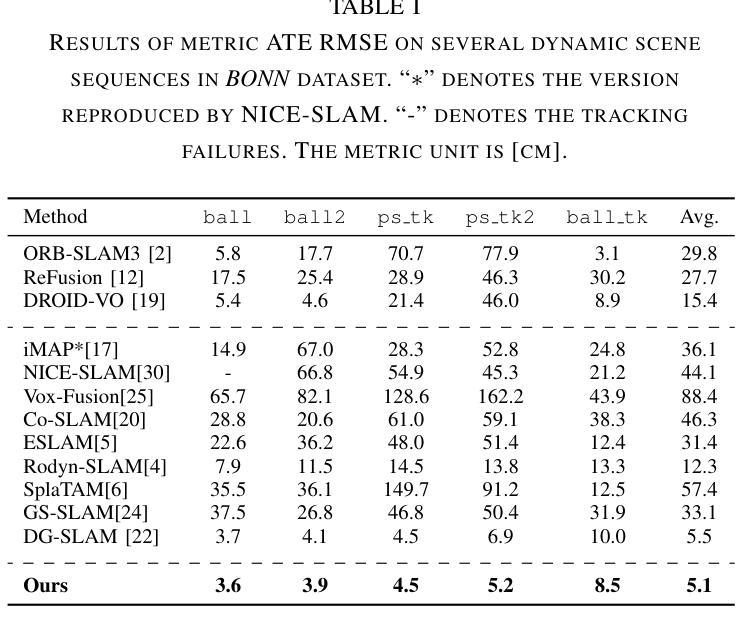

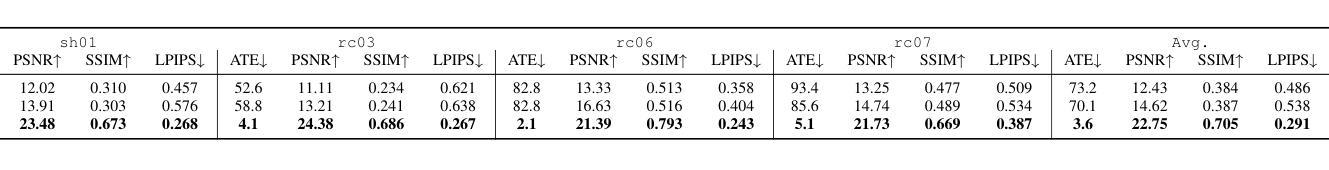
StableGS: A Floater-Free Framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Luchao Wang, Qian Ren, Kaimin Liao, Hua Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaohua Tang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) reconstructions are plagued by stubborn floater" artifacts that degrade their geometric and visual fidelity. We are the first to reveal the root cause: a fundamental conflict in the 3DGS optimization process where the opacity gradients of floaters vanish when their blended color reaches a pseudo-equilibrium of canceling errors against the background, trapping them in a spurious local minimum. To resolve this, we propose StableGS, a novel framework that decouples geometric regularization from final appearance rendering. Its core is a Dual Opacity architecture that creates two separate rendering paths: a Geometric Regularization Path” to bear strong depth-based constraints for structural correctness, and an ``Appearance Refinement Path” to generate high-fidelity details upon this stable foundation. We complement this with a synergistic set of geometric constraints: a self-supervised depth consistency loss and an external geometric prior enabled by our efficient global scale optimization algorithm. Experiments on multiple benchmarks show StableGS not only eliminates floaters but also resolves the common blur-artifact trade-off, achieving state-of-the-art geometric accuracy and visual quality.
3DGS重建过程中受到“漂浮物”问题的困扰,这个问题会导致其几何和视觉真实感降低。我们是首个揭示其原因的团队:在优化过程中存在一个基本冲突,即漂浮物的不透明度梯度在其混合颜色达到与背景相抵消的伪平衡状态时消失,使它们陷入一个虚假的局部最小值。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了StableGS,这是一个将几何正则化与最终外观渲染解耦的新型框架。其核心是双重不透明度架构,该架构创建了两条单独的渲染路径:“几何正则化路径”,用于承受基于深度的强大结构约束;“外观细化路径”,在稳定的基准上生成高保真细节。我们以一组协同几何约束来补充它:通过自我监督的深度一致性损失和由我们的高效全局尺度优化算法启用的外部几何先验。在多个基准测试上的实验表明,StableGS不仅消除了漂浮物问题,还解决了常见的模糊伪影权衡问题,实现了最先进的几何精度和视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)重建中存在的“浮子”伪影问题,分析其根本原因为优化过程中的基本冲突。为解决这一问题,提出StableGS框架,采用双重透明度架构,创建两个独立渲染路径,分别负责结构正确性的几何正则化和在此基础上生成高保真细节的外观优化路径。同时引入一系列几何约束,包括自监督深度一致性损失和由高效全局尺度优化算法实现的外部几何先验。实验表明,StableGS不仅能消除浮子伪影,还能解决常见的模糊伪影权衡问题,实现最先进的几何精度和视觉质量。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS重建存在“浮子”伪影问题,影响几何和视觉保真度。
- 浮子伪影的根本原因是优化过程中的基本冲突,导致透明度梯度消失。
- StableGS框架采用双重透明度架构,创建两个独立渲染路径:几何正则化和外观优化路径。
- StableGS引入自监督深度一致性损失和外部几何先验,提高结构正确性和高保真细节生成。
- StableGS解决了浮子伪影问题,实现了更精确的几何重建。
- StableGS在多个基准测试上的实验结果表明,其几何精度和视觉质量达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图


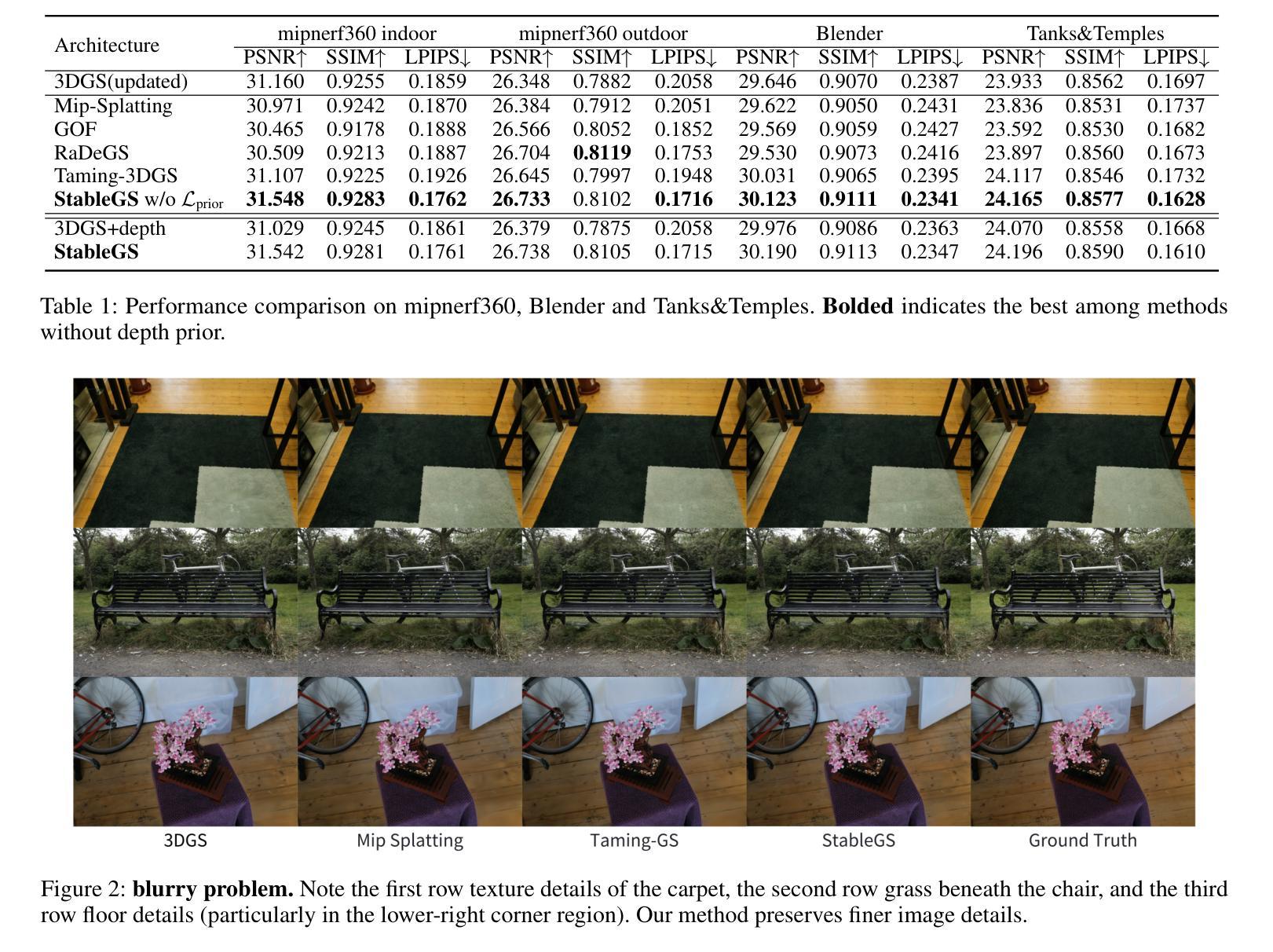

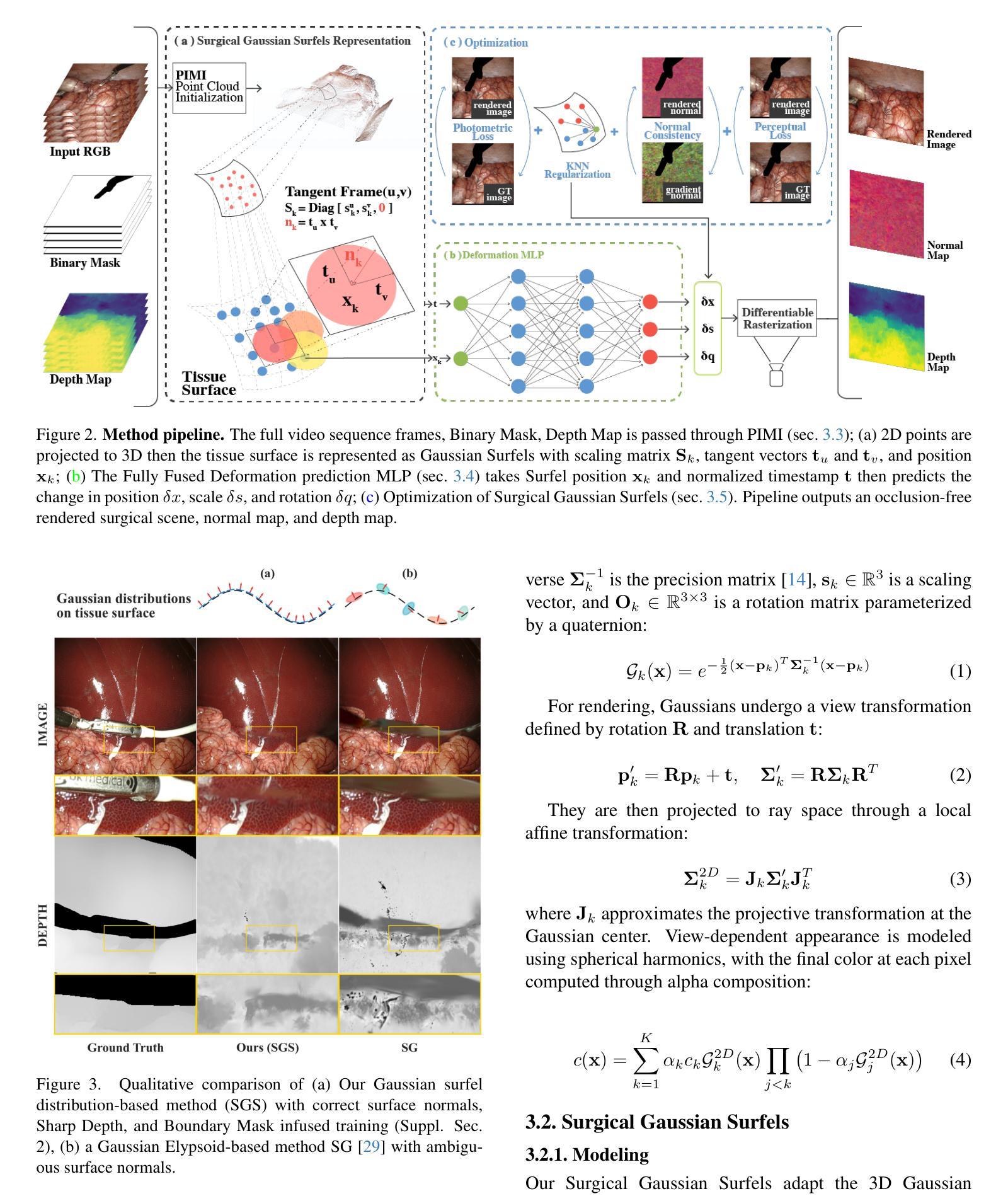
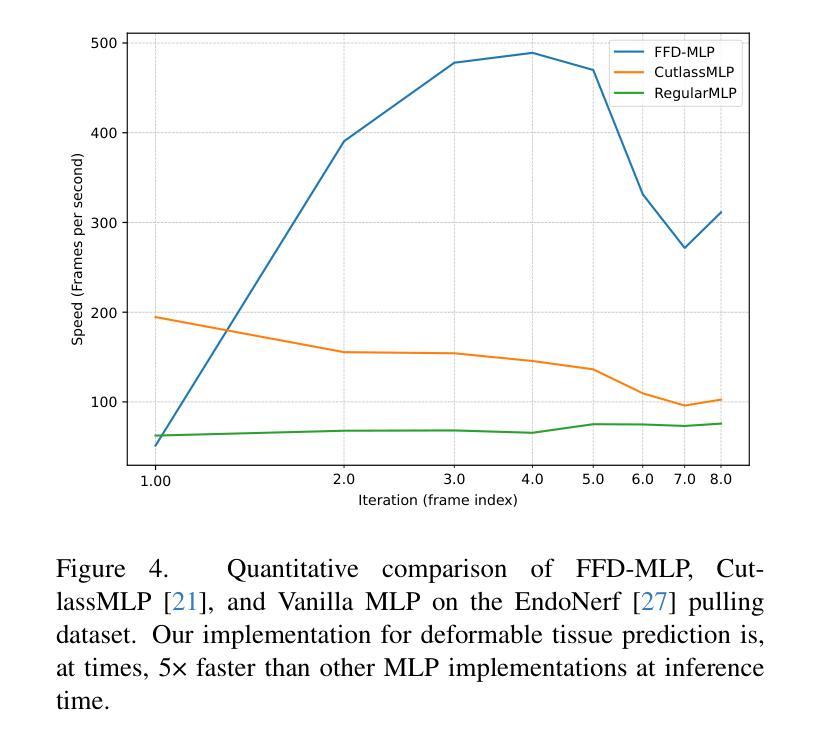
Surgical Gaussian Surfels: Highly Accurate Real-time Surgical Scene Rendering using Gaussian Surfels
Authors:Idris O. Sunmola, Zhenjun Zhao, Samuel Schmidgall, Yumeng Wang, Paul Maria Scheikl, Viet Pham, Axel Krieger
Accurate geometric reconstruction of deformable tissues in monocular endoscopic video remains a fundamental challenge in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Although recent volumetric and point primitive methods based on neural radiance fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian primitives have efficiently rendered surgical scenes, they still struggle with handling artifact-free tool occlusions and preserving fine anatomical details. These limitations stem from unrestricted Gaussian scaling and insufficient surface alignment constraints during reconstruction. To address these issues, we introduce Surgical Gaussian Surfels (SGS), which transform anisotropic point primitives into surface-aligned elliptical splats by constraining the scale component of the Gaussian covariance matrix along the view-aligned axis. We also introduce the Fully Fused Deformation Multilayer Perceptron (FFD-MLP), a lightweight Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) that predicts accurate surfel motion fields up to 5x faster than a standard MLP. This is coupled with locality constraints to handle complex tissue deformations. We use homodirectional view-space positional gradients to capture fine image details by splitting Gaussian Surfels in over-reconstructed regions. In addition, we define surface normals as the direction of the steepest density change within each Gaussian surfel primitive, enabling accurate normal estimation without requiring monocular normal priors. We evaluate our method on two in-vivo surgical datasets, where it outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in surface geometry, normal map quality, and rendering efficiency, while remaining competitive in real-time rendering performance. We make our code available at https://github.com/aloma85/SurgicalGaussianSurfels
在单目内窥镜视频中,可变形组织的精确几何重建仍然是机器人辅助微创手术中的一项基本挑战。尽管最近基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯原始点的体积和点原始方法已经有效地呈现了手术场景,但它们仍然在处理无工具遮挡物和保留精细解剖细节方面存在困难。这些局限性源于高斯缩放的无限制性和重建过程中表面对齐约束的不足。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了手术高斯曲面元素(Surgical Gaussian Surfels,SGS),它将各向异性的点原始元素通过约束高斯协方差矩阵的尺度成分在视图对齐轴上转换为表面对齐的椭圆平板。我们还引入了全融合变形多层感知器(Fully Fused Deformation Multilayer Perceptron,FFD-MLP),这是一个轻量级的多层感知器(MLP),它能够以比标准MLP快5倍的速度预测准确的曲面元素运动场。这与局部约束相结合,可以处理复杂的组织变形。我们通过将同方向视图空间位置梯度用于捕获图像细节,将高斯曲面元素在过度重建区域中拆分。此外,我们将表面法线定义为每个高斯曲面元素原始内部密度变化最陡峭的方向,从而能够在不需要单眼正常先验的情况下进行准确的法线估计。我们在两个体内手术数据集上评估了我们的方法,该方法在表面几何、法线图质量和渲染效率方面优于当前最新技术,同时在实时渲染性能方面保持竞争力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/aloma85/SurgicalGaussianSurfels获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在机器人辅助的微创手术中,基于神经辐射场和3D高斯原语的方法在处理工具遮挡和保留精细解剖细节方面的局限性。为解决这些问题,提出了Surgical Gaussian Surfels(SGS)方法,通过将各向异性点原始转换为表面对齐的椭圆平板,并约束高斯协方差矩阵的尺度成分来改进重建。同时,引入Fully Fused Deformation Multilayer Perceptron(FFD-MLP)网络,预测准确的surfel运动场,速度比标准MLP快5倍。此外,通过同方向视图空间位置梯度捕捉图像细节,并通过定义高斯surfel原语内最陡峭密度变化方向为表面法线,实现准确法线估计。实验表明,该方法在表面几何、法线图质量和渲染效率方面优于当前最先进的方案,并在实时渲染性能上保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 神径辐射场和高斯原始方法在手术场景重建中面临工具遮挡和解剖细节保留的挑战。
- Surgical Gaussian Surfels(SGS)通过约束高斯协方差矩阵的尺度成分来解决这些问题,并将各向异性点原始转换为表面对齐的椭圆平板。
- 引入Fully Fused Deformation Multilayer Perceptron(FFD-MLP)网络,预测准确的surfel运动场,速度更快。
- 通过同方向视图空间位置梯度捕捉图像细节,实现精细图像重建。
- 通过定义高斯surfel原语内的表面法线,实现准确法线估计,无需单眼法线先验。
- 在两个体内手术数据集上的实验表明,该方法在表面几何、法线图质量和渲染效率方面优于当前最先进的方案。
点此查看论文截图

AutoOcc: Automatic Open-Ended Semantic Occupancy Annotation via Vision-Language Guided Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xiaoyu Zhou, Jingqi Wang, Yongtao Wang, Yufei Wei, Nan Dong, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Obtaining high-quality 3D semantic occupancy from raw sensor data remains an essential yet challenging task, often requiring extensive manual labeling. In this work, we propose AutoOcc, a vision-centric automated pipeline for open-ended semantic occupancy annotation that integrates differentiable Gaussian splatting guided by vision-language models. We formulate the open-ended semantic 3D occupancy reconstruction task to automatically generate scene occupancy by combining attention maps from vision-language models and foundation vision models. We devise semantic-aware Gaussians as intermediate geometric descriptors and propose a cumulative Gaussian-to-voxel splatting algorithm that enables effective and efficient occupancy annotation. Our framework outperforms existing automated occupancy annotation methods without human labels. AutoOcc also enables open-ended semantic occupancy auto-labeling, achieving robust performance in both static and dynamically complex scenarios.
从原始传感器数据中获取高质量的三维语义占用仍然是一项重要而具有挑战性的任务,通常需要大量的手动标记。在这项工作中,我们提出了AutoOcc,这是一个以视觉为中心的开放式语义占用注释的自动化管道,它集成了由视觉语言模型引导的可区分的高斯拼贴。我们将开放式语义三维占用重建任务表述为通过结合视觉语言模型和基础视觉模型的注意力图来自动生成场景占用。我们设计语义感知高斯作为中间几何描述符,并提出一种累积的高斯到体素拼贴算法,以实现有效和高效的占用注释。我们的框架在不需要人工标签的情况下,优于现有的自动占用注释方法。AutoOcc还实现了开放式语义占用的自动标记,在静态和动态复杂的场景中都能实现稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Hightlight (main conference)
Summary
本文提出了AutoOcc,一个面向开放式语义占用的自动化注释管道。该方法结合了可微分的Gaussian splatting和视觉语言模型,用于自动生成场景占用。通过设计语义感知高斯作为中间几何描述符,并结合累积的高斯到体素splatting算法,实现了高效且有效的占用注释。该方法超越了现有无需人工标签的占用注释方法,并可在静态和动态复杂场景中实现稳健性能。
Key Takeaways
- AutoOcc是一个面向开放式语义占用的自动化注释管道,集成了可微分的Gaussian splatting和视觉语言模型。
- 通过结合注意力图和视觉语言模型,提出了场景占用的自动生成方法。
- 设计了语义感知高斯作为中间几何描述符,为占用注释提供了有效手段。
- 采用了累积的高斯到体素splatting算法,提高了占用注释的效率。
- 该方法超越了现有无需人工标签的占用注释方法。
- AutoOcc能够在复杂场景,包括静态和动态场景中实现稳健的占用注释性能。
点此查看论文截图

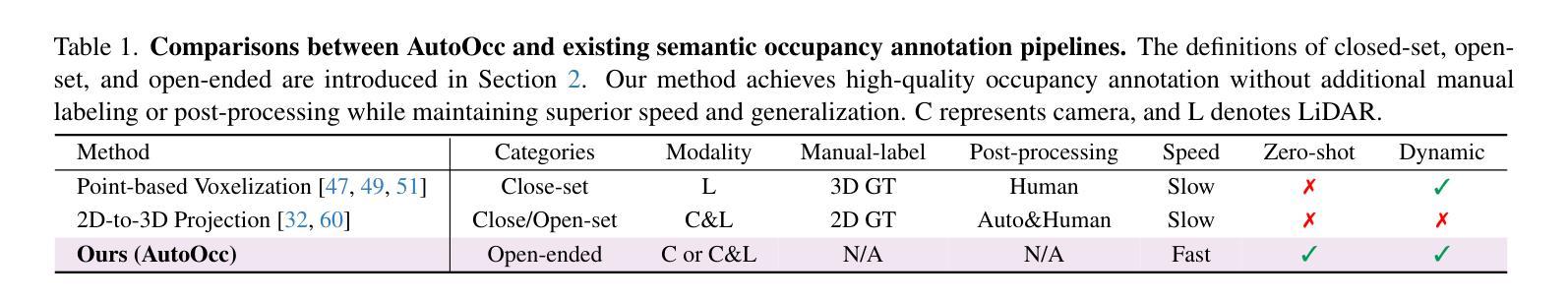
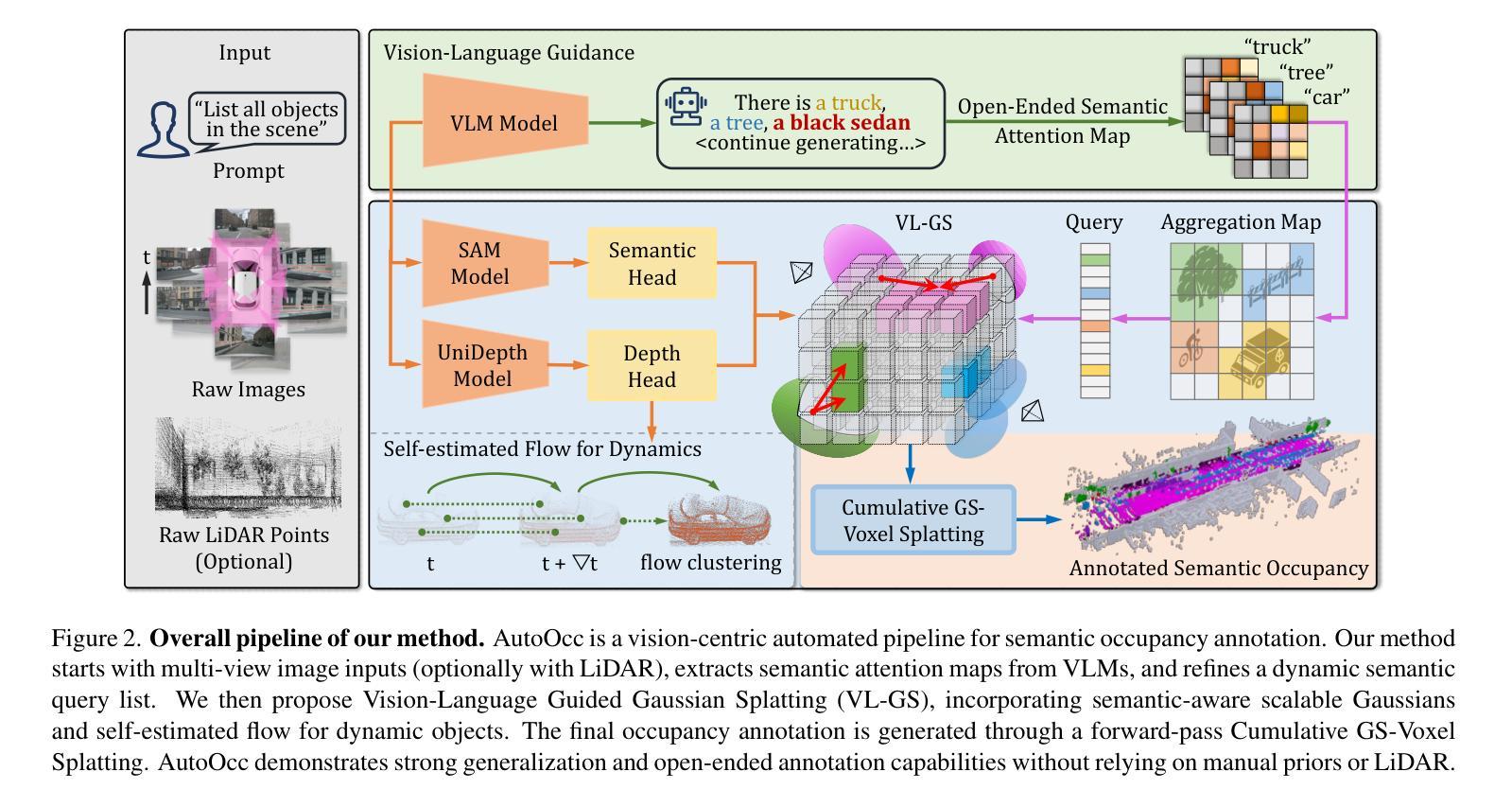
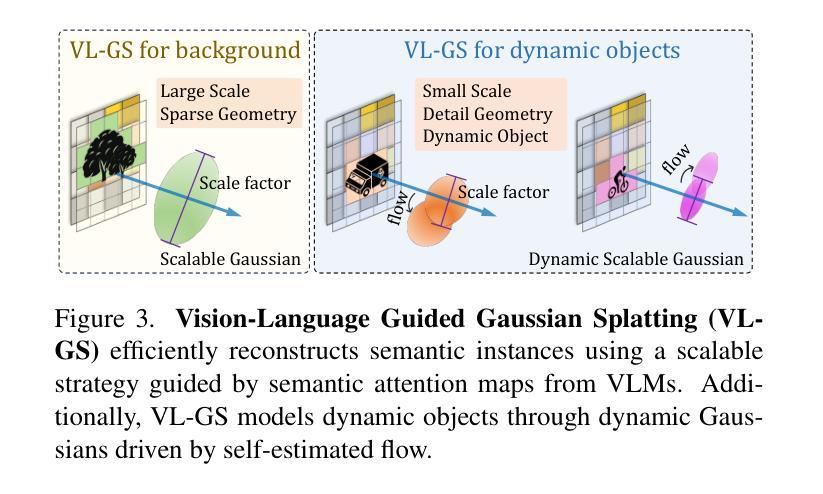
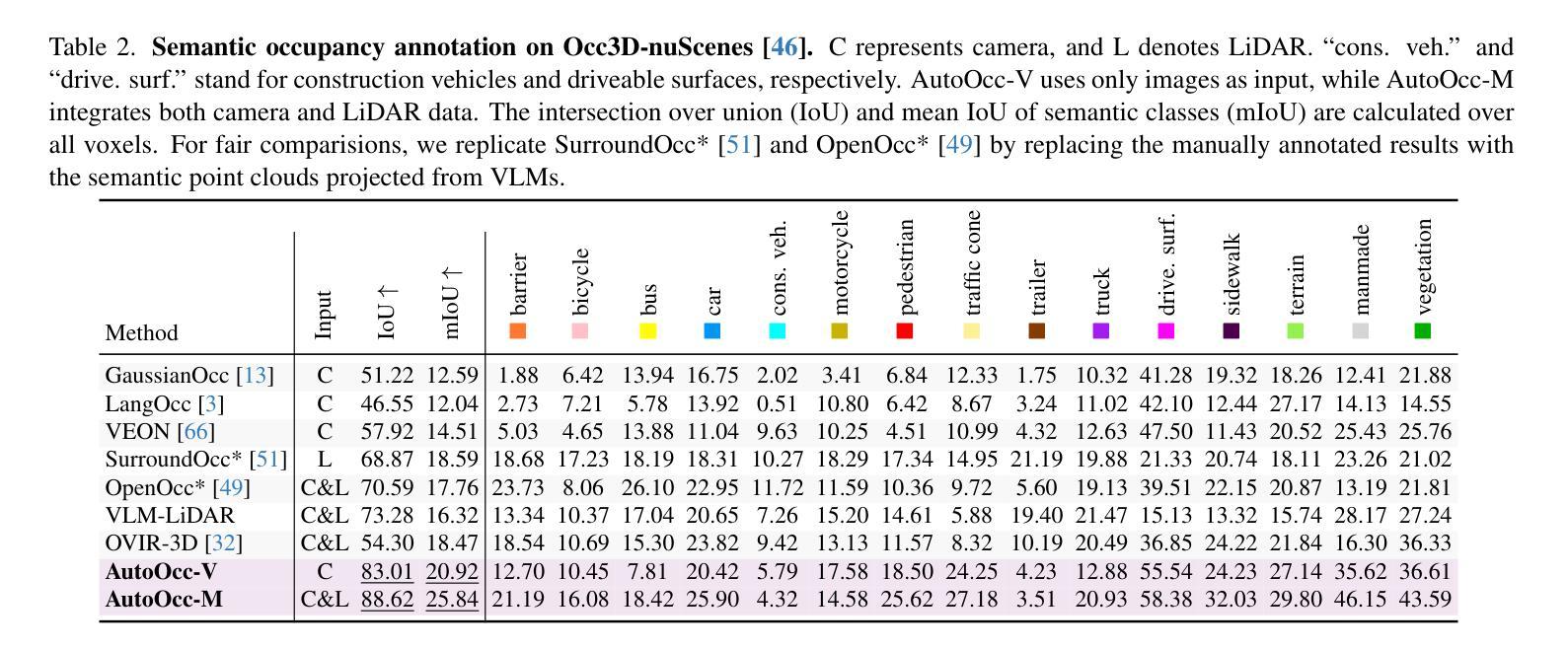
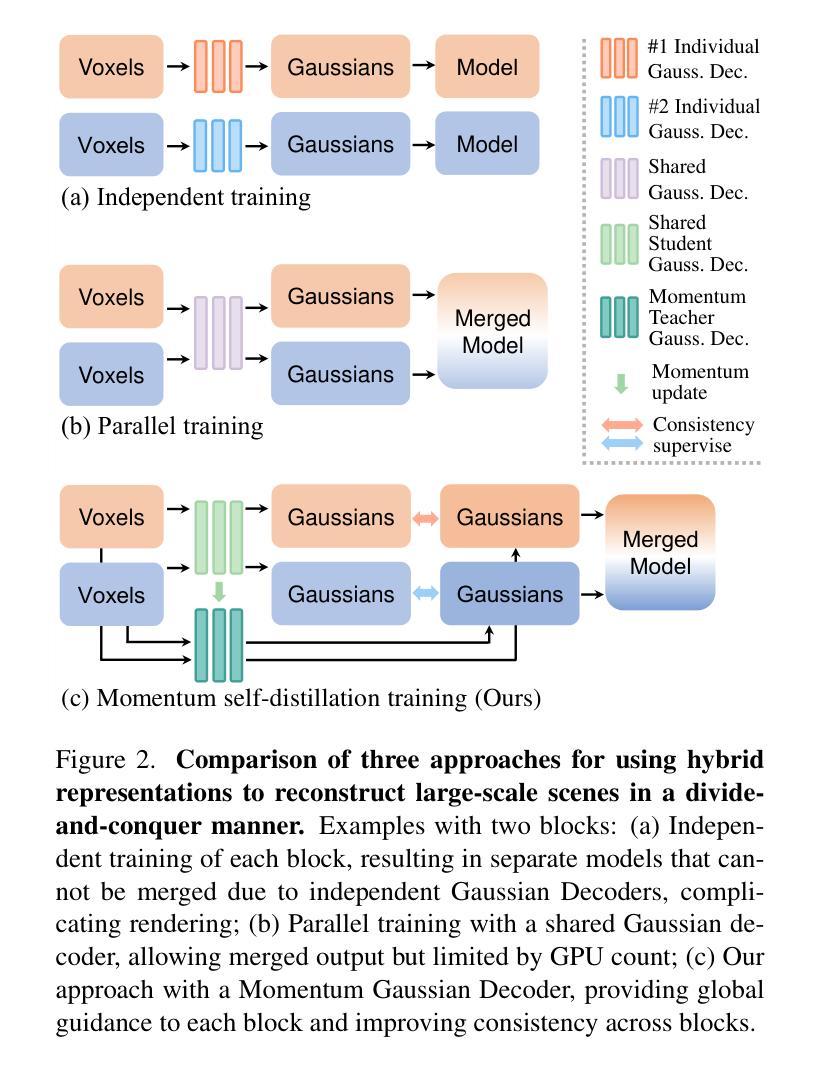
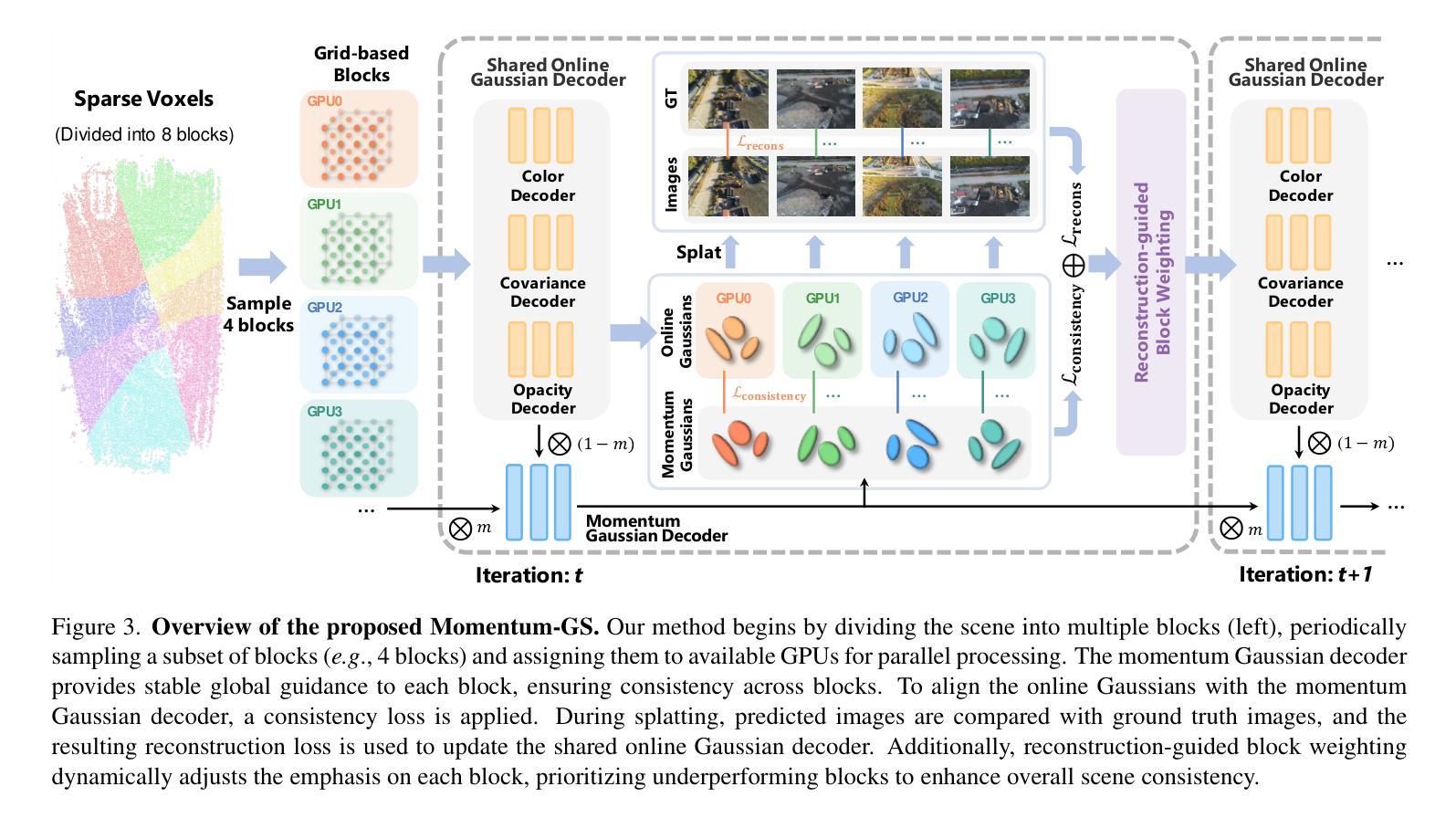
Momentum-GS: Momentum Gaussian Self-Distillation for High-Quality Large Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Jixuan Fan, Wanhua Li, Yifei Han, Tianru Dai, Yansong Tang
3D Gaussian Splatting has demonstrated notable success in large-scale scene reconstruction, but challenges persist due to high training memory consumption and storage overhead. Hybrid representations that integrate implicit and explicit features offer a way to mitigate these limitations. However, when applied in parallelized block-wise training, two critical issues arise since reconstruction accuracy deteriorates due to reduced data diversity when training each block independently, and parallel training restricts the number of divided blocks to the available number of GPUs. To address these issues, we propose Momentum-GS, a novel approach that leverages momentum-based self-distillation to promote consistency and accuracy across the blocks while decoupling the number of blocks from the physical GPU count. Our method maintains a teacher Gaussian decoder updated with momentum, ensuring a stable reference during training. This teacher provides each block with global guidance in a self-distillation manner, promoting spatial consistency in reconstruction. To further ensure consistency across the blocks, we incorporate block weighting, dynamically adjusting each block’s weight according to its reconstruction accuracy. Extensive experiments on large-scale scenes show that our method consistently outperforms existing techniques, achieving a 12.8% improvement in LPIPS over CityGaussian with much fewer divided blocks and establishing a new state of the art. Project page: https://jixuan-fan.github.io/Momentum-GS_Page/
3D高斯贴图在大规模场景重建中取得了显著的成功,但仍然存在挑战,因为存在较高的训练内存消耗和存储开销。融合隐式和显式特征的混合表示提供了一种缓解这些限制的方法。然而,在并行块式训练中应用时,会出现两个问题:一是重建精度因每个块独立训练时数据多样性减少而下降,二是并行训练将块的数量限制为可用的GPU数量。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Momentum-GS,这是一种基于动量自蒸馏技术的新方法,旨在促进块之间的一致性和准确性,同时解除块数量与物理GPU数量的耦合。我们的方法维护了一个使用动量更新的教师高斯解码器,以确保训练过程中的稳定参考。这位教师以自蒸馏的方式为每个块提供全局指导,促进重建的空间一致性。为了进一步增强块之间的一致性,我们引入了块权重,根据重建精度动态调整每个块的权重。在大规模场景上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于现有技术,在CityGaussian上的LPIPS提高了12.8%,并且使用的块更少,创下了新的世界纪录。项目页面:[https://jixuan-fan.github.io/Momentum-GS_Page/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大规模场景重建领域,3D高斯渲染技术已经取得显著进展,但仍有内存消耗大和存储开销的问题待解决。为此,研究者提出混合表示法以融合隐式和显式特征来解决这些问题。然而,在并行块级训练中,该方法面临两个关键问题:重建精度下降和数据多样性减少的问题。为了克服这些缺陷,研究者提出Momentum-GS方法,采用基于动量的自我蒸馏技术来提高各块之间的一致性和准确性,并将块的数目与实际的GPU数量分开计算。实验表明,该方法在大型场景上的表现优于现有技术,相较于CityGaussian提高了LPIPS得分12.8%,并实现了更少的块分割,成为业界新的领跑者。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯渲染技术在大型场景重建中取得显著进展,但仍面临内存消耗大和存储开销的问题。
- 混合表示法试图通过结合隐式和显式特征来解决上述问题。但在并行块级训练中重建精度和多样性的问题限制了其性能。
- Momentum-GS方法通过引入基于动量的自我蒸馏技术来提高块间的一致性和准确性。
- Momentum-GS解决了并行训练中的两个关键问题:重建精度下降和数据多样性减少的问题。它通过引入教师高斯解码器并提供全局指导来实现这一目标。此外,还引入了块权重机制来确保重建的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

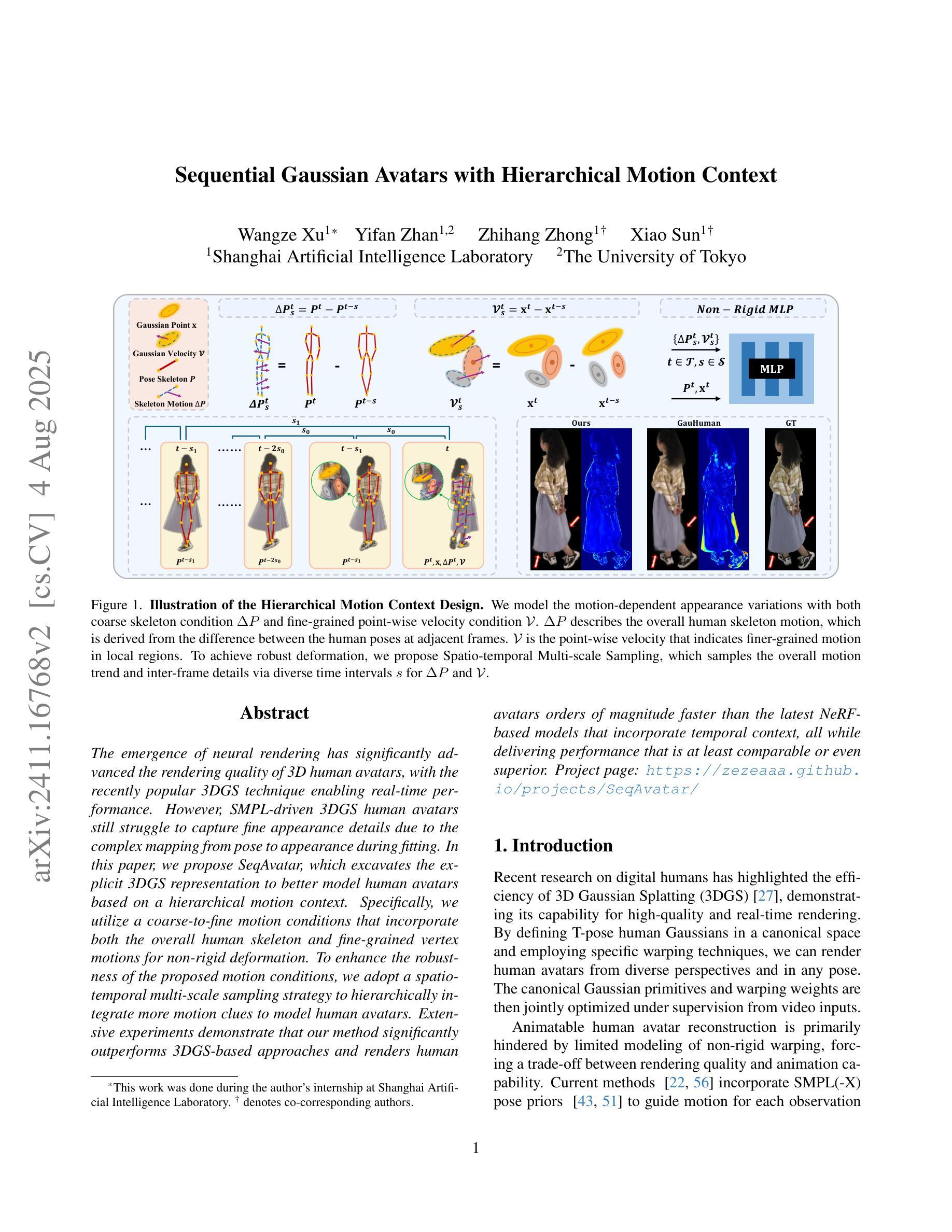
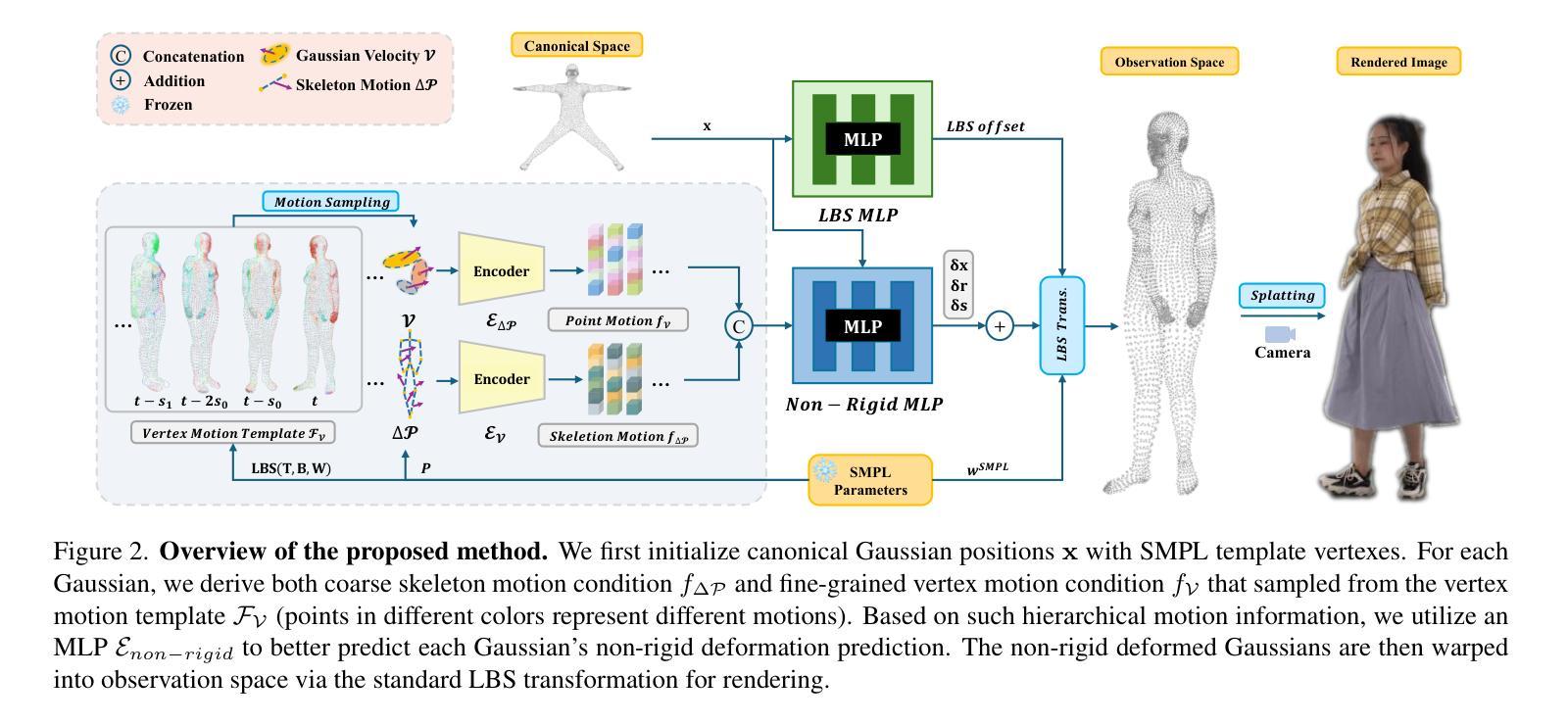
Sequential Gaussian Avatars with Hierarchical Motion Context
Authors:Wangze Xu, Yifan Zhan, Zhihang Zhong, Xiao Sun
The emergence of neural rendering has significantly advanced the rendering quality of 3D human avatars, with the recently popular 3DGS technique enabling real-time performance. However, SMPL-driven 3DGS human avatars still struggle to capture fine appearance details due to the complex mapping from pose to appearance during fitting. In this paper, we propose SeqAvatar, which excavates the explicit 3DGS representation to better model human avatars based on a hierarchical motion context. Specifically, we utilize a coarse-to-fine motion conditions that incorporate both the overall human skeleton and fine-grained vertex motions for non-rigid deformation. To enhance the robustness of the proposed motion conditions, we adopt a spatio-temporal multi-scale sampling strategy to hierarchically integrate more motion clues to model human avatars. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms 3DGS-based approaches and renders human avatars orders of magnitude faster than the latest NeRF-based models that incorporate temporal context, all while delivering performance that is at least comparable or even superior. Project page: https://zezeaaa.github.io/projects/SeqAvatar/
神经渲染的出现极大地提高了3D人类虚拟形象的渲染质量,最近流行的3DGS技术能够实现实时性能。然而,SMPL驱动的3DGS人类虚拟形象仍然难以捕捉精细的外观细节,因为在拟合过程中从姿势到外观的映射非常复杂。在本文中,我们提出了SeqAvatar,它挖掘了明确的3DGS表示,以基于分层运动上下文更好地建模人类虚拟形象。具体来说,我们利用从粗到细的运动条件,结合整体人类骨骼和精细顶点运动进行非刚性变形。为了提高所提出运动条件的稳健性,我们采用时空多尺度采样策略,分层融合更多运动线索来建模人类虚拟形象。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著优于基于3DGS的方法,并且与采用时间上下文的最新NeRF模型相比,渲染人类虚拟形象的速度要快得多,同时性能至少相当甚至更优。项目页面:https://zezeaaa.github.io/projects/SeqAvatar/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
神经网络渲染技术的出现显著提高了3D人类角色的渲染质量,特别是流行的3DGS技术能够实现实时性能。然而,基于SMPL的3DGS人类角色在拟合过程中仍然难以捕捉精细的外观细节。本文提出SeqAvatar,通过挖掘明确的3DGS表示并基于分层运动上下文对人物角色进行更好的建模来解决这个问题。具体而言,它采用从粗到细的运动条件,结合整体人物骨骼和精细顶点运动来实现非刚体变形。为了增强运动条件的稳健性,研究采用了时空多尺度采样策略来分层整合更多运动线索。实验表明,该方法显著优于基于3DGS的方法,并且渲染速度比最新结合时间上下文的NeRF模型快得多,同时性能至少与之相当或更优。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络渲染技术提高了3D人类角色的渲染质量,特别是3DGS技术可实现实时性能。
- 基于SMPL的3DGS方法在捕捉角色精细外观细节方面存在挑战。
- SeqAvatar通过挖掘明确的3DGS表示来解决这一问题,基于分层运动上下文对人物角色进行建模。
- SeqAvatar采用从粗到细的运动条件,结合整体人物骨骼和精细顶点运动来实现非刚体变形。
- 为了增强运动条件的稳健性,采用了时空多尺度采样策略。
- 实验显示SeqAvatar显著优于基于3DGS的方法,并且渲染速度更快。
点此查看论文截图
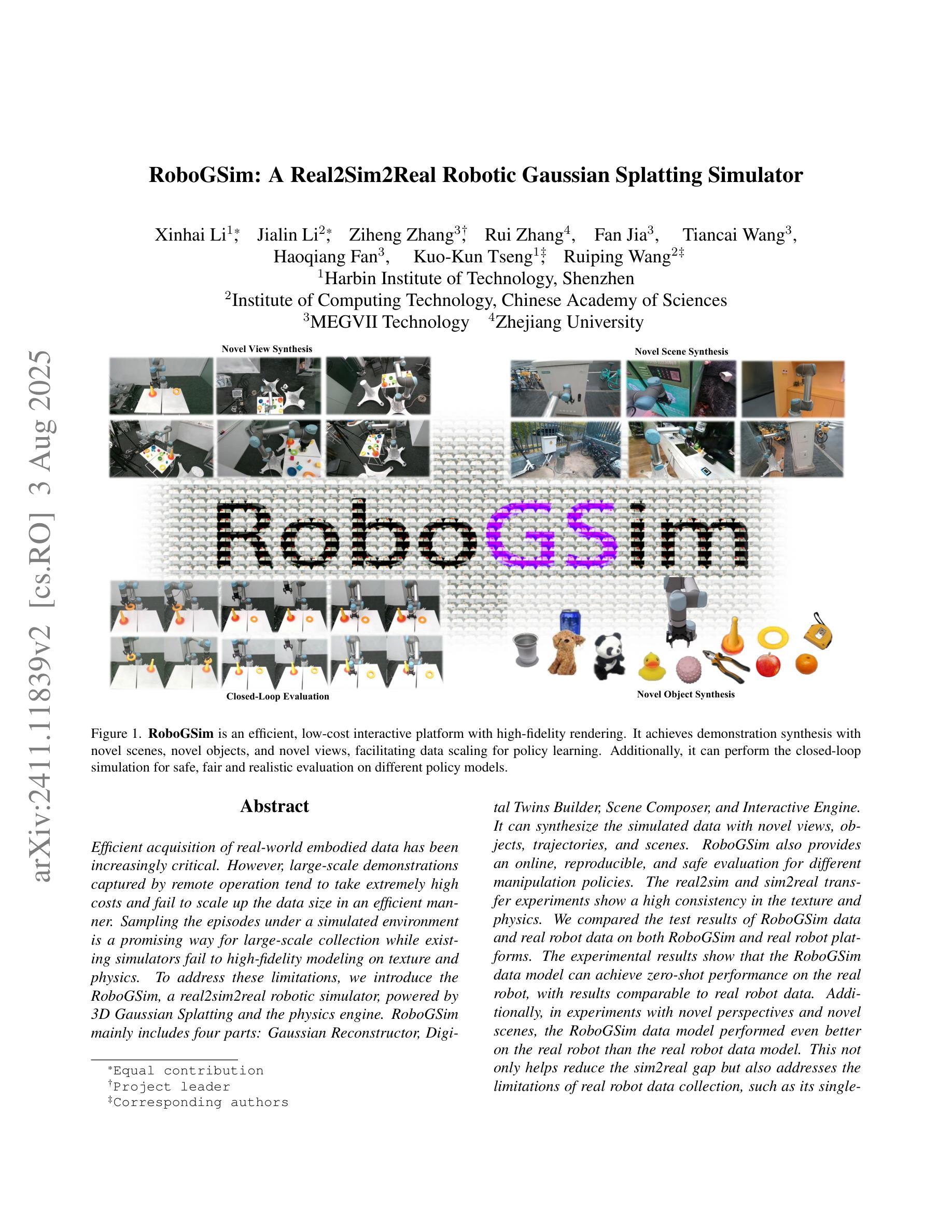
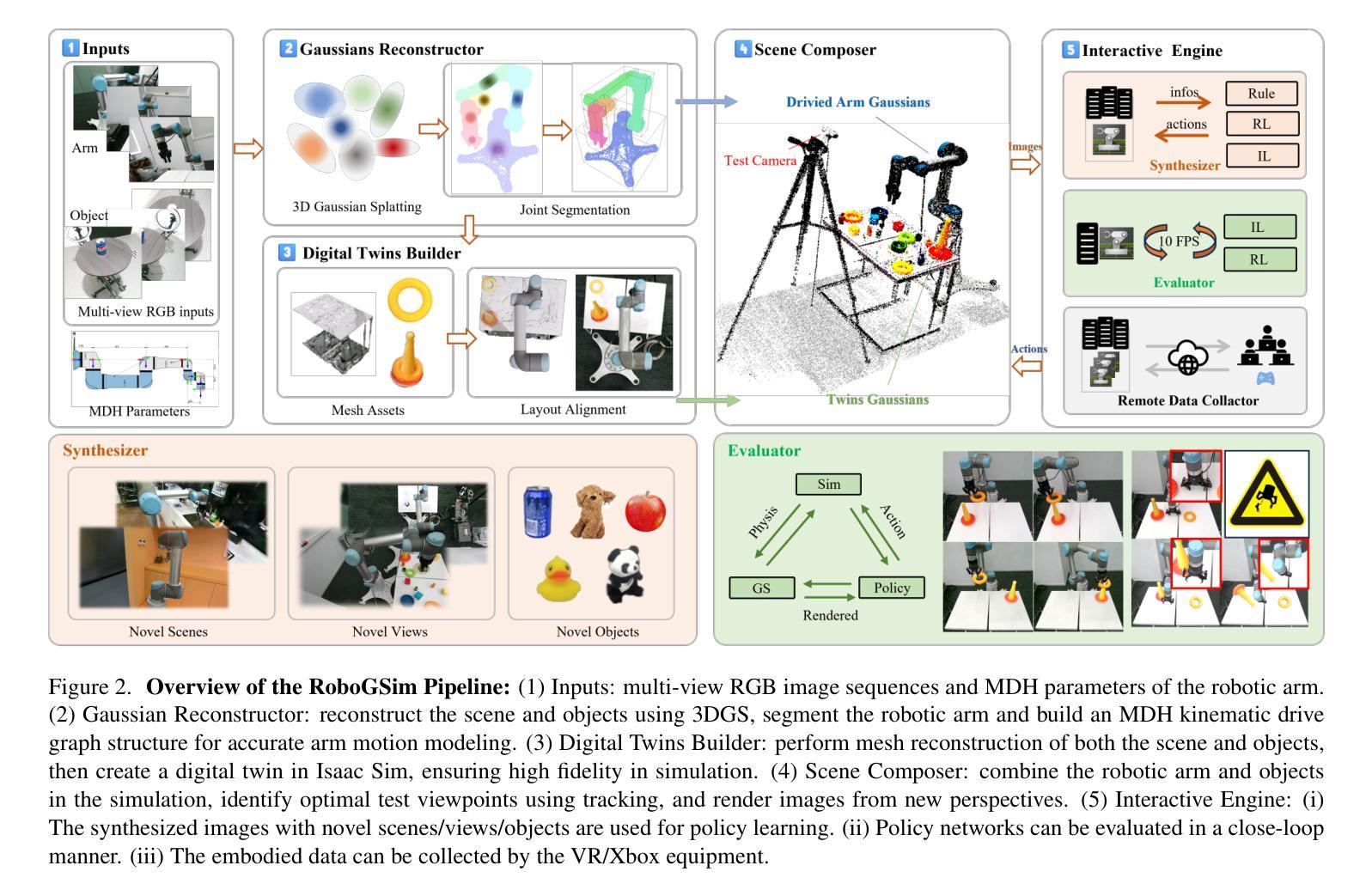
RoboGSim: A Real2Sim2Real Robotic Gaussian Splatting Simulator
Authors:Xinhai Li, Jialin Li, Ziheng Zhang, Rui Zhang, Fan Jia, Tiancai Wang, Haoqiang Fan, Kuo-Kun Tseng, Ruiping Wang
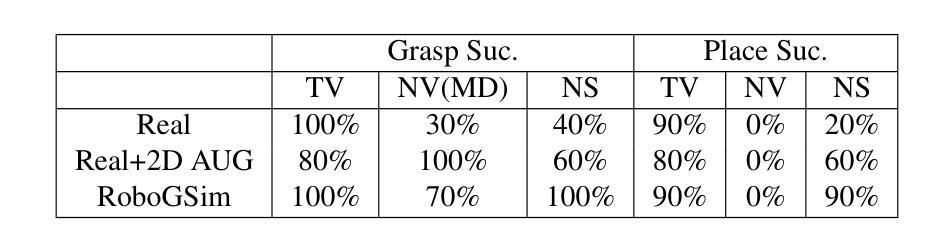
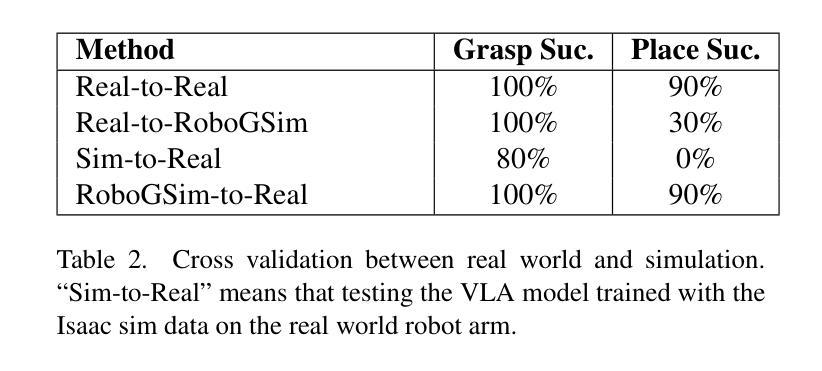
Efficient acquisition of real-world embodied data has been increasingly critical. However, large-scale demonstrations captured by remote operation tend to take extremely high costs and fail to scale up the data size in an efficient manner. Sampling the episodes under a simulated environment is a promising way for large-scale collection while existing simulators fail to high-fidelity modeling on texture and physics. To address these limitations, we introduce the RoboGSim, a real2sim2real robotic simulator, powered by 3D Gaussian Splatting and the physics engine. RoboGSim mainly includes four parts: Gaussian Reconstructor, Digital Twins Builder, Scene Composer, and Interactive Engine. It can synthesize the simulated data with novel views, objects, trajectories, and scenes. RoboGSim also provides an online, reproducible, and safe evaluation for different manipulation policies. The real2sim and sim2real transfer experiments show a high consistency in the texture and physics. We compared the test results of RoboGSim data and real robot data on both RoboGSim and real robot platforms. The experimental results show that the RoboGSim data model can achieve zero-shot performance on the real robot, with results comparable to real robot data. Additionally, in experiments with novel perspectives and novel scenes, the RoboGSim data model performed even better on the real robot than the real robot data model. This not only helps reduce the sim2real gap but also addresses the limitations of real robot data collection, such as its single-source and high cost. We hope RoboGSim serves as a closed-loop simulator for fair comparison on policy learning. More information can be found on our project page https://robogsim.github.io/.
现实世界体感数据的高效采集变得越来越关键。然而,通过远程操作捕获的大规模演示往往成本极高,且未能以高效的方式扩大数据量。在模拟环境下对情节进行采样是大规模采集的一种有前途的方式,但现有模拟器在纹理和物理方面的高保真建模存在不足。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了RoboGSim,这是一个由3D高斯拼贴和物理引擎驱动的real2sim2real机器人模拟器。RoboGSim主要包括四个部分:高斯重建器、数字孪生构建器、场景作曲家和交互引擎。它可以合成具有新颖视角、物体、轨迹和场景模拟数据。RoboGSim还为不同的操作策略提供了在线、可重复和安全的评估。纹理和物理的实拟与拟实转移实验表现出高度一致性。我们在RoboGSim平台和真实机器人平台上对RoboGSim数据和真实机器人数据进行了测试结果的比较。实验结果表明,RoboGSim数据模型能够在真实机器人上实现零射效果,其性能与真实机器人数据相当。此外,在具有新颖视角和场景的实验中,RoboGSim数据模型在真实机器人上的表现甚至比真实机器人数据模型更好。这不仅有助于缩小模拟与现实的差距,还解决了真实机器人数据采集的局限性,如单一来源和高成本的问题。我们希望RoboGSim能作为闭环模拟器,为策略学习的公平比较提供服务。更多信息请访问我们的项目页面https://robogsim.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了RoboGSim模拟器,通过利用3D高斯Splatting和物理引擎技术解决了远程操作大规模演示所面临的问题。该模拟器主要由高斯重建器、数字双胞胎建造器、场景组合器和交互引擎四部分组成,可以合成模拟数据并展示新颖的视图、物体、轨迹和场景。此外,RoboGSim提供了在线、可重复和安全的评估不同操作策略的平台。通过真实到模拟再到真实的转移实验,展现了其在纹理和物理方面的高度一致性。实验结果显示,RoboGSim数据模型能在真实机器人上实现零射击性能,与真实机器人数据结果相当。并且在新型视角和场景的实验中,RoboGSim数据模型甚至表现更佳。该模拟器不仅有助于缩小模拟与真实之间的差距,还解决了真实机器人数据采集的局限性,如单一来源和高成本问题。期望RoboGSim能作为闭环模拟器,为策略学习提供公平比较的平台。
关键见解
- RoboGSim是一个基于3D高斯Splatting和物理引擎技术的模拟器,旨在解决大规模收集现实机器人数据的高成本和无法有效扩展的问题。
- RoboGSim包括四个主要部分,能够合成模拟数据并展示不同的视图、物体、轨迹和场景。
- 该模拟器提供了在线、可重复和安全的评估平台,用于不同操作策略的评价。
- RoboGSim在真实到模拟再到真实的转移实验中展现了其在纹理和物理方面的高度一致性。
- 实验结果显示,RoboGSim数据模型在真实机器人上的性能与真实机器人数据相当,甚至在某些情况下表现更佳。
- 该模拟器有助于缩小模拟与真实机器人之间的差距,并解决真实机器人数据采集的局限性。
- RoboGSim的预期作用是为策略学习提供一个公平比较的平台,作为一个闭环模拟器。
点此查看论文截图