⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
From Pixels to Pathology: Restoration Diffusion for Diagnostic-Consistent Virtual IHC
Authors:Jingsong Liu, Xiaofeng Deng, Han Li, Azar Kazemi, Christian Grashei, Gesa Wilkens, Xin You, Tanja Groll, Nassir Navab, Carolin Mogler, Peter J. Schüffler
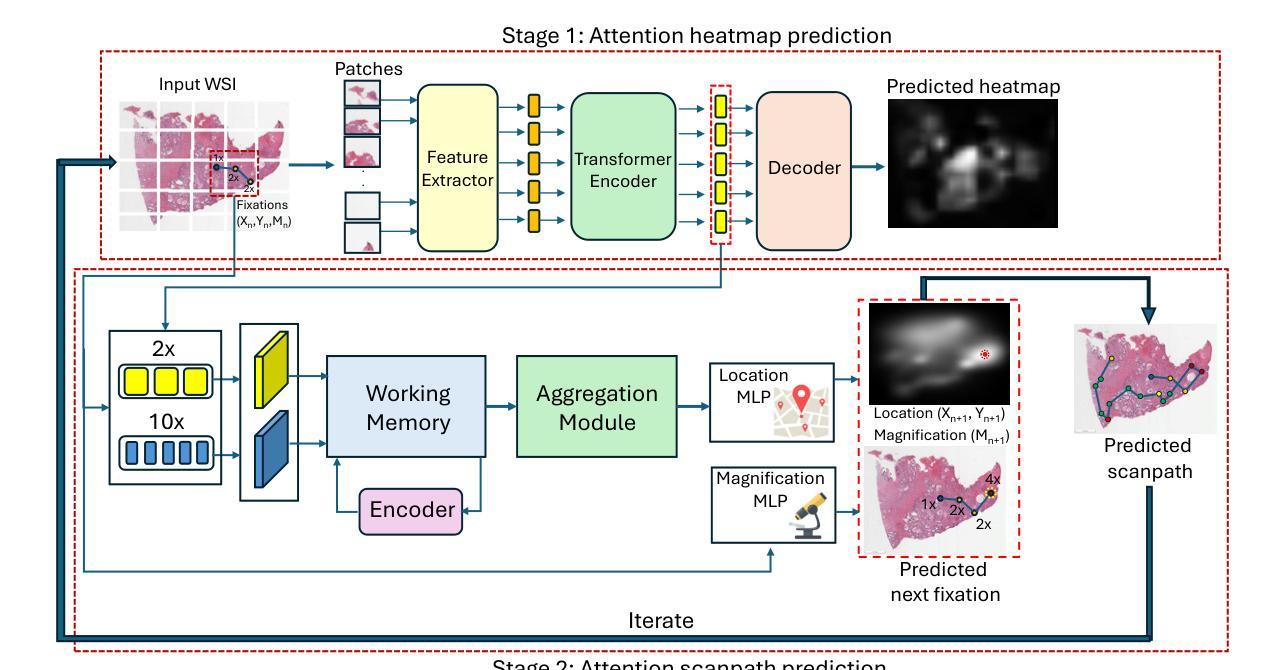
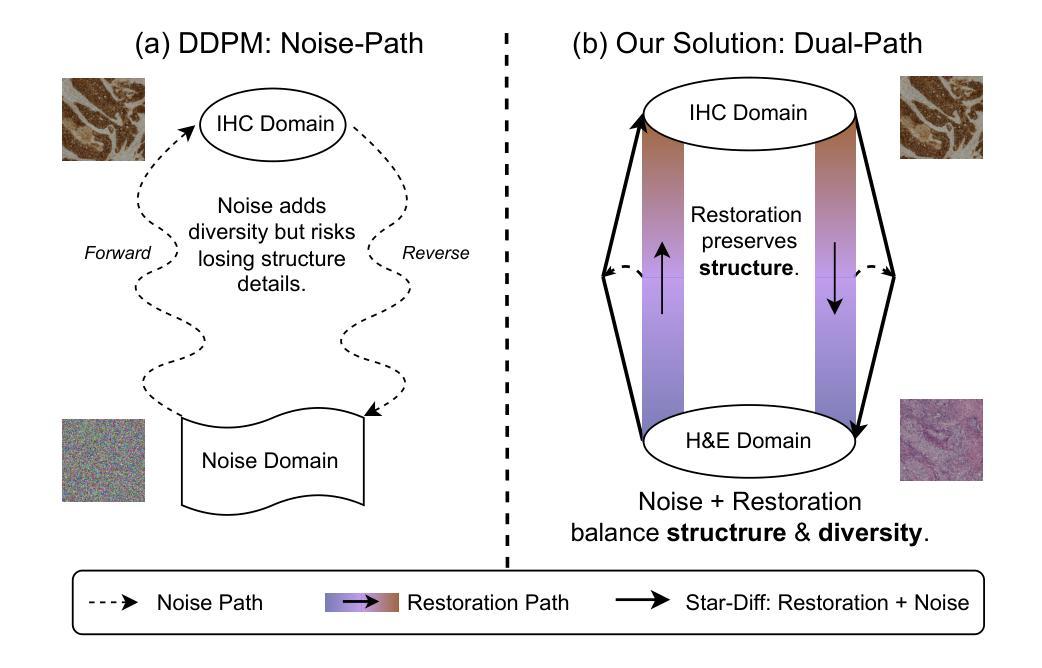
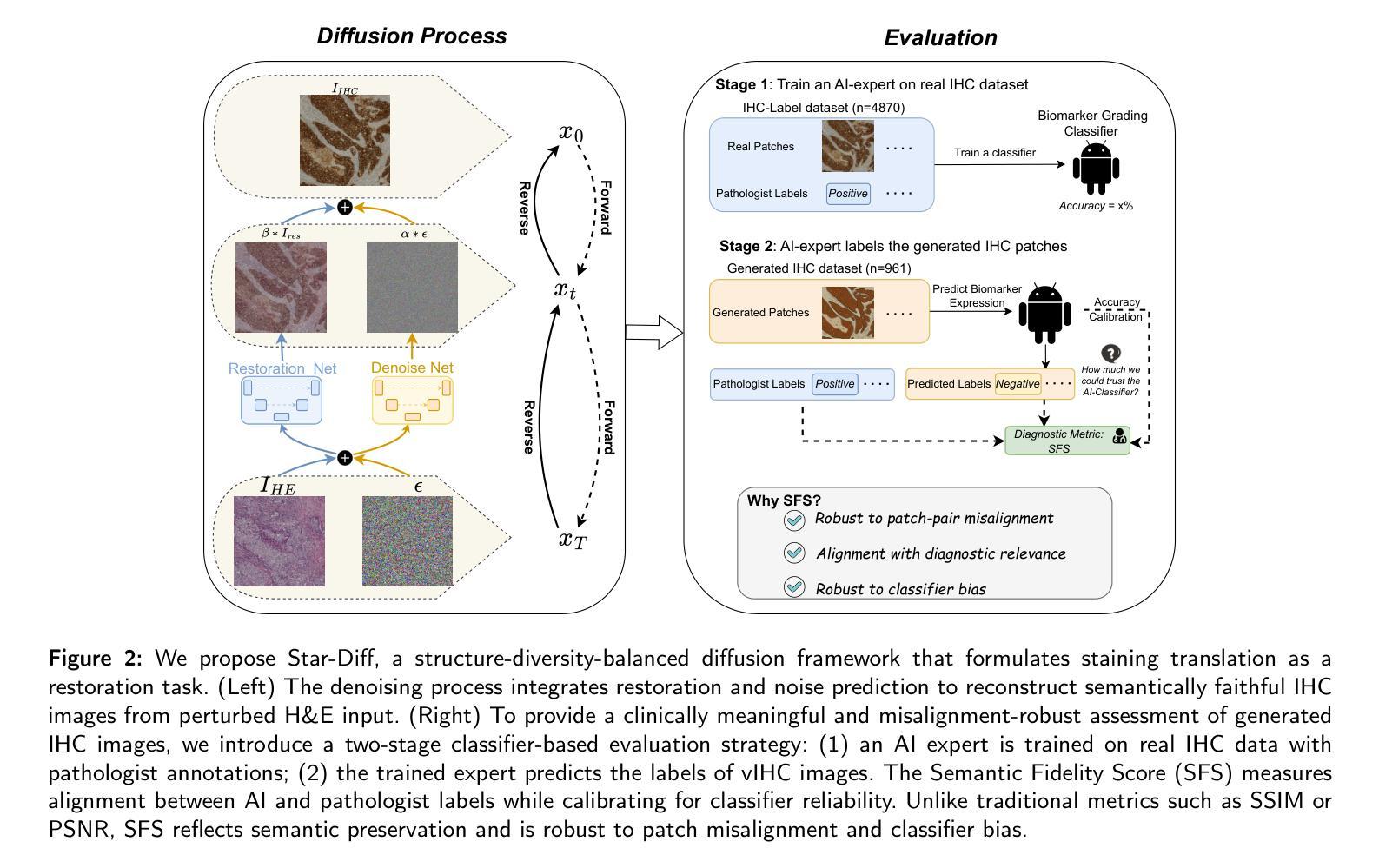
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the clinical standard for assessing tissue morphology, but it lacks molecular-level diagnostic information. In contrast, immunohistochemistry (IHC) provides crucial insights into biomarker expression, such as HER2 status for breast cancer grading, but remains costly and time-consuming, limiting its use in time-sensitive clinical workflows. To address this gap, virtual staining from H&E to IHC has emerged as a promising alternative, yet faces two core challenges: (1) Lack of fair evaluation of synthetic images against misaligned IHC ground truths, and (2) preserving structural integrity and biological variability during translation. To this end, we present an end-to-end framework encompassing both generation and evaluation in this work. We introduce Star-Diff, a structure-aware staining restoration diffusion model that reformulates virtual staining as an image restoration task. By combining residual and noise-based generation pathways, Star-Diff maintains tissue structure while modeling realistic biomarker variability. To evaluate the diagnostic consistency of the generated IHC patches, we propose the Semantic Fidelity Score (SFS), a clinical-grading-task-driven metric that quantifies class-wise semantic degradation based on biomarker classification accuracy. Unlike pixel-level metrics such as SSIM and PSNR, SFS remains robust under spatial misalignment and classifier uncertainty. Experiments on the BCI dataset demonstrate that Star-Diff achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in both visual fidelity and diagnostic relevance. With rapid inference and strong clinical alignment,it presents a practical solution for applications such as intraoperative virtual IHC synthesis.
苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色是评估组织形态的临床标准,但它缺乏分子水平的诊断信息。相比之下,免疫组织化学(IHC)为生物标志物表达提供了关键见解,如乳腺癌分级中的HER2状态,但其成本高昂且耗时,限制了其在时间敏感的临床工作流程中的应用。为了解决这一差距,从H&E到IHC的虚拟染色已成为一种有前途的替代方案,但面临两个核心挑战:(1)合成图像与错配的IHC真实值之间的公平评估缺失;(2)在翻译过程中保持结构完整性和生物变异性。为此,我们在工作中提出了一个涵盖生成和评估的端到端框架。我们介绍了Star-Diff,这是一个结构感知的染色恢复扩散模型,它将虚拟染色重新定义为图像恢复任务。通过结合残差和基于噪声的生成路径,Star-Diff在模拟现实生物标志物变异性的同时保持了组织结构。为了评估生成IHC补丁的诊断一致性,我们提出了语义保真度评分(SFS),这是一个基于临床分级任务的指标,它根据生物标志物分类准确性对类级语义降解进行量化。与SSIM和PSNR等像素级指标不同,SFS在空间错位和分类器不确定性下保持稳健。在BCI数据集上的实验表明,Star-Diff在视觉保真度和诊断相关性方面达到了最新水平。具有快速推理和强大的临床对齐能力,它为术中虚拟IHC合成等应用提供了实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
H&E染色是评估组织形态的临床标准,但缺乏分子水平的诊断信息。相比之下,免疫组织化学(IHC)为生物标志物表达提供关键见解,如乳腺癌分级中的HER2状态,但成本高昂且耗时,限制了其在时间敏感的临床工作流程中的应用。为了解决这一差距,从H&E到IHC的虚拟染色已成为一种有前途的替代方案,但面临两个核心挑战:(1)合成图像与错位的IHC真实值之间的公平评估不足;(2)在翻译过程中保持结构完整性和生物变异性。因此,我们在工作中提出了涵盖生成和评估的端到端框架。我们介绍了Star-Diff,这是一种结构感知染色恢复扩散模型,将虚拟染色重新定义为图像恢复任务。通过结合残差和基于噪声的生成路径,Star-Diff在模拟生物标志物变异性的同时保持了组织结构。为了评估生成IHC斑块的诊断一致性,我们提出了语义保真度评分(SFS),这是一种基于临床分级任务的指标,根据生物标志物分类准确性量化类级别的语义降解。与SSIM和PSNR等像素级指标不同,SFS在空间错位和分类器不确定性下保持稳健。在BCI数据集上的实验表明,Star-Diff在视觉保真度和诊断相关性方面达到了最新水平(SOTA)。其快速推理和强大的临床对齐能力为术中虚拟IHC合成等应用提供了切实可行的解决方案。
要点
- H&E染色在评估组织形态上是临床标准,但缺乏分子水平的诊断信息。
- 免疫组织化学(IHC)提供有关生物标志物表达的见解,但成本高昂且耗时。
- 虚拟染色技术作为从H&E到IHC的替代方案面临两个核心挑战:合成图像与真实IHC的评估及结构完整性和生物变异性的保持。
- Star-Diff是一种结构感知染色恢复扩散模型,能将虚拟染色作为图像恢复任务来处理。
- Star-Diff结合了残差和基于噪声的生成路径,以模拟生物标志物变异性和保持组织结构。
- 语义保真度评分(SFS)是一种新的评价指标,用于评估生成的IHC图像的诊断一致性,它基于临床分级任务并考虑生物标志物的分类准确性。
点此查看论文截图

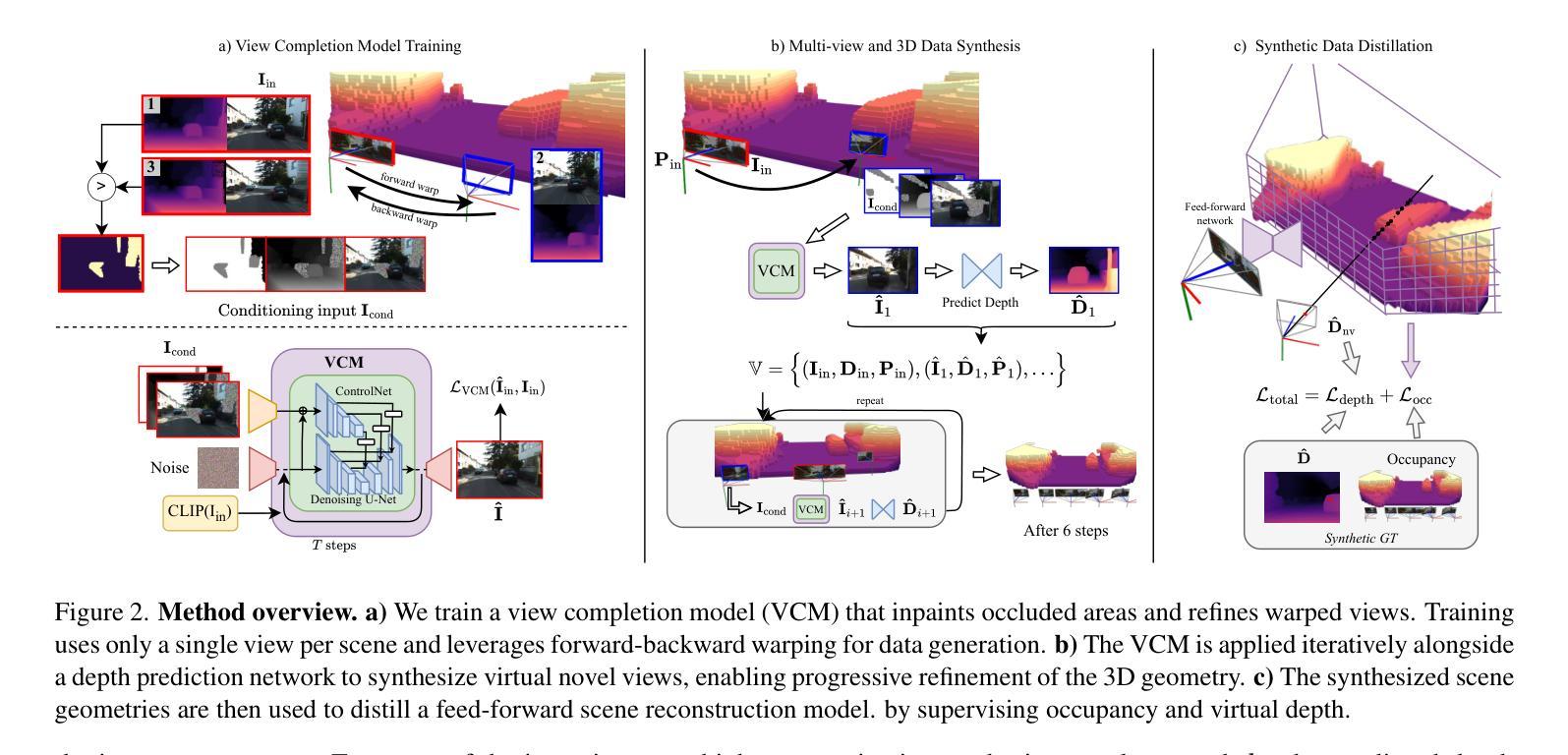
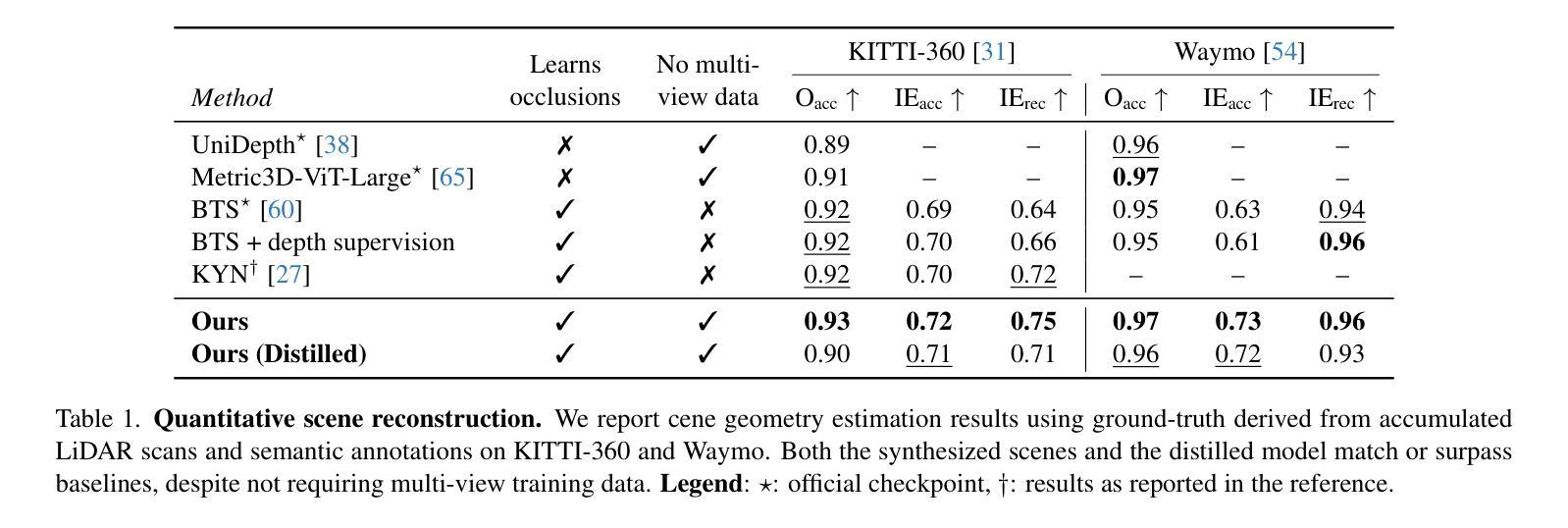
Dream-to-Recon: Monocular 3D Reconstruction with Diffusion-Depth Distillation from Single Images
Authors:Philipp Wulff, Felix Wimbauer, Dominik Muhle, Daniel Cremers
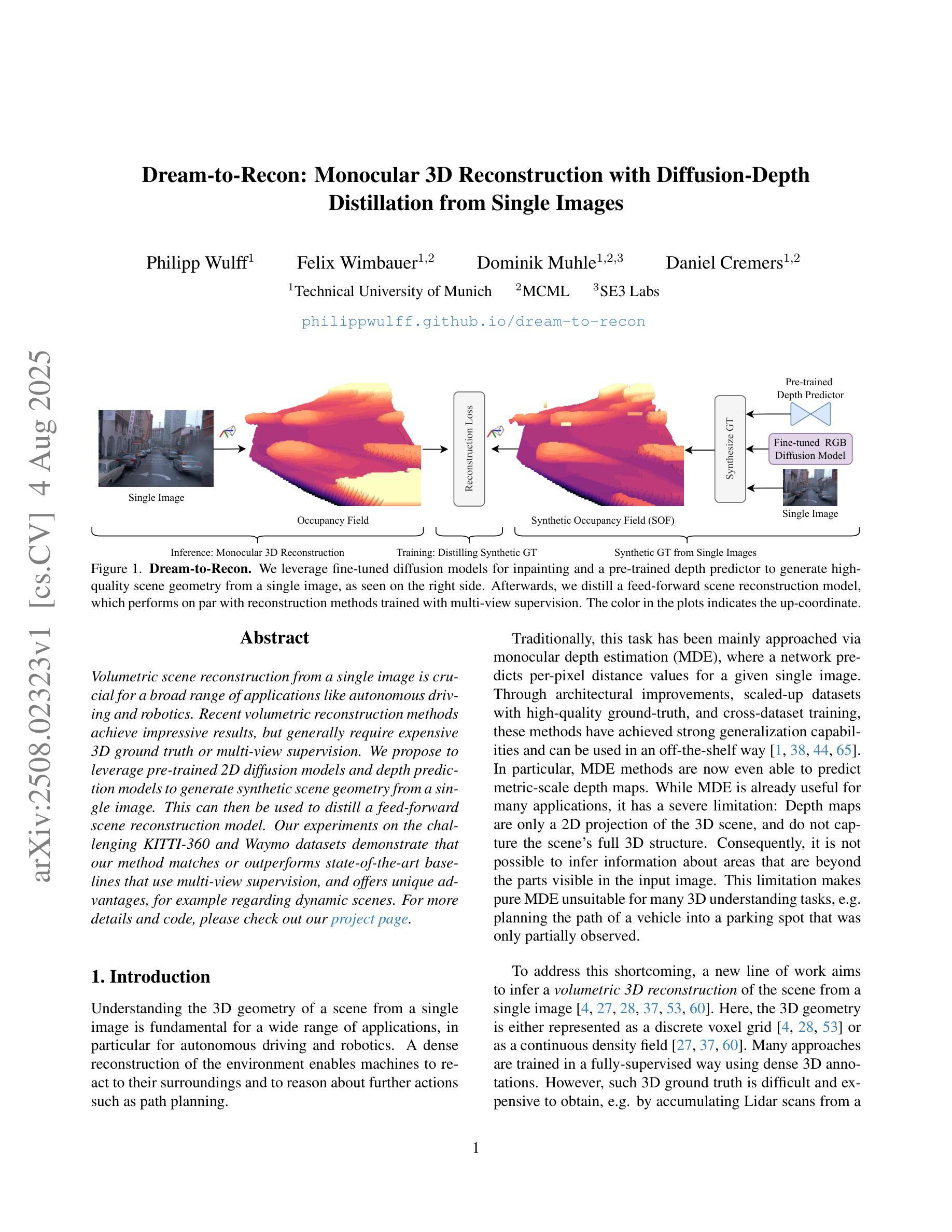
Volumetric scene reconstruction from a single image is crucial for a broad range of applications like autonomous driving and robotics. Recent volumetric reconstruction methods achieve impressive results, but generally require expensive 3D ground truth or multi-view supervision. We propose to leverage pre-trained 2D diffusion models and depth prediction models to generate synthetic scene geometry from a single image. This can then be used to distill a feed-forward scene reconstruction model. Our experiments on the challenging KITTI-360 and Waymo datasets demonstrate that our method matches or outperforms state-of-the-art baselines that use multi-view supervision, and offers unique advantages, for example regarding dynamic scenes.
从单张图像进行场景体积重建对于自动驾驶和机器人技术等广泛应用领域至关重要。虽然最近的体积重建方法取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但它们通常需要昂贵的3D真实数据或多视角监督。我们建议使用预训练的2D扩散模型和深度预测模型来从单张图像生成合成场景几何结构,然后可以用于提炼前馈场景重建模型。我们在具有挑战性的KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法与使用多视角监督的先进技术相比,性能相匹配或更胜一筹,并具有独特的优势,例如在动态场景方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Website: https://philippwulff.github.io/dream-to-recon
Summary
该文提出了利用预训练的2D扩散模型和深度预测模型,从单张图像生成合成场景几何的方法,用于蒸馏前馈场景重建模型。在具有挑战性的KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的实验表明,该方法匹配或超越了使用多视角监督的基线,并具有动态场景的独特优势。
Key Takeaways
- 文章讨论了从单张图像进行体积场景重建的重要性,并指出其在自动驾驶和机器人技术等领域的应用。
- 现有体积重建方法虽效果显著,但需要昂贵的3D真实数据或多视角监督。
- 文章提出了利用预训练的2D扩散模型和深度预测模型的方法,从单张图像生成合成场景几何。
- 该方法能够蒸馏出前馈场景重建模型。
- 在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性,与多视角监督的基线相比具有竞争力。
- 该方法在动态场景上具有独特优势。
点此查看论文截图
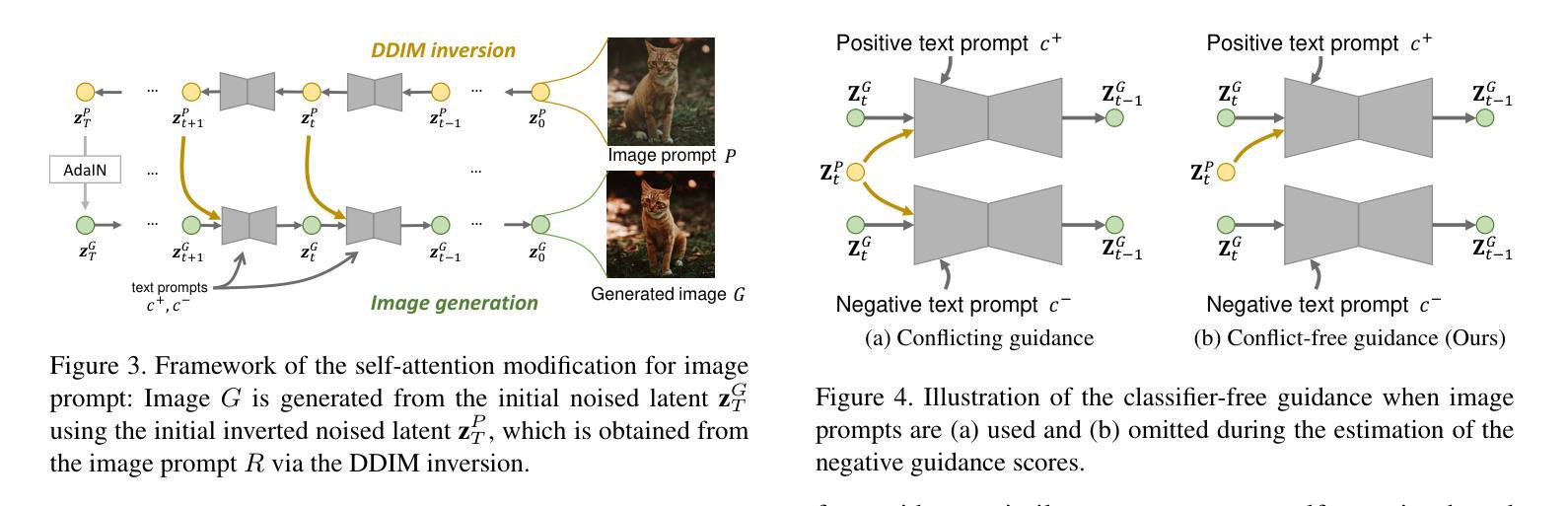
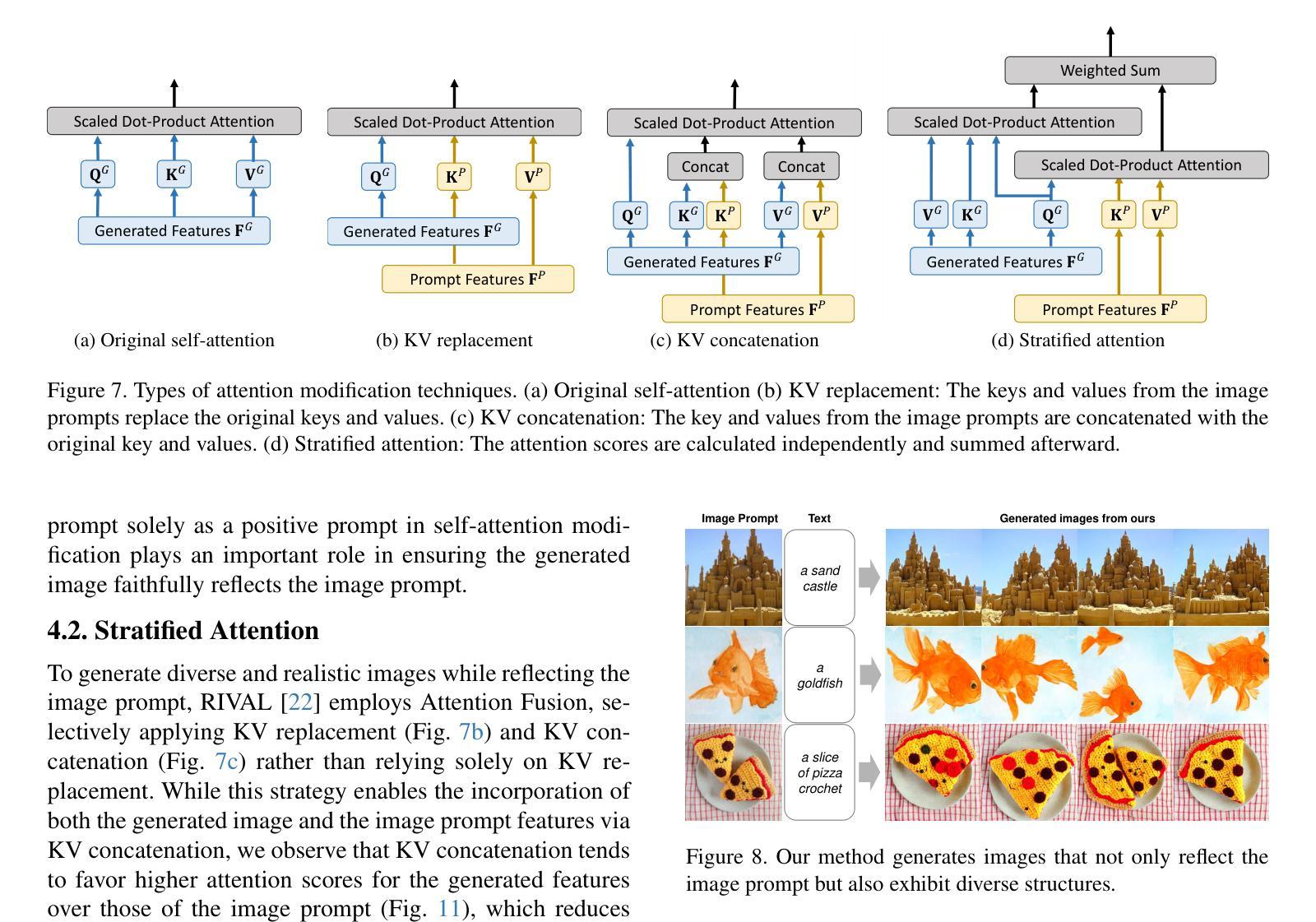
Devil is in the Detail: Towards Injecting Fine Details of Image Prompt in Image Generation via Conflict-free Guidance and Stratified Attention
Authors:Kyungmin Jo, Jooyeol Yun, Jaegul Choo
While large-scale text-to-image diffusion models enable the generation of high-quality, diverse images from text prompts, these prompts struggle to capture intricate details, such as textures, preventing the user intent from being reflected. This limitation has led to efforts to generate images conditioned on user-provided images, referred to as image prompts. Recent work modifies the self-attention mechanism to impose image conditions in generated images by replacing or concatenating the keys and values from the image prompt. This enables the self-attention layer to work like a cross-attention layer, generally used to incorporate text prompts. In this paper, we identify two common issues in existing methods of modifying self-attention to generate images that reflect the details of image prompts. First, existing approaches neglect the importance of image prompts in classifier-free guidance. Specifically, current methods use image prompts as both desired and undesired conditions in classifier-free guidance, causing conflicting signals. To resolve this, we propose conflict-free guidance by using image prompts only as desired conditions, ensuring that the generated image faithfully reflects the image prompt. In addition, we observe that the two most common self-attention modifications involve a trade-off between the realism of the generated image and alignment with the image prompt. Specifically, selecting more keys and values from the image prompt improves alignment, while selecting more from the generated image enhances realism. To balance both, we propose an new self-attention modification method, Stratified Attention to jointly use keys and values from both images rather than selecting between them. Through extensive experiments across three image generation tasks, we show that the proposed method outperforms existing image-prompting models in faithfully reflecting the image prompt.
虽然大规模文本到图像的扩散模型能够从文本提示中生成高质量、多样化的图像,但这些提示很难捕捉复杂的细节,如纹理,无法反映用户的意图。这一局限性促使人们努力根据用户提供的图像生成图像,称为图像提示。最近的工作通过修改自注意力机制,通过在生成的图像中替换或连接图像提示的键和值来施加图像条件。这使得自注意力层能够像用于融合文本提示的交叉注意力层那样工作。在本文中,我们发现了两种在现有方法中修改自注意力以生成反映图像提示细节的图像时存在的常见问题。首先,现有方法忽视了图像提示在分类器自由指导中的重要性。具体来说,当前的方法将图像提示既用作所需条件又用作非所需条件,产生相互矛盾的信息。为解决这一问题,我们通过仅使用图像提示作为所需条件,提出了无冲突指导方法,确保生成的图像忠实反映图像提示。此外,我们观察到最常见的两种自注意力修改涉及生成图像的逼真度和与图像提示对齐之间的权衡。具体来说,从图像提示中选择更多的键和值可以提高对齐性,而从生成的图像中选择更多则增强逼真度。为了平衡这两者,我们提出了一种新的自注意力修改方法——分层注意力,该方法能够同时使用来自两者的键和值,而不是在它们之间做出选择。通过三项图像生成任务的广泛实验,我们证明了所提出的方法在忠实反映图像提示方面优于现有的图像提示模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大规模文本到图像的扩散模型在生成图像时面临的挑战,即无法捕捉用户提供的图像提示中的细节。为此,研究人员改进了自注意力机制以引入图像条件,并指出了现有方法中的两个问题。首先,现有方法忽视了图像提示在分类器免费指导中的重要性,导致生成的图像无法忠实反映图像提示。为解决这一问题,本文提出了无冲突指导方法,仅将图像提示作为期望条件。其次,现有自注意力修改方法面临真实感和与图像提示对齐之间的权衡。为解决这一问题,本文提出了分层注意力方法,结合来自图像和生成图像的键和值。实验表明,该方法在忠实反映图像提示方面优于现有图像提示模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型虽能生成高质量、多样化的图像,但难以捕捉用户提供的图像提示中的细节。
- 现有方法忽视了图像提示在分类器免费指导中的重要性。
- 提出的无冲突指导方法仅将图像提示作为期望条件,确保生成的图像忠实反映图像提示。
- 现有自注意力修改方法在真实感和与图像提示对齐之间存在权衡。
- 提出的分层注意力方法结合来自图像和生成图像的键和值,以平衡真实性和对齐。
- 通过三个图像生成任务的广泛实验,新方法在忠实反映图像提示方面表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图




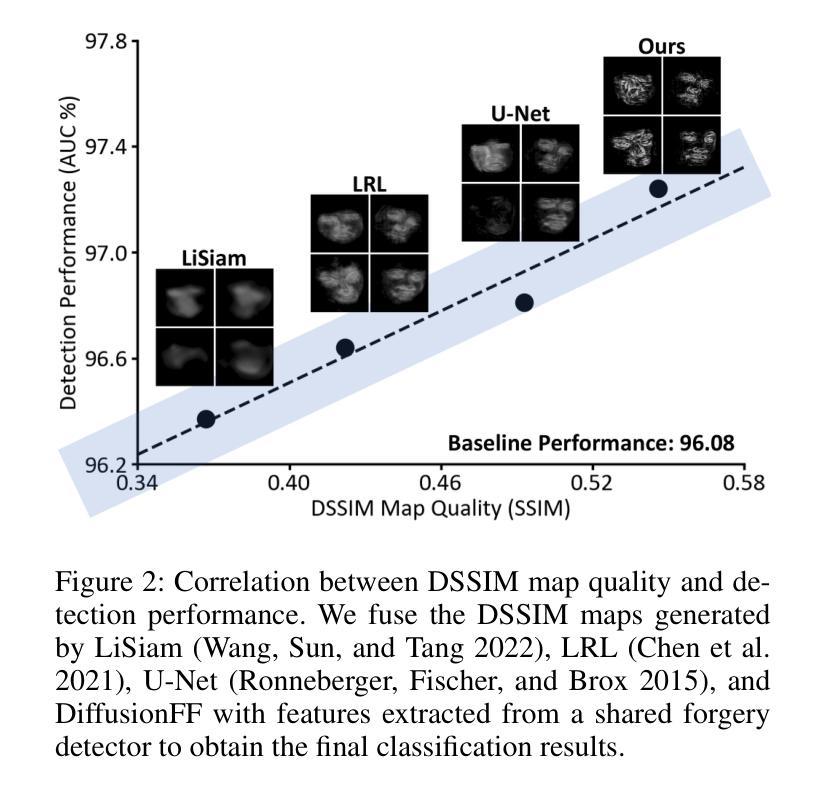
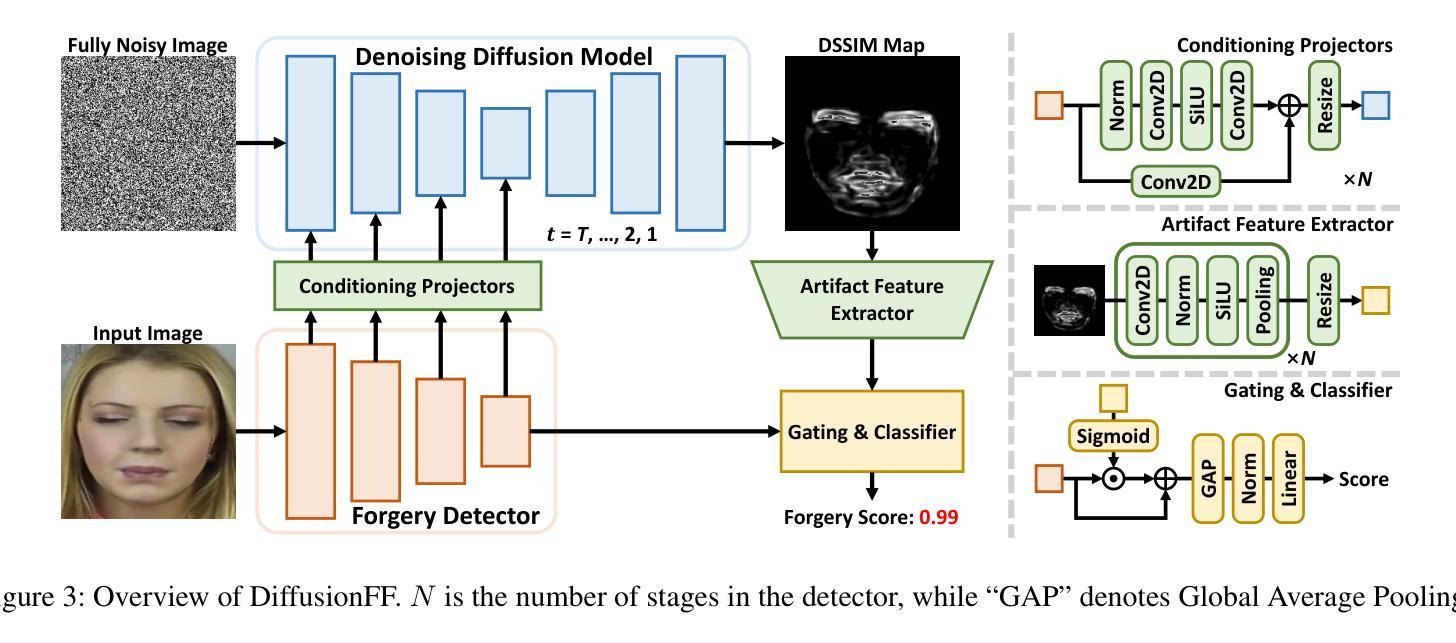
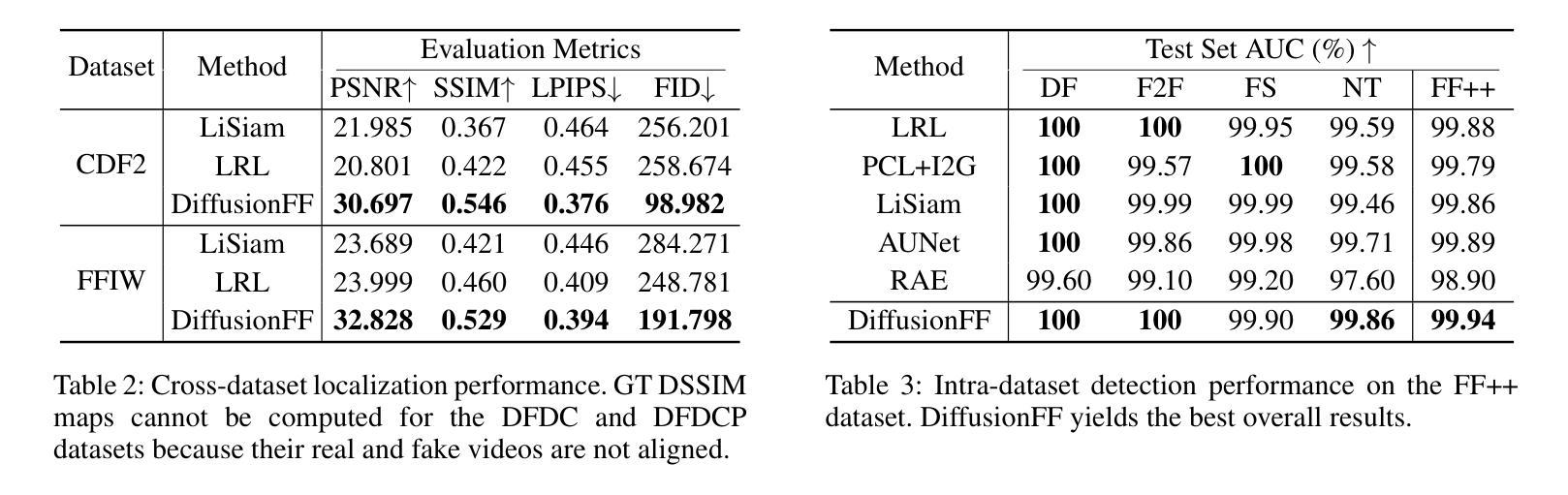
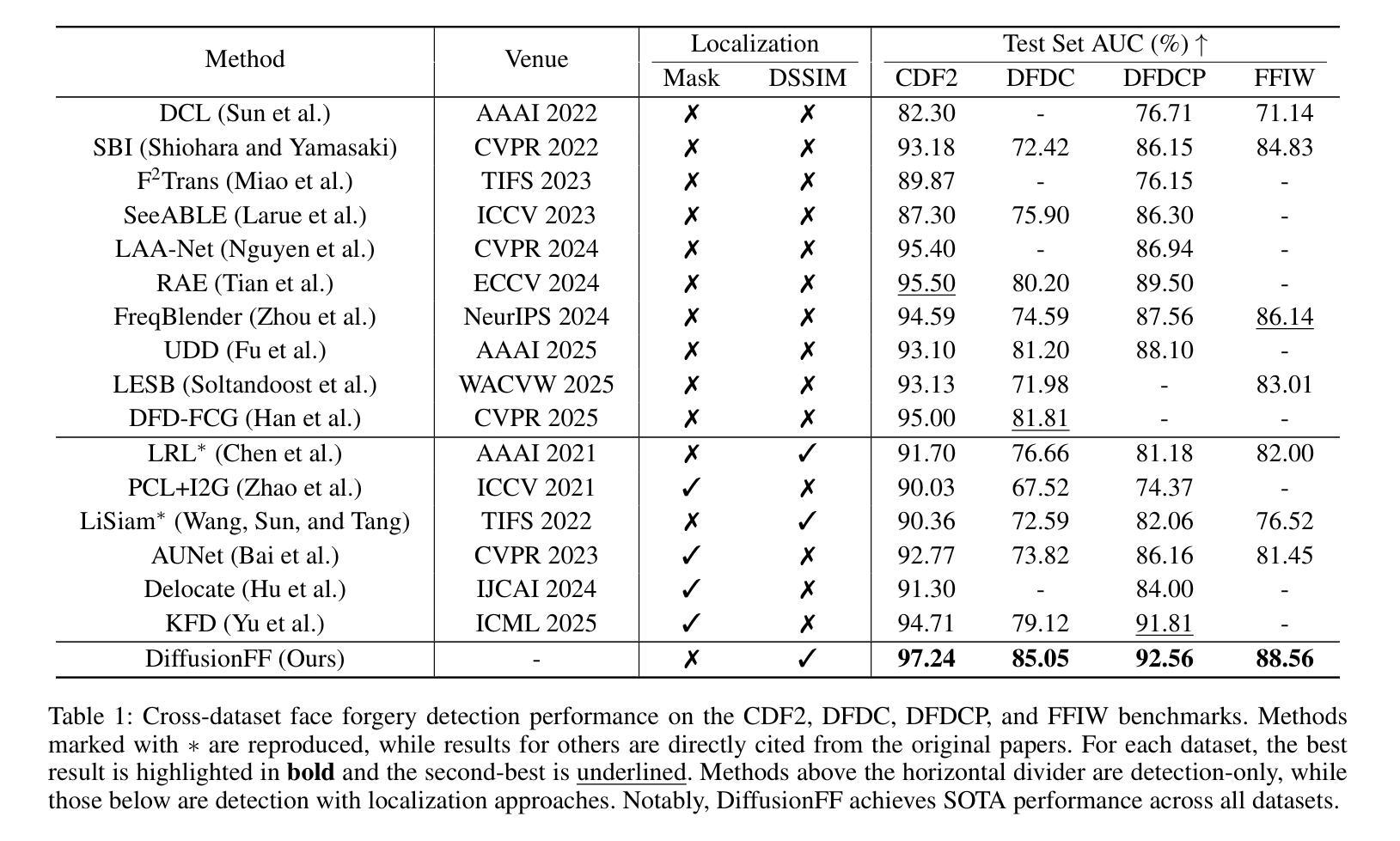
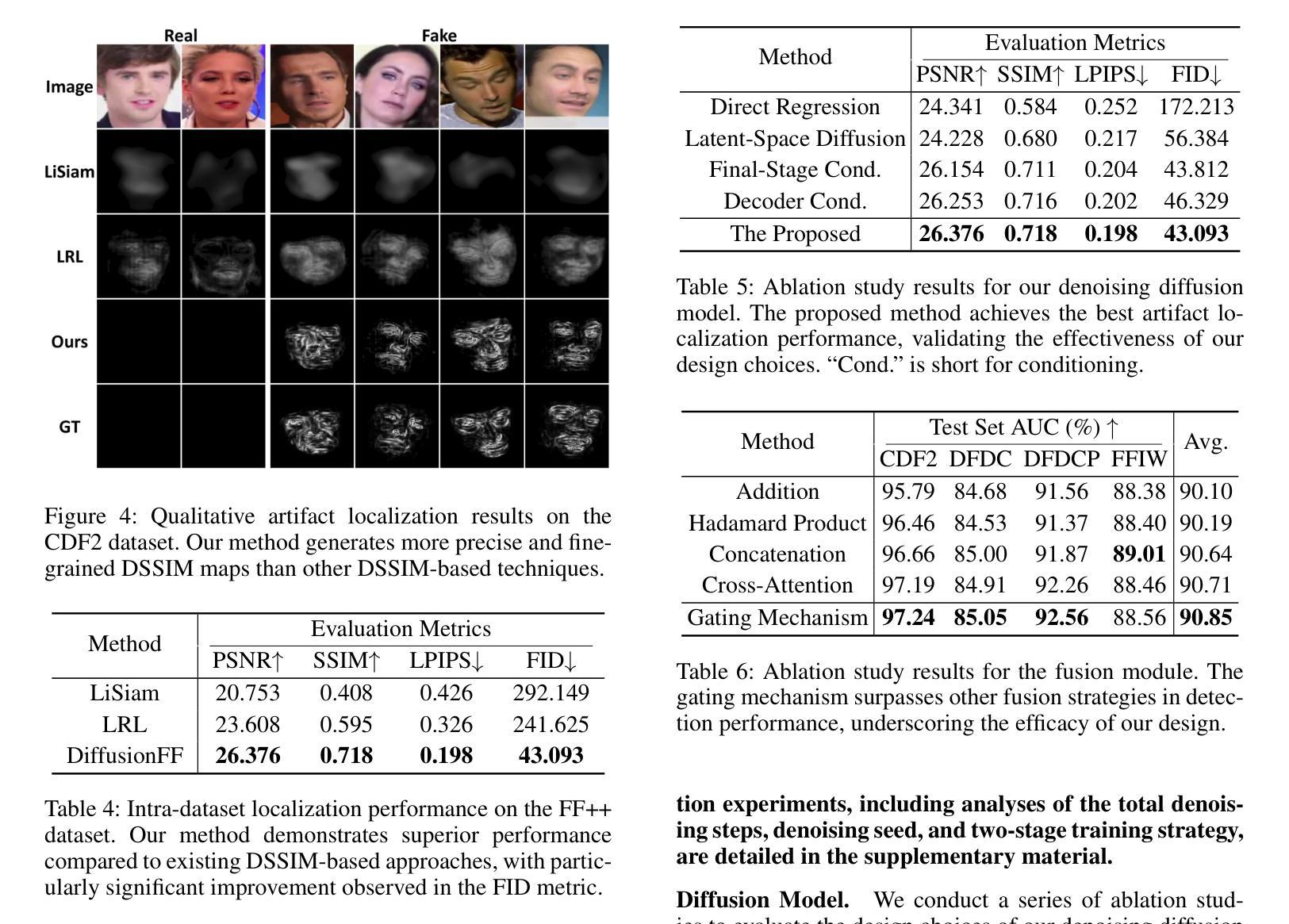
DiffusionFF: Face Forgery Detection via Diffusion-based Artifact Localization
Authors:Siran Peng, Haoyuan Zhang, Li Gao, Tianshuo Zhang, Bao Li, Zhen Lei
The rapid evolution of deepfake generation techniques demands robust and accurate face forgery detection algorithms. While determining whether an image has been manipulated remains essential, the ability to precisely localize forgery artifacts has become increasingly important for improving model explainability and fostering user trust. To address this challenge, we propose DiffusionFF, a novel framework that enhances face forgery detection through diffusion-based artifact localization. Our method utilizes a denoising diffusion model to generate high-quality Structural Dissimilarity (DSSIM) maps, which effectively capture subtle traces of manipulation. These DSSIM maps are then fused with high-level semantic features extracted by a pretrained forgery detector, leading to significant improvements in detection accuracy. Extensive experiments on both cross-dataset and intra-dataset benchmarks demonstrate that DiffusionFF not only achieves superior detection performance but also offers precise and fine-grained artifact localization, highlighting its overall effectiveness.
深度伪造生成技术的快速发展要求有稳健且准确的人脸伪造检测算法。确定图像是否被篡改仍然至关重要,但精确定位伪造痕迹的能力在提高模型解释性和促进用户信任方面变得日益重要。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了DiffusionFF这一新型框架,它通过基于扩散的痕迹定位技术来提高人脸伪造检测能力。我们的方法利用去噪扩散模型生成高质量的结构差异(DSSIM)图,有效捕捉细微的篡改痕迹。这些DSSIM图然后与由预训练伪造检测器提取的高级语义特征相融合,显著提高了检测精度。跨数据集和内部数据集的广泛实验表明,DiffusionFF不仅实现了卓越的检测性能,而且提供了精确和精细的痕迹定位,凸显了其整体有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度伪造生成技术的快速发展要求有稳健准确的面部伪造检测算法。除了判断图像是否被操纵外,能够精确定位伪造痕迹的能力对于提高模型解释性和增强用户信任度也变得越来越重要。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了DiffusionFF这一新型框架,它通过基于扩散的痕迹定位技术来提升面部伪造检测效果。该方法利用去噪扩散模型生成高质量的结构差异(DSSIM)图,有效捕捉微妙的操作痕迹。这些DSSIM图随后与预训练伪造检测器提取的高级语义特征融合,极大地提高了检测准确率。在跨数据集和内部数据集基准测试上的广泛实验表明,DiffusionFF不仅实现了出色的检测性能,而且提供了精确和精细的痕迹定位,凸显了其整体有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度伪造生成技术的快速发展要求有稳健准确的面部伪造检测算法。
- 除了判断图像是否被操纵外,定位伪造痕迹的能力日益重要,以提高模型解释性和用户信任度。
- DiffusionFF框架利用去噪扩散模型生成高质量的结构差异(DSSIM)图,以捕捉操作痕迹。
- DSSIM图与预训练伪造检测器的高级语义特征融合,提高了检测准确率。
- DiffusionFF实现了跨数据集和内部数据集的优异检测性能。
- DiffusionFF提供了精确和精细的伪造痕迹定位。
点此查看论文截图

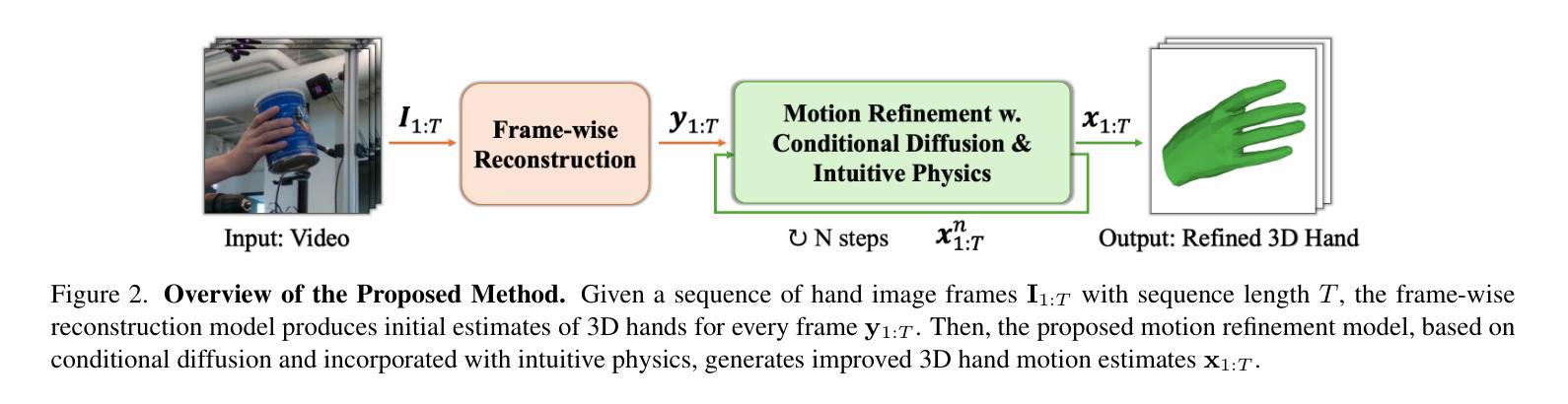
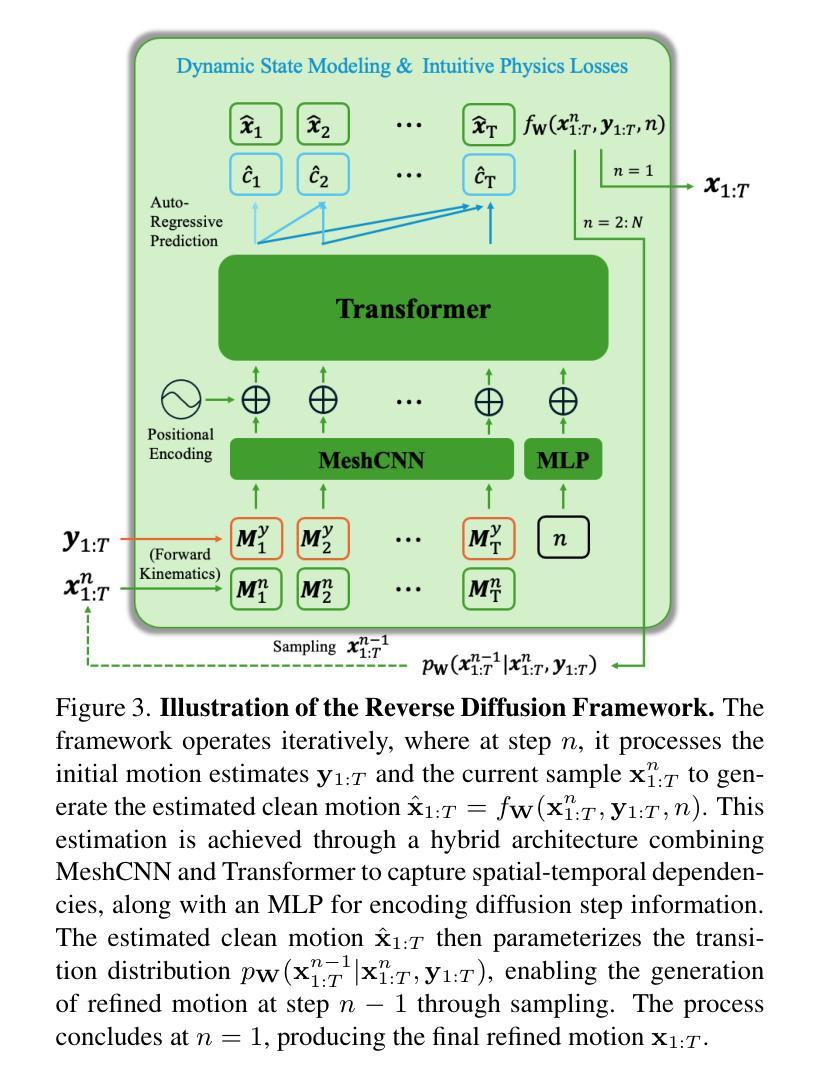
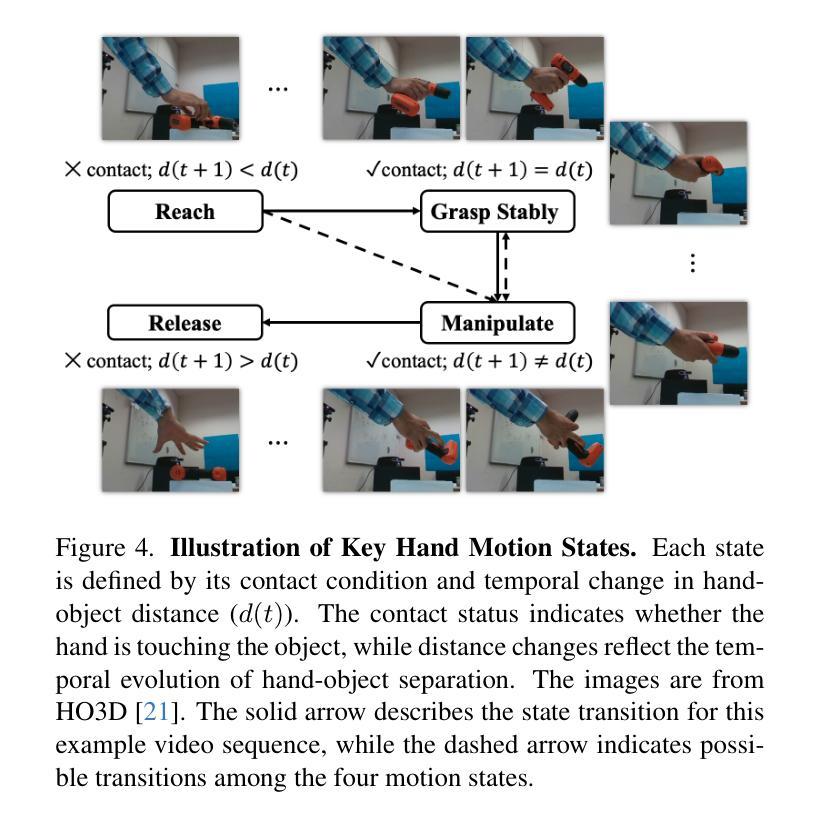
Diffusion-based 3D Hand Motion Recovery with Intuitive Physics
Authors:Yufei Zhang, Zijun Cui, Jeffrey O. Kephart, Qiang Ji
While 3D hand reconstruction from monocular images has made significant progress, generating accurate and temporally coherent motion estimates from videos remains challenging, particularly during hand-object interactions. In this paper, we present a novel 3D hand motion recovery framework that enhances image-based reconstructions through a diffusion-based and physics-augmented motion refinement model. Our model captures the distribution of refined motion estimates conditioned on initial ones, generating improved sequences through an iterative denoising process. Instead of relying on scarce annotated video data, we train our model only using motion capture data without images. We identify valuable intuitive physics knowledge during hand-object interactions, including key motion states and their associated motion constraints. We effectively integrate these physical insights into our diffusion model to improve its performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly improves various frame-wise reconstruction methods, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on existing benchmarks.
虽然从单目图像中重建3D手部已经取得了显著进展,但从视频中生成准确且时间连贯的运动估计仍然具有挑战性,特别是在手部与物体交互时。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的3D手部运动恢复框架,它通过基于扩散和物理增强的运动优化模型来增强基于图像的重建。我们的模型捕获了基于初始估计的精细运动估计的分布,并通过迭代去噪过程生成了改进序列。我们并没有依赖于稀缺的标注视频数据来训练模型,而是仅使用运动捕获数据进行训练,并不使用图像。我们确定了在手部与物体交互过程中的有价值的直观物理知识,包括关键运动状态及其相关的运动约束。我们有效地将这些物理见解集成到我们的扩散模型中,以提高其性能。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著改进了各种帧级重建方法,在现有基准测试中实现了最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的3D手部运动恢复框架,通过扩散模型和物理增强运动优化模型提升基于图像的重建效果。该模型能够捕捉初始运动估计的分布情况,并通过迭代去噪过程生成改进序列。研究团队利用运动捕捉数据进行训练,无需图像数据。此外,该研究还将手部与物体交互过程中的直觉物理知识融入扩散模型,提升模型性能。实验证明,该方法在现有基准测试中表现卓越,显著提高帧重建效果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新颖的3D手部运动恢复框架,结合了扩散模型和物理增强技术,提高了基于图像的重建效果。
- 通过捕捉初始运动估计的分布情况,并迭代去噪,生成改进的运动序列。
- 仅利用运动捕捉数据进行训练,无需图像数据。
- 融入直觉物理知识,包括关键运动状态和关联的运动约束,提升扩散模型的性能。
- 该方法显著提高帧重建效果,实现了对现有技术的超越。
- 提出的模型在现有基准测试中表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图

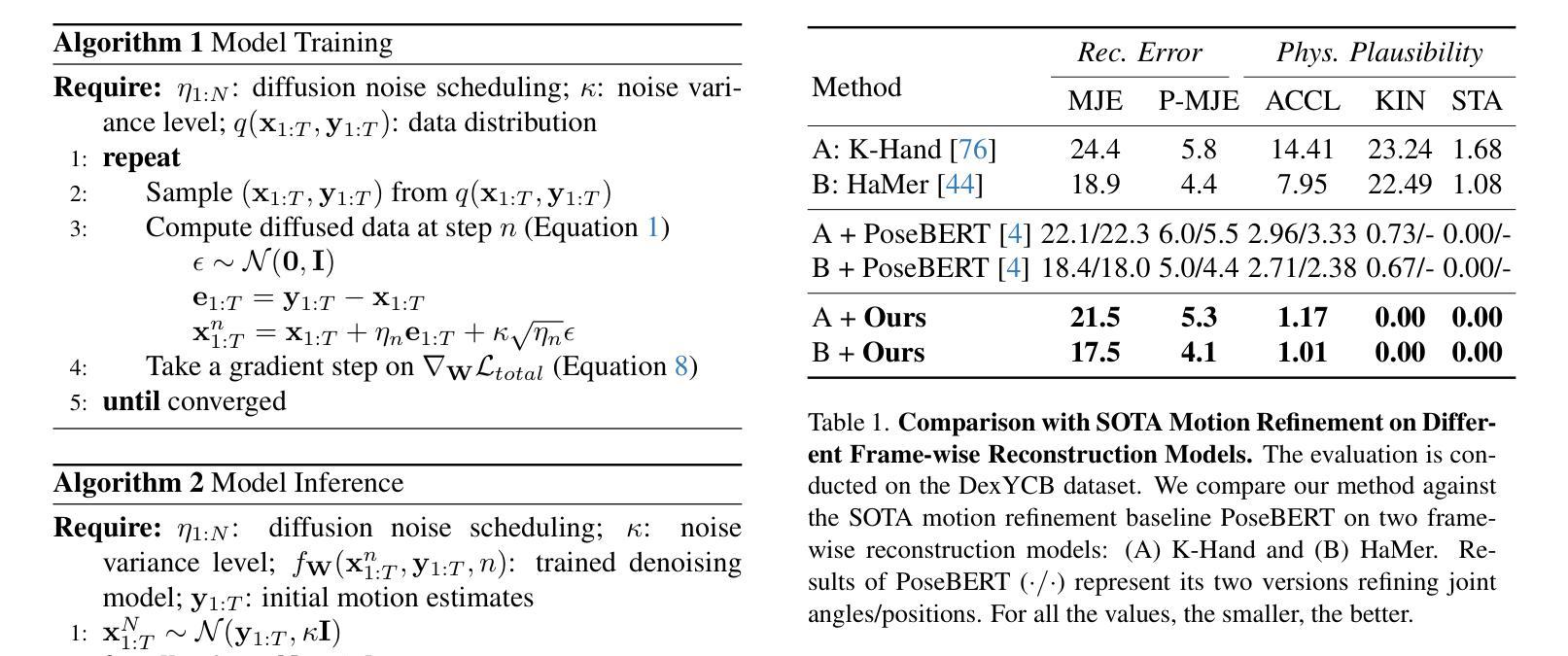
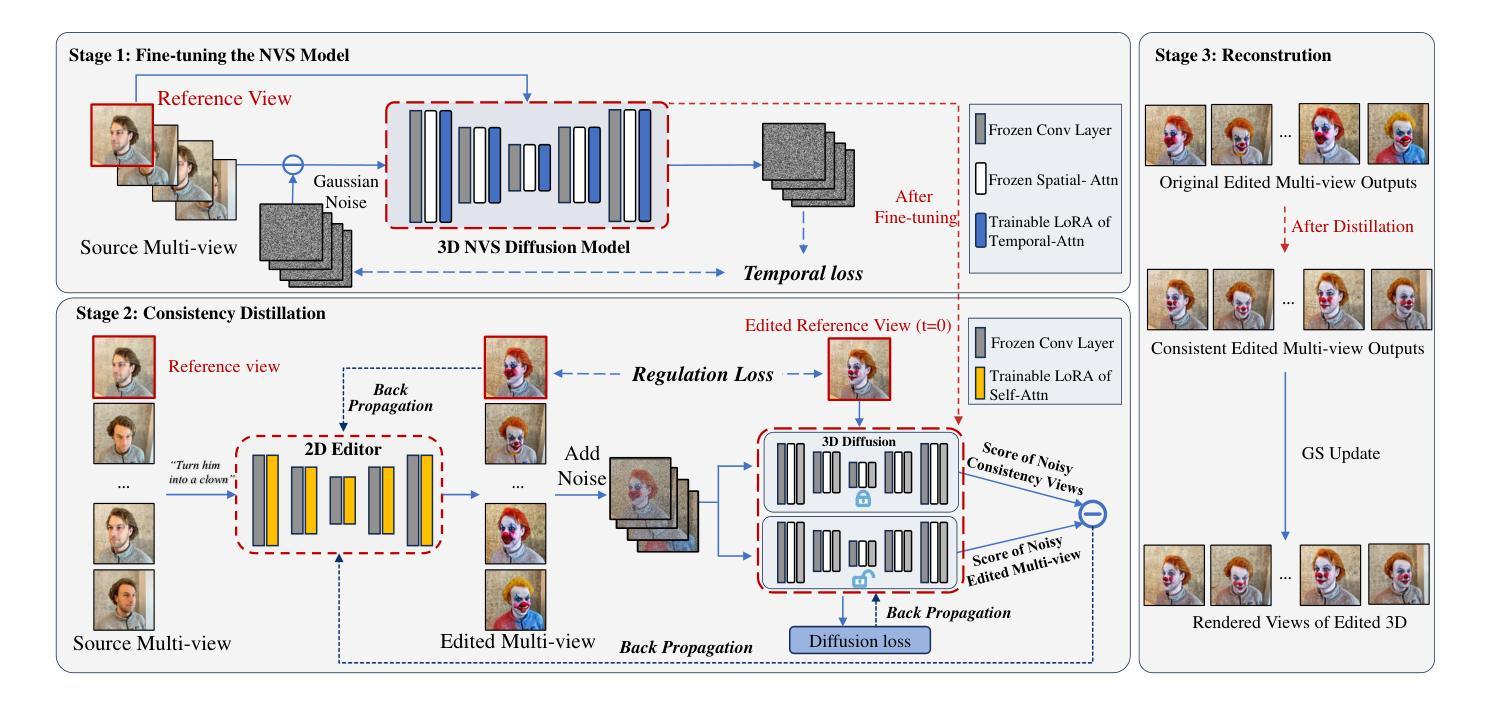
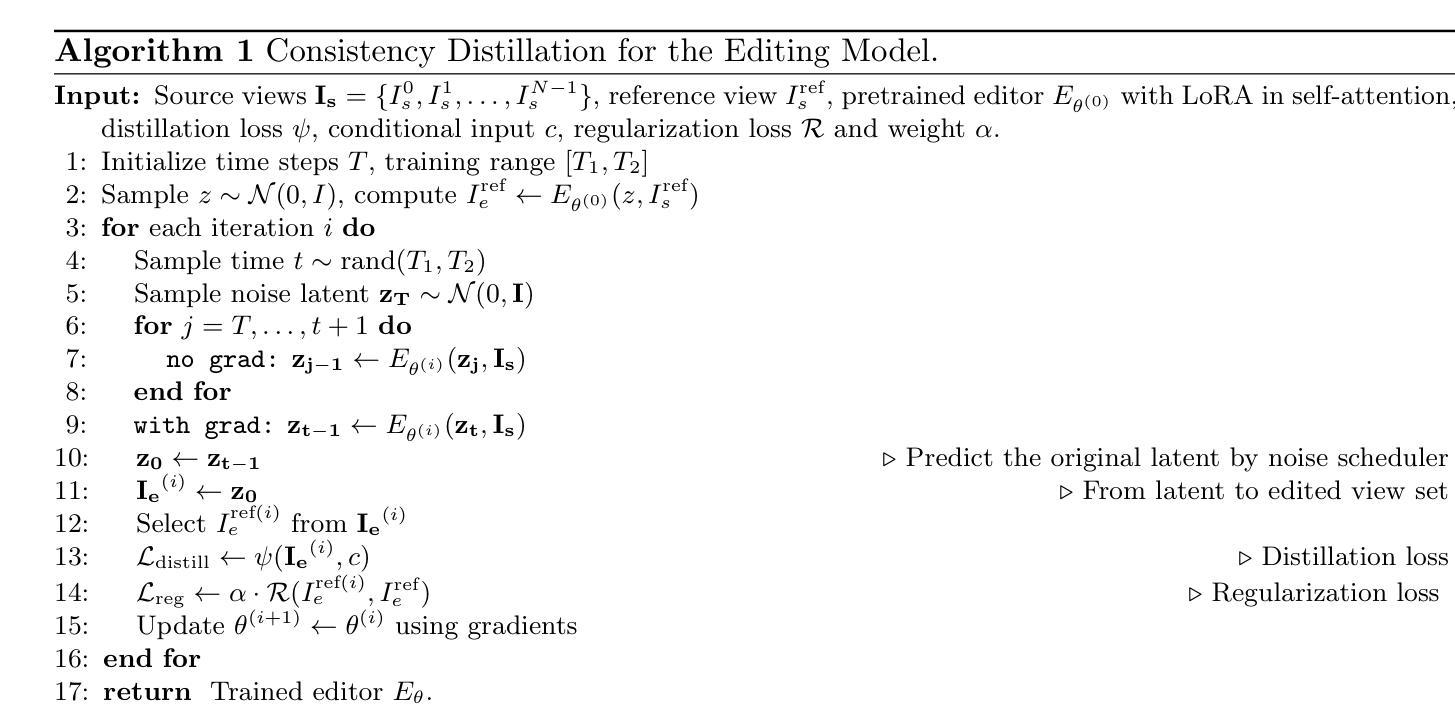
DisCo3D: Distilling Multi-View Consistency for 3D Scene Editing
Authors:Yufeng Chi, Huimin Ma, Kafeng Wang, Jianmin Li
While diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable progress in 2D image generation and editing, extending these capabilities to 3D editing remains challenging, particularly in maintaining multi-view consistency. Classical approaches typically update 3D representations through iterative refinement based on a single editing view. However, these methods often suffer from slow convergence and blurry artifacts caused by cross-view inconsistencies. Recent methods improve efficiency by propagating 2D editing attention features, yet still exhibit fine-grained inconsistencies and failure modes in complex scenes due to insufficient constraints. To address this, we propose \textbf{DisCo3D}, a novel framework that distills 3D consistency priors into a 2D editor. Our method first fine-tunes a 3D generator using multi-view inputs for scene adaptation, then trains a 2D editor through consistency distillation. The edited multi-view outputs are finally optimized into 3D representations via Gaussian Splatting. Experimental results show DisCo3D achieves stable multi-view consistency and outperforms state-of-the-art methods in editing quality.
虽然扩散模型在二维图像生成和编辑方面取得了显著的进步,但将这些能力扩展到三维编辑仍然具有挑战性,尤其是在保持多视图一致性方面。传统方法通常基于单个编辑视图通过迭代优化来更新三维表示。然而,这些方法通常存在收敛速度慢、由于跨视图不一致导致图像模糊等缺陷。最近的方法通过传播二维编辑注意力特征来提高效率,但由于约束不足,在复杂场景中仍然存在细微的不一致性和失败模式。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了新型框架DisCo3D,它通过蒸馏三维一致性先验知识来辅助二维编辑器。我们的方法首先使用多视图输入对三维生成器进行微调,以适应场景,然后通过一致性蒸馏来训练二维编辑器。最后,编辑后的多视图输出通过高斯拼贴优化为三维表示。实验结果表明,DisCo3D实现了稳定的多视图一致性,并在编辑质量方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为DisCo3D的新框架,它通过蒸馏3D一致性先验知识来改进二维编辑器在三维编辑中的性能。该框架通过微调三维生成器以适应场景,然后训练二维编辑器以保证一致性。最后,通过高斯映射优化编辑后的多视角输出到三维表示。DisCo3D实现了稳定的多视角一致性,并在编辑质量上超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在二维图像生成和编辑方面取得了显著进展,但在三维编辑方面的扩展仍然具有挑战性,尤其是在保持多视角一致性方面。
- 经典方法通常通过基于单一编辑视角的迭代优化来更新三维表示,但常常面临收敛速度慢和跨视角不一致导致的模糊伪影问题。
- 最近的方法通过传播二维编辑注意力特征提高了效率,但由于约束不足,在复杂场景中仍然存在细微的不一致性和失败模式。
- DisCo3D框架通过蒸馏3D一致性先验知识到二维编辑器来解决这些问题。
- DisCo3D首先使用多视角输入微调三维生成器以适应场景。
- 然后,它训练二维编辑器以保证一致性。
点此查看论文截图

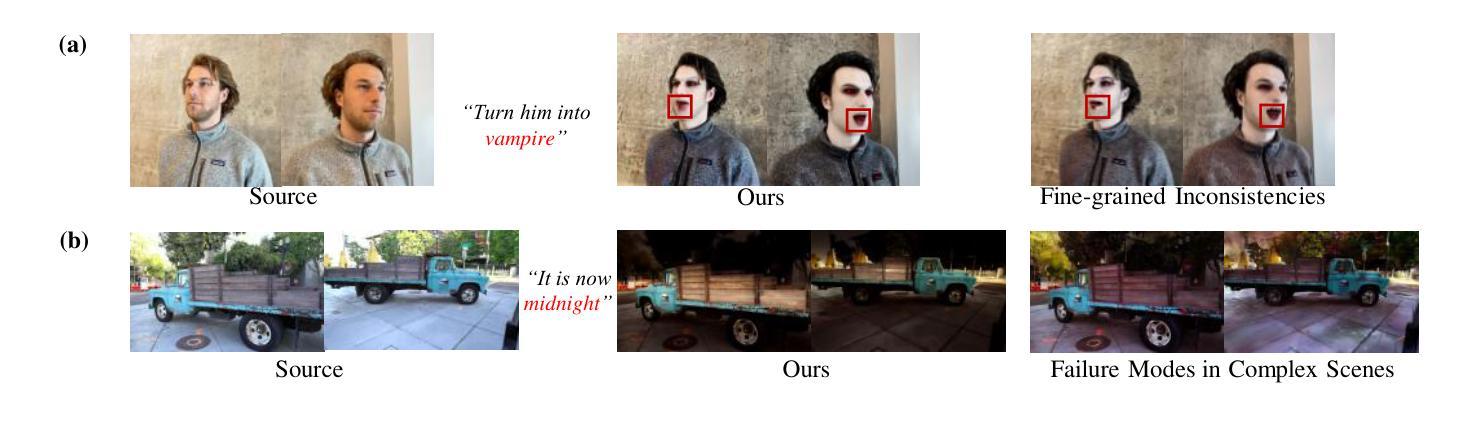
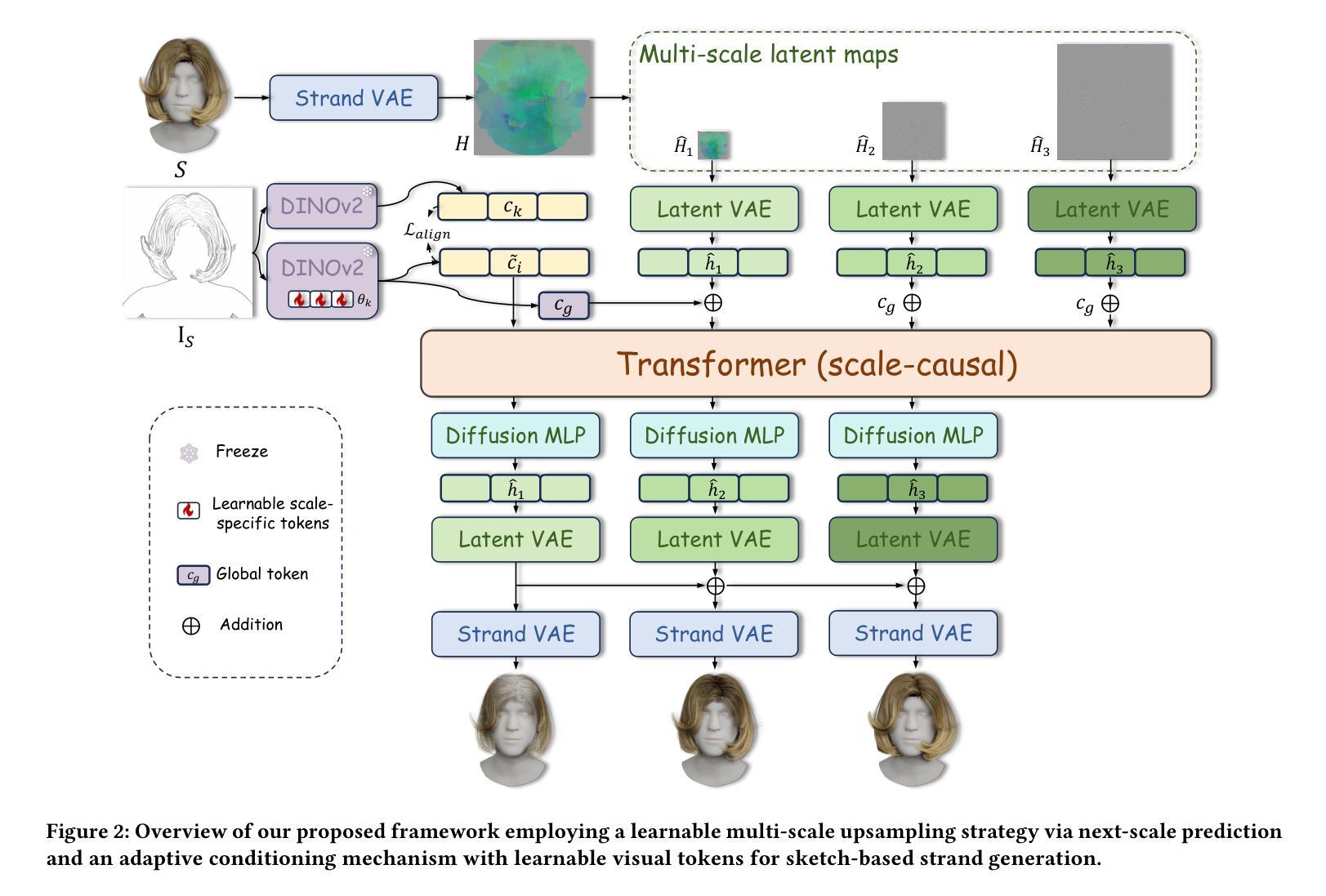
StrandDesigner: Towards Practical Strand Generation with Sketch Guidance
Authors:Na Zhang, Moran Li, Chengming Xu, Han Feng, Xiaobin Hu, Jiangning Zhang, Weijian Cao, Chengjie Wang, Yanwei Fu
Realistic hair strand generation is crucial for applications like computer graphics and virtual reality. While diffusion models can generate hairstyles from text or images, these inputs lack precision and user-friendliness. Instead, we propose the first sketch-based strand generation model, which offers finer control while remaining user-friendly. Our framework tackles key challenges, such as modeling complex strand interactions and diverse sketch patterns, through two main innovations: a learnable strand upsampling strategy that encodes 3D strands into multi-scale latent spaces, and a multi-scale adaptive conditioning mechanism using a transformer with diffusion heads to ensure consistency across granularity levels. Experiments on several benchmark datasets show our method outperforms existing approaches in realism and precision. Qualitative results further confirm its effectiveness. Code will be released at GitHub.
真实感的发丝生成对于计算机图形和虚拟现实等应用至关重要。虽然扩散模型可以从文本或图像生成发型,但这些输入缺乏精确性和用户友好性。相反,我们提出了基于草图的首个发丝生成模型,该模型在保持用户友好的同时提供了更精细的控制。我们的框架通过两个主要创新解决了建模复杂发丝交互和多样草图模式等关键挑战:一种可学习的发丝上采样策略,将3D发丝编码到多尺度潜在空间中;以及使用带有扩散头的变压器确保跨粒度层次一致性的多尺度自适应调节机制。在几个基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在真实感和精确度方面优于现有方法。定性结果进一步证实了其有效性。代码将在GitHub上发布(GitHub链接)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于草图技术的发丝生成模型,解决了传统扩散模型缺乏精度和用户友好性的问题。通过采用学习发丝上采样策略和自适应调节机制等技术手段,实现了发丝模型的精细控制和逼真生成。实验证明,该方法在真实感和精确度上超越了现有方法,可广泛应用于计算机图形和虚拟现实领域。代码已上传至GitHub仓库。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了首个基于草图技术的发丝生成模型,实现了精细控制和用户友好性。
- 通过学习发丝上采样策略和多尺度自适应调节机制,解决了复杂发丝交互和多样草图模式建模的挑战。
- 模型在多个基准数据集上的实验表现优异,实现了发丝模型的逼真生成和精细控制。
- 模型具备自适应调节机制,确保不同粒度级别的一致性。
- 定性结果证实了该模型的有效性。
- 代码已公开,方便研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图


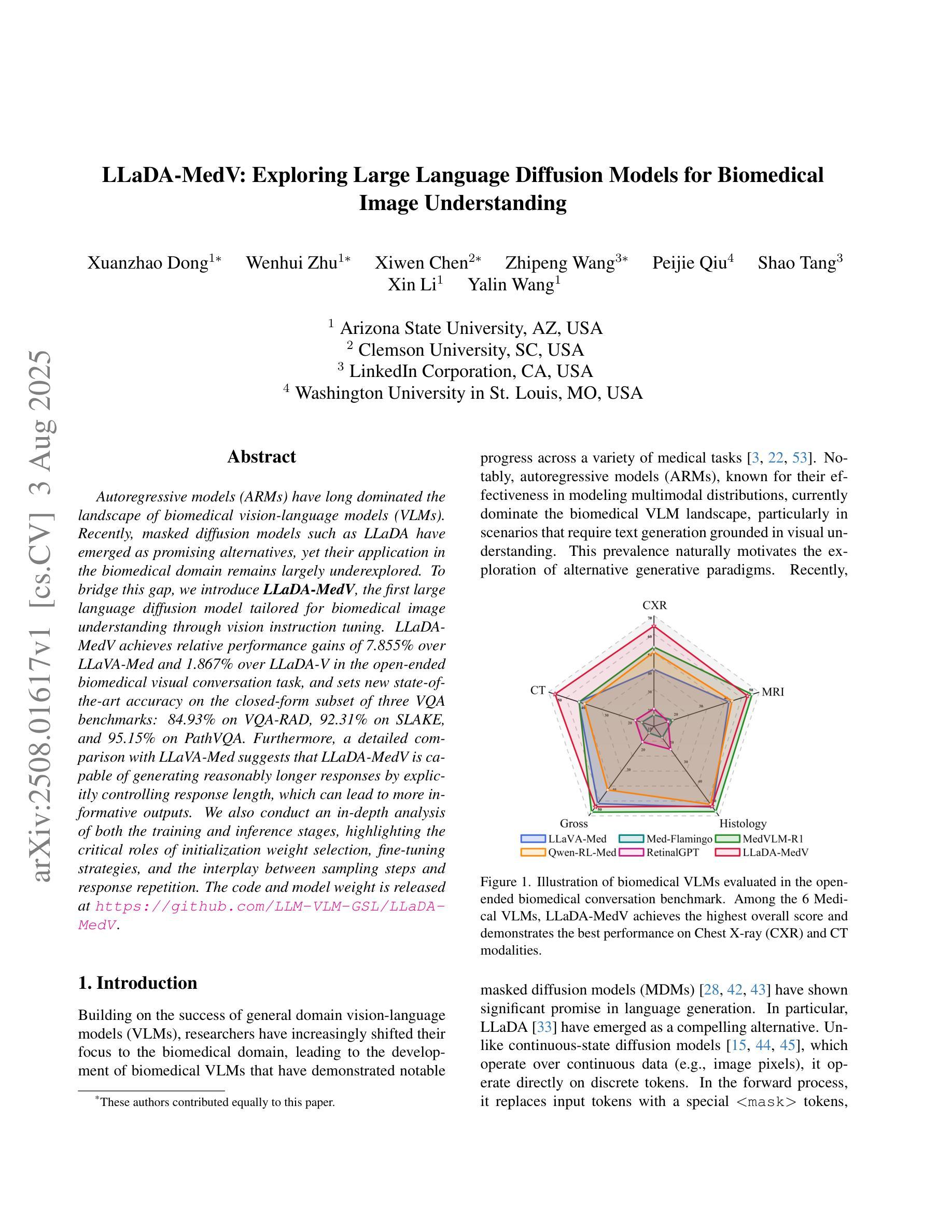
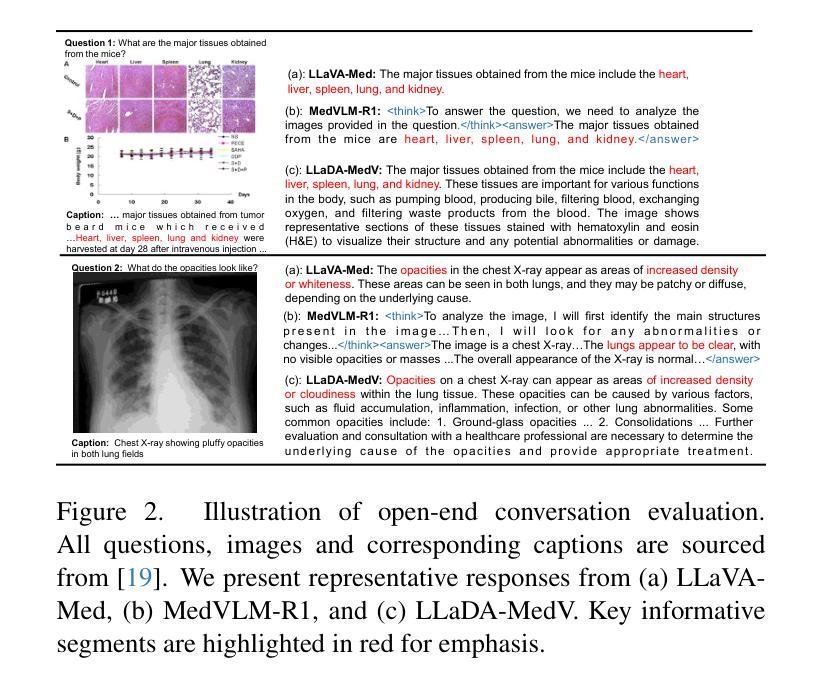
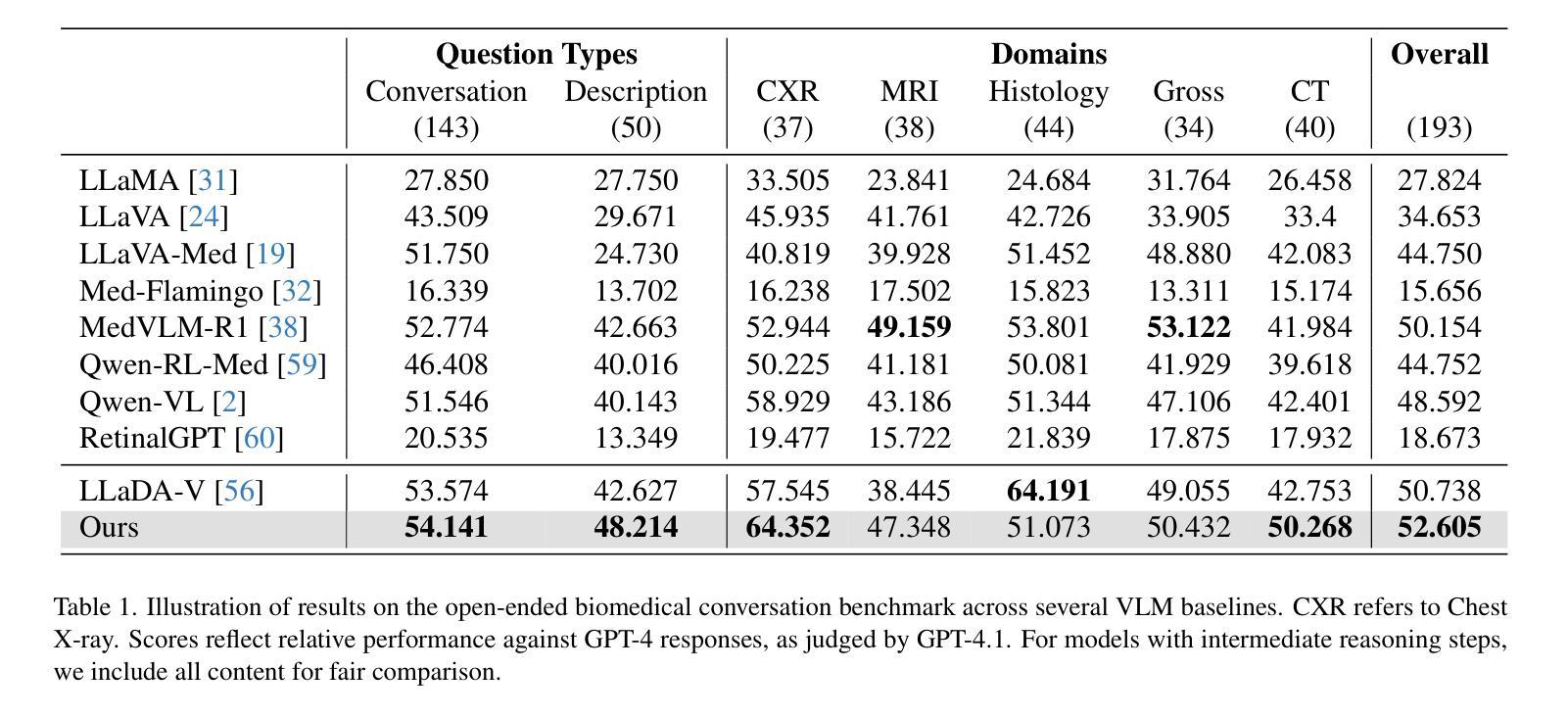
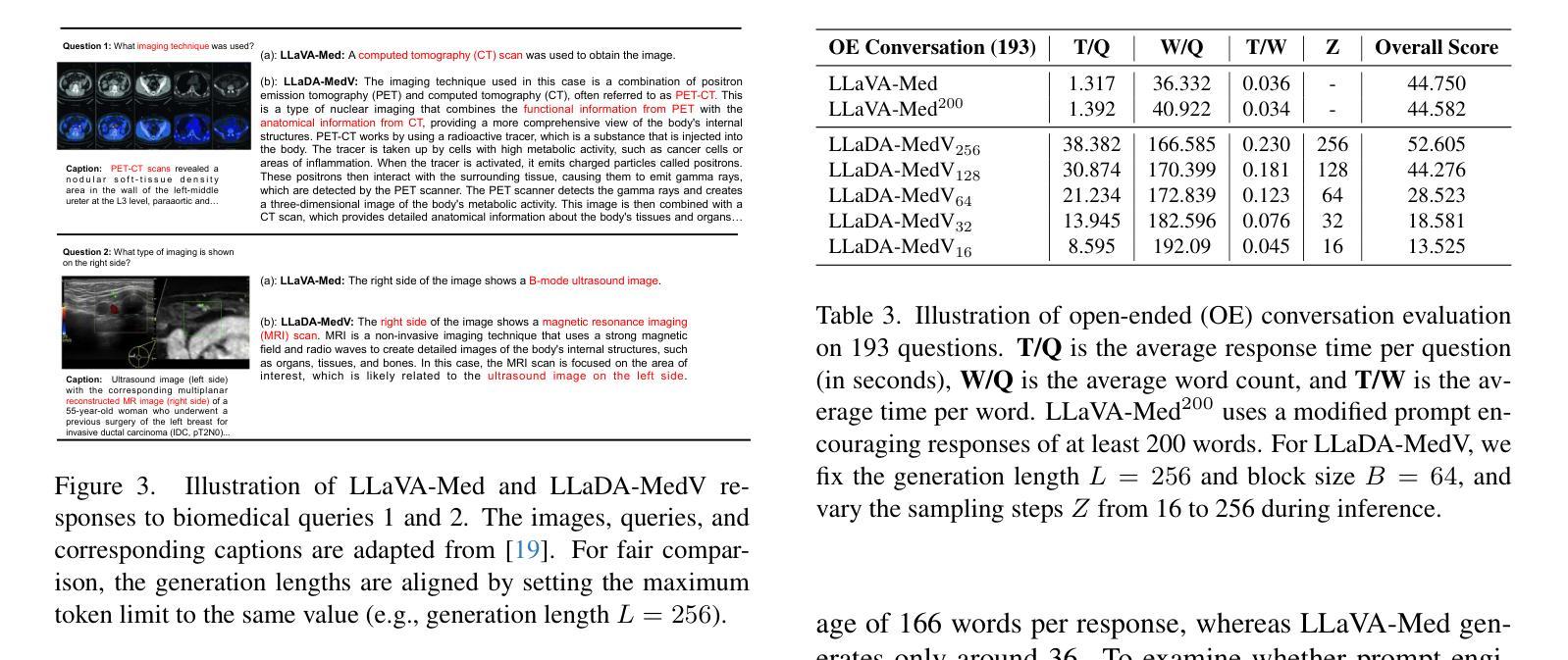
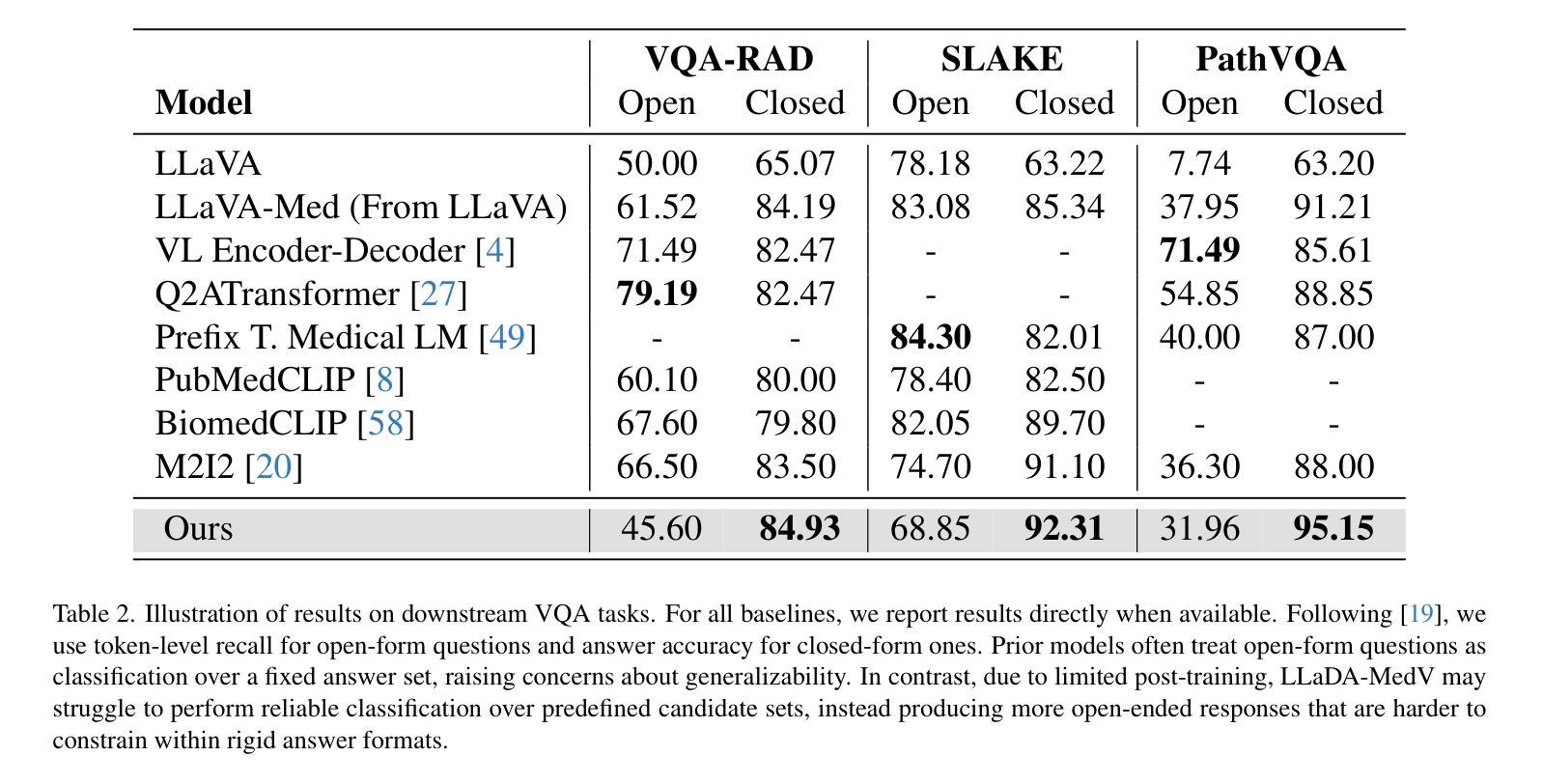
LLaDA-MedV: Exploring Large Language Diffusion Models for Biomedical Image Understanding
Authors:Xuanzhao Dong, Wenhui Zhu, Xiwen Chen, Zhipeng Wang, Peijie Qiu, Shao Tang, Xin Li, Yalin Wang
Autoregressive models (ARMs) have long dominated the landscape of biomedical vision-language models (VLMs). Recently, masked diffusion models such as LLaDA have emerged as promising alternatives, yet their application in the biomedical domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{LLaDA-MedV}, the first large language diffusion model tailored for biomedical image understanding through vision instruction tuning. LLaDA-MedV achieves relative performance gains of 7.855% over LLaVA-Med and 1.867% over LLaDA-V in the open-ended biomedical visual conversation task, and sets new state-of-the-art accuracy on the closed-form subset of three VQA benchmarks: 84.93% on VQA-RAD, 92.31% on SLAKE, and 95.15% on PathVQA. Furthermore, a detailed comparison with LLaVA-Med suggests that LLaDA-MedV is capable of generating reasonably longer responses by explicitly controlling response length, which can lead to more informative outputs. We also conduct an in-depth analysis of both the training and inference stages, highlighting the critical roles of initialization weight selection, fine-tuning strategies, and the interplay between sampling steps and response repetition. The code and model weight is released at https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV.
自回归模型(ARMs)长期以来在生物医学视觉语言模型(VLMs)领域占据主导地位。最近,如LLaDA之类的掩模扩散模型已成为有前景的替代品,然而它们在生物医学领域的应用仍被大大忽视。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了针对生物医学图像理解设计的语言扩散模型LLaDA-MedV。LLaDA-MedV在开放式生物医学视觉对话任务上相对于LLaVA-Med的性能提升了7.855%,相对于LLaDA-V的性能提升了1.867%,并在三个问答基准测试集的封闭式子集上达到了最新水平的准确性:在VQA-RAD上为84.93%,在SLAKE上为92.31%,在PathVQA上为95.15%。此外,与LLaVA-Med的详细比较表明,LLaDA-MedV能够通过明确控制响应长度来生成更长的合理响应,从而生成更具信息量的输出。我们还深入分析了训练和推理阶段,强调了初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤与响应重复之间的相互作用的重要性。代码和模型权重已在https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,针对生物医学图像理解的自动语言扩散模型LLaDA-MedV被提出。相较于其他模型,LLaDA-MedV在开放型生物医学视觉对话任务中具有更高的性能表现,同时在三个视觉问答基准测试中的准确率达到了最新水平。模型可以生成较长的回应并控制响应长度,提供更多信息输出。模型的关键训练与推理阶段也被深入分析。代码和模型权重已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- LLaDA-MedV是首个针对生物医学图像理解的大型语言扩散模型,通过视觉指令微调实现。
- LLaDA-MedV在开放型生物医学视觉对话任务中相对于LLaVA-Med和LLaDA-V有更高的性能表现。
- LLaDA-MedV在三个视觉问答基准测试上的准确率达到了最新水平,具体数据为:VQA-RAD的84.93%,SLAKE的92.31%,PathVQA的95.15%。
- LLaDA-MedV能够生成较长的回应并控制响应长度,提供更多信息输出。
- 模型的关键训练阶段包括初始化权重选择、微调策略等被详细分析。
- 模型推理阶段的采样步骤和响应重复之间的相互作用被深入探讨。
点此查看论文截图
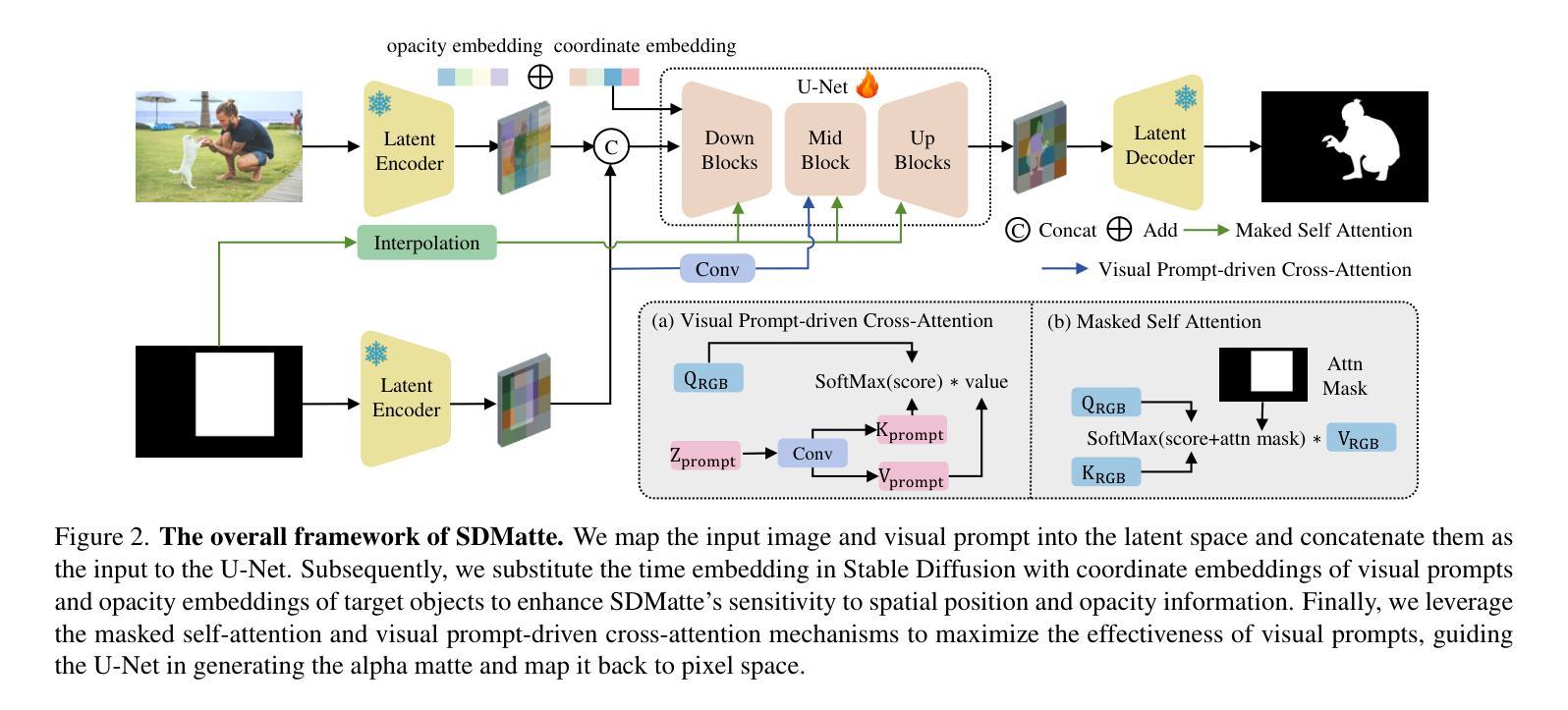
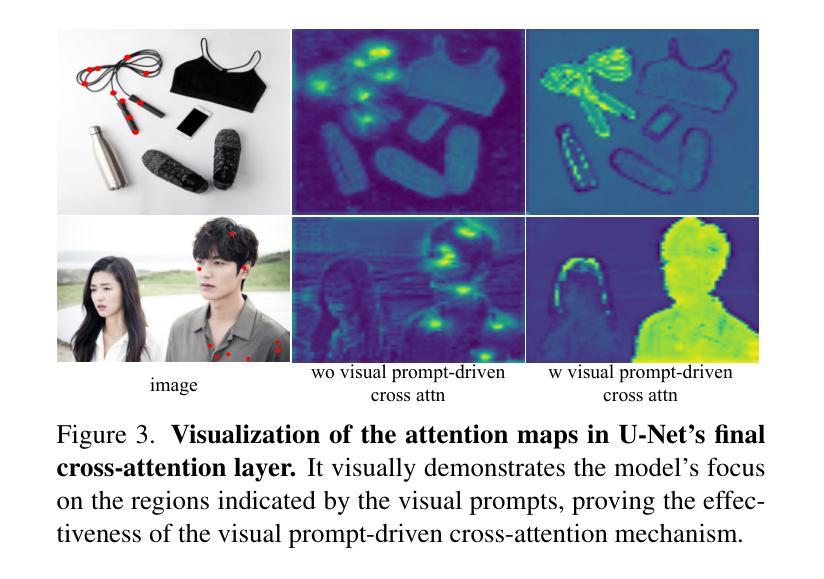
SDMatte: Grafting Diffusion Models for Interactive Matting
Authors:Longfei Huang, Yu Liang, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Wei Dong, Lunde Chen, Wanyu Liu, Bo Li, Peng-Tao Jiang
Recent interactive matting methods have shown satisfactory performance in capturing the primary regions of objects, but they fall short in extracting fine-grained details in edge regions. Diffusion models trained on billions of image-text pairs, demonstrate exceptional capability in modeling highly complex data distributions and synthesizing realistic texture details, while exhibiting robust text-driven interaction capabilities, making them an attractive solution for interactive matting. To this end, we propose SDMatte, a diffusion-driven interactive matting model, with three key contributions. First, we exploit the powerful priors of diffusion models and transform the text-driven interaction capability into visual prompt-driven interaction capability to enable interactive matting. Second, we integrate coordinate embeddings of visual prompts and opacity embeddings of target objects into U-Net, enhancing SDMatte’s sensitivity to spatial position information and opacity information. Third, we propose a masked self-attention mechanism that enables the model to focus on areas specified by visual prompts, leading to better performance. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method, validating its effectiveness in interactive matting. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/vivoCameraResearch/SDMatte.
近期交互式抠图方法已经展现出捕捉物体主要区域的满意性能,但在边缘区域提取精细细节方面存在不足。扩散模型经过数十亿图像文本对的训练,在建模高度复杂的数据分布和合成逼真的纹理细节方面表现出卓越的能力,同时展现出稳健的文本驱动交互能力,使其成为交互式抠图的理想解决方案。为此,我们提出SDMatte,一种基于扩散的交互式抠图模型,有三个主要贡献。首先,我们利用扩散模型的有力先验,将文本驱动的交互能力转化为视觉提示驱动的交互能力,以实现交互式抠图。其次,我们将视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入集成到U-Net中,提高SDMatte对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感度。第三,我们提出了一种掩膜自注意力机制,使模型能够关注视觉提示指定的区域,从而提高性能。在多个数据集上的广泛实验证明了我们方法的优越性,验证了其在交互式抠图中的有效性。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/vivoCameraResearch/SDMatte上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025, 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
文本提出了一种名为SDMatte的基于扩散模型的交互式抠图方法,具有三大贡献。首先,利用扩散模型的强大先验知识,将文本驱动交互能力转化为视觉提示驱动交互能力,实现交互式抠图。其次,将视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入整合到U-Net中,提高SDMatte对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感性。最后,提出了一种掩膜自注意力机制,使模型能够关注视觉提示指定的区域,从而提高性能。该方法在多个数据集上的实验验证了其优越性,展示了在交互式抠图任务中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型具有建模复杂数据分布和合成逼真纹理细节的能力,展现出在交互式抠图领域的潜力。
- SDMatte模型利用扩散模型的先验知识,实现文本驱动交互能力到视觉提示驱动交互能力的转化。
- 通过整合视觉提示的坐标嵌入和目标对象的透明度嵌入到U-Net中,SDMatte提高了对空间位置信息和透明度信息的敏感性。
- SDMatte提出的掩膜自注意力机制能关注视觉提示指定的区域,进一步提高性能。
- 相较于传统方法,SDMatte在多个数据集上的实验表现出卓越性能。
- SDMatte模型的有效性已在实践中得到验证,可应用于交互式抠图任务。
- SDMatte模型的代码和模型已公开在https://github.com/vivoCameraResearch/SDMatte。
点此查看论文截图

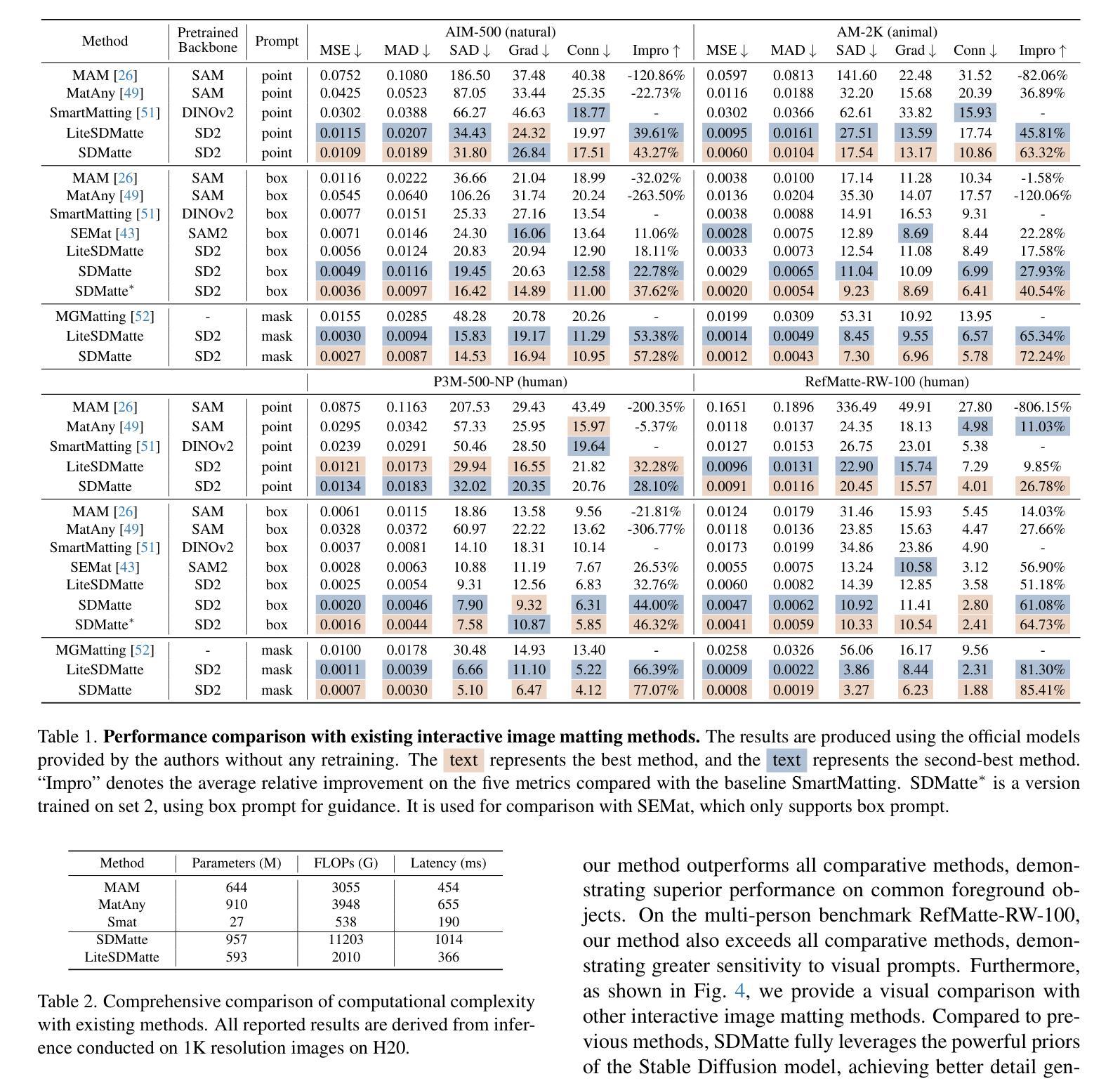
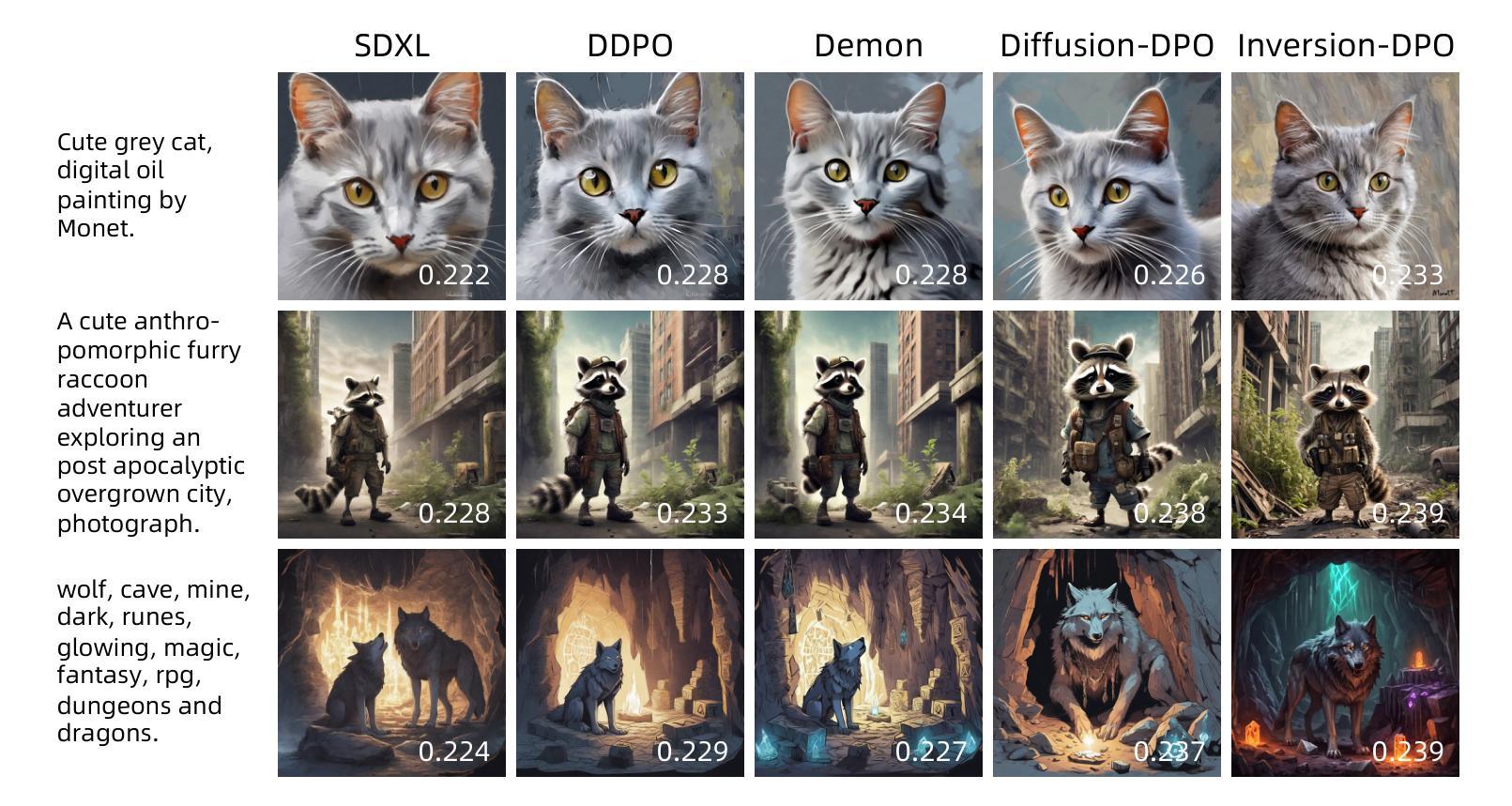
Inversion-DPO: Precise and Efficient Post-Training for Diffusion Models
Authors:Zejian Li, Yize Li, Chenye Meng, Zhongni Liu, Yang Ling, Shengyuan Zhang, Guang Yang, Changyuan Yang, Zhiyuan Yang, Lingyun Sun
Recent advancements in diffusion models (DMs) have been propelled by alignment methods that post-train models to better conform to human preferences. However, these approaches typically require computation-intensive training of a base model and a reward model, which not only incurs substantial computational overhead but may also compromise model accuracy and training efficiency. To address these limitations, we propose Inversion-DPO, a novel alignment framework that circumvents reward modeling by reformulating Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with DDIM inversion for DMs. Our method conducts intractable posterior sampling in Diffusion-DPO with the deterministic inversion from winning and losing samples to noise and thus derive a new post-training paradigm. This paradigm eliminates the need for auxiliary reward models or inaccurate appromixation, significantly enhancing both precision and efficiency of training. We apply Inversion-DPO to a basic task of text-to-image generation and a challenging task of compositional image generation. Extensive experiments show substantial performance improvements achieved by Inversion-DPO compared to existing post-training methods and highlight the ability of the trained generative models to generate high-fidelity compositionally coherent images. For the post-training of compostitional image geneation, we curate a paired dataset consisting of 11,140 images with complex structural annotations and comprehensive scores, designed to enhance the compositional capabilities of generative models. Inversion-DPO explores a new avenue for efficient, high-precision alignment in diffusion models, advancing their applicability to complex realistic generation tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/MIGHTYEZ/Inversion-DPO
近期扩散模型(DMs)的进展得益于通过对模型进行后训练以更好符合人类偏好的对齐方法。然而,这些方法通常需要计算密集的基础模型和奖励模型的训练,这不仅产生了大量的计算开销,还可能影响模型的准确性和训练效率。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Inversion-DPO,这是一种新的对齐框架,它通过重新制定扩散模型的直接偏好优化(DPO)与DDIM反转来规避奖励建模。我们的方法通过从获胜和失败样本到噪声的确定性反转来进行难以捉摸的后验采样,从而开创了新的后训练范式。这种方法消除了对辅助奖励模型或不精确近似计算的需求,显著提高了训练的准确性和效率。我们将Inversion-DPO应用于文本到图像生成的基本任务以及具有挑战性的组合图像生成任务。大量实验表明,与现有的后训练方法相比,Inversion-DPO取得了显著的性能提升,并展示了训练好的生成模型在生成高保真组合连贯图像方面的能力。对于组合图像生成的后训练,我们整理了一个包含11,140张带有复杂结构注释和全面分数的图像配对数据集,旨在提高生成模型的组合能力。Inversion-DPO为扩散模型的高效高精度对齐探索了一条新途径,提高了其在复杂现实生成任务中的适用性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/MIGHTYEZ/Inversion-DPO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM25
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型的新进展,提出了一种名为Inversion-DPO的新型对齐框架,该框架通过改革Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)与DDIM反演方法,规避了奖励建模,从而实现了扩散模型的后训练。新方法通过从获胜和失败样本中确定性地反演噪声来进行不可行后采样,开创了无需辅助奖励模型或不精确近似的新后训练范式。此范式提高了训练和精度效率。应用于文本到图像生成和基本任务以及更具挑战性的组合图像生成任务中,实验结果显示Inversion-DPO相较于现有后训练方法实现了显著的性能提升,并展示了生成模型生成高保真组合图像的能力。此外,为后训练组合图像生成,研究团队创建了一个包含复杂结构注释和评分的一对一图像数据集,旨在增强生成模型的组合能力。该研究为扩散模型的高效高精度对齐探索了新途径,提高了其在复杂现实生成任务中的应用性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)的最新进展通过对齐方法来更好地符合人类偏好。
- 当前方法需要计算密集的训练基础模型和奖励模型,带来计算开销并可能影响准确性和效率。
- 提出了一种新型对齐框架Inversion-DPO,通过改革Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)与DDIM反演规避奖励建模。
- Inversion-DPO实现了无需辅助奖励模型或不精确近似的新后训练范式。
- 该方法应用于文本到图像生成和基本任务以及更具挑战性的组合图像生成任务。
- Inversion-DPO显著提高了性能,并展示了生成高保真组合图像的能力。
点此查看论文截图


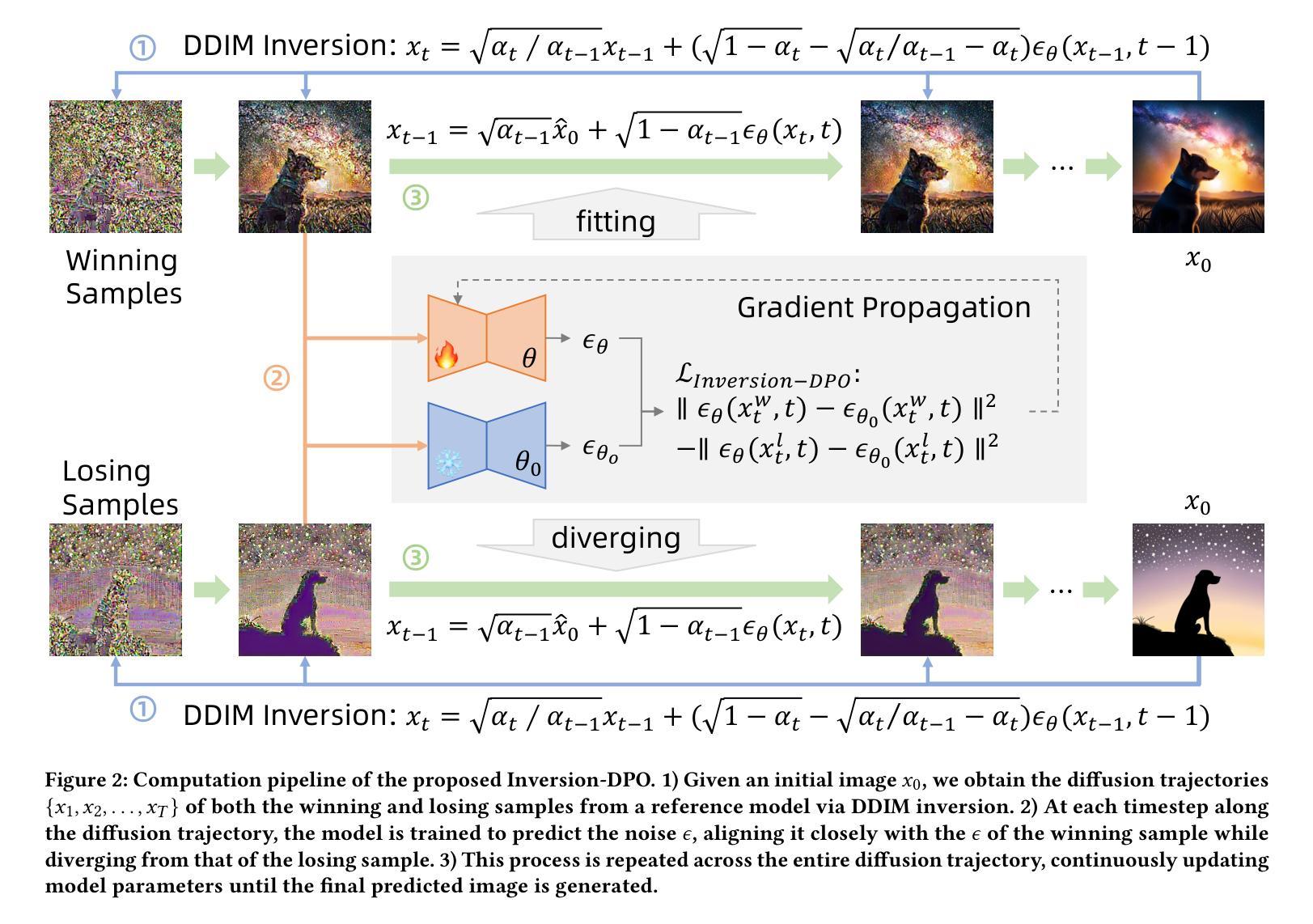
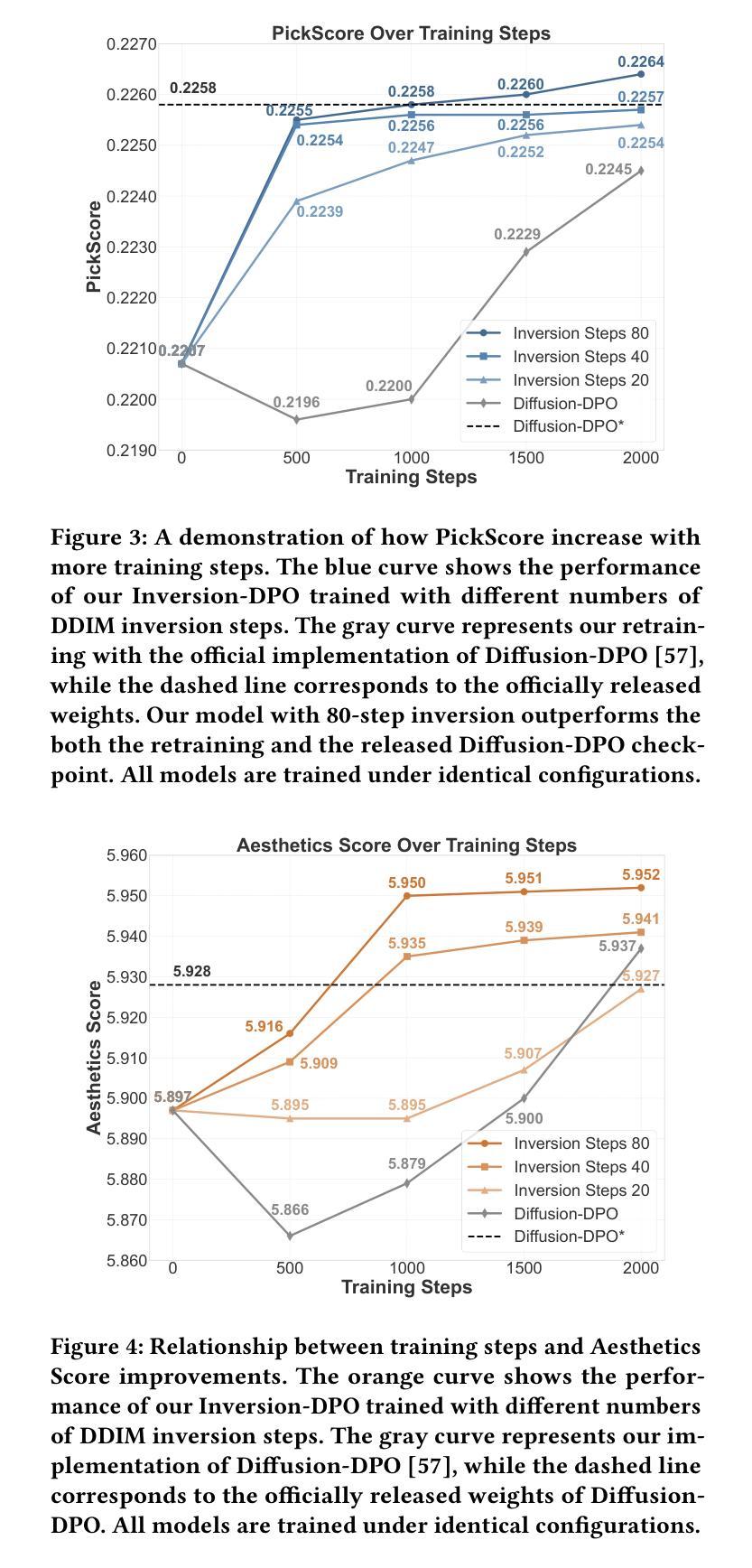
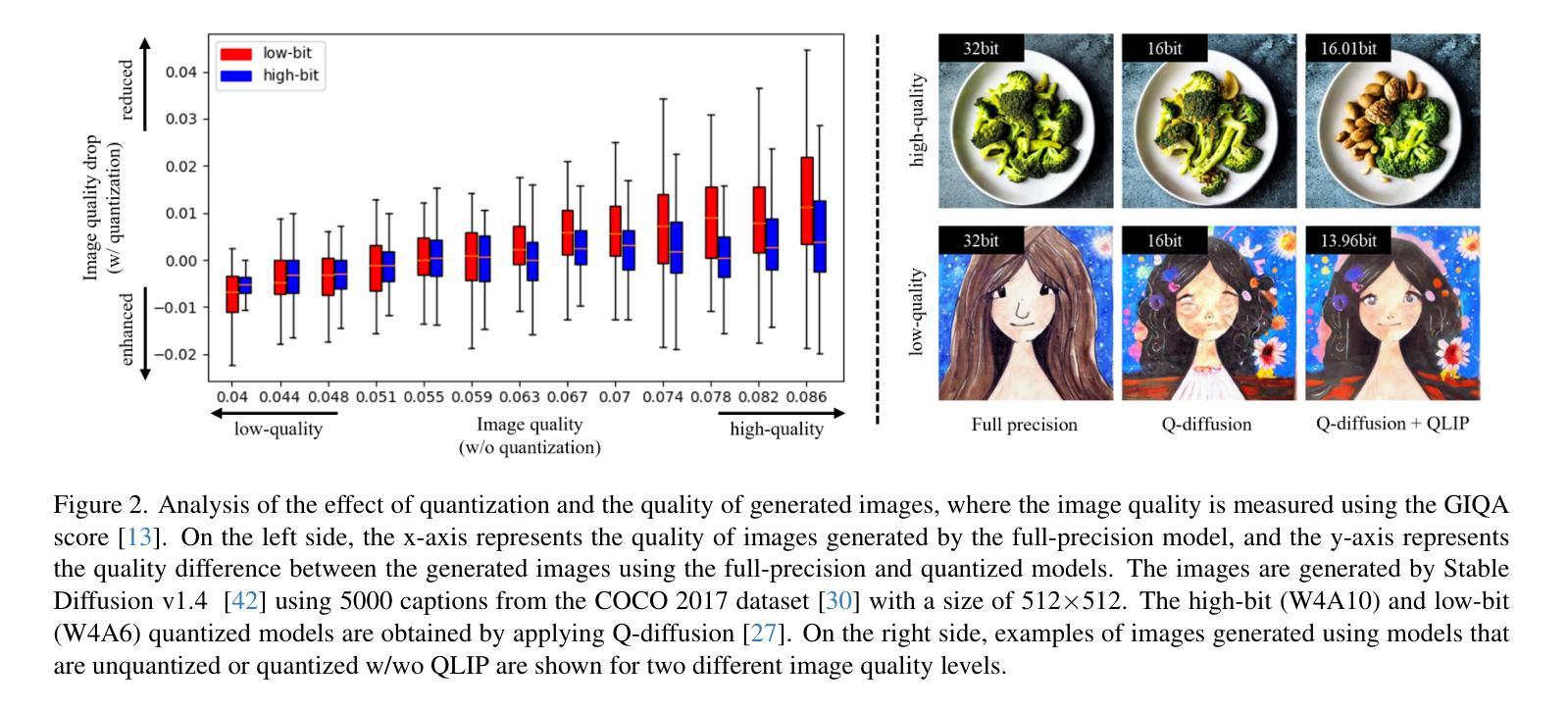
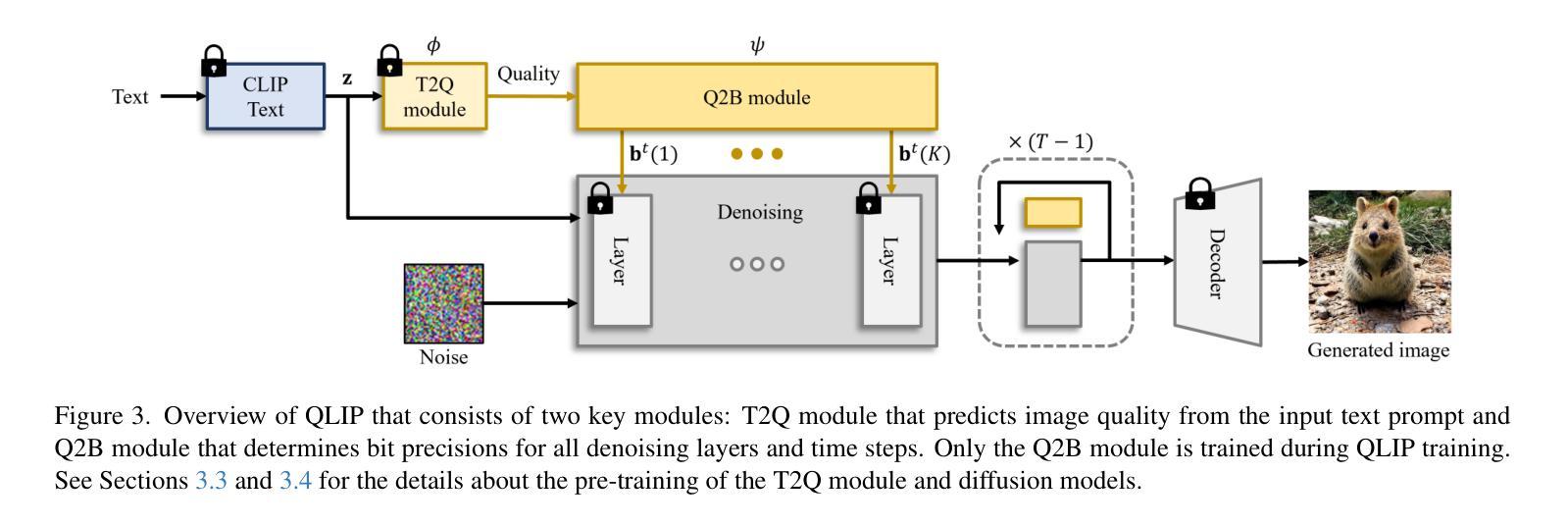
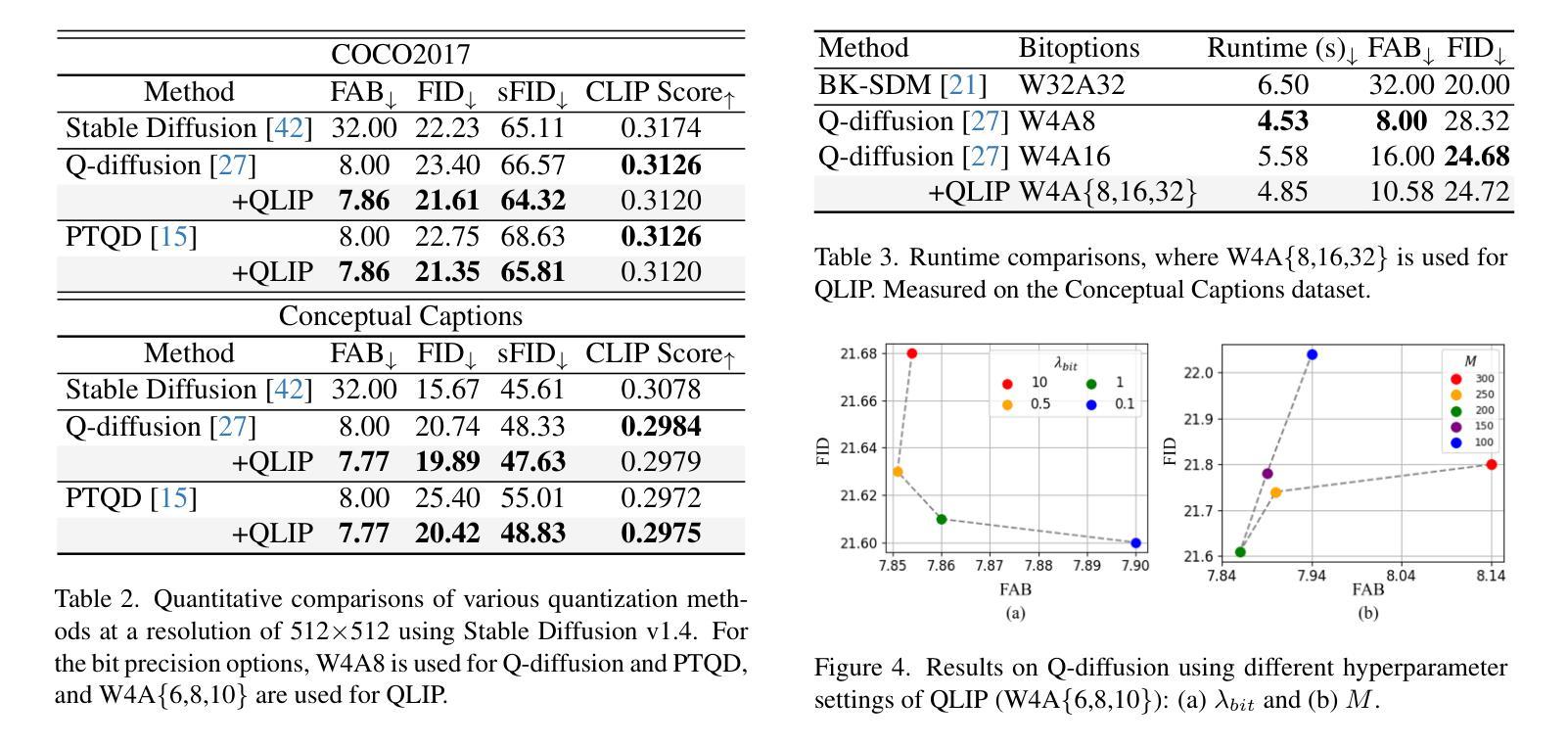
Text Embedding Knows How to Quantize Text-Guided Diffusion Models
Authors:Hongjae Lee, Myungjun Son, Dongjea Kang, Seung-Won Jung
Despite the success of diffusion models in image generation tasks such as text-to-image, the enormous computational complexity of diffusion models limits their use in resource-constrained environments. To address this, network quantization has emerged as a promising solution for designing efficient diffusion models. However, existing diffusion model quantization methods do not consider input conditions, such as text prompts, as an essential source of information for quantization. In this paper, we propose a novel quantization method dubbed Quantization of Language-to-Image diffusion models using text Prompts (QLIP). QLIP leverages text prompts to guide the selection of bit precision for every layer at each time step. In addition, QLIP can be seamlessly integrated into existing quantization methods to enhance quantization efficiency. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of QLIP in reducing computational complexity and improving the quality of the generated images across various datasets.
尽管扩散模型在文本到图像等图像生成任务中取得了成功,但其巨大的计算复杂度限制了其在资源受限环境中的应用。为了解决这一问题,网络量化作为设计高效扩散模型的有前途的解决方案而出现。然而,现有的扩散模型量化方法没有考虑输入条件,如文本提示,作为量化的重要信息来源。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的量化方法,称为使用文本提示的语言到图像扩散模型量化(QLIP)。QLIP利用文本提示来指导每个时间步长每一层的位精度的选择。此外,QLIP可以无缝集成到现有的量化方法中,以提高量化的效率。我们的广泛实验表明,QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高各种数据集生成图像的质量方面非常有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
扩散模型在网络量化技术的帮助下,在图像生成任务中取得了显著的成功,尤其是在文本到图像的任务中。然而,现有的扩散模型量化方法往往忽略了输入条件,如文本提示,作为量化的重要信息来源。本文提出了一种新的量化方法——利用文本提示的文本到图像扩散模型的量化(QLIP)。QLIP利用文本提示指导每一层每一步的位精度选择,并可以无缝集成到现有的量化方法中以提高量化效率。实验证明,QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高生成图像质量方面效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成任务中取得了成功,特别是在文本到图像的任务中。
- 网络量化是解决扩散模型在资源受限环境中使用的重要方法。
- 现有扩散模型量化方法忽略了文本提示等输入条件。
- QLIP是一种新的量化方法,利用文本提示指导每一层每一步的位精度选择。
- QLIP可以无缝集成到现有的量化方法中以提高量化效率。
- QLIP在降低计算复杂度和提高生成图像质量方面效果显著。
点此查看论文截图

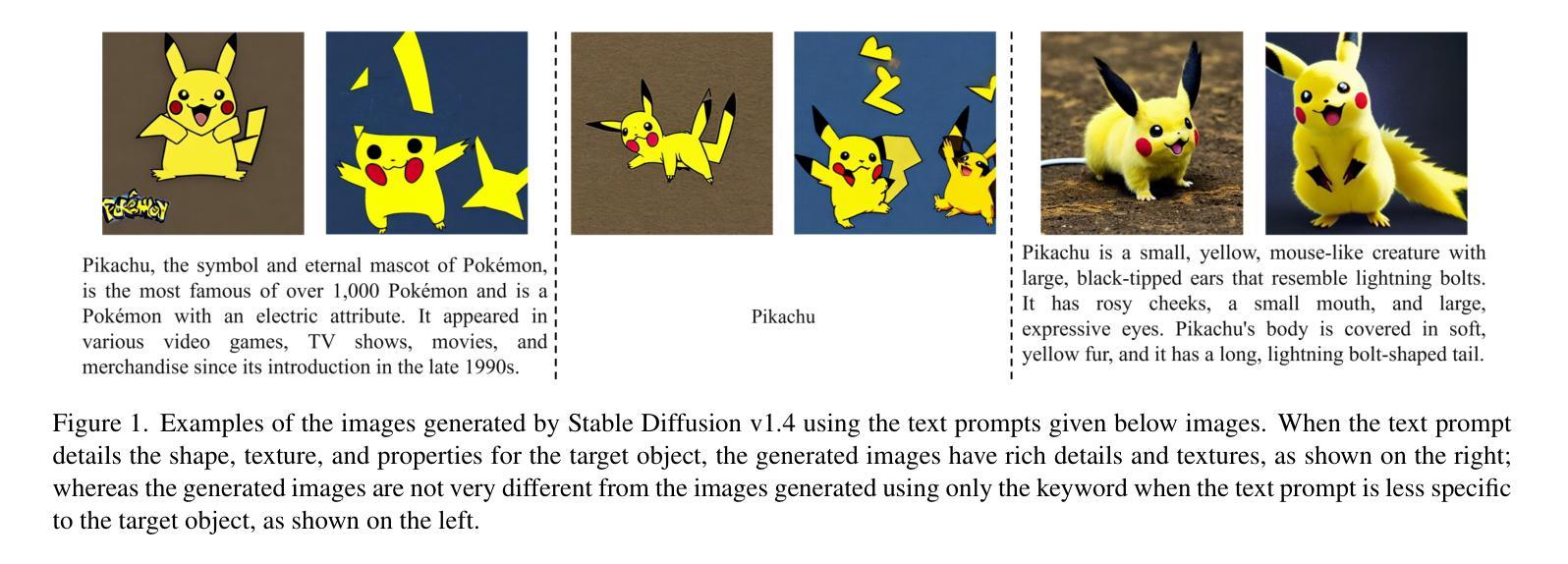
Subjective Camera 0.1: Bridging Human Cognition and Visual Reconstruction through Sequence-Aware Sketch-Guided Diffusion
Authors:Haoyang Chen, Dongfang Sun, Caoyuan Ma, Shiqin Wang, Kewei Zhang, Zheng Wang, Zhixiang Wang
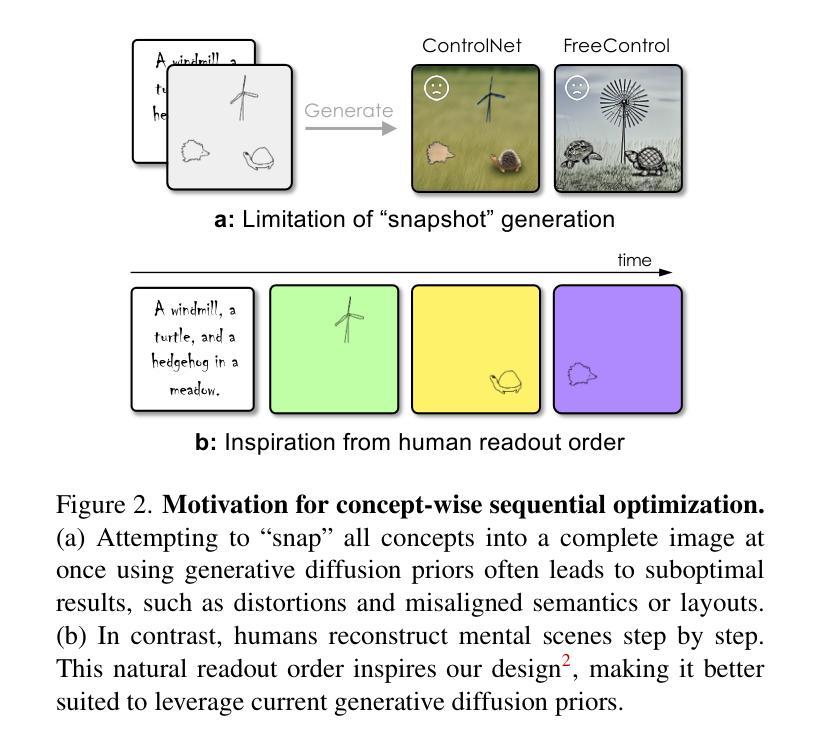
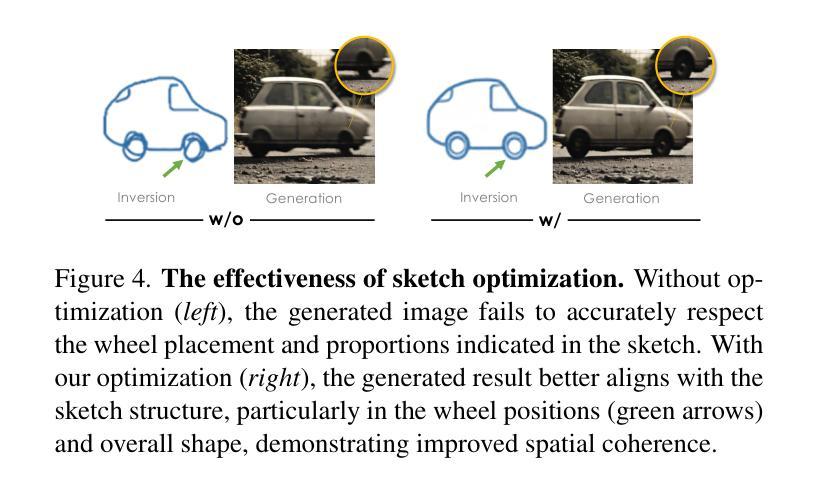
We introduce the concept of a subjective camera to reconstruct meaningful moments that physical cameras fail to capture. We propose Subjective Camera 0.1, a framework for reconstructing real-world scenes from readily accessible subjective readouts, i.e., textual descriptions and progressively drawn rough sketches. Built on optimization-based alignment of diffusion models, our approach avoids large-scale paired training data and mitigates generalization issues. To address the challenge of integrating multiple abstract concepts in real-world scenarios, we design a Sequence-Aware Sketch-Guided Diffusion framework with three loss terms for concept-wise sequential optimization, following the natural order of subjective readouts. Experiments on two datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in image quality as well as spatial and semantic alignment with target scenes. User studies with 40 participants further confirm that our approach is consistently preferred.Our project page is at: subjective-camera.github.io
我们引入主观相机的概念,以重建物理相机未能捕捉的有意义时刻。我们提出主观相机0.1,这是一个从易于获取的主观读数(如文本描述和逐步绘制的粗略草图)重建现实场景的框架。我们的方法建立在基于优化的扩散模型对齐之上,避免了大规模配对训练数据,并缓解了泛化问题。为了解决在现实场景中整合多个抽象概念的挑战,我们设计了一个序列感知草图引导扩散框架,包含三个用于概念级顺序优化的损失项,遵循主观读数的自然顺序。在两个数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在图像质量以及空间和时间与目标的场景语义对齐方面达到了最新技术水平。有40名参与者参与的用户研究进一步证实了我们方法的优越性。我们的项目页面是:主观相机官网。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种主观相机概念,用以重建物理相机无法捕捉的有意义时刻。我们提出了主观相机0.1框架,通过优化基于扩散模型的对齐方式,从易获取的主观读数(如文本描述和粗略草图)重建现实场景。为解决现实场景中整合多个抽象概念的问题,我们设计了序列感知草图引导扩散框架,包含三个用于概念级顺序优化的损失项,遵循主观读数的自然顺序。在两项数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在图像质量以及空间与语义对齐目标场景方面达到领先水平。40名参与者的用户研究进一步证实了我们方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入主观相机概念,旨在捕捉物理相机无法捕捉的有意义时刻。
- 提出Subjective Camera 0.1框架,利用文本描述和粗略草图重建现实场景。
- 基于优化对齐的扩散模型,无需大规模配对训练数据,减轻泛化问题。
- 设计序列感知草图引导扩散框架,通过三个损失项进行概念级顺序优化。
- 框架遵循主观读数的自然顺序,能更准确地重建场景。
- 在两个数据集上的实验证明,该方法在图像质量及空间、语义对齐方面表现优异。
- 用户研究证实该方法的一致优越性。
点此查看论文截图



DIP: Unsupervised Dense In-Context Post-training of Visual Representations
Authors:Sophia Sirko-Galouchenko, Spyros Gidaris, Antonin Vobecky, Andrei Bursuc, Nicolas Thome
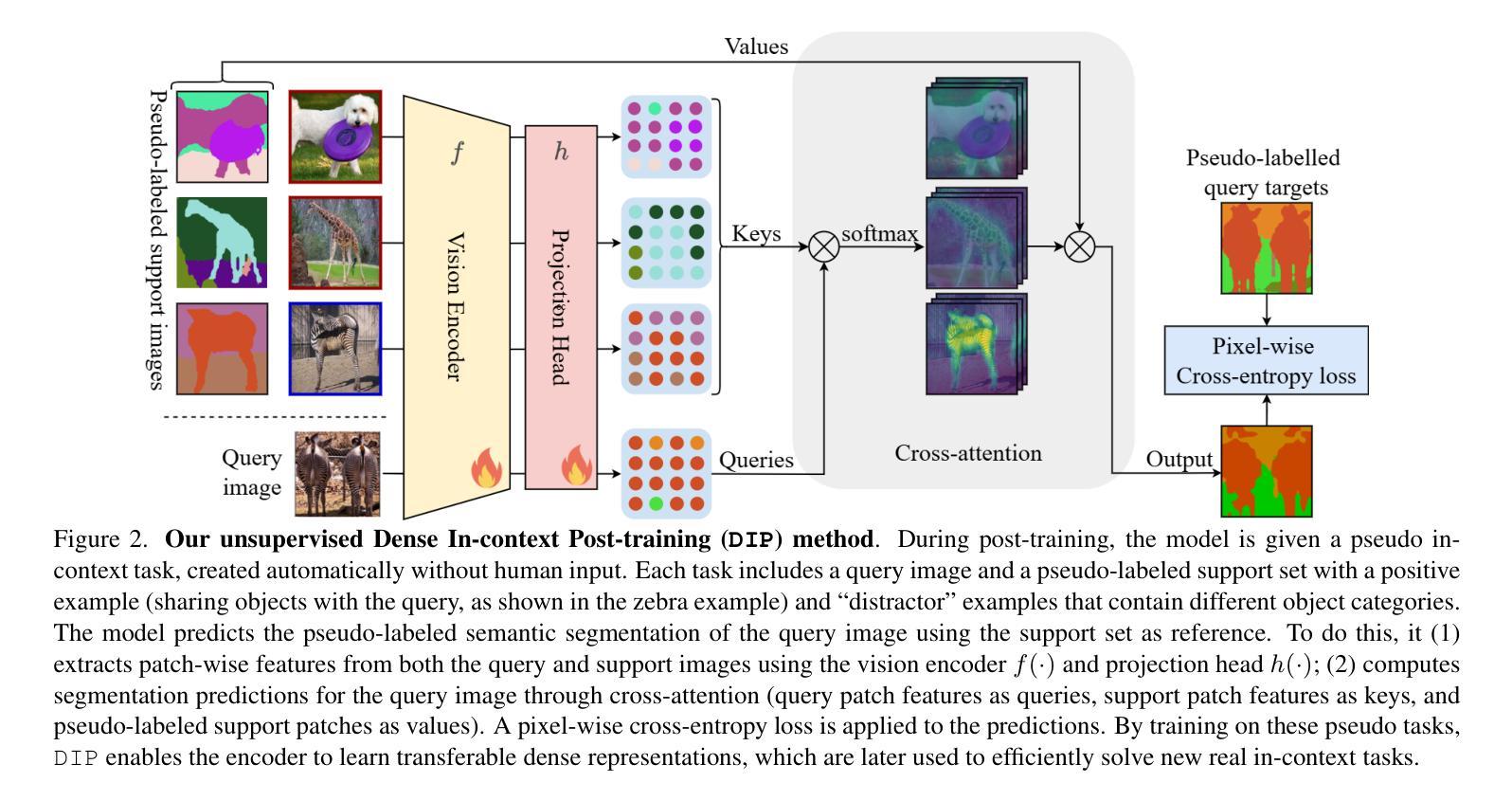
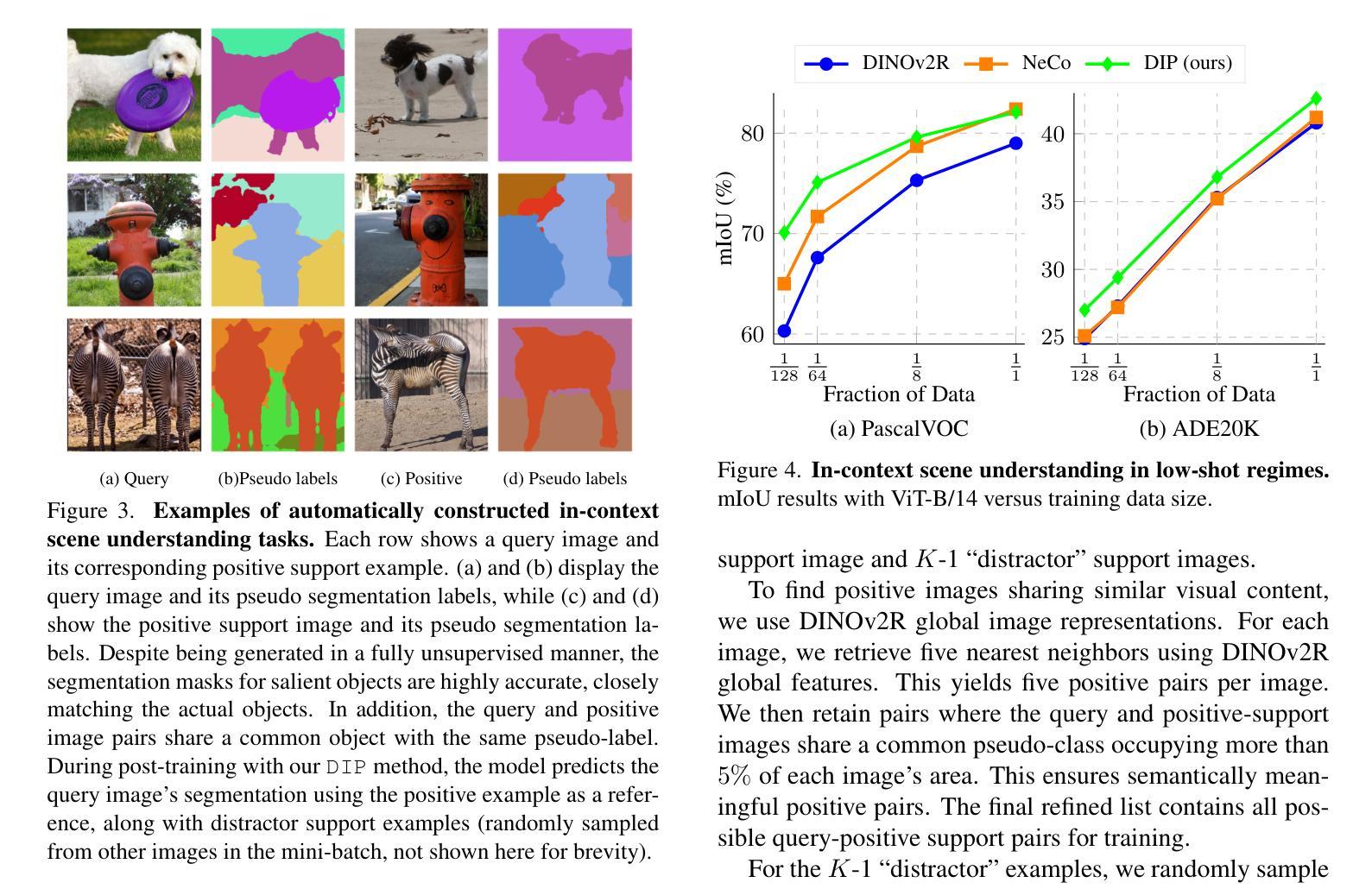
We introduce DIP, a novel unsupervised post-training method designed to enhance dense image representations in large-scale pretrained vision encoders for in-context scene understanding. Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex self-distillation architectures, our method trains the vision encoder using pseudo-tasks that explicitly simulate downstream in-context scenarios, inspired by meta-learning principles. To enable post-training on unlabeled data, we propose an automatic mechanism for generating in-context tasks that combines a pretrained diffusion model and the vision encoder itself. DIP is simple, unsupervised, and computationally efficient, requiring less than 9 hours on a single A100 GPU. By learning dense representations through pseudo in-context tasks, it achieves strong performance across a wide variety of downstream real-world in-context scene understanding tasks. It outperforms both the initial vision encoder and prior methods, offering a practical and effective solution for improving dense representations. Code available here: https://github.com/sirkosophia/DIP
我们介绍了DIP,这是一种新型的无监督后训练法,旨在增强大规模预训练视觉编码器的密集图像表示,以进行上下文场景理解。不同于依赖复杂自我蒸馏架构的先前方法,我们的方法使用伪任务来明确模拟下游上下文场景,这是受元学习原理的启发。为了在无标签数据上进行后训练,我们提出了一种生成上下文任务的自动机制,该机制结合了预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器本身。DIP简单、无监督且计算高效,在单个A100 GPU上不到9小时即可完成。它通过伪上下文任务学习密集表示,在多种下游现实世界上下文场景理解任务中表现出强大的性能。它优于初始的视觉编码器和先前的方法,为改进密集表示提供了实用有效的解决方案。代码可在https://github.com/sirkosophia/DIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了DIP,一种新型无监督的后训练技术,旨在增强大规模预训练视觉编码器的密集图像表示,以进行上下文场景理解。DIP采用伪任务模拟下游上下文场景,受元学习原理启发。通过预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器本身生成上下文任务,实现无监督数据后训练。DIP简单、高效,可在单个A100 GPU上不到9小时内完成。通过伪上下文任务学习密集表示,在多种下游现实场景理解任务中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- DIP是一种无监督后训练技术,用于增强预训练视觉编码器的图像表示能力。
- DIP通过模拟下游上下文场景生成伪任务,从而增强视觉编码器的性能。
- DIP采用元学习原理,利用预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器生成上下文任务。
- DIP在单个A100 GPU上计算效率高,训练时间短。
- DIP在多种下游现实场景理解任务中表现优异,优于初始视觉编码器和先前方法。
- DIP适用于改善密集表示,为场景理解提供了一种实用有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

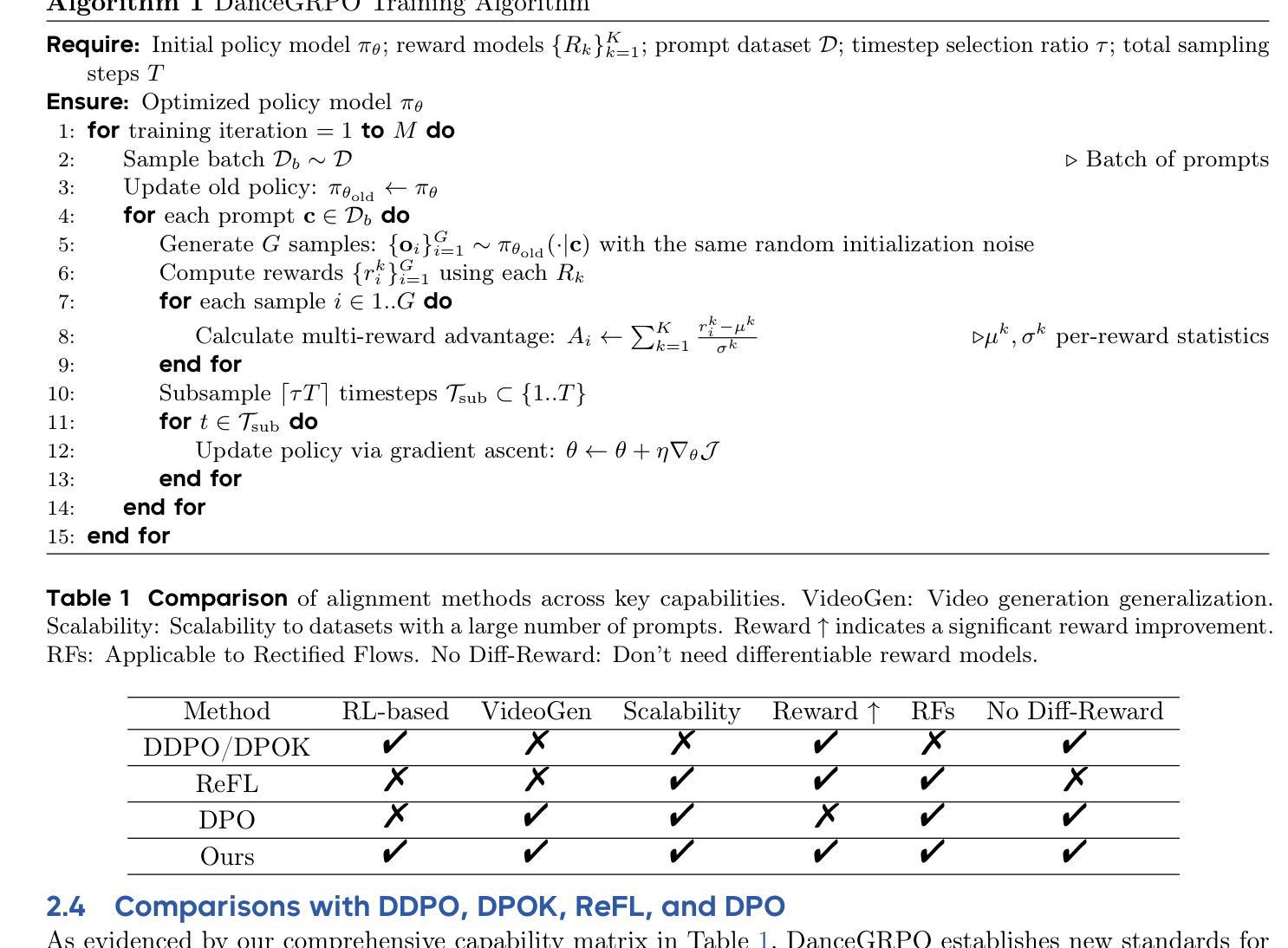
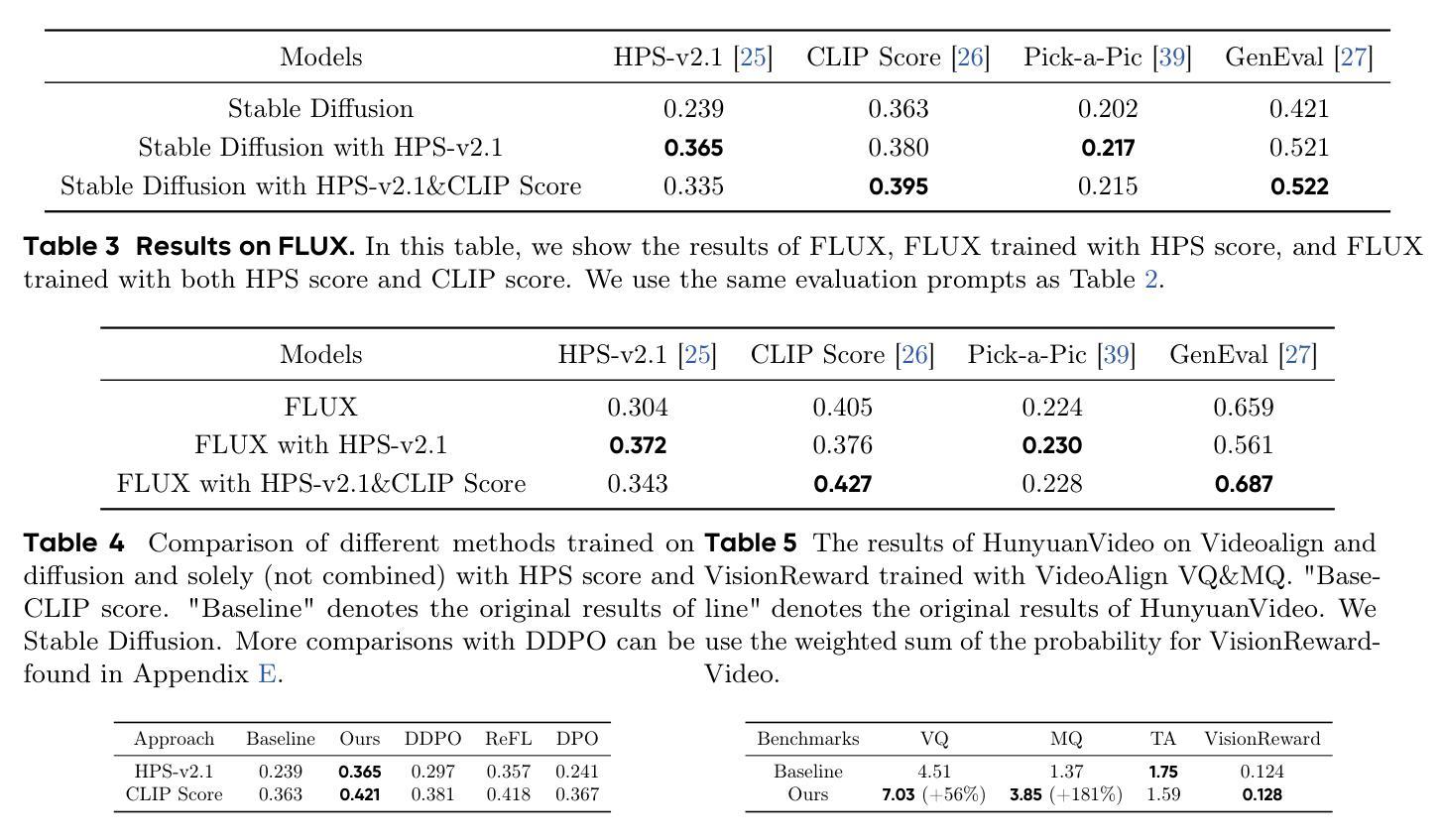
DanceGRPO: Unleashing GRPO on Visual Generation
Authors:Zeyue Xue, Jie Wu, Yu Gao, Fangyuan Kong, Lingting Zhu, Mengzhao Chen, Zhiheng Liu, Wei Liu, Qiushan Guo, Weilin Huang, Ping Luo
Recent breakthroughs in generative models-particularly diffusion models and rectified flows-have revolutionized visual content creation, yet aligning model outputs with human preferences remains a critical challenge. Existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods for visual generation face critical limitations: incompatibility with modern Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)-based sampling paradigms, instability in large-scale training, and lack of validation for video generation. This paper introduces DanceGRPO, the first unified framework to adapt Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to visual generation paradigms, unleashing one unified RL algorithm across two generative paradigms (diffusion models and rectified flows), three tasks (text-to-image, text-to-video, image-to-video), four foundation models (Stable Diffusion, HunyuanVideo, FLUX, SkyReels-I2V), and five reward models (image/video aesthetics, text-image alignment, video motion quality, and binary reward). To our knowledge, DanceGRPO is the first RL-based unified framework capable of seamless adaptation across diverse generative paradigms, tasks, foundational models, and reward models. DanceGRPO demonstrates consistent and substantial improvements, which outperform baselines by up to 181% on benchmarks such as HPS-v2.1, CLIP Score, VideoAlign, and GenEval. Notably, DanceGRPO not only can stabilize policy optimization for complex video generation, but also enables generative policy to better capture denoising trajectories for Best-of-N inference scaling and learn from sparse binary feedback. Our results establish DanceGRPO as a robust and versatile solution for scaling Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) tasks in visual generation, offering new insights into harmonizing reinforcement learning and visual synthesis. The code will be released.
近期生成模型——尤其是扩散模型和修正流——的突破为视觉内容创作带来了革命性的变化,但如何使模型输出符合人类偏好仍然是一个关键挑战。现有的基于强化学习(RL)的视觉生成方法面临重要局限:与现代基于常微分方程(ODE)的采样范式不兼容、大规模训练不稳定、以及视频生成的验证缺乏。本文介绍了DanceGRPO,这是第一个将集团相对政策优化(GRPO)适应于视觉生成范式的统一框架,释放了一种统一的强化学习算法,该算法涵盖了两种生成范式(扩散模型和修正流)、三种任务(文本到图像、文本到视频、图像到视频)、四种基础模型(Stable Diffusion、HuYuanVideo、FLUX、SkyReels-I2V),以及五种奖励模型(图像/视频美学、文本-图像对齐、视频运动质量、二元奖励)。据我们所知,DanceGRPO是第一个能够在多种生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型之间无缝适应的基于强化学习的统一框架。DanceGRPO表现出持续且显著的改进,在HPS-v2.1、CLIP Score、VideoAlign和GenEval等基准测试上的表现优于基线高达181%。值得一提的是,DanceGRPO不仅能够稳定复杂视频生成的策略优化,还能够使生成策略更好地捕捉去噪轨迹,用于Best-of-N推理扩展,并从稀疏的二元反馈中学习。我们的结果确立了DanceGRPO在视觉生成中扩展强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)任务的稳健性和通用性解决方案,为强化学习与合成视觉的和谐融合提供了新的见解。代码将被发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://dancegrpo.github.io/
摘要
近期生成模型(如扩散模型和校正流)的突破为视觉内容创作带来革命性变化,但如何使模型输出与人类偏好对齐仍是关键挑战。现有基于强化学习(RL)的视觉生成方法存在与现代基于常微分方程(ODEs)的采样范式不兼容、大规模训练不稳定、视频生成验证缺乏等问题。本文引入DanceGRPO框架,首次将组相对策略优化(GRPO)适应于视觉生成范式,实现统一RL算法在两种生成范式(扩散模型和校正流)、三种任务(文本转图像、文本转视频、图像转视频)、四种基础模型(Stable Diffusion、HunyuanVideo等)和五种奖励模型中的灵活应用。据我们所知,DanceGRPO是首个能够无缝适应多种生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型的RL统一框架。DanceGRPO在HPS-v2.1等基准测试中实现了与基线相比最高达181%的持续和实质性改进,同时显著提升了视频生成的策略优化稳定性,并能够更好地捕捉去噪轨迹用于Best-of-N推理扩展和从稀疏二元反馈中学习。我们的研究结果表明,DanceGRPO为强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)任务在视觉生成方面的应用提供了稳健且通用的解决方案,为强化学习与视觉合成的和谐融合提供了新的见解。代码将公开发布。
关键见解
- 突破性的生成模型(如扩散模型和校正流)在视觉内容创作领域具有革命性影响。
- 模型输出与人类偏好对齐仍是当前的重要挑战。
- 现有基于强化学习的视觉生成方法面临多种挑战,如与现代采样范式不兼容、训练不稳定、视频生成验证缺乏等。
- 引入DanceGRPO框架,首次实现统一RL算法在多种生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型中的应用。
- DanceGRPO实现了显著的性能改进,并在视频生成的政策优化稳定性方面有所提升。
- DanceGRPO能够捕捉去噪轨迹用于Best-of-N推理扩展。
点此查看论文截图
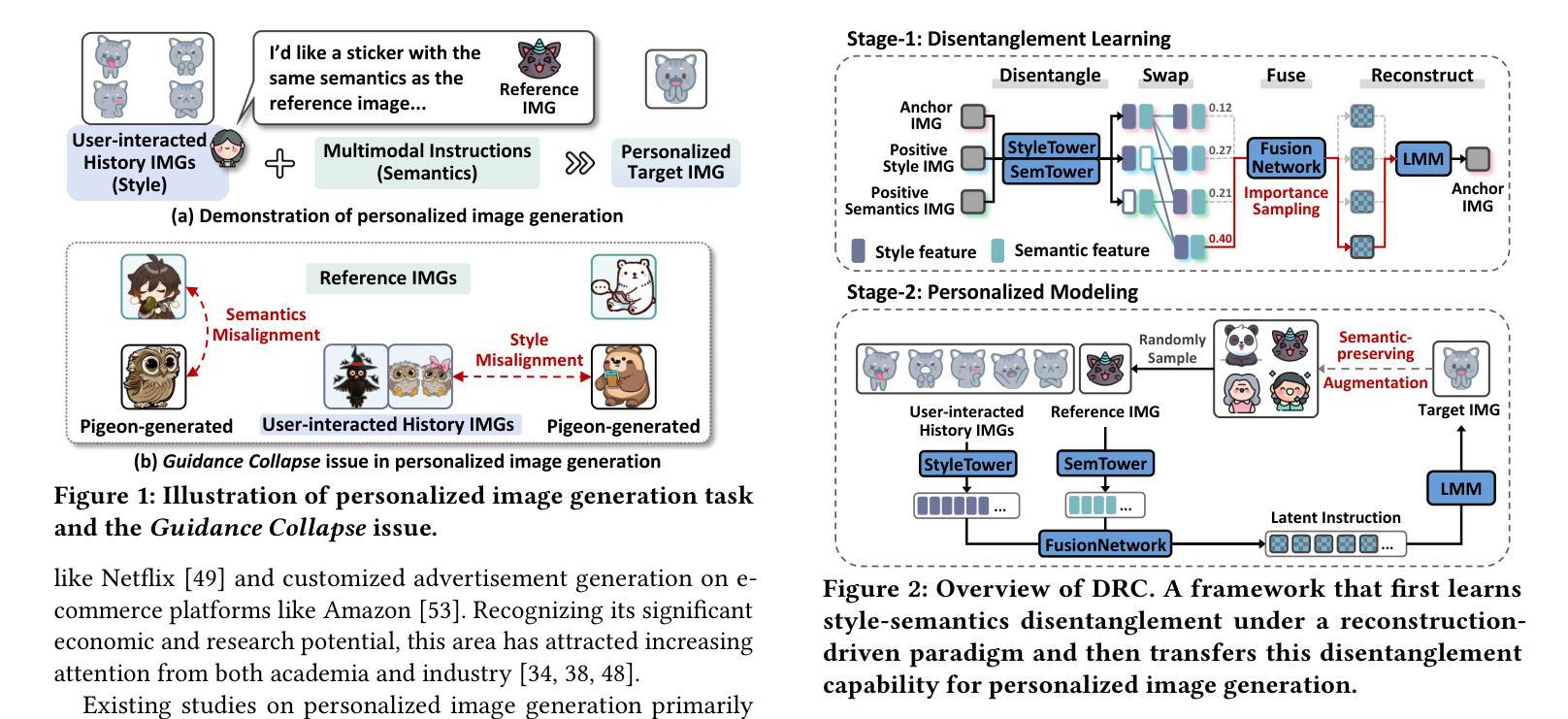
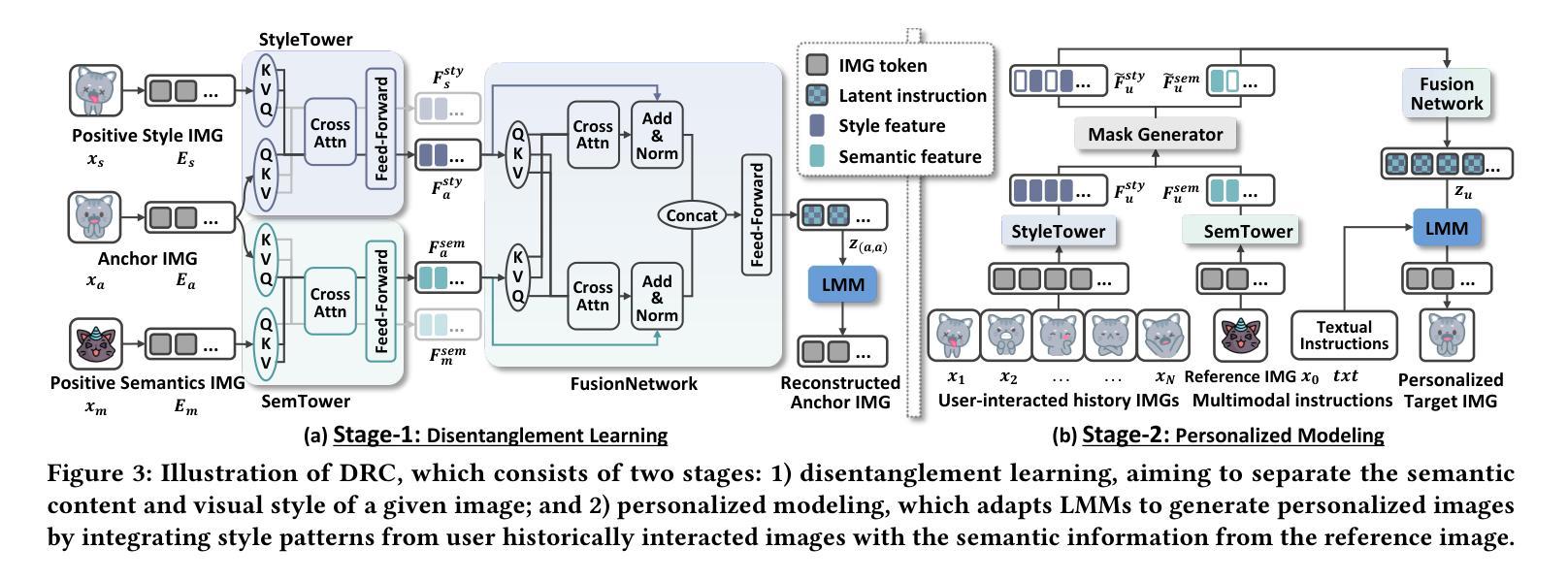
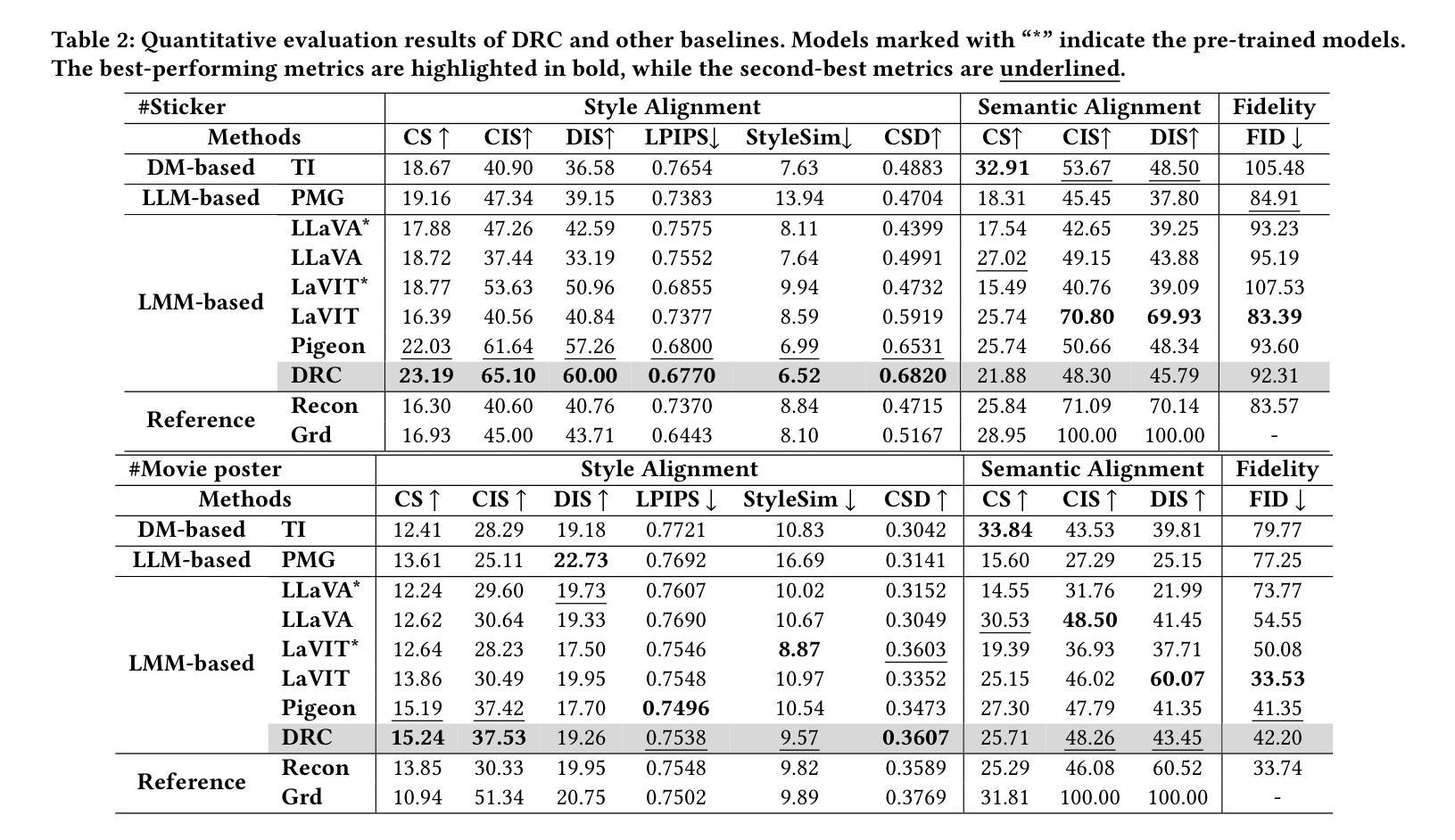
DRC: Enhancing Personalized Image Generation via Disentangled Representation Composition
Authors:Yiyan Xu, Wuqiang Zheng, Wenjie Wang, Fengbin Zhu, Xinting Hu, Yang Zhang, Fuli Feng, Tat-Seng Chua
Personalized image generation has emerged as a promising direction in multimodal content creation. It aims to synthesize images tailored to individual style preferences (e.g., color schemes, character appearances, layout) and semantic intentions (e.g., emotion, action, scene contexts) by leveraging user-interacted history images and multimodal instructions. Despite notable progress, existing methods – whether based on diffusion models, large language models, or Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) – struggle to accurately capture and fuse user style preferences and semantic intentions. In particular, the state-of-the-art LMM-based method suffers from the entanglement of visual features, leading to Guidance Collapse, where the generated images fail to preserve user-preferred styles or reflect the specified semantics. To address these limitations, we introduce DRC, a novel personalized image generation framework that enhances LMMs through Disentangled Representation Composition. DRC explicitly extracts user style preferences and semantic intentions from history images and the reference image, respectively, to form user-specific latent instructions that guide image generation within LMMs. Specifically, it involves two critical learning stages: 1) Disentanglement learning, which employs a dual-tower disentangler to explicitly separate style and semantic features, optimized via a reconstruction-driven paradigm with difficulty-aware importance sampling; and 2) Personalized modeling, which applies semantic-preserving augmentations to effectively adapt the disentangled representations for robust personalized generation. Extensive experiments on two benchmarks demonstrate that DRC shows competitive performance while effectively mitigating the guidance collapse issue, underscoring the importance of disentangled representation learning for controllable and effective personalized image generation.
个性化图像生成已成为多媒体内容创建的一个前景广阔的方向。它旨在通过利用用户交互的历史图像和多模态指令,合成符合个人风格偏好(如色彩方案、角色外观、布局)和语义意图(如情感、动作、场景上下文)的图像。尽管取得了显著的进展,但现有方法——无论是基于扩散模型、大型语言模型还是大型多媒体模型(LMM)——在准确捕捉和融合用户风格偏好和语义意图方面都存在困难。特别是最先进的基于LMM的方法受到视觉特征纠缠的影响,导致出现“指导崩溃”,生成的图像无法保持用户偏好的风格或反映指定的语义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in ACM MM’25
Summary
本文探讨个性化图像生成领域的研究进展,提出一种基于解纠缠表示组合(DRC)的新框架,旨在提高大型多模态模型(LMMs)在个性化图像生成方面的性能。该框架通过明确提取用户风格偏好和语义意图,形成用户特定的潜在指令,指导图像在LMMs内的生成。
Key Takeaways
- 个人化图像生成成为多模态内容创建的有前途的方向。
- 现有方法很难捕捉和融合用户的风格偏好和语义意图。
- 当前领先的大型多模态模型(LMMs)面临视觉特征纠缠的问题,导致生成的图像无法保持用户偏好的风格或反映指定的语义。
- DRC框架旨在通过解纠缠表示组合增强LMMs在个性化图像生成方面的性能。
- DRC框架包括两个关键学习阶段:解纠缠学习和个性化建模。
- 解纠缠学习阶段采用双塔解缠器明确分离风格与语义特征,并通过重建驱动范式和优化难度感知重要性采样进行优化。
- 个性化建模阶段应用语义保留增强,有效适应解缠表示,以实现稳健的个性化生成。
点此查看论文截图

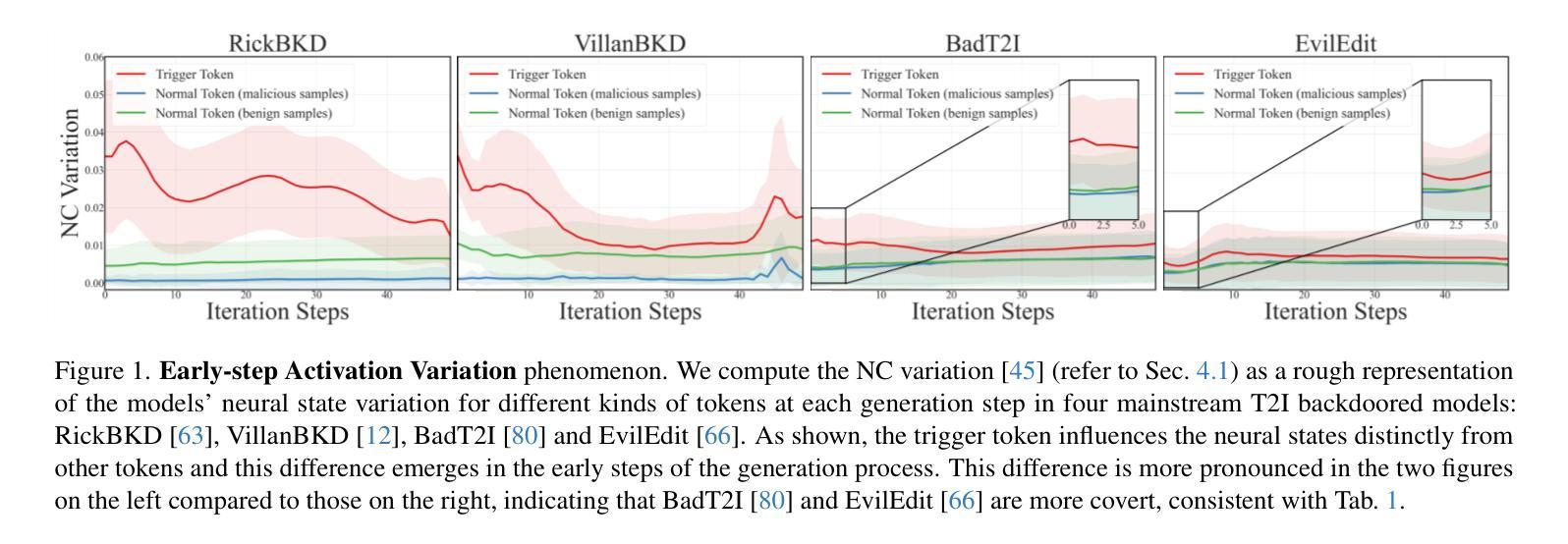
Efficient Input-level Backdoor Defense on Text-to-Image Synthesis via Neuron Activation Variation
Authors:Shengfang Zhai, Jiajun Li, Yue Liu, Huanran Chen, Zhihua Tian, Wenjie Qu, Qingni Shen, Ruoxi Jia, Yinpeng Dong, Jiaheng Zhang
In recent years, text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have gained significant attention for their ability to generate high quality images reflecting text prompts. However, their growing popularity has also led to the emergence of backdoor threats, posing substantial risks. Currently, effective defense strategies against such threats are lacking due to the diversity of backdoor targets in T2I synthesis. In this paper, we propose NaviT2I, an efficient input-level backdoor defense framework against diverse T2I backdoors. Our approach is based on the new observation that trigger tokens tend to induce significant neuron activation variation in the early stage of the diffusion generation process, a phenomenon we term Early-step Activation Variation. Leveraging this insight, NaviT2I navigates T2I models to prevent malicious inputs by analyzing Neuron activation variations caused by input tokens. Extensive experiments show that NaviT2I significantly outperforms the baselines in both effectiveness and efficiency across diverse datasets, various T2I backdoors, and different model architectures including UNet and DiT. Furthermore, we show that our method remains effective under potential adaptive attacks.
近年来,文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型因其能够生成反映文本提示的高质量图像而备受关注。然而,其日益普及也带来了后门威胁,带来了相当大的风险。由于T2I合成中的后门目标多样性,目前缺乏针对此类威胁的有效防御策略。在本文中,我们提出了NaviT2I,这是一种针对多种T2I后门的高效输入级后门防御框架。我们的方法基于一个新的观察结果,即触发令牌往往会在扩散生成过程的早期阶段引起神经元激活的显著变化,我们将这一现象称为“早期步骤激活变化”。利用这一见解,NaviT2I通过分析输入令牌引起的神经元激活变化,引导T2I模型防止恶意输入。大量实验表明,NaviT2I在多个数据集、多种T2I后门和不同模型架构(包括UNet和DiT)方面,在有效性和效率方面都显著优于基线。此外,我们还表明,我们的方法在潜在的适应性攻击下仍然有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages. ICCV 2025 (Highlight)
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型能够根据文本提示生成高质量图像,但近期出现的后门威胁给其带来了巨大风险。由于缺乏针对T2I合成中后门目标的防御策略,本文提出了NaviT2I,一个高效的输入级后门防御框架。NaviT2I基于新观察,触发令牌在扩散生成过程的早期阶段会引起神经元激活变化显著,我们称之为早期激活变化现象。利用这一洞察,NaviT2I通过分析输入令牌引起的神经元激活变化来防止恶意输入。实验表明,NaviT2I在多个数据集、各种T2I后门以及不同模型架构(包括UNet和DiT)上,在有效性和效率方面都显著优于基线方法,并且在潜在的自适应攻击下仍然保持有效。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型因能够根据文本提示生成高质量图像而受到广泛关注,但也存在后门威胁风险。
- 缺乏针对T2I合成中多样后门目标的防御策略。
- 本文提出了NaviT2I,一个高效的输入级后门防御框架,针对T2I模型进行防御。
- NaviT2I基于新观察:触发令牌在扩散模型的早期阶段会引起神经元激活显著变化。
- NaviT2I通过分析输入令牌引起的神经元激活变化来防止恶意输入。
- 实验表明,NaviT2I在多个方面显著优于基线方法,包括数据集、T2I后门类型、模型架构等。
点此查看论文截图


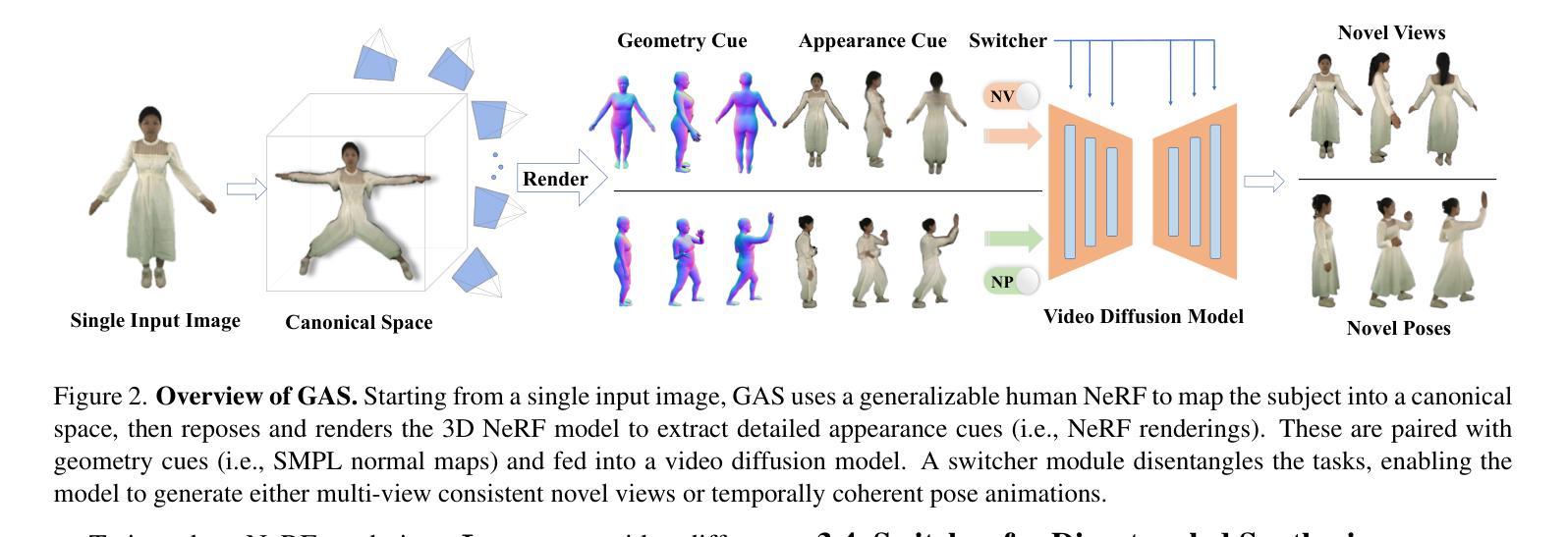
GAS: Generative Avatar Synthesis from a Single Image
Authors:Yixing Lu, Junting Dong, Youngjoong Kwon, Qin Zhao, Bo Dai, Fernando De la Torre
We present a unified and generalizable framework for synthesizing view-consistent and temporally coherent avatars from a single image, addressing the challenging task of single-image avatar generation. Existing diffusion-based methods often condition on sparse human templates (e.g., depth or normal maps), which leads to multi-view and temporal inconsistencies due to the mismatch between these signals and the true appearance of the subject. Our approach bridges this gap by combining the reconstruction power of regression-based 3D human reconstruction with the generative capabilities of a diffusion model. In a first step, an initial 3D reconstructed human through a generalized NeRF provides comprehensive conditioning, ensuring high-quality synthesis faithful to the reference appearance and structure. Subsequently, the derived geometry and appearance from the generalized NeRF serve as input to a video-based diffusion model. This strategic integration is pivotal for enforcing both multi-view and temporal consistency throughout the avatar’s generation. Empirical results underscore the superior generalization ability of our proposed method, demonstrating its effectiveness across diverse in-domain and out-of-domain in-the-wild datasets.
我们提出了一种统一且可推广的框架,可从单张图像中合成视角一致且时间连贯的虚拟角色,以解决单图像角色生成这一具有挑战性的任务。现有的基于扩散的方法通常依赖于稀疏的人体模板(例如深度或法线图),这会导致这些信号与主体的真实外观之间的不匹配,进而产生多视角和时间上的不一致性。我们的方法结合了基于回归的3D人体重建的重建能力与扩散模型的生成能力,以缩小这一差距。首先,通过通用的NeRF生成初始的3D重建人体,提供全面的条件,确保高质量且忠于参考外观和结构的合成。随后,从通用的NeRF中得出的几何形状和外观作为视频扩散模型的输入。这种战略性的整合对于在角色生成过程中强制执行多视角和时间一致性至关重要。经验结果强调了我们提出方法的卓越泛化能力,证明了它在各种领域内外、野生数据集上的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025; Project Page: https://humansensinglab.github.io/GAS/
Summary
本文提出了一种统一且通用的框架,用于从单张图像合成视角一致、时间连贯的虚拟角色。该框架解决了基于扩散的单图像虚拟角色生成中的不一致性问题,通过结合回归型三维人体重建的重建能力与扩散模型的生成能力,确保了高质量且忠于原始外观和结构的合成。首先,通过通用NeRF进行三维人体重建,为后续合成提供全面的条件。接着,将从NeRF中得出的几何和外观信息作为视频扩散模型的输入,强制实现多视角和时间上的连贯性。经验结果表明,该方法具有出色的泛化能力,在不同领域和野外数据集上都表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种统一框架,用于从单张图像合成视角一致、时间连贯的虚拟角色。
- 解决了现有扩散模型在虚拟角色生成中的多视角和时间不一致性问题。
- 结合了回归型三维人体重建的重建能力与扩散模型的生成能力。
- 使用通用NeRF进行初始三维人体重建,为后续合成提供全面条件。
- 从NeRF中得出的几何和外观信息作为视频扩散模型的输入。
- 通过策略性整合实现了多视角和时间连贯性的强制实施。
点此查看论文截图


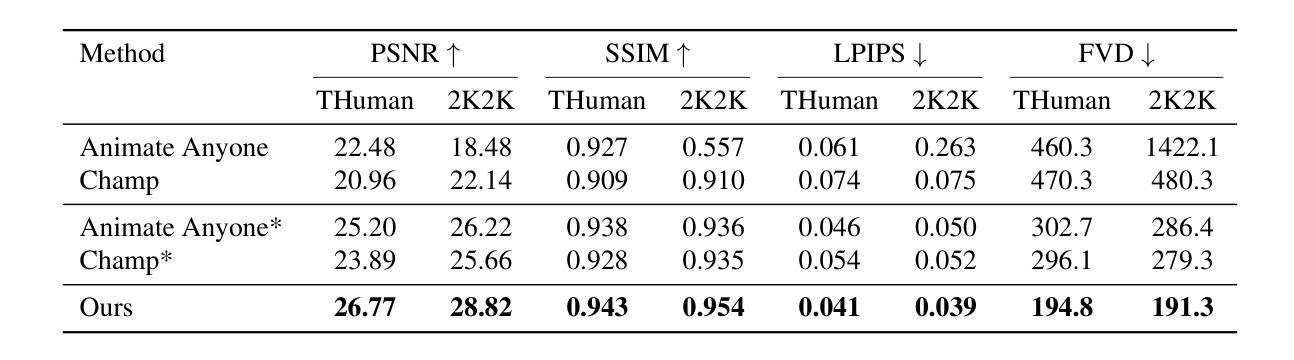
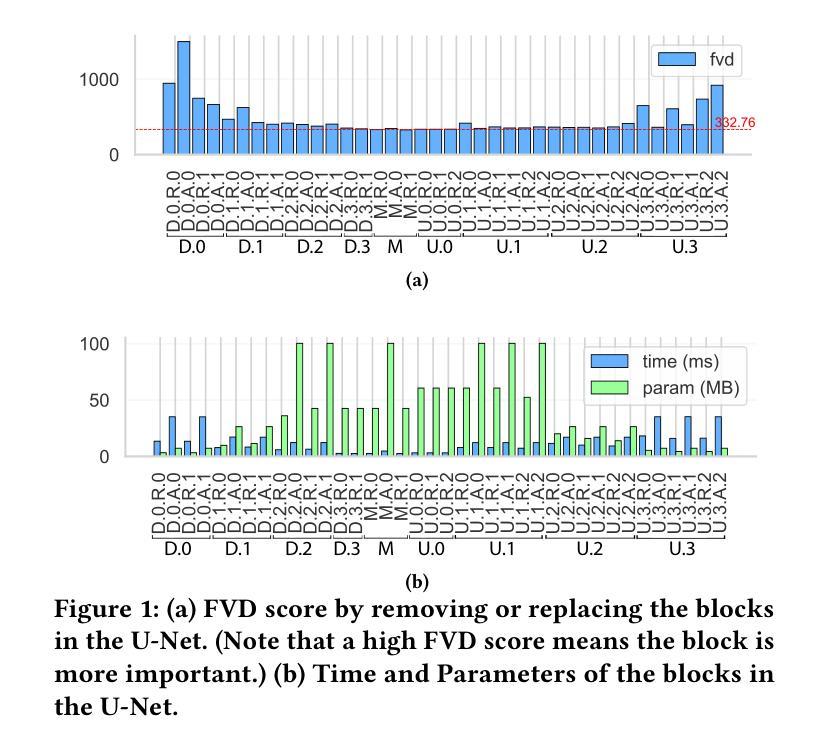
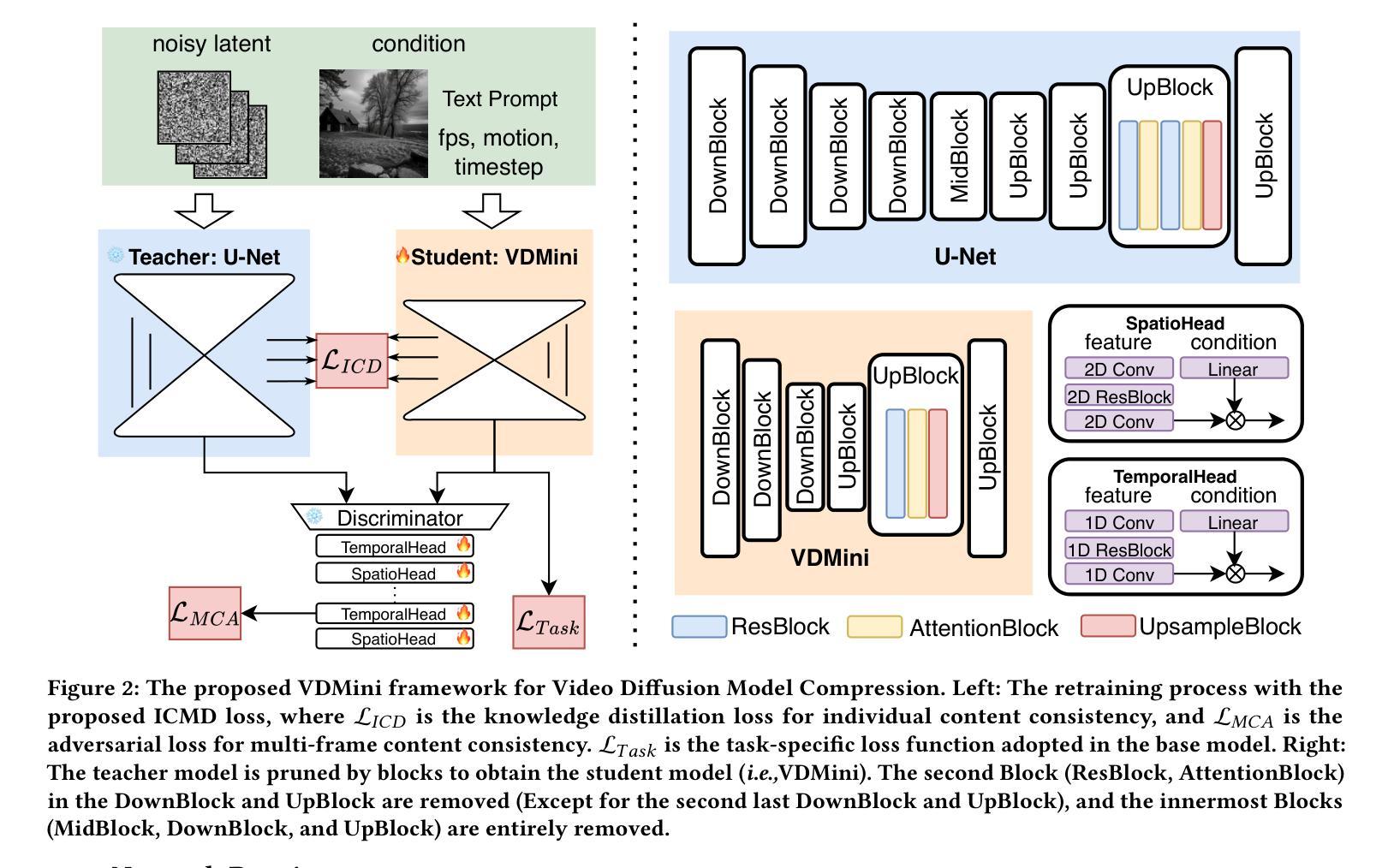
Individual Content and Motion Dynamics Preserved Pruning for Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Yiming Wu, Huan Wang, Zhenghao Chen, Dong Xu
The high computational cost and slow inference time are major obstacles to deploying Video Diffusion Models (VDMs). To overcome this, we introduce a new Video Diffusion Model Compression approach using individual content and motion dynamics preserved pruning and consistency loss. First, we empirically observe that deeper VDM layers are crucial for maintaining the quality of \textbf{motion dynamics} (\textit{e.g.,} coherence of the entire video), while shallower layers are more focused on \textbf{individual content} (\textit{e.g.,} individual frames). Therefore, we prune redundant blocks from the shallower layers while preserving more of the deeper layers, resulting in a lightweight VDM variant called VDMini. Moreover, we propose an \textbf{Individual Content and Motion Dynamics (ICMD)} Consistency Loss to gain comparable generation performance as larger VDM to VDMini. In particular, we first use the Individual Content Distillation (ICD) Loss to preserve the consistency in the features of each generated frame between the teacher and student models. Next, we introduce a Multi-frame Content Adversarial (MCA) Loss to enhance the motion dynamics across the generated video as a whole. This method significantly accelerates inference time while maintaining high-quality video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our VDMini on two important video generation tasks, Text-to-Video (T2V) and Image-to-Video (I2V), where we respectively achieve an average 2.5 $\times$, 1.4 $\times$, and 1.25 $\times$ speed up for the I2V method SF-V, the T2V method T2V-Turbo-v2, and the T2V method HunyuanVideo, while maintaining the quality of the generated videos on several benchmarks including UCF101, VBench-T2V, and VBench-I2V.
视频扩散模型(VDM)的高计算成本和缓慢的推理时间是其主要部署障碍。为了克服这一障碍,我们引入了一种新的视频扩散模型压缩方法,该方法保留了个人内容和运动动力学的修剪和一致性损失。首先,我们经验性地观察到,较深的VDM层对于维持运动动力学的质量(例如整个视频的一致性)至关重要,而较浅的层则更专注于个人内容(例如单个帧)。因此,我们从较浅的层中修剪掉多余的部分,同时保留更多的深层结构,从而得到一种轻量级的VDM变体,称为VDMini。此外,我们提出了一种个人内容和运动动力学(ICMD)一致性损失,以在大型VDM与VDMini之间获得相当的生成性能。具体来说,我们首先使用个人内容蒸馏(ICD)损失来保持教师模型和学生模型之间每个生成帧的特征一致性。接下来,我们引入了一种多帧内容对抗(MCA)损失,以提高整个生成视频的动态运动效果。该方法显著加速了推理时间,同时保持了高质量的视频生成。大量实验证明,我们的VDMini在两项重要的视频生成任务——文本到视频(T2V)和图像到视频(I2V)上效果显著。在I2V方法SF-V、T2V方法T2V-Turbo-v2以及T2V方法HunyuanVideo上,我们分别实现了平均2.5倍、1.4倍和1.25倍的加速,同时在包括UCF101、VBench-T2V和VBench-I2V等多个基准测试上保持了生成视频的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2025
Summary
视频扩散模型(VDM)面临高计算成本和慢推理时间的挑战。为此,我们引入了一种新的视频扩散模型压缩方法,采用个体内容和运动动态保留的修剪和一致性损失。通过实证观察,我们发现较深的VDM层对于保持运动动态质量至关重要,而较浅的层更专注于个体内容。因此,我们从较浅的层修剪冗余块,同时保留更多的深层,形成轻量级的VDM变体VDMini。此外,我们提出了个体内容和运动动态(ICMD)一致性损失,以在较大的VDM与VDMini之间获得相当的生产性能。通过个体内容蒸馏(ICD)损失保持教师和学生模型之间每个生成帧的特征一致性,并引入多帧内容对抗(MCA)损失以增强整个生成视频的运动动态。此方法在维持高质量视频生成的同时,显著加速了推理时间。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型(VDM)面临计算成本高和推理时间慢的问题。
- 引入了一种新的VDM压缩方法,结合个体内容和运动动态保留的修剪和一致性损失。
- 较深的VDM层对保持运动动态质量至关重要,而较浅的层更关注个体内容。
- 提出了VDMini,通过修剪浅层冗余块并保留更多深层,形成轻量级的VDM变体。
- 引入了ICMD一致性损失,以在大型VDM和VDMini之间实现相当的生产性能。
- 使用ICD损失保持特征一致性,并使用MCA损失增强整个生成视频的运动动态。
点此查看论文截图

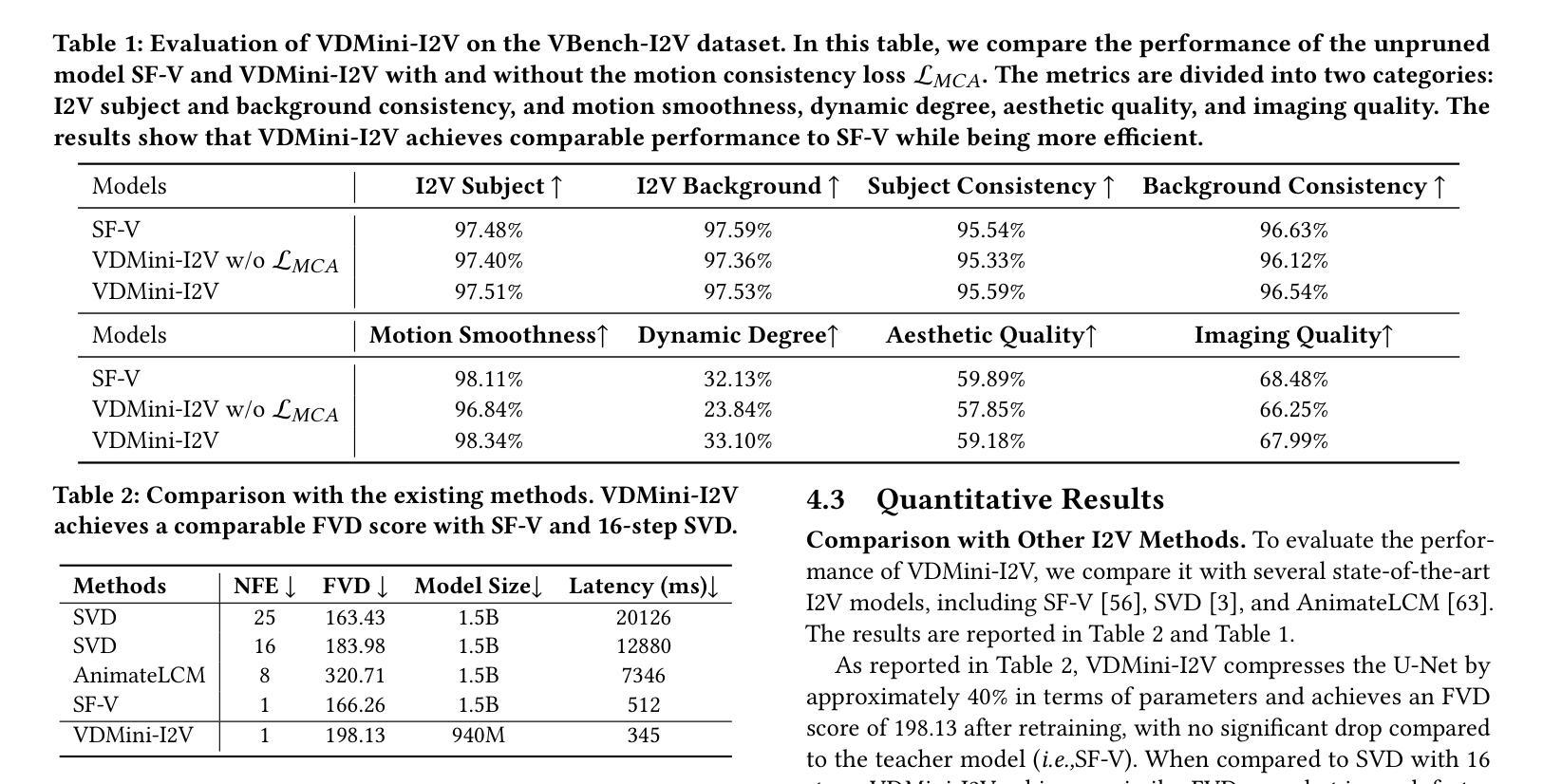
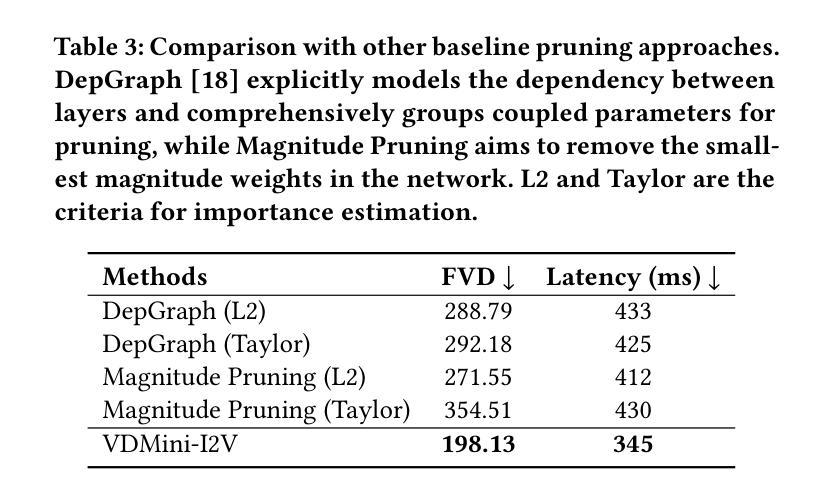
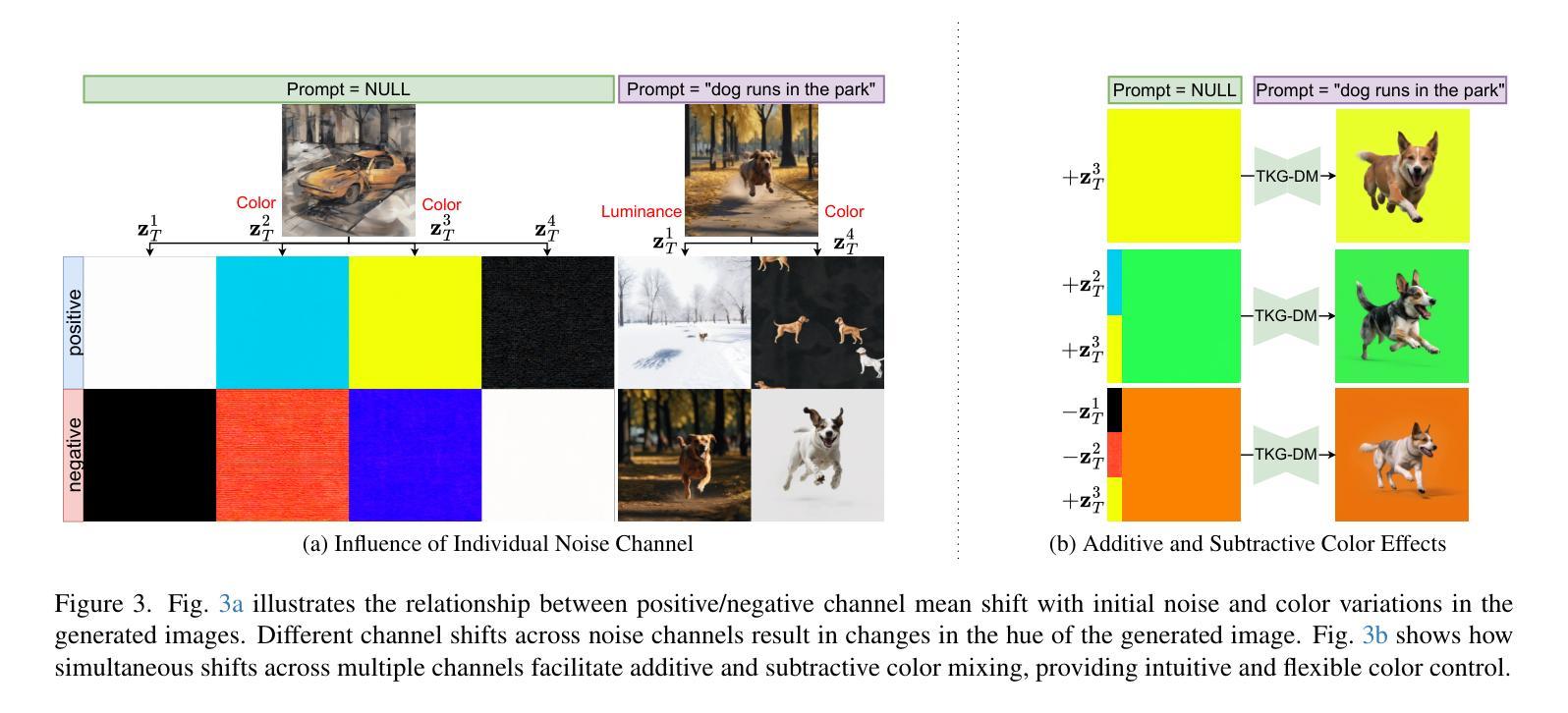
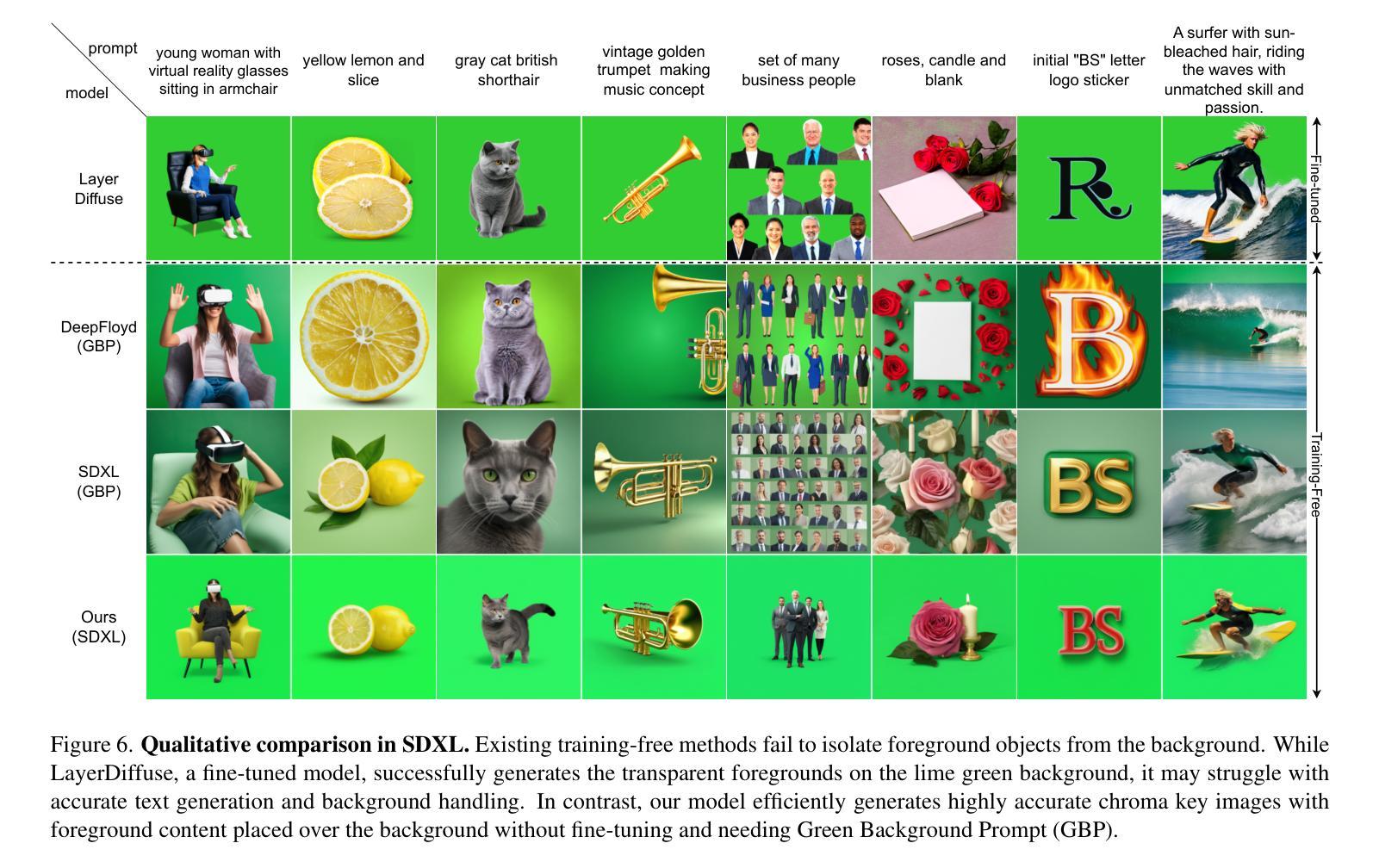
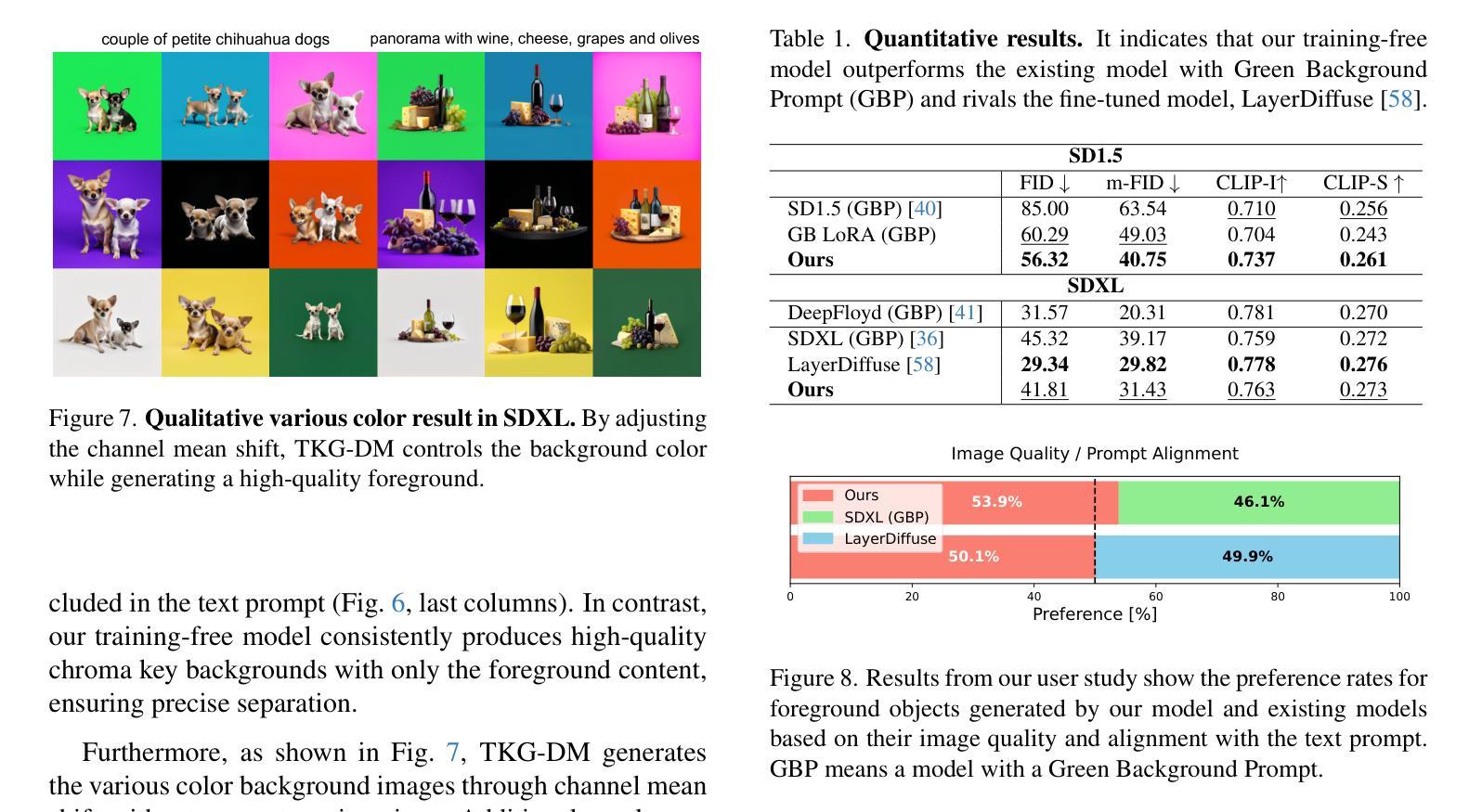
TKG-DM: Training-free Chroma Key Content Generation Diffusion Model
Authors:Ryugo Morita, Stanislav Frolov, Brian Bernhard Moser, Takahiro Shirakawa, Ko Watanabe, Andreas Dengel, Jinjia Zhou
Diffusion models have enabled the generation of high-quality images with a strong focus on realism and textual fidelity. Yet, large-scale text-to-image models, such as Stable Diffusion, struggle to generate images where foreground objects are placed over a chroma key background, limiting their ability to separate foreground and background elements without fine-tuning. To address this limitation, we present a novel Training-Free Chroma Key Content Generation Diffusion Model (TKG-DM), which optimizes the initial random noise to produce images with foreground objects on a specifiable color background. Our proposed method is the first to explore the manipulation of the color aspects in initial noise for controlled background generation, enabling precise separation of foreground and background without fine-tuning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our training-free method outperforms existing methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, matching or surpassing fine-tuned models. Finally, we successfully extend it to other tasks (e.g., consistency models and text-to-video), highlighting its transformative potential across various generative applications where independent control of foreground and background is crucial.
扩散模型已经能够生成高质量的图片,并强烈专注于现实感和文本忠实度。然而,大规模的文本到图像模型,如Stable Diffusion,在生成前景物体放置在色键背景上的图像时遇到困难,这限制了它们在未经微调的情况下分离前景和背景元素的能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种全新的无训练色键内容生成扩散模型(TKG-DM),它通过优化初始随机噪声来生成具有指定颜色背景的图像。我们提出的方法是第一个探索初始噪声中颜色方面的控制以用于背景生成的方法,能够在不微调的情况下实现前景和背景的精确分离。大量实验表明,我们的无训练方法在定性和定量评估中都优于现有方法,甚至超过了微调模型。最后,我们成功地将其扩展到其他任务(如一致性模型和文本到视频),突显其在各种生成应用程序中的变革潜力,尤其是在需要独立控制前景和背景的情况下至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR2025(Highlight). Code at: https://github.com/ryugo417/TKG-DM
Summary
本文介绍了Diffusion模型在生成高质量图像方面的应用,特别是在真实性和文本忠实度方面的优势。然而,大型文本到图像模型(如Stable Diffusion)在生成前景物体放置在色键背景上的图像时存在困难。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种无需训练的新型色键内容生成扩散模型(TKG-DM),它通过优化初始随机噪声来生成具有指定背景色的前景物体图像。该方法首次探索了初始噪声中颜色方面的操控,实现了无需精细调整的精确前景与背景分离。实验证明,该方法在定性和定量评估中都优于现有方法,甚至与精细调整的模型相匹配或超越。此外,该方法的潜力巨大,可广泛应用于各种生成任务,特别是在需要独立控制前景和背景的任务中表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion模型能生成高质量、逼真的图像。
- 大型文本到图像模型在生成特定背景(如色键背景)上的前景物体图像时存在挑战。
- 提出的Training-Free Chroma Key Content Generation Diffusion Model(TKG-DM)能优化初始随机噪声,生成具有指定背景色的前景物体图像。
- TKG-DM首次探索了初始噪声中颜色方面的操控,实现前景和背景的精确分离,无需精细调整。
- TKG-DM在定性和定量评估中都表现出优异的性能,甚至超越了某些经过精细调整的模型。
- TKG-DM可广泛应用于各种生成任务,特别是在需要独立控制前景和背景的任务中表现突出。
点此查看论文截图


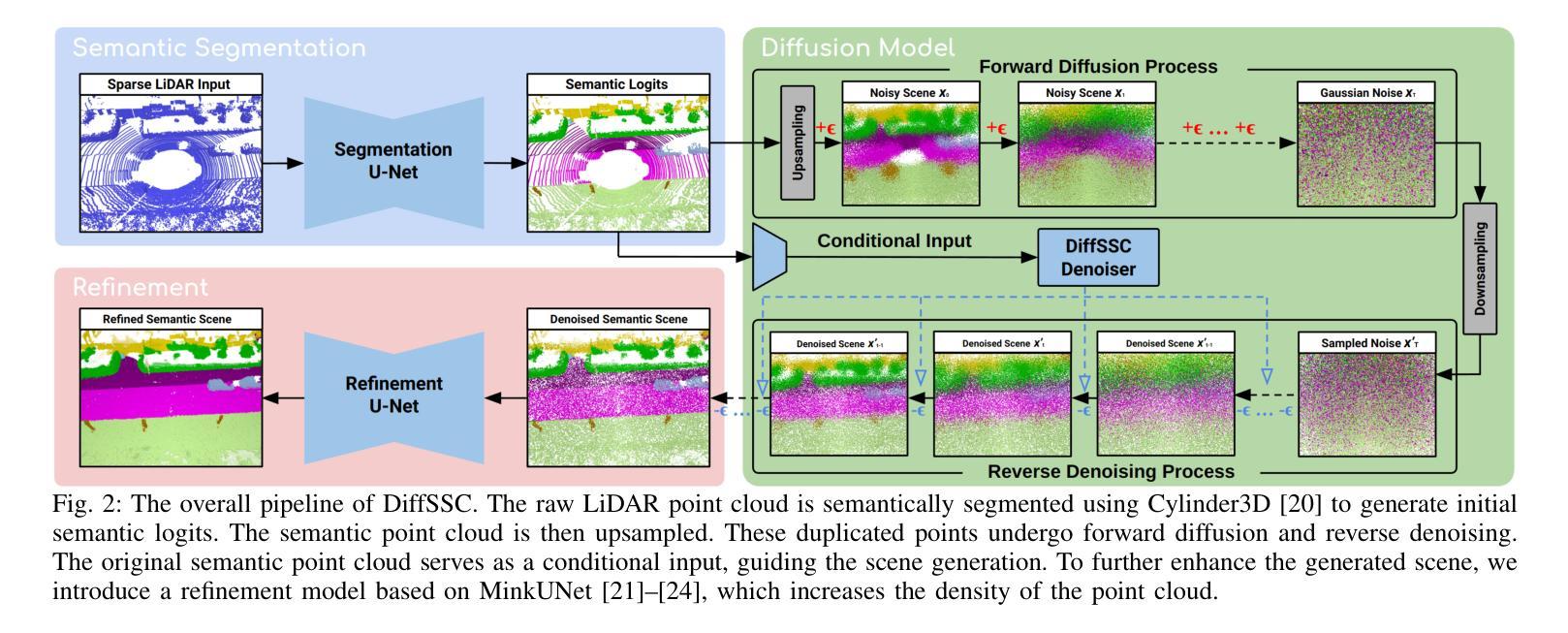
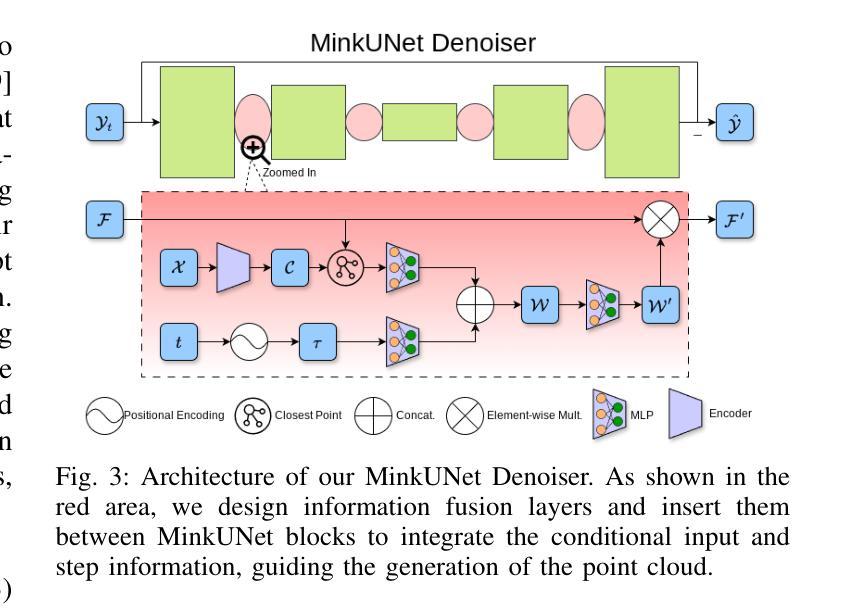
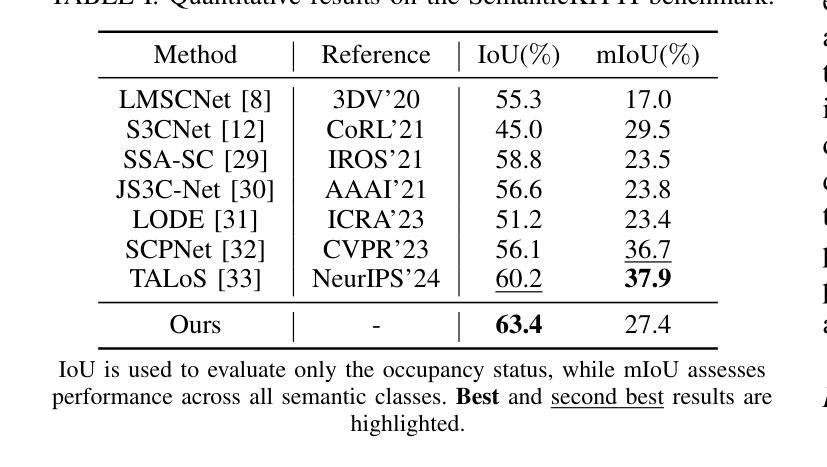
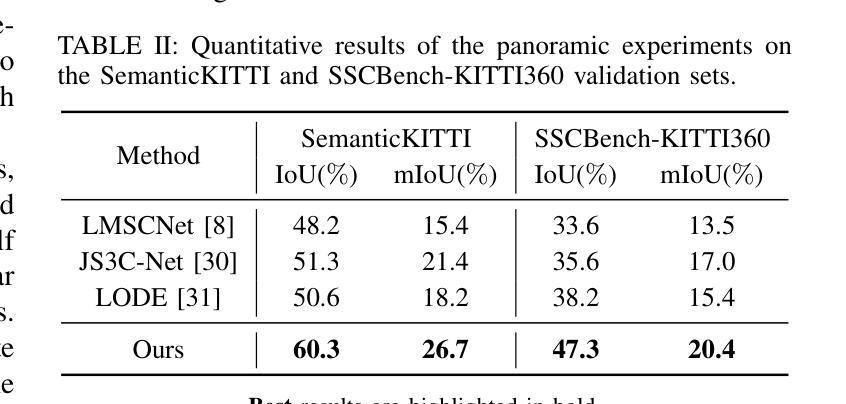
DiffSSC: Semantic LiDAR Scan Completion using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Authors:Helin Cao, Sven Behnke
Perception systems play a crucial role in autonomous driving, incorporating multiple sensors and corresponding computer vision algorithms. 3D LiDAR sensors are widely used to capture sparse point clouds of the vehicle’s surroundings. However, such systems struggle to perceive occluded areas and gaps in the scene due to the sparsity of these point clouds and their lack of semantics. To address these challenges, Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) jointly predicts unobserved geometry and semantics in the scene given raw LiDAR measurements, aiming for a more complete scene representation. Building on promising results of diffusion models in image generation and super-resolution tasks, we propose their extension to SSC by implementing the noising and denoising diffusion processes in the point and semantic spaces individually. To control the generation, we employ semantic LiDAR point clouds as conditional input and design local and global regularization losses to stabilize the denoising process. We evaluate our approach on autonomous driving datasets, and it achieves state-of-the-art performance for SSC, surpassing most existing methods.
感知系统在自动驾驶中扮演着至关重要的角色,它融合了多种传感器和相应的计算机视觉算法。3D激光雷达传感器被广泛应用于捕捉车辆周围稀疏的点云。然而,由于点云的稀疏性和缺乏语义信息,这样的系统在感知遮挡区域和场景中的间隙时面临困难。为了解决这些挑战,语义场景补全(SSC)能够根据原始的激光雷达测量联合预测场景中未观察到的几何形状和语义信息,旨在实现更完整的场景表示。基于扩散模型在图像生成和超分辨率任务中的出色表现,我们将其扩展到SSC,通过在点和语义空间上分别实现噪声和去噪声扩散过程。为了控制生成过程,我们使用语义激光雷达点云作为条件输入,并设计局部和全局正则化损失来稳定去噪声过程。我们在自动驾驶数据集上评估了我们的方法,它实现了最先进的SSC性能,超越了大多数现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2025), Hangzhou, China, Oct 2025
摘要
感知系统在自动驾驶中扮演着至关重要的角色,融合了多种传感器和计算机视觉算法。3D激光雷达传感器广泛应用于捕捉车辆周围稀疏的点云数据。然而,由于点云数据的稀疏性和缺乏语义信息,这类系统在感知遮挡区域和场景中的间隙时面临挑战。为了解决这些挑战,语义场景补全(SSC)旨在根据原始激光雷达测量联合预测未观察到的场景几何和语义,以实现更完整的场景表示。基于扩散模型在图像生成和超分辨率任务中的优异表现,我们将其扩展到SSC,通过在点和语义空间分别实现噪声和去噪声扩散过程。为了控制生成过程,我们使用语义激光雷达点云作为条件输入,并设计局部和全局正则化损失以稳定去噪声过程。我们在自动驾驶数据集上评估了我们的方法,它在SSC方面实现了最先进的性能,超越了大多数现有方法。
关键见解
- 感知系统在自动驾驶中起关键作用,融合多种传感器和计算机视觉算法。
- 3D激光雷达传感器广泛应用于捕捉车辆周围的稀疏点云数据,但存在感知遮挡区域和场景间隙的挑战。
- 语义场景补全(SSC)可联合预测未观察到的场景几何和语义,以实现更完整的场景表示。
- 扩散模型在图像生成和超分辨率任务中表现优异,可扩展到SSC。
- 在点和语义空间分别实现噪声和去噪声扩散过程。
- 使用语义激光雷达点云作为条件输入来控制生成过程。
点此查看论文截图