⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
Hierarchical Learning-Based Control for Multi-Agent Shepherding of Stochastic Autonomous Agents
Authors:Italo Napolitano, Stefano Covone, Andrea Lama, Francesco De Lellis, Mario di Bernardo
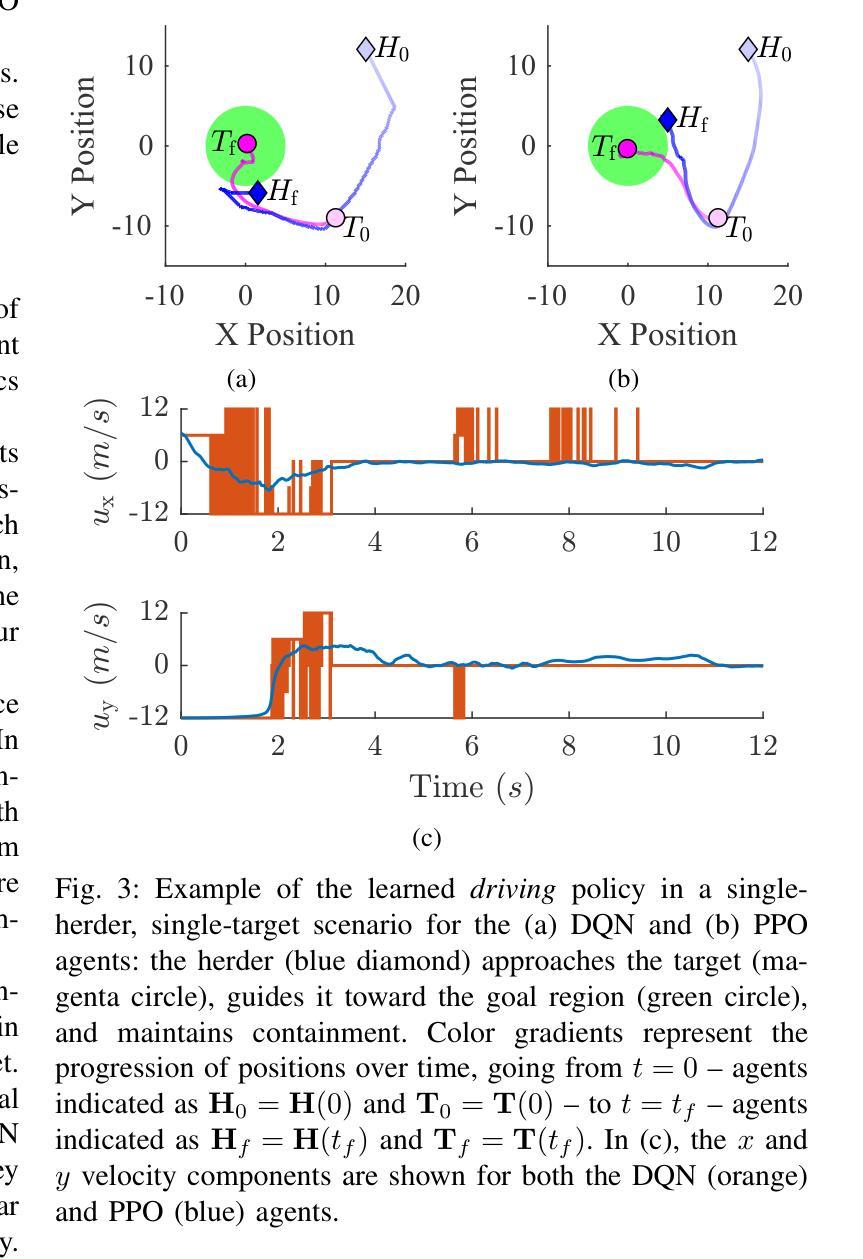
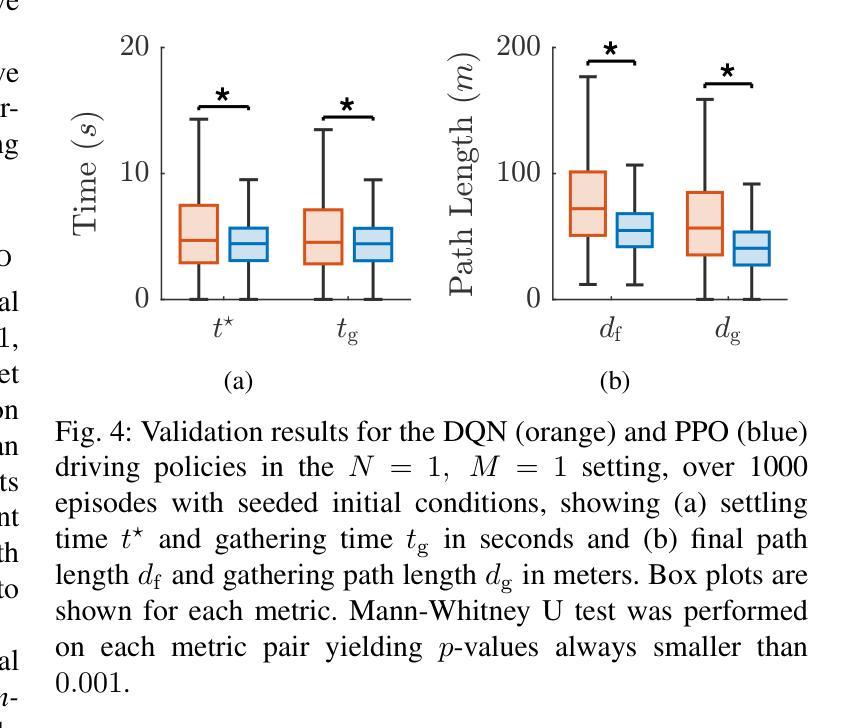
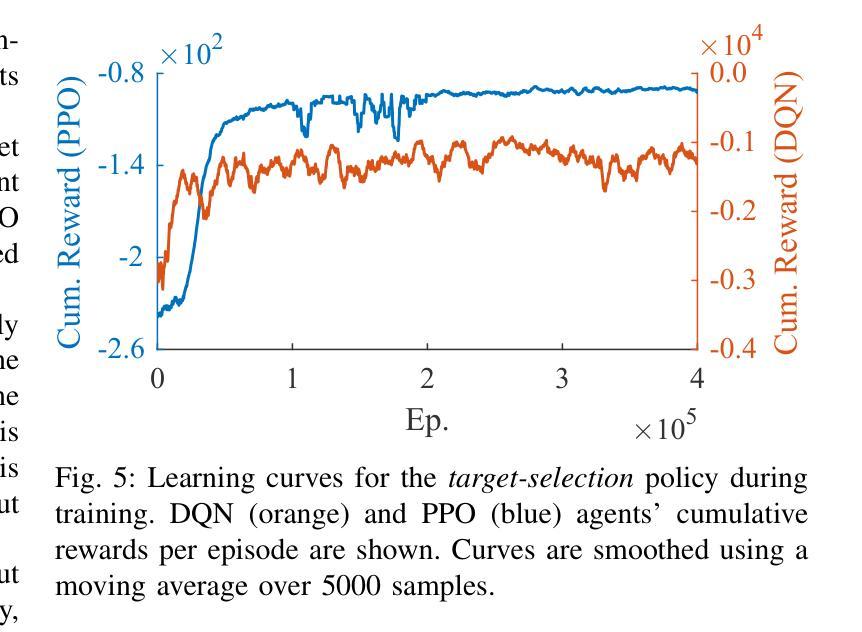
Multi-agent shepherding represents a challenging distributed control problem where herder agents must coordinate to guide independently moving targets to desired spatial configurations. Most existing control strategies assume cohesive target behavior, which frequently fails in practical applications where targets exhibit stochastic autonomous behavior. This paper presents a hierarchical learning-based control architecture that decomposes the shepherding problem into a high-level decision-making module and a low-level motion control component. The proposed distributed control system synthesizes effective control policies directly from closed-loop experience without requiring explicit inter-agent communication or prior knowledge of target dynamics. The decentralized architecture achieves cooperative control behavior through emergent coordination without centralized supervision. Experimental validation demonstrates superior closed-loop performance compared to state-of-the-art heuristic control methods, achieving 100% success rates with improved settling times and control efficiency. The control architecture scales beyond its design conditions, adapts to time-varying goal regions, and demonstrates practical implementation feasibility through real-time experiments on the Robotarium platform.
多智能体放牧代表了一个具有挑战性的分布式控制问题,其中牧羊人智能体必须协调行动,以引导独立移动的目标达到期望的空间配置。大多数现有的控制策略都假设目标行为是协调一致的,这在目标表现出随机自主行为的应用场景中往往会失败。本文提出了一种基于层次学习的控制架构,它将放牧问题分解为高层决策模块和底层运动控制组件。所提出的分布式控制系统直接从闭环经验中综合有效的控制策略,无需明确的智能体间通信或对目标动力学的先验知识。去中心化的架构通过涌现协调实现了无集中监管的合作控制行为。实验验证表明,与传统的启发式控制方法相比,该架构具有优越的闭环性能,实现了100%的成功率,缩短了稳定时间和提高了控制效率。该控制架构在设计条件之外进行了扩展,适应了时变目标区域,并通过Robotarium平台上的实时实验证明了其实施的可行性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于分层学习控制架构的多智能体牧羊问题解决方案。该架构分为高层决策模块和低层运动控制组件,可从闭环经验中直接合成有效的控制策略,无需明确的智能体间通信或对目标动力学的先验知识。该分散式架构通过突发协调实现控制行为,无需中央监督。实验验证表明,与传统的启发式控制方法相比,该架构具有优异的闭环性能,实现了更高的成功率、更快的结算时间和更高的控制效率。此外,该控制架构能够适应时间变化的目标区域,在Robotarium平台上进行实时实验,证明了其实施的可行性。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体牧羊问题是一个分布式控制挑战,需要智能体协调引导独立移动的目标达到期望的空间配置。
- 现有控制策略大多假设目标行为具有凝聚力,但在目标表现出随机自主行为时,这些策略常常会失效。
- 本文提出了一种基于分层学习控制架构的解决方案,该架构分为高层决策和低层运动控制。
- 该架构能从闭环经验中合成有效的控制策略,无需智能体间的明确通信或对目标动力学的先验知识。
- 分散式架构通过突发协调实现控制行为,无需中央监督,并通过实验验证其性能优于启发式控制方法。
- 控制架构具有良好的适应性,能够应对时间变化的目标区域。
点此查看论文截图

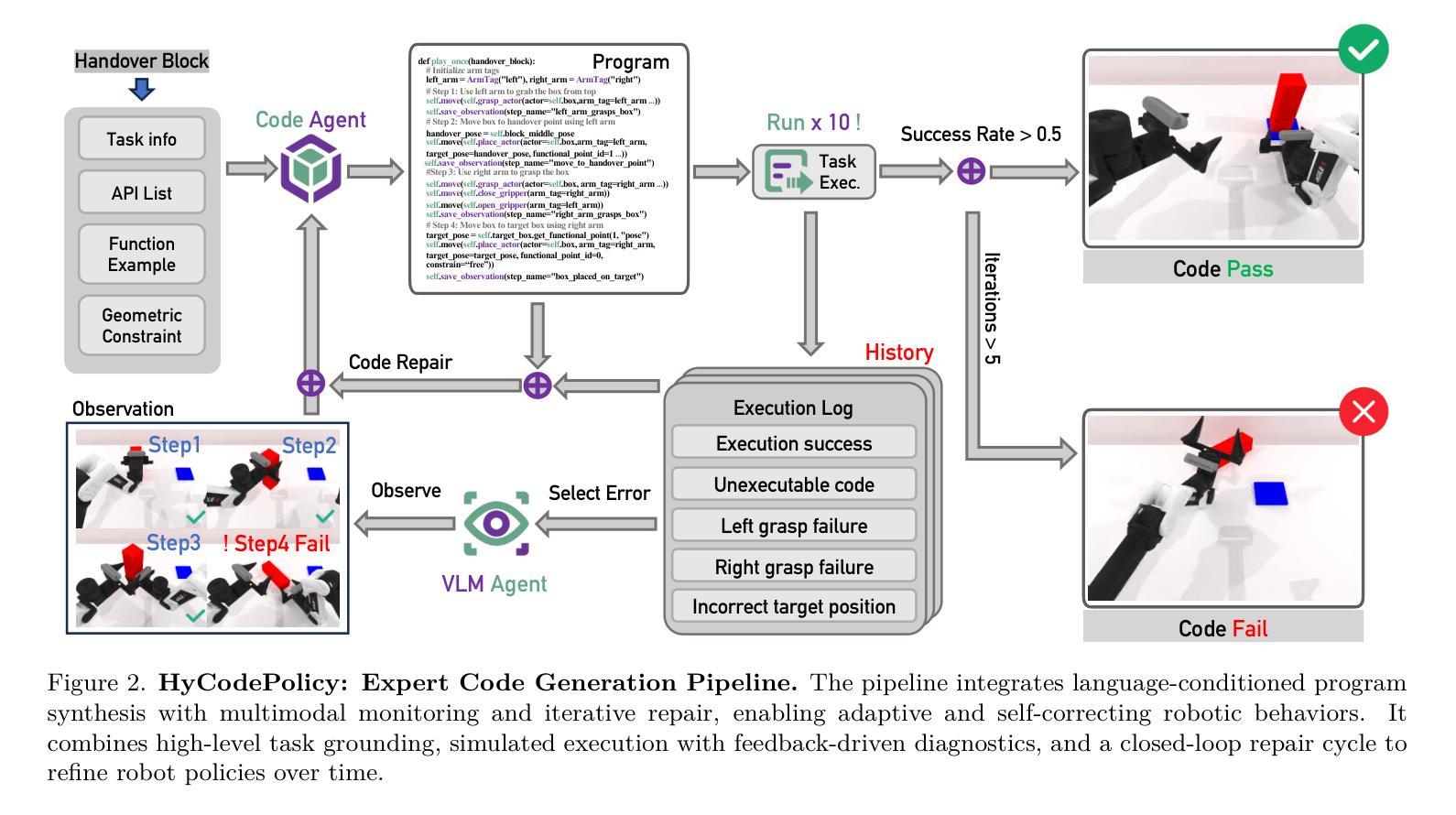
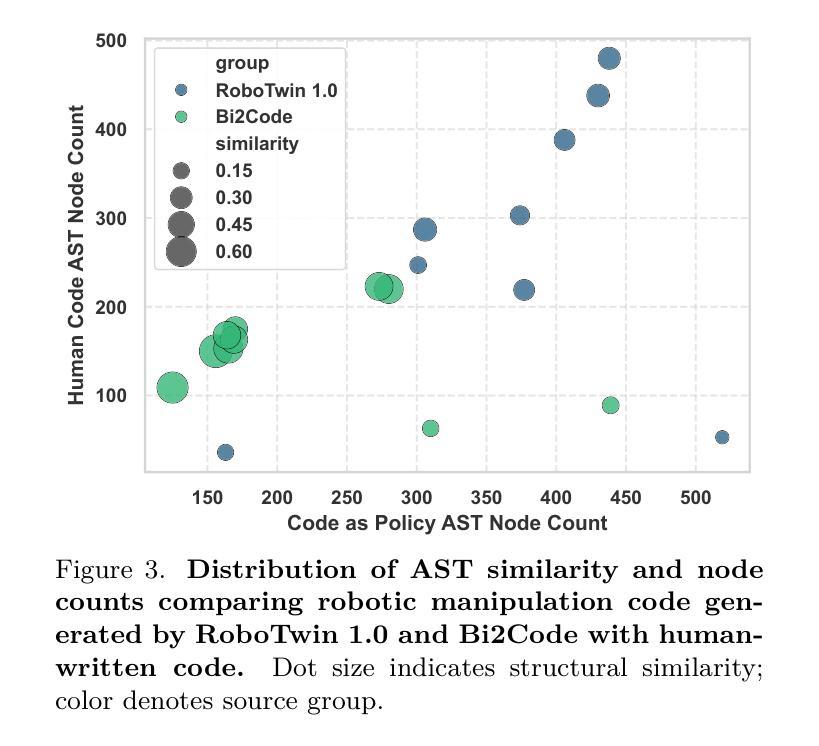
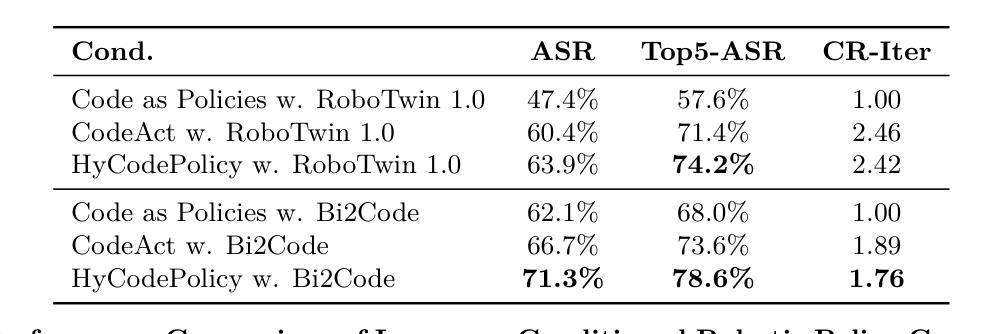
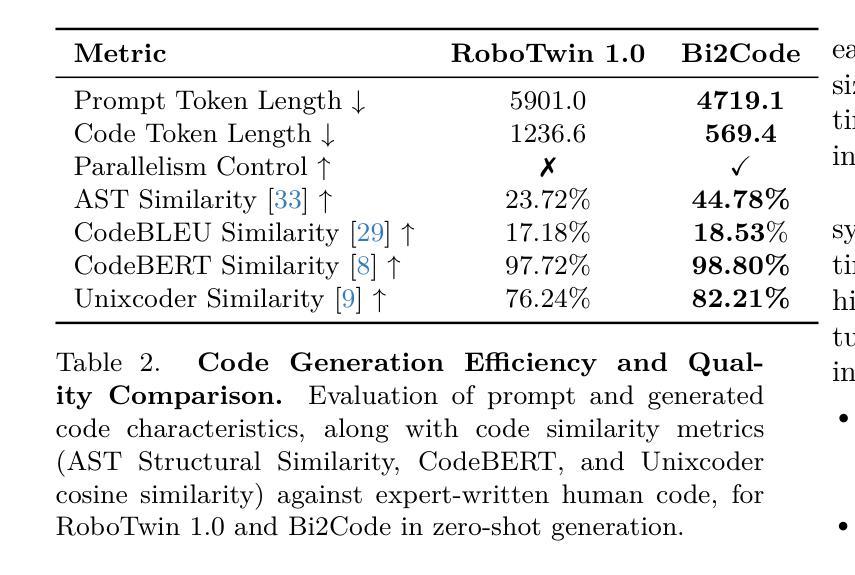
HyCodePolicy: Hybrid Language Controllers for Multimodal Monitoring and Decision in Embodied Agents
Authors:Yibin Liu, Zhixuan Liang, Zanxin Chen, Tianxing Chen, Mengkang Hu, Wanxi Dong, Congsheng Xu, Zhaoming Han, Yusen Qin, Yao Mu
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have enabled richer perceptual grounding for code policy generation in embodied agents. However, most existing systems lack effective mechanisms to adaptively monitor policy execution and repair codes during task completion. In this work, we introduce HyCodePolicy, a hybrid language-based control framework that systematically integrates code synthesis, geometric grounding, perceptual monitoring, and iterative repair into a closed-loop programming cycle for embodied agents. Technically, given a natural language instruction, our system first decomposes it into subgoals and generates an initial executable program grounded in object-centric geometric primitives. The program is then executed in simulation, while a vision-language model (VLM) observes selected checkpoints to detect and localize execution failures and infer failure reasons. By fusing structured execution traces capturing program-level events with VLM-based perceptual feedback, HyCodePolicy infers failure causes and repairs programs. This hybrid dual feedback mechanism enables self-correcting program synthesis with minimal human supervision. Our results demonstrate that HyCodePolicy significantly improves the robustness and sample efficiency of robot manipulation policies, offering a scalable strategy for integrating multimodal reasoning into autonomous decision-making pipelines.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的进步为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了更丰富的感知基础。然而,大多数现有系统缺乏有效的机制来在任务完成过程中自适应地监视策略执行和修复代码。在这项工作中,我们介绍了HyCodePolicy,这是一个基于混合语言的控制框架,它系统地集成了代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复,形成一个闭环编程周期,用于实体代理。从技术上讲,给定自然语言指令,我们的系统首先将其分解为子目标并生成基于对象为中心的几何原始数据的初始可执行程序。然后,该程序在仿真中执行,同时视觉语言模型(VLM)观察选定的检查点以检测和定位执行故障并推断故障原因。通过将捕获程序级事件的结构化执行轨迹与基于VLM的感知反馈相结合,HyCodePolicy可以推断出失败原因并修复程序。这种混合双重反馈机制实现了自我修正的程序合成,只需最少的人工监督。我们的结果表明,HyCodePolicy显著提高了机器人操作策略的稳健性和样本效率,为将多模态推理集成到自主决策管道中提供了可伸缩的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025 Workshop on Multi-Modal Reasoning for Agentic Intelligence
Summary
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的近期发展,为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了更丰富的感知基础。然而,大多数现有系统缺乏在任务完成过程中自适应地监控策略执行和修复代码的有效机制。在此工作中,我们引入了HyCodePolicy,这是一个基于语言的控制框架,系统地集成了代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复,为实体代理提供了一个闭环编程周期。给定自然语言指令,我们的系统首先将其分解为子目标并生成基于对象为中心的几何原始数据的初始可执行程序。该程序在模拟中执行,同时视觉语言模型(VLM)会观察选定检查点以检测和定位执行故障并推断故障原因。通过融合捕捉程序级事件的结构化执行轨迹与基于VLM的感知反馈,HyCodePolicy能够推断故障原因并修复程序。这种混合双重反馈机制实现了自我修正的程序合成,几乎无需人工监督。我们的结果表明,HyCodePolicy显著提高了机器人操作策略的稳健性和样本效率,为自主决策管道中多模式推理的集成提供了可扩展的策略。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了丰富的感知基础。
- 当前系统缺乏在任务执行过程中自适应监控和调整代码的能力。
- HyCodePolicy是一个基于语言的控制框架,集成了代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复。
- 系统通过分解自然语言指令生成初始可执行程序,该程序基于对象中心的几何原始数据。
- 程序在模拟环境中执行,期间由视觉语言模型(VLM)观察并检测执行故障。
- 通过结合结构化执行轨迹和基于VLM的感知反馈,HyCodePolicy能推断故障原因并进行程序修复。
点此查看论文截图
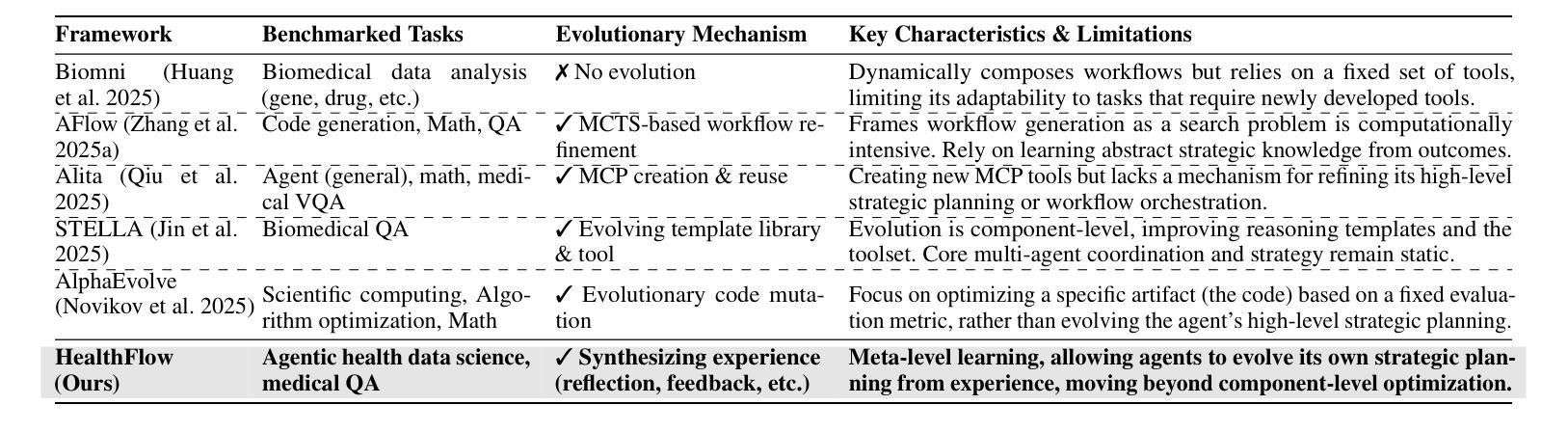
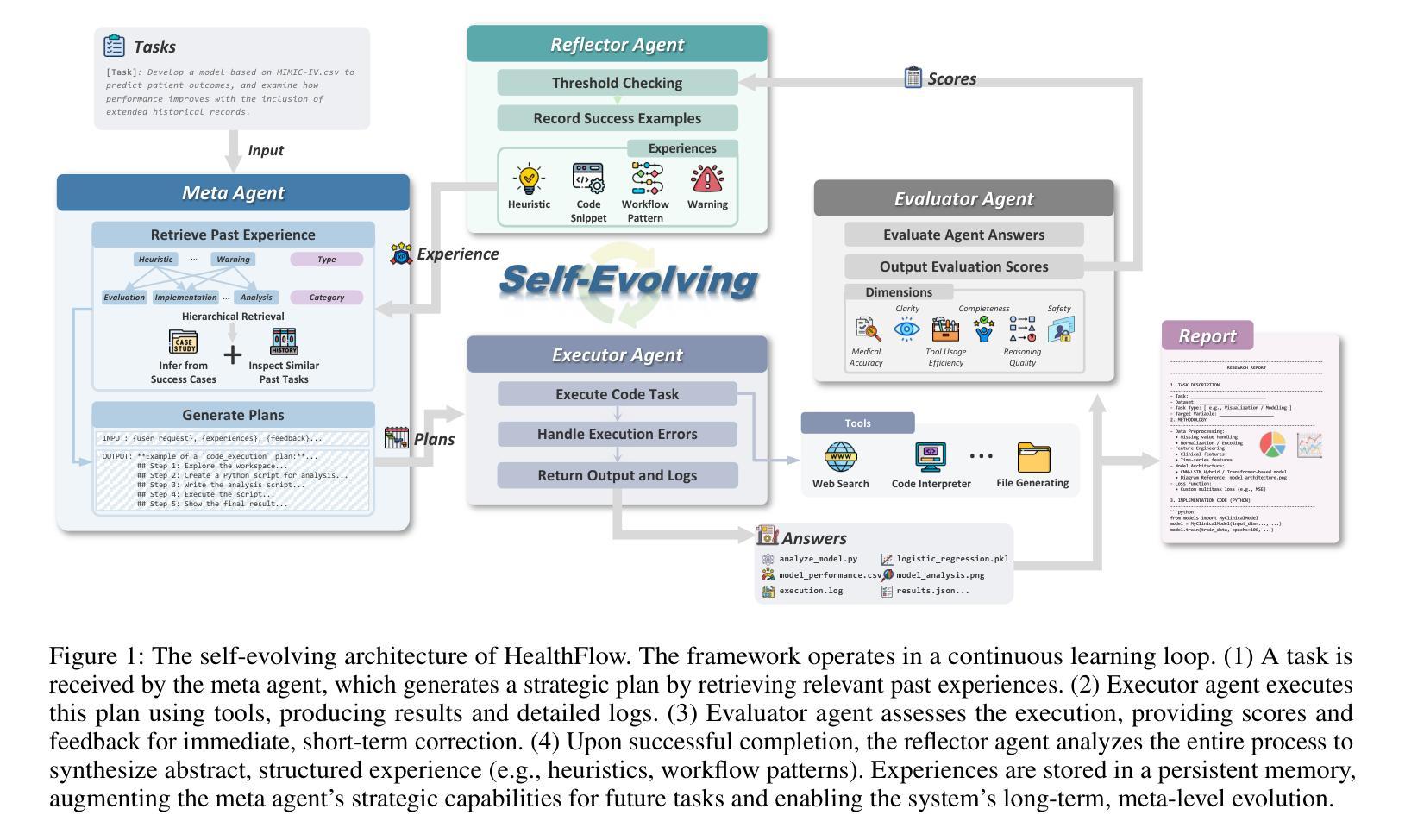
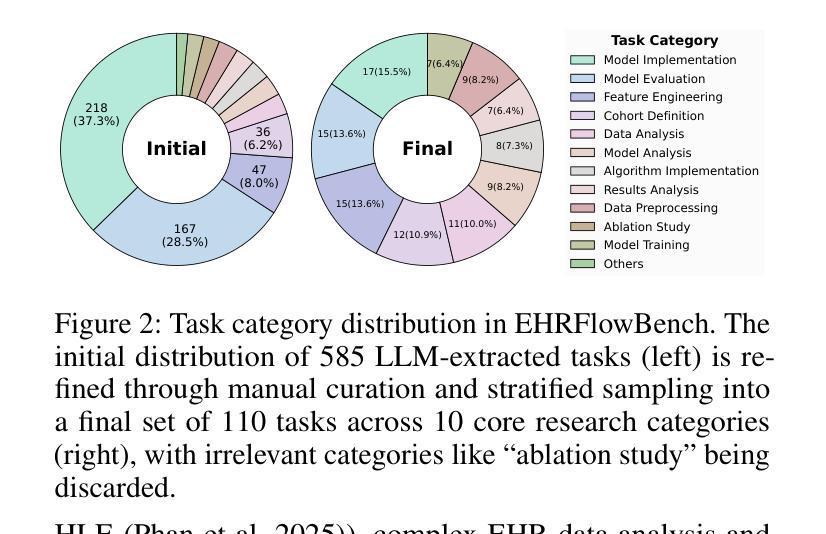
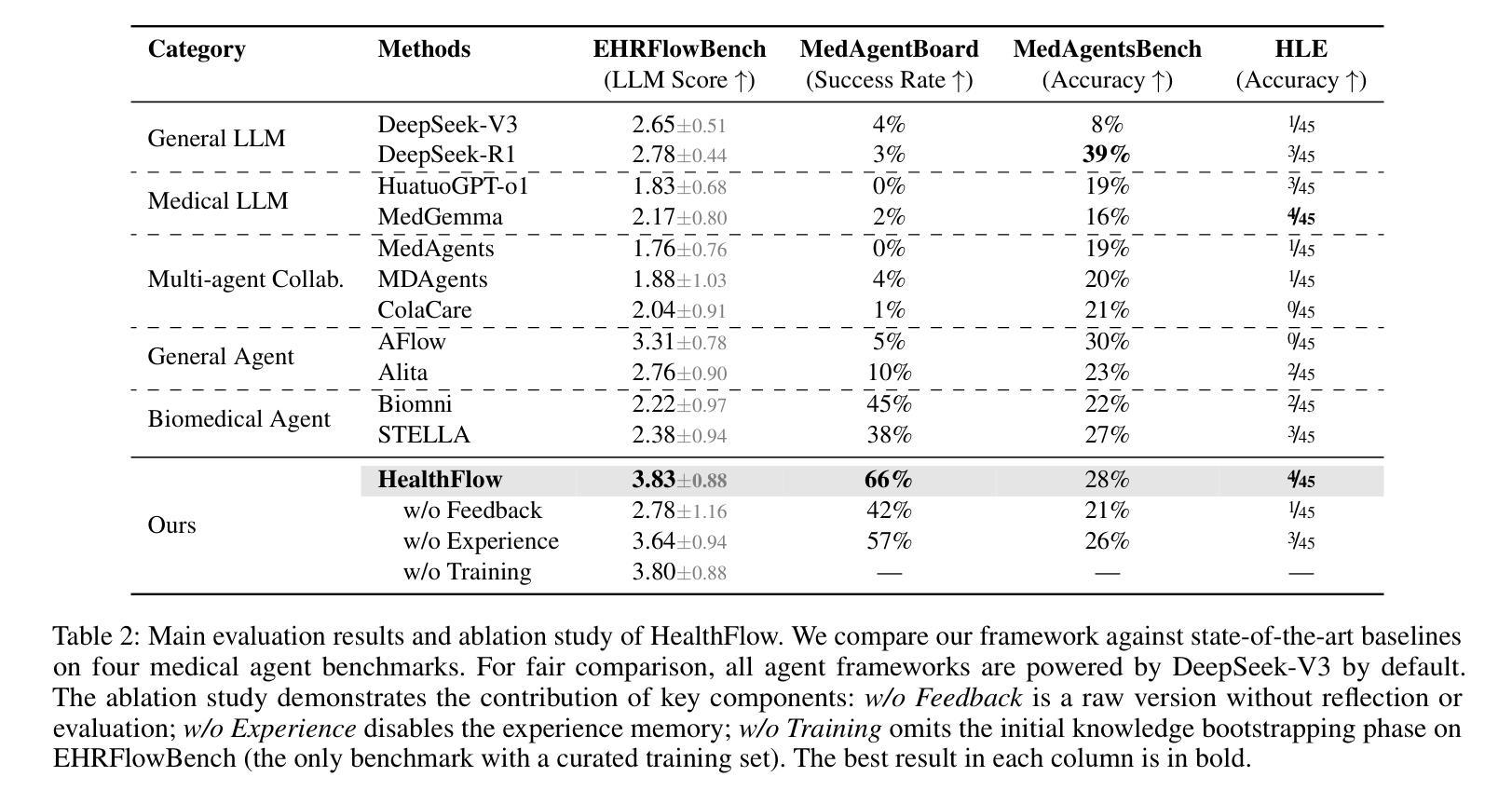
HealthFlow: A Self-Evolving AI Agent with Meta Planning for Autonomous Healthcare Research
Authors:Yinghao Zhu, Yifan Qi, Zixiang Wang, Lei Gu, Dehao Sui, Haoran Hu, Xichen Zhang, Ziyi He, Liantao Ma, Lequan Yu
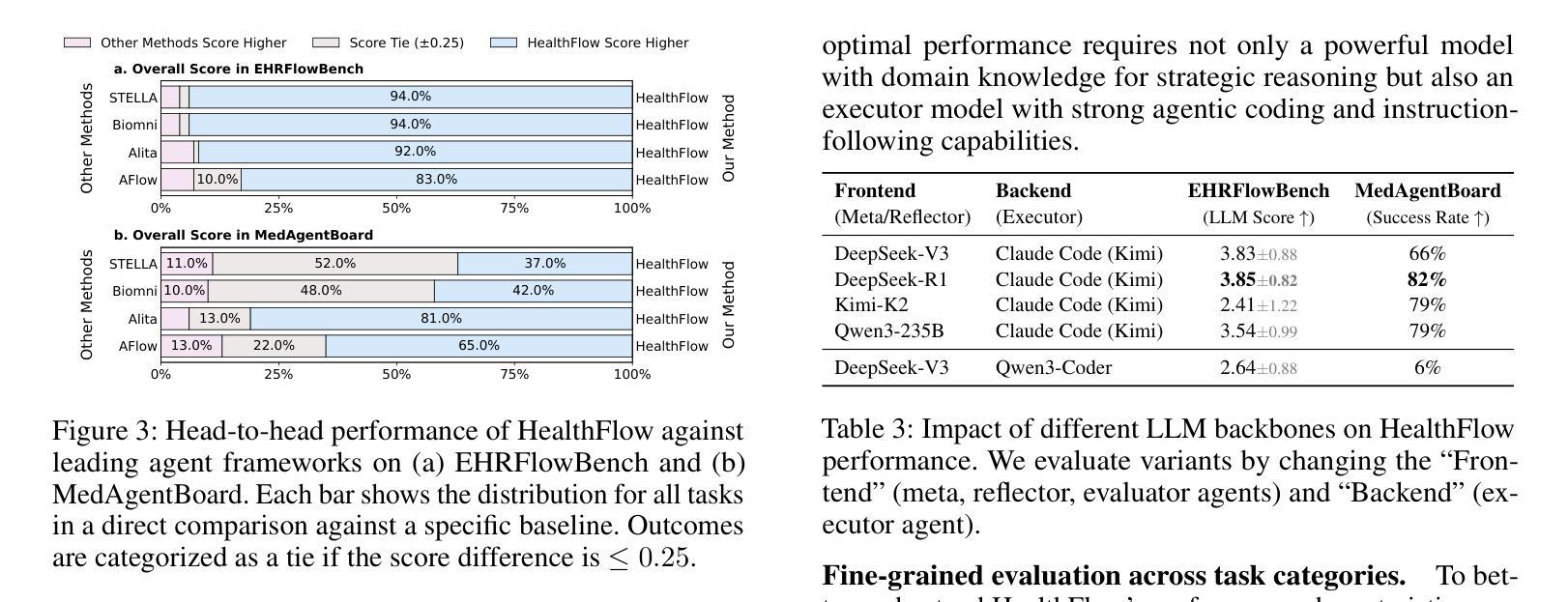
The efficacy of AI agents in healthcare research is hindered by their reliance on static, predefined strategies. This creates a critical limitation: agents can become better tool-users but cannot learn to become better strategic planners, a crucial skill for complex domains like healthcare. We introduce HealthFlow, a self-evolving AI agent that overcomes this limitation through a novel meta-level evolution mechanism. HealthFlow autonomously refines its own high-level problem-solving policies by distilling procedural successes and failures into a durable, strategic knowledge base. To anchor our research and facilitate reproducible evaluation, we introduce EHRFlowBench, a new benchmark featuring complex, realistic health data analysis tasks derived from peer-reviewed clinical research. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that HealthFlow’s self-evolving approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art agent frameworks. This work marks a necessary shift from building better tool-users to designing smarter, self-evolving task-managers, paving the way for more autonomous and effective AI for scientific discovery.
人工智能代理在医疗领域研究的效用受到其依赖静态、预设策略的阻碍。这产生了一个关键的局限性:代理可以变得更好的工具使用者,但不能学会成为更好的策略规划者,这对于医疗等复杂领域是一项至关重要的技能。我们引入了HealthFlow,这是一种自我进化的AI代理,它通过一种新的元级进化机制克服了这一局限性。HealthFlow自主地提炼其自己的高级问题解决策略,将程序的成功和失败转化为持久、战略性的知识库。为了巩固我们的研究并促进可重复评估,我们推出了EHRFlowBench,这是一个新的基准测试平台,它包含从同行评审的临床研究中得出的复杂且真实健康数据分析任务。我们的综合实验表明,HealthFlow的自我进化方法显著优于最新的代理框架。这项工作标志着从构建更好的工具使用者到设计更智能、自我进化的任务管理器的必要转变,为更自主、有效的AI科学发现铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/yhzhu99/HealthFlow
Summary
AI代理在医疗健康研究中的效能受限于其依赖静态、预设策略的问题。为解决这一瓶颈,我们推出HealthFlow,一种自我进化的AI代理,通过新型元级进化机制突破此限制。HealthFlow可自主优化其高级问题解决策略,将程序成功与失败经验提炼成持久、战略性的知识库。为支持研究并促进可重复评估,我们推出EHRFlowBench,以复杂、现实化的健康数据分析任务为特点的新基准测试,这些任务源自经过同行评审的临床研究。我们的综合实验显示,HealthFlow的自我进化方法显著优于当前最先进的代理框架。这项工作标志着从构建更好的工具用户转向设计更智能的自我进化任务管理器,为更自主和有效的AI科学发现铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- AI代理在医疗健康研究中的效能受限。
- 现有AI代理主要作为工具用户,缺乏战略规划能力。
- HealthFlow通过自我进化机制突破此限制,可自主优化高级问题解决策略。
- HealthFlow将经验提炼成持久、战略性的知识库。
- 推出EHRFlowBench作为新型基准测试,以支持研究和促进评估的可重复性。
- 综合实验显示HealthFlow显著优于当前最先进的代理框架。
点此查看论文截图

Emergence of Fair Leaders via Mediators in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Akshay Dodwadmath, Setareh Maghsudi
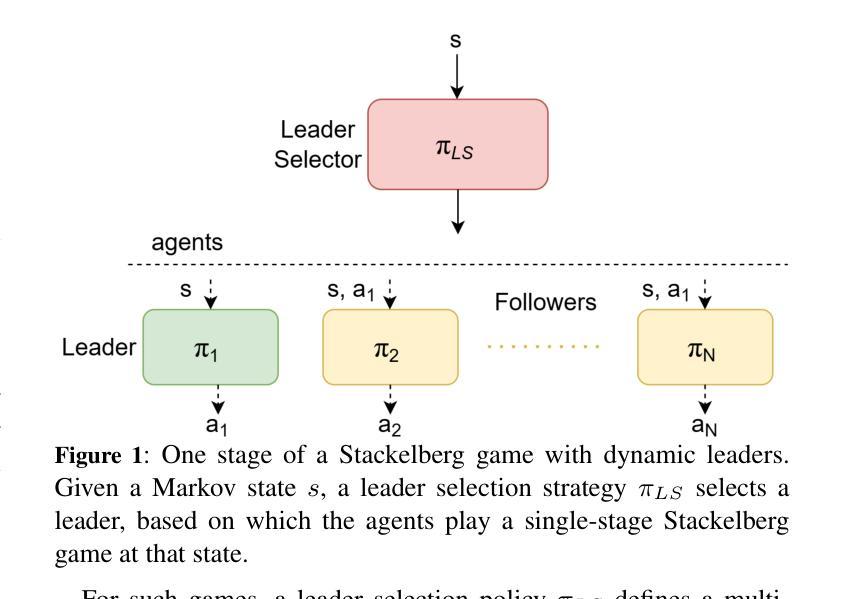
Stackelberg games and their resulting equilibria have received increasing attention in the multi-agent reinforcement learning literature. Each stage of a traditional Stackelberg game involves a leader(s) acting first, followed by the followers. In situations where the roles of leader(s) and followers can be interchanged, the designated role can have considerable advantages, for example, in first-mover advantage settings. Then the question arises: Who should be the leader and when? A bias in the leader selection process can lead to unfair outcomes. This problem is aggravated if the agents are self-interested and care only about their goals and rewards. We formally define this leader selection problem and show its relation to fairness in agents’ returns. Furthermore, we propose a multi-agent reinforcement learning framework that maximizes fairness by integrating mediators. Mediators have previously been used in the simultaneous action setting with varying levels of control, such as directly performing agents’ actions or just recommending them. Our framework integrates mediators in the Stackelberg setting with minimal control (leader selection). We show that the presence of mediators leads to self-interested agents taking fair actions, resulting in higher overall fairness in agents’ returns.
斯塔克尔伯格(Stackelberg)博弈及其产生的均衡状态在多智能体强化学习文献中受到了越来越多的关注。传统的斯塔克尔伯格博弈的每个阶段都涉及一个或多个领导者率先行动,随后是追随者。在领导者和追随者的角色可以互换的情况下,指定的角色可以带来巨大的优势,例如在先行优势环境中。然后会出现一个问题:谁应该是领导者,又应该在何时?领导者选择过程中的偏见可能导致不公平的结果。如果智能体是自私的,只关心他们的目标和回报,那么这个问题就会加剧。我们正式定义了这个问题并展示了它与智能体回报公平性的关系。此外,我们提出了一个多智能体强化学习框架,通过引入中介来最大化公平性。中介以前已被用于具有不同控制级别的同时行动设置,例如直接执行智能体的行动或仅仅是提出建议。我们的框架在斯塔克尔伯格背景下整合中介,控制力度最小(领导层选择)。我们表明,中介的存在导致自私的智能体采取公平的行动,从而提高了智能体回报的整体公平性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ECAI 2025
Summary
在多重代理强化学习文献中,斯塔克尔伯格博弈及其产生的均衡状态越来越受到关注。传统的斯塔克尔伯格博弈每个阶段都有领导者先行,随后是追随者。在领导者和追随者角色可以互换的情况下,指定角色可以带来巨大的优势,例如在先行优势设置中。因此产生了一个问题:谁应该成为领导者,何时成为领导者?领导选择过程中的偏见可能导致不公平的结果。如果代理人是自私的,只关心他们的目标和回报,这个问题会更加严重。我们正式定义了这个领导选择问题,并展示了它与代理回报公平性的关系。此外,我们提出了一种多代理强化学习框架,通过引入调解者来最大化公平性。调解者以前已被用于同时行动的环境中,具有不同程度的控制力,如直接执行代理的行动或仅提供建议。我们的框架将调解者纳入斯塔克尔伯格设置中,具有最小的控制力(领导选择)。我们表明,调解者的存在导致自私的代理人采取公平行动,从而提高代理回报的整体公平性。
Key Takeaways
- 斯塔克尔伯格博弈在多代理强化学习中受到关注。
- 领导者和追随者角色的互换在博弈中具有优势,特别是在先行优势场景中。
- 领导选择过程中的偏见可能导致不公平结果。
- 代理的自私性会加剧这一问题。
- 提出了领导选择问题的正式定义,并与代理回报的公平性相联系。
- 引入调解者的多代理强化学习框架可以最大化公平性。
点此查看论文截图

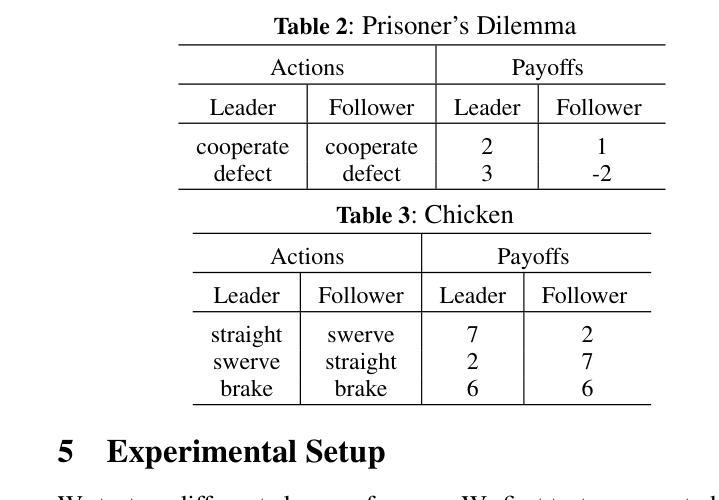
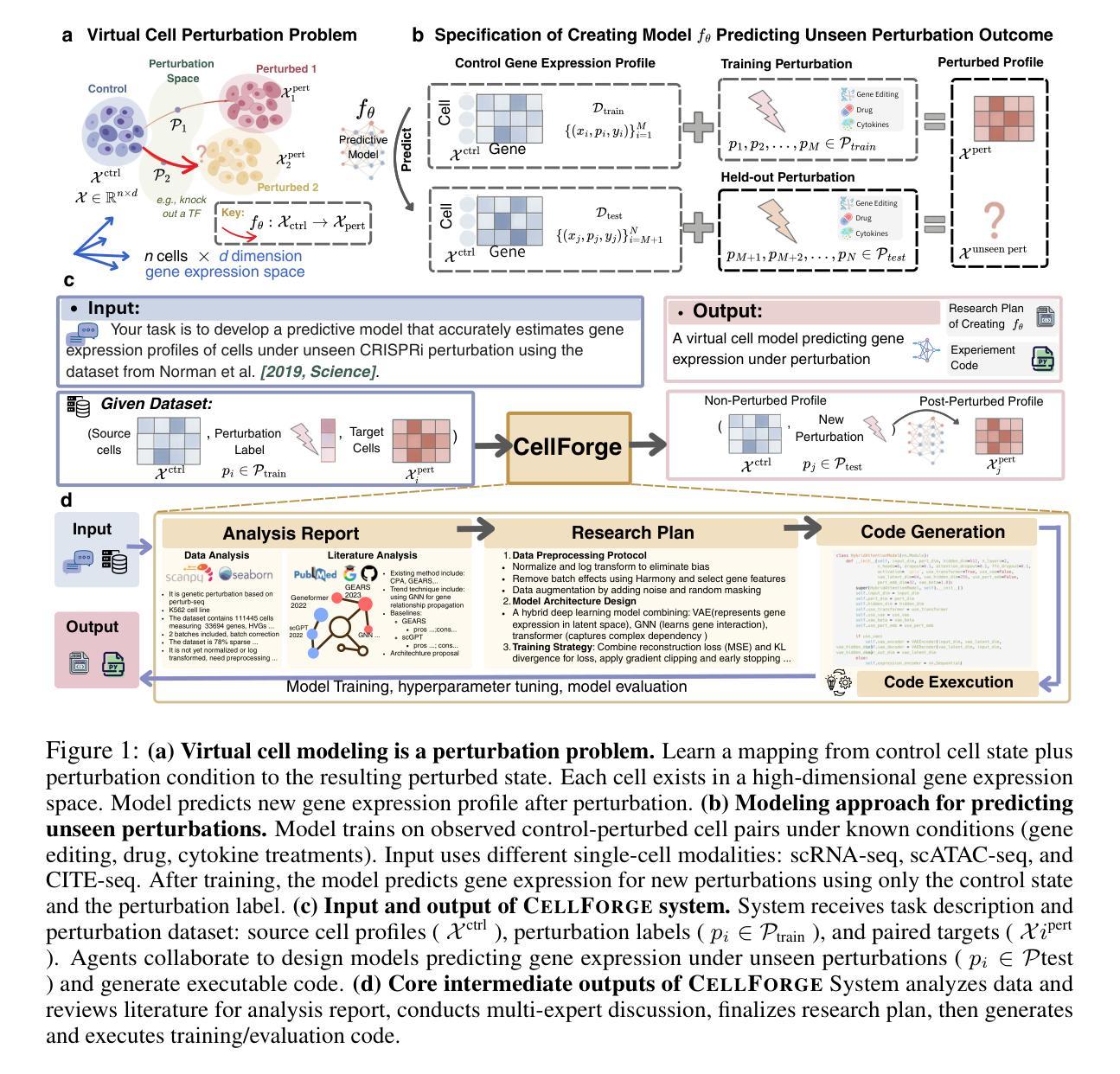
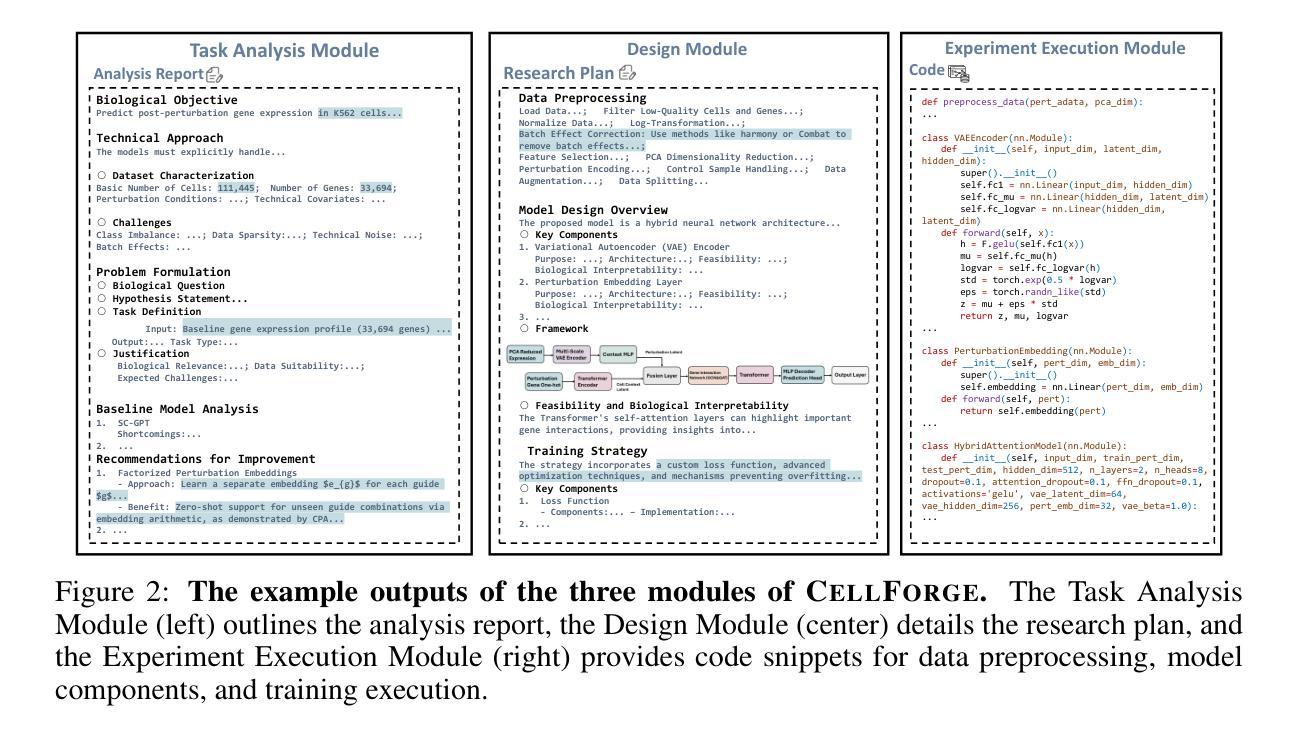
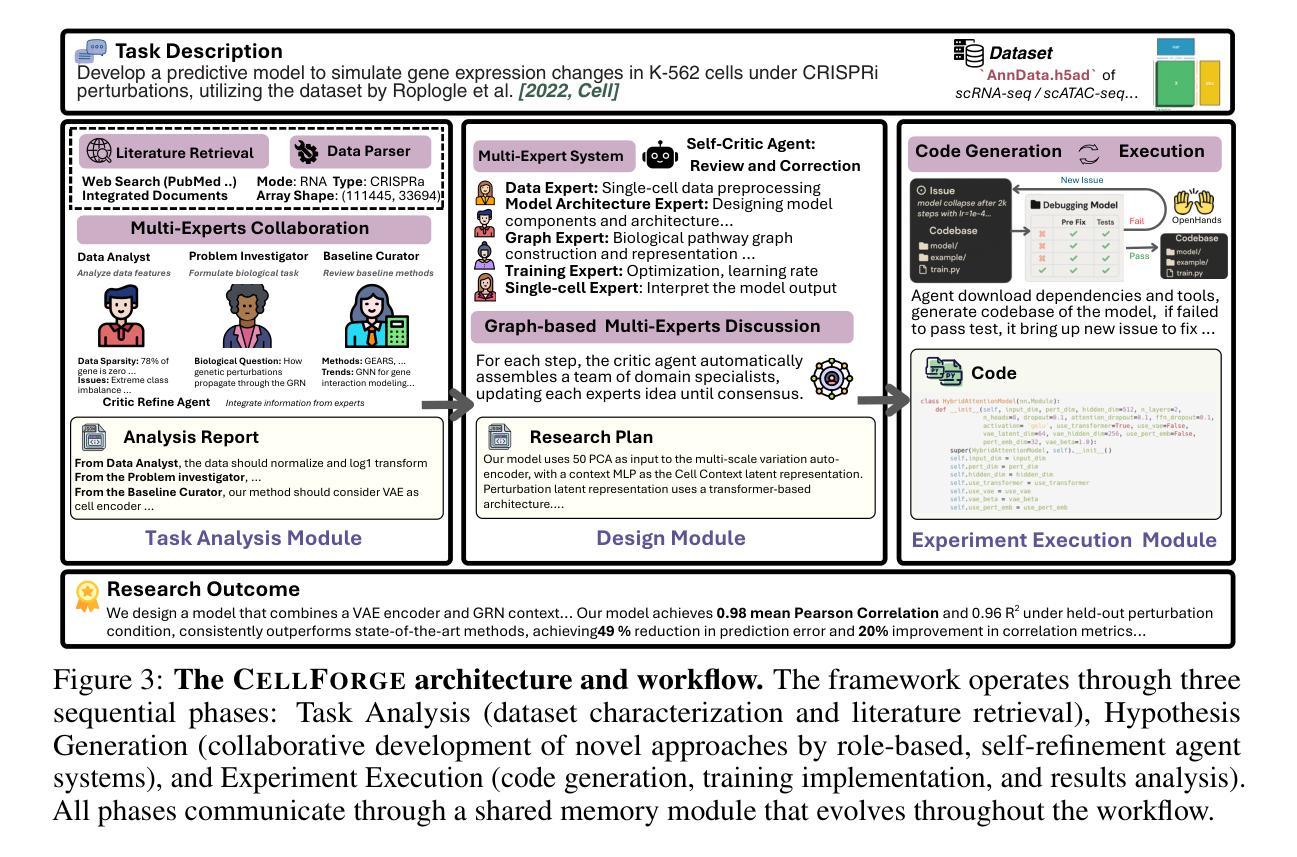
CellForge: Agentic Design of Virtual Cell Models
Authors:Xiangru Tang, Zhuoyun Yu, Jiapeng Chen, Yan Cui, Daniel Shao, Weixu Wang, Fang Wu, Yuchen Zhuang, Wenqi Shi, Zhi Huang, Arman Cohan, Xihong Lin, Fabian Theis, Smita Krishnaswamy, Mark Gerstein
Virtual cell modeling represents an emerging frontier at the intersection of artificial intelligence and biology, aiming to predict quantities such as responses to diverse perturbations quantitatively. However, autonomously building computational models for virtual cells is challenging due to the complexity of biological systems, the heterogeneity of data modalities, and the need for domain-specific expertise across multiple disciplines. Here, we introduce CellForge, an agentic system that leverages a multi-agent framework that transforms presented biological datasets and research objectives directly into optimized computational models for virtual cells. More specifically, given only raw single-cell multi-omics data and task descriptions as input, CellForge outputs both an optimized model architecture and executable code for training virtual cell models and inference. The framework integrates three core modules: Task Analysis for presented dataset characterization and relevant literature retrieval, Method Design, where specialized agents collaboratively develop optimized modeling strategies, and Experiment Execution for automated generation of code. The agents in the Design module are separated into experts with differing perspectives and a central moderator, and have to collaboratively exchange solutions until they achieve a reasonable consensus. We demonstrate CellForge’s capabilities in single-cell perturbation prediction, using six diverse datasets that encompass gene knockouts, drug treatments, and cytokine stimulations across multiple modalities. CellForge consistently outperforms task-specific state-of-the-art methods. Overall, CellForge demonstrates how iterative interaction between LLM agents with differing perspectives provides better solutions than directly addressing a modeling challenge. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/gersteinlab/CellForge.
虚拟细胞建模是人工智能和生物学交叉领域的新兴前沿,旨在定量预测对不同扰动的反应等数量。然而,由于生物系统的复杂性、数据模态的异质性和多学科领域专业知识的需求,自主构建虚拟细胞计算模型具有挑战性。在这里,我们介绍了CellForge,一个智能系统,它利用多智能体框架直接将呈现的生物学数据集和研究目标转化为优化的计算模型,用于虚拟细胞。更具体地说,CellForge仅接受原始的单细胞多组学数据和任务描述作为输入,输出的是优化后的模型架构和可用于训练虚拟细胞模型和进行推断的可执行代码。该框架集成了三个核心模块:任务分析,用于呈现数据集表征和相关文献检索;方法设计,其中专业智能体协同开发优化建模策略;实验执行,用于自动生成代码。设计模块中的智能体分为不同角度的专家和一个中央协调者,他们必须协同交流解决方案,直到达成合理共识。我们利用涵盖基因敲除、药物治疗和细胞因子刺激的六个不同数据集,展示了CellForge在单细胞扰动预测方面的能力。CellForge的性能始终优于特定任务的最先进方法。总的来说,CellForge展示了不同角度的LLM智能体之间的迭代交互如何提供比直接解决建模挑战更好的解决方案。我们的代码可在https://github.com/gersteinlab/CellForge公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
虚拟细胞建模是人工智能与生物学交叉领域的新兴前沿,旨在定量预测对多种扰动的响应。然而,自主构建虚拟细胞的计算模型具有挑战性,因为生物系统的复杂性、数据模态的异质性和多学科领域专业知识的需求。这里介绍CellForge,一个利用多智能体框架的agentic系统,可直接将呈现的生物学数据集和研究目标转化为优化的计算模型。CellForge接受原始单细胞多组学数据和任务描述作为输入,输出优化后的模型架构和可执行代码,用于训练和推断虚拟细胞模型。通过任务分析、方法设计和实验执行三个核心模块,实现了自动化生成代码。在单细胞扰动预测中,CellForge使用六个包含基因敲除、药物治疗和细胞因子刺激的多模态数据集进行演示,并始终优于特定任务的最先进方法。总体而言,CellForge展示了在不同视角的大型语言模型智能体之间的迭代交互如何提供比直接解决建模挑战更好的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟细胞建模是人工智能与生物学结合的新兴领域,旨在预测生物系统对扰动的响应。
- CellForge是一个多智能体系统,能将生物数据集和研究目标转化为虚拟细胞模型。
- CellForge接受原始单细胞多组学数据和任务描述为输入,并输出优化后的模型架构和训练代码。
- CellForge包括三个核心模块:任务分析、方法设计和实验执行。
- 在单细胞扰动预测中,CellForge表现出卓越的性能,优于现有方法。
- CellForge通过智能体间的迭代交互,实现了更好的解决方案。
- CellForge的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

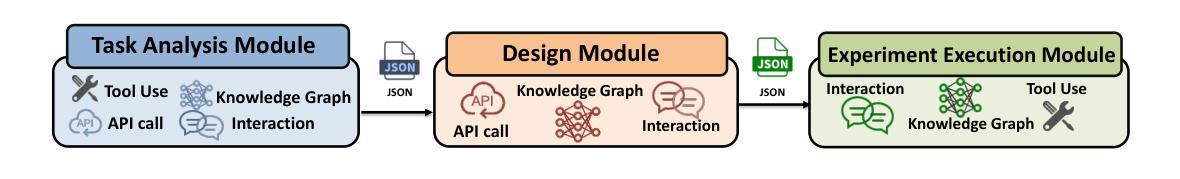
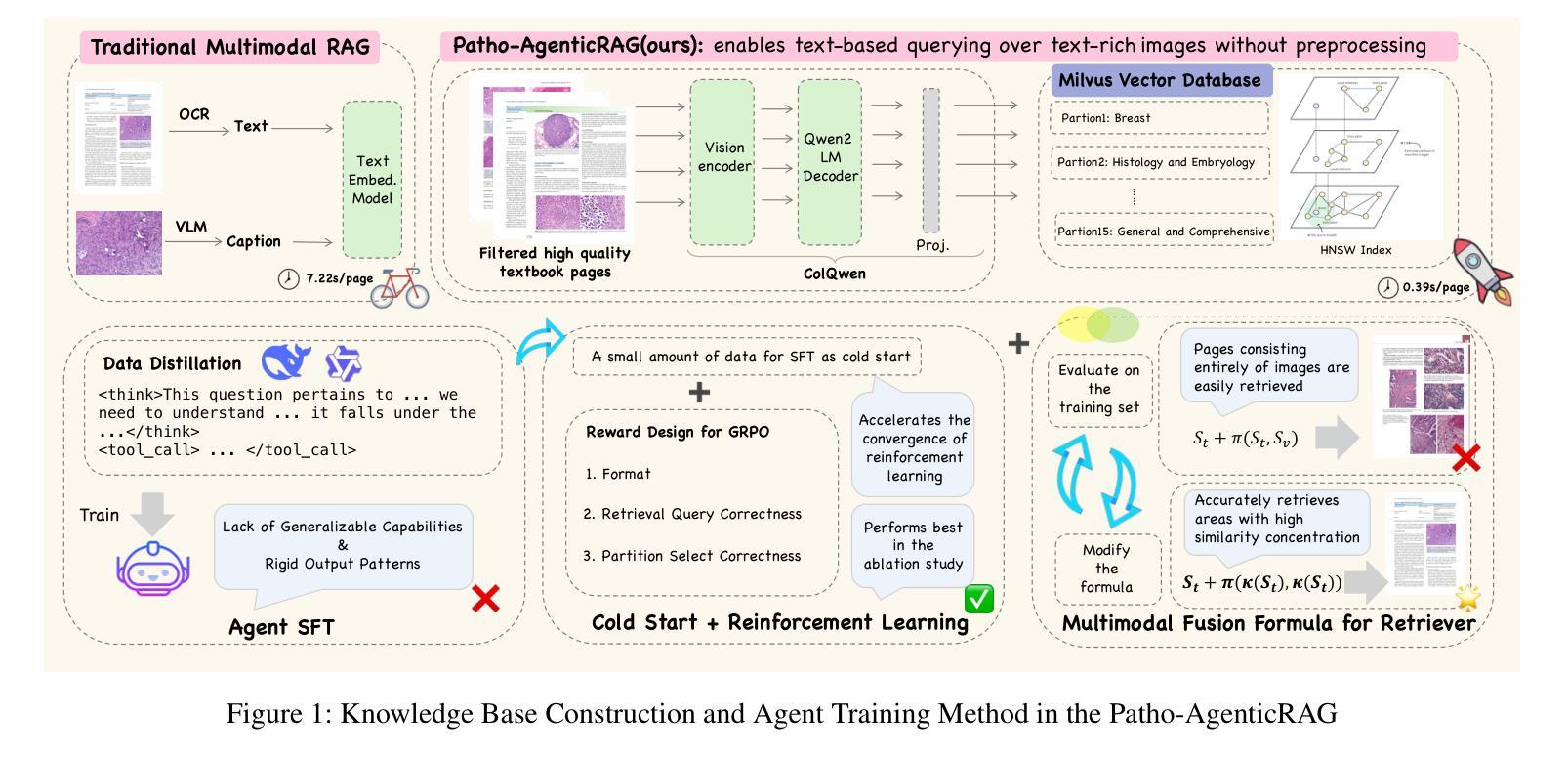
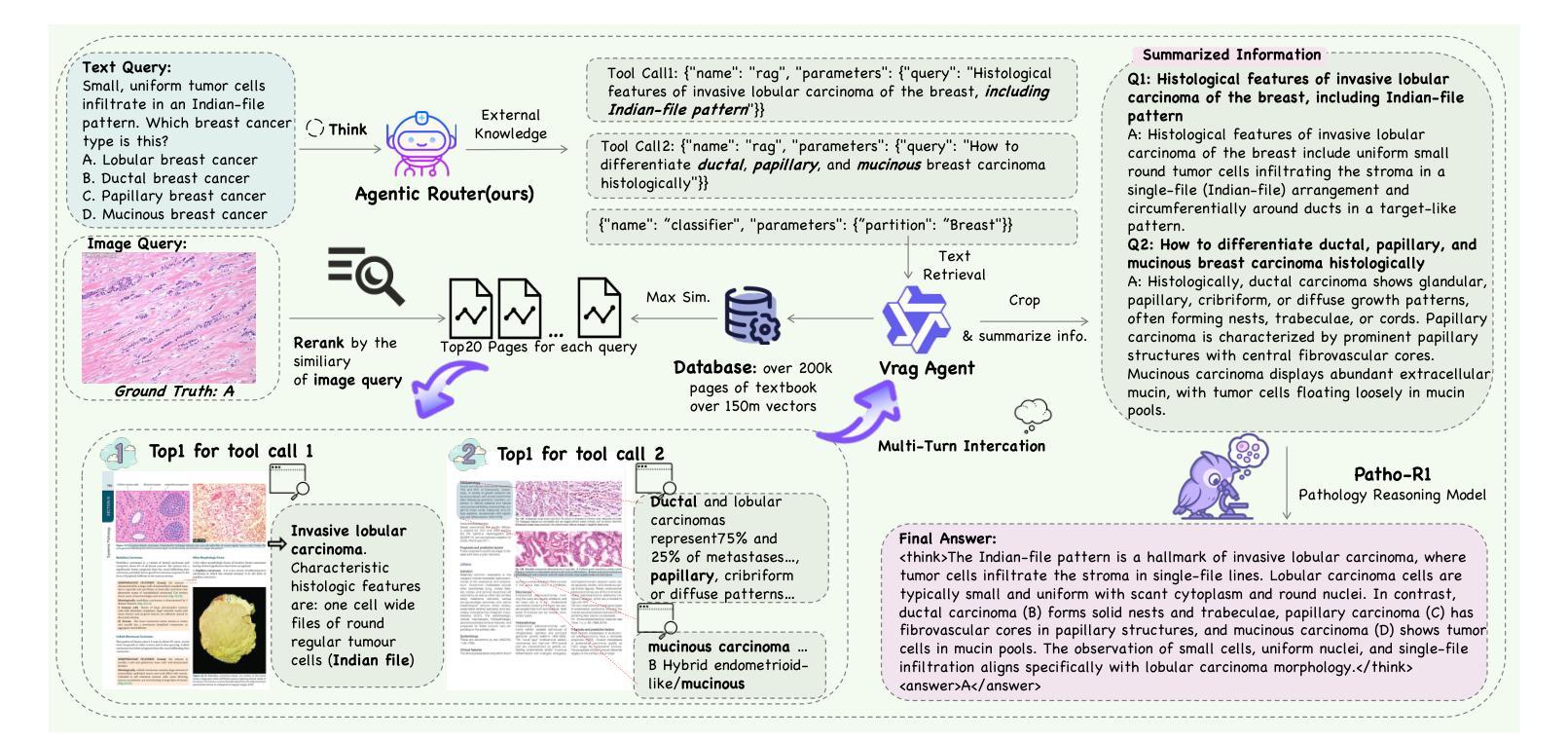
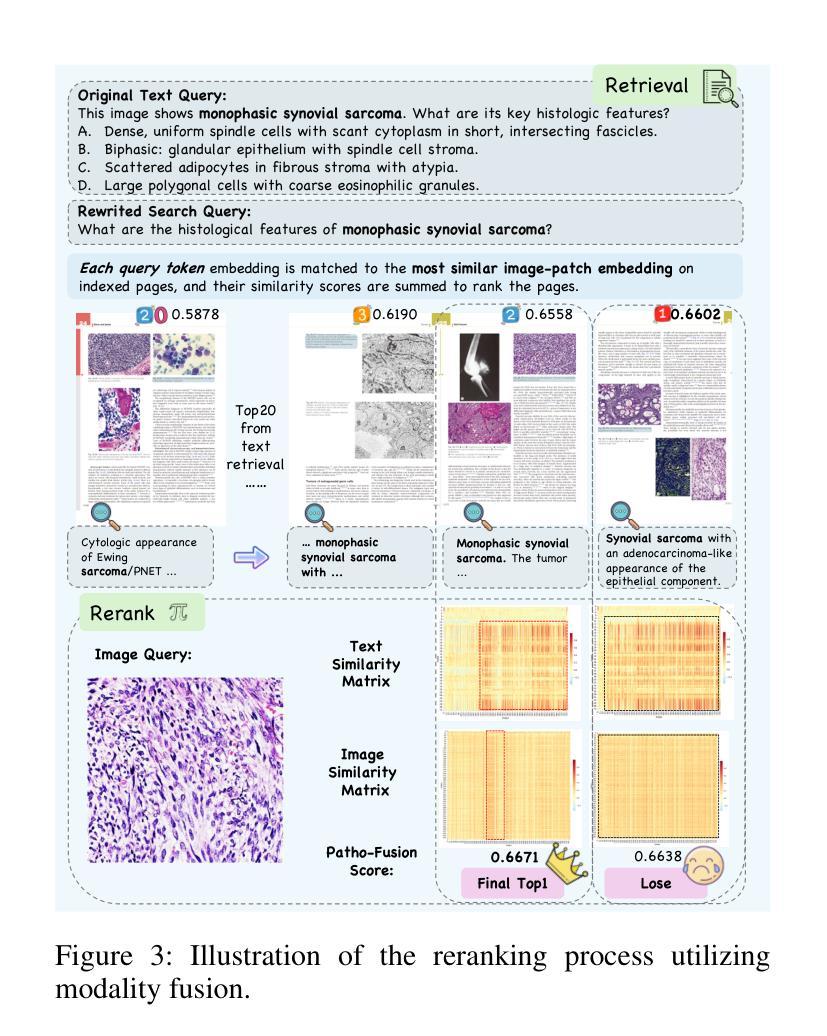
Patho-AgenticRAG: Towards Multimodal Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Pathology VLMs via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wenchuan Zhang, Jingru Guo, Hengzhe Zhang, Penghao Zhang, Jie Chen, Shuwan Zhang, Zhang Zhang, Yuhao Yi, Hong Bu
Although Vision Language Models (VLMs) have shown strong generalization in medical imaging, pathology presents unique challenges due to ultra-high resolution, complex tissue structures, and nuanced clinical semantics. These factors make pathology VLMs prone to hallucinations, i.e., generating outputs inconsistent with visual evidence, which undermines clinical trust. Existing RAG approaches in this domain largely depend on text-based knowledge bases, limiting their ability to leverage diagnostic visual cues. To address this, we propose Patho-AgenticRAG, a multimodal RAG framework with a database built on page-level embeddings from authoritative pathology textbooks. Unlike traditional text-only retrieval systems, it supports joint text-image search, enabling direct retrieval of textbook pages that contain both the queried text and relevant visual cues, thus avoiding the loss of critical image-based information. Patho-AgenticRAG also supports reasoning, task decomposition, and multi-turn search interactions, improving accuracy in complex diagnostic scenarios. Experiments show that Patho-AgenticRAG significantly outperforms existing multimodal models in complex pathology tasks like multiple-choice diagnosis and visual question answering. Our project is available at the Patho-AgenticRAG repository: https://github.com/Wenchuan-Zhang/Patho-AgenticRAG.
尽管视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学成像中表现出了强大的泛化能力,但由于超高分辨率、复杂的组织结构和微妙的临床语义,病理学还是面临着独特的挑战。这些因素使得病理学VLMs容易产生幻觉,即生成与视觉证据不一致的输出,这损害了临床信任。目前该领域的RAG方法大多依赖于基于文本的知识库,限制了它们利用诊断视觉线索的能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Patho-AgenticRAG,这是一个多模态RAG框架,其数据库建立在权威病理学教科书页面级别的嵌入之上。与传统的仅文本检索系统不同,它支持联合文本图像搜索,能够直接检索包含查询文本和相关视觉线索的教科书页面,从而避免了基于关键图像信息丢失的问题。Patho-AgenticRAG还支持推理、任务分解和多轮搜索交互,提高了复杂诊断场景中的准确性。实验表明,Patho-AgenticRAG在多项选择题诊断和视觉问答等复杂病理学任务上显著优于现有多模态模型。我们的项目可在Patho-AgenticRAG仓库中找到:https://github.com/Wenchuan-Zhang/Patho-AgenticRAG。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
病理视语言模型面临独特挑战,包括超高分辨率、复杂组织结构和细微临床语义。Patho-AgenticRAG是一个多模态RAG框架,支持联合文本图像搜索,避免丢失关键图像信息,提高复杂诊断场景的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 病理视语言模型(VLMs)在医学成像中具有良好的泛化能力,但在病理学领域面临独特挑战。
- 病理学的高分辨率、复杂组织结构和细微临床语义使模型易产生幻觉输出。
- 现有RAG方法主要依赖文本知识库,难以利用诊断视觉线索。
- Patho-AgenticRAG是一个多模态RAG框架,支持联合文本图像搜索,避免信息丢失。
- Patho-AgenticRAG能进行推理、任务分解和多轮搜索交互,提高复杂诊断场景的准确性。
- 实验显示,Patho-AgenticRAG在复杂病理学任务(如多选诊断和视觉问答)上显著优于现有多模态模型。
点此查看论文截图


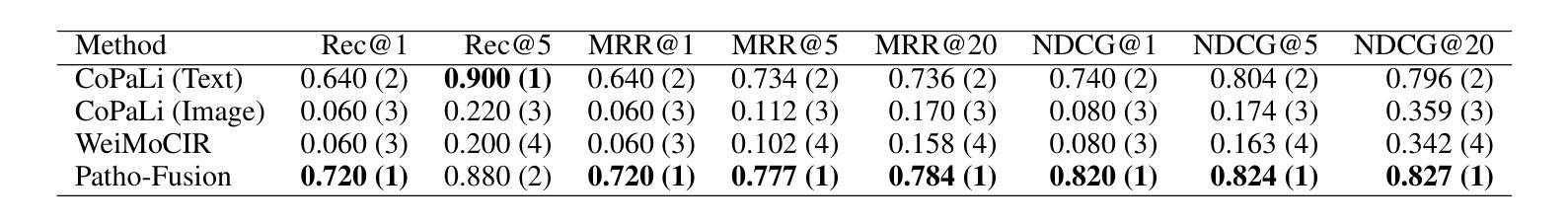
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
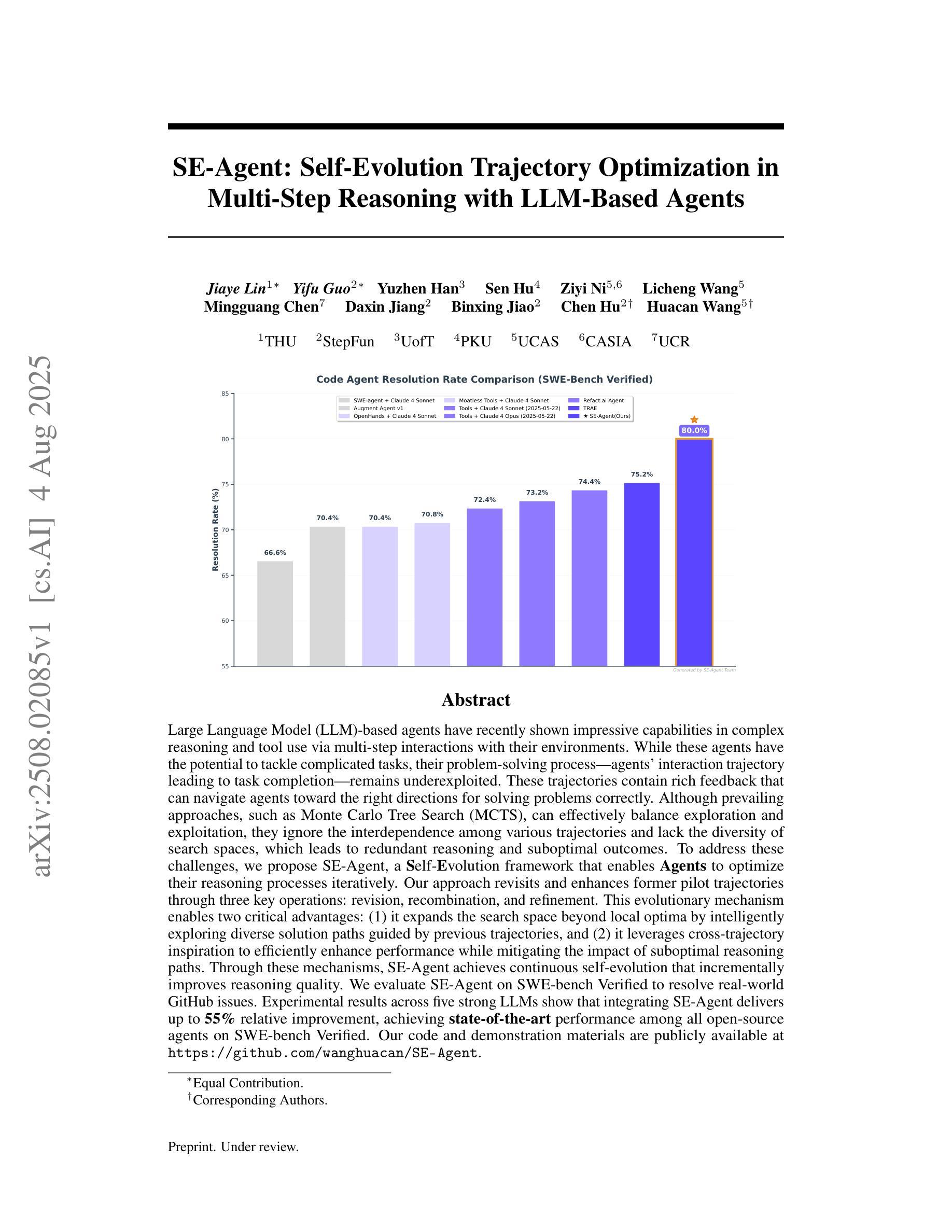
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/wanghuacan/SE-Agent.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理最近表现出通过多步骤与环境互动进行复杂推理和工具使用的惊人能力。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但他们的解决问题过程,即代理完成任务的互动轨迹,仍未得到充分探索。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理朝着正确方向解决问题。虽然现有的方法,如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了不同轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,这是一种自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作来重新审视和改进先前的轨迹:修订、重组和细化。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索以前轨迹引导的多样化解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了持续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的性能达到了开源代理中的最佳水平。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/wanghuacan/SE-Agent公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在复杂推理和工具使用方面展现出强大的能力,通过多步骤与环境的交互来完成任务。然而,这些代理的问题解决过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,尚未得到充分研究。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理正确解决问题。虽然现有的方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了不同轨迹之间的依赖性并缺乏搜索空间的多样性,导致冗余推理和次优结果。为解决这些问题,我们提出了SE-Agent,一个自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化其推理过程。通过修订、重组和细化等关键操作,该机制扩大了搜索空间并提高了性能。在SWE-bench Verified上评估SE-Agent解决GitHub实际问题的能力时,相较于五个主流LLM,其实现了高达55%的相对改进率并达到先进性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based agents demonstrate impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with environments.
- Agents’ problem-solving trajectories contain rich feedback that can guide them to solve problems correctly.
- Existing methods like MCTS ignore the interdependence among trajectories and lack search space diversity, leading to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes.
- SE-Agent framework enables iterative optimization of reasoning processes for agents through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement.
- SE-Agent expands search space beyond local optima and leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to enhance performance.
- SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution, incrementally improving reasoning quality.
点此查看论文截图
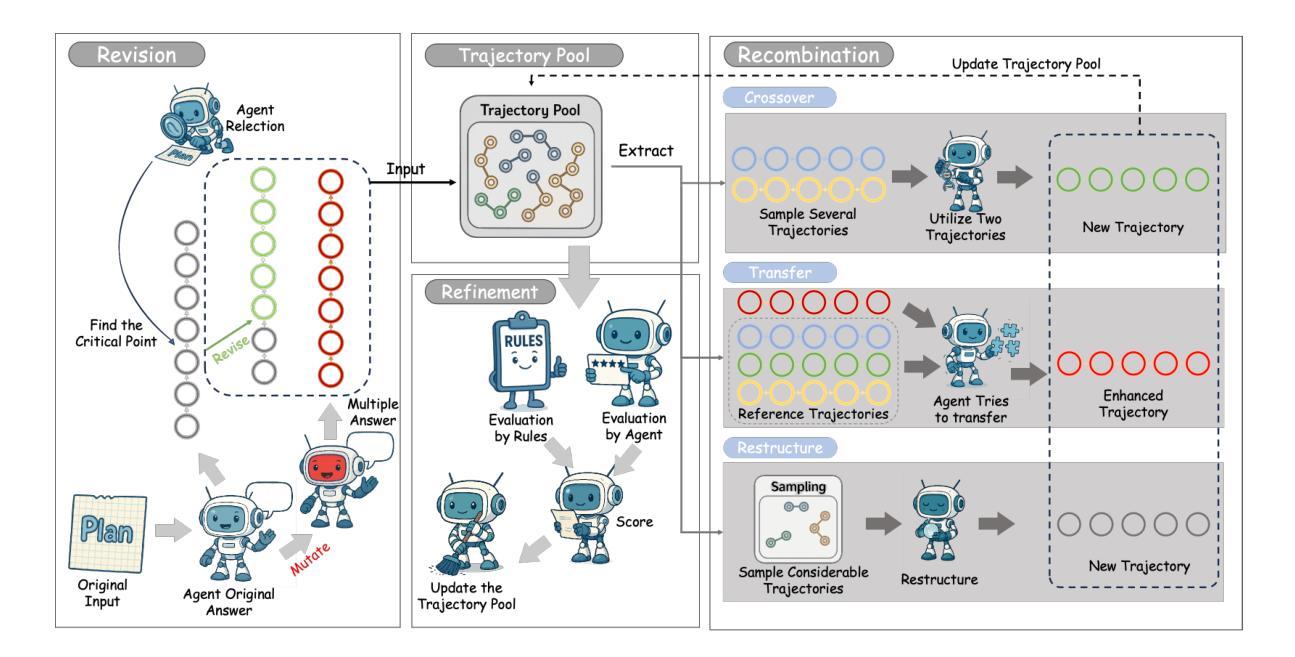
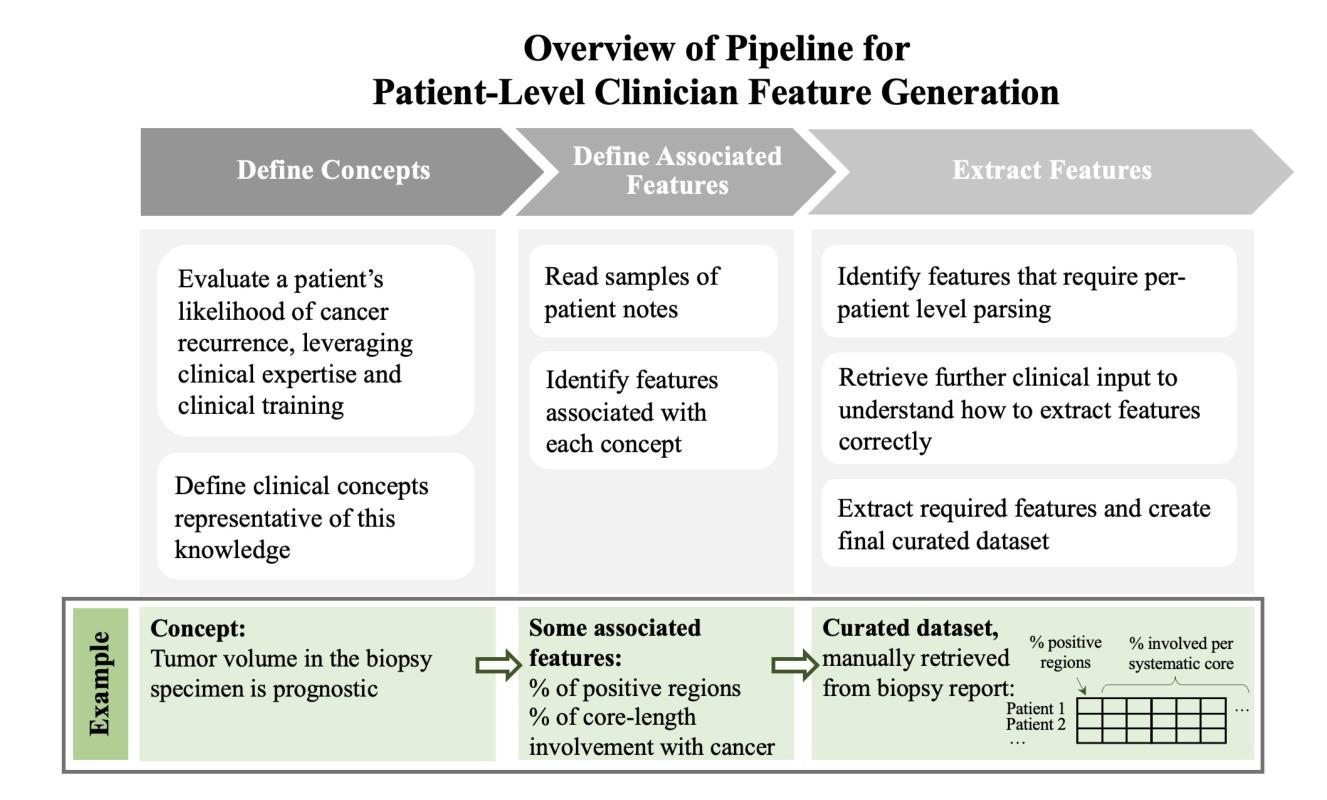
Agent-Based Feature Generation from Clinical Notes for Outcome Prediction
Authors:Jiayi Wang, Jacqueline Jil Vallon, Neil Panjwani, Xi Ling, Sushmita Vij, Sandy Srinivas, John Leppert, Mark K. Buyyounouski, Mohsen Bayati
Electronic health records (EHRs) contain rich unstructured clinical notes that could enhance predictive modeling, yet extracting meaningful features from these notes remains challenging. Current approaches range from labor-intensive manual clinician feature generation (CFG) to fully automated representational feature generation (RFG) that lack interpretability and clinical relevance. Here we introduce SNOW (Scalable Note-to-Outcome Workflow), a modular multi-agent system powered by large language models (LLMs) that autonomously generates structured clinical features from unstructured notes without human intervention. We evaluated SNOW against manual CFG, clinician-guided LLM approaches, and RFG methods for predicting 5-year prostate cancer recurrence in 147 patients from Stanford Healthcare. While manual CFG achieved the highest performance (AUC-ROC: 0.771), SNOW matched this performance (0.761) without requiring any clinical expertise, significantly outperforming both baseline features alone (0.691) and all RFG approaches. The clinician-guided LLM method also performed well (0.732) but still required expert input. SNOW’s specialized agents handle feature discovery, extraction, validation, post-processing, and aggregation, creating interpretable features that capture complex clinical information typically accessible only through manual review. Our findings demonstrate that autonomous LLM systems can replicate expert-level feature engineering at scale, potentially transforming how clinical ML models leverage unstructured EHR data while maintaining the interpretability essential for clinical deployment.
电子健康记录(EHRs)包含丰富的非结构化临床笔记,这些笔记可以增强预测模型的性能,然而从这些笔记中提取有意义的特征仍然是一个挑战。当前的方法范围从劳动密集型的手动临床医生特征生成(CFG)到缺乏可解释性和临床相关性的完全自动化的代表性特征生成(RFG)。在这里,我们介绍了SNOW(可扩展的笔记到结果工作流程),这是一个由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的模块化多代理系统,能够无需人工干预,从非结构化笔记中自主生成结构化临床特征。我们在斯坦福医疗健康的147名患者中,用SNOW与手动CFG、临床医生指导的LLM方法和RFG方法预测前列腺癌5年复发率进行比较评估。虽然手动CFG表现最佳(AUC-ROC:0.771),但SNOW与之相匹配(0.761),无需任何临床经验,显著优于基本特征(0.691)和所有RFG方法。临床医生指导的LLM方法表现良好(0.732),但仍需专家输入。SNOW的专用代理处理特征发现、提取、验证、后处理和聚合,创建可解释的特征,这些特征能够捕获通常只能通过手动审查才能获得的复杂临床信息。我们的研究结果表明,自主化的LLM系统能够在大规模上复制专家级的特征工程,有可能改变临床机器学习模型如何利用非结构化EHR数据的方式,同时保持对于临床部署至关重要的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了名为SNOW的模块化多智能体系统,该系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)从非结构化病历记录中提取结构化临床特征,用于预测前列腺癌复发的风险。在斯坦福医疗机构的测试中,尽管手动CFG表现最佳(AUC-ROC:0.771),但SNOW系统无需临床专家参与即实现了与之相当的性能(AUC-ROC:0.761),显著优于基本特征(AUC-ROC:0.691)和全自动RFG方法。SNOW系统由多个智能体组成,负责特征发现、提取、验证、后处理和聚合,可生成易于理解的特征,捕捉复杂临床信息,这通常是只能通过人工审查才能获取的。这些发现证明,自主的大型语言模型系统在大规模特征工程上可模拟专家级的表现,可能为临床部署中的机器学习模型提供更高效的非结构化病历数据利用方式并保持必要的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- SNOW系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)从非结构化病历记录中提取结构化临床特征。
- SNOW系统的性能与手动CFG相当,但无需临床专家参与。
- SNOW系统通过多个智能体进行特征发现、提取、验证、后处理和聚合。
- SNOW系统能够生成易于理解的特征,捕捉复杂临床信息。
- 自主的大型语言模型系统在特征工程上可模拟专家级的表现。
- SNOW系统的应用可提升临床机器学习模型对非结构化病历数据的利用。
点此查看论文截图

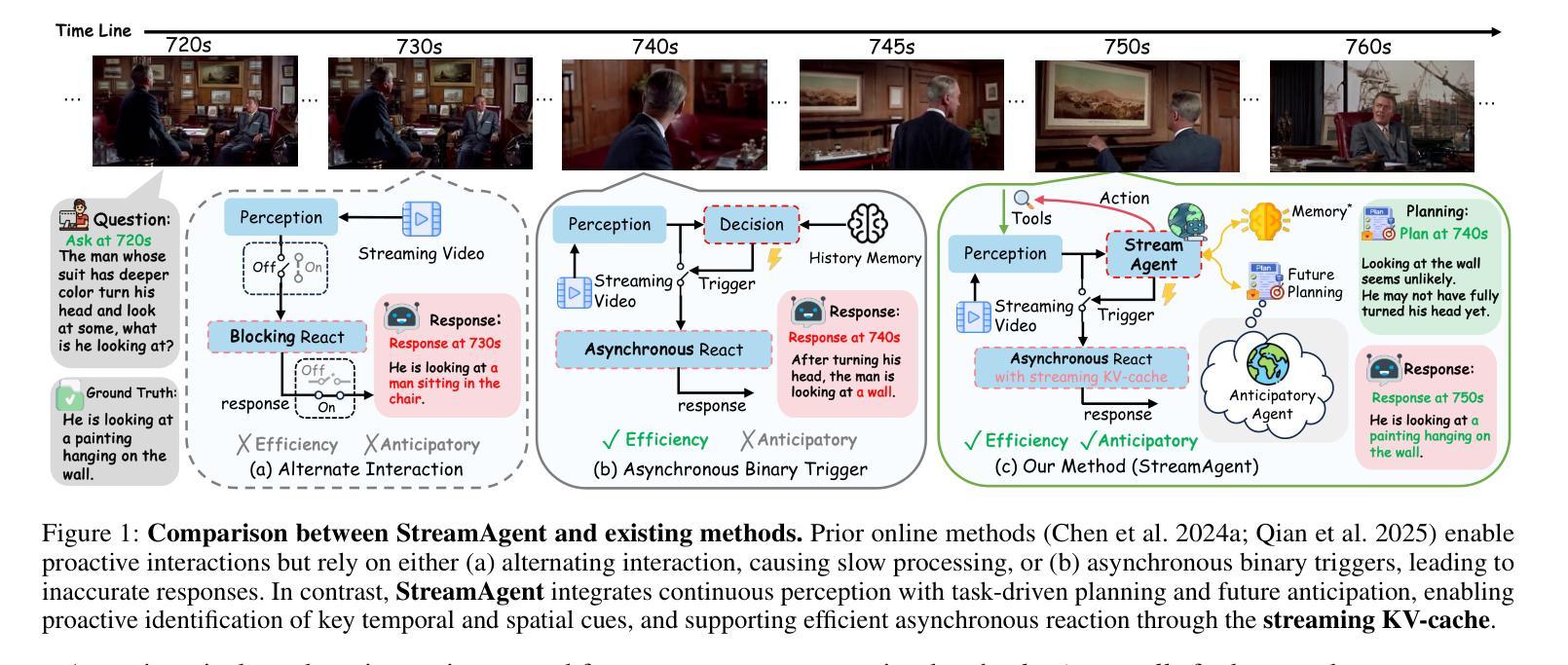
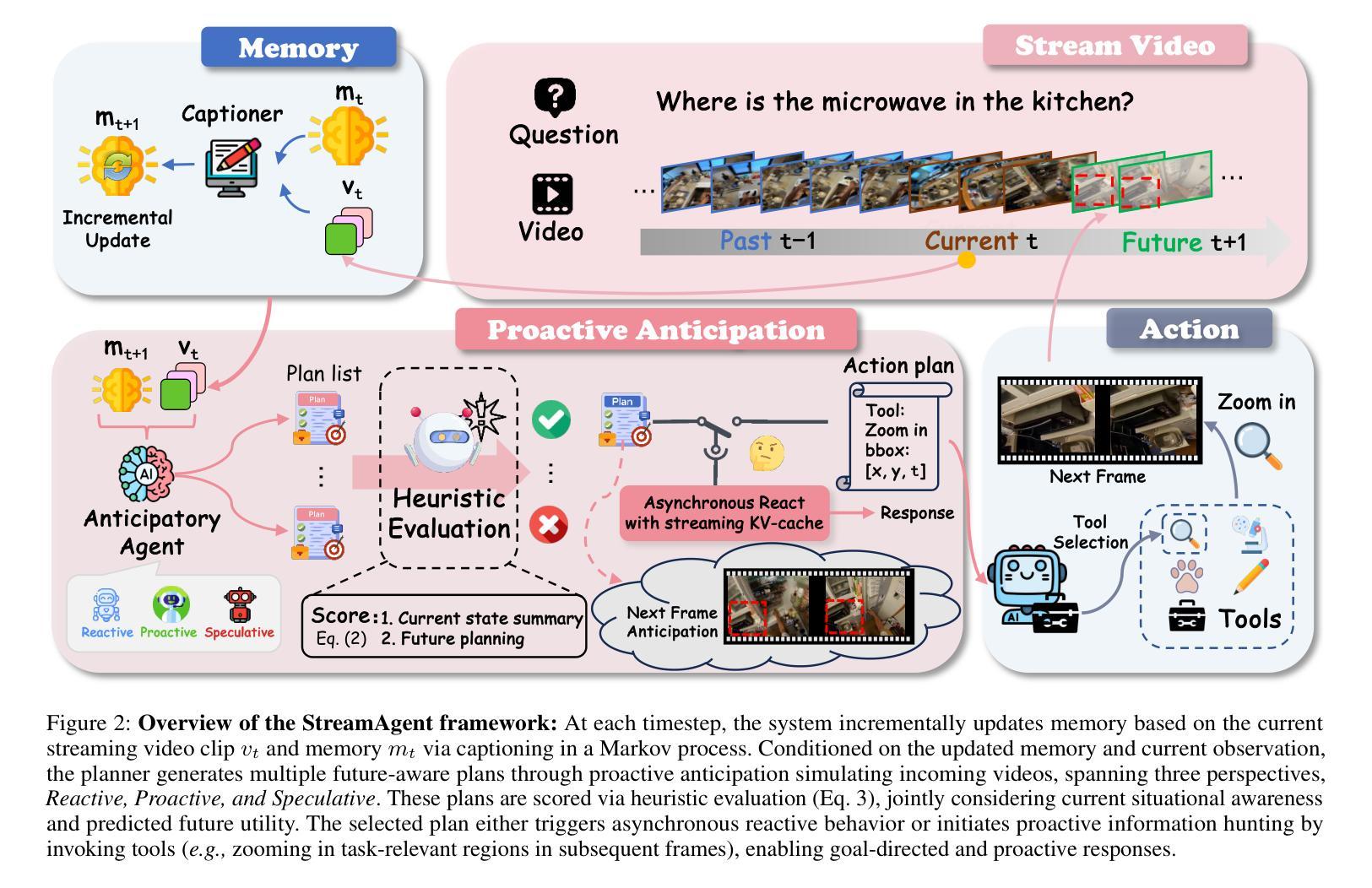
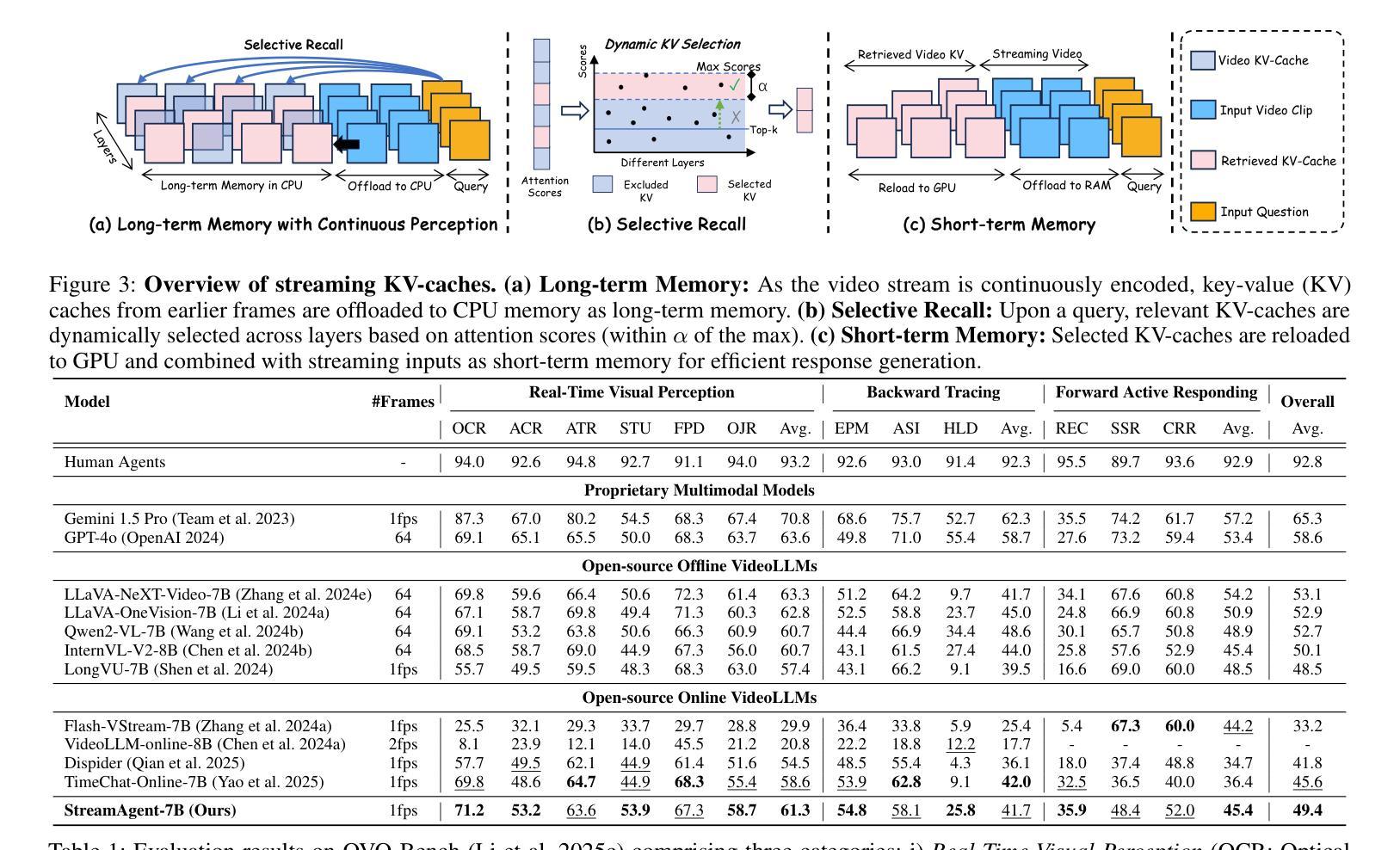
StreamAgent: Towards Anticipatory Agents for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Haolin Yang, Feilong Tang, Linxiao Zhao, Xiang An, Ming Hu, Huifa Li, Xinlin Zhuang, Boqian Wang, Yifan Lu, Xiaofeng Zhang, Abdalla Swikir, Junjun He, Zongyuan Ge, Imran Razzak
Real-time streaming video understanding in domains such as autonomous driving and intelligent surveillance poses challenges beyond conventional offline video processing, requiring continuous perception, proactive decision making, and responsive interaction based on dynamically evolving visual content. However, existing methods rely on alternating perception-reaction or asynchronous triggers, lacking task-driven planning and future anticipation, which limits their real-time responsiveness and proactive decision making in evolving video streams. To this end, we propose a StreamAgent that anticipates the temporal intervals and spatial regions expected to contain future task-relevant information to enable proactive and goal-driven responses. Specifically, we integrate question semantics and historical observations through prompting the anticipatory agent to anticipate the temporal progression of key events, align current observations with the expected future evidence, and subsequently adjust the perception action (e.g., attending to task-relevant regions or continuously tracking in subsequent frames). To enable efficient inference, we design a streaming KV-cache memory mechanism that constructs a hierarchical memory structure for selective recall of relevant tokens, enabling efficient semantic retrieval while reducing the overhead of storing all tokens in the traditional KV-cache. Extensive experiments on streaming and long video understanding tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods in response accuracy and real-time efficiency, highlighting its practical value for real-world streaming scenarios.
在自动驾驶和智能监控等领域,实时流媒体视频理解面临着超越传统离线视频处理的挑战。这需要我们进行连续感知、主动决策,以及基于动态演化视觉内容的响应交互。然而,现有方法依赖于交替感知反应或异步触发,缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预期,这限制了它们在实时流媒体中的实时响应能力和主动决策制定。为此,我们提出了StreamAgent,能够预测未来包含任务相关信息的时间间隔和空间区域,以实现以目标和主动的反应。具体来说,我们通过提示预测代理整合问题语义和历史观察,以预测关键事件的时间进展,将当前观察与预期的未来证据对齐,随后调整感知行为(例如,关注任务相关区域或在后续帧中持续跟踪)。为了实现高效推理,我们设计了一种流式KV缓存机制,构建了一种分层内存结构,用于选择性回忆相关令牌,实现在不存储所有令牌的传统KV缓存的同时进行高效语义检索。在流媒体和长视频理解任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在响应准确性和实时效率方面优于现有方法,凸显了其在真实世界流媒体场景中的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
实时流媒体视频理解在自动驾驶和智能监控等领域面临传统离线视频处理无法应对的挑战,需要持续感知、主动决策和基于动态演化视觉内容的响应交互。然而,现有方法依赖于交替感知反应或异步触发,缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预期,这限制了其在实时流媒体中的响应能力和主动决策。为此,我们提出了StreamAgent,可预测未来任务相关信息的预期时间间隔和空间区域,以实现目标驱动的响应。具体来说,我们通过整合问题语义和历史观察,促使预测代理预测关键事件的时间进展,将当前观察与预期的未来证据对齐,并据此调整感知行动(例如,关注任务相关区域或在后续帧中进行持续跟踪)。为提升推理效率,我们设计了一种流式KV缓存机制,构建分层内存结构以实现选择性召回相关令牌,从而在减少存储所有令牌的传统KV缓存开销的同时,实现高效语义检索。在流媒体和长视频理解任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在响应准确性和实时效率方面优于现有方法,突显其在真实世界流媒体场景中的实用价值。
关键见解
- 实时流媒体视频理解面临超越传统离线视频处理的挑战,需要持续感知、主动决策和响应交互。
- 现有方法缺乏任务驱动的规划和未来预期,限制了实时响应能力和主动决策。
- 提出的StreamAgent能够预测未来任务相关信息的预期时间间隔和空间区域。
- 通过整合问题语义和历史观察,StreamAgent可以促使预测代理预测关键事件的时间进展。
- StreamAgent能够调整感知行动,例如关注任务相关区域或在后续帧中进行持续跟踪。
- 设计了流式KV缓存机制,实现高效语义检索和减少存储开销。
- 在流媒体和长视频理解任务上的实验表明,StreamAgent在响应准确性和实时效率方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

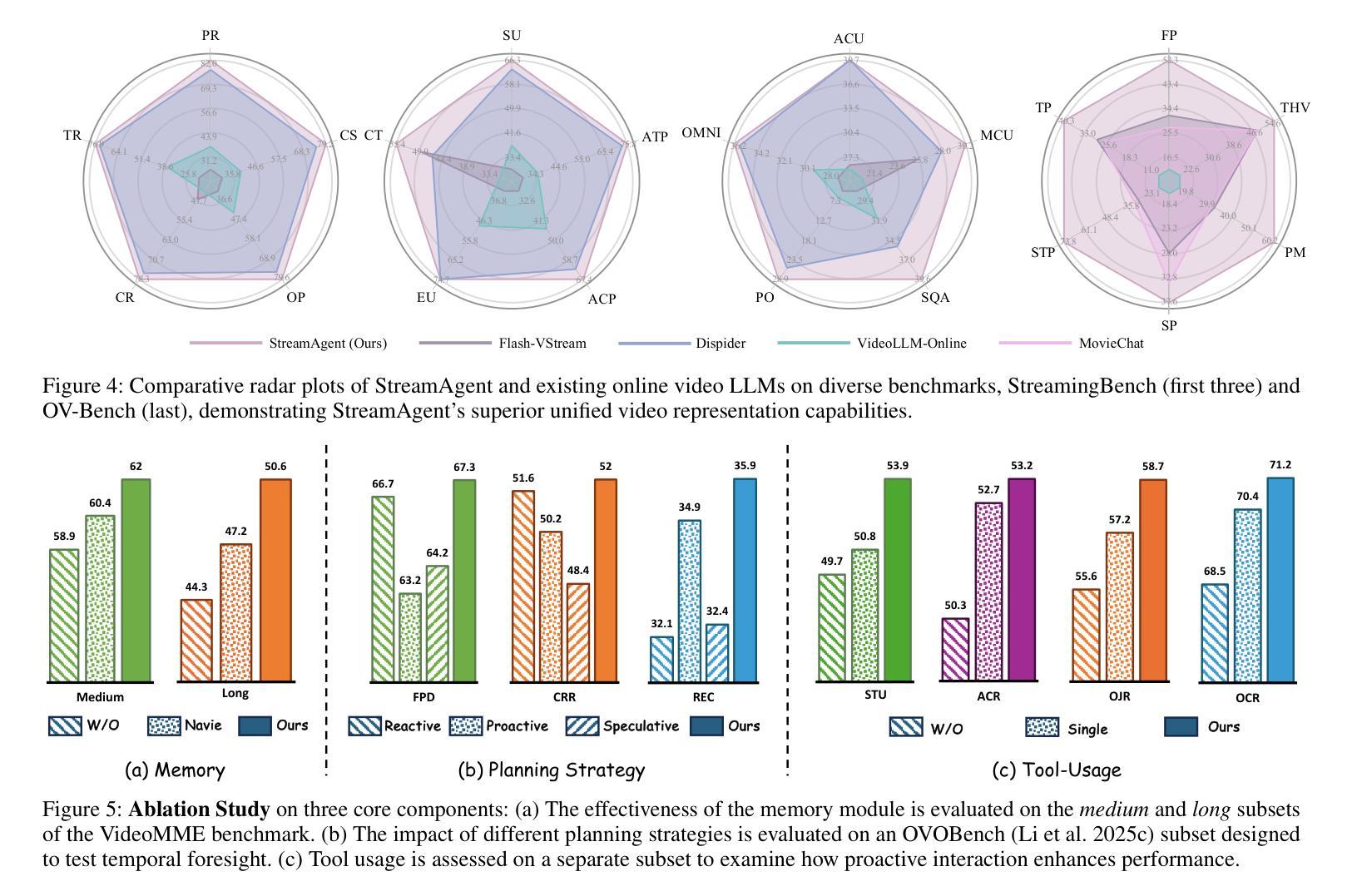
Web-CogReasoner: Towards Knowledge-Induced Cognitive Reasoning for Web Agents
Authors:Yuhan Guo, Cong Guo, Aiwen Sun, Hongliang He, Xinyu Yang, Yue Lu, Yingji Zhang, Xuntao Guo, Dong Zhang, Jianzhuang Liu, Jiang Duan, Yijia Xiao, Liangjian Wen, Hai-Ming Xu, Yong Dai
Multimodal large-scale models have significantly advanced the development of web agents, enabling perception and interaction with digital environments akin to human cognition. In this paper, we argue that web agents must first acquire sufficient knowledge to effectively engage in cognitive reasoning. Therefore, we decompose a web agent’s capabilities into two essential stages: knowledge content learning and cognitive processes. To formalize this, we propose Web-CogKnowledge Framework, categorizing knowledge as Factual, Conceptual, and Procedural. In this framework, knowledge content learning corresponds to the agent’s processes of Memorizing and Understanding, which rely on the first two knowledge types, representing the “what” of learning. Conversely, cognitive processes correspond to Exploring, grounded in Procedural knowledge, defining the “how” of reasoning and action. To facilitate knowledge acquisition, we construct the Web-CogDataset, a structured resource curated from 14 real-world websites, designed to systematically instill core knowledge necessary for web agent. This dataset serves as the agent’s conceptual grounding-the “nouns” upon which comprehension is built-as well as the basis for learning how to reason and act. Building on this foundation, we operationalize these processes through a novel knowledge-driven Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning framework, developing and training our proposed agent, the Web-CogReasoner. Extensive experimentation reveals its significant superiority over existing models, especially in generalizing to unseen tasks where structured knowledge is decisive. To enable rigorous evaluation, we introduce the Web-CogBench, a comprehensive evaluation suite designed to assess and compare agent performance across the delineated knowledge domains and cognitive capabilities. Our code and data is open sourced at https://github.com/Gnonymous/Web-CogReasoner
多模态大规模模型已经显著推动了网络代理的发展,使其能够感知和与数字环境进行类似于人类认知的交互。在本文中,我们认为网络代理必须首先获得足够的知识以有效地参与认知推理。因此,我们将网络代理的能力分解为两个关键阶段:知识内容学习和认知过程。为了正式提出这一点,我们提出了Web-CogKnowledge框架,将知识分类为事实、概念和程序三类。在此框架中,知识内容学习对应于代理的记忆和理解过程,这依赖于前两种知识类型,代表学习的“内容是什么”。相反,认知过程对应于基于程序知识的探索,定义了推理和行动方式的“如何”。为了促进知识获取,我们构建了Web-Cog数据集,这是一个从14个真实网站精心策划的结构化资源,旨在系统地灌输网络代理所需的核心知识。该数据集作为代理的概念基础——构建理解的“名词”,以及学习如何推理和行动的基础。在此基础上,我们通过新的知识驱动的思考链(CoT)推理框架来实施这些过程,开发和训练我们提出的代理——Web-CogReasoner。大量实验表明,与现有模型相比,它具有显著的优势,特别是在处理未见过的任务时,结构化知识是起决定性的。为了进行严格的评估,我们引入了Web-CogBench,这是一套全面的评估工具,旨在评估和比较代理在不同划分的知识领域和认知能力方面的表现。我们的代码和数据在https://github.com/Gnonymous/Web-CogReasoner开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code and data is open sourced at https://github.com/Gnonymous/Web-CogReasoner
Summary
本文主张Web代理需先获取充足知识再参与认知推理,提出Web-CogKnowledge Framework,将知识分为事实、概念与程序三类。为促使知识获取,构建Web-CogDataset,通过结构化资源教授核心知识。在此基础上提出Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理框架并训练Web-CogReasoner代理。实验证明其在未见任务上的表现优于现有模型。同时推出Web-CogBench评估套件来评估代理性能。
Key Takeaways
- Web代理在开发过程中,首先需要获取充足的知识来进行有效的认知推理。
- 提出Web-CogKnowledge Framework框架,将知识分为事实、概念和程序三类。
- 构建Web-CogDataset数据集,从真实世界的网站中挑选结构化资源,为代理提供核心知识的训练基础。
- 引入Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理框架,使代理能在获取的知识基础上进行推理操作。
- 训练出Web-CogReasoner代理,并在一系列实验中证明了其性能显著优于现有模型。
- 推出Web-CogBench评估套件,用于评估代理在不同知识领域和认知能力方面的表现。
点此查看论文截图
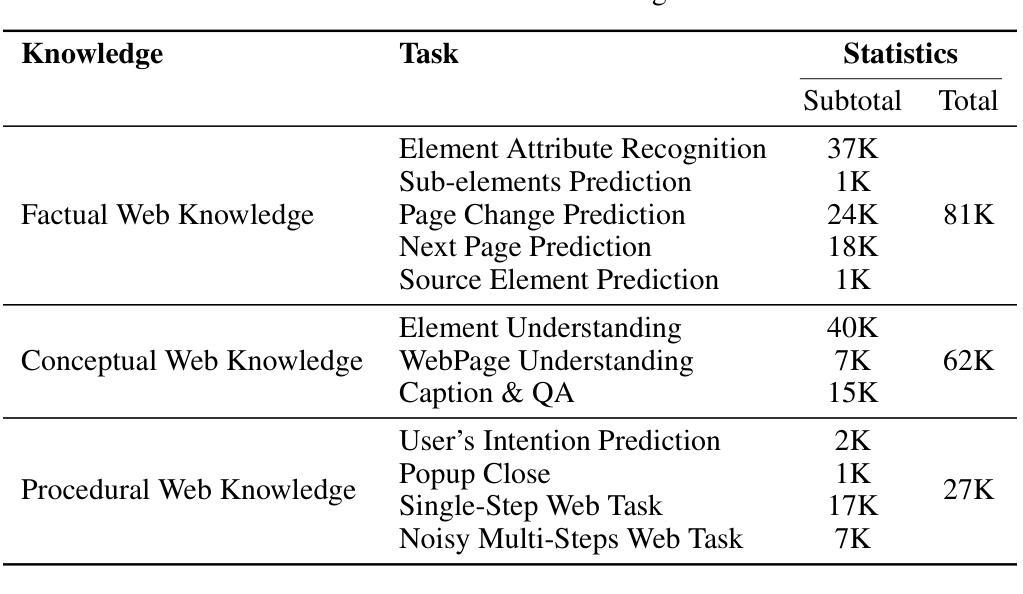
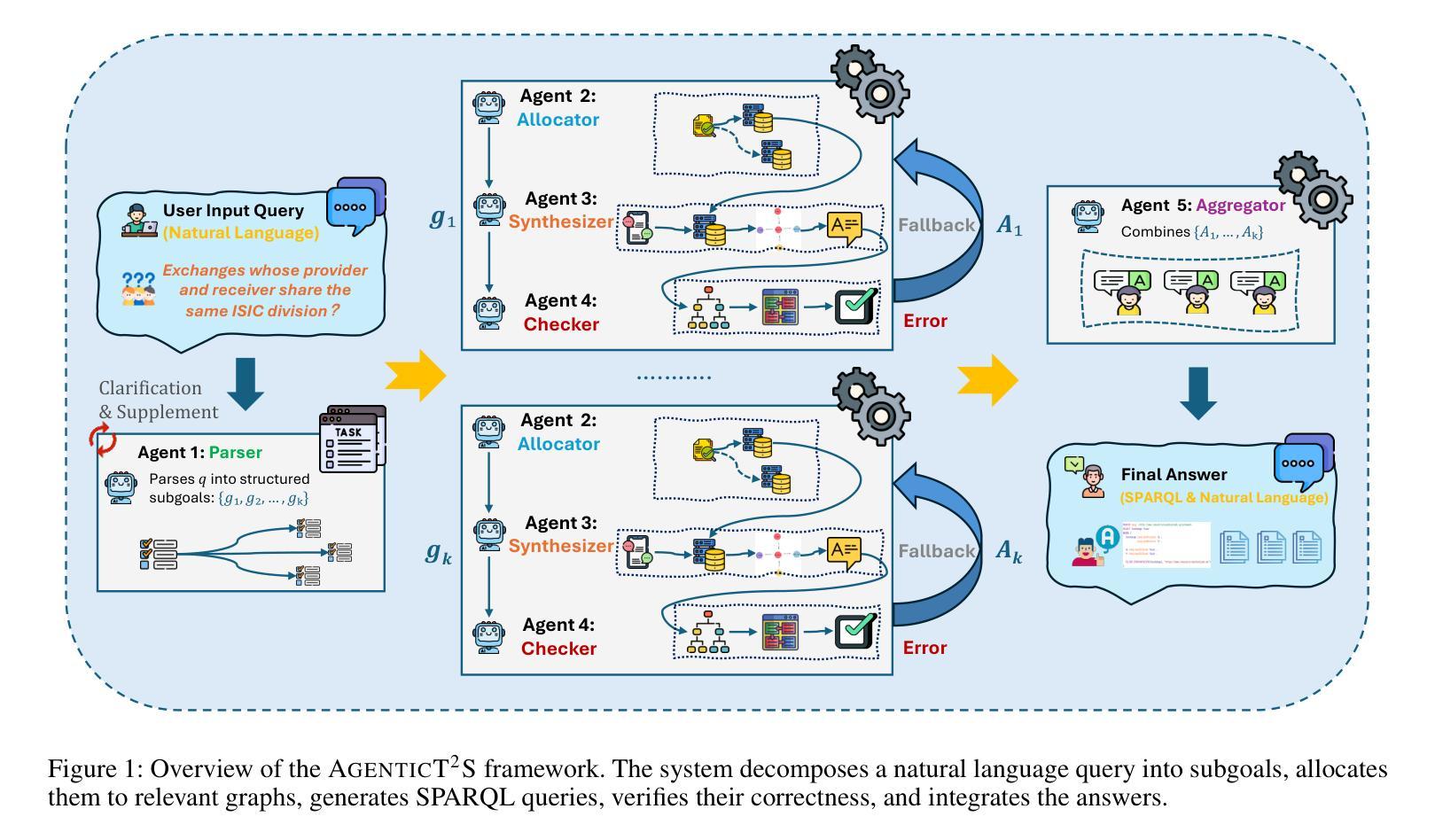
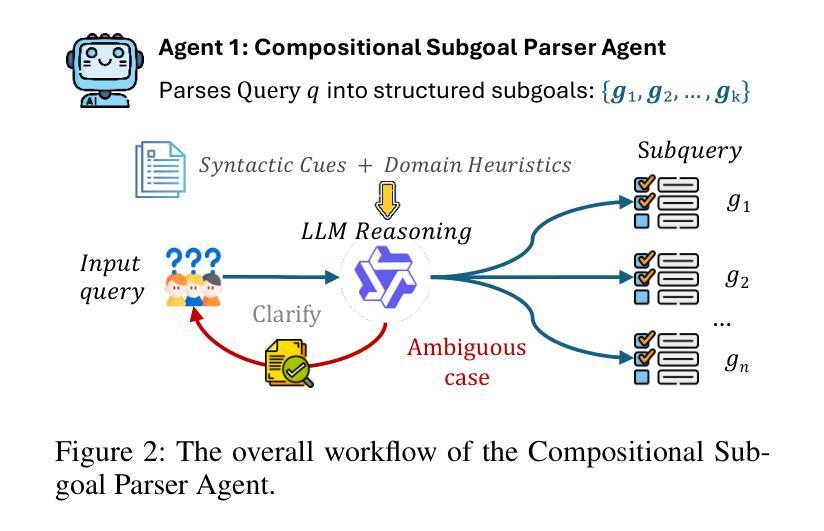
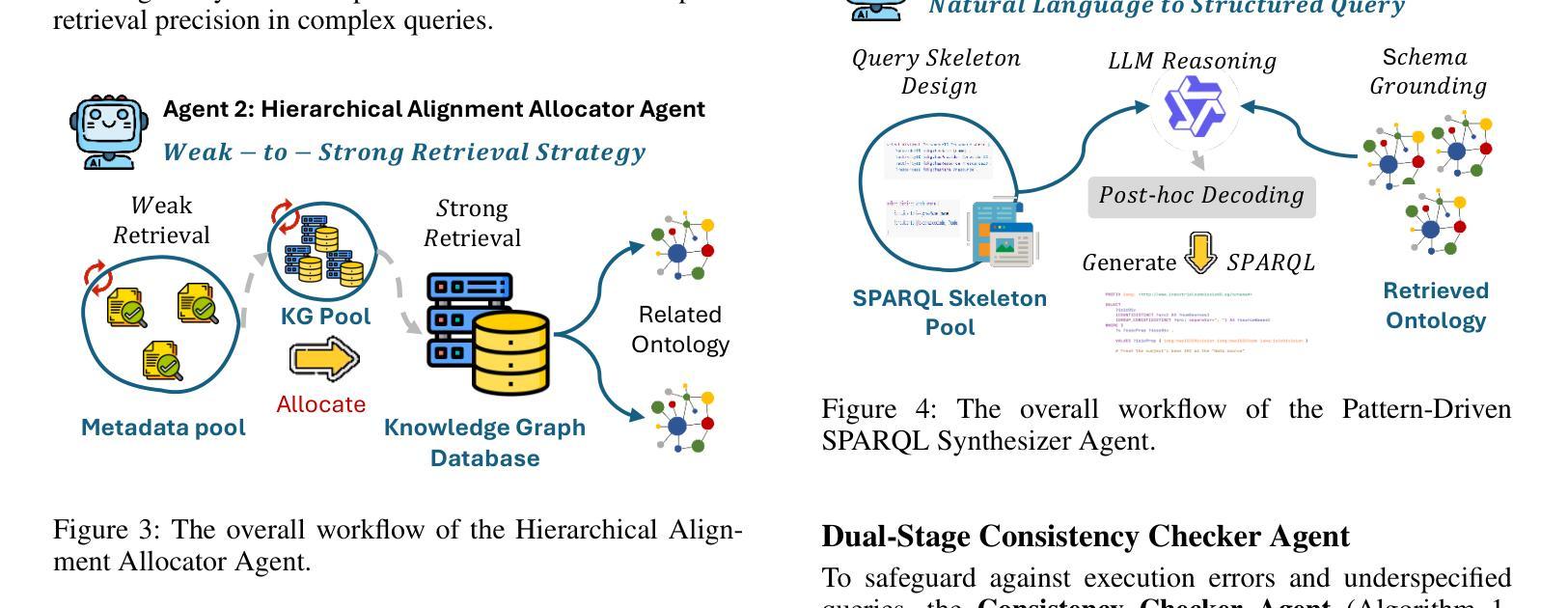
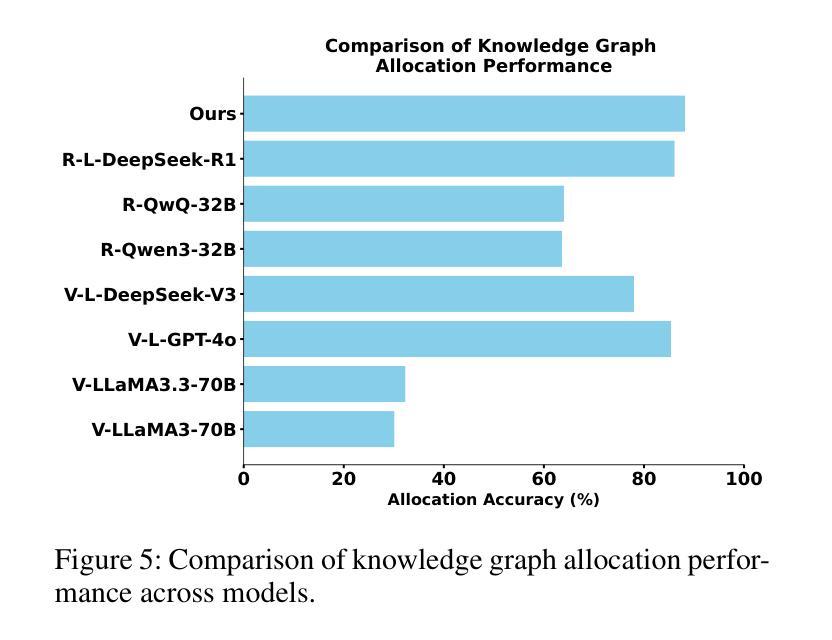
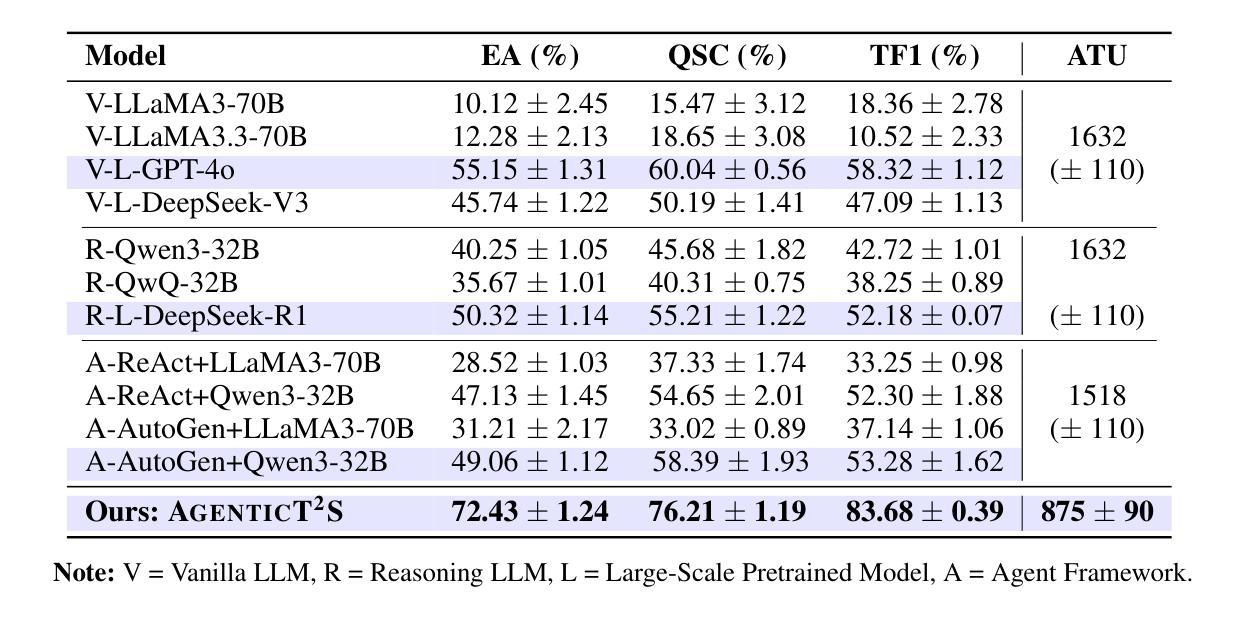
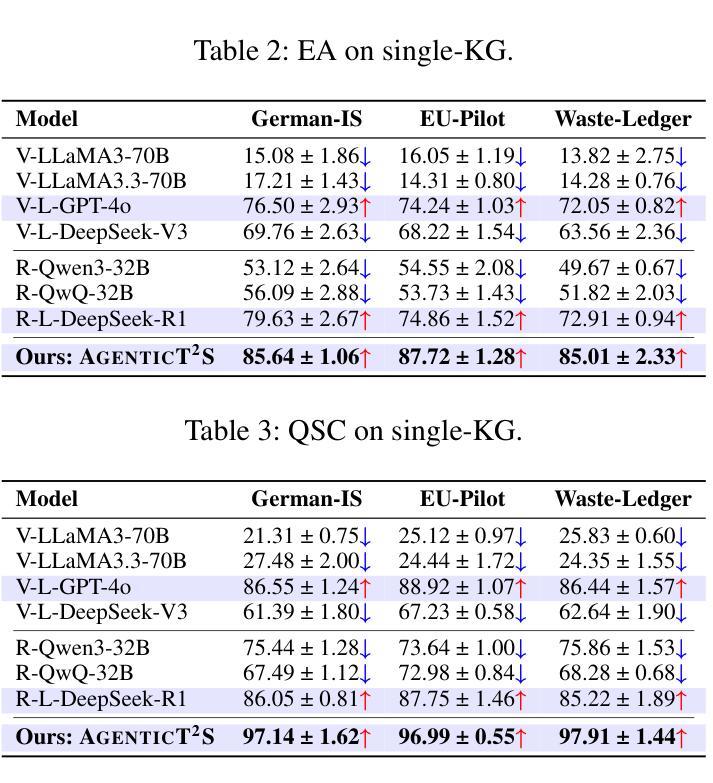
AGENTICT$^2$S:Robust Text-to-SPARQL via Agentic Collaborative Reasoning over Heterogeneous Knowledge Graphs for the Circular Economy
Authors:Yang Zhao, Chengxiao Dai, Wei Zhuo, Tan Chuan Fu, Yue Xiu, Dusit Niyato, Jonathan Z. Low, Eugene Ho Hong Zhuang, Daren Zong Loong Tan
Question answering over heterogeneous knowledge graphs (KGQA) involves reasoning across diverse schemas, incomplete alignments, and distributed data sources. Existing text-to-SPARQL approaches rely on large-scale domain-specific fine-tuning or operate within single-graph settings, limiting their generalizability in low-resource domains and their ability to handle queries spanning multiple graphs. These challenges are particularly relevant in domains such as the circular economy, where information about classifications, processes, and emissions is distributed across independently curated knowledge graphs (KGs). We present AgenticT$^2$S, a modular framework that decomposes KGQA into subtasks managed by specialized agents responsible for retrieval, query generation, and verification. A scheduler assigns subgoals to different graphs using weak-to-strong alignment strategies. A two-stage verifier detects structurally invalid and semantically underspecified queries through symbolic validation and counterfactual consistency checks. Experiments on real-world circular economy KGs demonstrate that AgenticT$^2$S improves execution accuracy by 17.3% and triple level F$_1$ by 25.4% over the best baseline, while reducing the average prompt length by 46.4%. These results demonstrate the benefits of agent-based schema-aware reasoning for scalable KGQA and support decision-making in sustainability domains through robust cross-graph reasoning.
问答系统在异质知识图谱(KGQA)中的应用涉及跨不同模式、不完整对齐和分布式数据源的推理。现有的文本到SPARQL的方法依赖于大规模的特定领域的微调,或者在单个图环境中运行,这在低资源领域中限制了其通用性,也限制了它们处理跨多个图的查询的能力。这些挑战在循环经济等领域尤为突出,循环经济中的分类、过程和排放信息分布在独立维护的知识图谱(KGs)中。我们提出了AgenticT$^2$S,这是一个模块化框架,它将KGQA分解成由专门代理负责检索、查询生成和验证的子任务。调度器使用弱到强的对齐策略将子目标分配给不同的图形。两阶段验证器通过符号验证和反向事实一致性检查来检测结构无效和语义未指定的查询。在现实世界循环经济知识图谱上的实验表明,与最佳基线相比,AgenticT$^2$S的执行精度提高了17.3%,三重F$_1$提高了25.4%,同时平均提示长度减少了46.4%。这些结果证明了基于代理的模式感知推理在可扩展的KGQA中的好处,并通过可靠的跨图推理支持可持续性领域的决策制定。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
知识图谱问答(KGQA)面临跨不同模式、不完全对齐和分布式数据源的推理挑战。现有文本到SPARQL的转换方法依赖于大规模特定领域的微调或在单一图谱环境中运行,这限制了其在低资源领域中的通用性以及处理跨多图谱查询的能力。特别是在循环经济等领域,信息分散在独立编制的知识图谱中。我们提出了AgenticT$^2$S,一个模块化框架,将KGQA分解成由专门代理负责检索、查询生成和验证的子任务。调度器使用弱到强的对齐策略将子目标分配给不同的图谱。两阶段验证器通过符号验证和反事实一致性检查检测结构和语义上未指定的查询。在真实循环经济知识图谱上的实验表明,AgenticT$^2$S相较于最佳基线,执行精度提高17.3%,三元组级别F$_1$提高25.4%,平均提示长度减少46.4%。这表明基于代理的模式感知推理对于可扩展的KGQA和可持续性领域的决策支持具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- KGQA面临跨不同知识图谱的推理挑战,需处理多样模式、不完全对齐和分布式数据源。
- 现有文本到SPARQL的转换方法缺乏通用性,难以处理跨多图谱查询。
- AgenticT$^2$S是一个模块化框架,通过专门代理处理KGQA的不同子任务,如检索、查询生成和验证。
- 调度器根据弱到强的对齐策略分配子目标到不同图谱。
- 两阶段验证器检测结构和语义上未指定的查询。
- 在真实循环经济知识图谱上的实验表明,AgenticT$^2$S较现有方法有明显性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

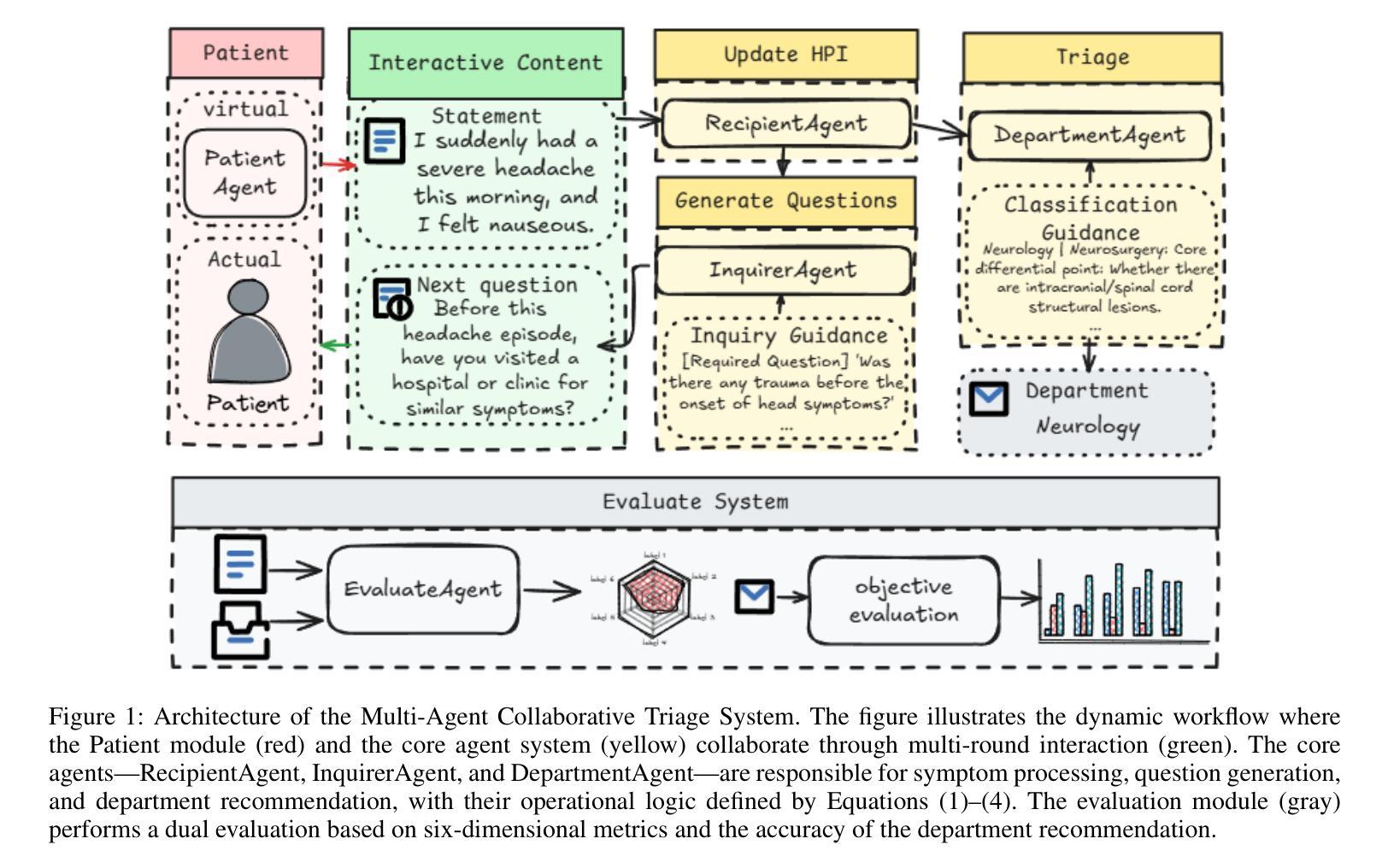
Collaborative Medical Triage under Uncertainty: A Multi-Agent Dynamic Matching Approach
Authors:Hongyan Cheng, Chengzhang Yu, Yanshu Shi, Chiyue Wang, Cong Liu, Zhanpeng Jin
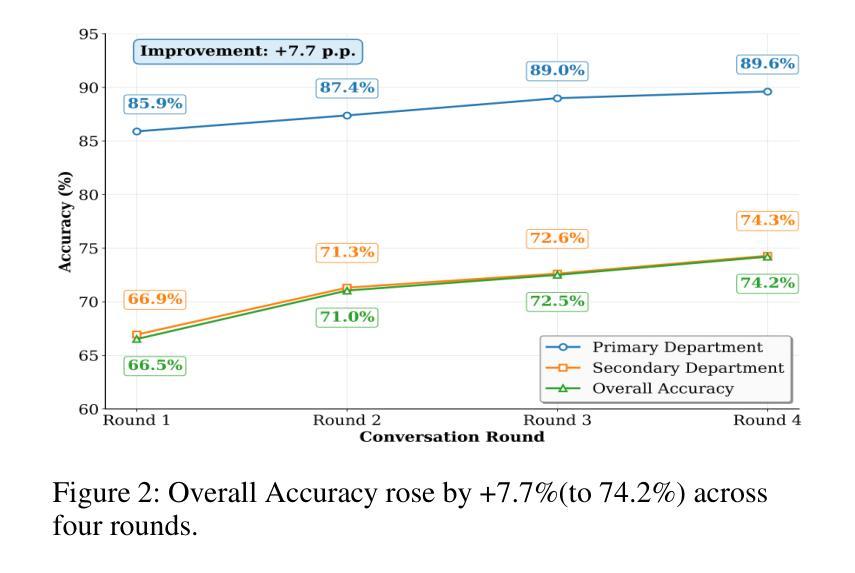
The post-pandemic surge in healthcare demand, coupled with critical nursing shortages, has placed unprecedented pressure on medical triage systems, necessitating innovative AI-driven solutions. We present a multi-agent interactive intelligent system for medical triage that addresses three fundamental challenges in current AI-based triage systems: inadequate medical specialization leading to misclassification, heterogeneous department structures across healthcare institutions, and inefficient detail-oriented questioning that impedes rapid triage decisions. Our system employs three specialized agents–RecipientAgent, InquirerAgent, and DepartmentAgent–that collaborate through Inquiry Guidance mechanism and Classification Guidance Mechanism to transform unstructured patient symptoms into accurate department recommendations. To ensure robust evaluation, we constructed a comprehensive Chinese medical triage dataset from “Ai Ai Yi Medical Network”, comprising 3,360 real-world cases spanning 9 primary departments and 62 secondary departments. Experimental results demonstrate that our multi-agent system achieves 89.6% accuracy in primary department classification and 74.3% accuracy in secondary department classification after four rounds of patient interaction. The system’s dynamic matching based guidance mechanisms enable efficient adaptation to diverse hospital configurations while maintaining high triage accuracy. We successfully developed this multi-agent triage system that not only adapts to organizational heterogeneity across healthcare institutions but also ensures clinically sound decision-making.
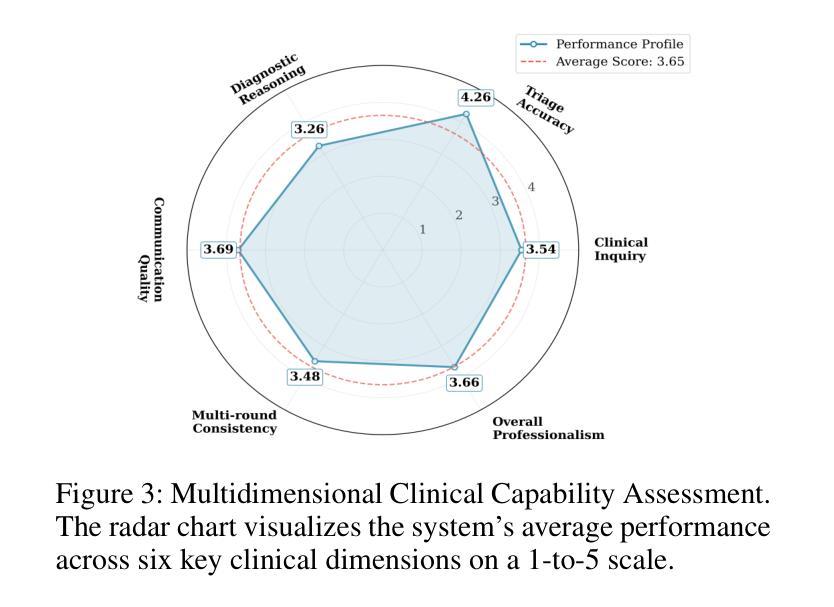
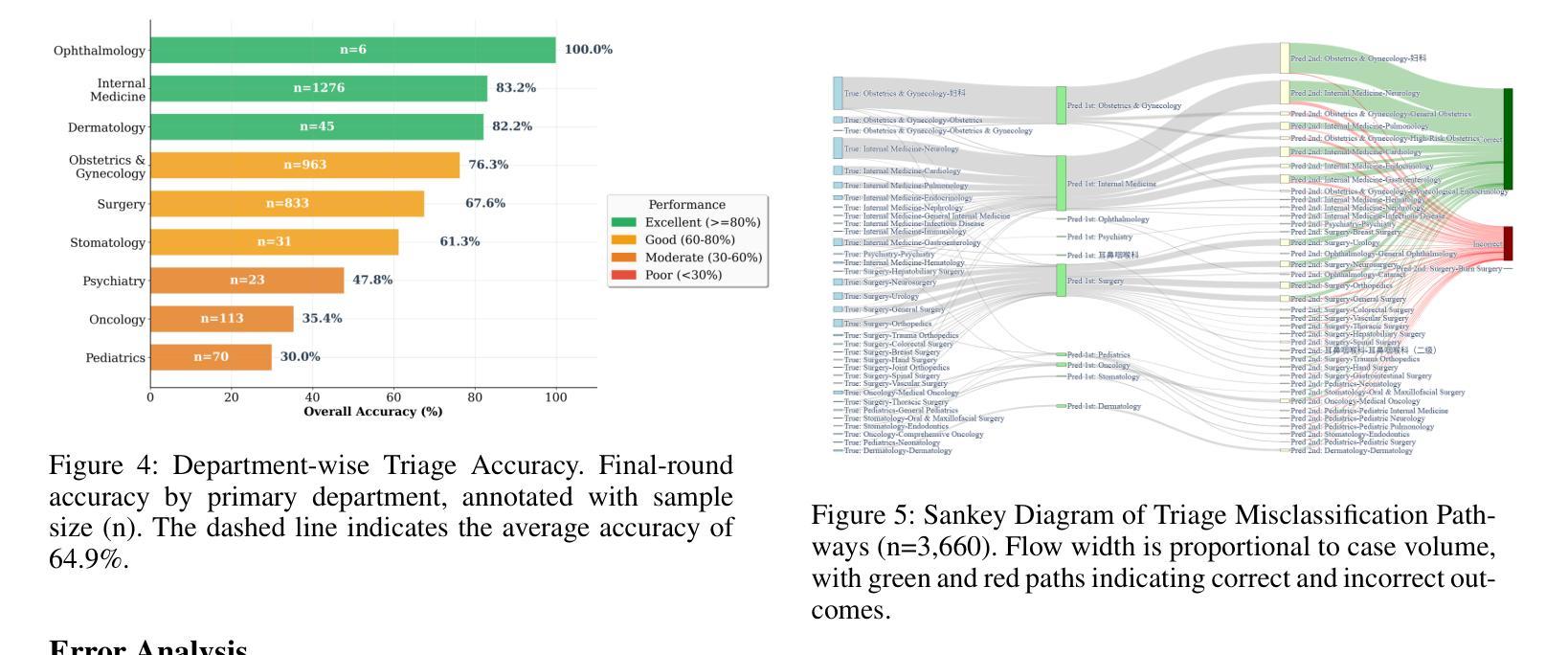
后疫情时代医疗需求的激增,加上护理人员的严重短缺,给医疗分流系统带来了前所未有的压力,急需创新的AI驱动解决方案。我们提出了一种用于医疗分流的多智能体交互式系统,解决了当前基于AI的分流系统中的三个基本挑战:医疗专业化不足导致误分类、医疗机构之间部门结构异质、以及效率低下、细节导向的提问阻碍快速分流决策。我们的系统采用三个专用智能体——RecipientAgent、InquirerAgent和DepartmentAgent,它们通过查询指导机制和分类指导机制进行协作,将非结构化的患者症状转化为准确的部门推荐。为确保稳健评估,我们从“爱爱医疗网”构建了一个全面的中文医疗分流数据集,包含3360个真实案例,涵盖9个主要部门和62个次要部门。实验结果表明,我们的多智能体系统在四轮患者互动后,在主要部门分类方面达到了89.6%的准确率,在次要部门分类方面达到了74.3%的准确率。该系统的动态匹配指导机制能够高效地适应不同的医院配置,同时保持较高的分流准确率。我们成功开发了这个多智能体分流系统,它不仅适应于医疗机构之间的组织异质性,而且确保临床决策的科学性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures, 2 table
总结
疫情后医疗保健需求的激增与护理人员的短缺给医疗分流系统带来了前所未有的压力,迫切需要创新的人工智能驱动解决方案。针对当前AI分流系统中的三个基本挑战,即医疗专业化不足导致的误分类、医疗机构之间部门结构差异大和不详尽的细节问题导致的分流决策效率低下等问题,我们提出了一种多智能体互动智能系统进行医疗分流。该系统采用三个专门代理:RecipientAgent、InquirerAgent和DepartmentAgent,通过询问指导和分类指导机制协同工作,将患者的不结构化症状转化为准确的科室推荐。为了确保有效的评估,我们从“爱爱医医疗网络”构建了一个全面的中文医疗分流数据集,包含涵盖9个主要科室和62个二级科室的3360个真实病例。实验结果显示,经过四轮的患者互动后,该多智能系统主要科室分类准确度达到了89.6%,二级科室分类准确度达到了74.3%。该系统的动态匹配指导机制能够实现高效的医院配置适应,同时保持较高的分流准确性。我们成功开发了这个多智能分流系统,不仅适应于医疗机构间的组织异质性,而且确保临床决策的科学性。
关键见解
- 疫情后的医疗保健需求激增和护理短缺给医疗分流系统带来了压力,需要AI解决方案。
- 当前AI医疗分流系统面临三大挑战:医疗专业化不足、医疗机构部门结构差异大和效率问题。
- 提出了一种多智能体互动智能系统,包括三个专门代理:RecipientAgent、InquirerAgent和DepartmentAgent。
- 通过询问指导和分类指导机制,智能系统可将患者的不结构化症状转化为准确的科室推荐。
- 在包含真实病例的中文医疗分流数据集上进行评估,该系统表现良好,主要科室分类准确度高。
- 系统的动态匹配指导机制能适应不同的医院配置,同时保持较高的分流准确性。
点此查看论文截图

GEM: Gaussian Embedding Modeling for Out-of-Distribution Detection in GUI Agents
Authors:Zheng Wu, Pengzhou Cheng, Zongru Wu, Lingzhong Dong, Zhuosheng Zhang
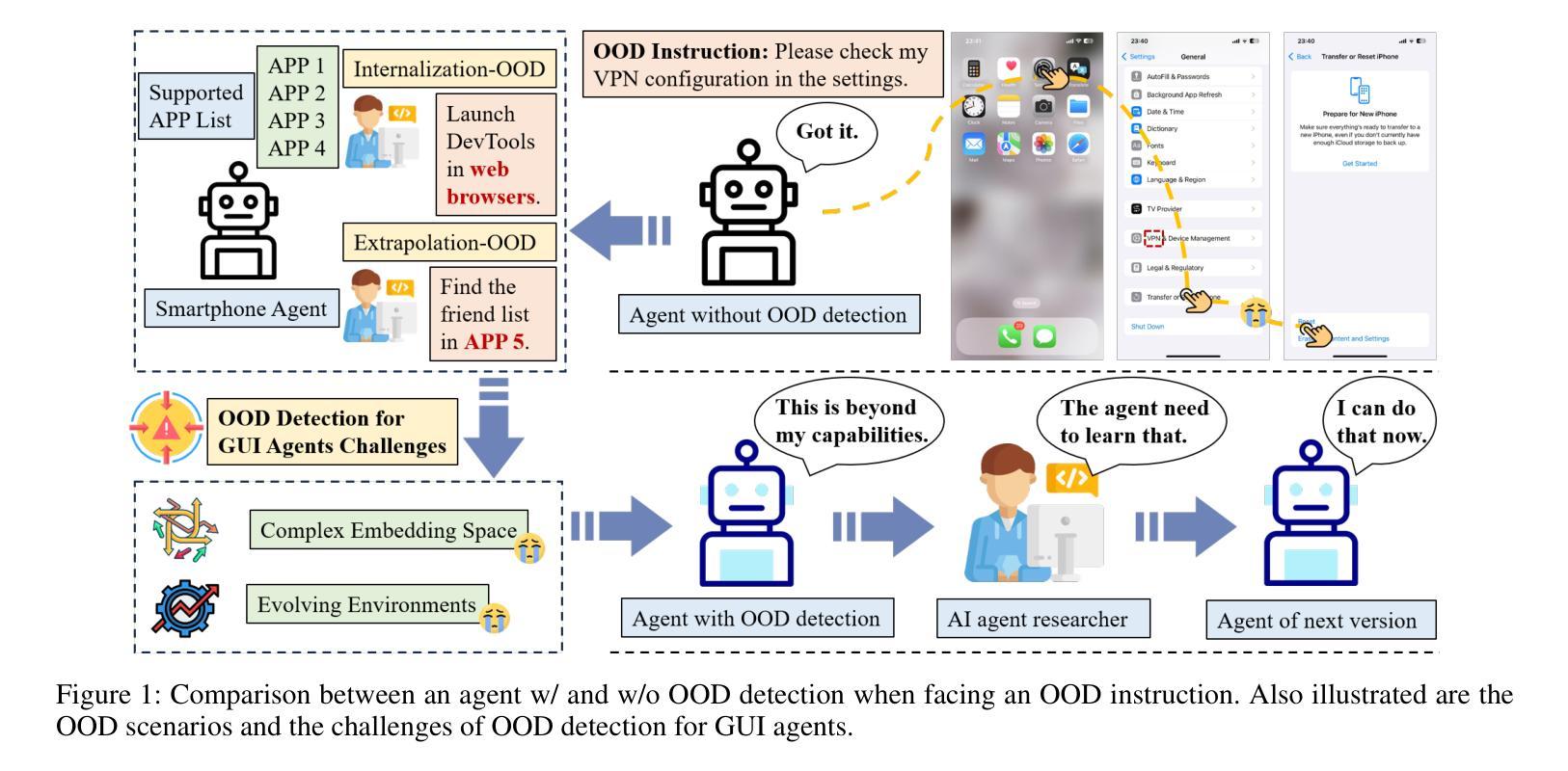
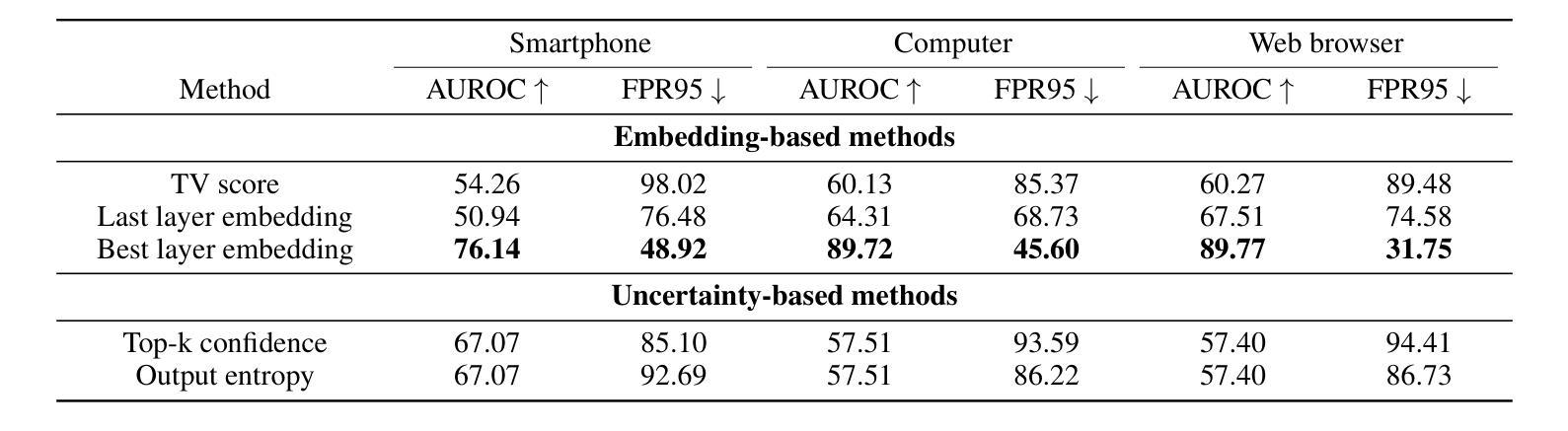
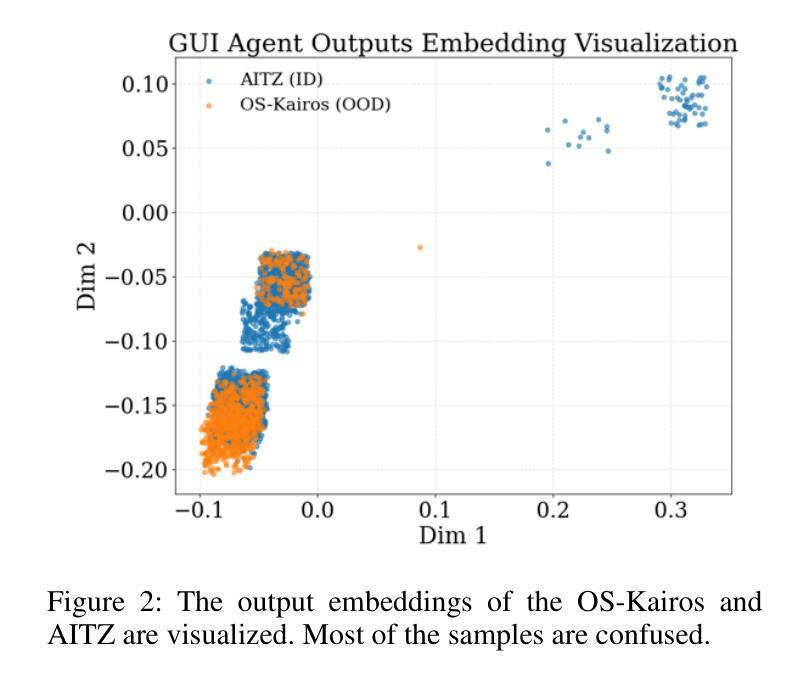
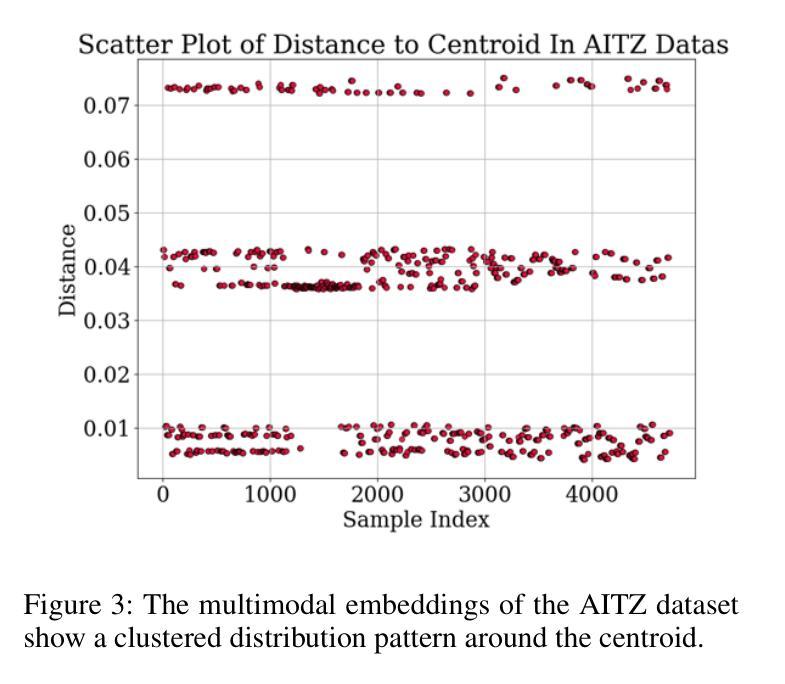
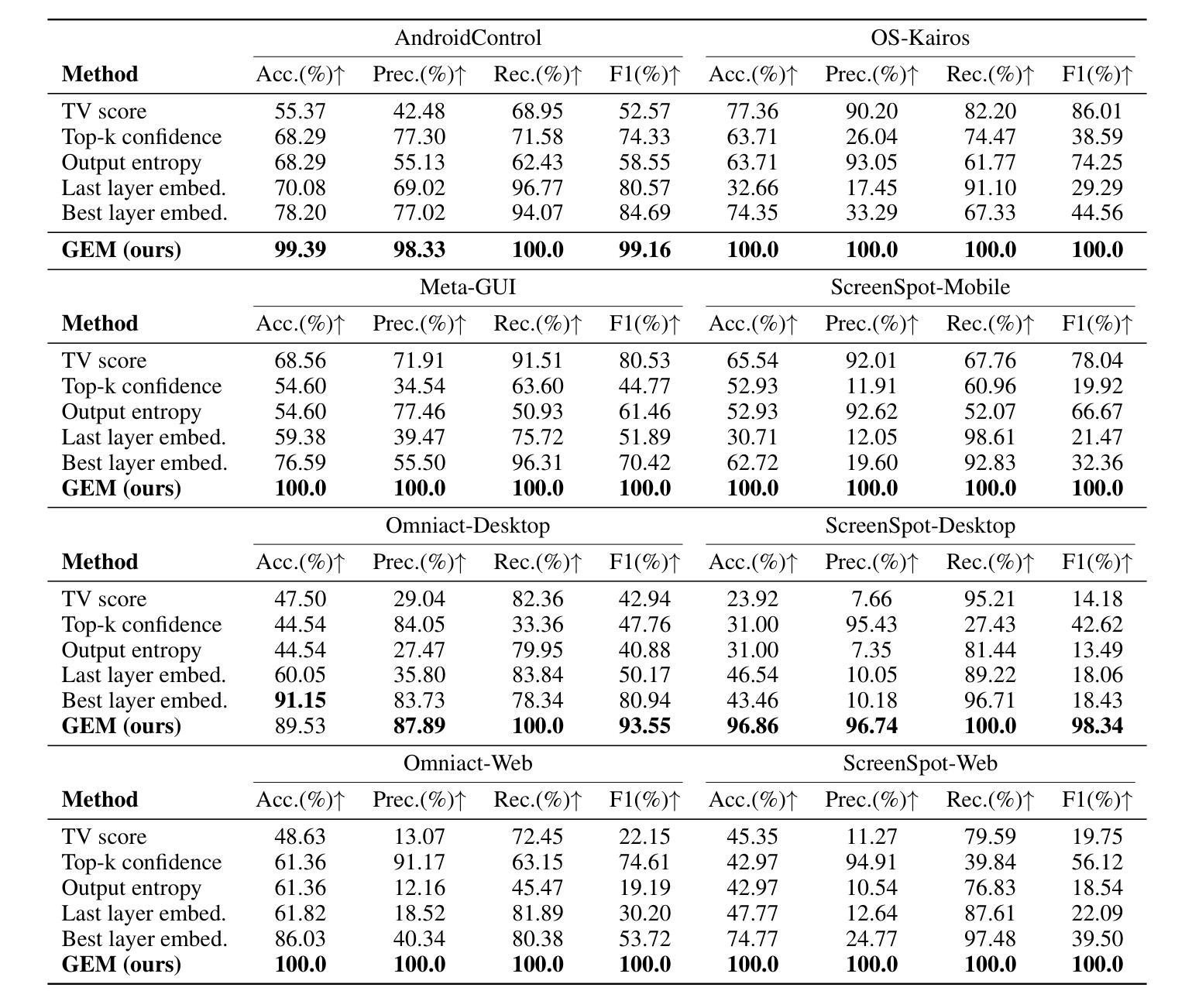
Graphical user interface (GUI) agents have recently emerged as an intriguing paradigm for human-computer interaction, capable of automatically executing user instructions to operate intelligent terminal devices. However, when encountering out-of-distribution (OOD) instructions that violate environmental constraints or exceed the current capabilities of agents, GUI agents may suffer task breakdowns or even pose security threats. Therefore, effective OOD detection for GUI agents is essential. Traditional OOD detection methods perform suboptimally in this domain due to the complex embedding space and evolving GUI environments. In this work, we observe that the in-distribution input semantic space of GUI agents exhibits a clustering pattern with respect to the distance from the centroid. Based on the finding, we propose GEM, a novel method based on fitting a Gaussian mixture model over input embedding distances extracted from the GUI agent that reflect its capability boundary. Evaluated on eight datasets spanning smartphones, computers, and web browsers, our method achieves an average accuracy improvement of 23.70% over the best-performing baseline while only increasing training time by 4.9% and testing time by 6.5%. We also experimentally demonstrate that GEM can improve the step-wise success rate by 9.40% by requesting assistance from the cloud model when encountering OOD samples. Analysis verifies the generalization ability of our method through experiments on nine different backbones. The codes are available at https://github.com/Wuzheng02/GEM-OODforGUIagents.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理作为人机交互的一种引人入胜的模式最近已经出现,它能够自动执行用户指令来操作智能终端设备。然而,当遇到超出分布(OOD)的指令,这些指令可能违反环境约束或超出代理的当前能力时,GUI代理可能会发生任务故障,甚至可能构成安全威胁。因此,有效的GUI代理的OOD检测至关重要。由于嵌入空间的复杂性和GUI环境的不断变化,传统的OOD检测方法在这个领域表现不佳。在这项工作中,我们发现GUI代理的内置分布输入语义空间在距离质心方面表现出聚类模式。基于这一发现,我们提出了基于高斯混合模型拟合的GEM新方法,该方法对从GUI代理提取的输入嵌入距离进行建模,反映了其能力边界。在涵盖智能手机、计算机和网页浏览器的八个数据集上评估,我们的方法在最先进的基线方法上平均提高了23.70%的准确率,同时仅将训练时间增加4.9%,测试时间增加6.5%。我们还通过实验证明,当遇到OOD样本时,通过请求云模型协助,GEM可以提高步骤成功率9.4%。分析并通过在九个不同主干网络上进行的实验验证了我们的方法的泛化能力。相关代码可通过链接https://github.com/Wuzheng02/GEM-OODforGUIagents访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨图形用户界面(GUI)代理在面临超出其能力范围或违反环境约束的未知指令时面临的挑战,并提出一种基于高斯混合模型的方法(GEM)进行异常检测。该方法能有效识别出GUI代理在智能手机、计算机和网页浏览器等不同平台上的异常输入,相较于现有最佳基线模型,其准确率平均提高23.70%,同时仅增加训练时间4.9%和测试时间6.5%。当遇到超出代理能力的样本时,通过请求云模型协助,可进一步提高步骤成功率9.40%。实验证明该方法具有良好的泛化能力,相关代码已公开于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理在面临超出其能力范围或违反环境约束的未知指令时可能出现问题。
- 传统OOD检测方法在GUI环境中表现不佳,主要由于环境复杂和变化性大。
- 本文观察到GUI代理的输入语义空间具有特定的聚类模式,基于此提出了基于高斯混合模型的GEM方法。
- GEM方法在不同平台上实现了较高的准确率提升,且对训练和测试时间的影响较小。
- 当遇到未知样本时,通过请求云模型协助,可进一步提高代理的性能。
- 实验证明GEM方法具有良好的泛化能力,并适用于多种不同的模型架构。
点此查看论文截图

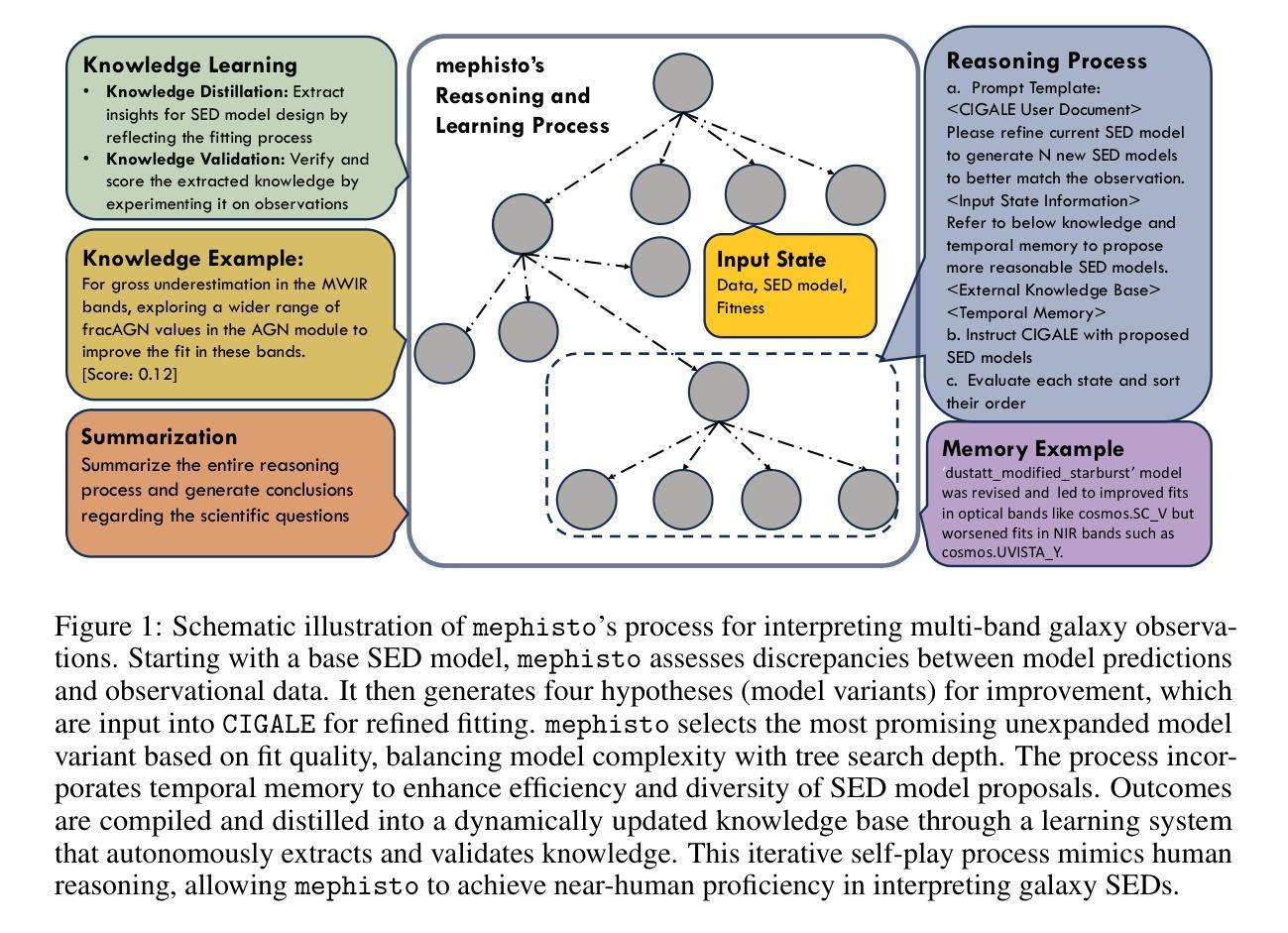
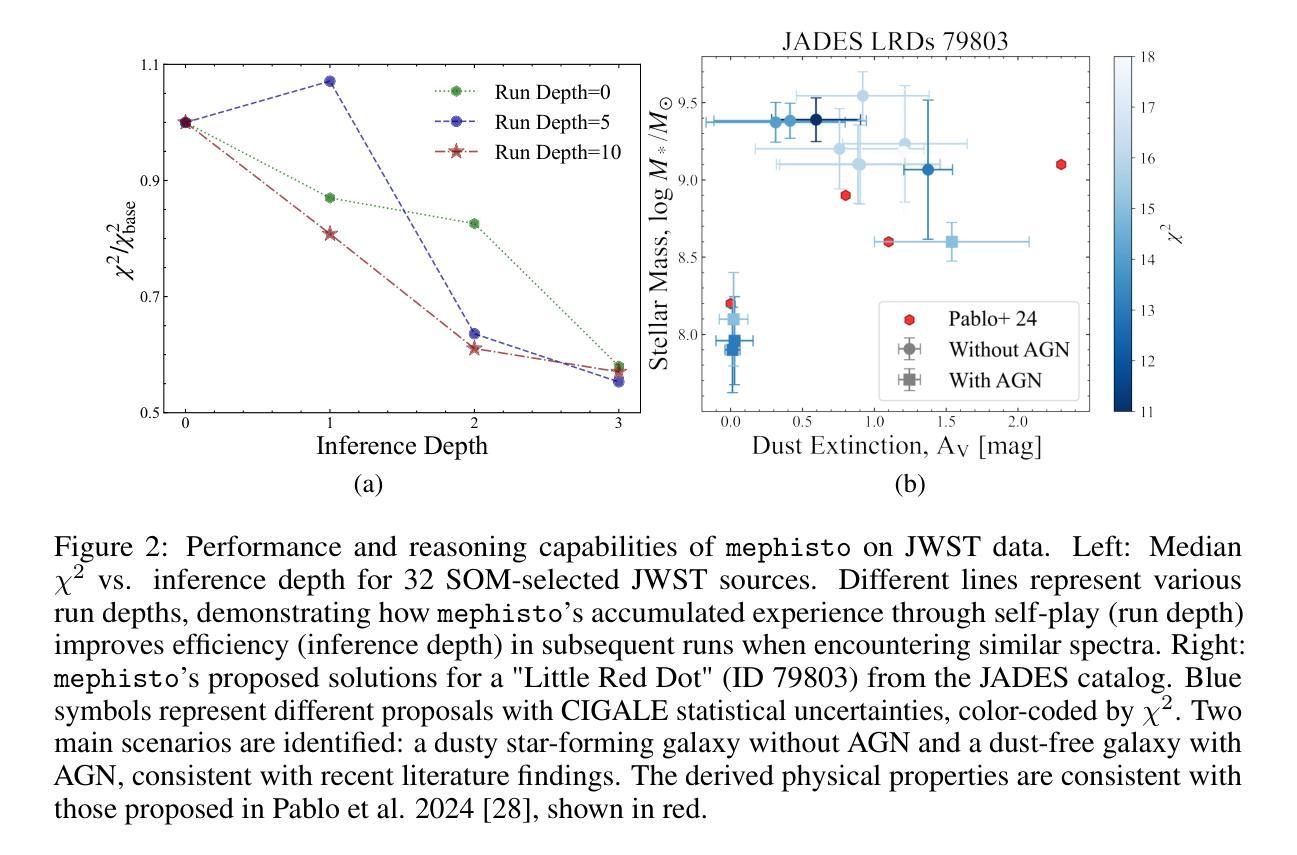
Interpreting Multi-band Galaxy Observations with Large Language Model-Based Agents
Authors:Zechang Sun, Yuan-Sen Ting, Yaobo Liang, Nan Duan, Song Huang, Zheng Cai
Astronomical research traditionally relies on extensive domain knowledge to interpret observations and narrow down hypotheses. We demonstrate that this process can be emulated using large language model-based agents to accelerate research workflows. We propose mephisto, a multi-agent collaboration framework that mimics human reasoning to interpret multi-band galaxy observations. mephisto interacts with the CIGALE codebase, which includes spectral energy distribution (SED) models to explain observations. In this open-world setting, mephisto learns from its self-play experience, performs tree search, and accumulates knowledge in a dynamically updated base. As a proof of concept, we apply mephisto to the latest data from the James Webb Space Telescope. mephisto attains near-human proficiency in reasoning about galaxies’ physical scenarios, even when dealing with a recently discovered population of “Little Red Dot” galaxies. This represents the first demonstration of agentic research in astronomy, advancing towards end-to-end research via LLM agents and potentially expediting astronomical discoveries.
传统的天文研究依赖于广泛的领域知识来解释观测结果并缩小假设范围。我们证明,这个过程可以使用基于大型语言模型的代理来加速研究工作流程。我们提出了模仿人类推理来解释多波段星系观测数据的智能体合作框架“墨菲斯托”。墨菲斯托与CIGALE代码库进行交互,该代码库包含光谱能量分布(SED)模型来解释观测结果。在这个开放世界环境中,墨菲斯托通过自我玩耍经验学习,进行树搜索,并在动态更新的基础上积累知识。作为概念验证,我们将墨菲斯托应用于詹姆斯韦伯太空望远镜的最新数据。墨菲斯托在处理最近发现的“小红点”星系群体时,在理解星系物理场景方面达到了近乎人类的熟练程度。这标志着天文领域智能研究的首次展示,朝着通过大型语言模型代理进行端到端研究的方向迈进,并有可能加速天文学发现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the NIPS ML4PS Workshop 2024. The journal version is in preparation. Code and data will be fully made public following the journal publication. We welcome any comments and feedback
Summary
基于大规模语言模型的代理能够模拟人类推理,加快天文研究流程。我们提出了一个名为mephisto的多代理协作框架,用于解释多波段星系观测结果。通过与包括光谱能量分布(SED)模型在内的CIGALE代码库互动,mephisto可以在开放世界环境中进行自我游戏经验学习,进行树状搜索并在动态更新的知识库中积累知识。在詹姆斯·韦伯太空望远镜的最新数据应用中,mephisto在关于星系物理场景的推理中达到了接近人类的熟练程度,即使在处理最新发现的“小红点”星系群体时也是如此。这标志着代理研究的首次在天文学领域的展示,朝着通过LLM代理进行端到端研究的方向迈进,并可能加速天文学发现。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型代理能模拟人类推理以加快天文学研究。
- 提出名为mephisto的多代理协作框架,用以解释多波段星系观测。
- mephisto与CIGALE代码库中的SED模型互动。
- mephisto在开放世界环境中进行自我游戏经验学习、树状搜索和知识积累。
- 在詹姆斯·韦伯太空望远镜数据中,mephisto展现出接近人类的推理能力,特别是在解释星系物理场景方面。
- 这是首次展示在天文学领域使用代理进行研究。
点此查看论文截图

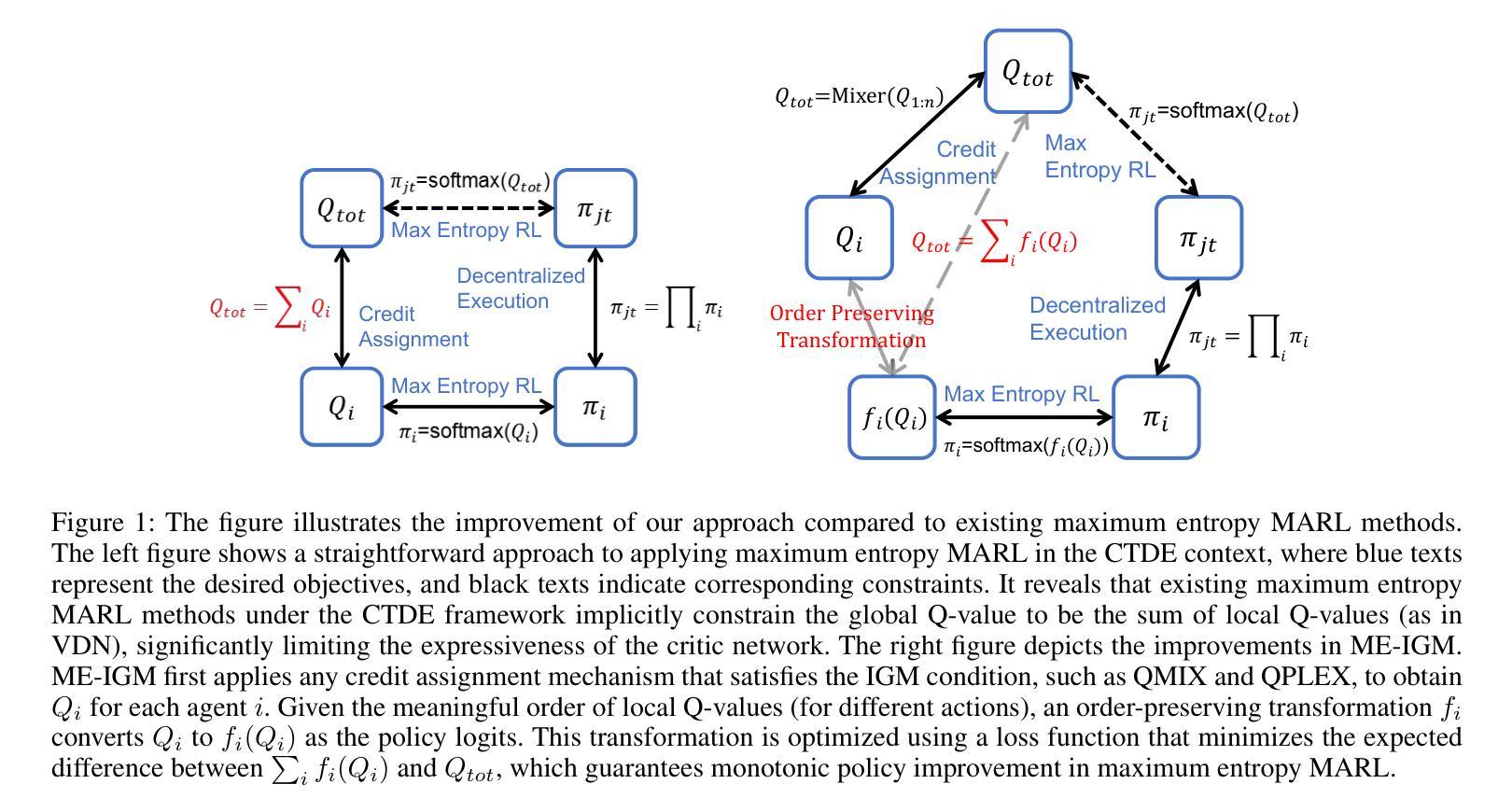
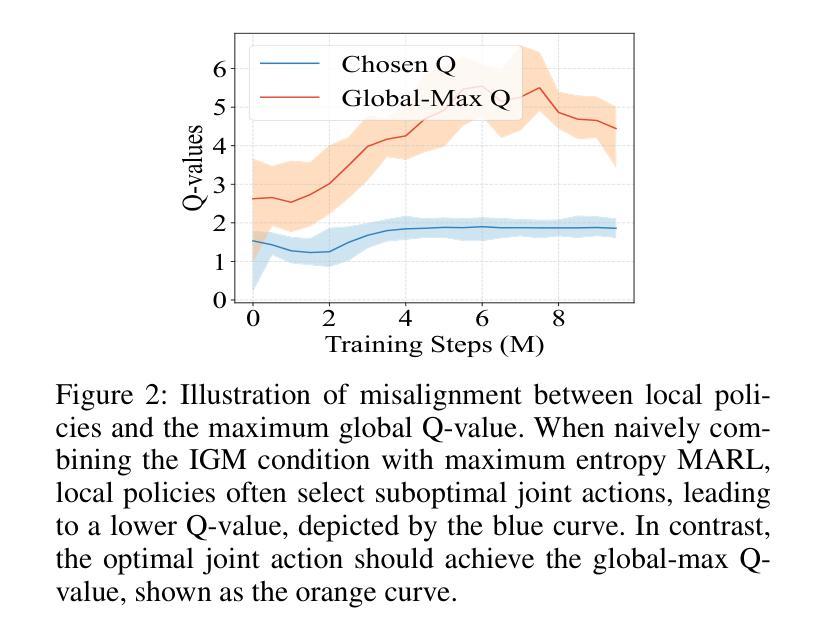
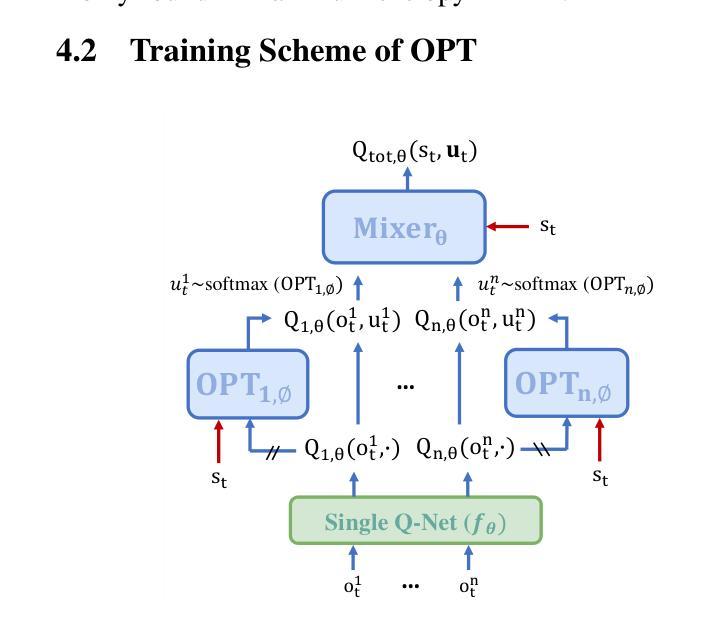
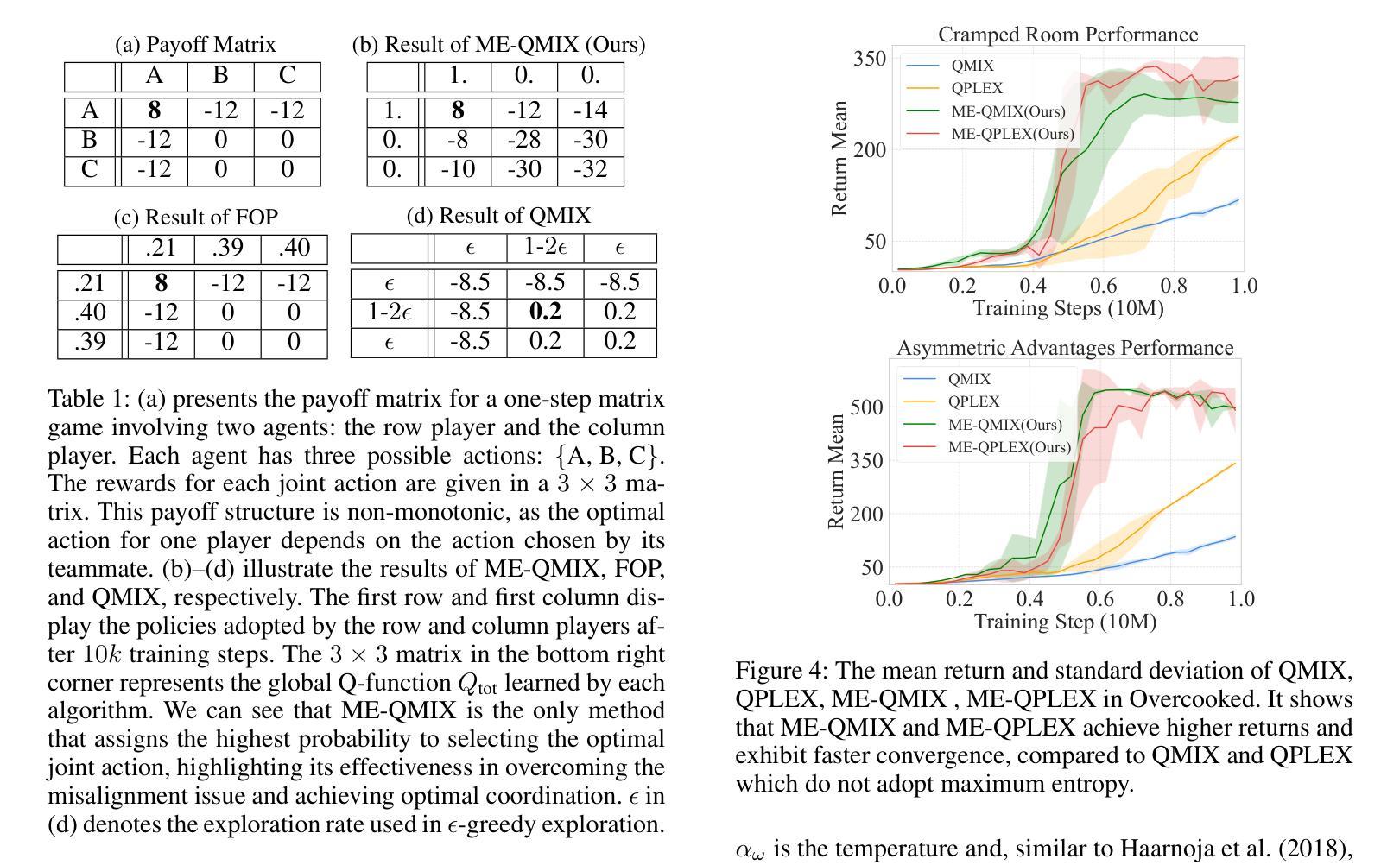
ME-IGM: Individual-Global-Max in Maximum Entropy Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wen-Tse Chen, Yuxuan Li, Shiyu Huang, Jiayu Chen, Jeff Schneider
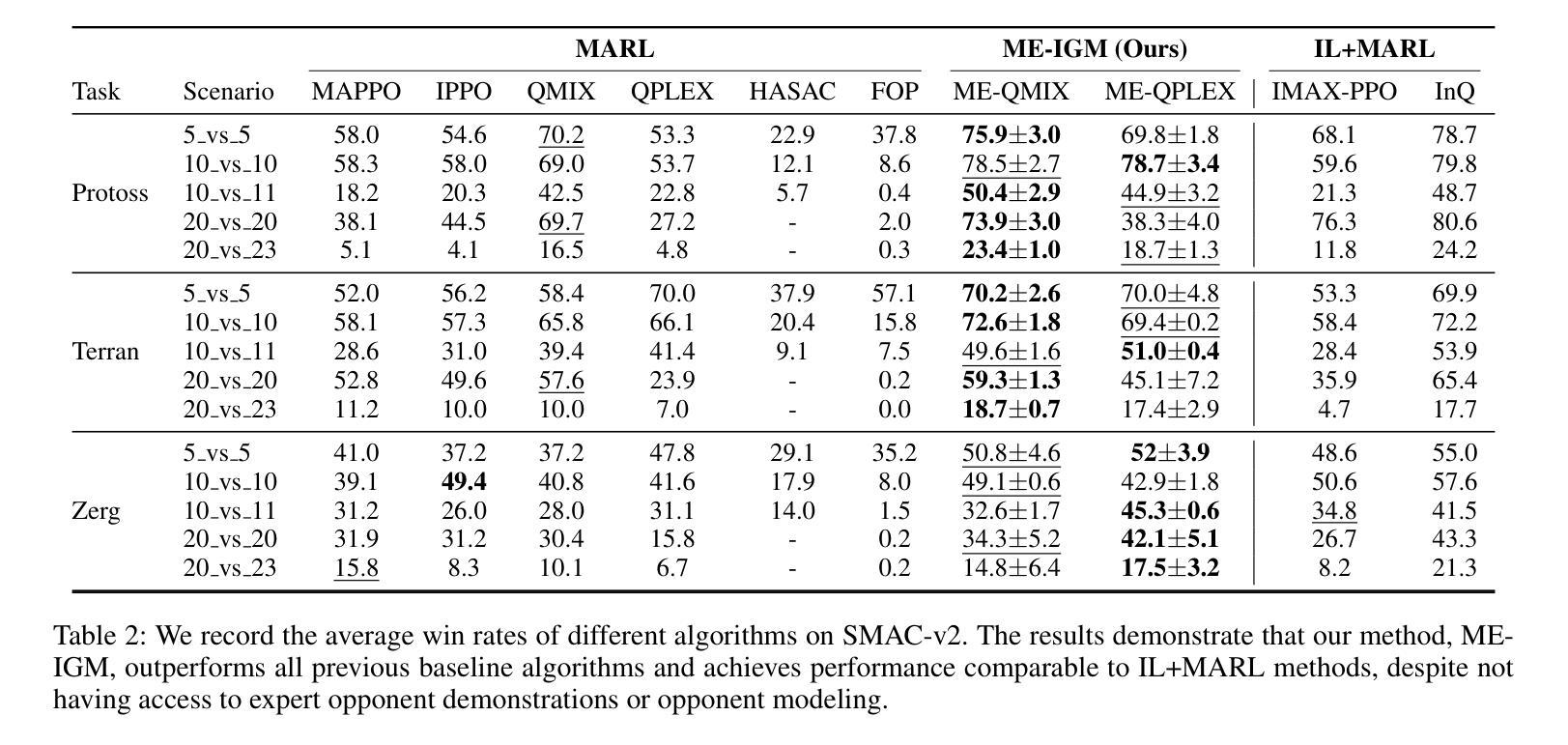
Multi-agent credit assignment is a fundamental challenge for cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), where a team of agents learn from shared reward signals. The Individual-Global-Max (IGM) condition is a widely used principle for multi-agent credit assignment, requiring that the joint action determined by individual Q-functions maximizes the global Q-value. Meanwhile, the principle of maximum entropy has been leveraged to enhance exploration in MARL. However, we identify a critical limitation in existing maximum entropy MARL methods: a misalignment arises between local policies and the joint policy that maximizes the global Q-value, leading to violations of the IGM condition. To address this misalignment, we propose an order-preserving transformation. Building on it, we introduce ME-IGM, a novel maximum entropy MARL algorithm compatible with any credit assignment mechanism that satisfies the IGM condition while enjoying the benefits of maximum entropy exploration. We empirically evaluate two variants of ME-IGM: ME-QMIX and ME-QPLEX, in non-monotonic matrix games, and demonstrate their state-of-the-art performance across 17 scenarios in SMAC-v2 and Overcooked.
多智能体信用分配是合作型多智能体强化学习(MARL)中的一个基本挑战,其中一组智能体从共享奖励信号中学习。个体-全局-最大化(IGM)条件是用于多智能体信用分配的一个广泛应用的原则,要求由个体Q函数决定的联合行动最大化全局Q值。同时,最大熵原则已被用于增强MARL中的探索。然而,我们发现了现有最大熵MARL方法的一个关键局限:局部政策和最大化全局Q值的联合政策之间出现不匹配,导致IGM条件的违反。为了解决这种不匹配,我们提出了一种保序变换。在此基础上,我们引入了ME-IGM,这是一种新型的最大熵MARL算法,与任何满足IGM条件的信用分配机制兼容,同时享受最大熵探索的优势。我们通过非单调矩阵游戏对ME-IGM的两个变体ME-QMIX和ME-QPLEX进行了实证评估,在SMAC-v2和Overcooked的17个场景中展示了它们的最先进性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了多智能体强化学习中的信用分配问题,并指出了现有最大熵多智能体强化学习方法中的关键局限性。为了解决这一局限性,本文提出了ME-IGM算法,该算法兼容任何满足IGM条件的信用分配机制,并享受最大熵探索的优势。经过在非单调矩阵游戏中的实证研究,ME-IGM的两个变体ME-QMIX和ME-QPLEX在SMAC-v2和Overcooked的17个场景中展现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习面临的核心挑战之一是信用分配问题,尤其在共享奖励信号的情境中尤为重要。
- 个体全局最大(IGM)条件广泛应用于多智能体信用分配原则中,它要求由个体Q函数决定的联合行动最大化全局Q值。
- 最大熵原则已用于增强多智能体强化学习中的探索能力。
- 然而,现有的最大熵多智能体强化学习方法存在一个关键局限:局部政策与最大化全局Q值的联合政策之间的不匹配导致IGM条件的违反。
- 为了解决这一不匹配问题,本文提出了一种顺序保留转换方法。
- 基于此转换方法,引入了ME-IGM算法,该算法与任何满足IGM条件的信用分配机制兼容,并享受最大熵探索的优势。
点此查看论文截图